
LXT970A
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
Datasheet
The LXT970A is an enhanced derivative of the LXT970 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet PHY
Transceiver that supports selectable driver strength capabilities and link-loss criteria. The
LXT970A supports 100BASE-TX, 10BASE-T, and 100BASE-FX applications. It provides a
Media Independent Interface (MII) for easy attachment to 10/100 Media Access Controllers
(MAC)s and a pseudo-ECL interface for use with 100BASE-FX fiber networks.
The LXT970A supports full-duplex operation at 10 and 100 Mbps. Its operating condition is set
using auto-negotiation, parallel detection or manual control. The encoder may be bypassed for
symbol mode applications.
The LXT970A is fabricated with an advanced CMOS process and requires only a single 5V
power supply. The MII may be operated independently with either a 5V or a 3.3V supply.
Applications
■ Combination 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX
Network Interface Cards (NICs)
■ 10/100 Switches, 10/100 Printservers
Product Features
■ IEEE 802.3 Compliant:
—10BASE-T and 100BASE-TX using a
single RJ-45 connection.
—Supports auto-negotiation and parallel
detection for legacy systems.
—MII interface with extended register
capability.
■ Robust baseline wander correction
performance.
■ 100BASE-FX fiber optic capable.
■ Standard CSMA/CD or full-duplex
operation.
■ Configurable via MII serial port or external
control pins.
■ 100BASE-FX Network Interface Cards
(NICs)
■ Configurable for DTE or switch
applications.
■ CMOS process with single 5Vsupply
operation
with provision for interface to 3.3V MII
bus.
■ Integrated LED drivers.
■ Integrated supply monitor and line
disconnect during low supply fault.
■ Available in:
—64-pin TQFP (LXT970ATC)
—64-pin PQFP (LXT970AQC)
■ Commercial temperature range (0 - 70
ambient).
o
C
As of January 15, 2001, this document replaces the Level One document Order Number: 249099-001
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver. January 2001

Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel® products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual
property rights is granted by this document. Except as provided in Intel’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability
whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to
fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not
intended for use in medical, life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The LXT970A may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current
characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained by calling 1-800-
548-4725 or by visiting Intel’s website at http://www.intel.com.
Copyright © Intel Corporation, 2001
*Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Datasheet

Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Contents
1.0 Pin Assignments and Signal Descriptions....................................................10
2.0 Functional Description...........................................................................................18
2.1 Introduction..........................................................................................................18
2.2 Interfaces (Network Media/Protocol Support) ..................................................... 19
2.2.1 Twisted-Pair Interface ............................................................................19
2.2.2 Fiber Interface ........................................................................................ 19
2.2.3 MII Interface ...........................................................................................20
2.2.3.1 Selectable Driver Levels............................................................20
2.2.3.2 MII Data Interface...................................................................... 21
2.2.3.3 Repeater Mode..........................................................................24
2.2.3.4 MII Management Interface ........................................................24
2.2.4 Hardware Control Interface ....................................................................26
2.3 Operating Requirements ..................................................................................... 27
2.3.1 Power Supply Requirements..................................................................27
2.3.1.1 Optional MII Power Supply........................................................ 27
2.3.2 Reference Clock Requirements .............................................................27
2.3.2.1 Master Clock Mode ...................................................................28
2.3.2.2 Slave Clock Mode .....................................................................28
2.3.3 Bias Circuit Requirements......................................................................29
2.4 Initialization..........................................................................................................29
2.4.1 Control Mode Selection ..........................................................................29
2.4.1.1 MDIO Control Mode ..................................................................29
2.4.1.2 Manual Control Mode ................................................................ 29
2.4.2 Link Configuration ..................................................................................29
2.4.2.1 Manual Configuration ................................................................ 30
2.4.2.2 Auto-Negotiation/Parallel Detection ..........................................30
2.5 Monitoring Operational Status.............................................................................31
2.5.1 Monitoring Status via MII Registers........................................................31
2.5.2 Monitoring Status via Indicator Pins ....................................................... 32
2.6 100BASE-X Operation ........................................................................................32
2.6.1 100BASE-X MII Operations....................................................................32
2.6.2 100BASE-X Network Operations ...........................................................33
2.7 10BASE-T Operation...........................................................................................35
2.7.1 10BASE-T MII Operations ...................................................................... 35
2.7.2 10BASE-T Network Operations..............................................................35
2.8 Protocol Sublayer Operations ............................................................................. 35
2.8.1 PCS Sublayer.........................................................................................35
2.8.1.1 100X Preamble Handling ..........................................................36
2.8.1.2 10T Preamble Handling.............................................................36
2.8.1.3 Data Errors (100X Only)............................................................36
2.8.1.4 Collision Indication ....................................................................37
2.8.1.5 SQE (10T Only) ......................................................................... 38
2.8.1.6 Jabber (10T Only) .....................................................................38
2.8.2 PMA Layer..............................................................................................38
2.8.2.1 100TX Link Options ................................................................... 38
2.8.2.2 10T Link Test.............................................................................38
Datasheet 3

LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
