
Broadband Router User Guide

Broadband Router User Guide
Dec. 2001
Limitation of Liability
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part.
The material contained herein is supplied without representation or warranty of any kind. Therefore assumes no
responsibility and shall have no liability of any kind arising from the supply or use of this document or the material
contained herein.
This manual copyright 2001. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be copied or re-used without prior
written consent

1Broadband Router
About This User Guide
Welcome to the Networking world of multifunction routers! Thank you for investing
in a Broadband Router. We are dedicated to provide the most efficient, easy to
configure, and trouble free equipment in the networking industry.
This manual is intended as a basic introduction to your Broadband Router. It supplies
enough information to make the Broadband Router operational in most common
environments: connecting to the Internet , receiving calls from dial-in users, or
connecting to another network through the telephone network.
We’ll describe how to use your web browser to configure the Broadband Router and
to perform some basic operations, e.g. upgrading the software, or viewing the
connection log, a task which may be useful in ongoing operations. Finally, we’ll tell
you how to obtain information and help for subjects that are beyond the scope of this
manual.
This manual consists of seven chapters and three appendixes:
Chapter One: Introduction, explains the features and capabilities of the Broadband
Router.
Chapter Two: Installing the Broadband Router, gives the simple steps you follow to
install the Broadband Router and configure your workstations.
Chapter Three: Configuring the Broadband Router, explains how to log in to the
ARM Manager, describes the browser screen, and provides the steps needed to
configure your Broadband Router for specific applications. It provides easy-to-follow
instructions for quick Internet access and provides a guide to the most popular
Broadband Router configurations.
Chapter Four: Advanced Configuration, provides information on advanced router
configuration setup.
Chapter Five: Managing the Broadband Router, explains the management features
of the Broadband Router.
Chapter Six: Messages, lists messages you may see in the ARM message window,
and what they mean.
Appendix A: Specifications
Appendix B: Glossary
Appendix C: Warranty, Copyright, FCC Notice
Safety Warnings
• The Broadband Router is not intended to be serviced by the user. Do not open
the case.
Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction
What’s in the box?
Overview of the Broadband Router
Broadband Router Applications
Accessing the Internet
Accessing Servers from the Public Network
Supporting Dial-in Access to Your Network
Accessing Internet and Dial-In Simultaneously
Creating Your Own Private Wide Area Network
Accessing Internet and LAN-to-LAN Simultaneously
Creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A Configuration Example
Security Overview
A Physical Look at the Broadband Router
The Connectors on the Back
The LEDs on the Front
Chapter 2 Installing the Broadband Router
Installing the Broadband Router
Setting Up a Windows PC for Configuring the Broadband Router
Connecting more Devices through a Hub to the Broadband Router
Chapter 3 Configuring the Broadband Router
Internet Access in Five Minutes
Using Setup Wizard
Overview of The ARM Browser Screen
What is a Connection Profile?
Internet Access Interface
Configuring a Basic Internet Access Profile via EWAN
Configuring Auto Backup
Configuring a Basic Internet Access Profile via Modem
Adding Internet Access Profiles
Deleting or Modifying Internet Access Profiles
Remote Office Access
Advanced Options for Remote Office Profiles
Deleting or Modifying Remote Office Access Profiles
Dial-in User Access
Dial-In User Advanced Options
Deleting Dial-in User Profiles
Internet Access Time Restrictions
Chapter 4 Advanced Configuration
NAT(Network Address Translation)
Virtual Server/DMZ (De-military Zone)
iii

Firewall (IP/IPX Filtering)
VPN (Virtual Private Network )
Bridging
Chapter 5 Managing the Broadband Router
System Status
Connection Log
About System
System Upgrade
Clear Configuration
Reset System
Change Password
System Time
Chapter 6 Messages
Messages
Appendix A Broadband Router Specifications
Appendix B Glossary
Appendix C Warranty, Copyrights, FCC Notice
Warranty
Copyrights
FCC Part 15 Notice
iv
1Broadband Router
1 Introduction
This chapter gives the introduction to the Broadband Router.
What’s in the Box?
Your Broadband Router box should contain the items listed below
• 1 Broadband Router
• 1 AC Adapter, AC 9V 1A
• 1 RS-232 serial cable with DB-9 (9 pin) male connector and RJ45 plug to
connect the Broadband Router Console/COM port and external ISDN TA/
Analog Modem
• 1 female to female 9 pin adaptor to connect the Broadband Router Console port
to a PC COM port.
• 1 CAT5 UTP cross-over LAN cable to connect the Broadband Router EWAN
port to an external ADSL or Cable Modem
Note: Some Cable Modems use straight LAN cable
• 1 CD-ROM containing the online documentation
• 1 Quick-Start Guide
Overview of the Broadband Router
The Broadband Router is a small desktop router that sits between your local Ethernet
network and a remote network (e.g., the Internet or a remote office). The Broadband
Router contains an EWAN port connecting to an external ADSL/Cable modem , a
Console/ COM port for connection to a console device(such as a PC COM port ), and
a four-port 10/100Mbps Ethernet switch for connection to PCs on your local network.
The Console/COM port can alsobe used to connect to the Internet(as a back-up such
as when the ADSL/Cable modem line is not operational) or a remote office via an
external ISDN TA or Analog Modem, and even allows a remote user(a tele-commuter
or a traveling sales person) to dial in and access your local network.
Data comes into the Broadband Router from the local LAN and then is “routed” to the
remote network, and vice versa.
Broadband Router Applications
The main functions of the Broadband Router
-to allow devices on your LAN to access the Internet,
-to allow access to the servers from the public network,
1-1
-to support remote users to directly dial in and access your LAN,
-to support direct dial-up communication with remote offices and share resources
between remnote LANs.
- to create Virtual Private Network (VPN) to allow remote LANs to share resources
with each other over the Internet.
Accessing the Internet
The most common use for the Broadband Router is to provide Internet access, so that
everyone on your LAN can surf the web and send/receive email or files.
The Broadband Router automatically acquires the necessary IP address when the
connection to the Internet is established. You don’t need to apply for and assign an IP
address to each PC or workstation on your network.
Accessing Servers from the Public Network
If you want special servers to be accessible by remote users across the Internet (e.g.,
an e-mail server, an FTP server, or a web server), you can configure the Broadband
Router to proxy the service from its own address. This means that the remote user can
address the router as if it were the special server and the Broadband Router will redirect this connection to the appropriate computer on the network.
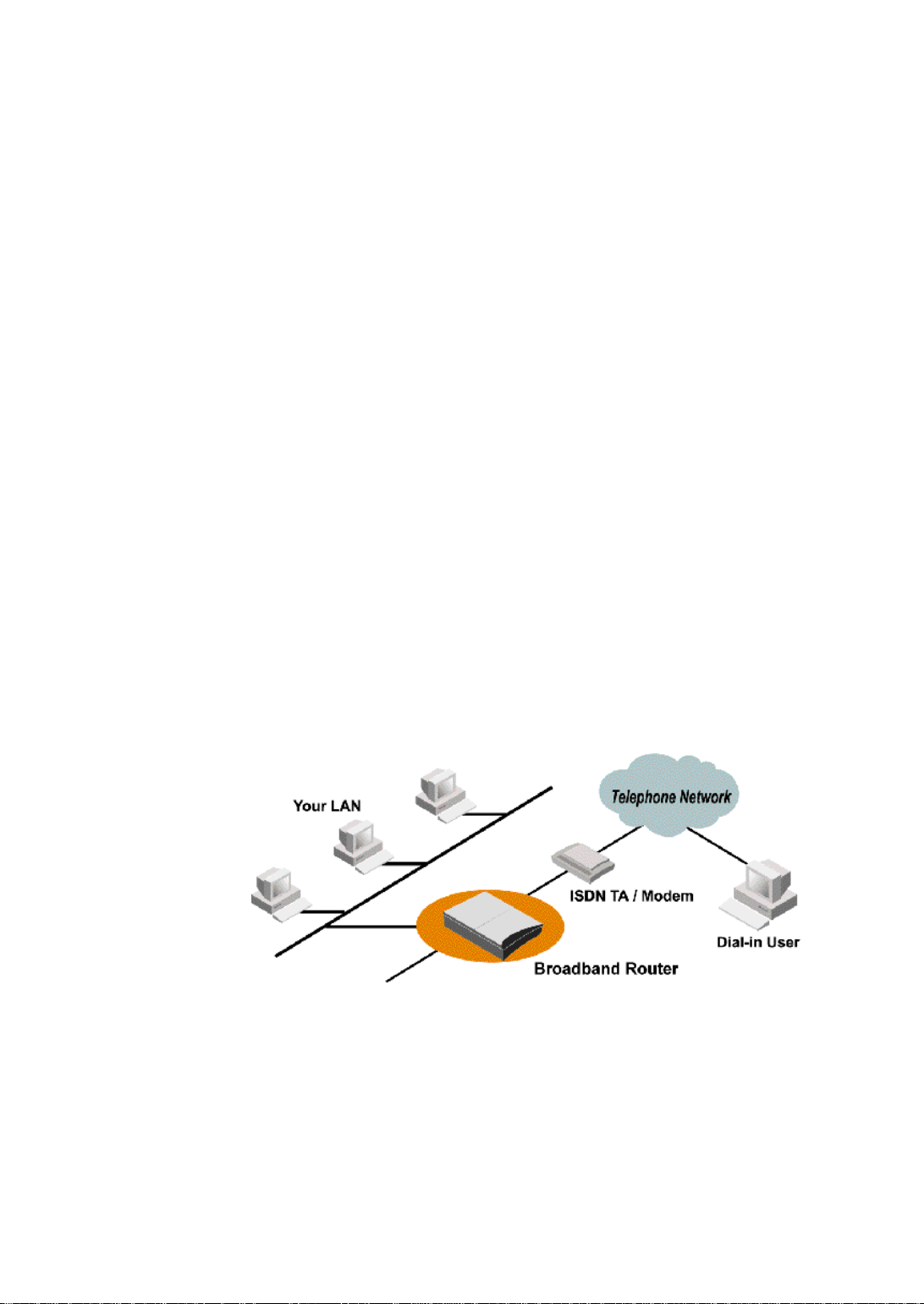
Supporting Dial-in Access to Your Network
You can set up your Broadband Router to allow users to connect to your network
and share resources from home or while they’re travelling. The Broadband Router
built-in configuration program makes the necessary setup a snap. As a security
feature, after a user calls in, the Broadband Router can hang up and call that user
back at a preconfigured telephone number.
1-2
Figure 1-1 Dial-in Access
You can set up the Broadband Router to provide Internet access for everyone on your
LAN and allow a remote user to dial in to your network via V.90 Modem or ISDN TA
simultaneously.
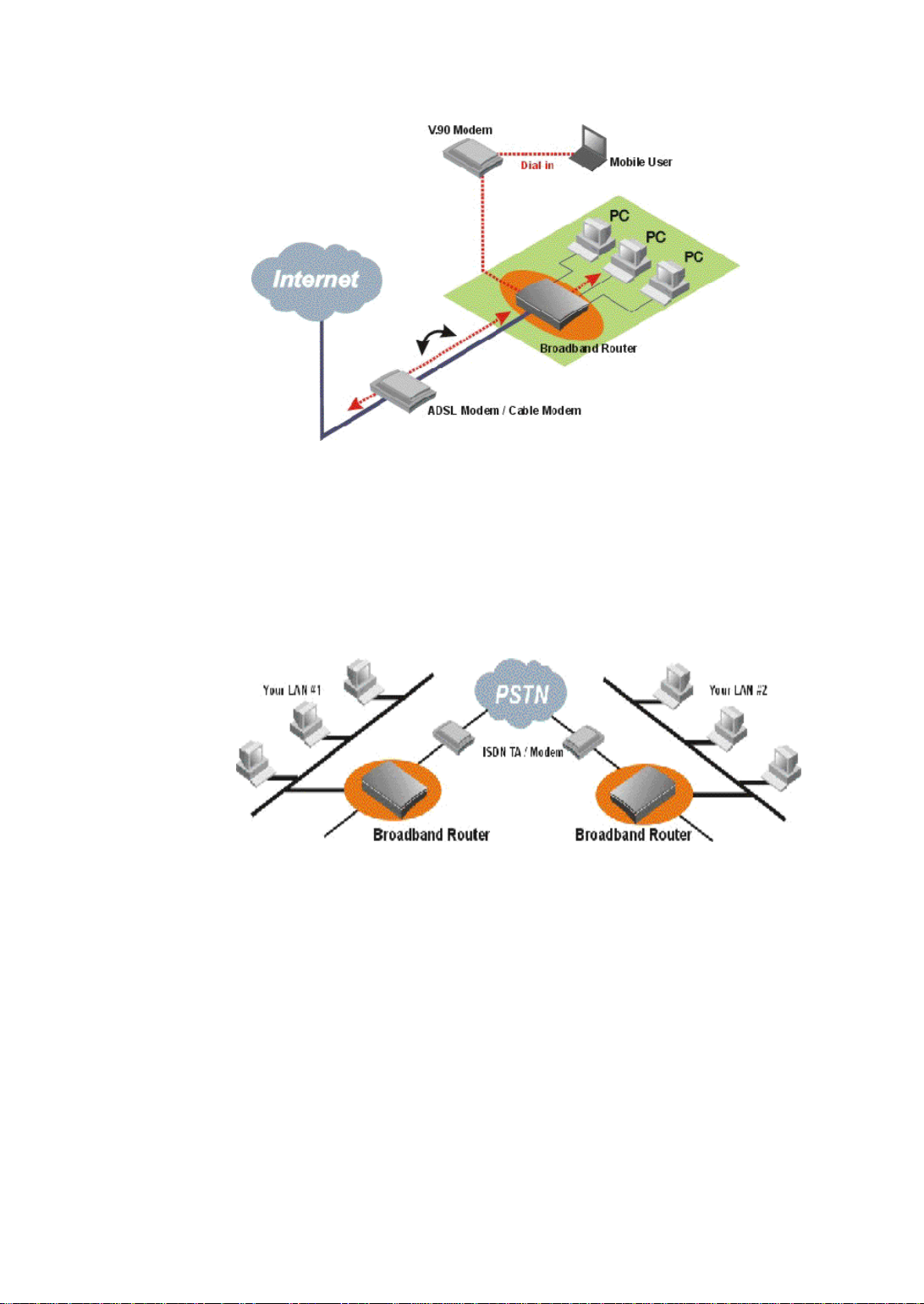
Figure 1-2 Internet Access and Dial-in Simultaneously
Creating Your Own Private Wide Area Network
You can create your own private wide area network with Broadband Router via
external ISDN TA / modem and allow two or more remote networks to connect to one
another and share resources. The remote network can use a broadband router even
though it is a different vendor - as long as it also supports LAN to LAN
communications.
Figure 1-3 Connecting Two Networks with Broadband Router
You can set up the Broadband Router to provide Internet access for everyone on your
LAN and create your own private wide area network via V.90 Modem or ISDN TA
simultaneously.
1-3
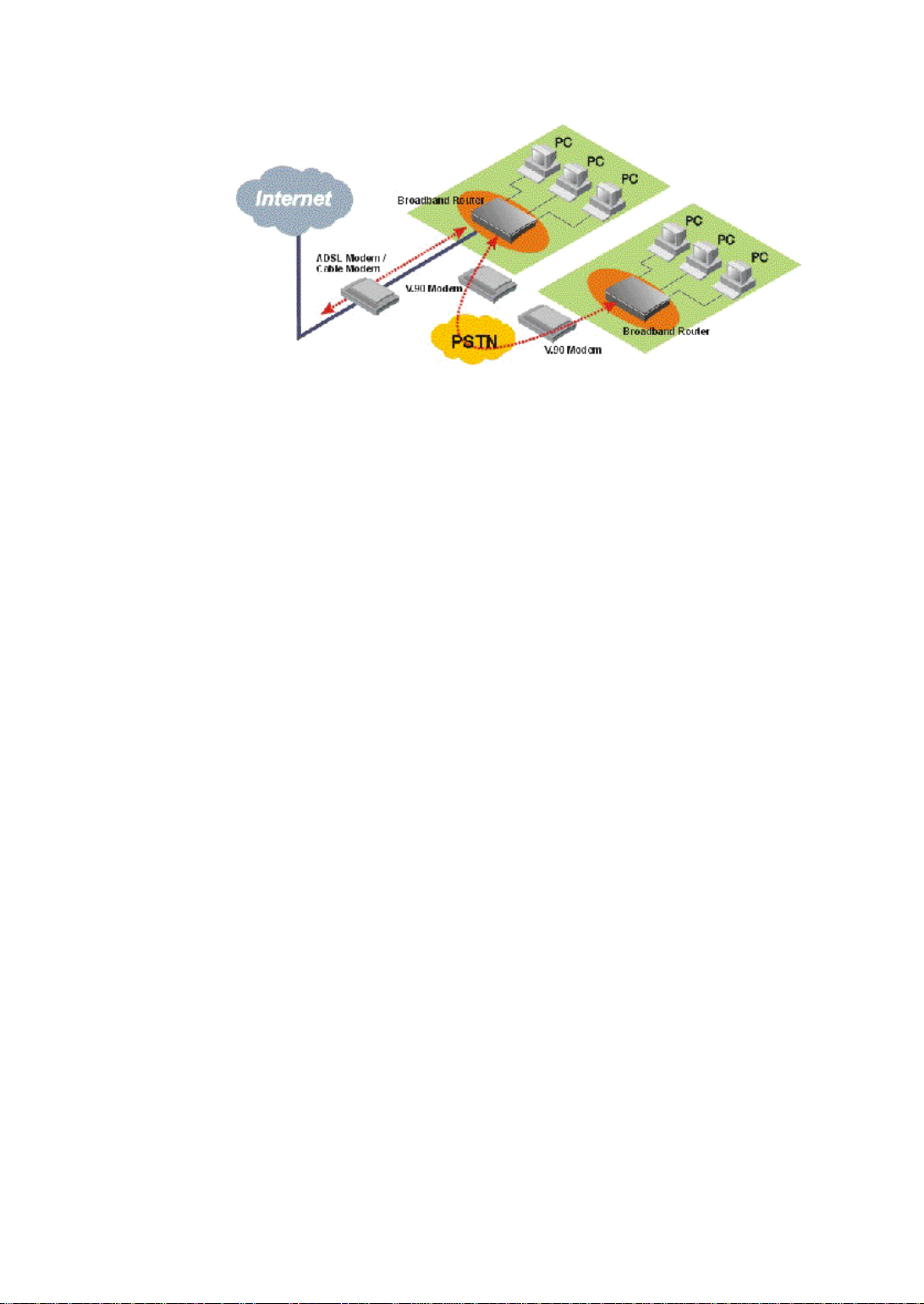
Figure 1-4 Internet Access and LAN-to-LAN Simultaneously
Creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN)
Virtual Private Networking (VPN) provides a means to connect remote LANs over
the Internet, while only local toll charges to an Internet Service Provider are incurred
even if the two LANs are physically remote to each other.
To create a VPN between two sites, a special connection called “tunnel” followed by
a VPN data session has to be set up over the Internet. After a VPN data session is set
up, data can be sent over it, optionally encrypted to prevent unauthorized access.
Additionally, VPN tunnels allow IP, IPX and Bridging traffic to flow across the
Internet, including NetBIOS information (for Windows networking) encapsulated
within IP or IPX packets.
All information required for a VPN is defined in a VPN profile, which contains, for
example, the IP address of the VPN partner and authentication information (including
the encryption key that is used).
When a PC from one site tries to communicate with a device on the other site for the
first time, the VPN tunnel and data session establishment process will be triggered
automatically. For the originating side, first the destination IP address will be used to
search for the corresponding VPN profile. Based on the information conifgured in the
matched VPN profile, a VPN tunnel is created, a VPN data session will be created
and authentication information exchanged, then data traffic can start to flow. For the
destination side, when a VPN data session creation is requested, the router will base
on the originating IP address to search for a matched profile. Once found, the
Broadband Router will use the information in the matched profile to authenticate the
incoming "call", after which data transfer can begin.
1-4
More than one VPN data sessions can be established over the same tunnel.
See chapter 4 for detailed configuration instructions.
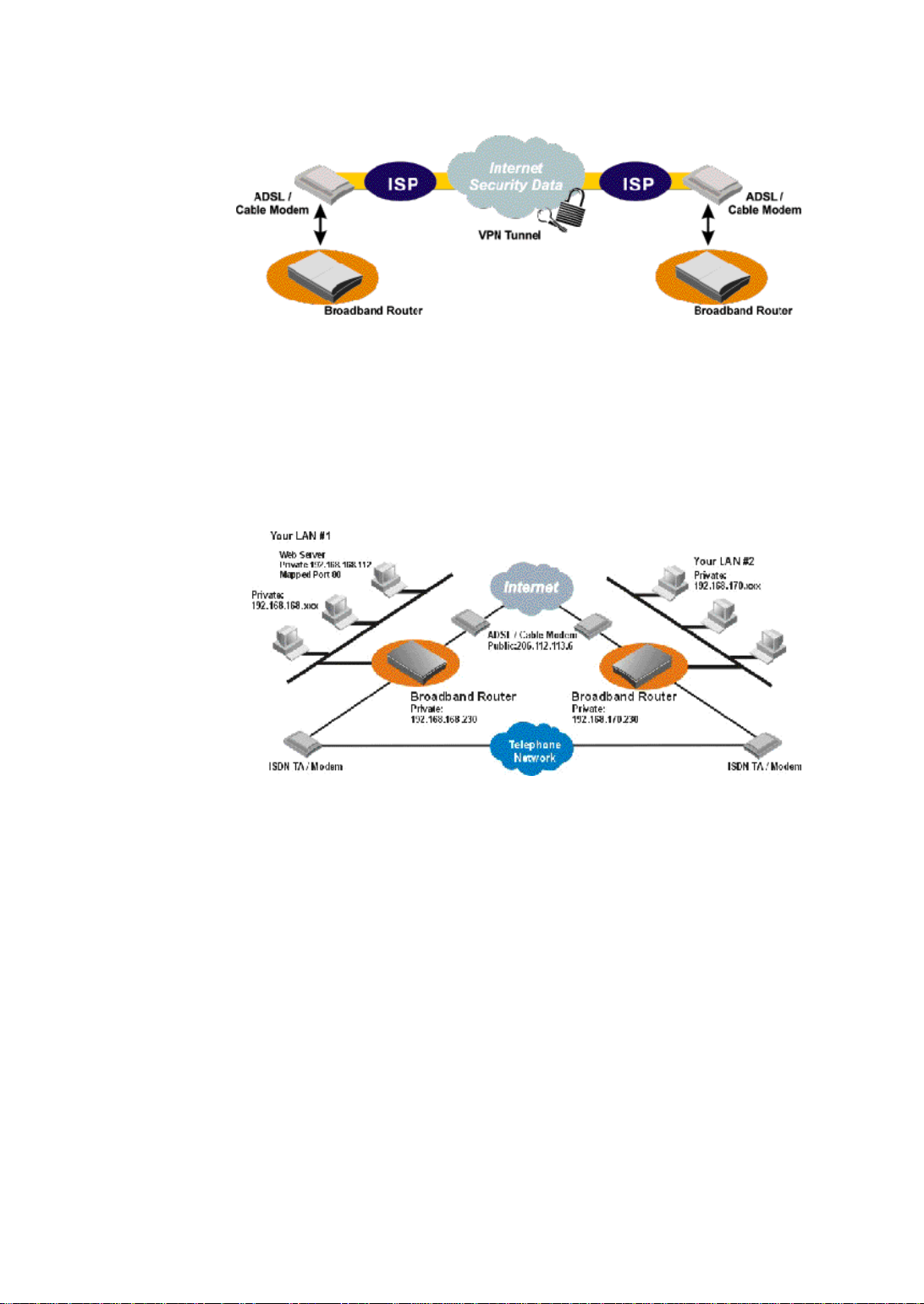
Figure 1-5 Creating a Virtual Private Network
A Configuration Example
In Figure 1-6, two Broadband Routers are installed in two different locations. They
are connected to the Internet via ADSL/Cable modem, allowing users to surf the
Web. They are also connected to each other through the telephone network, forming a
private company network.
Figure 1-6 Connecting Two Private Networks
This example illustrates an important feature of the Broadband Router: a private
device can be accessed from the Internet by mapping the application port number to a
port number on the Broadband Router. In this case, an Internet user accesses a web
server with IP address 206.112.113.6, which is the Broadband Router’s IP address.
When properly configured, the Broadband Router will translate that port 80 of that
address to port 80 of the private IP address, 192.168.168.112.
In this example, all devices on both LANs (except for the Web servers) are
configured to obtain their IP addresses automatically (i.e., from the built-in DHCP
server in the Broadband Router). It is important for the Web Server on LAN #1 to
have the same IP address all the time (so that users can use the same IP address to
access it), it also means the Broadband Router should also be assigned a static IP
address.
IP addresses assigned to the devices on the LAN are only used in the local LAN
environment (with default IP network address of 192.168.168.0), therefore these
devices naturally form a private network and are not accessible by users across the
Internet, unless they are mapped. It is still possible to assign public IP addresses
obtained from your ISP to devices on your LAN so that they can be accessed by users
1-5

