Page 1

Intel SSD DC S3500 Series Workload
Characterization in RAID Configurations
White Paper
December 2013
329903-001US
Page 2

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, E XPR ESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR
OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECT UAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GR ANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCE PT AS PR OVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND
CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOE VER AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IM PL IE D
WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR ANY APPLICATION IN
WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR.
Intel may make changes t o specifications and product descriptions at any time, wit h out n otice. Designers must not rel y on t h e abse n ce or
characterist ics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undef ined." Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no
responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from fu ture changes to them. The information here is subject to change without
notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cau se t h e product to dev iate from
published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distribu t or to obtai n t h e latest specifications and before p lacing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling 1-
800-548-4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm
Software and workloads used in p e rformance tests m ay have been optimized for perf ormance only on I ntel microproc essors. Any change t o a n y of
those factors may cause the results t o vary . You sh ou ld consult other information and performance tests to assist you i n fully evaluating your
contemplated purchases, including the performance of that product when combined with other products.
Intel and the I ntel logo are trademarks of Int e l Corporation in the U.S. and ot h er countries.
*Other names and brands may be clai m ed as t h e property of oth ers.
Copyright © 2013, Intel Corporation . All Righ t s R eserved.
White Paper December 2013
2 329903-001US
Page 3

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Contents
1.0 Revision Histor y ................................................................................................... 5
2.0 Supporting Documentation ................................................................................... 5
3.0 About This Guide .................................................................................................. 5
4.0 Overview .............................................................................................................. 5
4.1 What Impacts SSD IO Performance................................................................. 6
4.2 Queue Depth and Latency ............................................................................. 7
4.3 Why Mixed Workload Is Importan t .................................................................. 7
4.4 Drive Endurance ........................................................................................... 8
4.5 Selection of RAID Controller........................................................................... 8
5.0 RAID 1 .................................................................................................................. 9
5.1 Test System Specifications ............................................................................ 9
5.2 Intel SSD DC S3500 Series in RAID 1 Perform a nce Characterization Data ........... 10
5.3 RAID 1 Consistency ..................................................................................... 13
5.4 RAID 1 Performance Conclusions ................................................................... 13
6.0 RAID 5 ................................................................................................................ 14
6.1 Test System Specifications ........................................................................... 14
6.2 Intel SSD DC S3500 Series in RAID 5 Performance Characterization Data ........... 14
6.3 RAID 5 Performance Consistency ................................................................... 16
RAID 5 Performance Conclusions ................................................................... 17
6.4
7.0 Summary ............................................................................................................ 18
8.0 Appendix ............................................................................................................ 19
8.1 RAID Levels ................................................................................................ 19
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 3
Page 4

