Page 1

Intel® NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN
Technical Product Specification
September 2018
Intel® NUC Board NUC7i7DN may contain design defects or errors known as errata that may cause the product to deviate from published
specifications. Current characterized errata, if any, are documented in Intel NUC Board NUC7i7DN Specification Update.
Page 2
Revision History
Revision
Revision History
Date
102
Added clarifying information about supported technologies
June 2018
103
Added clarification to Wireless information in Feature Summary section
September 2018
100 First release of the Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification February 2018
101 Clarifications February 2018
Disclaimer
This product specification applies to only the standard Intel NUC Board with BIOS identifier DNKBLi7v.86A.
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT.
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO
LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR
USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS OTHERWISE AGREED IN WRITING BY INTEL, THE INTEL PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED NOR INTENDED FOR
ANY APPLICATION IN WHICH THE FAILURE OF THE INTEL PRODUCT COULD CREATE A SITUATION WHERE PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH MAY OCCUR.
All Intel NUC Boards are evaluated as Information Technology Equipment (I.T.E.) for use in personal computers (PC) for
installation in homes, offices, schools, computer rooms, and similar locations. The suitability of this product for other PC
or embedded non-PC applications or other environments, such as medical, industrial, alarm systems, test equipment, etc.
may not be supported without further evaluation by Intel.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property
rights that relate to the presented subject matter. The furnishing of documents and other materials and information does
not provide any license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or
other intellectual property rights.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or
“undefined.” Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or
incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each
processor family, not across different processor families: Go to:
Learn About Intel
Intel NUC may contain design defects or errors known as errata, which may cause the product to deviate from published
specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications before placing your product
order.
Intel, the Intel logo, Intel NUC and Intel Core are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
* Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright 2018 Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
®
Processor Numbers
Page 3

Board Identification Information
AA Revision
BIOS Revision
Notes
Device
Stepping
S-Spec Numbers
Intel Core i7
Y0
SR3L8
Product Name
Intel® NUC Board
NUC7i7DNKE
NUC7i7DNBE
Date
Type of Change
Description of Changes or Clarifications
2/2/2018
Clarification
Pin 1 designator on board silkscreen is incorrect for the following headers:
09/07/2018
Clarification
Added text to Wireless row of table in Feature Summary section:
Basic Intel® NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE Identification Information
J83500-00X DNKBLi7v.86A.0040 1,2
Notes:
1. The AA number is found on a small label on the component side of the board.
2. The Intel
®
Core™ i7-8650U processor is used on this AA revision consisting of the following component:
Production Identification Information
Intel® NUC Products NUC7i7DN{x} Identification Information
NUC7i7DNB NUC7i7DNHE
Specification Changes or Clarifications
The table below indicates the Specification Changes or Specification Clarifications that apply to
the Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN.
Specification Changes or Clarifications
USB 2.0, HDMI CEC, Serial Port, SATA Power, and eDP. The pinout information
and pin 1 designators in the TPS are correct for these headers.
“Pre-installed M.2 module”
Errata
Current characterized errata, if any, are documented in a separate Specification Update. See
http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/nuc/overview.html
for the latest documentation.
iii
Page 4
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Chapter
Description
1
A description of the hardware used on Intel® NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE
2
A map of the resources of the Intel® NUC Board
3
The features supported by the BIOS Setup program
4
A description of the BIOS error messages, beep codes, and POST codes
Preface
This Technical Product Specification (TPS) specifies the board layout, components, connectors,
power and environmental requirements, and the BIOS for Intel® NUC Board/Kits NUC7i7DN. Some
features are only available on Kit SKUs.
Intended Audience
The TPS is intended to provide detailed, technical information about Intel® NUC Board/Kit
NUC7i7DN and its components to the vendors, system integrators, and other engineers and
technicians who need this level of information. It is specifically not intended for general
audiences.
What This Document Contains
Typographical Conventions
This section contains information about the conventions used in this specification. Not all of
these symbols and abbreviations appear in all specifications of this type.
Notes, Cautions, and Warnings
NOTE
Notes call attention to important information.
CAUTION
Cautions are included to help you avoid damaging hardware or losing data.
iv
Page 5

Other Common Notation
GB
Gigabyte (1,073,741,824 bytes)
GB/s
Gigabytes per second
Gb/s
Gigabits per second
Kb
Kilobit (1024 bits)
kb/s
1000 bits per second
MB
Megabyte (1,048,576 bytes)
Mb
Megabit (1,048,576 bits)
Mb/s
Megabits per second
TDP
Thermal Design Power
x.x V
Volts. Voltages are DC unless otherwise specified.
x.x A
Amperes.
# Used after a signal name to identify an active-low signal (such as USBP0#)
KB Kilobyte (1024 bytes)
MB/s Megabytes per second
xxh An address or data value ending with a lowercase h indicates a hexadecimal value.
* This symbol is used to indicate third-party brands and names that are the property of their respective
owners.
v
Page 6

Contents
Revision History ............................................................................................................... ii
Disclaimer .................................................................................................................................................................. ii
Board Identification Information ..................................................................................................................... iii
Errata ........................................................................................................................................................................... iii
Intended Audience ................................................................................................................................................ iv
What This Document Contains ........................................................................................................................ iv
Typographical Conventions .............................................................................................................................. iv
Contents ............................................................................................................................ 6
1 Product Description ............................................................................................... 11
1.1 Overview ...................................................................................................................................................... 11
1.1.1 Feature Summary .................................................................................................................. 11
1.1.2 Board Layout (Top) ............................................................................................................... 13
1.1.3 Board Layout (Bottom) ........................................................................................................ 14
1.1.4 Block Diagram ......................................................................................................................... 16
1.2 Online Support .......................................................................................................................................... 17
1.3 Processor ..................................................................................................................................................... 17
1.4 System Memory ........................................................................................................................................ 17
1.5 Processor Graphics Subsystem .......................................................................................................... 20
1.5.1 Integrated Graphics .............................................................................................................. 20
1.6 USB ................................................................................................................................................................. 24
1.7 SATA Interface ........................................................................................................................................... 24
1.7.1 AHCI Mode ................................................................................................................................ 24
1.7.2 NVMe........................................................................................................................................... 25
1.7.3 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology / SATA RAID ......................................................... 25
1.7.4 Intel® Next Generation Storage Acceleration ............................................................. 25
Real-Time Clock Subsystem ........................................................................................................................... 26
1.8 Audio Subsystem Software .................................................................................................................. 26
1.8.1 Audio Subsystem Software ............................................................................................... 26
1.9 LAN Subsystem ......................................................................................................................................... 27
1.9.1 Intel® I219LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller .................................................................. 27
1.9.2 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs .............................................................. 28
1.9.3 Wireless Network Module .................................................................................................. 28
1.10 Hardware Management Subsystem ................................................................................................. 29
1.10.1 Hardware Monitoring ........................................................................................................... 29
1.10.2 Fan Monitoring ........................................................................................................................ 29
1.10.3 Thermal Solution ................................................................................................................... 29
1.11 Power Management ................................................................................................................................ 31
1.11.1 ACPI ............................................................................................................................................. 31
1.11.2 Hardware Support ................................................................................................................. 33
Page 7

Product Description
1.12 Intel® Security and Manageability Technologies ......................................................................... 35
1.12.1 Intel® vPro™ Technology ..................................................................................................... 35
2 Technical Reference ............................................................................................... 39
2.1 Memory Resources .................................................................................................................................. 39
2.1.1 Addressable Memory ........................................................................................................... 39
2.2 Connectors and Headers....................................................................................................................... 39
2.2.1 Front Panel Connectors ...................................................................................................... 40
2.2.2 Back Panel Connectors ....................................................................................................... 40
2.2.3 Connectors and Headers (Top) ........................................................................................ 41
2.2.4 Connectors and Headers (Bottom) ................................................................................. 42
2.3 BIOS Security Jumper ............................................................................................................................ 53
2.4 Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel® MEBX) Reset Header ......................... 55
2.5 Mechanical Considerations .................................................................................................................. 57
2.5.1 Form Factor .............................................................................................................................. 57
2.6 Electrical Considerations ...................................................................................................................... 59
2.6.1 Power Supply Considerations .......................................................................................... 59
2.6.2 Fan Header Current Capability ......................................................................................... 60
2.7 Thermal Considerations ........................................................................................................................ 61
2.8 Reliability ..................................................................................................................................................... 65
2.9 Environmental ........................................................................................................................................... 65
3 Overview of BIOS Features ................................................................................... 67
3.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................................ 67
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization ..................................................................................................... 67
3.3 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS) .............................................................................................. 67
3.4 Legacy USB Support ............................................................................................................................... 68
3.5 BIOS Updates ............................................................................................................................................. 68
3.5.1 Language Support ................................................................................................................. 69
3.5.2 BIOS Recovery ......................................................................................................................... 69
3.6 Boot Options .............................................................................................................................................. 70
3.6.1 Network Boot........................................................................................................................... 70
3.6.2 Booting Without Attached Devices ................................................................................ 70
3.6.3 Changing the Default Boot Device during POST ...................................................... 70
3.6.4 Power Button Menu .............................................................................................................. 70
3.7 Hard Disk Drive Password Security Feature .................................................................................. 72
3.8 BIOS Security Features .......................................................................................................................... 72
4 Error Messages and Blink Codes ......................................................................... 75
4.1 Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes ................................................................................................ 75
4.2 BIOS Error Messages ............................................................................................................................... 75
7
Page 8

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Figures
Figure 1. Major Board Components (Top) ....................................................................................................... 13
Figure 2. Major Board Components (Bottom) ................................................................................................ 14
Figure 3. Block Diagram ........................................................................................................................................... 16
Figure 4. Memory Channel and SO-DIMM Configuration.......................................................................... 19
Figure 5. eDP Connector on Bottom-side of the Board ............................................................................. 22
Figure 6. LAN Connector LED Locations........................................................................................................... 28
Figure 7. Thermal Solution and Fan Header ................................................................................................... 30
Figure 8. Location of the Standby Power LED ............................................................................................... 34
Figure 9. Front Panel Connectors ........................................................................................................................ 40
Figure 10. Back Panel Connectors ...................................................................................................................... 40
Figure 11. Connectors and Headers (Top) ....................................................................................................... 41
Figure 12. Connectors and Headers (Bottom) ............................................................................................... 42
Figure 13. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Header (2.0 mm Pitch) ............................................ 50
Figure 14. Connection Diagram for the Internal Power Supply Connector ....................................... 52
Figure 15. Location of the BIOS Security Jumper ........................................................................................ 53
Figure 16. Intel MEBX Reset Header .................................................................................................................. 56
Figure 17. Board Dimensions ................................................................................................................................ 57
Figure 18. Board Height Dimensions ................................................................................................................. 58
Figure 19. Localized High Temperature Zones ............................................................................................. 62
Figure 20. Installation Area of the Thermal Pad ........................................................................................... 63
8
Page 9

Product Description
Tables
Table 1. Feature Summary ..................................................................................................................................... 11
Table 2. Components Shown in Figure 2 ......................................................................................................... 15
Table 3. Supported Memory Configurations .................................................................................................. 18
Table 4. Unsupported Memory Configurations............................................................................................. 18
Table 5. LAN Connector LED States ................................................................................................................... 28
Table 6. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch ............................................................................................... 31
Table 7. Power States and Targeted System Power ................................................................................... 32
Table 8. Wake-up Devices and Events .............................................................................................................. 33
Table 9. Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 11 .............................................................................. 41
Table 10. Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 12 ........................................................................... 43
Table 11. SATA Power Header (1.25 mm pitch) ............................................................................................ 44
Table 12. Internal USB 2.0 Header (1.25 mm pitch) ..................................................................................... 44
Table 13. Internal USB 3.0 Header (1.25 mm pitch) ..................................................................................... 45
Table 14. Serial Port Header (1.25 mm pitch) ................................................................................................. 45
Table 15. HDMI CEC Header (1.25 mm pitch) ................................................................................................. 46
Table 16. M.2 2280 Module (Mechanical Key M) Connector .................................................................... 46
Table 17. M.2 2230 Module (Mechanical Key E) Connector .................................................................... 47
Table 18. 40-Pin eDP Connector ......................................................................................................................... 49
Table 19. Front Panel Header (2.0 mm Pitch) ................................................................................................ 49
Table 20. States for a One-Color Power LED ................................................................................................. 50
Table 21. States for a Dual-Color Power LED ................................................................................................ 51
Table 22. 12-24 V Internal Power Supply Connector ................................................................................ 51
Table 23. BIOS Security Jumper Settings ........................................................................................................ 54
Table 24. Intel MEBX Reset Header Signals .................................................................................................... 56
Table 25. Power Budget for Assessing the DC-to-DC Circuit’s Power Rating (worst
rd
case: Embedded board in 3
Table 26. Fan Header Current Capability ......................................................................................................... 60
Table 27. Thermal Considerations for Components ................................................................................... 64
Table 28. Tcontrol Values for Components ................................................................................................... 64
Table 29. Environmental Specifications ........................................................................................................... 65
Table 30. Acceptable Drives/Media Types for BIOS Recovery ............................................................... 69
Table 31. Boot Device Menu Options ................................................................................................................ 70
Table 32. Master Key and User Hard Drive Password Functions ........................................................... 72
Table 33. Supervisor and User Password Functions................................................................................... 73
Table 34. Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes ............................................................................................. 75
Table 35. BIOS Error Messages ............................................................................................................................ 75
party chassis) ........................................................................................... 59
9
Page 10

