Intel Corporation G28F016S3-150, G28F016S3-120, G28F008S3-150, G28F008S3-120 Datasheet
E
PRELIMINARY
December 1997
Order Number: 290598-004
n
SmartVoltage Technology
Smart 3 Flash: 2.7 V or 3.3 V V
CC
and 2.7 V, 3.3 V or 12 V V
PP
n
High-Performance
120 ns Read Access Time
n
Enhanced Data Protection Features
Absolute Protection with V
PP
= GND
Flexible Block Locking
Block Write Lockout during Power
Transitions
n
Enhanced Automated Suspend Options
Program Suspend to Read
Block Erase Suspend to Program
Block Erase Suspend to Read
n
Industry-Standard Packaging
40-Lead TSOP, 44-Lead PSOP
and 40 Bump µBGA* CSP
n
High-Density 64-Kbyte Symmetrical
Erase Block Architecture
4 Mbit: Eight Blocks
8 Mbit: Sixteen Blocks
16 Mbit: Thirty-Two Blocks
n
Extended Cycling Capability
100,000 Block Erase Cycles
n
Low Power Management
Deep Power-Down Mode
Automatic Power Savings Mode
Decreases I
CC
in Static Mode
n
Automated Program and Block Erase
Command User Interface
Status Register
n
SRAM-Compatible Write Interface
n
ETOX™ V Nonvolatile Flash
Technology
Intel’s byte-wide Smart 3 FlashFile™ memory family renders a variety of density offerings in the same
package. The 4-, 8-, and 16-Mbit byte-wide FlashFile memories provide high-density, low-cost, nonv olatile,
read/write storage solutions for a wide range of applications. Their symmetrically-blocked architecture, fl exible
voltage, and extended cyc ling provide highly flexible components s uitable for resident flash arrays , SIMMs,
and memory cards. Enhanced suspend capabilities provide an ideal solution for code or data storage
applications. For secure code storage applications, such as networking, where code is either directly
executed out of flash or downloaded t o DRAM, the 4-, 8-, and 16-Mbit FlashFile mem ories offer three lev els
of protection: absolute protection with V
PP
at GND, selective hardware block locking, or flexible software
block locking. These alternatives give designers ultimate control of their code security needs.
This family of products is manufactured on Intel’s 0.4 µm ETOX™ V process technology. They come in
industry-standard packages: the 40-lead TSOP, ideal for board-constrained applications, and the rugged
44-lead PSOP. Based on the 28F008SA architecture, the byte-wide Smart 3 FlashFile memory family
enables quick and easy upgrades for designs that demand state-of-the-art technology.
BYTE-WIDE
SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
4, 8, AND 16 MBIT
28F004S3, 28F008S3, 28F016S3
Includes Commercial and Extended Temperature Specifications

Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or
otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provi ded in Intel ’s Terms and Condi tions of
Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to
sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or
infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life
saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
The 28F004S3, 28F008S3, 28F016S 3 may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to
deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be
obtained from:
Intel Corporation
P.O. Box 5937
Denver, CO 80217-9808
or call 1-800-548-4725
or visit Intel’s Website at http:\\www.intel.com
COPYRIGHT © INTEL CORPORATION, 1997 CG-041493
*Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

E BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
3
PRELIMINARY
CONTENTS
PAGE PAGE
1.0 INTRODUCTION .............................................5
1.1 New Features...............................................5
1.2 Product Overview.........................................5
1.3 Pinout and Pin Description...........................6
2.0 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION .....................11
2.1 Data Protection ..........................................12
3.0 BUS OPERATION.........................................12
3.1 Read..........................................................12
3.2 Output Disable...........................................12
3.3 Standby......................................................12
3.4 Deep Power-Down.....................................12
3.5 Read Identifier Codes Operation................13
3.6 Write ..........................................................13
4.0 COMMAND DEFINITIONS............................13
4.1 Read Array Command................................16
4.2 Read Identifier Codes Command...............16
4.3 Read Status Register Command................16
4.4 Clear Status Register Command................16
4.5 Block Erase Command ..............................16
4.6 Program Command....................................17
4.7 Block Erase Suspend Command................17
4.8 Program Suspend Command.....................18
4.9 Set Block and Master Lock-Bit Commands 18
4.10 Clear Block Lock-Bits Command..............19
5.0 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS........................27
5.1 Three-Line Output Control..........................27
5.2 RY/BY# Hardware Detection......................27
5.3 Power Supply Decoupling..........................27
5.4 V
PP
Trace on Printed Circuit Boards...........27
5.5 V
CC
, VPP, RP# Transitions .........................27
5.6 Power-Up/Down Protection........................27
5.7 V
PP
Program and Erase Voltages on Sub-
0.4µ S3 Memory Family ............................28
6.0 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS..................29
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings........................29
6.2 Commercial Temperature Operating
Conditions.................................................29
6.3 Capacitance...............................................29
6.4 DC Characteristics— Commercial
Temperature..............................................30
6.5 AC Characteristics—Read-Only
Operations—Commercial Temperature.....34
6.6 AC Characteristics—Write Operations—
Commercial Temperature..........................36
6.7 Block Erase, Program, and Lock-Bit
Configuration Performance—Commercial
Temperature..............................................38
6.8 Extended Temperature Operating
Conditions.................................................39
6.9 DC Characteristics—Extended
Temperature..............................................39
6.10 AC Characteristics—Read-Only
Operations—Extended Temperature.........39
7.0 ORDERING INFORMATION..........................40
8.0 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.......................40
BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY E
4
PRELIMINARY
REVISION HISTORY
Number Description
-001 Original version
-002 Table 3 revised to reflect change in abbreviations from “W” for write to “P” for program.
Ordering information graphic (Appendix A) corrected: from PB = Ext. Temp. 44-Lead
PSOP to TB = Ext. Temp. 44-Lead PSOP
Updated Ordering Information and table
Correction to table, Section 6.2.3. Under I
LO
Test Conditions, previously read VIN = V
CC
or GND, corrected to V
OUT
= VCC or GND
Section 6.2.7, modified Program and Block Erase Suspend Latency Times
-003 Updated disclaimer
-004
Added 2.7 V V
PP
specifications.
