Page 1

WEB-MANAGED
GIGABIT ETHERNET
SWITCH
WITH 4 SFP PORTS
USER MANUAL
MODELS 560801 & 560818
Model 560801, 16-Port
Model 560818, 24-Port
INT-560801/560818-UM-1112-01
Page 2

Web Managed GbE Switch
2
FCC Certifications
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used
in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference received; including interference that may cause undesired operation.
CE Warning
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility, EN
55022 class A for ITE, the essential protection requirement of Council Directive 2004/108/EC on
the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to electromagnetic compatibility.
Trademarks:
All trade names and trademarks are the properties of their respective companies.
Page 3

Web Managed GbE Switch
3
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction ·····································································································6
1.1 General Description ································································································6
1.2 The Front Panel ······································································································7
1.3 LEDs Definition ·······································································································7
1.4 The Rear Panel·······································································································7
1.5 Installation···············································································································9
Chapter 2 Basic Web Management Information ···························································11
2.1 System login ·········································································································11
2.2 The Graphic User Interface ··················································································12
2.3 Logging Out of the Web Configurator ···································································16
3.1.2 Log··············································································································19
3.1.3 Port ·············································································································21
3.1.3.1 Port Statistics···················································································· 21
3.1.3.2 Port Counters ··················································································· 22
3.1.3.3 Port Error Disabled··········································································· 24
3.1.3.4 Bandwidth Utilization ········································································ 24
3.1.4 Trunk Group································································································25
3.1.5 MAC Address Table····················································································26
3.1.5.1 Dynamic Learned ············································································· 26
3.1.5.2 Static MAC························································································ 27
3.2 Network·················································································································28
3.2.1 IP Address ··································································································28
3.2.2 IPv6 Address ······························································································30
3.2.3 Time············································································································31
3.3 Switching···············································································································32
3.3.1 Port Setting································································································· 32
3.3.2 Port Mirroring······························································································ 33
3.3.3 Trunk···········································································································34
3.3.3.1 Trunk Group ····················································································· 34
3.3.3.2 LACP ································································································ 36
3.3.4 VLAN ··········································································································37
3.3.4.1 VLAN Setting···················································································· 37
Chapter 3 Web Management Configuration ··································································17
3.1 Status····················································································································17
3.1.1 System Information·····················································································17
Page 4

Web Managed GbE Switch
4
3.3.4.2 VLAN Port Setting ············································································ 38
3.3.4.3 VLAN Port Mode Setting ·································································· 39
3.3.4.4 VLAN Ingress Filter ·········································································· 40
3.3.5 SVLAN········································································································ 40
3.3.5.1 SVLAN Setting ················································································· 40
3.3.5.2 SVLAN Member Setting ··································································· 41
3.3.5.3 SVLAN PVID Setting ········································································ 42
3.3.5.4 SVLAN Service Port ········································································· 42
3.3.6 Bandwidth Control ······················································································43
3.3.6.1 Preamble Setting·············································································· 43
3.3.6.2 Port Rate Setting ·············································································· 44
3.3.7 IGMP Snooping ··························································································46
3.3.7.1 IGMP Setting ···················································································· 46
3.3.7.2 IGMP VLAN Setting·········································································· 47
3.3.7.3 Multicast Database··········································································· 48
3.3.7.4 Router Table····················································································· 49
3.3.8 Jumbo Frame······························································································49
3.3.9 STP·············································································································50
3.3.9.1 STP Global Setting··········································································· 50
3.3.9.2 STP Port Setting··············································································· 52
3.3.9.3 MST Configuration ··········································································· 53
3.3.9.4 MST Instance Setting ······································································· 55
3.3.9.5 MST Port Setting ·············································································· 55
3.4 Security················································································································· 57
3.4.1 Storm Control······························································································57
3.4.2 MAC Filtering······························································································ 58
3.4.3 802.1X ········································································································59
3.4.3.1 802.1X Setting·················································································· 59
3.4.3.2 802.1X Port Setting ·········································································· 61
3.4.4 Port Security ·······························································································62
3.4.5 Protected Ports··························································································· 63
3.4.6 Access ········································································································63
3.4.6.1 Console ···························································································· 63
3.4.6.2 Telnet································································································ 64
3.4.6.3 SSH ·································································································· 65
3.4.6.4 HTTP ································································································ 66
3.4.6.5 HTTPS······························································································ 66
3.5 ACL······················································································································· 67
3.5.1 ACL Setting·································································································67
Page 5

Web Managed GbE Switch
5
3.5.2 ACL Template Setting ················································································70
3.5.3 ACL Index Range Setting ···········································································71
3.5.4 ACL Policy Setting······················································································ 72
3.6 QoS·······················································································································72
3.6.1 Port-based Priority······················································································ 72
3.6.2 802.1 p- based Priority ···············································································73
3.6.3 DSCP - based Priority·················································································74
3.6.4 Priority to Queue Mapping·········································································· 75
3.6.5 Packet Scheduling······················································································ 77
3.6.6 Queue Weight Setting ················································································77
3.6.7 Queue Remarking Status ···········································································78
3.6.8 Queue Remarking Table ············································································79
3.7 Management········································································································· 80
3.7.1 SNMP ·········································································································80
3.7.1.1 SNMP Setting··················································································· 80
3.7.1.2 SNMP Community············································································ 81
3.7.1.3 SNMP Trap······················································································· 82
3.8 Diagnostics ···········································································································83
3.8.1 Ping Test·····································································································83
3.8.2 Ping6 Test···································································································84
3.8.3 Log Setting ·································································································85
3.8.3.1 Local Log·························································································· 85
3.8.3.2 Remote Log······················································································ 86
3.8.4 Factory Default ···························································································87
3.8.5 Reboot Switch·····························································································88
3.9 Maintenance ·········································································································88
3.9.1 Backup Manager ························································································88
3.9.2 Upgrade Manager·······················································································90
3.9.3 Configuration Manager ···············································································91
3.9.4 Account Manager ·······················································································92
3.9.5 Enable Password························································································93
Product Specifications ·······································································································95
Page 6

Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 General Description
High Performance
This 16/24 + 4 Layer 2 Gigabit Switch is a high-performance SNMP-managed device that provides
users with 16 or 24 10/100/1000 Mbps Ethernet and four additional Gigabit SFP ports. The
Web/SNMP management provides remote control capability, providing flexible network
management and monitoring options. Whether managed through an "in-band" SNMP management
station or an Internet Web browser, the Intellinet Gigabit switch facilitates network management
and problem diagnosis.
Flexible Network Management
The switch is easy to use and manage, designed to increase business productivity by reliably
supporting business applications. It features a Web-based GUI and supports SNMP, RMON and
Telnet. The impressive list of features includes, but is not limited to, ACL management,
sophisticated QoS-related settings, port mirroring, integrated IP-connectivity tools, logging, MAC
filtering, RADIUS authentication, port aggregation and detailed port rate configuration options.
Eliminate Bottlenecks
This switch offers plenty of performance for your computers, servers and other networking devices.
In addition, four small form-factor pluggable GBIC module slots (SFP) provide fiber connectivity for
greater distances. These are not shared combo-ports, but true Gigabit ports, pushing the total
available bandwidth up to 40 Gbps for Model 560801 and 56 Gbps for Model 560818.
Page 7

1.2 The Front Panel
The following figure shows the front panel of the switch.
The following table describes the port labels on the front panel.
LABEL
DESCRIPTON
16 / 24 10/100
RJ-45 Ethernet
Ports
Connect these ports to a computer, a hub, an Ethernet switch or router
Four
Mini-GBIC
Slots:
Use mini-GBIC transceivers in these slots for connections to backbone
Ethernet switches.
1.3 LEDs Definition
This device provides a full complement of LEDs to indicate the status of power, system functions
and ports. See the following description for reference:
LED
Status
Operation
Steady Green
The switch is powered on.
Power
Off
The switch is powered off.
Steady Green
Valid port connection.
Blinking Green
Valid port connection and there is data transmitting/ receiving.
Link/ACT
Off
Port disconnected.
The Restore Defaults (Reset) Button
Reset the switch to its factory default configuration using the Restore Defaults (Reset) button on
the front panel. Press the recessed button for one second and release. The switch automatically
reboots and reloads its factory configuration file.
1.4 The Rear Panel
The following figure shows the rear panel of the switch:
Power Receptacle
To be compatible with the electric service standards around the world, the switch is designed to
Page 8

Web Managed GbE Switch
8
afford the power supply in the range from 100 to 240 VAC, 50/60 Hz. Make sure that your outlet
standard is within this range.
To power on the switch, plug the female end of the power cord firmly into the receptacle of the
switch and the other end into an electric service outlet. After the power cord installation, confirm
that the power LED is lit indicating normal power status.
Page 9

1.5 Installation
This switch can be placed on your desktop or another flat surface or mounted in a rack. Refer to the
instructions for installation.
Before operating the switch, it’s recommended that:
1. The switch is placed within an appropriate ventilation environment. A minimum of 25 mm of
space around the unit is recommended.
2. The switch and the relevant components are away from sources of electrical noise such as radios,
transmitters and broadband amplifiers.
3. The switch is not placed in an excessively moist or humid environment.
Desktop Installation
1. Install the switch on a level surface that can support the weight of the unit and the relevant
components.
2. Connect the switch to the female end of the provided power cord and plug the male end into the
power outlet.
Rackmount Installation
The switch may be standalone or mounted in a rack. Rackmounting allows a more orderly installation
when you are going to install a series of networking devices.
Procedures for rackmounting the switch:
1. Disconnect all the cables from the switch.
2. Place the unit on a hard, flat surface with the front facing you.
3. Position a mounting bracket over the mounting holes on one side of the unit.
4. Insert the screws and fully tighten with a suitable screwdriver.
5. Repeat the two previous steps for the other side of the unit.
6. Insert the unit into the rack and secure with suitable screws.
7. Reconnect all the cables.
Installing Network Cables
1. Crossover or straight-through cable: All the ports on the switch support Auto-MDI/MDI-X
functionality. Both straight-through or crossover cables can be used as the media to connect the
switch with PCs as well as other devices like switches, hubs or routers.
Page 10
Web Managed GbE Switch
10
2. Category 3, 4, 5 or 5e, 6 UTP/STP cable: To make a valid connection and obtain the optimal
performance, an appropriate cable that corresponds to different transmitting/receiving speeds is
required. To choose a suitable cable, refer to the following table.
Media
Speed
Wiring
10 Mbps
Category 3,4,5 UTP/STP
100 Mbps
Category 5 UTP/STP
10/100/1000 Mbps
copper
1000 Mbps
Category 5e, 6 UTP/STP
1000 Mbps Fiber
(mini-GBIC
required)
1000 Mbps
The cable type differs from the mini-GBIC you choose. Refer to
the instructions that came with your mini-GBIC.
Page 11
Web Managed GbE Switch
11
Chapter 2 Basic Web Management Information
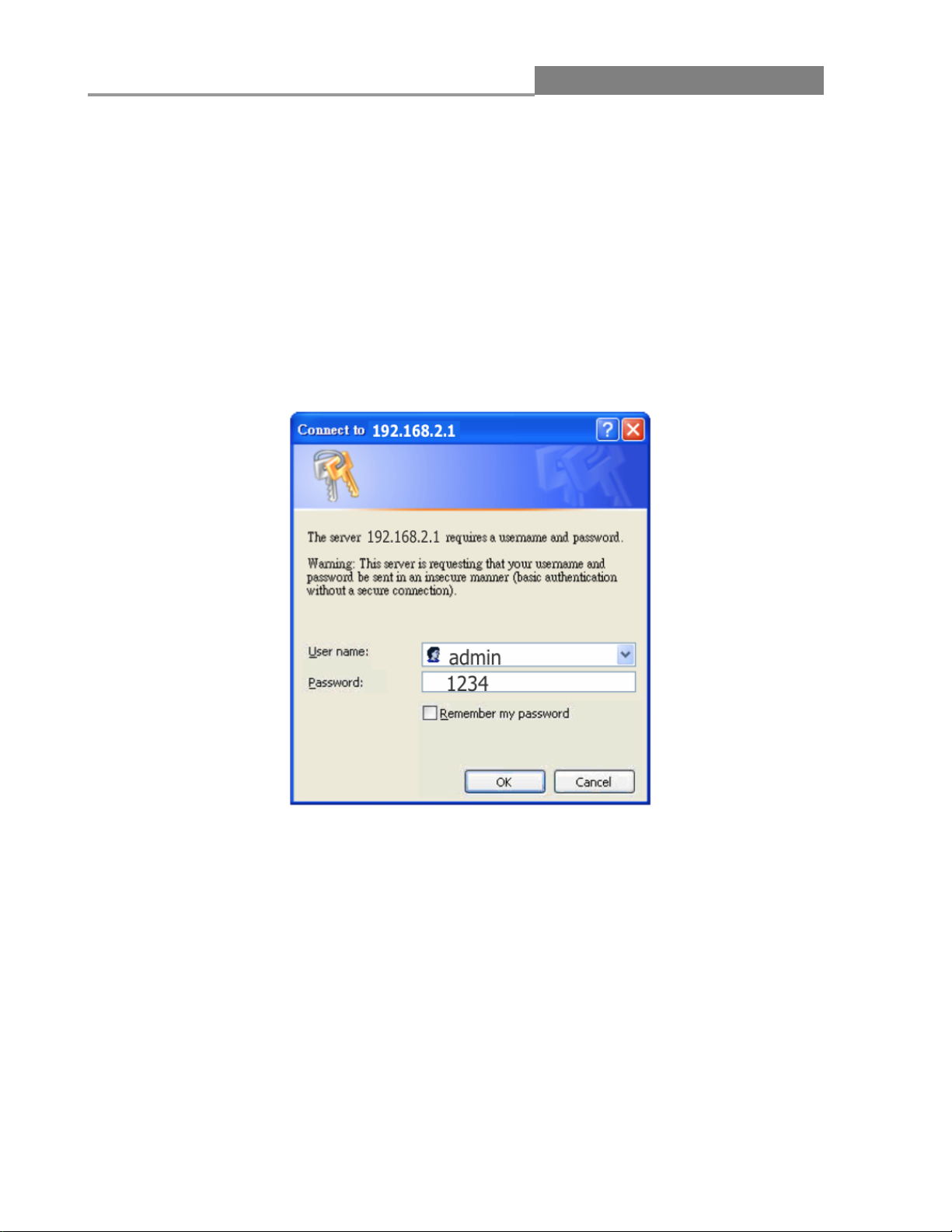
2.1 System login
1. Start your Web browser.
2. Type “http://”and the IP address of the switch (for example, the default management IP address
is 192.168.2.1) in the Location or Address field. Press [ENTER].
3. The login screen appears. The default username is “admin” and the password is “1234.”
Page 12
Web Managed GbE Switch
12
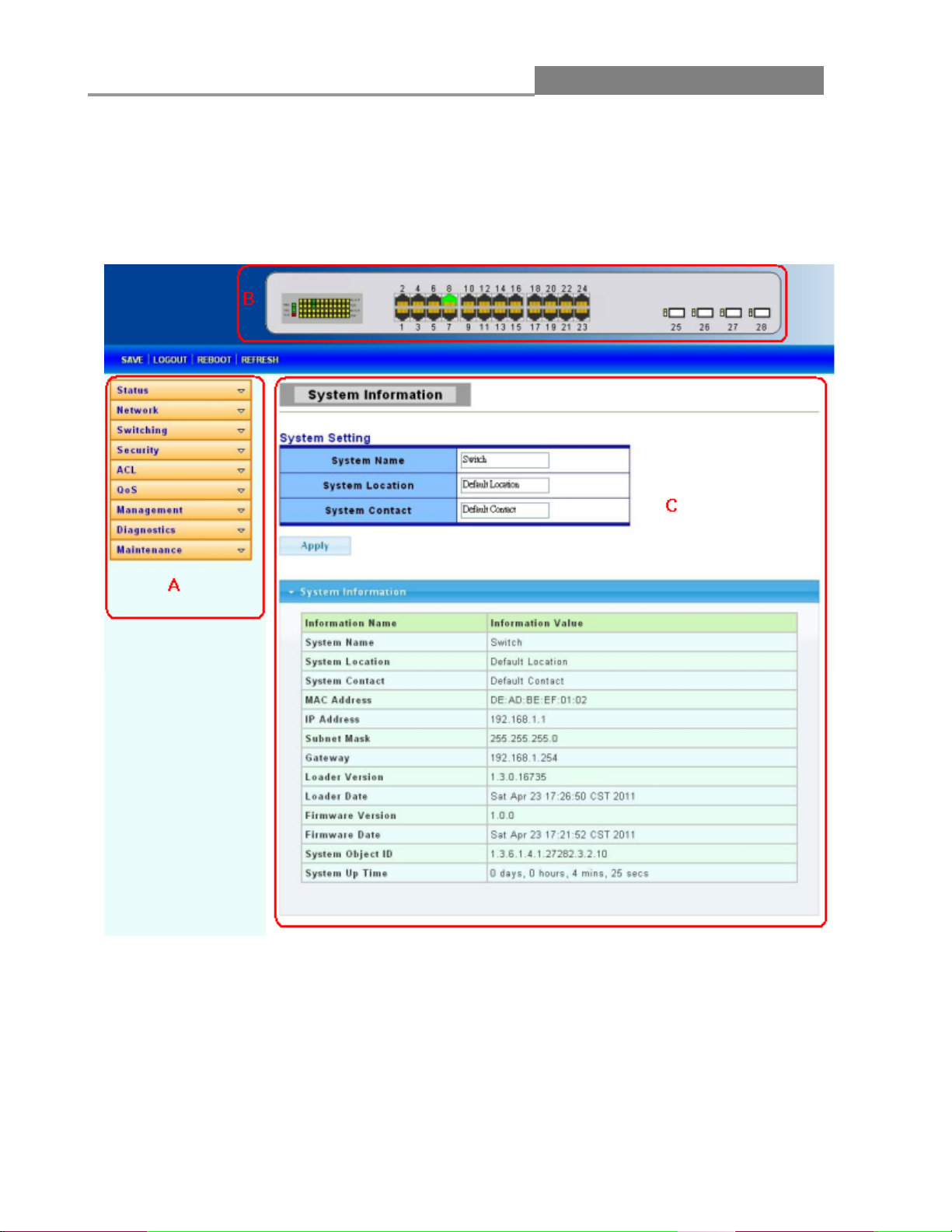
2.2 The Graphic User Interface
After the password authorization, the information page shows up. You may click on each folder on
the left column of each page to get access to each configuration page. The Graphic User Interface is
as follows:
A – Click the menu items to open submenu links, and then click on a submenu link to open the
screen in the main window.
B – It shows the switch’s current link status. Green squares indicate the port link is up, while black
squares indicate the port link is down.
C – Displays system information such as MAC address and firmware version.
Page 13

