Intellinet 522755 User Manual

2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11g
Super-G 108Mb
Wireless Access Point
User’s Guide

Contents
Contents............................................................................................................2
System Requirements For Configuration...........................................................3
Introduction........................................................................................................4
Connections ......................................................................................................5
LEDs .................................................................................................................6
Wireless Basics.................................................................................................7
Installation Considerations ................................................................................9
Getting Started................................................................................................10
Using the Web Configuration Utility.................................................................12
Setup Wizard...................................................................................................14
Advanced Setup..............................................................................................16
Configuration...................................................................................................16
Device Information ..........................................................................................17
WLAN Parameter Settings ..............................................................................18
WLAN Partition................................................................................................19
Access Control Settings ..................................................................................20
Security Settings .............................................................................................21
Administration..................................................................................................22
Misc.................................................................................................................22
Maintenance/Update Firmware .......................................................................23
Configuration File ............................................................................................23
Restart System................................................................................................24
Statistics..........................................................................................................24
Throughput......................................................................................................24
Transmitted .....................................................................................................25
Received .........................................................................................................25
WEP Frame Error............................................................................................26
Troubleshooting...............................................................................................27
Technical Specifications..................................................................................32
2

Package Contents
• Intellinet Super-G Wireless LAN Access Point
• Power Adapter – 5VDC, 2A
• Quick Installation Guide on CD
Note: Using a power supply with a different voltage rating than the one included with the
802.11g Wireless Access Point will cause damage and void the warranty for this product.
If any of the above items is missing, please contact your reseller.
System Requirements For Configuration
• Computer with Windows, Macintosh, or Linux-based operating system with an
installed Ethernet adapter
• Internet Explorer or Netscape Navigator version 6.0 or above, with JavaScript
enabled
• At least 128 MB of memory and a 500 MHz processor
3

Introduction
The Intellinet Super-G 802.11g Wireless Access Point provides the largest available
bandwidth available in an AP. Network members can connect to this AP using any of its
channels to transfer data at speeds never achievable before in a wireless device. The
802.11g Wireless Access Point operates seamlessly and simultaneously in the 2.4GHz
frequency spectrums supporting the 802.11b and the newer, faster 802.11g wireless
standards. For offices, schools or public hotspots that already use 802.11b devices, the
802.11g Wireless Access Point is a great way to expand an existing network and enable
even more users to communicate with one another, access data and the Internet. Now,
you can have an AP that will compliment your existing network and protect the
investment you made when you provided the convenience of wireless networking.
The 802.11g Wireless Access Point offers transfer rates up to 108Mbps in the 2.4GHz
band, large data packets travel from the router to a remote desktop or roaming laptop
PC at up to ten times the speed of previous wireless devices. Everyone can work faster
and more efficiently or watch a streaming video smoothly. Network administrators can
partition the usage of the 802.11g Wireless Access Point by segmenting the users on
the wireless network by frequency band. Users who require special networking privileges
— access to sensitive information, specific departments or videoconferencing — may
use just the 802.11b and 802.11g channels. This type of user segmentation optimizes
the AP’s performance and delivers the best network experience to each set of users.
The 802.11g Wireless Access Point is ideal for network administrators who require
additional management, firewall, and other network security features. All of the AP’s
settings are easily accessible in the operating system independent, Web-based software
user interface that also features a step-by-step Setup Wizard to get your router up and
running in just a matter of minutes. The 802.11g Wireless Access Point incorporates the
WPA* (Wi-Fi Protected Access) which dynamically encrypts data as it’s being sent.
