
PD - 96283
IRF7759L2TRPbF
IRF7759L2TR1PbF
l RoHS Compliant, Halogen Free
l Lead-Free (Qualified up to 260°C Reflow)
l Ideal for High Performance Isolated Converter
Primary Switch Socket
l Optimized for Synchronous Rectification
l Low Conduction Losses
l High Cdv/dt Immunity
DirectFET Power MOSFET
Typical values (unless otherwise specified)
V
DSS
75V min ±20V max
Q
g tot
200nC 62nC 3.0V
V
Q
GS
gd
R
DS(on)
1.8mΩ@ 10V
V
gs(th)
l Low Profile (<0.7mm)
l Dual Sided Cooling Compatible
l Compatible with existing Surface Mount Techniques
l Industrial Qualified
Applicable DirectFET Outline and Substrate Outline
D
G
S
S
S
S S
L8
S
S
D
S
DirectFET ISOMETRIC
SB SC M2 M4 L4 L6 L8
Description
The IRF7759L2TR/TR1PbF combines the latest HEXFET® Power MOSFET Silicon technology with the advanced DirectFETTM packaging to
achieve the lowest on-state resistance in a package that has a footprint smaller than a D2PAK and only 0.7 mm profile. The DirectFET package
is compatible with existing layout geometries used in power applications, PCB assembly equipment and vapor phase, infra-red or convection
soldering techniques, when application note AN-1035 is followed regarding the manufacturing methods and processes. The DirectFET package
allows dual sided cooling to maximize thermal transfer in power systems.
The IRF7759L2TR/TR1PbF is optimized for high frequency switching and synchronous rectification applications. The reduced total losses
in the device coupled with the high level of thermal performance enables high efficiency and low temperatures, which are key for system
reliability improvements, and makes this device ideal for high performance power converters.
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Units
V
DS
V
GS
I
@ TC = 25°C
D
ID @ TC = 100°C
ID @ TA = 25°C
ID @ TC = 25°C
I
DM
E
AS
I
AR
)
8
Ω
m
(
e
c
n
a
t
s
6
i
s
e
R
n
O
e
c
4
r
u
o
S
o
t
n
i
a
2
r
D
,
)
n
o
(
S
D
0
R
Fig 1. Typical On-Resistance vs. Gate Voltage
Notes:
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
Drain-to-Source Voltage
Gate-to-Source Voltage
Continuous Drain Current, V
Continuous Drain Current, V
Continuous Drain Current, V
Continuous Drain Current, V
Pulsed Drain Current
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
Avalanche Current
V
Gate -to -Source Voltage (V)
GS,
g
TJ = 125°C
TJ = 25°C
g
ID = 96A
@ 10V
GS
@ 10V
GS
@ 10V
GS
@ 10V
GS
h
Click on this section to link to the appropriate technical paper.
Click on this section to link to the DirectFET Website.
Surface mounted on 1 in. square Cu board, steady state.
(Silicon Limited)
(Silicon Limited)
(Silicon Limited)
(Package Limited)
T
f
f
e
C
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by max. junction temperature.
Starting T
f
1.95
)
Ω
m
(
R
l
a
c
i
p
y
T
TA= 25°C
1.85
)
n
o
(
S
D
1.75
1.65
15 30 45 60 75 90 105
Fig 2. Typical On-Resistance vs. Drain Current
measured with thermocouple mounted to top (Drain) of part.
= 25°C, L = 0.056mH, RG = 25Ω, I
J
Max.
