International Rectifier IRF7805, IRF7805A Datasheet
PD – 91746C
IRF7805/IRF7805A
HEXFET® Chip-Set for DC-DC Converters
• N Channel Application Specific MOSFETs
• Ideal for Mobile DC-DC Converters
• Low Conduction Losses
• Low Switching Losses
Description
These new devices employ advanced HEXFET Power
MOSFET technology to achieve an unprecedented
balance of on-resistance and gate charge. The
SO-8
S
S
S
1
2
3
4
Top View
reduced conduction and switching losses make them
ideal for high efficiency DC-DC Converters that power
the latest generation of mobile microprocessors.
Device Features
IRF7805 IRF7805A
The IRF7805/IRF7805A offers maximum efficiency for
mobile CPU core DC-DC converters.
Vds 30V 30V
Rds(on) 11mΩ 11mΩ
Qg 31nC 31nC
Qsw 11.5nC
Qoss 36nC 36nC
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol IRF7805 IRF7805A Units
Drain-Source V oltage V
Gate-Source Voltage V
Continuous Drain or Source 25°C I
Current (V
≥ 4.5V) 70°C 10 1 0
GS
Pulsed Drain Current I
Power Dissipation 25°C P
DS
GS
D
DM
D
13 13 A
100 100
30 V
±12
2.5 W
70°C 1.6
Junction & Storage Temperature Range TJ, T
Continuous Source Current (Body Diode) I
Pulsed source Current I
STG
S
SM
–55 to 150 °C
2.5 2.5 A
106 106
A
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
DG
Thermal Resistance
Parameter Max. Units
Maximum Junction-to-Ambient R
θJA
50 °C/W
www.irf.com 1
10/10/00
IRF7805/IRF7805A
Electrical Characteristics
IRF7805 IRF7805A
Parameter Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Drain-to-Source V
Breakdown Voltage*
Static Drain-Source R
on Resistance*
Gate Threshold Voltage* V
Drain-Source Leakage I
Current*
(BR)DSS
DS
GS
DSS
30 – – 30 – – V VGS = 0V, ID = 250µA
(on) 9. 2 11 9.2 11 mΩ VGS = 4.5V, ID = 7A
(th) 1.0 1.0 V VDS = VGS,ID = 250µA
30 30 µA VDS = 24V, VGS = 0
150 150 V
= 24V, VGS = 0,
DS
Tj = 100°C
Gate-Source Leakage I
GSS
±100 ±100 nA VGS = ±12V
Current*
T otal Gate Charge* Q
Pre-Vth Q
Gate-Source Charge
Post-Vth Q
Gate-Source Charge
Gate to Drain Charge Q
Switch Charge* Q
(Q
+ Qgd)
gs2
Output Charge* Q
Gate Resistance R
T urn-on Delay Time t
Rise Time t
T urn-off Delay Time t
Fall Time t
g
gs1
gs2
gd
SW
oss
g
(on) 16 16 VDD = 16V
d
r
(off) 38 38 Rg = 2Ω
d
f
22 31 22 31 VGS = 5V, ID = 7A
3.7 3.7 VDS = 16V, ID = 7A
1.4 1.4 nC
6.8 6.8
8.2 11.5 8.2
30 36 30 36 VDS = 16V, VGS = 0
1.7 1.7 Ω
20 20 ns ID = 7A
16 16 VGS = 4.5V
Resistive Load
Source-Drain Rating & Characteristics
Parameter Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units Conditions
Diode Forward V
Voltage*
Reverse Recovery Q
Charge VDS = 16V, VGS = 0V, IS = 7A
Reverse Recovery Q
Charge (with Parallel
SD
rr
rr(s)
Schotkky)
1.2 1.2 V IS = 7A, VGS = 0V
88 88 nC di/dt = 700A/µs
55 55
di/dt = 700A/µs
(with 10BQ040)
VDS = 16V, VGS = 0V, IS = 7A
Notes:
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by max. junction temperature.
Pulse width ≤ 300 µs; duty cycle ≤ 2%.
When mounted on 1 inch square copper board, t < 10 sec.
Measured at V
Typ = measured - Q
* Devices are 100% tested to these parameters.
< 100mV. This approximates actual operation of a synchronous rectifier.
DS
oss
www.irf.com2
)
Power MOSFET Selection for DC/DC
Converters
Control FET
Special attention has been given to the power losses
in the switching elements of the circuit - Q1 and Q2.
Pow er losses in the high side switch Q1, also called the
Control FET , are impacted by the R
but these conduction losses are only about one half of
the total losses.
