Page 1
POD-6552
5.25” Intel® Celeron® M SBC,
with CPU/ VGA/LCD, and Ethernet Interface
User’s Manual
Page 2

Copyright
This document is copyrighted, © 2005. All rights are reserved. The original manufacturer reserves the right to make improvements to the products
described in this manual at any time without notice.
No part of this manual may be reproduced, copied, translated or transmitted in any form or by any means without the prior written permission of
the original manufacturer. Information provided in this manual is
intended to be accurate and reliable. However, the original manufacturer
assumes no responsibility for its use, nor for any infringements upon the
rights of third parties that may result from such use.
Acknowledgements
Award is a trademark of Award Software International, Inc.
IBM, PC/AT, PS/2 and VGA are trademarks of International Business
Machines Corporation.
Intel and Celeron are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Microsoft Windows® is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corp.
RTL is a trademark of Realtek Semi-Conductor Co., Ltd.
ESS is a trademark of ESS Technology, Inc.
UMC is a trademark of United Microelectronics Corporation.
SMI is a trademark of Silicon Motion, Inc.
All other product names or trademarks are properties of their respective
owners.
For more information on this and other Advantech products, please visit
our websites at: http://www.advantech.com
http://www.advantech.com/eplatform
For technical support and service, please visit our support website at:
http://www.advantech.com.tw/support
This manual is for the POD-6552.
Part No.200K655210
1st Edition, June 2005
POD-6552 User’s Manual ii
Page 3

Packing List
Before you begin installing your card, please make sure that the following
materials have been shipped:
• 1 POD-6552 all-in one single board computer
• Mini Jumper(yellow) p/n: 1653300100
• Mini Jumper(black) p/n: 1653302122
Optional
• 1 startup manual
• 1 CD-ROM or disks for utility, drivers, and manual (in PDF format)
• 1 Wiring kit for POD-6552 p/n: POD-10586-K100
If any of these items are missing or damaged, contact your distributor or
sales representative immediately.
iii
Page 4

Model No. List Description
POD-6552L-M0A1 C-M 600 MHzM(0L2) SBC LAN/VGA/
LCD/TV/AT Eco
POD-6552F-M0A1 Same as POD-6552L-M0A1,w/cable/DSTN/
AT X
POD-6552L-00A1 Same as POD-6552L-M0A1,but with
SKT479
Additional Information and Assistance
Visit the Advantech web site at www.advantech.com where you can find
the latest information about the product.
Step 1. Contact your distributor, sales representative, or Advantech's cus-
tomer service center for technical support if you need additional
assistance. Please have the following information ready before
you call:
• Product name and serial number
• Description of your peripheral attachments
• Description of your software (operating system, version, application
software, etc.)
• A complete description of the problem
• The exact wording of any error messages
POD-6552 User’s Manual iv
Page 5

FCC
This device complies with the requirements in
part 15 of the FCC rules: Operation is subject to
the following two conditions:
1.This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference
received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation
This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment
is operated in a commercial environment. This
equipment generates, uses, and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instruction manual,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this device in a residential
area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct
the interference at his/her own expense. The
user is advised that any equipment changes or
modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance would void the
compliance to FCC regulations and therefore,
the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Caution!
Achtung!
There is a danger of a new battery exploding if it
is incorrectly installed. Do not attempt to
recharge, force open, or heat the battery.
Replace the battery only with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
Discard used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
v
Page 6

POD-6552 User’s Manual vi
Page 7

Contents
Chapter 1 General Information ........................................2
1.1 Introduction ....................................................................... 2
1.2 Features ............................................................................. 2
1.3 Specifications .................................................................... 3
1.3.1 Standard SBC Functions ................................................. 3
1.3.2 Display Interface............................................................. 3
1.3.3 Solid State disk ............................................................... 4
1.3.4 TV-Out............................................................................ 4
1.3.5 Ethernet interface ............................................................ 4
1.3.6 Mechanical and Environmental ...................................... 4
1.4 Board layout: dimensions.................................................. 5
Chapter 2 Installation ........................................................8
2.1 Jumpers.............................................................................. 8
2.2 Connectors......................................................................... 9
2.3 Locating Connectors(component side)........................... 10
2.4 Locating Connectors(solder side).................................... 11
2.5 Setting Jumpers ............................................................... 12
2.6 Clear CMOS (J8)............................................................. 13
2.7 COM2 232/422/485 Select(J1/J2/J3/J4)...........................14
2.8 Setting LCD Voltage(J5)..................................................14
2.9 SM BUS Connector(J6)....................................................15
2.10 PCI VIO(J7).....................................................................15
2.11 Installing DDR SODIMMs..............................................15
2.12 Printer port connector (CN28)......................................... 16
2.13 CompactFlash Card Socket(CN22)................................. 16
2.13.1 CompactFlash(CN22) ................................................... 16
2.14 Floppy drive connector (CN27) ...................................... 16
2.14.1 Connecting the floppy drive ......................................... 17
2.15 IDE connector(CN25, CN24).......................................... 17
2.15.1 Connecting the hard drive............................................. 17
2.16 VGA/LVDS interface connections.................................. 18
2.16.1 CRT display connector (CN1, CN7)............................ 18
2.16.2 LVDS LCD panel connector(CN14) ............................ 18
2.16.3 LCD Backlight connector(CN15)................................. 18
2.16.4 TTL LCD/DSTN connector(CN17).............................. 19
2.17 USB connectors (CN4,CN11,CN12) .............................. 19
2.18 Ethernet configuration..................................................... 19
2.18.1 LAN connector (CN6) .................................................. 19
2.18.2 Network boot ................................................................ 19
vii
Page 8

2.19 COM port connector (CN2,CN9).................................... 19
2.20 PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector (CN5)......................... 20
2.20.1 PS/2 connector(CN13).................................................. 20
2.21 Front Panel Connector (CN26) ....................................... 20
2.21.1 Reset (Pin 13 & Pin14) ................................................ 20
2.21.2 HDD LED (Pin 1 & Pin2)............................................. 20
2.21.3 Power LED (Pin 3 & Pin 4) .......................................... 20
2.21.4 Suspend LED (Pin 5 & Pin 6)....................................... 20
2.21.5 Power Button (Pin 11 & Pin12).................................... 20
2.21.6 Lan Active LED(Pin 7 & Pin 8) ................................... 21
2.21.7 Lan Linked LED(Pin 9 & Pin10).................................. 21
2.22 Audio interface................................................................ 21
2.22.1 Audio connector(CN8) ................................................. 21
2.22.2 CD-In connector(CN16) ............................................... 21
2.23 Printer port connector (CN28)......................................... 21
2.24 TV-out interface(CN3).................................................... 21
2.25 IR Connector(CN10)(Optional) ...................................... 22
2.26 Power connectors (CN20, CN21,CN23) ......................... 22
2.26.1 EBX power connector, +5 V, +/-12 V (CN20)............. 22
2.26.2 Power supply connector, -5V, -12V (CN21) ................ 22
2.26.3 ATX power connector (CN23) .................................... 22
Chapter 3 Software Configuration .................................24
3.1 Introduction ..................................................................... 24
3.2 VGA display firmware configuration ............................. 24
Figure 3.1:VGA setup screen........................................ 25
3.3 Connectors to Standard LCDs......................................... 25
3.3.1 AU M170EG01(1280 x1024 LVDS LCD).................. 26
Table 3.1:Connections to LCD/Flat Pannel (CN14)..... 26
Chapter 4 Award BIOS Setup.........................................28
4.1 System test and initialization........................................... 28
4.1.1 System configuration verification................................. 28
4.2 Award BIOS setup .......................................................... 29
4.2.1 Entering setup .............................................................. 29
Figure 4.1:BIOS setup program initial screen .............. 29
4.2.2 Standard CMOS Features setup .................................... 30
Figure 4.2:Standard CMOS Features setup .................. 30
4.2.3 Advanced BIOS Features setup .................................... 31
Figure 4.3:Advanced BIOS Features setup................... 31
4.2.4 Advanced Chipset Features setup ................................. 32
Figure 4.4:Advanced Chipset Features setup ............... 32
4.2.5 Integrated Peripherals ................................................... 33
Figure 4.5:Integrated Peripherals.................................. 33
4.2.6 Power Management Setup ............................................ 34
POD-6552 User’s Manual viii
Page 9

Figure 4.6:Power Management Setup........................... 34
4.2.7 PnP/PCI Configurations................................................ 35
Figure 4.7:PnP/PCI Configurations .............................. 35
4.2.8 Frequency/Voltage Control........................................... 36
Figure 4.8:Frequency/Voltage Control ......................... 36
4.2.9 Load Optimized Defaults .............................................. 37
Figure 4.9:Load BIOS defaults screen.......................... 37
4.2.10 Set Password ................................................................. 38
Figure 4.10:Set password.............................................. 39
4.2.11 Save & Exit Setup..........................................................40
Figure 4.11:Save & Exit Setup ..................................... 40
4.2.12 Exit Without Saving.......................................................41
Figure 4.12:Exit without saving.................................... 41
Chapter 5 PCI SVGA Setup ............................................44
5.1 Introduction ..................................................................... 44
5.1.1 Chipset .......................................................................... 44
5.1.2 Display memory............................................................ 44
5.1.3 Display types................................................................. 44
5.2 Installation of the SVGA Driver ..................................... 45
5.2.1 Installation for Windows 2000/XP ............................... 45
5.3 Further Information......................................................... 48
Chapter 6 Audio Setup.....................................................50
6.1 Introduction ..................................................................... 50
6.2 Driver installation............................................................ 50
6.2.1 Before you begin.......................................................... 50
6.2.2 Windows XP driver ..................................................... 50
Appendix A Pin Assignments ............................................54
A.1 ATX power connector (CN23)....................................... 54
Table A.1:ATX power connector(CN23) ..................... 54
A.2 Floppy connector (CN27)................................................ 55
Table A.2:Floppy Connector (CN27) ........................... 55
A.3 Primary IDE Connector (CN25) ..................................... 56
Table A.3:Primary IDE connector (CN25)................... 56
A.4 Secondary IDE Connector (CN24) ................................. 57
Table A.4:Secondary IDE connector (CN24)............... 57
A.5 CompactFlash socket(CN22) .......................................... 58
Table A.5:CompactFlash socket (CN22) ...................... 58
A.6 LAN,RJ45 connector(CN6).............................................59
Table A.6:LAN,RJ45 connector(CN6) ......................... 59
A.7 USB port 0, 1(CN4).........................................................59
Table A.7:USB 0, 1 connector(CN4)............................ 59
A.8 USB port 2, 3(CN12).......................................................59
Table A.8:USB 2, 3 connector(CN12).......................... 59
ix
Page 10