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Tables
Table 1 Typical Mixed Workloads in Data Center Application s ....................................... 7
Figures
Figure 1 RAID 1 Random 100% Write @ 4KB T r a nsfer Size with Average Latency ............ 11
Figure 2 RAID 1 Random 70% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with Average Latency ............. 11
Figure 3 RAID 1 Random 90% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with Average Latency ............. 12
Figure 4 RAID 1 Random 100% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with Average Latency ........... 12
Figure 5 RAID 1 Maximum Latency for 2-drive and 8-drive Configurations ...................... 13
Figure 6 RAID 5 Random 100% Write @ 4KB Transfer Size with A verage Latency ........... 15
Figure 7 RAID 5 Random 70% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with Average Latency ............. 15
Figure 8 RAID 5 Random 90% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with Average L a ten c y ............. 16
Figure 9 RAID 5 Random 100% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with Avera ge La tency ........... 16
Figure 10 RAID 5 Maximum Latency for 3-drive and 8-drive Configuration s ...................... 17
White Paper December 2013
4 329903-001US
Page 5
Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
1.0 Revision History
Document
Number
329903 001
Revision
Number
Description Revision Date
Initial release
2.0 Supporting Documentation
For more information on Intel SSDs, see the correspon ding documentation.
Document Document No./Location
®
Intel
Solid-State Drive DC S3500 Series Product Specification 328860
December 2013
3.0 About This Guide
This guide describes Intel® SSD DC S3500 Series performan c e characteristics in RAID
configurations across multiple workloads, an d provides analysis to help optimize
performance.
The audience is technical IT professionals: Systems, Storage, Database, and Application
Engineers.
4.0 Overview
The Intel SSD DC S3500 Series provides high random read and write storage
Input/Outpu t Operations per Second ( IOPS) across mixed read and wr ite workloads. This
high random performance and the consistency of IOPS under workload deliver robust
and scalable operation when used behind a RAID controller. Data centers can benefit in
both performance and TC O by using the Intel SSD DC S3500 Series in the appropriate
applications.
Compared to the approximately 200-300 random IOPS that a single 15K SAS hard disk
drive (HDD) can provide, an Intel SSD DC S3500 Series operates at much higher IOPS;
up to 75,000 IOPS for random 4KB reads and up to 11,500 I O P S for random 4KB writes,
over the entire span of the SSD. The Intel SSD performance nu m ber s a r e ba s ed on the
Intel product specification sheet, a s d er ived from internal Intel testing. With r e a l-world
workloads, the IOPS that any particular device c an produce will va r y depending on
several factors: the application’s ability to produce IOPS, the ratio of random to
sequential access, the block tra nsfer size, the queue depth, the read/write mix of the
workload, and ov e r a ll resource utilization in the server running the workload.
This guide presents data for RAID 1 and RAID 5 configurations due to their prom inence
in the datacenter. Additional RA ID levels are currently being tested and will be
presented in future revision s , or as separate papers.
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 5
Page 6

