Page 1

www.inter-m.com
MADE IN KOREA
2003.2 9017100300
SERVICE
MANUAL
STEREO/DUAL 31-BAND GRAPHIC
EQUALIZER
GEQ-1231D/2231D
Page 2

1
MICOM DATA
MM74HC4051 8-CHANNEL ANALOG MULTIPLEXER
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MM74HC4051, MM74HC4052 and MM74HC4053 Multiplexers are digitally controlled analog switches
implemented in advanced silicon-gate CMOS technology. These switches have low “on” resistance and
low “off” leakages. They are bidirectional switches, thus any analog input may be used as an output and
vice-versa. Also These switches contain linearization circuity which lowers the on resistance and increases
switch linearity. These devices allow control of up to ± 6V(peak) analog signals with digital control signals
of 0 to 6V. Three supply pins are provided for VCC, ground, and VEE. This enables the connection of 0-5V
logic signals when V
CC
= 5V and an analog input range of ± 5V when VEE= 5V. All three devices also have
an inhibit control which when HIGH will disable all switches to their off state. All analog inputs and outputs
and digital inputs are protected from electrostatic damage by diodes to V
CC
and ground.
This device connects together the outputs of 8 switches, thus achieving an 8 channel multiplexer. The
binary code placed on the A, B, and C select lines determines which one of the eight switches is “on”, and
connects one of the eight inputs to the common output.
FEATURES
• Wide analog input voltage range: ±6V
• Low
on resistance: 50 typ.(VCC-V
EE
= 4.5V), 30 typ.(VCC-V
EE
= 9V)
• Logic level translation to enable 5V logic with ± 5V analog signals
• Low quiescent current: 80µA maximum (74HC)
• Matched Switch characteristic
ORDERING CODE:
Devices also available in Tape and Reel. Specify by appending the suffix letter X to the ordering code.
Order Number
Package Number
Package Description
MM74HC4051M M16A
16-Lead Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC), JEDEC MS-012,0.150˝ Narrow
MM74HC4051WM M16B 16-Lead Small Outline Integrated Circuit (SOIC), JEDEC MS-013,0.300˝ Wide
MM74HC4051SJ M16D 16-Lead Small Outline Package (SOP), ELAJ TYPE ll, 5.3mm Wide
MM74HC4051MTC MTC16
16-Lead Thin Shrink Small Outline Package (TSSOP), JEDEC MO-153,4.4mm Wide
MM74HC4051N N16E 16-Lead Plastic Dual-In-Line Package (PDIP), JEDEC MS-0010.300˝ Wide
Micom Data 1 ~ 21
Specifications
22
Electrical Parts List 23 ~ 24
Top and Bottom View of P.C. Board
25 ~ 29
Wiring Diagram 30
Block Diagram 31~ 32
Schematic Diagram
33 ~ 50
Exploded View of Cabinet & Chassis / Mechanical Parts List
51 ~ 54
Ass’y Drawing 55 ~ 58
CONTENTS
Page 3

3
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS inches (millimeters) unless otherwise noted
2
TRUTH TABLES
LOGIC DIAGRAMS
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS (Pin Assignments for DIP, SOIC, SOP and TSSO)
Input
Inh C B A
“ON”
Channel
H
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
L
X
L
L
L
L
H
H
H
H
X
L
L
H
H
L
L
H
H
X
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
H
None
Y0
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Top V iew
Page 4

54
PIN CONFIGURATION
LOGIC SYMBOL (IEEE/IEC)
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin Number Symbol Function
1, 2 Dsa, D
sb
Date inputs
3, 4, 5, 6 Q
0
to Q
7
Outputs
10, 11, 12, 13
7 GND Ground(ov)
8 CP Clock input (LOW-to-HIGH, edge-trig-gered)
9 MR Master reset input (active LOW)
14 V
CC
Positive supply voltage
SV00381
LOGIC SYMBOL
FUNCTIONAL DIAGRAM
SV00382 SV00383
SV00384
NOTES 1: CPDis used to determine the dynamic power dissipation (PDin µW)
PD= CPD x V
CC
2
x fi + ∑(CL x V
CC
2
x fO) where:
fi= input frequency in MHz; CL= output load capacitance in pF;
fO= output frequency in MHz; VCC= supply voltage in V;
∑(C
L
x V
CC
2
x fO) = sum of the outputs.
2: The condition is V
l
= GND to V
CC
Symbol Parameter Conditions Typical Unit
t
PHL
, t
PLH
Propagation delay CL=15pF 12 ns
CP to Q
n
VCC=3.3V 12
MR to Q
n
f
max
Maximum clock frequency 78 MH
Z
C
l
Input capacitance 3.5 pF
C
PD
Power dissipation capacitance per gate VCC=3.3V 40 pF
Notes 1 and 2
ORDERING INFORMATION
Packages Temperature Range Outside North Amerlca North Amerlca Pkg. Dwg.#
14-Pin Plastic DIL
-40°C to + 125°C 74LV164N 74LV164N SOT27-1
14-Pin Plastic SO
-40°C to + 125°C 74LV164D 74LV164D SOT108-1
14-Pin Plastic SSOP Type II
-40°C to + 125°C 74LV164DB 74LV164DB SOT337-1
14-Pin Plastic TSSOP Type I
-40°C to + 125°C 74LV164PW 74LV164PW DH SOT402-1
74LV164 8-bit SERIAL-IN / PARALLEL-OUT SHIFT REGISTER
FEATURES
–Wide operating voltage: 1.0 to 5.5V
– Optimized for Low Voltage applications: 1.0 to 3.6V
– Accepts TTL input levels between VCC=2.7V and VCC=3.6V
–Typical V
OLP
(output ground bounce) < 0.8V@VCC=3.3V, T
amb
=25°C
–Typical V
OHV
(output VOHundershoot) > 2V@VCC=3.3V,T
amb
=25°C
– Gated serial data inputs – Asynchronous master reset
– Output capability: standard – I
CC
category: MSl
DESCRIPTION
The 74LV164 is a low-voltage Si-gate CMOS device and is pin and function compatible with the 74HC/HCT164.
The 74LV164 is an 8-bit edge-triggered shift register with serial data entry and an output from each of the
eight stages. Data is entered serially through one of two inputs(Dsaor Dsb); either input can be used as an
active HIGH enable for data entry through the other input. Both inputs must be connected together or an
unused input must be tied HIGH.
Data shifts one place to the right on each LOW-to-HIGH transition of the clock (CP) input and enters into Q
0
,
which is the logical AND of the two data inputs (D
sa
, Dsb) that existed one set-up time prior to the rising clock edge.
A LOW on the master reset (MR) input overrides all other inputs and clears the register asynchronously,
forcing all outputs LOW.
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
GND = OV; T
amb
= 25°C; tr=t
f
≤ 2.5ns
Page 5

76
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7819 is a high speed, microprocessor-compatible, 8-bit analog-to-digital converter with a maximum
throughput of 200kSPS. The converter operates off a single 2.7V to 5.5V supply and contains a 4.5µs
successive approximation A/D converter, track/hold circuitry, on-chip clock oscillator and 8-bit wide parallel
interface. The parallel interface is designed to allow easy interfacing to microprocessors and DSPs. Using
only address decoding logic the AD7819 is easily mapped into the microprocessor address space.
When used in its power-down mode, the AD7819 automatically powers down at the end of a conversion
and powers up at the start of a new conversion. This feature significantly reduces the power consumption
of the part at lower throughput rates. The AD7819 can also operate in a high speed mode where the part is
not powered down between conversions. In this mode of operation the part is capable of providing 200
kSPS throughput.
The part is available in a small, 16-lead 0.3" wide, plastic dual-in-line package (DIP); in a 6-lead, 0.15"
wide, narrow body small outline IC (SOIC) and in a 16-lead, narrow body, thin shrink small outline package
(TSSOP).
AD7819 2.7V to 5.5V, 200 kSPS 8-bit SAMPLING ADC
FEATURES
– 8-Bit ADC with 4.5 µs Conversion Time
– On-Chip Track and Hold
– Operating Supply Range : 2.7V to 5.5V
– Specifications at 2.7V-3.6V and 5V ± 10%
– 8-Bit Parallel Interface : 8-Bit Read
– Power Performance
Normal Operation : 10.5mW,VDD=3V
– Automatic Power-Down : 57.75µW@1kSPS,V
DD
=3V
– Analog Input Range : 0V to V
REF
– Reference Input Range : 1.2V to V
DD
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
SO14 : plastic small outline package; 14 leads; body width 3.9 mm
NOTE : Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.15 mm maximum per side are not included.
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
Unit
A
max.
A1A2A3bpcD
(1)E(1)
eHELLPQvwyz
(1)
European
Projection
Issue Date
SOT108-1 076E06S MS-012AB
91-08-13
95-01-23
mm
inches
1.75
0.069
0.25
0.10
0.0098
0.0039
0.49
0.36
0.019
0.014
4.0
3.8
0.16
0.15
6.2
5.8
0.24
0.23
1.05
0.041
0.25
0.01
0.25
0.01
0.1
0.004
8°
0°
0.7
0.3
0.028
0.012
1.0
0.4
0.039
0.016
0.7
0.6
0.028
0.024
1.27
0.050
8.75
8.55
0.35
0.34
0.25
0.19
0.0098
0.0075
1.45
1.25
0.057
0.049
0.25
0.01
Outline
Version
Iec Jedec Eiaj
References
Page 6

