Page 1

Intel® Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium Desktop Processor 6000 Series
Specification Update
January 2011
Reference Number: 322911-013
Page 2

Legal Lines and Disclaimers
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY
ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PRO PERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN
INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEV ER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES
RELATING T O FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical, life saving, life sust aining, critical control or safety systems, or
in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “un defined.” Intel reserves these for
future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The processor may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current
characterized errata are available on request. Contact your local I ntel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before
placing your product order.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiat e features within each processor family, not across
different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number for details. Over time processor numbers will increment based on
changes in clock, speed, cache, or other features, an d increment s are not inte nded to r epresent pro portional or quantit ative increases in a ny particular
feature. Current roadmap processor number progression is not necessarily representative of future roadmaps. See www.intel.com/products/
processor_number for details.
®
Active Management Technology requires the computer system to have an Intel(R) AMT-enabled chipset, network hardware and software, as
Intel
well as connection with a power source and a corporate network connection . Setu p req uires configu rat ion b y the purchaser and may require scripting
with the management console or further integration into existing security frameworks to enable certain functionality . I t may also require modifications
of implementation of new business processes. With regard to notebooks, Intel AMT may not be available or certain capabilities may be limited over a
host OS-based VPN or when connecting wirelessly, on battery power, sleeping, hibernating or powered off. For more information, see www.intel.com/
technology/platform-technology/intel-amt/
®
Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) requires a computer system with Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® Virtualization Technology
Intel
®
VT-x) and Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d)), a Intel TXT-enabled processor, chipset, BIOS, Authenticated Code
(Intel
Modules and an Intel TXT-compatible measured launched environment (MLE). The MLE could consist of a virtual machine monitor, an OS or an
application. In addition, Intel TXT requires the system to contain a TPM v1.2, as defined by the Trusted Computing Group and specific software for
some uses. For more information, see http://www.intel.com/technology/security
®
Intel
Virtualization Technology requires a computer system with an enabled Intel® processor, BIOS, virtual machine monitor (VMM) and, for some
uses, certain computer system software enabled for it. Functionality, performance or other benefits will vary depending on hardware and software
configurations and may require a BIOS update. Software applications may not be compatible with all operating systems. Please check with your
application vendor.
®
* Intel
Turbo Boost Technology requires a PC with a processor with Intel Turbo Boost Technology capability. Intel Turbo Boost Technology
performance varies depending on hardware, software and overall system configuration. Check with your PC manufacturer on whether your system
delivers Intel Turbo Boost Technology. For more information, see http://www.intel.com/technology/turboboost
®
Intel
Hyper-threading Technology requires a computer system with a processor supporting HT Technology and an HT Technology-enabled chipset,
BIOS, and operating system. Performance will vary depending on the specific hardware and software you use. For more information including details
on which processors support HT Technology, see http://www.intel.com/info/hyperthreading.
64-bit computing on Intel architecture requires a computer system with a processor, chipset, BIOS, operating system, device drivers and applications
enabled for Intel
®
64 architecture. Performance will vary depending on your hardware and software confi gurations. Consult with your system vendor
for more information.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literatur e may be obt ained by cal ling 1-8 00-548-
4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com.
Intel, Intel Core, Celeron, Pentium, Intel Xeon, Intel Atom, Intel SpeedStep, and the Intel logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel
Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2010-2011, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
2
Specification Update
Page 3

Contents
Contents
Revision History...............................................................................................................5
Preface ..............................................................................................................................6
Summary Tables of Changes..........................................................................................8
Identification Information..............................................................................................14
Errata...............................................................................................................................17
Specification Changes...................................................................................................49
Specification Clarifications...........................................................................................50
Documentation Changes...............................................................................................51
§
Specification Update
3
Page 4

Contents
4
Specification Update
Page 5
Revision History
Revision Description Date
-001 Initial Release January 2010
-002
-003
-004 Added Errataum AAU92. April 2010
-005
-006 Added Errata AAU93 - AAU97 April 2010
-007
-008 Added Errata AAU98-AAU102 July 2010
-009
-010
-011 Added Errata AAU103-AAU105 September 2010
-012
-013
Added Errata AAU85-AAU87.
Corrected Extended Model and Model Number register values in Component Identification
table.
Added Errata AAU88-AAU91.
Added Documentation Changes AAU1-AAU3.
Updated Processor Identification table to include the SKU information for the Intel® Core™
i5-680 processor.
Added processor K-0 stepping information.
Updated Processor Identification table to include the SKU information for the Intel® Core™
i5-655K and i3-550 processor.
Erratum AAU32 added to this product Specification Update in error, all erratum details
removed from the specification update doc ument.
Updated Processor Identification table to include the SKU information for the Intel® Core™
i3-560 processor.
Added Errata AAU106 - AAU108
Updated problem statement for erratum AAU36
Changed document title to reflect introduction of G6960 processor
Added Errata AAU109-AAU110
Erratum AAU98 added to this specification Update in error; all erratum
details removed from the specification update document.
February 2010
March 2010
April 2010
June 2010
August 2010
August 2010
November 2010
January 2011
Specification Update
5
Page 6
Preface
This document is an update to the specifications contained in the Affected Documents
table below. This document is a compilation of device and documentation errata,
specification clarifications and changes. It is intended for hardware system
manufacturers and software developers of applications, operating systems, or tools.
Information types defined in Nomenclature are consolidated into the specification
update and are no longer published in other documents.
This document may also contain information that was not previously published.
Affected Documents
®
Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium® Desktop
Intel
Processor 6000 Series Datasheet, Volume 1
®
Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium® Processor
Intel
G6950 Datasheet, Volume 2
Related Documents
AP-485, Intel® Processor Identification and the CPUID Instruction http://www.intel.com/
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Volume 1: Basic Architecture
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2A: Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 2B: Instruction Se t Reference Manual N-Z
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3A: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual,
Intel
Volume 3B: System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Intel Architecture Optimization Reference
Intel
Manual
®
Intel
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual
Documentation Changes
ACPI Specifications www.acpi.info
Document Title
Document Title
Document
Number
322909-006
322910-002
Document Number/
Location
design/processor/
applnots/241618.htm
http://www.intel.com/
products/processor/
manuals/index.htm
http://www.intel.com/
design/processor/
specupdt/252046.htm
6
Specification Update
Page 7

Nomenclature
Errata are design defects or errors. These may cause the processor behavior to
deviate from published specifications. Hardware and software designed to be used with
any given stepping must assume that all errata documented for that stepping are
present on all devices.
S-Spec Number is a five-digit code used to identify products. Products are
differentiated by their unique characteristics such as, core speed, L2 cache size,
package type, etc. as described in the processor identification information table. Read
all notes associated with each S-Spec number.
Specification Changes are modifications to the current published specifications.
These changes will be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Specification Clarifications describe a specification in greater detail or further
highlight a specification’s impact to a complex design situation. These clarifications will
be incorporated in any new release of the specification.
Documentation Changes include typos, errors, or omissions from the current
published specifications. These will be incorporated in any new release of the
specification.
Note: Errata remain in the specification update throughout the product’s lifecycle, or until a
particular stepping is no longer commercially available. Under these circumstances,
errata removed from the specification update are archived and available upon request.
Specification changes, specification clarifications and documentation changes are
removed from the specification update when the appropriate changes are made to the
appropriate product specification or user documentation (datasheets, manuals, etc.).
Specification Update
7
Page 8