4

Connections
• Straight-Through cable is required when connecting to a router or switch
• Cross-Over cable is required when connecting directly to an Ethernet adapter on a
computer for configuration
Features & Benefits
• Up to 54 Mbps - Means you can transfer large files up to 5 times more quickly than
was previously possible without signal interference
• 802.11b and 802.11g Compliant - Means you can mix devices from different
standards without sacrificing connectivity
• Better Security with WPA - Other 802.11g devices can connect securely using
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
5
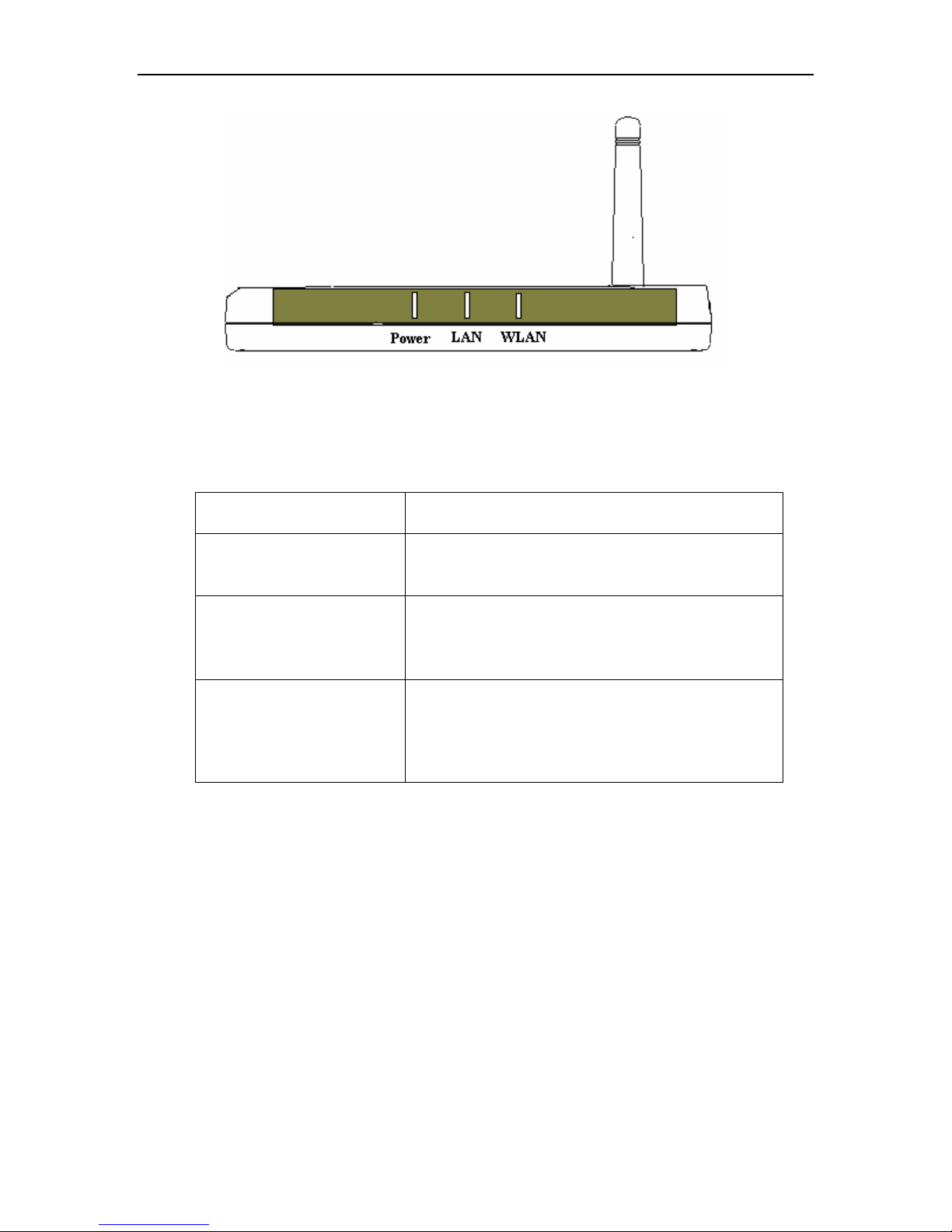
LEDs
LED stands for Light-Emitting Diode. The 802.11g Wireless Access Point has 3 Green
LEDs as shown below:
LED LED Activity
Power
A steady light indicates a connection to a
power source
LAN (10/100)
A steady light indicates a connection to the
Ethernet port; a blinking light indicates
activity
WLAN
(802.11b or
802.11g)
A blinking light indicates activity in the
respective wireless mode: 802.11b or
802.11g
6

Wireless Basics
The 802.11g Wireless Access Point is based on industry standards to provide easy-to
use and compatible high-speed wireless connectivity within your home, business or
public access wireless networks. Strictly adhering to the IEEE standard, the 802.11g
Wireless Access Point will allow you to securely access the data you want, when and
where you want it. You will be able to enjoy the freedom that wireless networking
delivers.
A wireless local area network (WLAN) is a cellular computer network that transmits and
receives data with radio signals instead of wires. Wireless LANs are used increasingly in
both home and office environments, and public areas such as airports, coffee shops and
universities. Innovative ways to utilize WLAN technology are helping people to work and
communicate more efficiently. Increased mobility and the absence of cabling and other
fixed infrastructure have proven to be beneficial for many users.
Wireless users can use the same applications they use on a wired network. Wireless
adapter cards used on laptop and desktop systems support the same protocols as
Ethernet adapter cards.