98
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charge as high as 4000V
readily accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge
without detection. Although the AD7819 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry,
permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic
discharges, Therefore, proper ESD precaution are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of
functionality.
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1V
REF
Reference Input, 1.2V to VDD.
2V
IN
Analog Input, 0V to V
REF
.
3 GND Analog and Digital Ground.
4 CONVST Convert Start. A low-to-high transition on this pin initiates a 1.5
µ
s pulse on an
internally generated CONVST signal. A high-to-low transition on this line initiates the
conversion process if the internal CONVST signal is low. Depending on the signal on
this pin at the end of a conversion, the AD7819 automatically powers down.
5CS Chip Select. This is a logic input. CS is used in conjunction with RD to enable outputs.
6RD Read Pin. This is a logic input. When CS is low and RD goes low, the DB7-DB0 leave
their high impedance state and data is driven onto the data bus.
7 BUSY ADC Bus y Sig nal. T his i s a lo gic output. This signal goes logic high during the
conversion process.
8-15 DB0-DB7 Data Bit 0 to 7. These outputs are three-state TTL-compatible.
16 V
DD
Positive power supply voltage, 2.7V to 5.5V.
PIN CONFIGURATION DIP/SOIC
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only;
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational sections of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Model Linearity Error(LSB) Package Description Package Option
AD7819YN ± 1 LSB Plastic DIP N-16
AD7819YR ± 1 LSB Small Outline IC R-16A
AD7819YRU ± 1 LSB Thin Shark Small RU-16
Outline (TSSOP)
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VDDto DGND ..............................................................................................................................-0.3V to + 7V
Digital Input Voltage to DGND
(CONVST, RD, CS)...............................................................................................................-0.3V, V
DD
+ 0.3V
Digital Output Voltage to DGND
(BUSY, DB0-DB7) .................................................................................................................-0.3V, V
DD
+ 0.3V
REF
IN
to AGND......................................................................................................................-0.3V, VDD+ 0.3V
Analog Input ..........................................................................................................................-0.3V, V
DD
+ 0.3V
Storage Temperature Range.................................................................................................-65
to + 150°C
Junction Temperature ........................................................................................................................... 150°C
Plastic DIP Package, Power Dissipation .............................................................................................450mW
JA
Thermal Impedance...................................................................................................................105°C/W
Lead Temperature, (Soldering 10 sec)................................................................................................260°C
SOIC Package, Power Dissipation ......................................................................................................450mW
JA
Thermal Impedance .....................................................................................................................75°C/W
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) ....................................................................................................................215°C
Infrared (15 sec)............................................................................................................................220°C
SSOP Package, Power Dissipation.....................................................................................................450mW
JA
Thermal Impedance ...................................................................................................................115°C/W
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) ....................................................................................................................215°C
Infrared (15 sec).............................................................................................................................220°C
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Digital Output Timing Specifications
Page 7

1110
BLOCK DIAGRAM
AK4524 24 bit 96kHz AUDIO CODEC
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AK4524 is a high performance 24bit CODEC for the 96kHz recording system. The ADC has an
Enhanced Dual Bit architecture with wide dynamic range. The DAC uses the new developed Advanced
Multi Bit architecture and achieves low outband noise and high jitter tolerance by use of SCF(switched
capacitor filter) techniques.The AK4524 has an input PGA and is well suited MD, DVTR system and
musical instruments.
FEATURES
• 24bit 2ch ADC
– 64x Oversampling
– Single-End inputs
– S/(N+D):90dB
– Dynamic Range, S/N:100dB
– Digital HPF for offset cancellation
– Input PGA with +8dB gain & 0.5dB step
– Input DATT with -72dB att
– I/F format:MSB justified or I2S
• 24bit 2ch DAC
– 128 x Oversampling
– 24bit 8 times Digital Filter
Ripple:±0.005dB, Attenuation:75dB
– SCF
– Differential Outputs
– S/(N+D):94dB
– Dynamic Range, S/N:110dB
– De-emphasis for 32kHz, 44.1kHz, 48kHz sampling
– Output DATT with -72dB att
– Soft Mute
– I/F format:MSB justified, LSB justified or l
2
S
• High Jitter Tolerance
• 3-wire Serial Interface for Volume Control
• Master Clock
– X’tal Oscillating Circuit
– 256fs/384fs/768fs/1024fs
• Master Mode/Slave Mode
• 5V operation
• 3V Power Supply Pin for 3V I/F
• Small 28pin VSOP package
PIN LAYOUT
ORDERING GUIDE
AK4524VF -10~+70°C 28pin VSOP (0.65mm pitch)
AKD4524 Evaluation Board
Page 8

1312
PACKAGE & LEAD FRAME MATERIAl
Package molding compound: Epoxy
Lead frame material: Cu
Lead frame surface treatment: Solder plate
PACKAGZ
Note : Dimension
“*” does not include moid flash.
ADSP-21065L DSP MICROCOMPUTER
SUMMARY
– High Performance Signal Computer for Communications, Audio, Automotive, Instrumentation and
Industrial Applications
– Super Harvard Architecture Computer (SHARC®)
Four Independent Buses for Dual Data, Instruction, and I/O Fetch on a Single Cycle
–32-Bit Fixed-Point Arithmetic; 32-Bit and 40-Bit Floating-Point Arithmetic
– 544 Kbits On-Chip SRAM Memory and Integrated I/O Peripheral
–I
2
S Support, for Eight Simultaneous Receive and Transmit Channels
KEY FEATURES
– 66 MIPS, 198 MFLOPS Peak, 132 MFLOPS Sustained Performance
– User-Configurable 544 Kbits On-Chip SRAM Memory
–Two External Port, DMA Channels and Eight Serial Port, DMA Channels
– SDRAM Controller for Glueless Interface to Low Cost External Memory (@66 MHz)
– 64M Words External Address Range
–12 Programmable I/O Pins and Two Timers with Event Capture Options
– Code-Compatible with ADSP-2106x Family
– 208-Lead MQFP or 196-Ball Mini-BGA Package
– 3.3 Volt Operation
Flexible Data Formats and 40-Bit Extended Precision
– 32-Bit Single-Precision and 40-Bit Extended-Precision IEEE Floating-Point Data Formats
–32-Bit Fixed-Point Data Format, Integer and Fractional, with Dual 80-Bit Accumulators
Parallel Computations
– Single-Cycle Multiply and ALU Operations in Parallel with Dual Memory Read/Writes and Instruction
Fetch
– Multiply with Add and Subtract for Accelerated FFT Butterfly Computation
– 1024-Point Complex FFT Benchmark: 0.274 ms (18,221 Cycles)
544 Kbits Configurable On-Chip SRAM
– Dual-Ported for Independent Access by Core Processor and DMA
– Configurable in Combinations of 16-, 32-, 48-Bit Data and Program Words in Block 0 and Block 1
DMA Controller
–Ten DMA Channels–Two Dedicated to the External Port and Eight Dedicated to the Serial Ports
– Background DMA Transfers at up to 66 MHz, in Parallel with Full Speed Processor Execution
– Performs Transfers Between:
Internal RAM and Host
Internal RAM and Serial Ports
Internal RAM and Master or Slave SHARC
Internal RAM and External Memory or I/O Devices
External Memory and External Devices
Host Processor Interface
–Efficient Interface to 8-, 16-, and 32-Bit Microprocessors
– Host Can Directly Read/Write ADSP-21065L IOP Registers
Page 9