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
10
Page 11
Form Factor
4.0 inches by 4.0 inches (101.60 millimeters by 101.60 millimeters)
Processor
Intel® NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE has a soldered-down 8th generation Intel® Core™ i7-8650U
Memory
Two 260-pin 1.2 V DDR4 SDRAM Small Outline Dual Inline Memory Module (SO-DIMM)
Graphics
Integrated graphics support for processors with Intel® Graphics Technology:
Intel® High Definition (Intel® HD) Audio via the HDMI v2.0a interface through the processor
Storage
SATA ports:
Peripheral Interfaces
USB 3.0 ports:
1 Product Description
1.1 Overview
1.1.1 Feature Summary
Table 1 summarizes the major features of Intel® NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE.
Table 1. Feature Summary
quad-core processor with up to 15 W TDP
― Intel® UHD Graphics 620
― Integrated memory controller
― Integrated PCH
sockets
― Support for DDR4 2400 MHz SO-DIMMs
― Support for 4 Gb and 8 Gb memory technology
― Support for up to 32 GB of system memory with two SO-DIMMs using 8 Gb memory
technology
― Support for non-ECC memory
― Support for 1.2 V low voltage JEDEC memory only
Note: 2 Gb memory technology (SDRAM Density) is not compatible
― Two High Definition Multimedia Interface* 2.0a (HDMI*) back panel connectors
― Flat panel displays via the internal Embedded DisplayPort* 1.4 (eDP) connector
Audio
― One SATA 6.0 Gb/s port (blue)
― One SATA 6.0 Gb/s port is reserved for an M.2 2280 module
Note: Intel® NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE supports key type M (PCI Express* x1/x2/x4 and
SATA)
― Two ports are implemented with external front panel connectors (blue)
― Two ports are implemented with external back panel connectors (blue)
― One port is implemented with an internal 1x10 1.25mm pitch header (white)
USB 2.0 ports:
― Two ports via two single-port internal 1x4 1.25 mm pitch headers (white)
― One port is reserved for an M.2 2230 Module (key type E)
Serial Port 1x9 1.25mm pitch header (black)
HDMI CEC 1x4 1.25 mm pitch header (black)
continued
Page 12
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Expansion Capabilities
One M.2 Module supporting M.2 2280 (key type M)
BIOS
Intel® BIOS resident in the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Flash device
Gigabit (10/100/1000 Mb/s) LAN subsystem using the Intel® I219LM Gigabit Ethernet
Hardware Monitor
Hardware monitoring subsystem, based on ITE Tech. ITE8987E-VG embedded controller,
Wireless (Kit only)
Intel® Dual Band Wireless-AC vPro 8265
Intel® vPro™
Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT) 11.6
Table 1. Feature Summary (continued)
One M.2 Module supporting M.2 2230 (key type E)
Support for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI), Plug and Play, and System
Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
LAN
Controller
Subsystem
Technologies
including:
Voltage sense to detect out of range power supply voltages
Thermal sense to detect out of range thermal values
One processor fan header
Fan sense input used to monitor fan activity
Fan speed control
― 802.11ac, Dual Band, 2x2 Wi-Fi + Bluetooth v4.2
― Maximum Transfer speed up to 867 Mbps
Supports Intel® Smart Connect Technology
Pre-installed M.2 module
Intel® Virtualization (Intel® VT-x)
Intel® Virtualization for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
Intel® Identity Protection Technology (Intel® IPT)
Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX)
Intel® Transparent Supply Chain (Intel® TSC)
Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 2.0
12
Page 13
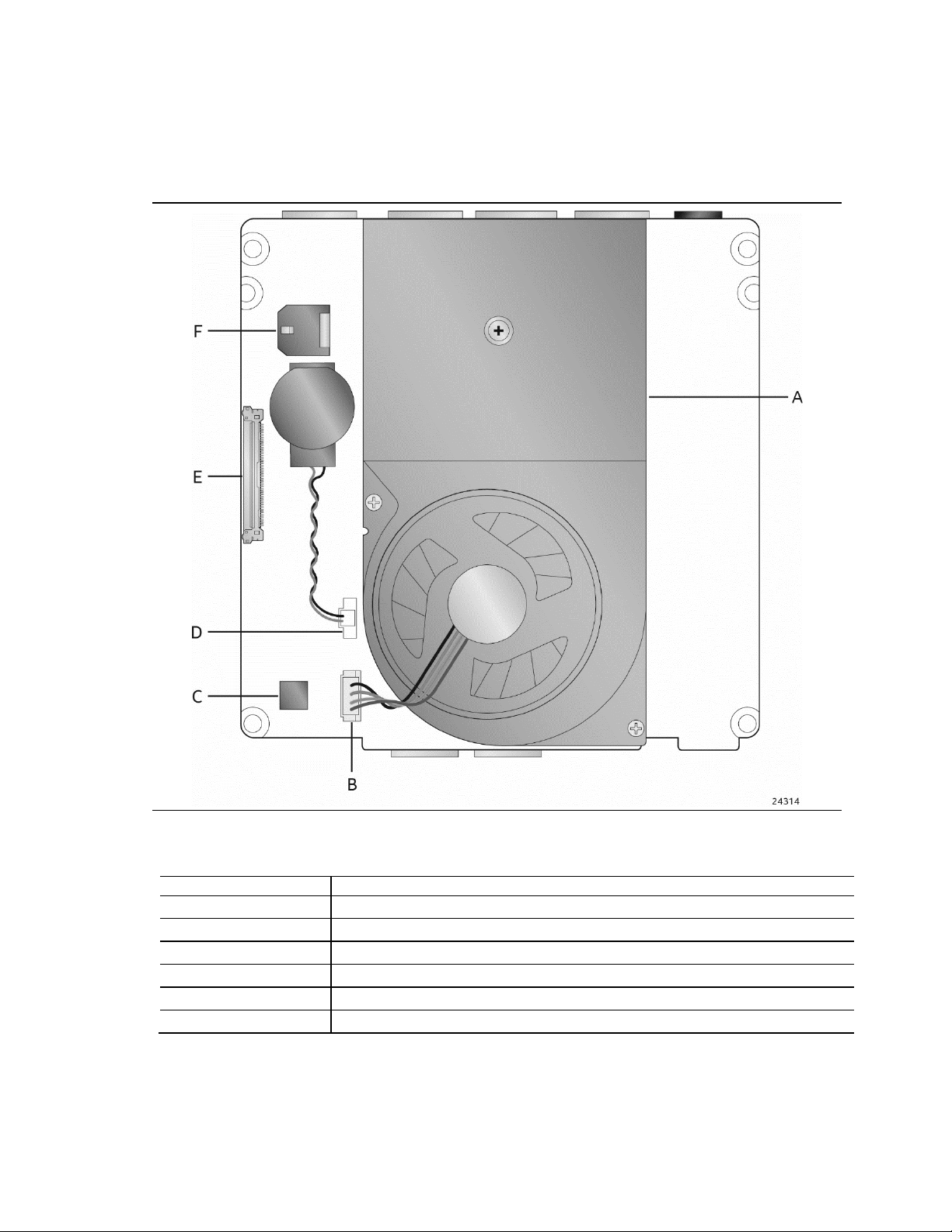
1.1.2 Board Layout (Top)
Item from Figure 1
Description
A
Thermal Solution
B
Processor Fan Header
E
eDP Connector
F
DC Internal Power Connector
Figure 1 shows the location of the major components on the top-side of Intel NUC Board
NUC7i7DNBE.
Product Description
Table 2. Components Shown in Figure 1
Figure 1. Major Board Components (Top)
C SPI
D Battery Header
13
Page 14
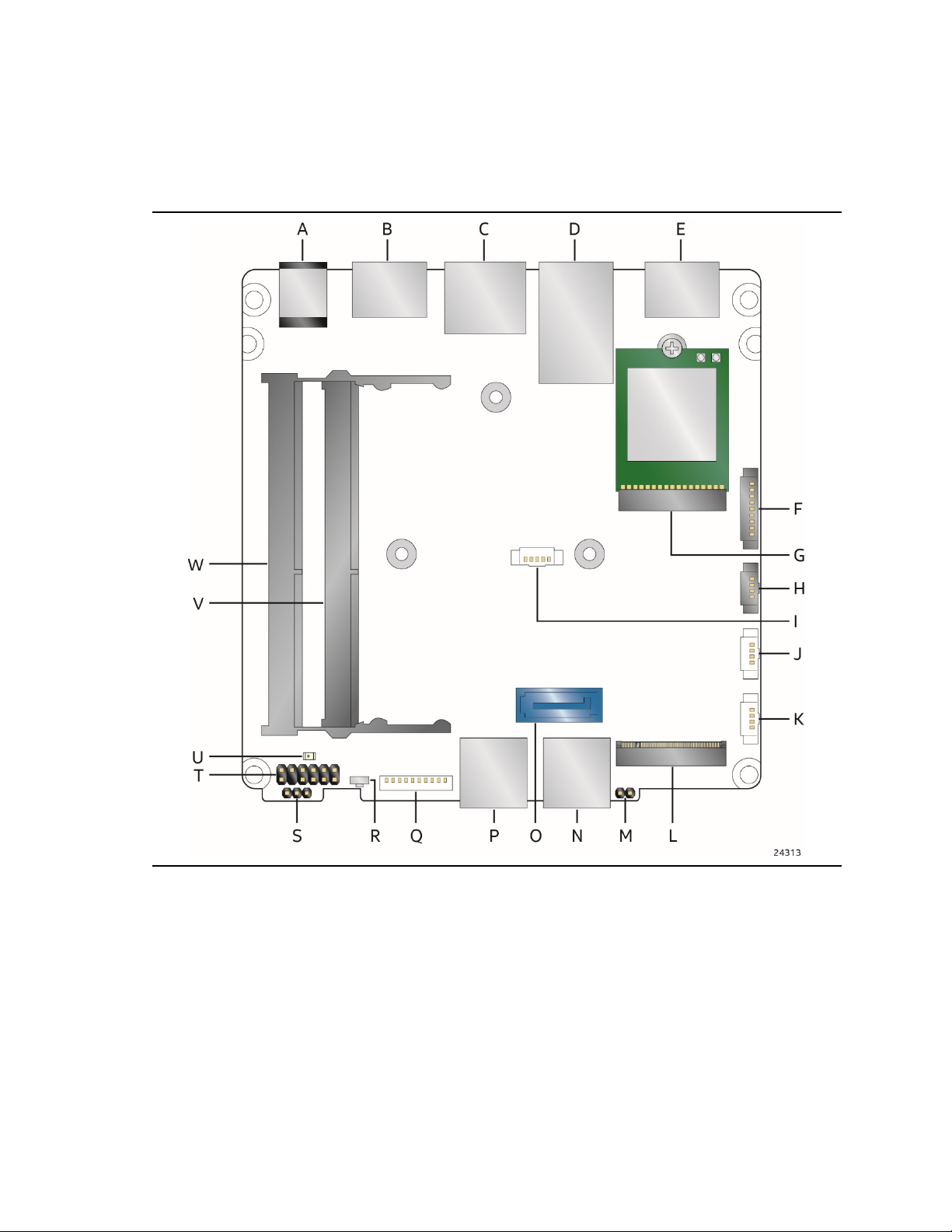
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
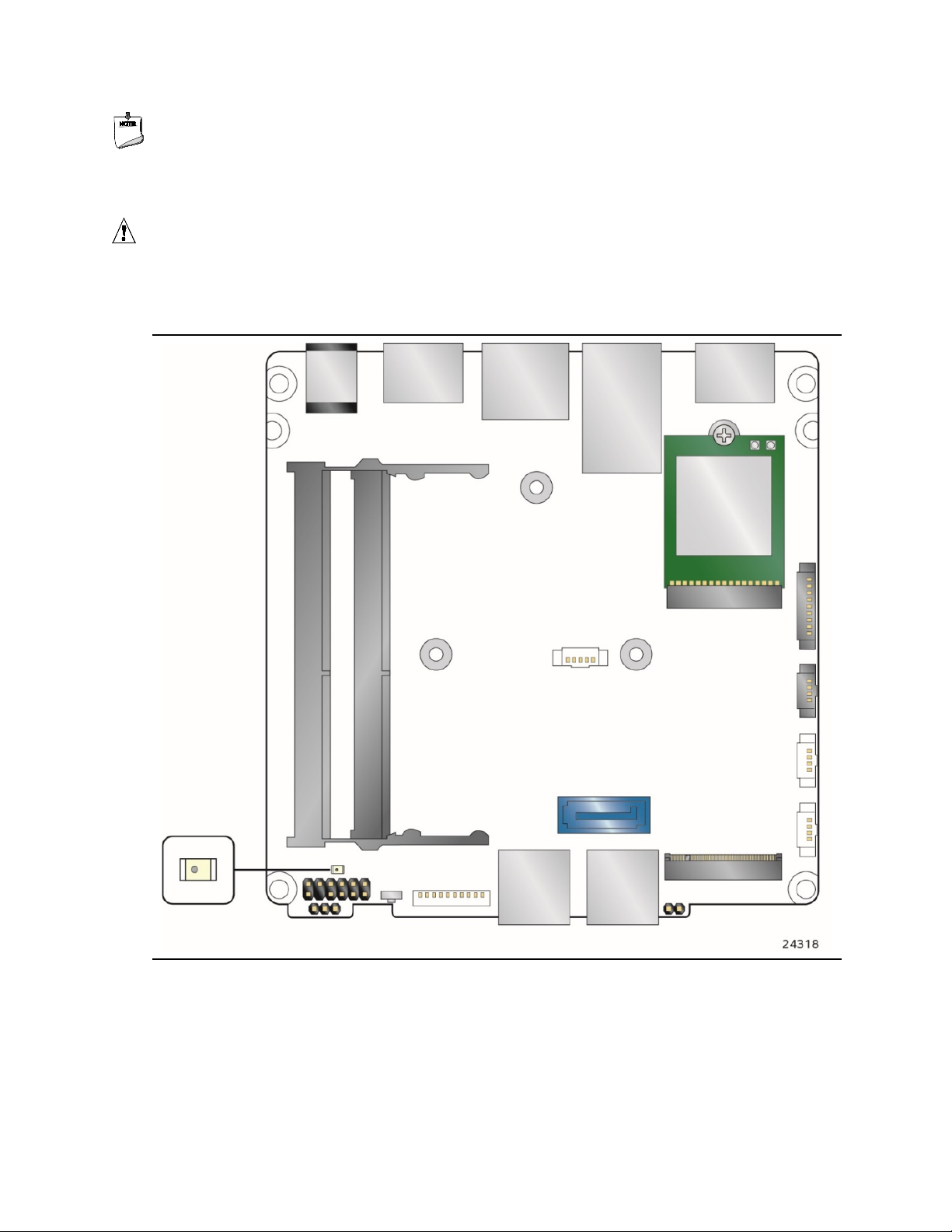
1.1.3 Board Layout (Bottom)
Figure 2 shows the location of the major components on the bottom-side of Intel NUC Board
NUC7i7DNBE.
14
Figure 2. Major Board Components (Bottom)
Page 15
Table 2. Components Shown in Figure 2
Item from Figure 2
Description
A
12-24 V DC Input Jack
B
HDMI 2.0a Port 1 with HDCP 2.2 Support and Built-In CEC Support
D
Back Panel USB 3.0
E
HDMI 2.0a Port 2
F
Serial Port Header
H
HDMI CEC
I
SATA Power Header
J
USB 2.0 Header
L
M.2 2280 Module Connector (Key Type M)
M
Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel® MEBX) Reset Header
N
Front Panel USB 3.0
P
Front Panel USB 3.0
Q
USB 3.0 Header
R
Front Panel Power Button
T
Front Panel Header
U
Standby Power LED
V
DDR4 SO-DIMM 2 Socket
C LAN Connector
G M.2 2230 Module Connector (Key Type E) (Wireless card on Kit only)
K USB 2.0 Header
O SATA 6.0 Gb/s Connector
Product Description
S BIOS Security Header
W DDR4 SO-DIMM 1 Socket
15
Page 16
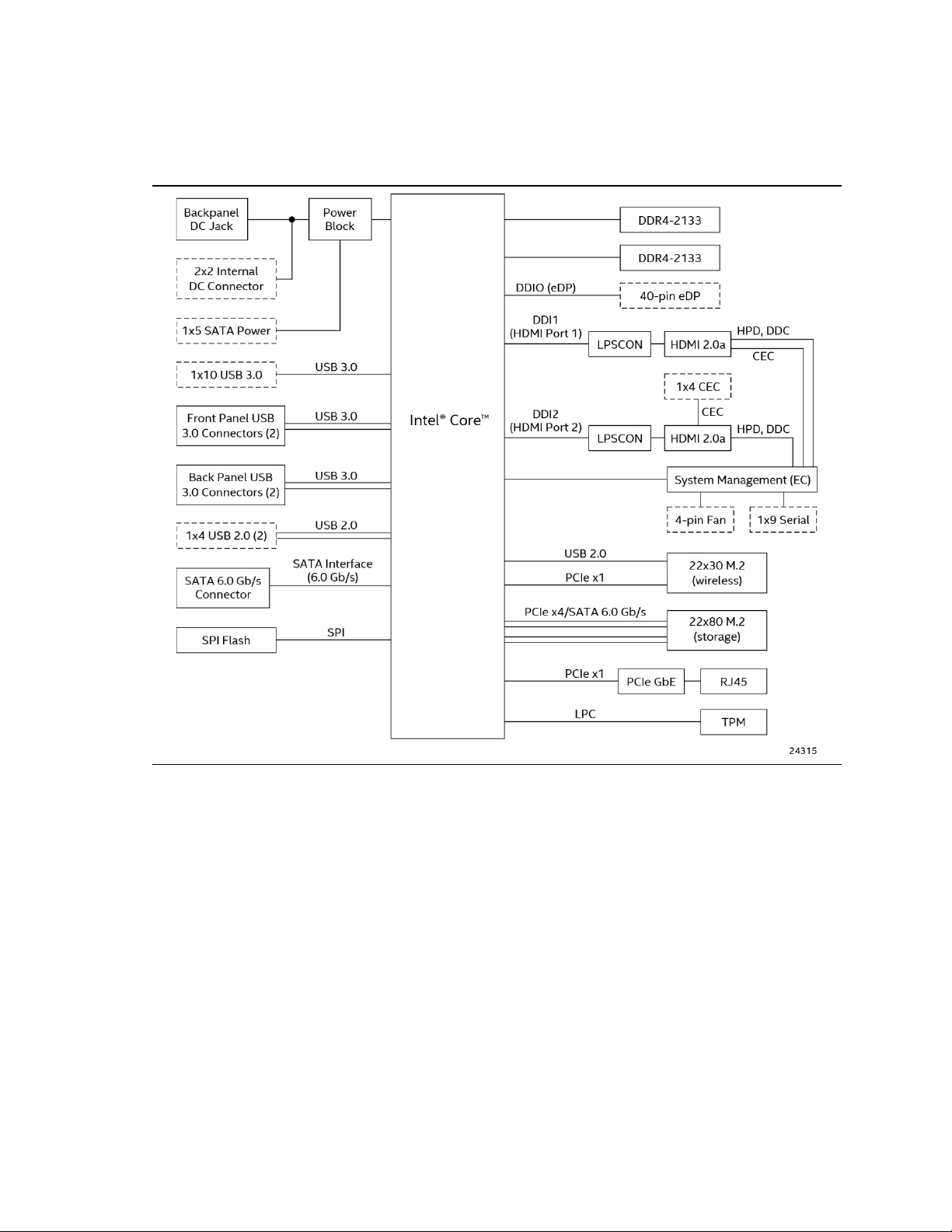
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
1.1.4 Block Diagram
Figure 3 is a block diagram of the major functional areas of the board.
i7-8650U
16
Figure 3. Block Diagram
Page 17