A.9 USB port 4, 5(CN11).......................................................60
Table A.9:USB 4, 5 connector(CN11).......................... 60
A.10 LVDS connector(CN14)..................................................61
Table A.10:LVDS connector (CN14) ........................... 61
A.11 Print port connector(CN28).............................................62
Table A.11:Print port connector(CN28) ....................... 62
A.12 COM port 1, 2 Connector (CN2).....................................62
Table A.12:COM port 1, 2 Connector(CN2)................ 62
A.13 COM port 3, 4 Connector (CN9)......................................63
Table A.13:COM port 3,4 Connector(CN9)................. 63
A.14 Audio connector(CN8).....................................................64
Table A.14:Audio connector(CN8) .............................. 64
A.15 D-SUB VGA connector(CN1)..........................................64
Table A.15:D-SUB VGA connector(CN1)................... 64
A.16 VGA connector(CN7)......................................................65
Table A.16:VGA connector(CN7)................................ 65
A.17 IrDA connector(CN10)....................................................65
Table A.17:IrDA connector(CN10).............................. 65
A.18 LCD Backlight connector(CN15)....................................65
Table A.18:LCD Backlight connector(CN15).............. 65
A.19 PS/2 connector(CN13).....................................................66
Table A.19:PS/2 connector(CN13) ............................... 66
A.20 CD-In connector(CN16)...................................................66
Table A.20:CD-In connector(CN16) ............................ 66
A.21 PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector(CN5)...........................66
Table A.21:PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector(CN5) .... 66
A.22 TTL LCD or DSTN connector(CN17)............................ 67
Table A.22:TTL LCD or DSTN connector (CN17) ..... 67
A.23 ISA slot(CN19) ............................................................... 68
Table A.23:ISA slot Connector (CN19) ....................... 68
A.24 EBX Power connector(CN20)..........................................69
Table A.24:EBX connector(CN20) .............................. 69
A.25 -5V and -12V connector(CN21).......................................69
Table A.25:-5V and -12V connector(CN21) ................ 69
A.26 Front Panel connector(CN26)...........................................70
Table A.26:Front Panel connector(CN26).................... 70
Appendix B System Assignments ......................................72
B.1 System I/O Ports.............................................................. 72
Table B.1:System I/O ports .......................................... 72
B.2 1st MB memory map....................................................... 73
Table B.2:1st MB memory map ................................... 73
B.3 DMA channel assignments.............................................. 73
Table B.3:DMA channel assignments .......................... 73
POD-6552 User’s Manual x
Page 11

B.4 Interrupt assignments ...................................................... 74
Table B.4:Interrupt assignments ................................... 74
Appendix C Programming the Watchdog Timer .............76
C.1 Supported Input Timing Modes ...................................... 76
xi
Page 12

POD-6552 User’s Manual xii
Page 13
1
CHAPTER
General Information
This chapter gives background
information on the POD-6552.
Sections include:
• Introduction
• Features
• Specifications
• Board layout and dimensions
1 Chapter 1 General Information
Page 14
Chapter 1 General Information
1.1 Introduction
The POD-6552 is a new Intel® Celeron® M 600 MHz(0L2) 5.25" Biscuit PC with enhanced graphics function. The POD-6552 comes with an
embedded high-performance Celeron® M 600 MHz processor on-board,
and one socket479 optional for Celeron-M CPU. For maximum performance, the POD-6552 supports one 200pin DDR SODIMM socket that
can accept up to 512 MB memory. On-board features include an Ethernet
interface, audio interface, socket for Compact Flash Card, Enhanced IDE
interface , Floppy interface, one parallel port, four serial ports (three RS232 ports and one RS-232/422/485 port), six USB 2.0 ports, IrDA interface and a PS/2 keyboard/mouse interface. The best specification of the
POD-6552 is its dual display(CRT+LVDS, CRT+TTL, LVDS+TV-Out,
CRT+TV-Out). The POD-6552 supports CRT up to 1600 x 1200, and also
supports 1 channel 18bit LVDS(2 channel 36bit optional) up to UXGA.
If you need any additional functions, the POD-6552 has a PC/104 connector, a 8-bit ISA slot and three PCI slots for future upgrades.
1.2 Features
• Onboard Intel® Celeron® M 600 MHz(0L2) CPU, Socket 479 for
Intel® Celeron® M and Pentium® M CPU(Optional)
• Fanless operation at 0~60°C (POD-6552F-M0A1,POD-6552L-
M0A1)
• 2 x PCI Slots onboard
• 4 x COM ports
• 1 x DDR SODIMM Socket, support up to 512MB
• 6 x 2.0 USB ports onboard
• Supports Compact Flash Card Type I/II
• Supports Independent Dual Display(CRT+LVDS, CRT+TTL,
LVDS+TV-Out, CRT+TV-Out)
POD-6552 User’s Manual 2
Page 15

1.3 Specifications
1.3.1 Standard SBC Functions
• CPU: Intel® Celeron® M 600 MHz w/o L2 cache. Socket479(Optional
for Celeron® M and Pentium® M CPU)
• System chipsets: Intel® 852GM/ICH4
• BIOS: Award 4Mbit Flash memory
• System memory:One DDR SODIMM socket, support up to 512MB
DRAM
• 2nd cache memory: N/A
• Enhanced IDE Interface: Supports four Enhanced IDE channels with
PIO/DMA-33 mode
• Serial Ports: Three RS232 ports, One RS232/422/485
Connection: 1*RS232 and 1*RS232/422/485 are realized by a dual
port D-sub, 2*RS232 are realized by two box headers
• Parallel Ports: One parallel port, support EPP/ECP mode
• Keyboard/Mouse Connector:Support standard PC/AT Keyboard and a
PS/2 mouse
• Power Management: APM 1.2 power management compliant, support
ACPI 1.0b,2.0
• FDD interface: Support 360K/1.2M/720K/1.44MB/2.88MB Two FDD
devices
• Watchdog Timer: 255 levels timer intervals
• Expansion Interface: 32-bit PCI Slot, 1*8 bit ISA slot, 1 * PC/104
• Battery: Lithium 3V/195 mAH
• USB: 6 USB ports, USB 2.0 compliant
• Audio:AC'97 version 2.0 compliant
• IrDA(Optional):115Kbps SIR, IrDA 1.0 compliant
1.3.2 Display Interface
• Chipset: Intel® 852GM chip integrated
• Memory size: Shared up to 64MB
• Interface: 4X AGP VGA/LCD interface,Support for 9,12,15,18bit TTL
TFT (Optional for 16 or 24bit DSTN panel)
• Display modes:
CRT Modes: 1024 x 768 @ 16bpp (85Hz);
LCD Modes: 1280 x 1024 @ 16bpp(60Hz)
1024 x 768 @ 16bpp (60Hz)
• LVD S: Support one channel 18bit LVDS interface (Optional for 2 channel 2 x 18bit LVDS)
• Dual Independent Display: CRT + LVDS, CRT + TV-Out, LVDS +
TV-Out
3 Chapter 1 General Information
Page 16