75
±20
160
113
26
375
640
257
96
VGS = 7.0V
VGS = 8.0V
VGS = 10V
VGS = 15V
ID, Drain Current (A)
AS
V
A
mJ
A
= 96A.
www.irf.com 1
11/16/09

IRF7759L2TR/TR1PbF
Static @ TJ = 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units
BV
DSS
V
/∆T
∆Β
DSS
R
DS(on)
V
GS(th)
∆V
/∆T
GS(th)
I
DSS
I
GSS
gfs Forward Transconductance 74 ––– ––– S
Q
g
Q
gs1
Q
gs2
Q
gd
Q
godr
Q
sw
Q
oss
R
G
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
C
oss
C
oss
Diode Characteristics
I
S
I
SM
V
SD
t
rr
Q
rr
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage 75 ––– ––– V
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient ––– 0.02 ––– V/°C
J
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance ––– 1.8 2.3
Gate Threshold Voltage 2.0 3.0 4.0 V
Gate Threshold Voltage Coefficient ––– -11 ––– mV/°C
J
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current ––– ––– 20
––– ––– 250
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage ––– ––– 100
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage ––– ––– -100
Total Gate Charge ––– 200 300
Pre-Vth Gate-to-Source Charge ––– 37 –––
Post-Vth Gate-to-Source Charge ––– 11 –––
Gate-to-Drain Charge ––– 62 93
Gate Charge Overdrive ––– 91 ––– See Fig. 9
Switch Charge (Q
gs2
+ Qgd)
––– 73 –––
Output Charge ––– 60 ––– nC
Gate Resistance ––– 1.1 ––– Ω
Turn-On Delay Time ––– 18 –––
Rise Time ––– 37 –––
Turn-Off Delay Time ––– 80 –––
Fall Time ––– 33 –––
Input Capacitance ––– 12222 –––
Output Capacitance ––– 1465 –––
Reverse Transfer Capacitance ––– 609 –––
Output Capacitance ––– 7457 –––
Output Capacitance ––– 955 –––
Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Units
Continuous Source Current
(Body Diode)
Pulsed Source Current
(Body Diode)
g
Diode Forward Voltage ––– ––– 1.3 V
Reverse Recovery Time ––– 64 96 ns
Reverse Recovery Charge ––– 150 225 nC
––– ––– 160
––– ––– 640
Conditions
VGS = 0V, ID = 250µA
Reference to 25°C, I
V
mΩ
µA
nA
nC
ns
= 10V, ID = 96A
GS
= VGS, ID = 250µA
V
DS
= 75V, VGS = 0V
V
DS
VDS = 60V, VGS = 0V, TJ = 125°C
VGS = 20V
V
= -20V
GS
V
= 25V, ID = 96A
DS
V
= 38V
DS
= 10V
V
GS
I
= 96A
D
= 16V, VGS = 0V
V
DS
V
= 38V, VGS = 10V
DD
I
= 96A
D
R
=1.8Ω
G
= 0V
V
GS
VDS = 25V
pF
ƒ = 1.0MHz
= 0V, VDS = 1.0V, f=1.0MHz
V
GS
VGS = 0V, VDS = 60V, f=1.0MHz
Conditions
MOSFET symbol
showing the
A
integral reverse
p-n junction diode.
= 25°C, IS = 96A, VGS = 0V
T
J
TJ = 25°C, IF = 96A, VDD = 38V
di/dt = 100A/µs
i
= 2mA
D
i
i
i
Notes:
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by max. junction temperature.
Pulse width ≤ 400µs; duty cycle ≤ 2%.
2 www.irf.com

τ
Absolute Maximum Ratings
PD @TC = 25°C
PD @TC = 100°C Power Dissipation
PD @TA = 25°C
T
P
T
J
T
STG
Power Dissipation
Power Dissipation
Peak Soldering Temperature
Operating Junction and
Storage Temperature Range
Thermal Resistance
R
R
R
R
R
θJA
θJA
θJA
θJ-Can
θJ-PCB
10
W
/
1
C
°
)
C
J
h
t
0.1
Z
(
e
s
n
o
p
0.01
s
e
R
l
a
m
r
e
0.001
h
T
0.0001
1E-006 1E-005 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1
Junction-to-Ambient
Junction-to-Ambient
Junction-to-Ambient
Junction-to-Can
fl
Junction-to-PCB Mounted ––– 0.5
D = 0.50
0.20
0.10
0.05
0.02
0.01
SINGLE PULSE
( THERMAL RESPONSE )
IRF7759L2TR/TR1PbF
Parameter Units
f
f
c
Parameter Typ. Max. Units
e
j
k
R
R
1
2
R
R
1
τ
J
τ
J
τ
1
τ
1
Ci= τi/Ri
2
τ
2
τ
2
t1 , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
––– 45
12.5 –––
––– 1.2
R
R
3
R
3
τ
τ
3
4
τ
3
Max.