Summary Tables of Changes
The following tables indicate the errata, specification changes, specification
clarifications, or documentation changes which apply to the processor. Intel may fix
some of the errata in a future stepping of the component, and account for the other
outstanding issues through documentation or specification changes as noted. These
tables uses the following notations:
Codes Used in Summary Tables
Stepping
Page
Status
Row
X: Errata exists in the stepping indicated. Specification Change or
Clarification that applies to this stepping.
(No mark)
or (Blank box): This erratum is fixed in listed stepping or specification change
does not apply to listed stepping.
(Page): Page location of item in this document.
Doc: Document change or update will be implemented.
Plan Fix: This erratum may be fixed in a future stepping of the product.
Fixed: This erratum has been previously fixed.
No Fix: There are no plans to fix this erratum.
Change bar to left of a table row indicates this erratum is either new or modified from
the previous version of the document.
8
Specification Update
Page 9
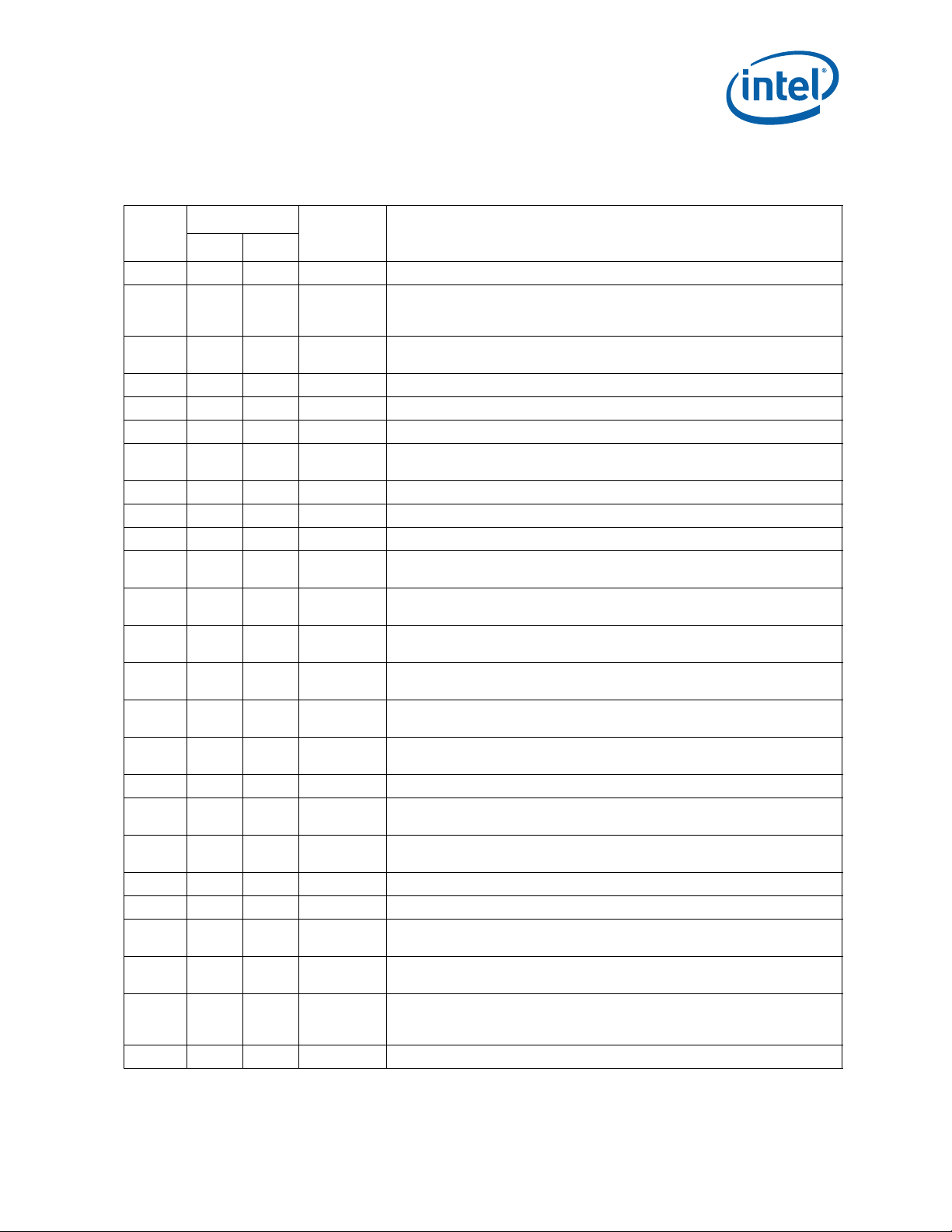
Errata (Sheet 1 of 5)
Number
AAU1
AAU2
AAU3
AAU4
AAU5
AAU6
AAU7
AAU8
AAU9
AAU10
AAU11
AAU12
AAU13
AAU14
AAU15
AAU16
AAU17
AAU18
AAU19
AAU20
AAU21
AAU22
AAU23
AAU24
AAU25
Steppings
C-2 K-0
Status ERRATA
XXNo FixThe Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing Page
XXNo Fix
Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an Incorrect Data Size or
Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations
XXNo Fix
Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May Be Serviced before Higher
Priority Interrupts/Exceptions and May Push the Wrong Address onto the Stack
XXNo FixPerformance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect Values
XXNo FixPremature Execution of a Load Operation Prior to Exception Handler Invocation
XXNo FixMOV To/From Debug Registers Causes Debug Exception
XXNo Fix
Incorrect Address Computed for Last Byte of FXSAVE/FXRSTOR Image Leads
to Partial Memory Update
XXNo FixValues for LBR/BTS/BTM Will Be Incorrect after an Exit from SMM
XXNo FixSingle Step Interrupts with Floating Point Exception Pending May Be Mishandled
XXNo FixFault on ENTER Instruction May Result in Unexpected Values on Stack Frame
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment Check
Exception
General Protection Fault (#GP) for Instructions Greater than 15 Bytes May be
Preempted
General Protection (#GP) Fault May Not Be Signaled on Data Segment Limit
Violation above 4-G Limit
LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/Interrupt
Occurs in 64-bit Mode
MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance of a DTLB
Error
Debug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled
Breakpoints
XXNo FixMONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in Hang
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning From Real
Mode to Protected Mode
Performance Monitoring Events for Read Miss to Level 3 Cache Fill Occupancy
Counter may be Incorrect
XXNo FixA VM Exit on MWAIT May Incorrectly Report the Monitoring Hardware as Armed
XXNo FixPerformance Monitor Event SEGMENT_REG_LOADS Counts Inaccurately
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
#GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical Boundary May
Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code
Improper Parity Error Signaled in the IQ Following Reset When a Code
Breakpoint is Set on a #GP Instruction
An Enabled Debug Breakpoint or Single Step Trap May Be Taken after MOV SS/
XXNo Fix
POP SS Instruction if it is Followed by an Instruction That Signals a Floating
Point Exception
XXNo FixIA32_MPERF Counter Stops Counting During On-Demand TM1
Specification Update
9
Page 10
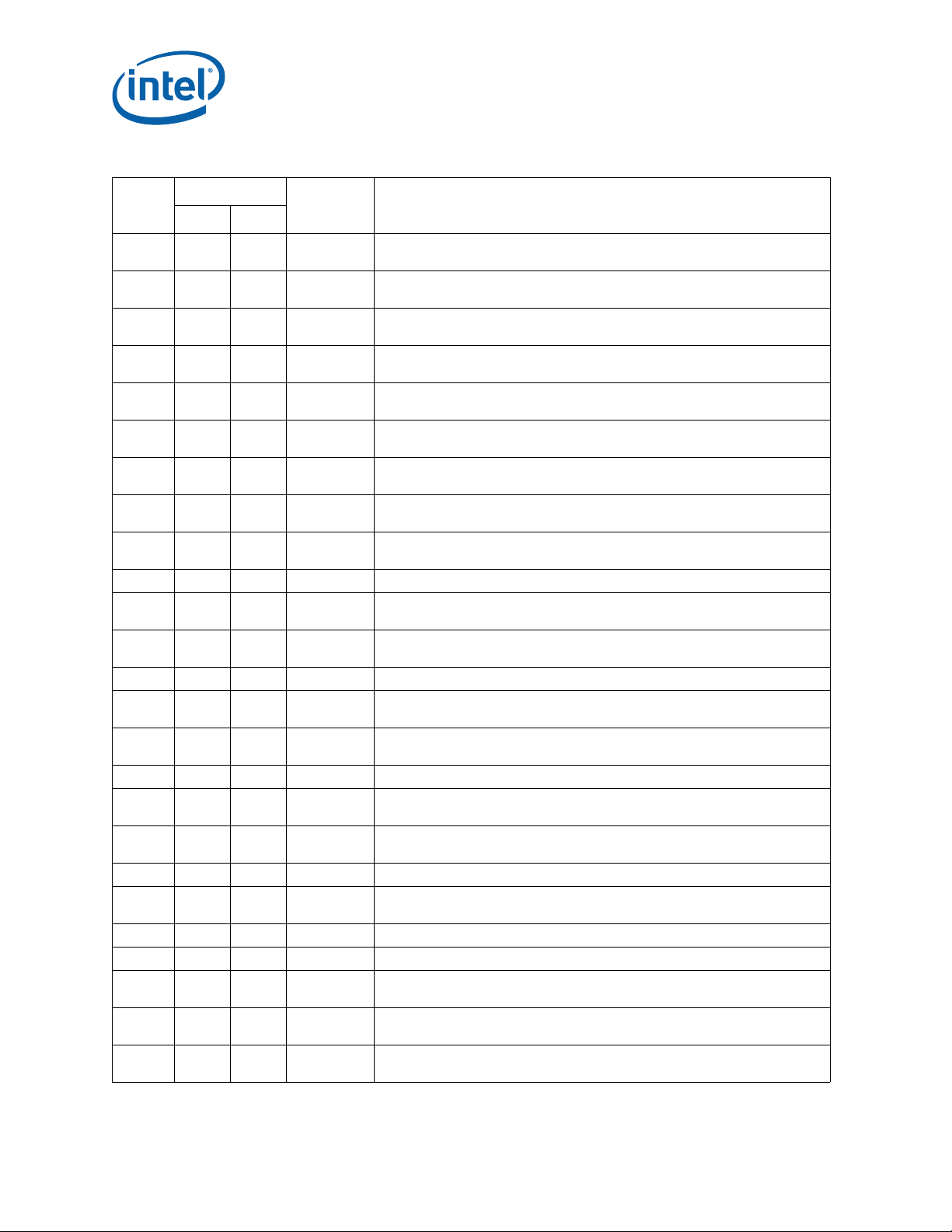
Errata (Sheet 2 of 5)
Number
AAU26
AAU27
AAU28
AAU29
AAU30
AAU31
Steppings
Status ERRATA
C-2 K-0
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
AAU32 X X No Fix
AAU33
AAU34
AAU35
AAU36
AAU37
AAU38
AAU39
AAU40
AAU41
AAU42
AAU43
AAU44
AAU45
AAU46
AAU47
AAU48
AAU49
AAU50
XFixed
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixTwo xAPIC Timer Event Interrupts May Unexpectedly Occur
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixAPIC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixIA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR May Be Incorrectly Initialized
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixFaulting Executions of FXRSTOR May Update State Inconsistently
XXNo Fix
XXNo FixMemory Aliasing of Code Pages May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
XXNo FixPerformance Monitor Counters May Count Incorrectly
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Synchronous Reset of IA32_APERF/IA32_MPERF Counters on Overflow Does
Not Work
Disabling Thermal Monitor While Processor is Hot, Then Re-enabling, May
Result in Stuck Core Operating Ratio
Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is Pending May Cause an
Unexpected Interrupt
xAPIC Timer May Decrement Too Quickly Following an Automatic Reload While
in Periodic Mode
Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and Referenced
Data Structures
Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead to
Memory-Ordering Violations
Erratum AAU32 added to this specification Update in error; all erratum details
removed from the specification update document.
Delivery of Certain Events Immediately Following a VM Exit May Push a
Corrupted RIP onto the Stack
Infinite Stream of Interrupts May Occur if an ExtINT Delivery Mode Interrupt is
Received while All Cores in C6
EOI Transaction May Not be Sent if Software Enters Core C6 During an Interrupt
Service Routine
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM Does Not Prevent Event From Pending PEBS During
SMM
DR6 May Contain Incorrect Information When the First Instruction After a MOV
SS,r/m or POP SS is a Store
An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May Also Result in a
System Hang
Performance Monitor Counter INST_RETIRED.STORES May Count Higher than
Expected
Sleeping Cores May Not be Woken Up on Logical Cluster Mode Broadcast IPI
Using Destination Field Instead of Shorthand
Performance Monitor Event EPT.EPDPE_MISS May be Counted While EPT is
Disable
Performance Monitor Event Offcore_response_0 (B7H) Does Not Count NT
Stores to Local DRAM Correctly
EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits after a
Translation Change
Back to Back Uncorrected Machine Check Errors May Overwrite
IA32_MC3_STATUS.MSCOD
10
Specification Update
Page 11
Errata (Sheet 3 of 5)
Number
AAU51
AAU52
AAU53
AAU54
AAU55
AAU56
AAU57
AAU58
AAU59
AAU60
AAU61
AAU62
AAU63
AAU64
AAU65
AAU66
AAU67
AAU68
AAU69
AAU70
AAU71
AAU72
AAU73
AAU74
AAU75
AAU76
Steppings
C-2 K-0
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Status ERRATA
Corrected Errors With a Yellow Error Indication May be Overwritten by Other
Corrected Errors
Performance Monitor Events DCACHE_CACHE_LD and DCACHE_CACHE_ST
May Overcount
XXNo FixRapid Core C3/C6 Transitions May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
XXNo FixAPIC Timer CCR May Report 0 in Periodic Mode
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Performance Monitor Events INSTR_RETIRED and MEM_INST_RETIRED May
Count Inaccurately
A Page Fault May Not be Generated When the PS bit is set to "1" in a PML4E or
PDPTE
BIST Results May be Additionally Reported After a GETSEC[WAKEUP] or INIT-
SIPI Sequence
XXNo FixPending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than Expected
XXNo FixVM Exits Due to "NMI-Window Exiting" May Be Delayed by One Instruction
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
The Memory Controller tTHROT_OPREF Timings May be Violated During Self
Refresh Entry
VM Exits Due to EPT Violations Do Not Record Information About Pre-IRET NMI
Blocking
Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of
IA32_FIXED_CTR2
XXNo FixLBRs May Not be Initialized During Power-On Reset of the Processor
XXNo Fix
LBR, BTM or BTS Records May have Incorrect Branch From Information After an
EIST Transition, T-states, C1E, or Adaptive Thermal Throttling
XXNo FixVMX-Preemption Timer Does Not Count Down at the Rate Specified
XXNo Fix
Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of Fixed
Counter 0
XXNo FixVM Exits Due to LIDT/LGDT/SIDT/SGDT Do Not Report Correct Operand Size
XXNo Fix
Performance Monitoring Events STORE_BLOCKS.NOT_STA and
STORE_BLOCKS.STA May Not Count Events Correctly
XXNo FixStorage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not Count
Some Transitions
INVLPG Following INVEPT or INVVPID May Fail to Flush All Translations for a
Large Page
Logical Processor May Use Incorrect VPID after VM Entry That Returns From
SMM
The Memory Controller May Hang Due to Uncorrectable ECC Errors or Parity
Errors Occurring on Both Channels in Mirror Channel Mode
MSR_TURBO_RATIO_LIMIT MSR May Return Intel® Turbo Boost Technology
Core Ratio Multipliers for Non-Existent Core Configurations
XFixedInternal Parity Error May Be Incorrectly Signaled during C6 Exit
XXNo FixPMIs during Core C6 Transitions May Cause the System to Hang
Specification Update
11
Page 12
Errata (Sheet 4 of 5)
Number
AAU77
AAU78
AAU79
AAU80
AAU82
AAU83
AAU84
AAU85
AAU86
AAU87
AAU88
AAU89
AAU90
AAU91
AAU92
AAU93
AAU94
AAU95
AAU96
AAU97
AAU98
AAU99
AAU100
AAU101
AAU102
AAU103
Steppings
C-2 K-0
XXNo Fix
Status ERRATA
2MB Page Split Lock Accesses Combined With Complex Internal Events May
Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
If the APIC timer Divide Configuration Register (Offset 03E0H) is written at the
XXNo Fix
same time that the APIC timer Current Count Register (Offset 0390H) reads 1H,
it is possible that the APIC timer will deliver two interrupts.
XFixedTXT.PUBLIC.KEY is Not Reliable
XFixed
XXNo Fix
8259 Virtual Wire B Mode Interrupt May Be Dropped When it Collides With
Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle From the Preceding Interrupt
The APIC Timer Current Count Register May Prematurely Read 0x0 While the
Timer is Still Running
XXNo FixSecondary PCIe Port May Not Train After A Warm Reset
XXNo FixThe PECI Bus May Be Tri-stated after System Reset
XXNo Fix
The Combination of a Page-Split Lock Access And Data Accesses That Are Split
Across Cacheline Boundaries May Lead to Processor Livelock
XXNo FixProcessor Hangs on Package C6 State Exit
XXNo FixA Synchronous SMI May be Delayed
FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP Access
XXNo Fix
Which Wraps a 4-Gbyte Boundary in Code That Uses 32-Bit Address Size in 64-
bit Mode
XXPlan Fix
PCI Express x16 Port Links May Fail to Dynamically Switch From 5.0GT/s to
2.5GT/s
XXNo FixPCI Express Cards May Not Train to x16 Link Width
XXNo Fix
Unexpected Graphics VID Transition During Warm Reset May Cause the System
to Hang
XXNo FixIO_SMI Indication in SMRAM State Save Area May Be Lost
XFixedVM Entry to 64-Bit Mode May Fail if Bits 48 And 47 of Guest RIP Are Different
XFixedVM Entry Loading an Unusable SS Might Not Set SS.B to 1
XFixed
XXNo Fix
FSW May Be Corrupted If an x87 Store Instruction Causes a Page Fault in VMX
Non-Root Operation
Under Certain Low Temperature Conditions, Some Uncore Performance
Monitoring Events May Report Incorrect Results
XXNo FixCKE May go Low Within tRFC(min) After a PD Exit
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Erratum AAU98 added to this specification Update in error; all erratum details
removed from the specification update document.
Performance Monitor Events for Hardware Prefetches Which Miss The L1 Data
Cache May be Over-Counted
XXNo FixVM Exit May Incorrectly Clear IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL [34:32]
XFixed
XXNo Fix
XXNo Fix
Correctable and Uncorrectable Cache Errors May be Reported Until the First
Core C6 Transition
Accesses to a VMCS May Not Operate Correctly If CR0.CD is Set on Any Logical
Processor of a Core
PCIe Port’s LTSSM May Not Transition Properly in the Presence of TS1 or TS2
Ordered Sets That Have Unexpected Symbols Within those Sets
12
Specification Update
Page 13
Errata (Sheet 5 of 5)
Number
AAU104
AAU105
Steppings
C-2 K-0
Status ERRATA
XXNo FixNTB/RP Link Will Send Extra TS2 Ordered Set During Link Training
XXNo Fix
PCIe Ports May Not Enter Slave Loopback Mode From the Configuration LTSSM
State
USB Devices May Not Function Properly With Integrated Graphics While
AAU106
XXNo Fix
Running Targeted Stress Graphics Workloads With Non-Matching Memory
Configurations
AAU107
AAU108
AAU109
AAU110
XXNo Fix
XNo Fix
XFixedExecution of VMPTRLD May Corrupt Memory If Current-VMCS Pointer is Invalid
XXNo Fix
VM Entry May Omit Consistency Checks Related to Bit 14 (BS) of the Pending
Debug Exception Field in Guest-State Area of the VMCS
Intel Turbo Boost Technology Ratio Changes May Cause Unpredictable System
Behavior
PerfMon Overflow Status Can Not be Cleared After Certain Conditions Have
Occurred
Specification Changes
Number SPECIFICATION CHANGES
None for this revision of this specification update.
Specification Clarifications
Number SPECIFICATION CLARIFICATIONS
None for this revision of this specification update.
Documentation Changes
Number DOCUMENTATION CHANGES
None for this revision of this specification update.
Specification Update
13
Page 14
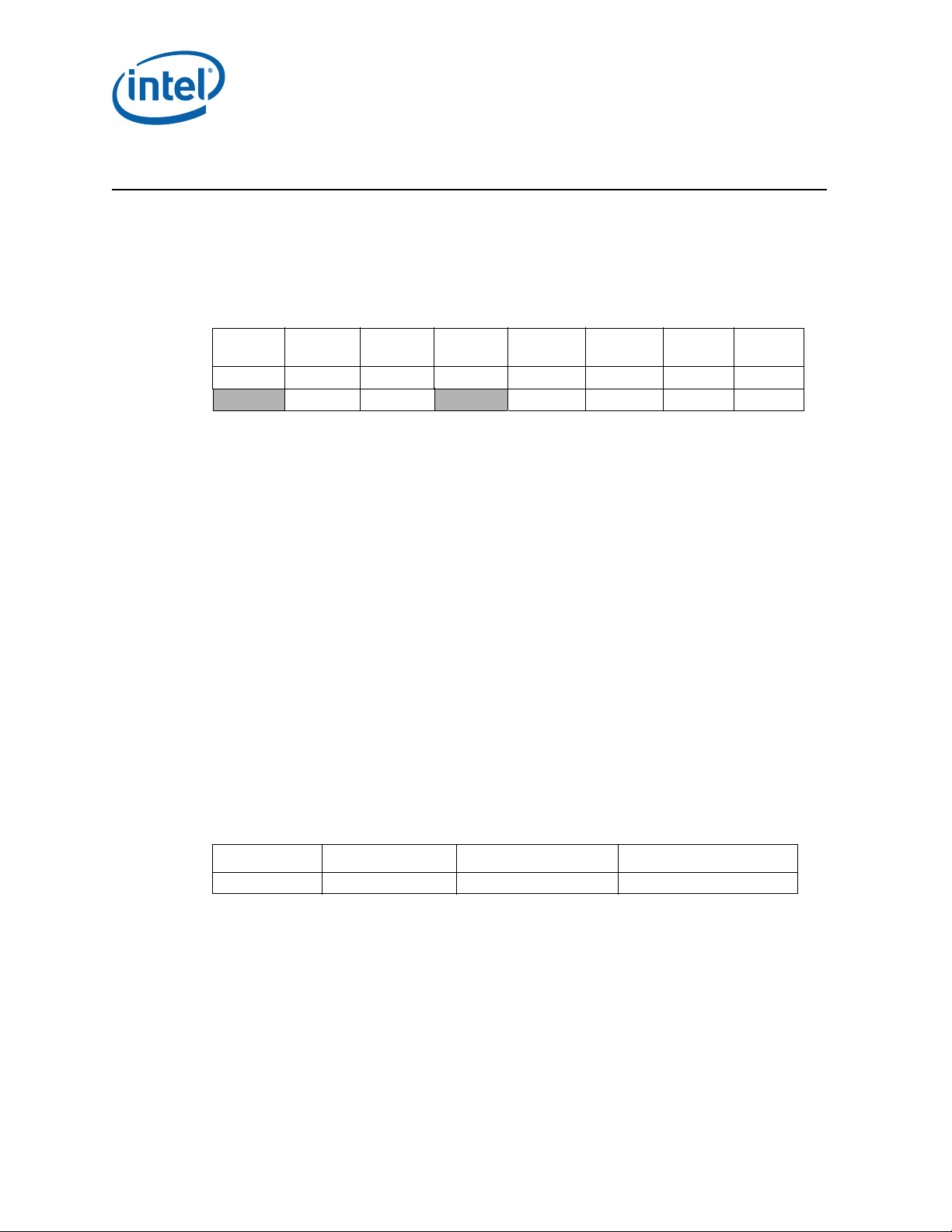
Identification Information
Component Identification using Programming Interface
The Intel® Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium®
Desktop Processor 6000 Series stepping can be identified by the following register
contents:
1
Extended
2
Model
Reserved
Reserved
31:28 27:20 19:16 15:14 13:12 11:8 7:4 3:0
Note:
1. The Extended Family , bits [27:20] are used in con junction with the F amily Code, specif ied in bits [11:8],
2. The Extended Model, bits [19:16] in conjunction with the Model Number, specified in bits [7:4], are
3. The Processor Type, specified in bits [13:12] indicates whether the processor is an original OEM
4. The Family Code corresponds to bits [11:8] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [11:8] of the EAX
5. The Model Number corresponds to bits [7:4] of the EDX register after RESET, bits [7:4] of the EAX
6. The Stepping ID in bits [3:0] indicates the revision number of that model. See Table 1 for the processor
Extended
Family
00000000b 0010b 00b 0110 0101b xxxxb
to indicate whether the processor belongs to the Intel386, Intel486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium 4,
®
or Intel
used to identify the model of the processor within the processor’s family.
processor, an OverDrive processor, or a dual processor (capable of being used in a dual processor
system).
register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the generation field of
the Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
register after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 1 in the EAX register, and the model field of the
Device ID register accessible through Boundary Scan.
stepping ID number in the CPUID information.
Core™ processor family.
Processor
Type
Family
3
Code
4
Model
Number
Stepping
5
ID
6
When EAX is initialized to a value of ‘1’, the CPUID instruction returns the Extended
Family, Extended Model, Processor Type, Family C ode, Mode l Number and Step ping ID
value in the EAX register. Note that the EDX processor signature value after reset is
equivalent to the processor signature output value in the EAX register.
Cache and TLB descriptor parameters are provided in the EAX, EBX, ECX and EDX
registers after the CPUID instruction is executed with a 2 in the EAX register.
14
The Intel® Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium®
Desktop Processor 6000 Series can be identified by the following register contents:
Stepping Vendor ID
C-2 8086h 0040h 12h
Notes:
1. The Vendor ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Vendor ID Register located at offset 00–01h in the PCI
2. The Device ID corresponds to bits 15:0 of the Device ID Register located at Device 0 offset 02–03h in
3. The Revision Number corresponds to bits 7:0 of the Revision ID Register located at offset 08h in the PCI
function 0 configuration space.
the PCI function 0 configuration space.
function 0 configuration space.
1
Device ID
2
Revision ID
3
Specification Update
Page 15
Component Marking Information
LOT NO S/N
INTEL ©'08 PROC#
BRAND
SLxxx [COO]
SPEED/CACHE/FMB
[FPO]
M
e4
The processor stepping can be identified by the following component markings.
Figure 1. Processor Production Top-side Markings (Example)
Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 1 of 2)
S-Spec
Number
SLBTM i5-680 K-0 20655h 3.60 / 1333 / 733
SLBLT i5-670 C-2 20652h 3.46 / 1333 / 733
SLBNE i5-661 C-2 20652h 3.33 / 1333 / 900
SLBLV i5-660 C-2 20652h 3.33 / 1333 / 733
SLBXL i5-655K K-0 20655h 3.20 / 1333 / 733
SLBLK i5-650 C-2 20652h 3.20 / 1333 / 733
SLBUD i3-550 K-0 2065 5h 3.20 / 1333 / 733 N/A 4 1, 3, 5, 8, 10
SLBY2 i3-560 K-0 20655h 3.33 / 1333 / 733 N/A 4
SLBMQ i3-540 C-2 20652h 3.06 / 1333 / 733 N/A 4
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
Core Frequency
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Integrated
Graphics
Frequency
(GHz)
®
2
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
Frequency
2 core: 3.73
1 core: 3.86
2 core: 3.60
1 core: 3.73
2 core: 3.46
1 core: 3.60
2 core: 3.46
1 core: 3.60
2 core: 3.33
1 core: 3.46
2 core: 3.33
1 core: 3.46
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
4
4
4
4
4
4
Notes
1, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 10
1, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 10
3, 5, 7, 8, 9,
10
1, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 10
1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7,
8, 10
1, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7,
8, 10
1, 3, 5, 8,
10
1, 3, 5, 8,
10
Specification Update
15
Page 16
Table 1. Processor Identification (Sheet 2 of 2)
S-Spec
Number
Processor
Number
Stepping
Processor
Signature
Core Frequency
(GHz) /
DDR3 (MHz) /
Integrated
Graphics
Frequency
Max Intel
Turbo Boost
Technology
Frequency
SLBLR i3-530 C-2 20652h 2.93 / 1333 / 733 N/A 4
(GHz)
2
®
Shared
L3 Cache
Size (MB)
Notes
1, 3, 5, 8,
10
SLBMS G6950 C-2 20652h 2.80 / 1066 / 533 N/A 3 1, 5, 10
SLBT6 G6960 C-2 20652h 2.93 / 1066 / 533 N/A 3 1, 5, 10
Notes:
1. This processor has TDP of 73 W.
2. This column indicates maximum Intel
3. Intel
4. Intel
5. Intel
6. Intel
7. Intel
8. Intel SSE4.1 and SSE4.2 enabled.
9. This processor has TDP of 87 W.
10. The core frequency reported in the pro cessor brand string is rounded to 2 decimal digits. (F o r examp le,
respectively.
®
Hyper-Threading Technology enabled.
®
Trusted Execution Technology (Intel® TXT) enabled.
®
Virtualization Technology for IA-32, Intel® 64 and Intel® Architecture (Intel® VT-x) enabled.
®
Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (Intel® VT-d) enabled.
®
AES-NI enabled.
core frequency of 3.4666, repeating 6, is reported as @3.47 in brand stri ng. Core fr equency o f 3.3333,
is reported as @3.33 in brand string.)
®
Turbo Boost Technology frequency (GHz) for 2 or 1 cores active
16
Specification Update
Page 17

