International Rectifier IRFSL17N20D, IRFS17N20D, IRFB17N20D Datasheet
SMPS MOSFET
PD- 93902A
IRFB17N20D
IRFS17N20D
IRFSL17N20D
HEXFET® Power MOSFET
Applications
l High frequency DC-DC converters
V
DSS
R
DS(on)
max I
200V 0.17Ω 16A
Benefits
l Low Gate-to-Drain Charge to Reduce
Switching Losses
l Fully Characterized Capacitance Including
Effective C
to Simplify Design, (See
OSS
App. Note AN1001)
l Fully Characterized Avalanche Voltage
and Current
TO-220AB
IRFB17N20D
D2Pak
IRFS17N20D
TO-262
IRFSL17N20D
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Max. Units
ID @ TC = 25°C Continuous Drain Current, VGS @ 10V 16
ID @ TC = 100°C Continuous Drain Current, VGS @ 10V 12 A
I
DM
PD @TA = 25°C Power Dissipation 3.8 W
PD @TC = 25°C Power Dissipation 140
V
GS
dv/dt Peak Diode Recovery dv/dt 2.7 V/ns
T
J
T
STG
Pulsed Drain Current 64
Linear Derating Factor 0.90 W/°C
Gate-to-Source Voltage ± 30 V
Operating Junction and -55 to + 175
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds 300 (1.6mm from case )
Mounting torqe, 6-32 or M3 screw 10 lbf•in (1.1N•m)
D
°C
Typical SMPS Topologies
l Telecom 48V input Forward Converter
Notes through are on page 11
www.irf.com 1
4/26/00
IRFB/IRFS/IRFSL17N20D
Static @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
V
(BR)DSS
∆V
(BR)DSS
R
DS(on)
V
GS(th)
I
DSS
I
GSS
Dynamic @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
g
fs
Q
g
Q
gs
Q
gd
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
C
oss
C
oss
C
eff. Effective Output Capacitance ––– 130 ––– VGS = 0V, VDS = 0V to 160V
oss
Avalanche Characteristics
E
AS
I
AR
E
AR
Thermal Resistance
R
θJC
R
θCS
R
θJA
R
θJA
Diode Characteristics
I
S
I
SM
V
SD
t
rr
Q
rr
t
on
2 www.irf.com
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage 200 ––– ––– V VGS = 0V, ID = 250µA
/∆T
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient
J
––– 0.25 ––– V/°C Reference to 25°C, ID = 1mA
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance ––– ––– 0.17 Ω VGS = 10V, ID = 9.8A
Gate Threshold Voltage 3.0 ––– 5.5 V VDS = VGS, ID = 250µA
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
––– ––– 25
––– ––– 250 VDS = 160V, VGS = 0V, TJ = 150°C
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage ––– ––– 10 0 VGS = 30V
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage ––– ––– -100
VDS = 200V, VGS = 0V
µA
nA
VGS = -30V
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
Forward Transconductance 5.3 ––– ––– S VDS = 50V, ID = 9.8A
Total Gate Charge ––– 33 50 ID = 9.8A
Gate-to-Source Charge ––– 8.4 13 nC VDS = 160V
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge ––– 16 24 VGS = 10V,
Turn-On Delay Time ––– 11 ––– VDD = 100V
Rise Time ––– 19 ––– ID = 9.8A
Turn-Off Delay Time ––– 18 ––– RG = 5.1Ω
ns
Fall Time ––– 6.6 ––– VGS = 10V
Input Capacitance ––– 1100 ––– VGS = 0V
Output Capacitance ––– 190 ––– VDS = 25V
Reverse Transfer Capacitance ––– 44 ––– pF ƒ = 1.0MHz
Output Capacitance ––– 1340 ––– VGS = 0V, VDS = 1.0V, ƒ = 1.0MHz
Output Capacitance ––– 76 ––– VGS = 0V, VDS = 160V, ƒ = 1.0MHz
Parameter Typ. Max. Units
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy ––– 240 mJ
Avalanche Current ––– 9.8 A
Repetitive Avalanche Energy ––– 14 mJ
Parameter Typ. Max. Units
Junction-to-Case ––– 1 .1
Case-to-Sink, Flat, Greased Surface 0.50 ––– °C/W
Junction-to-Ambient ––– 62
Junction-to-Ambient ––– 40
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
Continuous Source Current MOSFET symbol
(Body Diode)
Pulsed Source Current integral reverse
(Body Diode)
––– –––
––– –––
Diode Forward Voltage ––– ––– 1.3 V TJ = 25°C, IS = 9.8A, VGS = 0V
Reverse Recovery Time ––– 160 240 ns TJ = 25°C, IF = 9.8A
Reverse RecoveryCharge ––– 900 1350 nC di/dt = 100A/µs
Forward Turn-On Time Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by LS+LD)
64
16
showing the
A
p-n junction diode.