1514
Multiprocessing
– Distributed On-Chip Bus Arbitration for Glueless, Parallel Bus Connect Between Two ADSP-21065Ls
Plus Host
– 132 Mbytes/s Transfer Rate Over Parallel Bus
Serial Ports
– Independent Transmit and Receive Functions
–Programmable 3-Bit to 32-Bit Serial Word Width
–I2S Support Allowing Eight Transmit and Eight Receive Channels
– Glueless Interface to Industry Standard Codecs
–TDM Multichannel Mode with µ-Law/A-Law Hardware Companding
– Multichannel Signaling Protocol
BLOCK DIAGRAM
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
ADSP-21065L pin definitions are listed below. Inputs identified as synchronous (S) must meet timing
requirements with respect to CLKIN (or with respect to TCK for TMS, TDI). Inputs identified as
asynchronous (A) can be asserted asynchronously to CLKIN (or to TCK for TRST).
Unused inputs should be tied or pulled to VDD or GND, except for ADDR
23-0
, DATA
31-0
, FLAG
11-0
, SW, and
inputs that have internal pull-up or pull-down resistors (CPA, ACK, DTxX, DRxX, TCLKx, RCLKx, TMS, and
TDI)–these pins can be left floating. These pins have a logic-level hold circuit that prevents the input from
floating internally.
I=Input S=Synchronous P=Power Supply (O/D)=Open Drain
O=Output A=Asynchronous G=Ground (A/D)=Active Drive
T=Three-state (when SBTS is asserted, or when the ADSP-2106x is a bus slave)
Pin Type Function
ADDR
23-0
I/O/T External Bus Address. The ADSP-21065L outputs addresses for external
memory and peripherals on these pins. In a multiprocessor system the bus
master outputs addresses for read/writes of the IOP registers of the other
ADSP-21065L. The ADSP-21065L inputs addresses when a host processor
or multiprocessing bus master is reading or writing its IOP registers.
DATA
31-0
I/O/T External Bus Data. The ADSP-21065L inputs and outputs data and
instructions on these pins. The external data bus transfers 32-bit singleprecision floating-point data and 32-bit fixed-point data over bits 31-0. 16-bit
short word data is transferred over bits 15-0 of the bus. Pull-up resistors on
unused DATA pins are not necessary.
MS
3-0
I/O/T Memory Select Lines. These lines are asserted as chip selects for the
corresponding banks of external memory. Internal ADDR
25-24
are decoded
into MS
3-0
. The MS
3-0
lines are decoded memory address lines that change
at the same time as the other address lines. When no external memory
access is occurring the MS
3-0
lines are inactive; they are active, however,
when a conditional memory access instruction is executed, whether or not
the condition is true. Additionally, an MS
3-0
line which is mapped to SDRAM
may be asserted even when no SDRAM access is active. In a
multiprocessor system, the MS
3-0
lines are output by the bus master.
RD I/O/T Memory Read Strobe. This pin is asserted when the ADSP-21065L reads
from external memory devices or from the IOP register of another ADSP21065L. External devices (including another ADSP-21065L) must assert RD
to read from the ADSP-21065L’s IOP registers. In a multiprocessor system,
RD is output by the bus master and is input by another ADSP-21065L.
WR I/O/T Memory Write Strobe. This pin is asserted when the ADSP-21065L writes
to external memory devices or to the IOP register of another ADSP-21065L.
External devices must assert WR to write to the ADSP-21065L’s IOP
registers. In a multiprocessor system, WR is output by the bus master and is
input by the other ADSP-21065L.
SW I/O/T Synchronous Write Select. This signal interfaces the ADSP-21065L to
synchronous memory devices (including another ADSP-21065L). The
ADSP-21065L asserts SW to provide an early indication of an impending
write cycle, which can be aborted if WR is not later asserted (e.g., in a
conditional write instruction). In a multiprocessor system, SW is output by the
bus master and is input by the other ADSP-21065L to determine if the
multiprocessor access is a read or write. SW is asserted at the same time as
the address output.
ACK I/O/S Memory Acknowledge. External devices can deassert ACK to add wait
states to an external memory access. ACK is used by I/O devices, memory
controllers, or other peripherals to hold off completion of an external memory
Page 10

1716
Pin Type Function
access. The ADSP-21065L deasserts ACK as an output to add wait states to
a synchronous access of its IOP registers. In a multiprocessor system, a
slave ADSP-21065L deasserts the bus master’s ACK input to add wait
state(s) to an access of its IOP registers. The bus master has a keeper latch
on its ACK pin that maintains the input at the level to which it was last driven.
SBTS I/S Suspend Bus Three-State. External devices can assert SBTS to place the
external bus address, data, selects, and strobes–but not SDRAM control
pins–in a high impedance state for the following cycle. If the ADSP-21065L
attempts to access external memory while SBTS is asserted, the processor
will halt and the memory access will not finish until SBTS is deasserted.
SBTS should only be used to recover from host processor/ADSP-21065L
deadlock.
IRQ
2-0
I/A Interrupt Request Lines. May be either edge-triggered or level-sensitive.
FLAG
11-0
I/O/A Flag Pins. Each is configured via control bits as either an input or an output.
As an input, it can be tested as a condition. As an output, it can be used to
signal external peripherals.
HBR I/A Host Bus Request. Must be asserted by a host processor to request control
of the ADSP-21065L’s external bus. When HBR is asserted in a
multiprocessing system, the ADSP-21065L that is bus master will relinquish
the bus and assert HBG. To relinquish the bus, the ADSP-21065L places the
address, data, select, and strobe lines in a high impedance state. It does,
however, continue to drive the SDRAM control pins. HBR has priority over all
ADSP-21065L bus requests (BR
2-1
) in a multiprocessor system.
HBG I/O Host Bus Grant. Acknowledges an HBR bus request, indicating that the
host processor may take control of the external bus. HBG is asserted by the
ADSP-21065L until HBR is released. In a multiprocessor system, HBG is
output by the ADSP-21065L bus master.
CS I/A Chip Select. Asserted by host processor to select the ADSP-21065L.
REDY(O/D)
O Host Bus Acknowledge. The ADSP-21065L deasserts REDY to add wait
states to an asynchronous access of its internal memory or IOP registers by
a host. Open drain output (O/D) by default; can be programmed in ADREDY
bit of SYSCON register to be active drive (A/D). REDY will only be output if
the CS and HBR inputs are asserted.
DMAR
1
I/A DMA Request 1 (DMA Channel 9).
DMAR
2
I/A DMA Request 2 (DMA Channel 8).
DMAG
1
O/T DMA Grant 1 (DMA Channel 9).
DMAG
2
O/T DMA Grant 2 (DMA Channel 8).
BR
2-1
I/O/S Multiprocessing Bus Requests. Used by multiprocessing ADSP-21065L’s
to arbitrate for bus mastership. An ADSP-21065L drives its own BRx line
(corresponding to the value of its ID
2-0
inputs) only and monitors all others. In
a uniprocessor system, tie both BRx pins to VDD.
ID
1-0
I Multiprocessing ID. Determines which multiprocessor bus request
(BR
1
–BR2) is used by ADSP-21065L. ID=01 corresponds to BR1, ID=10
corresponds to BR
2
. ID=00 in single-processor systems. These lines are a
system configuration selection which should be hard-wired or changed only
at reset.
CPA (O/D) I/O Core Priority Access. Asserting its CPA pin allows the core processor of an
ADSP-21065L bus slave to interrupt background DMA transfers and gain
Pin Type Function
access. The ADSP-21065L deasserts ACK as an output to add wait states to
a synchronous access of its IOP registers. In a multiprocessor system, a
slave ADSP-21065L deasserts the bus master’s ACK input to add wait
state(s) to an access of its IOP registers. The bus master has a keeper latch
on its ACK pin that maintains the input at the level to which it was last driven.
SBTS I/S Suspend Bus Three-State. External devices can assert SBTS to place the
external bus address, data, selects, and strobes–but not SDRAM control
pins–in a high impedance state for the following cycle. If the ADSP-21065L
attempts to access external memory while SBTS is asserted, the processor
will halt and the memory access will not finish until SBTS is deasserted.
SBTS should only be used to recover from host processor/ADSP-21065L
deadlock.
IRQ
2-0
I/A Interrupt Request Lines. May be either edge-triggered or level-sensitive.
FLAG
11-0
I/O/A Flag Pins. Each is configured via control bits as either an input or an output.
As an input, it can be tested as a condition. As an output, it can be used to
signal external peripherals.
HBR I/A Host Bus Request. Must be asserted by a host processor to request control
of the ADSP-21065L’s external bus. When HBR is asserted in a
multiprocessing system, the ADSP-21065L that is bus master will relinquish
the bus and assert HBG. To relinquish the bus, the ADSP-21065L places the
address, data, select, and strobe lines in a high impedance state. It does,
however, continue to drive the SDRAM control pins. HBR has priority over all
ADSP-21065L bus requests (BR
2-1
) in a multiprocessor system.
HBG I/O Host Bus Grant. Acknowledges an HBR bus request, indicating that the
host processor may take control of the external bus. HBG is asserted by the
ADSP-21065L until HBR is released. In a multiprocessor system, HBG is
output by the ADSP-21065L bus master.
CS I/A Chip Select. Asserted by host processor to select the ADSP-21065L.
REDY(O/D)
O Host Bus Acknowledge. The ADSP-21065L deasserts REDY to add wait
states to an asynchronous access of its internal memory or IOP registers by
a host. Open drain output (O/D) by default; can be programmed in ADREDY
bit of SYSCON register to be active drive (A/D). REDY will only be output if
the CS and HBR inputs are asserted.
DMAR
1
I/A DMA Request 1 (DMA Channel 9).
DMAR
2
I/A DMA Request 2 (DMA Channel 8).
DMAG
1
O/T DMA Grant 1 (DMA Channel 9).
DMAG
2
O/T DMA Grant 2 (DMA Channel 8).
BR
2-1
I/O/S Multiprocessing Bus Requests. Used by multiprocessing ADSP-21065L’s
to arbitrate for bus mastership. An ADSP-21065L drives its own BRx line
(corresponding to the value of its ID
2-0
inputs) only and monitors all others. In
a uniprocessor system, tie both BRx pins to VDD.
ID
1-0
I Multiprocessing ID. Determines which multiprocessor bus request
(BR
1
–BR2) is used by ADSP-21065L. ID=01 corresponds to BR1, ID=10
corresponds to BR
2
. ID=00 in single-processor systems. These lines are a
system configuration selection which should be hard-wired or changed only
at reset.
CPA (O/D) I/O Core Priority Access. Asserting its CPA pin allows the core processor of an
ADSP-21065L bus slave to interrupt background DMA transfers and gain
Page 11