Errata
AAU1. The Processor May Report a #TS Instead of a #GP Fault
Problem: A jump to a busy TSS (Task-State Segment) may cause a #TS (invalid TSS exception)
instead of a #GP fault (general protection exception).
Implication: Operation systems that access a busy TSS may get invalid TSS fault instead of a #GP
fault. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU2. REP MOVS/STOS Executing with Fast Strings Enabled and Crossing
Page Boundaries with Inconsistent Memory Types may use an
Incorrect Data Size or Lead to Memory-Ordering Violations
Problem: Under certain conditions as described in the Software Developers Manual section "Out-
of-Order Stores For String Operations in Pentium 4, Intel Xeon, and P6 Family
Processors" the processor performs REP MOVS or REP STOS as fast strings. Due to this
erratum fast string REP MOVS/REP STOS instructions that cross page boundaries from
WB/WC memory types to UC/WP/WT memory types, may start using an incorrect data
size or may observe memory ordering violations.
Implication: Upon crossing the page boundary the following may occur, dependent on the new page
memory type:
• UC the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the
original data size.
• WP the data size of each write will now always be 8 bytes, as opposed to the
original data size and there may be a memory ordering violation.
• WT there may be a memory ordering violation.
Workaround: Software should avoid crossing page boundaries from WB or WC memory type to UC,
WP or WT memory type within a single REP MOVS or REP STOS instruction that will
execute with fast strings enabled.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
17
Page 18

