
E
ADVANCE INFORMATION
December 1997
Order Number: 290599-004
n
SmartVoltage Technology
Smart 5 Flash: 5 V Reads,
5 V or 12 V Writes
Increased Programming Throughput
at 12 V V
PP
n
Very High-Performance Read
2-, 4-Mbit: 60 ns Access Time
8-Mbit: 70 ns Access Time
n
x8 or x8/x16-Configurable Data Bus
n
Low Power Consumption
Max 60 mA Read Current at 5 V
Auto Power Savings: <1 mA Typical
Standby Current
n
Optimized Array Blocking Architecture
16-KB Protected Boot Block
Two 8-KB Parameter Blocks
96-KB and 128-KB Main Blocks
Top or Bottom Boot Locations
n
Extended Temperature Operation
–40 °C to +85 °C
n
Industry-Standard Packaging
40, 48-Lead TSOP, 44-Lead PSOP
n
Extended Block Erase Cycling
100,000 Cycles at Commercial Temp
10,000 Cycles at Extended Temp
n
Hardware Data Protection Feature
Absolute Hardware-Protection for
Boot Block
Write Lockout during Power
Transitions
n
Automated Word/Byte Program and
Block Erase
Command User Interface
Status Registers
Erase Suspend Capability
n
SRAM-Compatible Write Interface
n
Reset/Deep Power-Down Input
Provides Low-Power Mode and
Reset for Boot Operations
n
Pinout Compatible 2, 4, and 8 Mbit
n
ETOX™ Flash Technology
0.6 µ ETOX IV Initial Production
0.4 µ ETOX V Later Production
Intel’s Smart 5 boot block flas h memory family provides 2-, 4-, and 8-Mbit memories feat uring high-density,
low-cost, nonvolatile, read/write storage solutions for a wide range of applications. Their asymmetricallyblocked architecture, flexible voltage, and extended cycl ing provide highly flexible components s uitable for
embedded code execution applications, such as networking infrastructure and office automation.
Based on Intel’s boot block architecture, the Smart 5 boot block memory family enables quick and easy
upgrades for designs that demand state-of-the-art technology. This family of products comes in industrystandard packages: the 40-lead TS OP for very s pace-constrai ned 8-bit applicat ions, 48-lead TSOP, ideal for
board-constrained higher-performance 16-bit applications, and the rugged, easy to handle 44-lead PSOP.
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK
FLASH MEMORY FAMILY
2, 4, 8 MBIT
28F200B5, 28F400B5, 28F800B5, 28F004B5

Information in this document is provided in connection with Intel products. No license, express or implied, by estoppel or
otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this document. Except as provi ded in Intel ’s Terms and Condi tions of
Sale for such products, Intel assumes no liability whatsoever, and Intel disclaims any express or implied warranty, relating to
sale and/or use of Intel products including liability or warranties relating to fitness for a particular purpose, merchantability, or
infringement of any patent, copyright or other intellectual property right. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life
saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
The 28F200B5, 28F400/004B5, 28F800B5 may contain design defects or errors known are errata. Current characterized errata
are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be
obtained from:
Intel Corporation
P.O. Box 5937
Denver, CO 80217-9808
or call 1-800-548-4725
or visit Intel’s website at http://www.intel.com
COPYRIGHT © INTEL CORPORATION 1997, 1998 CG-041493
*Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.

E SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY
3
ADVANCE INFORMATION
CONTENTS
PAGE PAGE
1.0 INTRODUCTION .............................................5
1.1 New Features in the Smart 5 Memory
Products......................................................5
1.2 Product Overview.........................................5
2.0 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION..............................6
2.1 Pin Descriptions...........................................6
2.2 Pinouts.........................................................8
2.3 Memory Blocking Organization...................10
2.3.1 One 16-KB Boot Block.........................10
2.3.2 Two 8-KB Parameter Blocks................10
2.3.3 Main Blocks - One 96-KB + Additional
128-KB Blocks....................................10
3.0 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION .....................13
3.1 Bus Operations ..........................................13
3.1.1 Read....................................................13
3.1.2 Output Disable.....................................14
3.1.3 Standby...............................................14
3.1.4 Word/Byte Configuration......................14
3.1.5 Deep Power-Down/Reset....................14
3.1.6 Write....................................................14
3.2 Modes of Operation....................................16
3.2.1 Read Array..........................................16
3.2.2 Read Identifier.....................................16
3.2.3 Read Status Register ..........................16
3.2.4 Word/Byte Program.............................17
3.2.5 Block Erase.........................................17
3.3 Boot Block Locking ....................................23
3.3.1 V
PP
= VIL for Complete Protection .......24
3.3.2 WP# = V
IL
for Boot Block Locking .......24
3.3.3 RP# = V
HH
or WP# = VIH for Boot Block
Unlocking ...........................................24
3.3.4 Note for 8-Mbit 44-PSOP Package......24
4.0 DESIGN CONSIDERATIONS........................24
4.1 Power Consumption...................................24
4.1.1 Active Power .......................................24
4.1.2 Automatic Power Savings (APS) .........24
4.1.3 Standby Power....................................25
4.1.4 Deep Power-Down Mode.....................25
4.2 Power-Up/Down Operation.........................25
4.2.1 RP# Connected to System Reset ........25
4.3 Board Design .............................................25
4.3.1 Power Supply Decoupling....................25
4.3.2 VPP Trace on Printed Circuit Boards...25
5.0 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS..................26
5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings........................26
5.2 Operating Conditions..................................26
5.3 Capacitance...............................................27
5.4 DC Characteristics—Commercial and
Extended Temperature..............................27
5.5 AC Characteristics—Read Operations—
Commercial and Extended Temperature...31
5.6 Erase and Program Timings—Commercial
and Extended Temperature.......................32
5.7 AC Characteristics—Write Operations—
Commercial and Extended Temperature...33
6.0 ORDERING INFORMATION..........................35
7.0 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.......................36
APPENDIX A: Write State Machine: Current-
Next State Chart..........................................37
APPENDIX B: Product Block Diagram..............38
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY E
4
ADVANCE INFORMATION
REVISION HISTORY
Number Description
-001 Original Version
-002 Minor changes throughout document.