Added µBGA* CSP pinouts and corrected error in PSOP pinout
Added Design Consideration for V
PP
Program and Erase Voltages on future sub-0.4µ
devices.

E BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
5
PRELIMINARY
1.0 INTRODUCTION
This datasheet contains 4-, 8-, and 16-Mbi t Smart 3
FlashFile memory specifications. Section 1.0
provides a flash memory overview. Sections 2.0,
3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 describe t he memory organiz ation
and functionality. Section 6.0 covers electrical
specifications for commercial and extended
temperature product offerings. Ordering inform ation
is provided in Section 7.0. Finally, the byte-wide
Smart 3 FlashFile memory family documentation
also includes application notes and design tools
which are referenced in Section 8.0.
1.1 New Features
The byte-wide Smart 3 FlashFile memory family
maintains backwards-compatibility with Intel’s
28F008SA-L. Key enhancements include:
• SmartVoltage Technology
• Enhanced Suspend Capabilities
• In-System Block Locking
They share a compatible status register, software
commands, and pinouts. Thes e similarities enable
a clean upgrade from the 28F008SA-L to byte-wide
Smart 3 FlashFile products. When upgrading, it i s
important to note the following differences:
• Because of new feature and density options,
the devices have different device identifier
codes. This allows for software optimization.
• V
PPLK
has been lowered from 6.5 V to 1.5 V to
support low V
PP
voltages during block erase,
program, and lock-bit confi guration operations.
Designs that switch V
PP
off during read
operations should transition V
PP
to GND.
• To take advantage of SmartVoltage technology, allow V
PP
connection to 3.3 V.
For more details see application note
AP-625,
28F008SC Compatibility with 28F008SA
(order
number 292180)
.
1.2 Product Overview
The byte-wide Smart 3 FlashFile memory family
provides density upgrades with pinout compatibility
for the 4-, 8-, and 16-Mbit densities. The 28F004S3,
28F008S3, and 28F016S3 are high-performance
memories arranged as 512 Kbyte, 1 Mbyte, and
2 Mbyte of eight bits. This data is grouped i n eight,
sixteen, and thirty-two 64-Kbyte blocks which are
individually erasable, lockable, and unlockable insystem. Figure 5 illustrates the memory
organization.
SmartVoltage technology enables fast factory
programming and low power designs. Specifically
designed for 3 V systems, Smart 3 FlashFile
components support read operations at 2.7 V and
3.3 V V
CC
and block erase and program operations
at 2.7 V, 3.3 V and 12 V V
PP
. The 12 V VPP option
renders the fastest program perf ormance which will
increase your factory t hroughput. With the 2.7 V or
3.3 V V
PP
option, VCC and VPP can be tied together
for a simple, low-power 2.7 V or 3 V design. In
addition to the voltage flexibility, the dedicated V
PP
pin gives complete data protection when VPP ≤
V
PPLK
.
Internal V
PP
detection circuitry automatically
configures the device f or optimiz ed block eras e and
program operations.
A Command User Interface (CUI) serves as the
interface between the system processor and
internal operation of the device. A valid c ommand
sequence written to the CUI initiates device
automation. An internal Wri te State Machine (WSM)
automatically executes the algorithms and timings
necessary for block erase, program, and lock-bit
configuration operations.
A block erase operation erases one of the device’s
64-Kbyte blocks typically within 1.1 second
(12 V V
PP
), independent of other blocks. Each block
can be independently erased 100,000 times
(1.6 million block erases per device). A block erase
suspend operation allows system software to
suspend block erase to read data from or program
data to any other block.
Data is programmed in byte increments typically
within 7.6 µs (12 V V
PP
). A program suspend
operation permits system software to read data or
execute code from any other flash memory array
location.
BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY E
6
PRELIMINARY
To protect programmed data, each block can be
locked. This block locking mechanism uses a
combination of bits, block lock-bits and a master
lock-bit, to lock and unlock individual blocks. The
block lock-bits gate block erase and program
operations, while the master lock-bit gates block
lock-bit configuration operations. Lock-bit configuration operations (Set Bloc k Lock-Bit, Set M aster
Lock-Bit, and Clear Bloc k Loc k-Bit s c ommands) set
and clear lock-bits.
The status register and RY/BY# output indicate
whether or not the device is busy executing or
ready for a new command. Polling the status
register, system software retrieves WSM feedback.
The RY/BY# output gives an addi tional indicator of
WSM activity by provi ding a hardware st atus s ignal.
Like the status register, RY/BY#-low indicates that
the WSM is performing a bl ock erase, program, or
lock-bit configuration operation. RY/BY#-high
indicates that the WSM is ready for a new
command, block erase is suspended, program is
suspended, or the device is in deep power-down
mode.
The Automatic Power Savings (APS) feature
substantially reduces active current when the
device is in stati c mode (addresses not switching).
In APS mode, the typical I
CCR
current is 3 mA.
When CE# and RP# pins are at V
CC
, the
component enters a CMOS s tandby mode. Driving
RP# to GND enables a deep power-down mode
which significantly reduces power consumption,
provides write protection, resets the device, and
clears the status register. A reset time (t
PHQV
) is
required from RP# switching high until output s are
valid. Likewise, t he device has a wake time (t
PHEL
)
from RP#-high until writes to the CUI are
recognized.