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
A selection of work loads that represent both bes t-case performance and real-world
performance are presented in this white paper. These scenarios give th e IT professional
a better understanding of the capabilities of the Intel
®
SSD DC S3500 Series drive w hen
used in conjunction with a hardware RAID controller. More imp or ta ntly, it helps the IT
professional un d er stand a variety of workloads and circumstances in which Intel SSD
technologies will accelerate those workloads and provide business value for their
organization.
4.1 What Impacts SSD IO Performance
Although Intel SSDs excel in delivering random read and write IOPS, it is important to
remember that more IO ac tivity at the application level results in higher CPU utilization
in the applications’ host. In addition to the abilities of the SSD, IO performance in any
particular situation is dictated by how the particular applica tion scales, and the IO profile
of the workload produced by the application.
The following wor kload-specific characteristics have a direct impact on the ability of the
SSD to produce IO:
• Read/Write Mix – NAND programming (writes) and read timing (reads) differ
significantly a t the hardware level. Because of the higher controller overhead
required for processing writes, the number of read IOPS are often higher th a n
write IOPS. Real world workloads are most often a mix of read and write.
• Random/Sequen tia l Mix – IOPS can vary depending on the ratio of sequ ential
versus random accesses. With higher random write workloads, more data
movement and greater data management activity occurs in the drive. A s random
write activity increases, the IOPS serviceable to the host typically decreases.
• Queue Depth - Higher queue depths typically allow the SS D to gen er a te higher
IOPS through concurrent processing of commands. However, as the queue size
increases, latency will be negatively impacted.
• Random Transfer/Block Size - With a smaller transfer size, the S SD controller has
to work harder to ma intain the logical-to-physical address mappings. In addition,
the smaller the transfer size, the larger the logical space needed for its mapping.
Once logical space constraint is reached, background re-mapping will take place.
These frequent events s low IOPS.
• Available Spare Area – A larger spare area directly impacts random write and
mixed read/write performance by minimizing the frequency of reclaim activ ities
and freeing up processor cy c les to support more host read/write requests. You can
increase the spare area by ov er-provisioning the SSD. See the Intel® High
Performance SATA Solid-State Drive Over-Provisioning an Intel® SS D White Paper
for more information.
In summary, th e following principles of storage are often true concerning queu e depth ,
block size, randomness, a nd per-IO transactional latency:
• As queue depth increases, IOPS increase, and latency increases.
• As block size increases, throughput increases, and latency increases.
• As randomness increases, IOPS decreases, and latency increases.
White Paper December 2013
6 329903-001US
Page 7
Web-Servers
4KB/8KB/16KB+
~75%
~95%
Exchange Email
4KB
~95%
~70%
Database OLTP
4KB/8KB
~95%
~70%
Decision Support
16KB+
~95%
~95%
Video On Demand
16KB+
~95%
~95%
Search Engine
4KB/8KB/16KB
~95%
~95%
Cache
16KB+
~95%
~95%
Content Delivery Network
16KB+
~95%
~70%-95%
Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
4.2 Queue Depth and Latency
Latency – The amount of time needed to s e r vice one outstanding IO to the drive,
measured in milliseconds (ms) or, with SSDs, microseconds (µs).
The Intel
RAID array, the queue depth is multiplied by the number of drives in the RAID set .
Example: In a RAID 5 set of 8 drives, the maxim um total queue depth would be 256 (8
X 32). As more commands a r e queued in the SSD, average latency is impacted. Our
internal testing ind ic ates that average latency increases sharply with queue depths
beyond 8. However, these high queue depths can increase IOPS with read intensive
workloads.
Obtaining the best per formance for a particular application requires balance. The
challenge is to achieve high s peed or IOPS at an acceptable latency level. This white
paper presents lower qu eue depths of 1, 2, 4 and 8 per drive. The results shown
demonstrate favorable speed and IOPS generation without pushing latency to extreme
levels.
®
SSD DC S3500 Series supports a maximum queue depth of 32 per driv e. In a
4.3 Why Mixed Workload Is Important
Mixed random workloads are predom in a nt in data center and enterpr ise applications.
Intel SSDs ha ve been deployed in a variety of these applic ations ranging from content
delivery and video on demand n etw orks, to Internet datacenter portals and database
management servers. Although these applications see unique IO traffic across the
storage drive, there are commonalities in their usage of ra ndom and read/write mixed
workloads.
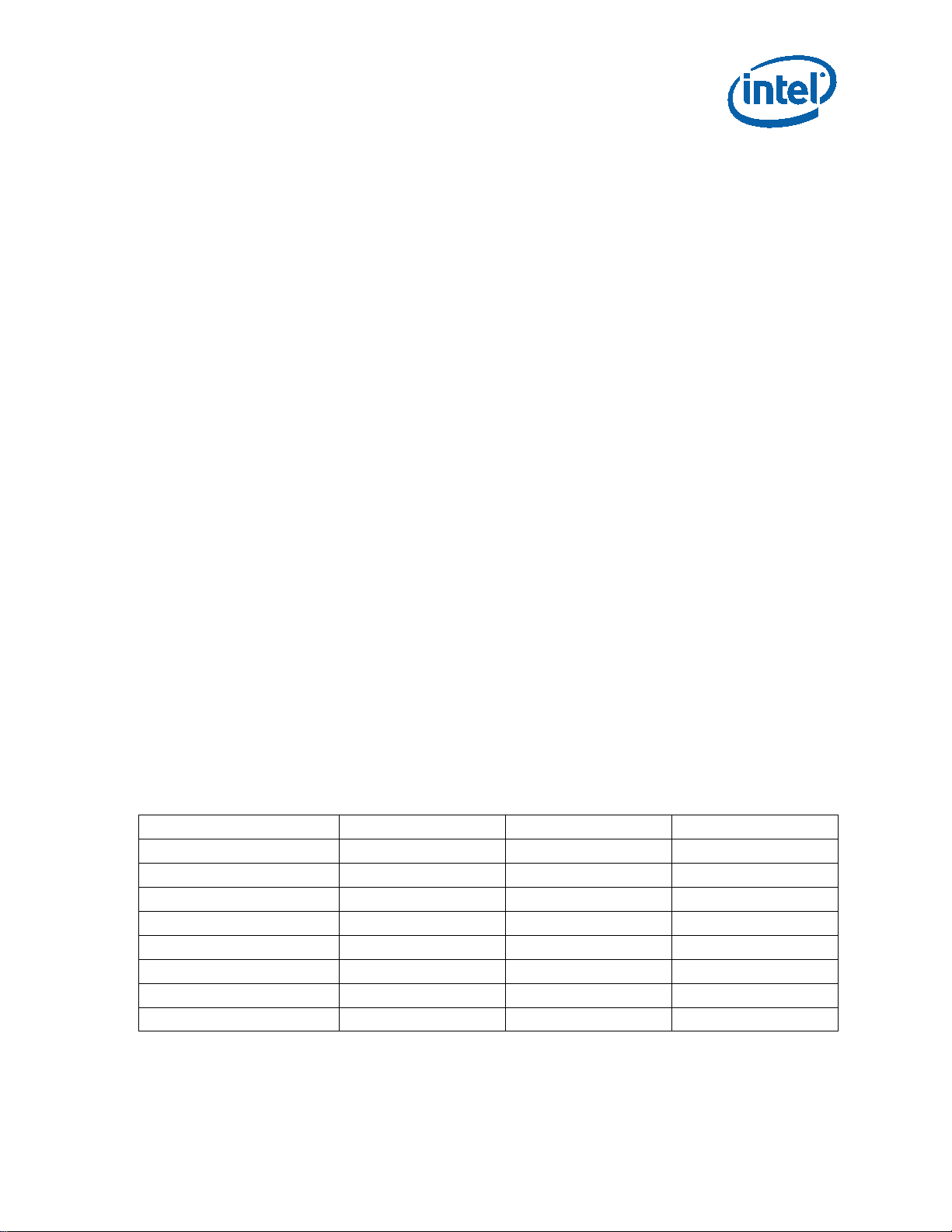
Table 1 shows an overview of transfer sizes, read/write mixes and randomness in
commonly used workloads in data center applications. These are based on commonly
available industr y information and information available through such benchmarks as,
TPC-C, TPC-E, TPC-H, and TPOX, which attempt to m imic these real world ap plications.
Table 1. Typical Mixed Workloads i n D a ta C e n ter Applications
Application Transfer Size %Random %Read
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 7
Based on these usage trends, small transfer sizes–ranging from 4KB to 16KB and
above–are common in enterprise an d data center application s . Also, much emphasis is
placed on random accesses, and although there are varied levels of read and write
Page 8