1.3.3 Solid State disk
• Supports CompactFlash Type I/II disks
1.3.4 TV-Out
• Chipset: Chrontel CH7009
• Supports TV output
• Supports NTSC and PAL formats
• Supports s-video
• TV output supports graphics resolutions up to 1024x768 pixels
1.3.5 Ethernet interface
• Chipset: RealTek 8100BL
• Connection: on-board RJ-45
• Interface: IEEE 802.3u(100BASE-T) protocol compatible
•
BootROM:
build-in-system
• I/O address switchless setting
1.3.6 Mechanical and Environmental
• Dimensions (L x W): 203 x 146 mm(8” x 5.75”)
• Power supply voltage: +5 V±5%, +12V ±5%
• Power requirements:
Max:(Win2000, Kpower)
2.8A @+5V (w/Celeron M 600 MHzMHz, 128MB DDR333)
0.25A @+12V (w/Celeron M 600 MHzMHz, 128MB DDR333)
Typical:(Win2000, Kpower)
1.9 A @ +5V(w/Celeron M 600 MHzMHz, 128MB DDR333)
0.10 A @ +12V(w/Celeron M 600 MHzMHz, 128MB DDR333)
• Operating temperature: 0 ~ 60°C (32 ~ 140°F),operation
• Operating humidity: 0% ~ 90% Relative Humidity, Non condensing
POD-6552 User’s Manual 4
Page 17
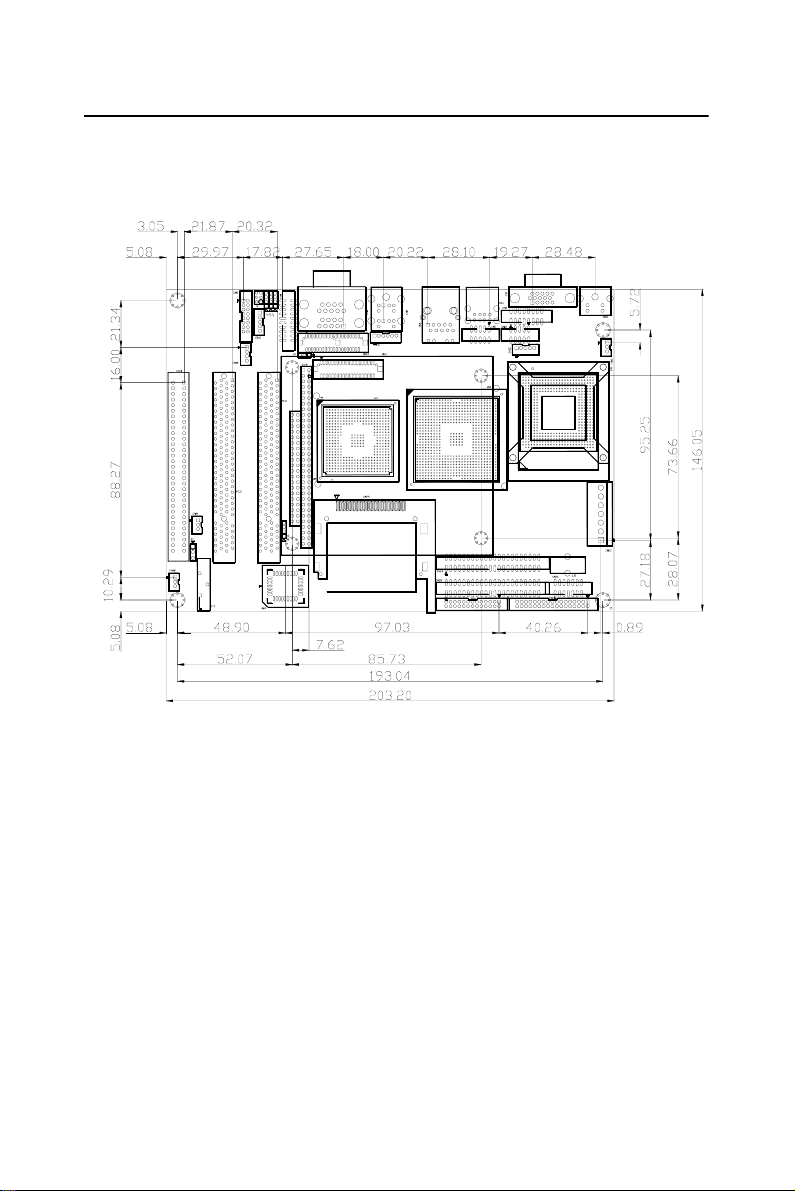
1.4 Board layout: dimensions
Figure 1.1: Board layout: dimensions (component side)
5 Chapter 1 General Information
Page 18
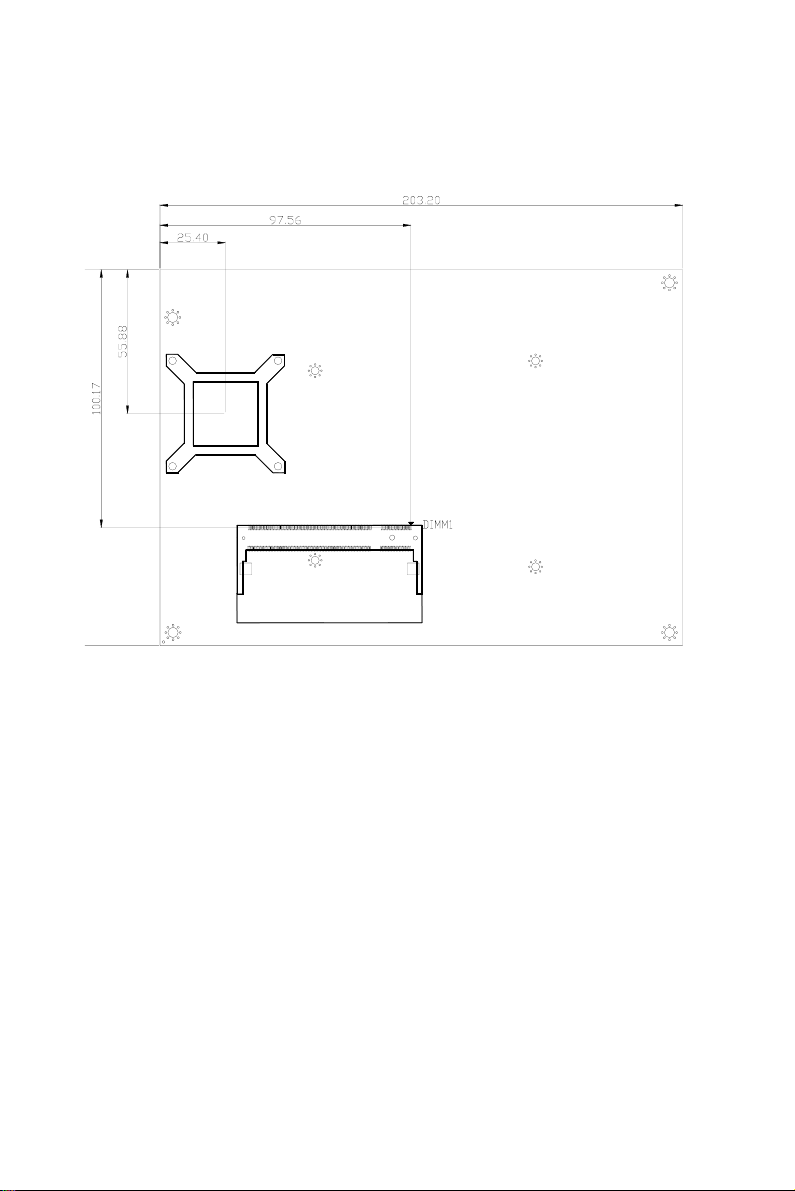
Figure 1.2: Board layout: dimensions (solder side)
POD-6552 User’s Manual 6
Page 19
2
CHAPTER
Installation
This chapter explains the setup procedures
of POD-6552 hardware, including instructions on setting jumpers and connecting
peripherals, switches and indicators. Be
sure to read all safety precautions before
you begin the installation procedure.
7 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 20

Chapter 2 Installation
2.1 Jumpers
The POD-6552 has a number of jumpers that allow you to configure your
system to suit your application. The table below lists the functions of the
various jumpers.
Table 2.1: Jumpers
Label Function
J1/J2/J3/J4 Setting COM2 RS232/422/485
J5 LCD voltage setting
J6 SM BUS connector
J7 PCI VIO setting
J8 CMOS setting
POD-6552 User’s Manual 8
Page 21

