Intel E5310 - Xeon 1.6 GHz 8M L2 Cache 1066MHz FSB LGA771 Active Quad-Core Processor, Xeon 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 1

Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor
5300 Series
Datasheet
November 2006
Order Number: 315569, Revision: 001
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER,
AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING
LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY
PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving,
life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel
reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future
changes to them.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the
product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Enabling Execute Disable Bit functionality requires a PC with a processor with Execute Disable Bit capability and a supporting
operating system. Check with your PC manufacturer on whether your system delivers Execute Disable Bit functionality. Further
details on Execute Disable can be found at http://www3.intel.com/cd/ids/developer/asmo-na/eng/149308.htm.
Intel® Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, virtual machine monitor (VMM) and
applications enabled for virtualization technology. Functionality, performance or other virtualization technology benefits will vary
depending on hardware and software configurations. Virtualization technology-enabled BIOS and VMM applications are currently in
development.
Intel® 64 architecture requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, OS, device drivers and applications enabled for
Intel® 64. Processor will not operate (including 32-bit operation) without an Intel EM64T-enabled BIOS. Performance will vary
depending on your hardware and software configurations. Intel EM64T-enabled OS, BIOS, device drivers and applications may not
be available. Check with your vendor for more information.
Copies of documents which have an ordering number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be
obtained by calling 1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Intel, Pentium, Intel Xeon, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology, Intel Virtualization Technology (Intel VT) and Intel logo are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2006, Intel Corporation
2 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction.................................................................................................................9
1.1 Terminology ..................................................................................................... 11
1.2 State of Data .................................................................................................... 13
1.3 References ....................................................................................................... 13
2 Electrical Specifications ............................................................................................... 15
2.1 Front Side Bus and GTLREF ................................................................................ 15
2.2 Power and Ground Lands.................................................................................... 16
2.3 Decoupling Guidelines........................................................................................ 16
2.3.1 VCC Decoupling...................................................................................... 16
2.3.2 VTT Decoupling ...................................................................................... 16
2.3.3 Front Side Bus AGTL+ Decoupling ............................................................ 17
2.4 Front Side Bus Clock (BCLK[1:0]) and Processor Clocking ....................................... 17
2.4.1 Front Side Bus Frequency Select Signals (BSEL[2:0]).................................. 18
2.4.2 PLL Power Supply................................................................................... 19
2.5 Voltage Identification (VID) ................................................................................ 19
2.6 Reserved, Unused, or Test Signals....................................................................... 21
2.7 Front Side Bus Signal Groups.............................................................................. 22
2.8 CMOS Asynchronous and Open Drain Asynchronous Signals .................................... 24
2.9 Test Access Port (TAP) Connection....................................................................... 24
2.10 Platform Environmental Control Interface (PECI) DC Specifications........................... 24
2.10.1 DC Characteristics .................................................................................. 24
2.10.2 Input Device Hysteresis .......................................................................... 25
2.11 Mixing Processors.............................................................................................. 26
2.12 Absolute Maximum and Minimum Ratings ............................................................. 26
2.13 Processor DC Specifications ................................................................................ 27
2.13.1 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines (FMB)...................................................... 27
2.13.2 VCC Overshoot Specification .................................................................... 33
2.13.3 Die Voltage Validation............................................................................. 34
2.14 AGTL+ FSB Specifications................................................................................... 34
3 Mechanical Specifications............................................................................................. 39
3.1 Package Mechanical Drawings ............................................................................. 39
3.2 Processor Component Keepout Zones................................................................... 43
3.3 Package Loading Specifications ........................................................................... 43
3.4 Package Handling Guidelines............................................................................... 44
3.5 Package Insertion Specifications.......................................................................... 44
3.6 Processor Mass Specifications ............................................................................. 44
3.7 Processor Materials............................................................................................ 44
3.8 Processor Markings............................................................................................ 45
3.9 Processor Land Coordinates ................................................................................ 45
4 Land Listing ............................................................................................................... 49
4.1 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Pin Assignments ........................... 49
4.1.1 Land Listing by Land Name...................................................................... 49
4.1.2 Land Listing by Land Number................................................................... 60
5 Signal Definitions ....................................................................................................... 71
5.1 Signal Definitions .............................................................................................. 71
6 Thermal Specifications ................................................................................................ 79
6.1 Package Thermal Specifications........................................................................... 79
6.1.1 Thermal Specifications ............................................................................ 79
6.1.2 Thermal Metrology ................................................................................. 83
6.2 Processor Thermal Features................................................................................ 84
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 3
Page 4

6.2.1 Thermal Monitor Features ........................................................................84
6.2.2 Thermal Monitor (TM1)............................................................................84
6.2.3 Thermal Monitor 2 ..................................................................................85
6.2.4 On-Demand Mode...................................................................................86
6.2.5 PROCHOT# Signal ..................................................................................87
6.2.6 FORCEPR# Signal ...................................................................................87
6.2.7 THERMTRIP# Signal................................................................................88
6.3 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) ......................................................88
6.3.1 Introduction...........................................................................................88
6.3.2 PECI Specifications .................................................................................89
7 Features ....................................................................................................................91
7.1 Power-On Configuration Options ..........................................................................91
7.2 Clock Control and Low Power States.....................................................................91
7.2.1 Normal State .........................................................................................92
7.2.2 HALT or Extended HALT State...................................................................92
7.2.3 Stop-Grant State ....................................................................................94
7.2.4 Extended HALT Snoop or HALT Snoop State, Stop Grant
Snoop State...........................................................................................94
7.3 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology...............................................................95
8 Boxed Processor Specifications .....................................................................................97
8.1 Introduction......................................................................................................97
8.2 Mechanical Specifications....................................................................................99
8.2.1 Boxed Processor Heat Sink Dimensions (CEK).............................................99
8.2.2 Boxed Processor Heat Sink Weight ..........................................................107
8.2.3 Boxed Processor Retention Mechanism and Heat Sink
Support (CEK)......................................................................................107
8.3 Electrical Requirements ....................................................................................107
8.3.1 Fan Power Supply (Active CEK)...............................................................107
8.3.2 Boxed Processor Cooling Requirements.................................................... 108
8.4 Boxed Processor Contents.................................................................................109
9 Debug Tools Specifications .........................................................................................111
9.1 Debug Port System Requirements......................................................................111
9.2 Target System Implementation..........................................................................111
9.2.1 System Implementation.........................................................................111
9.3 Logic Analyzer Interface (LAI) ...........................................................................111
9.3.1 Mechanical Considerations .....................................................................112
9.3.2 Electrical Considerations ........................................................................112
4 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 5

Figures
2-1 Input Device Hysteresis ..................................................................................... 25
2-2 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Load Current versus Time............. 29
2-3 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Load Current versus Time ............ 30
2-4 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series VCC Static and
Transient Tolerance Load Lines........................................................................... 31
2-5 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series VCC Static and
Transient Tolerance Load Lines........................................................................... 32
2-6 VCC Overshoot Example Waveform...................................................................... 34
2-7 Electrical Test Circuit ......................................................................................... 36
2-8 Differential Clock Waveform................................................................................ 36
2-9 Differential Clock Crosspoint Specification............................................................. 37
3-1 Processor Package Assembly Sketch .................................................................... 39
3-2 Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 3)............................................................ 40
3-3 Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 3)............................................................ 41
3-4 Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 3 of 3)............................................................ 42
3-5 Processor Top-side Markings (Example)................................................................ 45
3-6 Processor Land Coordinates, Top View.................................................................. 46
3-7 Processor Land Coordinates, Bottom View............................................................. 47
6-1 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Thermal Profile ........................... 81
6-2 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profiles.......................... 82
6-3 Case Temperature (TCASE) Measurement Location ................................................ 84
6-4 Thermal Monitor 2 Frequency and Voltage Ordering ............................................... 86
6-5 PECI Topology .................................................................................................. 88
6-6 Conceptual Fan Control Diagram For A PECI-Based Platform.................................... 89
7-1 Stop Clock State Machine ................................................................................... 93
8-1 Boxed Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series 1U Passive/3U+
Active Combination Heat Sink (With Removable Fan) ............................................. 97
8-2 Boxed Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series 2U Passive Heat Sink ........... 98
8-3 2U Passive Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Processor
Thermal Solution (Exploded View) ....................................................................... 98
8-4 Top Side Board Keepout Zones (Part 1).............................................................. 100
8-5 Top Side Board Keepout Zones (Part 2).............................................................. 101
8-6 Bottom Side Board Keepout Zones..................................................................... 102
8-7 Board Mounting-Hole Keepout Zones ................................................................. 103
8-8 Volumetric Height Keep-Ins .............................................................................. 104
8-9 4-Pin Fan Cable Connector (For Active CEK Heat Sink) ......................................... 105
8-10 4-Pin Base Board Fan Header (For Active CEK Heat Sink)...................................... 106
8-11 Fan Cable Connector Pin Out for 4-Pin Active CEK Thermal Solution ....................... 108
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 5
Page 6

Tables
1-1 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Features.......................................10
2-1 Core Frequency to FSB Multiplier Configuration ......................................................18
2-2 BSEL[2:0] Frequency Table.................................................................................18
2-3 Voltage Identification Definition ...........................................................................20
2-4 Loadline Selection Truth Table for LL_ID[1:0] ........................................................21
2-5 Market Segment Selection Truth Table for MS_ID[1:0] ...........................................21
2-6 FSB Signal Groups .............................................................................................22
2-7 AGTL+ Signal Description Table...........................................................................23
2-8 Non AGTL+ Signal Description Table.....................................................................23
2-9 Signal Reference Voltages...................................................................................24
2-10 PECI DC Electrical Limits.....................................................................................25
2-11 Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings ...................................................................26
2-12 Voltage and Current Specifications .......................................................................27
2-13 VCC Static and Transient Tolerance......................................................................30
2-14 AGTL+ Signal Group Specifications.......................................................................32
2-15 CMOS Signal Input/Output Group and TAP Signal Group DC Specifications.................33
2-16 Open Drain Output Signal Group DC Specifications .................................................33
2-17 VCC Overshoot Specifications ..............................................................................33
2-18 AGTL+ Bus Voltage Definitions ............................................................................35
2-19 FSB Differential BCLK Specifications .....................................................................35
3-1 Package Loading Specifications............................................................................43
3-2 Package Handling Guidelines ...............................................................................44
3-3 Processor Materials ............................................................................................44
4-1 Land Listing by Land Name .................................................................................49
4-2 Land Listing by Land Number ..............................................................................60
5-1 Signal Definitions...............................................................................................71
6-1 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Thermal Specifications..................80
6-2 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Thermal Profile Table ...................81
6-3 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Specifications .................82
6-4 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile A Table ................83
6-5 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile B Table ................83
6-6 GetTemp0() and GetTemp1() Error Codes.............................................................90
7-1 Power-On Configuration Option Lands...................................................................91
7-2 Extended HALT Maximum Power ..........................................................................93
8-1 PWM Fan Frequency Specifications for 4-Pin Active CEK Thermal Solution................ 108
8-2 Fan Specifications for 4-Pin Active CEK Thermal Solution.......................................108
8-3 Fan Cable Connector Pin Out for 4-Pin Active CEK Thermal Solution........................108
6 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 7

Revision History
Document
Number
315569 -001 Initial Release November 2006
Revision Description Date
§
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 7
Page 8

8 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 9

Introduction
1 Introduction
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series are 64-bit server/workstation
processors utilizing four Intel Core™ microarchitecture cores. These processors are
based on Intel’s 65 nanometer process technology combining high performance with
the power efficiencies of low-power Intel Core™ microarchitecture cores. The
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series consists of two die, each containing
two processor cores. All processors maintain the tradition of compatibility with IA-32
software. Some key features include on-die, 32 KB Level 1 instruction data caches per
core and 4 MB shared Level 2 cache per die (8 MB Total Cache per processor) with
Advanced Transfer Cache Architecture. The processor’s Data Prefetch Logic
speculatively fetches data to the L2 cache before an L1 cache requests occurs, resulting
in reduced bus cycle penalties and improved performance. The 1333 MHz Front Side
Bus (FSB) is a quad-pumped bus running off a 333 MHz system clock, which results in
10.6 GBytes per second data transfer. The 1066 MHz Front Side Bus is based on a
266 MHz system clock for an 8.5 GBytes per second data transfer rate. The Quad-Core
Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series offers higher clock frequencies than the
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series for platforms that are targeted for
the performance optimized segment..
Enhanced thermal and power management capabilities are implemented including
Thermal Monitor 1 (TM1), Thermal Monitor 2 (TM2) and Enhanced Intel SpeedStep®
Technology. TM1 and TM2 provide efficient and effective cooling in high temperature
situations. Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology provides power management
capabilities to servers and workstations.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series features include Advanced
Dynamic Execution, enhanced floating point and multi-media units, Streaming SIMD
Extensions 2 (SSE2) and Streaming SIMD Extensions 3 (SSE3). Advanced Dynamic
Execution improves speculative execution and branch prediction internal to the
processor. The floating point and multi-media units include 128-bit wide registers and a
separate register for data movement. SSE3 instructions provide highly efficient doubleprecision floating point, SIMD integer, and memory management operations.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series supports Intel® 64 architecture
as an enhancement to Intel's IA-32 architecture. This enhancement allows the
processor to execute operating systems and applications written to take advantage of
the 64-bit extension technology. Further details on Intel 64 architecture and its
programming model can be found in the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software
Developer's Manual.
In addition, the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series supports the Execute
Disable Bit functionality. When used in conjunction with a supporting operating system,
Execute Disable allows memory to be marked as executable or non executable. This
feature can prevent some classes of viruses that exploit buffer overrun vulnerabilities
and can thus help improve the overall security of the system. Further details on
Execute Disable can be found at:
http://www3.intel.com/cd/ids/developer/asmo-na/eng/149308.htm
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series supports Intel® Virtualization
Technology for hardware-assisted virtualization within the processor. Intel Virtualization
Technology is a set of hardware enhancements that can improve virtualization
solutions. Intel Virtualization Technology is used in conjunction with Virtual Machine
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 9
Page 10

Monitor software enabling multiple, independent software environments inside a single
platform. Further details on Intel Virtualization Technology can be found at
http://developer.intel.com/technology/virtualization/index.htm.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series are intended for high performance
server and workstation systems. The processors support a Dual Independent Bus (DIB)
architecture with one processor on each bus, up to two processor sockets in a system.
The DIB architecture provides improved performance by allowing increased FSB speeds
and bandwidth. The processors will be packaged in an FC-LGA6 Land Grid Array
package with 771 lands for improved power delivery. It utilizes a surface mount
LGA771 socket that supports Direct Socket Loading (DSL).
Table 1-1. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Features
Introduction
# of Processor
Cores
4 32 KB instruction
L1 Cache (per
core)
32 KB data
L2 Advanced
Transfer Cache
4MB Shared L2
Cache per die
8MB Total Cache
Front Side Bus
Frequency
1333 MHz
1066 MHz
Package
FC-LGA6
771 Lands
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series based platforms implement
independent core voltage (V
) power planes for each processor. FSB termination
CC
voltage (VTT) is shared and must connect to all FSB agents. The processor core voltage
utilizes power delivery guidelines specified by VRM/EVRD 11.0 and its associated load
line (see Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) and Enterprise Voltage Regulator-Down
(EVRD) 11.0 Design Guidelines for further details). VRM/EVRD 11.0 will support the
power requirements of all frequencies of the processors including Flexible Motherboard
Guidelines (FMB) (see Section 2.13.1). Refer to the appropriate platform design
guidelines for implementation details.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support either 1333 or 1066 MHz
Front Side Bus operation. The FSB utilizes a split-transaction, deferred reply protocol
and Source-Synchronous Transfer (SST) of address and data to improve performance.
The processor transfers data four times per bus clock (4X data transfer rate, as in AGP
4X). Along with the 4X data bus, the address bus can deliver addresses two times per
bus clock and is referred to as a ‘double-clocked’ or a 2X address bus. In addition, the
Request Phase completes in one clock cycle. Working together, the 4X data bus and 2X
address bus provide a data bus bandwidth of up to 10.66 GBytes (1333 MHz) or 8.5
GBytes (1066 MHz) per second. The FSB is also used to deliver interrupts.
Signals on the FSB use Assisted Gunning Transceiver Logic (AGTL+) level voltages.
Section 2.1 contains the electrical specifications of the FSB while implementation
details are fully described in the appropriate platform design guidelines (refer to
Section 1.3).
10 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 11

Introduction
1.1 Terminology
A ‘#’ symbol after a signal name refers to an active low signal, indicating a signal is in
the asserted state when driven to a low level. For example, when RESET# is low, a
reset has been requested. Conversely, when NMI is high, a nonmaskable interrupt has
occurred. In the case of signals where the name does not imply an active state but
describes part of a binary sequence (such as address or data), the ‘#’ symbol implies
that the signal is inverted. For example, D[3:0] = ‘HLHL’ refers to a hex ‘A’, and
D[3:0]# = ‘LHLH’ also refers to a hex ‘A’ (H= High logic level, L= Low logic level).
Commonly used terms are explained here for clarification:
• Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series – Intel 64-bit microprocessor
intended for dual processor servers and workstations. The Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor 5300 Series is based on Intel’s 65 nanometer process, in the
FC-LGA6 package with four processor cores. For this document, “processor” is used
as the generic term for the “Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series”. The
term ‘processors’ and “Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series” are
inclusive of Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series and Quad-Core
Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series.
• Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series – A mainstream
performance version of the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series. For
this document “Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series” is used to call
out specifications that are unique to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300
Series SKU.
• Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series – An accelerated
performance version of the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series. For
this document “Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series” is used to call
out specifications that are unique to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300
Series SKU.
• FC-LGA6 (Flip Chip Land Grid Array) Package – The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series package is a Land Grid Array, consisting of a processor core
mounted on a pinless substrate with 771 lands, and includes an integrated heat
spreader (IHS).
• LGA771 socket – The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series interfaces
to the baseboard through this surface mount, 771 Land socket. See the LGA771
Socket Design Guidelines for details regarding this socket.
• Processor core – Processor core with integrated L1 cache. L2 cache and system
bus interface are shared between the two cores on the die. All AC timing and signal
integrity specifications are at the pads of the processor die.
• FSB (Front Side Bus) – The electrical interface that connects the processor to the
chipset. Also referred to as the processor system bus or the system bus. All
memory and I/O transactions as well as interrupt messages pass between the
processor and chipset over the FSB.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 11
Page 12

Introduction
• Dual Independent Bus (DIB) – A front side bus architecture with one processor
on each bus, rather than a FSB shared between two processor agents. The DIB
architecture provides improved performance by allowing increased FSB speeds and
bandwidth.
• Flexible Motherboard Guidelines (FMB) – Are estimates of the maximum
values the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series will have over certain
time periods. The values are only estimates and actual specifications for future
processors may differ.
• Functional Operation – Refers to the normal operating conditions in which all
processor specifications, including DC, AC, FSB, signal quality, mechanical and
thermal are satisfied.
• Storage Conditions – Refers to a non-operational state. The processor may be
installed in a platform, in a tray, or loose. Processors may be sealed in packaging or
exposed to free air. Under these conditions, processor lands should not be
connected to any supply voltages, have any I/Os biased or receive any clocks.
Upon exposure to “free air” (that is, unsealed packaging or a device removed from
packaging material) the processor must be handled in accordance with moisture
sensitivity labeling (MSL) as indicated on the packaging material.
• Priority Agent – The priority agent is the host bridge to the processor and is
typically known as the chipset.
• Symmetric Agent – A symmetric agent is a processor which shares the same I/O
subsystem and memory array, and runs the same operating system as another
processor in a system. Systems using symmetric agents are known as Symmetric
Multiprocessing (SMP) systems.
• Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) – A component of the processor package used
to enhance the thermal performance of the package. Component thermal solutions
interface with the processor at the IHS surface.
• Thermal Design Power – Processor thermal solutions should be designed to meet
this target. It is the highest expected sustainable power while running known
power intensive real applications. TDP is not the maximum power that the
processor can dissipate.
• Intel® 64 Architecture – Instruction set architecture and programming
environment of Intel’s 64-bit processors, which are a superset of and compatible
with IA-32. This 64-bit instruction set architecture was formerly known as IA-32
with EM64T or Intel® EM64T.
• Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology – Technology that provides power
management capabilities to servers and workstations.
• Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) – A proprietary one-wire bus
interface that provides a communication channel between Intel processor and
chipset components to external thermal monitoring devices, for use in fan speed
control. PECI communicates readings from the processor’s Digital Thermal Sensor
(DTS). The replaces the thermal diode available in previous processors.
• Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT) – Processor virtualization which
when used in conjunction with Virtual Machine Monitor software enables multiple,
robust independent software environments inside a single platform.
• VRM (Voltage Regulator Module) – DC-DC converter built onto a module that
interfaces with a card edge socket and supplies the correct voltage and current to
the processor based on the logic state of the processor VID bits.
• EVRD (Enterprise Voltage Regulator Down) – DC-DC converter integrated onto
the system board that provides the correct voltage and current to the processor
based on the logic state of the processor VID bits.
12 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 13
Introduction
• V
• V
• V
– The processor core power supply.
CC
– The processor ground.
SS
– FSB termination voltage. (Note: In some Intel processor EMTS documents,
TT
VTT is instead called V
1.2 State of Data
The data contained within this document is the most accurate information available by
the publication date of this document.
1.3 References
Material and concepts available in the following documents may be beneficial when
reading this document:
AP-485, Intel® Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction 241618 1
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B
IA-32 Intel® Architecture Optimization Reference Manual 248966 1
Intel® Virtualization Technology Specification for the IA-32 Intel® Architecture C97063 1
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Specification Update 315338 1
Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) and Enterprise Voltage Regulator-Down (EVRD)
11.0 Design Guidelines
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 SeriesThermal/Mechanical Design
Guidelines
LGA771 Socket Mechanical Design Guide 313871 1
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Boundary Scan Description
Language (BSDL) Model
Debug Port Design Guide for UP/DP Systems 1
Notes:
1. Document is available publicly at http://developer.intel.com.
2. Document not available at the time of printing.
.)
CCP
Document
Document
Number
1
253665
253666
253667
253668
253669
315794 1
Notes
1
2
1
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 13
§
Page 14

Introduction
14 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 15

Electrical Specifications
2 Electrical Specifications
2.1 Front Side Bus and GTLREF
Most Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series FSB signals use Assisted
Gunning Transceiver Logic (AGTL+) signaling technology. This technology provides
improved noise margins and reduced ringing through low voltage swings and controlled
edge rates. AGTL+ buffers are open-drain and require pull-up resistors to provide the
high logic level and termination. AGTL+ output buffers differ from GTL+ buffers with
the addition of an active PMOS pull-up transistor to “assist” the pull-up resistors during
the first clock of a low-to-high voltage transition. Platforms implement a termination
voltage level for AGTL+ signals defined as V
power planes for each processor (and chipset), separate V
necessary. This configuration allows for improved noise tolerance as processor
frequency increases. Speed enhancements to data and address buses have made
signal integrity considerations and platform design methods even more critical than
with previous processor families. Design guidelines for the processor FSB are detailed
in the appropriate platform design guidelines (refer to Section 1.3).
The AGTL+ inputs require reference voltages (GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END,
GTLREF_ADD_MID and GTLREF_ADD_END) which are used by the receivers to
determine if a signal is a logical 0 or a logical 1. GTLREF_DATA_MID and
GTLREF_DATA_END are used for the 4X front side bus signaling group and
GTLREF_ADD_MID and GTLREF_ADD_END are used for the 2X and common clock front
side bus signaling groups. GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END,
GTLREF_ADD_MID, and GTLREF_ADD_END must be generated on the baseboard (See
Ta b le 2- 18 for GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END, GTLREF_ADD_MID and
GTLREF_ADD_END specifications). Refer to the applicable platform design guidelines
for details. Termination resistors (R
silicon and are terminated to VTT. The on-die termination resistors are always enabled
on the processor to control reflections on the transmission line. Intel chipsets also
provide on-die termination, thus eliminating the need to terminate the bus on the
baseboard for most AGTL+ signals.
) for AGTL+ signals are provided on the processor
TT
. Because platforms implement separate
TT
and V
CC
supplies are
TT
Some FSB signals do not include on-die termination (R
the baseboard. See Tab le 2- 7 and Tab le 2- 8 for details regarding these signals.
The AGTL+ bus depends on incident wave switching. Therefore, timing calculations for
AGTL+ signals are based on flight time as opposed to capacitive deratings. Analog
signal simulation of the FSB, including trace lengths, is highly recommended when
designing a system. Contact your Intel Field Representative to obtain the applicable
signal integrity models, which includes buffer and package models.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 15
) and must be terminated on
TT
Page 16

2.2 Power and Ground Lands
For clean on-chip processor core power distribution, the processor has 223 VCC (power)
and 267 V
plane, while all VSS lands must be connected to the system ground plane. The
processor V
Voltage IDentification (VID) signals. See Tab le 2- 3 for VID definitions.
Twenty two lands are specified as VTT, which provide termination for the FSB and
provides power to the I/O buffers. The platform must implement a separate supply for
these lands which meets the V
(ground) inputs. All VCC lands must be connected to the processor power
SS
lands must be supplied with the voltage determined by the processor
CC
specifications outlined in Ta b le 2- 1 2.
TT
2.3 Decoupling Guidelines
Due to its large number of transistors and high internal clock speeds, the processor is
capable of generating large average current swings between low and full power states.
This may cause voltages on power planes to sag below their minimum values if bulk
decoupling is not adequate. Larger bulk storage (C
supply current during longer lasting changes in current demand by the component,
such as coming out of an idle condition. Similarly, they act as a storage well for current
when entering an idle condition from a running condition. Care must be taken in the
baseboard design to ensure that the voltage provided to the processor remains within
the specifications listed in Ta b le 2- 1 2. Failure to do so can result in timing violations or
reduced lifetime of the component. For further information and guidelines, refer to the
appropriate platform design guidelines.
Electrical Specifications
), such as electrolytic capacitors,
BULK
2.3.1 V
Vcc regulator solutions need to provide bulk capacitance with a low Effective Series
Resistance (ESR), and the baseboard designer must assure a low interconnect
resistance from the regulator (EVRD or VRM pins) to the LGA771 socket. Bulk
decoupling must be provided on the baseboard to handle large current swings. The
power delivery solution must insure the voltage and current specifications are met (as
defined in Tab l e 2- 12 ). For further information regarding power delivery, decoupling
and layout guidelines, refer to the appropriate platform design guidelines.
2.3.2 V
Bulk decoupling must be provided on the baseboard. Decoupling solutions must be
sized to meet the expected load. To insure optimal performance, various factors
associated with the power delivery solution must be considered including regulator
type, power plane and trace sizing, and component placement. A conservative
decoupling solution consists of a combination of low ESR bulk capacitors and high
frequency ceramic capacitors. For further information regarding power delivery,
decoupling and layout guidelines, refer to the appropriate platform design guidelines.
Decoupling
CC
Decoupling
TT
16 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 17