1.2 Online Support
To find information about…
Visit this World Wide Web site:
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN
http://www.intel.com/NUC
Intel NUC Board/Kit Support
http://www.intel.com/NUCSupport
High level details for Intel NUC Board/Kit
http://ark.intel.com
BIOS and driver updates
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Tested memory
http://www.intel.com/NUCSupport
Integration information
http://www.intel.com/NUCSupport
Processor datasheet
http://ark.intel.com
Product Description
NUC7i7DN
1.3 Processor
Intel NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE has a soldered-down 8th generation Intel Core i7-8650U quad-core
processor with up to 15 W TDP:
• Intel® UHD Graphics 620
• Integrated memory controller
• Integrated PCH
NOTE
There are specific requirements for providing power to the processor. Refer to Section 2.6.1 on
page 59 for information on power supply requirements.
1.4 System Memory
The board has two 260-pin SO-DIMM sockets and supports the following memory features:
• 1.2 V DDR4 SDRAM SO-DIMMs with gold plated contacts
• Two independent memory channels with interleaved mode support
• Unbuffered, single-sided or double-sided SO-DIMMs
• 32 GB maximum total system memory (with 8 Gb memory technology). Refer to Section 2.1.1
on page 39 for information on the total amount of addressable memory.
• Minimum recommended total system memory: 2048 MB
• Non-ECC SO-DIMMs
• Serial Presence Detect
• DDR4 2400 MHz SDRAM SO-DIMMs
• Supports 4 Gb and 8 Gb memory technology (SDRAM Density)
17
Page 18

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
SO-DIMM
Capacity
Configuration
SDRAM
Density
SDRAM Organization
Front-side/Back-side
Number of SDRAM
Devices
2048 MB
SS
4 Gbit
512 M x4/empty
4
4096 MB
DS
4 Gbit
512 M x4/512 M x4
8
4096 MB
SS
8 Gbit
1024 M x4/empty
4
8192 MB
DS
4 Gbit
512 M x8/512 M x8
16
8192 MB
DS
8 Gbit
1024 M x4/1024 M x4
8
16384 MB
DS
8 Gbit
1024 M X8/1024 M x8
16
SO-DIMM
Capacity
Configuration
SDRAM
Density
SDRAM Organization
Front-side/Back-side
Number of SDRAM
Devices
1024 MB
SS
1 Gbit
128 M x8/empty
8
2048 MB
DS
1 Gbit
128 M x8/128 M x8
16
2048 MB
SS
2 Gbit
256 M x8/empty
8
4096 MB
DS
2 Gbit
256 M x8/256 M x8
16
For information about…
Refer to:
Tested Memory
http://www.intel.com/NUCSupport
NOTE
To be fully compliant with all applicable DDR SDRAM memory specifications, the board should be
populated with SO-DIMMs that support the Serial Presence Detect (SPD) data structure. This
allows the BIOS to read the SPD data and program the chipset to accurately configure memory
settings for optimum performance. If non-SPD memory is installed, the BIOS will attempt to
correctly configure the memory settings, but performance and reliability may be impacted or the
SO-DIMMs may not function under the determined frequency.
NOTE
Intel NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE supports only 4 Gb and 8 Gb memory technologies (also referred to
as “SDRAM density”). Table 3 lists the supported SO-DIMM configurations. Table 4
lists the SO-
DIMM configurations that are not supported.
Table 3. Supported Memory Configurations
(Note)
Note: “DS” refers to double-sided memory modules and “SS” refers to single-sided memory modules.
Table 4. Unsupported Memory Configurations
(Note)
Note: “DS” refers to double-sided memory modules and “SS” refers to single-sided memory modules.
18
Page 19
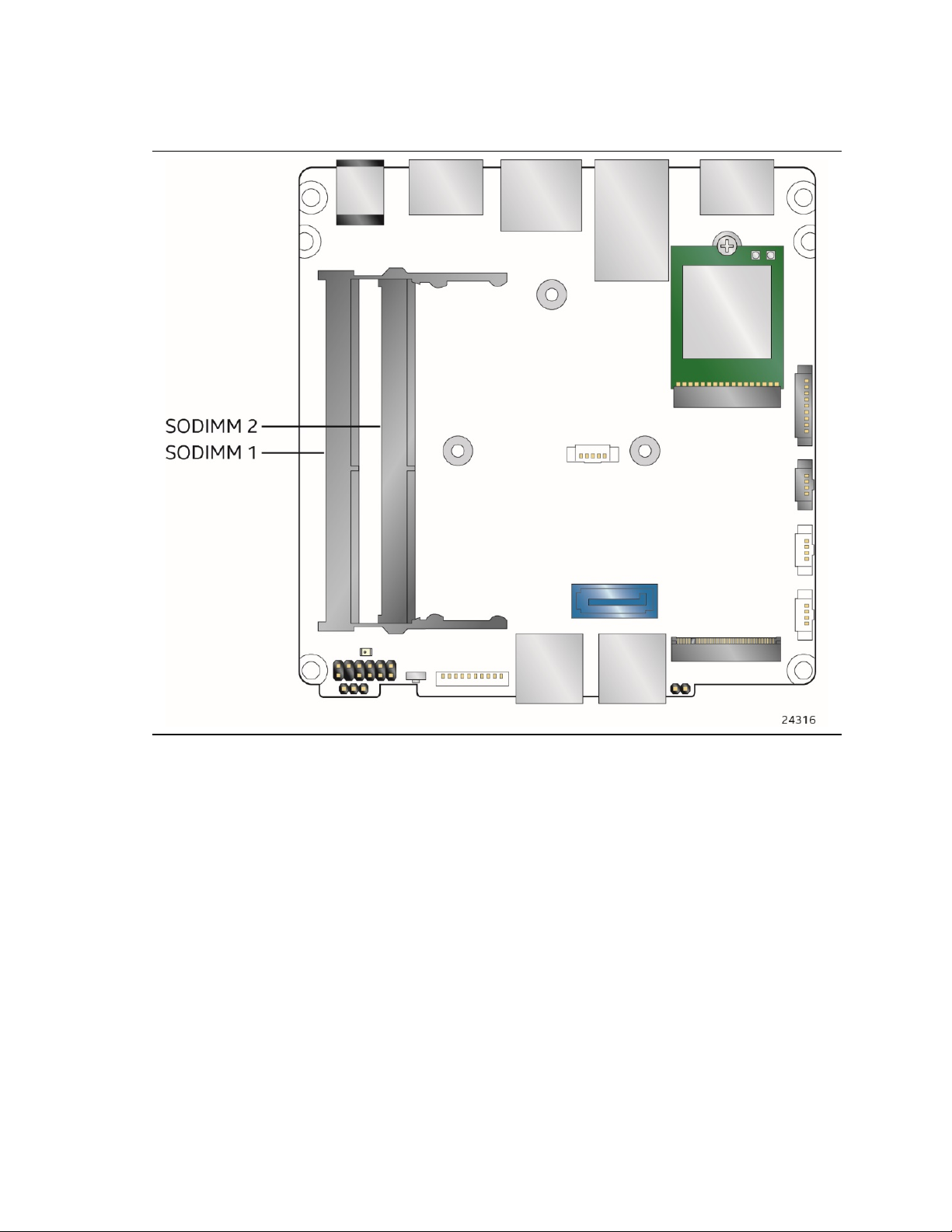
Figure 4 illustrates the memory channel and SO-DIMM configuration.
Product Description
Figure 4. Memory Channel and SO-DIMM Configuration
19
Page 20

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
For information about
Refer to
HDMI technology
http://www.hdmi.org
1.5 Processor Graphics Subsystem
The board supports graphics through Intel® UHD Graphics 620.
1.5.1 Integrated Graphics
The board supports integrated graphics via the processor.
1.5.1.1 Intel® High Definition (Intel® HD) Graphics
The Intel® UHD Graphics 620 controller features the following:
• 3D Features
DirectX* 12 support
OpenGL* 4.4 support
• Display
Supports eDP flat panel displays up to 3840 x 2160 at 60 Hz
Supports HDMI displays up to 4096 x 2160 at 60 Hz
• Next Generation Intel® Clear Video Technology HD support is a collection of video playback
and enhancement features that improve the end user’s viewing experience
• Encode/transcode HD content
• Playback of high definition content including Blu-ray* disc
• Superior image quality with sharper, more colorful images
• DirectX* Video Acceleration (DXVA) support for accelerating video processing
• Full AVC/VC1/MPEG2/HEVC/VP8/JPEG HW Decode
• Intel HD Graphics with Advanced Hardware Video Transcoding (Intel® Quick Sync Video)
• HDR 10 (High Dynamic Range 10 bit)
• HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection) 2.2
NOTE
Intel Quick Sync Video is enabled by an appropriate software application.
HDMI 2.0a enabled by a LSPCON (DisplayPort 1.2 to HDMI 2.0a controller). Stereo 3D (S3D)
technology is not supported.
1.5.1.2 High Definition Multimedia Interface* (HDMI*)
The HDMI ports are HDMI 2.0a specification compliant and support standard, enhanced, or high
definition video, plus multi-channel digital audio on a single cable. The port is compatible with all
ATSC and DVB HDTV standards and supports thirty-two full range channels of lossless audio
formats. The system can support up to two displays at the maximum supported resolution of
4096 x 2160 @ 60 Hz, 24bpp.
1.5.1.2.1 Integrated Audio Provided by the HDMI Interfaces
The following audio technologies are supported by the HDMI 2.0a interface:
20
Page 21

Product Description
• AC3 – Dolby* Digital
• Dolby Digital Plus
• DTS-HD*
• 192kHz/16-bit or 176.4 kHz/24-bit, 32 Channel
• Dolby True HD, DTS-HD Master Audio* (Lossless Blu-ray Disc* Audio Format)
1.5.1.2.2 HDMI Consumer Electronics Control (CEC)
The system provides built-in HDMI CEC support on port 1 (refer to Figure 2), as well as a header
rd
for 3
party HDMI CEC daughtercard support on HDMI port 2. The built-in HDMI CEC feature is
OS agnostic and supports bi-directional power on/off control between the system and the
attached display, as well as automatic HDMI input port detection from the display. This feature
can be enabled and configured in BIOS Setup (Advanced → Display tab). Additional HDMI CEC
capabilities can be implemented on HDMI port 2 using a 3
allow bi-directional power on/off control and other capabilities as supported by the
daughtercard, such as the use of the media buttons on the display’s remote controller.
For information about Refer to
HDMI CEC feature on NUC https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/arti
cles/000023500/mini-pcs/intel-nuc-kits.html
rd
party daughtercard, which would
1.5.1.2.3 High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP)
HDMI Port 1 supports HDCP 2.2. HDCP is the technology for protecting high definition content
against unauthorized copy or interception between a source (computer, digital set top boxes, etc.)
and the sink (panels, monitor, and TVs). The PCH supports HDCP 2.2 for content protection over
wired displays.
1.5.1.3 Flat Panel Display Interfaces
The board supports flat panel displays via the Embedded DisplayPort interface. Figure 5 shows
the flat panel connector on the bottom-side of the board.
21
Page 22
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Item
Description
A
Embedded DisplayPort Connector
A
Figure 5. eDP Connector on Bottom-side of the Board
1.5.1.3.1 Embedded DisplayPort (eDP) Interface
The Embedded DisplayPort 1.4 (eDP) flat panel display interface supports the following:
• Maximum resolution of 3840 x 2160 at 60 Hz
• 4-lane bandwidth at 5.4 GT/s
• Multiple EDID data source capability (panel, predefined, and custom payloads)
• 3.3V flat panel display voltage
• 0.6A of maximum backlight current capability
• Backlight power voltage same as NUC board DC power source
• Board connector used is I-PEX-20455-040E-12, or compatible.
• Mating plug is I-PEX 20453-040T, or compatible.
1.5.1.3.2 Configuration Modes
Video mode configuration for eDP displays is supported as follows:
• Panel: automatic panel identification via Extended Display Identification Data (EDID) for
panels with onboard EDID support
• Predefined: panel selection from common predefined panel types
• Custom payloads: custom EDID payload installation for ultimate parameter flexibility,
allowing custom definition of EDID data on panels without onboard EDID
In addition, BIOS setup provides the following configuration parameters for internal flat panel
displays:
22
Page 23