AAU3. Code Segment Limit/Canonical Faults on RSM May Be Serviced before
Higher Priority Interrupts/Exceptions and May Push the Wrong
Address onto the Stack
Problem: Normally, when the processor encounters a Segment Limit or Canonical Fault due to
code execution, a #GP (General Protection Exception) fault is generated after all higher
priority Interrupts and exceptions are serviced. Due to this erratum, if RSM (Resume
from System Management Mode) returns to execution flow that results in a Code
Segment Limit or Canonical Fault, the #GP fault may be serviced before a higher
priority Interrupt or Exception (e.g., NMI (Non-Maskable Interrupt), Debug
break(#DB), Machine Check (#MC), etc.). If the RSM attempts to return to a noncanonical address, the address pushed onto the stack for this #GP fault may not match
the non-canonical address that caused the fault.
Implication: Operating systems may observe a #GP fault being serviced before higher priority
Interrupts and Exceptions. Intel has not observed this erratum on any commercially-
available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU4. Performance Monitor SSE Retired Instructions May Return Incorrect
Values
Problem: Performance Monitoring counter SIMD_INST_RETIRED (Event: C7H) is used to track
retired SSE instructions. Due to this erratum, the processor may also count other types
of instructions resulting in higher than expected values.
Implication: Performance Monitoring counter SIMD_INST_RETIRED may report count higher than
expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU5. Premature Execution of a Load Operation Prior to Exception Handler
Invocation
Problem: If any of the below circumstances occur, it is possible that the load portion of the
instruction will have executed before the exception handler is entered.
• If an instruction that performs a memory load causes a code segment limit
violation.
• If a waiting X87 floating-point (FP) instruction or MMX™ technology (MMX)
instruction that performs a memory load has a floating-point exception pending.
• If an MMX o r SSE/SSE2/SSE3/SSSE3 extensions (SSE) i nstruction that performs a
memory load and has either CR0.EM=1 (Emulation bit set), or a floating-point Topof-Stack (FP TOS) not equal to 0, or a DNA exception pending.
Implication: In normal code execution where the target of the load operation is to write back
memory there is no impact from the load being prematurely executed, or from the
restart and subsequent re-execution of that instruction by the exception handler. If the
target of the load is to uncached memory that has a system side-effect, restarting the
instruction may cause unexpected system behavior due to the repetition of the sideeffect. Particularly, while CR0.TS [bit 3] is set, a MOVD/MOVQ with MMX/XMM register
operands may issue a memory load before getting the DNA exception.
Workaround: Code which performs loads from memory that has side-effects can effectively
workaround this behavior by using simple integer-based load instructions when
18
Specification Update
Page 19