Electrical Specifications
2.3.3 Front Side Bus AGTL+ Decoupling
The processor integrates signal termination on the die, as well as a portion of the
required high frequency decoupling capacitance on the processor package. However,
additional high frequency capacitance must be added to the baseboard to properly
decouple the return currents from the FSB. Bulk decoupling must also be provided by
the baseboard for proper AGTL+ bus operation. Decoupling guidelines are described in
the appropriate platform design guidelines.
2.4 Front Side Bus Clock (BCLK[1:0]) and Processor
Clocking
BCLK[1:0] directly controls the FSB interface speed as well as the core frequency of the
processor. As in previous processor generations, the processor core frequency is a
multiple of the BCLK[1:0] frequency. The processor bus ratio multiplier is set during
manufacturing. The default setting is for the maximum speed of the processor. It is
possible to override this setting using software (see the Intel® 64 and IA-32
Architectures Software Developer’s Manual). This permits operation at lower
frequencies than the processor’s tested frequency.
The processor core frequency is configured during reset by using values stored
internally during manufacturing. The stored value sets the highest bus fraction at which
the particular processor can operate. If lower speeds are desired, the appropriate ratio
can be configured via the CLOCK_FLEX_MAX Model Specific Register (MSR). For details
of operation at core frequencies lower than the maximum rated processor speed, refer
to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual.
Clock multiplying within the processor is provided by the internal phase locked loop
(PLL), which requires a constant frequency BCLK[1:0] input, with exceptions for spread
spectrum clocking. Processor DC and AC specifications for the BCLK[1:0] inputs are
provided in Tab le 2- 19 . These specifications must be met while also meeting signal
integrity requirements as outlined in Tab l e 2 - 19 . The processor utilizes differential
clocks. Tab le 2- 1 contains processor core frequency to FSB multipliers and their
corresponding core frequencies.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 17
Page 18

Table 2-1. Core Frequency to FSB Multiplier Configuration
Electrical Specifications
Core Frequency to FSB
Multiplier
1/6 2 GHz 1.60 GHz 1, 2, 3, 4
1/7 2.33 GHz 1.86 GHz 1, 2, 3
1/8 2.66 GHz 2.13 GHz 1, 2, 3
1/9 3 GHz 2.40 GHz 1, 2, 3
Notes:
1. Individual processors operate only at or below the frequency marked on the package.
2. Listed frequencies are not necessarily committed production frequencies.
3. For valid processor core frequencies, refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
Specification Update.
4. The lowest bus ratio supported is 1/6.
Core Frequency with
333.333 MHz Bus Clock
Core Frequency with
266.666 MHz Bus Clock
2.4.1 Front Side Bus Frequency Select Signals (BSEL[2:0])
Upon power up, the FSB frequency is set to the maximum supported by the individual
processor. BSEL[2:0] are CMOS outputs which must be pulled up to VTT, and are used
to select the FSB frequency. Please refer to Tab le 2-1 5 for DC specifications. Ta b le 2- 2
defines the possible combinations of the signals and the frequency associated with each
combination. The frequency is determined by the processor(s), chipset, and clock
synthesizer. All FSB agents must operate at the same core and FSB frequency. See the
appropriate platform design guidelines for further details.
Table 2-2. BSEL[2:0] Frequency Table
BSEL2 BSEL1 BSEL0 Bus Clock Frequency
0 0 0 266.666 MHz
0 0 1 Reserved
0 1 0 Reserved
0 1 1 Reserved
1 0 0 333.333 MHz
1 0 1 Reserved
1 1 0 Reserved
1 1 1 Reserved
Notes
18 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 19

Electrical Specifications
2.4.2 PLL Power Supply
An on-die PLL filter solution is implemented on the processor. The V
to provide power to the on chip PLL of the processor. Please refer to Tab le 2- 1 2 for DC
specifications. Refer to the appropriate platform design guidelines for decoupling and
routing guidelines.
2.5 Voltage Identification (VID)
The Voltage Identification (VID) specification for the processor is defined by the Voltage
Regulator Module (VRM) and Enterprise Voltage Regulator-Down (EVRD) 11.0 Design
Guidelines. The voltage set by the VID signals is the reference VR output voltage to be
delivered to the processor Vcc pins. Please refer to Tab le 2- 1 6 for the DC specifications
for these signals. A voltage range is provided in Tab l e 2- 1 2 and changes with
frequency. The specifications have been set such that one voltage regulator can
operate with all supported frequencies.
Individual processor VID values may be calibrated during manufacturing such that two
devices at the same core frequency may have different default VID settings. This is
reflected by the VID range values provided in Tab le 2-3 .
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series uses six voltage identification
signals, VID[6:1], to support automatic selection of power supply voltages. Tab l e 2- 3
specifies the voltage level corresponding to the state of VID[6:1]. A ‘1’ in this table
refers to a high voltage level and a ‘0’ refers to a low voltage level. The definition
provided in Tab l e 2 - 3 is not related in any way to previous Intel® Xeon® processors or
voltage regulator designs. If the processor socket is empty (VID[6:1] = 111111), or
the voltage regulation circuit cannot supply the voltage that is requested, the voltage
regulator must disable itself. See the Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) and Enterprise
Voltage Regulator-Down (EVRD) 11.0 Design Guidelines for further details.
input is used
CCPLL
Although the Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) and Enterprise Voltage Regulator-Down
(EVRD) 11.0 Design Guidelines defines VID [7:0], VID 7 and VID 0 are not used on the
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series. Please refer to the appropriate
platform design guide for details.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series provide the ability to operate
while transitioning to an adjacent VID and its associated processor core voltage (V
CC
).
This will represent a DC shift in the load line. It should be noted that a low-to-high or
high-to-low voltage state change may result in as many VID transitions as necessary to
reach the target core voltage. Transitions above the specified VID are not permitted.
Ta b le 2- 12 includes VID step sizes and DC shift ranges. Minimum and maximum
voltages must be maintained as shown in Tab l e 2- 13 .
The VRM or EVRD utilized must be capable of regulating its output to the value defined
by the new VID. DC specifications for dynamic VID transitions are included in
Ta b le 2- 12 .
Power source characteristics must be guaranteed to be stable whenever the supply to
the voltage regulator is stable.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 19
Page 20
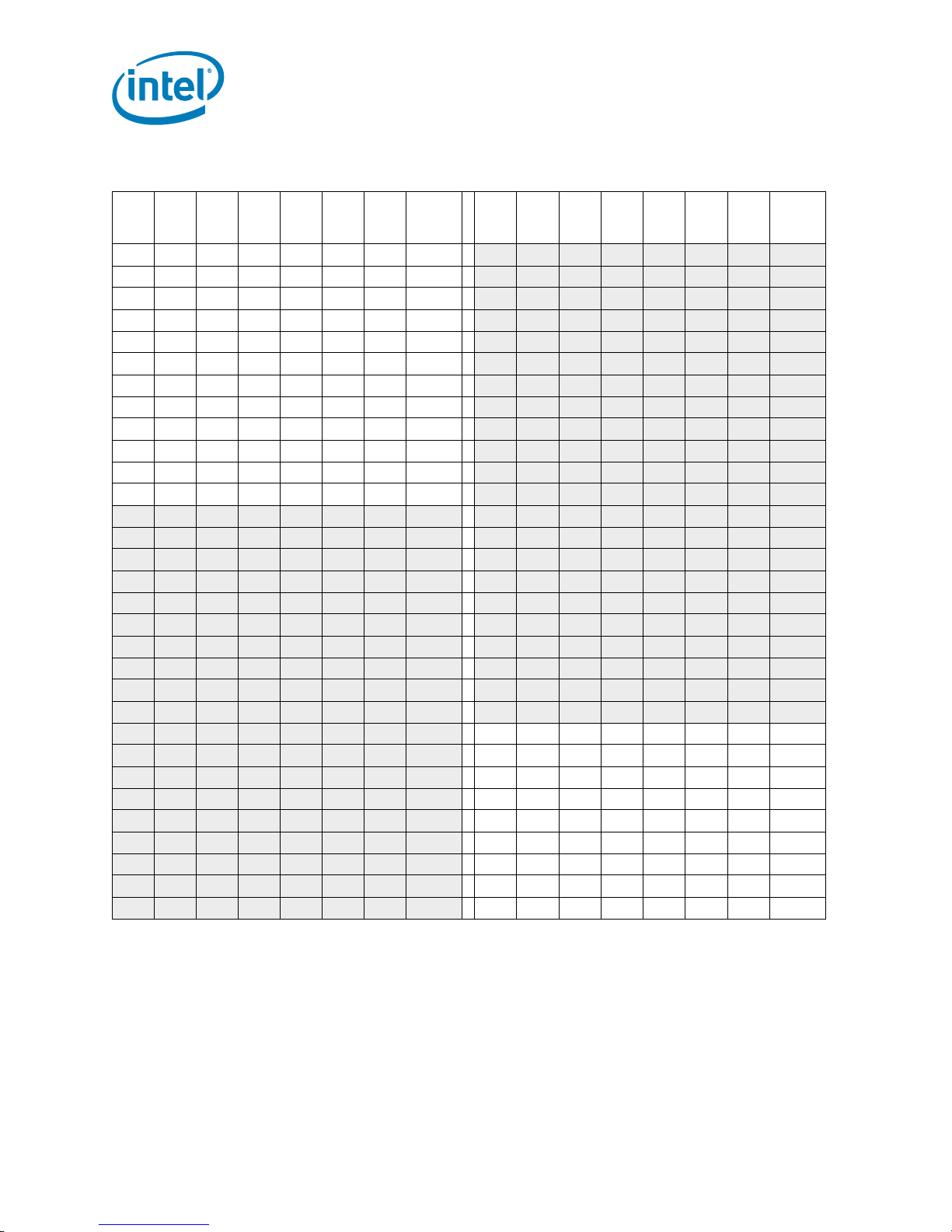
Table 2-3. Voltage Identification Definition
Electrical Specifications
HEX
VID6
400
mV
VID5
200
mV
VID4
100
mV
VID3
50
mV
VID2
25
mV
VID1
12.5 mVV
CC_MAX
HEX
VID6
400
mV
VID5
200
mV
VID4
100
mV
VID3
50
mV
VID2
25
mV
VID1
12.5 mVV
CC_MAX
7A111101 0.8500 3C 0 1 1 1 1 0 1.2375
7811110
7611101
7411101
7211100
7011100
6E11011
6C11011
6A11010
0 0.8625 3A 0 1 1 1 0 1 1.2500
1 0.8750 38 0 1 1 1 0 0 1.2625
0 0.8875 36 0 1 1 0 1 1 1.2750
1 0.9000 34 0 1 1 0 1 0 1.2875
0 0.9125 32 0 1 1 0 0 1 1.3000
1 0.9250 30 0 1 1 0 0 0 1.3125
0 0.9375 2E 0 1 0 1 1 1 1.3250
1 0.9500 2C 0 1 0 1 1 0 1.3375
68 1 1 0 1 0 0 0.9625 2A 0 1 0 1 0 1 1.3500
66 1 1 0 0 1 1 0.9750 28 0 1 0 1 0 0 1.3625
64 1 1 0 0 1 0 0.9875 26 0 1 0 0 1 1 1.3750
62 1 1 0 0 0 1 1.0000 24 0 1 0 0 1 0 1.3875
60 1 1 0 0 0 0 1.0125 22 0 1 0 0 0 1 1.4000
5E 1 0 1 1 1 1 1.0250 20 0 1 0 0 0 0 1.4125
5C 1 0 1 1 1 0 1.0375 1E 0 0 1 1 1 1 1.4250
5A 1 0 1 1 0 1 1.0500 1C 0 0 1 1 1 0 1.4375
58 1 0 1 1 0 0 1.0625 1A 0 0 1 1 0 1 1.4500
56 1 0 1 0 1 1 1.0750 18 0 0 1 1 0 0 1.4625
54 1 0 1 0 1 0 1.0875 16 0 0 1 0 1 1 1.4750
52 1 0 1 0 0 1 1.1000 14 0 0 1 0 1 0 1.4875
50 1 0 1 0 0 0 1.1125 12 0 0 1 0 0 1 1.5000
4E 1 0 0 1 1 1 1.1250 100010001.5125
4C 1 0 0 1 1 0 1.1375 0E0001111.5250
4A 1 0 0 1 0 1 1.1500 0C0001101.5375
48 1 0 0 1 0 0 1.1625 0A0001011.5500
46 1 0 0 0 1 1 1.1750 080001001.5625
44 1 0 0 0 1 0 1.1875 060000111.5750
42 1 0 0 0 0 1 1.2000 040000101.5875
40 1 0 0 0 0 0 1.2125 020000011.6000
3E 0 1 1 1 1 1 1.2250 00000000OFF
1
Notes:
1. When the “111111” VID pattern is observed, the voltage regulator output should be disabled.
2. Shading denotes the expected VID range of the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series.
3. The VID range includes VID transitions that may be initiated by thermal events, assertion of the FORCEPR# signal (see
Section 6.2.3), Extended HALT state transitions (see Section 7.2.2), or Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology transitions
(see Section 7.3). The Extended HALT state must be enabled for the processor to remain within its specifications.
4. Once the VRM/EVRD is operating after power-up, if either the Output Enable signal is de-asserted or a specific VID off code is
received, the VRM/EVRD must turn off its output (the output should go to high impedance) within 500 ms and latch off until
power is cycled.
20 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 21

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-4. Loadline Selection Truth Table for LL_ID[1:0]
LL_ID1 LL_ID0 Description
00Reserved
0 1 Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5000 Series
10Reserved
1 1 All Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
Note: The LL_ID[1:0] signals are used by the platform to select the correct loadline slope for the processor.
Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5100 Series
Table 2-5. Market Segment Selection Truth Table for MS_ID[1:0]
MS_ID1 MS_ID0 Description
0 0 Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5000 Series
0 1 Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5100 Series
1 0 All Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
11Reserved
Note: The MS_ID[1:0] signals are provided to indicate the Market Segment for the processor and may be
used for future processor compatibility or for keying.
2.6 Reserved, Unused, or Test Signals
All Reserved signals must remain unconnected. Connection of these signals to VCC, VTT,
, or to any other signal (including each other) can result in component malfunction
V
SS
or incompatibility with future processors. See Section 4 for a land listing of the
processor and the location of all Reserved signals.
For reliable operation, always connect unused inputs or bidirectional signals to an
appropriate signal level. Unused active high inputs, should be connected through a
resistor to ground (V
interfere with some TAP functions, complicate debug probing, and prevent boundary
scan testing. A resistor must be used when tying bidirectional signals to power or
ground. When tying any signal to power or ground, a resistor will also allow for system
testability. Resistor values should be within ± 20% of the impedance of the baseboard
trace for FSB signals, unless otherwise noticed in the appropriate platform design
guidelines. For unused AGTL+ input or I/O signals, use pull-up resistors of the same
value as the on-die termination resistors (R
TAP, Asynchronous GTL+ inputs, and Asynchronous GTL+ outputs do not include on-die
termination. Inputs and utilized outputs must be terminated on the baseboard. Unused
outputs may be terminated on the baseboard or left unconnected. Note that leaving
unused outputs unterminated may interfere with some TAP functions, complicate debug
probing, and prevent boundary scan testing. Signal termination for these signal types
is discussed in the appropriate platform design guidelines.
For each processor socket, connect the TESTIN1 and TESTIN2 signals together, then
terminate the net with a 51 Ω resistor to V
). Unused outputs can be left unconnected; however, this may
SS
). For details see Tab l e 2- 18 .
TT
.
TT
The TESTHI signals must be tied to the processor V
matched resistor has a resistance value within ± 20% of the impedance of the board
transmission line traces. For example, if the trace impedance is 50 Ω, then a value
between 40 Ω and 60 Ω is required.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 21
using a matched resistor, where a
TT
Page 22
The TESTHI signals may use individual pull-up resistors or be grouped together as
detailed below. A matched resistor must be used for each group:
• TESTHI[1:0] - can be grouped together with a single pull-up to V
• TESTHI[7:2] - can be grouped together with a single pull-up to V
• TESTHI10 – cannot be grouped with other TESTHI signals
• TESTHI11 – cannot be grouped with other TESTHI signals
2.7 Front Side Bus Signal Groups
The FSB signals have been combined into groups by buffer type. AGTL+ input signals
have differential input buffers, which use GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END,
GTLREF_ADD_MID, and GTLREF_ADD_END as reference levels. In this document, the
term “AGTL+ Input” refers to the AGTL+ input group as well as the AGTL+ I/O group
when receiving. Similarly, “AGTL+ Output” refers to the AGTL+ output group as well as
the AGTL+ I/O group when driving. AGTL+ asynchronous outputs can become active
anytime and include an active PMOS pull-up transistor to assist during the first clock of
a low-to-high voltage transition.
With the implementation of a source synchronous data bus comes the need to specify
two sets of timing parameters. One set is for common clock signals whose timings are
specified with respect to rising edge of BCLK0 (ADS#, HIT#, HITM#, etc.) and the
second set is for the source synchronous signals which are relative to their respective
strobe lines (data and address) as well as rising edge of BCLK0. Asynchronous signals
are still present (A20M#, IGNNE#, etc.) and can become active at any time during the
clock cycle. Tab le 2- 6 identifies which signals are common clock, source synchronous
and asynchronous.
Electrical Specifications
TT
TT
Table 2-6. FSB Signal Groups (Sheet 1 of 2)
Signal Group Type Signals
AGTL+ Common Clock Input Synchronous to
AGTL+ Common Clock Output Synchronous to
AGTL+ Common Clock I/O Synchronous to
AGTL+ Source Synchronous I/O Synchronous to assoc.
AGTL+ Strobes I/O Synchronous to
Open Drain Output Asynchronous FERR#/PBE#, IERR#, PROCHOT#, THERMTRIP#
BCLK[1:0]
BCLK[1:0]
BCLK[1:0]
strobe
BCLK[1:0]
1
BPRI#, DEFER#, RESET#, RS[2:0]#, RSP#,
TRDY#;
BPM4#, BPM[2:1]#, BPMb[2:1]#
2
ADS#, AP[1:0]#, BINIT#
BPM3#, BPM0#, BPMb3#, BPMb0#, BR[1:0]#,
DBSY#, DP[3:0]#, DRDY#, HIT#
LOCK#, MCERR#
Signals Associated Strobe
REQ[4:0]#,A[16:3]#,
A[37:36]#
A[35:17]# ADSTB1#
D[15:0]#, DBI0# DSTBP0#, DSTBN0#
D[31:16]#, DBI1# DSTBP1#, DSTBN1#
D[47:32]#, DBI2# DSTBP2#, DSTBN2#
D[63:48]#, DBI3# DSTBP3#, DSTBN3#
ADSTB[1:0]#, DSTBP[3:0]#, DSTBN[3:0]#
2
3
, BNR#2, BPM5#,
2
, HITM#2,
ADSTB0#
22 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 23
Electrical Specifications
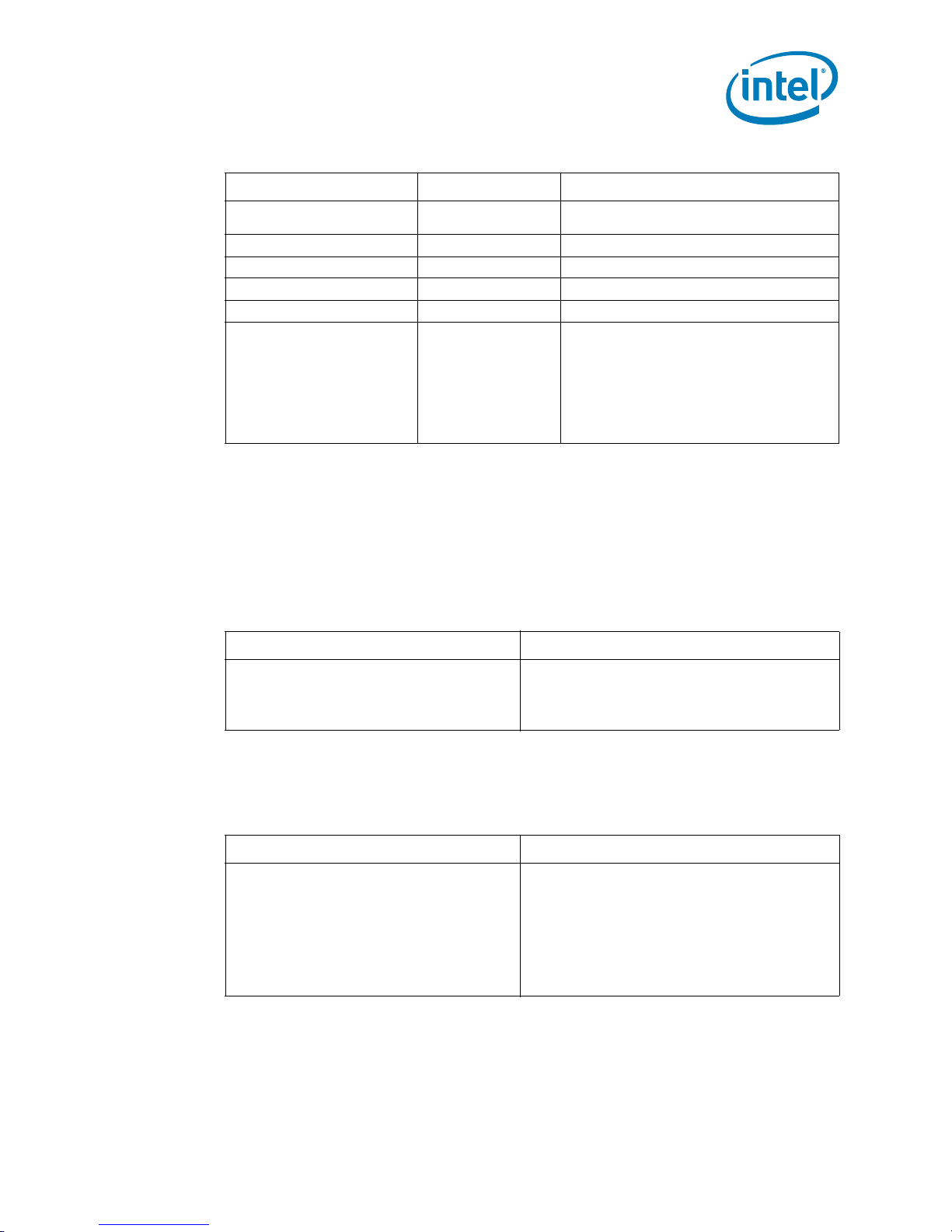
Table 2-6. FSB Signal Groups (Sheet 2 of 2)
Signal Group Type Signals
CMOS Asynchronous Input Asynchronous A20M#, FORCEPR#, IGNNE#, INIT#, LINT0/
CMOS Asynchronous Output Asynchronous BSEL[2:0], VID[6:1]
FSB Clock Clock BCLK[1:0]
TAP Input Synchronous to TCK TCK, TDI, TMS, TRST#
TAP Output Synchronous to TCK TDO
Power/Other Power/Other COMP[3:0], GTLREF_ADD_MID,
Notes:
1. Refer to Section 5 for signal descriptions.
2. These signals may be driven simultaneously by multiple agents (Wired-OR).
3. Not all Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support the additional signals A[37:36]#.
Processors that support these signals will be outlined in the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series Specification Update.
1
INTR, LINT1/NMI, PWRGOOD, SMI#, STPCLK#,
GTLREF_ADD_END, GTLREF_DATA_MID,
GTLREF_DATA_END, LL_ID[1:0], MS_ID[1:0],
PECI, RESERVED, SKTOCC#, TESTHI[11:10],
TESTHI[7:0], TESTIN1, TESTIN2, VCC,
VCC_DIE_SENSE, VCC_DIE_SENSE2, VCCPLL,
VID_SELECT, VSS_DIE_SENSE,
VSS_DIE_SENSE2, VSS, VTT, VTT_OUT,
VTT_SEL
Ta b le 2- 7 and Ta bl e 2- 8 outline the signals which include on-die termination (RTT).
Ta b le 2- 7 denotes AGTL+ signals, while Tab l e 2 - 8 outlines non AGTL+ signals including
open drain signals. Tab l e 2 - 9 provides signal reference voltages.
Table 2-7. AGTL+ Signal Description Table
AGTL+ signals with R
A[37:3]#1, ADS#, ADSTB[1:0]#, AP[1:0]#,
BINIT#, BNR#, BPRI#, D[63:0]#, DBI[3:0]#,
DBSY#, DEFER#, DP[3:0]#, DRDY#, DSTBN[3:0]#,
DSTBP[3:0]#, HIT#, HITM#, LOCK#, MCERR#,
REQ[4:0]#, RS[2:0]#, RSP#, TRDY#
Note:
1. Not all Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support the additional signals A[37:36]#.
Processors that support these signals will be outlined in the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series Specification Update.
TT
Table 2-8. Non AGTL+ Signal Description Table
Signals with R
FORCEPR#1, PROCHOT#
TT
1
AGTL+ signals with no R
BPM[5:0]#, BPMb[3:0]#, RESET#, BR[1:0]#
Signals with no R
A20M#, BCLK[1:0], BSEL[2:0], COMP[3:0], FERR#/
PBE#, GTLREF_ADD_MID, GTLREF_ADD_END,
GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END, IERR#,
IGNNE#, INIT#, LINT0/INTR, LINT1/NMI, LL_ID[1:0],
MS_ID[1:0], PECI, PWRGOOD, SKTOCC#, SMI#,
STPCLK#, TCK, TDI, TDO, TESTHI[11:10], TESTHI[7:0],
TESTIN1, TESTIN2, THERMTRIP#, TMS, TRST#,
VCC_DIE_SENSE, VCC_DIE_SENSE2, VID[6:1],
VID_SELECT, VSS_DIE_SENSE, VSS_DIE_SENSE2,
VTT_SEL
TT
TT
Note:
1. Signals that have a 50 Ω pullup to V
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 23
on package.
TT
Page 24
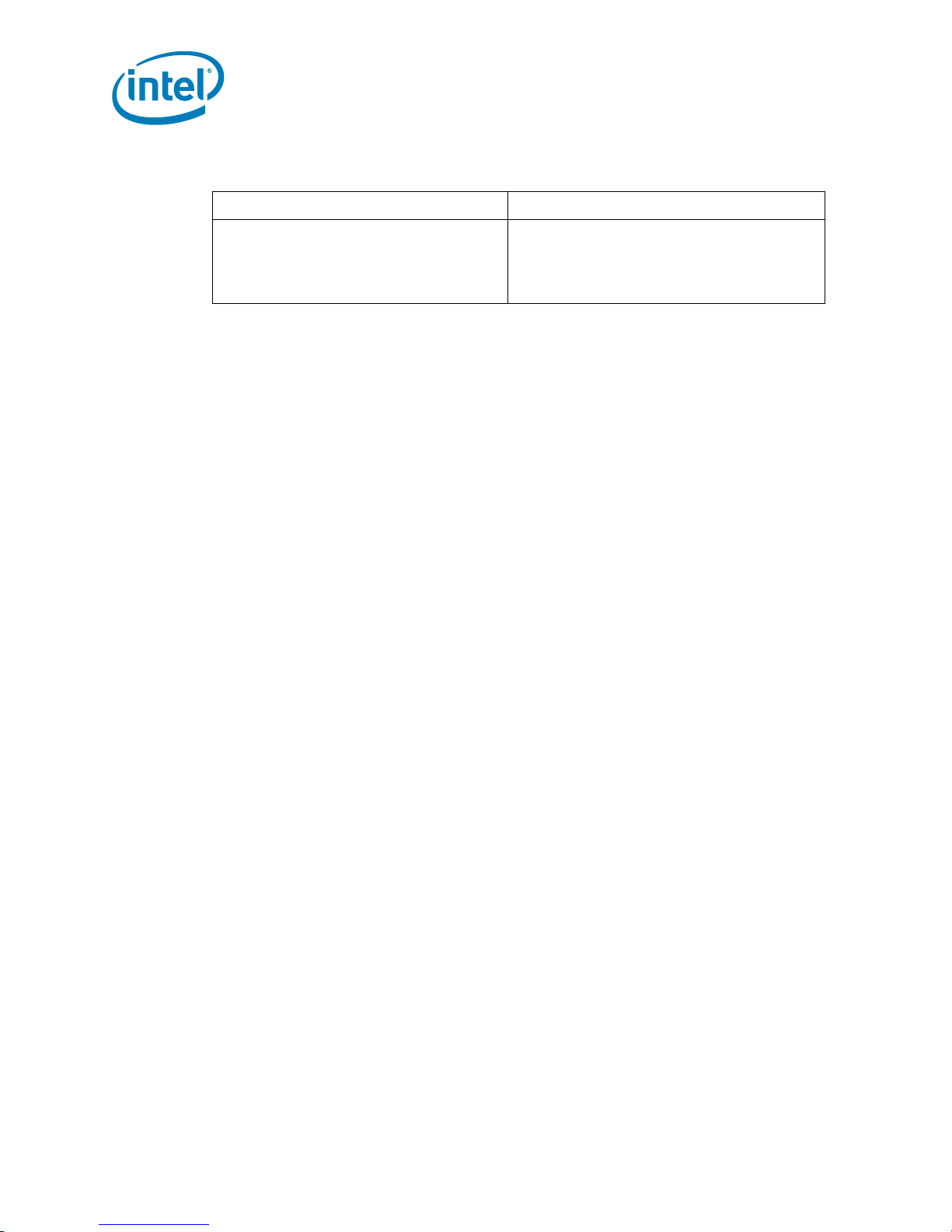
Table 2-9. Signal Reference Voltages
GTLREF CMOS
A[37:3]#
BINIT#, BNR#, BPM[5:0]#, BPMb[3:0]#, BPRI#,
BR[1:0]#, D[63:0]#, DBI[3:0]#, DBSY#, DEFER#,
DP[3:0]#, DRDY#, DSTBN[3:0]#, DSTBP[3:0]#,
HIT#, HITM#, LOCK#, MCERR#, RESET#,
REQ[4:0]#, RS[2:0]#, RSP#, TRDY#
Note:
1. Not all Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support the additional signals A[37:36]#.
1
, ADS#, ADSTB[1:0]#, AP[1:0]#,
Processors that support these signals will be outlined in the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series Specification Update.
A20M#, FORCEPR#, IGNNE#, INIT#, LINT0/INTR,
LINT1/NMI, PWRGOOD, SMI#, STPCLK#, TCK, TDI,
TMS, TRST#
2.8 CMOS Asynchronous and Open Drain
Asynchronous Signals
Legacy input signals such as A20M#, IGNNE#, INIT#, SMI#, and STPCLK# utilize
CMOS input buffers. Legacy output signals such as FERR#/PBE#, IERR#, PROCHOT#,
and THERMTRIP# utilize open drain output buffers. All of the CMOS and Open Drain
signals are required to be asserted/deasserted for at least eight BCLKs in order for the
processor to recognize the proper signal state. See Section 2.13 for the DC
specifications. See Section 7 for additional timing requirements for entering and
leaving the low power states.
Electrical Specifications
2.9 Test Access Port (TAP) Connection
Due to the voltage levels supported by other components in the Test Access Port (TAP)
logic, it is recommended that the processor(s) be first in the TAP chain and followed by
any other components within the system. A translation buffer should be used to
connect to the rest of the chain unless one of the other components is capable of
accepting an input of the appropriate voltage. Similar considerations must be made for
TCK, TDO, TMS, and TRST#. Two copies of each signal may be required with each
driving a different voltage level.
2.10 Platform Environmental Control Interface (PECI)
DC Specifications
PECI is an Intel proprietary one-wire interface that provides a communication channel
between Intel processor and external thermal monitoring devices. The Quad-Core
Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series contains Digital Thermal Sensors (DTS)
distributed throughout the die. These sensors are implemented as analog-to-digital
converters calibrated at the factor for reasonable accuracy to provide a digital
representation of relative processor temperature. PECI provides an interface to relay
the highest DTS temperature within a die to external management devices for thermal/
fan speed control.
2.10.1 DC Characteristics
A PECI device interface operates at a nominal voltage set by VTT. The set of DC
electrical specifications shown in Tab l e 2 - 10 is used with devices normally operating
from a V
PECI devices will operate at the V
system. For V
interface supply. VTT nominal levels will vary between processor families. All
TT
specifications, refer to Tab le 2- 1 2.
TT
level determined by the processor installed in the
TT
24 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 25
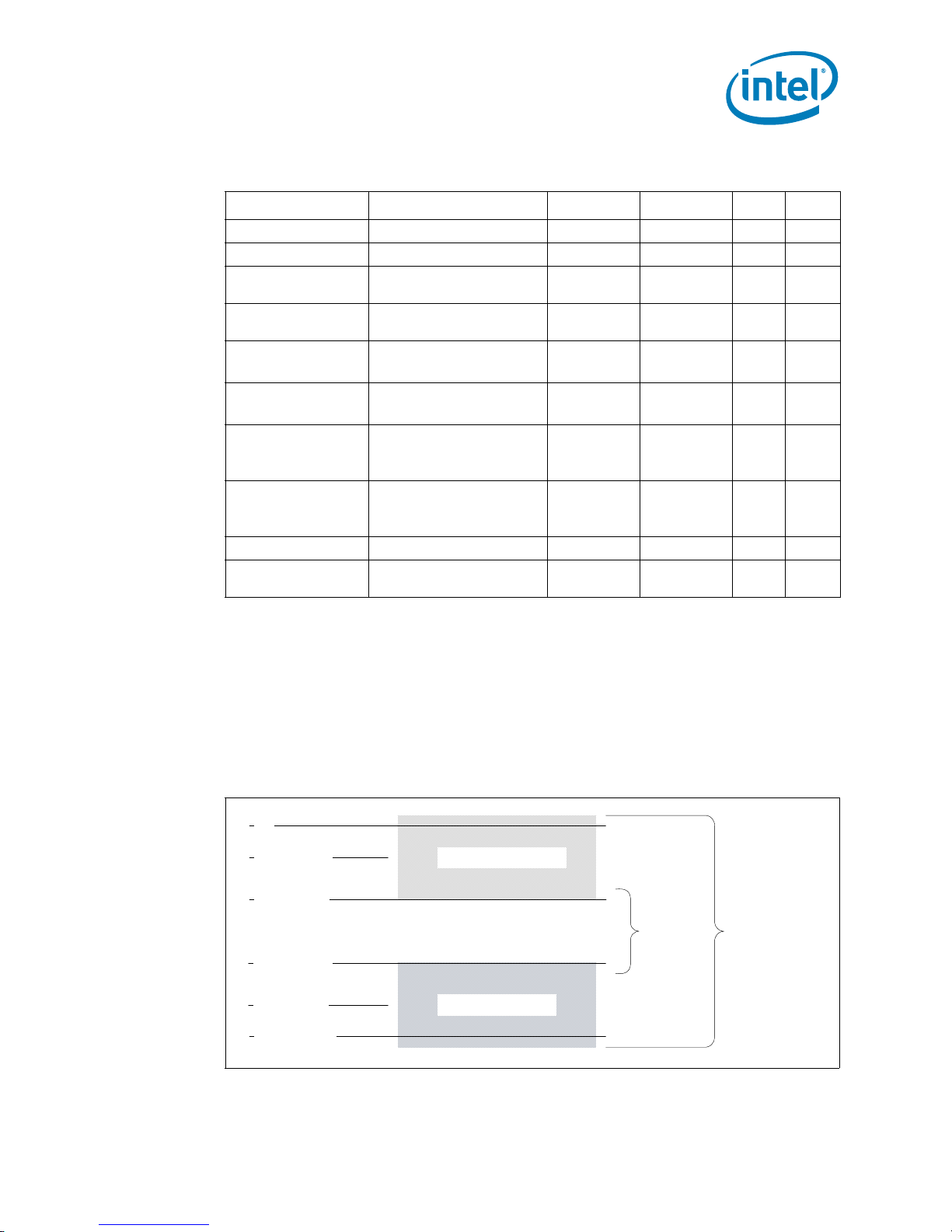
Electrical Specifications
Table 2-10. PECI DC Electrical Limits
Symbol Definition and Conditions Min Max Units Notes
V
in
V
hysteresis
V
N
V
p
I
source
I
sink
I
leak+
I
leak-
C
bus
V
noise
Input Voltage Range -0.150 V
Negative-edge threshold
Positive-edge threshold
High level output source
(V
Low level output sink
(V
High impedance state
High impedance leakage
Bus capacitance per node N/A 10 pF 3
Signal noise immunity
Hysteresis 0.1 * V
voltage
voltage
= 0.75 * VTT)
OH
= 0.25 * VTT)
OL
leakage to V
= VOL)
(V
leak
TT
0.275 * V
0.550 * V
to GND
= VOH)
(V
leak
above 300 MHz
0.1 * V
V
V
TT
V
TT
TT
TT
TT
TT
N/A V
0.500 * V
0.725 * V
-6.0 N/A mA
0.5 1.0 mA
N/A 50 µA 2
N/A 10 µA 2
TT
N/A V
p-p
1
Note:
1. V
2. The leakage specification applies to powered devices on the PECI bus.
3. One node is counted for each client and one node for the system host. Extended trace lengths might appear
supplies the PECI interface. PECI behavior does not affect VTT min/max specifications.
TT
as additional nodes.
2.10.2 Input Device Hysteresis
The input buffers in both client and host models must use a Schmitt-triggered input
design for improved noise immunity. Use Figure 2-1 as a guide for input buffer design.
Figure 2-1. Input Device Hysteresis
V
TT
Maximum V
Minimum V
Maximum V
Minimum V
PECI Ground
P
P
N
N
PECI High Range
PECI Low Range
Minimum
Hysteresis
Valid Input
Signal Range
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 25
Page 26