Section 3.1.5 and Figure 14 redone to clarify program/erase operation abort.
Information added to Table 2, Figure 1, and Section 3.3 to clarify WP# on 8-Mbit,
44-PSOP.
Read and Write Waveforms changed to numbered format.
Typical numbers removed from DC Characteristics and Erase/Program Timings.
-003 Minor text changes throughout document.
Figure 1, 44-PSOP pinout: mistake on pin 3 on 2-Mbit pinout corrected from A
17
to NC.
Specs t
EHQZ
and t
GHQZ
improved.
Explanations of program/erase abort commands reworked in Table 6, Command
Codes.
-004 Specifications for 28F004B5 40-TSOP version added; Erase suspend text and
flowchart updated for clarity (Section 3.2.5.1, Table 6, Figure 10)
E SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY
5
ADVANCE INFORMATION
1.0 INTRODUCTION
This datasheet contains specifications for 2-, 4-,
and 8-Mbit Smart 5 boot block flash memories.
Section 1.0 provides a feat ure overview. Sec tions
2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 describe the product and
functionality. Sect ion 5.0 details the electrical and
timing specifications for both commercial and
extended temperature operation. Final ly, Sections
6.0 and 7.0 provide ordering and reference
information.
1.1 New Features in the
Smart 5 Memory Products
The Smart 5 boot block flas h memory fami ly of fers
identical features with the BV/CV/BE/CE
SmartVoltage products, except the Smart 5 boot
block -B5 parts only support 5 V V
CC
read voltage.
The following differences dist inguish the Smart 5
boot block products from their predecessors:
• A delay is required if the part i s reset during an
in-progress program or erase operation.
• On the fly word-byte mode switching is no
longer supported. Word-byte mode must be
configured at power-up and remain stable
during operation.
• Write operations are no longer specified as
WE#- or CE#-controlled in favor of a simpler
“unified” write method, which is compatible
with either of the old methods.
1.2 Product Overview
The Smart 5 boot block memory family provides
pinout-compatible flash memories at the
2-, 4-, and 8-Mbit densities. The 28F200B5,
28F400B5, and 28F800B5 can be configured to
operate either in 16-bit or 8-bit bus mode, wit h the
data divided into individually erasable blocks. The
28F004B5 provides 8-bit operation in a compact
package.
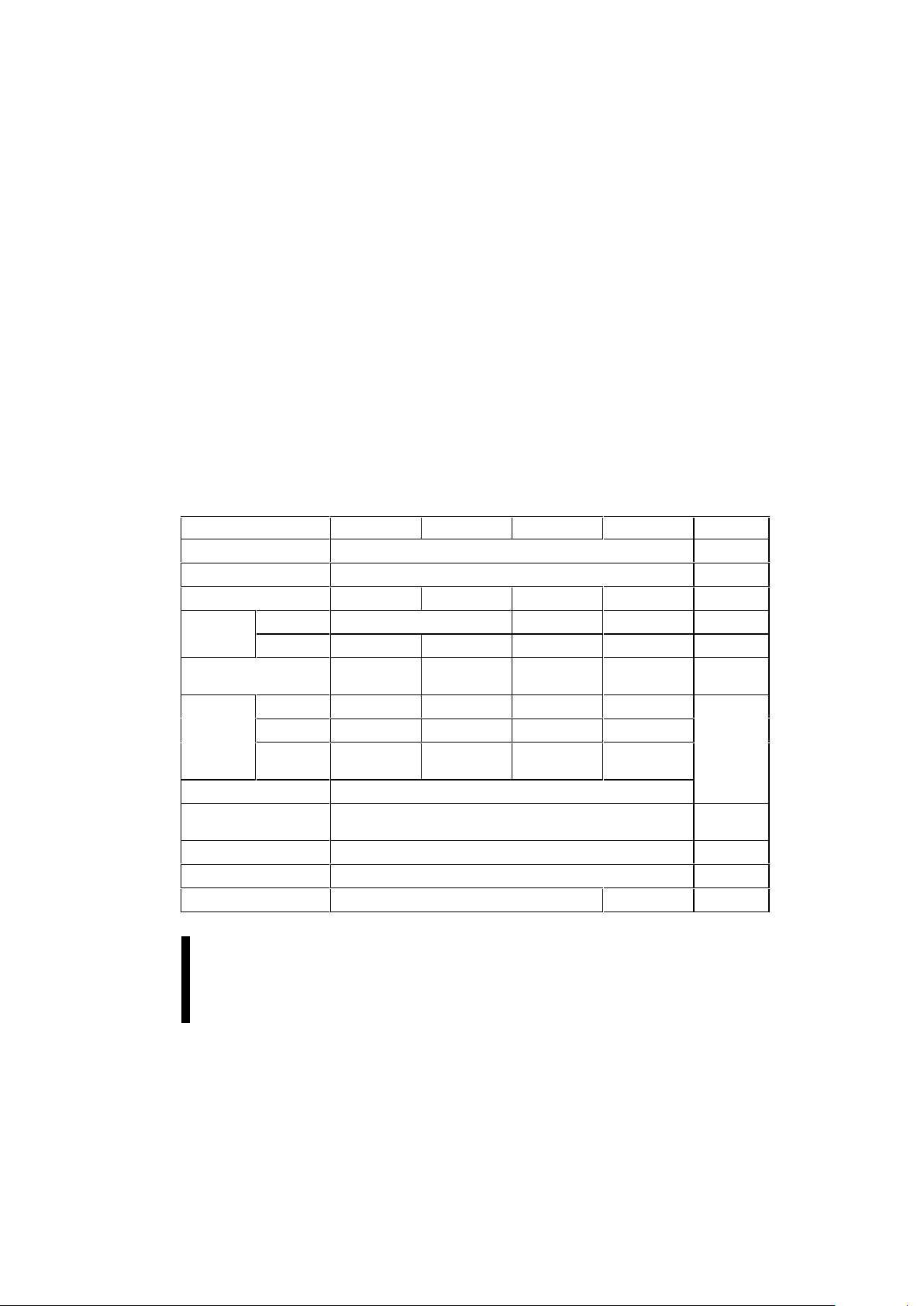
Table 1. Smart 5 Boot Block Family: Feature Summary
Feature 28F200B5 28F400B5 28F800B5 28F004B5 Reference
VCC Read Voltage 5 V ± 5%, 5 V ± 10% Section 5.2
VPP Prog/Erase Voltage 5 V ± 10% or 12 V ± 5%, auto-detected Section 5.2
Bus-width 8- or 16-bit 8- or 16-bit 8- or 16-bit 8-bit Table 2
Speed (ns) Commercial 60, 80 70, 90 60, 80 Section 5.6
Extended 80 80 90 not available Section 5.6
Memory Arrangement x8: 256K x 8
x16: 128K x 16
x8: 512K x 8
x16: 256K x 16
x8: 1M x 8
x16: 512K x 16
x8: 512K x 8
Blocking Boot 1 x 16 KB 1 x 16 KB 1 x 16 KB 1 x 16 KB Section 2.3,
Parameter 2 x 8 KB 2 x 8 KB 2 x 8 KB 2 x 8 KB Figs. 4-7
Main 1 x 96 KB
1 x 128 KB
1 x 96 KB
3 x 128 KB
1 x 96 KB
7 x 128 KB
1 x 96 KB
3 x 128 KB
Boot Location Top or Bottom boot locations available
Locking Boot Block lockable using WP# and/or RP#
All other blocks protectable using V
PP
switch
Section 3.3
Operating Temperature Commercial: 0 °C – +70 °C, Extended: -40 °C – +85 °C Section 5.2
Erase Cycling 100,000 cycles at Commercial, 10,000 cycles at Extended
Packages 44-PSOP, 48-TSOP 40-TSOP Figs. 1-2

SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY E
6
ADVANCE INFORMATION
SmartVoltage technology enables fast factory
programming and low-power designs. Specifically
designed for 5 V systems, Smart 5 components
support read operations at 5 V V