2.2 Connectors
On-board connectors link the POD-6552 to external devices such as hard
disk drives, a keyboard, or floppy drives. The table below lists the function of each of the board’s connectors.
Table 2.2: Connectors
Label Function
CN1
CN2 COM port 1,2
CN3 TV-Out connector
CN4 USB port 0,1
CN5 PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector
CN6 LAN connector
CN7 VGA connector
CN8 Audio connector
CN9 COM port 3,4
CN10 IrDA connector
CN11 USB port 4,5
CN12 USB port 2,3
CN13 PS/2 connector
CN14 LVDS connector
CN15 LCD Backlight connector
CN16 CD-IN connector
CN17 TTL LCD connector or DSTN connector
CN18 PC/104 connector
CN19 ISA slot
CN20 EBX Power connector
CN21 -5V & -12V connector
CN22 CompactFlash socket
CN23 ATX connector
CN24 Secondary IDE connector
CN25 Primary IDE connector
VGA D-SUB
9 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 22
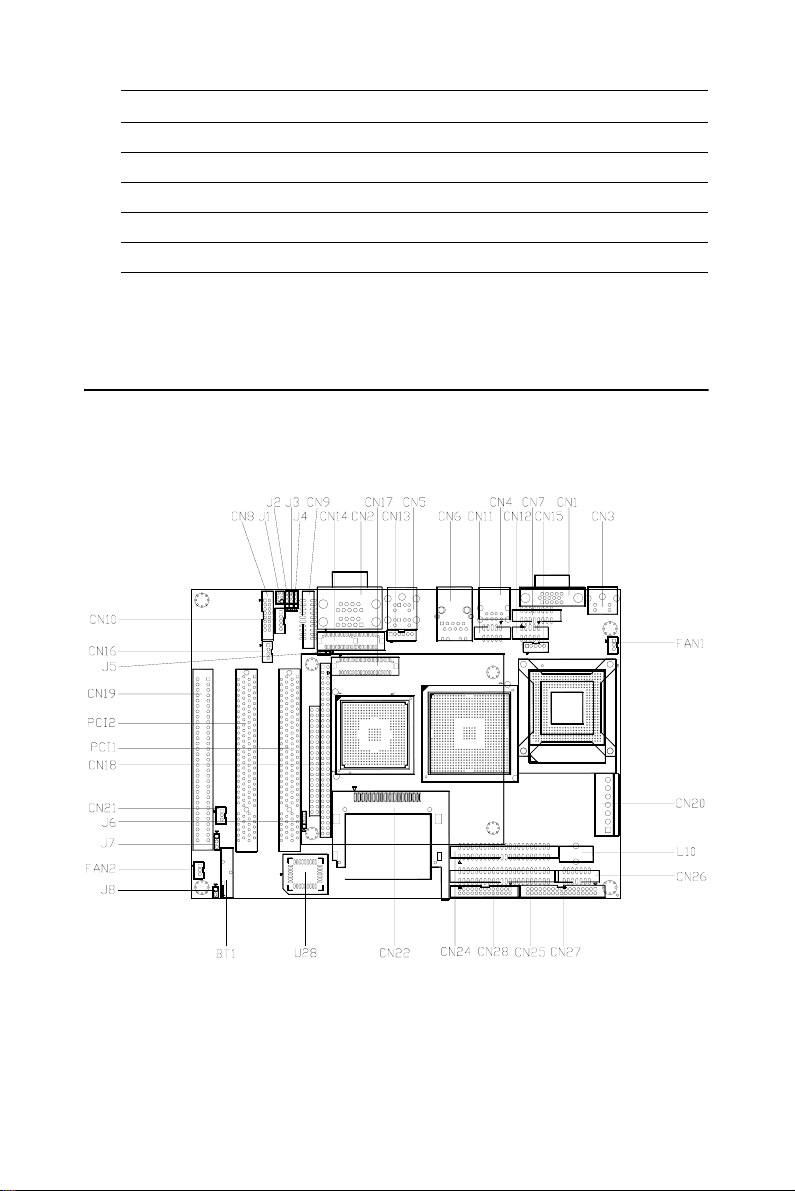
Table 2.2: Connectors
CN26 Front Panel connector
CN27 Floppy connector
CN28 Print connector
FAN 1,2 FAN connector
PCI 1,2 PCI slot
2.3 Locating Connectors(component side)
Figure 2.1: Jumper&Connector Locations
POD-6552 User’s Manual 10
Page 23
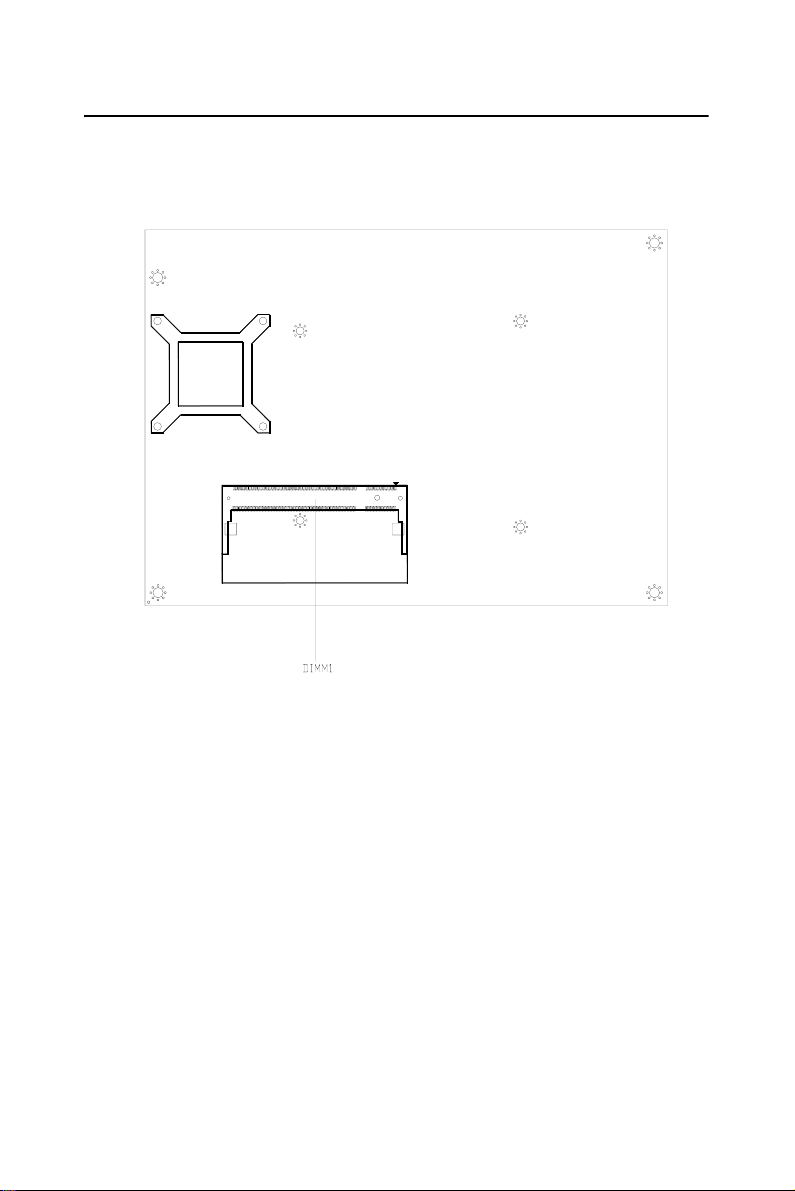
2.4 Locating Connectors(solder side)
Figure 2.2: Connectors (solder side)
11 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 24
2.5 Setting Jumpers
You may configure your card to match the needs of your application by
setting jumpers. A jumper is a metal bridge used to close an electric circuit. It consists of two metal pins and a small metal clip (often protected
by a plastic cover) that slides over the pins to connect them. To “close” a
jumper, you connect the pins with the clip. To “open” a jumper, you
remove the clip. Sometimes a jumper will have three pins, labeled 1, 2
and 3. In this case you would connect either pins 1 and 2, or 2 and 3.
open closed closed 2-3
The jumper settings are schematically depicted in this manual as follows:.
open closed closed 2-3
A pair of needle-nose pliers may be helpful when working with jumpers.
If you have any doubts about the best hardware configuration for your
application, contact your local distributor or sales representative before
you make any changes.
Generally, you simply need a standard cable to make most connections.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 12
Page 25
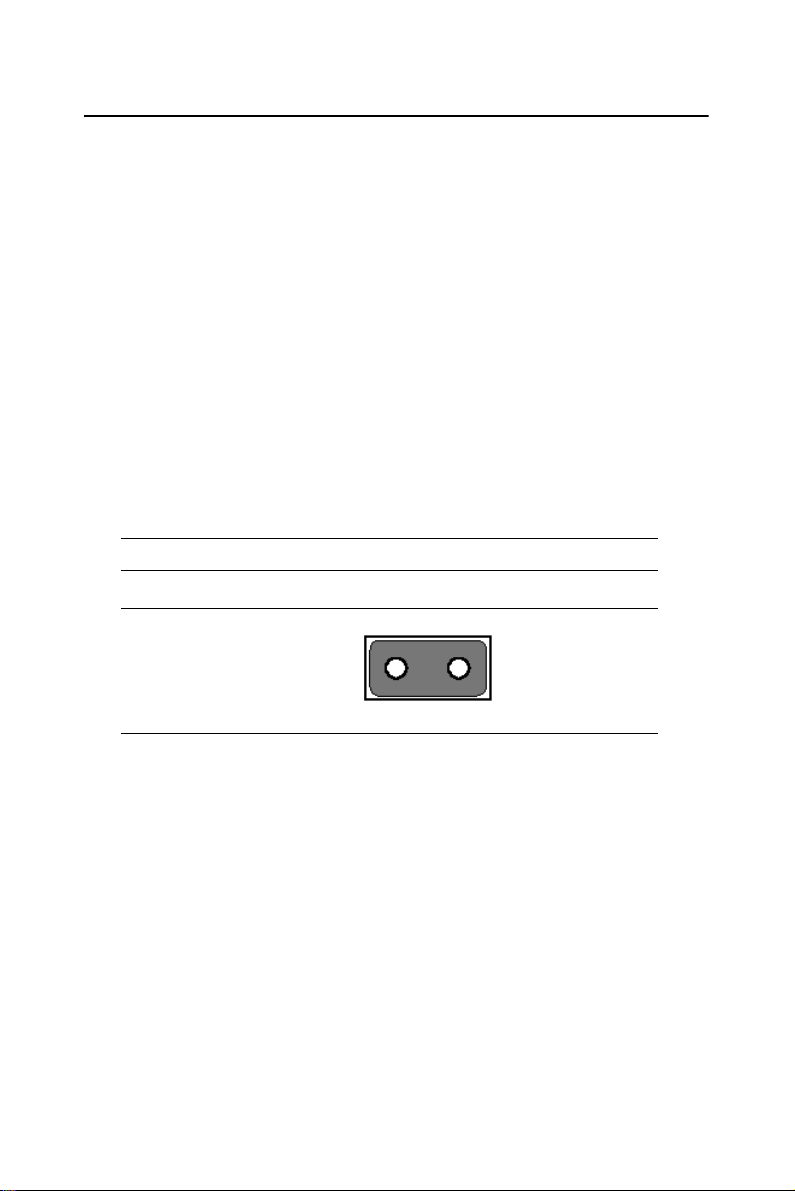
2.6 Clear CMOS (J8)
Warning! To avoid damaging the computer, always turn
off the power supply before setting “Clear
CMOS.” Before turning on the power supply,
set the jumper back to “3.0 V Battery On.”
This jumper is used to erase CMOS data and reset system BIOS information.
The procedure for clearing CMOS is:
1. Turn off the system.
2. Short pin 1 and pin 2.
3. Turn on the system. The BIOS is now reset to its default setting
Table 2.3: CMOS clear (J8)
clear CMOS
13 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 26
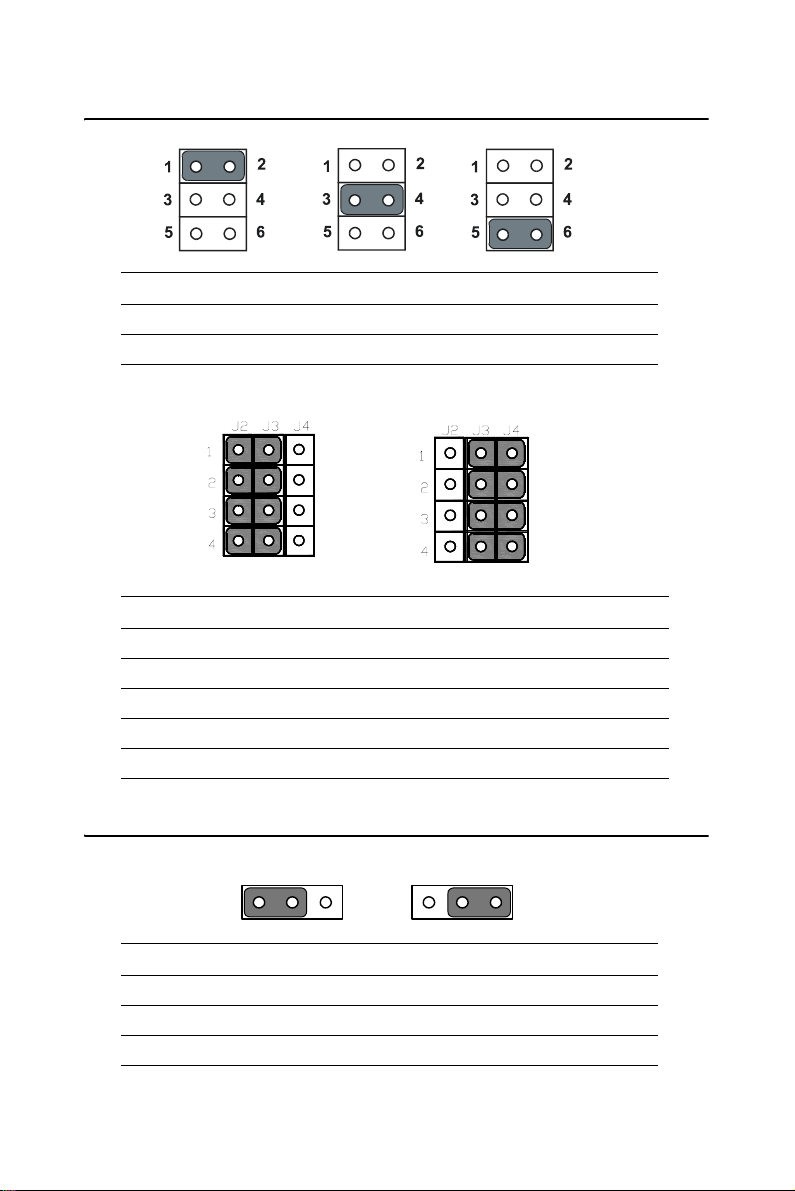
2.7 COM2 232/422/485 Select(J1/J2/J3/J4)
Table 2.4: COM2 232/422/485 Select(J1)
RS232 RS422 RS485
1-2(Default) 3-4 5-6
Table 2.5: COM2 232/422/485 Select(J2/J3/J4)
RS232 RS422/RS485
J2(1)-J3(1) J3(1)-J4(1)
J2(2)-J3(2) J3(2)-J4(2)
J2(3)-J3(3) J3(3)-J4(3)
J2(4)-J3(4) J3(4)-J4(4)
2.8 Setting LCD Voltage(J5)
123 1 23
Table 2.6: Setting LCD Voltage(J5)
Pin Function
1-2 +5V
2-3 +3.3V(Default)
POD-6552 User’s Manual 14
Page 27

2.9 SM BUS Connector(J6)
12 43
Table 2.7: SM BUS Connector(J6)
Pin Function
1+5V
2- SM_CLOCK
3SM_DATA
4GND
2.10 PCI VIO(J7)
123
1 23
Table 2.8: PCI VIO(J7)
Pin Function
1-2 +5V
2-3 +3.3V
2.11 Installing DDR SODIMMs
Notes The modules can only fit into a socket one way.
The gold pins must point down into the DDR
SODIMM socket.
The procedure for installing DDR SODIMMs appears below. Please
follow these steps carefully.
1. Make sure that all power supplies to the system are switched off
2. Install the DDR SODIMM card. Install the DDR SODIMM so that its
gold pins
point down into the DDR SODIMM socket.
15 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 28