across the Internet. These public addresses can co-exist with private IP address on the
same LAN.
In order for LAN to LAN communication to work in such configurations, the default
private network Broadband Routeraddress (192.168.168.0) for one of the above
Broadband Router has to be changed (to 192.168.170.0 in the above example). The
traffic between these two networks is secure because data are sent across the
telephone network via a direct phone call.
A Security Overview
More and more people are concerned about security of their data in the Internet
The Broadband Router provides many ways to help make your network and your
data secure:
• All dial-in users and LAN-to-LAN communications require PPP PAP/CHAP/
MS-CHAP authentication (basically user name and password)
• The Broadband Router also supports call-back for dial-in users - so that remote
user are really who they say they are
• The Broadband Router uses a private IP addressing scheme to prevent devices on
your LAN from access by outside users
• Console, Telnet and ARM support password protection
• DES encryption with PPP/ECP negotiation is supported for VPN connections
• IP packet filtering may be used to futher enhance security requirements
A Physical Look at the Broadband Router
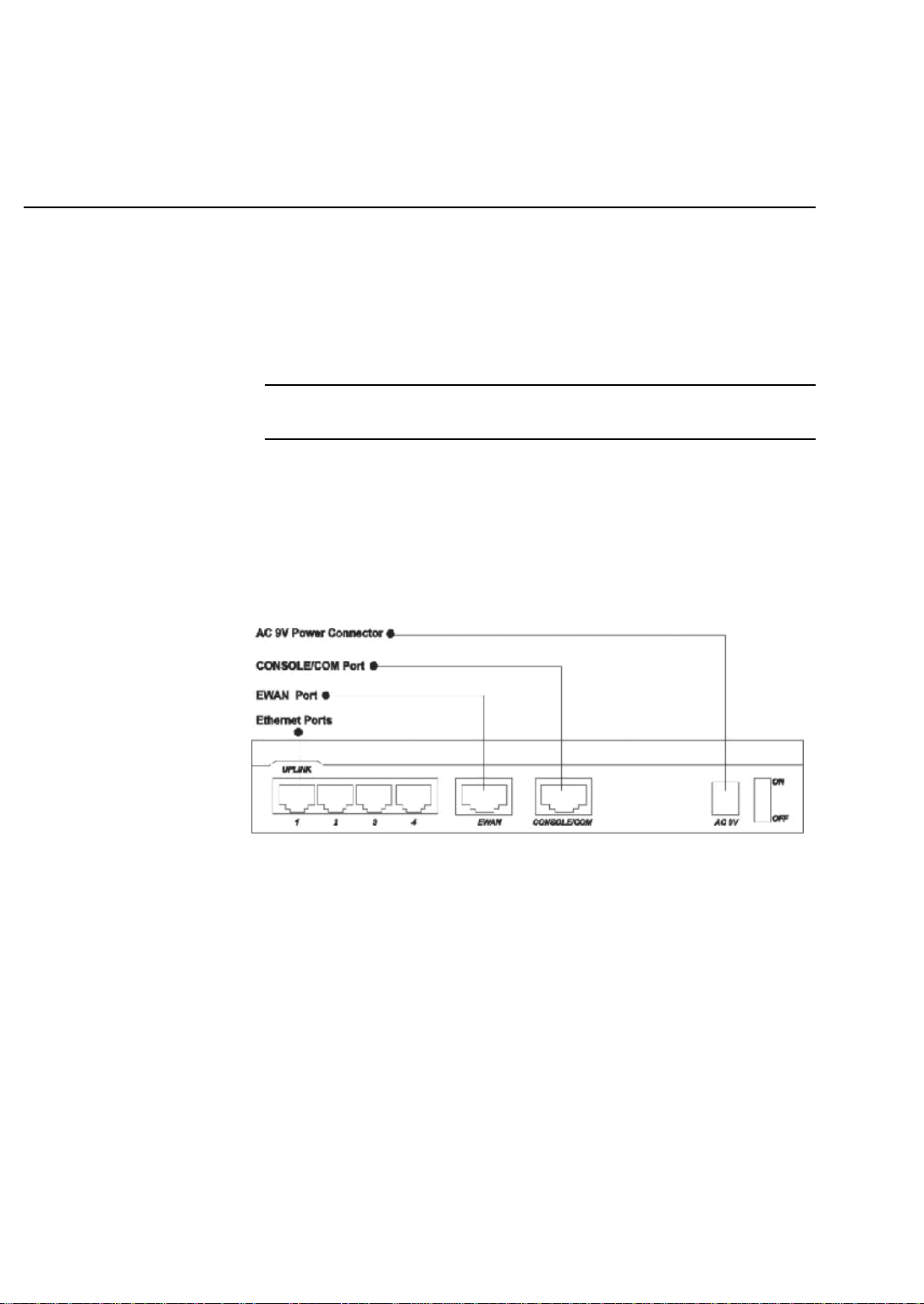
The Connectors on the Back
The following illustration shows the rear panel of Broadband Router.
(1 )4 RJ-45 10/100 Switch connectors for connecting to PCs and workstations or
connecting external Ethernet hub, or switch with uplink switch on port 1.
(2) 1 RJ-45 EWAN connector for connecting to Internet via ADSL/Cable modem
(3) 1 RJ-45 connector to be a COM port connecting to external ISDN TA/ modem
or to be a Console port connecting to PC.
(4) 1 AC power connector for connecting through an AC power adapter (included as
part of the product) to the wall power outlet
(5) 1 power ON/OFF switch
1-6
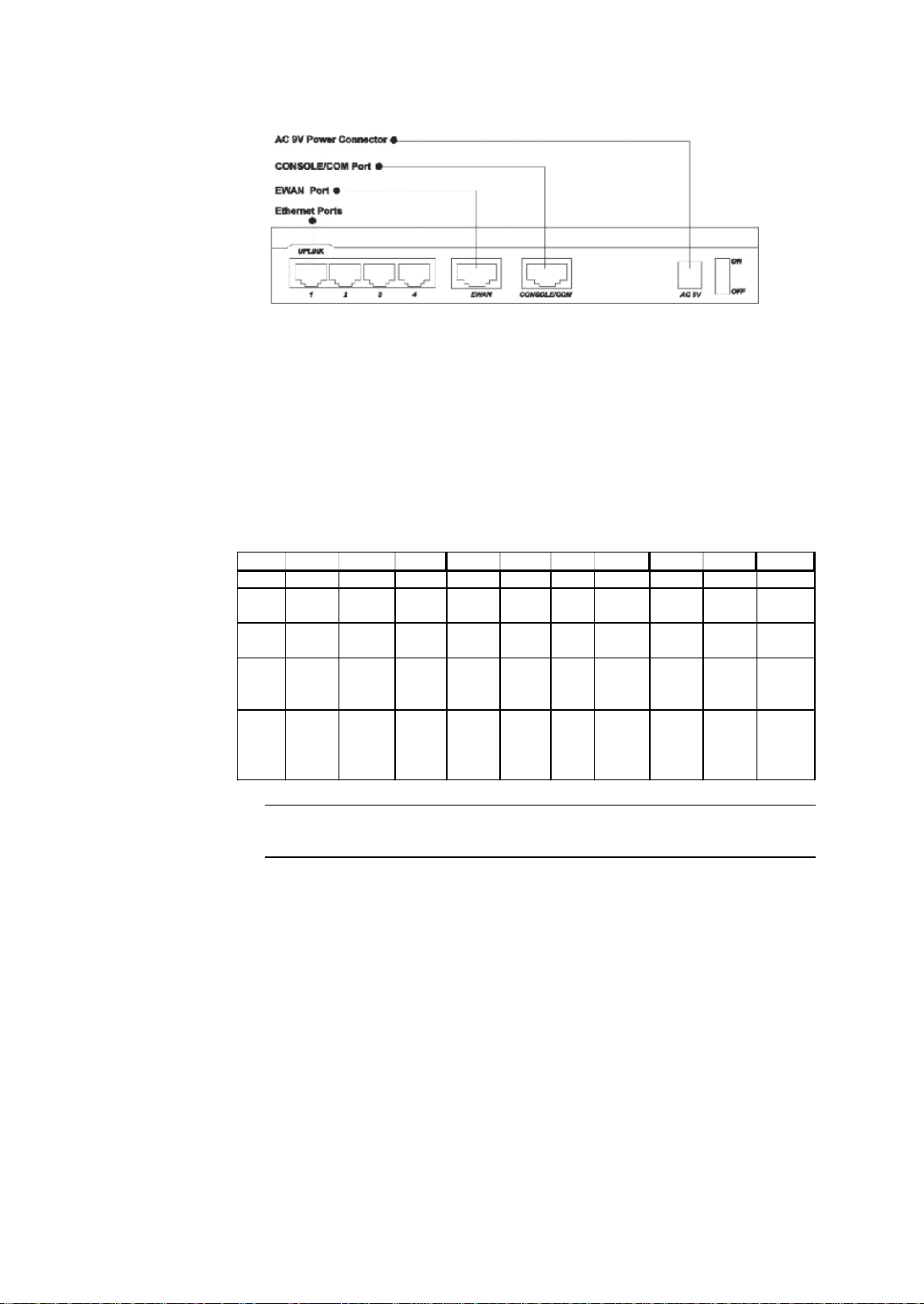
Figure 1-7 Broadband Router Connectors
The LEDs on the Front
There are 20 LEDs on the front of the Broadband Router that show connection and
traffic status of Power, PPPoE, COM, EWAN and LAN ports:
Figure 1-8 LEDs
LAN COM EWAN POWER
LED1 LED2 LED3 LED4 LED5 LED6 LED7 LED8 LED9 LED10
FDX/COLLNK/AC
T 100/10 RX TX CD OH
ON FDX
OFF HDX
FLASH Collision
Physical
Linkage 100Mbps N/A N/A
No
Physical
Linkage 10Mbps No Data No DataNoCarrier On-Hook N/A
Sending
or
Receiving N/A
Receivin
g Data
Carrier
Detect Off-Hook N/A
Sending
Data N/A N/A
Note: Some of the features above are optional. Please refer to Appendix A for
the details.
ACT/
LINK COL PPPoE
Physical
Linkage
Physical
Linkage
Sending
or
Receivin
g Packet N/A
PPPoE
Linkage
No
PPPoE
Linkage
Sending or
Receiving
Packet
No
1-7
2Broadband RouterBroadband Router
2 Installing the Broadband Router
Now you should be ready to connect your Broadband Router devices on your LAN .
Follow these steps to install the Broadband Router:
Step 1 Connect ADSL/Cable modem to the Broadband Router EWAN port using
crossover CAT5 UTP LAN cable.
Note: Some Cable Modems use straight LAN cables
Step 2 Connect a PC/Workstation to one of the LAN ports of the Broadband
Router, such as port 1 or port 2 (using a straight or cross-over LAN cable,
respectively). See below for more details of how to connect to an external
repeater hub or LAN switch.
Step 3 Connect the AC adapter to the Broadband Router and an electrical outlet.
Figure 2-1 Broadband Router Connectors
2-1
Setting Up a Windows PC for Configuring the
Broadband Router
This section describes how to configurea PC on the LAN in order to communicate with
the Broadband Router.
The PC need to have an Ethernet interface cards installed, and be connected to the
Broadband Router either directly(to its LAN ports) or indirectly through an external
LAN hub or switch. It should also h ave TCP/IP installed, enabled, and configured to
obtain an IP address automatically(i.e., through a DHCP server).
If TCP/IP is not already installed, follow the steps below for its installation.
Note: Any TCP/IP capable workstation can communicate with the Broadband
Router. To configure workstations other than Windows 95/98/NT, please consult the
manufacturer’s documentation.
Step 1 Connect your PC to one of the Broadband Router Switch ports. If you
connect to LAN port 1, you should use a straight LAN cable and set the
Uplink switch to the Normal position. or use a crossover LAN cable and set
the Uplink switch to Uplink. See Figure 2-3..
Step 2 From the Win95/98 Start Button, select Settings, then Control Panel. The
Win95/98 Control Panel displays.
Step 3 Double-click on the Network icon.
Step 4 Check your list of Network Components in the Network window
Configuration tab. If TCP/IP has already been installed, go to Step 8.
Otherwise, select Add to install it now.
Installed components
Look for TCP/IP
Add button
Client for Microsoft Networks
2-2
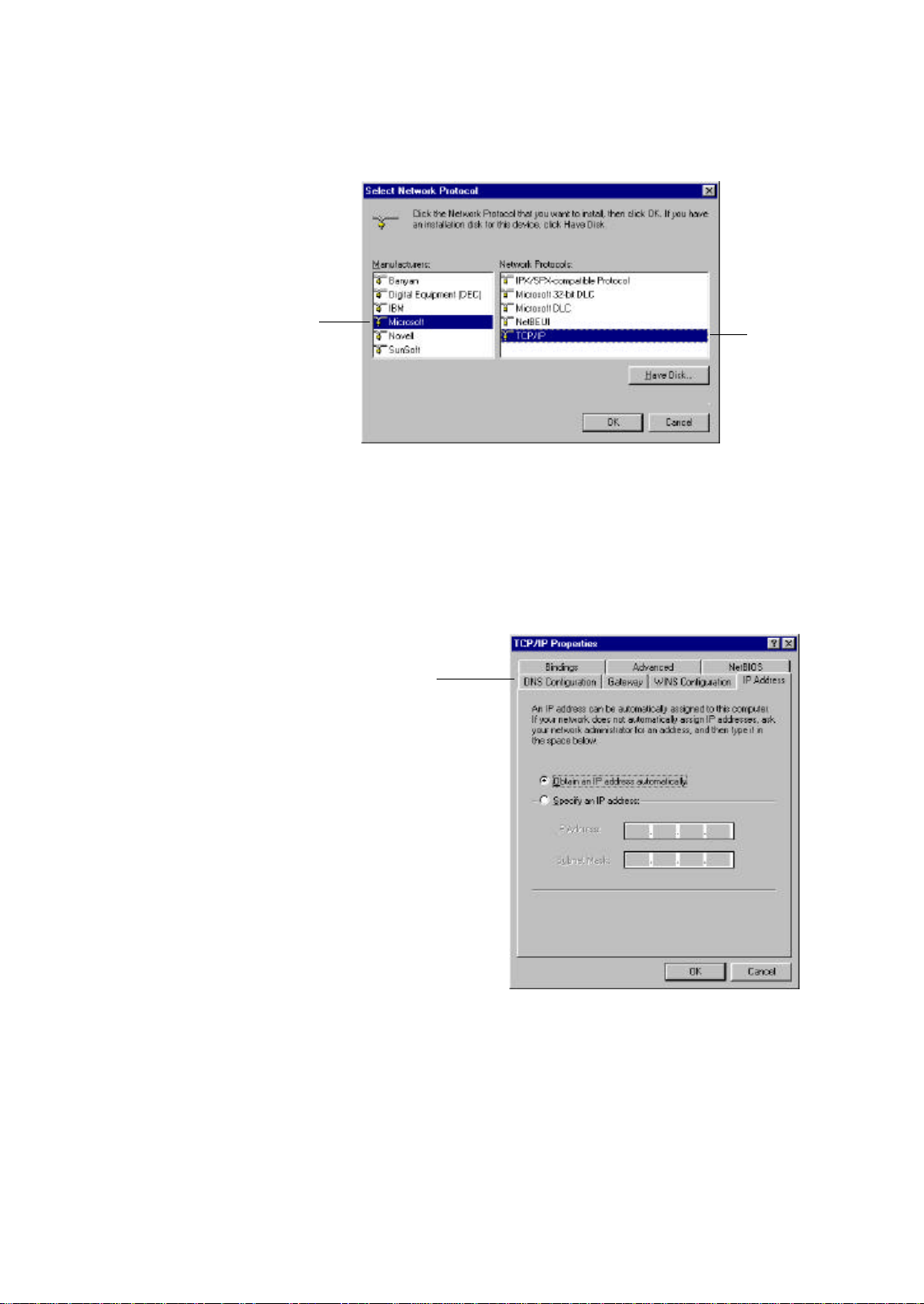
Step 5 In the new Network Component Type window, select Protocol.
Step 6 In the new Select Network Protocol window, select Microsoft in the
Manufacturers area.
Select
Microsoft
Select
TCP/IP
Step 7 In the Network Protocols area of the same window, select TCP/IP, then
click OK. You may need your Win95/98 CD to complete the installation.
After TCP/IP installation is complete, go back to the Network window
shown in Step 4.
Step 8 Select TCP/IP in the list of Network Components.
Step 9 Click Properties, and check the settings in each of the TCP/IP Properties
window:
TCP/IP Properties Tabs
(IP Address Tab shown)
-Bindings Tab: both Client for Microsoft Networks and File and printer
sharing for Microsoft Networks should be selected.
-Gateway Tab: All fields should be blank
-DNS Configuration Tab: Disable DNS should be selected
-IP Address Tab: Obtain IP address automatically should be selected
Step 10 When the Broadband Router connected to the LAN (and powered on),
reboot the PC. After the PC is re-booted, you should be ready to configure
the Broadband Router. See Chapter 3.
2-3
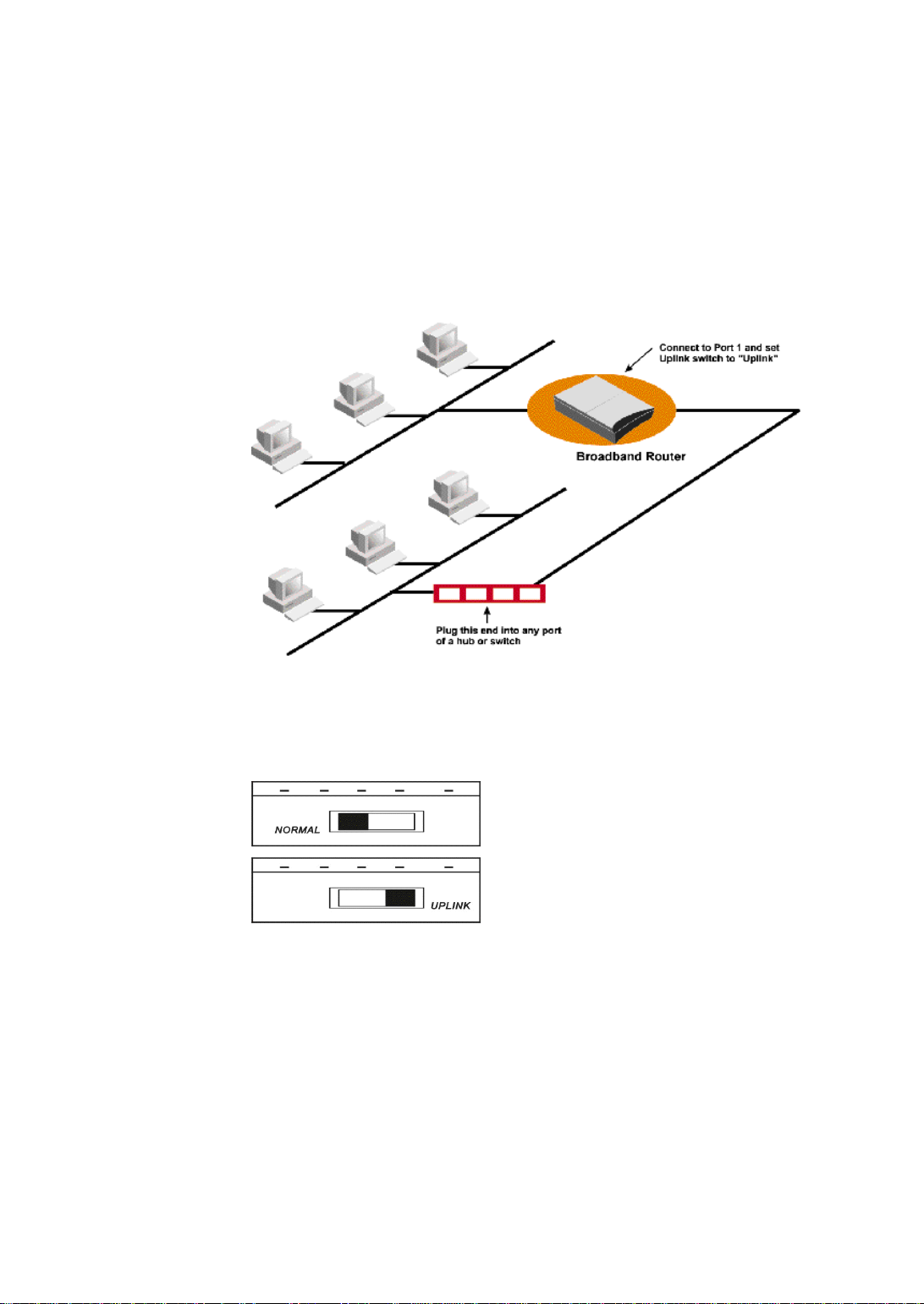
Connecting more Devices through a Hub to the
Broadband Router
The Broadband Router provides four LAN ports to allow up to four PCs or
Workstations to be connected to it directly. If you want to connect more devices, you
can connect an external hub or switch to LAN port 1 using a straight LAN cable if the
Uplink switch is set to the Uplink position, or using a cross-over LAN cable if the
Uplink switch is set to the Normal position.
Figure 2-2 Connecting a Hub or Switch to the Broadband Router
The uplink switch is shown in the following picture.
Figure 2-3 Uplink Switch
2-4