2.8.2.3 Carrier Sense (CRS) .................................................................38
2.8.3 Twisted-Pair PMD Layer ........................................................................39
2.8.3.1 Scrambler/Descrambler (100TX Only) ...................................... 39
2.8.3.2 Baseline Wander Correction
(100TX Only)39
2.8.3.3 Polarity Correction..................................................................... 39
2.8.4 Fiber PMD Layer ....................................................................................39
2.8.5 Additional Operating Features ............................................................... 40
2.8.6 Low-Voltage-Fault Detect....................................................................... 40
2.8.7 Power Down Mode.................................................................................40
2.8.8 Software Reset....................................................................................... 40
2.8.9 Hardware Reset ..................................................................................... 40
3.0 Application Information......................................................................................... 41
3.1 Magnetics Information ......................................................................................... 41
3.2 Crystal Information ..............................................................................................41
3.3 Design Recommendations ..................................................................................42
3.3.1 General Design Guidelines ....................................................................42
3.3.2 Power Supply Filtering ...........................................................................42
3.3.3 Ground Noise .........................................................................................43
3.3.4 Power and Ground Plane Layout Considerations ..................................43
3.3.5 Interfaces for Twisted-Pair /Fiber ...........................................................43
3.3.5.1 Twisted-Pair .............................................................................. 43
3.3.5.2 Fiber .......................................................................................... 44
3.3.6 Interface for the MII ................................................................................44
3.3.6.1 Transmit Hold Time Adjustment................................................44
3.3.6.2 MII Terminations........................................................................ 44
3.3.7 Typical Application .................................................................................45
3.3.7.1 Voltage Divider For MF Inputs................................................... 45
4.0 Test Specifications.................................................................................................. 47
5.0 Register Definitions ................................................................................................ 63
6.0 Mechanical Specifications ................................................................................... 73
4 Datasheet

Figures
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
1 LXT970A Block Diagram ....................................................................................... 9
2 LXT970A Pin Assignments .................................................................................10
3 Network Interface Card (NIC) Application ..........................................................18
4 MII Interface .......................................................................................................20
5 MII Data Interface ...............................................................................................21
6 Loopback Paths ..................................................................................................23
7 Repeater Block Diagram .................................................................................... 24
8 MDIO Interrupt Signaling ....................................................................................25
9 Management Interface - Read Frame Structure .................................................25
10 Management Interface - Write Frame Structure .................................................25
11 LXT970A Initialization Sequence .......................................................................30
12 Auto-Negotiation Operation ................................................................................ 31
13 100BASE-TX Frame Structure ...........................................................................33
14 100BASE-TX Data Flow ..................................................................................... 33
15 LXT970A Protocol Sublayers .............................................................................36
16 100BASE-TX Reception with No Errors .............................................................37
17 100BASE-TX Reception with Invalid Symbol ....................................................37
18 100BASE-TX Transmission with No Errors ....................................................... 37
19 100BASE-TX Transmission with Collision .........................................................37
20 Voltage Divider ...................................................................................................45
21 Typical Interface Circuitry ...................................................................................46
22 MII - 100BASE-TX Receive Timing / 4B Mode ...................................................51
23 MII - 100BASE-TX Transmit Timing / 4B Mode .................................................52
24 MII - 100BASE-TX Receive Timing / 5B Mode ...................................................53
25 100BASE-TX Transmit Timing / 5B Mode ..........................................................54
26 MII - 100BASE-FX Receive Timing / 4B Mode ...................................................55
27 MII - 100BASE-FX Transmit Timing / 4B Mode ..................................................56
28 MII - 10BASE-T Receiving Timing ......................................................................57
29 MII - 10BASE-T Transmit Timing ....................................................................... 58
30 10BASE-T SQE (Heartbeat) Timing ...................................................................59
31 10BASE-T Jab and Unjab Timing ...................................................................... 59
32 Auto Negotiation and Fast Link Pulse Timing .................................................... 60
33 Fast Link Pulse Timing ....................................................................................... 60
34 MDIO Timing when Sourced by STA .................................................................61
35 MDIO Timing when Sourced by PHY ................................................................. 61
36 Power-Down Recovery Timing (Over Recommended Range) ...........................62
37 PHY Identifier Bit Mapping ................................................................................. 66
38 64-Pin QFP Package Diagram ........................................................................... 73
39 64-Pin TQFP Package Diagram .........................................................................74
Datasheet 5

LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
Tables
1 LXT970A Power Supply Signal Descriptions ...................................................... 10
2 LXT970A MII Signal Descriptions .......................................................................11