3. Slip the DDR SODIMM into the socket at a 45 degree angle and care-
fully fit the bottom of the card against the connectors.
4. Gently push the DDR SODIMM into a perpendicular position until the
clips on the ends of the DDR SODIMM sockets snap into place.
5. Check to ensure that the DDR SODIMM is correctly seated and all
con-
nector contacts touch. The DDR SODIMM should not move around in its
socket.
2.12 Printer port connector (CN28)
Normally, the parallel port is used to connect the card to a printer. The
POD-6552 includes a multi-mode (ECP/EPP/SPP) parallel port accessed
via CN28 and a 26-pin flat-cable connector. You will need an adapter
cable if you use a traditional DB-25 connector. The adapter cable has a
26-pin connector on one end, and a DB-25 connector on the other.
The parallel port is designated as LPT1, and can be disabled or changed to
LPT2 or LPT3 in the system BIOS setup.
The parallel port interrupt channel is designated to be IRQ7.
You can select ECP/EPP DMA channel via BIOS setup.
2.13 CompactFlash Card Socket(CN22)
The POD-6552 provides a 50-pin socket for CompactFlash card type I/II
which is defaulted as a master device.
2.13.1 CompactFlash(CN22)
The CompactFlash card occupies a secondary IDE channel which can be
enabled/disabled via the BIOS settings.
2.14 Floppy drive connector (CN27)
You can attach up to two floppy drives to the POD-6552’s on-board controller. You can use any combination of 5.25” (360 KB and 1.2 MB) and/
or 3.5” (720 KB, 1.44 MB, and 2.88 MB) drives.
A 34-pin daisy-chain drive connector cable is required for a dual-drive
system. On one end of the cable is a 34-pin flat-cable connector. On the
other end are two sets of floppy disk drive connectors. Each set consists
POD-6552 User’s Manual 16
Page 29

of a 34-pin flat-cable connector (usually used for 3.5” drives) and a
printed-circuit board connector (usually used for 5.25” drives).
2.14.1 Connecting the floppy drive
1. Plug the 34-pin flat-cable connector into CN27. Make sure that the
red wire corresponds to pin one on the connector.
2. Attach the appropriate connector on the other end of the cable to
the floppy drive(s). You can use only one connector in the set. The
set on the end (after the twist in the cable) connects to the A: drive.
The set in the middle connects to the B: drive.
3. If you are connecting a 5.25” floppy drive, line up the slot in the
printed circuit board with the blocked-off part of the cable connec-
tor.
If you are connecting a 3.5” floppy drive, you may have trouble determining which pin is number one. Look for a number printed on the circuit
board indicating pin number one. In addition, the connector on the floppy
drive may have a slot. When the slot is up, pin number one should be on
the right. Check the documentation that came with the drive for more
information.
If you desire, connect the B: drive to the connectors in the middle of the
cable as described above.
In case you need to make your own cable, you can find the pin assignments for the board’s connector in Appendix A.
2.15 IDE connector(CN25, CN24)
The POD-6552 provides two IDE channels to which you can attach up to
four Enhanced Integrated Device Electronics hard disk drives or
CDROM to the POD-6552’s internal controller. The POD-6552's IDE
controller uses a PCI interface. This advanced IDE controller supports
faster data transfer, PIO Mode 3 or Mode 4, UDMA 33 mode.
2.15.1 Connecting the hard drive
Connecting drives is done in a daisy-chain fashion. It requires one of two
cables (not included in this package), depending on the drive size. 1.8"
and 2.5" drives need a 1 x 44-pin to 2 x 44-pin flat-cable connector. 3.5"
drives use a 1 x 44-pin to 2 x 40-pin connector.
Wire number 1 on the cable is red or blue, and the other wires are gray.
17 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 30

1. Connect one end of the cable to CN25,CN24. Make sure that the
red (or blue) wire corresponds to pin 1 on the connector, which is
labeled on the board (on the right side).
2. Plug the other end of the cable into the Enhanced IDE hard drive,
with pin 1 on the cable corresponding to pin 1 on the hard drive.
(See your hard drive’s documentation for the location of the con-
nector.)
If desired, connect a second drive as described above.
Unlike floppy drives, IDE hard drives can connect to either end of the
cable. If you install two drives, you will need to set one as the master and
one as the slave by using jumpers on the drives. If you install only one
drive, set it as the master.
2.16 VGA/LVDS interface connections
The POD-6552’s display interface can drive conventional CRT displays
and is capable of driving a wide range of LVDS flat panel displays as
well. The board has two display connectors: one for standard CRT VGA
monitors, and one for LVDS flat panel displays.
2.16.1 CRT display connector (CN1, CN7)
CN1 is a standard 16-pin DESUB connector used for conventional CRT
displays. Users can drive a standard progressive scan analog monitor with
pixel resolution up to 1600 MHz x 1200 at 85 Hz.
The POD-6552 also provides a box header CN7 which connects CRT display via a cable. Pin assignments for CRT display connector are detailed
in Appendix A.
2.16.2 LVDS LCD panel connector(CN14)
POD-6552 uses the Intel 852GM to supports single or dual-channel
LVDS panels up to UXGA panel resolution with frequency range from
25MHz to 112MHz.
The display mode can be one channel 18-bit LVDS LCD panel displays
Users can connector to 18-bit LVDS LCD with CN14. In addtion, CN14
can support 2 channels (2 x 18-bit) LVDS LCD panel (optional).
2.16.3 LCD Backlight connector(CN15)
CN15 provides +5V and +12V for LCD backlight.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 18
Page 31

2.16.4 TTL LCD/DSTN connector(CN17)
CN17 is a 40-pin connector for TTL LCD or DSTN. It could connect
TTL LCD or DSTN freely to meet your need.
2.17 USB connectors (CN4,CN11,CN12)
The POD-6552 board provides up to six USB (Universal Serial Bus)
ports. This gives complete Plug and Play, and hot attach/detach for up to
127 external devices. The USB interfaces comply with USB specification
Rev. 2.0, and are fuse protected.
The USB interface is accessed through the 5 x 2-pin flat-cable connector,
CN4(USB0, 1),CN12(USB2, 3),CN11(USB4,5). You will need an
adapter cable if you use a standard USB connector. The adapter cable has
a 5 x 2-pin connector on one end and a USB connector on the other.
The USB interfaces can be disabled in the system BIOS setup.
2.18 Ethernet configuration
The POD-6552 is equipped with a high performance 32-bit PCI-bus Ethernet interface which is fully compliant with IEEE 802.3U 10/100Mbps
CSMA/CD standards. It is supported by all major network operating systems.
The POD-6552 supports 10/100Base-T Ethernet connections with
onboard RJ-45 connectors(CN6).
2.18.1 LAN connector (CN6)
10/100 or 1000 Base-T connects to the POD-6552 via a cable to a standard RJ-45 connector.
2.18.2 Network boot
The Network Boot feature can be utilized by incorporating the Boot
ROM image files for the appropriate network operating system. The Boot
ROM BIOS files are included in the system BIOS, which is on the utility
CD disc.
2.19 COM port connector (CN2,CN9)
The POD-6552 provides four serial ports (COM1,COM3,COM4: RS-232
and COM2: RS232/RS422/RS485). CN2 supports COM1 and COM2;
CN9 supports COM3, COM4. and J1/J2/J3/J4 is for COM2 RS232/
RS422/RS485 selection. It provides connections for serial devices (a
19 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 32

mouse, etc.) or a communication network. You can find the pin assignments for the COM port connector in Appendix A.
2.20 PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector (CN5)
The POD-6552 board provides a keyboard connector that supports both a
keyboard and a PS/2 style mouse. In most cases, especially in embedded
applications, a keyboard is not used. If the keyboard is not present, the
standard PC/AT BIOS will report an error or fail during power-on selftest (POST) after a reset. The POD-6552’s BIOS standard setup menu
allows you to select "All, But Keyboard"under the "Halt On"selection.
This allows no-keyboard operation in embedded system applications,
without the system halting under POST.
2.20.1 PS/2 connector(CN13)
CN13 is a 6pin connector for PS/2.
2.21 Front Panel Connector (CN26)
Next is to install external switches to monitor and control the POD-6552.
These features are optional: install them only if necessary. CN26 is an
2x7 pin header, 180 degree, male.It provides connections for reset and
power & hard disk indicator.
2.21.1 Reset (Pin 13 & Pin14)
If a reset switch is installed, it should be an open single pole switch.
Momentarily pressing the switch will activate a reset. The switch should
be rated for 10 mA, 5 V.
2.21.2 HDD LED (Pin 1 & Pin2)
The HDD LED indicator for hard disk access is an active low signal (24
mA sink rate).
The HDD LED indicator would light when HDD works.
2.21.3 Power LED (Pin 3 & Pin 4)
The Power LED indicator would light when the power is on.
2.21.4 Suspend LED (Pin 5 & Pin 6)
The Suspend LED indicator would light when the computer is suspend.
2.21.5 Power Button (Pin 11 & Pin12)
The POD-6552 provides an ATX power input connector. When connected
with PIN 9 & PIN 10, it enables power On/Off from the chassis.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 20
Page 33

2.21.6 Lan Active LED(Pin 7 & Pin 8)
The LED would light when the Lan is active.
2.21.7 Lan Linked LED(Pin 9 & Pin10)
The LED would light when the Lan is linked.
2.22 Audio interface
2.22.1 Audio connector(CN8)
The Audio link is a 2x8 pin connector, the POD-6552can support
speaker-out, Line-IN, Line-out with Realtek ALC202, AC97 stereo
sound. Detailed pin assignment refer to Appendix A.
2.22.2 CD-In connector(CN16)
The POD-6552 can support CD-In via CN16.
2.23 Printer port connector (CN28)
Normally, the parallel port is used to connect the card to a printer. The
POD-6552 includes a multi-mode (ECP/EPP/SPP) parallel port accessed
via CN5 and a 26-pin flat-cable connector. You will need an adapter cable
if you use a traditional DB-25 connector. The adapter cable has a 26-pin
connector on one end, and a DB-25 connector on the other.
The parallel port is designated as LPT1, and can be disabled or changed to
LPT2 or LPT3 in the system BIOS setup.
The parallel port interrupt channel is designated to be IRQ7.
You can select ECP/EPP DMA channel via BIOS setup.
2.24 TV-out interface(CN3)
The POD-6552 board provides optional TV-out via CN3. This module
output supports S-video connectors. TV-out generators use both NTSC
and PAL formats with 640 x 480 or 800 x 600 MHz resolution.
To set up your video interface:
Run the appropriate installation program located on the utility disk.
That’s all there is to it.
21 Chapter 2 Installation
Page 34