30Broadband Router
3 Configuring the Broadband Router
Once you have completed the installation stage and have configured a PC properly as
described in chapter two, you are ready to configure the Broadband Router for actual
applications.
This chapter describes how to configure your Broadband Router for basic Internet
access.
Internet Access in Five Minutes
You can configure your Broadband Router quickly by the Setup Wizard at you
first time logging on the router.
Setup Wizard
The Wizard will lead you step by step to configure the router for your Internet Access
by connecting ADSL/Cable modem.
You can change your Internet Access configuration by clicking the Setup Wizard
item on the top of left side in ARM(Access Router Manager) menu.
1. Open your browser and type http://192.168.168.230 in the browser’s address
box, it is the default IP address of your router.
2. Logging On
After entering the default IP address as described above, a password prompt screen
will ask you to log on. If you are logging on for the first time, you should accept the
factory default password (which is “password”). The password is always displayed as
a string of asterisks (“*”). Clicking the Log On button will begin a Access Router
Manager (ARM) session. The next time you log in, even if you have modified the
password , the default password (“password”) will still be used as the default. You
need to change it to the correct password before you will be let in.
No matter what password you use, each character will always be displayed in the
logon prompt as a “*”.
If you forget the password, you need to follow steps described in chapter 5 to be able
to log on.
3-1
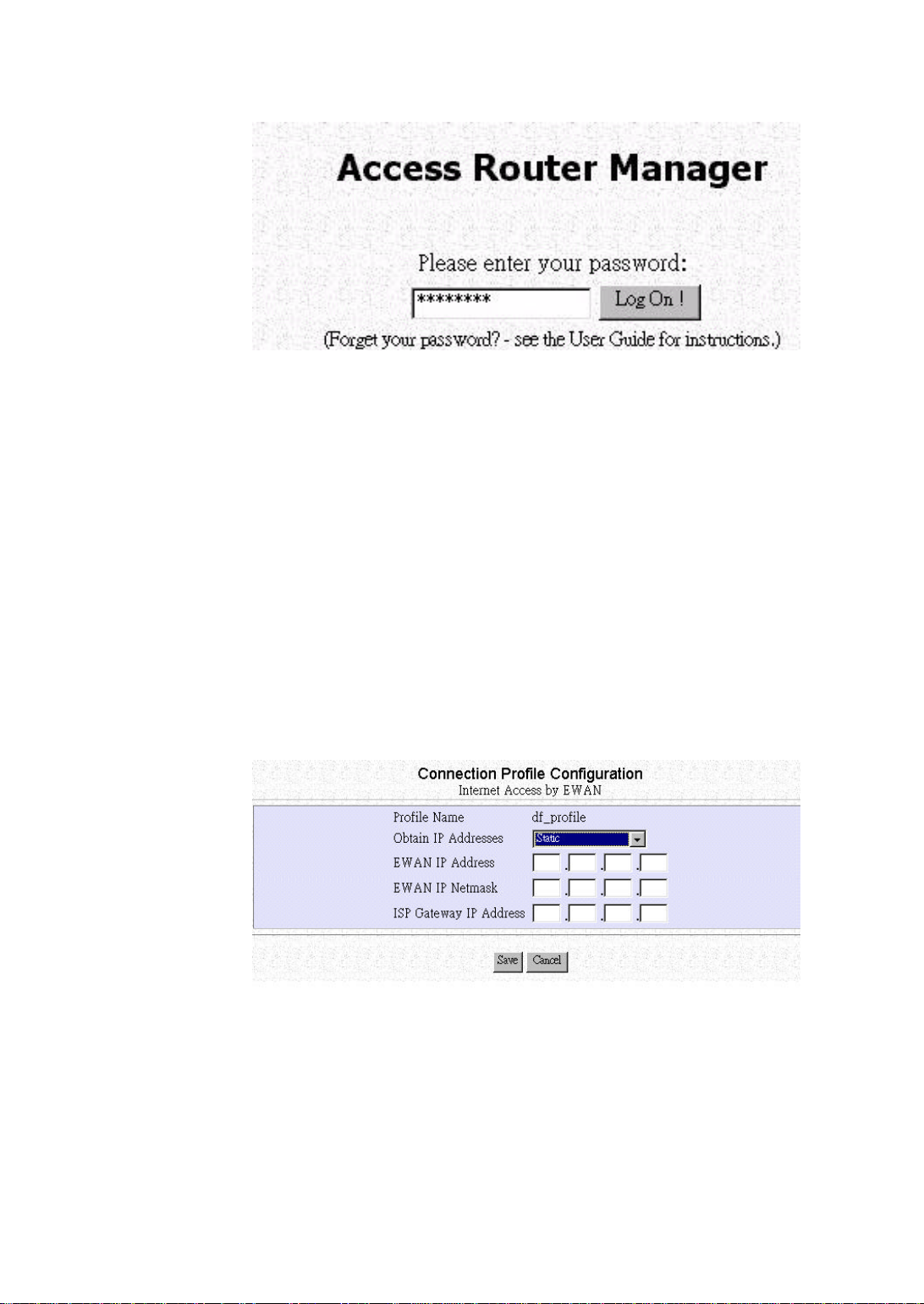
3. Enter your ISP information
There are 4 ways to connect to your ISP, these 4 methods can be found in the “Obtain
IP Addresses” section, they include:
(1) Static
(2) via DHCP
(3) via PPP over Ethernet
(4) via PPTP
(1) Some ISPs may give you a static IP, if this is the case you’ll need to select
Static in Obtain IP addresses and set the following settings.
After you finish your settings, please click Save.
3-2
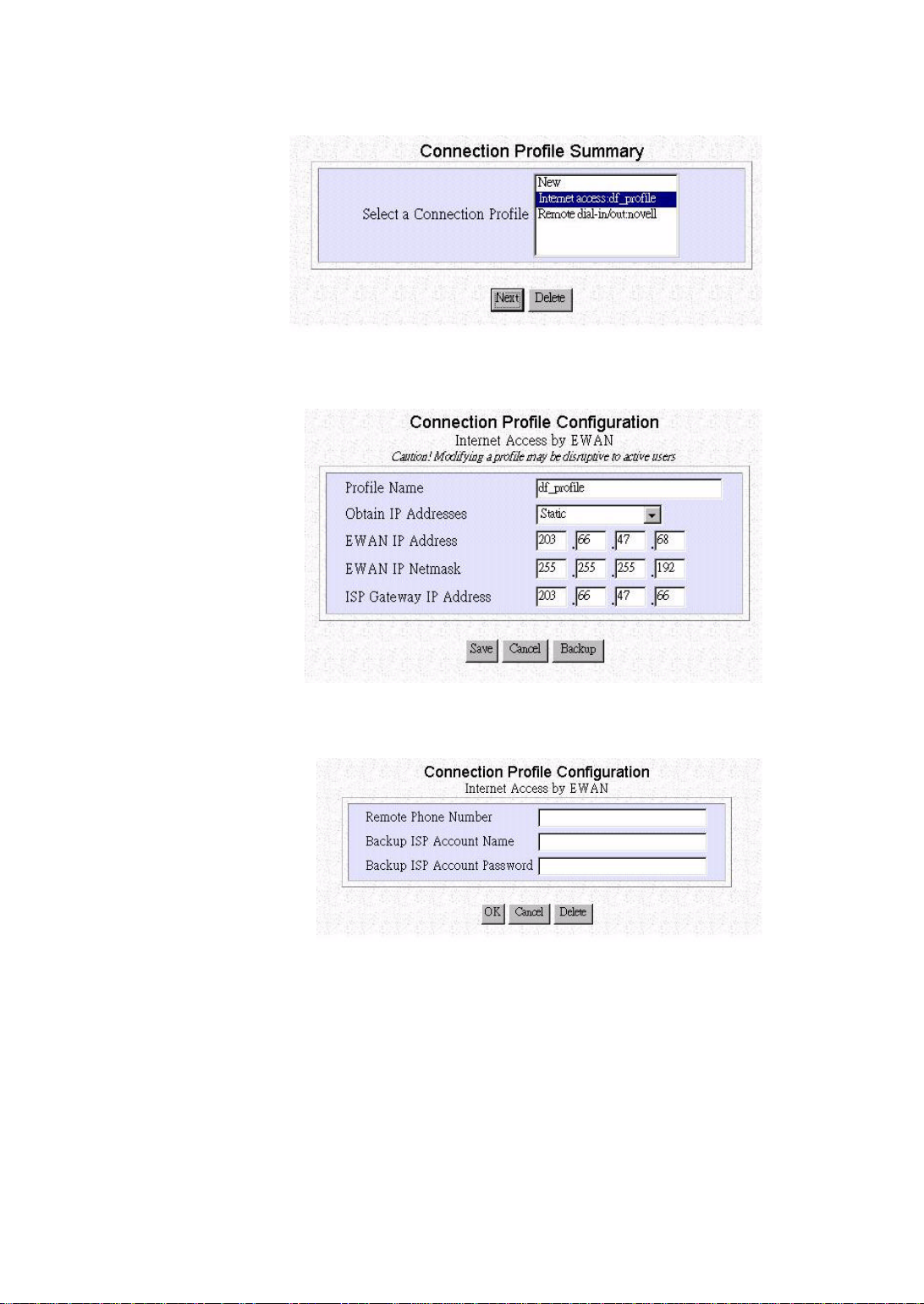
Enter the following information:
The file name “df_profile” is the default file name of your Internet Access
connection which is configured by Setup Wizard.
Obtain IP Addresses: The method you want to connect to your ISP.
EWAN IP Address: The IP Address of your EWAN.
EWAN IP Netmask: The IP Netmask of your EWAN.
ISP Gateway IP Address: The IP address of your ISP Gateway.
(2) If your ISP will automatically give you an IP address(Cable connections),
select via DHCP the following screen will appear.
Please enter the following information:
Obtain IP Address: via DHCP(will automatically get an IP from your ISP for you),
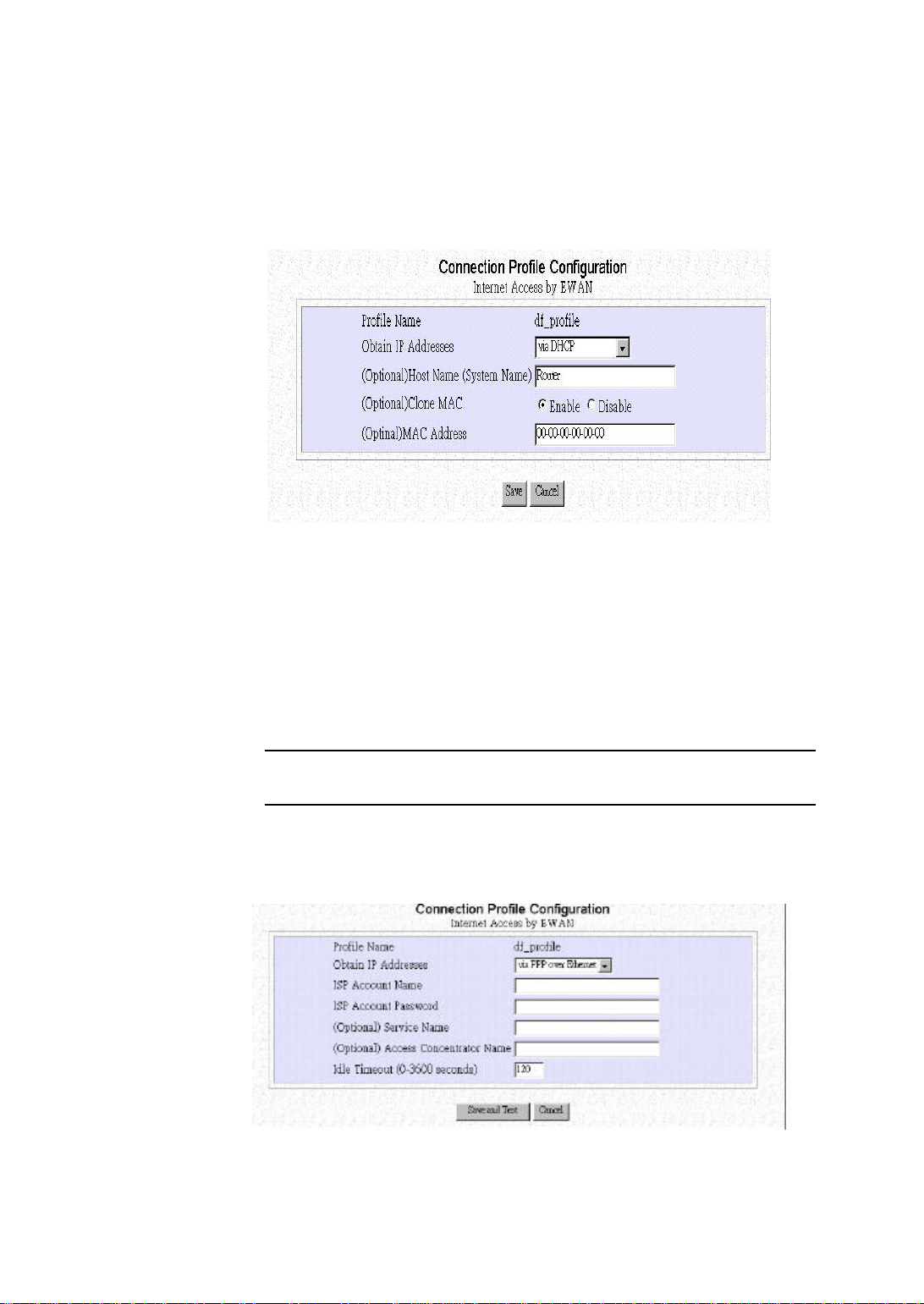
(Optional) Host Name(System Name): The Host Name provided by your system.
(Optional) Clone MAC: If you want to assign the router a cloned MAC address,
please select enable.
(Optional) MAC Address: Input the MAC address that the ISP requires to establish
a connection.
Note: Some ISPs require a specific MAC address in order to establish a
connection.
(3) Some ISP’s require the PPPoE protocol in order to connect to the Internet. If
you choose via PPP over Ethernet the following will appear.
Please enter the following information:
3-3