1918
Pin Type Function
TMS I/S Test Mode Select (JTAG). Used to control the test state machine. TMS has
a 20kΩ internal pull-up resistor.
TDI I/S Test Data Input (JTAG). Provides serial data for the boundary scan logic.
TDI has a 20kΩ internal pull-up resistor.
TDO O Test Data Output (JTAG). Serial scan output of the boundary scan path.
TRST I/A Test Reset (JTAG). Resets the test state machine. TRST must be asserted
(pulsed low) after power-up or held low for proper operation of the ADSP21065L. TRST has a 20kΩ internal pull-up resistor.
EMU (O/D) O Emulation Status. Must be connected to the ADSP-21065L EZ-ICE target
board connector only.
BMSTR O Bus Master Output. In a multiprocessor system, indicates whether the
ADSP-21065L is current bus master of the shared external bus. The ADSP21065L drives BMSTR high only while it is the bus master. In a singleprocessor system (ID=00), the processor drives this pin high.
CAS I/O/T SDRAM Column Access Strobe. Provides the column address. In
conjunction with RAS, MSx, SDWE, SDCLKx, and sometimes SDA10,
defines the operation for the SDRAM to perform.
RAS I/O/T SDRAM Row Access Strobe. Provides the row address. In conjunction with
CAS, MSx, SDWE, SDCLKx, and sometimes SDA10, defines the operation
for the SDRAM to perform.
SDWE I/O/T SDRAM Write Enable. In conjunction with CAS, RAS, MSx, SDCLKx and
sometimes SDA10, defines the operation for the SDRAM to perform.
DQM O/T SDRAM Data Mask. In write mode, DQM has a latency of zero and is used
to block write operations.
SDCLK
1-0
I/O/S/T SDRAM 2x Clock Output. In systems with multiple SDRAM devices
connected in parallel, supports the corresponding increased clock load
requirements, eliminating need of off-chip clock buffers. Either SDCLK
1
or
both SDCLKx pins can be three-stated.
SDCKE I/O/T SDRAM Clock Enable. Enables and disables the CLK signal. For details,
see the data sheet supplied with your SDRAM device.
SDA10 O/T SDRAM A10 Pin. Enables applications to refresh an SDRAM in parallel with
a host access.
XTAL O Crystal Oscillator Terminal. Used in conjunction with CLKIN to enable the
ADSP-21065L’s internal clock generator or to disable it to use an external
clock source. See CLKIN.
PWM_EVENT
1-0
I/O/A PWM Output/Event Capture. In PWMOUT mode, is an output pin and
functions as a timer counter. In WIDTH_CNT mode, is an input pin and
functions as a pulse counter/event capture.
VDD P Power Supply; nominally +3.3V dc. (33 pins)
GND G Power Supply Return. (37 pins)
NC Do Not Connect. Reserved pins that must be left open and unconnected. (7)
CLOCK SIGNALS
The ADSP-21065L can use an external clock or a crystal. See CLKIN pin description. You can configure the
ADSP-21065L to use its internal clock generator by connecting the necessary components to CLKIN and
XTAL. You can use either a crystal operating in the fundamental mode or a crystal operating at an overtone.
Figure shows the component connections used for a crystal operating in fundamental mode, and Figure 2
shows the component connections used for a crystal operating at an overtone.
TARGET BOARD CONNECTOR FOR EZ-ICE PROBE
The ADSP-2106x EZ-ICE emulator uses the IEEE 1149.1 JTAG test access port of the ADSP-2106x to
monitor and control the target board processor during emulation. The EZ-ICE probe requires the ADSP2106x’s CLKIN, TMS, TCK, TRST, TDI, TDO, EMU and GND signals be made accessible on the target
system via a 14-pin connector (a 2 row x 7 pin strip header) such as that shown in Figure 3. The EZ-ICE
probe plugs directly onto this connector for chip-on-board emulation. You must add this connector to your
target board design if you, intend to use the ADSP-2106x EZ-ICE.
The total trace length between the EZ-ICE
connector and the furthest device sharing the EZICE JTAG pins should be limited to 15 inches
maximum for guaranteed operation. This restriction
on length must include EZ-ICE JTAG signals, which
are routed to one or more 2106x devices or to a
combination of 2106xs and other JTAG devices on
the chain.
The 14-pin, 2-row pin strip header is keyed at the
Pin 3 location–you must remove Pin 3 from the
header. The pins must be 0.025 inch square and at
least 0.20 inch in length. Pin spacing should be
0.1x0.1 inches. Pin strip headers are available from
vendors such as 3M, McKenzie and Samtec.
Figure 1. 30 MHz Operation (Fundamental Mode Crystal)
SUGGESTED COMPONENTS FOR 30 MHz OPERATION:
ECLIPTEK EC2SM-33-30.000M (SURFACE MOUNT PACKAGE)
ECLIPTEK EC-33-30.000M (THRU-HOLE PACKAGE)
C1=33pF
C2=27pF
NOTE: C1 AND C2 ARE SPECIFIC TO CRYSTAL SPECIFIED FOR
X1.
CONTACT CRYSTAL MANUFACTURER FOR DETAILS.
Figure 2. 30 MHz Operation (3rd Overtone Crystal)
SUGGESTED COMPONENTS FOR 30 MHz OPERATION:
ECLIPTEK EC2SM-T-30.000M (SURFACE MOUNT PACKAGE)
ECLIPTEK ECT-30.000M (THRU-HOLE PACKAGE)
C1=18pF
C2=27pF
C3=75pF
L1=3300nH
Rs=SEE NOTE.
NOTE: C1, C2, C3, Rs AND L
1 ARE SPECIFIC TO CRYSTAL SPECIFIED
FOR X1.
CONTACT MANUFACTURER FOR DETAILS.
Figure 3. Target Board Connector for ADSP-2106x
EZ-ICE (JTAG Header)
Page 12
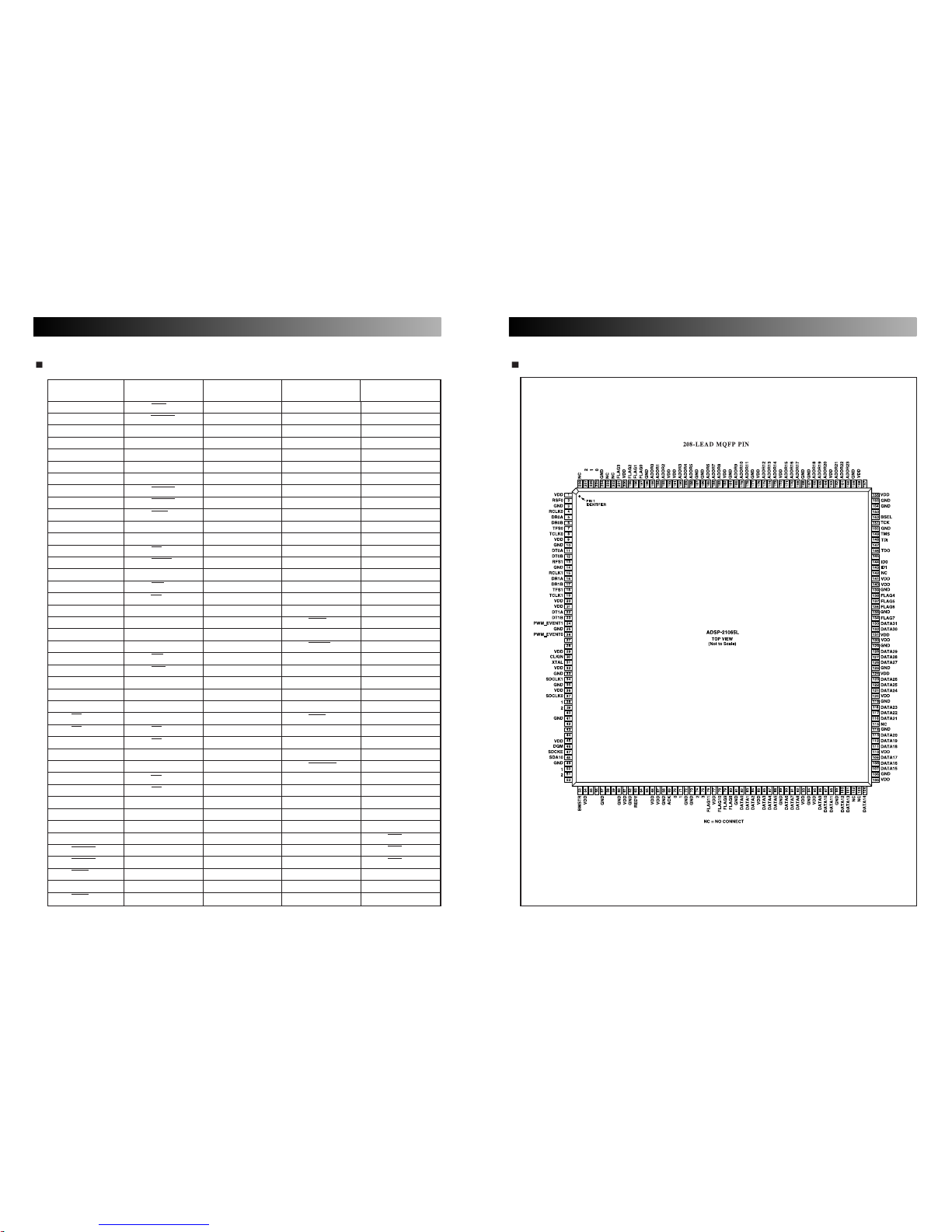
2120
208-LEAD MQFP PIN CONFIGURATION
Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin
No. Name No. Name No. Name No. Name No. Name
1 VDD
2 RFS0
3 GND
4 RCLK0
5 DR0A
6 DR0B
7 TFS0
8 TCLK0
9 VDD
10 GND
11 DT0A
12 DT0B
13 RFS1
14 GND
15 RCLK1
16 DR1A
17 DR1B
18 TFS1
19 TCLK1
20 VDD
21 VDD
22 DT1A
23 DT1B
24
PWM_EVENT1
25 GND
26
PWM_EVENT0
27 BR1
28 BR2
29 VDD
30 CLKIN
31 XTAL
32 VDD
33 GND
34 SDCLK1
35 GND
36 VDD
37 SDCLK0
38 DMAR1
39 DMAR2
40 HBR
41 GND
42 RAS
43 CAS
44 SDWE
45 VDD
46 DQM
47 SDCKE
48 SDA10
49 GND
50 DMAG1
51 DMAG2
52 HBG
53 BMSTR
54 VDD
55 CS
56 SBTS
57 GND
58 WR
59 RD
60 GND
61 VDD
62 GND
63 REDY
64 SW
65 CPA
66 VDD
67 VDD
68 GND
69 ACK
70 MS0
71 MS1
72 GND
73 GND
74 MS2
75 MS3
76 FLAG11
77 VDD
78 FLAG10
79 FLAG9
80 FLAG8
81 GND
82 DATA0
83 DATA1
84 DATA2
85 VDD
86 DATA3
87 DATA4
88 DATA5
89 GND
90 DATA6
91 DATA7
92 DATA8
93 VDD
94 GND
95 VDD
96 DATA9
97 DATA10