3 LXT970A Fiber Interface Signal Descriptions ..................................................... 12
4 LXT970A Twisted-Pair Interface Signal Descriptions .........................................13
5 LXT970A LED Indicator Signal Descriptions....................................................... 13
6 LXT970A Miscellaneous Signal Descriptions......................................................13
7 LXT970A Hardware Control Interface Signal Descriptions ................................. 14
8 MF Pin Function Settings1, 3 ..............................................................................16
9 LXT970A Auto-Negotiation Operating Speed/Full-Duplex
Advertisement Settings ....................................................................................... 17
10 Test Loopback Operation....................................................................................23
11 Carrier Sense, Loopback, and Collision Conditions............................................ 23
12 Configuring the LXT970A via Hardware Control .................................................26
13 LXT970A Operating Configurations / Auto-Negotiation Enabled ........................ 26
14 LXT970A Operating Configurations / Auto-Negotiation Disabled .......................27
15 Mode Control Settings......................................................................................... 29
16 LXT970A Status using FDS/LED Pins ................................................................ 32
17 4B/5B Coding ......................................................................................................34
18 Magnetics Requirements .................................................................................... 41
19 Crystal Requirements.......................................................................................... 41
20 Crystal Component Manufacturers ..................................................................... 41
21 Absolute Maximum Ratings ................................................................................ 47
22 Operating Conditions .......................................................................................... 47
23 Digital I/O Characteristics1.................................................................................. 48
24 Digital I/O Characteristics - MultiFunction Pins MF<4:0>.................................... 48
25 Required Clock Characteristics........................................................................... 48
26 Low Voltage Fault Detect Characteristics ...........................................................49
27 100BASE-TX Transceiver Characteristics ..........................................................49
28 100BASE-FX Transceiver Characteristics ..........................................................49
29 10BASE-T Transceiver Characteristics............................................................... 50
30 10BASE-T Link Integrity Timing Characteristics ................................................. 50
31 MII - 100BASE-TX Receive Timing Parameters / 4B Mode................................ 51
32 MII - 100BASE-TX Transmit Timing Parameters / 4B Mode............................... 52
33 MII - 100BASE-TX Receive Timing Parameters / 5B Mode................................ 53
34 MII - 100BASE-TX Transmit Timing Parameters / 5B Mode............................... 54
35 MII - 100BASE-FX Receive Timing Parameters / 4B Mode................................ 55
36 MII - 100BASE-FX Transmit Timing Parameters / 4B Mode............................... 56
37 MII - 10BASE-T Receive Timing Parameters...................................................... 57
38 MII - 10BASE-T Transmit Timing Parameters..................................................... 58
39 10BASE-T SQE (Heartbeat) Timing Parameters ................................................59
40 10BASE-T Jab and Unjab Timing Parameters.................................................... 59
41 Auto Negotiation and Fast Link Pulse Timing Parameters.................................. 60
42 MDIO Timing Parameters ................................................................................... 61
43 Power-Down Recovery Timing Parameters ........................................................ 62
44 Register Set ........................................................................................................63
45 Control Register (Address 0)............................................................................... 64
46 Status Register (Address 1)................................................................................65
47 PHY Identification Register 1 (Address 2)........................................................... 66
48 PHY Identification Register 2 (Address 3)........................................................... 66
6 Datasheet

Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
49 Auto Negotiation Advertisement Register (Address 4)........................................67
50 Auto Negotiation Link Partner Ability Register (Address 5).................................68
51 Auto Negotiation Expansion (Address 6) ............................................................ 69
52 Mirror Register (Address 16, Hex 10)..................................................................69
53 Interrupt Enable Register (Address 17, Hex 11) ................................................. 70
54 Interrupt Status Register (Address 18, Hex 12) ..................................................70
55 Configuration Register (Address 19, Hex 13)......................................................71
56 Chip Status Register (Address 20, Hex 14) ........................................................ 72
Datasheet 7
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
Revision History
Revision Date Description
8 Datasheet
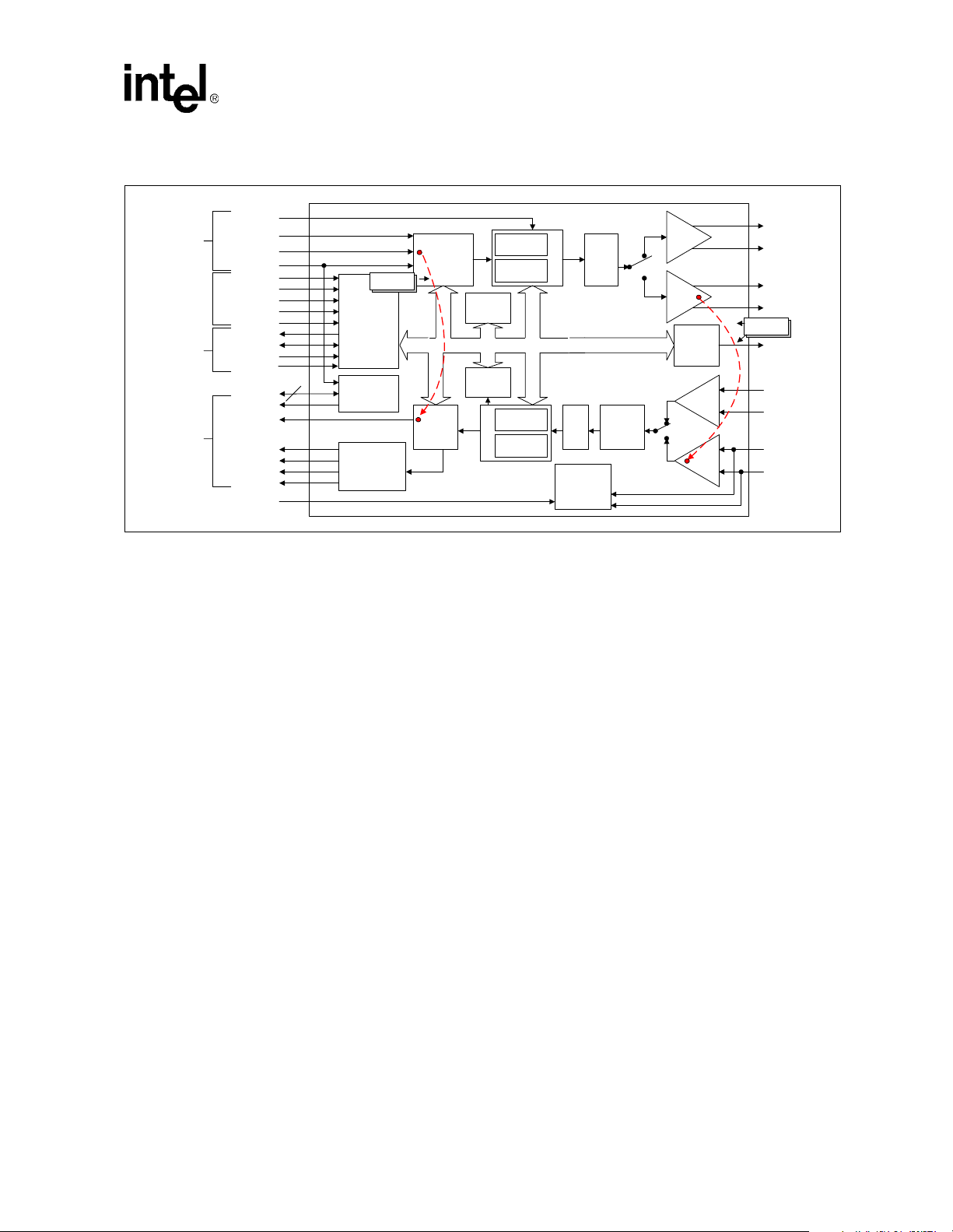
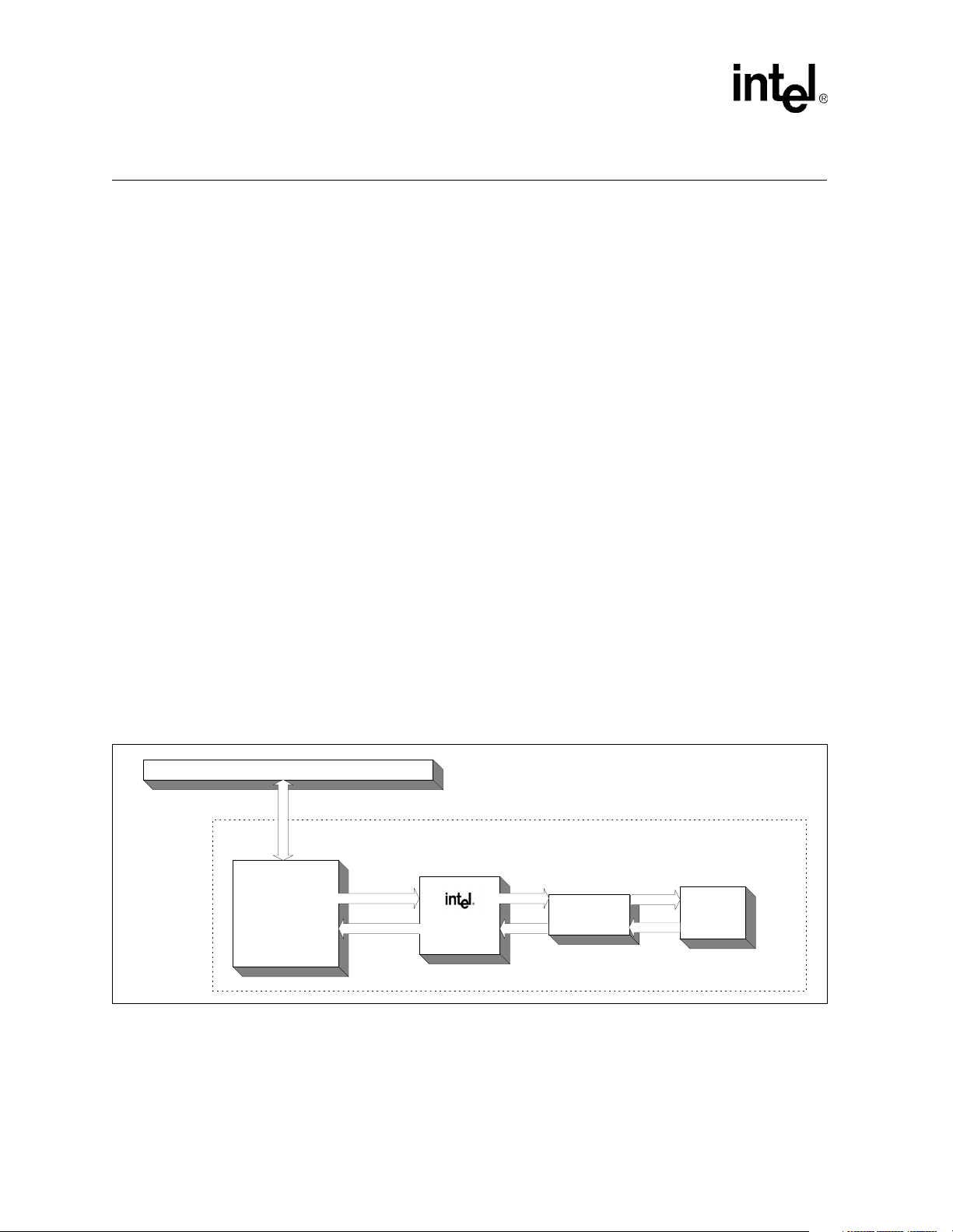
Figure 1. LXT970A Block Diagram
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
MII
TX
Hardware
Interface
MII
MGMT
MII
RX
TX_EN
TX_ER
TXD<0:4>
TX_CLK
MF<0:4>
CFG<0:1>
FDE
TRSTE
RESET
FDS/MDINT
MDIO
MDDIS
MDC
XTALI/O
RX_CLK
RXD<0:4>
CRS
COL
RX_DV
RX_ER
PWR_DWN
+
ECL
Driver
TP
Driver
LED
Drivers
ECL
Rcvr
TP
Rcvr
-
+
-
+
+
Auto
Negotiation
Clock
Generator
10
100
Manchester
Scrambler
& Encoder
Manchester
Decoder &
Descrambler
Parallel
to Serial
Converter
10Mbps
Loopback
Management/
Mode Select
Logic
2
Crystal Osc
& PLL
Carrier Sense
Collision Detect
Data Valid
Error Detect
Serial to
Parallel
Converter
Encoder
Decoder
10
100
Slicer
PwrDown/
Line Energy
Monitor
Pulse
Shaper
Baseline
Wander
Correction
FIBOP
FIBON
TPOP
TPON
100Mbps
Loopback
LED_
FIBIP
FIBIN
-
TPIP
TPIN
-
Datasheet 9
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
1.0 Pin Assignments and Signal Descriptions
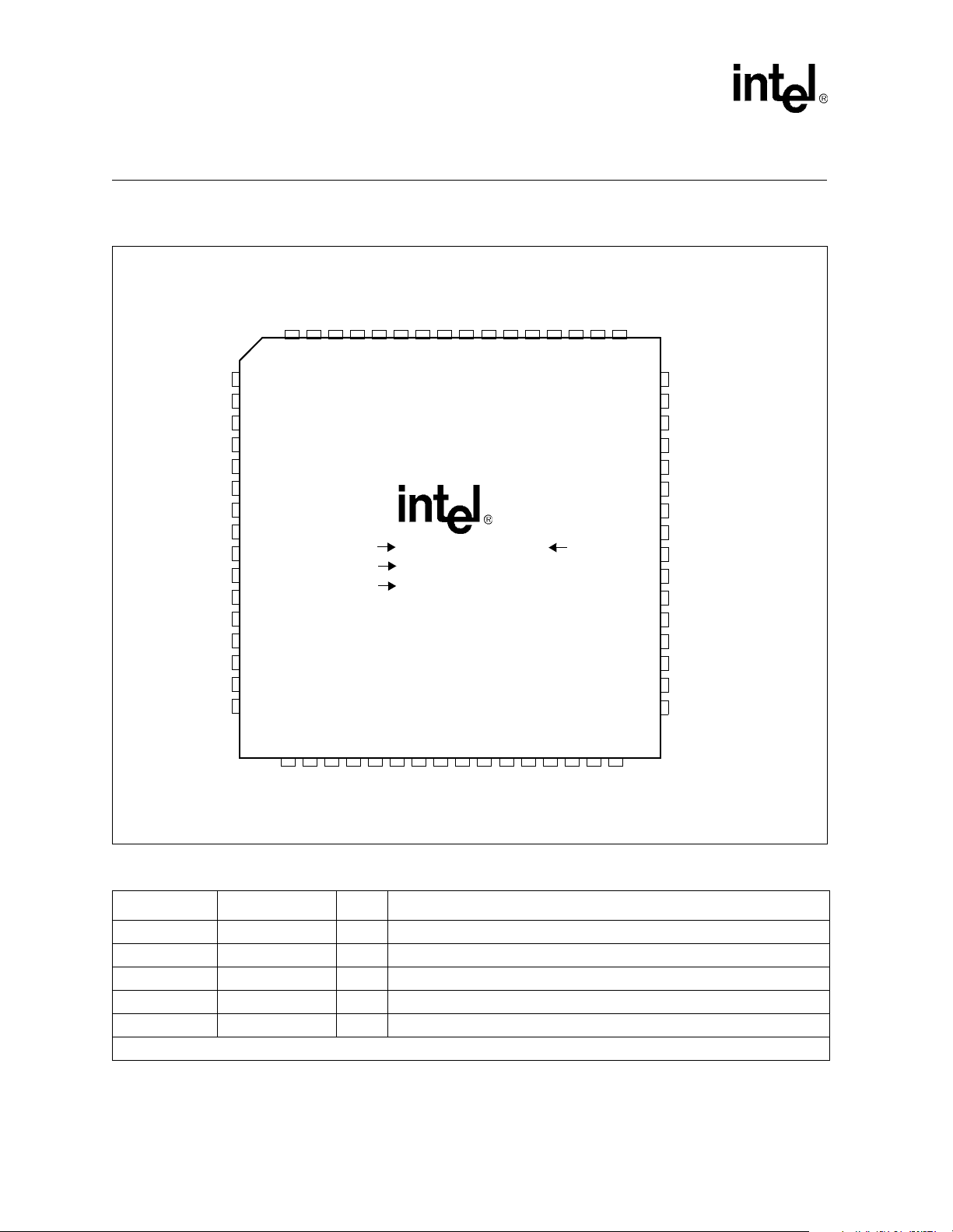
Figure 2. LXT970A Pin Assignments
COL
TXD4
TXD3
TXD2
TXD1
TXD0
TX_EN
TX_CLK
TX_ER
RX_ER
RX_CLK
VCCIO
GNDIO
RX_DV
RXD0
RXD1
CRS
FDS/MDINT
TRSTE
MF4
MF3
MF2
MF1
MF0
VCCD
TEST
XO
XI
FDE
CFG0
MDDIS
RESET
646362616059585756555453525150
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
Part #
LOT #
FPO #
LXT970AQC/ATC XX
XXXXXX
XXXXXXXX
12
13
14
15
16
171819202122232425262728293031
FIBOP
FIBON
VCCT
TREF
TPOP
GNDT
TPON
VCCA
FIBIP
GNDA
RBIAS
TPIP
FIBIN
Rev #
TPIN
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
N/C
GNDR
RXD2
RXD3
RXD4
MDC
MDIO
GNDD
LEDR
LEDT
LEDL
LEDC
LEDS
VCCR
N/C
N/C
PWRDWN
CFG1
Table 1. LXT970A Power Supply Signal Descriptions
1
Pin#
19, 22 VCCT, GNDT - Transmitter Supply (+5V) and Ground. (Analog plane)
37, 31 VCCR, NDR - Receiver Supply (+5V) and Ground. (Analog plane)
24, 26 VCCA, NDA - Analog Supply (+5V) and Ground.