Obtain IP Addresses: Some DSL-based ISPs use PPPoE to establish communication
with end-users.
ISP Account Name: The user name of your ISP account.
ISP Account Password: The password of your ISP account.
(Optional) Service Name: The Service Name provided by your ISP, if one is
required, otherwise, leave it empty.
(Optional) Access concentrator Name: The Access Concentrator Name provided by
your ISP, if one is required, otherwise, leave it empty.
Idle Timeout (0-3600 seconds): The default value of the idle timeout is 120 seconds,
which represents the number of seconds of inactivity over the connection. When this
value is reached, the Broadband Router will disconnect the call. You can change the
idle timeout value to anything between 0 to 3600 seconds. But if you select 0, the
connection will never be timed out.
(4) Some ISP’s require the PPTP protocol in order for you to connect to the Internet.
If you choose via PPTP the following screen will appear.
3-4
Obtain IP Addresses: Some DSL-based ISPs use PPTP to establish communication
with end-users.
(Optional) Host Name(System Name): You can give your router a name.
PPTP local IP Address: IP address of Broadband Router for the PPTP connection.
Consult your ISP for this information. check with your ISP to see if PPTP is used.
PPTP IP Netmask: IP network mask for the PPTP Tunnel. Consult your ISP for this
information.
PPTP Remote IP Address: IP address of the ISP for the PPTP Tunnel. consult your
ISP for this information.
ISP Account Name: The user name of your ISP account.
ISP Account password: The password of your ISP account.
Idle Timeout (0-3600 seconds): The default value of the idle timeout is 120seconds.
It represents the number of seconds of inactivity over the connection. When this value
is reached, the Broadband Router will disonnect the connection. You can change the
idle timeout value to anything between 0 to 3600 seconds. But if you select 0, the
connection will never be timed out.
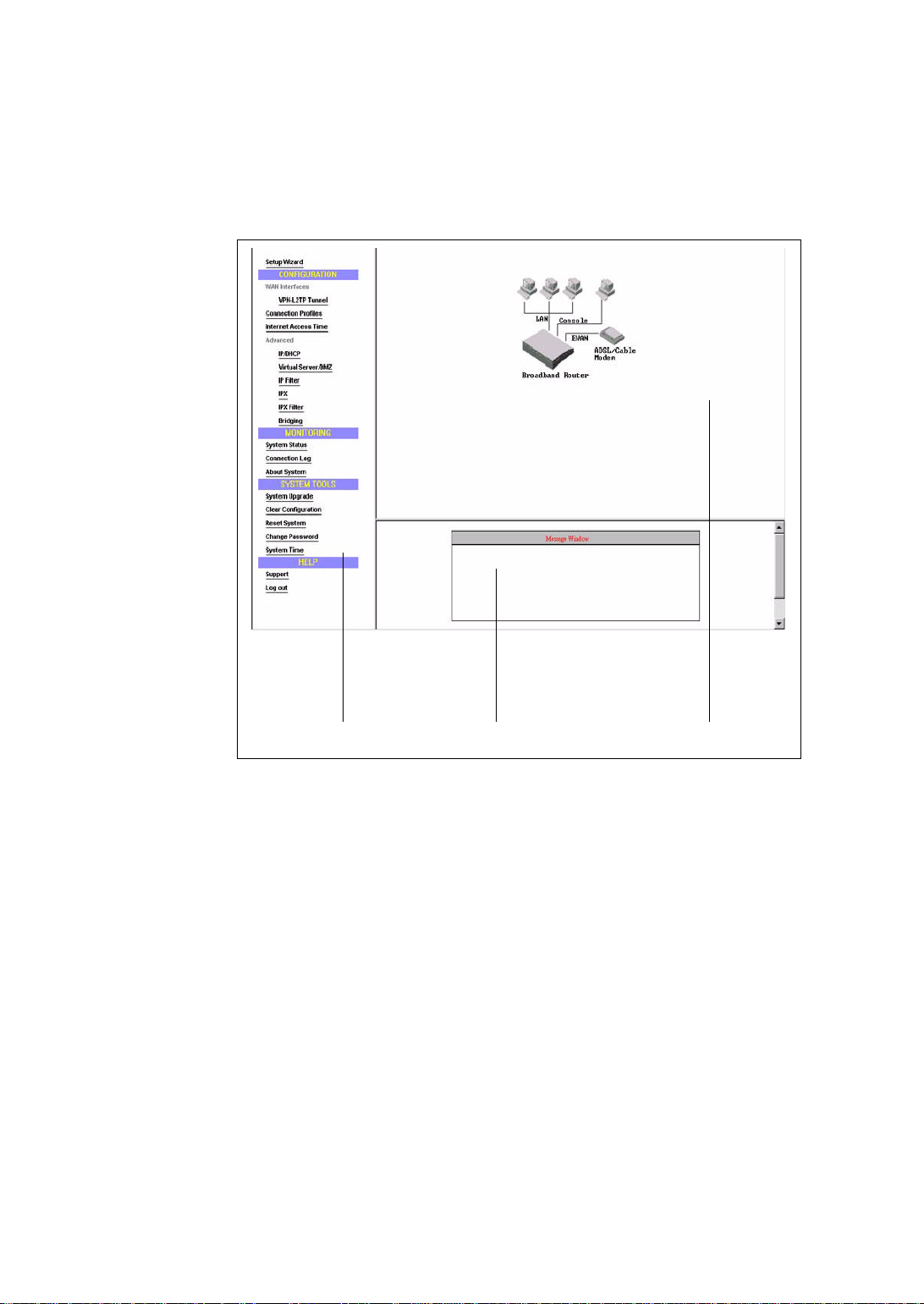
Overview of The ARM Browser Screen
Before you begin the configuration, take a moment to look at the ARM screen.
AAARM Menu
AAMessage Window AAConfiguration Window
ARM Menu
This part of the browser screen contains items you can click to display the various
screens for configuring your Broadband Router, including EWAN, connection
profiles, and protocols, as well as system monitoring, tools, and help.
Configuration Window
This is the window where the actual configuration screens appear. Before any
selection of the configuration is made, the window shows a picture of the Broadband
Router with cables and peripheral devices that can be connected to it.
Message Window
Whenever appropriate, the Broadband Router will display system status or error
messages in this window. For example, when you try to connect to the Internet, if
you had configured your password incorrectly, the message window will display an
appropriate message.
3-5
What is a Connection Profile?
To access the Internet, you need to apply for an account with an ISP (Internet Service
Provider), who will provide you the ISP Account name and ISP Account Password
that you need to call, as well as phone number if necessary to dial-up to your ISP.
You need to enter such information into a “connection profile” in the Broadband
Router. Likewise, a connection profile needs to be created for each dial-in user, each
remote office, or each VPN user.
Essentially, a connection profile contains all information that the Broadband Router
needs to access the Internet, or support a remote dial-in user, or set up a connection
with a remote office, or create a VPN. Such information includes dial-up phone
numbers, authentication information (the local user name and password and possibly
the remote site user name password), plus other information that may be required for
the communication.
Configuring an Internet Access Profile (via EWAN)
To configure an Internet access connection profile, from the ARM menu, press
Connection Profiles. If there are no other profiles at this point, you will immediately
enter a profile configuration screen. First decide what interface to use for Internet
access.
Selecting Internet Access Interface
Either EWAN or Modem can be used for Internet access. If you select the EWAN
port, you need to connect the EWAN port to an external ADSL/Cable Modem. If
you select the Modem interface, you need to connect the COM port to an external
ISDN TA/Analog Modem.
3-6
Now select Internet Access as the Access Type , then press Enter, which will cause
the following screen to show.
There are 4 ways to obtain an IP Address for your router, including via PPP over
Ethernet, via DHCP and “Static”, “PPTP”. Please refer to the configuration in
Setup Wizard.
Configuring Auto Backup
When the primary connection(ADSL/Cable) is down, the system will attempt to set
up the backup external ISDN or modem connection automatically. Only when the
backup connection disconnects(or idle timeout), then the router will attempt to
establish primary link again when there is user traffic to send.
Step 1 Configuration Profiles -- Internet Access: df_profile
Step 2 Select the Backup.
Step 3 Key in the following information.
Remote Phone Number: the telephone number of your ISP.
ISP Account Name: the username of your ISP account.
ISP Account Password: the password of your ISP account.
You can delete the backup profile by clicking Delete.
Step 4 Aftern configuration, please click OK, and then click Save, to save you
configuration.
You will see the your backup profile added in the Profile Summary.
3-7
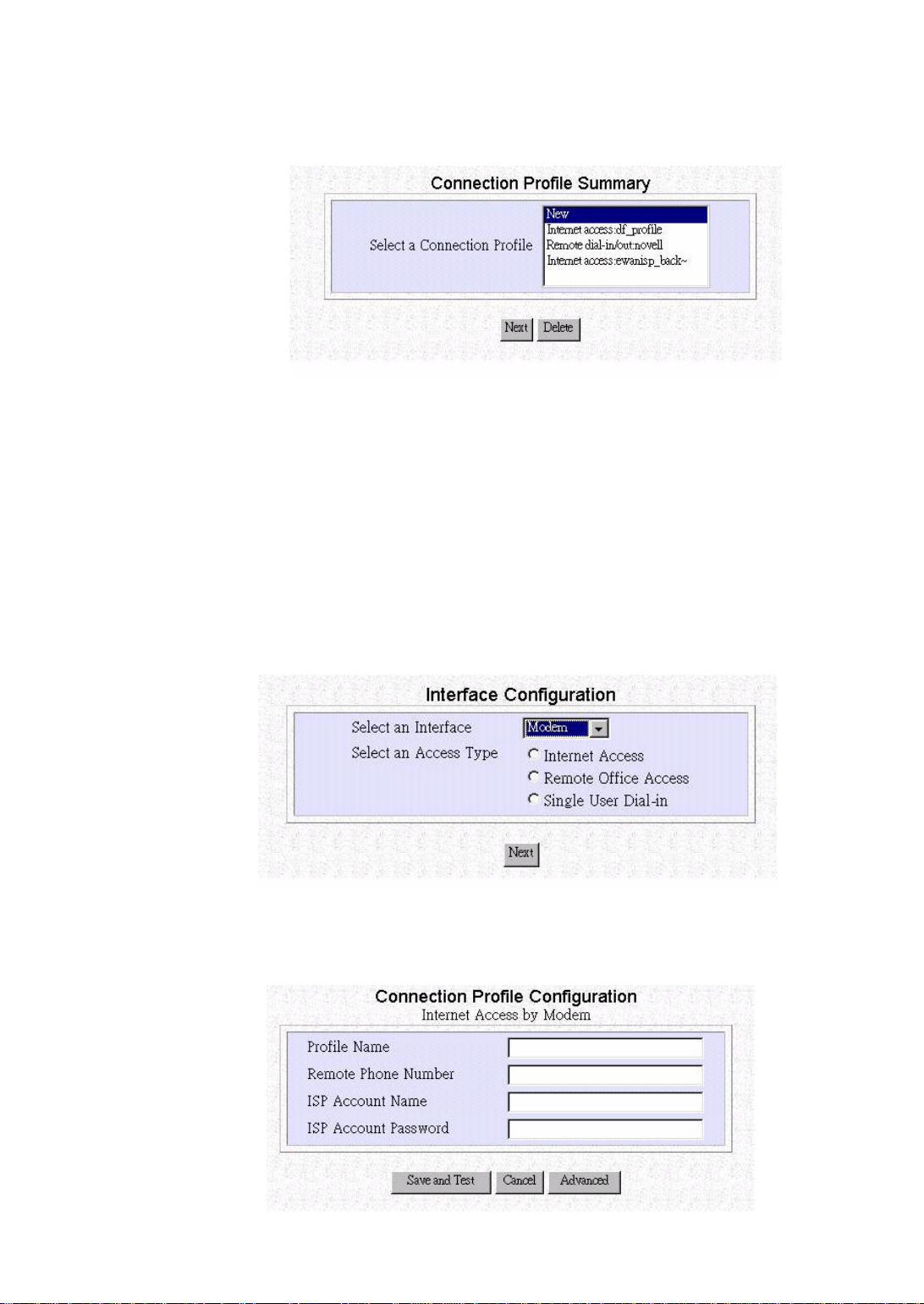
Configuring a Basic Internet Access Profile( via
Modem)
Except ADSL/Cable modem, you also can access Internet via V.90 or ISDN modem.
The following screen show you the interface configuration via Modem. Please select
Internet Access, and click Next .
The following screen will appear.
3-8

Step 1 Enter the following information:
Profile Name: the name that you will use to identify this Internet access
profile.
Remote Phone Number: the telephone number of your ISP.
ISP Account Name: the username of your ISP account.
ISP Account Password: the password of your ISP account.
Step 2 Click Advanced to get to the screen as below:
STAC Compression: allows outgoing data to be compressed to achieve
higher throughput, and compressed incoming data to be recognized. The
ability to use compression depends on the capabilities of the ISP.
Idle Timeout(0-3600):
This is where you specify the idle timeout
The default value of the idle timeout is 300 seconds. It represents the
number of seconds of inactivity over the connection: when this value is
reached, the Broadband Router will disconnect the call. You can change
the idle timeout value to anything between 0 to 3600 seconds. But if you
select 0, the connection will never time out.
After you make the change, click OK. You will are returned to the
previous screen
Step 3 Click Save and Test
Note: When you click Save and Test, the Broadband Router attempts to place a
call to your Internet Service Provider. Watch the Message Window for any messages.
If the test is successful, your users will be ready to access the Internet. If not, the
Broadband Router will try to give you enough information to let you know why the
connection is not successful.
If Save and Test is successful, users on your LAN can now start to access the
Internet. However, it is required that these devices have also been configured to
obtain IP addresses automatically, as described in Chapter 2. Users may need to reboot their computers in order to obtain the DNS information obtained during the Save
and Test operation.
Adding Internet Access Profiles
Step 1 If you want to add additional Internet access connection profiles, you need
to select Connection Profiles from the ARM Menu:
3-9
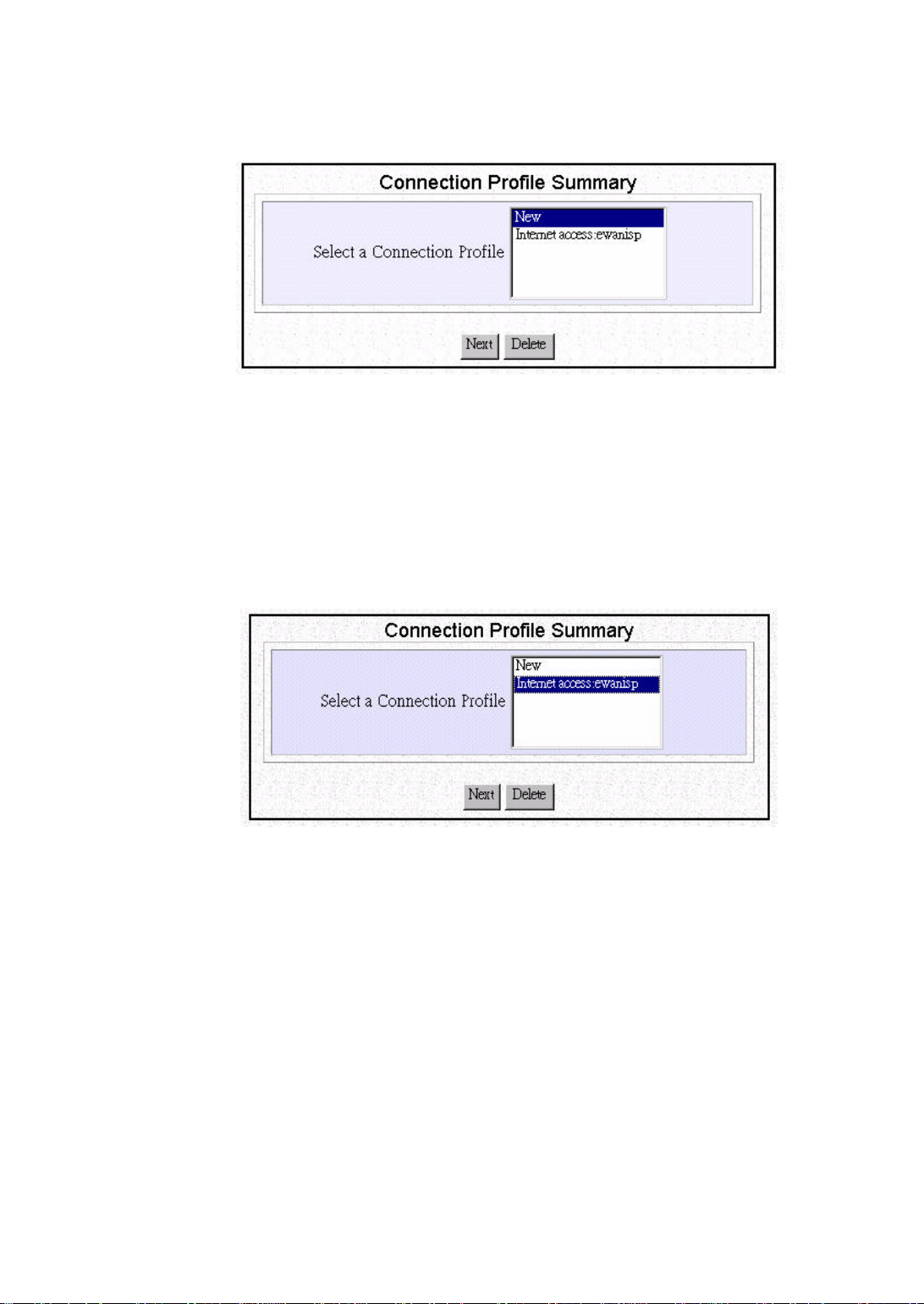
Configuration - Connection Profiles:
Then the following screen will show:
You should highlight New in the list, and then click NEXT, which will
lead you through the configuration as above.
Deleting or Modifying Internet Access Profiles
To delete or modify a Connection Profile:
Step 1 Select Connection Profiles from the ARM menu.
Configuration - Connection Profiles
The following screen will appear.
3-10
Step 2 Highlight the entry in the list, and click DELETE to delete the profile, or
click NEXT to modify the profile, in which case the same screen as
configured previously will appear.