98 DATA11
99 GND
100 DATA12
101 DATA13
102 NC
103 NC
104 DATA14
105 VDD
106 GND
107 DATA15
108 DATA16
109 DATA17
110 VDD
111 DATA1 8
112 DATA19
113 DATA20
114 GND
115 NC
116 DATA21
117 DATA22
118 DATA23
119 GND
120 VDD
121 DATA24
122 DATA25
123 DATA26
124 VDD
125 GND
126 DATA27
127 DATA28
128 DATA29
129 GND
130 VDD
131 VDD
132 DATA30
133 DATA31
134 FLAG7
135 GND
136 FLAG6
137 FLAG5
138 FLAG4
139 GND
140 VDD
141 VDD
142 NC
143 ID1
144 ID0
145 EMU
146 TDO
147 TRST
148 TDI
149 TMS
150 GND
151 TCK
152 BSEL
153 BMS
154 GND
155 GND
156 VDD
157 RESET
158 VDD
159 GND
160 ADDR23
161 ADDR22
162 ADDR21
163 VDD
164 ADDR20
165 ADDR19
166 ADDR18
167 GND
168 GND
169 ADDR17
170 ADDR16
171 ADDR15
172 VDD
173 ADDR14
174 ADDR13
175 ADDR12
176 VDD
177 GND
178 ADDR11
179 ADDR10
180 ADDR9
181 GND
182 VDD
183 ADDR8
184 ADDR7
185 ADDR6
186 GND
187 GND
188 ADDR5
189 ADDR4
190 ADDR3
191 VDD
192 VDD
193 ADDR2
194 ADDR1
195 ADDR0
196 GND
197 FLAG0
198 FLAG1
199 FLAG2
200 VDD
201 FLAG3
202 NC
203 NC
204 GND
205 IRQ0
206 IRQ1
207 IRQ2
208 NC
208-LEAD MQFP PIN
Page 13
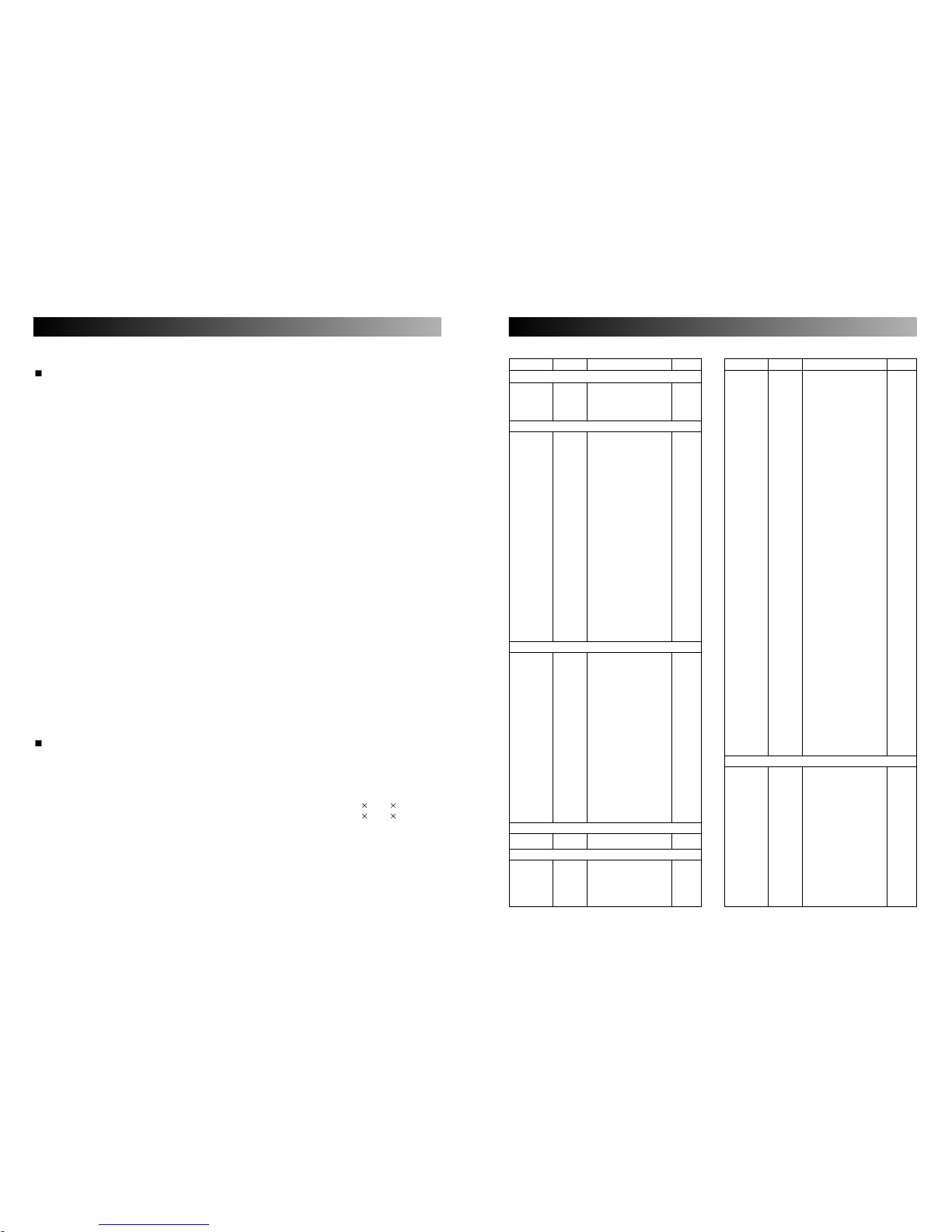
2322
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
Ref No. Part No. ValueDescription
AC INPUT B'D (4003482620)
C427 3509101130-T CAP CE SL 100PF 50V J 100p
C433-436 3689103219 CAP X7R 10N 10% 50V (LS5.08) 10n
C428 C432 3689102219 CAP X7R 1N 10% 50V (LS5.08) 1n
C310-317 3509331130-T CAP CE SL 330PF 50V J 330P
CN401-402 4428595005 LW5267/LWB0640/2.5MM-05P WAFER 5P
CN305 CN403 CN405
4428595002 LW5267/LWB0640/2.5MM-02P WAFER 2P
CN301-304 CN406 4428595003 LW5267/LWB0640/2.5MM-07P WAFER 3P
CN404 4428595007 CON WAFER A2505WV2-07P WAFER 7P
F402 3908609980 EMI FILTER 2200PF 22nF
D301-302 D401-402 2058100996 DIODE RECTIFIER LT1N4006(4007) 1N 4006
D405 D406
D407 2058304100 DIODE IN4148M 1N 4148
D403-404 2058100890 DIODE RECTIFIER IN5401 1N5401
C426 3409210033-T CAP E SE 10UF 16V 4*5 10/16
C430-431 3409210059-T CAP RG 10UF 50V 105C 10/50
C414-415 C424 3408210233 CAP RSD 1000UF 16V SNAP 10P 1000/16
C410-411 3419533265 CAP HC 3300UF 35V 3300/35
C422 3419568238 CAP AF HM 6800UF 16V 25P LUG 6800/16
FB301-308 2648609900 FERITE BEAD H5B FERRITE
FS401 0.125A/250V
FS402-403 5508212233 FUSE NB 20MM 1A/250V U/C 1AT
FS404 4458999110 FUSE CLIP 5*20 FUSE CLIP
JX302 JX304 4408194510 XLR JACK (F) (E303A0070N)
XLR JACK (F)
JX301 JX303 4408194610 XLR JACK (M) (E403A0090N)
XLR JACK (M)
JK301-304 4408194210 XLR JACK(M) E503A0130N
JACK PHONE
IC405 2168640979 IC LM311N (DIL8) FSC LM311N
IC402 2168640987 IC 7915 SAMSUNG 7915
IC404 2118089926 IC LM 350T LM350T
4 8
CN407 4235007210 GND TERMINAL (POWER B'D)
GND TERMINAL
P32 P36 P38-39
P41-42
P401-404 4465998210 TERMINAL(250)PCB TAB
TERMINAL TAB
JP1-2
JP301-304 4428590423 PIN HEADER 2X3POL (LS2.54) pinheader 3p
PT1 PT
R408 3004100953 RES CF 100 1/5W FN SMA-4000 100 1%
R403 R418 3001100953 RES CF 100K 1/5W F N 100K 1%
R417 R425 3005100953 RES CF 10 1/5W F N 10 1%
R420 3002150953 RES CF 15K 1/5W F N 15K 1%
R423 3003220953 RES CF 2.2K 1/5W F N 2.2K
R409 3003274953 RES CF 2.7K 1/5W F N 2.7K 1%
R410-411 R416 R419
3002220953 RES CF 22K 1/5W F N 22K 1%
R421
R404 3003330953 RES CF 3.3K 1/5W F N 3.3K 1%
R406 3003348953 RES CF 3.48K 1/5W FN SMA-4000 3.48K 1%
R401 3004390953 RES CF 390 1/5W FN 390 1%
R402 3004240953 RES CF 240 1/5W FN 240 1%
R413 3003470953 RES CF 4.7K 1/5W F N 4.7K 1%
R407 3002470953 RES CF 47K 1/5W F N 47K 1%
R415 3004470953 RES 470 1/5W FN 470 1%
R405 3009564973 RES CF 560K 1/5W J N 560K
RLY301-302 5528007800 RELAY AZ850-12 DC12V
RELAY DC12V
SW301-302 4625995510 SW SLIDE SSAF122NB011(9MM)
SW SLIDE(9MM)
S401 4648099310 POWER SWITCH (H8500VB) POWER SW
IC406 2128612400 IC TL431CLP (TO92) TIA TL431
Q401-402 2008405980-T KRA103M-AT KRC103M
IC605 S21281169601 IC AD7819 8BIT SAMPLING ADC AD7819
2IC620-621 S22300502001 DIODE BAT54S SOT-23 BAT54S
C529-530 C535-536
C538-542 C545-549
C606-630 C650-651 S35101045039 CAP X7R 100N 10% 63V 2012 100n
C655-659 C670-677
C683-684
C654 S35101025039 CAP NPO 1N 10% 63V 2012 1N
C505 C507 C510 C512
S35101014331 CAP CE C 100PF 50V J 0805(2012) 100P NPO
C531-532 S35201005020 CAP NPO 10p 10% 63V SMD 10p NPO
C601-603 S35102204339 CAP CL 22PF 50V J 2012 22P
C604 S35102704321 CAP CE C 27PF 50V J 0603(1608) 27P
C525-526 C551-552 S35203314030 CAP NPO 330P 5% 50V 2012 330P
C503-504 C513-514
C524 C527 C550 S35203324030 CAP NPO 3.3N 5% 50V 2012 3.3N
C553 C506 C511
C518-521 C556-559 S35103304321 CAP CL 33PF 50V J 1608 33P
C605
CN501 CN503-506 4428595003 LW5267/LWB0640/2.5MM-03P WAFER 3P
CN502 4428595007 LW5267/LWB0640/2.5MM-07P CON / 7P
Ref No. Part No. ValueDescription
FRONT B'D:GEQ-2231D (4003482400)
FRONT B'D:GEQ-1231D (400382500)
DIP S/W B'D (4003481200)
SHT B'D (4003482700)
POWER/IN-OUT B'D (4003482600)
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL
• ANALOG INPUT
XLR & 1/4˝ TRS, Electronically Balanced, RF Filtered, and fully unbalanced compatible
Impedance .......................................................................................................................................>10kΩ
Maximal Input Level .........................................................................................................................20dBu
• ANALOG OUTPUT
XLR & 1/4˝ TRS, Electronically Balanced, RF Filtered and fully unbalanced compatible
Impedance ......................................................................................................................................< 100Ω
Maximum Output Level @ > 600Ω ...................................................................................................20dBu
DIP Switch Selectable Output Attenuator in 3dB Steps ...................20dBu to 2dBu and Unity-Gain Mode
• GRAPHIC EQUALIZER
31-Band 1/3-Octave Interpolating Constant-Q Filter Bank
Selectable Boost/Cut Range ..........................±12dB/ ±6dB and 0 to -12dB/ 0 to -6dB (in Cut Only mode)
Input Gain Control .....................................................................................................................0 to +18dB