Web Managed GbE Switch
13
In the navigation panel, click a main link to reveal a list of submenu links shown as the following:
Status
Network
Switching
Security
ACL
QoS
Management
Diagnostics
Maintenance
Page 14
Web Managed GbE Switch
14
The following table describes the links in the navigation panel.
LINKS
DESCRIPTION
Status
System Information
This link takes you to a screen that displays general system
information.
Log
This sub-menu takes you to screens where you can view
and set up system logs.
Port
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
port information.
Trunk Group
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
trunk settings on a port.
MAC Address Table
This link takes you to screens where you can configure MAC
address options.
Network
IP Address
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
IP information.
IPv6 Address
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
IPv6 information.
Time
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
switch’s time settings.
Switching
Port Setting
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure
settings for individual switch ports.
Port Mirroring
This sub-menu takes you to screens where you can copy
traffic from one port or ports to another port in order that you
can examine the traffic from the first port without
interference.
Trunk
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
trunk settings on a port.
VLAN
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
VLAN (IEEE 802.1Q) settings on a port.
SVLAN
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
SVLAN settings on a port.
Bandwidth Control
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure
bandwidth limits on the switch.
IGMP Snooping
This sub-menu takes you to screens where you can
configure and revising the information of IGMP Snooping.
Jumbo Frame
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
Page 15
Web Managed GbE Switch
15
Jumbo Frame size.
STP
This sub-menu takes you to screens where you can
configure the STP to prevent network loops.
Security
Storm Control
This link takes you to a screen where you can limit the
number of broadcast, multicast and unknown unicast and
multicast packets the Switch receives per second on the
ports.
MAC Filtering
This sub-menu takes you to screens where you can
configure the accessed MAC address.
802.1X
This sub-menu takes you to screens where you can
configure IEEE 802.1x port authentication for clients
communicating via the switch.
Port Security
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
port security setting.
Protected Ports
This link takes you to a screen to setting and revising the
protected ports.
Access
This link takes you a way to access the switch.
ACL
ACL Setting
This link takes you to a screen to setting and revising the
basic setting of ASL.
ACL Template Setting
This link takes you to a screen to setting and revising the
template setting of ASL.
ACL Index Range Setting
This link takes you to a screen to setting and revising the
index range setting of ASL.
ACL Policy Setting
This link takes you to a screen to setting and revising the
policy setting of ASL.
QoS
Port-based Priority
This link takes you to a screen where you can assign a IEEE
802.1p priority to packets based on the ingress (incoming)
port of the packet.
802.1p-based Priority
This link takes you to a screen where you can assign a IEEE
802.1p-based priority to packets based on the ingress
(incoming) port of the packet.
DSCP-based Priority
This link takes you to a screen where you can assign priority
to packets based on their Differentiated Services Code
Points (DSCPs).
Priority to Queue Mapping
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure the
priority level-to-physical queue mapping.
Packet Scheduling
Packet Scheduling is used to help solve performance
degradation when there is network congestion. Use this
screen to configure queuing algorithms for outgoing traffic.
Queue Weight Setting
This link takes you to a screen where you can assign a
queue weight to packets based on the ingress (incoming)
port of the packet.
Page 16
Web Managed GbE Switch
16
QoS Remarking Status
This link takes you to a screen where you can assign a QoS
remarking status to packets based on the ingress (incoming)
port of the packet.
QoS Remarking Table
This link takes you to a screen where you can assign a QoS
remarking table to packets based on the ingress (incoming)
port of the packet.
Management
SNMP
This link takes you to a screen where you can set and revise
the SNMP.
Diagnostics
Ping Test
This link takes you to a screen where you can do Ping test.
Ping6 Test
This link takes you to a screen where you can do Ping6 test.
Log Setting
This link takes you to a screen where you can configure log
settings.
Factory Default
This link takes you back to the factory default configuration.
Reboot Switch
This link takes you to a screen where you can reboot the
switch.
Maintenance
Backup Manager
This link takes you to a screen where you can back up the
settings you have made.
Upgrade Manager
This link takes you to a screen where you can upgrade the
switch settings.
Configuration Manager
This link takes you to a screen where you can save all the
configurations you have made to the switch.
Account Manager
This link takes you to a screen where you can change the
Web configurator login account.
Enable Password
This link takes you to a screen where you can change the
login password.
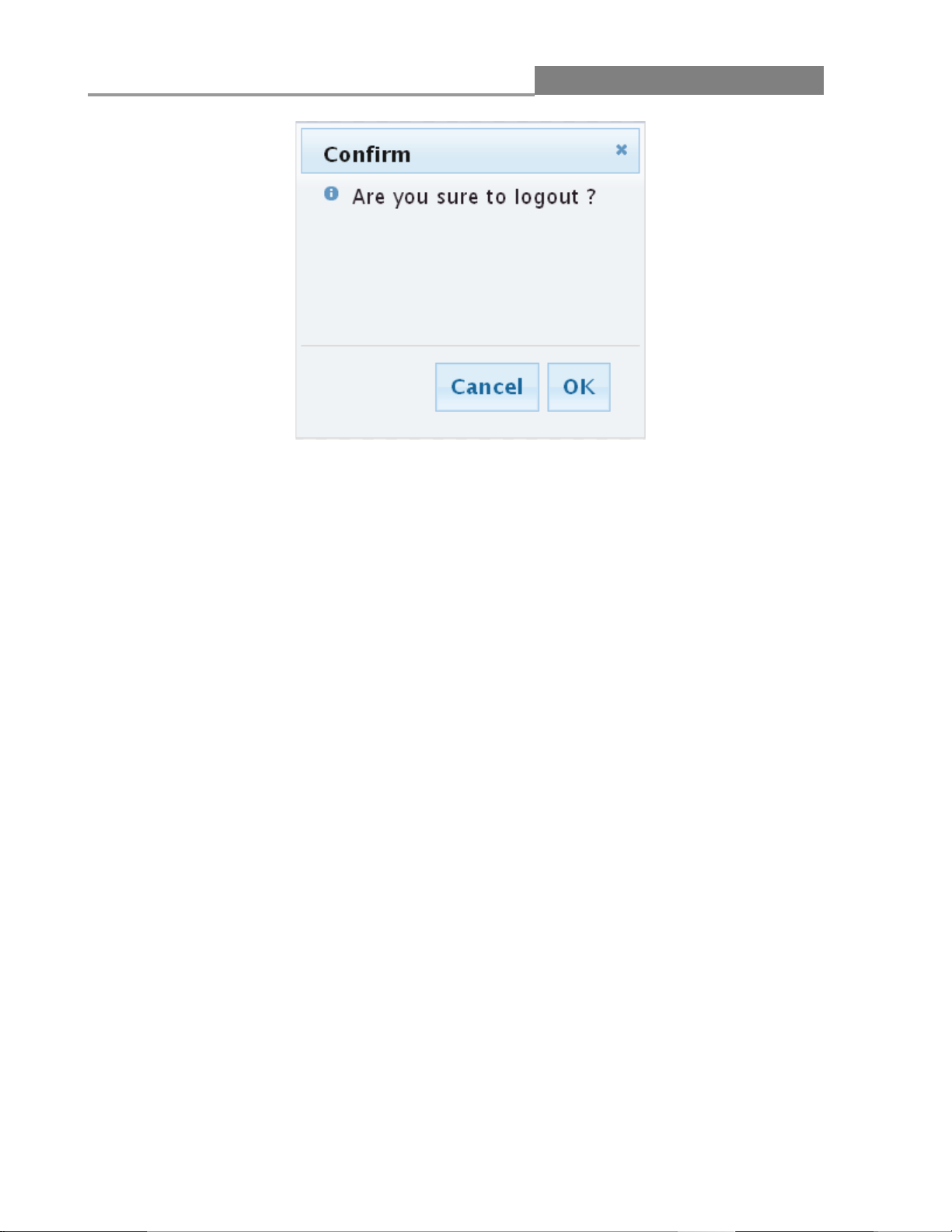
2.3 Logging Out of the Web Configurator
Click Logout in the navigation panel to exit the Web configurator. You have to log in with your
