Intel Corporation E28F008SA-L200 Datasheet

*Other brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, including infringement of any patent or
copyright, for sale and use of Intel products except as provided in Intel’s Terms and Conditions of Sale for such products. Intel retains the right to make
changes to these specifications at any time, without notice. Microcomputer Products may have minor variations to this specification known as errata.
December 1995COPYRIGHT©INTEL CORPORATION, 1995 Order Number: 290435-005
28F008SA-L
8-MBIT (1 MBIT x 8) FLASHFILETMMEMORY
Y
High-Density Symmetrically-Blocked
Architecture
Ð Sixteen 64-Kbyte Blocks
Y
Low-Voltage Operation
Ð
b
3.3Vg0.3V or 5.0Vg10% V
CC
Y
Extended Cycling Capability
Ð 10,000 Block Erase Cycles
Ð 160,000 Block Erase
Cycles per Chip
Y
Automated Byte Write and Block Erase
Ð Command User Interface
Ð Status Register
Y
System Performance Enhancements
Ð RY/BY
Ý
Status Output
Ð Erase Suspend Capability
Y
High-Performance Read
Ð 200 ns Maximum Access Time
Y
Deep Power-Down Mode
Ð 0.20 mAI
CC
Typical
Y
SRAM-Compatible Write Interface
Y
Hardware Data Protection Feature
Ð Erase/Write Lockout during Power
Transitions
Y
Industry Standard Packaging
Ð 40-Lead TSOP, 44-Lead PSOP
Y
ETOXTMIII Nonvolatile Flash
Technology
Ð 12V Byte Write/Block Erase
Intel’s 28F008SA-L 8 Mbit FlashFileTMMemory is the highest density nonvolatile read/write solution for solidstate storage. The 28F008SA-L’s extended cycling, symmetrically-blocked architecture, fast access time, write
automation and very low power consumption provide a more reliable, lower power, lighter weight and higher
performance alternative to traditional rotating disk technology. The 28F008SA-L brings new capabilities to
portable computing. Application and operating system software stored in resident flash memory arrays provide
instant-on, rapid execute-in-place and protection from obsolescence through in-system software updates.
Resident software also extends system battery life and increases reliability by reducing disk drive accesses.
For high-density data acquisition applications, the 28F008SA-L offers a more cost-effective and reliable alternative to SRAM and battery. Traditional high-density embedded applications, such as telecommunications,
can take advantage of the 28F008SA-L’s nonvolatility, blocking and minimal system code requirements for
flexible firmware and modular software designs.
The 28F008SA-L is offered in 40-lead TSOP (standard and reverse) and 44-lead PSOP packages. Pin assignments simplify board layout when integrating multiple devices in a flash memory array or subsystem. This
device uses an integrated Command User Interface and state machine for simplified block erasure and byte
write. The 28F008SA-L memory map consists of 16 separately erasable 64-Kbyte blocks.
Intel’s 28F008SA-L employs advanced CMOS circuitry for systems requiring low power consumption and
noise immunity. Its 200 ns access time provides superior performance when compared with magnetic storage
media. A deep power-down mode lowers power consumption to 0.66 mW typical thru V
CC
, crucial in portable
computing, handheld instrumentation and other low-power applications. The RP
Ý
power control input also
provides absolute data protection during system power-up/down.
Manufactured on Intel’s 0.8 micron ETOX process, the 28F008SA-L provides the highest levels of quality,
reliability and cost-effectiveness.
*Other brands and names are property of their respective owners.

28F008SA-L
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
The 28F008SA-L is a high-performance 8-Mbit
(8,388,608-bit) memory organized as 1 Mbyte
(1,048,576 bytes) of 8 bits each. Sixteen 64-Kbyte
(65,536-byte) blocks are included on the
28F008SA-L. A memory map is shown in Figure 6 of
this specification. A block erase operation erases
one of the sixteen blocks of memory in typically 2.0
seconds, independent of the remaining blocks.
