International Rectifier IRFSL4710, IRFS4710, IRFB4710 Datasheet
PD- 94080
IRFB4710
IRFS4710
IRFSL4710
HEXFET® Power MOSFET
Applications
l High frequency DC-DC converters
l Motor Control
l Uninterrutible Power Supplies
V
DSS
R
DS(on)
max I
100V 0.014Ω 75A
Benefits
l Low Gate-to-Drain Charge to Reduce
Switching Losses
l Fully Characterized Capacitance Including
Effective C
App. Note AN1001)
l Fully Characterized Avalanche Voltage
and Current
to Simplify Design, (See
OSS
TO-220AB
IRFB4710
D2Pak
IRFS4710
TO-262
IRFSL4710
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Max. Units
ID @ TC = 25°C Continuous Drain Current, VGS @ 10V 75
ID @ TC = 100°C Continuous Drain Current, VGS @ 10V 53 A
I
DM
PD @TA = 25°C Power Dissipation 3.8 W
PD @TC = 25°C Power Dissipation 200
V
GS
dv/dt Peak Diode Recovery dv/dt 8.2 V/ns
T
J
T
STG
Pulsed Drain Current 300
Linear Derating Factor 1.4 W/°C
Gate-to-Source Voltage ± 20 V
Operating Junction and -55 to + 175
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds 300 (1.6mm from case )
Mounting torqe, 6-32 or M3 screw 10 lbf•in (1.1N•m)
D
°C
Thermal Resistance
Parameter Typ. Max. Units
R
θJC
R
θCS
R
θJA
R
θJA
Notes through are on page 11
Junction-to-Case ––– 0.74
Case-to-Sink, Flat, Greased Surface 0.50 ––– °C/W
Junction-to-Ambient ––– 62
Junction-to-Ambient ––– 40
www.irf.com 1
3/16/01
IRFB/IRFS/IRFL4710
Static @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
V
(BR)DSS
∆V
(BR)DSS
R
DS(on)
V
GS(th)
I
DSS
I
GSS
Dynamic @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
g
fs
Q
g
Q
gs
Q
gd
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
C
oss
C
oss
C
eff. Effective Output Capacitance ––– 430 ––– VGS = 0V, VDS = 0V to 80V
oss
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage 100 –– – ––– V VGS = 0V, ID = 250µA
/∆T
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient
J
––– 0.11 ––– V/°C Reference to 25°C, ID = 1mA
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance ––– 0.011 0.014 Ω VGS = 10V, ID = 45A
Gate Threshold Voltage 3.5 –– – 5.5 V VDS = VGS, ID = 250µA
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
––– ––– 1.0
––– ––– 250 VDS = 80V, VGS = 0V, TJ = 150°C
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage ––– ––– 100 VGS = 20V
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage ––– ––– -100
VDS = 95V, VGS = 0V
µA
nA
VGS = -20V
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
Forward Transconductance 35 ––– ––– S VDS = 50V, ID = 45A
Total Gate Charge ––– 110 170 ID = 45A
Gate-to-Source Charge ––– 43 ––– nC VDS = 50V
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge ––– 40 ––– VGS = 10V,
Turn-On Delay Time ––– 35 –– – VDD = 50V
Rise Time ––– 130 ––– ID = 45A
Turn-Off Delay Time ––– 41 ––– RG = 4.5Ω
ns
Fall Time ––– 38 ––– VGS = 10V
Input Capacitance ––– 6160 ––– VGS = 0V
Output Capacitance ––– 440 ––– VDS = 25V
Reverse Transfer Capacitance ––– 250 ––– pF ƒ = 1.0MHz
Output Capacitance ––– 1580 ––– VGS = 0V, VDS = 1.0V, ƒ = 1.0MHz
Output Capacitance ––– 280 ––– VGS = 0V, VDS = 80V, ƒ = 1.0MHz
Avalanche Characteristics
Parameter Typ. Max. Units
E
AS
I
AR
E
AR
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy ––– 190 mJ
Avalanche Current ––– 45 A
Repetitive Avalanche Energy ––– 20 mJ
Diode Characteristics
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units Conditions
I
S
I
SM
V
SD
t
rr
Q
rr
t
on
Continuous Source Current MOSFET symbol
(Body Diode)
Pulsed Source Current integral reverse
(Body Diode)
––– –––
––– –––
75
300
showing the
A
p-n junction diode.
