Intermax SVF1-400 Instruction Manual

Variable Frequency Welding
Controller
SVF1-400
Instruction Manual
Intermax, Co.
(630) 717-8610
1365 Middleburg Rd.
Naperville Il, 60540
http://www.intermax.com.tw
intermax@dpliv.net
!
Ver. 5.5

Table of Contents
I. Introduction 1
II. Variable Frequency Controller 1
1. Variable Frequency vs. Normal Frequency Controller Comparison 2
III. Welding Controller Configuration 3
1. Main features: 4
2. Technical parameters: 4
IV. Operation Description 4
1. Spot Welding 4
2. Repeated Spot Welding 5
3. Seam Welding Mode 5
V. Stepper Function 6
VI. Electric Current Monitoring 8
VII.Programmable Welding Pressure 10
VIII.Programming Console Manual 10
1. Programming Console Screen 10
2. Programming Console 11
3. Modes 12
4. “Programming”, “Test”, and “Weld” Mode Parameter List 12
5. “Monitor” Mode Parameters List 14
IX. DIP Switch Configuration 14
1. S1, S4, S5, S6, S7, S8 14
2. Programmable Pressure Control Combinations (S2, S3) 15
X. Error Messages and Troubleshooting 15
XI. Fig.1 Motherboard Terminal Wiring Diagram 16
XII.Fig. 2 System Wiring Diagram 17
!

XIII.Fig. 3 Schedule Selection 17
!
I. Introduction
Inverter Welding Controller Advantages
The output for the middle frequency inverter is direct-current waveform. This results
in more straightforward control of the welding process, shorter welding time, and
more consistent welding quality. The welding controller power source frequency is 1