2.11 Mixing Processors
Intel supports and validates dual processor configurations only in which both
processors operate with the same FSB frequency, core frequency, number of cores, and
have the same internal cache sizes. Mixing components operating at different internal
clock frequencies is not supported and will not be validated by Intel. Combining
processors from different power segments is also not supported.
Electrical Specifications
Note: Processors within a system must operate at the same frequency per bits [12:8] of the
CLOCK_FLEX_MAX MSR; however this does not apply to frequency transitions initiated
due to thermal events, Extended HALT, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
transitions, or assertion of the FORCEPR# signal.
Not all operating systems can support dual processors with mixed frequencies. Mixing
processors of different steppings but the same model (as per CPUID instruction) is
supported. Details regarding the CPUID instruction are provided in the AP-485 Intel®
Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction application note.
2.12 Absolute Maximum and Minimum Ratings
Tab le 2- 1 1 specifies absolute maximum and minimum ratings only, which lie outside
the functional limits of the processor. Only within specified operation limits, can
functionality and long-term reliability be expected.
At conditions outside functional operation condition limits, but within absolute
maximum and minimum ratings, neither functionality nor long-term reliability can be
expected. If a device is returned to conditions within functional operation limits after
having been subjected to conditions outside these limits, but within the absolute
maximum and minimum ratings, the device may be functional, but with its lifetime
degraded depending on exposure to conditions exceeding the functional operation
condition limits.
At conditions exceeding absolute maximum and minimum ratings, neither functionality
nor long-term reliability can be expected. Moreover, if a device is subjected to these
conditions for any length of time then, when returned to conditions within the
functional operating condition limits, it will either not function or its reliability will be
severely degraded.
Although the processor contains protective circuitry to resist damage from static
electric discharge, precautions should always be taken to avoid high static voltages or
.
electric fields.
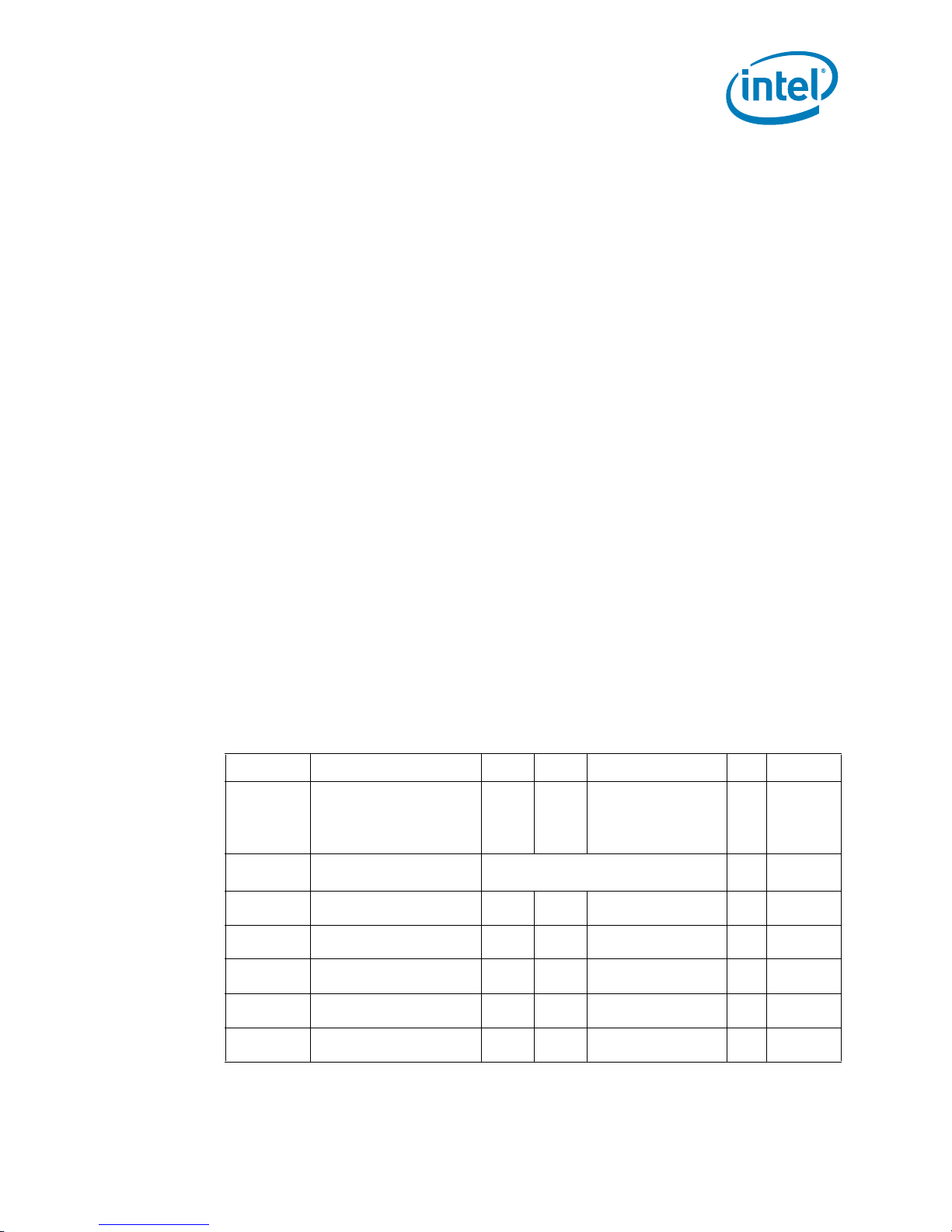
Table 2-11. Processor Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit Notes
V
CC
V
TT
T
CASE
T
STORAGE
Notes:
1. For functional operation, all processor electrical, signal quality, mechanical and thermal specifications must
be satisfied.
2. Overshoot and undershoot voltage guidelines for input, output, and I/O signals are outlined in Section 3.
Excessive overshoot or undershoot on any signal will likely result in permanent damage to the processor.
26 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Core voltage with respect to VSS -0.30 1.55 V
FSB termination voltage with respect to
V
SS
Processor case temperature See
Storage temperature -40 85 °C3, 4, 5
-0.30 1.55 V
Section 6
See
Section 6
1, 2
°C
Page 27
Electrical Specifications
3. Storage temperature is applicable to storage conditions only. In this scenario, the processor must not
receive a clock, and no lands can be connected to a voltage bias. Storage within these limits will not affect
the long-term reliability of the device. For functional operation, please refer to the processor case
temperature specifications.
4. This rating applies to the processor and does not include any tray or packaging.
5. Failure to adhere to this specification can affect the long-term reliability of the processor.
2.13 Processor DC Specifications
The processor DC specifications in this section are defined at the processor die
(pads) unless noted otherwise. See Tab le 4- 1 for the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series land listings and Ta bl e 5 -1 for signal definitions. Voltage and
current specifications are detailed in Ta b le 2- 1 2. For platform planning refer to
Ta b le 2- 13 , which provides V
is presented graphically in Figure 2-4 and Figure 2-5 .
The FSB clock signal group is detailed in Tab l e 2- 19 . The DC specifications for the
AGTL+ signals are listed in Ta b le 2- 1 4. Legacy signals and Test Access Port (TAP)
signals follow DC specifications similar to GTL+. The DC specifications for the
PWRGOOD input and TAP signal group are listed in Tab le 2- 1 5.
Ta b le 2- 12 through Tab le 2- 1 6 list the DC specifications for the processor and are valid
only while meeting specifications for case temperature (T
clock frequency, and input voltages. Care should be taken to read all notes associated
with each parameter.
Static and Transient Tolerances. This same information
CC
as specified in Section 6),
CASE
2.13.1 Flexible Motherboard Guidelines (FMB)
The Flexible Motherboard (FMB) guidelines are estimates of the maximum values the
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series will have over certain time periods.
The values are only estimates and actual specifications for future processors may differ.
Processors may or may not have specifications equal to the FMB value in the
foreseeable future. System designers should meet the FMB values to ensure their
systems will be compatible with future processors.
Table 2-12. Voltage and Current Specifications (Sheet 1 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
VID VID range for Quad-Core
V
CC
V
CC_BOOT
V
VID_STEP
V
VID_SHIFT
V
TT
V
CCPLL
Intel® Xeon® Processor
E5300 Series and Quad-Core
Intel® Xeon® Processor
X5300 Series
VCC for processor core
Launch - FMB
Default VCC Voltage for initial
power up 1.10 V 2
VID step size during a
transition ± 12.5 mV
Total allowable DC load line
shift from VID steps 450 mV 10
FSB termination voltage
(DC + AC specification) 1.14 1.20 1.26 V 8,13
PLL supply voltage (DC + AC
specification) 1.455 1.500 1.605 V
1.0000 1.5000 V
See Ta b le 2- 1 3, Figure 2-4, Figure 2-5
V
1,11
2, 3, 4, 6, 9
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 27
Page 28
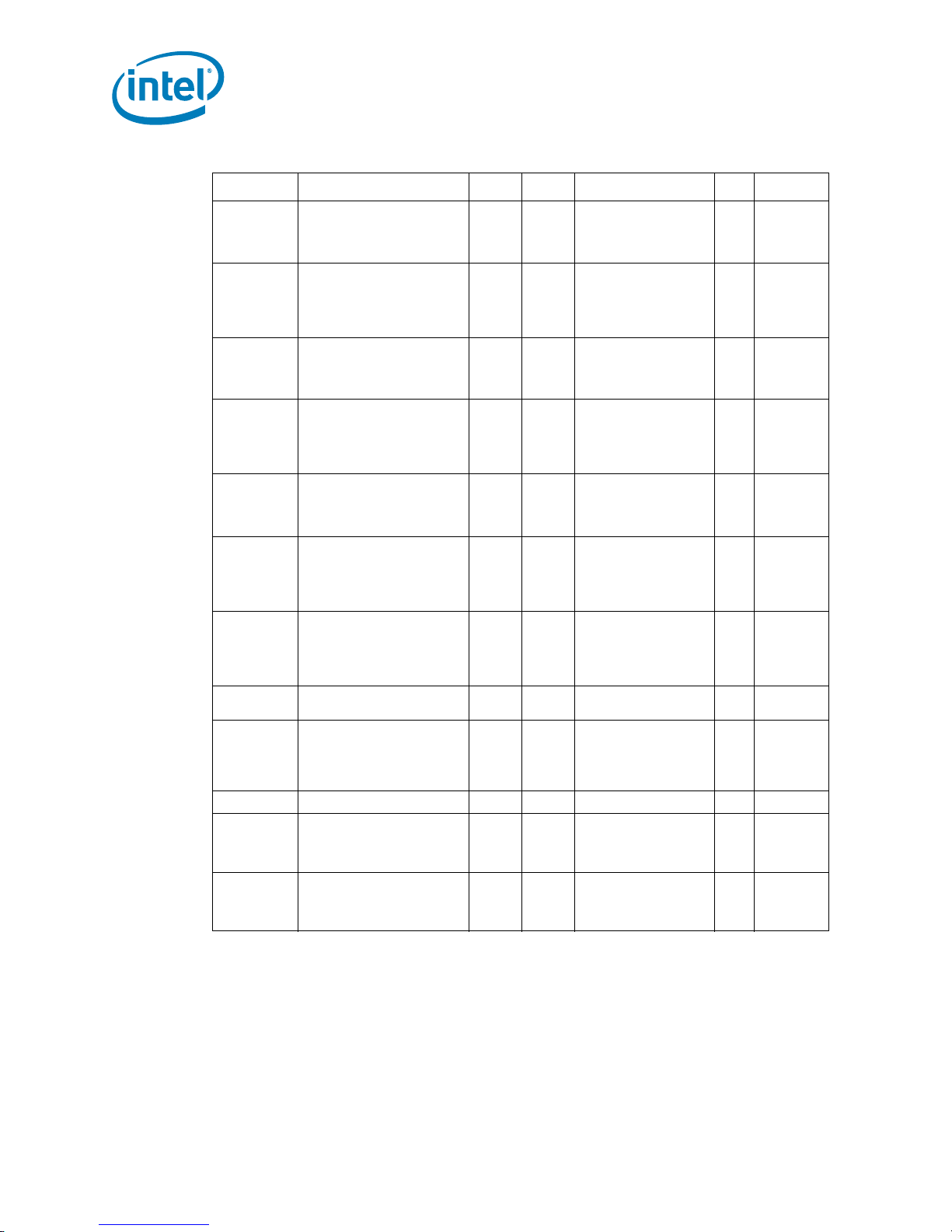
Table 2-12. Voltage and Current Specifications (Sheet 2 of 2)
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
I
CC
I
CC_RESET
I
CC
I
CC_RESET
I
TT
I
CC_TDC
I
CC_TDC
I
CC_VTT_OUT
I
CC_GTLREF
I
CC_VCCPLL
I
TCC
I
TCC
ICC for Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor E5300
Series core with multiple VID
Launch - FMB
I
Intel® Xeon® Processor
E5300 Series core with
multiple VID
CC_RESET
for Quad-Core
Launch - FMB
ICC for Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor X5300
Series core with multiple VID
Launch - FMB 125 A 4,5,6,9
I
Intel® Xeon® Processor
X5300 Series core with
CC_RESET
for Quad-Core
multiple VID
Launch - FMB
ICC for VTT supply before VCC
stable
for VTT supply after VCC
I
CC
stable
Thermal Design Current
(TDC) Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor E5300
Series
Launch - FMB
Thermal Design Current
(TDC) Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor X5300
Series
Launch - FMB
DC current that may be
drawn from V
ICC for
GTLREF_DATA_MID,
GTLREF_DATA_END,
GTLREF_ADD_MID,
per land 580 mA 16
TT_OU T
GTLREF_ADD_END 200 µA 7
ICC for PLL supply 260 mA 12
I
for Quad-Core Intel®
CC
Xeon® Processor E5300
Series during active thermal
control circuit (TCC)
I
for Quad-Core Intel®
CC
Xeon® Processor X5300
Series during active thermal
control circuit (TCC) 125 A
Electrical Specifications
90 A 4,5,6,9
90 A 17
125 A 17
8.0
7.0
A
15
A
70 A 6,14
110 A 6,14
90 A
1,11
Notes:
1. Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in this table are based on final silicon characterization data.
2. These voltages are targets only. A variable voltage source should exist on systems in the event that a
different voltage is required. See Section 2.5 for more information.
3. The voltage specification requirements are measured across the VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE
lands and across the VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands with an oscilloscope set to 100 MHz
bandwidth, 1.5 pF maximum probe capacitance, and 1 MΩ minimum impedance. The maximum length of
ground wire on the probe should be less than 5 mm. Ensure external noise from the system is not coupled
in the scope probe.
4. The processor must not be subjected to any static V
particular current. Failure to adhere to this specification can shorten processor lifetime.
5. I
specification is based on maximum V
CC_MAX
capable of drawing I
average processor current draw over various time durations.
28 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
level that exceeds the V
CC
loadline Refer to Figure 2-6 for details. The processor is
for up to 10 ms. Refer to Figure 2-2 and Figure 2-3 for further details on the
CC_MAX
CC
associated with any
CC_MAX
Page 29
Electrical Specifications
6. FMB is the flexible motherboard guideline. These guidelines are for estimation purposes only. See
Section 2.13.1 for further details on FMB guidelines.
7. This specification represents the total current for GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END,
GTLREF_ADD_MID, and GTLREF_ADD_END.
must be provided via a separate voltage source and must not be connected to VCC. This specification is
8. V
TT
measured at the land.
9. Minimum V
in Figure 6-1.
10. This specification refers to the total reduction of the load line due to VID transitions below the specified
VID.
11. Individual processor VID values may be calibrated during manufacturing such that two devices at the same
frequency may have different VID settings.
12. This specification applies to the VCCPLL land.
13. Baseboard bandwidth is limited to 20 MHz.
14. I
CC_TDC
should be used for the voltage regulator temperature assessment. The voltage regulator is responsible for
monitoring its temperature and asserting the necessary signal to inform the processor of a thermal
excursion. Please see the applicable design guidelines for further details. The processor is capable of
drawing I
current draw over various time durations. This parameter is based on design characterization and is not
tested.
15. This is the maximum total current drawn from the V
specification does not include the current coming from on-board termination (R
Refer to the appropriate platform design guide and the Voltage Regulator Design Guidelines to determine
the total I
16. I
CC_VTT_OUT
17. I
.
CC_RESET
and maximum ICC are specified at the maximum processor case temperature (T
CC
CASE
) shown
is the sustained (DC equivalent) current that the processor is capable of drawing indefinitely and
indefinitely. Refer to Figure 2-2 and Figure 2-3 for further details on the average processor
CC_TDC
plane by only one processor with RTT enabled. This
TT
drawn by the system. This parameter is based on design characterization and is not tested.
TT
is specified at 1.2 V.
), through the signal line.
TT
is specified while PWRGOOD and RESET# are asserted.
Figure 2-2. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Load Current versus Time
10 0
95
90
85
80
75
70
Sustained Current (A)
65
60
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Time Duration (s)
Notes:
1. Processor or voltage regulator thermal protection circuitry should not trip for load currents greater than
2. Not 100% tested. Specified by design characterization.
I
CC_TDC
.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 29
Page 30
Electrical Specifications
Figure 2-3. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Load Current versus Time
13 0
12 5
12 0
115
110
10 5
Sustained Current (A)
10 0
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Time Duration (s)
Notes:
1. Processor or voltage regulator thermal protection circuitry should not trip for load currents greater than
2. Not 100% tested. Specified by design characterization.
I
CC_TDC
.
Table 2-13. VCC Static and Transient Tolerance (Sheet 1 of 2)
ICC (A) V
(V) V
CC_Max
(V) V
CC_Typ
(V) Notes
CC_Min
0 VID - 0.000 VID - 0.015 VID - 0.030 1, 2, 3
5 VID - 0.006 VID - 0.021 VID - 0.036 1, 2, 3
10 VID - 0.013 VID - 0.028 VID - 0.043 1, 2, 3
15 VID - 0.019 VID - 0.034 VID - 0.049 1, 2, 3
20 VID - 0.025 VID - 0.040 VID - 0.055 1, 2, 3
25 VID - 0.031 VID - 0.046 VID - 0.061 1, 2, 3
30 VID - 0.038 VID - 0.053 VID - 0.068 1, 2, 3
35 VID - 0.044 VID - 0.059 VID - 0.074 1, 2, 3
40 VID - 0.050 VID - 0.065 VID - 0.080 1, 2, 3
45 VID - 0.056 VID - 0.071 VID - 0.086 1, 2, 3
50 VID - 0.069 VID - 0.084 VID - 0.099 1, 2, 3
55 VID - 0.069 VID - 0.077 VID - 0.093 1, 2, 3
60 VID - 0.075 VID - 0.090 VID - 0.105 1, 2, 3
65 VID - 0.081 VID - 0.096 VID - 0.111 1, 2, 3
70 VID - 0.087 VID - 0.103 VID - 0.118 1, 2, 3
75 VID - 0.094 VID - 0.109 VID - 0.124 1, 2, 3
80 VID - 0.100 VID - 0.115 VID - 0.130 1, 2, 3
85 VID - 0.106 VID - 0.121 VID - 0.136 1, 2, 3
90 VID - 0.113 VID - 0.128 VID - 0.143 1, 2, 3,
95 VID - 0.119 VID - 0.134 VID - 0.149 1, 2, 3, 4
100 VID - 0.125 VID - 0.140 VID - 0.155 1, 2, 3, 4
105 VID - 0.131 VID - 0.146 VID - 0.161 1, 2, 3, 4
110 VID - 0.138 VID - 0.153 VID - 0.168 1, 2, 3, 4
115 VID - 0.144 VID - 0.159 VID - 0.174 1, 2, 3, 4
30 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 31

