March 1997
CDP1855,
CDP1855C
8-Bit Programmable
Multiply/Divide Unit
Features
• Cascadable Up to 4 Units for 32-Bit by 32-Bit Multiply
or 64
÷ 32-Bit Divide
• 8-Bit by 8-Bit Multiply or 16
÷ 8-Bit Divide in 5.6µs at
5V or 2.8µs at 10V
• Direct Interface to CDP1800-Series Microprocessors
• Easy Interface to Other 8-Bit Microprocessors
• Significantly Increases Throughput of Microprocessor
Used for Arithmetic Calculations
Ordering Information
PKG.
PACKAGE TEMP. RANGE 5V 10V
PDIP -40oC to +85oC CDP1855CE CDP1855E E28.6
Burn-In CDP1855CEX - E28.6
SBDIP -40oC to +85oC CDP1855CD CDP1855D D28.6
Burn-In CDP1855CDX - D28.6
NO.
Description
The CDP1855 and CDP1855C are CMOS 8-bit multiply/divide units which can be used to greatly increase the
capabilities of 8-bit microprocessors. They perform multiply
and divide operations on unsigned, binary operators. In
general, microprocessors do not contain multiply or divide
instructions and even efficiently coded multiply or divide
subroutines require considerable memory and execution
time. These multiply/divide units directly interface to the
CDP1800-series microprocessors via the N-lines and can
easily be configured to fit in either the memory or I/O space
of other 8-bit microprocessors.
The multiple/divide unit is based on a method of multiplying
by add and shift right operations and dividing by subtract and
shift left operations. The device is structured to permit cascading identical units to handle operands up to 32 bits.
The CDP1855 and CDP1855C are functionally identical.
They differ in that the CDP1855 has a recommended
operating voltage range of 4V to 10.5V, and the CDP1855C,
a recommended operating voltage range of 4V to 6.5V.
The CDP1855 and CDP1855C types are supplied in a 28
lead hermetic dual-in-line ceramic package (D suffix) and in
a 28 lead dual-in-line plastic package (E suffix). The
CDP1855C is also available in chip form (H suffix).
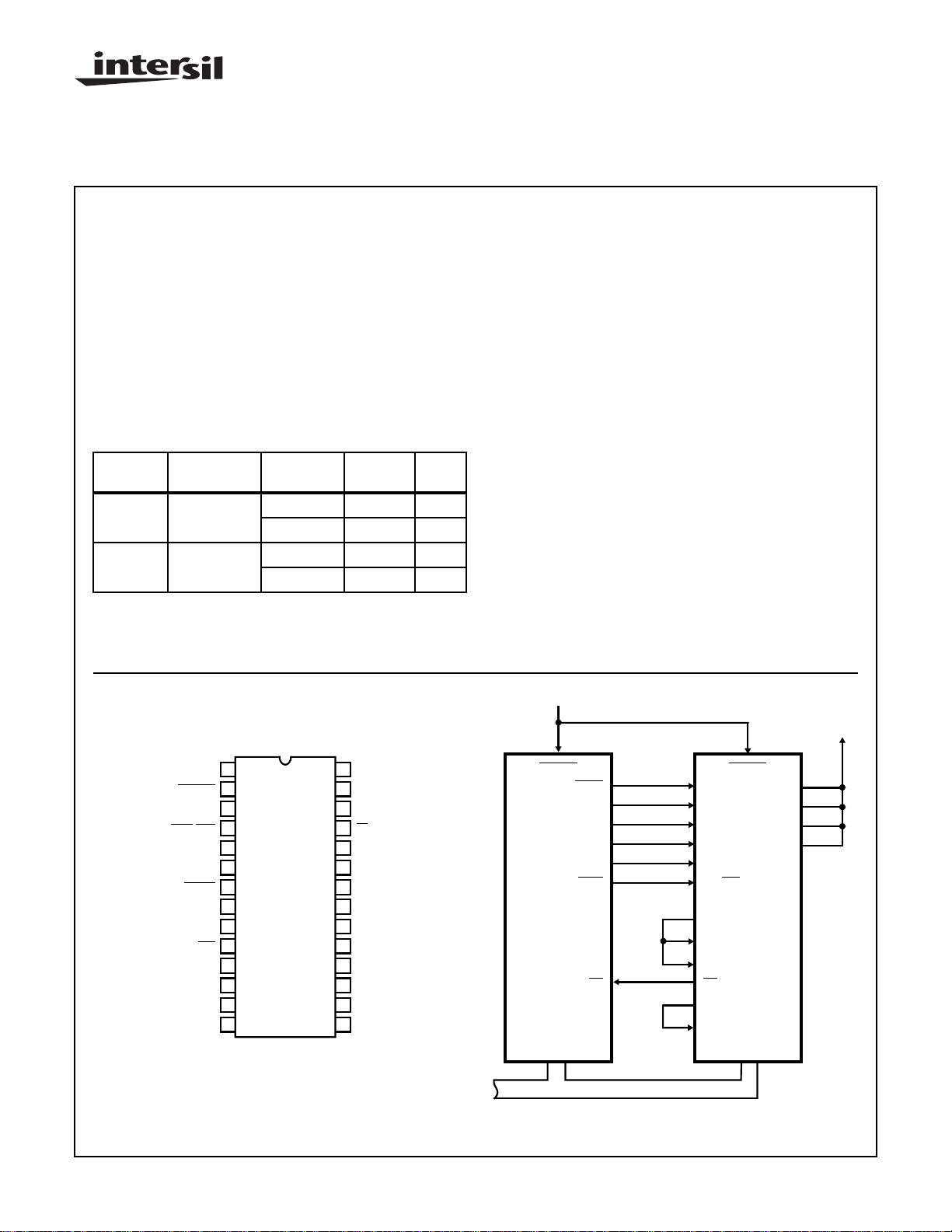