Under many circumstances, it may be desirable for mobile network devices to link to a
conventional Ethernet LAN in order to use servers, printers or an Internet connection
supplied through the wired LAN. A Wireless Access Point (AP) is a device used to
provide this link.
People use wireless LAN technology for many different purposes:
Mobility - Productivity increases when people have access to data in any location within
the operating range of the WLAN. Management decisions based on real-time information
can significantly improve worker efficiency.
Low Implementation Costs – WLANs are easy to set up, manage, change and
relocate. Networks that frequently change can benefit from WLANs ease of
implementation. WLANs can operate in locations where installation of wiring may be
impractical.
Installation and Network Expansion - Installing a WLAN system can be fast and easy
and can eliminate the need to pull cable through walls and ceilings. Wireless technology
allows the network to go where wires cannot go - even outside the home or office.
Inexpensive Solution – Wireless network devices are as competitively priced as
conventional Ethernet network devices.
Scalability – WLANs can be configured in a variety of ways to meet the needs of
specific applications and installations. Configurations are easily changed and range from
peer-to-peer networks suitable for a small number of users to larger infrastructure
networks to accommodate hundreds or thousands of users, depending on the number of
wireless devices deployed.
7

The 802.11g Wireless Access Point is compatible with the following IEEE802.11g
wireless products: 802.11g Wireless Cardbus Adapters used with laptop computers
and 802.11g Wireless PCI cards used with desktop computers
Standards-Based Technology
The 802.11g Wireless Access Point utilizes the 802.11b and 802.11g standards.
The IEEE 802.11g standard is an extension of the 802.11b standard. It increases the
data rate up to 54 Mbps within the 2.4GHz band. 802.11g utilizing OFDM technology.
This means that in most environments, within the specified range of this device, you will
be able to transfer large files quickly or even watch a movie in MPEG format over your
network without noticeable delays. This technology works by transmitting high-speed
digital data over a radio wave utilizing OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division
Multiplexing) technology. OFDM works by splitting the radio signal into multiple smaller
sub-signals that are then transmitted simultaneously at different frequencies to the
receiver. OFDM reduces the amount of crosstalk (interference) in signal transmissions.
The 802.11g Wireless Access Point offers the most advanced network security features
available today, including: WPA.
In addition to its compatibility with 802.11g devices, the 802.11g Wireless Access Point
is compatible with 802.11b devices. This means that if you have an existing 802.11b
network, or a network with a mixture of 802.11g and 802.11b, the devices in that network
will be compatible with the 802.11g Wireless Access Point.
8

Installation Considerations
Desktop and laptop computers with wireless network adapters installed can access the
802.11g Wireless Access Point from virtually anywhere within its operating range. Keep
in mind, however, that the number, thickness and location of walls, ceilings, or other
objects that the wireless signals must pass through, may limit the range. Typical ranges
vary depending on the types of materials and background RF (radio frequency) noise in
your home or business. The key to maximizing wireless range is to follow these basic
guidelines:
1
Keep the number of walls and ceilings between the 802.11g Wireless Access Point and
other network devices to a minimum - each wall or ceiling can reduce your wireless
product’s range from 3-90 feet (1-30 meters.) Position your devices so that the number
of walls or ceilings is minimized.
2
Be aware of the direct line between network devices. A wall that is 1.5 feet thick (.5
meters), at a 45-degree angle appears to be almost 3 feet (1 meter) thick. At a 2-degree
angle it looks over 42 feet (14 meters) thick! Position devices so that the signal will travel
straight through a wall or ceiling (instead of at an angle) for better reception.
3
Building materials can impede the wireless signal - a solid metal door or aluminum studs
may have a negative effect on range. Try to position wireless devices and computers
with wireless adapters so that the signal passes through drywall or open doorways and
not other materials.
4
Keep your product away (at least 3-6 feet or 1-2 meters) from electrical devices or
appliances that may generate extreme RF noise.
9
y
Getting Started
A. First, connect the power adapter to the receptor at the back panel of
the 802.11g Wireless Access Point and then plug the other end of the power adapter to
a wall outlet or power strip. The Power LED will turn ON to indicate the device has
detected power.
B. Connect your 802.11g Wireless Access Point LAN port with your straight-through
Ethernet cable into a switch/router. The Link LED for the LAN Port will illuminate to
indicate a proper connection.
C. Desktop or laptop computers with 802.11b or 802.11g wireless adapters can connect
to the 802.11g Wireless Access Point.
Right out of the box with its default settings, the 802.11g Wireless Access
Point will automaticall
connect with other wireless products.
Note: If you are using a DHCP-capable router in your network setup you will
not need to assign a static IP Address.