2.25 IR Connector(CN10)(Optional)
This connector supports the optional wireless infrared transmitting and
receiving module. This module mounts on the system case. You must
configure th setting through BIOS setup. Detailed pin definition you will
find in Appendix A.
Important Make sure that J1 DO NOT equipped with any
jumper when you use IR connector. J2, J3 and
J4 would help to set COM2 RS232/422/485.
2.26 Power connectors (CN20, CN21,CN23)
2.26.1 EBX power connector, +5 V, +/-12 V (CN20)
Supplies main power to the POD-6552 (+5 V), and to devices that require
+12 V. The POD-6552 supports AT power via CN20.
2.26.2 Power supply connector, -5V, -12V (CN21)
Supplies secondary power to devices that require -5 V and -12 V.
2.26.3 ATX power connector (CN23)
The POD-6552 supports ATX power via CN23 and CN20. CN23 supplies
main power (5VSB), and it is a 3 x 1 power connector, w/Fixed Lock
4200-WS-A1.
Important Make sure that the ATX power supply can take
at least a 10 mA load on the 5 V standby lead
(5VSB). If not, you may have difficulty powering on your system.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 22
Page 35

3
CHAPTER
Software Configuration
This chapter details the software configuration information. It shows you
how to configure the card to match
your application requirements. Award
System BIOS will be covered in
Chapter 4.
Sections include:
• Introduction
• VGA display software configuration
Page 36

Chapter 3 Software Configuration
3.1 Introduction
The system BIOS and custom drivers are located in a
512 KB, 32-pin (JEDEC spec.) Flash ROM device, designated U28. A
single Flash chip holds the system BIOS, VGA BIOS, and network Boot
ROM image. The display can be configured via software. This method
minimizes the number of chips and eases configuration. You can change
the display BIOS simply by reprogramming the Flash chip.
3.2 VGA display firmware configuration
The board’s on-board VGA interface supports a wide range of popular
LCD, EL, gas plasma flat panel displays and traditional analog CRT monitors. The 852GM chip with optimized Shared Memory Architecture,
supports up to 64 MB frame buffer using system memory to provide
LVDS mode up to 1280 x 1024 @ 48bpp, the interface can drive CRT displays with resolutions up to 1600 MHz x 1200 @ 24bpp.
The VGA interface is configured completely via the software utility, so
you do not have to set any jumpers. Configure the VGA display as follows:
1. Apply power to the board with a color TFT display attached. This
is the default setting for this board. Ensure that the AWD-
FLASH.EXE and *.BIN files are located in the working drive.
NOTE: Ensure that you do not run AWDFLASH.EXE
while your system is operating in EMM386
mode.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 24
Page 37

2. At the prompt, type AWDFLASH.EXE and press <Enter>. The
VGA configuration program will then display the following:
Figure 3.1: VGA setup screen
3. At the prompt, enter the new BIN file which supports your display.
When you are sure that you have entered the file name correctly
press <Enter>.
4. The screen will ask “Do you want to save BIOS?”. If you change
your mind or have made a mistake, press N to abort and end the
setup procedure. Press Y if you wish to save the existing configura-
tion before changing it. Then type the name under which you want
to save the current configuration.
5. The prompt will then ask “Are you sure to program?”. Press Y if
you want the new file to be written into the BIOS. Press N to exit
the program.
The new VGA configuration will then write to the ROM BIOS chip. This
configuration will remain the same until you run the AWDFLASH.EXE
program and change the settings.
3.3 Connectors to Standard LCDs
The following table illustrate typical LCD connection pinouts for the
POD-6552.
25 Chapter 3
Page 38

3.3.1 AU M170EG01(1280 x1024 LVDS LCD)
Table 3.1: Connections to LCD/Flat Pannel (CN14)
LCD Connector Flat Pannel Connector
JAE FI-X30C2L DF13-40P
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 RxOIN0- 7 OD02 RxOIN0+ 9 OD0+
3 RxOIN1- 13 OD14 RxOIN1+ 15 OD1+
5 RxOIN2- 19 OD26 RxOIN2+ 21 OD2+
7VSS 23GND
8 RxOCLKIN- 25 OCK9 RxOCLKIN+ 27 OCK+
10 RxOIN3- 35 OD311 RxOIN3+ 37 OD3+
12 RxEIN0- 8 ED013 RxEIN0+ 10 ED0+
14 VSS 4 WP#
15 RxEIN1- 14 ED116 RxEIN1+ 16 ED1+
17 VSS 12 GND
18 RxEIN2- 20 ED219 RxEIN2+ 22 ED2+
20 RxECLKIN- 26 ECK21 RxECLKIN+ 28 ECK+
22 RxEIN3- 36 ED323 RxEIN3+ 38 ED3+
24 VSS 34 GND
25 VSS 30 GND
26 NC X
27 VSS 34 GND
28 +5V 1 VCC_LCD
29 +5V 2 VCC_LCD
POD-6552 User’s Manual 26
Page 39

Chapter 4 Ducks that Need Love!
4
Award BIOS Setup
This chapter describes how to set BIOS
configuration data.
CHAPTER
27
Page 40

Chapter 4 Award BIOS Setup
4.1 System test and initialization
These routines test and initialize board hardware. If the routines encounter an error during the tests, you will either hear a few short beeps or see
an error message on the screen. There are two kinds of errors: fatal and
non-fatal. The system can usually continue the boot up sequence with
non-fatal errors. Non-fatal error messages usually appear on the screen
along with the following instructions:
press <F1> to CONTINUE
Write down the message and press the F1 key to continue the bootup
sequence.
4.1.1 System configuration verification
These routines check the current system configuration against the values
stored in the board’s CMOS memory. If they do not match, the program
outputs an error message. You will then need to run the BIOS setup program to set the configuration information in memory.
There are three situations in which you will need to change the CMOS
settings:
1. You are starting your system for the first time
2. You have changed the hardware attached to your system
3. The CMOS memory has lost power and the configuration informa-
tion has been erased.
The POD-6552 Series' CMOS memory has an integral lithium battery
backup. The battery backup should at least three years in normal service,
but when it finally runs down, you will need to replace the complete unit.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 28
Page 41

4.2 Award BIOS setup
Award’s BIOS ROM has a built-in Setup program that allows users to
modify the basic system configuration. This type of information is stored
in battery-backed CMOS RAM so that it retains the Setup information
when the power is turned off.
4.2.1 Entering setup
Power on the computer and press <Del> immediately. This will allow you
to enter Setup.
Figure 4.1: BIOS setup program initial screen
29
Page 42

4.2.2 Standard CMOS Features setup
When you choose the Standard CMOS Features option from the Initial
Setup Screen menu, the screen shown below is displayed. This standard
Setup Menu allows users to configure system components such as date,
time, hard disk drive, floppy drive and display. Once a field is highlighted, on-line help information is displayed in the right top of the Menu
screen.
Figure 4.2: Standard CMOS Features setup
POD-6552 User’s Manual 30
Page 43
4.2.3 Advanced BIOS Features setup
By choosing the Advanced BIOS Features Setup option from the Initial
Setup Screen menu, the screen below is displayed. This sample screen
contains the manufacturer’s default values for the POD-6552 Series.
Figure 4.3: Advanced BIOS Features setup
31
Page 44

4.2.4 Advanced Chipset Features setup
By choosing the Advanced Chipset Features option from the Initial Setup
Screen menu, the screen below is displayed. This sample screen contains
the manufacturer’s default values for the POD-6552 Series.
Figure 4.4: Advanced Chipset Features setup
POD-6552 User’s Manual 32
Page 45

4.2.5 Integrated Peripherals
Choosing the Integrated Peripherals option from the Initial Setup Screen
menu should produce the screen below. Here we see the manufacturer’s
default values for the POD-6552 Series.
Figure 4.5: Integrated Peripherals
33
Page 46

4.2.6 Power Management Setup
By choosing the Power Management Setup option from the Initial Setup
Screen menu, the screen below is displayed. This sample screen contains
the manufacturer’s default values for the POD-6552 Series.
Figure 4.6: Power Management Setup
POD-6552 User’s Manual 34
Page 47

4.2.7 PnP/PCI Configurations
By choosing the PnP/PCI Configurations option from the Initial Setup
Screen menu, the screen below is displayed. This sample screen contains
the manufacturer’s default values for the POD-6552 Series.
Figure 4.7: PnP/PCI Configurations
35
Page 48

4.2.8 Frequency/Voltage Control
By choosing the Frequency/Voltage Control option from the Initial Setup
Screen menu, the screen below is displayed. This sample screen contains
the manufacturer’s default values for the POD-6552
Figure 4.8: Frequency/Voltage Control
Caution Incorrect settings in Frequency/Voltage Control
may damage the system CPU, video adapter,
or other hardware.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 36
Page 49

4.2.9 Load Optimized Defaults
Load Optimized Defaults loads the default system values directly from
ROM. If the stored record created by the Setup program should ever
become corrupted (and therefore unusable), these defaults will load automatically when you turn the POD-6552 Series system on.
Figure 4.9: Load BIOS defaults screen
37
Page 50

4.2.10 Set Password
Note To enable this feature, you should first go to the
Advanced BIOS Features menu, choose the
Security Option, and select either Setup or
System, depending on which aspect you want
password protected. Setup requires a password only to enter Setup. System requires the
password either to enter Setup or to boot the
system.
A password may be at most 8 characters long.
To Establish Password
1. Choose the Set Password option from the CMOS Setup Utility
main menu and press <Enter>.
2. When you see “Enter Password,” enter the desired password and
press <Enter>.
3. At the “Confirm Password” prompt, retype the desired password,
then press <Enter>.
4. Select Save to CMOS and EXIT, type <Y>, then <Enter>.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 38
Page 51

Figure 4.10: Set password
To Change Password
1. Choose the Set Password option from the CMOS Setup Utility
main menu and press <Enter>.
2. When you see “Enter Password,” enter the existing password and
press <Enter>.
3. You will see “Confirm Password.” Type it again, and press
<Enter>.
4. Select Set Password again, and at the “Enter Password” prompt,
enter the new password and press <Enter>.
5. At the “Confirm Password” prompt, retype the new password, and
press <Enter>.
6. Select Save to CMOS and EXIT, type <Y>, then <Enter>.
39
Page 52

To Disable Password
1. Choose the Set Password option from the CMOS Setup Utility
main menu and press <Enter>.
2. When you see “Enter Password,” enter the existing password and
press <Enter>.
3. You will see “Confirm Password.” Type it again, and press
<Enter>.
4. Select Set Password again, and at the “Enter Password” prompt,
don’t enter anything; just press <Enter>.
5. At the “Confirm Password” prompt, again don’t type in anything;
just press <Enter>.
6. Select Save to CMOS and EXIT, type <Y>, then <Enter>.
4.2.11 Save & Exit Setup
Figure 4.11: Save & Exit Setup
POD-6552 User’s Manual 40
Page 53