Pinout
CE
CLEAR
CTL
C.O./O.F.
Y
Z
SHIFT
CLK
STB
WE
RD/
RA2
RA1
RA0
V
SS
1
2
3
4
5
L
6
L
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28 LEAD DIP
TOP VIEW
Circuit Configuration
+V
28
V
DD
27
CN0
CN1
26
CI
25
24
Y
R
Z
23
R
BUS 7
22
BUS 6
21
20
BUS 5
BUS 4
19
BUS 3
18
BUS 2
17
16
BUS 1
15
BUS 0
CLEAR
XTAL
N0
N1
N2
TPB
MRD
CDP1802
EF
BUS
FIGURE 1. MDU ADDRESSED AS I/O DEVICE
CLK
RA0
RA1
RA2
STB
RD/
Y
L
Z
R
CTL
C0
Y
R
Z
L
CLEAR
CE
C1
CN0
CN1
WE
CDP1855
BUS
CAUTION: These devices are sensitive to electrostatic discharge; follow proper IC Handling Procedures.
http://www.intersil.com or 407-727-9207
| Copyright © Intersil Corporation 1999
4-47
File Number 1053.2
CDP1855, CDP1855C
Absolute Maximum Ratings Thermal Information
DC Supply Voltage Range, (VDD)
(All voltage values referenced to VSS terminal)
CDP1855 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5V to +11V
CDP1855C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -0.5V to +7V
Input Voltage Range, All Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . .-0.5V to VDD +0.5V
DC Input Current, Any One Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .±10mA
CAUTION: Stresses above those listed in “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress only rating and operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
Thermal Resistance (Typical) θJA (oC/W) θJC (oC/W)
PDIP Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55 N/A
SBDIP Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50 12
Device Dissipation Per Output Transistor
For TA = Full Package-Temperature Range
(All Package Types). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100mW
Operating Temperature Range (TA) . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40oC to +85oC
Storage Temperature Range (T
) . . . . . . . . . . . .-65oC to +150oC
STg
Lead Temperature (During Soldering)
At distance 1/16 ± 1/32 In. (1.59 ± 0.79mm)