1.3 Pinout and Pin Description
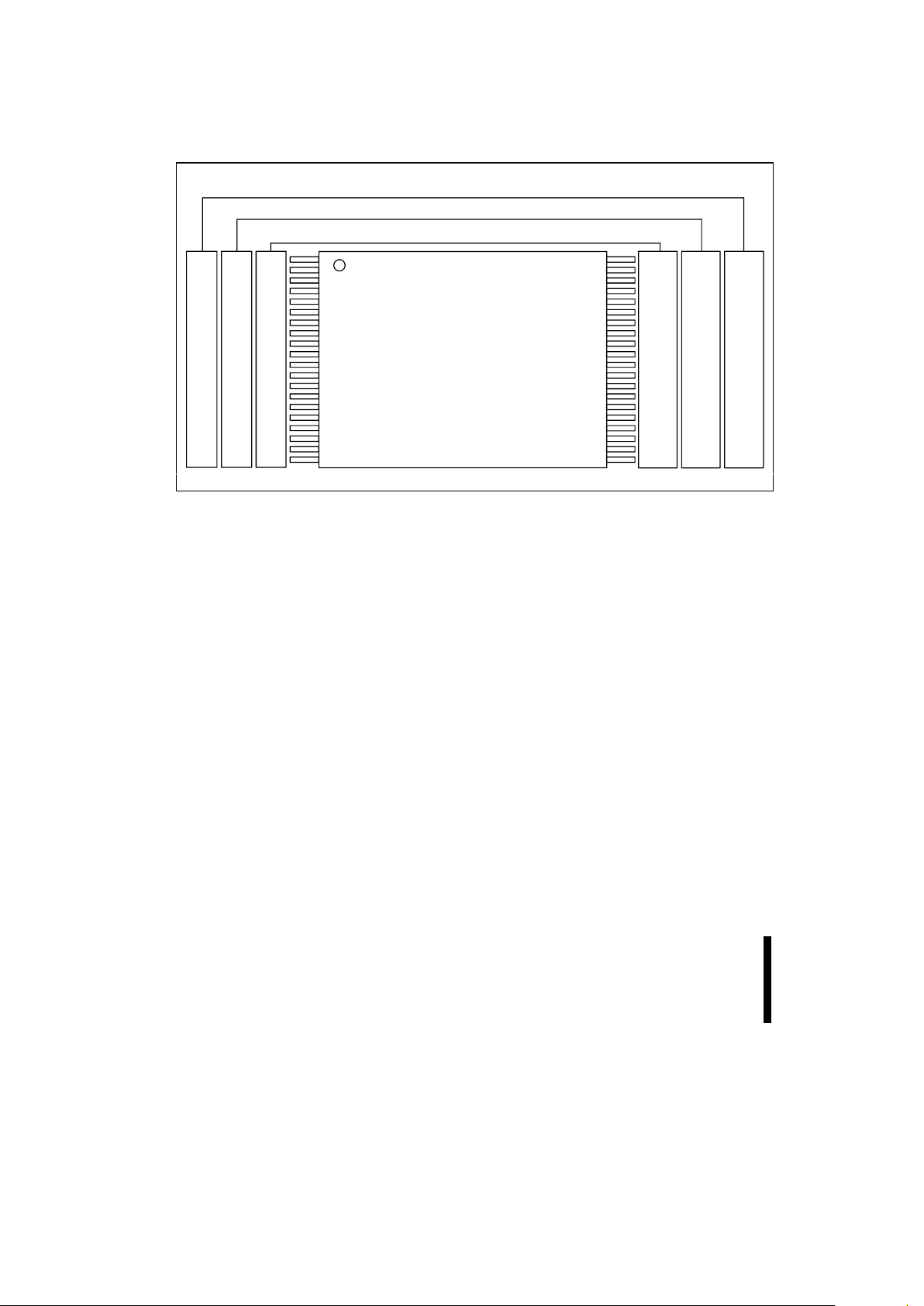
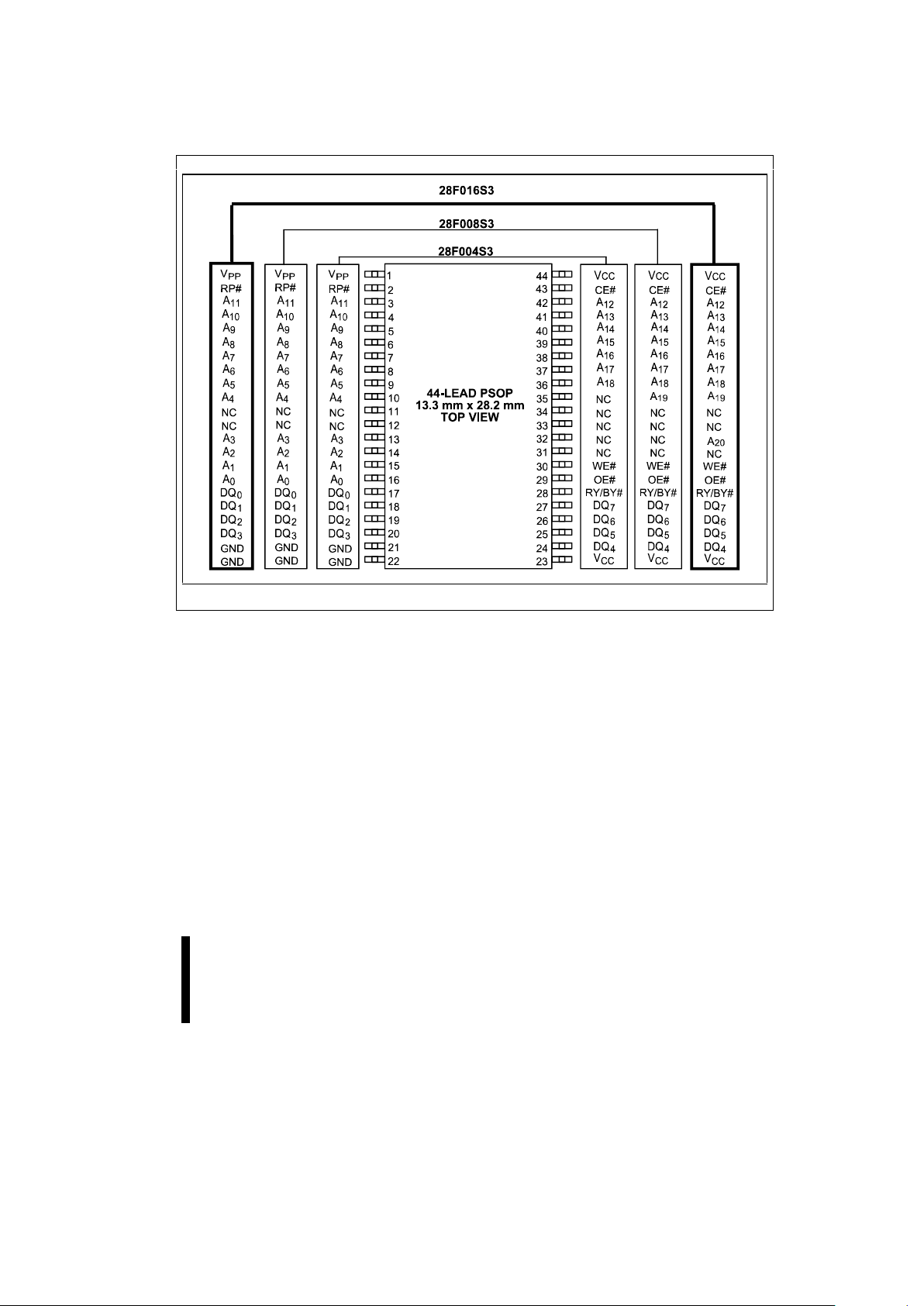
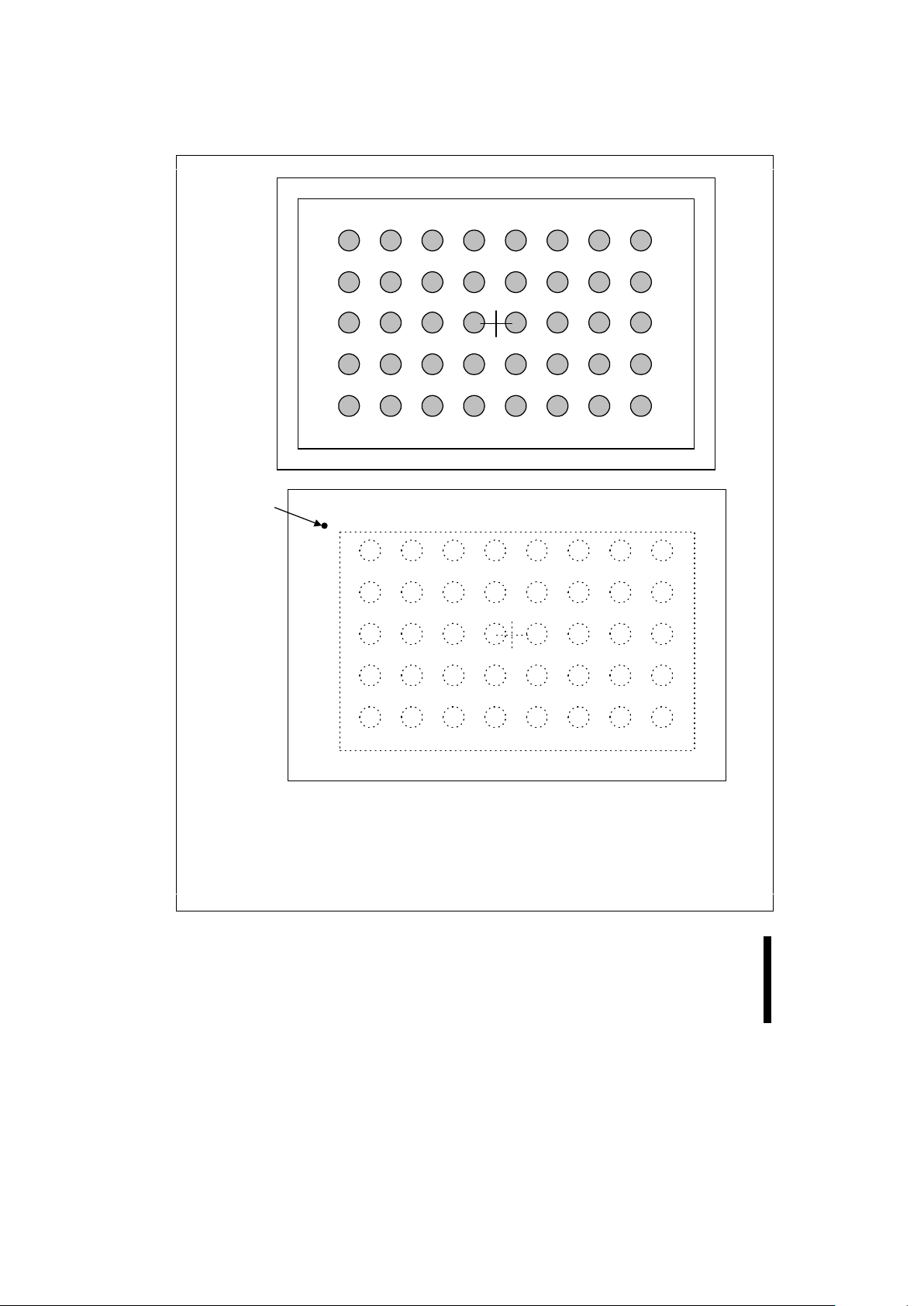
The family of devices is availabl e in 40-lead TSOP
(Thin Small Outline Package, 1.2 mm thick), 44lead PSOP (Plastic Sm all Out line P ack age) and 40bump µBGA* CSP (28F008S3 and 28F016S3 only).
Pinouts are shown in Figures 2, 3 and 4.