Product Description
• Color Depth: allows the system integrator to select whether the panel is 24 bpp with VESA or
JEIDA color mapping, or 18 bpp.
• eDP Interface Type: allows the system integrator to select whether the eDP panel is a single-
lane, dual-lane, or quad-lane display.
• eDP Data Rate: allows the system integrator to select whether the eDP panel runs at
1.62 Gb/s, 2.7 Gb/s, or 5.4 Gb/s.
• Inverter Frequency and Polarity: allows the system integrator to set the operating frequency
and polarity of the panel inverter board.
• Maximum and Minimum Inverter Current Limit (%): allows the system integrator to set
maximum PWM%, as appropriate, according to the power requirements of the internal flat
panel display and the selected inverter board.
NOTE
Support for flat panel display configuration complies with the following:
1. Internal flat panel display settings will be preserved across BIOS updates.
2. Backlight inverter voltage option “Vin” refers to board input voltage as provided to board
power input connector.
1.5.1.4 EDID Emulation Modes
The board supports emulation of displays so that the system may be remotely accessed in a
headless configuration, or be capable of tolerating display connectivity interruptions without
the operating system redetecting and rearranging the overall display layout. The display
emulation feature may be enabled in BIOS Setup (Advanced → Video → “Display Emulation”
drop down menu), with the following options:
• “No display emulation” (default selection): the system operates normally.
• “Headless display emulation”: the system creates a virtual 1280x1024 display when it boots
with no displays connected.
• “Persistent display emulation”: the system is trained with the EDID information from each
display connected on the first boot after selecting this option, and retains such parameters
regardless of display power or connectivity interruptions. The EDID information from each
display will even remain programmed through S3, S4, and S5 power states, until the feature
is disabled or a power cycle event (G3 global state) occurs.
NOTE
“Persistent display emulation” is not compatible with HDCP 2.2 displays.
When using “Persistent display emulation” it would be expected behavior for the system not to
properly drive displays different than those connected when the feature was enabled, as the
EDID parameters of the initially connected displays are still being driven by the system. In
order to retrain “Persistent display emulation” with a different display configuration a power
cycle (AC power loss) is required.
23
Page 24

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
For information about
Refer to
The location of the USB connectors on the back panel
Figure 10, page 40
The location of the front panel USB headers
Figure 9, page 40
The location of the internal connectors
Figure 12, page 42
1.6 USB
The board supports eight USB ports. All eight ports are high-speed, full-speed, and low-speed
capable. The port arrangement is as follows:
• USB 3.0 ports:
Two ports are implemented with external front panel connectors (blue)
Two ports are implemented with external back panel connectors (blue)
One port is implemented with a 1x10 1.25mm internal header (white)
• USB 2.0 ports:
Two ports via two single-port internal 1x4 1.25 mm pitch headers (white)
One port is reserved for the M.2 2230 Module Connector (Key Type E) (Wireless card on
Kit only)
NOTE
Computer systems that have an unshielded cable attached to a USB port may not meet FCC
Class B requirements, even if no device is attached to the cable. Use a shielded cable that meets
the requirements for full-speed devices.
1.7 SATA Interface
The board provides the following SATA interfaces:
• One internal M.2 SATA port supporting M.2 2280 (key type M) modules
• One SATA 6.0 Gb/s port (blue)
The PCH provides independent SATA ports with a theoretical maximum transfer rate of 6 Gb/s. A
point-to-point interface is used for host to device connections.
1.7.1 AHCI Mode
The board supports AHCI storage mode.
NOTE
In order to use AHCI mode, AHCI must be enabled in the BIOS. Microsoft* Windows* 10 includes
the necessary AHCI drivers without the need to install separate AHCI drivers during the operating
system installation process; however, it is always good practice to update the AHCI drivers to the
latest available by Intel.
24
Page 25

Product Description
1.7.2 NVMe
The board supports M.2 NVM Express* (NVMe) drives. NVMe is an optimized, high-performance
scalable host controller interface designed to utilize PCIe-based solid-state storage. NVMe is
designed to provide efficient access to storage devices built with non-volatile memory, from
current NAND flash technology to future, higher performing persistent memory technologies like
Optane. NVMe is designed to meet serial bandwidth requirements and very high IOPs. It is based
on PCIe Gen 3 and can deliver up to 4GB/s bandwidth. Current NVMe is based on version 1.3 of
the specification.
1.7.3 Intel® Rapid Storage Technology / SATA RAID
The PCH supports Intel® Rapid Storage Technology, providing both AHCI and integrated RAID
functionality. The RAID capability provides high-performance RAID 0 and 1 functionality on all
SATA ports. Other RAID features include hot spare support, SMART alerting, and RAID 0 auto
replace. Software components include an Option ROM for pre-boot configuration and boot
functionality, a Microsoft Windows compatible driver, and a user interface for configuration and
management of the RAID capability of the PCH.
NOTE
Intel Rapid Storage Technology / SATA RAID is only supported if an M.2 SATA SSD module is
used with the onboard SATA interface. RAID is not available with an M.2 NVMe SSD module and
onboard SATA interface. Supported on chassis with 2.5 inch SATA HDD capability.
1.7.4 Intel® Next Generation Storage Acceleration
Intel® Next Generation Storage Acceleration with Intel® Optane™ Technology is a disk caching
solution that can provide improved computer system performance with improved power savings. It
allows configuration of a computer system with the advantage of having HDDs for maximum
storage capacity and with Intel® Optane™ Technology for improved system performance.
Supported on chassis with 2.5 inch SATA HDD capability.
For more information on Intel® Optane™ Technology, go to
http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-technology/non-volatilememory.html
25
Page 26

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
For information about
Refer to
Obtaining NUC software and drivers
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Real-Time Clock Subsystem
A coin-cell battery (CR2032) powers the real-time clock and CMOS memory. When the computer
is not plugged into a wall socket, the battery has an estimated life of three years. When the
computer is plugged in, the standby current from the power supply extends the life of the battery.
The clock is accurate to ± 13 minutes/year at 25 ºC with 3.3 VSB applied via the power supply 5 V
STBY rail.
NOTE
If the battery and AC power fail, date and time values will be reset and the user will be notified
during the POST.
When the voltage drops below a certain level, the BIOS Setup program settings stored in CMOS
RAM (for example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the battery with an
equivalent one. Figure 1 on page 13 shows the location of the battery.
CAUTION
Risk of explosion if the battery is replaced with an incorrect type. Batteries should be recycled
where possible. Disposal of used batteries must be in accordance with local environmental
regulations.
1.8 Audio Subsystem Software
Audio is supported through the HDMI 2.0a ports interface through the processor and supports
eight full range channels of lossless audio formats per port. When using an encoded format (such
as DTS-HD MA or Dolby True HD) the board supports a single 7.1 stream. When using an unencoded format the board supports 8 discrete, un-encoded channels per HDMI port
simultaneously, for a total of 16 discrete/un-encoded channels.
1.8.1 Audio Subsystem Software
Audio drivers are built into the Graphics driver and are available from Intel’s website.
26
Page 27

1.9 LAN Subsystem
The LAN subsystem consists of the following:
• Intel I219LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller (10/100/1000 Mb/s)
• RJ-45 LAN connector with integrated status LEDs
Additional features of the LAN subsystem include:
• CSMA/CD protocol engine
• LAN connect interface between the Processor and the LAN controller
• Power management capabilities
ACPI technology support
LAN wake capabilities
• LAN subsystem software
Product Description
For information about
LAN software and drivers http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Refer to
1.9.1 Intel® I219LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller
The Intel I219LM Gigabit Ethernet Controller supports the following features:
• Compliant with the 1 Gb/s Ethernet 802.3, 802.3u, 802.3z, 802.3ab specifications
• Multi-speed operation: 10/100/1000 Mb/s
• Full-duplex operation at 10/100/1000 Mb/s; Half-duplex operation at 10/100 Mb/s
• Flow control support compliant with the 802.3X specification as well as the specific operation
of asymmetrical flow control defined by 802.3z
• VLAN support compliant with the 802.3q specification
• Supports Jumbo Frames (up to 9 kB)
IEEE 1588 supports (Precision Time protocol)
• MAC address filters: perfect match unicast filters, multicast hash filtering, broadcast filter, and
promiscuous mode
27
Page 28
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Item
Description
LED
LED Color
LED State
Condition
On
LAN link is established.
Blinking
LAN activity is occurring.
Off
10 Mb/s data rate is selected.
Yellow
1000 Mb/s data rate is selected.
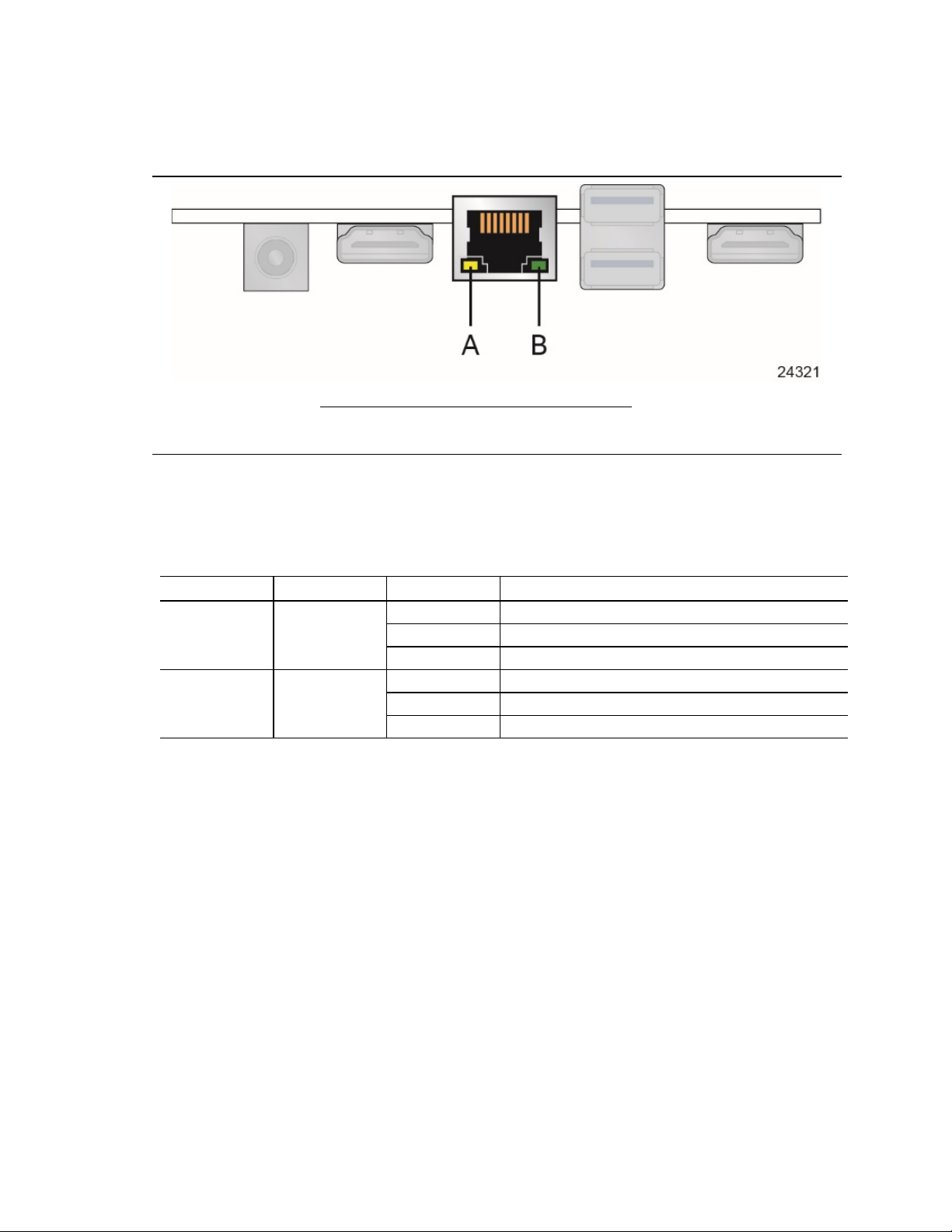
1.9.2 RJ-45 LAN Connector with Integrated LEDs
Two LEDs are built into the RJ-45 LAN connector (shown in Figure 6).
A Link LED (Green)
B Data Rate LED (Green/Yellow)
Figure 6. LAN Connector LED Locations
Table 5 describes the LED states when the board is powered up and the LAN subsystem is
operating.
Table 5. LAN Connector LED States
Off LAN link is not established.
Link Green
Data Rate Green/Yellow
Green 100 Mb/s data rate is selected.
1.9.3 Wireless Network Module
The Intel Dual Band Wireless-AC vPro 8265 module provides hi-speed wireless connectivity
provided with the following capabilities and is supported by Intel vPro Technology. The wireless
module is included with Kit SKUs only:
• Compliant IEEE 802.11a/b/g/n/ac, 802.11d, 802.11e, 802.11i, 802.11w, 802.11r, 802.11k,
802.11v (pending OS support) specifications
• Maximum bandwidth of 867 Mbps
• Dual Mode Bluetooth* 4.2
• Wi-Fi Direct* for peer to peer device connections
• Wi-Fi Miracast* as Source
• Authentication: WPA and WPA2, 802.1X (EAP-TLS, TTLS, PEAP, LEAP, EAP-FAST), EAP-SIM,
EAP-AKA
• Encryption: 64-bit and 128-bit WEP, 128-bit AES-CCMP
28
Page 29