If you need to assign IP Addresses to the computers on the network, please
remember that the IP Address for each computer must be in the same IP
Address range as all the computers in the network, and the Subnet mask
must be exactly the same for all the computers in the network.
For example: If the first computer is assigned an IP Address of 10.0.0.2 with
a Subnet Mask of 255.0.0.0, then the second computer can be assigned an
IP Address of 10.0.0.3 with a Subnet Mask of 255.0.0.0, etc.
IMPORTANT: If computers or other devices are assigned the same IP
Address, one or more of the devices may not be visible on the network.
IP ADDRESS
10
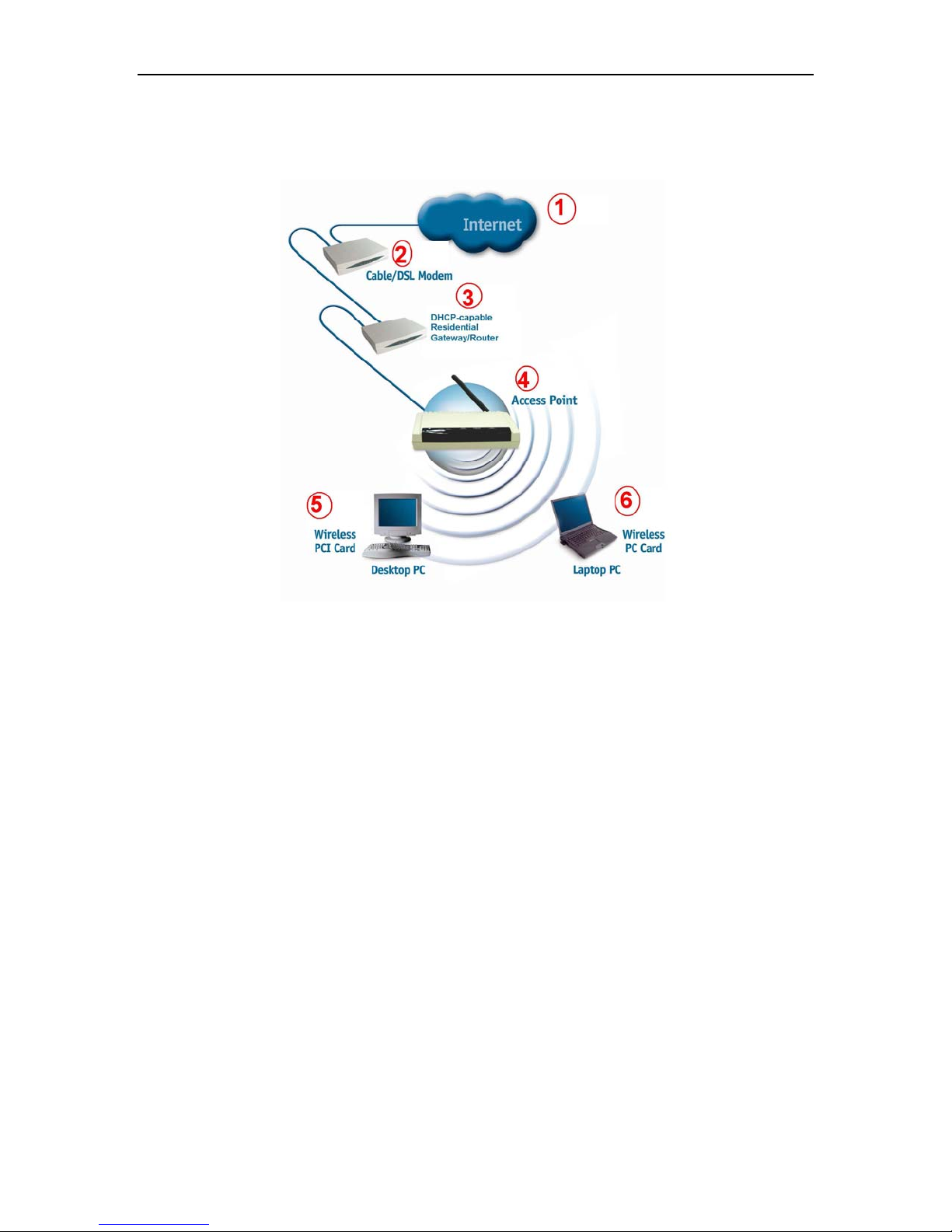
An Infrastructure wireless network contains an Access Point or Router. The
Infrastructure Network example, shown here, contains the following network devices:
For a typical wireless setup (as shown above), please do the following:
1. You will need a broadband Internet access (Cable/DSL) subscription
2. Consult with your Cable/DSL provider for proper installation of the modem
3. Connect the modem to an Ethernet broadband router.
4. Connect the router to the 802.11g Wireless Access Point.
5. If you are connecting a desktop computer in your network, you can install any 11g
compliant wireless PCI adapter into an available PCI slot, or install a WLAN 11g
CardBus card into a Notebook PC.