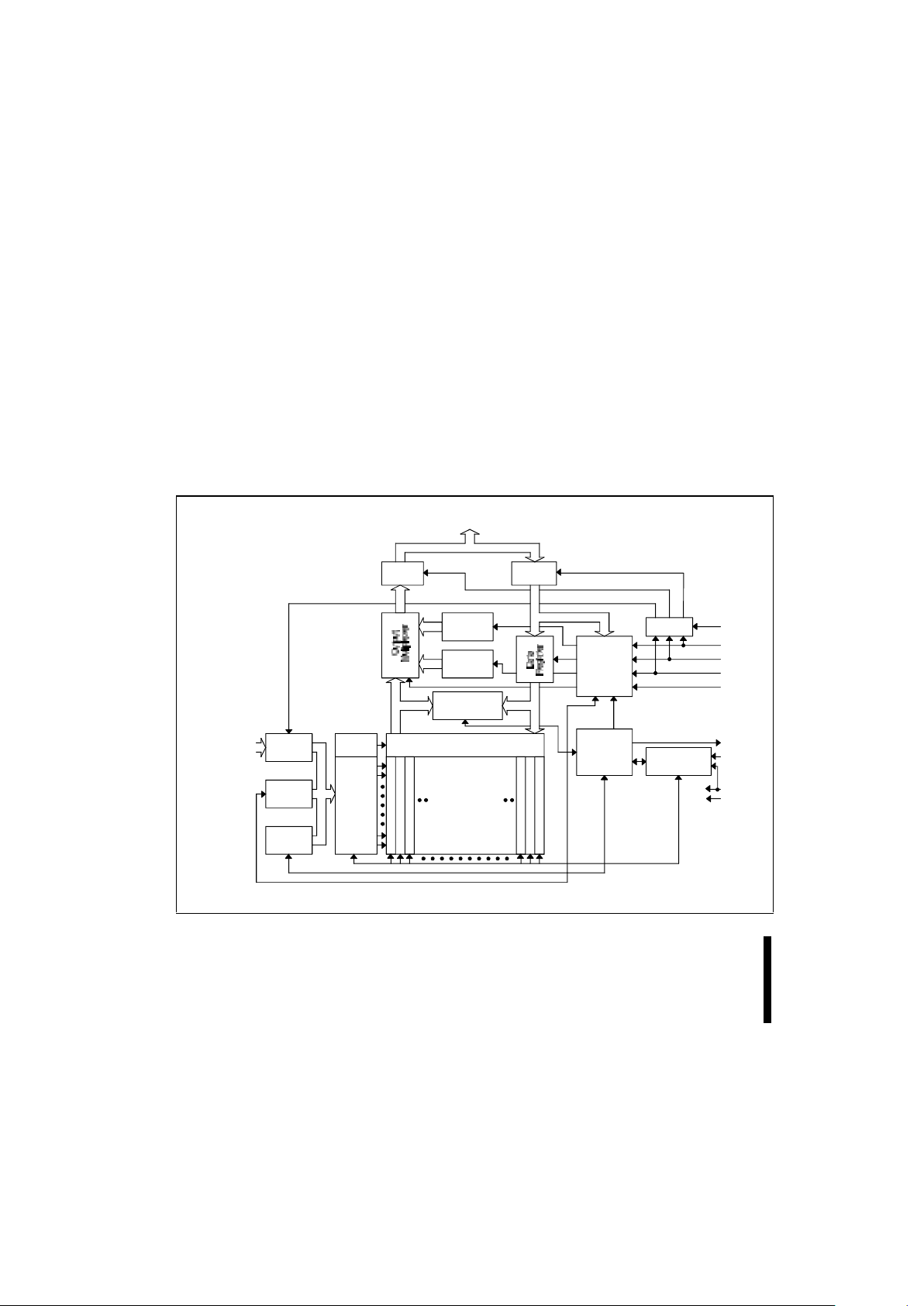
4-Mbit: A - A ,
8-Mbit: A - A ,
16-Mbit: A - A
0
18
0
19
020
Input
Buffer
Output
Buffer
Identifier
Register
Status
Register
Command
Register
I/O Logic
Data
Comparator
Input
Buffer
Address
Latch
Address
Counter
Y
Decoder
X
Decoder
Y Gating
4-Mbit: Eight
8-Mbit : S ixteen
16-Mbit: Thirty-Two
64-Kbyte Blocks
Write State
Machine
Program/Erase
Voltage Switch
CE#
WE#
OE#
RP#
RY/BY#
V
V
GND
DQ - DQ
PP
CC
V
CC
07
Figure 1. Block Diagram
E BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
7
PRELIMINARY
Table 1. Pin Descriptions
Sym Type Name and Function
A0–A
20
INPUT ADDRESS INPUTS: Inputs for addresses during read and write operations.
Addresses are internally latched during a write cycle.
4 Mbit → A
0
–A
8 Mbit → A0–A
16 Mbit → A0–A
20
DQ0–DQ7INPUT/
OUTPUT
DATA INPUT/OUTPUTS: Inputs data and commands during CUI write cycles;
outputs data during memory array, status register, and identifier code read cycles.
Data pins float to high-impedance when the chip is deselected or outputs are
disabled. Data is internally latched during a write cycle.
CE# INPUT CHIP ENABLE: Activates the device’s control logic, input buffers, decoders, and
sense amplifiers. CE#-high deselects the device and reduces power consumption to
standby levels.
RP# INPUT RESET/DEEP POWER-DOWN: When driven low, RP# inhibits write operations
which provides data protection during power transitions, puts the device in deep
power-down mode, and resets internal automation. RP#-high enables normal
operation. Exit from deep power-down sets the device to read array mode.
RP# at V
HH
enables setting of the master lock-bit and enables configuration of block
lock-bits when the master lock-bit is set. RP# = V
HH
overrides block lock-bits,
thereby enabling block erase and program operations to locked memory blocks.
Block erase, program, or lock-bit configuration with V
IH
< RP# < VHH produce
spurious results and should not be attempted.
OE# INPUT OUTPUT ENABLE: Gates the device’s outputs during a read cycle.
WE# INPUT WRITE ENABLE: Controls writes to the CUI and array blocks. Addresses and data
are latched on the rising edge of the WE# pulse.
RY/BY# OUTPUT READY/BUSY#: Indicates the status of the internal WSM. When low, the WSM is
performing an internal operation (block erase, program, or lock-bit). RY/BY#-high
indicates that the WSM is ready for new commands, block erase or program is
suspended, or the device is in deep power-down mode. RY/BY# is always active.
V
PP
SUPPLY BLOCK ERASE, PROGRAM, LOCK-BIT CONFIGURATION POWER SUPPLY:
For erasing array blocks, programming data, or configuring lock-bits.
Smart 3 Flash → 2.7 V, 3.3 V and 12 V V
PP
With VPP ≤ V
PPLK
, memory contents cannot be altered. Block erase, program, and
lock-bit configuration with an invalid V
PP
(see
DC Characteristics
) produce spurious
results and should not be attempted.
V
CC
SUPPLY DEVICE POWER SUPPLY: Internal detection automatically configures the device
for optimized read performance. Do not float any power pins.
Smart 3 Flash → 2.7 V and 3.3 V V
CC
With VCC ≤ V
LKO
, all write attempts to the flash memory are inhibited. Device
operations at invalid V
CC
voltages (see
DC Characteristics
) produce spurious
results and should not be attempted. Block erase, program, and lock-bit
configuration operations with V
CC
< 2.7 V are not supported.
GND SUPPLY GROUND: Do not float any ground pins.
NC NO CONNECT: Lead is not internally connected; it may be driven or floated.
BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY E
8
PRELIMINARY
28F004S3
28F008S3
28F016S3
NC
CE#
RP#
A
18
A
13
A
17
A
14
A
16
A
15
A
12
A
11
A
10
A
9
A
8
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
V
CC
V
PP
NC
WE#
OE#
RY/BY#
GND
GND
DQ
6
DQ
7
DQ
5
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
DQ
3
DQ
2
DQ
1
DQ
0
NC
V
CC
A
19A19
DQ
4
A
20
40-LEAD TSOP
STANDARD PINOUT
10 mm x 20 mm
TOP VIEW
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
CE#
RP#
A
18
A
13
A
17
A
14
A
16
A
15
A
12
A
11
A
10
A
9
A
8
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
V
CC
V
PP
CE#
RP#
A
18
A
13
A
17
A
14
A
16
A
15
A
12
A
11
A
10
A
9
A
8
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
V
CC
V
PP
NC
WE#
OE#
RY/BY#
GND
GND
DQ
6
DQ
7
DQ
5
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
DQ
3
DQ
2
DQ
1
DQ
0
NC
V
CC
DQ
4
NC
WE#
OE#
RY/BY#
GND
GND
DQ
6
DQ
7
DQ
5
A
0
A
1
A
2
A
3
DQ
3
DQ
2
DQ
1
DQ
0
V
CC
DQ
4
Figure 2. TSOP 40-Lead Pinout
E BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
9
PRELIMINARY
Figure 3. PSOP 44-Lead Pinout
BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY E
10
PRELIMINARY
A
9
A
7
RP# V
PP
V
CC
A
12
A
17
A
18
A
16
A
14
CE# A
13
A
11
A
10
A
6
A
4
RY/BY#A
3
NCA
8
A
19
A
5
A
20
A
2
A
0
D
4
D3GNDD
1
D6WE#
OE#D
7
D
2
V
CC
GND D
5
D
0
A
1
A
15
87654321
A
B
C
D
E
A
B
C
D
E
A
15
A
17
A
12
V
CC
V
PP
RP# A
7
A
6
A
10
A
11
CE#A
13
A
14
A
16
A
18
NC RY/BY# A
19
NC A
8
A
3
A
5
A
4
A
2
A
0
D
1
D
3
GNDD
4
D
6
WE#
OE# D
7
D
5
V
CC
GND D
2
D
0
A
1
A
9
12345678
Pin #1
Indicator
Top View - Bump Side Down
Bottom View - Bump Side Up
This is the view of the package as surface mounted on the board.
Note that the signals are mirror images of bottom view.
NOTES:
1. Figures are not drawn to scale.
2. Address A20 is not included in the 28F008S3.
3. More information on µBGA* packages is available by contacting your Intel/Distribution sales office.
Figure 4. µBGA* CSP 40-Bump Pinout (28F008S3 and 28F016S3)
E BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
11
PRELIMINARY
2.0 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
The byte-wide Smart 3 FlashFile memories i nclude
an on-chip WSM to manage block erase, program,
and lock-bit configuration functions. It allows for:
100% TTL-level control inputs, f ixed power s upplies
during block erasure, program, and lock-bit
configuration, and minimal process or overhead with
RAM-like interface timings.
After initial device power-up or return from deep
power-down mode (see
Bus Operations
), the
device defaults to read array mode. Mani pulation of
external memory control pins allow array read,
standby, and output disable operations.
Status register and identifier codes can be
accessed through the CUI independent of the V
PP
voltage. High voltage on VPP enables successful
block erasure, program, and lock-bit c onfiguration.
All functions associated with altering memory
contents—block erase, program, lock-bit
configuration, status, and identifier codes—are
accessed via the CUI and verified through the
status register.
Commands are written using standard microprocessor write timings . The CUI cont ents s erve as
input to the WSM that controls block erase,
program, and lock-bit configuration operati ons. The
internal algorithms are regulated by the WSM,
including pulse repetition, internal verification, and
margining of data. Addresses and data are
internally latched during write cycles. Writing the
appropriate command outputs array dat a, acces ses
the identifier codes, or outputs status register data.
Interface software that initiates and polls progress
of block erase, program, and lock-bit configuration
can be stored in any block. This code is c opied to
and executed from system RAM during flash
memory updates. After successful completion,
reads are again possible via the Read Array
command. Block erase suspend allows system
software to suspend a block erase to read data
from or program data to any other block . Program
suspend allows system software to suspend a
program to read data from any other flash memory
array location.
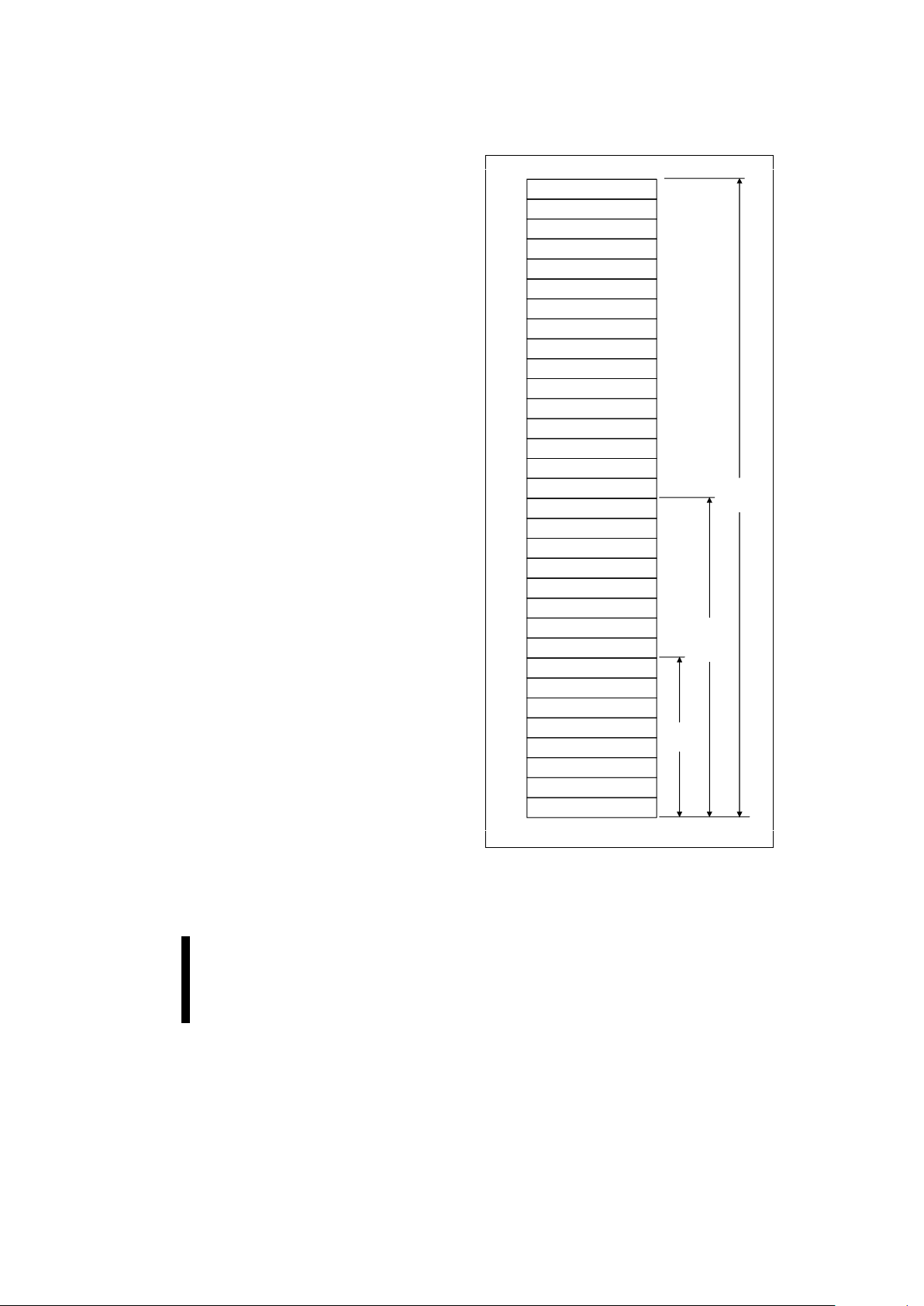
64-Kbyte Block
1FFFFF
31
1F0000
1EFFFF
1E0000
1DFFFF
1D0000
1CFFFF
1C0000
1BFFFF
30
29
28
27
1B0000
1AFFFF
1A0000
19FFFF
190000
18FFFF
180000
17FFFF
26
25
24
23
170000
16FFFF
160000
15FFFF
150000
14FFFF
140000
13FFFF
22
21
20
19
130000
12FFFF
120000