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-13. V
Static and Transient Tolerance (Sheet 2 of 2)
CC
ICC (A) V
(V) V
CC_Max
(V) V
CC_Typ
(V) Notes
CC_Min
120 VID - 0.150 VID - 0.165 VID - 0.180 1, 2, 3, 4
125 VID - 0.156 VID - 0.171 VID - 0.186 1, 2, 3, 4
Notes:
1. The V
V
CC
2. This table is intended to aid in reading discrete points on Figure 2-4 for Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor E5300 Series, Figure 2-5 for Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series.
3. The loadlines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE
lands and across the VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands. Voltage regulation feedback for
voltage regulator circuits must also be taken from processor VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE
lands and VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands.
value greater than 90 A is not applicable for the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series.
4. I
cc
and V
CC_MIN
overshoot specifications.
loadlines represent static and transient limits. Please see Section 2.13.2 for
CC_MAX
Figure 2-4. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series VCC Static and
Transient Tolerance Load Lines
Icc [A]
VID - 0.000
VID - 0.020
VID - 0.040
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90
V
CC
Maximum
VID - 0.060
VID - 0.080
Vcc [V]
VID - 0.100
V
VID - 0.120
VID - 0.140
VID - 0.160
Notes:
1. The V
overshoot specifications.
2. Refer to Tab le 2 -1 2 for processor VID information.
3. Refer to Tab le 2 -1 3 for V
4. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE
lands and the VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands. Voltage regulation feedback for voltage
regulator circuits must also be taken from processor VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE lands and
VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands. Please refer to the appropriate platform design guide for
CC_MIN
and V
CC_MAX
CC
Typical
V
CC
Minimum
loadlines represent static and transient limits. Please see Section 2.13.2 for VCC
Static and Transient Tolerance
CC
details on VR implementation.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 31
Page 32

Electrical Specifications
Figure 2-5. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series VCC Static and
Transient Tolerance Load Lines
V
CC
Minimum
Icc [A ]
V
CC
Maximum
VID - 0.000
VID - 0.020
VID - 0.040
VID - 0.060
VID - 0.080
VID - 0.100
Vcc [V]
VID - 0.120
VID - 0.140
VID - 0.160
VID - 0.180
VID - 0.200
Notes:
1. The V
overshoot specifications.
2. Refer to Tab le 2 -1 2 for processor VID information.
3. Refer to Tab le 2 -1 3 for V
4. The load lines specify voltage limits at the die measured at the VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE
lands and the VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands. Voltage regulation feedback for voltage
regulator circuits must also be taken from processor VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE lands and
VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands. Please refer to the appropriate platform design guide for
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 120 125
V
CC
Typical
CC_MIN
and V
loadlines represent static and transient limits. Please see Section 2.13.2 for VCC
CC_MAX
Static and Transient Tolerance
CC
details on VR implementation.
Table 2-14. AGTL+ Signal Group Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OH
R
ON
I
LI
Notes:
1. Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in this table apply to all processor frequencies.
is defined as the maximum voltage level at a receiving agent that will be interpreted as a logical low
2. V
IL
value.
is defined as the minimum voltage level at a receiving agent that will be interpreted as a logical high
3. V
IH
value.
and VOH may experience excursions above VTT. However, input signal drivers must comply with the
4. V
IH
signal quality specifications.
5. This is the pull down driver resistance. Refer to processor I/O Buffer Models for I/V characteristics.
Measured at 0.31*V
6. GTLREF should be generated from V
specifications is the instantaneous V
7. Specified when on-die R
8. This is the measurement at the pin.
Input Low Voltage -0.10 0 GTLREF-0.10 V 2,4,6
Input High Voltage GTLREF+0.10 V
Output High Voltage V
- 0.10 N/A V
TT
TT
VTT+0.10 V 3,6
TT
V4,6
Buffer On Resistance 10.00 11.50 13.00 W 5
Input Leakage Current N/A N/A +/- 200 μA7,8
. RON (min) = 0.225*RTT. RON (typ) = 0.250*RTT. RON (max) = 0.275*RTT.
TT
and RON are turned off. VIN between 0 and VTT.
TT
with a 1% tolerance resistor divider. The VTT referred to in these
TT
.
TT
32 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
1
Page 33

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-15. CMOS Signal Input/Output Group and TAP Signal Group DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Notes
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
I
OL
I
OH
I
LI
Notes:
1. Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in this table apply to all processor frequencies.
2. The V
3. Refer to the processor I/O Buffer Models for I/V characteristics.
4. Measured at 0.1*V
5. Measured at 0.9*V
6. For Vin between 0 V and V
7. This is the measurement at the pin.
Input Low Voltage -0.10 0.00 0.3*V
Input High Voltage 0.7*V
TT
V
TT
VTT+0.1 V 2
Output Low Voltage -0.10 0 0.1*V
Output High Voltage 0.9*V
TT
V
TT
VTT+0.1 V 2
TT
TT
V2,3
V2
Output Low Current 1.70 N/A 4.70 mA 4
Output High Current 1.70 N/A 4.70 mA 5
Input Leakage Current N/A N/A +/- 200 μA6,7
referred to in these specifications refers to instantaneous VTT.
TT
.
TT
.
TT
. Measured when the driver is tristated.
TT
Table 2-16. Open Drain Output Signal Group DC Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Units Notes
V
OL
V
OH
I
OL
I
LO
Output Low Voltage N/A 0.20 V 3
Output High Voltage 0.95 * V
TT
V
TT
1.05 * V
TT
V
Output Low Current 16 N/A 50 mA 2
Leakage Current N/A N/A +/- 400 μA4,5
1
1
Notes:
1. Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in this table apply to all processor frequencies.
2. Measured at 0.2*V
3. V
4. For V
5. This is the measurement at the pin.
is determined by value of the external pullup resistor to VTT. Please refer to platform design guide for
OH
details.
between 0 V and VOH.
IN
.
TT
2.13.2 VCC Overshoot Specification
Processors can tolerate short transient overshoot events where VCC exceeds the VID
voltage when transitioning from a high-to-low current load condition. This overshoot
cannot exceed VID + V
OS_MAX
VID). These specifications apply to the processor die voltage as measured across the
VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE lands and across the VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and
VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands.
Table 2-17. VCC Overshoot Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Max Units Figure Notes
V
OS_MAX
T
OS_MAX
Magnitude of VCC overshoot above VID 50 mV 2-6
Time duration of VCC overshoot above VID 25 µs 2-6
(V
OS_MAX
is the maximum allowable overshoot above
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 33
Page 34

Electrical Specifications
Figure 2-6. V
Overshoot Example Waveform
CC
VID + 0.050
Voltage [V]
VID - 0.000
0 5 10 15 20 25
Notes:
1. V
2. T
is the measured overshoot voltage.
OS
is the measured time duration above VID.
OS
Example Overshoot Waveform
V
OS
T
OS
Time [us]
TOS: Overshoot time abo ve VID
: Overshoot above VID
V
OS
2.13.3 Die Voltage Validation
Core voltage (VCC) overshoot events at the processor must meet the specifications in
Tab le 2- 1 7 when measured across the VCC_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE lands
and across the VCC_DIE_SENSE2 and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 lands. Overshoot events that
are < 10 ns in duration may be ignored. These measurements of processor die level
overshoot should be taken with a 100 MHz bandwidth limited oscilloscope.
2.14 AGTL+ FSB Specifications
Routing topologies are dependent on the processors supported and the chipset used in
the design. Please refer to the appropriate platform design guidelines for specific
implementation details. In most cases, termination resistors are not required as these
are integrated into the processor silicon. See Tab l e 2 -7 for details on which signals do
not include on-die termination. Please refer to Tab l e 2 - 18 for R
Valid high and low levels are determined by the input buffers via comparing with a
reference voltage called GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END, GTLREF_ADD_MID,
and GTLREF_ADD_END. GTLREF_DATA_MID and GTLREF_DATA_END are the reference
voltage for the FSB 4X data signals, GTLREF_ADD_MID and GTLREF_ADD_END are the
reference voltage for the FSB 2X address signals and common clock signals. Ta b le 2- 18
lists the GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END, GTLREF_ADD_MID, and
GTLREF_ADD_END specifications.
The AGTL+ reference voltages (GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END,
GTLREF_ADD_MID, and GTLREF_ADD_END) must be generated on the baseboard
using high precision voltage divider circuits. Refer to the appropriate platform design
guidelines for implementation details.
values.
TT
34 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 35

Electrical Specifications
Table 2-18. AGTL+ Bus Voltage Definitions
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
GTLREF_DATA_MID
GTLREF_DATA_END
GTLREF_ADD_MID
GTLREF_ADD_END
R
TT
COMP COMP
Note:
1. Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in this table apply to all processor frequencies.
2. The tolerances for this specification have been stated generically to enable system designer to calculate the
minimum values across the range of V
3. GTLREF_DATA_MID, GTLREF_DATA_END, GTLREF_ADD_MID, and GTLREF_ADD_END is generated from V
on the baseboard by a voltage divider of 1% resistors. The minimum and maximum specifications account
for this resistor tolerance. Refer to the appropriate platform design guidelines for implementation details.
referred to in these specifications is the instantaneous VTT.
The V
TT
is the on-die termination resistance measured at VOL of the AGTL+ output driver. Measured at
4. R
TT
0.31*V
5. COMP resistance must be provided on the system board with +/- 1% resistors. See the applicable platform
. RTT is connected to VTT on die. Refer to processor I/O Buffer Models for I/V characteristics.
TT
design guide for implementation details.
Data Bus
Reference
Voltag e
Address Bus
Reference
Voltag e
Termination
Resistance
(pull up)
Resistance
0.98 * 0.67 * V
0.98 * 0.67 * V
0.67 * VTT1.02 * 0.67 * V
TT
0.67 * VTT1.02 * 0.67 * V
TT
V2, 3
TT
V2, 3
TT
45 50 55 Ω 4
49.4 49.9 50.4 Ω 5
.
TT
1
TT
Table 2-19. FSB Differential BCLK Specifications
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Figure Notes
V
L
V
H
V
CROSS(abs)
V
CROSS(rel)
CROSS Range of
Δ V
V
OS
V
US
V
RBM
V
TR
I
LI
Note:
1. Unless otherwise noted, all specifications in this table apply to all processor frequencies.
2. Rise and fall times are measured single-ended between 245 mV and 455 mV of the clock swing.
3. Crossing Voltage is defined as the instantaneous voltage value when the rising edge of BCLK0 is equal to
the falling edge of BCLK1.
4. V
Havg
5. Overshoot is defined as the absolute value of the maximum voltage.
6. Undershoot is defined as the absolute value of the minimum voltage.
7. Ringback Margin is defined as the absolute voltage difference between the maximum Rising Edge Ringback
and the maximum Falling Edge Ringback.
Input Low
Voltag e
Input High
Voltag e
Absolute
Crossing
Point
Relative
Crossing
Point
Crossing
Points
-0.150 0.0 N/A V 2-8
0.660 0.710 0.850 V 2-8
0.250 0.350 0.550 V 2-8, 2-9 3,9
0.250 +
0.5 * (V
Havg
- 0.700)
N/A N/A 0.140 V 2-8, 2-9 12
Overshoot N/A N/A VH + 0.300 V 2-8 5
Undershoot -0.300 N/A N/A V 2-8 6
Ringback
Margin
Threshold
Region
Input
Leakage
Current
0.200 N/A N/A V 2-8 7
V
- 0.100 N/A V
CROSS
N/A N/A +/- 100 μA11
is the statistical average of the VH measured by the oscilloscope.
N/A
0.550 +
0.5 * (V
- 0.700)
Havg
+ 0.100 V 2-8 8
CROSS
V 2-8, 2-9 4,9,10
1,2
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 35
Page 36

8. Threshold Region is defined as a region entered around the crossing point voltage in which the differential
receiver switches. It includes input threshold hysteresis.
9. The crossing point must meet the absolute and relative crossing point specifications simultaneously.
10. V
11. For V
12. ΔV
can be measured directly using “Vtop” on Agilent and “High” on Tektronix oscilloscopes.
Havg
between 0 V and VH.
IN
is defined as the total variation of all crossing voltages as defined in Note 3.
CROSS
Figure 2-7. Electrical Test Circuit
Electrical Specifications
Figure 2-8. Differential Clock Waveform
BCLK1
Threshold
Region
BCLK0
Tp = T1: BCLK[1:0] period
Crossing
Voltage
Tp
Crossing
Voltage
Overshoot
VH
Rising Edge
Ringback
Ringback
Margin
Falling Edge
Ringback,
VL
Undershoot
36 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 37

Electrical Specifications
Figure 2-9. Differential Clock Crosspoint Specification
650
600
550
500
450
400
350
Crossin g Point (mV)
300
250
200
550 + 0.5 (VHavg - 700)
250 + 0.5 (VHavg - 700)
250 mV
660 670 680 690 700 710 720 730 740 750 760 770 780 790 800 810 820 830 840 850
VHavg (mV)
Note: Please refer to Tab l e 2 -1 5 for TAP Signal Group DC specifications for TAP Signal Group AC specifications.
§
550 mV
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 37
Page 38

Electrical Specifications
38 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 39

Mechanical Specifications
3 Mechanical Specifications
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series are packaged in a Flip Chip Land
Grid Array (FC-LGA6) package that interfaces to the baseboard via a LGA771 socket.
The package consists of two processor dies mounted on a pinless substrate with 771
lands. An integrated heat spreader (IHS) is attached to the package substrate and core
and serves as the interface for processor component thermal solutions such as a
heatsink. Figure 3-1 shows a sketch of the processor package components and how
they are assembled together. Refer to the LGA771 Socket Design Guidelines for
complete details on the LGA771 socket.
The package components shown in Figure 3-1 include the following:
• Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS)
• Thermal Interface Material (TIM)
• Processor Die
• Package Substrate
• Landside capacitors
•Package Lands
Figure 3-1. Processor Package Assembly Sketch
Core (die)
IHS
IHS
Substrate
Substrate
Package Lands
Package Lands
System Board
System Board
Note: This drawing is not to scale and is for reference only.
Core (die)
3.1 Package Mechanical Drawings
The package mechanical drawings are shown in Figure 3-2 through Figure 3-4. The
drawings include dimensions necessary to design a thermal solution for the processor
including:
• Package reference and tolerance dimensions (total height, length, width, and so
forth)
• IHS parallelism and tilt
• Land dimensions
• Top-side and back-side component keepout dimensions
• Reference datums
TIM
TIM
Capacitors
Capacitors
LGA771 Socket
LGA771 Socket
Note: All drawing dimensions are in mm [in.].
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 39
Page 40

Figure 3-2. Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 1 of 3)
Mechanical Specifications
Note: Guidelines on potential IHS flatness variation with socket load plate actuation and installation of the cooling solution is
40 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
available in the processor Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines.
Page 41

Mechanical Specifications
Figure 3-3. Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 2 of 3)
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 41
Page 42

Figure 3-4. Processor Package Drawing (Sheet 3 of 3)
Mechanical Specifications
42 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 43

Mechanical Specifications
3.2 Processor Component Keepout Zones
The processor may contain components on the substrate that define component
keepout zone requirements. A thermal and mechanical solution design must not intrude
into the required keepout zones. Decoupling capacitors are typically mounted to either
the topside or landside of the package substrate. See Figure 3-4 for keepout zones.
3.3 Package Loading Specifications
Ta b le 3- 1 provides dynamic and static load specifications for the processor package.
These mechanical load limits should not be exceeded during heatsink assembly,
mechanical stress testing or standard drop and shipping conditions. The heatsink
attach solutions must not include continuous stress onto the processor with the
exception of a uniform load to maintain the heatsink-to-processor thermal interface.
Also, any mechanical system or component testing should not exceed these limits. The
processor package substrate should not be used as a mechanical reference or loadbearing surface for thermal or mechanical solutions.
Table 3-1. Package Loading Specifications
Parameter
Static Compressive Load 1.57 mm
Dynamic Compressive
Load
Transient Bend Limits 1.57 mm
Notes:
1. These specifications apply to uniform compressive loading in a direction perpendicular to the IHS top
surface.
2. This is the minimum and maximum static force that can be applied by the heatsink and retention solution
to maintain the heatsink and processor interface.
3. These specifications are based on limited testing for design characterization. Loading limits are for the
LGA771 socket.
4. Dynamic compressive load applies to all board thickness.
5. Dynamic loading is defined as an 11 ms duration average load superimposed on the static load
requirement.
6. Test condition used a heatsink mass of 1 lbm with 50 g acceleration measured at heatsink mass. The
dynamic portion of this specification in the product application can have flexibility in specific values, but the
ultimate product of mass times acceleration should not exceed this dynamic load.
7. Transient bend is defined as the transient board deflection during manufacturing such as board assembly
and system integration. It is a relatively slow bending event compared to shock and vibration tests.
8. For more information on the transient bend limits, please refer to the MAS document entitled
Manufacturing with Intel® Components using 771-land LGA Package that Interfaces with the Motherboard
via a LGA771 Socket.
9. Refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines for
information on heatsink clip load metrology.
Board
Thickness
0.062”
2.16 mm
0.085”
2.54 mm
0.100”
NA NA 311 N (max
0.062”
Min Max Unit Notes
80
18
111
25
133
30
compressive
load) + 222 N
dynamic loading
70 lbf (max
compressive
load) + 50 lbf
dynamic loading
NA 750 me 1,3,7,8
311
70
311
70
311
70
static
static
lbf
lbf
lbf
lbf
N
N
N
N
1,2,3,9
1,3,4,5,6
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 43
Page 44

3.4 Package Handling Guidelines
Tab le 3- 2 includes a list of guidelines on a package handling in terms of recommended
maximum loading on the processor IHS relative to a fixed substrate. These package
handling loads may be experienced during heatsink removal.
Table 3-2. Package Handling Guidelines
Parameter Maximum Recommended Units Notes
Shear 311
Tensile 111
Torque 3.95
Notes:
1. A shear load is defined as a load applied to the IHS in a direction parallel to the IHS top surface.
2. A tensile load is defined as a pulling load applied to the IHS in a direction normal to the IHS surface.
3. A torque load is defined as a twisting load applied to the IHS in an axis of rotation normal to the IHS top
surface.
4. These guidelines are based on limited testing for design characterization and incidental applications (one
time only).
5. Handling guidelines are for the package only and do not include the limits of the processor socket.
70
25
35
N
lbf
N
lbf
N-m
LBF-in
Mechanical Specifications
1,4,5
2,4,5
3,4,5
3.5 Package Insertion Specifications
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series can be inserted and removed 15
times from an LGA771 socket, which meets the criteria outlined in the LGA771 Socket
Design Guidelines.
3.6 Processor Mass Specifications
The typical mass of the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series is 21.5 g
(0.76 oz). This includes all components which make up the entire processor product.
3.7 Processor Materials
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series are assembled from several
components. The basic material properties are described in Ta b le 3- 3 .
Table 3-3. Processor Materials
Component Material
Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) Nickel over copper
Substrate Fiber-reinforced resin
Substrate Lands Gold over nickel
44 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 45

Mechanical Specifications
3.8 Processor Markings
Figure 3-5 shows the topside markings on the processor. This diagram aids in the
identification of the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series.
Figure 3-5. Processor Top-side Markings (Example)
Legend:
GROUP1LINE1
GROUP1LINE2
GROUP1LINE3
GROUP1LINE4
GROUP1LINE5
ATPO
ATPO
LOT NO
S/N
S/N
S/N
Notes:
1. 2D matrix is required for engineering samples only (encoded with ATPO-S/N)
GROUP1LINE1
GROUP1LINE2
GROUP1LINE3
GROUP1LINE4
GROUP1LINE5
Legend:
GROUP1LINE1
GROUP1LINE2
GROUP1LINE3
GROUP1LINE4
GROUP1LINE5
3.9 Processor Land Coordinates
Figure 3-6 and Figure 3-7 show the top and bottom view of the processor land
coordinates, respectively. The coordinates are referred to throughout the document to
identify processor lands.
Mark Text (Production Mark):
2.66GHZ/8M/1333
Intel ® Xeon®
SXXX XXXXX
i (M) © ’05 x53XX
(FPO)
Mark Text (Engineering Mark):
INTEL CONFIDENTIAL
QXXX ES XXXXX
i (M) © ‘05 HH80563KJ0678M
(FPO) e4
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 45
Page 46

Figure 3-6. Processor Land Coordinates, Top View
Mechanical Specifications
VCC/ V
AN
AM
AL
AK
AJ
AH
AG
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
Y
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
VTT/ Clocks
SS
Socket 771
Quadrants
Top View
Data
6789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
12345
AN
AM
AL
AK
AJ
AH
AG
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
Y
W
V
U
R
P
N
M
K
H
G
E
D
C
B
A
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930
Address /
Common Clock /
T
L
J
F
Async
46 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 47

Mechanical Specifications
Figure 3-7. Processor Land Coordinates, Bottom View
Address /
Common Clock /
Async
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
AN
AM
AL
AK
AJ
AH
AG
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
Y
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
Socket 771
Quadrants
Bottom View
Data
VCC/ V
SS
VTT/ Clocks
AN
AM
AL
AK
AJ
AH
AG
AF
AE
AD
AC
AB
AA
Y
W
V
U
T
R
P
N
M
L
K
J
H
G
F
E
D
C
B
A
§
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 47
Page 48

Mechanical Specifications
48 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 49

Land Listing
4 Land Listing
4.1 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
Pin Assignments
This section provides sorted land list in Tab le 4-1 and Ta bl e 4 -2 . Tab le 4- 1 is a listing of
all processor lands ordered alphabetically by land name. Ta b l e 4- 2 is a listing of all
processor lands ordered by land number.
4.1.1 Land Listing by Land Name
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 1 of 22)
Pin Name
A03# M5 Source Sync Input/
A04# P6 Source Sync Input/
A05# L5 Source Sync Input/
A06# L4 Source Sync Input/
A07# M4 Source Sync Input/
A08# R4 Source Sync Input/
A09# T5 Source Sync Input/
A10# U6 Source Sync Input/
A11# T4 Source Sync Input/
A12# U5 Source Sync Input/
A13# U4 Source Sync Input/
A14# V5 Source Sync Input/
A15# V4 Source Sync Input/
A16# W5 Source Sync Input/
A17# AB6 Source Sync Input/
A18# W6 Source Sync Input/
A19# Y6 Source Sync Input/
A20# Y4 Source Sync Input/
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 2 of 22)
Pin Name
A20M# K3 ASync GTL+ Input
A21# AA4 Source Sync Input/
A22# AD6 Source Sync Input/
A23# AA5 Source Sync Input/
A24# AB5 Source Sync Input/
A25# AC5 Source Sync Input/
A26# AB4 Source Sync Input/
A27# AF5 Source Sync Input/
A28# AF4 Source Sync Input/
A29# AG6 Source Sync Input/
A30# AG4 Source Sync Input/
A31# AG5 Source Sync Input/
A32# AH4 Source Sync Input/
A33# AH5 Source Sync Input/
A34# AJ5 Source Sync Input/
A35# AJ6 Source Sync Input/
A36# N4 Source Sync Input/
A37# P5 Source Sync Input/
ADS# D2 Common Clk Input/
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 49
Page 50

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 3 of 22)
Pin Name
ADSTB0# R6 Source Sync Input/
ADSTB1# AD5 Source Sync Input/
AP0# U2 Common Clk Input/
AP1# U3 Common Clk Input/
BCLK0 F28 Clk Input
BCLK1 G28 Clk Input
BINIT# AD3 Common Clk Input/
BNR# C2 Common Clk Input/
BPM0# AJ2 Common Clk Input/
BPM1# AJ1 Common Clk Output
BPM2# AD2 Common Clk Output
BPM3# AG2 Common Clk Input/
BPM4# AF2 Common Clk Output
BPM5# AG3 Common Clk Input/
BPMb0# G1 Common Clk Input/
BPMb1# C9 Common Clk Output
BPMb2# G4 Common Clk Output
BPMb3# G3 Common Clk Input/
BPRI# G8 Common Clk Input
BR0# F3 Common Clk Input/
BR1# H5 Common Clk Input
BSEL0 G29 Power/Other Output
BSEL1 H30 Power/Other Output
BSEL2 G30 Power/Other Output
COMP0 A13 Power/Other Input
COMP1 T1 Power/Other Input
COMP2 G2 Power/Other Input
COMP3 R1 Power/Other Input
D00# B4 Source Sync Input/
D01# C5 Source Sync Input/
D02# A4 Source Sync Input/
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 4 of 22)
Pin Name
D03# C6 Source Sync Input/
D04# A5 Source Sync Input/
D05# B6 Source Sync Input/
D06# B7 Source Sync Input/
D07# A7 Source Sync Input/
D08# A10 Source Sync Input/
D09# A11 Source Sync Input/
D10# B10 Source Sync Input/
D11# C11 Source Sync Input/
D12# D8 Source Sync Input/
D13# B12 Source Sync Input/
D14# C12 Source Sync Input/
D15# D11 Source Sync Input/
D16# G9 Source Sync Input/
D17# F8 Source Sync Input/
D18# F9 Source Sync Input/
D19# E9 Source Sync Input/
D20# D7 Source Sync Input/
D21# E10 Source Sync Input/
D22# D10 Source Sync Input/
D23# F11 Source Sync Input/
D24# F12 Source Sync Input/
D25# D13 Source Sync Input/
D26# E13 Source Sync Input/
D27# G13 Source Sync Input/
D28# F14 Source Sync Input/
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
50 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 51

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 5 of 22)
Pin Name
D29# G14 Source Sync Input/
D30# F15 Source Sync Input/
D31# G15 Source Sync Input/
D32# G16 Source Sync Input/
D33# E15 Source Sync Input/
D34# E16 Source Sync Input/
D35# G18 Source Sync Input/
D36# G17 Source Sync Input/
D37# F17 Source Sync Input/
D38# F18 Source Sync Input/
D39# E18 Source Sync Input/
D40# E19 Source Sync Input/
D41# F20 Source Sync Input/
D42# E21 Source Sync Input/
D43# F21 Source Sync Input/
D44# G21 Source Sync Input/
D45# E22 Source Sync Input/
D46# D22 Source Sync Input/
D47# G22 Source Sync Input/
D48# D20 Source Sync Input/
D49# D17 Source Sync Input/
D50# A14 Source Sync Input/
D51# C15 Source Sync Input/
D52# C14 Source Sync Input/
D53# B15 Source Sync Input/
D54# C18 Source Sync Input/
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 6 of 22)
Pin Name
D55# B16 Source Sync Input/
D56# A17 Source Sync Input/
D57# B18 Source Sync Input/
D58# C21 Source Sync Input/
D59# B21 Source Sync Input/
D60# B19 Source Sync Input/
D61# A19 Source Sync Input/
D62# A22 Source Sync Input/
D63# B22 Source Sync Input/
DBI0# A8 Source Sync Input/
DBI1# G11 Source Sync Input/
DBI2# D19 Source Sync Input/
DBI3# C20 Source Sync Input/
DBR# AC2 Power/Other Output
DBSY# B2 Common Clk Input/
DEFER# G7 Common Clk Input
DP0# J16 Common Clk Input/
DP1# H15 Common Clk Input/
DP2# H16 Common Clk Input/
DP3# J17 Common Clk Input/
DRDY# C1 Common Clk Input/
DSTBN0# C8 Source Sync Input/
DSTBN1# G12 Source Sync Input/
DSTBN2# G20 Source Sync Input/
DSTBN3# A16 Source Sync Input/
DSTBP0# B9 Source Sync Input/
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 51
Page 52