kHz, as opposed to the traditional 50 Hz power source, which allows for much more
precise heat control.
Inverter output voltage Corresponding Output welding current
Compared to traditional welding controllers, the middle frequency inverter has the
following advantages:
1. The welding current is DC, therefore the welding current is less influenced by
inductance from the secondary circuit.
2. Smaller welding transformer is required
3. Increased electrode life cycle
4. Thinner materials, three-layer materials, and materials such as aluminum and
zinc-plated metal can be welded with good results
5. Precision welding
6. Minimized explosions
7. Spot weld quality improves greatly due to better electric current control
II. Variable Frequency Controller
Page 1
1
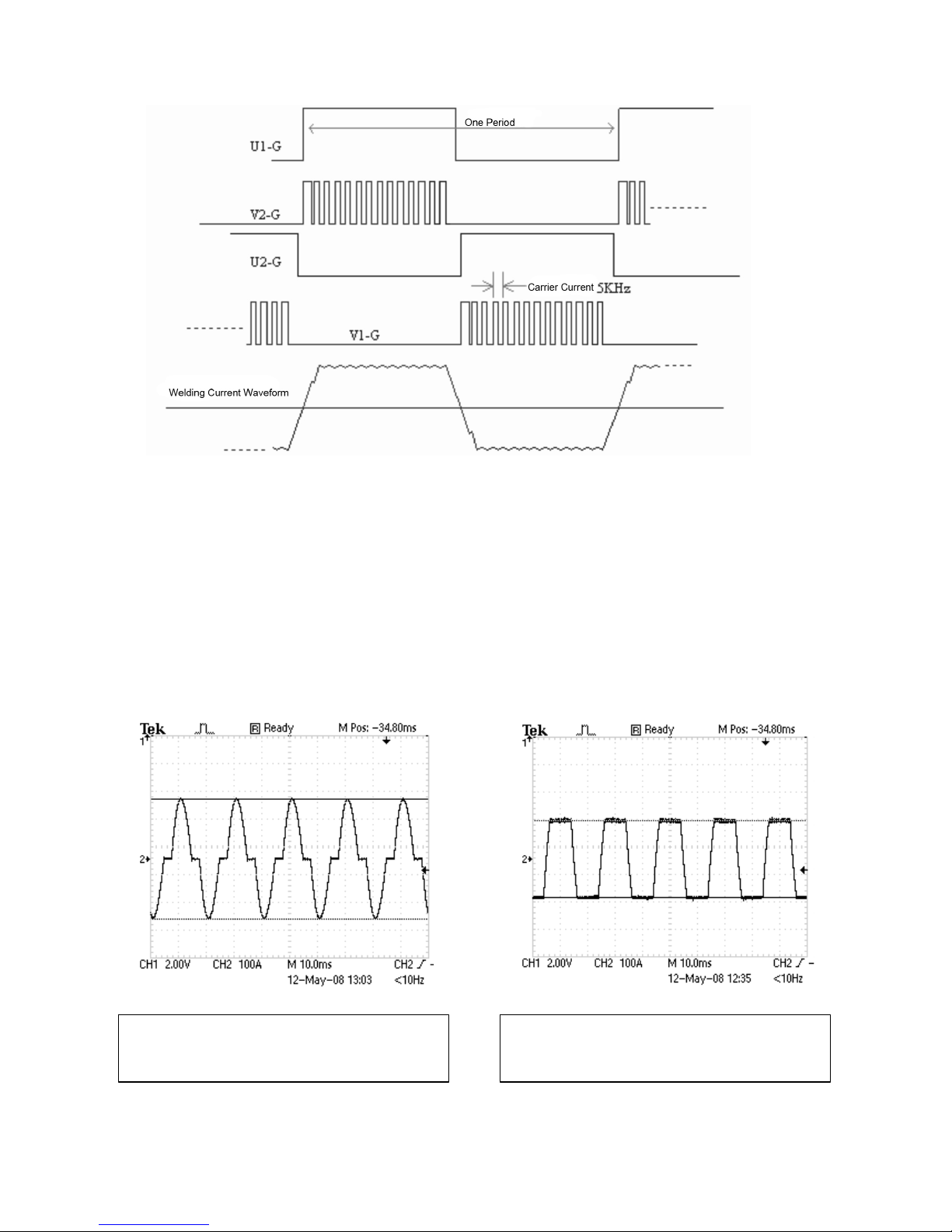
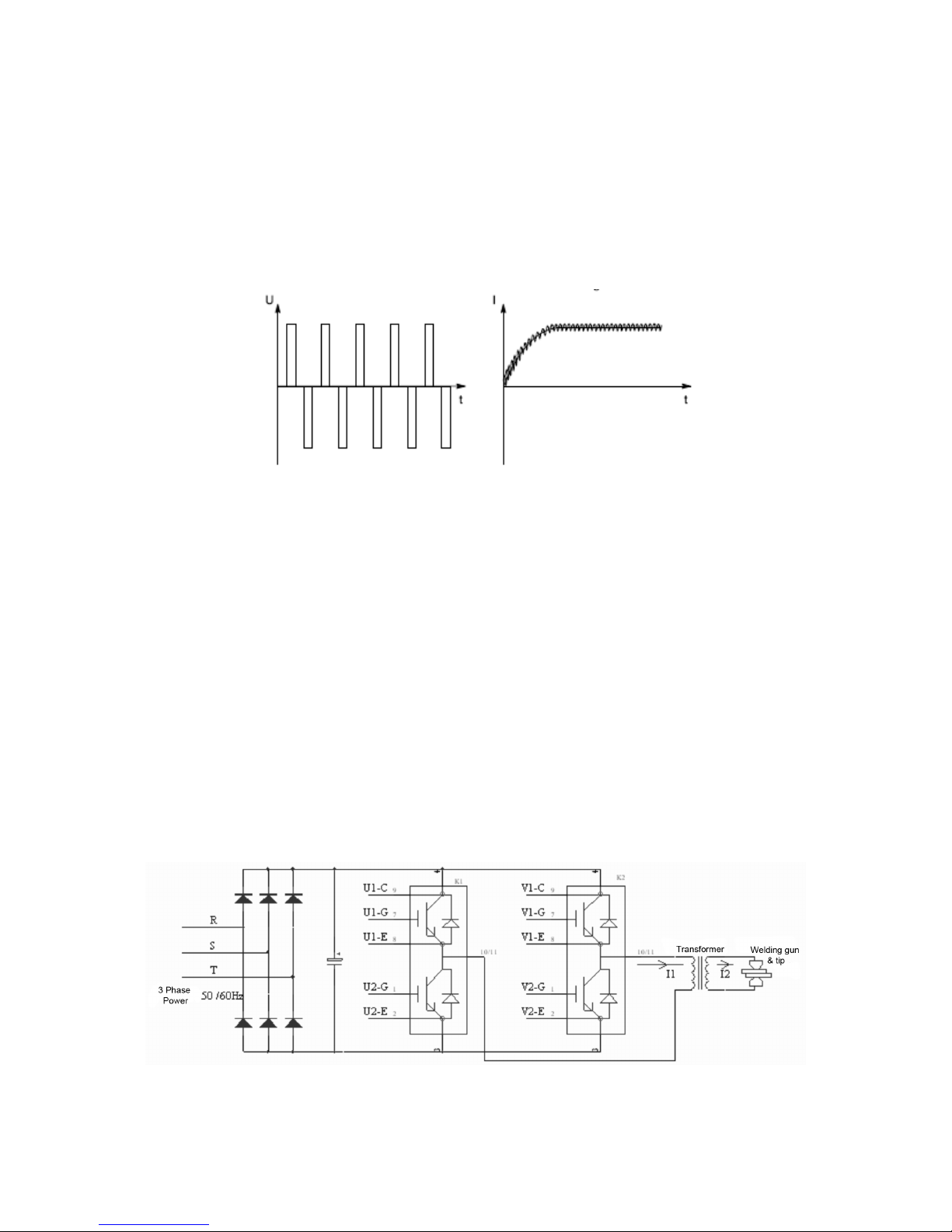
After the three-phase AC 50/60Hz input goes through the rectifier, the filter turns the
smooth direct current, makes the switch component by IGBT/K1 to have the
alternate voltage output, realizes the hypothesis welding current output through the
adjustment high frequency (5KHz) work's IGBT/K2 clear pulse width.
1. Variable Frequency vs. Normal Frequency Controller Comparison
Compared to common power welding controller shows the variable frequency
welding controller to have higher heating efficiency and lower peak current.
Page 2
2