Each block can be independently erased and written
10,000 cycles. Erase Suspend mode allows system software to suspend block erase to read data or
execute code from any other block of the
28F008SA-L.
The 28F008SA-L is available in the 40-lead TSOP
(Thin Small Outline Package, 1.2 mm thick) and 44-
lead PSOP (Plastic Small Outline) packages. Pinouts are shown in Figures 2 and 4 of this specification.
The Command User Interface serves as the interface between the microprocessor or microcontroller
and the internal operation of the 28F008SA-L.
Byte Write and Block Erase Automation allow
byte write and block erase operations to be executed using a two-write command sequence to the
Command User Interface. The internal Write State
Machine (WSM) automatically executes the algorithms and timings necessary for byte write and
block erase operations, including verifications,
thereby unburdening the microprocessor or microcontroller. Writing of memory data is performed in
byte increments typically within 11 ms, I
PP
byte
write and block erase currents are 10 mA typical,
30 mA maximum. V
PP
byte write and block erase
voltage is 11.4V to 12.6V.
The Status Register indicates the status of the
WSM and when the WSM successfully completes
the desired byte write or block erase operation.
The RY/BY
Ý
output gives an additional indicator of
WSM activity, providing capability for both hardware
signal of status (versus software polling) and status
masking (interrupt masking for background erase,
for example). Status polling using RY/BYÝminimizes both CPU overhead and system power consumption. When low, RY/BY
Ý
indicates that the
WSM is performing a block erase or byte write operation. RY/BY
Ý
high indicates that the WSM is ready
for new commands, block erase is suspended or the
device is in deep powerdown mode.
Maximum access time is 200 ns (t
ACC
) over the
commercial temperature range (0
§
Ctoa70§C) and
over V
CC
supply voltage range (3.0V to 3.6V and
4.5V to 5.5V). I
CC
active current (CMOS Read) is
5 mA typical, 12 mA maximum at 5 MHz,