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
mixes, read-intensive workloads a r e m or e p r om inent. In summary, it is important to
select the proper SSD for a particular workload.
The examples presented here use 100% write and 100% read workload s to show the
maximum performance in these areas. Also, 70%/30% r ea d/ write and 90%/10%
read/write are us ed in order to simulate typical workloads in the da tacenter.
4.4 Drive Endurance
Drive endurance, or w ea r , is an important consideration when selecting an SSD for a
particular application. The Intel
enterprise class drive, designed for read-heavy workloads. It is important to understand
how drive wear is affected by the RAID level.
A RAID level that uses dedicated parity, such as RA I D 4, will write all parity to a single
drive. This can potentially cause the pa r ity drive to wear faster than the other driv es in
the set. Distributed parity RAID levels (RAID 5 and RAID 6) reduce this issue.
RAID 1 and RAID 5, as tested in this example, shows very consistent wear across all
drives in the RAID sets. This is due to the tests using the full LBA space of the RAID set,
thereby not creating any hotspot activity.
®
SSD DC S3500 Series drive is a s tandard endurance,
4.5 Selection of RAID Controller
There are many quality RAI D controllers on the market today, with varying levels of
performance, features a nd price points. Below are the important features cons idered in
selecting the RAI D c ontroller for this sample test:
• RAID levels ava ila b le
• Controller chipset
• PCIe* version
• SAS/SATA speed
• Internal/Ex ter nal ports
• Compatibility with SS D s
Within these categories, the LSI* MegaRAID 9265-8i was chosen for th e following
reasons:
• RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 50, 60 are supported
• LSISAS2208 Dual-Core RAID on Chip (ROC)
• 1 GB 1333MHz DDR3 SDRAM Cache
• x8 PCIe 2.0
• 6Gb/s per port
• 8 internal SAS ports
• SSD support
• Relative availability/ pop ularity in the industry
White Paper December 2013
8 329903-001US
Page 9