password again after you log out. This is recommended after you finish a management session for
security reasons.
Page 17
Web Managed GbE Switch
17
Page 18
Web Managed GbE Switch
18
Chapter 3 Web Management Configuration
3.1 Status
Use the Status pages to view system information and status.
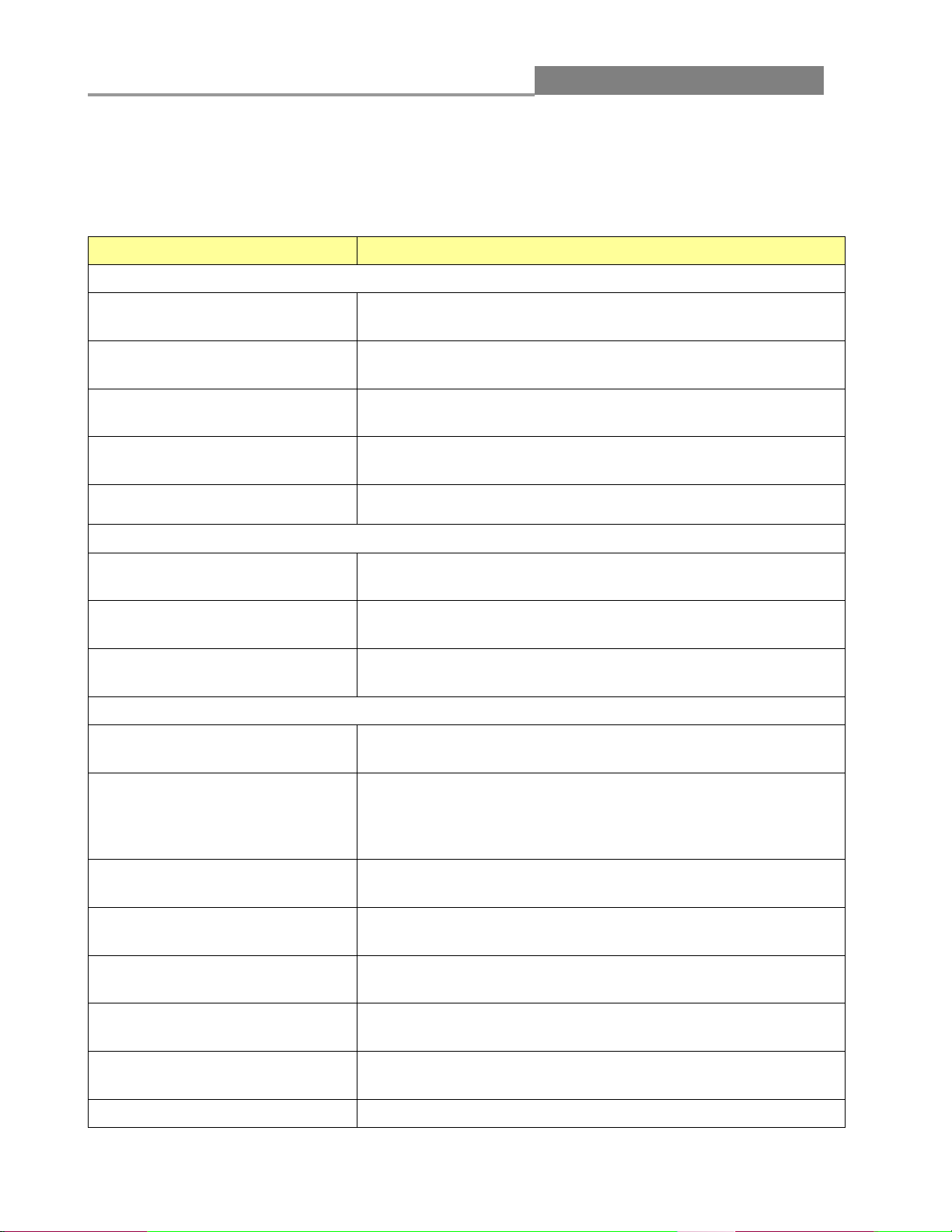
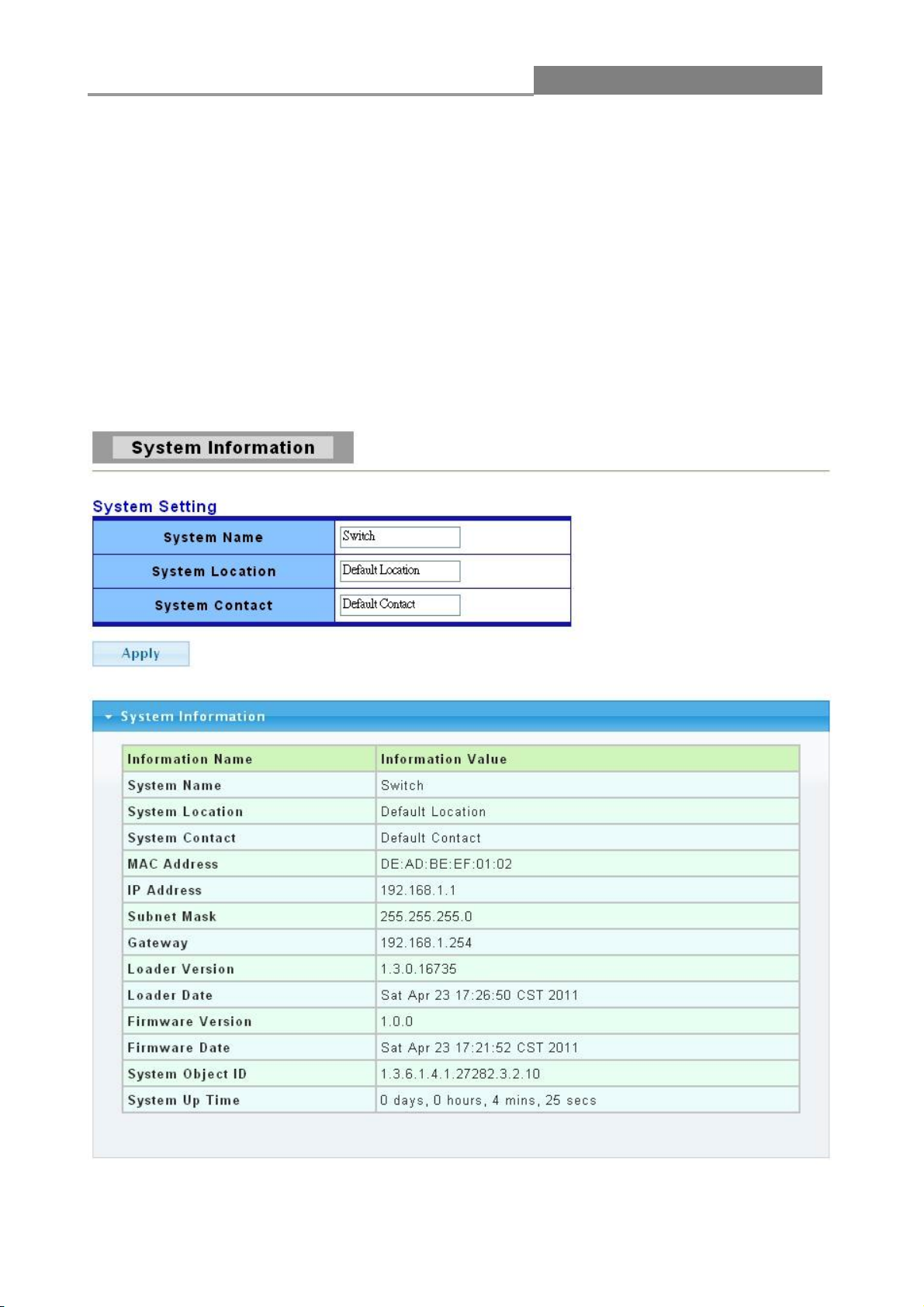
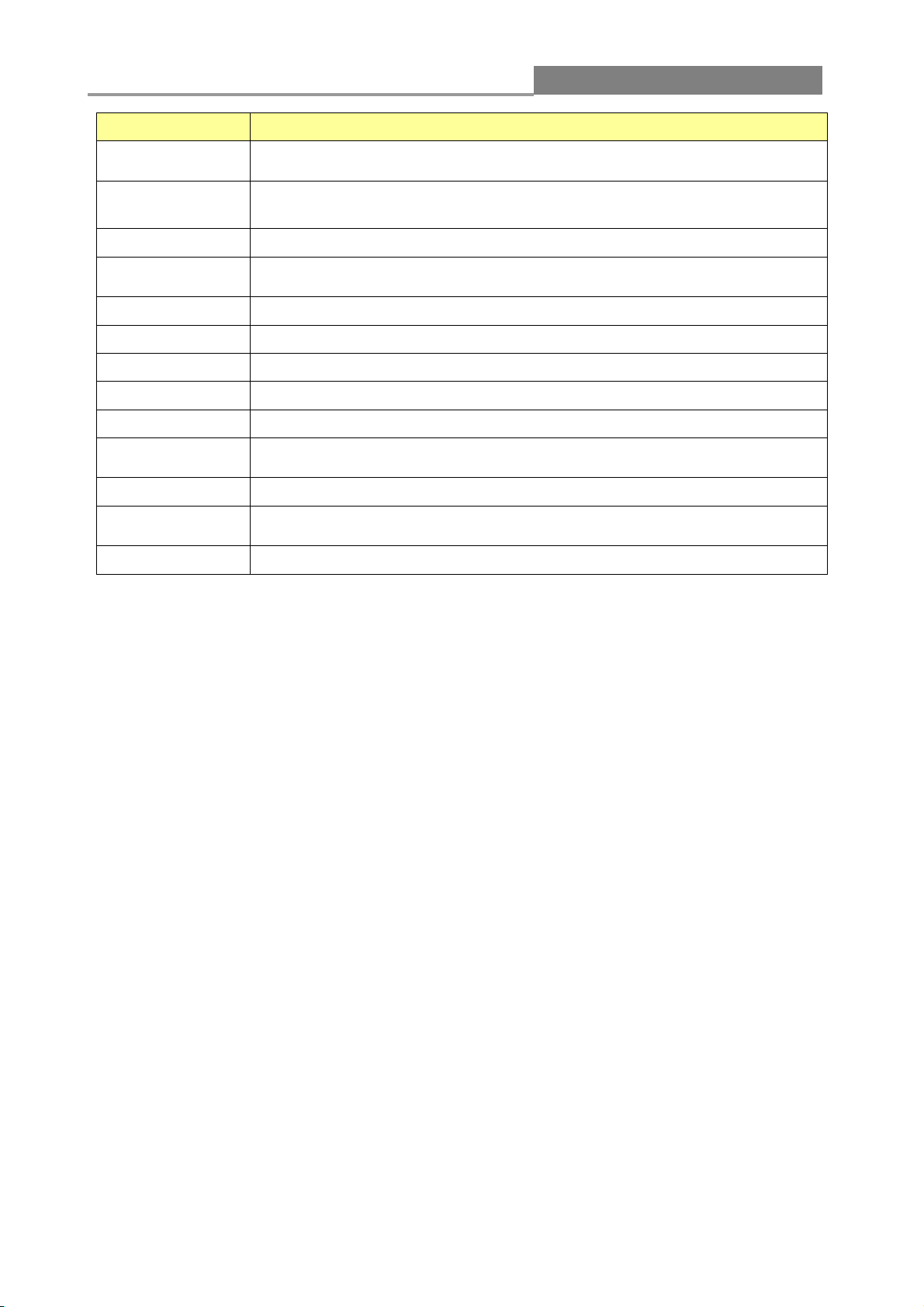
3.1.1 System Information
In the navigation panel, click Status > System Information to display the screen as shown below.
This page allow user to configure and browse some system information such as MAC address, IP
address, loader version and firmware version.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 19
Web Managed GbE Switch
19
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
System Name
This field displays the descriptive name of the switch for identification
purposes.
System
Location
This field displays the system location of the switch.
System Contact
This field displays the system contact of the switch.
MAC Address
This field refers to the Ethernet MAC (Media Access Control) address of
the switch.
IP Address
This field displays the IP address of the switch.
Subnet Mask
This field displays the subnet mask of the switch.
Gateway
This field displays the IP address of the gateway.
Loader Version
This field displays the loader version of the switch.
Loader Date
This field displays the loader date of the switch.
Firmware
Version
This field displays the version number of the switch’s current firmware.
Firmware Date
This field displays the switch’s firmware created date.
System Object
ID
This field displays the system object ID of the switch.
System Up Time
This field displays the system up time.
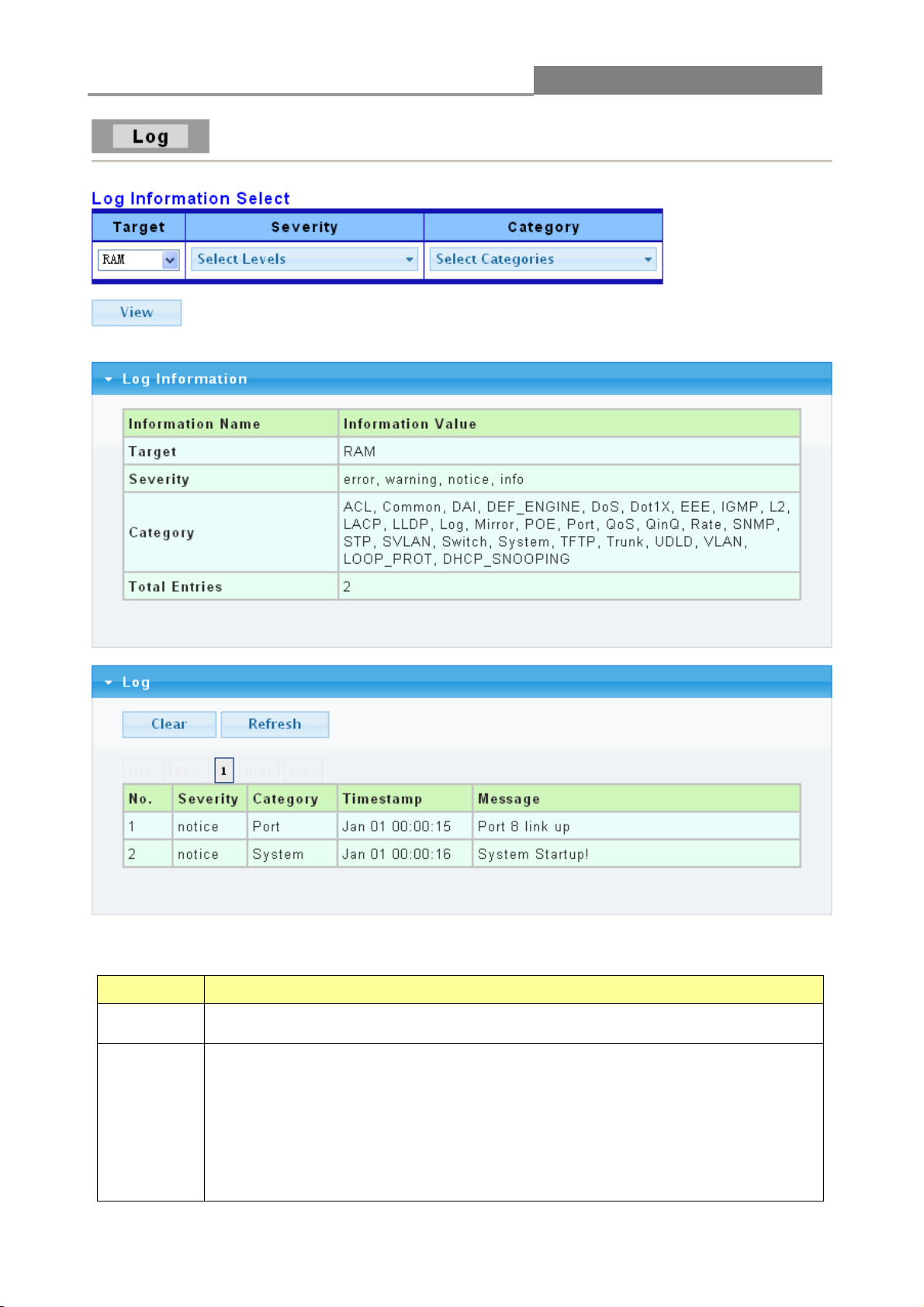
3.1.2 Log
Use this screen to display the switch logs. Click Status > Log in the navigation panel to display the
screen shown below.
Page 20
Web Managed GbE Switch
20
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Target
Select RAM to display only the logs stored in the RAM.
Select Flash to display only the logs stored in the Flash memory.
Severity
Select severity level(s) to filter log messages. The possible severity levels are:
Error - to record system failures, such as events which will cause the
switch to malfunction and events such as invalid user input in the
Web configurator.
Warning - to record non-critical errors on the Switch. The Switch will
continue to function when warnings are recorded.
Info - to record regular system events, such as configuration changes or
logins.
Page 21
Web Managed GbE Switch
21
Notice- to record the error that needs attention.
Category
Select Category to filter log messages. The categories are based on software
and hardware features of the switch. For example, the category MIRROR
records events which deal with the Port Mirroring features you set up and the
category SYSTEM records events which deal with the overall operation of the
switch.
View
Click the View button to display the logs according the criteria specified in the
fields above.
No.
This is the index number for the log entry.
Severity
This field displays the severity level of the log entry.
Category
This field displays what category the log entry fits into.
Timestamp
This field specifies the time when the switch recorded the log event. The
switch resets its internal clock when it is restarted.
Message
This field displays an explanation for the log entry.
3.1.3 Port
The Port configuration page displays port summary and status information.
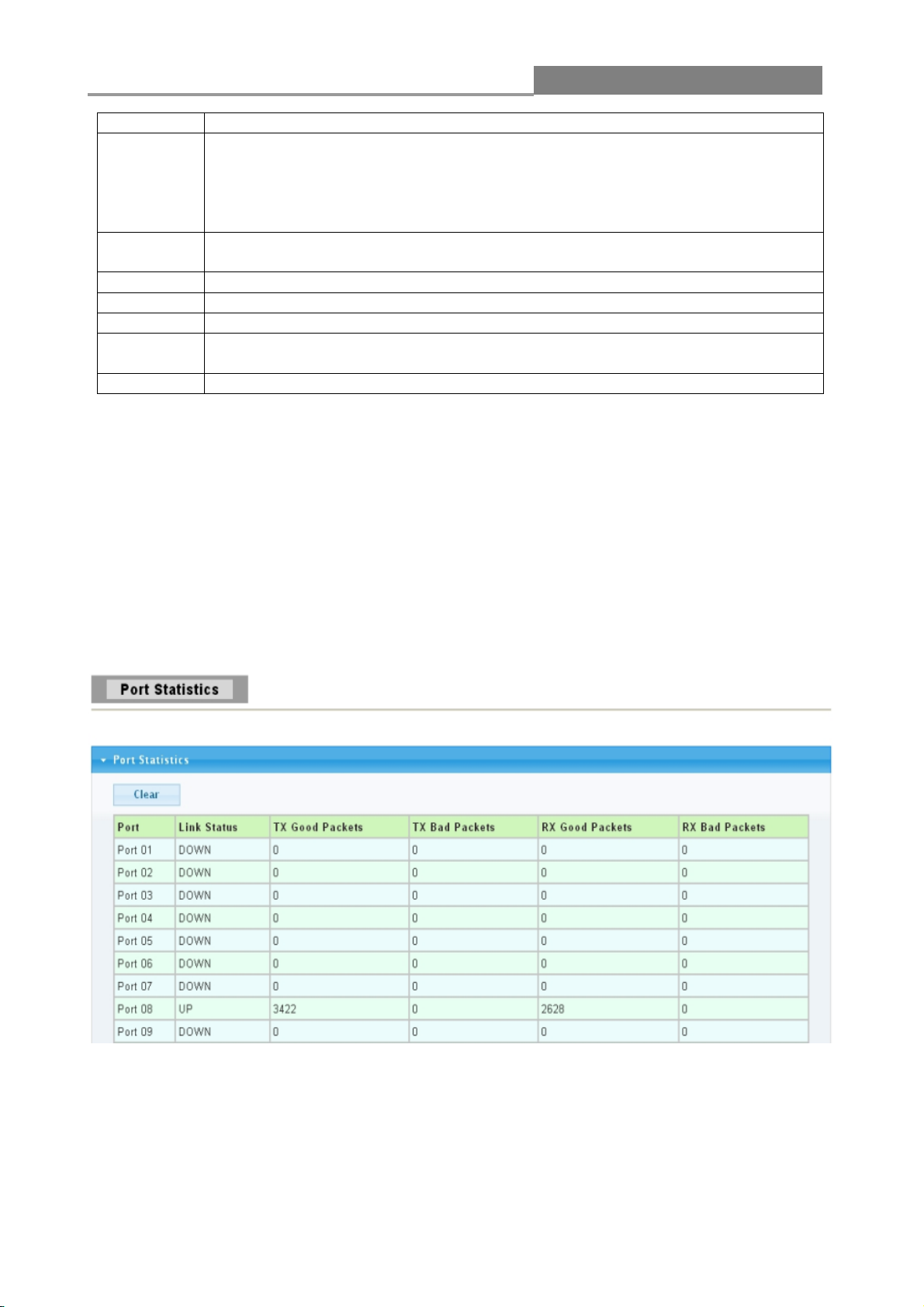
3.1.3.1 Port Statistics
Use this screen to display the Switch port statistics. Click Status->Port > Port Statistics to view
the screen shown below.
Page 22
Web Managed GbE Switch
22
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
This identifies the Ethernet port.
Link Status
This field displays Link Up if the port is currently in use. Otherwise it
displays Link Down.
Tx Good Pkt
This field shows the number of frames successfully transmitted on this port.
Tx Bad Pkt
This field shows the number of frames unsuccessfully transmitted on this
port.
Rx Good Pkt
This field shows the number of frames successfully received on this port.
Rx Bad Pkt
This field shows the number of frames unsuccessfully received on this port.
Clear
Click the Clear button to reset the port statistics.
3.1.3.2 Port Counters
Click Status->Port > Port Counters to view the screen shown below.
This page displays standard counters on network traffic from the Interface, Etherlike and RMON
MIB. Interface and Etherlike counters display errors on the traffic passing through each port.
RMON counters provide a total count of different frame types and sizes passing through each port.
Page 23
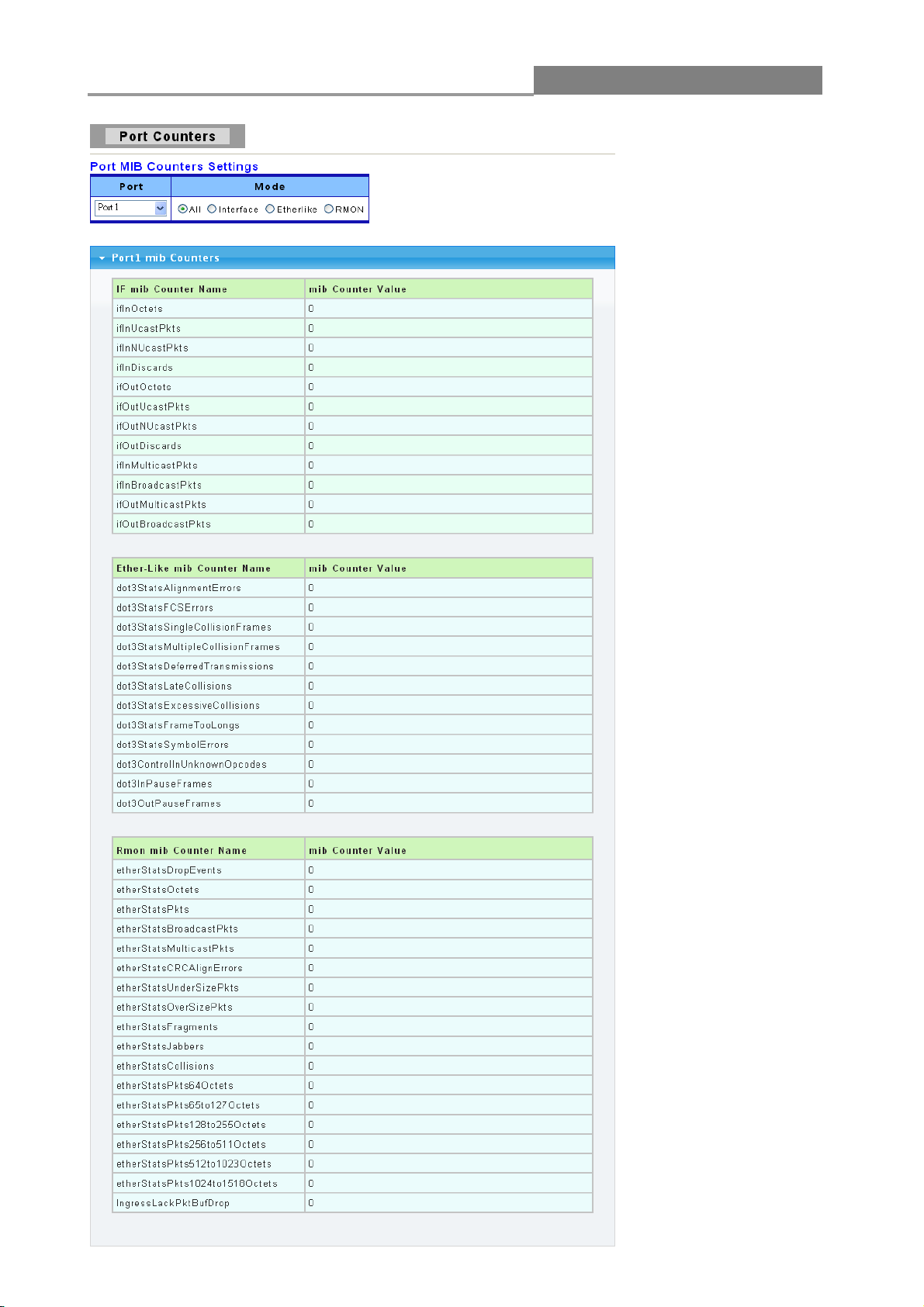
Web Managed GbE Switch
23
Page 24
Web Managed GbE Switch
24
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
This identifies the Ethernet port.
Mode
You have four choices: All, Interface, Etherlike and RMON.
3.1.3.3 Port Error Disabled
This page allow the user to browse ports that are disabled by some protocols, such as BPDU
Guard, Loopback and UDLD.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port Name
This shows the disabled Ethernet port.
Error Disabled
Reason
This shows the reasons for the error(s).
Recover
Click this button to enable those error-disabled ports.
3.1.3.4 Bandwidth Utilization
Page 25
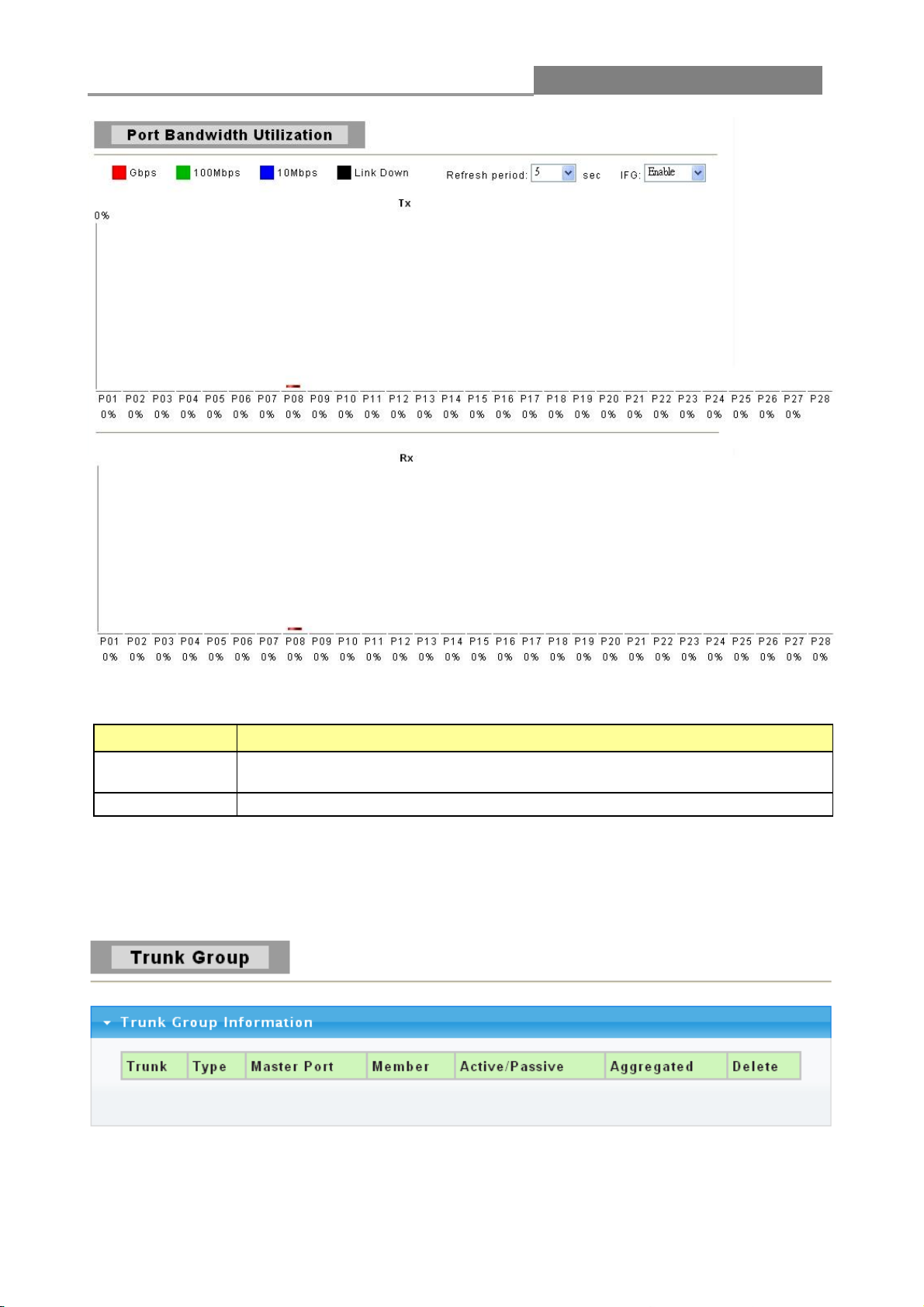
Web Managed GbE Switch
25
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Refresh Period
This shows the period interval between last and next refresh. You have