11FFFF
110000
10FFFF
100000
0FFFFF
18
17
16
15
0F0000
0EFFFF
0E0000
0DFFFF
0D0000
0CFFFF
0C0000
0BFFFF
14
13
12
11
0B0000
0AFFFF
0A0000
09FFFF
090000
08FFFF
080000
07FFFF
10
9
8
7
070000
06FFFF
060000
05FFFF
050000
04FFFF
040000
03FFFF
6
5
4
3
030000
02FFFF
020000
01FFFF
010000
00FFFF
000000
2
1
0
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
64-Kbyte Block
8-Mbit
16-Mbit
4-Mbit
Figure 5. Memory Map

BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY E
12
PRELIMINARY
2.1 Data Protection
Depending on the application, the system designer
may choose to make the V
PP
power supply
switchable (available only when memory block
erase, program, or lock-bit configurat ion operations
are required) or hardwired to V
PPH1/2
. The device
accommodates either design practice and
encourages optimization of the processor-memory
interface.
When V
PP
≤ V
PPLK
, memory contents cannot be
altered. When high voltage is applied to V
PP
, the
two-step block erase, program, or lock-bit
configuration command sequences provides protection from unwanted operations. All write
functions are disabled when V
CC
voltage is below
the write lockout voltage V
LKO
or when RP# is at
V
IL
. The device’s block locking capabilit y provides
additional protection from i nadvertent code or data
alteration by gating erase and program operations.
3.0 BUS OPERATION
The local CPU reads and writes flash memory
in-system. All bus cycles to or from the flash
memory conform to standard microprocessor bus
cycles.
3.1 Read
Block information, i dent i fier codes, or status register
can be read independent of the V
PP
voltage. RP#
can be at either V
IH
or VHH.
The first task is to write the appropriat e read-mode
command (Read Array, Read Identifier Codes, or
Read Status Register) to the CUI. Upon initial
device power-up or after exit from deep powerdown mode, the device automati cally resets t o read
array mode. Four control pins dictate the data flow
in and out of the component: CE#, OE#, WE#, and
RP#. CE# and OE# must be driven active to obtai n
data at the outputs. CE# is the device selection
control, and when active enables the selected
memory device. OE# is the data out put (DQ
0
–DQ7)
control and when active drives the selected
memory data onto the I/O bus . WE # must be at V
IH
and RP# must be at VIH or VHH. Figure 17
illustrates a read cycle.
3.2 Output Disable
With OE# at a logic-high level (VIH), the device
outputs are disabled. Output pins DQ
0
–DQ7 are
placed in a high-impedance state.
3.3 Standby
CE# at a logic-high level (VIH) places the device in
standby mode which substantially reduces device
power consumption. DQ
0
–DQ7 outputs are placed
in a high-impedance state independent of OE#. If
deselected during block erase, program, or lock-bit
configuration, the devic e continues functioning and
consuming active power until the operation
completes.
3.4 Deep Power-Down
RP# at VIL initiates the deep power-down mode.
In read mode, RP#-low deselects the memory,
places output drivers in a high-impedance state,
and turns off all internal c ircuits. RP# mus t be held
low for time t
PLPH
. Time t
PHQV
is required after
return from power-down until initial m emory access
outputs are valid. After this wake-up interval,
normal operation is restored. The CUI resets to
read array mode, and the status regi ster is set to
80H.
During block erase, program, or lock-bit
configuration, RP#-low will abort the operation.
RY/BY# remains low until the reset operation is
complete. Memory contents being altered are no
longer valid; the data may be partially erased or
written. Time t
PHWL
is required after RP# goes to
logic-high (V
IH
) before another command can be
written.
As with any automated device, it is important to
assert RP# during system reset. When the system
comes out of reset, i t ex pect s t o read from t he f las h
memory. Automated flash memori es provide status
information when accessed during block erase,
program, or lock-bit confi guration modes. If a CPU
reset occurs with no flash memory reset, proper
CPU initialization may not occur because the flas h
memory may be providing status information
instead of array data. Int el’s flash memories allow
proper CPU initialization following a system reset
through the use of the RP# input. I n this applicati on,
RP# is controlled by the same RESET# signal that
resets the system CPU.