9, 43 VCCD, GNDD - Digital Supply (+5V) and Ground.
53, 52 VCCIO, GNDIO - MII Supply (+3.3V or +5V) and Ground. (Digital plane)
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
Pin Name I/O Signal Description
10 Datasheet
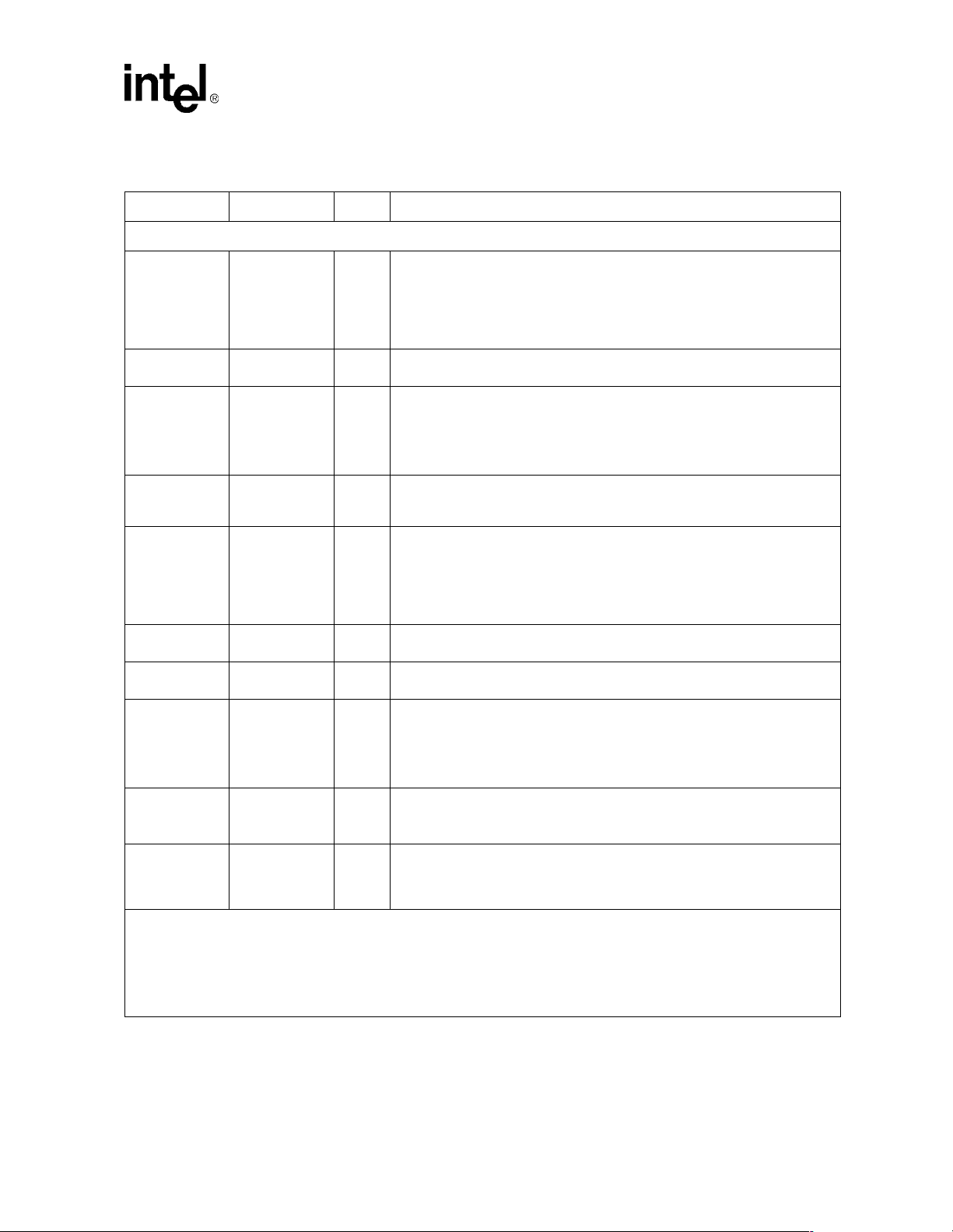
Table 2. LXT970A MII Signal Descriptions
Pin#
1
Pin Name I/O
2,3
MII Data Interface Pins
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Signal Description
4
63
62
61
60
59
58 TX_EN I
57 TX_CLK I/O
56 TX_ER I
46
47
48
49
50
51 RX_DV O
55 RX_ER O
54 RX_CLK O
64 COL O
1 CRS O
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
3. If bit 17.3 = 0, 55
on short traces.
If bit 17.3 = 1, termination resistors are not required.
4. The LXT970A supports the 802.3 MDIO register set. Specific bits in the registers are referenced using an “X.Y” notation,
where X is the register number (0-6 or 16-20) and Y is the bit number (0-15).
TXD4
TXD3
TXD2
TXD1
TXD0
RXD4
RXD3
RXD2
RXD1
RXD0
Ω series termination resistors are recommended on all output signals to avoid undershoot/overshoot, even
Transmit Data. The Media Access Controller (MAC) drives data to the
I
LXT970A using these inputs. TXD4 is monitored only in Symbol (5B) Mode.
These signals must be synchronized to the TX_CLK.
Transmit Enable. The MAC asserts this signal when it drives valid data on the
TXD inputs. This signal must be synchronized to the TX_CLK.
Transmit Clock. Normally the LXT970A drives TX_CLK; in Slave Clock Mode,
TX_CLK is an input. Refer to the Clock Requirements discussion in the
Functional Description section on page 18.
25 MHz for 100 Mbps operation.
2.5 MHz for 10 Mbps operation.
Transmit Coding Error. The MAC asserts this input when an error has
occurred in the transmit data stream. When the LXT970A is operating at 100
Mbps, the LXT970A responds by sending invalid code symbols on the line.
Receive Data. The LXT970A drives received data on these outputs,
synchronous to RX_CLK.
O
RXD4 is driven only in Symbol (5B) Mode.
Receive Data Valid. The LXT970A asserts this signal when it drives valid data
on RXD. This output is synchronous to RX_CLK.