three choices: 2 sec, 5 sec and 10 sec.
IFG
You can enable or disable this function.
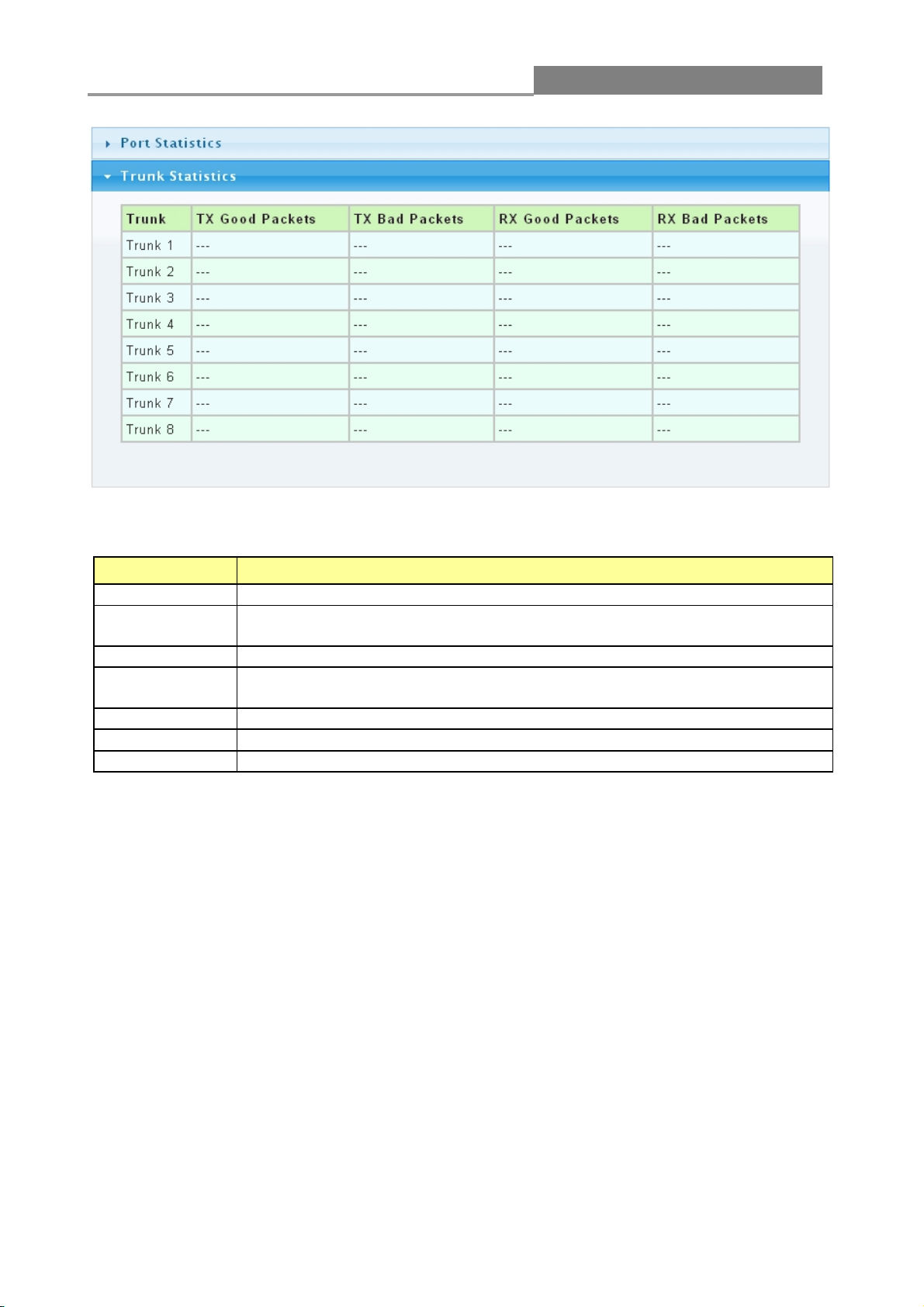
3.1.4 Trunk Group
Click Status > Trunk Group in the navigation panel to view the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 26
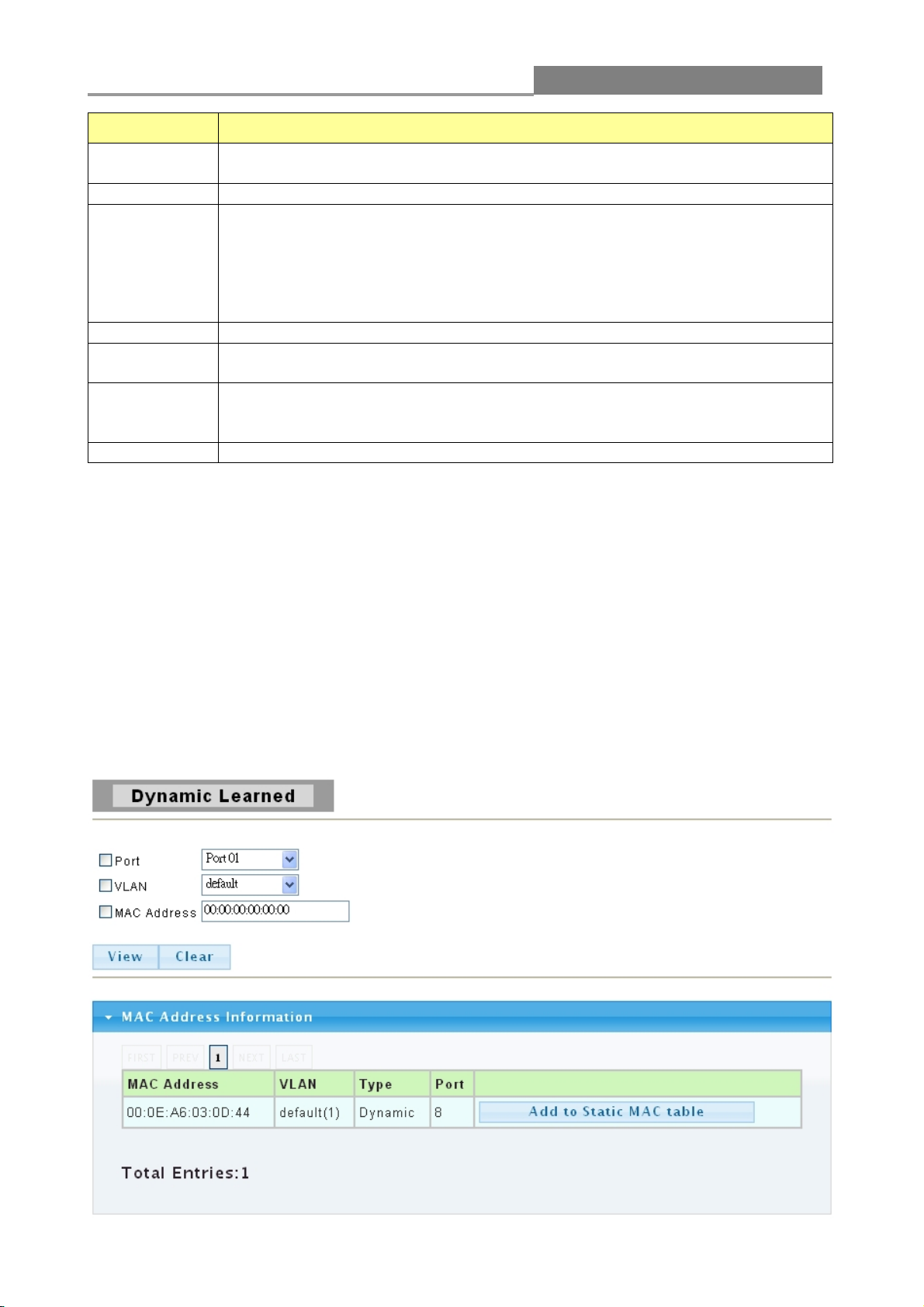
Web Managed GbE Switch
26
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Trunk
This field displays the trunk to identify a trunk group; that is, one logical link
containing multiple ports.
Type
This field displays the type of the trunk group: a static trunk or an LACP trunk.
Master port
This field displays which ports are master ports of the trunk. The port with
lowest port ID is designated to be master port of the trunk. To synchronize the
settings of trunk member ports, the configuration of the trunk master port
would be applied to all trunk member ports. Other member ports are slave
ports that cannot be configured individually in most settings (such as VLAN,
port ability and so on.) but follow the configuration of the master port.
Member
This field shows the member ports of the trunk.
Active/
Passive
If the trunk is an LACP trunk, this field shows the LACP active and passive
ports. The LACP active port would send LACP PDU periodically.
Aggregated
This field displays the ports that aggregated in a trunk group. A static trunk
would be aggregated immediately; an LACP trunk exchanges LACP PDU to
link partner to aggregate.
Delete
Click this button to delete the trunk.
3.1.5 MAC Address Table
Use the MAC Address Table pages to show dynamic MAC table and configure settings for static
MAC entries.
3.1.5.1 Dynamic Learned
Click Status > MAC Address Table > Dynamic Learned in the navigation panel to bring up the
screen shown below.
Page 27
Web Managed GbE Switch
27
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the port number to show or clear dynamic MAC entries. If not
selecting any port, VLAN or MAC address, the whole dynamic MAC table
will be displayed or cleared.
VLAN
This is the VLAN group to which the MAC address belongs. Select the
VLAN to show or clear dynamic MAC entries. If not selecting any port,
VLAN or MAC address, the whole dynamic MAC table will be displayed or
cleared.
MAC Address
This field displays the MAC address that will be forwarded. Select the MAC
address to show or clear dynamic MAC entries. If not selecting any port,
VLAN or MAC address, the whole dynamic MAC table will be displayed or
cleared.
View
Click the View button to display the logs according to the criteria specified
in the fields above.
Clear
Click this button to remove any dynamically learned MAC address
forwarding entries.
Type
This shows whether the MAC address is Dynamic (learned by the Switch)
or Static Unicast (manually entered in the Static MAC Forwarding
screen).
Port
This field displays the port where the MAC address will be forwarded.
Add to Static
MAC table
Click this button to add any port into the static MAC table.
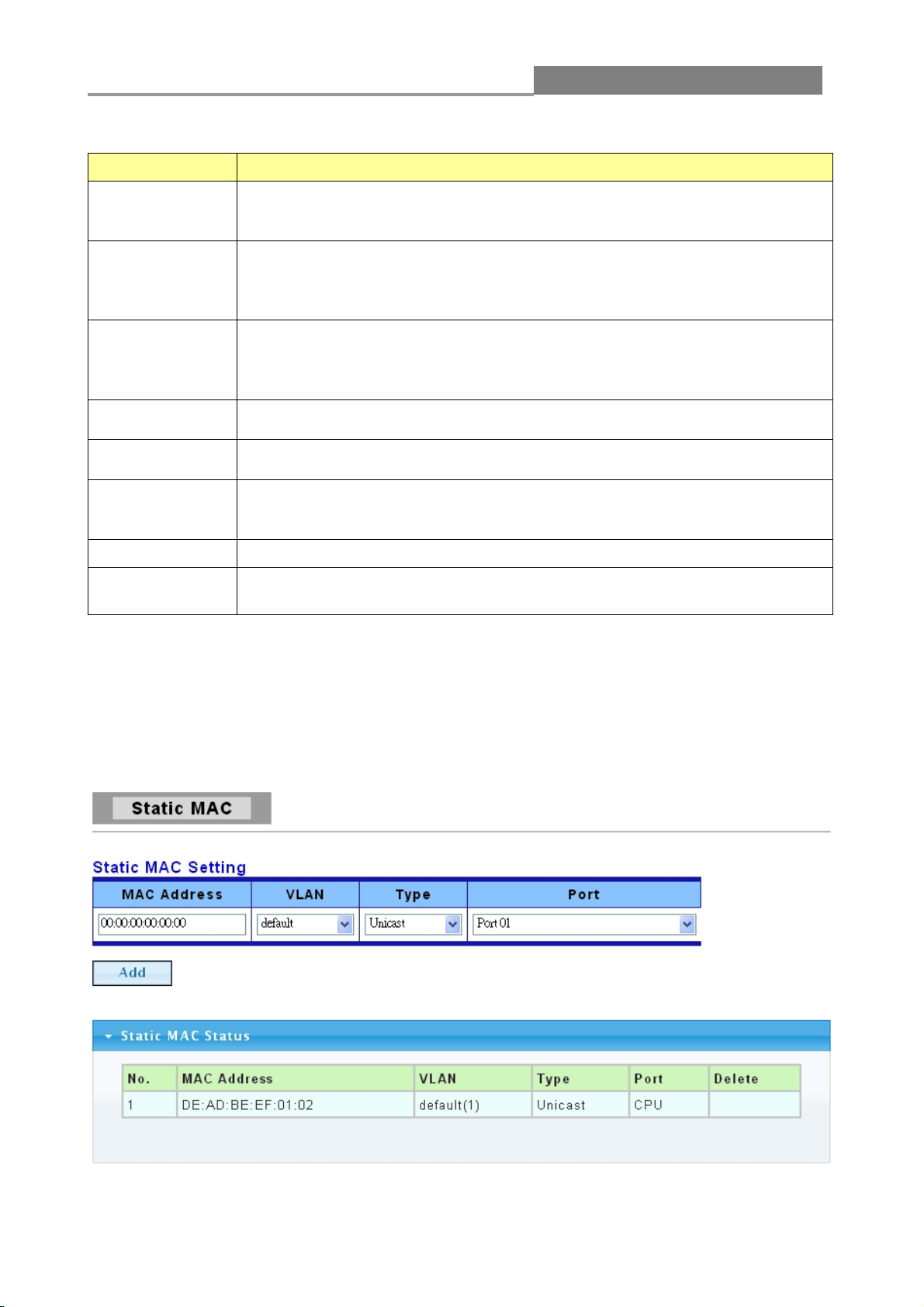
3.1.5.2 Static MAC
Click Status > MAC Address Table > Static MAC in the navigation panel to bring up the screen
shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 28
Web Managed GbE Switch
28
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
MAC Address
Enter the MAC address in valid MAC address format; that is, six hexadecimal
character pairs. Static MAC addresses do not age out.
VLAN
Enter the VLAN identification number the MAC address belongs to.
Type
There are two types of MAC entry:
Unicast: add a unicast MAC entry.
Multicast: add a multicast MAC entry.
Port
If Type is unicast, select the port number of the MAC entry;
If Type is multicast, select the port list of the MAC entry.
Add
Click Add to add any port into the static MAC address table.
No.
This is the index number for the MAC address forwarding entries.
Delete
To delete any selected MAC address entries.
3.2 Network
Use the Network pages to configure settings for the switch network interface and how the switch
connects to a remote server to get services.
3.2.1 IP Address
Use the IP Setting screen to configure the switch IP address and the default gateway device. The
gateway field specifies the IP address of the gateway (next hop) for outgoing traffic.
The switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. The factory default IP
address is 192.168.2.1. The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address.
The factory default subnet mask is 255.255.255.0.
Click Network > IP Address in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
Page 29
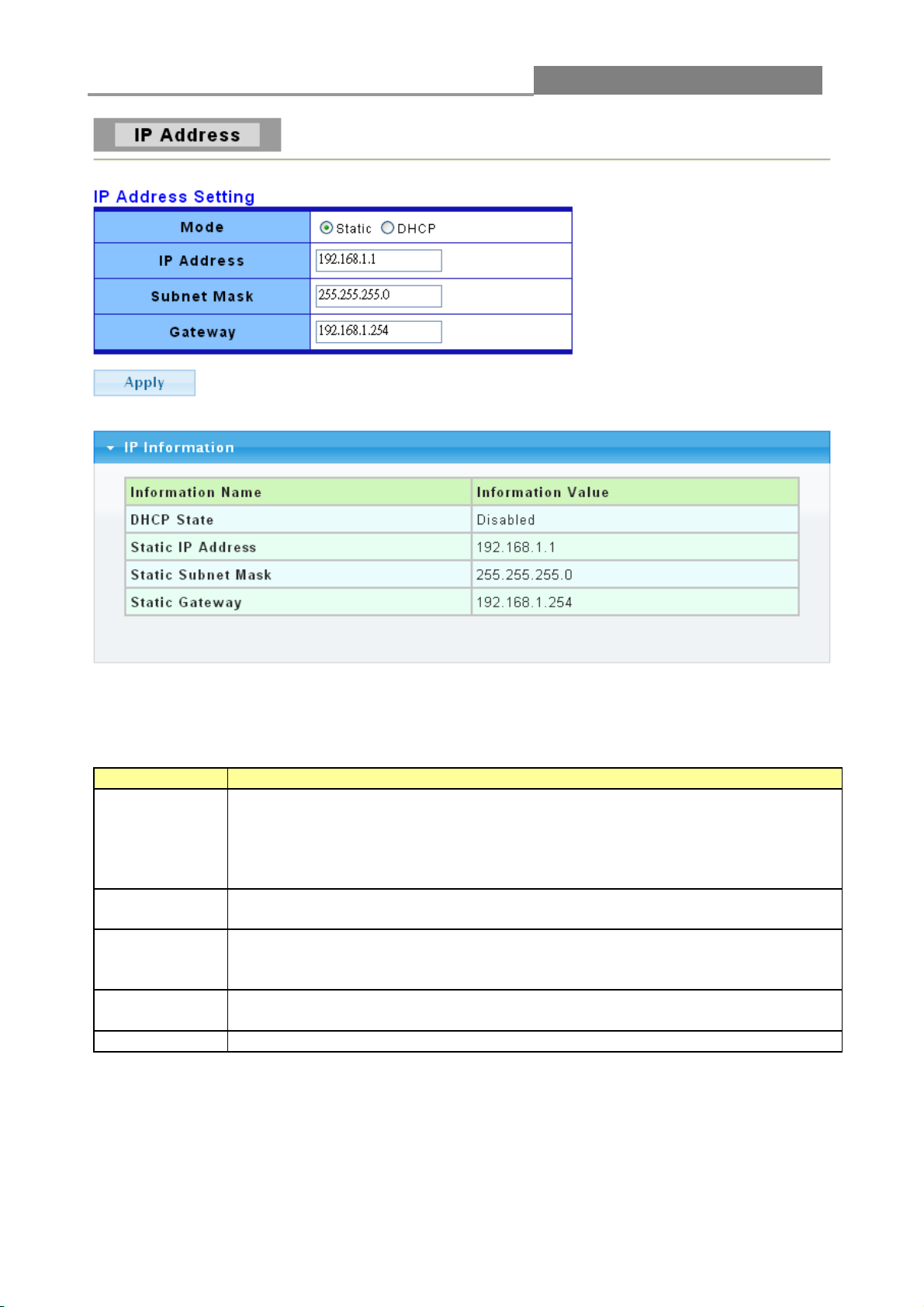
Web Managed GbE Switch
29
The screen shot shows sample data. The actual values may differ.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Mode
Select Static from the drop-down box if you don’t have a DHCP server or if
you wish to assign static IP address information to the switch. You need to fill
in the following fields when you select this option.
Select the DHCP option if you have a DHCP server that can assign the switch
an IP address, a subnet mask and a gateway IP address automatically.
IP Address
Enter the IP address of your switch in dotted decimal notation; for example,
192.168.2.1. If static mode is enabled, enter the IP address in this field.
Subnet Mask
Enter the IP subnet mask of your switch in dotted decimal notation; for
example, 255.255.255.0. If static mode is enabled, enter the subnet mask in
this field.
Gateway
Enter the IP address of the gateway in dotted decimal notation. If static mode
is enabled, enter the gateway address in this field.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Page 30