3.3V
g
0.3V.
When the CE
Ý
and RPÝpins are at VCC, the I
CC
CMOS Standby mode is enabled.
A Deep Powerdown mode is enabled when the
RP
Ý
pin is at GND, minimizing power consumption
and providing write protection. I
CC
current in deep
powerdown is 0.20 mA typical. Reset time of 500 ns
is required from RP
Ý
switching high until outputs are
valid to read attempts. Equivalently, the device has a
wake time of 1 ms from RP
Ý
high until writes to the
Command User Interface are recognized by the
28F008SA-L. With RP
Ý
at GND, the WSM is reset
and the Status Register is cleared.
2
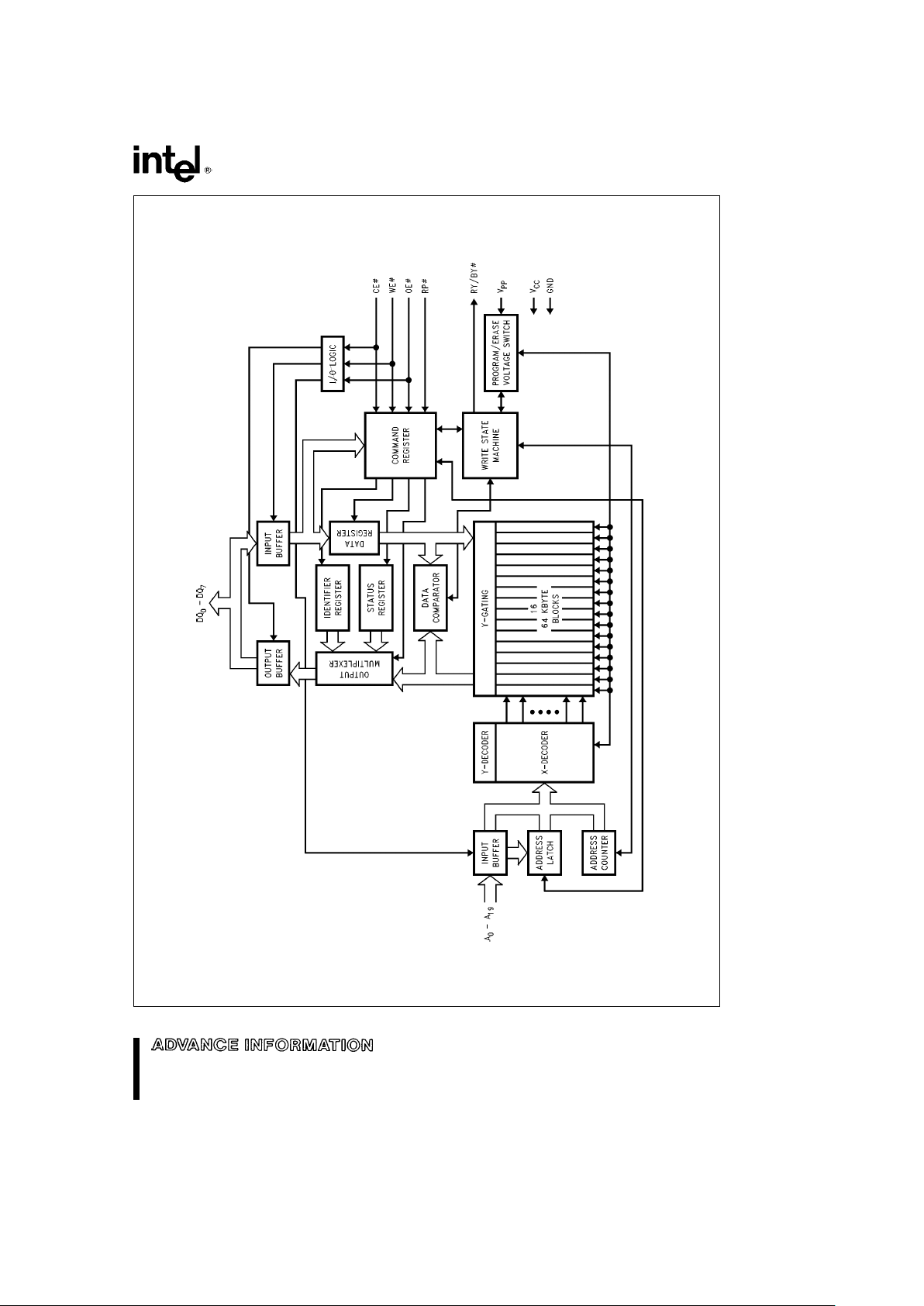
28F008SA-L
Figure 1. Block Diagram
290435– 1
3

28F008SA-L
Table 1. Pin Description
Symbol Type Name and Function
A0–A
19
INPUT ADDRESS INPUTS for memory addresses. Addresses are internally
latched during a write cycle.
DQ0–DQ7INPUT/OUTPUT DATA INPUT/OUTPUTS: Inputs data and commands during Command
User Interface write cycles; outputs data during memory array, Status
Register and Identifier read cycles. The data pins are active high and
float to tri-state off when the chip is deselected or the outputs are
disabled. Data is internally latched during a write cycle.
CE
Ý
INPUT CHIP ENABLE: Activates the device’s control logic, input buffers,
decoders, and sense amplifiers. CE
Ý
is active low; CEÝhigh deselects
the memory device and reduces power consumption to standby levels.
RP
Ý
INPUT RESET/ DEEP POWERDOWN: Puts the device in deep powerdown
mode. RP
Ý
is active low; RPÝhigh gates normal operation. RPÝalso
locks out block erase or byte write operations when active low, providing
data protection during power transitions. RP
Ý
active resets internal
automation. Exit from Deep Powerdown sets device to read-array mode.
OE
Ý
INPUT OUTPUT ENABLE: Gates the device’s outputs through the data buffers
during a read cycle. OE
Ý
is active low.
WE
Ý
INPUT WRITE ENABLE: Controls writes to the Command User Interface and
array blocks. WE
Ý
is active low. Addresses and data are latched on the
rising edge of the WEÝpulse.