CC
and internally
configure to program/erase at 5 V or 12 V. The 12 V
V
PP
option renders the fastest program and erase
performance which will increase your factory
throughput. With the 5 V V
PP
option, VCC and V
PP
can be tied together for a simple 5 V design. In
addition, the dedicated V
PP
pin gives complete dat a
protection when V
PP
≤ V
PPLK
.
The memory array is asymmetrically divided into
blocks in an asymmetrical architecture to
accommodate microprocessors that boot from the
top (denoted by -T suffix ) or the bottom (-B suffix)
of the memory map. The blocks include a
hardware-lockable boot block (16,384 bytes), two
parameter blocks (8,192 bytes each) and main
blocks (one block of 98,304 bytes and additional
block(s) of 131,072 bytes). See Figures 4–7 for
memory maps. Each block can be independently
erased and programmed 100,000 times at
commercial temperature or 10,000 times at
extended temperature. Unlike erase operations,
which erase all locations within a block
simultaneously, each byte or word in the flash
memory can be programmed independentl y of other
memory locations.
The hardware-lockable boot block provides
complete code security for the k ernel code required
for system initialization. Locking and unlocking of
the boot block is controlled by WP# and/or RP#
(see Section 3.3 for details).
The system processor interfaces to the flash device
through a Command User Interface (CUI), using
valid command sequences to initiate device
automation. An internal Wri te State Machi ne (WSM)
automatically executes the algorithms and timings
necessary for program and erase operations. The
Status Register (SR) indicates the status of the
WSM and whether it successfully completed the
desired program or erase operation.
The Automatic Power Savings (APS) feature
substantially reduces active current when the
device is in stati c mode (addresses not switching).
In APS mode, the typical I
CCR
current is 1 mA.
When CE# and RP# pins are at V
CC
, the
component enters a CMOS s tandby mode. Driving
RP# to GND enables a deep power-down mode
which significantly reduces power consumption,
provides write protection, resets the device, and
clears the status register. A reset time (t
PHQV
) is
required from RP# switching high until output s are
valid. Likewise, t he device has a wake time (t
PHEL
)
from RP#-high until writes to the CUI are
recognized. See Section 4.2.
The deep power-down mode can also be used as a
device reset, allowing the flash to be reset along
with the rest of the system. For example, when the
flash memory powers-up, it automatically defaults
to the read array mode, but during a warm system
reset, where power continues uninterrupted to the
system components, the flash memory could
remain in a non-read mode, such as erase.
Consequently, the system Reset signal should be
tied to RP# to reset the memory to normal read
mode upon activation of the Res et signal. Thi s also
provides protection against unwanted command
writes due to invalid system bus conditions during
system reset or power-up/down sequences.
These devices are configurable at power-up for
either byte-wide or word-wide input/output using the
BYTE# pin. Please see Table 2 for a detailed
description of BYTE# operations, especially the
usage of the DQ
15/A–1
pin.
These Smart 5 memory products are available in
the 44-lead PSOP (Plasti c Small Outline P ackage),
which is ROM/EPROM-com patible, and the 48-lead
TSOP (Thin Small Outline Pack age, 1.2 mm thick)
as shown in Figure 1, and 2, respectively.
2.0 PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
This section describes the pinout and block
architecture of the device family.