Web Managed GbE Switch
30
3.2.2 IPv6 Address
Click Network> IPv6 Address in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Auto
Configuration
Select Enable or Disable this function.
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 address of your switch. If auto configuration mode is
disabled, enter the IPv6 address in this field.
Gateway
Enter the IP address of the gateway in dotted decimal notation. If auto
configuration mode is disabled, enter the IPv6 gateway address in this field.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Auto
Configuration
It displays whether the auto configuration function is opened or not.
IPv6 In Use
Address
It displays the in-use address information of IPv6.
IPv6 In Use
Router
It displays the in-use router information of IPv6.
IPv6 Static
Address
It displays the static address of IPv6.
IPv6 Static
router
It displays the static router of IPv6.
Page 31

Web Managed GbE Switch
31
3.2.3 Time
Click Network> Time in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
SNTP State
Select Enable to use Simple Network Time Protocol (SNTP) or Disable
to set the time manually.
SNTP Server
Address
If SNTP is enabled, enter the IP address of the time server you will use.
SNTP Server
Port
It shows the Port Number of SNTP server.
Time
(HH:MM:SS)
If SNTP is disabled, enter the new time in hour, minute and second
format.
Date
(YYYY-MM-DD)
If SNTP is disabled, enter the new date in year, month and day format.
Page 32