RY/BY
Ý
OUTPUT READY/BUSYÝ: Indicates the status of the internal Write State
Machine. When low, it indicates that the WSM is performing a block
erase or byte write operation. RY/BY
Ý
high indicates that the WSM is
ready for new commands, block erase is suspended or the device is in
deep powerdown mode. RY/BY
Ý
is always active and does NOT float
to tri-state off when the chip is deselected or data outputs are disabled.
V
PP
BLOCK ERASE/BYTE WRITE POWER SUPPLY for erasing blocks of
the array or writing bytes of each block.
NOTE:
With V
PP
k
V
PPLMAX
, memory contents cannot be altered.
V
CC
DEVICE POWER SUPPLY (3.3Vg0.3V, 5Vg10%)
GND GROUND
4
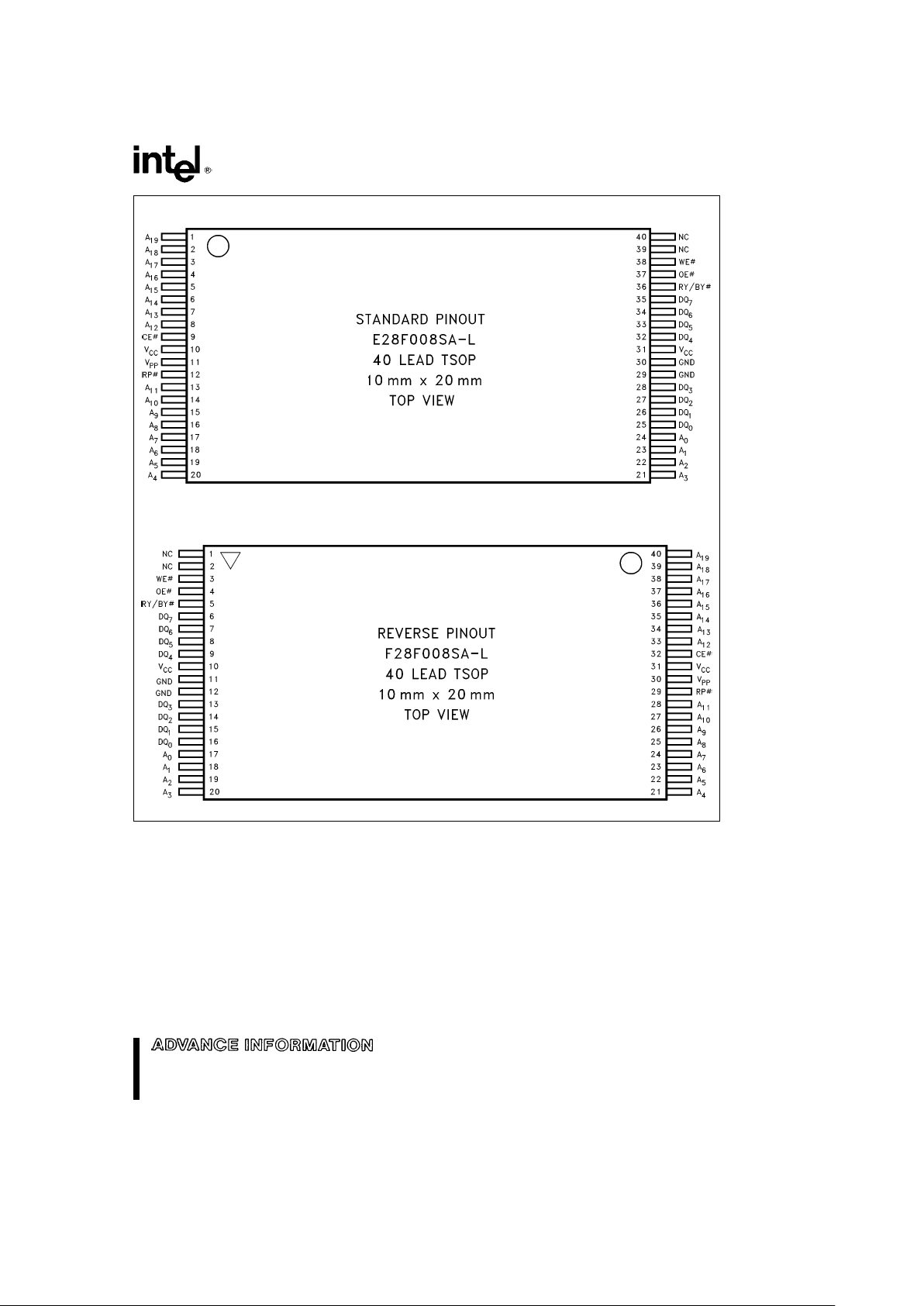
28F008SA-L
Standard Pinout
290435– 2
Reverse Pinout
290435– 3
Figure 2. TSOP Lead Configurations
5
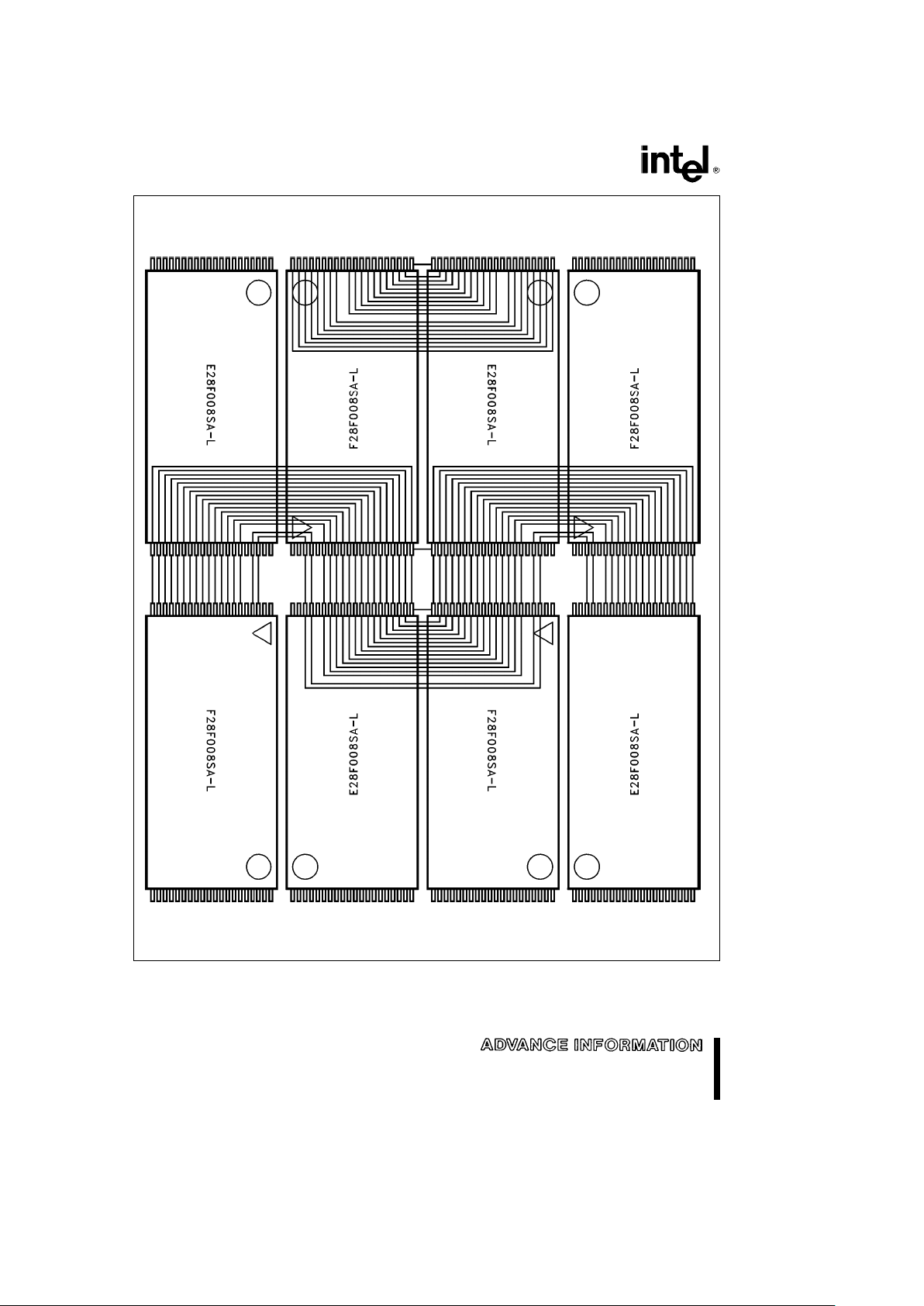
28F008SA-L
Figure 3. TSOP Serpentine Layout
NOTE:
1. Connect all V
CC
and GND pins of each device to common power supply outputs. DO NOT leave VCCor GND inputs
disconnected.