Receive Error. The LXT970A asserts this output when it receives invalid
symbols from the network. This signal is synchronous to RX_CLK.
Receive Clock. This continuous clock provides reference for RXD, RX_DV, and
RX_ER signals. Refer to the Clock Requirements discussion in the Functional
Description section.
25 MHz for 100 Mbps operation.
2.5 MHz for 10 Mbps operation.
Collision Detected. The LXT970A asserts this output when detecting a
collision. This output remains High for the duration of the collision.
This signal is asynchronous and inactive during full-duplex operation.
Carrier Sense. During half-duplex operation (bit 0.8 = 0), the LXT970A asserts
this output when either transmit or receive medium is non-idle. During fullduplex operation (bit 0.8 = 1) or repeater operation
(bit 19.13 = 1), CRS is asserted only when the receive medium is non-idle.
Datasheet 11
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
Table 2. LXT970A MII Signal Descriptions (Continued)
1
Pin#
Pin Name I/O
3TRSTEI
15 MDDIS I
45 MDC I
44 MDIO I/O
2 FDS/MDINT OD
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
3. If bit 17.3 = 0, 55
Ω series termination resistors are recommended on all output signals to avoid undershoot/overshoot, even
on short traces.
If bit 17.3 = 1, termination resistors are not required.
4. The LXT970A supports the 802.3 MDIO register set. Specific bits in the registers are referenced using an “X.Y” notation,
where X is the register number (0-6 or 16-20) and Y is the bit number (0-15).
2,3
Signal Description
4
Tri-state. In DTE Mode (19.13 = 0), when TRSTE input is High, the LXT970A
isolates itself from the MII Data Interface, and controls the MDIO register bit
0.10 (Isolate bit).
When MDDIS is High, TRSTE provides continuous control over bit 0.10. When
MDDIS is Low, TRSTE sets initial (default) values only and reverts control back
to the MDIO interface.
In Repeater Mode (19.13 = 1), when TRSTE input is High, the LXT970A tristates the receive outputs of the MII (RXD<4:0>, RX_DV, RX_ER, RX_CLK).
MII Control Interface Pins
Management Disable. When MDDIS is High, the MDIO is restricted to Read
Only and the MF<4:0>, CFG<1:0>, and FDE pins provide continual control of
their respective bits. When MDDIS is Low at power up or Reset, the MF<4:0>,
CFG<1:0>, and FDE pins control only the initial or “default” values of their
respective register bits. After the power-up/reset cycle is complete, bit control
reverts to the MDIO serial channel.
Management Data Clock. Clock for the MDIO serial data channel. Maximum
frequency is 2.5 MHz.
Management Data Input/Output. Bidirectional serial data channel for PHY/
STA communication.
Full-Duplex Status. When bit 17.1 = 0 (default), this pin indicates full-duplex
status. (High = full-duplex, Low = half-duplex)
This pin can drive a high efficiency LED. (See Table 23 for detail specifications).
Management Data Interrupt. When bit 17.1 = 1, an active Low output on this
pin indicates status change.
Interrupt is cleared by sequentially reading Register 1, then Register 18.
Table 3. LXT970A Fiber Interface Signal Descriptions
1
Pin#
17
18
27
28
Pin Name I/O
FIBOP
FIBON
FIBIP
FIBIN
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
2
Fiber Output, Positive and Negative. Differential pseudo-ECL driver pair compatible with
O
standard fiber transceiver for 100BASE-FX.
Fiber Input, Positive and Negative. Differential pseudo-ECL receive pair compatible with
I
standard fiber transceiver for 100BASE-FX.
Signal Description
12 Datasheet
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Table 4. LXT970A Twisted-Pair Interface Signal Descriptions
1
Pin#
21
23
Pin Name I/O
TPOP
TPON
20 TREF AO Transmit Reference. Tie to center tap of output transformer.
29
30
TPIP
TPIN
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog
2
Twisted-Pair Output, Positive and Negative. Differential driver pair produces 802.3-
AO
compliant pulses for either 100BASE-TX or 10BASE-T transmission.
Twisted-Pair Input, Positive and Negative. Differential input pair for either 100BASE-TX
AI
or 10BASE-T reception.
Signal Description
Table 5. LXT970A LED Indicator Signal Descriptions
1
Pin#
Pin Name I/O
38 LEDS O Speed LED. Active Low output indicates 100 Mbps operation is selected.
42 LEDR O Receive LED. Active Low output indicates that receiver is active.
41 LEDT O Transmit LED. Active Low output indicates transmitter is active.
40 LEDL O
39 LEDC O
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
3. LEDs are read at power-up to determine scrambler seed values.
2
Signal Description
3
Link LED. Active Low output;
During 100 Mbps operation, indicates scrambler lock and receipt of valid Idle codes.
During 10 Mbps operation, indicates Link Valid status.
Collision LED. In default mode, active Low output indicates collision. However, LEDC is
programmable and may be set for other indications. For programming options, see
Configuration Register 19 in Table 55, “Configuration Register (Address 19, Hex 13)” on
page 71.
Table 6. LXT970A Miscellaneous Signal Descriptions
1
Pin#
Pin Name I/O
10 TEST I Test. Must be tied Low.
12
11
XI
XO
25 RBIAS AI
16 RESET I
34 PWRDWN I
32, 35,
36
N/C - No Connection. Leave open.
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
2
Crystal Input and Output. Use a clock at XI or connect a 25 MHz crystal oscillator across
I
XI and XO. Refer to the Functional Description section for detailed clock requirements on
O
page 18.
Bias Control. Controls operating circuit bias via an external 22.1 k
Signal Description
Ω, 1% resistor to
ground.
Reset. This active Low input is OR’ed with the control register Reset bit (0.15). The
LXT970A reset cycle is extended 300
µs (nominal) after Reset is de-asserted.
Power Down. When High, forces LXT970A into power down mode. This pin is OR’ed with
the Power Down bit (0.11). Refer to Table 45 for more information.
Datasheet 13
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
Table 7. LXT970A Hardware Control Interface Signal Descriptions
Pin#
8
7
6
5
4
1
Pin Name I/O
MF0
MF1
MF2
MF3
MF4
2
Signal Description
Multi-Function (MF). Five dual-function configuration inputs. Each pin accepts one of four
input voltage levels (V
MF1 = 5V, VMF2 = 3.5V, VMF3 = 1.5V, VMF4 = 0V).
A simple resistor divider network, as shown in Figure 20 on page 45, is required to establish
Mid-level (V
MF2 and VMF3) settings. VMF1 and VMF4 (default) settings, can be established
with the LXT970A standard power supply and do not require a voltage divider. One voltage
divider may be used to drive the MF pins in designs using multiple LXT970A’s.
Each MF pin internally drives two different configuration functions. The first function
determines the 5-bit address that the LXT970A responds to on the MDIO line. The second
function determines a particular operational mode of the LXT970A. Each MF pin also
determines the state of a particular bit in the MII registers. The MDDIS input determines if this
effect occurs only at initialization (MDDIS = 0) or continuously (MDDIS = 1). The relationship
between the input levels and the two configuration functions are shown in Table 8 on page 16
and Table 9 on page 17.
The operating functions of MF4, CFGO, and CFG1 change depending on the state of MF0
(Auto-Negotiation enabled or disabled). The functions of MF4, CFG1 and FDE are
interrelated.
I
The functions of the five MF inputs are as follows:
Pin MII Address MII Bit Operating Function
MF0 0 0.12 Auto-Negotiation
MF1 1 19.13 Repeater Mode (Disabling DTE Mode)
MF2 2 19.4 5B Symbol Mode (Disabling 4B Nibble Mode)
MF3 3 19.3 Scrambler Operation (Disabling Scrambler)
4.7
Auto-Negotiation Enabled - Advertise 100 Mbps
MF4 4
4.8
19.2 Auto-Negotiation Disabled - Selects TX/FX
3
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
3. FDE, CFG0, and CFG1 are affected by the MDDIS input pin. When MDDIS = 0, these inputs determine only the initial state
of the function they control. When MDDIS = 1, these inputs provide continuous hardware control over their corresponding
functions.