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 7 of 22)
Pin Name
DSTBP1# E12 Source Sync Input/
DSTBP2# G19 Source Sync Input/
DSTBP3# C17 Source Sync Input/
FERR#/PBE# R3 ASync GTL+ Output
FORCEPR# AK6 ASync GTL+ Input
GTLREF_ADD_END G10 Power/Other Input
GTLREF_ADD_MID F2 Power/Other Input
GTLREF_DATA_END H1 Power/Other Input
GTLREF_DATA_MID H2 Power/Other Input
HIT# D4 Common Clk Input/
HITM# E4 Common Clk Input/
IERR# AB2 ASync GTL+ Output
IGNNE# N2 ASync GTL+ Input
INIT# P3 ASync GTL+ Input
LINT0 K1 ASync GTL+ Input
LINT1 L1 ASync GTL+ Input
LL_ID0 V2 Power/Other Output
LL_ID1 AA2 Power/Other Output
LOCK# C3 Common Clk Input/
MCERR# AB3 Common Clk Input/
MS_ID0 W1 Power/Other Output
MS_ID1 V1 Power/Other Output
PECI G5 Power/Other Input/
PROCHOT# AL2 ASync GTL+ Output
PWRGOOD N1 Power/Other Input
REQ0# K4 Source Sync Input/
REQ1# J5 Source Sync Input/
REQ2# M6 Source Sync Input/
REQ3# K6 Source Sync Input/
REQ4# J6 Source Sync Input/
RESERVED A20
RESERVED A23
RESERVED A24
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Output
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 8 of 22)
Pin Name
RESERVED AC4
RESERVED AE3
RESERVED AE4
RESERVED AE6
RESERVED AH2
RESERVED AH7
RESERVED AJ3
RESERVED AJ7
RESERVED AK1
RESERVED AK3
RESERVED AL1
RESERVED AM2
RESERVED AM6
RESERVED AN5
RESERVED AN6
RESERVED B13
RESERVED B23
RESERVED C23
RESERVED D1
RESERVED D14
RESERVED D16
RESERVED E1
RESERVED E23
RESERVED E24
RESERVED E29
RESERVED E5
RESERVED E6
RESERVED E7
RESERVED F23
RESERVED F29
RESERVED F6
RESERVED G6
RESERVED J2
RESERVED J3
RESERVED N5
RESERVED T2
RESERVED Y1
RESERVED Y3
RESET# G23 Common Clk Input
RS0# B3 Common Clk Input
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
52 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 53

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 9 of 22)
Pin Name
RS1# F5 Common Clk Input
RS2# A3 Common Clk Input
RSP# H4 Common Clk Input
SKTOCC# AE8 Power/Other Output
SMI# P2 ASync GTL+ Input
STPCLK# M3 ASync GTL+ Input
TCK AE1 TAP Input
TDI AD1 TAP Input
TDO AF1 TAP Output
TESTHI00 F26 Power/Other Input
TESTHI01 W3 Power/Other Input
TESTHI02 F25 Power/Other Input
TESTHI03 G25 Power/Other Input
TESTHI04 G27 Power/Other Input
TESTHI05 G26 Power/Other Input
TESTHI06 G24 Power/Other Input
TESTHI07 F24 Power/Other Input
TESTHI10 P1 Power/Other Input
TESTHI11 L2 Power/Other Input
TESTIN1 W2 Power/Other Input
TESTIN2 U1 Power/Other Input
THERMTRIP# M2 ASync GTL+ Output
TMS AC1 TAP Input
TRDY# E3 Common Clk Input
TRST# AG1 TAP Input
VCC AA8 Power/Other
VCC AB8 Power/Other
VCC AC23 Power/Other
VCC AC24 Power/Other
VCC AC25 Power/Other
VCC AC26 Power/Other
VCC AC27 Power/Other
VCC AC28 Power/Other
VCC AC29 Power/Other
VCC AC30 Power/Other
VCC AC8 Power/Other
VCC AD23 Power/Other
VCC AD24 Power/Other
VCC AD25 Power/Other
VCC AD26 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 10 of 22)
Pin Name
VCC AD27 Power/Other
VCC AD28 Power/Other
VCC AD29 Power/Other
VCC AD30 Power/Other
VCC AD8 Power/Other
VCC AE11 Power/Other
VCC AE12 Power/Other
VCC AE14 Power/Other
VCC AE15 Power/Other
VCC AE18 Power/Other
VCC AE19 Power/Other
VCC AE21 Power/Other
VCC AE22 Power/Other
VCC AE23 Power/Other
VCC AE9 Power/Other
VCC AF11 Power/Other
VCC AF12 Power/Other
VCC AF14 Power/Other
VCC AF15 Power/Other
VCC AF18 Power/Other
VCC AF19 Power/Other
VCC AF21 Power/Other
VCC AF22 Power/Other
VCC AF8 Power/Other
VCC AF9 Power/Other
VCC AG11 Power/Other
VCC AG12 Power/Other
VCC AG14 Power/Other
VCC AG15 Power/Other
VCC AG18 Power/Other
VCC AG19 Power/Other
VCC AG21 Power/Other
VCC AG22 Power/Other
VCC AG25 Power/Other
VCC AG26 Power/Other
VCC AG27 Power/Other
VCC AG28 Power/Other
VCC AG29 Power/Other
VCC AG30 Power/Other
VCC AG8 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 53
Page 54

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 11 of 22)
Pin Name
VCC AG9 Power/Other
VCC AH11 Power/Other
VCC AH12 Power/Other
VCC AH14 Power/Other
VCC AH15 Power/Other
VCC AH18 Power/Other
VCC AH19 Power/Other
VCC AH21 Power/Other
VCC AH22 Power/Other
VCC AH25 Power/Other
VCC AH26 Power/Other
VCC AH27 Power/Other
VCC AH28 Power/Other
VCC AH29 Power/Other
VCC AH30 Power/Other
VCC AH8 Power/Other
VCC AH9 Power/Other
VCC AJ11 Power/Other
VCC AJ12 Power/Other
VCC AJ14 Power/Other
VCC AJ15 Power/Other
VCC AJ18 Power/Other
VCC AJ19 Power/Other
VCC AJ21 Power/Other
VCC AJ22 Power/Other
VCC AJ25 Power/Other
VCC AJ26 Power/Other
VCC AJ8 Power/Other
VCC AJ9 Power/Other
VCC AK11 Power/Other
VCC AK12 Power/Other
VCC AK14 Power/Other
VCC AK15 Power/Other
VCC AK18 Power/Other
VCC AK19 Power/Other
VCC AK21 Power/Other
VCC AK22 Power/Other
VCC AK25 Power/Other
VCC AK26 Power/Other
VCC AK8 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 12 of 22)
Pin Name
VCC AK9 Power/Other
VCC AL11 Power/Other
VCC AL12 Power/Other
VCC AL14 Power/Other
VCC AL15 Power/Other
VCC AL18 Power/Other
VCC AL19 Power/Other
VCC AL21 Power/Other
VCC AL22 Power/Other
VCC AL25 Power/Other
VCC AL26 Power/Other
VCC AL29 Power/Other
VCC AL30 Power/Other
VCC AL9 Power/Other
VCC AM11 Power/Other
VCC AM12 Power/Other
VCC AM14 Power/Other
VCC AM15 Power/Other
VCC AM18 Power/Other
VCC AM19 Power/Other
VCC AM21 Power/Other
VCC AM22 Power/Other
VCC AM25 Power/Other
VCC AM26 Power/Other
VCC AM29 Power/Other
VCC AM30 Power/Other
VCC AM8 Power/Other
VCC AM9 Power/Other
VCC AN11 Power/Other
VCC AN12 Power/Other
VCC AN14 Power/Other
VCC AN15 Power/Other
VCC AN18 Power/Other
VCC AN19 Power/Other
VCC AN21 Power/Other
VCC AN22 Power/Other
VCC AN25 Power/Other
VCC AN26 Power/Other
VCC AN8 Power/Other
VCC AN9 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
54 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 55

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 13 of 22)
Pin Name
VCC J10 Power/Other
VCC J11 Power/Other
VCC J12 Power/Other
VCC J13 Power/Other
VCC J14 Power/Other
VCC J15 Power/Other
VCC J18 Power/Other
VCC J19 Power/Other
VCC J20 Power/Other
VCC J21 Power/Other
VCC J22 Power/Other
VCC J23 Power/Other
VCC J24 Power/Other
VCC J25 Power/Other
VCC J26 Power/Other
VCC J27 Power/Other
VCC J28 Power/Other
VCC J29 Power/Other
VCC J30 Power/Other
VCC J8 Power/Other
VCC J9 Power/Other
VCC K23 Power/Other
VCC K24 Power/Other
VCC K25 Power/Other
VCC K26 Power/Other
VCC K27 Power/Other
VCC K28 Power/Other
VCC K29 Power/Other
VCC K30 Power/Other
VCC K8 Power/Other
VCC L8 Power/Other
VCC M23 Power/Other
VCC M24 Power/Other
VCC M25 Power/Other
VCC M26 Power/Other
VCC M27 Power/Other
VCC M28 Power/Other
VCC M29 Power/Other
VCC M30 Power/Other
VCC M8 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 14 of 22)
Pin Name
VCC N23 Power/Other
VCC N24 Power/Other
VCC N25 Power/Other
VCC N26 Power/Other
VCC N27 Power/Other
VCC N28 Power/Other
VCC N29 Power/Other
VCC N30 Power/Other
VCC N8 Power/Other
VCC P8 Power/Other
VCC R8 Power/Other
VCC T23 Power/Other
VCC T24 Power/Other
VCC T25 Power/Other
VCC T26 Power/Other
VCC T27 Power/Other
VCC T28 Power/Other
VCC T29 Power/Other
VCC T30 Power/Other
VCC T8 Power/Other
VCC U23 Power/Other
VCC U24 Power/Other
VCC U25 Power/Other
VCC U26 Power/Other
VCC U27 Power/Other
VCC U28 Power/Other
VCC U29 Power/Other
VCC U30 Power/Other
VCC U8 Power/Other
VCC V8 Power/Other
VCC W23 Power/Other
VCC W24 Power/Other
VCC W25 Power/Other
VCC W26 Power/Other
VCC W27 Power/Other
VCC W28 Power/Other
VCC W29 Power/Other
VCC W30 Power/Other
VCC W8 Power/Other
VCC Y23 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 55
Page 56

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 15 of 22)
Pin Name
VCC Y24 Power/Other
VCC Y25 Power/Other
VCC Y26 Power/Other
VCC Y27 Power/Other
VCC Y28 Power/Other
VCC Y29 Power/Other
VCC Y30 Power/Other
VCC Y8 Power/Other
VCC_DIE_SENSE AN3 Power/Other Output
VCC_DIE_SENSE2 AL8 Power/Other Output
VCCPLL D23 Power/Other Input
VID_SELECT AN7 Power/Other Output
VID1 AL5 Power/Other Output
VID2 AM3 Power/Other Output
VID3 AL6 Power/Other Output
VID4 AK4 Power/Other Output
VID5 AL4 Power/Other Output
VID6 AM5 Power/Other Output
VSS A12 Power/Other
VSS A15 Power/Other
VSS A18 Power/Other
VSS A2 Power/Other
VSS A21 Power/Other
VSS A6 Power/Other
VSS A9 Power/Other
VSS AA23 Power/Other
VSS AA24 Power/Other
VSS AA25 Power/Other
VSS AA26 Power/Other
VSS AA27 Power/Other
VSS AA28 Power/Other
VSS AA29 Power/Other
VSS AA3 Power/Other
VSS AA30 Power/Other
VSS AA6 Power/Other
VSS AA7 Power/Other
VSS AB1 Power/Other
VSS AB23 Power/Other
VSS AB24 Power/Other
VSS AB25 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 16 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS AB26 Power/Other
VSS AB27 Power/Other
VSS AB28 Power/Other
VSS AB29 Power/Other
VSS AB30 Power/Other
VSS AB7 Power/Other
VSS AC3 Power/Other
VSS AC6 Power/Other
VSS AC7 Power/Other
VSS AD4 Power/Other
VSS AD7 Power/Other
VSS AE10 Power/Other
VSS AE13 Power/Other
VSS AE16 Power/Other
VSS AE17 Power/Other
VSS AE2 Power/Other
VSS AE20 Power/Other
VSS AE24 Power/Other
VSS AE25 Power/Other
VSS AE26 Power/Other
VSS AE27 Power/Other
VSS AE28 Power/Other
VSS AE29 Power/Other
VSS AE30 Power/Other
VSS AE5 Power/Other
VSS AE7 Power/Other
VSS AF10 Power/Other
VSS AF13 Power/Other
VSS AF16 Power/Other
VSS AF17 Power/Other
VSS AF20 Power/Other
VSS AF23 Power/Other
VSS AF24 Power/Other
VSS AF25 Power/Other
VSS AF26 Power/Other
VSS AF27 Power/Other
VSS AF28 Power/Other
VSS AF29 Power/Other
VSS AF3 Power/Other
VSS AF30 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
56 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 57

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 17 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS AF6 Power/Other
VSS AF7 Power/Other
VSS AG10 Power/Other
VSS AG13 Power/Other
VSS AG16 Power/Other
VSS AG17 Power/Other
VSS AG20 Power/Other
VSS AG23 Power/Other
VSS AG24 Power/Other
VSS AG7 Power/Other
VSS AH1 Power/Other
VSS AH10 Power/Other
VSS AH13 Power/Other
VSS AH16 Power/Other
VSS AH17 Power/Other
VSS AH20 Power/Other
VSS AH23 Power/Other
VSS AH24 Power/Other
VSS AH3 Power/Other
VSS AH6 Power/Other
VSS AJ10 Power/Other
VSS AJ13 Power/Other
VSS AJ16 Power/Other
VSS AJ17 Power/Other
VSS AJ20 Power/Other
VSS AJ23 Power/Other
VSS AJ24 Power/Other
VSS AJ27 Power/Other
VSS AJ28 Power/Other
VSS AJ29 Power/Other
VSS AJ30 Power/Other
VSS AJ4 Power/Other
VSS AK10 Power/Other
VSS AK13 Power/Other
VSS AK16 Power/Other
VSS AK17 Power/Other
VSS AK2 Power/Other
VSS AK20 Power/Other
VSS AK23 Power/Other
VSS AK24 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 18 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS AK27 Power/Other
VSS AK28 Power/Other
VSS AK29 Power/Other
VSS AK30 Power/Other
VSS AK5 Power/Other
VSS AK7 Power/Other
VSS AL10 Power/Other
VSS AL13 Power/Other
VSS AL16 Power/Other
VSS AL17 Power/Other
VSS AL20 Power/Other
VSS AL23 Power/Other
VSS AL24 Power/Other
VSS AL27 Power/Other
VSS AL28 Power/Other
VSS AL3 Power/Other
VSS AM1 Power/Other
VSS AM10 Power/Other
VSS AM13 Power/Other
VSS AM16 Power/Other
VSS AM17 Power/Other
VSS AM20 Power/Other
VSS AM23 Power/Other
VSS AM24 Power/Other
VSS AM27 Power/Other
VSS AM28 Power/Other
VSS AM4 Power/Other
VSS AM7 Power/Other
VSS AN1 Power/Other
VSS AN10 Power/Other
VSS AN13 Power/Other
VSS AN16 Power/Other
VSS AN17 Power/Other
VSS AN2 Power/Other
VSS AN20 Power/Other
VSS AN23 Power/Other
VSS AN24 Power/Other
VSS B1 Power/Other
VSS B11 Power/Other
VSS B14 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 57
Page 58

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 19 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS B17 Power/Other
VSS B20 Power/Other
VSS B24 Power/Other
VSS B5 Power/Other
VSS B8 Power/Other
VSS C10 Power/Other
VSS C13 Power/Other
VSS C16 Power/Other
VSS C19 Power/Other
VSS C22 Power/Other
VSS C24 Power/Other
VSS C4 Power/Other
VSS C7 Power/Other
VSS D12 Power/Other
VSS D15 Power/Other
VSS D18 Power/Other
VSS D21 Power/Other
VSS D24 Power/Other
VSS D3 Power/Other
VSS D5 Power/Other
VSS D6 Power/Other
VSS D9 Power/Other
VSS E11 Power/Other
VSS E14 Power/Other
VSS E17 Power/Other
VSS E2 Power/Other
VSS E20 Power/Other
VSS E25 Power/Other
VSS E26 Power/Other
VSS E27 Power/Other
VSS E28 Power/Other
VSS E8 Power/Other
VSS F1 Power/Other
VSS F10 Power/Other
VSS F13 Power/Other
VSS F16 Power/Other
VSS F19 Power/Other
VSS F22 Power/Other
VSS F4 Power/Other
VSS F7 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 20 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS H10 Power/Other
VSS H11 Power/Other
VSS H12 Power/Other
VSS H13 Power/Other
VSS H14 Power/Other
VSS H17 Power/Other
VSS H18 Power/Other
VSS H19 Power/Other
VSS H20 Power/Other
VSS H21 Power/Other
VSS H22 Power/Other
VSS H23 Power/Other
VSS H24 Power/Other
VSS H25 Power/Other
VSS H26 Power/Other
VSS H27 Power/Other
VSS H28 Power/Other
VSS H29 Power/Other
VSS H3 Power/Other
VSS H6 Power/Other
VSS H7 Power/Other
VSS H8 Power/Other
VSS H9 Power/Other
VSS J4 Power/Other
VSS J7 Power/Other
VSS K2 Power/Other
VSS K5 Power/Other
VSS K7 Power/Other
VSS L23 Power/Other
VSS L24 Power/Other
VSS L25 Power/Other
VSS L26 Power/Other
VSS L27 Power/Other
VSS L28 Power/Other
VSS L29 Power/Other
VSS L3 Power/Other
VSS L30 Power/Other
VSS L6 Power/Other
VSS L7 Power/Other
VSS M1 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
58 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 59

Land Listing
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 21 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS M7 Power/Other
VSS N3 Power/Other
VSS N6 Power/Other
VSS N7 Power/Other
VSS P23 Power/Other
VSS P24 Power/Other
VSS P25 Power/Other
VSS P26 Power/Other
VSS P27 Power/Other
VSS P28 Power/Other
VSS P29 Power/Other
VSS P30 Power/Other
VSS P4 Power/Other
VSS P7 Power/Other
VSS R2 Power/Other
VSS R23 Power/Other
VSS R24 Power/Other
VSS R25 Power/Other
VSS R26 Power/Other
VSS R27 Power/Other
VSS R28 Power/Other
VSS R29 Power/Other
VSS R30 Power/Other
VSS R5 Power/Other
VSS R7 Power/Other
VSS T3 Power/Other
VSS T6 Power/Other
VSS T7 Power/Other
VSS U7 Power/Other
VSS V23 Power/Other
VSS V24 Power/Other
VSS V25 Power/Other
VSS V26 Power/Other
VSS V27 Power/Other
VSS V28 Power/Other
VSS V29 Power/Other
VSS V3 Power/Other
VSS V30 Power/Other
VSS V6 Power/Other
VSS V7 Power/Other
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-1. Land Listing by Land Name
(Sheet 22 of 22)
Pin Name
VSS W4 Power/Other
VSS W7 Power/Other
VSS Y2 Power/Other
VSS Y5 Power/Other
VSS Y7 Power/Other
VSS_DIE_SENSE AN4 Power/Other Output
VSS_DIE_SENSE2 AL7 Power/Other Output
VTT A25 Power/Other
VTT A26 Power/Other
VTT B25 Power/Other
VTT B26 Power/Other
VTT B27 Power/Other
VTT B28 Power/Other
VTT B29 Power/Other
VTT B30 Power/Other
VTT C25 Power/Other
VTT C26 Power/Other
VTT C27 Power/Other
VTT C28 Power/Other
VTT C29 Power/Other
VTT C30 Power/Other
VTT D25 Power/Other
VTT D26 Power/Other
VTT D27 Power/Other
VTT D28 Power/Other
VTT D29 Power/Other
VTT D30 Power/Other
VTT E30 Power/Other
VTT F30 Power/Other
VTT_OUT AA1 Power/Other Output
VTT_OUT J1 Power/Other Output
VTT_SEL F27 Power/Other Output
Pin
No.
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 59
Page 60

4.1.2 Land Listing by Land Number
Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 1 of 20)
Pin
No.
A10 D08# Source Sync Input/Output
A11 D09# Source Sync Input/Output
A12 VSS Power/Other
A13 COMP0 Power/Other Input
A14 D50# Source Sync Input/Output
A15 VSS Power/Other
A16 DSTBN3# Source Sync Input/Output
A17 D56# Source Sync Input/Output
A18 VSS Power/Other
A19 D61# Source Sync Input/Output
A2 VSS Power/Other
A20 RESERVED
A21 VSS Power/Other
A22 D62# Source Sync Input/Output
A23 RESERVED
A24 RESERVED
A25 VTT Power/Other
A26 VTT Power/Other
A3 RS2# Common Clk Input
A4 D02# Source Sync Input/Output
A5 D04# Source Sync Input/Output
A6 VSS Power/Other
A7 D07# Source Sync Input/Output
A8 DBI0# Source Sync Input/Output
A9 VSS Power/Other
AA1 VTT_OUT Power/Other Output
AA2 LL_ID1 Power/Other Output
AA23 VSS Power/Other
AA24 VSS Power/Other
AA25 VSS Power/Other
AA26 VSS Power/Other
AA27 VSS Power/Other
AA28 VSS Power/Other
AA29 VSS Power/Other
AA3 VSS Power/Other
AA30 VSS Power/Other
AA4 A21# Source Sync Input/Output
AA5 A23# Source Sync Input/Output
AA6 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 2 of 20)
Pin
No.
AA7 VSS Power/Other
AA8 VCC Power/Other
AB1 VSS Power/Other
AB2 IERR# ASync GTL+ Output
AB23 VSS Power/Other
AB24 VSS Power/Other
AB25 VSS Power/Other
AB26 VSS Power/Other
AB27 VSS Power/Other
AB28 VSS Power/Other
AB29 VSS Power/Other
AB3 MCERR# Common Clk Input/Output
AB30 VSS Power/Other
AB4 A26# Source Sync Input/Output
AB5 A24# Source Sync Input/Output
AB6 A17# Source Sync Input/Output
AB7 VSS Power/Other
AB8 VCC Power/Other
AC1 TMS TAP Input
AC2 DBR# Power/Other Output
AC23 VCC Power/Other
AC24 VCC Power/Other
AC25 VCC Power/Other
AC26 VCC Power/Other
AC27 VCC Power/Other
AC28 VCC Power/Other
AC29 VCC Power/Other
AC3 VSS Power/Other
AC30 VCC Power/Other
AC4 RESERVED
AC5 A25# Source Sync Input/Output
AC6 VSS Power/Other
AC7 VSS Power/Other
AC8 VCC Power/Other
AD1 TDI TAP Input
AD2 BPM2# Common Clk Output
AD23 VCC Power/Other
AD24 VCC Power/Other
AD25 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
60 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 61

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 3 of 20)
Pin
No.
AD26 VCC Power/Other
AD27 VCC Power/Other
AD28 VCC Power/Other
AD29 VCC Power/Other
AD3 BINIT# Common Clk Input/Output
AD30 VCC Power/Other
AD4 VSS Power/Other
AD5 ADSTB1# Source Sync Input/Output
AD6 A22# Source Sync Input/Output
AD7 VSS Power/Other
AD8 VCC Power/Other
AE1 TCK TAP Input
AE10 VSS Power/Other
AE11 VCC Power/Other
AE12 VCC Power/Other
AE13 VSS Power/Other
AE14 VCC Power/Other
AE15 VCC Power/Other
AE16 VSS Power/Other
AE17 VSS Power/Other
AE18 VCC Power/Other
AE19 VCC Power/Other
AE2 VSS Power/Other
AE20 VSS Power/Other
AE21 VCC Power/Other
AE22 VCC Power/Other
AE23 VCC Power/Other
AE24 VSS Power/Other
AE25 VSS Power/Other
AE26 VSS Power/Other
AE27 VSS Power/Other
AE28 VSS Power/Other
AE29 VSS Power/Other
AE3 RESERVED
AE30 VSS Power/Other
AE4 RESERVED
AE5 VSS Power/Other
AE6 RESERVED
AE7 VSS Power/Other
AE8 SKTOCC# Power/Other Output
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 4 of 20)
Pin
No.
AE9 VCC Power/Other
AF1 TDO TAP Output
AF10 VSS Power/Other
AF11 VCC Power/Other
AF12 VCC Power/Other
AF13 VSS Power/Other
AF14 VCC Power/Other
AF15 VCC Power/Other
AF16 VSS Power/Other
AF17 VSS Power/Other
AF18 VCC Power/Other
AF19 VCC Power/Other
AF2 BPM4# Common Clk Output
AF20 VSS Power/Other
AF21 VCC Power/Other
AF22 VCC Power/Other
AF23 VSS Power/Other
AF24 VSS Power/Other
AF25 VSS Power/Other
AF26 VSS Power/Other
AF27 VSS Power/Other
AF28 VSS Power/Other
AF29 VSS Power/Other
AF3 VSS Power/Other
AF30 VSS Power/Other
AF4 A28# Source Sync Input/Output
AF5 A27# Source Sync Input/Output
AF6 VSS Power/Other
AF7 VSS Power/Other
AF8 VCC Power/Other
AF9 VCC Power/Other
AG1 TRST# TAP Input
AG10 VSS Power/Other
AG11 VCC Power/Other
AG12 VCC Power/Other
AG13 VSS Power/Other
AG14 VCC Power/Other
AG15 VCC Power/Other
AG16 VSS Power/Other
AG17 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 61
Page 62

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 5 of 20)
Pin
No.
AG18 VCC Power/Other
AG19 VCC Power/Other
AG2 BPM3# Common Clk Input/Output
AG20 VSS Power/Other
AG21 VCC Power/Other
AG22 VCC Power/Other
AG23 VSS Power/Other
AG24 VSS Power/Other
AG25 VCC Power/Other
AG26 VCC Power/Other
AG27 VCC Power/Other
AG28 VCC Power/Other
AG29 VCC Power/Other
AG3 BPM5# Common Clk Input/Output
AG30 VCC Power/Other
AG4 A30# Source Sync Input/Output
AG5 A31# Source Sync Input/Output
AG6 A29# Source Sync Input/Output
AG7 VSS Power/Other
AG8 VCC Power/Other
AG9 VCC Power/Other
AH1 VSS Power/Other
AH10 VSS Power/Other
AH11 VCC Power/Other
AH12 VCC Power/Other
AH13 VSS Power/Other
AH14 VCC Power/Other
AH15 VCC Power/Other
AH16 VSS Power/Other
AH17 VSS Power/Other
AH18 VCC Power/Other
AH19 VCC Power/Other
AH2 RESERVED
AH20 VSS Power/Other
AH21 VCC Power/Other
AH22 VCC Power/Other
AH23 VSS Power/Other
AH24 VSS Power/Other
AH25 VCC Power/Other
AH26 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 6 of 20)
Pin
No.
AH27 VCC Power/Other
AH28 VCC Power/Other
AH29 VCC Power/Other
AH3 VSS Power/Other
AH30 VCC Power/Other
AH4 A32# Source Sync Input/Output
AH5 A33# Source Sync Input/Output
AH6 VSS Power/Other
AH7 RESERVED
AH8 VCC Power/Other
AH9 VCC Power/Other
AJ1 BPM1# Common Clk Output
AJ10 VSS Power/Other
AJ11 VCC Power/Other
AJ12 VCC Power/Other
AJ13 VSS Power/Other
AJ14 VCC Power/Other
AJ15 VCC Power/Other
AJ16 VSS Power/Other
AJ17 VSS Power/Other
AJ18 VCC Power/Other
AJ19 VCC Power/Other
AJ2 BPM0# Common Clk Input/Output
AJ20 VSS Power/Other
AJ21 VCC Power/Other
AJ22 VCC Power/Other
AJ23 VSS Power/Other
AJ24 VSS Power/Other
AJ25 VCC Power/Other
AJ26 VCC Power/Other
AJ27 VSS Power/Other
AJ28 VSS Power/Other
AJ29 VSS Power/Other
AJ3 RESERVED
AJ30 VSS Power/Other
AJ4 VSS Power/Other
AJ5 A34# Source Sync Input/Output
AJ6 A35# Source Sync Input/Output
AJ7 RESERVED
AJ8 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
62 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 63