290435– 4
6
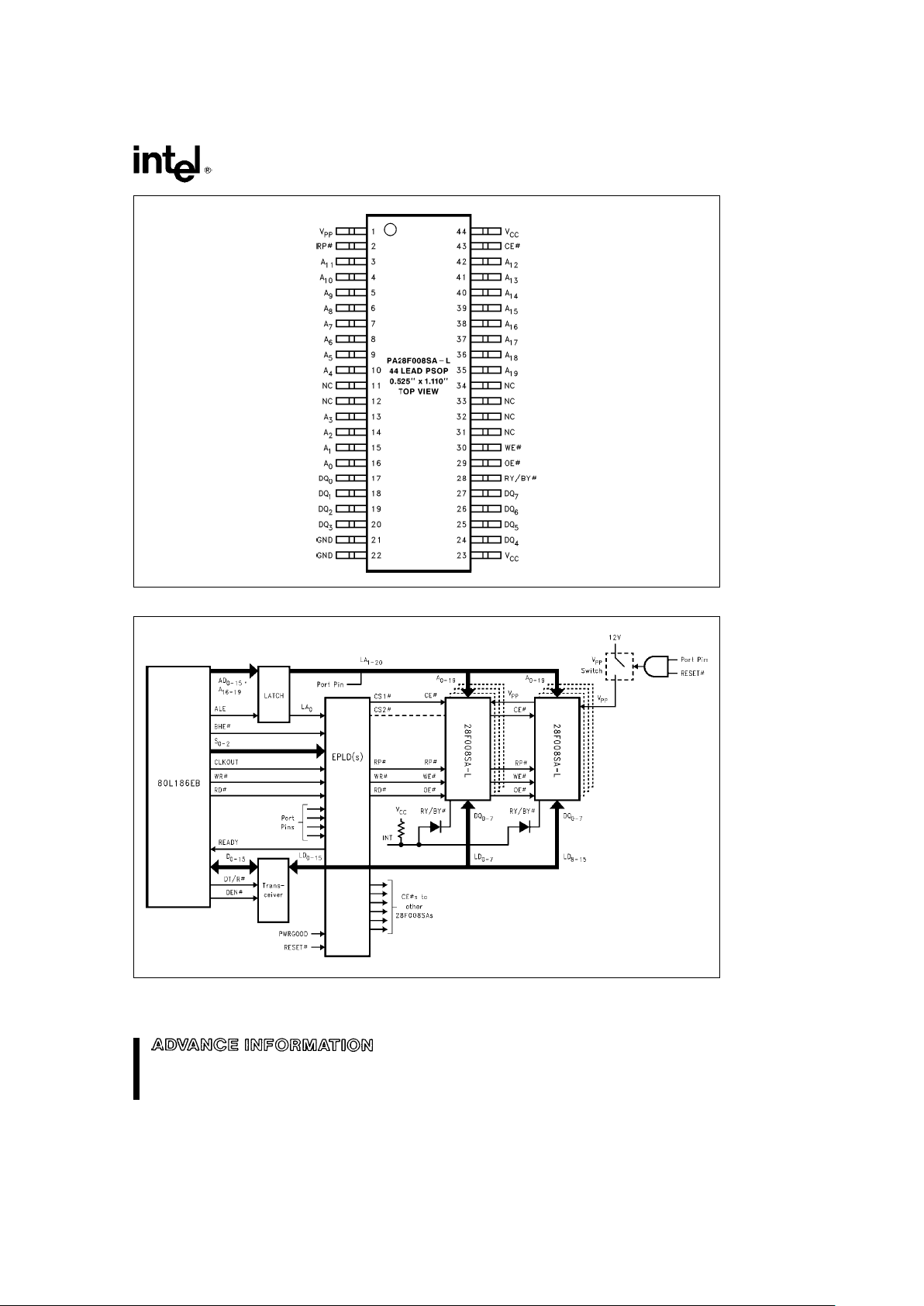
28F008SA-L
290435– 5
Figure 4. PSOP Lead Configuration
290435– 6
Figure 5. 28F008SA-L Array Interface to Intel3.3V 80L186EB Embedded Microprocessor
7
28F008SA-L
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
The 28F008SA-L includes on-chip write automation
to manage write and erase functions. The Write
State Machine allows for: 100% TTL-level control
inputs; fixed power supplies during block erasure
and byte write; and minimal processor overhead with
RAM-like interface timings.
After initial device powerup, or after return from
deep powerdown mode (see Bus Operations), the
28F008SA-L functions as a read-only memory. Manipulation of external memory-control pins allow array read, standby and output disable operations.
Both Status Register and intelligent identifiers can
also be accessed through the Command User Interface when V
PP
e
V
PPL
.
This same subset of operations is also available
when high voltage is applied to the V
PP
pin. In addi-
tion, high voltage on V
PP
enables successful block
erasure and byte writing of the device. All functions
associated with altering memory contentsÐbyte
write, block erase, status and intelligent identifierÐ
are accessed via the Command User Interface and
verified thru the Status Register.
Commands are written using standard microprocessor write timings. Command User Interface contents
serve as input to the WSM, which controls the block
erase and byte write circuitry. Write cycles also internally latch addresses and data needed for byte write
or block erase operations. With the appropriate command written to the register, standard microprocessor read timings output array data, access the Intelligent Identifier codes, or output byte write and block