from case for 10s max. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +265oC
Static Electrical Specifications At T
= -40 to +85oC, VDD±10%, Unless Otherwise Specified
A
CONDITIONS LIMITS
PARAMETER
Quiescent Device
Current
Output Low Drive (Sink)
Current
Output High Drive
(Source) Current
Output Voltage Low Level
(Note 2)
Output Voltage High Level
(Note 2)
Input Low Voltage V
V
O
(V)
I
DD
- 0, 5 5 - 0.01 50 - 0.02 200 µA
- 0, 10 10 - 1 200 - - - µA
I
OL
0.4 0, 5 5 1.6 3.2 - 1.6 3.2 - mA
0.5 0, 10 10 2.6 5.2 - - - - mA
I
OH
4.6 0, 5 5 -1.15 -2.3 - -1.15 -2.3 - mA
9.5 0, 10 10 -2.6 -5.2 - - - - mA
V
OL
- 0, 5 5 - 0 0.1 - 0 0.1 V
- 0, 10 10 - 0 0.1 - - - V
V
OH
- 0, 5 5 4.9 5 - 4.9 5 - V
- 0, 10 10 9.9 10 - - - - V
0.5, 4.5 - 5 - - 1.5 - - 1.5 V
IL
V
(V)
IN
0.5, 9.5 - 10 - - 3 - - - V
Input High Voltage V
0.5, 4.5 - 5 3.5 - - 3.5 - - V
IH
0.5, 9.5 - 10 7 - - - - - V
Input Leakage Current I
IN
- 0, 5 5 - - ±1- - ±1 µA
- 0, 10 10 - - ±1- - -µA
Three-State Output
Leakage Current
Operating Current
(Note 3)
Input Capacitance C
Output Capacitance C
I
OUT
I
DD1
OUT
0, 5 0, 5 5 - - ±1- - ±1 µA
0, 10 0, 10 10 - - ±10 - - - µA
- 0, 5 5 - 1.5 - - 1.5 3 mA
- 0, 10 10 - 6 12 - - - mA
IN
- - - - 5 7.5 - 5 7.5 pF
- - - - 10 15 - 10 15 pF
NOTES:
1. Typical values are for TA = +25oC and nominal VDD.
2. IOL = IOH = 1µA
3. Operating current is measured at 3.2MHz with open outputs.
V
(V)
DD
CDP1855 CDP1855C
(NOTE1)
MIN
TYP MAX MIN
(NOTE1)
TYP MAX
UNITS
4-48
CDP1855, CDP1855C
Recommended Operating Conditions At T
= Full package temperature range. For maximum reliability, operating conditions
A
should be selected so that operation is always within the following ranges:
LIMITS
CDP1855 CDP1855C
MIN MAX MIN MAX
UNITS
PARAMETER
V
DD
(V)
DC Operating Voltage Range - 4 10.5 4 6.5 V
Input Voltage Range - V
SS
V
DD
V
SS
V
DD
Maximum Clock Input Frequency 5 3.2 - 3.2 - MHz
10 6.4 - - - MHz
Minimum 8 x 8 Multiply (16 ÷ 8 Divide) Time 5 - 5.6 - 5.6 µs