If you select this option and press <Y> then <Enter>, the values entered
in the setup utilities will be recorded in the chipset’s CMOS memory. The
microprocessor will check this every time you turn your system on and
use the settings to configure the system. This record is required for the
system to operate.
4.2.12 Exit Without Saving
Figure 4.12: Exit without saving
Selecting this option and pressing <Enter> lets you exit the Setup program without recording any new values or changing old ones.
41
Page 54

POD-6552 User’s Manual 42
Page 55

PCI SVGA Setup
Introduction
Installation of SVGA drivers
-for Windows XP
Further information
CHAPTER
5
Page 56

Chapter 5 PCI SVGA Setup
5.1 Introduction
The board has an onboard interface. The specifications and features are
described as follows:
5.1.1 Chipset
The POD-6552 uses a Intel 852GM + ICH4 chipset for its graphic controller. It supports LVDS LCD displays, conventional CRT monitors.
5.1.2 Display memory
The 852GM chip with optimized Shared Memory Architecture, supports
up to 64 MB frame buffer using system memory to provide LVDS mode
up to 1280 x 1024 @ 36bpp with frequency range from 25-MHz to 112MHz. the interface can drive CRT displays with resolutions up to 1600
MHz x 1200 @ 24 bpp 75 Hz.
5.1.3 Display types
CRT and panel displays can be used simultaneously. The board can be set
in one of three configurations: on a CRT, on a flat panel display, or on
both simultaneously. The system is initially set to simultaneous display
mode. If you want to enable the CRT display only or the flat panel display
only, please contact Intel Corporation LTD., or our sales representative
for detailed information.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 44
Page 57

5.2 Installation of the SVGA Driver
Complete the following steps to install the SVGA driver. Follow the procedures in the flow chart that apply to the operating system that you are
using within your board.
Notes: 1. The windows illustrations in this chapter are
intended as examples only. Please follow the
listed steps, and pay attention to the instructions which appear on your screen.
2. For convenience, the CD-ROM drive is designated as "D" throughout this chapter.
5.2.1 Installation for Windows 2000/XP
To install SVGA driver for Window 2000/XP, please run the setup wizard
1
"Intel Extreme Graphic 2" in CD-ROM. Example of installation is shown
as bellow:
1. Select the path: G:\POD-6552\2_VGA, then double click
"win2k_xp169" to run "Install Shield Wizard".
45 Chapter 5
Page 58

2. Press the "Next" button.
3. Press the "Next" button.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 46
Page 59

4. In order to continue setup, you must accept the agreement, press
the "Yes" button and wait a minute.
5. Choose the option "Yes, I want to restart my computer now." and
press the "Finish" button.
47 Chapter 5
Page 60

5.3 Further Information
For further information about the AGP/VGA installation in your POD6552, including driver updates, troubleshooting guides and FAQ lists,
visit the following web resources:
Intel website: www.intel.com.
Advantech websites: www.advantech.com
www.advantech.com.tw
POD-6552 User’s Manual 48
Page 61

Audio Setup
• Introduction
• Installation of audio driver for Windows XP
CHAPTER
6
49 Chapter 6
Page 62

Chapter 6 Audio Setup
6.1 Introduction
The POD-6552 supports AC97 stereo sound without Amplifier and supports speaker-out, CD-input, Line-in, Line-out and Microphone..
6.2 Driver installation
6.2.1 Before you begin
Please read the instructions in this chapter carefully before you attempt
installation. The audio drivers for the POD-6552 board are located on the
audio driver CD. Run the supplied SETUP program to install the drivers;
don't copy the files manually.
Note: The files on the software installation diskette are compressed. Do
not attempt to install the drivers by copying the files manually. You must
use the supplied SETUP program to install the drivers.
6.2.2 Windows XP driver
To install audio driver for Window XP, please run the setup wizard in CDROM. Example of installation is shown as bellow:
1. Select the path: G:\POD-6552\wdm_a357, then double click to run
"Install Shield Wizard".
POD-6552 User’s Manual 50
Page 63

2. Press the "Next" button and wait for a moment.
3. Choose the option "Continue Anyway”.
51 Chapter 6
Page 64

4. Choose the option "Yes, I want to restart my computer now", then click
"Finish" button to reboot your computer.
POD-6552 User’s Manual 52
Page 65

A
Appendix
Pin Assignments
This appendix contains information of a
detailed or specialized nature. It includes:
• Floppy Drive Connector
• Primary IDE Connector
• LPT Connector
• Secondary IDE(Slave) Connector
• ATX Power Connector
• COM3/COM4 output
• USB0, 1 Connector
• USB2, 3Connector
• USB4, 5Connector
• D-SUB VGA Connector
• LAN, RJ45 Connector
• COM1 Connector
• COM2 Connector
• TTL LCD/DSTN Connector
• LVDS Connector
• Audio I/F Connector
• IR Connector
• PS/2 Mouse/KB Connector
• PC/104 Connector
• ISA Slot
• CompactFlash card Connector
• CD-IN Connector
53 Appx. A
Page 66

Appendix A Pin Assignments
A.1 ATX power connector (CN23)
1 23
Table A.1: ATX power connector(CN23)
Pin Signal
1 5VSB
2NC
3PS_ON
POD-6552 User’s Manual 54
Page 67

A.2 Floppy connector (CN27)
Table A.2: Floppy Connector (CN27)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1GND 2RWC#
3GND 4NC
5GND 6DS
7 GND 8 Index#
9GND 10MOA#
11 GND 12 DSB#
13 GND 14 DSA#
14 GND 16 MOB#
17 GND 18 DIR#
19 GND 20 STEP#
21 GND 22 WD#
23 GND 24 WE#
25 GND 26 Track0#
27 GND 28 WP#
29 GND 30 RDATA#
31 GND 32 HEAD#
33 GND 34 DSKCHG#
*low active
55 Appx. A
Page 68

A.3 Primary IDE Connector (CN25)
Table A.3: Primary IDE connector (CN25)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 IDE RESET 2 GND
3D7 4D8
5D6 6D9
7D5 8D10
9D4 10D11
11 D3 12 D12
13 D2 14 D13
15 D1 16 D14
17 D0 18 D15
19 GND 20 NC
21 REQ 22 GND
23 IOW 24 GND
25 IOR 26 GND
27 READY 28 Cable Select
29 DACK 30 GND
31 IRQ14 32 NC
33 A1 34 ATA check
35 A0 36 A2
37 CS1# 38 CS3#
39 Active 40 GND
1
34
2
3837
4039
POD-6552 User’s Manual 56
Page 69

A.4 Secondary IDE Connector (CN24)
Table A.4: Secondary IDE connector (CN24)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 IDE RESET 2 GND
3D7 4D8
5D6 6D9
7D5 8D10
9D4 10D11
11 D3 12 D12
13 D2 14 D13
15 D1 16 D14
17 D0 18 D15
19 GND 20 NC
21 REQ 22 GND
23 IOW 24 GND
25 IOR 26 GND
27 READY 28 Cable Select
29 DACK 30 GND
31 IRQ14 32 NC
33 A1 34 ATA check
35 A0 36 A2
37 CS1# 38 CS3#
39 Active 40 GND
41 +5V 42 +5V
43 GND 44 NC
1
34
2
4241
4443
57 Appx. A
Page 70

A.5 CompactFlash socket(CN22)
Table A.5: CompactFlash socket (CN22)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 GND 26 #CD1
2D3 27D11
3D4 28D12
4D5 29D13
5D6 30D14
6D7 31D15
7#CE 32#CE2
8 A10 33 #VS14
9#OE 34#IORD
10 A9 35 #IOWR
11 A 8 36 # WE
12 A7 37 #IRQ
13 +5V 38 +5V
14 A6 39 #CSEL
15 A5 40 #VS2
16 A4 41 RESET
17 A3 42 #WAIT
18 A2 43 #INPACK
19 A1 44 #REG
20 A0 45 BVD2
21 D0 46 BVD1
22 D1 47 D8
23 D2 48 D9
24 IOCS16 49 D10
25 #CD2 50 GND
POD-6552 User’s Manual 58
Page 71

A.6 LAN,RJ45 connector(CN6)
Table A.6: LAN,RJ45 connector(CN6)
10/100M
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1TX+ 5NC
2TX- 6RX3RX+ 7NC
4NC 8NC
A.7 USB port 0, 1(CN4)
Table A.7: USB 0, 1 connector(CN4)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1+5V 2+5V
3 USB0- 4 USB15 USB0+ 6 USB1+
7 USB GND 8 USB GND
9 GND 10 NC
A.8 USB port 2, 3(CN12)
64528
10
1
3
9
7
Table A.8: USB 2, 3 connector(CN12)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1+5V 2+5V
3 USB0- 4 USB15 USB0+ 6 USB1+
7 USB GND 8 USB GND
9 GND 10 NC
59 Appx. A
Page 72

A.9 USB port 4, 5(CN11)
64528
10
1
3
9
7
Table A.9: USB 4, 5 connector(CN11)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1+5V 2+5V
3 USB0- 4 USB15 USB0+ 6 USB1+
7 USB GND 8 USB GND
9 GND 10 NC
POD-6552 User’s Manual 60
Page 73

A.10 LVDS connector(CN14)
Table A.10: LVDS connector (CN14)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 VCC_LCD 2 VCC_LCD
3 GND 4 GND
5 LVDS0_N0 6 LVDS0_P0
7 GND 8 LVDS0_N1
9 LVDS0_P1 10 GND
11 LVDS0_N2 12 LVDS0_P2
13 GND 14 LVDS0_CLK0N
15 LVDS0_CLK0P 16 GND
17 LVDS0_N3 18 LVDS1_N2
19 GND 20 GND
21 LVDS0_P3 22 LVDS1_P2
23 GND 24 GND
25 LVDS1_N0 26 LVDS1_CLK0N
27 LVDS1_P0 28 LVDS1_CLK0P
29 GND 30 GND
31 LVDS_CLK 32 LVDS_DATA
33 GND 34 GND
35 LVDS1_N1 36 LVDS1_N3
37 LVDS1_P1 38 LVDS1_P3
39 NC 40 VCON
1
34
2
3837
4039
61 Appx. A
Page 74