6-LED Input Level Meter ..................................-40dBu, -24dBu, -15dBu, -8dBu,- 3dBu, Peak (> +18dBu)
• CUT FILTERS
Low-Cut Frequency Range .................................................................................................12.5Hz~200Hz
Low-Cut Slope .....................................................................................................18dB/octave Butterworth
High-Cut Frequency Range ..............................................................................................3.3kHz~29.5kHz
High-Cut Slope ....................................................................................................18dB/octave Butterworth
• PEAK-LIMITER
Type ......................................................................................................................Maximizer with Soft Clip
Threshold ..................................................................................................................................0 to 19dBu
3-LED Gain Reduction Meter .......................................................................................................1, 3, 6dB
Output Clip Indicator ...................................................................................................................> +19dBu
Limiter Link (GEQ-2231D only) .....................................................................................................ON/OFF
Channel Link (GEQ-2231D only) ..................................................................................................ON/OFF
• SYSTEM PERFORMANCE
Frequency Response (-0.5dB) ............................................................................................10Hz~31.5kHz
Dynamic Range .......................................................................................................................... > 95dB-A
THD+N ........................................................................................................................................< 0.003%
GENERAL
• Power Source .....................................................................................AC 100V/120V/230V/240V, 50/60Hz
• Power Consumption ..............................................................................................................................10W
• Weight ............................................................................................................................GEQ-1231D: 3.5kg
........................................................................................................................................GEQ-2231D: 5.0kg
• Dimensions ...........................................................GEQ-1231D (1HU Rack): 482(W)
44(H) 280(D) mm
.............................................................................. GEQ-2231D (2HU Rack): 482(W)
88(H) 280(D) mm
* Due to continuous improvements specifications and design are subject to change without prior notice.
C402-403 3549222091 CAP DE7100F 222MVAI-KC 2.2n/250
C404-405 3549472092 CAP DE7100F472MVAI-KC 4.7n/250
TR301 2658399940
COMON MODE CHOKE COIL MEQ-2000
CHOKE COIL
P1 P3 P14 P27 4465998210 TERMINAL(250)PCB TAB TERMINAL
4458999110 FUSE CLIP 5*20 FUSE CLIP
IC115-116 S21225165401 IC 74LCX 138(SOP16)PHI 74LCX138
C110-140 C142-197
S35101045039 CAP X7R 100N 10% 63V 2012 100n
C202-207 C209-211
C101-102 S35102204321 CAP CL 22PF 50V J 1608 22p
F101 S39006999944 EMI NFM60(SMD) NFM60R
C201 C208 S34121000422 CAP RC 10UF 16V 10u
IC106-114 S21225160201 IC 74HC4051 SOIC 74HC4051
IC101-105 IC120 S21224147701 IC 74LV164 SOT108-1 74LVC164
D101-103 D142 S22400502001 DIODE BAW56 SOT23 BAW56
D6 D8-13 D104-111
2309770100 LED BL-S4548-TBS22A 1.8MM LED1.8MM
D120-122 D128 D140
D116-117 D132-133
2300031100 LED LTL-1CHY LITEON
LED3MM-YELLOW
D14 D113 D123-124
D114 D129-131 2300032100 LED LTL-1CHG LITEON
LED3MM-GREEN
D115 D141
D126-127 D118-119
2300030000 LED LTL-1CHEE LITEON
LED3MM-RED
D112 D125
R102 R133 30101017121 RES TF 100 1/16W 1608 100
R104-119 R211-221
30101517121 RES TF 150 1/16W 1608 150
R223-225 R240-242
R101 R103
R135-158 R165-210
30101027121 RES TF 1K 1/16W 1608 1K
R230 R243
T101-108 4628980110 PUSH SWITCH PUSH S/W
Q101-103 S20510482001 TR MMBT4124 SOT-23 mmBT4124
SVR101-116
SVR119-132 3238010324 VR RS20111D6 10KB ALP SVR 10KB
SVR134-167
SVR168-173 3208010324 VR RK09K11330CC9 10KB ALP VR 10KB
J101 S44410510626
CON FFC/FPC 26P ZIP ANGLE CON 26P
4355735800 FLAT CABLE 1.0 140MM 26P ASS'Y
IC110 S21225165401 IC 74LCX 138M (SOP16) FSC 74LCX138
C108-112 C117-156
S35101045039 CAP X7R 100N 10% 63V 2012 100n
C158-161 C163
C100-101 S35102204321 CAP CL 22PF 50V J 1608 22p
F101 S39006999944 EMI NFM60(SMD) NFM60R
J101 S44410510626 CON FFC/FPC 26P ZIP ANGLE WAFER 26P
C157 C162 S34121000632 CAP RC 10UF 25V 10u
IC105-109 S21225160201 IC 74HC4051 SOIC 74HC4051
IC101-103 S21224147701 IC 74LV164 SOT108-1 74LV164
D117-118 S22400502001 DIODE BAW56 SOT-23 BAW56
D1-3 D100-102 S20510482001 LED BL-S4548-TBS22A 1.8MM LED1.8MM
D103-104 D110-112
2300032100 LED LTL-1CHG LITEON
LED3MM-GREEN
D109 D105-107
2300030000 LED LTL-1CHEE LITEON
LED3MM-RED
D115-116
D113-114 2300031100 LED LTL-1CHY LITEON
LED3MM-YELLOW
R118 R155 S30101017121 RES TF 100 1/16W 1608 100
R101-116 S30101517121 RES TF 150 1/16W 1608 150
R100 R123-154
S30101027121 RES TF 1K 1/16W 1608
R157-160
T101-103 4628980110 PUSH SWITCH PUSH S/W
Q101 S20510482001
TR MMBT4124 SOT-23 mmBT4124
SVR101-132 3238010324 VR RS20111D6 10KB SVR 10KB
SVR133-135 3208010324 VR RK09K11330CC9 10KB VR 10KB
J101 S44410510626
CON FFC/FPC 26P ZIP ANGLE CON 26P
4355735900 FLAT CABLE 1.0 80MM 26P ASS'Y
DS701 4698099610 SW DIP 4 WAY JEC DIP SW
4355738616 CON ASS'Y 5P 360MM ASS'Y
IC401 2168640988 IC 7815 SAMSUNG 7815
AC101 4308991810 AC CORD DOM 12A INLET AC INPUT
BD401 2058100976 DIODE BRIDGE KBP202G/KBP203G KBP02
C301-303 C307-309 3609104120-T CAP MA 0.1UF 100V J 0.1u
C412-413 C416-417 3689104219 CAP X7R 100N 10% 63V (LS5.08) 100n
C423 C425 C429
Page 14