10 - 2.8 - - µs
RA2 RA1 RA0CE
11
12 131
REGISTER
SELECT CONTROL
SELECT Z
SELECT Y
SELECT LOGIC
SELECT X
X SEQUENCE
COUNTER
RESET
OUT
SELECT STATUS
X REGISTER
LOAD
V
CLOCK
8
CN1
26
CN0
27
CHIP
NO.
8
SUBTRACT
Y REGISTER
RESET
Z REGISTER
RESET
CONTROL
LOAD
10729
ADD/
C.O.
8
REGISTER
14
V
V
28
BUS
22
SS
DD
7
STATUS
REG
8
8
BUS
6
21
Y SEQUENCE
COUNTER
RESET
Z SEQUENCE
COUNTER
RESET
SHIFT
GENERATOR
OUT
OUT
8
SHIFT
LOAD
SHIFT
LOAD
RD/WESHIFTCLEARSTB
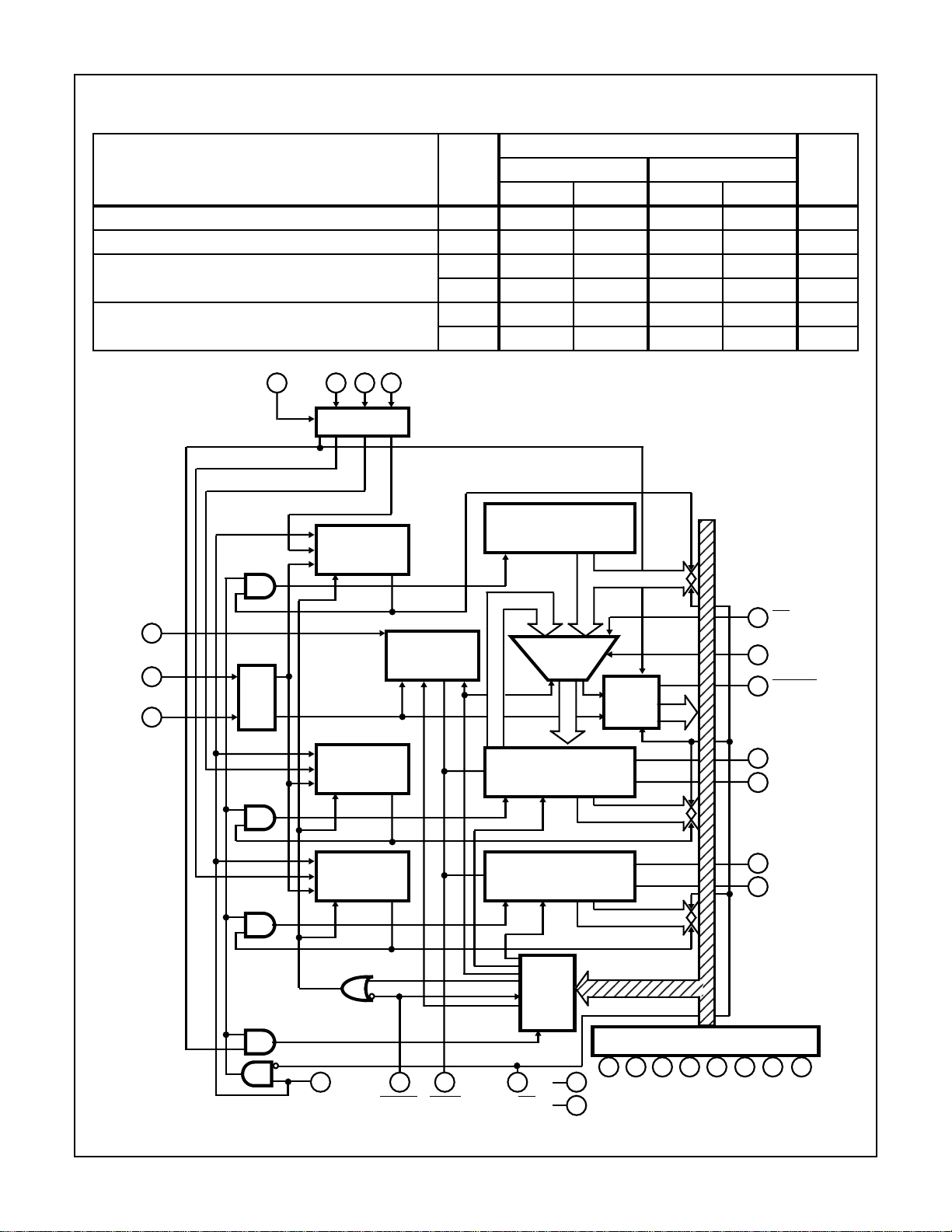
FIGURE 2. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF CDP1855 AND CDP1855C
BUS
5
20
BUS
4
19
BUS
3
18
BUS
2
17
25
3
4
5
24
6
23
BUS
C.I.
CTL.
C.O./O.F.
Y
L
Y
R
Z
L
Z
R
BUS
1
16
0
15
4-49
Functional Description
CDP1855, CDP1855C
The CDP1855 is a multiply-divide unit (MDU) designed to be
compatible with CDP1800 series microprocessor systems. It
can, in fact, be interfaced to most 8-bit microprocessors (see
Figure 5). The CDP1855 performs binary multiply or divide
operations as directed by the microprocessor. It can do a
16N-bit by 8N-bit divide yielding a 8N-bit result plus and 8Nbit remainder. The multiply is an 8N-bit by 8N-bit operation
with a 16N-bit result. The “N” represent the number of
cascaded CDP1855's and can be 1, 2, 3 or 4. All operations
require 8N + 1 shift pulses (See “DELAY NEEDED WITH
AND WITHOUT PRESCALER”).
The CDP1855 contains three registers, X, Y, and Z, which
are loaded with the operands prior to an operation and
contain the results at the completion. In addition, the control
register must be loaded to initiate a multiply or divide. There
is also a status register which contains an overflow flag as
shown in the “CONTROL REGISTER BIT ASSIGNMENT
TABLE”. The register address lines (RA0-RA1) are used to
select the appropriate register for loading or reading. The
RD/
WE and STB lines are used in conjunction with the RA
lines to determine the exact MDU response (See
“CONTROL TRUTH TABLE”).