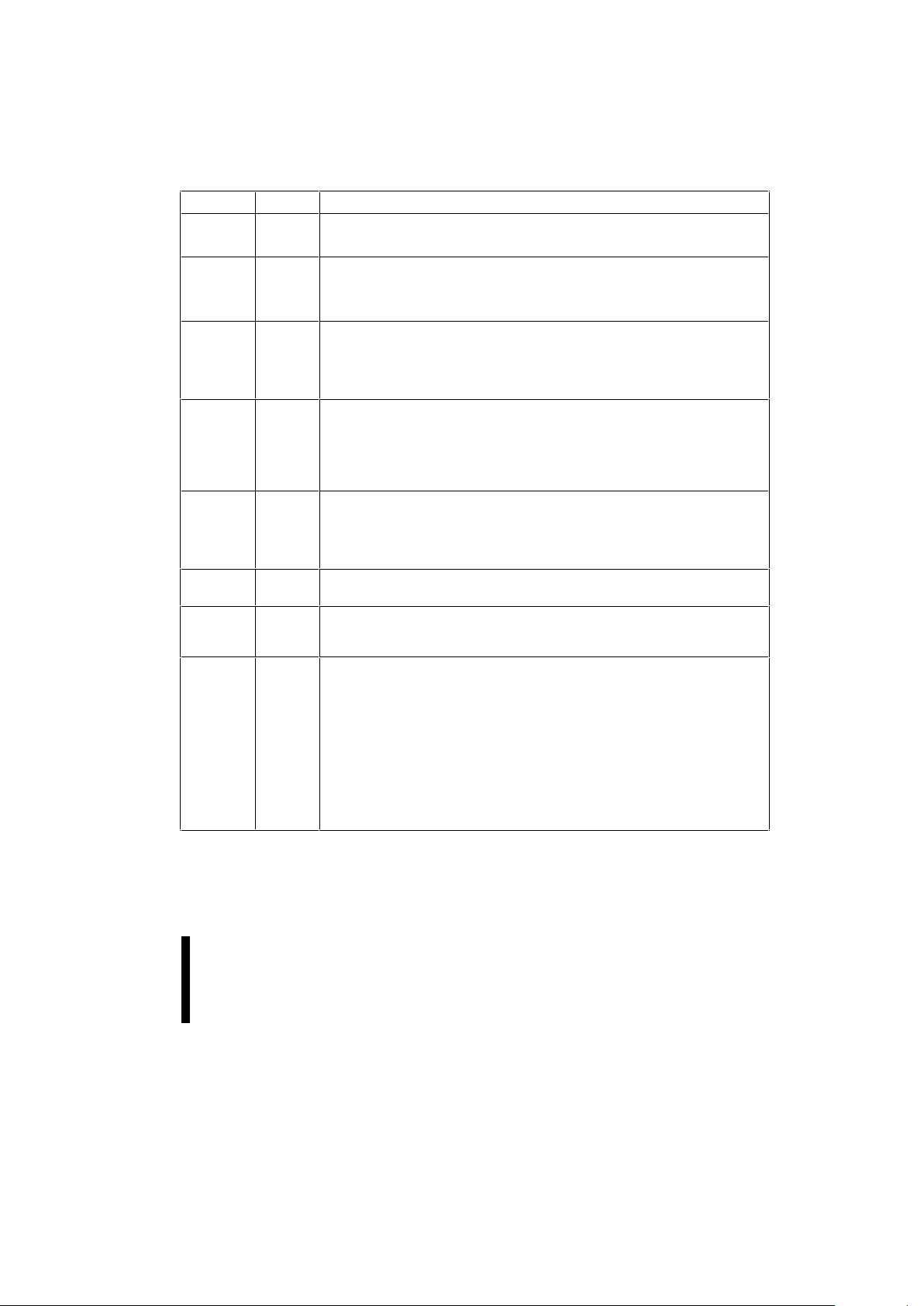
2.1 Pin Descriptions
The pin descriptions table details t he usage of eac h
of the device pins.
E SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY
7
ADVANCE INFORMATION
Table 2. Pin Descriptions
Symbol Type Name and Function
A0–A
18
INPUT
ADDRESS INPUTS for memory addresses. Addresses are internally latched
during a write cycle.
28F200: A[0–16], 28F400: A[0–17], 28F800: A[0–18], 28F004: A[0–18]
A
9
INPUT ADDRESS INPUT: When A9 is at VHH the signature mode is accessed. During
this mode, A
0
decodes between the manufacturer and device IDs. When BYTE#
is at a logic low, only the lower byte of the signatures are read. DQ
15/A–1
is a
don’t care in the signature mode when BYTE# is low.
DQ0–DQ
7
INPUT/
OUTPUT
DATA INPUTS/OUTPUTS: Inputs array data on the second CE# and WE# cycle
during a Program command. Inputs commands to the Command User Interface
when CE# and WE# are active. Data is internally latched during the write cycle.
Outputs array, intelligent identifier and status register data. The data pins float to
tri-state when the chip is de-selected or the outputs are disabled.
DQ8–DQ
15
INPUT/
OUTPUT
DATA INPUTS/OUTPUTS: Inputs array data on the second CE# and WE# cycle
during a Program command. Data is internally latched during the write cycle.
Outputs array data. The data pins float to tri-state when the chip is de-selected or
the outputs are disabled as in the byte-wide mode (BYTE# = “0”). In the byte-wide
mode DQ
15/A–1
becomes the lowest order address for data output on DQ0–DQ7.
Not applicable to 28F004B5.
CE# INPUT CHIP ENABLE: Activates the device’s control logic, input buffers, decoders and
sense amplifiers. CE# is active low. CE# high de-selects the memory device and
reduces power consumption to standby levels. If CE# and RP# are high, but not
at a CMOS high level, the standby current will increase due to current flow
through the CE# and RP# input stages.
OE# INPUT OUTPUT ENABLE: Enables the device’s outputs through the data buffers during
a read cycle. OE# is active low.
WE# INPUT WRITE ENABLE: Controls writes to the command register and array blocks. WE#
is active low. Addresses and data are latched on the rising edge of the WE#
pulse.
RP# INPUT RESET/DEEP POWER-DOWN: Uses three voltage levels (VIL, VIH, and VHH) to
control two different functions: reset/deep power-down mode and boot block
unlocking. It is backwards-compatible with the BX/BL/BV products.
When RP# is at logic low, the device is in reset/deep power-down mode,
which puts the outputs at High-Z, resets the Write State Machine, and draws
minimum current.
When RP# is at logic high, the device is in standard operation. When RP#
transitions from logic-low to logic-high, the device defaults to the read array mode.
When RP# is at V
HH
, the boot block is unlocked and can be programmed or
erased. This overrides any control from the WP# input.