Product Description
For information about
Refer to
Obtaining WLAN software and drivers
http://downloadcenter.intel.com
Full Specifications
http://intel.com/wireless
1.10 Hardware Management Subsystem
The board has several hardware management features, including thermal and voltage monitoring.
1.10.1 Hardware Monitoring
The hardware monitoring and fan control subsystem is based on an ITE Tech. ITE8987E-VG
embedded controller, which supports the following:
• Processor and system ambient temperature monitoring
• Fan speed monitoring
• Voltage monitoring of CPU IO Vcc (+Vccio), Memory Vcc (V_SM), CPU IN Vcc (+Vccp)
• SMBus communication with internal components
1.10.2 Fan Monitoring
Fan monitoring can be implemented using third-party software.
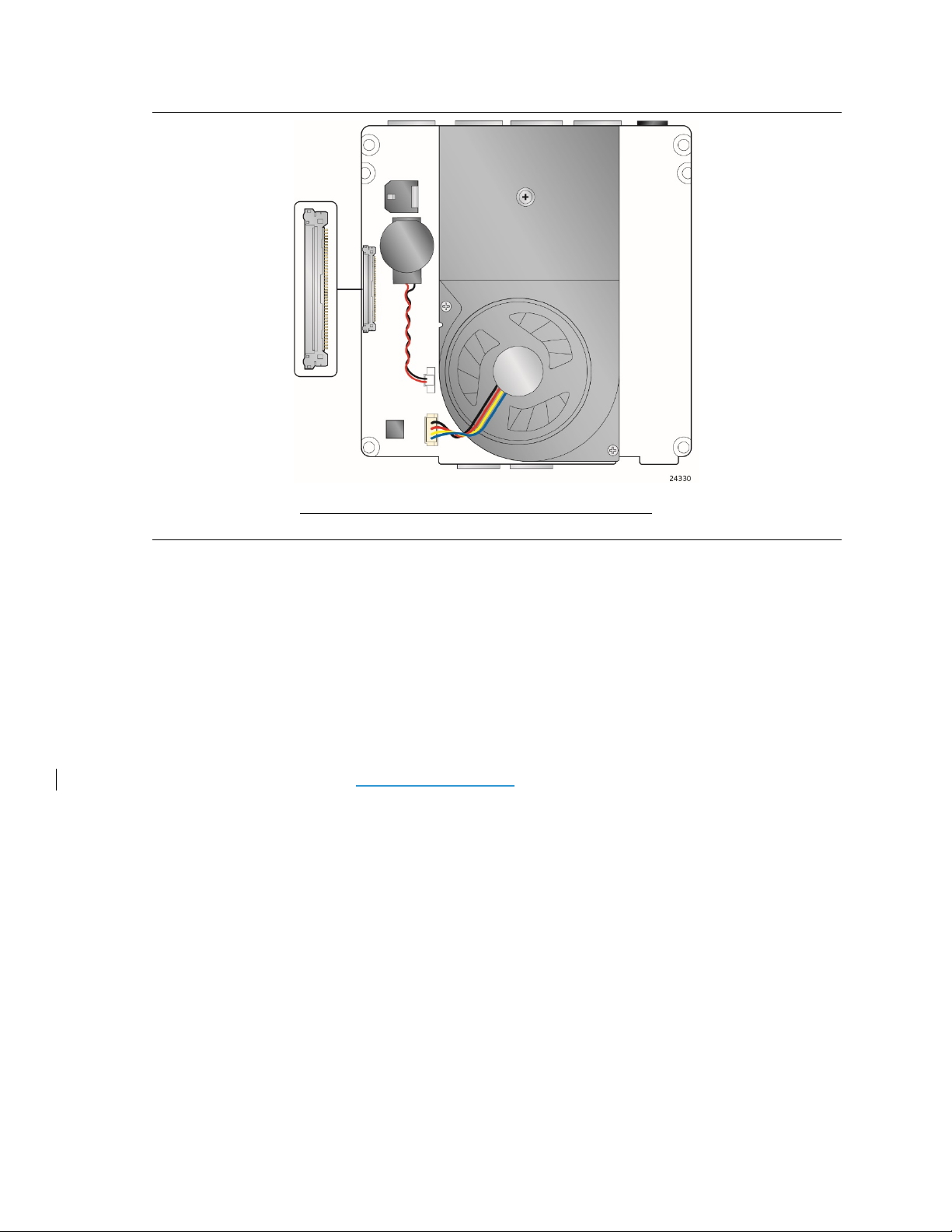
1.10.3 Thermal Solution
Figure 7 shows the location of the thermal solution and processor fan header.
29
Page 30

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Item
Description
B
Processor Fan Header
A Thermal Solution
Figure 7. Thermal Solution and Fan Header
30
Page 31

Product Description
…and the power switch is
Off
Power-on
On
Less than four seconds
Soft-off/Standby
On
More than six seconds
Fail safe power-off
Sleep
Less than four seconds
Wake-up
1.11 Power Management
Power management is implemented at several levels, including:
• Software support through Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI)
• Hardware support:
Power Input
LAN wake capabilities
Wake from USB
+5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
1.11.1 ACPI
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug and Play
functions of a computer. The use of ACPI with this board requires an operating system that
provides full ACPI support. ACPI features include:
• Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration)
• Power management control of individual devices, add-in boards (some add-in boards may
require an ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives
• Methods for achieving less than 15-watt system operation in the power-on/standby
sleeping state
• A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power-off the computer
• Support for multiple wake-up events (see Table 8 on page 33)
• Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch
Table 6 lists the system states based on how long the power switch is pressed, depending on how
ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware operating system.
Table 6. Effects of Pressing the Power Switch
If the system is in this state…
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Sleep
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
Note: Depending on power management settings in the operating system.
pressed for
Less than four seconds
More than six seconds
…the system enters this state
(ACPI G0 – working state)
(ACPI G1 – sleeping state)
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
(ACPI G0 – working state)
Power-off
(ACPI G2/G5 – Soft off)
Note
31
Page 32
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Processor
G1 – sleeping state
S3 – Suspend to RAM.
No power
D3 – no power except for wake-up
G1 – sleeping state
S4 – Suspend to disk.
No power
D3 – no power except for wake-up
G2/S5
S5 – Soft off. Context not
No power
D3 – no power except for wake-up
1.11.1.1 System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The
operating system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and
knowledge of how devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can be
turned off. The operating system uses information from applications and user settings to put the
system as a whole into a low-power state.
Table 7 lists the power states supported by the board along with the associated system power
targets. See the ACPI specification for a complete description of the various system and power
states.
Table 7. Power States and Targeted System Power
Global States
G0 – working state S0 – working C0 – working D0 – working state.
G3 – mechanical off
AC power is disconnected
from the computer.
Notes:
1. Total system power is dependent on the system configuration, including add-in boards and peripherals powered by
the system chassis’ power supply.
2. Dependent on the standby power consumption of wake-up devices used in the system.
Sleeping States
Context saved to RAM.
Context saved to disk.
saved. Cold boot is required.
No power to the system. No power D3 – no power for wake-up logic,
States
Device States
logic.
logic.
logic.
except when provided by battery
or external source.
32
Page 33

1.11.1.2 Wake-up Devices and Events
Devices/events that wake up the
…from this sleep
Comments
Table 8 lists the devices or specific events that can wake the computer from specific states.
Table 8. Wake-up Devices and Events
Product Description
system…
Power switch S3, S4, S51
RTC alarm S3, S4, S51 Monitor to remain in sleep state
LAN S3, S4, S5
WIFI S3, S4, S5
Bluetooth S31
USB S3, S4, S5
HDMI CEC S3, S4, S51 Emulates power button push
Serial N/A Wake from Serial is not supported
Notes:
1. S4 implies operating system support only.
2. Will not wake from Deep S4/S5. USB S4/S5 Power is controlled by BIOS. USB S5 wake is controlled by BIOS. USB S4
wake is controlled by OS driver, not just BIOS option.
3. Windows Fast startup will block wake from LAN and USB from S5.
NOTE
state
1, 3
“S5 WOL after G3” must be supported;
monitor to remain in sleep state
1, 3
“S5 WOL after G3” must be supported;
monitor to remain in sleep state
1, 2, 3
Wake S4, S5 controlled by BIOS option
(not after G3)
The use of these wake-up events from an ACPI state requires an operating system that provides
full ACPI support. In addition, software, drivers, and peripherals must fully support ACPI wake
events.
1.11.2 Hardware Support
The board provides several power management hardware features, including:
• Wake from Power Button signal
When resuming from an AC power failure, the computer returns to the power state
defined in the BIOS. Available states are “Power On”, “Stay Off”, and “Last State”.
• LAN wake capabilities
Enables remote wake-up of the computer through a network. The LAN subsystem
monitors network traffic at the Media Independent Interface. Upon detecting a Magic
Packet* frame, the LAN subsystem asserts a wake-up signal that powers up the computer.
• Wake from USB
USB bus activity wakes the computer from an ACPI S3 state (not after G3).
• +5 V Standby Power Indicator LED
The standby power indicator LED shows that power is still present even when the
computer appears to be off. Figure 8 shows the location of the standby power LED.
33
Page 34
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
NOTE
The use of Wake from USB from an ACPI state requires an operating system that provides full
ACPI support. Wake from USB requires the use of a USB peripheral that supports Wake from USB.
CAUTION
If AC power has been switched off and the standby power indicator is still lit, disconnect the power
cord before installing or removing any devices connected to the board. Failure to do so could
damage the board and any attached devices.
34
Figure 8. Location of the Standby Power LED
Page 35

Product Description
For information about
Refer to
Intel® vPro Technology
http://support.intel.com/support/vpro/
1.12 Intel® Security and Manageability Technologies
Intel® Security and Manageability Technologies provides tools and resources to help small
business owners and IT organizations protect and manage their assets in a business or
institutional environment.
NOTE
Software with security and/or manageability capability is required to take advantage of Intel
platform security and/or management technologies.
1.12.1 Intel® vPro™ Technology
Intel® vPro™ Technology is a collection of platform capabilities that support enhanced
manageability, security, virtualization and power efficiency. The key platform capabilities include:
• Intel® Active Management Technology (Intel® AMT) 11.6
• Intel® Virtualization (Intel® VT-x)
• Intel® Virtualization for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)
• Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT)
• Intel® Identity Protection Technology (Intel® IPT)
• Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX)
• Intel® Transparent Supply Chain (Intel® TSC)
• Trusted Platform Module 2.0 (TPM)
1.12.1.1 Intel® Active Management Technology 11.6
When used with third-party management and security applications, Intel Active Management
Technology (Intel® AMT) allows business owners and IT organizations to better discover, heal, and
protect their networked computing assets.
Some of the features of Intel AMT include:
• Out-of-band (OOB) system access, to discover assets even while PCs are powered off
• Remote trouble-shooting and recovery, which allows remote diagnosis and recovery of
systems after OS failures
• Hardware-based agent presence checking that automatically detects and alerts when critical
software agents have been stopped or are missing
• Proactive network defense, which uses filters to block incoming threats while isolating
infected clients before they impact the network
• Remote hardware and software asset tracking, helping to track computer assets and keep
virus protection up-to-date
• Keyboard, video and mouse (KVM) remote control, which allows redirection of a managed
system’s video to a remote console which can then interact with it using the console’s own
mouse and keyboard
35
Page 36

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
For information about
Refer to
Intel® Active Management Technology
http://www.intel.com/technology/platform-technology/intel-
For information about
Refer to
For information about
Refer to
NOTE
Intel AMT requires a network connector and an Intel AMT enabled remote management console.
Setup requires additional configuration of the platform.
amt/index.htm
1.12.1.2 Intel® Virtualization Technology
Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT-x) is a hardware-assisted technology that, when
combined with software-based virtualization solutions, provides maximum system utilization by
consolidating multiple environments into a single server or client.
NOTE
A processor with Intel VT does not guarantee that virtualization will work on your system. Intel VT
requires a computer system with a chipset, BIOS, enabling software and/or operating system,
device drivers, and applications designed for this feature.
Intel® Virtualization Technology http://www.intel.com/technology/virtualization/technology.htm
1.12.1.3 Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d) allows addresses in incoming I/O
device memory transactions to be remapped to different host addresses. This provides Virtual
Machine Monitor (VMM) software with:
• Improved reliability and security through device isolation using hardware assisted remapping.
• Improved I/O performance and availability by direct assignment of devices.
Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O https://software.intel.com/en-
us/node/139035?wapkw=vt+directed+io
36
Page 37

Product Description
For information about
Refer to
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology
http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/architecture-and-
For information about
Refer to
Intel® Identity Protection Technology
http://ipt.intel.com
For information about
Refer to
Intel® Software Guard Extensions
https://software.intel.com/en-us/sgx
For information about
Refer to
1.12.1.4 Intel® Trusted Execution Technology
Intel® Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) is a hardware security solution that protects
systems against software-based attacks by validating the behavior of key components at startup
against a known good source. It requires that Intel VT be enabled and the presence of a TPM.
technology/trusted-execution-technology/malware-reductiongeneral-technology.html
1.12.1.5 Intel® Identity Protection Technology
Intel® Identity Protection Technology (Intel® IPT) provides a simple way for websites and
enterprises to validate that a user is logging in from a trusted computer. This is accomplished by
using the Intel Manageability Engine embedded in the chipset to generate a six-digit number that,
when coupled with a user name and password, will generate a One-Time Password (OTP) when
visiting Intel IPT-enabled websites. Intel IPT eliminates the need for the additional token or key fob
required previously for two-factor authentication.
1.12.1.6 Intel® Software Guard Extensions
Intel® Software Guard Extensions (Intel® SGX) is for application developers who are seeking to
protect select code and data from disclosure or modification. Intel SGX makes such protections
possible through the use of enclaves, which are protected areas of execution in memory.
Application code can be put into an enclave by special instructions and software made available
to developers via the Intel SGX Software Development Kit (SDK).
1.12.1.7 Intel® Transparent Supply Chain (TSC)
Intel® Transparent Supply Chain is being able to prove that all components used for Intel
products were sourced from approved manufacturers and purchased from authorized suppliers
or distributors. The components will be traceable to each finished goods serial number. TSC data
aids in the detection of counterfeit, gray market, and/or components that do not conform to spec.
Intel® Transparent Supply Chain https://tsc.intel.com
37
Page 38

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
For information about
Refer to
Infineon SLB9665VQ2.0 TPM v2.0
www.infineon.com/cms/en/product/channel.html?channel=db3
1.12.1.8 Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
The TPM version 2.0 component is specifically designed to enhance platform security above-andbeyond the capabilities of today’s software by providing a protected space for key operations and
other security critical tasks. Using both hardware and software, the TPM protects encryption and
signature keys at their most vulnerable stages—operations when the keys are being used
unencrypted in plain-text form. The TPM shields unencrypted keys and platform authentication
information from software-based attacks.
NOTE
Support for TPM v2.0 requires a UEFI-enabled operating system, such as Microsoft Windows 10.
a30433efacd9a013f10d3ded64daf
38
Page 39

2 Technical Reference
2.1 Memory Resources
2.1.1 Addressable Memory
The system has been validated with up to 32 GB of addressable system memory. Typically the
address space that is allocated for PCI Express configuration space, BIOS (SPI Flash device), and
chipset overhead resides above the top of DRAM (total system memory). On a system that has 16
GB of system memory installed, it is not possible to use all of the installed memory due to system
address space being allocated for other system critical functions. These functions include the
following:
• BIOS/SPI Flash device (16 MB)
• Local APIC (19 MB)
• Direct Media Interface (40 MB)
• PCI Express configuration space (256 MB)
• PCH base address registers PCI Express ports (up to 256 MB)
• Memory-mapped I/O that is dynamically allocated for M.2 add-in cards (256 MB)
• Integrated graphics shared memory (up to 1.5 GB; 64 MB by default)
2.2 Connectors and Headers
CAUTION
Only the following connectors and headers have overcurrent protection: back panel USB, front
panel USB, and internal USB headers.
All other connectors and headers are not overcurrent protected and should connect only to
devices inside the computer’s chassis, such as fans and internal peripherals. Do not use these
connectors or headers to power devices external to the computer’s chassis. A fault in the load
presented by the external devices could cause damage to the computer, the power cable, and the
external devices themselves.
Furthermore, improper connection of USB header single wire connectors may eventually overload
the overcurrent protection and cause damage to the board.
This section describes the board’s connectors and headers. The connectors and headers can be
divided into these groups:
• Front panel I/O connectors
• Back panel I/O connectors
• On-board I/O connectors and headers (see page 41 and 42)
NOTE
Unless otherwise noted, all 2.0 mm headers are dual-row, straight, surface mount with each twopin section measuring 2.0 mm x 4.0 mm, with a pin height of 4.0 mm.
Page 40