14 Datasheet
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Table 7. LXT970A Hardware Control Interface Signal Descriptions (Continued)
1
Pin#
13 FDE I
14 CFG0 I
33 CFG1 I
1. Pin numbers apply to all package types.
2. I/O Column Coding: I = Input, O = Output, OD = Open Drain, A = Analog.
3. FDE, CFG0, and CFG1 are affected by the MDDIS input pin. When MDDIS = 0, these inputs determine only the initial state
of the function they control. When MDDIS = 1, these inputs provide continuous hardware control over their corresponding
functions.
Pin Name I/O
2
Full-Duplex Enable.
When A/N is enabled, FDE determines full-duplex advertisement capability in combination
with MF4 and CFG1.
When A/N is disabled, FDE directly affects full-duplex operation and determines the value of
bit 0.8 (Duplex Mode).
When FDE is High, full-duplex is enabled and 0.8 = 1.
When FDE is Low, full-duplex is disabled and 0.8 = 0.
Configuration Control 0.
When A/N is enabled, Low-to-High transition on CFG0 causes auto-negotiate to re-start and
0.9 = 1.
When A/N is disabled, this input selects operating speed and directly affects bit 0.13.
When CFG0 is High, 100 Mbps is selected and 0.13 = 1. If FX Operation is selected, this
input must be tied High.
When CFG0 is Low, 10 Mbps is selected and 0.13 = 0.
Configuration Control 1.
When A/N is enabled, CFG1 determines operating speed advertisement capabilities in
combination with MF4.
When A/N is disabled, CFG1 enables 10 Mbps link test function and directly affects bit 19.8.
When CFG1 is High, 10 Mbps link test is disabled and 19.8 = 1.
When CFG1 is Low, 10 Mbps link test is enabled and 19.8 = 0.
Signal Description
3
Datasheet 15
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
Table 8 summarizes the relationship between input voltage levels (V
MF1, VMF2, VMF3, VMF4) and
the configuration function for each of the MF input pins. Each MF pin shows two configuration
inputs; configuration function and MII address. The initial setting of the corresponding bit is also
shown.
Table 8. MF Pin Function Settings
Pin Function VMF1 (5V) VMF2 (3.5V) VMF3 (1.5V) VMF4 (0V)
MII Address Bit 0 1100
MF0
Auto-Negotiation
Sets the initial value of bit
0.12
MII Address Bit 1 1100
MF1
Repeater / DTE Mode
Sets the initial value of bit
19.13
MII Address Bit 2 1100
MF2
Nibble (4B) / Symbol (5B) Mode
Sets the initial value of bit
19.4
MII Address Bit 3 1100
MF3
Scrambler Operation
Sets the initial value of bit
19.3
MII Address Bit 4 1100
1, 3
Disabled
(0.12 = 0)
DTE
(19.13 = 0)
Nibble (4B)
(19.4 = 0)
Enabled
(19.3 = 0)
Input Voltage Levels
Enabled
(0.12 = 1)
Repeater
(19.13 = 1)
Symbol (5B)
(19.4 = 1)
Bypassed
(19.3 = 1)
2
Enabled
(0.12 = 1)
Repeater
(19.13 = 1)
Symbol (5B)
(19.4 = 1)
Bypassed
(19.3 = 1)
Disabled
(0.12 = 0)
DTE
(19.13 = 0)
Nibble (4B)
(19.4 = 0)
Enabled
(19.3 = 0)
If Auto-Negotiate Enabled via
MF0, MF4 works in combination
with CFG1 to control operating
speed and duplex advertisement
MF4
capabilities via bits 4.5 - 4.8.
If Auto-Negotiate Disabled via
MF0, MF4 selects either
TX or FX Mode
Sets the initial value of bit
19.2
1. In MDIO Control Mode, the MF pins control only the initial or default value for the respective register bits. In Manual Control
mode, the MF pins provide continuous control of the respective register bits.
2. Input Voltage Levels (V
3. See Table 12 through Table 14 for operating configuration set-up.
MF1, VMF2, VMF3, VMF4) for MF pins.
100TX
(19.2 = 0)
See Table 9 for details.
100FX
(19.2 = 1)
100FX
(19.2 = 1)
100TX
(19.2 = 0)
16 Datasheet
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Table 9. LXT970A Auto-Negotiation Operating Speed/Full-Duplex
Advertisement Settings
Desired Configuration
Advertise all capabilities
Ignore FDE
Advertise 10 Mbps only
Advertise FD
Advertise 10 Mbps only
Do Not Advertise FD
Advertise 100 Mbps only
Advertised FD
Advertise 100 Mbps only
Do Not Advertise FD
Advertise 10/100 Mbps
Advertise FD
Advertise 10/100 Mbps
Do Not Advertise FD
Input Value
MF4 CFG1 FDE
V
MF1, VMF4 Low – Sets 4.5, 4.6, 4.7 and 4.8 = 1
Sets 4.5 = 1
V
MF1, VMF4 High High
V
MF2, VMF3 Low High
V
MF2, VMF3 High High
Low
Low
Low
Sets 4.7 and 4.8 = 0
Sets 4.6 = 1
Sets 4.5 = 1
Sets 4.7 and 4.8 = 0
Sets 4.6 = 0
Sets 4.7 = 1
Sets 4.5 and 4.6 = 0
Sets 4.8 = 1
Sets 4.7 = 1
Sets 4.5 and 4.6 = 0
Sets 4.8 = 0
Sets 4.5 and 4.7 = 1
Sets 4.6 and 4.8 = 1
Sets 4.5 and 4.7 = 1
Sets 4.6 and 4.8 = 0
MDIO Registers
Datasheet 17
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
2.0 Functional Description
2.1 Introduction
The LXT970A, a new-generation version of the LXT970 10/100 PHY Fast Ethernet Transceiver
incorporates several functional enhancements for a more robust Ethernet solution. The LXT970A
supports optional MII driver strength capabilities and link-loss criteria selectable via the MDIO
register set.
The LXT970A can directly drive a twisted-pair cable for up to 100 meters. The LXT970A also
provides a pseudo-ECL interface for driving a 100BASE-FX fiber connection. On power-up, the
LXT970A uses auto-negotiation with parallel detection to automatically determine line operating
conditions. If the PHY device on the other side of the link supports auto-negotiation, the
LXT970A auto-negotiates using Fast Link Pulse (FLP) bursts. If the PHY partner does not support
auto-negotiation, the LXT970A automatically detects the presence of either link pulses (10 Mbps
PHY) or Idle symbols (100 Mbps PHY) and set its operating speed accordingly. When the line
speed selection is made via the parallel detection method, the duplex mode sets to half. The user
may later select full-duplex operation by subsequent writes to the appropriate MDIO register. Line
operation can also be set using the Hardware Control Interface.
The LXT970A interfaces to a 10/100 MAC through the MII interface. The LXT970A performs all
functions of the Physical Coding Sublayer (PCS) and Physical Media Attachment (PMA) sublayer
as defined in the IEEE 802.3 100BASE-X specification. It also performs all Physical Media
Dependent (PMD) sublayer functions for 100BASE-TX connections. The MII speed is
automatically set once line operating conditions have been determined.
See Figure 3 for a typical Network Interface Card (NIC). The LXT970A supports NIC, repeater,
and switch applications. It provides half- and full-duplex operation at 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps. The
LXT970A supports the 802.3 MDIO register set. Specific bits in the registers are referenced using
an “X.Y” notation, where X is the register address (0-6 or 16-20) and Y is the bit number (0:15).
Figure 3. Network Interface Card (NIC) Application
PC Bus (EISA,PCI)
MAC Controller
LXT970A
Magnetic
RJ-45
Connection
18 Datasheet

Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
2.2 Interfaces (Network Media/Protocol Support)
The LXT970A provides the following interfaces:
• A Twisted-Pair Interface which directly supports 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications.
• A pseudo-ECL (PECL) Fiber Interface which supports 100BASE-FX applications through an
external fiber transceiver.
• An MII (Media Independent Interface) for interfacing 10/100 Media Access Controllers
(MACs).
• A Hardware Control Interface to configure various operating characteristics.
2.2.1 Twisted-Pair Interface
The Twisted-Pair Interface directly supports both 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T applications. The
interface is capable of directly driving an RJ-45 interface through magnetics and termination
resistors. The interface uses two signal pairs - one for transmit and one for receive. A third output,
TREF, connects to the center-tap of the transmit transformer. The same signal pairs, magnetics, and
termination resistors are used for both 10 and 100 Mbps operation.
When the LXT970A is operating as a 100 Mbps device, it transmits and receives a 125 Mbps, 5Bencoded, scrambled MLT-3 waveform on this interface. The MLT-3 waveform is continuous.