E BYTE-WIDE SMART 3 FlashFile™ MEMORY FAMILY
13
PRELIMINARY
000000
Block 0
Master Lock Configuration
000001
000002
000003
010000
010002
00FFFF
Device Code
Block 0 Lock Configuration
Manufacturer Code
Reserved For
Future Implementation
Block 1
Block 1 Lock Configuration
Reserved for
Future Implementation
01FFFF
Reserved for
Future Implementation
1F0000
1F0002
Block 31 Lock Configuration
Reserved for
Future Implementation
1FFFFF
Block 31
(Blocks 16 through 30)
(Blocks 8 through 14)
(Blocks 2 through 14)
070000
070002
Block 7
Block 7 Lock Configuration
Reserved for
Future Implementation
07FFFF
Reserved for
Future Implementation
0F0000
0F0002
Block 15
Block 15 Lock Configuration
Reserved for
Future Implementation
0FFFFF
8-Mbit
16-Mbit
4-Mbit
Reserved for
Future Implementation
Reserved for
Future Implementation
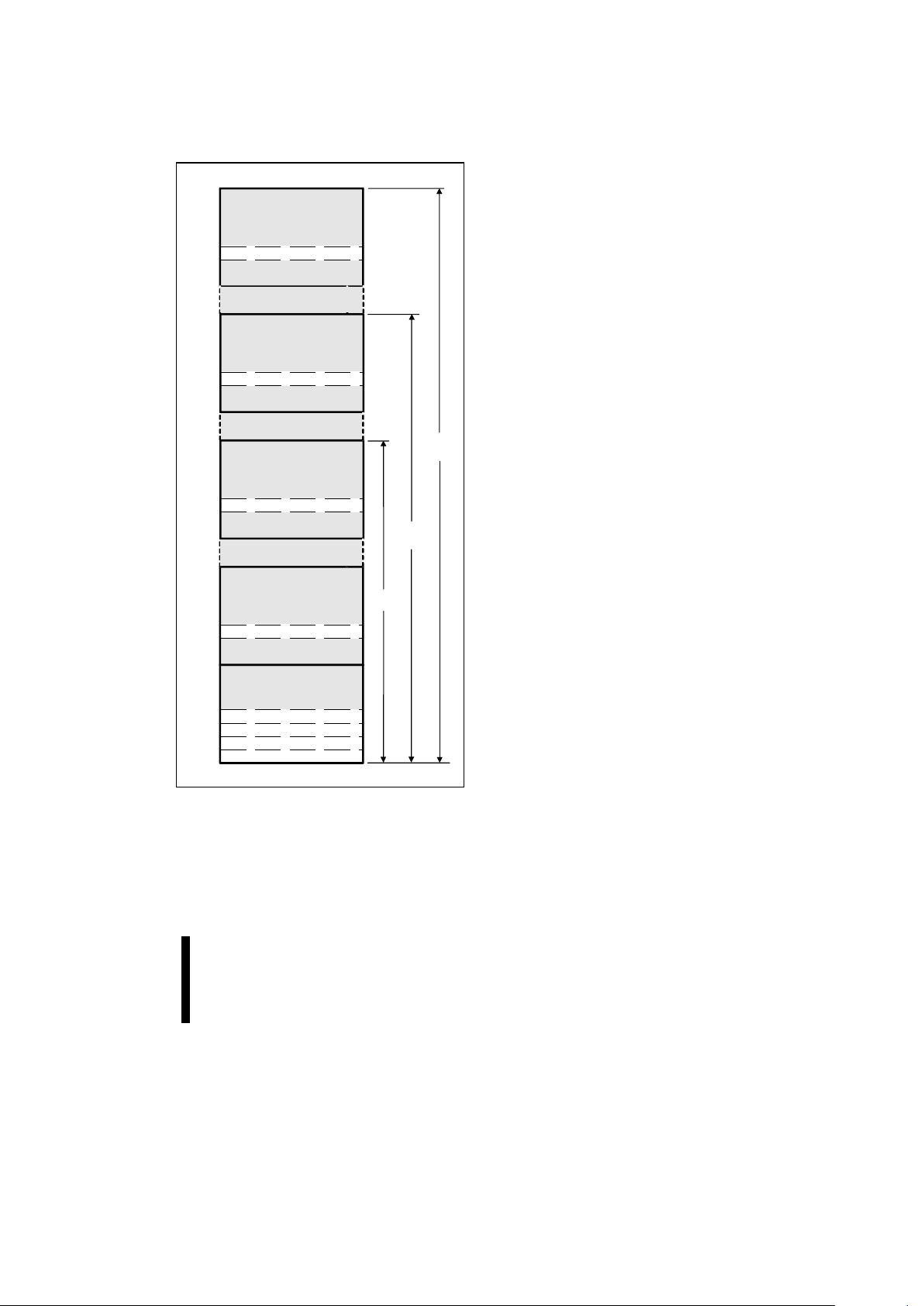
Figure 6. Device Identifier Code Memory Map
3.5 Read Identifier Codes
Operation
The read identifier codes operation outputs the
manufacturer code, device code, block lock
configuration codes for each bloc k, and mas ter lock
configuration code (see Figure 6). Using the
manufacturer and device codes, the system
software can automatical l y match the device with i ts
proper algorithms. The block lock and master lock
configuration codes identify locked and unlocked
blocks and master lock-bit setting.
3.6 Write
The CUI does not occupy an address able memory
location. It is wri tten when WE# and CE# are acti ve
and OE# = V
IH
. The address and data needed to
execute a command are latched on the risi ng edge
of WE# or CE# (whichever goes high first).
Standard microprocessor write timings are used.
Figure 18 illustrates a write operation.
4.0 COMMAND DEFINITIONS
When the VPP voltage ≤ V
PPLK
, read operations
from the status register, identif ier codes, or blocks
are enabled. Placing V
PPH1/2
on VPP enables
successful block erase, program, and lock-bit
configuration operations.
Device operations are selected by writing specific
commands into the CUI. Table 3 defines these
commands.
 Loading...
Loading...