Web Managed GbE Switch
32
Time Zone
Select system time zone by hours and minutes. “+” means after-UTC and
“-” means before-UTC.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3 Switching
Use the Switching pages to configure settings for the switch ports, trunk and other switch features.
3.3.1 Port Setting
This page allow the user to configure switch port settings and show port current status.
Click Switching > Port Setting in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port Select
Select the port(s) from the list box that you will change the port settings
for.
Name
It allows you to give a description of the port.
Enabled
Select Enable from the drop-down box to enable a port. The factory
default for all ports is enabled. A port must be enabled for data
transmission to occur. Select Disable to not use a port.
Speed
Port speed capabilities:
Auto: Auto speed with all capabilities.
Auto-10M: Auto speed with 10M ability only.
Auto-100M: Auto speed with 100M ability only.
Auto-1000M: Auto speed with 1000M ability only.
Auto-10/100M: Auto speed with 10/100M ability.
Page 33

Web Managed GbE Switch
33
10M: Force speed with 10M ability.
100M: Force speed with 100M ability.
1000M: Force speed with 1000M ability.
Selecting Auto (auto-negotiation) allows one port to negotiate with a peer
port automatically to obtain the connection speed and duplex mode that
both ends support. When auto-negotiation is turned on, a port on the
switch negotiates with the peer automatically to determine the connection
speed and duplex mode. If the peer port does not support
auto-negotiation or turns off this feature, the switch determines the
connection speed by detecting the signal on the cable and using half
duplex mode. When the switch’s auto-negotiation is turned off, a port uses
the pre-configured speed and duplex mode when making a connection,
thus requiring you to make sure that the settings of the peer port are the
same in order to connect.
Duplex
Port duplex capabilities:
Auto: Auto duplex with all capabilities.
Half: Auto speed with 10M ability only.
Full: Auto speed with 100M ability only.
Flow Control
A concentration of traffic on a port decreases port bandwidth and
overflows buffer memory, causing packet discards and frame losses. Flow
Control is used to regulate transmission of signals to match the bandwidth
of the receiving port. The switch uses IEEE802.3x flow control in full
duplex mode and backpressure flow control in half duplex mode.
IEEE802.3x flow control is used in full duplex mode to send a pause
signal to the sending port, causing it to temporarily stop sending signals
when the receiving port memory buffers fill. Back Pressure flow control is
typically used in half duplex mode to send a "collision" signal to the
sending port (mimicking a state of packet collision) causing the sending
port to temporarily stop sending signals and resend later.
Select “Enabled” to enable it. Or select “Disabled” to disable it.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Flow Control
Config
The Config column displays if Flow Control has been configured to be
turned On or Off for the port.
Flow Control
Status
The column displays the port’s current Flow Control status.
3.3.2 Port Mirroring
The Mirror function copies all the packets that are transmitted by the source port to the destination
port. It allows administrators to analyze and monitor the traffic of the monitored ports.
The Mirror Configuration steps are as follows:
1. Choose “enable” or “disable” this function in “State” column
2. Select those ports that are going to be monitored by marking the check boxes in “Monitoring
Port” column.
3. Click the “TX” or “RX” or “Both” in the drop list of the “Sniffer Mode” column. Select the
packet types that are going to be monitored (transferred or received packets or both).
4. Click “Apply” to activate.
Page 34

Web Managed GbE Switch
34
(a) Destination port: Theoretically, it’s possible to set more than one destination port in a network.
Actually, the port mirroring function will lower the network throughput; therefore, it’s recommended
to set “only one” destination port in a network.
(b) Mirroring Port: (1)RX: means copy the incoming packets of the selected source port to the
selected destination port. (2)TX: means copy the outgoing packets of the selected source port to
the selected destination port. (3)Rx & Tx: means the combination of Rx and Tx.
(c) Source port: the traffic source that will be copied to the destination port.
3.3.3 Trunk
3.3.3.1 Trunk Group
Click Switching> Trunk > Trunk Group in the navigation panel to view the screen shown below.
Page 35

Web Managed GbE Switch
35
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Trunk
This field displays the trunk group number to identify a trunk group; that is,
one logical link containing multiple ports.
Type
Select the type of the trunk group: a static trunk or an LACP trunk. A static
trunk would be aggregated immediately; an LACP trunk exchanges LACP
PDU to link partner to aggregate.
Ports
Select the ports to be added to the trunk group. There are the following
limitations for choosing the member ports:
A member port cannot be bandwidth limited.
A member port cannot be a mirroring port.
Member ports should join the same VLANs.
A member port cannot join more than one trunk group.
A member port cannot be in 802.1x force-authed or auth mode.
There could be at most 8 member ports in a trunk.
LACP Active
Select the LACP active ports to be added to the trunk group. This field is
active when LACP is selected as the Type.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Trunk
This field displays the trunk number to identify a trunk group; that is, one
logical link containing multiple ports.
Type
Here displays the type of the trunk group: a static trunk or an LACP trunk.
Master Port
This field displays the master port’s information.
The port with lowest port ID is designated to be master port of the trunk. To
synchronize the settings of trunk member ports, the configuration of the
trunk master port would be applied to all trunk member ports. Other member
ports are slave ports that cannot be configured individually in most settings
(such as VLAN, port ability and so on.) but follow the configuration of the
master port.
Member
This field displays the ports that are part of the trunk group.
Active/
Passive
If the trunk is an LACP trunk, this field shows the LACP active and passive
ports. The LACP active port would send LACP PDU periodically.
Page 36

Web Managed GbE Switch
36
Aggregated
This field displays the ports that are aggregated in a trunk group.
A static trunk would be aggregated immediately; an LACP trunk exchanges
LACP PDU to link partner to aggregate.
Delete
Click this button to delete the trunk.
3.3.3.2 LACP
Click Switching > Trunk > LACP to display the screen shown below.
LACP: Link Aggregation Control Protocol.
Note: Do not configure this screen unless you want to enable dynamic link aggregation.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
LACP Enable
Select Enable from the drop-down box to enable Link Aggregation
Control Protocol (LACP). Select Disable to not use LACP.
System Priority
LACP system priority is a number between 0 and 65,535. The switch with
the lowest system priority (and lowest port number if system priority is the
same) becomes the LACP “server.” The LACP “server” controls the
operation of LACP setup. Enter a number to set the priority of an active
port using Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP). The smaller the
number, the higher the priority level.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
Page 37

Web Managed GbE Switch
37
3.3.4 VLAN
Each VLAN in a network has an associated VLAN ID, which displays in the IEEE 802.1Q tag in
the L2 header of packets transmitted on a VLAN.
3.3.4.1 VLAN Setting
This page allows the user to add, edit or delete VLAN settings.
Click Switching > VLAN > VLAN Setting to access the screen below to configure and view VLAN
parameters for the switch.
The following table describes the related labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
VLAN ID
A unique number (between 1 and 4094) that identifies a particular VLAN.
VLAN Name
A 32-character alphanumeric name associated with a VLAN ID. The VLAN
Name is intended to make user-defined VLANs easier to identify and
remember.
Untagged
Ports Select
Select Untagged to make the port a permanent member of this VLAN
group. All outgoing frames will be transmitted without a VLAN Group ID
tag.
Tagged Ports
Select
Select Tagged to make the port a permanent member of this VLAN group.
All outgoing frames will be transmitted with the VLAN Group ID tag.
Add
Click Add to save your changes to the Switch.
VLAN ID
This field displays the unique identification number of the VLAN group.
VLAN Name
This field displays the descriptive name for this VLAN group.
Untagged
Ports
This field displays all the ports that will transmit outgoing frames without a
VLAN group ID tag.
Tagged Ports
This field displays all the ports that will transmit outgoing frames with a
VLAN group ID tag.
Modify
Click Edit to modify the tagged and untagged ports.
Page 38

Web Managed GbE Switch
38
3.3.4.2 VLAN Port Setting
This page allow user to configure VLAN port related settings.
Click Switching > VLAN > VLAN Port Setting to access the screen below.
A PVID (Port VLAN ID) is a tag that adds to incoming untagged frames received on a port so that
the frames are forwarded to the VLAN group that the tag defines.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port Select
Select the ports to change the PVID for.
PVID
Enter a number between 1 and 4094 as the port VLAN ID (PVID).
Accepted Type
Select the accepted type of the VLAN port:
All: Accept tagged and untagged frames.
Tag only: Only accept tagged frame.
Untag only: Only accept untagged frame.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Port
This field displays the port number.
PVID
This field displays the port VLAN ID (PVID).
Page 39

Web Managed GbE Switch
39
Accepted Frame
Type
This field displays the accepted frame type of the VLAN port.
3.3.4.3 VLAN Port Mode Setting
This page allow user to configure VLAN port tag mode setting.
Click Switching > VLAN > VLAN Port Mode Setting to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port Select
Select the ports you’re changing the settings for.
Tag Mode
Port tag mode:
Original: Tag depends on VLAN settings.
Keep-Format: Keep tag as packet received.
Priority-Tag: Always append priority-tag on packet.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Port
This field displays the port number.
Tag Mode
It displays the tag mode you have chosen.
Page 40

Web Managed GbE Switch
40
3.3.4.4 VLAN Ingress Filter
This page allow user to configure VLAN ingress filter setting.
Click Switching > VLAN > VLAN Ingress Filter to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
State
Select Enabled from the drop-down box to enable VLAN Ingress Filter.
Select Disabled to not use VLAN Ingress Filter.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.5 SVLAN
3.3.5.1 SVLAN Setting
This page allows the user to configure VLAN stacking tag protocol identifiers.
Click Switching->SVLAN->SVLAN Setting to access the screen below.
Page 41

Web Managed GbE Switch
41
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
TPID
VLAN stacking tag protocol identifier (0x0000~0xFFFF).
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.5.2 SVLAN Member Setting
This page allows the user to configure VLAN stacking members.
Click Switching->SVLAN->SVLAN Member Setting to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 42

Web Managed GbE Switch
42
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
SVLAN ID
Stacking VLAN ID.
Member Port
Select one or multiple ports as member ports of the SVLAN.
Add
Click Add to add any member port into the SVLAN.
3.3.5.3 SVLAN PVID Setting
This page allows the user to add or set port VLAN stacking entries in the VLAN stacking table.
Click Switching->SVLAN->SVLAN PVID Setting to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the port(s) to configure the SVLAN PVID settings for.
PVID
Set VLAN ID for selected ports.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.5.4 SVLAN Service Port
This page allows the user to configure VLAN stacking-aware ports.
Page 43

Web Managed GbE Switch
43
Click Switching->SVLAN->SVLAN Service Port to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the port(s) to configure the settings for.
Enabled
Set VLAN stacking aware state:
Enabled: Set as VLAN stacking aware.
Disabled: Set as VLAN stacking unaware.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.6 Bandwidth Control
3.3.6.1 Preamble Setting
Click Switching > Bandwidth Control->Preamble Setting in the navigation panel to bring up the
screen shown below.
Page 44

Web Managed GbE Switch
44
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Ingress Preamble
& IFG
Select the mode of ingress preamble & IFG:
Excluded: exclude preamble & IFG (20 bytes) when count ingress
bandwidth rate.
Included: include preamble & IFG (20 bytes) when count ingress
bandwidth rate.
Egress Preamble
& IFG
Select the mode of egress preamble & IFG:
Excluded: exclude preamble & IFG (20 bytes) when count egress
bandwidth rate.
Included: include preamble & IFG (20 bytes) when count egress
bandwidth rate.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.6.2 Port Rate Setting
Click Switching > Bandwidth Control-> Port Rate Setting in the navigation panel to bring up the
screen shown below.
Page 45

Web Managed GbE Switch
45
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the ports to enable bandwidth control on.
Type
Select the type of traffic to control: Ingress (incoming) or Egress
(outgoing).
State
Select Enable to activate bandwidth control on the selected ports.
Select Disable to turn off bandwidth control on the selected ports.
Rate (Kbit/sec)
Configure the desired bandwidth available to the port’s traffic flow. Traffic
that exceeds the maximum bandwidth allocated (in cases where the
network is congested) is dropped. Specify the bandwidth in kilobits per
second (kbps). Enter a number between 0 and 1048544. The number must
be a multiple of 16.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Port
This field displays the port number.
Ingress Rate
(Kbit/sec)
This field displays the maximum bandwidth allowed for incoming traffic on
the port in kilobits per second (kbps). The default setting is Unlimited.
Egress Rate
(Kbit/sec)
This field displays the maximum bandwidth allowed for outgoing traffic on
the port in kilobits per second (kbps). The default setting is Unlimited.
Page 46

Web Managed GbE Switch
46
3.3.7 IGMP Snooping
Use the Switching pages to configure settings for the switch network interface and how the switch
connects to a remote server to get services.
3.3.7.1 IGMP Setting
Click Switching > IGMP Snooping > IGMP Setting to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 47

Web Managed GbE Switch
47
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
IGMP Snooping
Select Enable from the drop-down box to enable IGMP Snooping.
Select Disable to not to use IGMP Snooping.
When enabled, it simply monitors the IGMP packets passing through it,
picks out the group registration information, and configures the multicast
filters accordingly.
Fastleave
Select Enable from the drop-down box to enable IGMP Fast-Leave.
Select Disable to not to use IGMP Fast-Leave.
Unknown
Multicast Action
Unknown multicast message to the switch. Enable Drop to throw away
the unknown multicast message. Enable Flood to flood the packets.
Query Interval
The query interval is the amount of time in seconds between IGMP
General Query messages sent by the router (if the router is the querier
on this subnet). You can also click the scroll arrows to select a new
setting. The default query interval is 125 seconds.
Response Time
The time a generic system or functional unit takes to react to a given
input. The default value is 10s.
Router Timeout
Save the time of the router port timer in the form. The default value is
125s.
Last Member
Query Interval
The interval that Querier-switch sends Group-Specific Queriers when it
receives a Leave Group message for a group.
Robustness
Variable
The robustness variable is a way of indicating how susceptible the
subnet is to lost packets. IGMP can recover from robustness variable
minus 1 lost IGMP packets. You can also click the scroll arrows to select
a new setting. The robustness variable should be set to a value of 2 or
greater. The default robustness variable value is 2.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Host Timeout
Save the timer related to the host and its member. The default value is
260s.
Querier Election
Time
It displays the querier election time.
3.3.7.2 IGMP VLAN Setting
Click Switching > IGMP Snooping > IGMP VLAN Setting to access the screen below.
Page 48

Web Managed GbE Switch
48
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
VLAN ID
Select the VLANs to configure.
Snooping State
Select Enable from the drop-down box to enable IGMP.
Select Disable to not use IGMP.
Querier State
Select Enable from the drop-down box to enable IGMP Querier
Election.
Select Disable to not use IGMP Querier Election.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Querier Status
It displays the status of querier.
Querier IP
It shows the Querier IP of IGMP VLAN.
3.3.7.3 Multicast Database
Click Switching > IGMP Snooping > Multicast Database to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 49

Web Managed GbE Switch
49
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
DIP Address
This field displays IP address of this group.
VID
This field displays ID of configured VLAN (1~4094).
Member Port
This field displays the ports that selected in the group address.
Life(Sec)
This field displays the life time of this group.
3.3.7.4 Router Table
Click Switching > IGMP Snooping > Router Table to access the screen below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
VID
The VLAN ID that has router port.
Port
Router port (i.e., the port ID where IGMP Query message received).
Expiry Time(Sec)
This field displays the expiry time of the router port.
3.3.8 Jumbo Frame
This page allows the user to configure switch port jumbo frame settings.
Click Switching > Jumbo Frame in the navigation panel to bring up the screen shown below.
Page 50

Web Managed GbE Switch
50
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Jumbo Frame
(Bytes)
Specify the maximum Jumbo Frame size in bytes from 0 to 9216.
Apply
Click Apply to save any changes to the switch.
3.3.9 STP
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology for any
bridged Ethernet local area network.
3.3.9.1 STP Global Setting
Use the SPT Global Setting screen to activate one of the STP modes on the switch.
Click Switching > STP > STP Global Setting.
Page 51

Web Managed GbE Switch
51
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Enabled
Select Enabled to use Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) or Rapid Spanning
Tree Protocol (RSTP). Select Disabled to not use STP or RSTP.
Force Version
Select the operating mode of STP.
STP-Compatible: 802.1D STP operation.
RSTP-Operation: 802.1w operation.
MSTP-Operation: 802.1s operation.
Max Hops
Set the value of the maximum number of hops in the region. Enter a
number between 1 and 40 as the max number of hops.
Forward Delay
Set the delay time an interface takes to change from blocking state to
forwarding state.
This is the maximum time (in seconds) the switch will wait before
changing states. This delay is required because every switch must
receive information about topology changes before it starts to forward
frames. In addition, each port needs time to listen for conflicting
information that would make it return to a blocking state; otherwise,
temporary data loops might result. The allowed range is 4 to 30 seconds.
Page 52

Web Managed GbE Switch
52
As a general rule:
Note: 2 * (Forward Delay – 1) >= Max Age >= 2 * (Hello Time + 1)
Max Age
Set the time any switch should wait before trying to change the STP
topology after unhearing Hello BPDU.
Tx Hold Count
Set the Transmit Hold Count used to limit BPDU transmission rate. Enter
a number between 1 and 10 as the Tx hold count.
Hello Time
Set the interval between periodic transmissions of BPDU by Designated
Ports.
This is the time interval (in seconds) at which the root switch transmits a
configuration message. The root bridge determines Hello Time, Max Age
and Forward Delay.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.9.2 STP Port Setting
Click Switching > STP > STP Port Setting.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port Select
Select the port(s) to change Spanning Tree Protocol settings for.
External
Path cost is the cost of transmitting a frame on to a LAN through that port. It is
Page 53