When there is no data to send, “IDLE” symbols are sent and received.
When the LXT970A is operating as a 10 Mbps device, it transmits and receives 10 Mbps
Manchester-encoded data. The waveform is not continuous. When there is no data to send, the
line is left in an idle state. Link pulses are transmitted periodically to keep the link up.
The LXT970A supports both fixed operation and auto-negotiation with parallel detection on this
interface. Fixed operation allows the designer to specify the line speed and duplex mode. With
auto-negotiation enabled, the LXT970A automatically determines line speed and duplex state by
exchanging capability “pages” with its link partner.
A 4 k
Ω passive load is always present across the twisted-pair inputs. When enabled, the twisted-
pair inputs are actively biased to approximately 2.8V.
In applications where the Twisted-Pair Interface is not used, the inputs and outputs may be left
unconnected.
The Twisted-Pair Interface is disabled in power down mode, when the Fiber Interface is selected,
or when the transmit disconnect (bit 19.0) is set. When the Twisted-Pair Interface is disabled its
outputs are tri-stated and inputs are unbiased.
2.2.2 Fiber Interface
The pseudo-ECL Fiber Interface is suitable for driving 100BASE-FX applications through an
external fiber transceiver. This interface consists of a transmit and receive pair. The LXT970A
sends and receives a continuous 125 Mbps, 5B-encoded NRZI stream on this interface.
Scrambling and MLT-3 are not used in fiber connections.
There is no industry standard for auto-negotiation on 100BASE-FX. The LXT970A only supports
forced operation on the Fiber Interface. The LXT970A does not support 10FL (10 Mbps fiber)
applications.
Datasheet 19
LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
The LXT970A does not support the Signal Detect Function. However, the PMA functions of the
LXT970A guarantee that it will detect invalid link conditions and break down a link, even without
the Signal Detect function.
In applications where the Fiber Interface is not used, the inputs and outputs may be left
unconnected. The Fiber Interface is disabled in power down mode and when the Twisted-Pair
Interface is enabled. When the Fiber Interface is disabled its outputs are pulled to ground.
2.2.3 MII Interface
The LXT970A implements the Media Independent Interface (MII) as defined in the IEEE 802.3.
This interface consists of a data interface and a management interface as shown in Figure 4. The
data interface is used for exchanging data between a 10/100 802.3 compliant Ethernet Media
Access Controller (MAC) and the LXT970A. The management portion of the interface allows
network management functions to control and monitor the LXT970A.
2.2.3.1 Selectable Driver Levels
The LXT970A supports two options for driver-strength capabilities that can be selected via bit
17.3.
High-strength (bit 17.3 = 0, default) MII driver level can effectively source 50 - 60 mA. To avoid
undershoot or overshoot, series termination resistors are recommended on all output signals when
this driver level is selected.
Reduced (bit 17.3 = 1) MII driver level relaxes the pull-down strength of the MII signals by a
factor of ten and the pull-up strength by a factor of eight. Termination resistors are not required on
the MII outputs when this driver level is selected.
Figure 4. MII Interface
Media Independent
Media Access Controller
Interface (MII)
LXT970A
DataMgmt
20 Datasheet

2.2.3.2 MII Data Interface
Figure 5 shows the data portion of the MII interface. Separate channels are provided for
transmitting data from the MAC to the LXT970A (TXD), and for receiving data (RXD) from the
line.
Each channel has its own clock, data bus and control signals. The LXT970A supplies both clock
signals as well as separate outputs for carrier sense and collision.
Normal data transmission across the MII is implemented in 4-bit wide nibbles known as 4B Nibble
Mode. In 5B Symbol Mode, a fifth bit allows 5-bit symbols to be sent across the MII. Refer to the
100 Mbps Operation section on page 32 for additional information.
Figure 5. MII Data Interface
LXT970A
TX_CLK
TX_EN
TXD<3:0>
TX_ER
RX_CLK
RX_DV
RXD<3:0>
RX_ER
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Media Access
Controller
MAC
CRS
COL
Transmit Clock
The transmit clock (TX_CLK) is normally generated by the LXT970A from the master 25 MHz
reference source at the XI input. However, when the XI input is grounded, TX_CLK becomes the
master reference clock input.
The transmit data and control signals must always be synchronized to TX_CLK by the MAC. The
LXT970A normally samples these signals on the rising edge of TX_CLK. However, Advanced
TX_CLK Mode is available by setting MII register bit 19.5=1. In this mode, the LXT970A
samples the transmit data and control signals on the falling edge of TX_CLK.
Further details of clock modes can be found in the Operating Requirements section on page 27.
Receive Clock
The source of the receive clock varies depending on operating conditions. For 100BASE-TX and
100BASE-FX links, receive clock is continuously recovered from the line. If the link goes down,
and auto-negotiation is disabled, receive clock operates off the master input clock (XI or
TX_CLK).
For 10T links, receive clock is recovered from the line while carrier is active and operates from the
master input clock when the line is idle.
Datasheet 21

LXT970A — Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver
The LXT970A synchronizes the receive data and control signals to RX_CLK. The LXT970A
always changes these signals on the falling edge of RX_CLK in order to stabilize the signals at the
rising edge of the clock with 10 ns setup and hold times.
Transmit Enable
The MAC must assert TX_EN the same time as the first nibble of preamble, and de-assert TX_EN
after the last bit of the packet.
Receive Data Valid
The LXT970A asserts RX_DV when it receives a valid packet. Timing changes depend on line
operating speed and MII mode:
• For 100TX and 100FX links with the MII in 4B mode, RX_DV is asserted from the first nibble
of preamble to the last nibble of the data packet.
• For 100TX and 100FX links with the MII in 5B mode, RX_DV is asserted starting with the /K
symbol and ending with the /T symbol.
• For 10BT links, the entire preamble is truncated. RX_DV is asserted with the first nibble of
the SFD “5D” and remains asserted until the end of the packet.
Error Signals
In 100TX mode, when the LXT970A receives an errored symbol from the network, it asserts
RX_ER and drives “1110” (4B) or “01110” (5B) on the RXD pins.
When the MAC asserts TX_ER, the LXT970A drives “H” symbols out on the line.
There are no error functions in 10T mode.
Carrier Sense
Carrier sense (CRS) is an asynchronous output. It is always generated when a packet is received
from the line and in some modes when a packet is transmitted.
On transmit CRS is asserted on a 10BT, half-duplex link when MII Register 19.11 = 0 (default
state), or on any 100 Mbps half-duplex link. Carrier sense is not generated on transmit when the
link operation is full-duplex, or with 10BT half-duplex links when 19.11=1.
Usage of CRS for Interframe Gap (IFG) timing is not recommended for the following reasons:
• De-assertion time for CRS is slightly longer than assertion time. This causes the IFG interval
to appear somewhat shorter to the MAC than it actually is on the wire.
• CRS de-assertion is not aligned with TX_EN de-assertion on transmit loopbacks in half-
duplex mode.
Operational Loopback
Operational loopback is provided for 10 Mbps half-duplex links when bit 19.11 = 0. Data
transmitted by the MAC will be looped back on the receive side of the MII. Operational loopback
is not provided for 100 Mbps links, full-duplex links, or when 19.11 = 1.