11
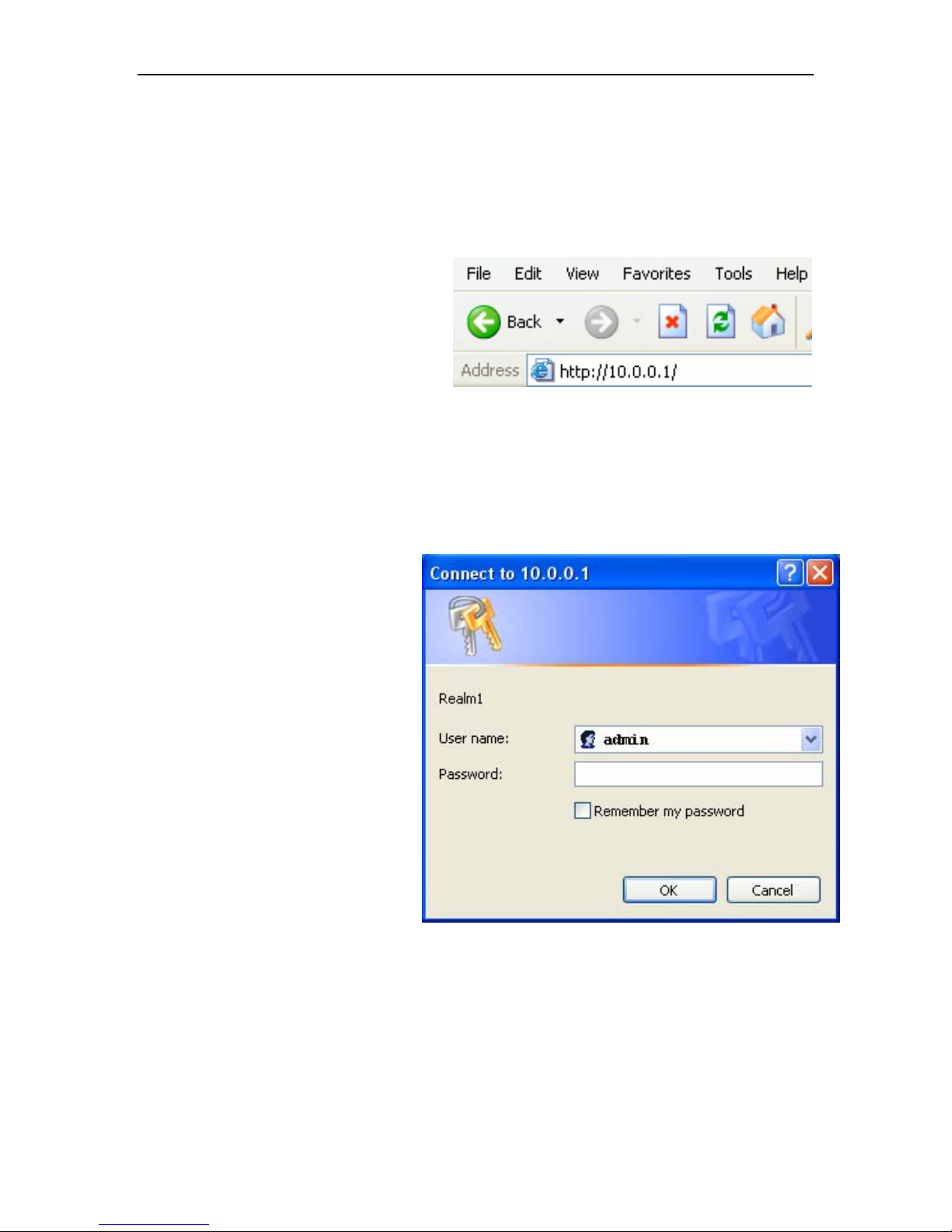
Using the Web Configuration Utility
The easiest and quickest way to connect to a wireless network using your Intellinet
802.11g Wireless Access Point is to use the Configuration Utility. Open your web-
browser and type in the IP Address of the Intellinet 802.11g Wireless Access Point:
default IP Address is shown below:
• Open the web browser
• Type in the IP Address of the
Access Point
Note: if you have changed the default IP Address assigned to the 802.11g Wireless
Access Point, make sure to enter the correct IP Address.
• Type admin in the User
Name field
• Leave the Password blank
• Click OK
12
 Loading...
Loading...