G
Diode Forward Voltage ––– ––– 1.3 V TJ = 25°C, IS = 45A, VGS = 0V
Reverse Recovery Time ––– 74 110 n s TJ = 25°C, IF = 45A
Reverse RecoveryCharge ––– 180 260 nC di/dt = 100A/µs
Forward Turn-On Time Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by LS+LD)
2 www.irf.com
D
S
IRFB/IRFS/IRFL4710
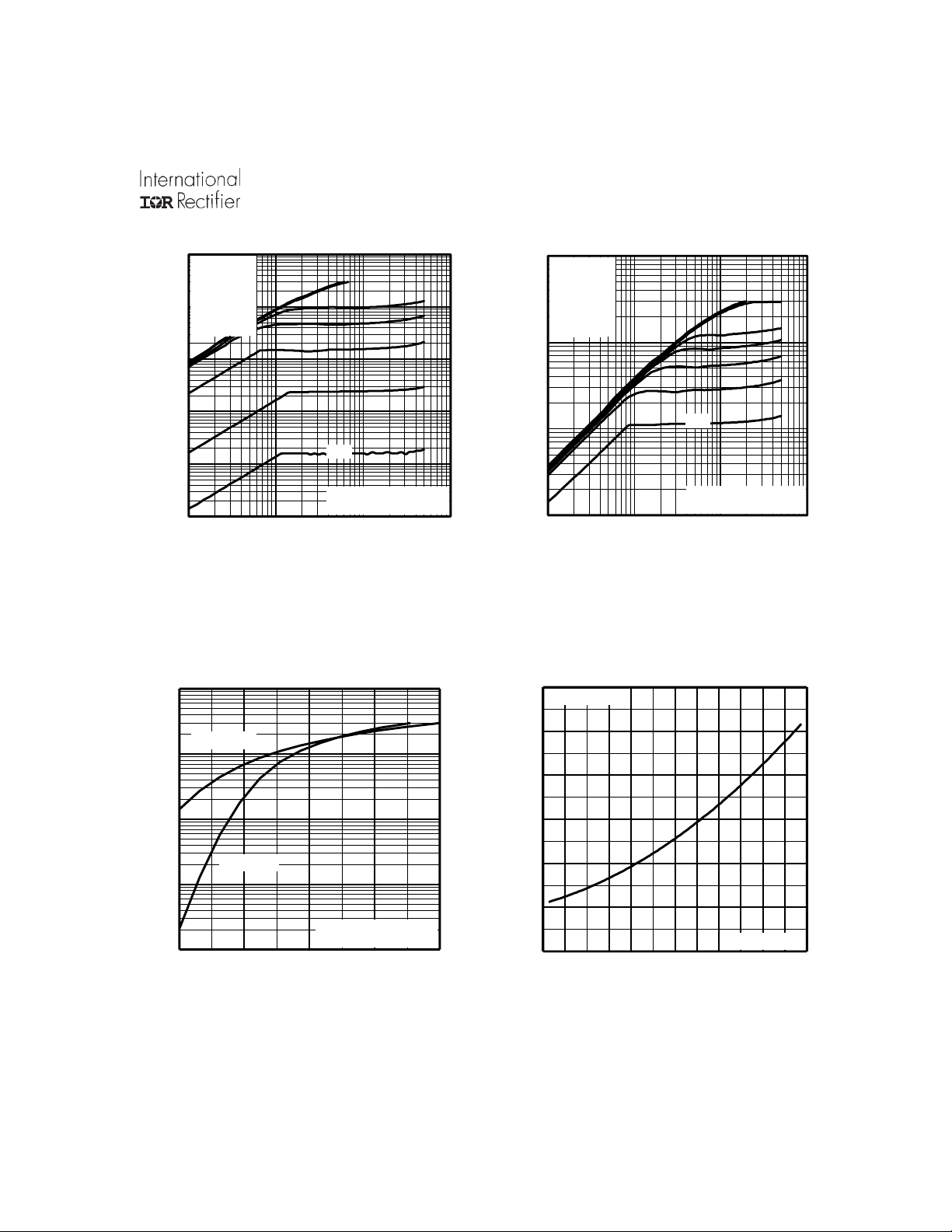
1000
100
10
1
0.1
D
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
0.01
0.1 1 10 100
1000
VGS
TOP
15V
12V
10V
8.0V
7.5V
7.0V
6.5V
BOTTOM
6.0V
6.0V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
T = 25 C
J
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
DS
1000
100
10
D
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
°
1
0.1 1 10 100
VGS
TOP
15V
12V
10V
8.0V
7.5V
7.0V
6.5V
BOTTOM
6.0V
6.0V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
T = 175 C
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
DS
°
J
Fig 2. Typical Output CharacteristicsFig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
3.0
75A
I =
D
°
T = 175 C
100
D
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
J
10
°
T = 25 C
J
1
V = 50V
DS
0.1
6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0
V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
GS
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
2.5
2.0
1.5
(Normalized)
1.0