22 Datasheet
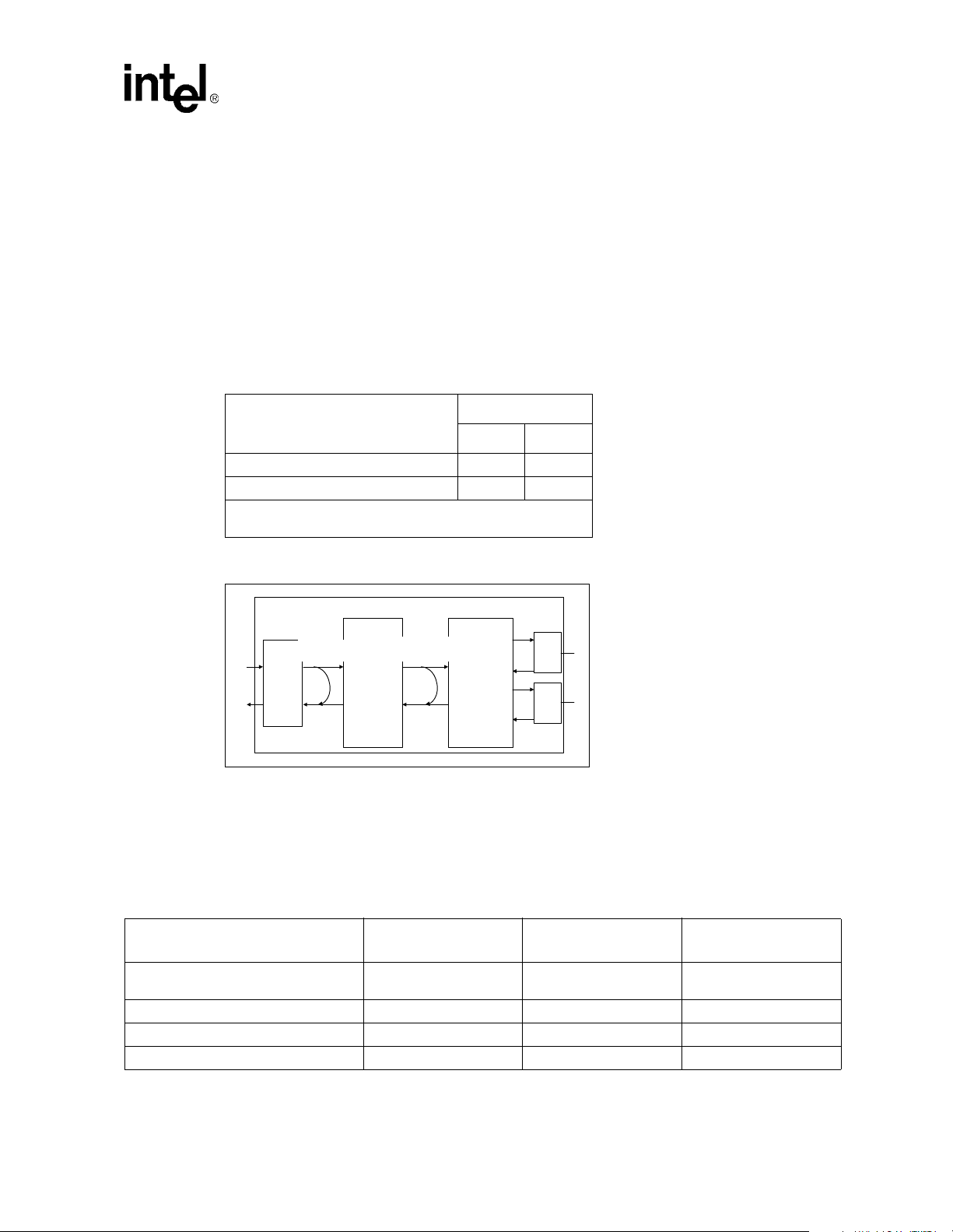
Test Loopback
A test loopback function is provided for diagnostic testing of the LXT970A. During test loopback
the twisted-pair interface is disabled. Data transmitted by the MAC is internally looped back by
the LXT970A and returned to the MAC.
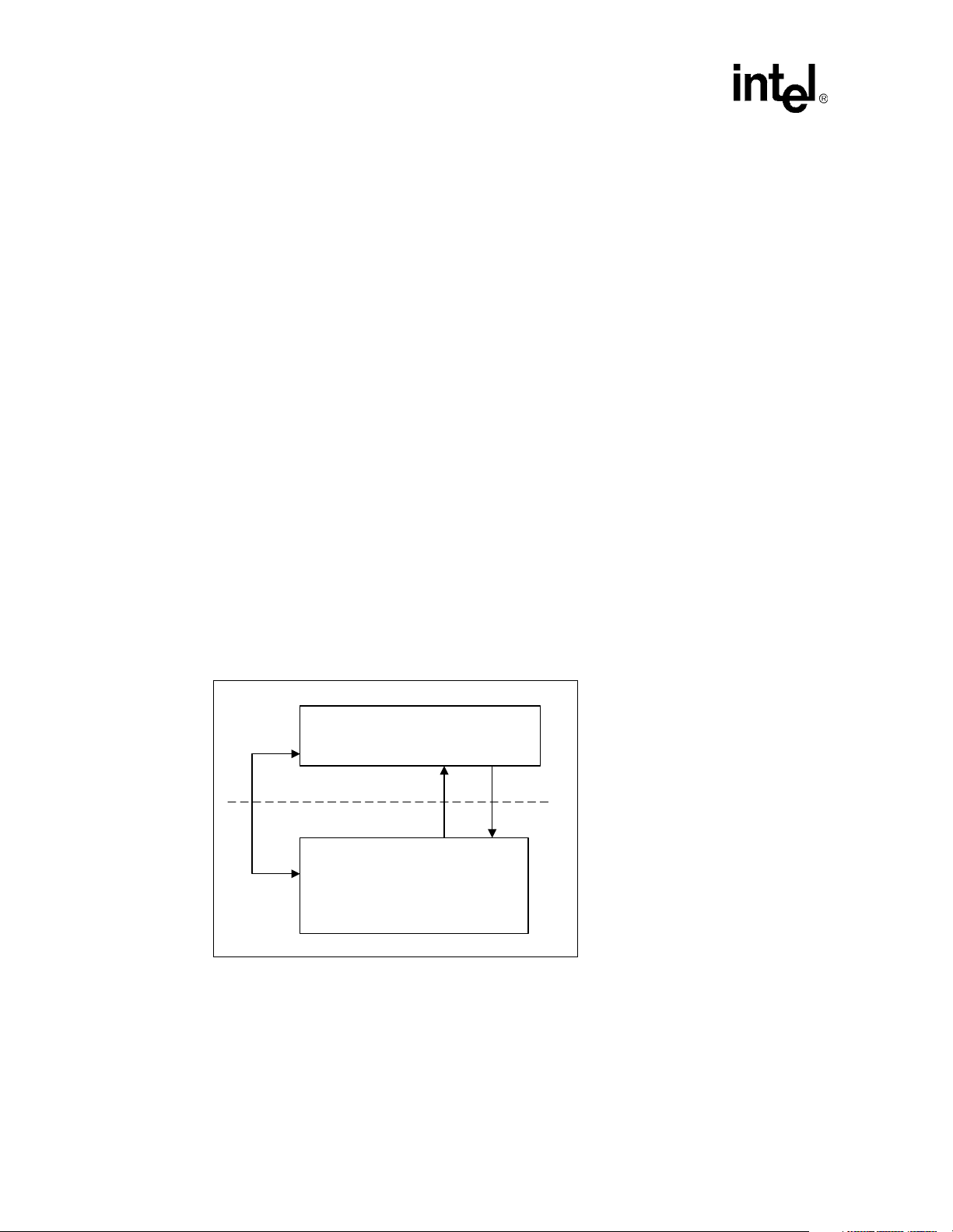
Test loopback is available for 100 Mbps and 10 Mbps operation. Loopback paths for the two modes
of operation are shown in Figure 6.
Test loopback is enabled by setting bit 0.14 = 1 (loopback), bit 0.8 = 1 (full-duplex), and bit 0.12 =
0 (disable auto-negotiation). The desired mode of operation for test loopback is set using bits 0.13
Table 10. Test Loopback Operation
and 19.2 as shown in Table 10.
Dual-Speed Fast Ethernet Transceiver — LXT970A
Mode of Operation
10 Mbps Test Loopback 0 0
100 Mbps Test Loopback 1 1
1. Also set bit 0.14 = 1, bit 0.8 = 1, and 0.12 = 0 to enable Test
Loopback.
Figure 6. Loopback Paths
10 Mbps
Loopback
MII
Collision
The LXT970A asserts its collision signal, asynchronously to any clock, whenever the line state is
half-duplex and the transmitter and receiver are active at the same time. Table 11 summarizes the
conditions for assertion of carrier sense, collision, and data loopback signals.
Digital
Block
100 Mbps
Loopback
Bit
19.2 0.13
Driver
Analog
Block
Driver
FX
TX
Table 11. Carrier Sense, Loopback, and Collision Conditions
Speed & Duplex Condition Carrier Sense
Full-Duplex at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps
Repeater Mode
100 Mbps, Half-Duplex Transmit or Receive None Transmit and Receive
10 Mbps, Half-Duplex, 19.11 = 0 Transmit or Receive Yes Transmit and Receive
10 Mbps, Half-Duplex, 19.11 = 1 Receive only None Transmit and Receive
Receive only None None
Operational
Loopback
Collision
Datasheet 23
 Loading...
Loading...