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
5.0 RAID 1
5.1 Test System Specifications¹
The system used for RAID 1 testing include the following:
• Intel
• Intel
• 2x Intel
• Intel
• 192GB DDR3-1333 memory
• Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2*, 64-bit
• LSI MegaRAID 9265-8i* contr olle r c ard
• 2x up to 8x Intel
®
R2208GZ4GC-IDD 2U rack mount server
®
S2600GZ server board
®
Xeon® E5-2690 8-core CPUs (2.9 GHz)
®
C602 chipset
®
SSD DC S3500 Series 480GB drives
BIOS configuration changes:
• Hyper-Threading disabled²
RAID controller c onfiguration:
• 256KB Striping (default)
• No Read-Ahead³
• Write-Through³
• Direct I/O
Windows Drive Configuration:
• Basic disk
• GUID partition table
• Simple volume
• Use full available space
• NTFS format
Test Software configuration:
• IOMeter 2009.10.22
• 1x worker per drive in RAID set⁴
Notes:
1. The system was selected to make sure the performance of the RAID car d and the SSDs would not be inhibited by the se rver.
2. Hyper-Threading is disabled in this test sy s te m s p e c i f ic a lly due to additional latency introduced during benchmark te s ting . In any practical applic ation, Hyper-Threading would NOT be disabled.
3. In the configuration of the RAID set, No Rea d A he a d and Write-through are used d ue to the speed
of the SSDs. Re ad and write caching was des i g ne d for use with HDDs. Ca c hing w i th S S D s introduces
additional overhe ad thus interfering with the S S Ds performance .
4. One thread, or worker, per drive was used in order to simulate the manner in which ma ny applications utilize storage and also to attempt to saturate the communication cha nne ls to the S S Ds.
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 9
Page 10

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
5.2 Intel® SSD DC S3500 Series in RAID 1 Performance Characterization Data
This section prov ides performance characterization data for the Intel® SSD DC S3500
Series in RAID 1 configurations.
To establish baseline expectations f or IOPS, the Intel SSD DC S3500 Series 480GB
drives were evaluated in RAID 1 sets of 2, 4, 6 & 8 drives. The data collected was ba s ed
on a different mix of read and write random and sequential workloads. Since high er
queue depths can sometimes yield higher IOPS, queue depths of 1, 2, 4, & 8 per drive
were chosen in the test setup. Multiple transfer sizes were tested, however, only
selected data is presented here. All tests w e r e don e using the entire LBA range of the
virtual drive. T ests were repeated at leas t twice to validate results.
Drives were prepared using I O Meter to fill the entire user area of the drive with data.
Then, the fir s t workload of each type (Sequential or Random) was 100% write
performed for 120 minutes. Ea c h subsequent workload was run for 12 minutes, with
average IOPS collected over th e las t 10 minutes of the run.
The following figures show the different levels of performance for a selection of
configurations.
Note: The scale of the IOPS charts is variable to clarify the changes that occur as drives are
added.
White Paper December 2013
10 329903-001US
Page 11

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Figure 1. RAID 1 Random 100% Write @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
Notes:
As more drives are added, the write performance scales linearly. At four drives, the perfo rmance is
At a queue depth of 1, the average latency for 100% write a t 4 KB transfer size is less than 200 µs.
Figure 1 - The write performance of the two drive RAID 1 set matches the write performance of a
single Intel
2x that of a single dr ive, at six drives, it is 3x higher and at eight d r ives it is 4x. This is true at all
queue depths tested and at transfer sizes fr om 4KB to 128KB. In this case, queue d e pth does not
affect performance significantly.
Latency increases as the queue deepens, ending at 1.4ms for a queue of 8. It is interesting to note
that latency is not affec te d by the number of drives.
®
DC S3500 drive. This indicates very low latenc y introduced by the RAID controller .
Figure 2. RAID 1 Random 70% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 11
Page 12