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY E
8
ADVANCE INFORMATION
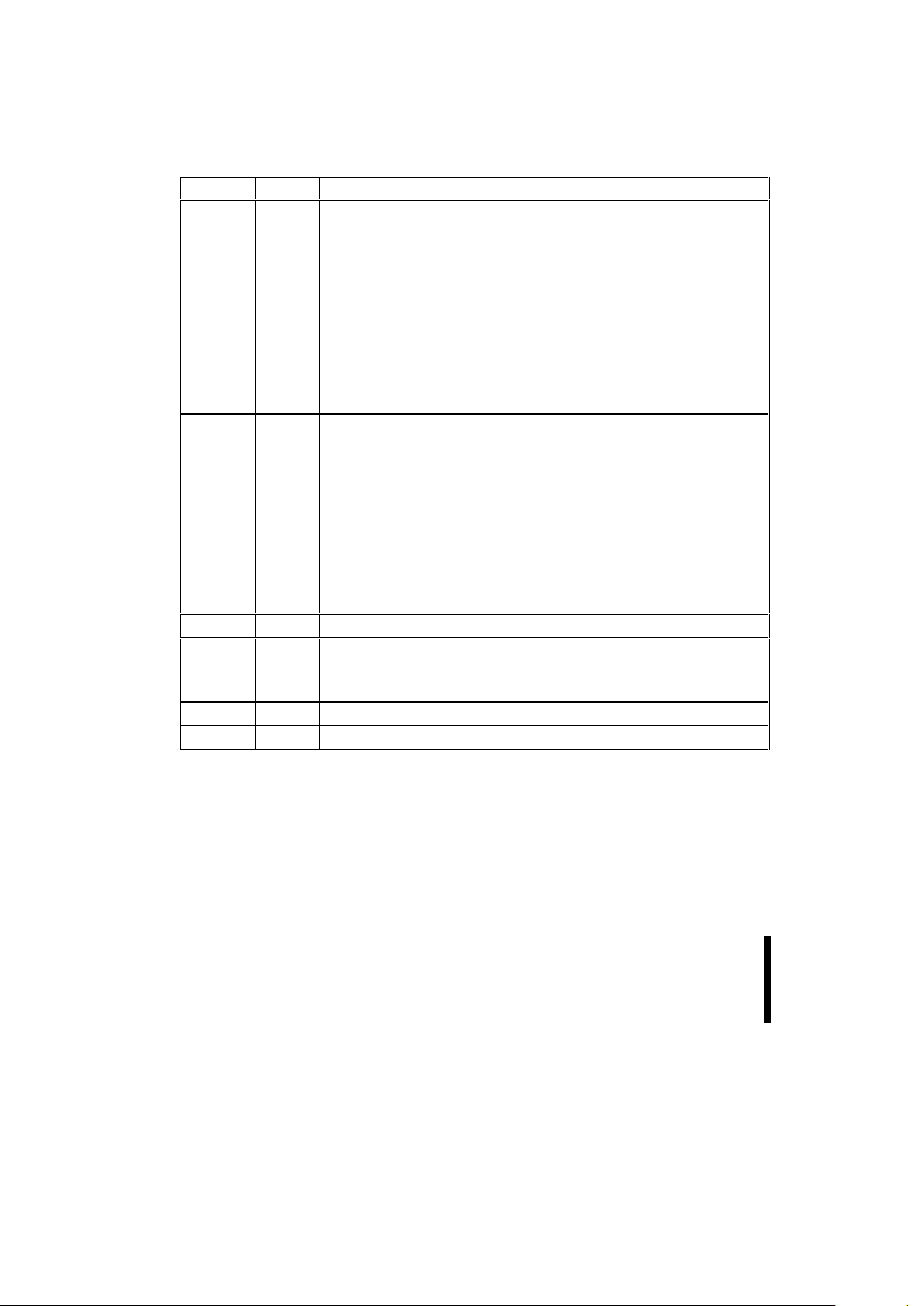
Table 2. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Symbol Type Name and Function
WP# INPUT WRITE PROTECT: Provides a method for unlocking the boot block with a logic
level signal in a system without a 12 V supply.
When WP# is at logic low, the boot block is locked, preventing program and
erase operations to the boot block. If a program or erase operation is attempted
on the boot block when WP# is low, the corresponding status bit (bit 4 for
program, bit 5 for erase) will be set in the status register to indicate the operation
failed.
When WP# is at logic high, the boot block is unlocked and can be
programmed or erased.
NOTE: This feature is overridden and the boot block unlocked when RP# is at
V
HH
. This pin can not be left floating. Because the 8-Mbit 44-PSOP package does
not have enough pins, it does not include this pin and thus 12 V on RP# is
required to unlock the boot block. See Section 3.3 for details on write protection.
BYTE# INPUT BYTE# ENABLE: Configures whether the device operates in byte-wide mode (x8)
or word-wide mode (x16). This pin must be set at power-up or return from deep
power-down and not changed during device operation. BYTE# pin must be
controlled at CMOS levels to meet the CMOS current specification in standby
mode.
When BYTE# is at logic low, the byte-wide mode is enabled, where data is
read and programmed on DQ
0
–DQ7 and DQ15/A–1 becomes the lowest order
address that decodes between the upper and lower byte. DQ
8
–DQ14 are tri-stated
during the byte-wide mode.
When BYTE# is at logic high, the word-wide mode is enabled, where data is
read and programmed on DQ
0
–DQ15.
Not applicable to 28F004B5.
V
CC
DEVICE POWER SUPPLY: 5.0 V ± 10%
V
PP
PROGRAM/ERASE POWER SUPPLY: For erasing memory array blocks or
programming data in each block, a voltage either of 5 V ± 10% or 12 V ± 5% must
be applied to this pin. When V
PP
< V
PPLK
all blocks are locked and protected
against Program and Erase commands.
GND GROUND: For all internal circuitry.
NC NO CONNECT: Pin may be driven or left floating.
2.2 Pinouts
Intel’s Smart 5 boot block architecture provides
upgrade paths in each package pinout up to the
8-Mbit density. The 44-lead PSOP pinout follows
the industry-standard ROM/EPROM pinout, as
shown in Figure 1. Designs with space concerns
should consider the 48-lead pinout shown in
Figure 2. Applications using an 8-bit bus can use
the 40-lead TSOP, which is av ailable for the 4-Mbi t
device only.
Pinouts for the corresponding 2-, 4-, and 8-Mbit
components are provided on the same di agram for
convenient reference. 2-Mbit pinouts are given on
the chip illustration in the center, with 4-Mbit and
8-Mbit pinouts going outward from the center.