When multiple MDU's are cascaded, the loading of each register is done sequentially. For example, the first selection of
register X for loading loads the most significant CDP1855,
the second loads the next significant, and so on. Registers
are also read out sequentially. This is accomplished by internal counters on each MDU which are decremented by STB
during each register selection. When the counter matches
the chip number (CN1, CN0 lines), the device is selected.
These counters must be cleared with a clear on pin 2 or with
bit 6 in the control word (See “CONTROL REGISTER BIT
ASSIGNMENT TABLE”) in order to star t each sequence of
accesses with the most significant device.
The CDP1855 has a built in clock prescaler which can be
selected via bit 7 in the control register. The prescaler may
be necessary in cascaded systems operating at high
frequencies or in systems where a suitable clock frequency
is not readily available. Without the prescaler select, the shift
frequency is equal to the clock input frequency. With the
prescaler selected, the rate depends on the number of
MDU's as defined by bits 4 and 5 of the control word (See
“CONTROL REGISTER BIT ASSIGNMENT TABLE”).
1. For one MDU, the clock frequency is divided by 2.
2. For two MDU's the clock frequency is divided by 4.
3. For 3 or 4 MDU's, the clock frequency is divided by 8.
Operation
1. Initialization and Controls
The CDP1855 must be cleared by a low on pin 2 during
power-on which prevents bus contention problems at the Y
Y
and ZL, ZR terminals and also resets the sequence
R
counters and the shift pulse generator.
Prior to loading any other registers the control register must
be loaded to specify the number of MDU's being used (See
“CONTROL REGISTER BIT ASSIGNMENT TABLE”).
Once the number of devices has been specified and the
sequence counters cleared with a clear pulse or bit 6 of the
control word, the X, Y, and Z registers can be loaded as
defined in the “CONTROL TRUTH TABLE”. All bytes of the X
register can be loaded, then all bytes of the Y, and then all
bytes of the Z, or they can be loaded randomly. Successive
loads to a given register will always proceed sequentially
from the most significant byte to the least significant byte, as
previously described. Resetting the sequence counters
select the most significant MDU. In a four MDU system, loading all MDU's results in the sequence counter pointing to the
first MDU again. In all other configurations (1, 2, or 3
MDU's), the sequence counter must be reset prior to each
series of register reads or writes.
2. Divide Operation
For the divide operation, the divisor is loaded in the X
register. The dividend is loaded in the Y and Z registers with
the more significant half in the Y register and the less significant half in the Z register. These registers may be loaded in
any order, and after loading is completed, a control word is
loaded to specify a divide operation and the number of
MDU's and also to reset the sequence counters and Y or Z
register and select the clock option if desired. Clearing the
sequence counters with bit 6 will set the MDU's up for reading the results.
The X register will be unaltered by the operation. The
quotient will be in the Z register while the remainder will be in
the Y register. An overflow will be indicated by the
of the most significant MDU and can also be determined by
reading the status byte.
While the CDP1855 is specified to perform 16 by 8-bit
divides, if the quotient of a divide operation exceeds the size
of the Z register(s) (8N-bits - where N is the number of
cascaded CDP1855's) the overflow bit in the Status Register
will be set. Neither the quotient in Z nor the remainder in Y
will represent a valid answer. This will always be the result of
a division performed when the divisor (X) is equal to or less
than the most significant 8N-bits of the dividend (Y).
The MDU can still be used for such computations if the
divide is done in two steps. The dividend is split into two
parts-the more significant 8N-bits and the less significant
8N-bits-and a divide done on each part. Each step yields an
8N-bit result for a total quotient of 16N-bits.
The first step consists of dividing the more significant 8Nbits by the divisor. This is done by clearing the Y register(s),
loading the Z register(s) with the more significant 8N-bits of
the dividend, and loading the X register(s) with the divisor. A
division is performed and the resultant value in Z represents
,
L
the more significant 8N-bits of the final quotient. The Z register(s) value must be unloaded and saved by the processor.
C.O./O.F.
4-50
CDP1855, CDP1855C
A second division is performed using the remainder from the
first division (in Y) as the more significant 8N-bits of the dividend and the less significant half of the original dividend
loaded into the Z register. The divisor in X remains unaltered
and is, by definition, larger than the remainder from the first
division which is in Y. The resulting value in Z becomes the
less significant 8N-bits of the final quotient and the value in Y
is, as usual, the remainder.