accessing side-effect memory and by ensuring that all code is written such that a code
segment limit violation cannot occur as a part of reading from side-effect memory.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU6. MOV To/From Debug Registers Causes Debug Exception
Problem: When in V86 mode, if a MOV instruction is executed to/from a debug registers, a
general-protection exception (#GP) should be generated. However, in the case when
the general detect enable flag (GD) bit is set, the observed behavior is that a debug
exception (#DB) is generated instead.
Implication: With debug-register protection enabled (i.e., the GD bit set), when attempting to
execute a MOV on debug registers in V86 mode, a debug exception will be generated
instead of the expected general-protection fault.
Workaround: In general, operating systems do not set the GD bit when they are in V86 mode. The
GD bit is generally set and used by debuggers. The debug exception handler should
check that the exception did not occur in V86 mode before continuing. If the exception
did occur in V86 mode, the exception may be directed to the general-protection
exception handler.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU7. Incorrect Address Computed for Last Byte of FXSAVE/FXRSTOR Image
Leads to Partial Memory Update
Problem: A partial memory state save of the 512-byte FXSAVE image or a partial memory state
restore of the FXRSTOR image may occur if a memory address exceeds the 64KB limit
while the processor is operating in 16-bit mode or if a memory address exceeds the
4GB limit while the processor is operating in 32-bit mode.
Implication: FXSAVE/FXRSTOR will incur a #GP fault due to the memory limit violation as expected
but the memory state may be only partially saved or restored.
Workaround: Software should avoid memory accesses that wrap around the respective 16-bit and
32-bit mode memory limits.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU8. Values for LBR/BTS/BTM Will Be Incorrect after an Exit from SMM
Problem: After a return from SMM (System Management Mode), the CPU will incorrectly update
the LBR (Last Branch Record) and the BTS (Branch Trace Store), hence rendering their
data invalid. The corresponding data if sent out as a B TM on the system bus will also be
incorrect.
Problem: Note: This issue would only occur when one of the 3 above mentioned debug support
facilities are used.
Implication: The value of the LBR, BTS, and BTM immediately after an RSM operation should not be
used.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
19
Page 20