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 7 of 20)
Pin
No.
AJ9 VCC Power/Other
AK1 RESERVED
AK10 VSS Power/Other
AK11 VCC Power/Other
AK12 VCC Power/Other
AK13 VSS Power/Other
AK14 VCC Power/Other
AK15 VCC Power/Other
AK16 VSS Power/Other
AK17 VSS Power/Other
AK18 VCC Power/Other
AK19 VCC Power/Other
AK2 VSS Power/Other
AK20 VSS Power/Other
AK21 VCC Power/Other
AK22 VCC Power/Other
AK23 VSS Power/Other
AK24 VSS Power/Other
AK25 VCC Power/Other
AK26 VCC Power/Other
AK27 VSS Power/Other
AK28 VSS Power/Other
AK29 VSS Power/Other
AK3 RESERVED
AK30 VSS Power/Other
AK4 VID4 Power/Other Output
AK5 VSS Power/Other
AK6 FORCEPR# ASync GTL+ Input
AK7 VSS Power/Other
AK8 VCC Power/Other
AK9 VCC Power/Other
AL1 RESERVED
AL10 VSS Power/Other
AL11 VCC Power/Other
AL12 VCC Power/Other
AL13 VSS Power/Other
AL14 VCC Power/Other
AL15 VCC Power/Other
AL16 VSS Power/Other
AL17 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 8 of 20)
Pin
No.
AL18 VCC Power/Other
AL19 VCC Power/Other
AL2 PROCHOT# ASync GTL+ Output
AL20 VSS Power/Other
AL21 VCC Power/Other
AL22 VCC Power/Other
AL23 VSS Power/Other
AL24 VSS Power/Other
AL25 VCC Power/Other
AL26 VCC Power/Other
AL27 VSS Power/Other
AL28 VSS Power/Other
AL29 VCC Power/Other
AL3 VSS Power/Other
AL30 VCC Power/Other
AL4 VID5 Power/Other Output
AL5 VID1 Power/Other Output
AL6 VID3 Power/Other Output
AL7 VSS_DIE_SENSE2 Power/Other
AL8 VCC_DIE_SENSE2 Power/Other
AL9 VCC Power/Other
AM1 VSS Power/Other
AM10 VSS Power/Other
AM11 VCC Power/Other
AM12 VCC Power/Other
AM13 VSS Power/Other
AM14 VCC Power/Other
AM15 VCC Power/Other
AM16 VSS Power/Other
AM17 VSS Power/Other
AM18 VCC Power/Other
AM19 VCC Power/Other
AM2 RESERVED
AM20 VSS Power/Other
AM21 VCC Power/Other
AM22 VCC Power/Other
AM23 VSS Power/Other
AM24 VSS Power/Other
AM25 VCC Power/Other
AM26 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 63
Page 64

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 9 of 20)
Pin
No.
AM27 VSS Power/Other
AM28 VSS Power/Other
AM29 VCC Power/Other
AM3 VID2 Power/Other Output
AM30 VCC Power/Other
AM4 VSS Power/Other
AM5 VID6 Power/Other Output
AM6 RESERVED
AM7 VSS Power/Other
AM8 VCC Power/Other
AM9 VCC Power/Other
AN1 VSS Power/Other
AN10 VSS Power/Other
AN11 VCC Power/Other
AN12 VCC Power/Other
AN13 VSS Power/Other
AN14 VCC Power/Other
AN15 VCC Power/Other
AN16 VSS Power/Other
AN17 VSS Power/Other
AN18 VCC Power/Other
AN19 VCC Power/Other
AN2 VSS Power/Other
AN20 VSS Power/Other
AN21 VCC Power/Other
AN22 VCC Power/Other
AN23 VSS Power/Other
AN24 VSS Power/Other
AN25 VCC Power/Other
AN26 VCC Power/Other
AN3 VCC_DIE_SENSE Power/Other Output
AN4 VSS_DIE_SENSE Power/Other Output
AN5 RESERVED
AN6 RESERVED
AN7 VID_SELECT Power/Other Output
AN8 VCC Power/Other
AN9 VCC Power/Other
B1 VSS Power/Other
B10 D10# Source Sync Input/Output
B11 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 10 of 20)
Pin
No.
B12 D13# Source Sync Input/Output
B13 RESERVED
B14 VSS Power/Other
B15 D53# Source Sync Input/Output
B16 D55# Source Sync Input/Output
B17 VSS Power/Other
B18 D57# Source Sync Input/Output
B19 D60# Source Sync Input/Output
B2 DBSY# Common Clk Input/Output
B20 VSS Power/Other
B21 D59# Source Sync Input/Output
B22 D63# Source Sync Input/Output
B23 RESERVED
B24 VSS Power/Other
B25 VTT Power/Other
B26 VTT Power/Other
B27 VTT Power/Other
B28 VTT Power/Other
B29 VTT Power/Other
B3 RS0# Common Clk Input
B30 VTT Power/Other
B4 D00# Source Sync Input/Output
B5 VSS Power/Other
B6 D05# Source Sync Input/Output
B7 D06# Source Sync Input/Output
B8 VSS Power/Other
B9 DSTBP0# Source Sync Input/Output
C1 DRDY# Common Clk Input/Output
C10 VSS Power/Other
C11 D11# Source Sync Input/Output
C12 D14# Source Sync Input/Output
C13 VSS Power/Other
C14 D52# Source Sync Input/Output
C15 D51# Source Sync Input/Output
C16 VSS Power/Other
C17 DSTBP3# Source Sync Input/Output
C18 D54# Source Sync Input/Output
C19 VSS Power/Other
C2 BNR# Common Clk Input/Output
C20 DBI3# Source Sync Input/Output
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
64 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 65

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 11 of 20)
Pin
No.
C21 D58# Source Sync Input/Output
C22 VSS Power/Other
C23 RESERVED
C24 VSS Power/Other
C25 VTT Power/Other
C26 VTT Power/Other
C27 VTT Power/Other
C28 VTT Power/Other
C29 VTT Power/Other
C3 LOCK# Common Clk Input/Output
C30 VTT Power/Other
C4 VSS Power/Other
C5 D01# Source Sync Input/Output
C6 D03# Source Sync Input/Output
C7 VSS Power/Other
C8 DSTBN0# Source Sync Input/Output
C9 BPMb1# Common Clk Output
D1 RESERVED
D10 D22# Source Sync Input/Output
D11 D15# Source Sync Input/Output
D12 VSS Power/Other
D13 D25# Source Sync Input/Output
D14 RESERVED
D15 VSS Power/Other
D16 RESERVED
D17 D49# Source Sync Input/Output
D18 VSS Power/Other
D19 DBI2# Source Sync Input/Output
D2 ADS# Common Clk Input/Output
D20 D48# Source Sync Input/Output
D21 VSS Power/Other
D22 D46# Source Sync Input/Output
D23 VCCPLL Power/Other Input
D24 VSS Power/Other
D25 VTT Power/Other
D26 VTT Power/Other
D27 VTT Power/Other
D28 VTT Power/Other
D29 VTT Power/Other
D3 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 12 of 20)
Pin
No.
D30 VTT Power/Other
D4 HIT# Common Clk Input/Output
D5 VSS Power/Other
D6 VSS Power/Other
D7 D20# Source Sync Input/Output
D8 D12# Source Sync Input/Output
D9 VSS Power/Other
E1 RESERVED Power/Other
E10 D21# Source Sync Input/Output
E11 VSS Power/Other
E12 DSTBP1# Source Sync Input/Output
E13 D26# Source Sync Input/Output
E14 VSS Power/Other
E15 D33# Source Sync Input/Output
E16 D34# Source Sync Input/Output
E17 VSS Power/Other
E18 D39# Source Sync Input/Output
E19 D40# Source Sync Input/Output
E2 VSS Power/Other
E20 VSS Power/Other
E21 D42# Source Sync Input/Output
E22 D45# Source Sync Input/Output
E23 RESERVED
E24 RESERVED
E25 VSS Power/Other
E26 VSS Power/Other
E27 VSS Power/Other
E28 VSS Power/Other
E29 RESERVED
E3 TRDY# Common Clk Input
E30 VTT Power/Other
E4 HITM# Common Clk Input/Output
E5 RESERVED
E6 RESERVED
E7 RESERVED
E8 VSS Power/Other
E9 D19# Source Sync Input/Output
F1 VSS Power/Other
F10 VSS Power/Other
F11 D23# Source Sync Input/Output
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 65
Page 66

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 13 of 20)
Pin
No.
F12 D24# Source Sync Input/Output
F13 VSS Power/Other
F14 D28# Source Sync Input/Output
F15 D30# Source Sync Input/Output
F16 VSS Power/Other
F17 D37# Source Sync Input/Output
F18 D38# Source Sync Input/Output
F19 VSS Power/Other
F2 GTLREF_ADD_MID Power/Other Input
F20 D41# Source Sync Input/Output
F21 D43# Source Sync Input/Output
F22 VSS Power/Other
F23 RESERVED
F24 TESTHI07 Power/Other Input
F25 TESTHI02 Power/Other Input
F26 TESTHI00 Power/Other Input
F27 VTT_SEL Power/Other Output
F28 BCLK0 Clk Input
F29 RESERVED
F3 BR0# Common Clk Input/Output
F30 VTT Power/Other
F4 VSS Power/Other
F5 RS1# Common Clk Input
F6 RESERVED
F7 VSS Power/Other
F8 D17# Source Sync Input/Output
F9 D18# Source Sync Input/Output
G1 BPMb0# Power/Other Input/Output
G10 GTLREF_ADD_END Power/Other Input
G11 DBI1# Source Sync Input/Output
G12 DSTBN1# Source Sync Input/Output
G13 D27# Source Sync Input/Output
G14 D29# Source Sync Input/Output
G15 D31# Source Sync Input/Output
G16 D32# Source Sync Input/Output
G17 D36# Source Sync Input/Output
G18 D35# Source Sync Input/Output
G19 DSTBP2# Source Sync Input/Output
G2 COMP2 Power/Other Input
G20 DSTBN2# Source Sync Input/Output
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 14 of 20)
Pin
No.
G21 D44# Source Sync Input/Output
G22 D47# Source Sync Input/Output
G23 RESET# Common Clk Input
G24 TESTHI06 Power/Other Input
G25 TESTHI03 Power/Other Input
G26 TESTHI05 Power/Other Input
G27 TESTHI04 Power/Other Input
G28 BCLK1 Clk Input
G29 BSEL0 Power/Other Output
G3 BPMb3# Common Clk Input/Output
G30 BSEL2 Power/Other Output
G4 BPMb2# Common Clk Output
G5 PECI Power/Other Input/Output
G6 RESERVED
G7 DEFER# Common Clk Input
G8 BPRI# Common Clk Input
G9 D16# Source Sync Input/Output
H1 GTLREF_DATA_END Power/Other Input
H10 VSS Power/Other
H11 VSS Power/Other
H12 VSS Power/Other
H13 VSS Power/Other
H14 VSS Power/Other
H15 DP1# Common Clk Input/Output
H16 DP2# Common Clk Input/Output
H17 VSS Power/Other
H18 VSS Power/Other
H19 VSS Power/Other
H2 GTLREF_DATA_MID Power/Other Input
H20 VSS Power/Other
H21 VSS Power/Other
H22 VSS Power/Other
H23 VSS Power/Other
H24 VSS Power/Other
H25 VSS Power/Other
H26 VSS Power/Other
H27 VSS Power/Other
H28 VSS Power/Other
H29 VSS Power/Other
H3 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
66 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 67

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 15 of 20)
Pin
No.
H30 BSEL1 Power/Other Output
H4 RSP# Common Clk Input
H5 BR1# Common Clk Input
H6 VSS Power/Other
H7 VSS Power/Other
H8 VSS Power/Other
H9 VSS Power/Other
J1 VTT_OUT Power/Other Output
J10 VCC Power/Other
J11 VCC Power/Other
J12 VCC Power/Other
J13 VCC Power/Other
J14 VCC Power/Other
J15 VCC Power/Other
J16 DP0# Common Clk Input/Output
J17 DP3# Common Clk Input/Output
J18 VCC Power/Other
J19 VCC Power/Other
J2 RESERVED
J20 VCC Power/Other
J21 VCC Power/Other
J22 VCC Power/Other
J23 VCC Power/Other
J24 VCC Power/Other
J25 VCC Power/Other
J26 VCC Power/Other
J27 VCC Power/Other
J28 VCC Power/Other
J29 VCC Power/Other
J3 RESERVED
J30 VCC Power/Other
J4 VSS Power/Other
J5 REQ1# Source Sync Input/Output
J6 REQ4# Source Sync Input/Output
J7 VSS Power/Other
J8 VCC Power/Other
J9 VCC Power/Other
K1 LINT0 ASync GTL+ Input
K2 VSS Power/Other
K23 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 16 of 20)
Pin
No.
K24 VCC Power/Other
K25 VCC Power/Other
K26 VCC Power/Other
K27 VCC Power/Other
K28 VCC Power/Other
K29 VCC Power/Other
K3 A20M# ASync GTL+ Input
K30 VCC Power/Other
K4 REQ0# Source Sync Input/Output
K5 VSS Power/Other
K6 REQ3# Source Sync Input/Output
K7 VSS Power/Other
K8 VCC Power/Other
L1 LINT1 ASync GTL+ Input
L2 TESTHI11 ASync GTL+ Input
L23 VSS Power/Other
L24 VSS Power/Other
L25 VSS Power/Other
L26 VSS Power/Other
L27 VSS Power/Other
L28 VSS Power/Other
L29 VSS Power/Other
L3 VSS Power/Other
L30 VSS Power/Other
L4 A06# Source Sync Input/Output
L5 A05# Source Sync Input/Output
L6 VSS Power/Other
L7 VSS Power/Other
L8 VCC Power/Other
M1 VSS Power/Other
M2 THERMTRIP# ASync GTL+ Output
M23 VCC Power/Other
M24 VCC Power/Other
M25 VCC Power/Other
M26 VCC Power/Other
M27 VCC Power/Other
M28 VCC Power/Other
M29 VCC Power/Other
M3 STPCLK# ASync GTL+ Input
M30 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 67
Page 68

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 17 of 20)
Pin
No.
M4 A07# Source Sync Input/Output
M5 A03# Source Sync Input/Output
M6 REQ2# Source Sync Input/Output
M7 VSS Power/Other
M8 VCC Power/Other
N1 PWRGOOD Power/Other Input
N2 IGNNE# ASync GTL+ Input
N23 VCC Power/Other
N24 VCC Power/Other
N25 VCC Power/Other
N26 VCC Power/Other
N27 VCC Power/Other
N28 VCC Power/Other
N29 VCC Power/Other
N3 VSS Power/Other
N30 VCC Power/Other
N4 A36# Source Sync Input/Output
N5 RESERVED
N6 VSS Power/Other
N7 VSS Power/Other
N8 VCC Power/Other
P1 TESTHI10 Power/Other Input
P2 SMI# ASync GTL+ Input
P23 VSS Power/Other
P24 VSS Power/Other
P25 VSS Power/Other
P26 VSS Power/Other
P27 VSS Power/Other
P28 VSS Power/Other
P29 VSS Power/Other
P3 INIT# ASync GTL+ Input
P30 VSS Power/Other
P4 VSS Power/Other
P5 A37# Source Sync Input/Output
P6 A04# Source Sync Input/Output
P7 VSS Power/Other
P8 VCC Power/Other
R1 COMP3 Power/Other Input
R2 VSS Power/Other
R23 VSS Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 18 of 20)
Pin
No.
R24 VSS Power/Other
R25 VSS Power/Other
R26 VSS Power/Other
R27 VSS Power/Other
R28 VSS Power/Other
R29 VSS Power/Other
R3 FERR#/PBE# ASync GTL+ Output
R30 VSS Power/Other
R4 A08# Source Sync Input/Output
R5 VSS Power/Other
R6 ADSTB0# Source Sync Input/Output
R7 VSS Power/Other
R8 VCC Power/Other
T1 COMP1 Power/Other Input
T2 RESERVED
T23 VCC Power/Other
T24 VCC Power/Other
T25 VCC Power/Other
T26 VCC Power/Other
T27 VCC Power/Other
T28 VCC Power/Other
T29 VCC Power/Other
T3 VSS Power/Other
T30 VCC Power/Other
T4 A11# Source Sync Input/Output
T5 A09# Source Sync Input/Output
T6 VSS Power/Other
T7 VSS Power/Other
T8 VCC Power/Other
U1 TESTIN2 Power/Other Input
U2 AP0# Common Clk Input/Output
U23 VCC Power/Other
U24 VCC Power/Other
U25 VCC Power/Other
U26 VCC Power/Other
U27 VCC Power/Other
U28 VCC Power/Other
U29 VCC Power/Other
U3 AP1# Common Clk Input/Output
U30 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
68 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 69

Land Listing
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 19 of 20)
Pin
No.
U4 A13# Source Sync Input/Output
U5 A12# Source Sync Input/Output
U6 A10# Source Sync Input/Output
U7 VSS Power/Other
U8 VCC Power/Other
V1 MS_ID1 Power/Other Output
V2 LL_ID0 Power/Other Output
V23 VSS Power/Other
V24 VSS Power/Other
V25 VSS Power/Other
V26 VSS Power/Other
V27 VSS Power/Other
V28 VSS Power/Other
V29 VSS Power/Other
V3 VSS Power/Other
V30 VSS Power/Other
V4 A15# Source Sync Input/Output
V5 A14# Source Sync Input/Output
V6 VSS Power/Other
V7 VSS Power/Other
V8 VCC Power/Other
W1 MS_ID0 Power/Other Output
W2 TESTIN1 Power/Other Input
W23 VCC Power/Other
W24 VCC Power/Other
W25 VCC Power/Other
W26 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Table 4-2. Land Listing by Land Number
(Sheet 20 of 20)
Pin
No.
W27 VCC Power/Other
W28 VCC Power/Other
W29 VCC Power/Other
W3 TESTHI01 Power/Other Input
W30 VCC Power/Other
W4 VSS Power/Other
W5 A16# Source Sync Input/Output
W6 A18# Source Sync Input/Output
W7 VSS Power/Other
W8 VCC Power/Other
Y1 RESERVED
Y2 VSS Power/Other
Y23 VCC Power/Other
Y24 VCC Power/Other
Y25 VCC Power/Other
Y26 VCC Power/Other
Y27 VCC Power/Other
Y28 VCC Power/Other
Y29 VCC Power/Other
Y3 RESERVED
Y30 VCC Power/Other
Y4 A20# Source Sync Input/Output
Y5 VSS Power/Other
Y6 A19# Source Sync Input/Output
Y7 VSS Power/Other
Y8 VCC Power/Other
Pin Name
Signal
Buffer Type
Direction
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 69
§
Page 70

Land Listing
70 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 71

Signal Definitions
5 Signal Definitions
5.1 Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 1 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
A[37:3]# I/O A[37:3]# (Address) define a 2
A20M# I If A20M# (Address-20 Mask) is asserted, the processor masks physical address bit 20
ADS# I/O ADS# (Address Strobe) is asserted to indicate the validity of the transaction address
ADSTB[1:0]# I/O Address strobes are used to latch A[37:3]#
1 of the address phase, these signals transmit the address of a transaction. In subphase 2, these signals transmit transaction type information. These signals must
connect the appropriate pins of all agents on the FSB. A[37:3]#
parity signals AP[1:0]#. A[37:3]#
into the receiving buffers by ADSTB[1:0]#.
On the active-to-inactive transition of RESET#, the processors sample a subset of the
A[37:3]#
(A20#) before looking up a line in any internal cache and before driving a read/write
transaction on the bus. Asserting A20M# emulates the 8086 processor's address
wrap-around at the 1 MB boundary. Assertion of A20M# is only supported in real
mode.
A20M# is an asynchronous signal. However, to ensure recognition of this signal
following an I/O write instruction, it must be valid along with the TRDY# assertion of
the corresponding I/O write bus transaction.
on the A[37:3]#
checking, protocol checking, address decode, internal snoop, or deferred reply ID
match operations associated with the new transaction. This signal must be connected
to the appropriate pins on all Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series FSB
agents.
edge. Strobes are associated with signals as shown below.
4
lands to determine their power-on configuration. See Section 7.1.
4
lands. All bus agents observe the ADS# activation to begin parity
38
-byte physical memory address space. In sub-phase
4
4
are source synchronous signals and are latched
4
and REQ[4:0]# on their rising and falling
are protected by
3,4
2
3
3,4
Signals Associated Strobes
REQ[4:0], A[16:3]#,
A[37:36]#
A[35:17]# ADSTB1#
AP[1:0]# I/O AP[1:0]# (Address Parity) are driven by the request initiator along with ADS#,
BCLK[1:0] I The differential bus clock pair BCLK[1:0] (Bus Clock) determines the FSB frequency.
A[37:3]#
is high if an even number of covered signals are low and low if an odd number of
covered signals are low. This allows parity to be high when all the covered signals are
high. AP[1:0]# must be connected to the appropriate pins of all Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor 5300 Series FSB agents. The following table defines the coverage
model of these signals.
Request Signals Subphase 1 Subphase 2
A[37:24]#
A[23:3]# AP1# AP0#
REQ[4:0]# AP1# AP0#
All processor FSB agents must receive these signals to drive their outputs and latch
their inputs.
All external timing parameters are specified with respect to the rising edge of BCLK0
crossing V
4
4
, and the transaction type on the REQ[4:0]# signals. A correct parity signal
4
.
CROSS
ADSTB0#
AP0# AP1#
3,4
3
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 71
Page 72

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 2 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
BINIT# I/O BINIT# (Bus Initialization) may be observed and driven by all processor FSB agents
BNR# I/O BNR# (Block Next Request) is used to assert a bus stall by any bus agent who is
BPM5#
BPM4#
BPM3#
BPM[2:1]#
BPM0#
BPMb3#
BPMb[2:1]#
BPMb0#
BPRI# I BPRI# (Bus Priority Request) is used to arbitrate for ownership of the processor FSB.
BR[1:0]# I/O The BR[1:0]# signals are sampled on the active-to-inactive transition of RESET#. The
BSEL[2:0] O The BCLK[1:0] frequency select signals BSEL[2:0] are used to select the processor
COMP[3:0] I COMP[3:0] must be terminated to VSS on the baseboard using precision resistors.
and if used, must connect the appropriate pins of all such agents. If the BINIT# driver
is enabled during power on configuration, BINIT# is asserted to signal any bus
condition that prevents reliable future operation.
If BINIT# observation is enabled during power-on configuration (see Section 7.1) and
BINIT# is sampled asserted, symmetric agents reset their bus LOCK# activity and
bus request arbitration state machines. The bus agents do not reset their I/O Queue
(IOQ) and transaction tracking state machines upon observation of BINIT# assertion.
Once the BINIT# assertion has been observed, the bus agents will re-arbitrate for the
FSB and attempt completion of their bus queue and IOQ entries.
If BINIT# observation is disabled during power-on configuration, a priority agent may
handle an assertion of BINIT# as appropriate to the error handling architecture of the
system.
unable to accept new bus transactions. During a bus stall, the current bus owner
cannot issue any new transactions.
Since multiple agents might need to request a bus stall at the same time, BNR# is a
wired-OR signal which must connect the appropriate pins of all processor FSB agents.
In order to avoid wired-OR glitches associated with simultaneous edge transitions
driven by multiple drivers, BNR# is activated on specific clock edges and sampled on
specific clock edges.
I/O
BPM[5:0]# (Breakpoint Monitor) are breakpoint and performance monitor signals.
They are outputs from the processor which indicate the status of breakpoints and
O
programmable counters used for monitoring processor performance. BPM[5:0]#
I/O
should connect the appropriate pins of all FSB agents.
O
BPM4# provides PRDY# (Probe Ready) functionality for the TAP port. PRDY# is a
I/O
processor output used by debug tools to determine processor debug readiness.
BPM5# provides PREQ# (Probe Request) functionality for the TAP port. PREQ# is used
by debug tools to request debug operation of the processors.
BPM[5:4]# must be bussed to all bus agents. Please refer to the appropriate platform
design guidelines for more detailed information.
I/O
BPMb[3:0]# (Breakpoint Monitor) are a second set of breakpoint and performance
monitor signals. They are additional outputs from the processor which indicate the
O
status of breakpoints and programmable counters used for monitoring processor
I/O
performance. BPMb[3:0]# should connect the appropriate pins of all FSB agents.
It must connect the appropriate pins of all processor FSB agents. Observing BPRI#
active (as asserted by the priority agent) causes all other agents to stop issuing new
requests, unless such requests are part of an ongoing locked operation. The priority
agent keeps BPRI# asserted until all of its requests are completed, then releases the
bus by deasserting BPRI#.
signal which the agent samples asserted determines its agent ID. BR0# drives the
BREQ0# signal in the system and is used by the processor to request the bus.
These signals do not have on-die termination and must be terminated.
input clock frequency. Tabl e 2- 2 defines the possible combinations of the signals and
the frequency associated with each combination. The required frequency is
determined by the processors, chipset, and clock synthesizer. All FSB agents must
operate at the same frequency. For more information about these signals, including
termination recommendations, refer to the appropriate platform design guideline.
These inputs configure the AGTL+ drivers of the processor. Refer to the appropriate
platform design guidelines for implementation details.
3
3
2
2
3
3
72 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 73

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 3 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
D[63:0]# I/O D[63:0]# (Data) are the data signals. These signals provide a 64-bit data path
between the processor FSB agents, and must connect the appropriate pins on all such
agents. The data driver asserts DRDY# to indicate a valid data transfer.
D[63:0]# are quad-pumped signals, and will thus be driven four times in a
common clock period. D[63:0]# are latched off the falling edge of both
DSTBP[3:0]# and DSTBN[3:0]#. Each group of 16 data signals correspond
to a pair of one DSTBP# and one DSTBN#. The following table shows the
grouping of data signals to strobes and DBI#.
3
Data Group
D[15:0]# 0 0
D[31:16]# 1 1
D[47:32]# 2 2
D[63:48]# 3 3
DSTBN#/
DSTBP#
DBI#
Furthermore, the DBI# signals determine the polarity of the data signals.
Each group of 16 data signals corresponds to one DBI# signal. When the
DBI# signal is active, the corresponding data group is inverted and
therefore sampled active high.
DBI[3:0]# I/O DBI[3:0]# (Data Bus Inversion) are source synchronous and indicate the polarity of
DBR# O DBR# is used only in systems where no debug port connector is implemented on the
DBSY# I/O DBSY# (Data Bus Busy) is asserted by the agent responsible for driving data on the
DEFER# I DEFER# is asserted by an agent to indicate that a transaction cannot be guaranteed
DP[3:0]# I/O DP[3:0]# (Data Parity) provide parity protection for the D[63:0]# signals. They are
DRDY# I/O DRDY# (Data Ready) is asserted by the data driver on each data transfer, indicating
the D[63:0]# signals. The DBI[3:0]# signals are activated when the data on the data
bus is inverted. If more than half the data bits, within, within a 16-bit group, would
have been asserted electronically low, the bus agent may invert the data bus signals
for that particular sub-phase for that 16-bit group.
DBI[3:0] Assignment to Data Bus
Bus Signal Data Bus Signals
DBI0# D[15:0]#
DBI1# D[31:16]#
DBI2# D[47:32]#
DBI3# D[63:48]#
system board. DBR# is used by a debug port interposer so that an in-target probe can
drive reset. If a debug port connector is implemented in the system, DBR# is a noconnect on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series package. DBR# is not
a processor signal.
processor FSB to indicate that the data bus is in use. The data bus is released after
DBSY# is deasserted. This signal must connect the appropriate pins on all processor
FSB agents.
in-order completion. Assertion of DEFER# is normally the responsibility of the
addressed memory or I/O agent. This signal must connect the appropriate pins of all
processor FSB agents.
driven by the agent responsible for driving D[63:0]#, and must connect the
appropriate pins of all processor FSB agents.
valid data on the data bus. In a multi-common clock data transfer, DRDY# may be
deasserted to insert idle clocks. This signal must connect the appropriate pins of all
processor FSB agents.
3
3
3
3
3
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 73
Page 74