Web Managed GbE Switch
53
Cost
recommended to assign this value according to the speed of the bridge. The
slower the media, the higher the cost. Entering 0 means the switch will
automatically assign a value.
Edge Port
Set the edge port configuration:
No: Force to false state (as link to a bridge).
Yes: Force to true state (as link to a host).
Auto: Auto-detect.
BPDU Filter
Set the BPDU Filter configuration:
No: Disable BPDU Filter function.
Yes: Enable BPDU Filter function.
To avoid transmitting BPDU from the specified ports
BPDU
Guard
Set the BPDU Guard configuration:
No: Disable BPDU Guard function.
Yes: Enable BPDU Guard function.
To drop directly the received BPDU from the specified ports
P2P MAC
Set the Point-to-Point port configuration:
No: Force to false state.
Yes: Force to true state.
Auto: Auto-detect (according to duplex).
Migrate
Click the square choice box to enable this function.
Force to try to use the new MST/RST BPDUs, and hence to test the
hypothesis that all legacy systems that do not understand the new BPDU
formats have been removed from the LAN segment on the port(s).
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.3.9.3 MST Configuration
MST is the acronym of Minimum Spanning Tree.
Click Switching > STP > MST Configuration.
Page 54

Web Managed GbE Switch
54
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Configuration
Name
You can manually set the configuration name for identification.
Configuration
Revision
You can manually set the configuration revision for identification. (Range:
0-65535)
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
MSTI ID
MSTI is MST Configuration ID. Enter a number between 1 and 15 as the MSTI
ID.
Action Type
Select the action type:
Add VID: Add the VLANs in the VLAN list to the specified MST instance.
Remove VID: Remove the VLANs in the VLAN list from the specified
MST instance.
VLAN List
Enter a number between 1 and 4094 as the VLAN List..
MSTI
It displays the CIST’s number.
VLAN List
It displays the list of VLANs.
VLAN Count
It displays the count number of VLANs.
Page 55

Web Managed GbE Switch
55
3.3.9.4 MST Instance Setting
Click Switching > STP > MST Instance Setting.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
MST ID
You can manually set the MST ID to specify MST instance.
Priority
You can manually set the Bridge Priority in the specified MST instance.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
MSTI
It displays the CIST’s number.
Instance
Status
It displays the status of MST instance.
Instance
Priority
It displays the priority of MST instance.
View Status
Click View to view the status of MST instance.
3.3.9.5 MST Port Setting
Click Switching > STP > MST Port Setting.
Page 56

Web Managed GbE Switch
56
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port Select
Select the port(s) that will use MST setting.
MST ID
You can manually set the MST ID to specify MST instance.
Internal Path
Cost
You can manually set the internal path cost to the selected ports in the
specified MST instance. (0 means “Auto”)
Priority
You can manually set the priority to the selected ports in the specified MST
instance.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Port
It displays the port you have chosen.
MSTI ID
It displays the MSTI ID of the chosen port.
Designed
Bridge
It displays the designed bridge of the chosen port.
Page 57

Web Managed GbE Switch
57
Internal Path
Cost
It displays the internal path cost of the chosen port.
Port Priority
It displays the port priority you have set.
Port Role
It displays the port role of the chosen port.
Port State
It displays the port state of the chosen port.
3.4 Security
3.4.1 Storm Control
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the port(s) that will use storm control.
Storm Type
Select the type of packets to be limited with the Storm Control feature.
Broadcast: Broadcast packet
Multicast: All multicast packet, including known and unknown multicast.
Unknown Unicast: Unknown unicast packet.
Unknown Multicast: Unknown multicast packet.
State
Select On to enable traffic storm control on the Switch.
Select Off to disable this feature.
Rate (pps)
Type a packet per second (pps) rate between 0 and 1000000. This is the
maximum amount of packets of the type selected previously allowed to be
transferred to the Switch per second. Any subsequent packets are
discarded.
Page 58

Web Managed GbE Switch
58
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
Port
This field displays the port number.
Broadcast
(pps)
This field displays how many broadcast packets the port can receive per
second.
Multicast
(pps)
This field displays how many multicast packets the port can receive per
second.
Unknown
Unicast (pps)
This field displays how many unknown unicast packets the port can receive
per second.
Unknown
Multicast
(pps)
This field displays how many unknown multicast packets the port can
receive per second.
3.4.2 MAC Filtering
Use this screen to create rules for traffic going through the switch.
Click Security> MAC Filtering in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
MAC Address
Type a MAC address to which packets will be filtered in valid MAC
address format; that is, six hexadecimal character pairs. And this must be
a unicast MAC address.
VLAN
The VLAN ID number of the VLAN on which the above MAC address
resides.
This function is set default in this switch.
Filter
Select Source MAC to drop the frames with the source MAC address
(specified in the MAC Address field).
Select Destination MAC to drop the frames with the destination MAC
address (specified in the MAC Address field).
Select Both to drop frames with the source MAC address and destination
MAC address specified in the MAC Address field.
Page 59

Web Managed GbE Switch
59
Name
Enter a descriptive name (up to 32 printable ASCII characters) for this
filtering rule. This is for identification only.
Add
Click Add to add any port into the MAC filtering table.
No.
This is the index number for the MAC filtering rules.
MAC Address
This field displays the MAC address that will be filtered.
VLAN
This is the VLAN group to which the MAC address belongs.
Filter
This field displays the action of the filter.
Name
This field displays the descriptive name for this rule. This is for
identification purpose only.
Select
Click on the check box for the MAC filtering rule you want to delete.
3.4.3 802.1X
3.4.3.1 802.1X Setting
Use this screen to activate IEEE 802.1x security and configure RADIUS server settings.
Click Security > 802.1x > 802.1x Setting to display the configuration screen shown below.
Page 60

Web Managed GbE Switch
60
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
802.1X
Select Enable from the drop-down list box to activate IEEE 802.1x port
authentication.
Select Disable to disable this function.
Radius Server IP
Enter the IP address of an external RADIUS server in dotted decimal
notation.
Server Port
(1024-65535)
The default port of a RADIUS server for authentication is 1812. You
need not change this value unless your network administrator instructs
you to do so.
Shared Key
(max. 30
characters)
Specify a password (up to 32 alphanumeric characters) as the key to be
shared between the external RADIUS server and the Switch. This key is
not sent over the network. This key must be the same on the external
RADIUS server and the Switch.
Retype Shared
Key
Retype the key specified above to ensure it has been entered correctly.
Reauthentication
enable
Specify if a subscriber has to periodically re-enter his or her username
and password to stay connected to the port.
Select Enable and the user has to re-enter his/her username and
Page 61

Web Managed GbE Switch
61
password.
Reauthentication
Period
(30-65535 sec)
Specify how often a client has to re-enter his or her username and
password to stay connected to the port.
Set the reauthentication period of 802.1X if reauthentication is enabled.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.4.3.2 802.1X Port Setting
Click Security > 802.1x > 802.1x Port Setting to display the configuration screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Specify the ports to activate IEEE 802.1x port authentication on.
Mode
Select Force Unauthorized to always force this port to be
unauthorized.
Select Force Authorized to always force this port to be authorized.
Select Authorization to enable 802.1x port authentication.
Select No Authorization to disable 802.1x port authentication.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
Port
This field displays the port number.
Mode
This field displays the port’s current 802.1x setting.
Status
This field displays the current stage of the 802.1x port authentication
procedure.
Page 62

Web Managed GbE Switch
3.4.4 Port Security
Click Security > Port Security to display the configuration screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Select
Security Port security function. 6HOHFWRQHRIWKHWZRRSWLRQV
Max L2 Entry Maximum number of Layer 2 entries that assign the MAC address to
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
Port Name
Enable State
L2 Entry Num
Action
Select the port(s) to configure this setting
En
Disable: Disable port security function.
the port.
This field displays the port number.
This field displays the state of this function (whether it has been
enabled or not).
This field displays the maximum number of Layer 2 entries of the MAC
addresses.
This field displays the action of the port.
able: En
able port security function.
62
Page 63

Web Managed GbE Switch
63
3.4.5 Protected Ports
This page allows the user to configure protected port settings to prevent the selected ports from
communicating with each other.
Click Security > Protected Ports to display the configuration screen as shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port List
To select the port to be protected.
Port Type
Configure port protect type:
Unprotected: The unprotected port can communicate with all
ports.
Protected: Prevent protected ports from communicating with each
other.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
3.4.6 Access
3.4.6.1 Console
Page 64

Web Managed GbE Switch
64
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Session Timeout
Set session timeout minutes for user access of the CLI from the console
line. If the user doesn’t respond after session timeout, the CLI will log out
automatically.
Enter a number between 0 and 1440 as the session timeout. 0 minutes
means never time out.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
3.4.6.2 Telnet
Telnet is the TCP/IP standard protocol for remote terminal service. Telnet allows a user at one site
to interact with a remote timesharing system at another site as if the user’s keyboard and display
were connected directly to the remote machine.
Page 65

Web Managed GbE Switch
65
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Session Timeout
Set session timeout minutes for user access of the CLI from a Telnet
line. If the user doesn’t respond after the session timeout minutes, the
CLI will log out automatically.
Enter a number between 0 and 1440 as the session timeout. 0 minutes
means never time out.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
3.4.6.3 SSH
SSH stands for Secure Shell.
Page 66

Web Managed GbE Switch
66
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Session Timeout
Set session timeout minutes for user access to the CLI from an SSH
line. If the user doesn’t respond after the session timeout minutes, the
CLI will log out automatically.
Enter a number between 0 and 1440 as the session timeout. 0 minutes
means never time out.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
3.4.6.4 HTTP
HTTP is the acronym for Hyper Text Transfer Protocol.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Session Timeout
Set session timeout minutes for user access to the Web using the
HTTP protocol. If the user doesn’t respond after the designated session
timeout minutes, the Web UI will log out automatically. Enter a number
between 0 and 1440 as the session timeout. 0 minutes means never
time out.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
3.4.6.5 HTTPS
HTTPS is the acronym for Hypertext Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer.
Page 67

Web Managed GbE Switch
67
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Session Timeout
Set session timeout minutes for user access to the Web using the
HTTPS protocol. If the user doesn’t respond after the designated
session timeout minutes, the Web UI will log out automatically. Enter a
number between 0 and 1440 as the session timeout. 0 minutes means
never time out.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
3.5 ACL
Use the ACL pages to configure settings for the Access Control List.
3.5.1 ACL Setting
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
Page 68

Web Managed GbE Switch
68
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
ACL Index
You can manually set the ACL Index.
Add
Click Add to add the basic information of ACL Index.
Index
It displays the index information.
Name
It displays the name of the index.
Port List
It displays the list of the port.
VLAN List
It displays the list of the VLAN.
Policy Index
It displays the policy index.
Modify
Click Modify to modify any setting.
Delete
Click Delete to delete any setting.
Click ACL->ACL Setting->Add button and the ACL Content Web page displays.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Page 69

Web Managed GbE Switch
69
Name
Enter ACL name in this field
Comment
Enter ACL comment in this field.
Interface
Select the interface to bind:
Port number: Enter port number.
VLAN ID: Enter VLAN ID.
Policy: Enter policy index.
ACE Index
Enter ACE index in this field to configure ACE.
Click ACL > ACL Setting > Add > Add (in ACE Setting) button and the ACE Content Web page
displays.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Comment
Enter ACE comment in this field.
src-mac
Enter source MAC data and mask in this field.
dst-mac
Enter destination MAC data and mask in this field.
ethertype
Enter ethernet type in this field.
src-ip
Enter source IP data and mask in this field.
dst-ip
Enter destination IP data and mask in this field.
ip-protocol
Enter IP protocol in this field.
Page 70

Web Managed GbE Switch
tos Enter ToS in this field.
14-src-port Enter Layer 4 source port in this field.
14-dst-port Enter Layer 4 destination port in this field.
tcp-flag Enter TCP flag in this field.
Action Select the action to take:
Permit: permit packet to pass through.
Deny: drop packet.
Click Apply.
3.5.2 ACL Template Setting
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Template Index
Get To get the basic information of the policy index.
src-mac Click in the square box to set source MAC into Template.
dst-mac Click in the square box to set destination MAC into Template.
ethertype Click in the square box to set ethernet type into Template.
src-ip Click in the square box to set source IP into Template.
dst-ip Click in the square box to set destination IP into Template.
ip-protocol Click in the square box to set IP protocol into Template.
tos Click in the square box to set ToS into Template.
70
You can choose the template index.
Page 71

Web Managed GbE Switch
71
14-src-port
Click in the square box to set Layer 4 source port into Template.
14-dst-port
Click in the square box to set Layer 4 destination port into Template.
tcp-flag
Click in the square box to set TCP flag into Template.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.5.3 ACL Index Range Setting
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
ACL Index Range
It displays the 16 types of ACL index range.
Template Index
Enter Template index mapping to specify the range of the ACL index in
this field.
Enter a number between 1 and 16 as the template index.
Page 72

Web Managed GbE Switch
3.5.4 ACL Policy Setting
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Policy Index You can choose the policy index.
Get To get the basic information of the policy index.
VLAN ID Enter a VLAN ID.
Port Number Enter a port number
Action Select the action to take:
Mirror Index: mirror the packet via the configuration of the
specified mirror index.
Rate Limit: limit the packet rate 7he LQFUHPHQW is 16kbps.
Priority: change the packet priority.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.6 QoS
Use the QoS pages to configure settings for the switch QoS interface and how the switch connects
to a remote server to get services.
3.6.1 Port-based Priority
You can configure the switch to assign an IEEE 802.1p priority to packets based on the ingress
(incoming) port of the packet.
Click QoS > Port-based Priority in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
72
Page 73

Web Managed GbE Switch
73
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the number of the port for which you want to assign IEEE 802.1p
priority to incoming frames.
Priority
Select the QoS port-based priority you want to assign to the packets
coming into the switch on the ports specified in the port field.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Port
This field displays the port number.
Priority
This field indicates what IEEE 802.1p priority is assigned to the incoming
packets from the port.
3.6.2 802.1p-based Priority
Click QoS > 802.1p-based Priority in the navigation panel to display the screen shown below.
Page 74

Web Managed GbE Switch
74
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
802.1 p
Select the 802.1p value to mapping to the priority and drop precedence.
The 802.1p range is 0 to 7.
Priority
Select the IEEE 802.1p priority you want to assign to the packets coming
into the switch on the ports specified in the port field. The priority range is
0 to 7.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
802.1 p
This field displays the 802.1p priority level which you’ve choosed..
Priority
This field indicates what IEEE 802.1p priority is assigned to the incoming
packets from the port.
3.6.3 DSCP - based Priority
You can configure the switch to assign an IEEE 802.1p priority to packets coming into the switch
with DSCPs assigned to them.
Click QoS > DSCP-based Priority to display the screen shown below.
Page 75

Web Managed GbE Switch
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DSCP
Priority
Apply
DSCP
Priority
Select the DSCP value IRUZKLFK\RXZDQWWRGHILQHDSULRULW\YDOXH.
The DSCP range is 0 to 63.
Select the priority value that the DSCP is mapped to. The priority range
is 0 to 7.
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
This field displays the DSCP classification identification numbers.
This field displays the DSCP classification identification number’s IEEE
802.1p Priority.
3.6.4 Priority to Queue Mapping
Click QoS > Priority to Queue Mapping to display the screen as shown next.
IEEE 802.1p defines up to eight separate traffic types by inserting a tag into a MAC-layer frame
that contains bits to define the class of service. Frames without an explicit priority tag are given the
default priority of the ingress port. Use the next screen to configure the priority level-to-physical-
queue mapping.
The Switch has eight physical queues that you can map to the eight priority levels. On the Switch,
75
Page 76