0.5
DS(on)
R , Drain-to-Source On Resistance
0.0
-60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
T , Junction Temperature ( C)
J
Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance
V =
10V
GS
°
Vs. Temperature
www.irf.com 3
IRFB/IRFS/IRFL4710
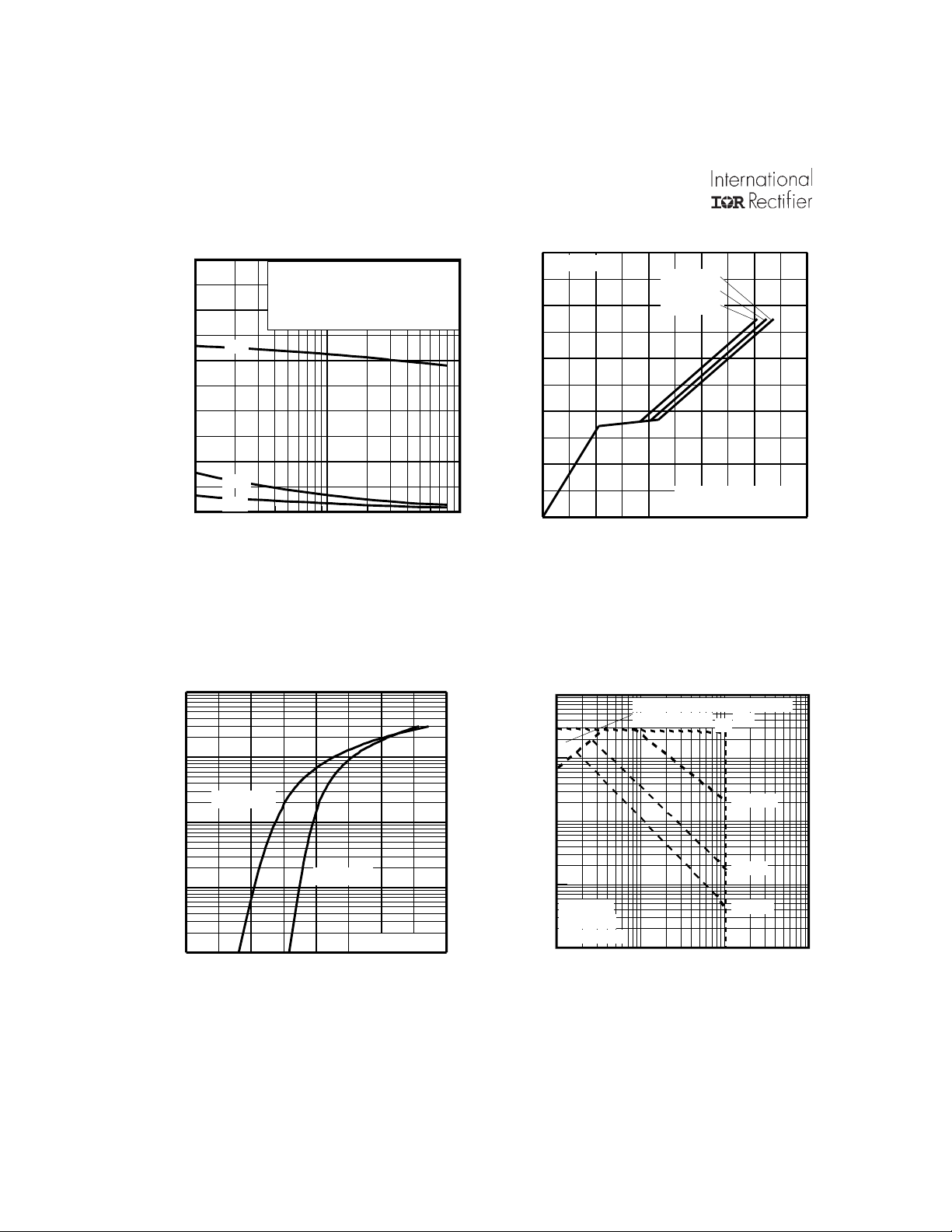
10000
8000
6000
4000
C, Capacitance(pF)
2000
0
Ciss
Coss
Crss
1 10 100
V
= 0V, f = 1 MHZ
GS
C
= C
= C
= C
+ Cgd, C
gs
gd
+ C
ds
gd
iss
C
rss
C
oss
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance Vs.
Drain-to-Source Voltage
1000
SHORTED
ds
20
I =
45A
D
16
12
8
4
GS
V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
0
0 40 80 120 160 200
Q , Total Gate Charge (nC)
G
V = 80V
DS
V = 50V
DS
V = 20V
DS
FOR TEST CIRCUIT
SEE FIGURE
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
1000
OPERATION IN THIS AREA
LIMITED BY RDS(on)
13
100
°
T = 175 C
J
10
°
T = 25 C
1
SD
I , Reverse Drain Current (A)
0.1
0.0 0.4 0.8 1.2 1.6
V ,Source-to-Drain Voltage (V)
SD
J
V = 0 V
GS
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
100
100µsec
10
1msec
1
, Drain-to-Source Current (A)
D
I
Tc = 25°C
Tj = 175°C
Single Pulse
0.1
1 10 100 1000
V
, Drain-toSource Voltage (V)
DS
10msec
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Forward Voltage
4 www.irf.com
 Loading...
Loading...