125
63
3.3
270
-55 to + 175
20 ––– °C/W
Ri (°C/W) τi (sec)
4
R
4
0.10804 0.000171
τ
C
0.61403 0.053914
τ
4
0.45202 0.006099
0.00001 0.036168
Notes:
1. Duty Factor D = t1/t2
2. Peak Tj = P dm x Zthjc + Tc
W
°C
Fig 3. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case
Notes:
Surface mounted on 1 in. square Cu board, steady state.
T
measured with thermocouple incontact with top (Drain) of part.
C
Used double sided cooling, mounting pad with large heatsink.
Surface mounted on 1 in. square Cu
board (still air).
www.irf.com 3
Mounted on minimum footprint full size board with metalized
back and with small clip heatsink. (still air)
Mounted on minimum footprint full size board with metalized
back and with small clip heatsink.
R
is measured at T
θ
of approximately 90°C.
J
IRF7759L2TR/TR1PbF
1000
TOP 15V
)
100
A
(
t
n
e
r
r
u
10
C
e
c
r
u
o
S
-
1
o
t
n
i
a
r
D
,
0.1
D
I
60µs
≤
3.75V
PULSE WIDTH
BOTTOM 3.75V
Tj = 25°C
0.01
0.1 1 10 100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
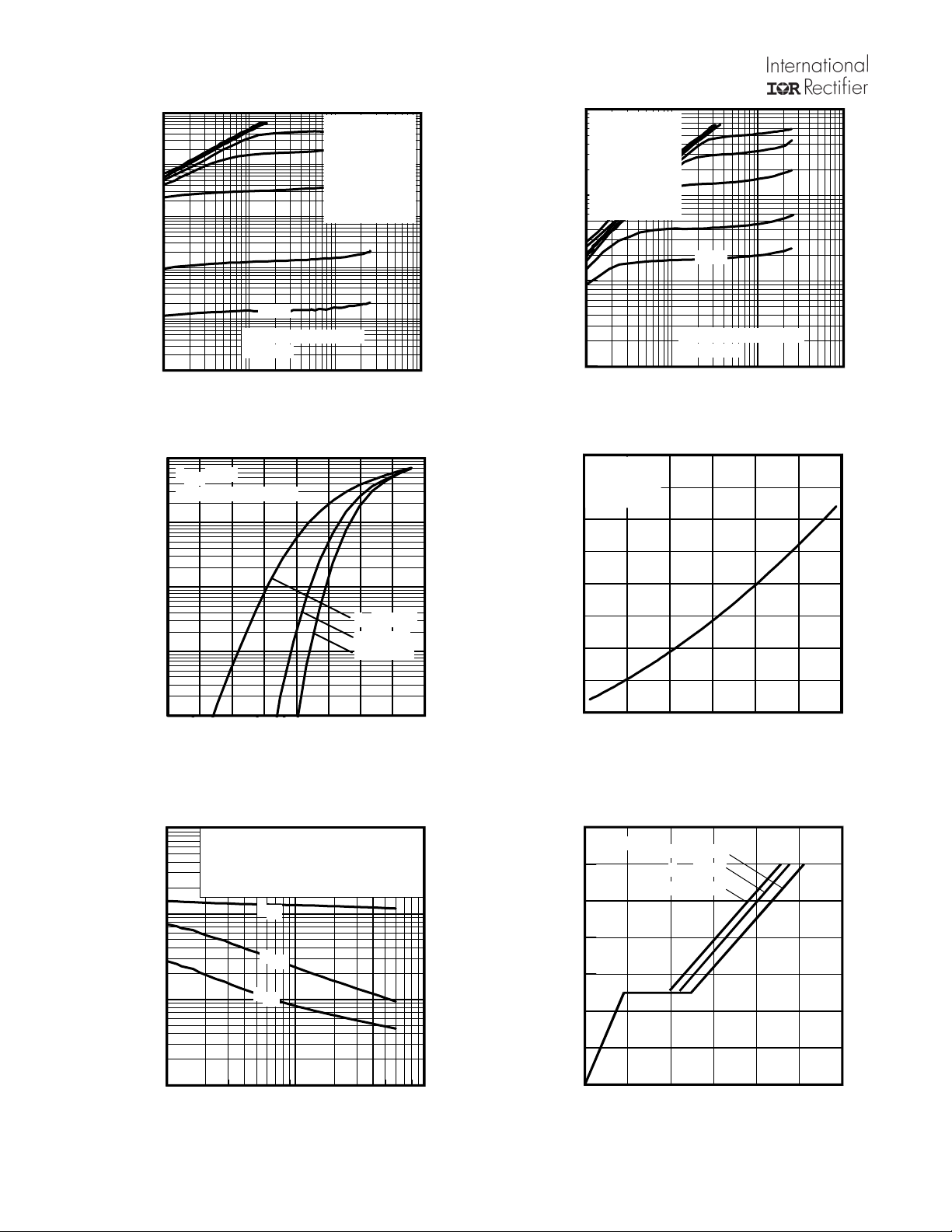
Fig 4. Typical Output Characteristics
1000
V
= 25V
DS
≤
)
A
(
t
100
n
e
r
r
u
C
e
c
r
u
o
S
o
t
n
i
a
r
D
,
D
I
60µs PULSE WIDTH
10
1
TJ = 175°C
TJ = 25°C
TJ = -40°C
0.1
2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5 6