erase status for verification.
Interface software to initiate and poll progress of internal byte write and block erase can be stored in
any of the 28F008SA-L blocks. This code is copied
to, and executed from, system RAM during actual
flash memory update. After successful completion of
byte write and/or block erase, code/data reads from
the 28F008SA-L are again possible via the Read Array command. Erase suspend/resume capability allows system software to suspend block erase to
read data and execute code from any other block.
FFFFF
64-Kbyte Block
EFFFF
F0000
64-Kbyte Block
DFFFF
E0000
64-Kbyte Block
CFFFF
D0000
64-Kbyte Block
BFFFF
C0000
64-byte Block
AFFFF
B0000
64-Kbyte Block
9FFFF
A0000
64-Kbyte Block
8FFFF
90000
64-Kbyte Block
7FFFF
80000
64-Kbyte Block
6FFFF
70000
64-Kbyte Block
5FFFF
60000
64-Kbyte Block
4FFFF
50000
64-Kbyte Block
3FFFF
40000
64-Kbyte Block
2FFFF
30000
64-Kbyte Block
1FFFF
20000
64-Kbyte Block
0FFFF
10000
64-Kbyte Block
00000
Figure 6. Memory Map
Command User Interface and Write
Automation
An on-chip state machine controls block erase and
byte write, freeing the system processor for other
tasks. After receiving the Erase Setup and Erase
Confirm commands, the state machine controls
block pre-conditioning and erase, returning progress
via the Status Register and RY/BY
Ý
output. Byte
write is similarly controlled, after destination address
and expected data are supplied. The program and
erase algorithms of past Intel flash memories are
now regulated by the state machine, including pulse
repetition where required and internal verification
and margining of data.