Remote Office Access
In order for the local LAN to access a remote LAN, you need to configure a remote
office access connection profile for the router on each site (the remote router and the
local router).
Note that the remote site does not have to have a Broadband Router, and may not be
configurable by the local administrator. In either case, make sure the configuration of
the Broadband Router matches the requirements of the remote site.
Note: You need to change the private IP network when you want to create a
private WAN with your remote offices (without using public IP addresses), so that all
LANs in the private WAN will have IP addresses on a unique network. It is not
necessary to modify the private IP address if you do not intend to communicate with
other private networks such as a remote office.
Step 1 Select Connection Profiles from the ARM menu:
Configuration - Connection Profiles
Please select Connection Profiles, the Interface Configuration screen
will appear.
Step 2 Click NEXT to continue. The following screen appears.
3-11

Profile Name: the name that you will use to identify this profile.
Call Direction: If the remote site will be dialing in only, select Incoming.
If the Broadband Router will only be dialing out to the remote site, select
Outgoing. Select Both if either side can initiate the connection. The
default setting is Both. Depending on the direction selected, some of the
fields will not be displayed.
Call Back: specifies the call back option, either Yes or No. If Call Back is
enabled (select Yes), the Broadband Router checks the Remote Account
Name and Remote Account Password. If authentication passes, the
Broadband Router disconnects the incoming call, and calls theremote site
back using the number specified in the Call Back field.
If Call Back is not set (Select No), the Call Back Number field will not
be displayed. If the Call Direction is Outgoing only, Call Back options
are not displayed.
Remote Phone Number: the phone number of the remote router
connected to the remote LAN.
My Account Name: the name that the remote system will use to
authenticate the local system.
My Account Password: the password of the remote system will use to
authenticate the local system.
Remote Account Name: the name of the remote system.
Remote Account Password: the password that the local system will use
to authenticate the remote system.
3-12
Note: Make sure the remote site is configured with your Account Name and
Account Password.
Step 3 Click Save and Test or go to “Advanced Options for Remote Office
Profiles”, shown below for more choices.

Note: When you click Save and T est, the Broadband Router attempts to place a
call to the remote LAN and log in. Watch the Message Window for any messages.
Advanced Options for Remote Office Profiles
Step 1 Key in the following information:
STAC Compression: allows outgoing data to be compressed to achieve
higher throughput, and compressed incoming data to be recognized. The
ability to use compression depends on the capabilities of the ISP
Idle Timeout: the number of seconds of inactivity over the connection.
When this value is reached, the Broadband Router will disconnect the call.
You can set the idle timeout from 0 to 3600 seconds. The default setting is
300 seconds. If you select 0, the connection will never time out.
Enable IP: select Yes to allow IP routing over a connection using this
profile
IP RIP: enable or disable IP Routing Information Protocol.
IP RIP Version: select RIP-I if the Routing Information Protocol,
version 1 is to be used, or RIP-II if the Routing Information Protocol,
version 2 is to be used for this connection.
Note: The use of RIP-I or RIP-II depends upon the System-wide setting of
RIP. If the system-wide setting is Disable, the RIP setting for all connection
profiles will be disabled. If the system-wide setting is RIP-I, only RIP-I may be
selected in any profile. If the system-wide setting is RIP-II, either RIP-I or RIP-II
may be selected in any individual profile.
3-13

Set as IP Default Route (e.g., for Internet Access): select Yes if you
want users on your local LAN to get their Internet access through a
connection to the remote LAN or if this connection is to be used to locate
an IP resource not otherwise defined in the IP Routing Table. If Yes is
selected, the Remote IP Address and Netmask fields do not appear.
Note: If you allow Internet access in this manner, make sure you do not have
any Internet Access configuration profiles set up on the Broadband Router.
Remote IP Address: the IP address of a destination computer on a
network reachable through this connection.
Remote IP Netmask: the IP subnet mask of the Remote IP Address
Enable IPX: select Yes to allow IPX routing over a connection using this
profile
IPX RIP/SAP: enable or disable IPX Routing Information Protocol and
Service Advertising Protocol.
Set as IPX Default Route: if this parameter is set to Yes, then the
Broadband Router uses this connection if no other route for an IPX packet
can be found in the routing table.
Remote IPX Network Number: the IPX network number of a network
reachable through this connection. If you set this connection as the default
IPX route, an entry in this field is not required.
Enable Bridging: select Enable to bridge other protocols, for example,
SNA, Appletalk, and NetBEUI.
Deleting or Modifying Remote Office Access
Profiles
To delete or modify a Connection Profile:
Step 1 Select Connection Profiles from the ARM menu.
Configuration - Connection Profiles
The following screen appears.
Highlight the entry in the list you want to delete or modify, and click DELETE to
delete the profile or click NEXT to modify the profile.
Dial-in User Access
Step 1 Select Connection Profiles from the ARM menu:
Configuration - Connection Profiles
3-14

Information about each dial-in user who is allowed access is stored in a
“connection profile.” When you select Connection Profiles, the
Connection Profile Summary screen appears only if you have existing
Connection Profiles The following screen appears.
Step 2 Highight the New and click the Next.
You may see a screen as the following:
Step 3 Select Modem as the interface, then select
Single User Dial-in from the list of access types.
3-15

Step 4 Click NEXT to continue and display the following screen.
Step 5 Enter the following information:
Profile Name: a name that you will use to identify this profile.
Call Back: sets the call back option. If selected, the Broadband Router
disconnects after authenticating the dial-in user, and dials the remote
user’s call back phone number to reconnect.
Call Back Phone Number: the number the Broadband Router calls if
Call Back is Yes. This field will not appeare if Call Back is not selected.
User Name: the username that is dialing in.
User Password: the password for the remote dial-in user. Note that
Authentication is CHAP,MS-CHAP (MicroSoft Challenge Handshake
Authentication Protocol) or PAP (the Password Authentication Protocol).
CHAP,or MS-CHAP will be first tried to authenticate the incoming call,
and if that fails, PAP will be used.
3-16
Step 6 Click Save to add the connection profile to the Broadband Router
database, or select ADVANCED for more options.

User Dial-In Advanced Options
STAC Compression: allows outgoing data to be compressed to achieve
higher throughput, and compressed incoming data to be recognized. The
ability to use compression depends on the capabilities of the ISP
Idle Timeout: the number of seconds of inactivity over the connection.
When this value is reached, the Broadband Router will disconnect the call.
You can set the idle timeout from 0 to 3600 seconds. The default setting is
300 seconds. If you select 0, the connection will never time out.
Enable IP: select YES to allow IP routing over a connection using this
profile
Dynamic IP Assignment: Suggest you choose Yes to get IP address
automatically. If you coose No, you have to set a static IP address by
Dialer IP Address and Router IP address.
Dialer IP Address: Please key in the private IP address reserved for the
dialer.
Router IP Address: Please key in a private IP address for the router, not
the default IPaddress. e.g. 192.168.168.1.
Enable IPX: select YES to allow IPX routing over a connection using this
profile
Dynamic IPX network Number Assign: sets the IPX network number as
a random or manually.
Remote IPX Network Number: sets the IPX network number on the
remote workstation. If you set “YES” for the Dynamic IPX network
Number , this field is not displayed.
Enable Bridging: select Enable to bridge other protocols, for example,
SNA, Appletalk, and NetBEUI (or IP and/or IPX if they are not routed)
To add additional dial-in profiles, repeat steps 2 through 7.
To modify an existing dial-in profile, select the corresponding profile name in Step 3
instead, which will lead to Step 5 directly.
3-17

.Deleting Dial-in User Profiles
To delete a Connection Profile:
Step 1 Select Connection Profiles from the ARM menu.
Configuration - Connection Profiles
The Connection Profile Summary screen appears.
3-18
Highlight the entry in the list you want to delete, and click DELETE.

Internet Access Time Restrictions
For cost, security and efficiency reasons, you may want to adjust the times when the
Broadband Router will be allowed to automatically connect to the Internet. A simple
setup screen is used to enter the days of the week and the hours of the day during
which Internet access is allowed. The Broadband Router will not connect to the
Internet outside of the configured times.
In order for this feature to be effective, the Broadband Router must be configured for
the current local time. To do this, see the section, “Setting the System Time”, above.
Note, however, that if for some reason the Broadband Router is reset or powercycled, the previous time setting will be lost. Until you once again set the time, the
Broadband Router will either allow Internet access or not, depending upon a setting
which is configured below.
To view or change Internet access time restriction settings, select Internet Access
Time from the menu:
Configuration - Internet Access Time
The following screen is displayed:
Step 1 Set the days of the week during which Internet access is allowed. Select
Day Range if you want to specify a range of days. If you select All,
Internet access will be allowed every day.
Step 2 Set the time during which Internet access will be allowed. Not that this
setting is based upon a 24 hour clock. Select Time Range to enter a
consecutive period of time between which Internet access is allowed. If
you select All, Internet access will be allowed from midnight to midnight
on the days selected in Step 1.
Step 3 Enter the default setting for Internet access if the router is power-cycled or
reset. If you enter “Yes” (the default), then Internet access will be allowed
unconditionally until the clock is set. If you enter “No”, then Internet
access will not be allowed until the clock is set.
Step 4 Click Save to enable your settings.
3-19

4Broadband Router
4 Advanced Configuration
NAT(Network Address Translation)
NAT let you share one public IP address to lower ADSL/Cable cost for your Internet
access.
You can use the IP/DHCP screen button from the ARM(under Advanced) menu to
enter a public IP address, modify the private IP address, modify or enter DNS
addresses configure WINS addresses and node type or enable/disable the DHCP
service.
Step 1 Select IP/DHCP from the ARM menu:
Configuration - Advanced IP/DHCP
Then the following screen displays:
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Note: To install publicly addressed servers on your network (e.g., Web or ftp
servers), you need to apply for an IP address for each server plus one for the LAN
port of the Broadband Router. All these public IP addresses have to belong to the
same IP network.
4-1

Public IP Address: the public IP address for the LAN interface on the
Broadband Router.
Internet
Modem or EWAN Interface
(IP address usually assigned by ISP)
LAN Interface
Public IP address Private IP address
Public computers
on your public
network
Private
workstations on
your private
network
Public IP Netmask: the network mask for the public network address on
your LAN.
Private IP Address: the private IP address for the LAN interface on the
Broadband Router. The default private IP address is 192.168.168.230. If
you want to create your own private network through other Broadband
Router at remote office locations, you need to make sure that each
Broadband Router on each LAN is assigned an address in a unique private
IP network .
Note: If you use a PC (that obtains an IP address automatically) to change the
private IP address (e.g., from the default of 192.168.168.230 to 192.168.167.230)
either from the browser or through a telnet session, right after the change is
made, you will no longer be able to communicate with your Broadband Router.
To reconnect, you need to re-boot your computer, so that your device will reacquire a new IP address and the default Gateway from the Broadband Router
based on the new private IP network address. Your device will then again be able
to communicate with your Broadband Router. For the same reason, all devices on
the LAN need to be restarted before they can access the Internet again.
Private IP Netmask: the network mask for your private network. Its
value is 255.255.255.0 and can be changed.
The Broadband Router private address of 192.168.xxx.yyy is called a
“Class C” IP address. This means that changing xxx will change the
network while changing yyy will assign a different address in the same
network.
Primary DNS IP Address: the IP address of the primary Domain Name
Server (DNS). If properly configured, when a computer re-boots and
acquires the IP address from the Broadband Router, the IP addresses of
both the primary and the secondary DNS server will be provided to
requesting client workstations. This field will reflect the DNS addresses
acquired from the ISP and will be used to assign to requesting DHCP
clients (see below). You may change this address if you want another
address to be assigned instead. The Broadband Router will save any
4-2

manually configured DNS addresses.
Secondary DNS IP Address: the IP address of the secondary Domain
Name Server.
Note: When a Broadband Router connects to the ISP, it will automatically be
assigned the IP address of a primary Domain Name Server (DNS), as well as the
IP address for a secondary DNS.
DHCP: you can enable or disable the DHCP server feature provided by
the Broadband Router. If you want the Broadband Router to act as a
DHCP server and assign private IP addresses to requesting DHCP clients,
you need to enable the DHCP (this is the default). When enabled, the
Broadband Router will provide an IP address, network mask, gateway’s IP
address (the Broadband Router’s private IP address), DNS addresses, the
WINS server IP address, and Window’s node type to clients on the LAN
making DHCP requests.
Note: Devices that require public IP addresses on your network are by
definition not DHCP clients. Therefore, you need to assign their IP addresses,
network mask, default gateway’s IP address, primary and secondary DNS IP
addresses manually.
Configure WINS Server: select Yes if you want the DHCP server to
assign WINS Server addresses and NetBIOS Node Type. This will cause
the following fields to appear.
Primary WINS Server: enter the IP address of a WINS Server to be
assigned to a requesting DHCP client.
Secondary WINS Server: enter the IP address of a second WINS Server
to be assigned to a requesting DHCP client.
NodeType: select a NetBIOS Node Type to be assigned to a requesting
DHCP client. For a definition of these node types, consult your Microsoft
documentation
b: Broad cast
p: Peer to Peer
m: Mix-node
h: Hybrid
IP Address Assignment - High: Addresses are assigned dynamically to
DHCP clients and dial-in users from the range of private addresses as
defined by the IP Address Assignment - High/Low. The high address
defaults to the highest address in the subnet. This is adjustable by the
administrator using this configuration item.
If the private network is reconfigured outside the current range, the
dynamic assignment range is reset to default values.
IP Address Assignment - Low: This is the lower end of the dial-in single
user address assignment range described above. This range defaults at the
low end to the high address minus 253. This is adjustable by the
administrator using this configuration item.
4-3

The IP Routing Table
The IP routing table contains all the information that the Broadband Router needs to
route an IP data packet. You can view the IP routing table by clicking on the IP
Routing Table button at the bottom of the System IP Configuration screen. From this
screen, you can also add new routing entries to the table. The following screen shows
an example of the IP routing table.
When an IP packet arrives in the Broadband Router, IP tries to determine if the
destination IP address contained in the packet is within the network defined by the
“Dest IP” and “Netmask” pair of an entry in the routing table. If a match is found, the
packet is forwarded to the interface or profile specified in the “Ifname” field.
The “Hops” field is the number of routers the packet must travel through in order to
reach its final destination. If this value is zero, the destination is in a network directly
attached to this router, such as a LAN.
If no match is found with a destination network, then a special entry called the
“Default IP Route” may be used. This normally is set to a path where another router
can be reached that has additional information about other networks not known to the
local router, such as the interface to the Internet. If no match is found and a default IP
route is not defined, the IP packet is discarded and will go nowhere.
An entry for a specific host or network may be added manually. This “static route” is
indicated by an “S” in the Flags field. Other flag field entries are “H” for host, and
“G” for gateway.
Note: To delete a static route, select it in the routing table and click the Delete
button. You cannot delete Host or Gateway routes.
Adding the Default Route or a Static Route
To add/change the default route or add a static route:
Step 1 Click the ADD button in the IP Routing Table screen to display the
4-4

following screen:
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Add Default Route: select if you want to specify a new default route.
Note that the Remote IP Address and Remote IP netmask fields do not
appear if you select this option.
Note: Mis-configuring the default route may result in abnormal system
behavior and/or unnecessary telephone charges.
Add IP: If you want to add a static route, please select Static Route.
Remote IP Address: the remote IP address of the new route.
Remote IP Netmask: the IP netmask of the new route.
Gateway: select whether the gateway is an IP address or interface.
Hop Count: the maximum number of hops for this route.
Step 3 Click Save.
Static DHCP assignments
In certain LAN environments, it is desirable for some PCs to be assigned the same
address each time it requires a DHCP server. Broadband Router is capable of
configuring up to 20 PCs for static assinments.
Each PC is to be assigned a static address requires an entry to be configured in the
DHCP static Assignment Table.
Please click Static DHCP button in System IP Configuration, the following screen
will appear.
4-5

Please click Add button to add a static entry in the following screen.
Name: Enter a convenient display name for this reosurce.
IP Address: The IP address to be consistently assigned to this device.
MAC Address: The hardware address associated with the Ehternet adapter which is
permanently assigned to this machine. Note that dashes must separate each pair of
hexadecimal digits.
To Configure IPX Settings
4-6
Step 1 To select IPX Protocol, select IPX from the Menu:

Configuration - Advanced Features - IPX:
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Ethernet Frame Type: the Ethernet frame type on the LAN, normally
detected automatically by the Broadband Router, however you may
change this selection. Options are Ethernet_802.3, Ethernet_802.2,
Ethernet_II, and Ethernet_SNAP.
Network Number: a unique identifier for the IPX network on your LAN.
Normally, this is automatically detected by the Broadband Router.
IPX RIP/SAP: enables or disables IPX Routing Information Protocol and
Service Advertising Protocol, used for exchanging routing tables and
server information among IPX RIP/SAP agents.
Step 3 Press Save to save the changes to the Broadband Router, or press IPX
Routing Table to display or modify the IP Routing Table or press IPX
SAP Table to display or modify the IPX SAP Table.
The IPX Routing Table
The IPX routing table contains all the information that the Broadband Router needs to
route an IPX data packet. You can view the IPX routing table by clicking on the IPX
Routing Table button at the bottom of the System IPX Configuration screen. From
this screen, you can also add new routing entries to the table. The following screen
shows an example of the IPX routing table.
When an IPX packet arrives in the Broadband Router, IPX tries to determine if the
destination IPX Network Number contained in the packet is within the network
4-7

defined by the “Network Number” in an entry in the routing table. If a match is found,
the packet is forwarded to the interface or profile specified in the “Gateway IfName”
field.
The “Hops” field is the number of routers the packet must travel through in order to
reach its final destination. If this value is zero, the destination is in a network directly
attached to this router, such as a LAN.
If no match is found with a destination network, then a special entry called the
“Default IPX Route” is used. This normally is set to a path where another router can
be reached that has additional information about other networks not known to the
local router. If no match is found and a default IPX route is not defined, the IPX
packet is discarded and will go nowhere.
An entry for a specific host or network may be added manually. This “static route” is
indicated by an “S” in the Flags field.
Note: To delete a static route, select it in the routing table and click the Delete
button. You cannot delete a non-static route.
Adding the Default IPX Route or a Static IPX Route
The procedure to add or change the IPX default route or to add an IPX static route is
as follows:
Step 1 Click the ADD button at the bottom of the IPX Routing Table screen to
display the following screen:
4-8
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Add IPX: select the type of entry to be added. If you specify a Default
Route, the Destination Network Number and Hop Count fields do not
appear. Select Static Route if you want to add a static route.
Note: Mis-configuring the IPX default route may result in abnormal system
behavior and/or unnecessary telephone charges.
Destination Network Number: the IPX Network Number reachable
through this new route.