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Figure 3. RAID 1 Random 90% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
Figure 4. RAID 1 Random 100% Read @ 4KB transfer size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
Notes:
Figures 2, 3 - In mixed wo rkloads, 70% re ad and 90% read, IOPS increase with additional drives
and show slightly exponential growth with d e e per queues.
Figures 2, 3, 4 - Average late nc y for 70% read s tarts out similar to 100 % w rite, but the progres s ion
is not as steep throug h deeper queues, end ing between 500-600 µS. Average latency for 90% read
and 100% read c ontinue to improve due to the higher speed of reads over writes.
Figures 2, 3, 4 - The latency of the two drive set is lower than other drive counts as r e ad
percentage incre a s e s d ue to the ma nne r in which the LSI controlle r deals with the additional d r i v e s .
This is expected b e havior. For more information, please co nta c t LS I for details.
Figure 4 - At 100% read the IOPS performance s c a le s line arly. In other wor ds, the IOPS for f our
drives is doub le that of two drives, six drives is triple tha t o f two drives, and eight drives is four
times that of two drives.
White Paper December 2013
12 329903-001US
Page 13

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
5.3 RAID 1 Consistency
Consistency behind a RAID controller is very importa nt because the performance of any
RAID set is limited by the lowest performing drive. As a RAID set increases in number of
drives, the probability of any given drive performing poorly incr ea s es . Therefore, if the
model of drive used is inconsistent in its performance, the inconsistency increases with
the size of the RA ID set.
The Intel
single drive. Figure 5 illustrates the consistent of DC S3500 in RAID sets. Notice that the
maximum latenc y is grouped very tightly for both the two-drive and eight-drive RAID
sets, indicating there is very little change in consistency as more SSDs are added.
Figure 5. RAID 1 Maximum Latency for 2-drive and 8-drive
®
SSD DC S3500 Series drive has shown excellent consistency when used as a
Configurations
Intel internal testing, October 2013
5.4 RAID 1 Performance Conclusions
RAID 1 is a very good choice for d a ta needing robust replic a tion. The RAID controller
used shows good bandwidth with low latency causing little to no effect on read and write
speeds of the SSDs. The linear scaling of r e a d a nd write performance with additional
drives shows that adding more drives wou ld provide good ROI in most applications. The
highest throughput seen in this test was 2300 MB/s during 100% read using eight drives
with transfer size of 128KB and a queue of 8 per drive. This means the theoretical
bandwidth limit of th e PCIe lanes was not reached (4000 MB/s for x8 PCIe 2.0). It is
theoretically possible that more than eight drives could be used and obtain an increase
in performance, depending on the latency in tr odu c ed by the necessary SAS expan der.
The consistenc y of the drives is well demonstrated in th es e tests and shows that
Intel SSD DC S3500 Series drives provide high performance with exc e llent stability,
even behind a RAID c on tr oller.
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 13
Page 14

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
6.0 RAID 5
6.1 Test System Specifications
The system used for RAID 5 testing wa s identical to the system us ed for RAID 1 testing except the following changes:
• 2x Intel Xeon E5-2680 8-core CPUs (2.7 GHz)
• 3x up to 8x Intel SSD DC S 3500 S er ies 800G B drives
Note: For this test, 800GB drives were used. The rated performance of the Intel SSD DC S3500
Series drive in 800GB, 600GB, and 480GB capacities are nearly identical, per internal Intel testing.
6.2 Intel SSD DC S3500 Series in RAID 5 Performance Characterization Data
This section prov ides performance characterization data for the Intel S SD DC S3500
Series in RAID 5 configurations .
To establish baseline expectations for IOPS, the Intel SSD DC S3500 Series 800 GB
drives were evaluated in RAID 5 sets of 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 and 8 drives. Th e da ta c ollected
was based on a different mix of read and wr ite ra ndom and sequential workloads. Since
higher queue depths can sometimes yield higher IOP S, queue depths of 1, 2, 4, and 8
per drive were used in the test setup. Multiple transfer sizes were tested, however, only
selected data is presented here. All tes ts were done using the entire Logical Block
Address (LBA) range of the virtual drive. Tests were repeated at least twice to validate
results.
Drives were prepared using I O Meter to fill the entire user area of the drive with da ta .
Then, the fir s t workload of each type (Sequential or Random) was 100% write
performed for 120 minutes. Each subsequent workload was run for 12 minutes, with
average IOPS collected over th e final 10 minutes of the run.
The following figures sh ow different levels of performance for a selection of
configurations.
Note: The scale of the IO PS c ha r ts is variable in order to c le arly show the change as d rives are added.
White Paper December 2013
14 329903-001US
Page 15