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Item
Description
Item
Description
A
12-24 V DC Input Jack
C
LAN Connector
2.2.1 Front Panel Connectors
Figure 9 shows the location of the front panel connectors for the board.
A Front Panel Power Button
B USB 3.0 Port (blue)
C USB 3.0 Port (blue)
Figure 9. Front Panel Connectors
2.2.2 Back Panel Connectors
Figure 10 shows the location of the back panel connectors for the board.
B HDMI Port 1
40
D USB 3.0 Ports (blue)
E HDMI Port 2
Figure 10. Back Panel Connectors
Page 41

2.2.3 Connectors and Headers (Top)
Item from Figure 11
Description
A
Processor Fan Header
B
eDP Connector
Figure 11 shows the location of the connectors and headers on the top-side of the board.
Technical Reference
Figure 11. Connectors and Headers (Top)
Table 9. Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 11
41
Page 42

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
2.2.4 Connectors and Headers (Bottom)
Figure 12 shows the locations of the connectors and headers on the bottom-side of the board.
1
1
1
1
1
Figure 12. Connectors and Headers (Bottom)
42
Page 43

Table 10 lists the connectors and headers identified in Figure 12.
Item from
B
M.2 2230 Module Connector (Key Type E) (Wireless card on Kit only)
D
SATA Power Header
F
USB 2.0 Header
H
Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel® MEBX) Reset Header
J
USB 3.0 Header
L
Front Panel Header
Table 10. Connectors and Headers Shown in Figure 12
Technical Reference
Figure 12
A Serial Port Header
C HDMI CEC
E USB 2.0 Header
G M.2 2280 Module Connector (Key Type M)
I SATA 6.0 Gb/s Connector
K BIOS Security Header
Description
43
Page 44
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
2.2.4.1 Signal Tables for the Connectors and Headers
Table 11. SATA Power Header (1.25 mm pitch)
1 5 V (1.5A total for pins 1, 2)
2 5 V (1.5A total for pins 1, 2)
3 3.3 V
4 GND
5 GND
Connector is Molex part number 53398-0571, 1.25mm Pitch PicoBlade* Header, Surface Mount,
Vertical, Lead-Free, 5 Circuits.
Table 12. Internal USB 2.0 Header (1.25 mm pitch)
1 5 V 1
2 D -
3 D +
4 GND
1
The two USB 2.0 headers on the board can deliver a combined power rating of 1.5 A, with any one of the headers
supplying 1 A and the other supplying 500 mA.
Connector is Molex part number 53398-0471, 1.25mm Pitch PicoBlade* Header, Surface Mount,
Vertical, Lead-Free, 4 Circuits.
44
Page 45
Table 13. Internal USB 3.0 Header (1.25 mm pitch)
Pin
Signal Name
1
USB_VBUS
2
USB1_N
3
USB1_P
4
GND 5 USBSS1_TX_N
6
USBSS1_TX_P
7
GND 8 USBSS1_RX_N
9
USBSS1_RX_P
10
Host/Device ID Switch
1
Pin
Signal Name
Description
IO Type
1
DCD
Data Carrier Detect
RS-232
2
RXD#
Receive Data
RS-232
3
TXD#
Transmit Data
5V TTL
4
DTR
Data Terminal Ready
5V TTL
5
GND
Ground
Ground
Data Set Ready
RS-232
RTS
Request to Send
5V TTL
1
Wiring requirement for pin 10 (“Host/Device ID Switch) is as follows:
Port Type Pin 10 wired to… Port automatically configured as…
Technical Reference
Type A or internal
USB peripheral
Type B Not connected Device port
Micro B or Micro AB ID pin on attached port Dynamic configuration as host or device port (depending on attached
Ground Host port
peripheral)
Connector is 1x10 1.25mm Pitch PicoBlade* Header, Surface Mount, Vertical, Lead-Free, 10
Circuits.
Table 14. Serial Port Header (1.25 mm pitch)
6 DSR
7
8 CTS
9 RI
Clear to Send RS-232
Ring Indicator RS-232
Connector is 1x9 1.25mm Pitch PicoBlade* Header, Surface Mount, Vertical, Lead-Free, 9 Circuits.
45
Page 46

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Pin
Signal Name
1
5VSTBY
2
GND 3 POWER_SWITCH#
4
HDMI_CEC (Port 1)
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
74
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 70, 4, 2)
75
GND
70
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 70, 4, 2)
71
GND
68
SUSCLK(32kHz) (O)(0/3.3V)
69
PEDET (NC-PCIe/GND-SATA)
66
Connector Key
67
N/C
64
Connector Key
65
Connector Key
62
Connector Key
63
Connector Key
60
Connector Key
61
Connector Key
58
N/C
59
Connector Key
56
N/C
57
GND
54
PEWAKE# (I/O)(0/3.3V) or N/C
55
REFCLKP
52
CLKREQ# (I/O)(0/3.3V) or N/C
53
REFCLKN
48
N/C
49
PETp0/SATA-A+
46
N/C
47
PETn0/SATA-A-
44
N/C
45
GND
42
N/C
43
PERp0/SATA-B-
40
N/C
41
PERn0/SATA-B+
38
DEVSLP (O)
39
GND
36
N/C
37
PETp1
34
N/C
35
PETn1
32
N/C
33
GND
30
N/C
31
PERp1
28
N/C
29
PERn1
26
N/C
27
GND
24
N/C
25
PETp2
22
N/C
23
PETn2
20
N/C
21
GND
18
3.3V
19
PERp2
16
3.3V
17
PERn2
Table 15. HDMI CEC Header (1.25 mm pitch)
Connector is 1x4 1.25mm Pitch PicoBlade* Header, Surface Mount, Vertical, Lead-Free, 4 Circuits.
Table 16. M.2 2280 Module (Mechanical Key M) Connector
72 3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 70, 4, 2) 73 GND
50 PERST# (O)(0/3.3V) or N/C 51 GND
46
Page 47

14 3.3V 15 GND
12
3.3V
13
PETp3
10
DAS/DSS# (I/O)/LED1# (I)(0/3.3V)
11
PETn3
8
N/C 9 GND 6 N/C 7 PERp3
4
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 70, 4, 2)
5
PERn3
2
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 70, 4, 2)
3
GND
1
GND
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
74
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 4, 2)
75
GND
72
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 4, 2)
73
RESERVED/REFCLKN1
70
UIM_POWER_SRC/GPIO1/PEWAKE1#
71
RESERVED/REFCLKP1
66
UIM_SWP/PERST1#
67
RESERVED/PERn1
64
RESERVED
65
RESERVED/PERp1
62
ALERT# (I)(0/3.3)
63
GND
60
I2C CLK (O)(0/3.3)
61
RESERVED/PETn1
58
I2C DATA (I/O)(0/3.3)
59
RESERVED/PETp1
56
W_DISABLE1# (O)(0/3.3V)
57
GND
54
W_DISABLE2# (O)(0/3.3V)
55
PEWAKE0# (I/O)(0/3.3V)
52
PERST0# (O)(0/3.3V)
53
CLKREQ0# (I/O)(0/3.3V)
50
SUSCLK(32kHz) (O)(0/3.3V)
51
GND
48
COEX1 (I/O)(0/1.8V)
49
REFCLKN0
44
COEX3(I/O)(0/1.8V)
45
GND
42
CLink_CLK (I/O)
43
PERn0
40
CLink_DATA (I/O)
41
PERp0
38
C-Link RESET* (I) (0/3.3V)
39
GND
36
UART CTS (I) (0/1.8V)
37
PETn0
34
UART RTS (O) (0/1.8V)
35
PETp0
32
UART RXD (I) (0/1.8V)
33
GPIO_2 (I/O)(0/1.8V*)
30
Connector Key
31
Connector Key
28
Connector Key
29
Connector Key
26
Connector Key
27
Connector Key
24
Connector Key
25
Connector Key
22
UART TXD (O) (0/1.8V)
23
RESERVED
20
UART WAKE# (O) (0/3.3V)
21
RESERVED
18
GND
19
RESERVED
16
ANTCTL0 (I)(0/1.8V)
17
RESERVED
Table 17. M.2 2230 Module (Mechanical Key E) Connector
68 UIM_POWER_SNK/CLKREQ1# 69 GND
Technical Reference
46
COEX2(I/O)(0/1.8V) 47 REFCLKP0
47
Page 48
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
12
ANTCTL2 (I)(0/1.8V)
13
RESERVED
10
ANTCTL3 (I)(0/1.8V)
11
RESERVED
8
RESET# (O)(0/1.8V)
9
RESERVED
6
CONFIG_1
7
GND
4
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 4, 2)
5
USB_D-
2
3.3V (2.75A total for pins 74, 72, 4, 2)
3
USB_D+
1
GND
14
ANTCTL1 (I)(0/1.8V) 15 RESERVED
48
Page 49
Table 18. 40-Pin eDP Connector
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
NC – Reserved
21
LCD_VCC (2.0A total for pins 21, 20, 19, 18)
2
H_GND
22
NC
3
23
4
Lane3_P
24
LCD_GND
5
H_GND
25
LCD_GND
6
Lane2_N
26
LCD_GND
7
Lane2_P
27
HPD 8 H_GND
28
BL_GND
9
Lane1_N
29
BL_GND
10
Lane1_P
30
BL_GND
11
H_GND
31
BL_GND
12
Lane0_N
32
BL_ENABLE
13
Lane0_P
33
BL_PWM_DIM
14
34
15
AUX_CH_P
35
NC - RESERVED
16
AUX_CH_N
36
BL_PWR (0.6A total for pins 39, 38, 37, 36)
17
H_GND
37
BL_PWR (0.6A total for pins 39, 38, 37, 36)
18
LCD_VCC (2.0A total for pins 21, 20, 19, 18)
38
BL_PWR (0.6A total for pins 39, 38, 37, 36)
19
LCD_VCC (2.0A total for pins 21, 20, 19, 18)
39
BL_PWR (0.6A total for pins 39, 38, 37, 36)
20
LCD_VCC (2.0A total for pins 21, 20, 19, 18)
40
NC - RESERVED
Pin
Signal Name
Description
Pin
Signal Name
Description
1
HDD_POWER_LED
Pull-up 750 Ω to +5V
2
POWER_LED_MAIN
[Out] Front panel LED (main
3
HDD_LED#
[Out] HDD activity LED
4
POWER_LED_ALT
[Out] Front panel LED (alt
5
GROUND
Ground
6
POWER_SWITCH#
[In] Power switch
7
RESET_SWITCH#
[In] Reset switch
8
GROUND
Ground
9
+5V_DC (1A) (Vcc)
VCC5 (1A current rating)
10
Key
No pin
Technical Reference
Lane3_N
H_GND
LCD_GND
NC - RESERVED
Connector used is right-angled I-PEX-20455-040E-12, 1x40 eDP connector.
2.2.4.2 Add-in Card Connectors
The board supports M.2 2230 (key type E) (WLAN) and 2280 (key type M) (SSD) Modules.
• M.2 2230 (key type E) (WLAN): Supports PCIe x1, USB 2.0
• M.2 2280 (key type M) (SSD): Supports PCIe x4 and SATA
2.2.4.3 Front Panel Header (2.0 mm Pitch)
This section describes the functions of the front panel header. Table 19 lists the signal names of
the front panel header. Figure 9 is a connection diagram for the front panel header.
Table 19. Front Panel Header (2.0 mm Pitch)
color)
color)
49
Page 50

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
11
5Vsby (2A)
5VSB (2A current rating)
12
3.3Vsby (1A)
3VSB (1A current rating)
LED State
Description
Off
Power off
Blinking
Standby
Steady
Normal operation
Figure 13. Connection Diagram for Front Panel Header (2.0 mm Pitch)
2.2.4.3.1 Hard Drive Activity LED Header
Pins 1 and 3 can be connected to an LED to provide a visual indicator that data is being read from
or written to a hard drive. Proper LED function requires a SATA hard drive or optical drive
connected to an onboard SATA connector.
2.2.4.3.2 Reset Switch Header
Pins 5 and 7 can be connected to a momentary single pole, single throw (SPST) type switch that is
normally open. When the switch is closed, the board resets and runs the POST.
2.2.4.3.3 Power/Sleep LED Header
Pins 2 and 4 can be connected to a one- or two-color LED. Table 20 and Table 21 show the
possible LED states.
Table 20. States for a One-Color Power LED
50
Page 51

Technical Reference
LED State
Description
Off
Power off
Blinking (white)
Standby
Pins
Signal Name
3, 4
Ground
Table 21. States for a Dual-Color Power LED
Steady (white) Normal operation
NOTE
The LED behavior shown in Table 20 is default – other patterns may be set via BIOS setup.
2.2.4.3.4 Power Switch Header
Pins 6 and 8 can be connected to a front panel momentary-contact power switch. The switch
must pull the SW_ON# pin to ground for at least 50 ms to signal the power supply to switch on or
off (the time requirement is due to internal debounce circuitry on the board). At least two seconds
must pass before the power supply will recognize another on/off signal.
2.2.4.4 Power Supply Connectors
The board has the following power supply connectors:
• External Power Supply – the board can be powered through a 12-24 V DC connector on the
back panel. The back panel DC connector is compatible with a 5.5 mm/OD (outer diameter)
and 2.5 mm/ID (inner diameter) plug, where the inner contact is +12-24 (±10%) V DC and the
shell is GND. The maximum current rating is 10 A.
NOTE
• Internal Power Supply – the board can alternatively be powered via the internal 12-24 V DC
Table 22. 12-24 V Internal Power Supply Connector
1, 2 +12-24 V (±10%)
External power voltage, 12-24 V DC, is dependent on the type of power brick used.
2 x 2 power connector, where pins 1 and 2 are +12-24 (±10%) V DC and pins 3 and 4 are
GND. The maximum current rating is 10 A.
The connector used is Molex Micro-Fit (3mm pitch), right-angled, 4-pos/dual row (2x2).
51
Page 52