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 4 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
DSTBN[3:0]# I/O Data strobe used to latch in D[63:0]#. 3
Signals Associated Strobes
D[15:0]#, DBI0# DSTBN0#
D[31:16]#, DBI1# DSTBN1#
D[47:32]#, DBI2# DSTBN2#
D[63:48]#, DBI3# DSTBN3#
DSTBP[3:0]# I/O Data strobe used to latch in D[63:0]#. 3
Signals Associated Strobes
D[15:0]#, DBI0# DSTBP0#
D[31:16]#, DBI1# DSTBP1#
D[47:32]#, DBI2# DSTBP2#
D[63:48]#, DBI3# DSTBP3#
FERR#/PBE# O FERR#/PBE# (floating-point error/pending break event) is a multiplexed signal and
FORCEPR# I The FORCEPR# (force power reduction) input can be used by the platform to cause
GTLREF_ADD_MID
GTLREF_ADD_END
GTLREF_DATA_MID
GTLREF_DATA_END
HIT#
HITM#
IERR# O IERR# (Internal Error) is asserted by a processor as the result of an internal error.
its meaning is qualified by STPCLK#. When STPCLK# is not asserted, FERR#/PBE#
indicates a floating-point error and will be asserted when the processor detects an
unmasked floating-point error. When STPCLK# is not asserted, FERR#/PBE# is similar
to the ERROR# signal on the Intel 387 coprocessor, and is included for compatibility
with systems using MS-DOS*-type floating-point error reporting. When STPCLK# is
asserted, an assertion of FERR#/PBE# indicates that the processor has a pending
break event waiting for service. The assertion of FERR#/PBE# indicates that the
processor should be returned to the Normal state. For additional information on the
pending break event functionality, including the identification of support of the feature
and enable/disable information, refer to Vol. 3 of the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel®
Architecture Software Developer’s Manual and the AP-485 Intel® Processor
Identification and the CPUID Instruction application note.
the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series to activate the Thermal Control
Circuit (TCC).
I GTLREF_ADD determines the signal reference level for AGTL+ address and common
clock input lands. GTLREF_ADD is used by the AGTL+ receivers to determine if a
signal is a logical 0 or a logical 1. Please refer to Tabl e 2- 1 8 and the appropriate
platform design guidelines for additional details.
I GTLREF_DATA determines the signal reference level for AGTL+ data input lands.
GTLREF_DATA is used by the AGTL+ receivers to determine if a signal is a logical 0 or
a logical 1. Please refer to Tab le 2 -1 8 and the appropriate platform design guidelines
for additional details.
I/O
HIT# (Snoop Hit) and HITM# (Hit Modified) convey transaction snoop operation
results. Any FSB agent may assert both HIT# and HITM# together to indicate that it
I/O
requires a snoop stall, which can be continued by reasserting HIT# and HITM#
together.
Assertion of IERR# is usually accompanied by a SHUTDOWN transaction on the
processor FSB. This transaction may optionally be converted to an external error
signal (e.g., NMI) by system core logic. The processor will keep IERR# asserted until
the assertion of RESET#.
This signal does not have on-die termination.
2
3
2
74 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 75

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 5 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
IGNNE# I IGNNE# (Ignore Numeric Error) is asserted to force the processor to ignore a numeric
INIT# I INIT# (Initialization), when asserted, resets integer registers inside all processors
LINT[1:0] I LINT[1:0] (Local APIC Interrupt) must connect the appropriate pins of all FSB agents.
LL_ID[1:0] O The LL_ID[1:0] signals are used to select the correct loadline slope for the processor.
LOCK# I/O LOCK# indicates to the system that a transaction must occur atomically. This signal
MCERR# I/O
MS_ID[1:0] O These signals are provided to indicate the Market Segment for the processor and may
PECI I/O PECI is a proprietary one-wire bus interface that provides a communication channel
PROCHOT# O PROCHOT# (Processor Hot) will go active when the processor’s temperature
error and continue to execute noncontrol floating-point instructions. If IGNNE# is
deasserted, the processor generates an exception on a noncontrol floating-point
instruction if a previous floating-point instruction caused an error. IGNNE# has no
effect when the NE bit in control register 0 (CR0) is set.
IGNNE# is an asynchronous signal. However, to ensure recognition of this signal
following an I/O write instruction, it must be valid along with the TRDY# assertion of
the corresponding I/O write bus transaction.
without affecting their internal caches or floating-point registers. Each processor then
begins execution at the power-on Reset vector configured during power-on
configuration. The processor continues to handle snoop requests during INIT#
assertion. INIT# is an asynchronous signal and must connect the appropriate pins of
all processor FSB agents.
When the APIC functionality is disabled, the LINT0/INTR signal becomes INTR, a
maskable interrupt request signal, and LINT1/NMI becomes NMI, a nonmaskable
interrupt. INTR and NMI are backward compatible with the signals of those names on
the Pentium
These signals must be software configured via BIOS programming of the APIC register
space to be used either as NMI/INTR or LINT[1:0]. Because the APIC is enabled by
default after Reset, operation of these pins as LINT[1:0] is the default configuration.
These signals are not connected to the processor die. A logic 0 is pulled to ground and
a logic 1 is a no-connect on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
package.
must connect the appropriate pins of all processor FSB agents. For a locked sequence
of transactions, LOCK# is asserted from the beginning of the first transaction to the
end of the last transaction.
When the priority agent asserts BPRI# to arbitrate for ownership of the processor
FSB, it will wait until it observes LOCK# deasserted. This enables symmetric agents to
retain ownership of the processor FSB throughout the bus locked operation and
ensure the atomicity of lock.
MCERR# (Machine Check Error) is asserted to indicate an unrecoverable
error without a bus protocol violation. It may be driven by all processor
FSB agents.
MCERR# assertion conditions are configurable at a system level. Assertion
options are defined by the following options:
• Enabled or disabled.
• Asserted, if configured, for internal errors along with IERR#.
• Asserted, if configured, by the request initiator of a bus transaction after it
• Asserted by any bus agent when it observes an error in a bus transaction.
For more details regarding machine check architecture, refer to the Intel® 64 and
IA-32 Intel® Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3: System
Programming Guide.
be used for future processor compatibility or for keying. These signals are not
connected to the processor die. A logic 0 is pulled to ground and a logic 1 is a noconnect on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series package.
between Intel processor and chipset components to external thermal monitoring
devices. See Section 6.3, “Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)” for more
on the PECI interface.
monitoring sensor detects that the processor has reached its maximum safe operating
temperature. This indicates that the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) has been
activated, if enabled. The TCC will remain active until shortly after the processor
deasserts PROCHOT#. See Section 6.2.5 for more details.
®
processor. Both signals are asynchronous.
observes an error.
2
2
2
3
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 75
Page 76

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 6 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
PWRGOOD I PWRGOOD (Power Good) is an input. The processor requires this signal to be a clean
REQ[4:0]# I/O REQ[4:0]# (Request Command) must connect the appropriate pins of all processor
RESET# I Asserting the RESET# signal resets all processors to known states and invalidates
RS[2:0]# I RS[2:0]# (Response Status) are driven by the response agent (the agent responsible
RSP# I RSP# (Response Parity) is driven by the response agent (the agent responsible for
SKTOCC# O SKTOCC# (Socket occupied) will be pulled to ground by the processor to indicate that
SMI# I SMI# (System Management Interrupt) is asserted asynchronously by system logic.
STPCLK# I STPCLK# (Stop Clock), when asserted, causes processors to enter a low power Stop-
TCK I TCK (Test Clock) provides the clock input for the processor Test Bus (also known as
TDI I TDI (Test Data In) transfers serial test data into the processor. TDI provides the serial
TDO O TDO (Test Data Out) transfers serial test data out of the processor. TDO provides the
indication that all processor clocks and power supplies are stable and within their
specifications. “Clean” implies that the signal will remain low (capable of sinking
leakage current), without glitches, from the time that the power supplies are turned
on until they come within specification. The signal must then transition monotonically
to a high state. PWRGOOD can be driven inactive at any time, but clocks and power
must again be stable before a subsequent rising edge of PWRGOOD. It must also
meet the minimum pulse width specification in Ta bl e 2 -17 , and be followed by a 110 ms RESET# pulse.
The PWRGOOD signal must be supplied to the processor; it is used to protect internal
circuits against voltage sequencing issues. It should be driven high throughout
boundary scan operation.
FSB agents. They are asserted by the current bus owner to define the currently active
transaction type. These signals are source synchronous to ADSTB[1:0]#. Refer to the
AP[1:0]# signal description for details on parity checking of these signals.
their internal caches without writing back any of their contents. For a power-on Reset,
RESET# must stay active for at least 1 ms after V
proper specifications. On observing active RESET#, all FSB agents will deassert their
outputs within two clocks. RESET# must not be kept asserted for more than 10 ms
while PWRGOOD is asserted.
A number of bus signals are sampled at the active-to-inactive transition of RESET#
for power-on configuration. These configuration options are described in the
Section 7.1.
This signal does not have on-die termination and must be terminated on the system
board.
for completion of the current transaction), and must connect the appropriate pins of
all processor FSB agents.
completion of the current transaction) during assertion of RS[2:0]#, the signals for
which RSP# provides parity protection. It must connect to the appropriate pins of all
processor FSB agents.
A correct parity signal is high if an even number of covered signals are low and low if
an odd number of covered signals are low. While RS[2:0]# = 000, RSP# is also high,
since this indicates it is not being driven by any agent guaranteeing correct parity.
the processor is present. There is no connection to the processor silicon for this
signal.
On accepting a System Management Interrupt, processors save the current state and
enter System Management Mode (SMM). An SMI Acknowledge transaction is issued,
and the processor begins program execution from the SMM handler.
If SMI# is asserted during the deassertion of RESET# the processor will tri-state its
outputs. See Section 7.1.
Grant state. The processor issues a Stop-Grant Acknowledge transaction, and stops
providing internal clock signals to all processor core units except the FSB and APIC
units. The processor continues to snoop bus transactions and service interrupts while
in Stop-Grant state. When STPCLK# is deasserted, the processor restarts its internal
clock to all units and resumes execution. The assertion of STPCLK# has no effect on
the bus clock; STPCLK# is an asynchronous input.
the Test Access Port).
input needed for JTAG specification support.
serial output needed for JTAG specification support.
CC and BCLK have reached their
2
3
3
3
3
2
2
76 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 77

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 7 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
TESTHI[11:10]
TESTHI[7:0],
TESTIN1
TESTIN2
THERMTRIP# O Assertion of THERMTRIP# (Thermal Trip) indicates the processor junction
TMS I TMS (Test Mode Select) is a JTAG specification support signal used by debug tools.
TRDY# I TRDY# (Target Ready) is asserted by the target to indicate that it is ready to receive a
TRST# I TRST# (Test Reset) resets the Test Access Port (TAP) logic. TRST# must be driven low
V
CCPLL
VCC_DIE_SENSE
VCC_DIE_SENSE2
VID[6:1] O VID[6:1] (Voltage ID) pins are used to support automatic selection of power supply
VID_SELECT O VID_SELECT is an output from the processor which selects the appropriate VID table
VSS_DIE_SENSE
VSS_DIE_SENSE2
I TESTHI[11:10] and TESTHI[7:0],must be connected to a V
resistor for proper processor operation. Refer to Section 2.6 for TESTHI grouping
restrictions.
I
TESTIN1 must be connected to a VTT power source through a resistor as well as to
the TESTIN2 land of the same socket for proper processor operation.
I
TESTIN2 must be connected to a VTT power source through a resistor as well as to
power source through a
TT
the TESTIN1 land of the same socket for proper processor operation.
Refer to Section 2.6 for TESTIN restrictions.
temperature has reached a temperature beyond which permanent silicon damage
may occur. Measurement of the temperature is accomplished through an internal
thermal sensor. Upon assertion of THERMTRIP#, the processor will shut off its internal
clocks (thus halting program execution) in an attempt to reduce the processor
junction temperature. To protect the processor its core voltage (V
removed following the assertion of THERMTRIP#. Intel also recommends the removal
when THERMTRIP# is asserted.
of V
TT
Driving of the THERMTRIP# signals is enabled within 10 μs of the assertion of
PWRGOOD and is disabled on de-assertion of PWRGOOD. Once activated,
THERMTRIP# remains latched until PWRGOOD is de-asserted. While the de-assertion
of the PWRGOOD signal will de-assert THERMTRIP#, if the processor’s junction
temperature remains at or above the trip level, THERMTRIP# will again be asserted
within 10 μs of the assertion of PWRGOOD.
) must be
CC
See the Debug Port Design Guide for Blackford and Greencreek Systems (External
Version) for further information.
write or implicit writeback data transfer. TRDY# must connect the appropriate pins of
all FSB agents.
during power on Reset.
I The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series implement an on-die PLL filter
solution. The V
input is used as a PLL supply voltage.
CCPLL
O VCC_DIE_SENSE and VCC_DIE_SENSE2 provides an isolated, low impedance
connection to the processor core power and ground. This signal should be connected
to the voltage regulator feedback signal, which insures the output voltage (that is,
processor voltage) remains within specification. Please see the applicable platform
design guide for implementation details.
voltages (V
pulled up through a resistor. Conversely, the voltage regulator output must be
disabled prior to the voltage supply for these pins becomes invalid. The VID pins are
needed to support processor voltage specification variations. See Ta b l e 2 -3 for
definitions of these pins. The VR must supply the voltage that is requested by these
pins, or disable itself.
for the Voltage Regulator. This signal is not connected to the processor die. This signal
is a no-connect on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series package.
O VSS_DIE_SENSE and VSS_DIE_SENSE2 provides an isolated, low impedance
connection to the processor core power and ground. This signal should be connected
to the voltage regulator feedback signal, which insures the output voltage (that is,
processor voltage) remains within specification. Please see the applicable platform
design guide for implementation details.
). These are CMOS signals that are driven by the processor and must be
CC
1
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 77
Page 78

Signal Definitions
Table 5-1. Signal Definitions (Sheet 8 of 8)
Name Type Description Notes
VTT P The FSB termination voltage input pins. Refer to Ta bl e 2 -1 2 for further details.
VTT_OUT O The VTT_OUT signals are included in order to provide a local V
require termination to V
VTT_SEL O The VTT_SEL signal is used to select the correct V
VTT_SEL is a no-connect on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
package.
Notes:
1. For this processor land on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series, the maximum number of symmetric agents is
one. Maximum number of priority agents is zero.
2. For this processor land on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series, the maximum number of symmetric agents is
two. Maximum number of priority agents is zero.
3. For this processor land on the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series, the maximum number of symmetric agents is
two. Maximum number of priority agents is one.
4. Not all Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support signals A[37:36]#. Processors that support these signals will
be outlined in the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Specification Update.
on the motherboard.
TT
voltage level for the processor.
TT
for some signals that
TT
§
78 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 79

Thermal Specifications
6 Thermal Specifications
6.1 Package Thermal Specifications
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series requires a thermal solution to
maintain temperatures within its operating limits. Any attempt to operate the processor
outside these operating limits may result in permanent damage to the processor and
potentially other components within the system. As processor technology changes,
thermal management becomes increasingly crucial when building computer systems.
Maintaining the proper thermal environment is key to reliable, long-term system
operation.
A complete solution includes both component and system level thermal management
features. Component level thermal solutions can include active or passive heatsinks
attached to the processor integrated heat spreader (IHS). Typical system level thermal
solutions may consist of system fans combined with ducting and venting.
This section provides data necessary for developing a complete thermal solution. For
more information on designing a component level thermal solution, refer to the
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical Design
Guidelines.
Note: The boxed processor will ship with a component thermal solution. Refer to Section 8 for
details on the boxed processor.
6.1.1 Thermal Specifications
To allow the optimal operation and long-term reliability of Intel processor-based
systems, the processor must remain within the minimum and maximum case
temperature (T
Ta b le 6- 1 and Figure 6-1 for Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series and
Ta b le 6- 3 and Figure 6-2 for Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series).
Thermal solutions not designed to provide this level of thermal capability may affect the
long-term reliability of the processor and system. For more details on thermal solution
design, please refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Thermal/
Mechanical Design Guidelines.
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series implement a methodology for
managing processor temperatures which is intended to support acoustic noise
reduction through fan speed control and to assure processor reliability. Selection of the
appropriate fan speed is based on the relative temperature data reported by the
processor’s Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI) bus as described in
Section 6.3. The temperature reported over PECI is always a negative value and
represents a delta below the onset of thermal control circuit (TCC) activation, as
indicated by PROCHOT# (see Section 6.2, Processor Thermal Features). Systems that
implement fan speed control must be designed to use this data. Systems that do not
alter the fan speed only need to guarantee the case temperature meets the thermal
profile specifications.
) specifications as defined by the applicable thermal profile (see
CASE
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series (see Figure 6-1; Tab le 6- 2 )
supports a single Thermal Profile. For these processors, it is expected that the Thermal
Control Circuit (TCC) would only be activated for very brief periods of time when
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 79
Page 80

Thermal Specifications
running the most power-intensive applications. Refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines for details on system
thermal solution design, thermal profiles and environmental considerations.
For the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series, Intel has developed two
thermal profiles, either of which can be implemented. Both ensure adherence to Intel
reliability requirements. Thermal Profile A (see Figure 6-2; Tab le 6- 4) is representative
of a volumetrically unconstrained thermal solution (that is, industry enabled 2U
heatsink). In this scenario, it is expected that the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) would
only be activated for very brief periods of time when running the most power intensive
applications. Thermal Profile B (see Figure 6-2; Tabl e 6- 5 ) is indicative of a constrained
thermal environment (that is, 1U form factor). Because of the reduced cooling
capability represented by this thermal solution, the probability of TCC activation and
performance loss is increased. Additionally, utilization of a thermal solution that does
not meet Thermal Profile B will violate the thermal specifications and may result in
permanent damage to the processor. Refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor
5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines for details on system thermal
solution design, thermal profiles and environmental considerations.
The upper point of the thermal profile consists of the Thermal Design Power (TDP) and
the associated T
value. It should be noted that the upper point associated with the
CASE
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile B (x = TDP and y =
T
CASE_MAX_B
@ TDP) represents a thermal solution design point. In actuality the
processor case temperature will not reach this value due to TCC activation (see
Figure 6-2 for Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series). The lower point of
the thermal profile consists of x = P
P
_PROFILE_MIN
is defined as the processor power at which T
_PROFILE_MIN
and y = T
CASE_MAX
CASE
@ P
_PROFILE_MIN
, calculated from the
.
thermal profile, is equal to 50°C.
Analysis indicates that real applications are unlikely to cause the processor to consume
maximum power dissipation for sustained time periods. Intel recommends that
complete thermal solution designs target the Thermal Design Power (TDP), instead of
the maximum processor power consumption. The Thermal Monitor feature is intended
to help protect the processor in the event that an application exceeds the TDP
recommendation for a sustained time period. For more details on this feature, refer to
Section 6.2. To ensure maximum flexibility for future requirements, systems should be
designed to the Flexible Motherboard (FMB) guidelines, even if a processor with lower
power dissipation is currently planned. Thermal Monitor 1 and Thermal Monitor 2
feature must be enabled for the processor to remain within its specifications.
Table 6-1. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Thermal Specifications
Core
Frequency
Launch to FMB 80 5 See Figure 6-1;
Notes:
1. These values are specified at V
the processor is not to be subjected to any static V
specified I
2. Maximum Power is the highest power the processor will dissipate, regardless of its VID. Maximum Power is
measured at maximum T
3. Thermal Design Power (TDP) should be used for processor thermal solution design targets. TDP is not the
maximum power that the processor can dissipate. TDP is measured at maximum T
4. These specifications are based on initial silicon characterization. These specifications may be further
updated as more characterization data becomes available.
5. Power specifications are defined at all VIDs found in Tab le 2 -3 . The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor
E5300 Series may be shipped under multiple VIDs for each frequency.
CC
Thermal Design
Power
(W)
CC_MAX
. Please refer to the loadline specifications in Section 2.
.
CASE
Minimum
CASE
T
(°C)
for all processor frequencies. Systems must be designed to ensure
and ICC combination wherein VCC exceeds V
CC
Maximum
CASE
T
(°C)
Tab le 6 -2
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
.
CASE
Notes
CC_MAX
at
80 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 81

Thermal Specifications
6. FMB, or Flexible Motherboard, guidelines provide a design target for meeting all planned processor
frequency requirements.
Figure 6-1.Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Thermal Profile
70
70
65
65
60
60
55
55
Tcase [C]
Tcase [C]
50
50
45
45
Thermal Profile
Thermal Profile
Y = 0.293*x + 42.6
Y = 0.293*x + 42.6
40
40
0 1020304050607080
0 1020304050607080
Power [W]
Power [W]
Notes:
1. Please refer to Ta bl e 6 - 2 for discrete points that constitute the thermal profile.
2. Refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines for
system and environmental implementation details.
Table 6-2. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300 Series Thermal Profile Table
Power (W) T
P
_PROFILE_MIN
=25.3 50.0
30 51.4
35 52.9
40 54.3
45 55.8
50 57.3
55 58.7
60 60.2
65 61.6
70 63.1
75 64.6
80 66.0
CASE_MAX
(°C)
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 81
Page 82

Thermal Specifications
Table 6-3. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Specifications
Core
Frequency
Launch to FMB 120 5 See Figure 6-2;
Notes:
1. These values are specified at V
the processor is not to be subjected to any static V
specified I
2. Maximum Power is the highest power the processor will dissipate, regardless of its VID. Maximum Power is
measured at maximum T
3. Thermal Design Power (TDP) should be used for processor thermal solution design targets. TDP is not the
maximum power that the processor can dissipate. TDP is measured at maximum T
4. These specifications are based on initial silicon characterization. These specifications may be further
updated as more characterization data becomes available.
5. Power specifications are defined at all VIDs found in Tab le 2 -3 . The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor
X5300 Series may be shipped under multiple VIDs for each frequency.
6. FMB, or Flexible Motherboard, guidelines provide a design target for meeting all planned processor
frequency requirements.
CC
Thermal Design
Power
(W)
CC_MAX
. Please refer to the loadline specifications in Section 2.
.
CASE
Minimum
CASE
T
(°C)
for all processor frequencies. Systems must be designed to ensure
and ICC combination wherein VCC exceeds V
CC
Maximum
CASE
T
(°C)
Tab l e 6 -4 ; Tab le 6 -5
CASE
Figure 6-2.Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profiles
TCASE_MAX is a thermal solution design point.
75
75
70
70
65
65
TCASE_MAX is a thermal solution design point.
In actuality, units will not significantly exceed
In actuality, units will not significantly exceed
TCASE_MAX_A d ue to T CC activa t io n .
TCASE_MAX_A d ue to T CC activa t io n .
Notes
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
CC_MAX
.
at
60
60
Tcase [C]
Tcase [C]
55
55
50
50
45
45
40
40
0 102030405060 708090100110120
0 102030405060708090100110120
Notes:
1. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile A is representative of a volumetrically
unconstrained platform. Please refer to Tab le 6- 4 for discrete points that constitute the thermal profile.
2. Implementation of Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile A should result in
virtually no TCC activation. Furthermore, utilization of thermal solutions that do not meet processor
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile A will result in increased probability of
TCC activation and may incur measurable performance loss. (See Section 6.2 for details on TCC activation).
3. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile B is representative of a volumetrically
constrained platform. Please refer to Tab le 6 - 5 for discrete points that constitute the thermal profile.
4. Implementation of Thermal Profile B will result in increased probability of TCC activation and measurable
performance loss. Furthermore, utilization of thermal solutions that do not meet Thermal Profile B do not
meet the processor's thermal specifications and may result in permanent damage to the processor.
5. Refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines for
system and environmental implementation details.
Thermal Profile B
Thermal Profile B
Y = 0.224*x + 43.1
Y = 0.224*x + 43.1
Pow er [W]
Pow er [W]
Thermal Profile A
Thermal Profile A
Y = 0.171*x + 42.5
Y = 0.171*x + 42.5
82 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 83

Thermal Specifications
Table 6-4. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile A Table
Power (W) T
P
_PROFILE_MIN_A
=43.9 50.0
45 50.2
50 51.1
55 51.9
60 52.8
65 53.6
70 54.5
75 55.3
80 56.2
85 57.0
90 57.9
95 58.7
100 59.6
105 60.5
110 61.3
115 62.2
120 63.0
CASE_MAX
(°C)
Table 6-5. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile B Table
Power (W) T
P
_PROFILE_MIN_B
=30.8 50.0
35 50.9
40 52.1
45 53.2
50 54.3
55 55.4
60 56.5
65 57.7
70 58.8
75 59.9
80 61.0
85 62.1
90 63.3
95 64.4
100 65.5
105 66.6
110 67.7
115 68.9
120 70.0
CASE_MAX
(°C)
6.1.2 Thermal Metrology
The minimum and maximum case temperatures (T
through Tab l e 6 - 5 and are measured at the geometric top center of the processor
integrated heat spreader (IHS). Figure 6-3 illustrates the location where T
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 83
) are specified in Tab le 6- 1 ,
CASE
CASE
Page 84

Thermal Specifications
temperature measurements should be made. For detailed guidelines on temperature
measurement methodology, refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series Thermal/Mechanical Design Guidelines.
Figure 6-3. Case Temperature (T
) Measurement Location
CASE
Note: Figure is not to scale and is for reference only.
6.2 Processor Thermal Features
6.2.1 Thermal Monitor Features
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series provide two thermal monitor features,
Thermal Monitor (TM1) and Enhanced Thermal Monitor (TM2). The TM1 and TM2 must
both be enabled in BIOS for the processor to be operating within specifications. When
both are enabled, TM2 will be activated first and TM1 will be added if TM2 is not
effective.
6.2.2 Thermal Monitor (TM1)
The Thermal Monitor (TM1) feature helps control the processor temperature by
activating the Thermal Control Circuit (TCC) when the processor silicon reaches its
maximum operating temperature. The TCC reduces processor power consumption as
needed by modulating (starting and stopping) the internal processor core clocks. The
temperature at which Thermal Monitor activates the thermal control circuit is not user
84 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 85