AAU9. Single Step Interrupts with Floating Point Exception Pending May Be
Mishandled
Problem: In certain circumstances, when a floating point exception (#MF) is pending during
single-step execution, processing of the single-step debug exception (#DB) may be
mishandled.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, #DB will be incorrectly handled as follows:
• #DB is signaled before the pending higher priority #MF (Interrupt 16)
• #DB is generated twice on the same instruction
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU10. Fault on ENTER Instruction May Result in Unexpected Values on Stack
Frame
Problem: The ENTER instruction is used to create a procedure stack frame. Due to this erratum,
if execution of the ENTER instruction results in a fault, the dynamic storage area of the
resultant stack frame may contain unexpected values (i.e., residual stack data as a
result of processing the fault).
Implication: Data in the created stack frame may be altered following a fault on the ENTER
instruction. Refer to "Procedure Calls For Block-Structured Languages" in IA-32 Intel
Architecture Software Developer's Manual, V ol. 1, Basic Architecture, for information on
the usage of the ENTER instructions. This erratum is not expected to occur in Ring 3.
Faults are usually processed in Ring 0 and stack switch occurs when transferring to
Ring 0. Intel has not observed this erratum on any commercially-available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
AAU11. IRET under Certain Conditions May Cause an Unexpected Alignment
Check Exception
Problem: In IA-32e mode, it is possible to get an Alignment Check Exception (#AC) on the IRET
instruction even though alignment checks were disabled at the start of the IRET. This
can only occur if the IRET instruction is returning from CPL3 code to CPL3 code. IRETs
from CPL0/1/2 are not affected. This erratum can occur if the EFLAGS value on the
stack has the AC flag set, and the interrupt handler's stack is misaligned. In IA-32e
mode, RSP is aligned to a 16-byte boundary before pushing the stack frame.
Implication: In IA-32e mode, under the conditions given above, an IRET can get a #AC even if
alignment checks are disabled at the start of the IRET. This erratum can only be
observed with a software generated stack frame.
Workaround: Software should not generate misaligned stack frames for use with IRET.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
20
Specification Update
Page 21