Web Managed GbE Switch
76
traffic assigned to higher-index queues gets through faster while traffic in lower-index queues is
dropped if the network is congested.
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Priority
Select the priority value to mapping to the Queue ID. The priority range is 0
to 7.
0
Typically used for best-effort traffic.
1
This is typically used for non-critical “background” traffic such as bulk
transfers that are allowed but that should not affect other applications and
users.
2
This is for “spare” bandwidth.
3
Typically used for “excellent effort” or better than best effort, and would
include important business traffic that can tolerate some delay.
4
Typically used for controlled-load, latency-sensitive traffic such as SNA
(Systems Network Architecture) transactions.
5
Typically used for video that consumes high bandwidth and is sensitive to
jitter.
6
Typically used for voice traffic that is especially sensitive to jitter (jitter is
the variations in delay).
7
Typically used for network control traffic such as router configuration
messages.
Queue ID
Select the Queue ID for which the Priority should be applied. The Queue ID
range is 1 to 8.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the Switch.
Priority
This field displays the priority for each Queue ID.
Queue ID
This field displays the Queue ID.
Page 77

Web Managed GbE Switch
3.6.5 Packet Scheduling
Click QoS > Packet Scheduling to display the screen shown below.
Packet Scheduling is used to help solve performance degradation when there is network
congestion. Use this screen to configure queuing algorithms for outgoing traffic.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Port Select the number of the port for which you want to assign IEEE 802.1p
priority to incoming frames.
Scheduling
Algorithm
Apply
Select the algorithm of packet scheduling:
WFQ:
WRR:
Note: Weighted Fair Queuing is used to guarantee each queue's minimum
bandwidth based on its bandwidth portion (weight: the number you configure
in the weight field). Queues with larger weights get more guaranteed
bandwidth than queues with smaller weights. Weighted Round Robin
Scheduling services queues on a rotating basis based on their queue weight
(the number you configure in the queue weight field). Queues with larger
weights get more service than queues with smaller weights.
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.6.6 Queue Weight Setting
Click QoS > Queue Weight Setting to display the screen shown below.
77
Page 78

Web Managed GbE Switch
78
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the number of the port for which you want to assign IEEE 802.1p
priority to incoming frames.
Queue ID
Select the Queue ID for configuration it’s weighted. The Queue ID range
is 1 to 8.
Weight
Configure the queue scheduling weight of specified ports. Range is valid
as following:
0: means the queue is strict mode.
1-127: means the queue weight of the scheduling.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Weight
This field displays the weight of the queue.
3.6.7 Queue Remarking Status
Click QoS > Queue Remarking Status to display the screen shown below.
Page 79

Web Managed GbE Switch
79
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Port
Select the number of the port for which you want to assign IEEE 802.1p
priority to incoming frames.
802.1p Priority
Remarking
Click Enabled to enable this function on specified ports.
Click Disabled to disable this function on specified ports.
DSCP Remarking
Click Enabled to enable this function on specified ports.
Click Disabled to disable this function on specified ports.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.6.8 Queue Remarking Table
Click QoS > Queue Remarking Table to display the screen shown below.
Page 80

Web Managed GbE Switch
80
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Priority
Select the priority value to mapping to new 802.1p, new 802.1ad and
DSCP value. The priority range is 0 to 7.
New 802.1p
Priority
Remark to the new 802.1p priority that the priority and drop precedence
mapped to. The new 802.1p priority is 0 to 7.
New DSCP Value
Remark to the new DSCP priority that the priority and drop precedence
mapped to. The new DSCP priority is 0 to 63.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.7 Management
3.7.1 SNMP
3.7.1.1 SNMP Setting
Click Management > SNMP > SNMP Setting to display the screen shown below.
Page 81

Web Managed GbE Switch
81
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
State
SNMP daemon state:
Select Enabled to activate SNMP daemon.
Select Disabled to not use SNMP daemon.
3.7.1.2 SNMP Community
Click Management > SNMP > SNMP Community to display the screen shown below.
Page 82

Web Managed GbE Switch
82
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Community
Enter a Community string. This will act as a password for requests from
the management station.
Type
SNMP community type:
Read-Only: Read all objects only. It can allow the SNMP manager
using this string to collect information from the switch.
Read-Write: Read and write all objects. It can allow the SNMP
manager using this string to create or edit MIBs (configure
settings on the switch).
Add
Click Add to add any other community.
No
It displays the port number in the community.
Community
This field displays the community strings.
Access Type
This field displays the community string’s type. This will either be
read-only or read-write.
Delete
Click Delete to remove any selected community strings.
3.7.1.3 SNMP Trap
This page allows the user to add or delete an SNMP trap receiver IP address and community
name.
Click Management > SNMP > SNMP Trap to display the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
IP Address
Enter the IP addresses to send your SNMP traps to.
Page 83

Web Managed GbE Switch
83
Community
Enter a Community string, which is the password sent with each trap to
the SNMP manager.
Add
Click Add to add any trap receiver.
IP Address
This field displays the IP address where the traps from the switch are
sent.
Community Type
This field displays the password sent with each trap to the SNMP
manager.
Delete
Click Delete to remove any selected trap receiver entries.
3.8 Diagnostics
Use the Diagnostics pages to configure settings for the switch diagnostics feature or operating
diagnostic utilities.
3.8.1 Ping Test
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
IP Address
Enter the IP addresses of the test destination.
Page 84

Web Managed GbE Switch
84
Count
It displays how many times to send ping request packet.
Enter a number between 1 and 5 as the count. The default configuration
is 1.
Interval
It displays time interval between each ping request packet.
Enter a number between 1 and 5 as the interval. The default
configuration is 1.
Size
It displays the size of ping packet.
Enter a number between 0 and 5120 as the size. The default
configuration is 0.
Ping Results
After a ping is finished, results will show in this field.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.8.2 Ping6 Test
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
IPv6 Address
Enter the IPv6 addresses of the test destination.
Count
It displays how many times to send ping request packet.
Enter a number between 1 and 5 as the count. The default
configuration is 1.
Interval
It displays time interval between each ping request packet.
Enter a number between 1 and 5 as the interval. The default
Page 85

Web Managed GbE Switch
85
configuration is 1.
Size
It displays the size of ping packet.
Enter a number between 0 and 5120 as the size. The default
configuration is 0.
Ping Results
After a ping finished, results will show in this field.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
3.8.3 Log Setting
3.8.3.1 Local Log
Use this screen to display the switch logs.
Click Diagnostics > Log Setting > Local Log to view the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Target
Select the target to store log message:
RAM: store the log messages on the RAM disk. All log messages will
disappear after a system reboot.
Flash: store the log messages in the Flash memory. Log messages will
not disappear after a system reboot.
Severity
Select the severity level(s) of the log entries you want to display. The
possible severity levels are:
Error - to record system failures, such as events which will cause the
switch to malfunction and events such as invalid user input in the
Web configurator.
Warning - to record non-critical errors on the Switch. The Switch will
Page 86

Web Managed GbE Switch
86
continue to function when warnings are recorded.
Info - to record regular system events, such as configuration changes or
logins.
Debug - to record events that can be helpful for engineering debugging
of the switch’s function. This field is not recommended for tracking,
as it creates many messages not helpful to typical users.
Notice- to record errors that need attention.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Status
It displays the status of local log settings.
Target
It displays the target you’ve chosen.
Severity
It displays the severity status.
Action
Click enable to enable this function.
Click disable to disable this function.
3.8.3.2 Remote Log
Click Diagnostics > Log Setting > Remote Log to view the screen shown below.
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Server Index
Select the index of the remote log server. System supports four remote log
servers. When a server is set and enabled, log messages will send to this
server.
Server IP
The IP address of the remote log server.
Server Port
Enter a number between 1 and 65535 as the server port.
Page 87

Web Managed GbE Switch
87
Severity
Select the severity level(s) of the log entries you want to display. The
possible severity levels are:
Error - to record system failures, such as events that will cause the
switch to malfunction and events such as invalid user input in the
Web configurator.
Warning - to record non-critical errors on the Switch. The Switch will
continue to function when warnings are recorded.
Info - to record regular system events, such as configuration changes or
logins.
Debug - to record events that can be helpful for engineering debugging
of the switch’s function. This field is not recommended for tracking,
as it creates many messages not helpful to typical users.
Notice- to record errors that need attention.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Status
It displays the status of local log settings.
Server
Information
It displays the server information.
Severity
It displays the severity status.
Action
It displays the action status.
3.8.4 Factory Default
Follow the steps below to restore the switch to the factory defaults.
1. Click Diagnostics -> Factory Default to view the screen shown below.
2. Click the Restore button and the confirm interface displays.
3. Click OK to restore all switch configurations to the factory defaults and the switch will reboot.
Page 88

Web Managed GbE Switch
88
3.8.5 Reboot Switch
Reboot allows you to restart the switch without physically turning the power off.
Follow the steps below to reboot the switch.
1. Click Diagnostics > Reboot Switch to view the screen shown below.
2. Click the Reboot button and the following interface displays.
3. When finished, the switch will have been restarted.
3.9 Maintenance
3.9.1 Backup Manager
This page allows the user to back up the firmware image or configuration file on the switch to a
remote TFTP server or host file system through the HTTP protocol.
Click Maintenance > Backup Manager to view the screen shown below.
Backup Image with TFTP Page
Page 89

Web Managed GbE Switch
89
Backup Config with TFTP Page
Backup Image with HTTP Page
Backup Config with HTTP Page
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Backup
Select the backup method:
Page 90

Web Managed GbE Switch
90
Method
TFTP: Use TFTP to back up.
HTTP: Use HTTP to back up.
Server IP
IP address of the TFTP server. If the TFTP backup method is selected,
the IP address of the TFTP server must be assigned.
Backup Type
Select backup type:
Image: Firmware image of current system.
Configuration: Configuration file.
Configuration
If the Configuration backup type is selected, one of the configuration files
in the current system can be selected for backup.
Backup
Click Backup to save the current switch configuration to the local address
specified.
3.9.2 Upgrade Manager
This page allows the user to upgrade a new firmware image or configuration file to the switch from
a remote TFTP server or a select file from the Web browser.
Click Maintenance > Upgrade Manager to view the screen shown below.
Upgrade with TFTP Page
Upgrade with HTTP Page
Page 91

Web Managed GbE Switch
91
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Upgrade
Method
Select the upgrade method:
TFTP: Use TFTP to upgrade.
HTTP: Use HTTP to upgrade.
Server IP
IP address of the TFTP server. If the TFTP upgrade method is selected, the
IP address of the TFTP server must be assigned.
File Name
Firmware image or configuration file name on remote TFTP server. If the
TFTP upgrade method is selected, the file name must be specified.
Browse File
If the HTTP upgrade method is selected, the browse file field allows you to
select any file on the host operating system.
Upgrade
Type
Select upgrade type:
Image: Firmware image of current system.
Configuration: Configuration file.
Upgrade
Click Upgrade to update the file specified above and install the new
firmware.
3.9.3 Configuration Manager
This page allows the user to save running configurations to any file specified by pushing the “Save
Configuration” button. Click “Set Startup” to select any existing configuration file as the startup
configuration. The “Delete” button allows the user to delete the selected configuration file.
Click Maintenance > Configuration Manager to view the screen shown below.
Configuration Manager Page
Page 92

Web Managed GbE Switch
92
Configuration Manager with new file name Page
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Configuration
You have two choices: startup-config.cfg and New Configuration
New Config Name
Configuration file name. Our system will save it with a sub-file name .cfg
automatically.
Save
Configuration
Click Save Configuration to save running configurations to any file the
user specified.
Set Startup
Click Set startup to select any existing configuration file as the startup
configuration.
File Name
It displays the name of the file.
File Size
It displays the size of the file.
Delete
Click Delete to delete the selected configuration file.
3.9.4 Account Manager
This page allows the user to add or delete switch local user database for authenticating.
Click Maintenance > Account Manager in the navigation panel to display the screen shown
below.
Page 93

Web Managed GbE Switch
93
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
User name
Enter your user name for new account.
Password Type
Select password type for new account:
Clear Text: Password without encryption.
Encrypted: Password with encryption.
No Password: No password for new account.
Password
If the password type is other than “No Password,” the password must be
specified.
Retype Password
Retype the password to make sure the password is exactly what you
typed before in the “Password” field.
Privilege Type
Select a privilege level for new account:
Admin: Allow to make changes in switch settings.
User: See switch settings only. Do not allow changes.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Modify
Click Delete to modify any configuration.
3.9.5 Enable Password
This page allows the user to modify the enable password. In the command line interface, the user
can usethe “enable” command to change the privilege level to “Admin.” After the “enable”
command is issued, the user needs to type the enable password to change the privilege level.
Click Maintenance > Enable Password in the navigation panel to display the screen shown
below.
Note: It is highly recommended that you change the default password.
Page 94

Web Managed GbE Switch
94
The following table describes the labels on this screen.
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Password Type
Select password type for the enable password function:
Clear Text: Password without encryption.
Encrypted: Password with encryption.
Password
Enter your new system password.
Retype Password
Retype the password to make sure the password is exactly what you
typed before in the “Password” field.
Apply
Click Apply to save your changes to the switch.
Page 95

Web Managed GbE Switch
95
Specifications
Standards
• IEEE 802.1d (Spanning Tree Protocol)
• IEEE 802.1p (Traffic Prioritization)
• IEEE 802.1q (VLAN Tagging)
• IEEE 802.1s (Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP))
• IEEE 802.3ad (Link Aggregation)
• IEEE 802.3 (10Base-T Ethernet)
• IEEE 802.3ab (Twisted Pair Gigabit Ethernet)
• IEEE 802.3ad (Link Aggregation Control Protocol LACP)
• IEEE 802.3az (Energy Efficient Ethernet EEE)
• IEEE 802.3u (100Base-TX Fast Ethernet)
• IEEE 802.3x (Flow Control, for full duplex mode)
• SNMPv1/v2/v3 (Simple Network Management Protocol)
General
• Media support:
- 10Base-T Cat3, 4, 5 UTP/STP RJ45
- 100Base-TX Cat5 UTP/STP RJ45
- 1000Base-T Cat5e UTP/STP RJ45
• Packet filter/forwarding rate:
- 1,488,000 pps (1000 Mbps)
- 148,800 pps (100 Mbps)
- 14,880 pps (10 Mbps)
• MAC address table: 16k
• Buffer memory: 448 kBytes
• Backplane speed / switch fabric: 40 Gbps for 16-port; 56 Gbps for 24-port
• Switch architecture: store and forward
• Configuration options:
- Port link speed: 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 1000 Mbps or auto-negotiation
- Flow control on/off per port
- VLAN, S-VLAN
- Rate limiting (ingress rate and egress rate)
- Rate limiting: policy-based or port-based bandwidth control, 16 kbps steps up to 1 Gbps
maximum
- Port Mirroring
- ACL (Access Control List)
- Port Aggregation/LACP: 8 groups
Page 96

Web Managed GbE Switch
96
- Broadcast Storm configuration with broadcast rate, multicast rate, and flooded unicast rate
- IGMP Snooping
- Event Logging / Remote Logging
- Quality of Service (QoS): port-based, 802.1p or DSCP
- Integrated ICMP Ping client sends ping requests to other network nodes
- SNMPv1/v2/v3 (Simple Network Management Protocol)
- LAN settings (IP address, gateway, etc.)
• Certifications: FCC Class A, CE
LEDs
• Power
• Link/activity
Power
• Input: 100 – 240 V AC, 50 – 60 Hz
• Power consumption: 30 watts (maximum)
Environmental
• Metal housing
• Dimensions: 440 (W) x 130 (L) x 44 (H) mm (17.3 x 5.1 x 1.7 in.)
• Weight: 2.9 kg (6.4 lbs.)
• Operating temperature: 0 – 40°C (32 – 104°F)
• Operating humidity: 10 – 90% RH, non-condensing
• Storage temperature: -40 – 70°C (-40 – 158°F)
Package Contents
• Web-Managed Gigabit Ethernet Switch with 4 SFP Ports
• Power cable
• 19" rackmount brackets
• User manual
 Loading...
Loading...