G
D
S
IRFB/IRFS/IRFSL17N20D
100
10
1
0.1
D
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
0.01
0.1 1 10 100
100
VGS
TOP
15V
12V
10V
8.0V
7.0V
6.0V
5.5V
BOTTOM
5.0V
5.0V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
T = 25 C
J
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
DS
°
100
10
D
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
1
0.1 1 10 100
VGS
TOP
15V
12V
10V
8.0V
7.0V
6.0V
5.5V
BOTTOM
5.0V
5.0V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
T = 175 C
J
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
DS
°
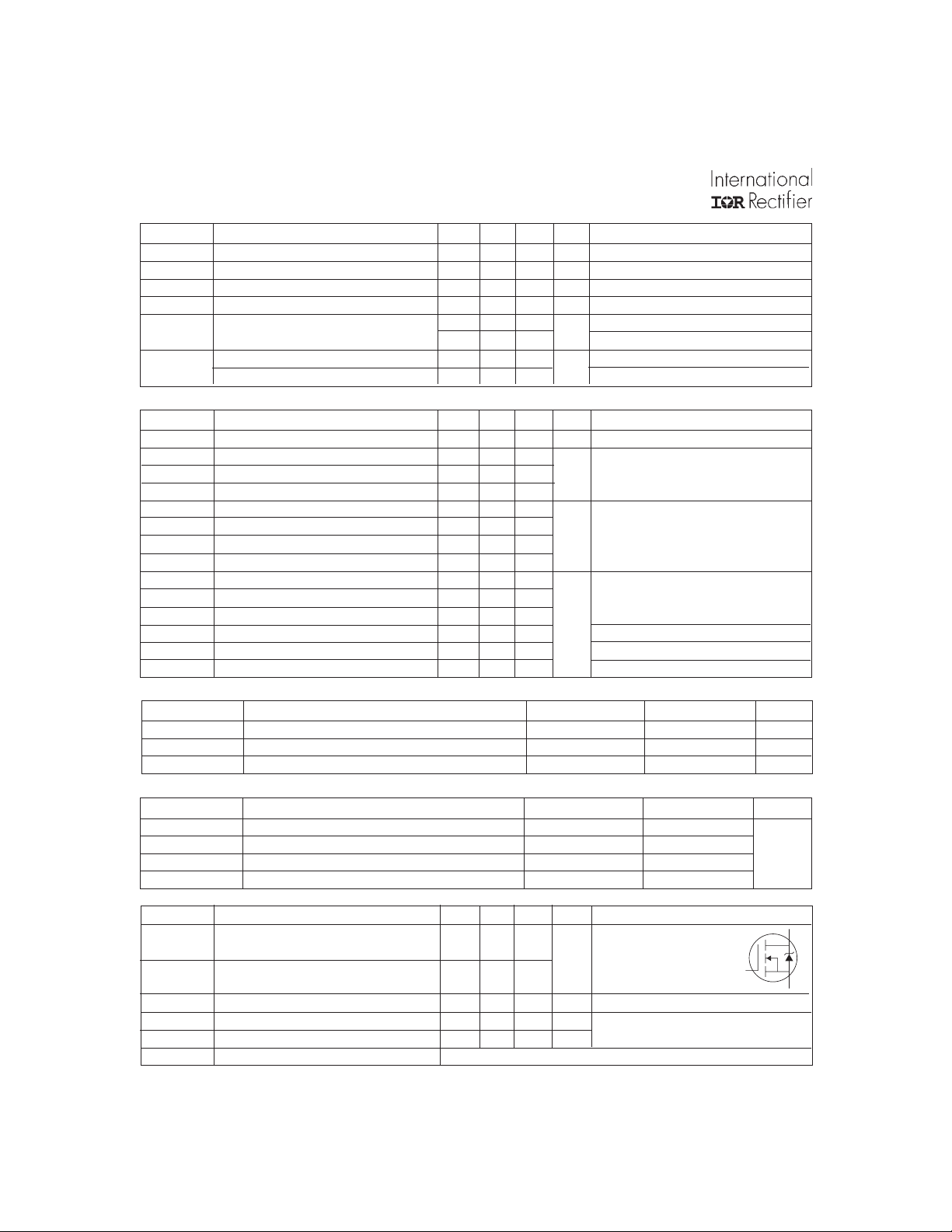
Fig 2. Typical Output CharacteristicsFig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
3.5
I =
D
16A
3.0
°
T = 175 C
J
10
°
T = 25 C
J
1
D
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
V = 50V
DS
0.1
5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0
V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
GS
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
2.5
2.0
1.5
(Normalized)
1.0
0.5
DS(on)
R , Drain-to-Source On Resistance
0.0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
T , Junction Temperature ( C)
J
Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance
V =
GS
°
10V
Vs. Temperature
www.irf.com 3
IRFB/IRFS/IRFSL17N20D
10000
1000
V
= 0V, f = 1 MHZ
GS
C
= C
iss
gs
C
= C
rss
gd
C
= C
oss
ds
Ciss
+ Cgd, C
+ C
gd
ds
Coss
100
C, Capacitance (pF)
Crss
10
1 10 100 1000
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
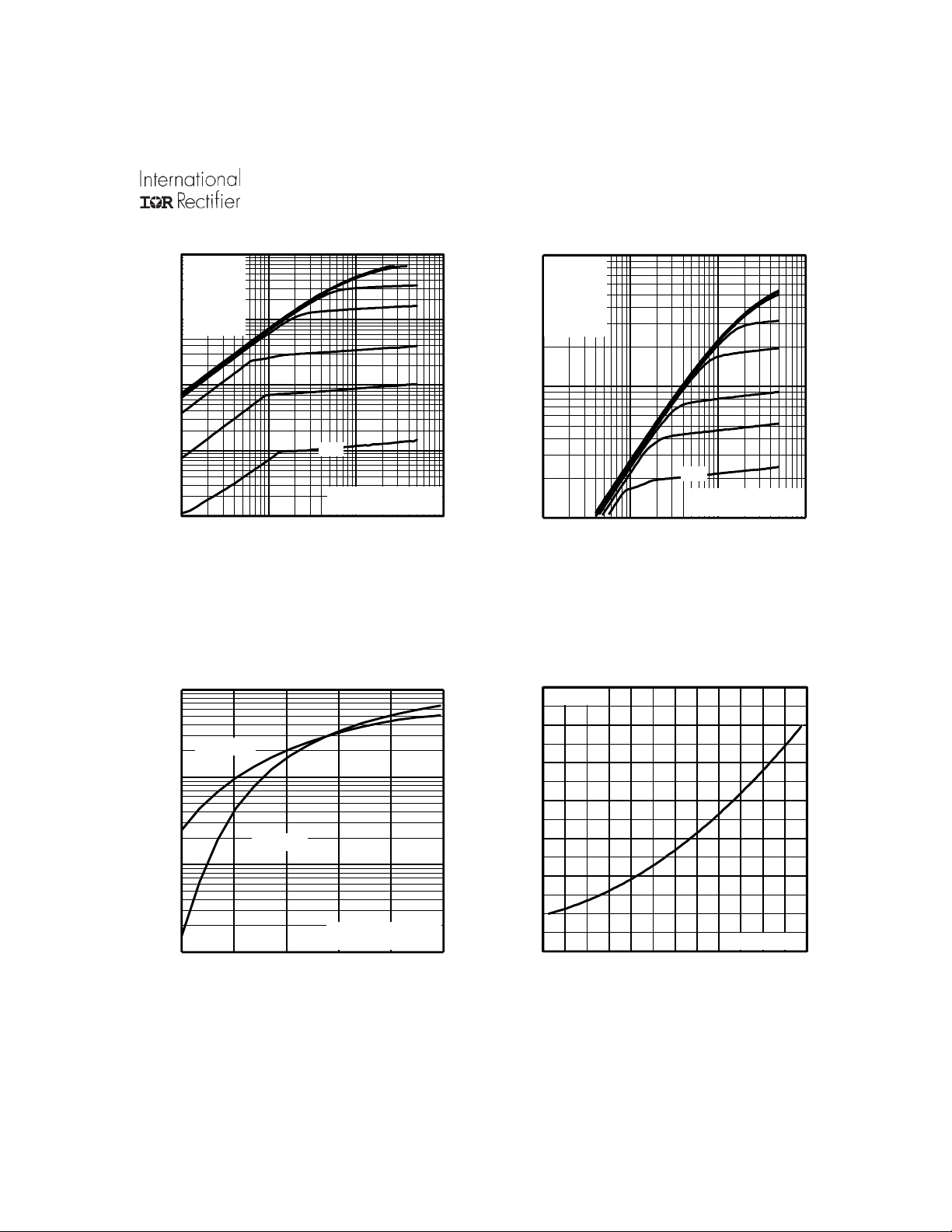
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance Vs.
Drain-to-Source Voltage
100
°
T = 175 C
J
10
SHORTED
20
I =
9.8A
D
16
12
8
4
GS
V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
V = 160V
DS
V = 100V
DS
V = 40V
DS
FOR TEST CIRCUIT
0
0 10 20 30 40 50
Q , Total Gate Charge (nC)
G
SEE FIGURE
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
1000
OPERATION IN THIS AREA LIMITED
100
BY R
DS(on)
13
10us
100us
1ms
10ms
°
T = 25 C
J
1
SD
I , Reverse Drain Current (A)
V = 0 V
0.1
0.2 0.5 0.8 1.1 1.4
V ,Source-to-Drain Voltage (V)
SD
GS
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
10
D
I , Drain Current (A)I , Drain Current (A)
1
°
= 25 C
C
T T= 175 C
Single Pulse
0.1
1 10 100 1000
°
J
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
DS
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Forward Voltage
4 www.irf.com
 Loading...
Loading...