Gateway Interface Name: this specifies the interface through which the
destination network can be reached. This is either the LAN or a profile
name.
Gateway MAC Address: identifies the MAC address of the gateway on
the LAN through which the Destination Network Number can be
reached. This field only appears if the Gateway Interface Name is the
LAN.
Hop Count: the maximum number of hops for this route.
Step 3 Click Save.
The IPX SAP Table
The IPX SAP table contains Service Advertising information gathered from adjacent
routers or configured statically. This information provides requesting IPX clients with
the services available on their network and a path to reach that service. You can view
the IPX SAP table by clicking on the IPX SAP Table button at the bottom of the
System IPX Configuration screen. From this screen, you can also add new SAP
entries to the table. The following screen shows an example of the IPX SAP table.
SAP table entries contain the following pieces of information:
- Server Name: This is a string of up to 48 characters that identifies the
device providing the service
- Network Number: This is the identification of the network on which the
Server resides
- Node: The node address of the device providing the service. Note that this
node address may correspond to the device’s physical MAC address, or it
may be an internal node number
- Socket: The two byte (four hexadecimal digit) address of the IPX socket
providing the service
- Type: The Service Type. Well-known service types include:
Service Type
Unknown 0000
Hexadecimal
Value
4-9

Service Type
Print Queue 0003
File Server 0004
Job Server 0005
Print Server 0007
Archive Server 0009
Remote Bridge Server 0024
Advertising Print Server 0047
Hexadecimal
Value
- IfName: The name of the interface through which this resource may be
accessed. This is either the LAN or a connection profile name
- Hops: The number of routers the packet must travel through in order to
reach its final destination. If this value is zero, the destination is in a network
directly attached to this router, i.e., the LAN.
- Flags: An “S” denotes a static IPX route
The Broadband Router will respond to a workstation request for the names and
address information of servers of a specific service types or all service types. The
router will search the SAP table for these entries and respond with the necessary
information that the workstation can use to communicate with the desired service.
An entry for a specific service may be added manually. This “static SAP entry” is
indicated by an “S” in the Flags field.
Note: To delete a static SAP entry, select it in the SAP table and click the Delete
button. You cannot delete non-static entries.
Adding a Static SAP Entry
The procedure to add an IPX static SAP entry is as follows:
Step 1 Click the ADD button at the bottom of the IPX SAP Table screen to
4-10

display the following screen:
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Server Name: The name of the server offering the service. This name
may be up to 48 characters.
IPX Network Number: The network number on which the server resides.
Up to eight hexadecimal digits may be entered.
IPX Node Number: The node number of the server. This is entered as six
pairs of hexadecimal digits.
IPX Socket Number: The socket number used to reach this service (up to
four hexadecimal digits).
IPX Service Type: The type of service offered. See the table above for
typical Service Types. Up to four hexadecimal digits are accepted. The
value “FFFF” is not valid.
Hop Count: the number of hops to reach this device.
Step 3 Click Save.
Virtual Server/DMZ(De-military Zone)
NAT feature makes all hosts behind this product are invisable. You can make some of
them accessible by enabling the Virtual Server mapping.
A virtual server is defined as a service port, and all requests to this port will be
redirected to the PC specified by teh server IP.
Step 1 Select Virtual Server/DMZ from the Menu:
4-11

Configuration - Virtual Server/DMZ
Step 2 Enter the following information:
DMZ: Key in the private IP for your DMZ host.
HTTP(port 80): Key in the private IP and re-mapped port number.
FTP, TELNET, SMTP, POP3 services have well-known port number as shown. IF
you want to add other services, you can click Add other PAT, to key in the service
port Number, the private IP and re-mapped port number.
Please check the samll box ahead of the PAT which you want to be active.
Note: The Maximum of Add other PAT is 23.
Firewall (IP/IPX Filtering)
This section describes the packet filtering feature.
Note: Packet filtering is a sophisticated feature that can substantially impact your
Broadband Router operation. Therefore be sure that you fully understand the
description in this chapter before you start to configure and use this feature, since if
you make any mistakes, it may produce drastic and potentially undesired results.
A Packet Filtering Overview
4-12
The Broadband Router already provides you with many different ways to ensure the
security of your data in your local environment. Packet filtering is a security feature
that allows you to selectively pass or throw away data traffic between your local LAN
and the wide area network (e.g., the Internet). Packet Filtering allows each IP or IPX

packet exiting a router interface to be examined for a match with a configured set of rules
and an action to be taken depending upon whether the packet statisfies any rule or not.
In the browser manager, a set of rules may be configured over any existing interface
as represented by a WAN profile. To configure a set of rules for packets exiting the
LAN interface (in addition to any WAN interface), you must use the Filtering
commands in the Command Line Interface. If the contents of the packet do not match
any rule for that interface, then the packet is either forwarded or discarded, depending
upon the filter default for that interface. Otherwise, the exception action is taken, i.e.,
the packet is discarded or forwarded, the opposite of the default action.
The Broadband Router maintains separate filtering tables for IP and IPX traffic.
These filters are configured separately. Configuration commands allow you to define:
- each and every IP or IPX packet to be inspected to determine if it should be
allowed or disallowed to be transmitted over a WAN interface
alternatively.
Due to the conflicting nature of allow and disallow, only one of the above two
choices can be made for each WAN interface. After the choice is made, you can
define selection rules to “select” which packets will be allowed (or disallowed).
Each packet selection rule consists of
- an IP protocol and set of local IP addresses/ports or an IPX Packet Type and
a set of local IPX network number(s), node(s) and socket(s)
- a set of remote IP addresses/ports or remote IPX network numbers/nodes/
sockets
The following table indicates the types of values that may be configured for each rule
condition.
4-13

Protocol
IP
IPX
Condition
Parameter
Configuration
Formats
Protocol TCP/UDP/
ICMP/IGMP/
Any
Address Single/Range/
Network/Any
Port Single/Range/
Any
Packet Type Single/Any
Network
Number
Single/Range/
Any
Node Number Single/Any
Socket Single/Range/
Any
Therefore packet filtering simply defines sets of rules of what to allow or disallow
through a set of parameters highlighted below:
For IP,
remote devices with IP addresses/port numbers
are allowed (or disallowed) to communicate with
local devices with IP addresses/port numbers over
a WAN connection and using a specific IP protocol.
For IPX,
remote devices with IPX network numbers/nodes/sockets
are allowed (or disallowed) to communicate with
local devices with IPX network numbers/nodes/sockets over
a WAN connection.
4-14
Examples of packet filtering requirements are:
1. “I want to block any user in my remote office from being able to access my
local NetWare server”.
The corresponding “translated” packet rule is:
All IPX communication with my remote office is allowed EXCEPT
remote devices with Any IPX network number and Any IPX node number
and Any IPX socket which are disallowed from communicating with the local
NetWare server (identified by its IPX network number, IPX Node Number
and Any socket number over my specified remote office connection profile

using any IPX packet type.
2. “I want to disallow people in the manufacturing department to access the
Internet“.
The corresponding “translated” packet rule is:
All access to the Internet is allowed EXCEPT
remote devices with the range of IP addresses in the manufacturing
department and any port number which are disallowed to communicate with
any IP address/port number over my Internet connection using any IP
protocol.
Configuring IP Packet Rules
To add a new IP packet rule or to edit an existing one, select IP Filter from the ARM
menu:
Configuration - Advanced - IP Filter
Step 1 From the IP Filtering Configuration screen, select the WAN profile of
interest from the pull down menu. For example, if your only need is to
control access to the Internet, you should only select the Internet access
profile.
Step 2 Select discarded or sent as the default action as desired, which is
equivalent to disallow and allow, respectively.
Step 3 If you are just starting, click Add to add a new selection rule. If you have
previously defined rules, you will see those rules shown as entries in the
rule table, and you can edit the rule by first highlighting the desired entry
in the rule table followed by clicking the Edit button.
4-15

Step 4 In case of adding a new selection rule, the following screen shows:
Step 5 Enter the following information:
Rule No.: a number used for identification purposes.
Rule Name: a name by which you will refer to this rule.
Interface: the specific WAN interface to which this new selection rule
applies.
IP Protocol: the IP protocol to which this rule applies. You can select
TCP, UDP, ICMP, IGMP, or any of these protocols.
Source IP Address: the IP address(es) of the local devices this new rule
will apply to. You can select a single IP address, a range of IP addresses,
a network, or any IP addresses. The screen may change to show fields
you need to fill out accordingly. For example, if you select range, you will
also see (From) and (To) fields where you need to fill out the starting IP
address and the ending IP address.
Source Port: the port number(s) of the local devices this new rule will
apply to. See Table 4-1 for some examples of TCP/IP port assignments.
This field does not appear if either ICMP or IGMP is selected as the IP
Protocol.
Dest. IP Address: the IP address(es) of the remote devices this new rule
will apply to. You can select a single IP address, a range of IP addresses,
a network, or any IP addresses. The screen may change to show fields
you need to fill out accordingly. For example, if you select range, you will
also see (From) and (To) fields where you need to fill out the starting IP
address and the ending IP address.
Dest. Port: the port number(s) of the remote devices this new rule will
apply to. See Table 4-1 for some examples of TCP/IP port assignments.
This field does not appear if either ICMP or IGMP is selected as the IP
Protocol.
If you highlighted an existing entry (by selecting the Select to Edit
button) and clicked Edit instead, a similar screen will display, with all
fields already filled out by you previously. Then you can make changes as
necessary.If you highlighted an existing entry and clicked Delete instead,
4-16

the corresponding entry in the rule table will be removed.
TCP/IP
Service
Type
BootP/DHCP 67-68
DNS 53
Finger 79
FTP 20-21
HTTP 80/8080
NetBIOS 137-139
NNTP 119
RIP 520
SMTP 25
SNMP 161-162
Sun RPC 111
Port Range
Telnet 23
TFTP 69
Whois 43
Table 4-1 TCP/IP Port Assignments
Configuring IPX Packet Rules
To add a new IPX packet rule or to edit an existing one, select IPX Filter from the
ARM menu:
Configuration - Advanced - IPX Filter
Step 1 From the IPX Filtering Configuration screen, select the WAN profile of
interest from the pull down menu.
Step 2 Select discarded or sent as the default action as desired, which is
equivalent to allow and disallow, respectively.
Step 3 If you are just starting, click Add to add a new selection rule. If you have
previously defined rules, you will see those rules shown as entries in the
rule table, and you can edit the rule by first highlighting the desired entry
4-17

in the rule table followed by clicking the Edit button.
Step 4 In case of adding a new selection rule, the following screen shows:
4-18
Step 5 Enter the following information:
Rule No.: a number used for identification purposes.
Rule Name: a name by which you will refer to this rule.
Interface: the specific WAN interface this new selection rule will apply
to.
IPX Packet Type: The packet type to which the rule applies. This value is
specified as a two digit hexadecimal number. Some standard IPX Packet
Types are listed in Table 4-2
Source IPX Network Number: the IPX Network Number(s) of the local
devices to which this new rule applies. You can select a single IPX
Network Number, a range of IPX Network Numbers, or any IPX
Network Number. The screen may change to show fields you need to fill
out accordingly. For example, if you select range, you will also see
(From) and (To) fields where you need to fill out the starting IPX
Network Number and the ending IPX Network Number.
Source IPX Node Number: the IPX Node Number of the local device(s)
to which this new rule applies. You may select an individual Network

Node or any Network Node. An individual Network Node is entered as six
pairs of hexadecimal digits, such as 11-22-33-aa-bb-cc.
Source IPX Socket Number: the local IPX Socket Number(s) of the local
devices to which this rule applies. You can select a single IPX Socket
Number, a range of IPX Socket Numbers, or any IPX Socket Number.
This value is specified as a four digit hexadecimal number.
Dest. IPX Network Number: the IPX Network Number(s) of the remote
devices to which this new rule applies. You can select a single IPX
Network Number, a range of IPX Network Numbers, or any IPX
Network Number. The screen may change to show fields you need to fill
out accordingly. For example, if you select range, you will also see
(From) and (To) fields where you need to fill out the starting IPX
Network Number and the ending IPX Network Number.
Dest. IPX Node Number: the IPX Node Number of the remote device(s)
to which this new rule applies. You may select an individual Network
Node or any Network Node. An individual Network Node is entered as six
pairs of hexadecimal digits, such as 11-22-33-aa-bb-cc.
Dest. IPX Socket Number: the remote IPX Socket Number(s) of the
local devices to which this rule applies. You can select a single IPX
Socket Number, a range of IPX Socket Numbers, or any IPX Socket
Number. This value is specified as a four digit hexadecimal number.
Packet Type
Unknown 00
Routing Information 01
Service Advertising 04
Sequenced Packet 05
NetWare Core Protocol 11
Propagated (NetBIOS) 14
If you highlighted an existing entry (by selecting the Select to Edit button) and
clicked Edit instead, a similar screen will display, with all fields already filled out by
you previously. Then you can make changes as necessary.
If you highlighted an existing entry and clicked Delete instead, the corresponding
entry in the rule table will be removed.
VPN (Virtual Private Network )
Before continuing on with this section, be sure you’ve reviewed the section,
“Creating a Virtual Private Network (VPN)” in Chapter 1.
Hexadecimal
Value
Also, make sure you have properly configured the Internet access profile(as detailed
in Chapter 3) before attempting to send traffic through VPN tunnels
When you set up your VPN, keep in mind that the VPN connection (the “tunnel”)
4-19

emulates an actual hardware wide area network port. After setting up your VPN
tunnel, you can create a connection profile to allow access to and from a remote site.
VPN connections are created automatically as a result of a reference by a LAN user to
a resource reachable through a VPN connection.
To Configure VPN Remote Office Access Profiles
In order to set up access to and from a remote site, be sure to configure both ends of
the VPN tunnel appropriately (the remote router and the local router). Broadband
Router supports for the Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol(L2TP), which was the original
open standard for Vitual Private Networking. If you selected Access to/from
Remote Site from the ARM Configuration screen, follow the steps in this section.
Note: When communicating with a remote office, the private IP network must be
different on both sides of the connection. To do this, follow the steps indicated in the
section.
Step 1 Configure a VPN tunnel. Select VPN-L2TP Tunnel from the menu:
Configuration - WAN Interface - VPN-L2TP Tunnel
4-20
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Tunnel ID: a ID by which you will refer to this VPN tunnel.
Call Direction: the direction of the call in the tunnel. If the remote site
will always be creating the tunnel, select Incoming Only. If the
Broadband Router will always initiate the connection to the remote site,
select Outgoing Only. Select Both if either side can initiate the
connection.The default setting is Both.
Remote IP Address: Key in your remote side IP address when you set
Call Direction to Both or Outgoing
Note: If you set Call Direction to Incoming Only, the Remote IP Address
field does not display.

My Tunnel Name: the name that the remote system will use to recognize
your network.
My Tunnel Password: the password the remote system will use to
authenticate your system.If the remote site does not require tunnel
authentication, leave this field blank.
Note: Make sure the remote site is configured with your Tunnel Name (and
Tunnel Password, if used).
Remote Tunnel Name: the name of the remote network that is dialing in.
Remote Tunnel Password: the password that your Broadband Router
will expect to see from the remote system. If you do not require tunnel
authentication, leave this field blank.
Step 3 Click Save.
Set up a VPN Connection Profile
Step 1 Set up a VPN Connection Profile. Select Connection Profiles from the
Menu:
Configuration - Connection Profiles
Step 2 When you select Connection Profiles, the Connection Profile Summary
screen appears only if you have existing Connection Profiles.
Step 3 Select New from the pull-down menu, and click NEXT. The Interface
Configuration screen appears. For example:
Note: If VPN-L2TP is selected as the interface, the Remote Office Access is the
only Configuration Type displayed.
Step 4 Select VPN-L2TP as the interface, and check Remote Office Access
from the list of configuration types.
Step 5 Click NEXT to continue. The Connection Profile Configuration screen
4-21

appears.
Step 6 Enter the following information:
Profile Name: the name that you will use to identify this remote office
dial-in/dial-out profile.
Call Direction: the direction of the call in the tunnel. If the remote site
will be dialing in, select Incoming Only. If the Broadband Router will be
dialing out to the remote site, select Outgoing Only. Select Both if either
side can initiate the connection.The default setting is Both.
Note: If you set Call Direction to Incoming Only, the My Account Name
and My Account Password fields do not display. If you set Call Direction to
Outgoing Only, the Remote Account Name and Remote Account Password
fields do not display
My Account Name: the name that the remote system will use to recognize
your network.
My Account Password: the password the remote system will use to
authenticate your system
Note: Make sure the VPN Connection Profile at the remote site is configured
with your Account Name and Account Password.
Remote Account Name: the name of the remote network that is dialing
in.
Remote Account Password: the password that your Broadband Router
will expect to see from the remote system.
VPN-L2TP Tunnel: the VPN Tunnel you will use for this profile. This is
one of the tunnel configurations set up earlier.
Step 7 Click Save and Test when you are done, or select Advanced to enter
advanced options.
4-22

Step 1 Enter the following information:
Enable IP: allows IP routing over a connection using this profile.
Remote IP Address: the IP address of a destination computer on a
network reachable through this connection.
Remote IP Netmask: the IP subnet mask of the Remote IP Address.
Enable IPX: allows IPX routing over a connection using this profile.
IPX RIP/SAP: enables or disables IPX Routing Information Protocol and
Service Advertising Protocol.
Set as IPX Default Route: specifies whether this connection is used as
the default IPX route if no other route for an IPX packet can be found in
the routing table.
Remote IPX Network Number: the IPX network number of a network
reachable through this connection. If you set this connection as the default
IPX route, this field is not displayed.
Enable Bridging: enables or disables bridging to bridge other protocols,
for example, SNA, Appletalk, and NetBEUI.
Enable Encryption: allows DES encryption. If you select DES
encryption you must enter a DES Encryption key.
Encryption key: the DES encryption key used by other systems to
establish contact with your system. This must be a hexadecimal number
(0-9, a-f) with up to 16 digits, depending upon the strength of encryption
licensed for your site.
Confirm Encryption key: re-enter the DES encryption key to confirm its
correct entry.
Note: For security reasons, encryption options only appear if you are
connected to the Broadband Router over a local LAN and if encryption is
enabled on your system.
4-23

5
5 Managing the Broadband Router
System Status
This section displays statistics and the status of all interfaces. You can click
Monitoring - System Status from the ARM Menu.
The following status/statistical information is provided for each interface:
Device: lists all interfaces, including both the physical interface (i.e., the LAN port,
the EWAN port).
Status: indicates the current state of the interface:
(I) For LAN: this will always show Up.
(II) For EWAN:
(i) PPPoE:
profile name: Sow the profile you used if the interface is up and
functioning.
No call: Means that this interface is not connected and the profile of
EWAN port is idle.
Down: Means that this interface is not connected and no EWAN profile
added.
(ii) DHCP & No:
profile name: Show the profile you used if the interface is up and
functioning.
Down: Means that this interface is not connected.
Xmt Pkts: indicates the number of packets that have been transmitted through the
interface.
Rcv Pkts: indicates the number of packets that the interface has received.
5-1

Err Pkts: indicates the number of error (bad) packets that have been received.
Disconnect: if an active interface has been selected (highlighted), clicking this button
will cause the connection to be taken down. The LAN interface is not affected by this
operation. When EWAN is configured to be DHCP interface, it's not affected either.
Clear: resets the selected statistics values to zero.
Connection Log
The Broadband Router provides a connection log that you can use to track the
connections in establlished both out of or into your Broadband Router. Connect and
disconnect messages can be useful in determining connection costs, Trigger messages
are useful in determining the particular device and application that triggered the
connection.
To view the Connection Log, select Connection Log from the menu:
Monitoring - Connection Log
The Connection Log displays in the Main window:
5-2
There are several types of messages that appear in the Connection Log:
Connected and Disconnected messages: Shows the date, time, port (channel) and
profile when a connection is established or disconnected.
Trigger messages: Shows the date, time and details of an event that triggers a
connection.
VPN messages: Shows the detail of Virtual Private Networking sessions.