Thermal Specifications
configurable and is not software visible. Bus traffic is snooped in the normal manner,
and interrupt requests are latched (and serviced during the time that the clocks are on)
while the TCC is active.
When the TM1 is enabled, and a high temperature situation exists (that is, TCC is
active), the clocks will be modulated by alternately turning off and on at a duty cycle
specific to the processor (typically 30 - 50%). Cycle times are processor speed
dependent and will decrease as processor core frequencies increase. A small amount of
hysteresis has been included to prevent rapid active/inactive transitions of the TCC
when the processor temperature is near its maximum operating temperature. Once the
temperature has dropped below the maximum operating temperature, and the
hysteresis timer has expired, the TCC goes inactive and clock modulation ceases.
With thermal solutions designed to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor E5300
Series Thermal Profile, or Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal
Profile A it is anticipated that the TCC would only be activated for very short periods of
time when running the most power intensive applications. The processor performance
impact due to these brief periods of TCC activation is expected to be so minor that it
would be immeasurable. A thermal solution that is designed to Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor X5300 Series Thermal Profile B may cause a noticeable performance
loss due to increased TCC activation. Thermal Solutions that exceed Thermal Profile B
will exceed the maximum temperature specification and affect the long-term reliability
of the processor. In addition, a thermal solution that is significantly under designed
may not be capable of cooling the processor even when the TCC is active continuously
Refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Thermal/Mechanical
Design Guidelines for information on designing a thermal solution.
The duty cycle for the TCC, when activated by the TM1, is factory configured and
cannot be modified. The TM1 does not require any additional hardware, software
drivers, or interrupt handling routines.
6.2.3 Thermal Monitor 2
The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series adds support for an Enhanced
Thermal Monitor capability known as Thermal Monitor 2 (TM2). This mechanism
provides an efficient means for limiting the processor temperature by reducing the
power consumption within the processor. TM2 requires support for dynamic VID
transitions in the platform.
When TM2 is enabled, and a high temperature situation is detected, the Thermal
Control Circuit (TCC) will be activated for all processor cores. The TCC causes the
processor to adjust its operating frequency (via the bus multiplier) and input voltage
(via the VID signals). This combination of reduced frequency and VID results in a
reduction to the processor power consumption.
A processor enabled for TM2 includes two operating points, each consisting of a specific
operating frequency and voltage, which is identical for both processor dies. The first
operating point represents the normal operating condition for the processor. Under this
condition, the core-frequency-to-system-bus multiplier utilized by the processor is that
contained in the CLOCK_FLEX_MAX MSR and the VID that is specified in Tab le 2- 3 .
The second operating point consists of both a lower operating frequency and voltage.
The lowest operating frequency is determined by the lowest supported bus ratio (1/6
for the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series). When the TCC is activated,
the processor automatically transitions to the new frequency. This transition occurs
rapidly, on the order of 5 µs. During the frequency transition, the processor is unable to
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 85
Page 86

service any bus requests, and consequently, all bus traffic is blocked. Edge-triggered
interrupts will be latched and kept pending until the processor resumes operation at the
new frequency.
Once the new operating frequency is engaged, the processor will transition to the new
core operating voltage by issuing a new VID code to the voltage regulator. The voltage
regulator must support dynamic VID steps in order to support Thermal Monitor 2.
During the voltage change, it will be necessary to transition through multiple VID codes
to reach the target operating voltage. Each step will be one VID table entry (see
Tab le 2- 3 ). The processor continues to execute instructions during the voltage
transition. Operation at the lower voltage reduces the power consumption of the
processor.
A small amount of hysteresis has been included to prevent rapid active/inactive
transitions of the TCC when the processor temperature is near its maximum operating
temperature. Once the temperature has dropped below the maximum operating
temperature, and the hysteresis timer has expired, the operating frequency and
voltage transition back to the normal system operating point. Transition of the VID code
will occur first, in order to insure proper operation once the processor reaches its
normal operating frequency. Refer to Figure 6-4 for an illustration of this ordering.
Figure 6-4. Thermal Monitor 2 Frequency and Voltage Ordering
Thermal Specifications
T
T
TM2
TM2
f
f
MAX
MAX
f
f
TM2
TM2
V
V
NOM
NOM
V
V
TM2
TM2
The PROCHOT# signal is asserted when a high temperature situation is detected,
regardless of whether TM1 or TM2 is enabled.
6.2.4 On-Demand Mode
The processor provides an auxiliary mechanism that allows system software to force
the processor to reduce its power consumption. This mechanism is referred to as “OnDemand” mode and is distinct from the Thermal Monitor 1 and Thermal Monitor 2
features. On-Demand mode is intended as a means to reduce system level power
consumption. Systems utilizing the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
must not rely on software usage of this mechanism to limit the processor temperature.
If bit 4 of the IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION MSR is set to a ‘1’, the processor will
immediately reduce its power consumption via modulation (starting and stopping) of
the internal core clock, independent of the processor temperature. When using OnDemand mode, the duty cycle of the clock modulation is programmable via bits 3:1 of
the same IA32_CLOCK_MODULATION MSR. In On-Demand mode, the duty cycle can
Temperature
Temperature
Frequency
Frequency
Vcc
Vcc
Time
Time
T(hysterisis)
T(hysterisis)
86 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 87

Thermal Specifications
be programmed from 12.5% on/ 87.5% off to 87.5% on/12.5% off in 12.5%
increments. On-Demand mode may be used in conjunction with the Thermal Monitor;
however, if the system tries to enable On-Demand mode at the same time the TCC is
engaged, the factory configured duty cycle of the TCC will override the duty cycle
selected by the On-Demand mode.
6.2.5 PROCHOT# Signal
An external signal, PROCHOT# (processor hot) is asserted when the processor die
temperature of any processor cores has reached its factory configured trip point. If
Thermal Monitor is enabled (note that Thermal Monitor must be enabled for the
processor to be operating within specification), the TCC will be active when PROCHOT#
is asserted. The processor can be configured to generate an interrupt upon the
assertion or de-assertion of PROCHOT#. Refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture
Software Developer’s Manual for specific register and programming details.
PROCHOT# is designed to assert at or a few degrees higher than maximum T
specified by Thermal Profile A) when dissipating TDP power, and cannot be interpreted
as an indication of processor case temperature. This temperature delta accounts for
processor package, lifetime and manufacturing variations and attempts to ensure the
Thermal Control Circuit is not activated below maximum T
power. There is no defined or fixed correlation between the PROCHOT# trip
temperature, or the case temperature. Thermal solutions must be designed to the
processor specifications and cannot be adjusted based on experimental measurements
of T
, or PROCHOT#.
CASE
6.2.6 FORCEPR# Signal
The FORCEPR# (force power reduction) input can be used by the platform to cause the
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series to activate the TCC. If the processor
supports Thermal Monitor 2 (TM2), and has Thermal Monitor 2 and Thermal Monitor
(TM) properly enabled, assertion of the FORCEPR# signal will immediately activate
Thermal Monitor 2. If the processor does not support Thermal Monitor 2, but has
Thermal Monitor properly enabled, FORCEPR# signal assertion will cause Thermal
Monitor to become active. Please refer to the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series Specification Update to determine which processors support TM2 and Intel® 64
and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer’s Manual for details on enabling these
capabilities. Assertion of the FORCEPR# signal will activate TCC for all processor cores.
The TCC will remain active until the system deasserts FORCEPR#.
FORCEPR# is an asynchronous input, which can be employed to thermally protect other
system components. To use the voltage regulator (VR) as an example, TCC circuit
activation will reduce the current consumption of the processor and the corresponding
temperature of the VR.
when dissipating TDP
CASE
CASE
(as
It should be noted that assertion of FORCEPR# does not automatically assert
PROCHOT#. As mentioned previously, the PROCHOT# signal is asserted when a high
temperature situation is detected. A minimum pulse width of 500
when FORCEPR# is asserted by the system. Sustained activation of the FORCEPR#
signal may cause noticeable platform performance degradation.
Refer to the appropriate platform design guidelines for details on implementing the
FORCEPR# signal feature.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 87
µs is recommended
Page 88

Thermal Specifications
6.2.7 THERMTRIP# Signal
Regardless of whether or not TM1 or TM2 is enabled, in the event of a catastrophic
cooling failure, the processor will automatically shut down when the silicon has reached
an elevated temperature (refer to the THERMTRIP# definition in Tabl e 5 -1 ). At this
point, the FSB signal THERMTRIP# will go active and stay active as described in
Tab le 5- 1 . THERMTRIP# activation is independent of processor activity and does not
generate any bus cycles. Intel also recommends the removal of V
TT
.
6.3 Platform Environment Control Interface (PECI)
6.3.1 Introduction
PECI offers an interface for thermal monitoring of Intel processor and chipset
components. It uses a single wire, thus alleviating routing congestion issues.
Figure 6-5 shows an example of the PECI topology in a system with Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor 5300 Series. PECI uses CRC checking on the host side to ensure
reliable transfers between the host and client devices. Also, data transfer speeds across
the PECI interface are negotiable within a wide range (2 Kbps to 2 Mbps). The PECI
interface on Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series is disabled by default and
must be enabled through BIOS. More information on this can be found in the Intel® 64
and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer’s Manual.
Figure 6-5. PECI Topology
6.3.1.1 T
CONTROL
and TCC Activation on PECI-Based Systems
Fan speed control solutions based on PECI utilize a T
processor IA32_TEMPERATURE_TARGET MSR. This MSR uses the same offset
temperature format as PECI, though it contains no sign bit. Thermal management
devices should infer the T
should utilize the relative temperature value delivered over PECI in conjunction with the
MSR value to control or optimize fan speeds. Figure 6-6 shows a conceptual fan control
diagram using PECI temperatures.
PECI Host
C o nt ro ller
CONTROL
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series
(So c ke t 0 )
0
x
Domain0
G5
G5
3
0
0
x
Domain1
3
0
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series
(So ck e t 1)
0
x
Domain0
3
1
0
x
Domain1
3
1
CONTROL
value stored in the
value as negative. Thermal management algorithms
88 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 89

Thermal Specifications
Figure 6-6. Conceptual Fan Control Diagram For A PECI-Based Platform
T
T
CONTROL
CONTROL
Setting
Setting
Max
Max
Fan Speed
Fan Speed
(RPM)
(RPM)
PECI = -10
PECI = -10
Min
Min
PECI = -20
PECI = -20
Temperature
Temperature
(not intended to depict actual implementation)
(not intended to depict actual implementation)
6.3.1.2 Processor Thermal Data Sample Rate and Filtering
The DTS provides an improved capability to monitor device hot spots, which inherently
leads to more varying temperature readings over short time intervals. The DTS sample
interval range can be modified, and a data filtering algorithm can be activated to help
moderate this. The DTS sample interval range is 82 ms (default) to 20 ms (max). This
value can be set in BIOS.
To reduce the sample rate requirements on PECI and improve thermal data stability vs.
time the processor DTS also implements an averaging algorithm that filters the
incoming data. This is an alpha-beta filter with coefficients of 0.5, and is expressed
mathematically as: Current_filtered_temp = (Previous_filtered_temp / 2) +
(new_sensor_temp / 2). This filtering algorithm is fixed and cannot be changed. It is on
by default and can be turned off in BIOS.
TCC Activation
TCC Activation
Temperature
Temperature
PECI = 0
PECI = 0
Host controllers should utilize the min/max sample times to determine the appropriate
sample rate based on the controller's fan control algorithm and targeted response rate.
The key items to take into account when settling on a fan control algorithm are the DTS
sample rate, whether the temperature filter is enabled, how often the PECI host will
poll the processor for temperature data, and the rate at which fan speed is changed.
Depending on the designer’s specific requirements the DTS sample rate and alpha-beta
filter may have no effect on the fan control algorithm.
6.3.2 PECI Specifications
6.3.2.1 PECI Device Address
The PECI device address for socket 0 is 0x30 and socket 1 is 0x31. Please note that
each address also supports two domains (Domain 0 and Domain 1).
6.3.2.2 PECI Fault Handling Requirements
PECI is largely a fault tolerant interface, including noise immunity and error checking
improvements over other compatible industry standard interfaces. The PECI client is as
reliable as the device that it is embedded within, and thus given operating conditions
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 89
Page 90

that fall under the specification, the PECI client will always respond to requests and the
protocol itself can be relied upon to detect any transmission failures. There are,
however, certain scenarios where PECI is known to be unresponsive.
Prior to a power on RESET# and during RESET# assertion, PECI is not guaranteed to
provide reliable thermal data. System designs should implement a default power-on
condition that ensures proper processor operation during the time frame when reliable
data is not available via PECI.
To protect platforms from potential operational or safety issues due to an abnormal
condition on PECI, the PECI host controller should take action to protect the system
from possible damage. It is recommended that the PECI host controller take
appropriate action to protect the client processor device if valid temperature readings
have not been obtained in response to three consecutive gettemp()s or for a one
second time interval. The PECI host controller may also implement an alert to software
in the event of a critical or continuous fault condition.
6.3.2.3 PECI GetTemp0() and GetTemp1() Error Code Support
The error codes supported for the processor GetTemp0() and GetTemp1() command
are listed in Tab le 6- 6 below:
Table 6-6. GetTemp0() and GetTemp1() Error Codes
Thermal Specifications
Error Code Description
0x8000 General sensor error
0x8002
Sensor is operational, but has detected a temperature below its operational range
(underflow).
§
90 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 91

Features
7 Features
7.1 Power-On Configuration Options
Several configuration options can be configured by hardware. Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series sample its hardware configuration at reset, on the active-toinactive transition of RESET#. For specifics on these options, please refer to Tab l e 7 - 1.
The sampled information configures the processor for subsequent operation. These
configuration options cannot be changed except by another reset. All resets reconfigure
the processor, for reset purposes, the processor does not distinguish between a “warm”
reset (PWRGOOD signal remains asserted) and a “power-on” reset.
Table 7-1. Power-On Configuration Option Lands
Configuration Option Land Name Notes
Output tri state SMI# 1,2,3
Execute BIST (Built-In Self Test) A3# 1,2
Disable MCERR# observation A9# 1,2
Disable BINIT# observation A10# 1,2
Symmetric agent arbitration ID BR[1:0]# 1,2
Notes:
1. Asserting this signal during RESET# will select the corresponding option.
2. Address lands not identified in this table as configuration options should not be asserted during RESET#.
3. Requires de-assertion of PWRGOOD.
Disabling of any of the cores within the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300
Series must be handled by configuring the EXT_CONFIG Model Specific Register (MSR).
This MSR will allow for the disabling of a single core per die within the Quad-Core
Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series package. Additional details can be found in the
Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer’s Manual.
7.2 Clock Control and Low Power States
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support the Extended HALT state (also
referred to as C1E) in addition to the HALT state and Stop-Grant state to reduce power
consumption by stopping the clock to internal sections of the processor, depending on
each particular state. See Figure 7-1 for a visual representation of the processor low
power states. The Extended HALT state is a lower power state than the HALT state or
Stop Grant state.
The Extended HALT state must be enabled via the BIOS for the processor to
remain within its specifications. Refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture
Software Developer’s Manual. For processors that are already running at the lowest bus
to core frequency ratio for its nominal operating point, the processor will transition to
the HALT state instead of the Extended HALT state.
The Stop Grant state requires chipset and BIOS support on multiprocessor systems. In
a multiprocessor system, all the STPCLK# signals are bussed together, thus all
processors are affected in unison. When the STPCLK# signal is asserted, the processor
enters the Stop Grant state, issuing a Stop Grant Special Bus Cycle (SBC) for each
processor. The chipset needs to account for a variable number of processors asserting
the Stop Grant SBC on the bus before allowing the processor to be transitioned into one
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 91
Page 92

of the lower processor power states. Refer to the applicable chipset specification and
the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer’s Manual for more
information.
7.2.1 Normal State
This is the normal operating state for the processor.
7.2.2 HALT or Extended HALT State
The Extended HALT state (C1E) is enabled via the BIOS. Refer to the Intel® 64 and
IA-32 Architecture Software Developer’s Manual. The Extended HALT state must be
enabled for the processor to remain within its specifications. The Extended HALT
state requires support for dynamic VID transitions in the platform.
7.2.2.1 HALT State
HALT is a low power state entered when the processor has executed the HALT or
MWAIT instruction. When one of the processor cores execute the HALT or MWAIT
instruction, that processor core is halted; however, the other processor continues
normal operation. The processor will transition to the Normal state upon the occurrence
of SMI#, BINIT#, INIT#, LINT[1:0] (NMI, INTR), or an interrupt delivered over the
front side bus. RESET# will cause the processor to immediately initialize itself.
Features
The return from a System Management Interrupt (SMI) handler can be to either
Normal Mode or the HALT state. See the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Intel® Architecture
Software Developer's Manual, Volume III: System Programming Guide for more
information.
The system can generate a STPCLK# while the processor is in the HALT state. When the
system deasserts STPCLK#, the processor will return execution to the HALT state.
While in HALT state, the processor will process front side bus snoops and interrupts.
7.2.2.2 Extended HALT State
Extended HALT state is a low power state entered when all four processor cores have
executed the HALT or MWAIT instructions and Extended HALT state has been enabled
via the BIOS. When one of the processor cores executes the HALT instruction, that
processor core is halted; however, the other processor cores continue normal
operation. The Extended HALT state is a lower power state than the HALT state or Stop
Grant state. The Extended HALT state must be enabled for the processor to remain
within its specifications.
The processor will automatically transition to a lower core frequency and voltage
operating point before entering the Extended HALT state. Note that the processor FSB
frequency is not altered; only the internal core frequency is changed. When entering
the low power state, the processor will first switch to the lower bus to core frequency
ratio and then transition to the lower voltage (VID).
While in the Extended HALT state, the processor will process bus snoops.
92 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 93

Features
Table 7-2. Extended HALT Maximum Power
Symbol Parameter Min Typ Max Unit Notes
P
EXTENDED_HALT
Quad-Core Intel®
Xeon® Processor
E5300 Series
P
EXTENDED_HALT
Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor X5300
Series
Quad-
Extended HALT
State Power
Extended HALT
State Power
30/34 W 1,2,3
50 W 1,2
Notes:
1. The specification is at T
VID while running in HALT state.
2. This specification is characterized by design.
3. Processors running in the lowest bus ratio will enter the HALT state when the processor has executed the
HALT and MWAIT instruction since the processor is already in the lowest core frequency and voltage
operating point. Values represent SKUs with Extended HALT state (30 W) and without Extended HALT state
(34 W).
= 50°C and nominal VCC. The VID setting represents the maximum expected
CASE
The processor exits the Extended HALT state when a break event occurs. When the
processor exits the Extended HALT state, it will first transition the VID to the original
value and then change the bus to core frequency ratio back to the original value.
Figure 7-1. Stop Clock State Machine
Normal State
Normal execution
STPCLK#
Asserted
STPCLK#
De-asserted
HALT or MWA IT Instruction and
HALT Bus Cycle Generated
INIT # , B INIT#, IN T R , N MI, SM I# ,
RESET#, FSB interrupts
#
K
L
d
C
e
t
P
r
T
e
S
s
s
A
#
d
K
e
t
L
r
e
C
s
P
s
T
a
-
S
e
D
Extended HALT or HALT State
BCLK running
Snoops and interrupts allowed
Snoop
Event
Occurs
Snoop
Event
Serviced
Stop Grant State
BCLK running
Snoops and interrupts allowed
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 93
Snoop Event Occurs
Snoop Event Serviced
Extended HALT Snoop or HALT
Snoop State
BCLK running
Service snoops to caches
Stop Grant Snoop State
BCLK running
Service snoops to caches
Page 94

7.2.3 Stop-Grant State
When the STPCLK# pin is asserted, the Stop-Grant state of the processor is entered
20 bus clocks after the response phase of the processor issued Stop Grant
Acknowledge special bus cycle. The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series
will issue two Stop Grant Acknowledge special bus cycles, once for each die. Once the
STPCLK# pin has been asserted, it may only be deasserted once the processor is in the
Stop Grant state. All processor cores will enter the Stop-Grant state once the STPCLK#
pin is asserted. Additionally, all processor cores must be in the Stop Grant state before
the deassertion of STPCLK#.
Since the AGTL+ signal pins receive power from the front side bus, these pins should
not be driven (allowing the level to return to V
termination resistors in this state. In addition, all other input pins on the front side bus
should be driven to the inactive state.
BINIT# will not be serviced while the processor is in Stop-Grant state. The event will be
latched and can be serviced by software upon exit from the Stop Grant state.
RESET# will cause the processor to immediately initialize itself, but the processor will
stay in Stop-Grant state. A transition back to the Normal state will occur with the deassertion of the STPCLK# signal.
A transition to the Grant Snoop state will occur when the processor detects a snoop on
the front side bus (see Section 7.2.4.1).
Features
TT) for minimum power drawn by the
While in the Stop-Grant state, SMI#, INIT#, BINIT# and LINT[1:0] will be latched by
the processor, and only serviced when the processor returns to the Normal state. Only
one occurrence of each event will be recognized upon return to the Normal state.
While in Stop-Grant state, the processor will process snoops on the front side bus and it
will latch interrupts delivered on the front side bus.
The PBE# signal can be driven when the processor is in Stop-Grant state. PBE# will be
asserted if there is any pending interrupt latched within the processor. Pending
interrupts that are blocked by the EFLAGS.IF bit being clear will still cause assertion of
PBE#. Assertion of PBE# indicates to system logic that it should return the processor to
the Normal state.
7.2.4 Extended HALT Snoop or HALT Snoop State, Stop Grant
Snoop State
The Extended HALT Snoop state is used in conjunction with the Extended HALT state. If
the Extended HALT state is not enabled in the BIOS, the default Snoop state entered
will be the HALT Snoop state. Refer to the sections below for details on HALT Snoop
state, Stop Grant Snoop state and Extended HALT Snoop state.
7.2.4.1 HALT Snoop State, Stop Grant Snoop State
The processor will respond to snoop or interrupt transactions on the front side bus
while in Stop-Grant state or in HALT state. During a snoop or interrupt transaction, the
processor enters the HALT/Grant Snoop state. The processor will stay in this state until
the snoop on the front side bus has been serviced (whether by the processor or another
agent on the front side bus) or the interrupt has been latched. After the snoop is
serviced or the interrupt is latched, the processor will return to the Stop-Grant state or
HALT state, as appropriate.
94 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 95

Features
7.2.4.2 Extended HALT Snoop State
The Extended HALT Snoop state is the default Snoop state when the Extended HALT
state is enabled via the BIOS. The processor will remain in the lower bus to core
frequency ratio and VID operating point of the Extended HALT state.
While in the Extended HALT Snoop state, snoops and interrupt transactions are handled
the same way as in the HALT Snoop state. After the snoop is serviced or the interrupt is
latched, the processor will return to the Extended HALT state.
7.3 Enhanced Intel SpeedStep® Technology
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series support Enhanced Intel SpeedStep®
Technology. This technology enables the processor to switch between multiple
frequency and voltage points, which results in platform power savings. Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep Technology requires support for dynamic VID transitions in the platform.
Switching between voltage/frequency states is software controlled. For more
configuration details also refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software
Developer’s Manual.
Note: Not all Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series are capable of supporting
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology. More details on which processor frequencies will
support this feature will be provided in future releases of the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series Specification Update when available.
Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology creates processor performance states (P-states)
or voltage/frequency operating points. P-states are lower power capability states within
the Normal state as shown in Figure 7-1. Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology
enables real-time dynamic switching between frequency and voltage points. It alters
the performance of the processor by changing the bus to core frequency ratio and
voltage. This allows the processor to run at different core frequencies and voltages to
best serve the performance and power requirements of the processor and system. The
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series have hardware logic that coordinates
the requested voltage (VID) between the processor cores. The highest voltage that is
requested from the four processor cores is selected for that processor package. Note
that the front side bus is not altered; only the internal core frequency is changed. In
order to run at reduced power consumption, the voltage is altered in step with the bus
ratio.
The following are key features of Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology:
• Multiple voltage/frequency operating points provide optimal performance at
reduced power consumption.
• Voltage/frequency selection is software controlled by writing to processor MSR’s
(Model Specific Registers), thus eliminating chipset dependency.
— If the target frequency is higher than the current frequency, V
in steps (+12.5 mV) by placing a new value on the VID signals and the
is incremented
CC
processor shifts to the new frequency. Note that the top frequency for the
processor can not be exceeded.
— If the target frequency is lower than the current frequency, the processor shifts
to the new frequency and V
changing the target VID through the VID signals.
is then decremented in steps (-12.5 mV) by
CC
Refer to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer’s Manual for specific
information to enable and configure Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology in BIOS.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 95
§
Page 96

Features
96 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Page 97

Boxed Processor Specifications
8 Boxed Processor Specifications
8.1 Introduction
Intel boxed processors are intended for system integrators who build systems from
components available through distribution channels. The Quad-Core Intel® Xeon®
Processor 5300 Series will be offered as an Intel boxed processor.
Intel will offer the Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series boxed processor
with two heat sink configurations available for each processor frequency: 1U passive/
3U+ active combination solution and a 2U passive only solution. The 1U passive/3U+
active combination solution is based on a 1U passive heat sink with a removable fan
that will be pre-attached at shipping. This heat sink solution is intended to be used as
either a 1U passive heat sink, or a 3U+ active heat sink. Although the active
combination solution with removable fan mechanically fits into a 2U keepout, its use is
not recommended in that configuration.
The 1U passive/3U+ active combination solution in the active fan configuration is
primarily designed to be used in a pedestal chassis where sufficient air inlet space is
present and strong side directional airflow is not an issue. The 1U passive/3U+ active
combination solution with the fan removed and the 2U passive thermal solution require
the use of chassis ducting and are targeted for use in rack mount or pedestal servers.
The retention solution used for these products is called the Common Enabling Kit, or
CEK. The CEK base is compatible with both thermal solutions and uses the same hole
locations as the Dual-Core Intel® Xeon® processor 5100 series.
The 1U passive/3U+ active combination solution will utilize a removable fan capable of
4-pin pulse width modulated (PWM) control. Use of a 4-pin PWM controlled active
thermal solution helps customers meet acoustic targets in pedestal platforms through
the motherboards’s ability to directly control the RPM of the processor heat sink fan.
See Section 8.3 for more details on fan speed control, and see Section 6.3 for more on
the PWM and PECI interface along with Digital Thermal Sensors (DTS). Figure 8-1
through Figure 8-3 are representations of the two heat sink solutions.
Figure 8-1. Boxed Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series 1U Passive/3U+
Active Combination Heat Sink (With Removable Fan)
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 97
Page 98

Boxed Processor Specifications
Figure 8-2. Boxed Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series 2U Passive Heat Sink
Figure 8-3. 2U Passive Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Processor
Thermal Solution (Exploded View)
Heat sink screw
Heat sink
Heat sink
screws
screws
Motherboard
Motherboard
and
and
processor
processor
Heat sink screw
springs
springs
Heat sink
Heat sink
Heat sink standoffs
Heat sink standoffs
Therm al Interface
Therm al Interface
Material
Material
Protective Tape
Protective Tape
CEK spring
CEK spring
Note:
1. The heat sinks and fan assemblies represented in Figure 8-1, Figure 8-2, and Figure 8-3 are for reference
only, and may not represent the final boxed processor heat sinks.
2. The screws, springs, and standoffs will be captive to the heat sink. This image shows all of the components
in an exploded view.
3. It is intended that the CEK spring will ship with the base board and be pre-attached prior to shipping.
98 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
Chassis pan
Chassis pan
Page 99

Boxed Processor Specifications
8.2 Mechanical Specifications
This section documents the mechanical specifications of the boxed processor.
8.2.1 Boxed Processor Heat Sink Dimensions (CEK)
The boxed processor will be shipped with an unattached thermal solution. Clearance is
required around the thermal solution to ensure unimpeded airflow for proper cooling.
The physical space requirements and dimensions for the boxed processor and
assembled heat sink are shown in Figure 8-4 through Figure 8-8. Figure 8-9 through
Figure 8-10 are the mechanical drawings for the 4-pin board fan header and 4-pin
connector used for the active CEK fan heat sink solution.
Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet 99
Page 100

Figure 8-4. Top Side Board Keepout Zones (Part 1)
Boxed Processor Specifications
100 Quad-Core Intel® Xeon® Processor 5300 Series Datasheet
 Loading...
Loading...