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
For information about
Refer to
Figure 14. Connection Diagram for the Internal Power Supply Connector
2.2.4.4.1 Power Sensing Circuit
The board has a power sensing circuit that:
• manages CPU power usage to maintain system power consumption below 65 W
• is designed and tested for use with the provided 65 W AC-DC adapters
NOTE
It is recommended that you disable this feature (via BIOS option) when using an AC-DC
Power supply considerations Section 2.6.1, page 59
adapter greater than 65 W.
52
Page 53
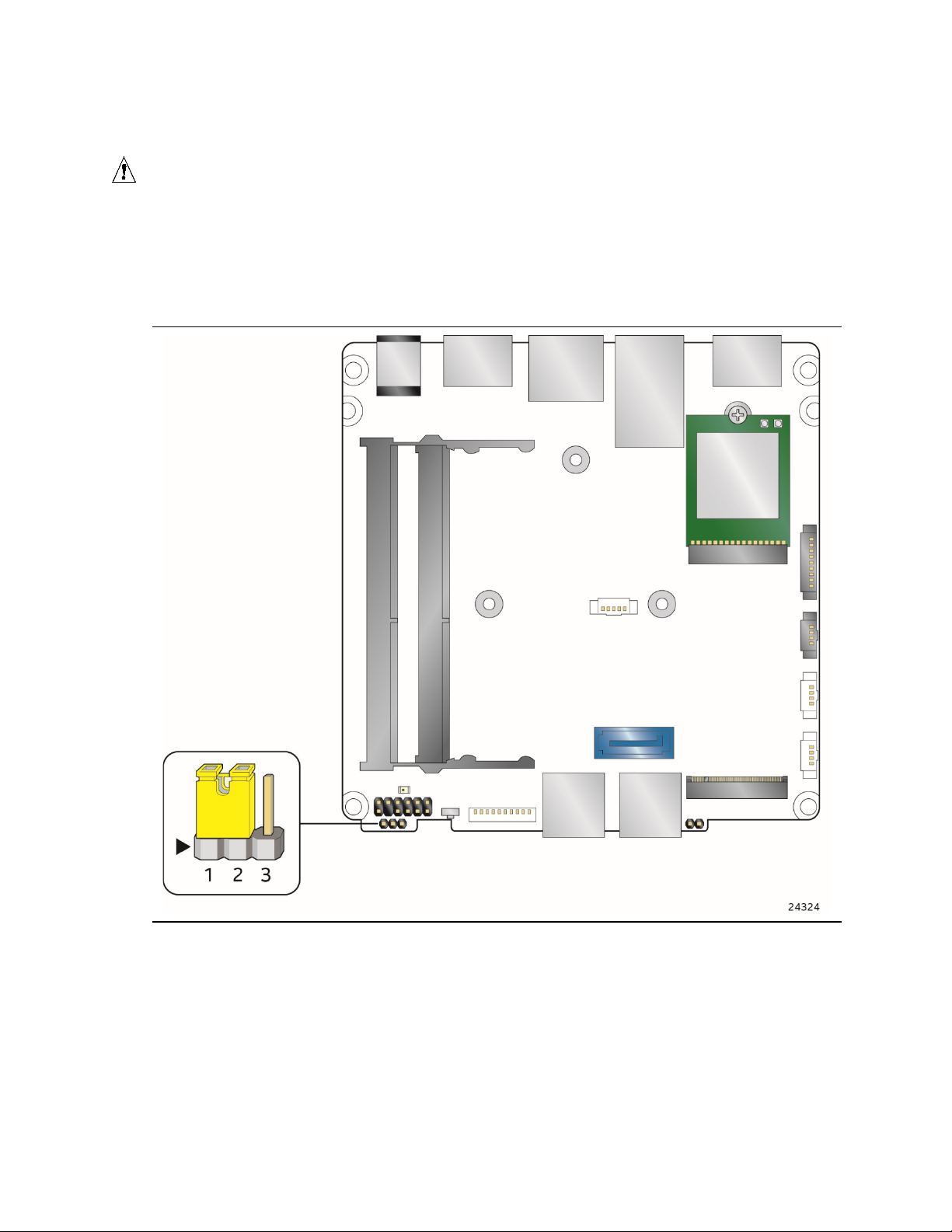
Technical Reference
2.3 BIOS Security Jumper
CAUTION
Do not move a jumper with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug the power cord
from the computer before changing a jumper setting. Otherwise, the board could be damaged.
Figure 15 shows the location of the BIOS Security Jumper. The 3-pin jumper determines the BIOS
Security program’s mode.
Figure 15. Location of the BIOS Security Jumper
Table 23 describes the jumper settings for the three modes: normal, lockdown, and configuration.
53
Page 54

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Function/Mode
Jumper Setting
Configuration
Normal
1-2
The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords for
Lockdown
2-3
The BIOS uses current configuration information and passwords for
Table 23. BIOS Security Jumper Settings
booting.
booting, except:
• All POST Hotkeys are suppressed (prompts are not displayed and keys
are not accepted. For example, F2 for Setup, F10 for the Boot Menu).
• Power Button Menu is not available (see Section 3.6.4 Power Button
Menu).
BIOS updates are not available except for automatic Recovery due to
flash corruption.
Configuration None BIOS Recovery Update process if a matching *.bio file is found. Recovery
Update can be cancelled by pressing the Esc key.
If the Recovery Update was cancelled or a matching *.bio file was not
found, a Config Menu will be displayed. The Config Menu consists of the
following (followed by the Power Button Menu selections):
[1] Suppress this menu until the BIOS Security Jumper is replaced.
[2] Clear BIOS User and Supervisor Passwords.
[3] Reset Intel® AMT to default factory settings.
[4] Clear Trusted Platform Module.
Warning: Data encrypted with the TPM will no longer be accessible
if the TPM is cleared.
[F2] Intel® Visual BIOS.
[F4] BIOS Recovery.
See Section 3.6.4 Power Button Menu.
54
Page 55

Technical Reference
2.4 Intel® Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel®
MEBX) Reset Header
The Intel® MEBX reset header (see Figure 16) allows you to reset the Intel ME configuration to the
factory defaults. Momentarily shorting pins 1 and 2 with a jumper (not supplied) will accomplish
the following:
• Return all Intel ME parameters to their default values.
• Reset the Intel MEBX password to the default value (admin).
• Unconfigure Intel AMT.
CAUTION
Always turn off the power and unplug the power cord from the computer before installing an
MEBX reset jumper. The jumper must be removed before reapplying power. The system must be
allowed to reach end of POST before reset is complete. Otherwise, the board could be damaged.
NOTE
After using the MEBX Reset, a “CMOS battery failure” warning will occur during the next POST.
This is expected and does not indicate a component failure.
NOTE
The MEBX_RESET header has a non-conductive protective cap installed. This must be removed
before installing the MEBX_RESET jumper, and reinstalled before reassembling the system. Failure
to do so may result in inadvertent shorting of the bottom cover screw to the header during bottom
cover reassembly (see Figure 16).
55
Page 56
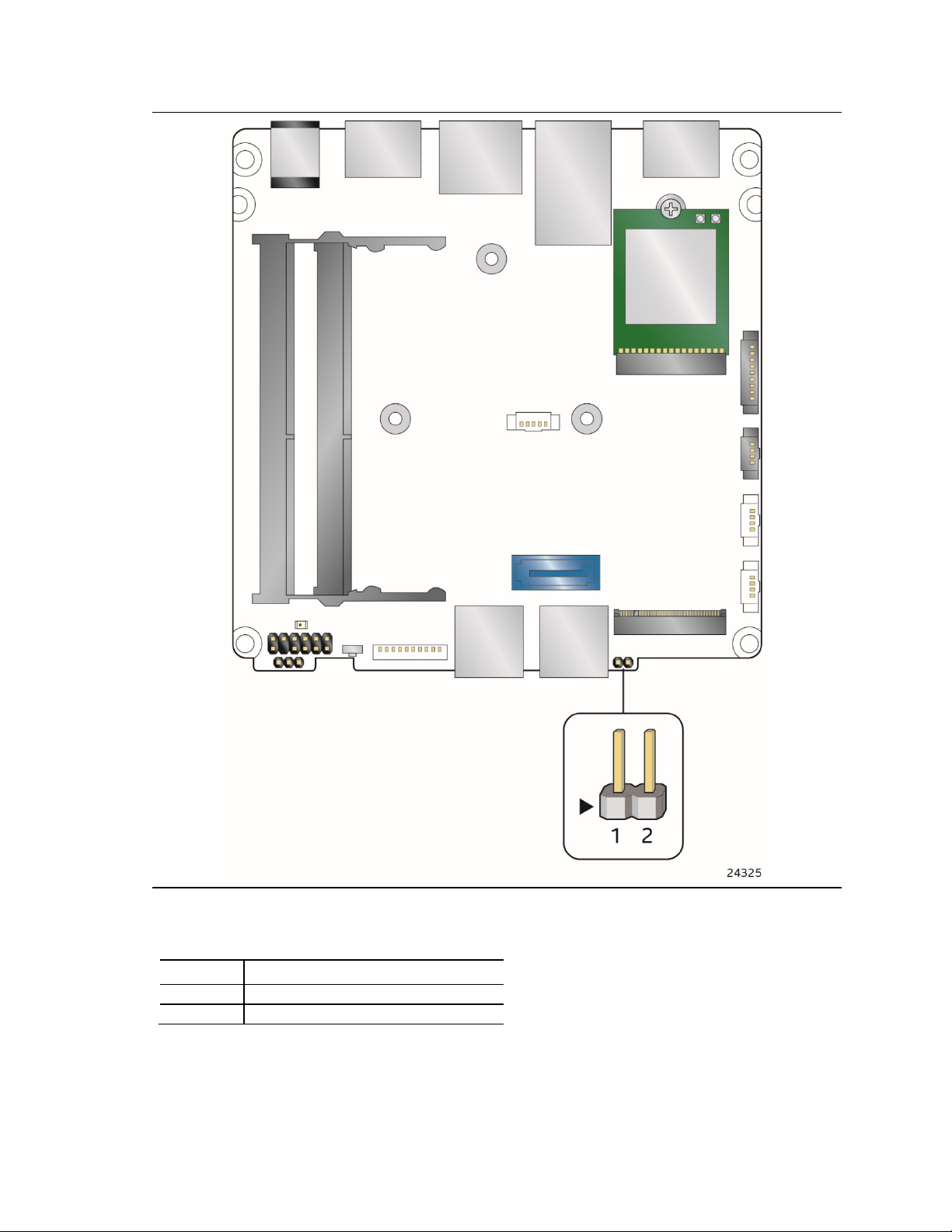
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Pin
Function
1
RTCRST
2
Ground
Figure 16. Intel MEBX Reset Header
Table 24. Intel MEBX Reset Header Signals
56
Page 57

Technical Reference
2.5 Mechanical Considerations
2.5.1 Form Factor
The board is designed to fit into a custom chassis. Figure 17 illustrates the mechanical form factor
for the board. Dimensions are given in inches [millimeters]. The outer dimensions are 4.0 inches
by 4.0 inches [101.60 millimeters by 101.60 millimeters].
Figure 17. Board Dimensions
57
Page 58

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Figure 18 shows the height dimensions of the board. Dimensions are in mm.
Figure 18. Board Height Dimensions
58
Page 59

Technical Reference
2.6 Electrical Considerations
2.6.1 Power Supply Considerations
System power requirements will depend on actual system configurations chosen by the
integrator, as well as end user expansion preferences. It is the system integrator’s responsibility to
ensure an appropriate power budget for the system configuration is properly assessed based on
the system-level components chosen. See Section 2.2.4.4 Power Supply Connector for more
information.
• The back panel input range is 12-24 V DC
• The internal power connector input range is 12-24 V DC
CAUTION
The external DC jack is the primary power input connector of Intel NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE.
However, the board also provides an internal 2 x 2 power connector that can be used in customdeveloped systems that have an internal power supply. The internal 2 x 2 power connector is a
Molex Micro-Fit (3mm pitch), right-angled, 4-pos/dual row connector.
There is no isolation circuitry between the external DC jack and the internal 2 x 2 power connector.
It is the system integrator’s responsibility to ensure no more than one power supply unit is or can
be attached to the board at any time and to ensure the external DC jack is covered if the internal 2
x 2 power connector is to be used. Simultaneous connection of both external and internal power
supply units could result in potential damage to the board, power supplies, or other hardware.
Table 25. Power Budget for Assessing the DC-to-DC Circuit’s Power Rating (worst case:
Embedded board in 3
rd
NUC7i7DNBE (3
CPU KBL-U 15 W SoC 15
Chipset 2.38
2 x DDR4 SODIMM 7.99
WLAN 0.40
2 x USB 2.0 (Internal) 2.78
USB 3.0 (Internal) 2.50
4 x USB 3.0 20
2 x HDMI 2.0 0.06
M.2 2280 Module 3.03
SATA HDD 2.5” 4.43
LAN 0.07
Front Panel 0.56
HDMI CEC 0.11
party chassis)
rd
party chassis)
Estimated Adapter Power
Consumption (W)
59
Page 60
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Fan Header
Maximum Available Current
Processor fan
.6 A
2.6.2 Fan Header Current Capability
Table 35 lists the current capability of the fan headers.
Table 26. Fan Header Current Capability
60
Page 61

Technical Reference
2.7 Thermal Considerations
CAUTION
Failure to ensure appropriate airflow may result in reduced performance of both the processor
and/or voltage regulator or, in some instances, damage to the board.
All responsibility for determining the adequacy of any thermal or system design remains solely
with the system integrator. Intel makes no warranties or representations that merely following the
instructions presented in this document will result in a system with adequate thermal
performance.
CAUTION
Ensure that the ambient temperature does not exceed the board’s maximum operating
temperature. Failure to do so could cause components to exceed their maximum case temperature
and malfunction. For information about the maximum operating temperature, see the
environmental specifications in Section 0.
CAUTION
Ensure that proper airflow is maintained in the processor voltage regulator circuit. Failure to do
so may result in shorter than expected product lifetime.
61
Page 62

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Item
Description
A
Thermal Solution
Figure 19 shows the locations of the localized high temperature zones.
62
B Processor Voltage Regulator Area
Figure 19. Localized High Temperature Zones
Page 63

Technical Reference
B
Thermal Pad Installation Area
A thermal pad has been installed for the bottom of the chassis to improve the thermal
performance when using M.2 devices that operate at higher temperatures. If the thermal pad ever
needs to be replaced, Figure 24 shows the installation area of the thermal pad.
Item Description
A Thermal Pad
Figure 20. Installation Area of the Thermal Pad
63
Page 64
Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Component
Maximum Case Temperature
Processor
For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and processor
Component
Tcontrol
For information about
Refer to
Processor datasheets and specification updates
Section 1.4, page 17
Table 27 provides maximum case temperatures for the components that are sensitive to thermal
changes. The operating temperature, current load, or operating frequency could affect case
temperatures. Maximum case temperatures are important when considering proper airflow to
cool the board.
Table 27. Thermal Considerations for Components
specification updates
To ensure functionality and reliability, the component is specified for proper operation when
Case Temperature is maintained at or below the maximum temperature listed in Table 28. This is
a requirement for sustained power dissipation equal to Thermal Design Power (TDP is specified
as the maximum sustainable power to be dissipated by the components). When the component is
dissipating less than TDP, the case temperature should be below the Maximum Case
Temperature. The surface temperature at the geometric center of the component corresponds to
Case Temperature.
It is important to note that the temperature measurement in the system BIOS is a value reported
by embedded thermal sensors in the components and does not directly correspond to the
Maximum Case Temperature. The upper operating limit when monitoring this thermal sensor is
Tcontrol.
Table 28. Tcontrol Values for Components
Processor For processor case temperature, see processor datasheets and processor
specification updates
64
Page 65