2524
TOP AND BOTTOM VIEW OF P.C BOARD
F601-604 S39006999944 EMI NFM60(SMD) NFM60R
J603 4428592510 WAFER BOX TPHB03-1419-10A WAFER 10P
J602 4428592520 WAFER BOX TPHB03-1419-20A WAFER 20P
J101 S4410510626 CON FFC/FPC 26P ZIP ANGLE WAFER 26P
S601 4428590807 PIN HEADER 2X7PIN
2*7 pin header
X602 3938000860 CRYSTAL 24.576MHz (ATS-49U) 24.576MHz
X601 3938000830 CRYSTAL 33MHz (ATS-49U) 33MHz
C528 C534
C543-544 C561
S34121000422 CAP RC 10UF 16V
C652-653 C685-687 10 / 16
C689
C517 C522 C555
3409210149-T CAP RG 100UF 25V 105C 100 / 25
C560
C537 S34114700232 CAP SC 47UF 6.3V SAMWHA 47 / 6.3
C680-682 S34104700642 CAP SC 47UF 25V SAMWHA 47 / 25
C501-502 C508-509
C515-516 C523 3409247041-T CAP AF RSG 47UF 25V 5 P 47 / 25
C554
IC607 S21229069401 IC DS2401P(TSOC)DALLAS DS2401
IC602 S21235328101 SST28VF040A-200-4C-NH FALSH ROM
IC604 S21210009801 IC ALG265QL 4009 ROUTER TQFP100 QL4009
IC608 S21102030402 IC NJM78L05UA-TE1 JRC 78I05
IC603 S21243862501 IC K4S64323C-TC/L70 SRAM
IC606 S21265055402 IC TPS3801(SOT-323) TIA TPS3801
IC601 S21213009601 IC ADSP21065LKS-264 66MH ADI adsp 21065
IC614 S21286282701 IC AKM4524 24BIT 96kHz CODEC AKM4524
IC609 IC611-613 S21101083204 IC NJM 5532 DMP-8 JRC 5532DD
J3 J5 S30100007231 RES TF 0 1/10W 2012 0
R614 R628-630 S30100007121 RES TF 0 1/16W 1608 0
R503-504 R523-524 S30331505121 RES MF 1.5K F 1/16W 1608 1.5K 1%
R658 R680-681 S30101017231 RES TF 100 1/10W 2012 100
R501-502 R525-528
S30311005121 RES MF 100K 1/16W 1608 100K 1%
R573-574
R548-550 R615
R617-619 R625-627
S30101037121 RES TF 10K 1/16W 1608 10K
R652 R671-673
R607-609
R536 R565
S303320110120
RES MF 18.7K F 1608 18.7K 1%
R670 S30101007121 RES TF 10 1/16W 1608 10
R507-512 R515-520
R532-533 R539-540 S30333305121 RES MF 3.3K F 1/16 1608 3.3K 1%
R561-562 R568-569
R543-544 R557-558 S30336345120 RES MF 6.34K F 1608 6.34K 1%
R551-554 R650-651
R654-657
S30103907121 RES TF 39 1/16W 1608 39
R610-613 R616
R620-623 R601-606
R513-514 R529
S30104707121 RES MF 47 1/16W 1608 47
R538 R563 R572
R547 S30104797121 RES TF 4.7 1/16W 1608 4.7
R530-531 R534-535
S30318255120 RES MF 8.25K F 1608 8.25K 1%
R566-567 R570
R537 R564 S30321025120 RES MF 10.2K F 1608 10.2K1%
R541 R545 R556 S30318255120 RES MF 768 F 1608 768 1%
R560 4.7
R542 R546 R555
R559 S30332110120 RES MF 11K F1608 11K 1%
R505-506 R521-522
D601 2308660126 LED TLM-2100 RED SOT-23 (SMD) TLM2100
T601-602 4628988710 SW TACT THHV501BAA SW TACT
S44410013632 SOCKET IC PLCC 32 (SMD) SOCKET
4408194800 CON JUMP CON JMP
CN508 4428595005 LW5267/LWB0640/2.5MM-05P WAFER 5P
Ref No. Part No. ValueDescription
Page 15