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Figure 6. RAID 5 Random 100% Write @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
NOTES: There are gains in write performance as drives are added to the RAID 5 set. The change at q ue ue
depth 1 from three drives to six drives is appr oximately 58% increase in IOPS. For eight drives,
the change is 97% increase in IOPS over the three drive set.
At a queue depth of 1, latency increases as more drives are added to the RAID set, most likely
caused by the additional overhead of ca lc ulating parity and striping across more drives. This
increases as the queue deepens.
Figure 7. RAID 5 Random 70% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 15
Page 16

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Figure 8. RAID 5 Random 90% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
Figure 9. RAID 5 Random 100% Read @ 4KB Transfer Size with
Average Latency
Intel internal testing, October 2013
Notes:
Figures 7, 8, 9 - As the workloads become more read intensive, there is a steady increase in
performance both as drives are added and as the queue deepens.
Figures 7, 8, 9 – As read percentage increas e s , the e xponential increase in latenc y is not as
prominent with deep e r queues. This is due to the speed at which reads are performed.
6.3 RAID 5 Consistency
Consistency behind a RAID controller is very importa nt because the performance of any
RAID set is limited by the lowest performing drive. As the num ber of dif ferent drives in a
RAID set increases, so does the likelihood of any given drive performing poorly .
Therefore, if the model of drive used is inconsistent in its performance, the inconsistency
increases with the size of the RAID set.
The Intel
®
SSD DC S3500 Series drive h a s s hown excellent consistency when used as a
single drive. Figure 10 illus tr a te s that the DC S3500 is also very consistent in RAID sets.
The three-drive and eight-drive data shows the maximum latency is grouped very
tightly; indicating that adding more drives would have little impact on consistency.
White Paper December 2013
16 329903-001US
Page 17

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
Figure 10. RAID 5 Maximum Latency for 3-drive and 8-drive
Configurations
Intel internal testing, October 2013
6.4 RAID 5 Performance Conclusions
The RAID 5 write performance data illustrates th e additional processing power required
of the RAID controller to calculate parity and stripe data across multiple drives. There is
diminished performance gain be a ddin g dr iv es when compared to RAID 1. Intel’s data
also shows that in mixed workloads and in pure reads, RAID 5 perf orm s well, reaching
over 300K IOPS in 100% read at a queue of 8 per drive on eight drives. As the
workloads become more rea d heavy, latency drops from a high of 2.2 ms (100% wr ite)
to a low of 140 µs (100% read). The h ighest throughput achieved was 2400 MB/s with
eight drives, 100% read, 128KB transfer size, and queu e depth of 8. This leaves room
for possible improvement by adding more driv es to th e R AID set.
In configurations where RAID 5 would traditionally be used, SSDs would provide
significant performance gain over HDDs. Additionally, RAID 5 with SSDs c ould be used in
situations wher e RAID 5 with HDDs would not perform well.
The consistenc y of the drives is well demonstrated in these tests and shows that
®
Intel
SSD DC S3500 Series drives consistently off e r higher perf orm a nce with excellent
stability, even behind a RAID controller.
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 17
Page 18