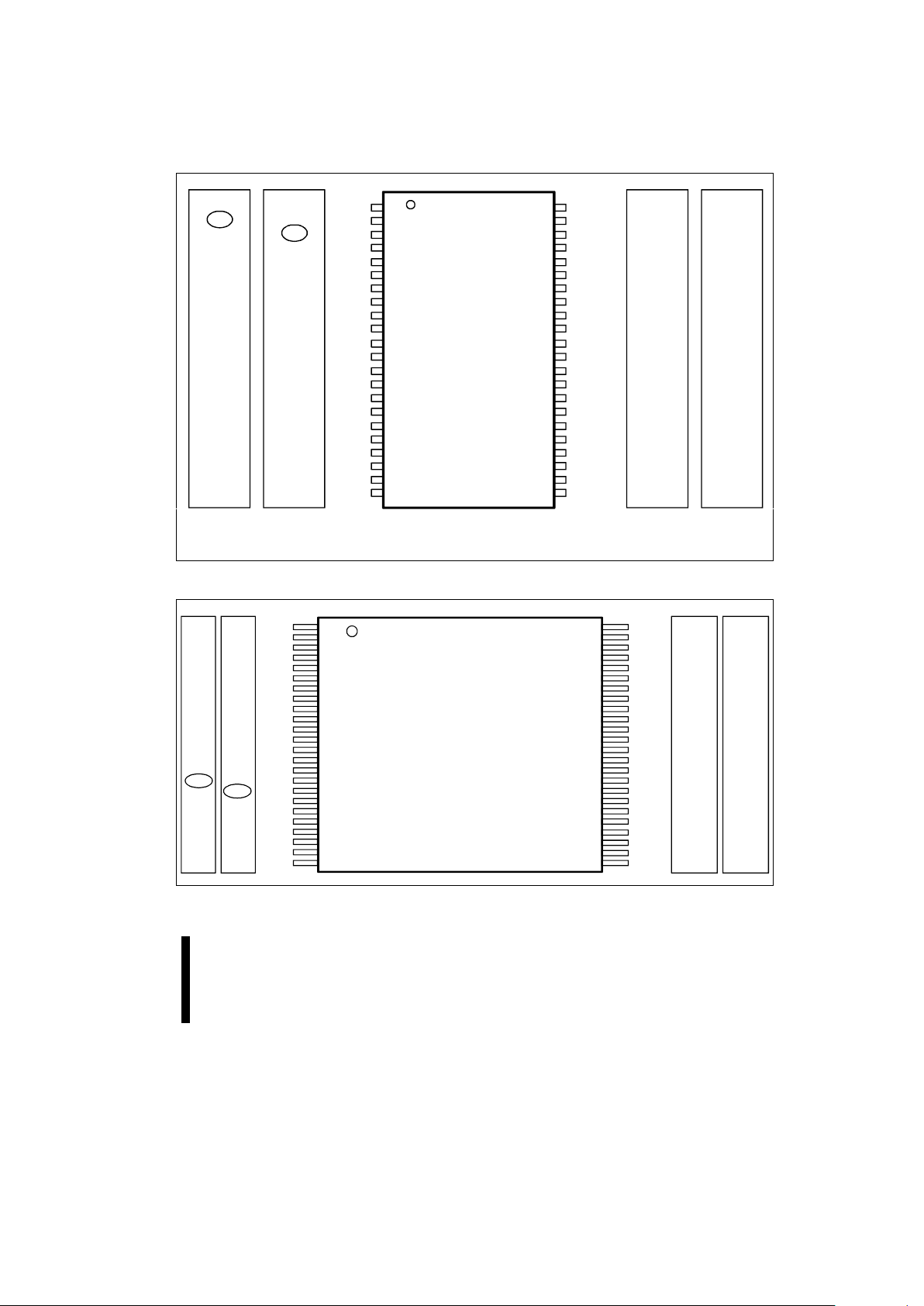
E SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY
9
ADVANCE INFORMATION
PA28F200
Boot Block
44-Lead PSOP
0.525" x 1.110"
TOP VIEW
GND
WE#
RP#
BYTE#
A
8
A
9
A
11
A
12
A
13
A
14
A
16
DQ
7
DQ
14
DQ
6
DQ
13
DQ
12
DQ
4
V
CC
DQ
5
A
10
A
15
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
22
21
20
19
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
28F400 28F400
DQ
15 -1
/A
CE#
GND
OE#
V
PP
28F800 28F800
A
17
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
A
2
A
1
A
0
DQ
0
DQ
8
DQ
1
DQ
9
DQ
2
DQ
10
DQ
3
DQ
11
A
18
CE#
GND
OE#
V
PP
A
17
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
A
2
A
1
A
0
DQ
0
DQ
8
DQ
1
DQ
9
DQ
2
DQ
10
DQ
3
DQ
11
WP#
CE#
GND
OE#
V
PP
NC
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
3
A
2
A
1
A
0
DQ
0
DQ
8
DQ
1
DQ
9
DQ
2
DQ
10
DQ
3
DQ
11
WP#
GND
WE#
RP#
BYTE#
A
8
A
9
A
11
A
12
A
13
A
14
A
16
DQ
7
DQ
14
DQ
6
DQ
13
DQ
12
DQ
4
V
CC
DQ
5
A
10
A
15
DQ
15 -1
/A
GND
WE#
RP#
BYTE#
A
8
A
9
A
11
A
12
A
13
A
14
A
16
DQ
7
DQ
14
DQ
6
DQ
13
DQ
12
DQ
4
V
CC
DQ
5
A
10
A
15
DQ
15 -1
/A
0599-01
NOTE: Pin 2 is WP# on 2- and 4-Mbit devices but A18 on the 8-Mbit because no other pins were available for the high order
address. Thus, the 8-Mbit in 44-PSOP cannot unlock the boot block without RP# = VHH. See Section 3.3 for details. To allow
upgrades to 8-Mbit from 2/4-Mbit in this package design pin 2 to control WP# at the 2/4-Mbit level and A18 at the 8-Mbit density.