A.11 Print port connector(CN28)
14 25
15 26
2
121
13
Table A.11: Print port connector(CN28)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1STB# 2AFD#
3D0 4ERR
5 D1 6 INIT#
7D2 8SLIN
9D3 10GND
11 D 4 12 GND
13 D5 14 GND
15 D6 16 GND
17 D7 18 GND
19 ACK# 20 GND
21 BUSY 22 GND
23 PE 24 GND
25 SLCT 26 NC
A.12 COM port 1, 2 Connector (CN2)
Table A.12: COM port 1, 2 Connector(CN2)
Com1 Com2
Rs232 Rs232 Rs422 Rs485
1 DCD DCD TXD- DATA2 SINA SINA TXD+ DATA+
3SOUTSOUT RXD- NC
4DTR DTR RXD+ NC
5 GND GND GND GND
6DSR DSR NC NC
7RTS RTS NC NC
8CTS CTS NC NC
9RI RI NC
POD-6552 User’s Manual 62
Page 75

A.13 COM port 3, 4 Connector (CN9)
218
420
3
171
19
Table A.13: COM port 3,4 Connector(CN9)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 DCD3 2 DSR3
3SIN3 4RTS3
5 SOUT3 6 CTS3
7DTR3 8RI3
9GND 10GND
11 DCD4 12 DSR4
13 SIN4 14 RTS4
15 SOUT4 16 CTS4
17 DTR4 18 RI4
19 GND 20 GND
63 Appx. A
Page 76

A.14 Audio connector(CN8)
4
123
14 16
13 15
Table A.14: Audio connector(CN8)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Right Speak out+ 2 Right speak out3 Left speak out+ 4 Left speak out5 Right Line out 6 Left line out
7 Ground 8 Ground
9 Right line in 10 Left line in
11 Ground 12 Ground
13 NC 14 NC
15 MIC IN 16 Ground
A.15 D-SUB VGA connector(CN1)
5
15 11
Table A.15: D-SUB VGA connector(CN1)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1R 9+5V
2G 10GND
3B 11NC
4NC 12S-DATA
5 GND 13 HSYNC
6 GND 14 VSYNC
7 GND 15 S-CLK
8GND
1
POD-6552 User’s Manual 64
Page 77

A.16 VGA connector(CN7)
4
123
14 16
13 15
Table A.16: VGA connector(CN7)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1R 2+5V
3G 4GND
5B 6NC
7 NC 8 D2_DATA
9 GND 10 HS
11 G ND 1 2 VS
13 GND 14 D2_ CLOCK
15 GND 16 NC
A.17 IrDA connector(CN10)
12 43 5
Table A.17: IrDA connector(CN10)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1+5V 2NC
3 IRRX 4 GND
5IRTX
A.18 LCD Backlight connector(CN15)
12 43 5
Table A.18: LCD Backlight connector(CN15)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 +12V 2 GND
3 BACKLIGHT ENABLE 4 NC
5+5V
65 Appx. A
Page 78

A.19 PS/2 connector(CN13)
54 2316
Table A.19: PS/2 connector(CN13)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 PS/2 KB CLOCK 2 PS/2 KB DATA
3 PS/2 MOUSE CLOCK 4 GND
5 +5V 6 PS/2 MOUSE DATA
A.20 CD-In connector(CN16)
12 43
Table A.20: CD-In connector(CN16)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 CD in left 2 GND
3 GND 4 CD in right
A.21 PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector(CN5)
Table A.21: PS/2 Mouse/Keyboard connector(CN5)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 K DATA 7 MD ATA
2NC 8NC
3NC 9NC
4+5V 10+5V
5 KCLOCK 11 MCLOCK
6NC 12NC
POD-6552 User’s Manual 66
Page 79

A.22 TTL LCD or DSTN connector(CN17)
Table A.22: TTL LCD or DSTN connector (CN17)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 VCC_LCD 2 VCC_LCD
3GND 4GND
5 VCC_LCD 6 VCC_LCD
7NC 8GND
9PD0 10PD1
11 PD 2 12 PD3
13 PD4 14 PD5
15 PD6 16 PD7
17 PD8 18 PD9
19 PD10 20 PD11
21 PD12 22 PD13
23 PD14 24 PD15
25 PD16 26 PD17
27 PD18 28 PD19
29 PD20 30 PD21
31 PD22 32 PD23
33 GND 34 GND
35 SFCLK 36 FLM
37 M 38 LP
39 GND 40 ENABL
1
34
2
3837
4039
67 Appx. A
Page 80

A.23 ISA slot(CN19)
Table A.23: ISA slot Connector (CN19)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
A1 IOCHECK B1 GND
A2 SD7 B2 RESETDRV
A3 SD6 B3 +5V
A4 SD5 B4 IRQ9
A5 SD4 B5 -5V
A6 SD3 B6 DRQ2
A7 SD2 B7 -12V
A8 SD1 B8 ENDFXR
A9 SD0 B9 +12V
A10 IOCHRDY B10 GND
A11 AEN B11 SMEMW
A12 SA19 B12 SMEMR
A13 SA18 B13 IOW
A14 SA17 B14 IOR
A15 SA16 B15 DACK3
A16 SA15 B16 DRQ3
A17 SA14 B17 DACK1
A18 SA13 B18 DRQ1
A19 SA12 B19 REFRESH
A20 SA11 B20 SYSCLK
A21 SA10 B21 IRQ7
A22 SA9 B22 IRQ6
A23 SA8 B23 IRQ5
A24 SA7 B24 IRQ4
A25 SA6 B25 IRQ3
A26 SA5 B26 DACK2
A27 SA4 B27 TC
A28 SA3 B28 ALE
A29 SA2 B29 +5V
A30 SA1 B30 OSC
A31 SA0 B31 GND
POD-6552 User’s Manual 68
Page 81

A.24 EBX Power connector(CN20)
Table A.24: EBX connector(CN20)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1+5V 2GND
3GND 4+12V
5-12V 6GND
7+5V
A.25 -5V and -12V connector(CN21)
1 23
Table A.25: -5V and -12V connector(CN21)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1-5V 2GND
3-12V
69 Appx. A
Page 82

A.26 Front Panel connector(CN26)
14
12
10
8
6
4
2
13
11
9
7
5
3
1
Table A.26: Front Panel connector(CN26)
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 +5V 2 HDD_LED
3+5V 4GND
5SUSLED 6GND
73.3V 8LAN_ACT
9 3.3V 10 LAN_LINK
11 POWER BUTTON 12 GND
13 GND 14 RESET
POD-6552 User’s Manual 70
Page 83

B
Appendix
System Assignments
This appendix contains information of a
detailed nature. It includes:
• System I/O ports
• 1st MB memory map
• DMA channel assignments
• Interrupt assignments
71 Appx. B
Page 84

Appendix B System Assignments
B.1 System I/O Ports
Table B.1: System I/O ports
Addr. range (Hex) Device
00-0F Master DMA controller
20-21F Master Interrupt controller
2E-2F Configuration Index/Data
40-5F Timer/Counter
60-6F Keyboard controller
(60h) KBC Data
(61h) Misc Funtions & Spkr Ctrl
(64h) KBC Command/Status
70-77 RTC/COMS/NMI-Disable
78-7F -available for system use80 -reserved-(debug port)
81-8F DMA Page Registers
90-91 -available for system use92 System Control
93-9F -available for system useA0-A1H Slave Interrupt Controller
C0-DF Slave DMA Controller
E0-FF -available for system use100-1EF -available for system use170-178 Secondary IDE Control
1F0-1F8 Primary IDE Control
200-20F Game Port
2E8-2EF COM4
2F8-2FF COM2
378-37F Parallel Port(Standard & AFF)
3C0-3CF EGA
3D0-3DF VGA
3E8-3EF COM3
3F0-3F7 Floppy Controller
3F8-3FF COM1
778-77A Parallel Port(ECP Extensions)(Port 378+400)
870-871 Hardware Monitor
POD-6552 User’s Manual 72
Page 85

Table B.1: System I/O ports
Addr. range (Hex) Device
CF8-CFB PCI Configuration Address
CFC-CFF PCI Configuration Data
D00-FFFF -available for system use-
B.2 1st MB memory map
Table B.2: 1st MB memory map
Addr. range (Hex) Device
F0000h - FFFFFh System ROM
*D0000h - EFFFFh Unused (reserved for Ethernet ROM)
C0000h - CFFFFh Expansion ROM (for VGA BIOS)
B8000h - BFFFFh CGA/EGA/VGA text
B0000h - B7FFFh Unused
A0000h - AFFFFh EGA/VGA graphics
00000h - 9FFFFh Base memory
If Ethernet boot ROM is disabled (Ethernet ROM occupies about 16 KB)
*
* E0000 - EFFFF is reserved for BIOS POST
B.3 DMA channel assignments
Table B.3: DMA channel assignments
Channel Function
0 Available
1 Available (audio)
2 Floppy disk (8-bit transfer)
3 Available (parallel port)
4 Cascade for DMA controller 1
5 Available
6 Available
7 Available
* Parallel port ECP mode DMA select 1 or 3
73 Appx. B
Page 86

B.4 Interrupt assignments
Table B.4: Interrupt assignments
Interrupt# Interrupt source
IRQ 0 Interval timer
IRQ 1 Keyboard
IRQ 2 Interrupt from controller 2 (cascade)
IRQ 3 COM2
IRQ 4 COM1
IRQ 5 COM4
IRQ 6 FDD
IRQ 7 LPT1
IRQ 8 RTC
IRQ 9 Reserved (audio)
IRQ 10 COM3
IRQ 11 Reserved for watchdog timer
IRQ 12 PS/2 mouse
IRQ 13 INT from co-processor
IRQ 14 Primary IDE
IRQ 15 Secondary IDE for CFC
POD-6552 User’s Manual 74
Page 87

Appendix
Programming the
Watchdog Timer
The board is equipped with a watchdog
timer that resets the CPU or generates
an interrupt if processing comes to a
standstill for any reason. This feature
ensures system reliability in industrial
standalone or unmanned environments.
C
Page 88

Appendix C Programming the Watchdog
Timer
C.1 Supported Input Timing Modes
In order to program the watchdog timer, you must write a program which
writes I/O port address 866 (hex). The output data is a value of time interval. The value range is from 01 (hex) to FF (hex), and the related time
interval is 1 sec. to 255 sec.
Data Time Interval
00 Disable
01 1 sec.
02 2 sec.
03 3 sec.
04 4 sec.
.
.
.
FF 255 sec.
After data entry, your program must refresh the watchdog timer by
rewriting the I/O port 866 (hex) while simultaneously setting it.
When you want to disable the watchdog timer, your program
should write I/O port 866 (hex) to 00.
Pod-6552 User’s Manual 76
Page 89

The following example shows how you might program the watchdog
timer in ASSEMBLY:
;Watchdog timer example program
MOV DX, 865H ; set the time unit as second
MOV AL, 80H
OUT DX, AL
MOV DX,866H
MOV AL, data ; data=1~255 Second
OUT DX, AL
77 Appendix C
Page 90

Pod-6552 User’s Manual 78
 Loading...
Loading...