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
7.0 Summary
The Intel® SSD DC S3500 Series drive has proven itself in many applications where
speed and reliability are essential. The data in this paper shows that this drive is very
robust behind a RAID controller.
In RAID 1 configurations, write performance is as expected for this setup; that is, a two
drive set matches the single drive specification, and increases linearly as drives are
added to the set. With eight drives a t qu eue depth 1 per drive, this configuration
processes over 50K write IOPS with 4KB blocks. The RAID controller adds very little
latency, but latency does incr ea s e a s th e queue depth grows and, as more drives are
added to the array. Read performance in c r ea s es with additional drives and with queue
depth, reaching over 200K read IOPS with eight drives, a queue of 8 per drive and 4KB
blocks. More importantly, the performance on mixed wor kloads was excellent and
increased as more drives were added. Th e 70% r ea d workload topped out at close to
110K IOPS with 4KB blocks, and the 90% went to n ea rly 150K IOPS with 4KB blocks
(both at queue of 8 per drive). The highest throughpu t s een in this test was 2300 MB/s
during 100% read using eight drives with transfer size of 128KB and a queue of 8 per
drive. This means the bandwidth limit of the PCIe lanes was not reached (4000 MB/s for
x8 PCIe 2.0). It is theoretically possible that more than eight drives could be used a nd
an increase in performance obtained.
In RAID 5 configurations, write operations increase both as drives are added and as th e
queue depth increases. T he increase in write performance with queue depth is somewhat
surprising and is most likely attributed to the RAID controller and the scaling effect of
the cache in each drive. This may be due to the way the controller write s the stripes to
the drive set, possibly consolidating the 4KB blocks into the 256KB stripes. Read
performance is a ls o very good, with eight drives reaching 300K IO P S with 4KB blocks
and queue depth 8 per drive. Mixed workloads show very good performance with 70%
read hitting 75K IOPS at queue of 8 per drive and 90% read coming in at almost 140K,
both with 4KB blocks. Latency on all workloads is very manageable, alth ough, as the
queue depth increases, so does the latency. The graphs show that as queues grow,
latency increases at an increasingly higher rate.
To summarize:
• In both RAID 1 and RAID 5, the Intel SSD DC S3500 Series dr ive shows
excellent scalability , performance, and consistency.
• Very little latency was introduced by the RAI D c ontroller in RAID 1. In RAID 5,
the overhead and latency are slightly higher.
• In random, mixed read/write workloads, S SDs perform significantly (as much as
100 times) better than H D D s in a similar situation.
• With this RAID controller, there is the possibility of greater performance by
adding more than eight drives in both RAID 1 and RAID 5 configura tions.
White Paper December 2013
18 329903-001US
Page 19

Intel SSD DC S3500 Workload Characterization in RAID Configurations
8.0 Appendix
8.1 RAID Levels
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks), developed in 1988 to improve
performance, r eliability and scalability of hard disk storage systems has become a
standard in datacenters beca use of these qualities. There ar e m a ny types, or levels, of
RAID.
RAID 0 uses bloc k level striping to span one or more drives. T his does improve
performance, and increases capacity when more than one dr iv e is used. However, there
is no fault toleran c e , so failure of an y one drive will cause full data loss.
RAID 1, also ca lled m ir r or ing, writes data identically to two drives, produ c ing a mirrored
set. Reads can be serviced by either drive, and writes occur in un ison on both drives. If
one drive has a hardware failure, the data is protected in the mirrored copy. RAID 1
requires two drives. Man y modern RAID controllers support RAID 1 sets of m or e than
two drives, however, the original specification was for only two. Because of the 50%
overhead, RAID 1 is the m os t ex pensive RAID type.
RAID 2 uses bit-level strip ing with dedicated Hamming-code parity. This is a theoretical
model and not used in practice.
RAID3 uses byte-level strip ing with dedicated parity. This level is not commonly used.
RAID 4 uses block-level striping with dedica ted parity. All parity da ta is on a single drive.
I/O requests are han dled in pa r a llel, increasing performance.
RAID 5 uses block-level striping with distributed parity. Data and parity are distributed
among all drives and requires a ll but one drive to be present. RAID 5 requires at least
three drives and can survive a single drive failure.
RAID 6 uses block-level striping with double dis tributed parity. Ide ntical to RAID 5 in the
way it writes data, however, parity is written twice in different locations. RAID 6 can
survive 2 drive failures ; therefore it is often used for larger sets of drives.
RAID levels can also be nes ted for improved performance or fault tolerance. RAID 10,
0+1, 50 and 60 are common combin a tions .
December 2013 White Paper
329903-001US 19
 Loading...
Loading...