AAU12. General Protection Fault (#GP) for Instructions Greater than 15 Bytes
May be Preempted
Problem: When the processor encounters an instruction that is greater than 15 bytes in length, a
#GP is signaled when the instruction is decoded. Under some circumstances, the #GP
fault may be preempted by another lower priority fault (e.g., Page Fault (#PF)).
However, if the preempting lower priority faults are resolved by the operating system
and the instruction retried, a #GP fault will occur.
Implication: Software may observe a lower-priority fault occurring before or in lieu of a #GP fault.
Instructions of greater than 15 bytes in length can only occur if redundant prefixes are
placed before the instruction.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU13. General Protection (#GP) Fault May Not Be Signaled on Data Segment
Limit Violation above 4-G Limit
Problem: In 32-bit mode, memory accesses to flat data segments (base = 00000000h) that
occur above the 4-G limit (0ffffffffh) may not signal a #GP fault.
Implication: When such memory accesses occur in 32-bit mode, the system may not issue a #GP
fault.
Workaround: Software should ensure that memory accesses in 32-bit mode do not occur above the
4-G limit (0ffffffffh).
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU14. LBR, BTS, BTM May Report a Wrong Address when an Exception/
Interrupt Occurs in 64-bit Mode
Problem: An exception/interrupt event should be transparent to the LBR (Last Branch Record),
BTS (Branch Trace Store) and BTM (Branch Trace Message) mechanisms. However,
during a specific boundary condition where the exception/interrupt occurs right after
the execution of an instruction at the lower canonical boundary (0x00007FFFFFFFFFFF)
in 64-bit mode, the LBR return registers will save a wrong return address with Bits 63
to 48 incorrectly sign extended to all 1's. Subsequent BTS and BTM operations which
report the LBR will also be incorrect.
Implication: LBR, BTS and BTM may report incorrect information in the event of an exception/
interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU15. MCi_Status Overflow Bit May Be Incorrectly Set on a Single Instance
of a DTLB Error
Problem: A single Data Translation Look Aside Buffer (DTLB) error can incorrectly set the
Overflow (bit [62]) in the MCi_Status register. A DTLB error is indicated by MCA error
code (bits [15:0]) appearing as binary value, 000x 0000 0001 0100, in the MCi_Status
register.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the Overflow bit in the MCi_Status register may not be an accur ate
indication of multiple occurrences of DTLB errors. There is no other impact to normal
processor functionality.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
21
Page 22

AAU16. Debug Exception Flags DR6.B0-B3 Flags May be Incorrect for Disabled
Breakpoints
Problem: When a debug exception is signaled on a load that crosses cache lines with data
forwarded from a store and whose corresponding breakpoint enable flags are disabled
(DR7.G0-G3 and DR7.L0-L3), the DR6.B0-B3 flags may be incorrect.
Implication: The debug exception DR6.B0-B3 flags may be incorrect for the load if the
corresponding breakpoint enable flag in DR7 is disabled.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU17. MONITOR or CLFLUSH on the Local XAPIC's Address Space Results in
Hang
Problem: If the target linear address range for a MONITOR or CLFLUSH is mapped to the local
xAPIC's address space, the processor will hang.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, the processor will hang. The local xAPIC's address space
must be uncached. The MONITOR instruction only functions correctly if the specified
linear address range is of the type write-back. CLFLUSH flushes data from the cache.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially-available software.
Workaround: Do not execute MONITOR or CLFLUSH instructions on the local xAPIC address space.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU18. Corruption of CS Segment Register During RSM While Transitioning
From Real Mode to Protected Mode
Problem: During the transition from real mode to protected mode, if an SMI (System
Management Interrupt) occurs between the MOV to CR0 that sets PE (Protection
Enable, bit 0) and the first FAR JMP, the subsequent RSM (Resume from System
Management Mode) may cause the lower two bits of CS segment register to be
corrupted.
Implication: The corruption of the bottom two bits of the CS segment register will have no impact
unless software explicitly examines the CS segment register between enabling
protected mode and the first FAR JMP. Intel
Developer’s Manual Volume 3A: System Programming Guide, Part 1, in the section
titled "Switching to Protected Mode" recommends the FAR JMP immediately follows the
write to CR0 to enable protected mode. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially-available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
64 and IA-32 Architectures Software
AAU19. Performance Monitoring Events for Read Miss to Level 3 Cache Fill
Occupancy Counter may be Incorrect
Problem: Whenever an Level 3 cache fill conflicts with another request's address, the miss to fill
occupancy counter, UNC_GQ_ALLOC.RT_LLC_MISS (Event 02H), will provide erroneous
results.
Implication: The Performance Monitoring UNC_GQ_ALLOC.RT_LLC_MISS event may count a value
higher than expected. The extent to which the value is higher than expected is
determined by the frequency of the L3 address conflict.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
22
Specification Update
Page 23