Figure 1. 44-Lead PSOP Pinout Diagram
28F200
Boot Block
48-Lead TSOP
12 mm x 20 mm
TOP VIEW
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
24
23
22
21
20
19
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
CE#
OE#
GND
A
0
V
CC
GND
BYTE#
A
16
DQ
15
/A
-1
DQ
7
DQ
14
DQ
6
DQ
13
DQ
5
DQ
12
DQ
4
DQ
11
DQ
10
DQ
2
DQ
9
DQ
1
DQ
8
DQ
0
DQ
3
CE#
OE#
GND
A
0
V
CC
GND
BYTE#
A
16
DQ
15
/A
-1
DQ
7
DQ
14
DQ
6
DQ
13
DQ
5
DQ
12
DQ
4
DQ
11
DQ
10
DQ
2
DQ
9
DQ
1
DQ
8
DQ
0
DQ
3
CE#
OE#
GND
A
0
V
CC
GND
BYTE#
A
16
DQ
15
/A
-1
DQ
7
DQ
14
DQ
6
DQ
13
DQ
5
DQ
12
DQ
4
DQ
11
DQ
10
DQ
2
DQ
9
DQ
1
DQ
8
DQ
0
DQ
3
28F400 28F80028F40028F800
RP#
WE#
NC
NC
NC
WP#
A
15
A
14
A
13
A
12
A
11
A
10
A
9
A
8
V
PP
A
17
A
6
A
7
A
4
A
5
A
3
A
2
RP#
WE#
NC
NC
NC
WP#
A
15
A
14
A
13
A
12
A
11
A
10
A
9
A
8
V
PP
A
6
A
7
A
4
A
5
A
3
A
2
RP#
WE#
NC
NC
NC
WP#
A
18
A
15
A
14
A
13
A
12
A
11
A
10
A
9
A
8
V
PP
A
17
A
6
A
7
A
4
A
5
A
3
A
2
NC
NC
NC
1
A
1
A
1
A
0599-02
Figure 2. 48-Lead TSOP Pinout Diagram
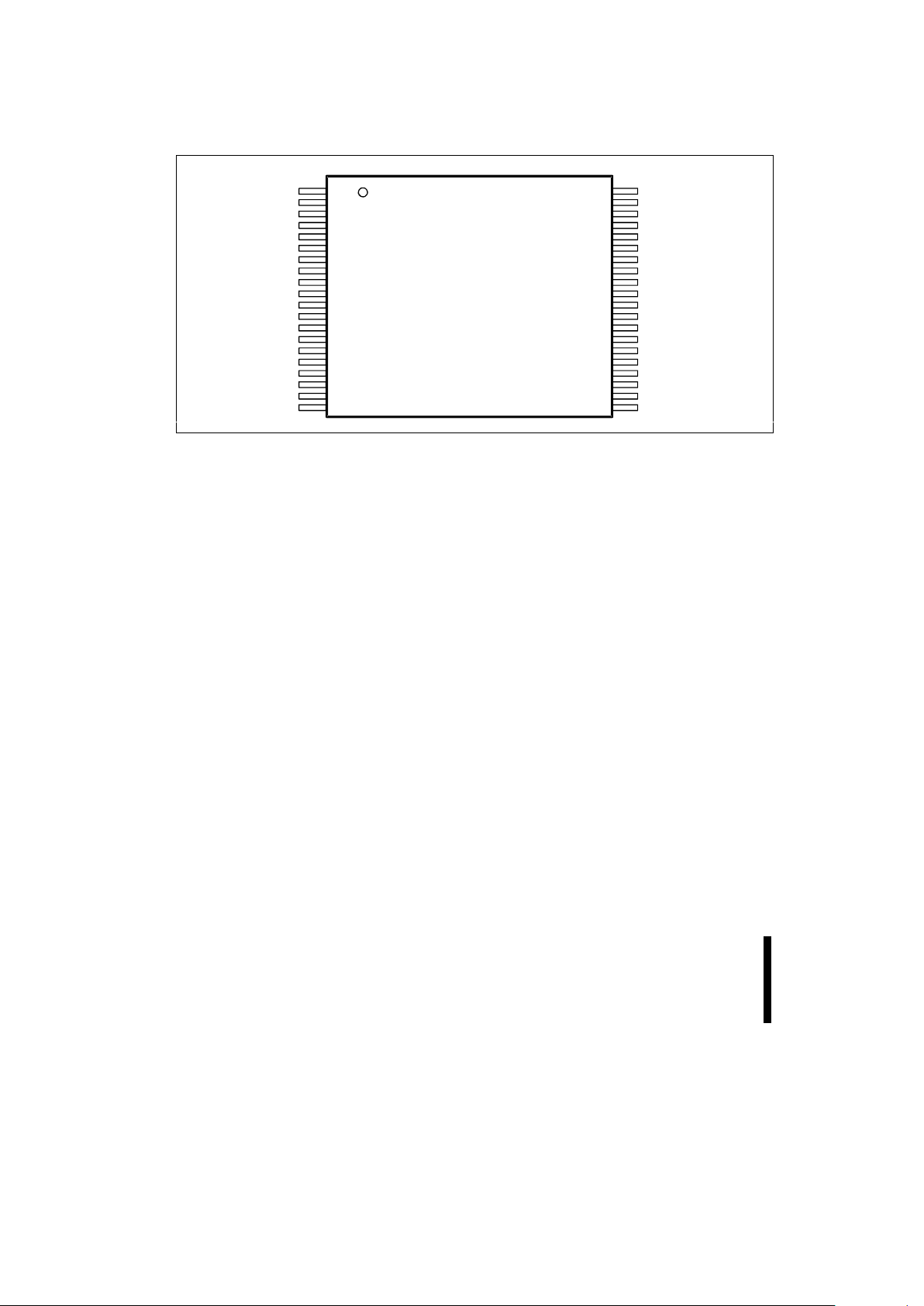
SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY E
10
ADVANCE INFORMATION
28F004 B5
Boot Block
40-Lead TSOP
10mmx20mm
TOPVIEW
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
20
19
17
18
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
16
15
A
1
A
2
A
3
RP#
WE#
V
PP
A
16
A
15
A
7
A
6
A
5
A
4
A
14
A
13
A
8
A
9
A
11
A
12
WP#
DQ
7
CE#
OE#
GND
A
0
DQ
6
DQ
5
DQ
4
DQ
2
DQ
1
DQ
0
V
CC
DQ
3
A
17
GND
NC
A
10
NC
NC
A
18
V
CC
Figure 3. 40-Lead TSOP Pinout Diagram (Available in 4-Mbit Only)
2.3 Memory Blocking Organization
The boot block product family features an
asymmetrically-blocked architecture providing
system memory integration. Each erase block can
be erased independently of the others up to
100,000 times for commerc ial temperature or up to
10,000 times for extended tem perature. The block
sizes have been chosen to optimize their
functionality for common appli cations of nonvolatile
storage. The combination of block sizes in the boot
block architecture allow the integration of several
memories into a single chip. For the address
locations of the blocks, see the memory maps in
Figures 4, 5, 6 and 7.