of the MOSFET ,
ds(on)
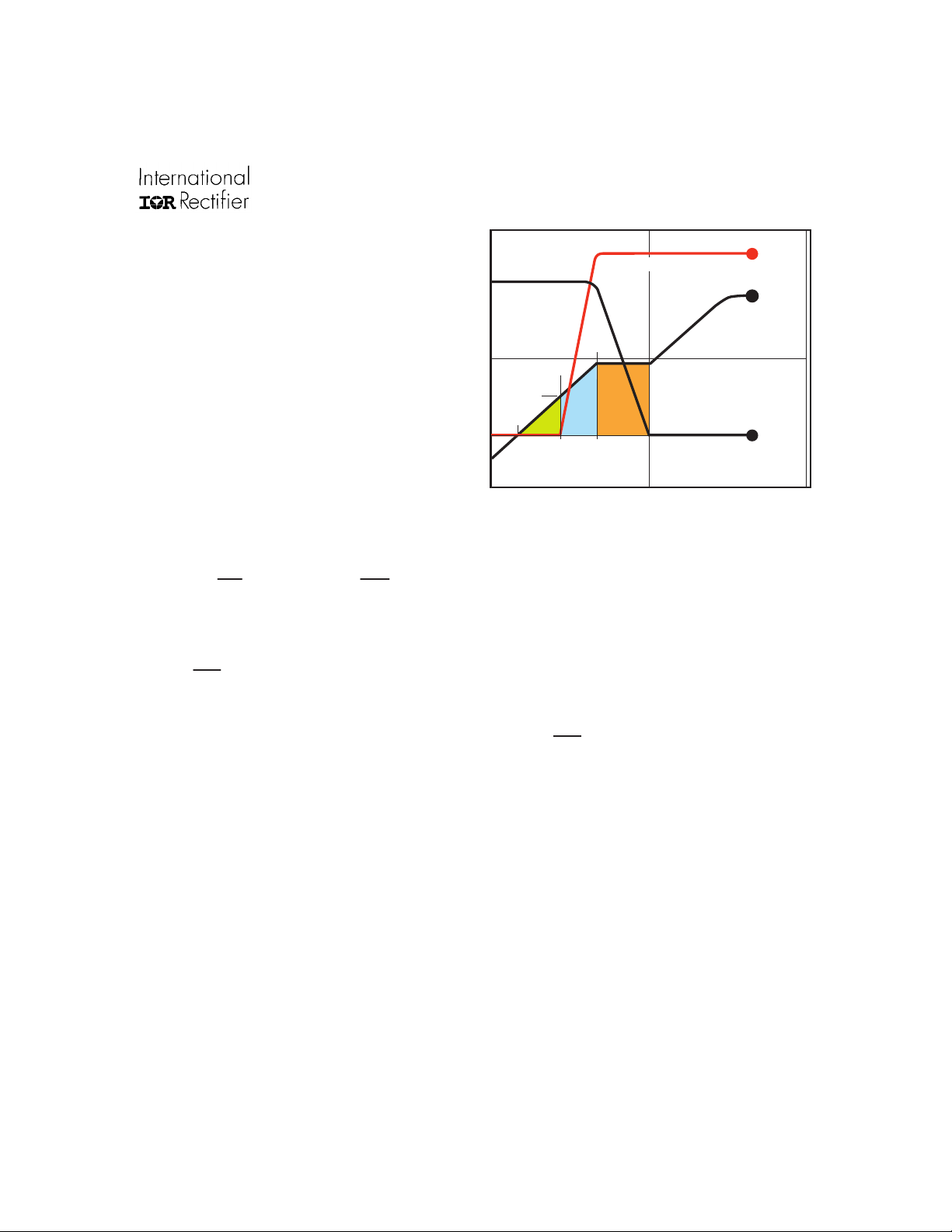
IRF7805/IRF7805A
Drain Current
Gate V oltage
t2
t3
t1
V
GTH
4
1
Pow er losses in the control s witch Q1 are given b y;
P
= P
loss
This can be expanded and approximated by;
P
loss
conduction
I
=
()
rms
+I
+Q
()
g
Q
+
This simplified loss equation includes the terms Q
and Q
that is included in all MOSFET data sheets. The importance of splitting this gate-source charge into two sub
elements, Q
the gate driver between the time that the threshold voltage has been reached (t1) and the time the drain current rises to I
begins to change. Minimizing Q
reducing switching losses in Q1.
capacitance of the MOSFET during every switching
cycle. Figure 2 shows how Q
lel combination of the voltage dependant (non-linear)
capacitance’s Cds and Cdg when multiplied by the power
supply input buss voltage.
which are new to P ower MOSFET data sheets.
oss
Q
is a sub element of traditional gate-source charge
gs2
Q
indicates the charge that must be supplied by
gs2
Q
is the charge that must be supplied to the output
oss
+ P
2
R
×
ds(on)
Q
gd
×
×
oss
2
V
×
in
i
g
V
f
×
g
V
×
×
in
and Q
gs1
gs2
(t2) at which time the drain voltage
dmax
+ P
switching
f
×
+I×
f
, can be seen from Fig 1.
oss
+ P
drive
Q
gs2
i
g
is a critical factor in
gs2
is formed by the paral-
output
×
V
f
×
in
gs2
t0
2
*
P
+
output
f
+
(
Drain V oltage
Q
V
×
rr
×
in
GS1QGS2QGD
Q
Figure 1: Typical MOSFET switching wavef orm
Synchronous FET
The power loss equation for Q2 is approximated
by;
P
P
=
loss
conduction
2
I
=
rms
()
()
g
Q
oss
+
2
P
loss
+Q
*dissipated primarily in Q1.
P
+
drive
R
×
ds(on)
V
×
f
×
g
V
×
×
in
f
www.irf.com 3
 Loading...
Loading...