About System
You can check the information of the Broadband Router by clicking About System
from the menu.
Monitoiring - About System
WAN IP: It indicates the WAN IP address of your Boradband Router.
Submask: The submask of the WAN IP address.
Gateway: The gateway of your ISP.
WAN MAC address: It indicates the WAN MAC IP address of your Boradband
Router.
LAN IP address: It indicates the WAN IP address of your Boradband Router.
LAN MAC address: It indicates the LAN MAC IP address of your Boradband
Router.
System Uptime: It indicates the time you start your system.
Firmware Version: It indicates the Firmware current version of your router.
System Upgrade
You can upgrade your firmware (the software that controls the router’s operations).
Normally, this is done when you discover a problem which is resolved in a different
version of firmware that contains new features that you need. Both types of system
upgrade can be performed through the ARM System Upgrade option as follows:
Step 1 Select System Upgrade from the menu:
System Tools - System Upgrade
5-3

The following screen is displayed:
Step 2 To update the Broadband Router software, download the software from
distributor’s web site and install the software in your local environment
first, then from the above screen enter a path or filename (e.g.,
a:\P17v500.sig), or click Browse to select the path for the firmware. Next,
Click the Upgrade button.
The new firmware will begin loading across the network. After a message
appears telling you that the operation is complete, you need to reset the
system to have the new firmware take effect.
Note: 1. In addition, you can also upgrade the firmware by console port.
Please refer to the Command Line Interface Manual in the CD for
the detail procedure.
2.What if you crash your router’s firmware, you can download the
“Recovery” firmware from your CD to recover your router. Though
the CD’s firmware maybe not updatest, you can get the updatest one
from distributor’s website after recovering the system.
The download procedure is as follows:
1. Connecting the RS232 cable with female-to female adapter to your
PC card and the console port of router.
2. In windows “start” menu, select “Program Files” ----”Accessories” -
--”Hyper Terminal” -----select the com port you connect.
3. Setting baudrate to “19200”.
4. To log in the CLI mode, the default password “password”.
5. Clicking “Receive Files” and browsing the path to the Recovery folder
in the CD.
You can use the Clear Configuration features to clear your configuration (i.e., to
restore to its factor default configuration).
Step 1 Select Clear Configuration from the menu:
System Tools - Clear Configuration
5-4

Step 2 Please click Yes for confirmation, if you change your mind, please click
Reset System
If your router is not operating correctly, upi can choose this option to display the
Reset System screen as follows.
Step 1 Select Reset System from the menu:
The following screen displays:
The following screen displays:
No to cancel.
System Tools - Reset System
Step 2 Click YES to reset the Broadband Router. If you do not want to reset the
system, Click No.
Note: Resetting the Broadband Router disconnects any active calls, and
therefore may disrupt current data traffic. Unless you manually save the
configuration. All saved configuration changes are restored after the system reinitializes.
Change Password
After you start using the Broadband Router, you should change the factory default
password as follows:
Step 1 Select Change Password from the menu:
System Tools - Change Password
5-5

The following screen displays:
Step 2 Enter the following information:
Current Password: the current password for the Broadband Router.
New Password: the new password for the Broadband Router
Confirm Password: the new password for the Broadband Router, entered
again for confirmation.
Note: 1. The factory default password is “password”.
2. You can also change the password by console port. Please reder to
the Command Line Interface manual .
Step 3 Click Submit.
What if I Forget the Password?
If you forget the password, the only way to recover is to clear the entire configuration
and return the unit to its original state as shipped from the factory. Unfortunately, this
means that you have to re-enter all of your configuration data.
To clear the configuration and restore the password to the default, follow these steps:
Step 1 Using the supplied Null Modem Cable, connect a console (or a PC
running a terminal emulation program such as HyperTerminal) to the
Broadband Router console port. The default port settings are 19200, 8,
None, 1, None.
5-6
Step 2 Turn off the Broadband Router, then turn it on again. In the console
window, you’ll see the message “Loading firmware...”.

Step 3 When you see the message "Ready", immediately (within one second)
press Control-C.
Step 4 The Broadband Router resets. When this is complete, the Broadband
Router will return all settings to the factory default. The password will
once again be “password”.
Note: Keep in mind that anyone who can physically access the router can
perform this and thereby compromise the security in your network.
5-7

6
6 Messages
This chapter lists messages you may see in the ARM message window.
System Messages
****** has to be an integer [0123456789]
The entered field (******) is not a valid integer.
****** has to be valid IP address
The entered field (******) is an invalid IP address format or an invalid IP address
value.
A
"Account name and/or password not accepted"
User name or password failed authentication by the ISP or the remote site.
"Address already in use"
A duplicate Static Route has been found in the IP Routing Table.
"Advanced Configuration not applied. Duplicate remote IP
address entered"
The IP address entered in the "Optional Remote IP Address" field is either invalid or a
duplicate of an existing entry in the IP Routing Table.
"Advanced Configuration not applied. Duplicate remote IPX
network number entered"
The IPX network number entered in the "Optional Remote IPX Network Number"
field is either invalid or a duplicate of an existing entry in the IPX Routing Table.
"Advanced Configuration not applied. Invalid Remote IP
Address"
The IP address entered in the "Remote IP Address" field is invalid.
"Advanced Configuration not applied. Invalid Remote IPX
Network Number"
The IP network number entered in the "IPX Network number" field is invalid.
"An IPX Network Number is an 8 digits hexadecimal number"
6-1

A valid IPX network number may only contain hexadecimal numbers, (0-9, a-f) and
may be up to 8 characters in length.
B
"Browser failed to send out user’s command. Please try again."
A temporary error has occurred while trying to communicate with the router. Please
repeat the operation.
"Browser’s connection has been lost. You can reconnect system
by opening ’http://***.***.***.***’ "
You must re-enter the indicated IP address in order to re-establish a management
session with the router.
"Browser’s passing command failed. Please try again"
A transient error occurred during the communication between the browser PC and the
router. Re-try the operation.
C
"Connection attempt failed. Acquired IP address conflicts with
the router configuration"
The IP address obtained from the EWAN Internet connection was in conflict with an
IP address subnet already defined for an interface of the router. Either change the IP
address subnet for the interface, or contact your ISP for a different address
assignment
"Call operation in progress. Request ignored"
An "Apply and Test" or "Connect" is pressed when a call is already connected.
"Cannot perform operation. Port or profile is currently disabled"
An outgoing call was attempted on a port or profile that has been disabled.
"Cannot disconnect LAN"
This message is displayed when "Disconnect" button is pressed for the LAN
interface.
"Cannot disconnect this type of connection."
An attempt has been made to disconnect a non-switched connection. This type of
profile connection cannot be disconnected.
"Clearing system configuration and restarting, please wait..."
6-2
This message is displayed when the router is in the process of clearing all system
configuration and then resetting.

"The confirmed encryption key doesn't match"
The encryption key entered in the "Confirm Encryption Key" field is not the same as
the key in "Encryption key" field.
"Invalid DHCP static IP address"
An Invalid static DHCP IP address has been detected. This is not permitted. Please
select another address or modify the original entry.
"Conflict with dial-in address"
An IP address has been entered which is in conflict with the pool of IP addresses
reserved for dial in users. You must select another IP address, or modify the dial in
address range (from the IP browser screen, or from the Command Line Interface
using the “set user” command).
"Invalid private IP address"
The specified IP address is an invalid private IP address.
"Connection profile limit reached"
The maximum number of profiles that can be defined in the system is 20 Remote
Offices and Internet Access profiles or up to 48 Single User Dial-In profiles. To add
another of either type, you must delete an existing profile from the same type.
"Conversion integer/character failure."
An internal error occurred. Please report this to customer support.
"Current password is wrong. The correct password is required"
The password entered is incorrect. Please re-enter the password.
D
"Destination not currently reachable or call back configured"
Either the phone line is not operational, the destination is busy or doesn’t answer, or
the remote profile is configured for call back and has disconnected the call.
"Detecting IPX network number..."
The system is attempting to automatically detect the IPX network number. This
occurs when a zero or a blank is entered as the IPX network number.
"DHCP static assignment table is full, no more actions allowed"
The maximum number of static DHCP entries has configured. You must delete a
static entry before a new one can be added.
"Disconnecting... Please wait. This action may take some
minutes."
This message is displayed whenever the link is in the process of disconnecting. This
6-3

operation may take up to several minutes, depending upon the modem responses.
"Download firmware, please wait (2 minutes)..."
System is downloading new firmware. It takes about two minutes to complete the
operation.
"Duplicate public port"
The specified public port is already used in a static NAT Table entry
"Duplicate static assignment"
The specified Name, MAC address or IP address already exists in the static DHCP
assignment table.
"Duplicate Public Port"
The public port number entered in the “IP Address Translation Configuration” screen
has been configured in another entry. The port number must be unique.
E
"Encryption key is invalid. Please re-enter"
A valid encryption key may only contain hexadecimal numbers, (0-9, a-f) and may be
up to 16 digits in length, depending upon the strength of encryption licensed for the
router site.
"File Invalid"
The firmware file entered is either missing or invalid.
"External logon attempt rejected"
Another browser elsewhere in the network has attempted to open the router’s HTTP
page. This attempt was rejected. Only one HTTTP configuration session allowed at a
given time.
F
"Failed to disconnect. Link is unconfigured"
An attempt was made to "Disconnect" an unconfigured interface.
"Failed to add DHCP static lease entry"
The system could not add a new DHCP entry. Please try again.
"Failed to clear statistics"
6-4
The clear statistics operation could not be completed. Please try again.
"Failed to configure IP routing table"

An invalid IP route has entered. Please check the parameters entered and try again.
"Failed to configure system IPX. Please check input and try
again"
The IPX Network Number entered is not valid. IPX Network Numbers consist of
eight hexadecimal digits (0-9, a-f).
"Failed to remove DHCP lease entry"
The system could not successfully delete a DHCP entry. Please try again.
"Feature key is invalid re-enter or contact vendor"
The feature key entered is not valid, or all system features have been enabled.
"Duplicate IP Filter Name. Please use another name"
A duplicate filter name has been detected. A filter name must be unique.
G
"General read failure"
An error has occurred while communicating with the router. Please use the “Reload”
or “Refresh” button to load this page again.
H
I
"The Internet access time has been configured successfully"
This message is displayed when the Internet access time configuration is accepted by
the router.
"Interface is not available"
An invalid interface type was specified during an IP filter configuration.
"Invalid access type selected. Please select again"
You must select one profile type from the list to configure.
"Invalid address range"
The configured IP address range is not valid. Ex: The range should include at least
two private IP addresses between 192.168.xxx.231 and 192.168.xxx.254.
"Invalid DHCP static IP address"
The configured IP address either conflicts with an IP address of an existing entry or is
not in the valid IP address range.
"Invalid entry index"
6-5

Current DHCP entry can’t be accessed.
"Invalid Filter IP Address"
This message is displayed when an IP address with a syntax error is entered. An IP
address should be a set of four three-digit numbers. Each three-digit number should
be between 0 and 255, inclusive. For example, a correct IP address is 192.168.100.2.
"Invalid Entry: Private Port"
The private port number entered is not valid. It must be a number in the range of 1 to
65535. Or, the user has entered a port number that is reserved or outside of the legal
range for TCP/UDP ports.
"Invalid Entry: Public Port"
The public port number entered is not valid. It must be a number in the range of 1 to
65535. Or, the user has entered a port number that is reserved or outside of the legal
range for TCP/UDP ports.
"Invalid Filter IP Address"
This message is displayed when an IP address with a syntax error is entered. An IP
address should be a set of four three-digit numbers. Each three-digit number should
be between 0 and 255, inclusive. For example, a correct IP address is 192.168.100.2.
"Filter name is a string up to 30 characters"
The Filter Name entered is not valid. A Filter Name should be between one and 30
characters(numbers, letters, dashes or underscores).
"Invalid gateway configuration"
An invalid value has been entered in the "Gateway" field while attempting to add a
static IP or IPX route.
"Invalid IP address"
The IP address entered is not valid.
"Invalid MAC address"
The format of MAC address entered in the DHCP Static Assignment Table is not
correct. It should consist of 6 pairs of hexadecimal digits (0-9, and a-f) separated by
dashes, as xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx.
"Invalid profile name, please use another"
The selected profile name is reserved by the system. Please use another name.
"Invalid remote IP address"
6-6
The remote IP address entered in the VPN tunnel configuration is not valid.
"Invalid static DHCP IP address"

The IP address entered in the static DHCP configuration form is invalid. Please check
all parameters entered.
"Remote Tunnel Name is required"
Each tunnel configuration requires a remote system name for authentication. If such a
name is not provided or is invalid, this message will be displayed.
"IP Address is invalid"
The IP address entered as the public or private address was not valid.
J
K
L
"Link is Disconnected"
This message is displayed after the modem link disconnection operation is completed.
"Link is already disconnected"
This message is displayed when an attempt is made to disconnect an inactive modem
port.
"Lower bound address is out of range (231-254)"
The IP address entered in "Dial In IP Address-Low", is not valid. It must be a number
in the range from 231 to 254, and at least one lower than the upper bound IP address
configured.
M
"My Tunnel Name is required"
The Local Name of a tunnel is required.
"Maximum number of tunnels reached. No more are added"
The maximum number of tunnels has been reached. To configure another, an existing
tunnel must be deleted.
"MAC Address not specified"
The MAC address in the static DHCP entry configuration must be 12 hexadecimal
digits (0-9, a-f).
"Management session time out"
The message is displayed when HTTP management session is idle for more than the
idle time out value(default is 10 minutes).
6-7

"The menu option you clicked on can’t be found. Please try
again."
An internal error has occurred. Please try this operation again.
N
"NAT translation failed. Procotol not supported."
A Network Address Translation operation failed because the packet protocol type was
unknown or is not supported.
"NAT translation failed. NAT table entry not found for an outgoing
ICMP error message."
An attempt to perform a Network Address Translation operation on an ICMP packet
(e.g., "ping") has failed. The Network Address Translation Table entry could not be
found.
"NAT fails to get proxy entry. Null proxy structure"
An internal error occurred. Please contact customer support.
“The new password does not match the confirmed password”
The re-entered password is not the same as the previous password entered during the
change password operation.
“The new password is the same as the old password”
The new password is the same as the old password.
"Not a static route"
The message is displayed when attempt to delete a non-static route in the IP Routing
Table is made. Only Static Routes may be deleted.
O
"Only one EWAN profile is supported"
The adminstrator is attempting to add a second profile over the EWAN port
"Only 8 rules allowed"
The maximum number of Filtering rules, system-wide, has been exceeded. To add an
additional rule, one must be deleted.
P
Parameter changes applied
6-8
Changed parameters have been applied to the router configuration.