VGS, Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
Fig 6. Typical Transfer Characteristics
VGS
10V
7.00V
5.50V
5.00V
4.50V
4.00V
1000
VGS
10V
7.00V
5.50V
5.00V
4.50V
4.00V
60µs
≤
3.75V
PULSE WIDTH
)
A
(
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
e
c
r
u
o
S
o
t
n
i
a
r
D
,
I
TOP 15V
100
BOTTOM 3.75V
10
D
Tj = 175°C
1
0.1 1 10 100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
Fig 5. Typical Output Characteristics
2.5
e
c
n
a
t
s
i
s
e
R
n
O
e
c
r
u
o
S
o
t
n
i
a
r
D
,
)
n
o
(
S
D
R
ID = 96A
V
= 10V
GS
2.0
)
d
e
z
i
l
1.5
a
m
r
o
N
(
1.0
0.5
-60 -20 20 60 100 140 180
TJ , Junction Temperature (°C)
Fig 7. Normalized On-Resistance vs. Temperature
100000
)
F
10000
p
(
e
c
n
a
t
i
c
a
p
a
C
1000
,
C
V
= 0V, f = 1 MHZ
GS
C
= C
iss
rss
oss
= C
= C
gs
gd
ds
C
C
C
C
C
+ Cgd, C
+ C
iss
oss
rss
SHORTED
ds
gd
100
1 10 100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
Fig 8. Typical Capacitance vs.Drain-to-Source Voltage
14
ID= 96A
12
)
V
(
e
g
10
a
t
l
o
V
e
8
c
r
u
o
S
-
6
o
t
e
t
a
4
G
,
S
G
V
2
VDS= 60V
VDS= 38V
VDS= 15V
0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300
QG, Total Gate Charge (nC)
Fig 9. Typical Total Gate Charge vs
Gate-to-Source Voltage
4 www.irf.com
 Loading...
Loading...