2726
Page 16
2928
Page 17
3130
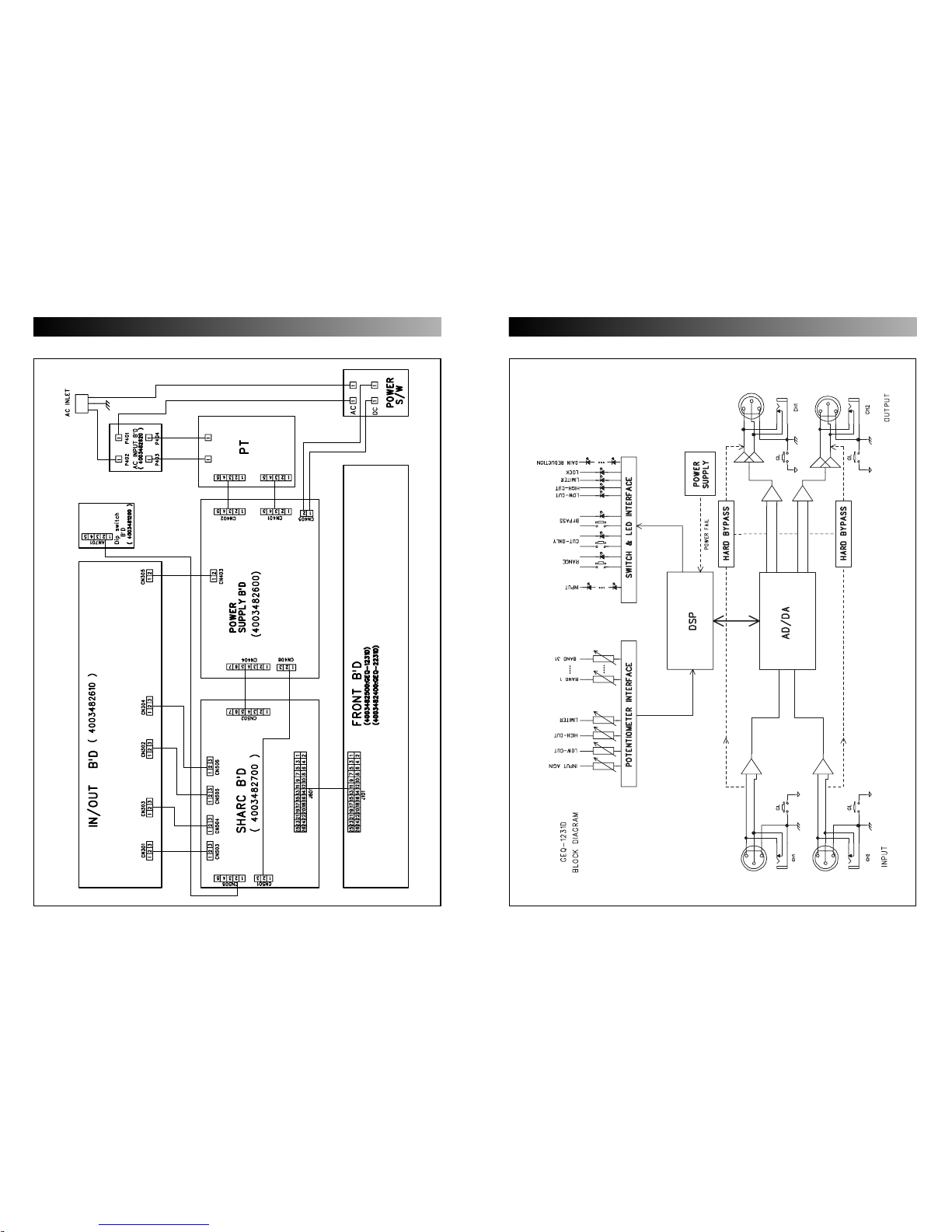
BLOCK DIAGRAMWIRING DIAGRAM
Page 18

32
Page 19

3433
SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM
GEQ - 1231D
FRONT B D
Page 20

3635
GEQ - 2231D
FRONT B D 1/2
Page 21
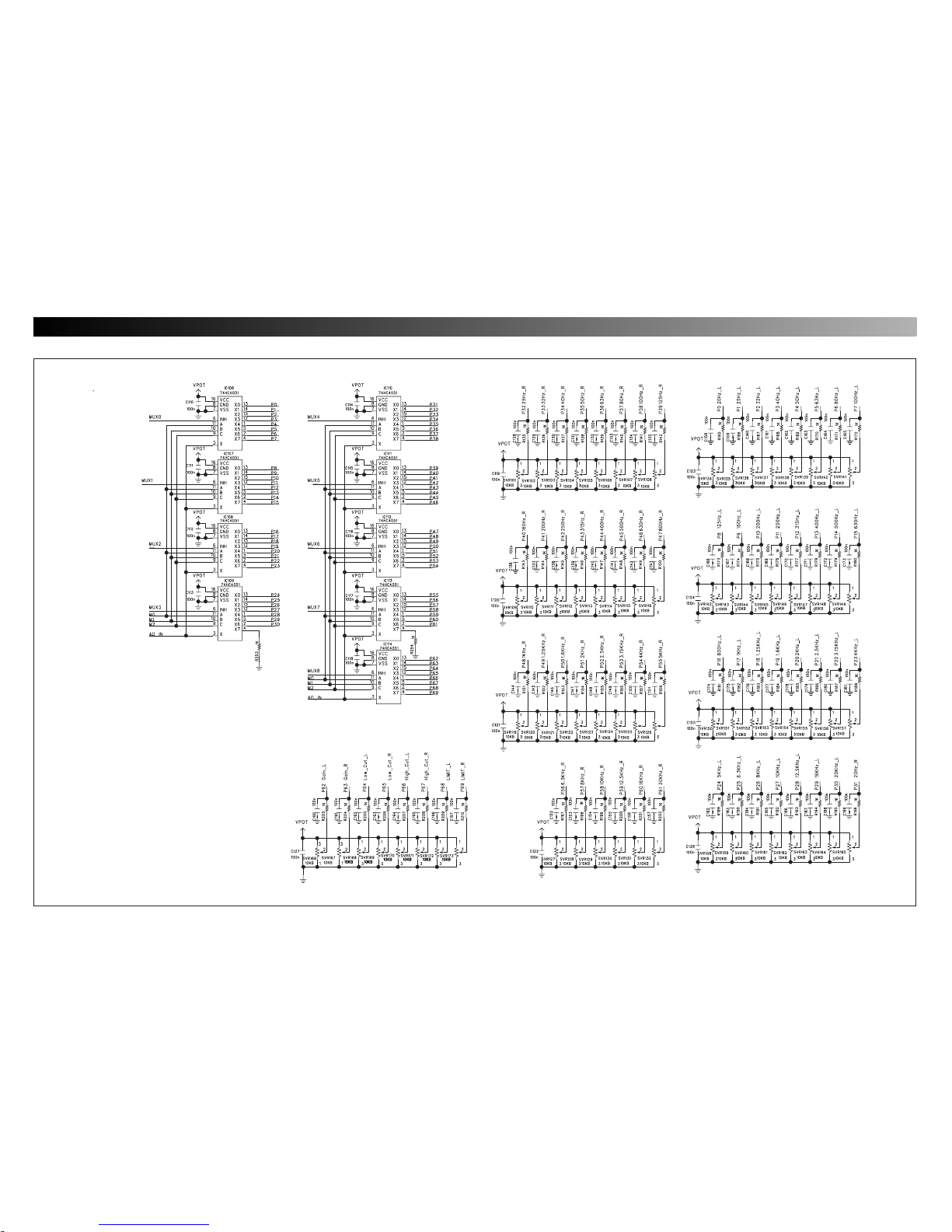
3837
GEQ - 2231D
FRONT B D 2/2
Page 22

4039
IN/OUT B D
Page 23

4241
POWER B D
Page 24

4443
SHT B D 1/4
Page 25

4645
SHT B D 2/4
Page 26

4847
SHT B D 3/4
Page 27

5049
SHT B D 4/4
Page 28
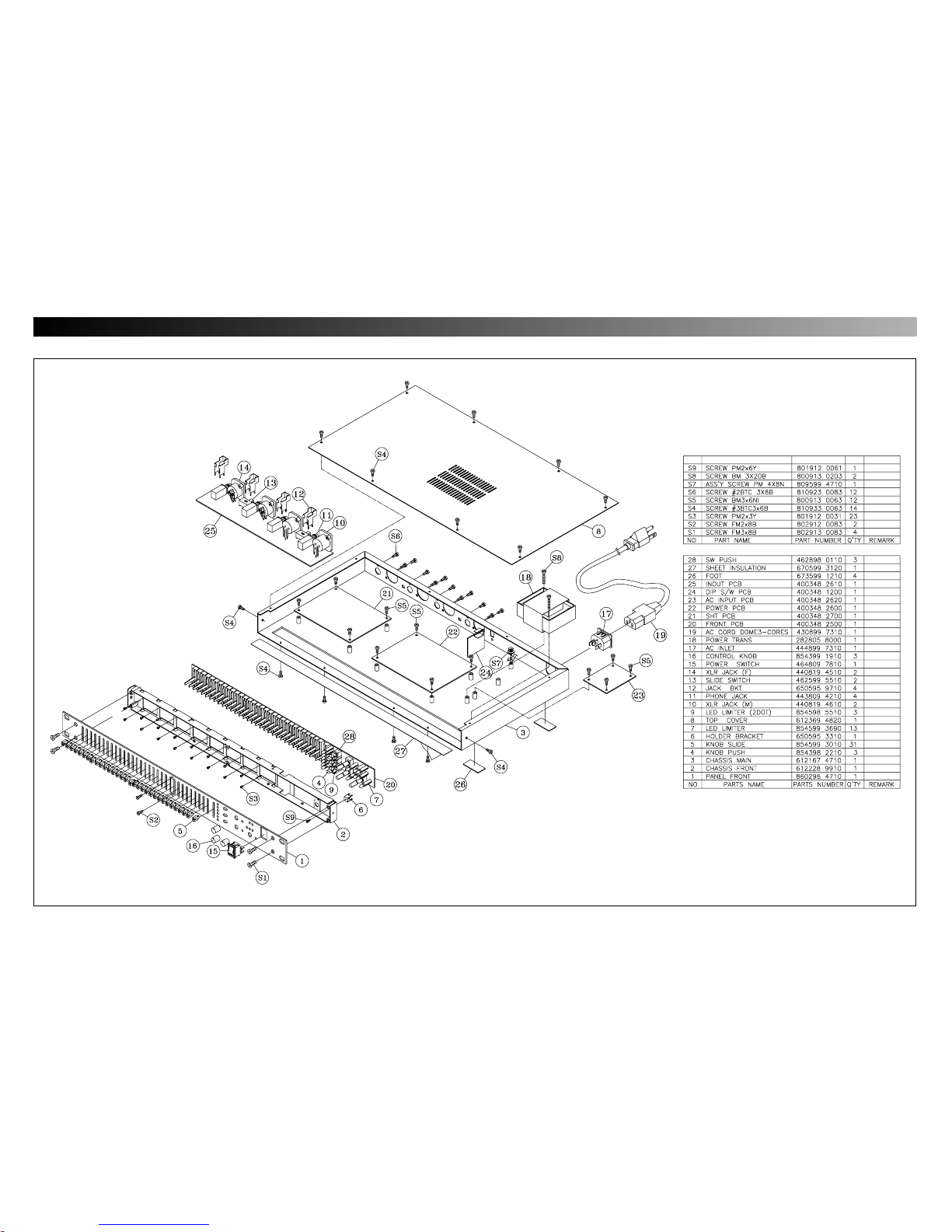
5251
EXPLODED CIEW OF CABINET & CHASSIS / MACHANICAL PARTS LIST
Page 29

5453
Page 30

5655
ASS’Y DRAWING
Page 31

5857
Page 32

NOTE
 Loading...
Loading...