Technical Reference
Parameter
Specification
Sustained Storage
Limits (i.e. warehouse)
-20 °C to +40 °C
Short Duration Limits
(i.e. shipping)
-40 °C to +60 °C
Ambient Operating –
0 °C to +40 °C
Ambient Operating –
0 °C to +50 °C
* Processor performance may automatically decrease when the system operates in the top
5 °C of the ambient operating temperature ranges above.
Unpackaged
50 g trapezoidal waveform
Velocity change of 170 inches/s²
Packaged
Product Weight (pounds)
Non-palletized Product
Palletized drop heights (single
<20
36
N/A
41-80
24
N/A 81-100
18
12
>120
9 9
Vibration Unpackaged
5 Hz to 20 Hz: 0.01 g² Hz sloping up to 0.02 g² Hz
Packaged
5 Hz to 40 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz (flat)
40 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.015 g² Hz sloping down to 0.00015 g² Hz
2.8 Reliability
The demonstrated Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is done through 24/7 testing. Full Intel®
NUC systems in chassis with memory, SSD or HDD, and a fan are ran at 100% on time for 90 days
continuously while running system wide stress inducing software in a 40 °C ambient air
temperature chamber. The demonstrated MTBF for Intel NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE is 50,000
hours.
2.9 Environmental
Table 29 lists the environmental specifications for the board.
Table 29. Environmental Specifications
Temperature
NUC Kit*
NUC Board*
Shock
21-40 30 N/A
100-120 12 9
20 Hz to 500 Hz: 0.02 g² Hz (flat)
drop height (inches)
product) (inches)
Note: The operating temperature of the board may be determined by measuring the air temperature from the junction of
the heatsink fins and fan, next to the attachment screw, in a closed chassis, while the system is in operation.
65
Page 66

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Note: Before attempting to operate this board, the overall temperature of the board must be above the minimum
operating temperature specified. It is recommended that the board temperature be at least room temperature
before attempting to power on the board. The operating and non-operating environment must avoid condensing
humidity.
CAUTION
If the external ambient temperature exceeds 40 oC, further thermal testing is required to ensure
components do not exceed their maximum operating temperature.
66
Page 67

3 Overview of BIOS Features
3.1 Introduction
The board uses Intel Visual BIOS that is stored in the Serial Peripheral Interface Flash Memory
(SPI Flash) and can be updated using a disk-based program. The SPI Flash contains the Visual
BIOS Setup program, POST, the PCI auto-configuration utility, LAN EEPROM information, and
Plug and Play support.
The BIOS displays a message during POST identifying the type of BIOS and a revision code.
The Visual BIOS Setup program can be used to view and change the BIOS settings for the
computer. The BIOS Setup program is accessed by pressing the <F2> key after the Power-On
Self-Test (POST) memory test begins and before the operating system boot begins.
NOTE
The maintenance menu is displayed only when the board is in configure mode. Section 2.3 on
page 53 shows how to put the board in configure mode.
3.2 BIOS Flash Memory Organization
The Serial Peripheral Interface Flash Memory (SPI Flash) includes a 16 MB flash memory device.
3.3 System Management BIOS (SMBIOS)
SMBIOS is a Desktop Management Interface (DMI) compliant method for managing computers in
a managed network.
The main component of SMBIOS is the Management Information Format (MIF) database, which
contains information about the computing system and its components. Using SMBIOS, a system
administrator can obtain the system types, capabilities, operational status, and installation dates
for system components. The MIF database defines the data and provides the method for
accessing this information. The BIOS enables applications such as third-party management
software to use SMBIOS. The BIOS stores and reports the following SMBIOS information:
• BIOS data, such as the BIOS revision level
• Fixed-system data, such as peripherals, serial numbers, and asset tags
• Resource data, such as memory size, cache size, and processor speed
• Dynamic data, such as event detection and error logging
Non-Plug and Play operating systems require an additional interface for obtaining the SMBIOS
information. The BIOS supports an SMBIOS table interface for such operating systems. Using this
support, an SMBIOS service-level application running on a non-Plug and Play operating system
can obtain the SMBIOS information. Additional board information can be found in the BIOS under
the Additional Information header under the Main BIOS page.
Page 68

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
3.4 Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB support enables USB devices to be used even when the operating system’s USB
drivers are not yet available. Legacy USB support is used to access the BIOS Setup program, and
to install an operating system that supports USB. By default, Legacy USB support is set to
Enabled.
Legacy USB support operates as follows:
1. When you apply power to the computer, legacy support is disabled.
2. POST begins.
3. Legacy USB support is enabled by the BIOS allowing you to use a USB keyboard to enter and
configure the BIOS Setup program and the maintenance menu.
4. POST completes.
5. The operating system loads. While the operating system is loading, USB keyboards and mice
are recognized and may be used to configure the operating system. (Keyboards and mice are
not recognized during this period if Legacy USB support was set to Disabled in the BIOS
Setup program.)
6. After the operating system loads the USB drivers, all legacy and non-legacy USB devices are
recognized by the operating system, and Legacy USB support from the BIOS is no longer
used.
To install an operating system that supports USB, verify that Legacy USB support in the BIOS
Setup program is set to Enabled and follow the operating system’s installation instructions.
3.5 BIOS Updates
The BIOS can be updated using one of the following methods:
• Intel® Express BIOS Update utility, which enables automated updating while in the Windows
environment. Using this utility, the BIOS can be updated from a file on a hard disk, a USB
drive, a CD-ROM, or from the file location on the Web.
• Intel® Flash Memory Update Utility, which requires booting from DOS. In order to boot from
DOS the legacy boot option in the BIOS has to be checked. Using this utility, the BIOS can be
updated from a file on a hard disk or a USB drive.
• Intel®
• Intel® Visual BIOS has an option to update the BIOS from a valid .bio file located on a hard
Both utilities verify that the updated BIOS matches the target system to prevent accidentally
installing an incompatible BIOS.
F7 switch during POST allows a user to select where the BIOS .bio file is located and
perform the update from that location/device. Similar to performing a BIOS Recovery without
removing the BIOS configuration jumper. The F7 switch supports FAT, FAT32, and NTFS
format storage.
disk or USB drive. Enter Intel Visual BIOS by pressing <F2> during POST.
NOTE
Review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before attempting a BIOS update.
68
Page 69
Overview of BIOS Features
For information about
Refer to
BIOS update utilities
http://support.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/CS-
Media Type
(Note)
Can be used for BIOS recovery?
USB flash drive
Yes
For information about
Refer to
034499.htm
3.5.1 Language Support
The BIOS Setup program and help messages are supported in US English. Check the Intel web
site for support.
3.5.2 BIOS Recovery
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt a BIOS update; however, if an interruption occurs, the
BIOS could be damaged. Table 30 lists the drives and media types that can and cannot be used
for BIOS recovery. The BIOS recovery media does not need to be made bootable.
Table 30. Acceptable Drives/Media Types for BIOS Recovery
Hard disk drive (connected to SATA or USB) Yes
NOTE
Supported file systems for BIOS recovery:
• NTFS (sparse, compressed, or encrypted files are not supported)
• FAT32
• FAT16
• FAT12
• ISO 9660
BIOS recovery http://www.intel.com/support/motherboards/desktop/sb/cs-034524.htm
69
Page 70

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Boot Device Menu Function Keys
Description
<↑> or <↓>
Selects a default boot device
<Enter>
Exits the menu, and boots from the selected device
<Esc>
Exits the menu and boots according to the boot priority defined
3.6 Boot Options
In the BIOS Setup program, the user can choose to boot from a hard drive, optical drive,
removable drive, or the network. The default setting is for the optical drive to be the first boot
device, the hard drive second, removable drive third, and the network fourth.
NOTE
Optical drives are not supported by the onboard SATA connectors. Optical drives are supported
only via the USB interfaces.
3.6.1 Network Boot
The network can be selected as a boot device. This selection allows booting from the onboard
LAN or a network add-in card with a remote boot ROM installed.
Pressing the <F12> key during POST automatically forces booting from the LAN. To use this key
during POST, the User Access Level in the BIOS Setup program's Security menu must be set to
Full.
3.6.2 Booting Without Attached Devices
For use in embedded applications, the BIOS has been designed so that after passing the POST,
the operating system loader is invoked even if the following devices are not present:
• Video adapter
• Keyboard
• Mouse
3.6.3 Changing the Default Boot Device during POST
Pressing the <F10> key during POST causes a boot device menu to be displayed. This menu
displays the list of available boot devices. Table 31 lists the boot device menu options.
Table 31. Boot Device Menu Options
through BIOS setup
3.6.4 Power Button Menu
As an alternative to Back-to-BIOS Mode or normal POST Hotkeys, the user can use the power
button to access a menu. The Power Button Menu is accessible via the following sequence:
1. System is in S4/S5 (not G3)
2. User pushes the power button and holds it down for 3 seconds
70
Page 71

Overview of BIOS Features
3. The system will emit three short beeps from the front panel (FP) audio port, then stop to
signal the user to release the power button. The FP power button LED will also change from
Blue to Amber when the user can release the power button.
4. User releases the power button before the 4-second shutdown override
If this boot path is taken, the BIOS will use default settings, ignoring settings in VPD where
possible.
At the point where Setup Entry/Boot would be in the normal boot path, the BIOS will display the
following prompt and wait for a keystroke:
[ESC] Normal Boot
[F2] Intel Visual BIOS
[F3] Disable Fast Boot
[F4] BIOS Recovery
[F7] Update BIOS
[F10] Enter Boot Menu
[F12] Network Boot
[F2] Enter Setup is displayed instead if Visual BIOS is not supported.
[F3] Disable Fast Boot is only displayed if at least one Fast Boot optimization is enabled.
[F9] Remote Assistance is only displayed if Remote Assistance is supported.
If an unrecognized key is hit, then the BIOS will beep and wait for another keystroke. If one of the
listed hotkeys is hit, the BIOS will follow the indicated boot path. Password requirements must
still be honored.
If Disable Fast Boot is selected, the BIOS will disable all Fast Boot optimizations and reset the
system.
71
Page 72

Intel NUC Board/Kit NUC7i7DN Technical Product Specification
Password Set
Password During Boot
Neither
None
Master only
None
User only
User only
Master and User Set
Master or User
3.7 Hard Disk Drive Password Security Feature
The Hard Disk Drive Password Security feature blocks read and write accesses to the hard disk
drive until the correct password is given. Hard Disk Drive Passwords are set in BIOS SETUP and
are prompted for during BIOS POST. For convenient support of S3 resume, the system BIOS will
automatically unlock drives on resume from S3. Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9.
Passwords may be up to 19 characters in length.
The User hard disk drive password, when installed, will be required upon each power-cycle until
the Master Key or User hard disk drive password is submitted.
The Master Key hard disk drive password, when installed, will not lock the drive. The Master Key
hard disk drive password exists as an unlock override in the event that the User hard disk drive
password is forgotten. Only the installation of the User hard disk drive password will cause a hard
disk to be locked upon a system power-cycle.
Table 32 shows the effects of setting the Hard Disk Drive Passwords.
Table 32. Master Key and User Hard Drive Password Functions
During every POST, if a User hard disk drive password is set, POST execution will pause with the
following prompt to force the user to enter the Master Key or User hard disk drive password:
“Enter Hard Disk Drive Password:”
Upon successful entry of the Master Key or User hard disk drive password, the system will
continue with normal POST.
If the hard disk drive password is not correctly entered, the system will go back to the above
prompt. The user will have three attempts to correctly enter the hard disk drive password. After
the third unsuccessful hard disk drive password attempt, the system will halt with the message:
“Hard Disk Drive Password Entry Error”
A manual power cycle will be required to resume system operation.
NOTE
As implemented on Intel NUC Board NUC7i7DNBE, Hard Disk Drive Password Security is only
supported on either SATA Port 0 (M.2) or SATA Port 1 (onboard SATA connector). The passwords
are stored on the hard disk drive so if the drive is relocated to another computer that does not
support Hard Disk Drive Password Security feature, the drive will not be accessible.
3.8 BIOS Security Features
72
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program and who can
boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be set for the BIOS Setup
program and for booting the computer, with the following restrictions:
Page 73

Overview of BIOS Features
Supervisor
Password to
Password
Neither
Can change all
Can change all
None
None
None
Supervisor only
Can change all
Can change a
Supervisor Password
Supervisor
None
User only
N/A
Can change all
Enter Password
User
User
Supervisor and
Can change all
Can change a
Supervisor Password
Supervisor or
Supervisor or
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the Setup options
in the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
• The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options in the BIOS
Setup program. This is the user mode.
• If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password prompt of
the BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the supervisor
password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to Setup respective to
which password is entered.
• Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password prompt will be
displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor password is set, the
computer boots without asking for a password. If both passwords are set, the user can enter
either password to boot the computer.
• For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user passwords.
• Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9. Passwords may be up to 16 characters in
length.
• To clear a set password, enter a blank password after entering the existing password.
Table 33 shows the effects of setting the supervisor password and user password. This table is for
reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
Table 33. Supervisor and User Password Functions
Password Set
user set
Note: If no password is set, any user can change all Setup options.
Mode
options
options
options
(Note)
User Mode Setup Options
options
limited number
of options
options
limited number
of options
(Note)
Clear User Password
Enter Password
Enter Setup
user
During Boot
user
73
Page 74

Page 75

(Note)
On-off (1.0 second each) two times, then 2.5-second
When no VGA option ROM is
Memory error
On-off (1.0 second each) three times, then 2.5-second
Error Message
Explanation
CMOS Battery Low
The battery may be losing power. Replace the battery soon.
CMOS Checksum Bad
The CMOS checksum is incorrect. CMOS memory may have been
Memory Size Decreased
Memory size has decreased since the last boot. If no memory was
4 Error Messages and Blink Codes
4.1 Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes
Whenever a recoverable error occurs during POST, the BIOS causes the board’s front panel
power LED to blink an error message describing the problem (see Table 34).
Table 34. Front-panel Power LED Blink Codes
Type Pattern Note
BIOS update in progress Off when the update begins, then on for 0.5 seconds,
then off for 0.5 seconds. The pattern repeats until the
BIOS update is complete.
Video error
Thermal trip warning Each beep will be accompanied by the following blink
Note: Disabled per default BIOS setup option.
pause (off), entire pattern repeats (blink and pause)
until the system is powered off.
pause (off), entire pattern repeats (blinks and pause)
until the system is powered off.
pattern: .25 seconds on, .25 seconds off,
.25 seconds on, .25 seconds off. This will result in a
total of 16 blinks.
found.
4.2 BIOS Error Messages
Table 35 lists the error messages and provides a brief description of each.
Table 35. BIOS Error Messages
corrupted. Run Setup to reset values.
removed, then memory may be bad.
No Boot Device Available System did not find a device to boot.
 Loading...
Loading...