"Passwords are 6 - 15 characters (numbers, letters, dashes,
underscores, dashes or colons) starting with a letter or a
number"
The password entered is invalid. A passwords must be more than 6 characters and less
than 15 characters. They can be digits, letters, dashes, underscores, dashes or colons,
and must begin with a letter or a digits.
"The password has been changed"
The new password is configured. Your new password will take effect the next time
you logon.
"Phone number or data service type seems to be incorrect"
After an "Apply and Test" button is pressed, the router detected a problem with either
the remote phone number or the data service type configured.
"Phone number up to 15, limit characters to 123456789,;-[]!*#"
The phone number field has been configured incorrectly. Up to 15 characters may be
entered. Only the numbers from 0 to 9, and the characters ",", ";","-","[", "]",, "*",
"#"and "!" may be entered.
"Placing VPN call. Please wait..."
The router is in the process of establishing a Virtual Private Networking session.
"Please add a filter to this interface first before setting ’sent’ or
’discarded’"
A Filtering Rule must be configured before the Default Rule (’Forward’ or ’Discard’)
can be set.
"Please select an access type"
The type of Connection Profile to be configured must be selected from the Access
Type list.
"The Port number should be 1 ~ 65535"
The port number entered in a filter rule should be in the range of 1 to 65535.
"The profile name is used by another profile"
A duplicate profile name is entered. Profile names must be unique.
"Primary WINS server IP Address is required"
If the user has selected “Yes” for “Configure WINS server”, then at least a primary
WINS server IP address must be entered. Otherwise, change the “Configure WINS
server” choice to “No”.
"The Public Port Number Has Been Reserved By System"
The port number entered is reserved and may not be mapped. The following port
6-9

numbers have been reserved by the system: 9800, 9801, 9802, 17783, and 17784.
Q
R
"Remote call back phone number unspecified"
“Call Back” is selected but a “Call Back Phone Number” is not provided.
"Remote name unspecified"
Please enter a Remote Name. This is a required parameter in a VPN tunnel
configuration.
"Remote phone number is unspecified"
A Remote Phone Number is required.
"Remote phone number is unspecified"
This message is displayed when the required remote phone number has not been
entered.
"The remote account name already exists. Please change to
another user name"
A duplicate user name is entered. Dial-In user names must be unique.
"Resetting system, please wait..."
The message is displayed when the router is in the process of resetting. You can logon
to the router after about 30 seconds.
S
"Save configuration failed. Please try again"
The system failed to save the configuration. Please try again.
"Save configuration succeeded"
The configuration was saved to flash memory successfully.
"Searched entry exists"
The IP route being added already exists.
"Search failed"
6-10
An internal error has occurred.
"The specified tunnel is incoming only"

A tunnel profile defined as "Incoming Only" cannot be used in an outgoing VPN
profile.
"Static entry not found"
An attempt was made to locate an entry which does not exist .
"Statistics Cleared"
The Broadband Router has completed a clear statistics operation on the link selected
in the System Status Monitoring Window.
"Static DHCP Entry Not Found"
A DHCP entry must be selected to “Edit” or “Delete”.
"Static routes to single user profiles not allowed"
You have entered an illegal configuration. Static routes can only be configured over
Internet Access or Remote Office Access profiles. You cannot configure a static route
to a Single User Dial-in profile.
"System received incompleted user's command. Please try
again"
An internal error has occurred. Please retry the operation.
T
"The system is disconnecting"
A "disconnect" button is pressed, while the system is in the process of disconnecting
an active modem link.
"The system time has been configured successfully"
The time has been configured successfully.
"The Gateway IP Address has been set as the IP Default Route"
The Internet access profile has been configured in the router and the configured ISP
Gateway IP Addrress is now set as the IP Default Route
"This interface has been configured to support a Remote Office
profile. You must use the Command Line Interface for this type of
configuration"
An EWAN profile has been configured to support Office-to-Office communication.
This type of profiles can only be configured using the Command Line Interface.
“This operation will cause a system reset upon completion. All
unsaved configuration changes will be lost. ”
A "Download Firmware" operation through a directly connected Command Line
Interface session will cause a system reset after the operation is complete. This
6-11

message informs the user that ongoing operations may be interrupted and that any
configuration changes made within the last 30 minutes (the default time period for
automatic configuration saves), may be lost as a result.
"This profile no longer exists"
The profile being configured no longer exists in the system. Please reload or refresh
the browser page and try again.
"Tunnel does not exist"
This message is displayed when an attempt is made to delete a non-existent tunnel.
V
"Value for idle time is invalid - choose between [0, 3600] seconds"
The idle timeout value entered was incorrect. The correct values are 0 (if no idle
timeout is desired) or 1 to 3600 seconds.
W
"Warning! You have changed the default HTTP port used by
remote Internet users of the Web browser configuration tool. In
order to access this tool remotely through the Internet, you must
re-assign the router's HTTP port (e.g., to 8080). LAN users may
continue to access the Web browser configuration tool as usual."
The administrator has assigned port 80 to another LAN device. Since this is the
default HTTP port for remote Internet users, this message appears to remind users
that the Web browser configuration tool is no longer accessible until HTTP is reassigned to another port. If the user has issued this command from a remote location,
through the Internet, then connectivity is lost immediately. At that point the user can
still use telnet through port 23 to issue a CLI command to do this. If port 23 has been
re-assigned, the administrator must re-assign the HTTP port using the CLI through a
new Telnet router port (if available), from a LAN-attached device, or through a nonInternet connection.
Note: Address Translation only applies to Internet connections
"Warning! You have changed the default TELNET port used by
remote Internet users of the CLI. In order to access the CLI
remotely through the Internet, you must re-assign the router's
Telnet port (e.g., to 8023). LAN users may continue to access the
CLI or the Web browser configuration tool as usual"
The administrator has assigned port 23 to another LAN device. Since this is the
default Telnet port for remote Internet user Command Line Interface configuration,
this message appears to remind users that the Command Line Interface is no longer
accessible over the Internet until Telnet is re-assigned to another port. If the user has
issued this command from a remote location, through the Internet, then connectivity
is lost immediately. At that point the user can still use HTTP through port 80 to access
the Web browser configuration tool to do this. If port 80 has been re-assigned, the
administrator must re-assign the Telnet port from a newly re-assigned router's HTTP
6-12

port (if available), from a LAN-attached device, or through a non-Internet connection.
Note: Address Translation only applies to Internet connections
6-13

A
A Specifications
• Internet Access via Cable or xDSL
• Accessing Servers from the Public Network
• Supporting Inter-office Communication
• Supporting Dial-In Access to your Network
• Supporting Multimedia Applications
• Creating Virtual Private Network
Features
Internet Access, Multimedia Applications and Virtual Server
• Multiple users to share Internet Access
• IP routing and NAT/PAT support
• Supporting PPPoE client function for xDSL connection
• Supporting Mac clone for cable modem connection
• Supporting Multimedia application(ICQ, Netmeeting, CUSeeMe, Quick Time,
etc)
• Supporting Virtual Server
Protocol Support
• PPP
• PPPoE
• IP routing, RIP-1/2
• NAT/PAT
• IPX
• Transparent bridging
• L2TP
Management
• Cisco-like Command Line Interface(CLI)
• Embedded Telnet server for remote Console management
• Customized Web-based GUI
• Firmware upgrade via Web-based GUI/Console port
• Configuration data upload and download via TFTP
• Internet Access time restriction feature
• Support DHCP server/client
• SNMP MIB support, easily for MIS staff
• Multiple connection profile
A-1

Monitoring
• Runtime traffic monitoring
• Connection log
• Syslog
Security
• Natural firewall, private IP addresses not accessible from the Internet
• IP Packet filtering (IP address/ Protocol/Port number)
• IPX Packet filtering( Network number/Node number/Socket number)
• PPP PAP/CHAP/MS-CHAP authentication
• DES Encryption with L2TP protocol support
RAS and WAN Port Redundancy
• COM port interface for connecting an external modem or ISDN TA for remote
dial-in and WAN-port redundancy
• Virtual server feature to setup public Server
VPN
• L2TP with DES Encryption
Physical Specification
• Electrical Specification
External power adapter with AC 9V/1A input
• Dimensions
H:33.6mm W:215mm D:149mm
• Weight
1013g
• EMI Certification
FCC part 15, CE, VCCI Class B
Hardware Configuration
• LAN: 4-Port 10BaseT/100BaseT Ethernet switch, with Uplink Switch
• EWAN: 1 10BaseT RJ-45 EWAN port for connecting Internet through ADSL/
Cable modem
• Console/COM: 1 RJ-45 port direct connection of management console or directly
connect to external modem/ISDN TA
• LED: 20 LEDs for Power. PPPoE. EWAN:LNK, ACT. COM:OH, CD, TX, RX.
LAN:10/100, LNK/ACT, FDX/COL for port 1, 2, 3, 4
• 1 power jack for AC Adapter 9V/1A
• 1 Power Switch
A-2

B
B Glossary
This section provides some common networking terms you may find in this user
guide.
ARP, ARP Table
To send an IP packet to another device on the same LAN, the source device needs to
know the MAC address of the destination device first.
If such information is already maintained in the ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
table, the corresponding MAC address will be used to transmit the data packet.
Otherwise, the data will be queued up first, and an ARP broadcast packet sent out to
the LAN. The device that has a matching IP address will respond with the IP-to-MAC
mapping information. When the response is received, the data that was previously
queued up will be transmitted, and the mapping information stored into the ARP
cache table for re-use later.
ARP table is a cache table that contains MAC-address-to-IP-address mapping
information.
Bit, Byte
These are units of information as stored in computers. A bit has a binary value of 0
and 1, which is the most basic unit for representing information. A byte consists of 8
bits, and therefore can have a value of between 0 and 255. A byte can represent any
character you can see on a computer keyboard, including upper case and lower case
characters. Therefore a document of a certain number of characters can be represented
in a computer as the same number of bytes plus some additional bytes that represent
other information such as the font of each character and the format of the document.
BootP
The Bootstrap Protocol (BootP) is an older version of the Dynamic Host Control
Protocol (see DHCP).
Bridge
A bridge is an intelligent, internetworking device that forwards or filters packets
between different networks based on data link layer (MAC) address information.
Bridge Address Table
A table containing association information between MAC addresses and interfaces in
a bridge. The bridge learns the association by inspecting each and every packet it sees
from each interface. The table is used to decide whether to filter or forward each
packet it receives from each interface.
B-1

Broadcast, Unicast
A data packet contains data, the sender’s address and the receiver’s address - just like
a letter to be mailed.
There is a special type of data packet that is delivered to every destination on the
network. This is called a broadcast packet. When there is only a single receiving
party, it is called a unicast packet.
CHAP
CHAP stands for Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol. It is an
authentication protocol used in PPP for communication devices to authenticate each
other remotely. The password is first encrypted before it is sent to the remote side.
This is as opposed to the PAP protocol, which sends the password in clear text.
Compression
Since data bandwidth over the WAN is usually quite expensive, data is usually
compressed first before it is sent out over the WAN, and decompressed when data is
received from the WAN.
Different types of compression algorithms are oriented towards different types of
data, but generally, certain data patterns are recognized and are abbreviated before
transmission. At the receiving end, the abbreviation is restored to the full data pattern.
A good compression algorithm can achieve a compression ratio of 4 to 1, depending
on the nature of the data being compressed.
Connection Profile
A connection profile contains all necessary information required to set up a dial-up
connection. For example, an Internet access connection profile contains the ISP’s
phone number, the account name and the account password, among other
information.
CPE
CPE stands for Customer Premises Equipment. It refers to any equipment that resides
on the customer premises.
Default IP Route
The default route is a special IP route in the IP routing table. When a packet is
received by the router, if destination network cannot be found in its routing table, the
packet will be forwarded over the default route to the next-hop IP router. Such a
router often has a more complete routing table, and therefore is “more
knowledgeable” about how to route the packet.
Default Gateway (Router)
Every non-router IP device needs to configure a default gateway’s IP address. When
the device sends out an IP packet, if the destination is not on the same network, the
device has to send the packet to its default gateway, which will then send it out
towards the destination.
B-2

DHCP, DHCP Client, DHCP Server
DHCP (the Dynamic Host Control Protocol) is the protocol that a DHCP client uses
to communicate with a DHCP server to ask for an IP address to be assigned. Other
network parameters that can be assigned using the DHCP protocol include network
mask, the primary DNS IP address, the secondary DNS IP address, the default
gateway IP address, WINS Server addresses, NetBIOS Node Type, etc.
Edge Router
A router that resides at the edge of a network. It is like a gateway that is used to
communicate with the outside network.
Encryption
A method for scrambling data which inhibits unauthorized snooping. To ensure
privacy of data sent over the network, the data is often encrypted before it is sent out,
and decrypted when it is received. This is used to protect private data from being
pirated, especially when data is sent over the WAN.
Dial-on-Demand, Bandwidth-on-Demand
If the user uses a switched (dial-up) service to access the Internet, the associated
telecomm cost is often directly proportional to the amount of time the user uses the
network service to connect to the Internet. Therefore often it is designed so that the
connection will be triggered only when there is a need - such as when a user tries to
use a web browser to access the Internet.
For ISDN, when there is a demand, the device will first bring up one B channel to
provide 64Kbps (or 56Kbps) data bandwidth. If traffic is heavy, such as when more
users want to access the Internet, the user can configure the device to bring up the
second B channel to provide higher data bandwidth. Such a capability is called
Bandwidth-on-Demand.
EWAN
The EWAN(Ethernet Wide Area Network) Port is where you will connect your cable
or DSL modem
Flash Memory
This is a special read-write memory in a computer system that allows the computer
program (firmware) or the user configuration data to be stored. Its content will
continue to exist even when the power is turned off.
ICMP
The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is part of the TCP/IP protocol suite,
which is often used for error reporting and control purposes, including the use of the
diagnostic PING command.
Idle Timeout
The Idle Timeout is an amount of time during which no productive data transfer
B-3

occurs. If the user uses a dial-up service to access the Internet, the associated
telecommunication cost is often directly proportional to the amount of time the user
uses the network service to connect to the Internet. Therefore, the Idle Timeout is
designed so that after there is no traffic to the Internet for a pre-configured amount of
time, the connection will automatically be taken down.
IGMP
IP Group Multicast Protocol, a protocol that is used as part of the IP multicast
protocol.
Internet Access and ISP Accounts
To access the Internet, first you need to have a device (such as a router or a modem)
that you can use to connect to the Internet using a dial-up services such as modem or
ISDN or a fixed connection service such as a leased line or a frame relay network.
Then you need to find a local ISP and apply for an ISP account, so that you can get an
account name and the associated password that you need to access the Internet.
Generally speaking, only one device can directly use a modem or an ISDN line to
access the Internet. But if you use a router, you can allow multiple users to share the
router to access the Internet.
IP Address and Network Mask
IP address is a unique identifier for a device in the IP network. It consists of 2
portions: the IP network address, and the host identifier.
The IP address is a 32-bit binary pattern, which can be represented as four cascaded
decimal numbers separated by “.”: aaa.aaa.aaa.aaa, where each “aaa” can be anything
from 000 to 255, or as four cascaded binary numbers separated by “.”:
bbbbbbbb.bbbbbbbb.bbbbbbbb.bbbbbbbb, where each “b” can either be 0 or 1.
A network mask is also a 32-bit binary pattern, and consists of consecutive leading
1’s followed by consecutive trailing 0’s, such as
11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000. Therefore sometimes a network mask can
also be described simply as “x” number of leading 1’s.
When both are represented side by side in their binary forms, all bits in the IP address
that correspond to 1’s in the network mask become part of the IP network address,
and the remaining bits correspond to the host ID. For example, if the IP address for a
device is, in its binary form,
11011001.10110000.10010000.00000111, and if its network mask is,
11111111.11111111.11110000.00000000
It means the device’s network address is
11011001.10110000.10010000.00000000, and its host ID is,
00000000.00000000.00000000.00000111.
IP Packet Filter
A feature that allows selective IP packets to be filtered (thrown away). This feature
means each and every packet to or from an outside network will be inspected to see if
it matches the user defined criteria. When there is a match, the packet will either be
filtered or forwarded depending on the configuration.
B-4

This feature can be used to block certain types of data, such as for security reasons, or
when parents want to make sure that their children do not access certain web sites.
IP Multicast
A protocol that allows only one copy of data to be sent out for multiple destinations in
the network. This allows the network bandwidth to be used most effectively for
multimedia applications.
IPX Address
The network layer address for the IPX protocol, which contains a 4-byte network
number (unique for each LAN segment and frame type combination), the 6-byte
MAC address of the device, and the 2-byte socket number that maps to the particular
application in the device.
IPX Network Number
A unique identifier for an IPX network, which is also the beginning 4-bytes of a 12byte IPX address. It is unique for each LAN segment and frame type combination.
IPX RIP
The IPX Routing Information Protocol, which is used for exchanging and
maintaining the IPX routing table with neighboring routers.
IPX SAP
IPX SAP (Service Advertising Protocol) is a protocol used for advertising services
available from IPX devices and for exchanging server tables among IPX SAP devices
(agents). For example, the SAP table is broadcasted either periodically or whenever
there is a change in the SAP table, or when the IPX SAP device receives SAP table
queries from other IPX SAP devices.
LAN & WAN
Local Area Network & Wide Area Network. Common LAN technologies include
Ethernet, Token Ring, Fast Ethernet. WAN technologies include analog modem,
leased lines, ISDN, frame relay, and ATM.
LAN to LAN Communication
When two physically disjoint offices of the same company need to communicate and
share data resources with each other, they can use one router on each side and perform
LAN to LAN communication - to allow users on one LAN to access resources on the
other.
MAC Address
The Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier for a device with an
Ethernet interface. It is comprised of two parts: 3 bytes of data that corresponds to the
Manufacturer ID (unique for each manufacturer), plus 3 bytes that are often used as
the product serial number.
B-5

Cyear
C Warranty, Copyrights, FCC Notice
Warranty
Broadband Router Products are provided with a limited one year Warranty. Details of
the warranty and return process are explained in the Warranty Policy below. Warranty
service is subject to the terms and conditions of company Warranty Policy.
1. WARRANTY:
Broadband Router (the "Product") carry a one (1) year limited warranty, except for
the power supply units, which carry a one (1) year limited warranty (collectively the
Warranty).
The Warranty covers:
(1) Defects in materials and workmanship of the Product under normal use and
service (Product Defects).
(2) Failure of the Product to perform in accordance with product specifications
published by company (Product Performance).
This Warranty is in lieu of all other express warranties that might otherwise arise with
respect to the Product. No individual or organization of whatever form, connected to
company or not, has authority to change or add to this Warranty.
This Warranty does not apply to any failure of the Product which results from
accident, abuse, misapplication, alteration, or failure due to attached equipment, and
company assumes no liability as a consequence of such events under the terms of this
Warranty. While company has made every effort to provide clear and accurate
technical information about the application of the Product, company assumes no
liability for any event arising out of the use of this technical information.
INCIDENTAL AND CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES CAUSED BY
MALFUNCTION, DESIGN DEFECT, OR OTHERWISE WITH RESPECT TO
BREACH OF THIS WARRANTY, OR ANY OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY, ARE NOT THE RESPONSIBILITY AND HEREBY EXCLUDED
BOTH FOR PROPERTY AND FOR PERSONAL INJURY DAMAGE.
C-1
2. PERIOD OF WARRANTY COVERAGE:
The period of coverage is one (1) year from the date the equipment is purchased.
There shall be no warranty after expiration of the period of coverage. ANY AND
ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR
PARTICULAR USE SHALL HAVE NO GREATER DURATION THAN THE
PERIOD OF COVERAGE STATED HEREIN AND SHALL TERMINATE
AUTOMATICALLY UPON THE EXPIRATION OF SUCH PERIOD.
3. REPAIR, REPLACEMENT AND REFUND:
In the event of a malfunction attributable directly to Product Defect or Product
Performance, company will, at its option, repair or replace the Product to whatever
extent company deems necessary to restore the Product to proper operating condition

without charge to the customer. If, in the company opinion, it is impractical for any
reason to repair or replace the Product, company may at its option refund or pay an
amount equal to the lesser of (1) the purchase price paid for the product or (2) the then
effective company estimated purchase price for the Product. The company may
replace the Product with a new or re-manufactured functionally equivalent product of
equal value at the company option.
4. HARDWARE SERVICE:
To obtain hardware service, contact the dealer from whom you purchased the
Product. Product under warranty will be repaired or replaced according to the terms
of the company Warranty Policy. After expiration of the warranty, you may elect to
have the Product repaired, in accordance with the terms of this Warranty, except that
you shall be responsible for all costs of repair, replacement and shipping and
handling.
5. SHIPPING AND HANDLING:
For equipment covered by warranty, Customers are responsible for shipping of
products requiring repair or replacement to and from the company Center, and for all
shipping and handling charges incurred.
Copyrights
A number of trademarks and registered trademarks appear in this manual. The
company acknowledges all trademarks and the rights of the trademarks owned by the
companies referred to herein. The following list of trademarks may not include all
trademarks referenced in this manual.
Windows, Windows 95, Windows NT, Windows NT Server, and Windows NT
Workstation,Windows ME, Windows 2000 are registered trademarks of Microsoft
Corporation. All other trademarks, service marks, registered trademarks, or registered
service marks mentioned in this manual are the property of their respective owners.
FCC Part 15 Notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy, and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at their
own expense.
The authority to operate this equipment is conditioned by the requirement that no
modifications will be made to the equipment unless the changes or modifications are
expressly approved .
C-2
 Loading...
Loading...