2.3.1 ONE 16-KB BOOT BLOCK
The boot block is intended to repl ace a dedicated
boot PROM in a microprocess or or microcontrollerbased system. The 16-Kbyte (16,384 bytes) boot
block is located at either the top (denoted by -T
suffix) or the bottom (-B suffix) of the address m ap
to accommodate different microproces sor protocols
for boot code location. This boot block features
hardware controllable write-protection to protec t the
crucial microprocessor boot code from accidental
modification. The protection of the boot block is
controlled using a combinati on of the V
PP
, RP#, and
WP# pins, as is detailed in Section 3.3.
2.3.2 TWO 8-KB PARAMETER BLOCKS
Each boot block component c ontains two parameter
blocks of 8 Kbytes (8,192 bytes) each to facilitate
storage of frequently updated s mall param eters t hat
would normally require an EEPROM. By using
software techniques, the byte-rewrite functionality
of EEPROMs can be emulated. These tec hniques
are detailed in Intel’s application note,
AP-604
Using Intel’s Boot B lock Flash Memory Parameter
Blocks to Replace EEPROM
. The parameter blocks
are not write-protectable.
2.3.3 MAIN BLOCKS - ONE 96-KB +
ADDITIONAL 128-KB BLOCKS
After the allocation of address space to the boot
and parameter blocks, the remainder is divided into
main blocks for data or code storage. Each device
contains one 96-Kbyte (98,304 byte) block and
additional 128-Kbyte (131,072 byte) blocks. The
2-Mbit has one 128-KB block; the 4-M bit , t hree; and
the 8-Mbit, seven.

E SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY
11
ADVANCE INFORMATION
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
00000H
0FFFFH
10000H
1FFFFH
20000H
2FFFFH
30000H
3FFFFH
40000H
4FFFFH
50000H
5FFFFH
60000H
6FFFFH
70000H
7BFFFH
7C000H
7CFFFH
7D000H
7DFFFH
7E000H
7FFFFH
28F800-T
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
00000H
0FFFFH
10000H
1FFFFH
20000H
2FFFFH
30000H
3BFFFH
3C000H
3CFFFH
3D000H
3DFFFH
3E000H
3FFFFH
28F400-T
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
00000H
0FFFFH
10000H
1BFFFH
1C000H
1CFFFH
1D000H
1DFFFH
1E000H
1FFFFH
28F200-T
0599-03
NOTE: Word addresses shown.
Figure 4. Word-Wide x16-Mode Memory Maps (Top Boot)
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
7FFFFH
70000H
6FFFFH
60000H
5FFFFH
50000H
4FFFFH
40000H
3FFFFH
30000H
2FFFFH
20000H
1FFFFH
10000H
0FFFFH
04000H
03FFFH
03000H
02FFFH
02000H
01FFFH
00000H
28F800-B
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
3FFFFH
30000H
2FFFFH
20000H
1FFFFH
10000H
0FFFFH
04000H
03FFFH
03000H
02FFFH
02000H
01FFFH
00000H
28F400-B
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
1FFFFH
10000H
0FFFFH
04000H
03FFFH
03000H
02FFFH
02000H
01FFFH
00000H
28F200-B
0599-04
NOTE: Word addresses shown.
Figure 5. Word-Wide x16-Mode Memory Maps (Bottom Boot)

SMART 5 BOOT BLOCK MEMORY FAMILY E
12
ADVANCE INFORMATION
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
00000H
1FFFFH
20000H
3FFFFH
40000H
5FFFFH
60000H
7FFFFH
80000H
9FFFFH
A0000H
BFFFFH
C0000H
DFFFFH
E0000H
F7FFFH
F8000H
F9FFFH
FA000H
FBFFFH
FC000H
FFFFFH
28F800-T
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
00000H
1FFFFH
20000H
3FFFFH
40000H
5FFFFH
60000H
77FFFH
78000H
79FFFH
7A000H
7BFFFH
7C000H
7FFFFH
28F400-T
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
00000H
1FFFFH
20000H
37FFFH
38000H
39FFFH
3A000H
3BFFFH
3C000H
3FFFFH
28F200-T
Byte-Mode Addresses
0599-05
NOTE: In x8 operation, the least significant system address should be connected to A-1.
Figure 6. Byte-Wide x8-Mode Memory Maps (Top Boot)
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
28F200-B
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
28F400-B
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
16-Kbyte BOOT BLOCK
8-Kbyte PARAMETER BLOCK
96-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
128-Kbyte MAIN BLOCK
FFFFFH
E0000H
DFFFFH
C0000H
BFFFFH
A0000H
9FFFFH
80000H
7FFFFH
60000H
5FFFFH
40000H
3FFFFH
20000H
1FFFFH
08000H
07FFFH
06000H
05FFFH
04000H
03FFFH
00000H
28F800-B
7FFFFH
60000H
5FFFFH
40000H
3FFFFH
20000H
1FFFFH
08000H
07FFFH
06000H
05FFFH
04000H
03FFFH
00000H
3FFFFH
20000H
1FFFFH
08000H
07FFFH
06000H
05FFFH
04000H
03FFFH
00000H
Byte-Mode Addresses
0599-06
NOTE: In x8 operation, the least significant system address should be connected to A-1.
Figure 7. Byte-Wide x8-Mode Memory Maps (Bottom Boot)
 Loading...
Loading...