Variable Frequency at 50Hz, secondary
current: 10.0KA, the transformer ratio: 80
Common power frequency at 50HZ,
secondary current: 10.0KA, the
transformer ratio: 80
Compared to common power frequency controller, the variable frequency conversion
controller has the following advantages:
1. The three-phase AC mains input, more balanced power usage; higher power
factor
2. To the same welding work piece, the weld period reduces, saves electricity;
Welding stability region enlarges; The electrode life grows
3. Can weld with good results: aluminum, the galvanized sheet, high-tensile
steel, stainless steel, magnesium alloy, carbon steel, titanium, etc.
4. Can weld with good results: three-layer materials, and thin materials
5. Less sparking
6. Higher weld spot quality due to faster electric current control response
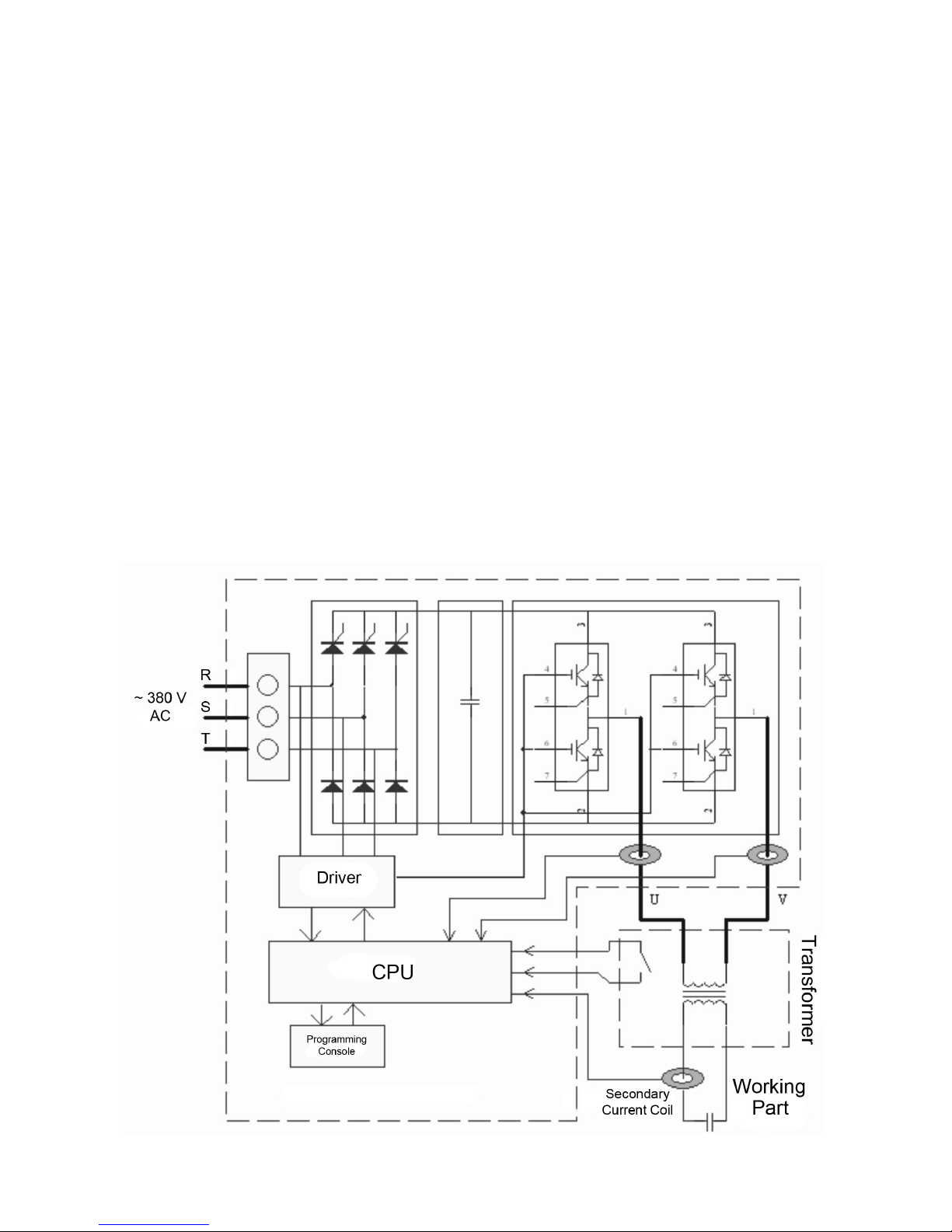
III. Welding Controller Configuration
The entire control system consists of: the welding controller, the welding
transformer, and the welding gun. The welding controller consists of: the power
supply, the rectifier, the capacitor, IGBT, and the CPU.
Page 3
3

! 1. Main features:
1. Welding frequency: programmable between 25.0Hz ~400.0Hz
2. Up to 64 sets of programmable welding condition
3. Three section of thermal processes: Preheating, welding, tempering;
Each process has its own stepper
4. The programmable pressure control, able to define up to 10 pressure