Extending this technique to more steps allows division of any
size number by an 8N-bit divisor.
Note that division by zero is never permitted and must be
tested for and handled in software.
The following example illustrates the use of this algorithm.
Example:
Assume three MDU's capable of a by 24-bit division. The
problem is to divide 00F273, 491C06H by 0003B4H.
Step 1: 000000 , 00F273 / 0003B4 = 000041 R=0001BF
Y Z(MS) X Z1 Y1
Step 2: 0001BF , 491C06 / 0003B4 = 78C936 R=00000E
Y1 Z(LS) X Z2 Y2
Result: 000041 , 78C936 R=00000E
Z1 Z2 Y2
The Z register can simply be reset using bit 2 of the control
word and another divide can be done in order to further
divide the remainder.
3. Multiply Operation
For a multiply operation the two numbers to be m ultiplied are
loaded in the X and Z registers. The result is in the Y and Z
register with Y being the more significant half and Z the less
significant half. The X register will be unchanged after the
operation is completed.
The original contents of the Y register are added to the
product of X and Z. Bit 3 of the control word will reset
register Y to 0 if desired.
Functional Description of
CDP1855 Terminals
CE - Chip Enable (Input):
ZR of the least significant CDP1855 MDU. This signal is
used to indicate whether the registers are to be operated on
or only shifted.
C.O./O.F. - Carry Out/Over Flow (Output):
This is a three-state output pin. It is the CDP1855
signal and is connected to
Cl (CARRY-IN) of the next more
Carry Out
significant CDP1855 MDU, except for on the most significant
MDU. On that MDU it is an overflow indicator and is enabled
when chip enables is true. A low on this pin indicates that an
overflow has occurred. The overflow signal is latched each
time the control register is loaded, but is only meaningful
after a divide command.
Y
, YR - Y-Left, Y-Right:
L
These are three-state bi-directional pins for data transfer
between the Y registers of cascaded CDP1855 MDU's. The
Y
pin is an output and YL is an input during a multiply and
R
the reverse is true at all other times. The Y
connected to the Y
An exception is that the Y
pin of the next more significant MDU.
R
pin of the most significant
L
CDP1855 MDU must be connected to the Z
pin must be
L
pin of the least
R
significant MDU and to the CTL pins of all MDU's. Also the
Y
pin of the least significant MDU is tied to the ZL pin of the
R
most significant MDU.
Z
, ZR - Z-Left, Z-Right:
L
These are three-state bi-directional pins for data transfers
between the “Z” registers of cascaded MDU's. The Z
an output and Z
reverse is true at all other times. The Z
the Y
pin of the next more significant MDU. An exception is
R
that the Z
L
nected to the Y
Z
pin of the least significant MDU is tied to the YL of the
R
is an input during a multiply and the
L
pin must be tied to
L
in of the most significant MDU must be con-
pin of the least significant MDU. Also, the
R
pin is
R
most significant MDU.
Shift - Shift Clock:
This is a three-state bi-directional pin. It is an output on the
most significant MDU. And an input on all other MDU's. It
provides the MDU system timing pulses. All
SHIFT pins must
be connected together for cascaded operation. A maximum
of the 8N +1 shifts are required for an operation where "N"
equals the number of MDU devices that are cascaded.
A high on this pin enables the CDP1855 MDU to respond to
the select lines. All cascaded MDU's must be enabled
together. CE also controls the three-state
C.O./O.F., output
of the most significant MDU.
Clear (Input):
The CDP1855 MDU(s) must be cleared upon power-on with
a low-on this pin. The clear signal resets the sequence
counters, the shift pulse generator, and bits 0 and 1 of the
control register.
CTL - Control (Input):
This is an input pin. All CTL pins must be wired together and
to the Y
of the most significant CDP1855 MDU and to the
L
CLK - Clock (Input):
This pin should be grounded on all but the most significant
MDU. There is an optional reduction of clock frequency a v ailable on this pin if so desired, controlled by bit 7 of the control
byte.
STB - Strobe (Input):
When RD/WE is low, data is latched from bus lines on the
falling edge of this signal. It may be asynchronous to the
clock. Strobe also increments the selected register's
sequence counter during reads and writes. TPB would be
used in CDP1800 systems.
4-51
 Loading...
Loading...