8

28F008SA-L
Data Protection
Depending on the application, the system designer
may choose to make the V
PP
power supply switchable (available only when memory byte writes/block
erases are required) or hardwired to V
PPH
. When
V
PP
e
V
PPL
, memory contents cannot be altered.
The 28F008SA-L Command User Interface architecture provides protection from unwanted byte write or
block erase operations even when high voltage is
applied to VPP. Additionally, all functions are disabled whenever V
CC
is below the write lockout volt-
age V
LKO
, or when RPÝis at VIL. The 28F008SA-L
accommodates either design practice and encourages optimization of the processor-memory interface.
The two-step byte write/block erase Command User
Interface write sequence provides additional software write protection.
BUS OPERATION
Flash memory reads, erases and writes in-system
via the local CPU. All bus cycles to or from the flash
memory conform to standard microprocessor bus
cycles.
Read
The 28F008SA-L has three read modes. The memory can be read from any of its blocks, and information can be read from the Intelligent Identifier or
Status Register. V
PP
can be at either V
PPL
or V
PPH
.
The first task is to write the appropriate read mode
command to the Command User Interface (array, Intelligent Identifier, or Status Register). The
28F008SA-L automatically resets to Read Array
mode upon initial device powerup or after exit from
deep powerdown. The 28F008SA-L has four control
pins, two of which must be logically active to obtain
data at the outputs. Chip Enable (CE
Ý
) is the device
selection control, and when active enables the selected memory device. Output Enable (OE
Ý
)isthe
data input/output (DQ
0
–DQ7) direction control, and
when active drives data from the selected memory
onto the I/O bus. RP
Ý
and WEÝmust also be at
V
IH
. Figure 10 illustrates read bus cycle waveforms.
Output Disable
With OEÝat a logic-high level (VIH), the device outputs are disabled. Output pins (DQ
0
–DQ7) are
placed in a high-impedance state.
Standby
CEÝat a logic-high level (VIH) places the
28F008SA-L in standby mode. Standby operation
disables much of the 28F008SA-L’s circuitry and
substantially reduces device power consumption.
The outputs (DQ
0
–DQ7) are placed in a high-impe-
dence state independent of the status of OE
Ý
.Ifthe
28F008SA-L is deselected during block erase or
byte write, the device will continue functioning and
consuming normal active power until the operation
completes.
Table 2. Bus Operations
Mode Notes RPÝCEÝOEÝWEÝA0VPPDQ
0–7
RY/BY
Ý
Read 1, 2, 3 V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
XXD
OUT
X
Output Disable 1, 2, 3 V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
X X High Z X
Standby 1, 2, 3 V
IH
V
IH
X X X X High Z X
Deep PowerDown 1, 2 V
IL
X X X X X High Z V
OH
Intelligent Identifier (Mfr) 1, 2 V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IHVIL
X 89H V
OH
Intelligent Identifier (Device) 1, 2 V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
VIHV
IH
X A1H V
OH
Write 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 V
IH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
XX DINX
NOTES:
1. Refer to DC Characteristics. When V
PP
e
V
PPL
, memory contents can be read but not written or erased.
2. X can be V
IL
or VIHfor control pins and addresses, and V
PPL
or V
PPH
for VPP. See DC Characteristics for V
PPL
and V
PPH
voltages.
3. RY/BY
Ý
is VOLwhen the Write State Machine is executing internal block erase or byte write algorithms. It is VOHwhen
the WSM is not busy, in Erase Suspend mode or deep powerdown mode.
4. Command writes involving block erase or byte write are only successfully executed when V
PP
e
V
PPH
.
5. Refer to Table 3 for valid D
IN
during a write operation.
9
 Loading...
Loading...