sections
5. Programmable output: 3 ways of outputs with PLC, robot, etc.
6. Spot weld count function.
! 2. Technical parameters:
1. Input voltage: Three-phase 380V, 50Hz/60Hz, power variation +10%, 20%
2. Output voltage: Single-phase PWM outputs 500V
3. Output current: Peak current 400A
4. Cooling water: Minimum capacity 6L/min, temperature ≤ 30℃
5. Working condition temperature: 0~50℃
6. Air valve voltage: DC24V
IV.Operation Description
The controller has two welding modes: Spot welding and seam welding.
1. Spot Welding
The welding start signal (X10 -10) will start the solenoid valve, but the
controller will not begin the welding process until the welding enable (X10 - 7) is
switched on. The Weld/No Weld (X10 - 5) is closed, the welding heat will start,
otherwise the welding process will start but with not current. The start signal will
begin the welding process. This welding process includes initial squeeze, squeeze,
heat 1, cool 1, up slope, heat 2, cool 2, down slope, heat 3, cool 3, hold time, off
time. After the welding has finished, the controller sends out a welding end signal.
Each welding schedule has its own “prohibit start” parameter. This parameter permits
or forbids the welding schedule to sequence, When this parameter is ON it will not
allow welding; When OFF, the welding schedule starts.
The spot welding welding sequence time chart is shown below:
Page 4
4
 Loading...
Loading...