AAU20. A VM Exit on MWAIT May Incorrectly Report the Monitoring Hardware
as Armed
Problem: A processor write to the address range armed by the MONITOR instruction may not
immediately trigger the monitoring hardware. Consequently, a VM exit on a later
MWAIT may incorrectly report the monitoring hardware as armed, when it should be
reported as unarmed due to the write occurring prior to the MWAIT.
Implication: If a write to the range armed by the MONITOR instruction occurs between the
MONITOR and the MWAIT, the MWAIT instruction may start executing before the
monitoring hardware is triggered. If the MWAIT instruction causes a VM exit, this could
cause its exit qualification to incorrectly report 0x1. In the recommended usage model
for MONITOR/MWAIT, there is no write to the range armed by the MONITOR instruction
between the MONITOR and the MWAIT.
Workaround: Software should never write to the address range armed by the MONITOR instruction
between the MONITOR and the subsequent MWAIT.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU21. Performance Monitor Event SEGMENT_REG_LOADS Counts
Inaccurately
Problem: The performance monitor event SEGMENT_REG_LOADS (Event 06H) counts
instructions that load new values into segment registers. The value of the count may be
inaccurate.
Implication: The performance monitor event SEGMENT_REG_LOADS may reflect a count higher or
lower than the actual number of events.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU22. #GP on Segment Selector Descriptor that Straddles Canonical
Boundary May Not Provide Correct Exception Error Code
Problem: During a #GP (General Protection Exception), the processor pushes an error code on to
the exception handler’s stack. If the segment selector descriptor straddles the
canonical boundary, the error code pushed onto the stack may be incorrect.
Status: An incorrect error code may be pushed onto the stack. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially-available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU23. Improper Parity Error Signaled in the IQ Following Reset When a Code
Breakpoint is Set on a #GP Instruction
Problem: While coming out of cold reset or exiting from C6, if the processor encounters an
instruction longer than 15 bytes (which causes a #GP) and a code breakpoint is
enabled on that instruction, an IQ (Instruction Queue) parity error may be incorrectly
logged resulting in an MCE (Machine Check Exception).
Implication: When this erratum occurs, an MCE may be incorrectly signaled.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
23
Page 24

AAU24. An Ena bled Debug Breakpo i nt or Single Step Trap May Be Taken after
MOV SS/POP SS Instruction if it is Followed by an Instruction That
Signals a Floating Point Exception
Problem: A MOV SS/POP SS instruction should inhibit all interrupts including debug breakpoints
until after execution of the following instruction. This is intended to allow the sequential
execution of MOV SS/POP SS and MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP instructions without having an
invalid stack during interrupt handling. However, an enabled debug breakpoint or single
step trap may be taken after MOV SS/POP SS if this instruction is followed by an
instruction that signals a floating point exception rather than a MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP
instruction. This results in a debug exception being signaled on an unexpected
instruction boundary since the MOV SS/POP SS and the following instruction should be
executed atomically.
Implication: This can result in incorrect signaling of a debug exception and possibly a mismatched
Stack Segment and Stack Pointer. If MOV SS/POP SS is not followed by a MOV [r/e]SP,
[r/e]BP, there may be a mismatched Stack Segment and Stack Pointer on any
exception. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially-available
software or system.
®
Workaround: As recommended in the IA32 Intel
Architecture Software Developer’s Manual, the use
of MOV SS/POP SS in conjunction with MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP will avoid the failure since
the MOV [r/e]SP, [r/e]BP will not generate a floating point exception. Developers of
debug tools should be aware of the potential incorrect debug event signaling created by
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU25. IA32_MPERF Counter Stops Counting During On-Demand TM1
Problem: According to the Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual
Volume 3A: System Programming Guide, the ratio of IA32_MPERF (MSR E7H) to
IA32_APERF (MSR E8H) should reflect actual performance while TM1 or on-demand
throttling is activated. Due to this erratum, IA32_MPERF MSR stops counting while TM1
or on-demand throttling is activated, and the ratio of the two will indicate higher
processor performance than actual.
Implication: The incorrect ratio of IA32_APERF/IA32_MPERF can mislead software P-state
(performance state) management algorithms under the conditions described above. It
is possible for the Operating System to observe higher processor utilization than actual,
which could lead the OS into raising the P-state. During TM1 activation, the OS P-state
request is irrelevant and while on-demand throttling is enabled, it is expected that the
OS will not be changing the P-state. This erratum should result in no practical
implication to software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU26. Synchronous Reset of IA32_APERF/IA32_MPER F Cou n ters on
Overflow Does Not Work
Problem: When either the IA32_MPERF or IA32_APERF MSR (E7H, E8H) increments to its
maximum value of 0xFFFF_FFFF_FFFF_FFFF, both MSRs are supposed to synchronously
reset to 0x0 on the next clock. This synchronous reset does not work. Instead, both
MSRs increment and overflow independently.
Implication: Software can not rely on synchronous reset of the IA32_APERF/IA32_MPERF registers.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
24
Specification Update
Page 25

AAU27. Disabling Thermal Monitor While Processor is Hot, Then Re-enabling,
May Result in Stuck Core Operating Ratio
Problem: If a processor is at its TCC (Thermal Control Circuit) activation temperature and then
Thermal Monitor is disabled by a write to IA32_MISC_ENABLES MSR (1A0H) bit [3], a
subsequent re-enable of Thermal Monitor will result in an artificial ceiling on the
maximum core P-state. The ceiling is based on the core frequency at the time of
Thermal Monitor disable. This condition will only correct itself once the processor
reaches its TCC activation temperature again.
Implication: Since Intel requires that Thermal Monitor be enabled in order to be operating within
specification, this erratum should never be seen during normal operation.
Workaround: Software should not disable Thermal Monitor during processor operation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU28. Writing the Local Vector Table (LVT) when an Interrupt is Pending
May Cause an Unexpected Interrupt
Problem: If a local interrupt is pending when the LVT entry is written, an interrupt may be taken
on the new interrupt vector even if the mask bit is set.
Implication: An interrupt may immediately be generated with the new vector when a LVT entry is
written, even if the new L VT entry has the mask bit set. If there is no Interrupt Service
Routine (ISR) set up for that vector the system will GP fault. If the ISR does not do an
End of Interrupt (EOI) the bit for the vector will be left set in the in-service register and
mask all interrupts at the same or lower priority.
Workaround: Any vector programmed into an LVT entry must have an ISR associated with it, even if
that vector was programmed as masked. This ISR routine must do an EOI to clear any
unexpected interrupts that may occur. The ISR associated with the spurious vector
does not generate an EOI, therefore the spurious vector should not be used when
writing the LVT.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU29. xAPIC Timer May Decrement Too Quickly Following an Automatic
Reload While in Periodic Mode
Problem: When the xAPIC Timer is automatically reloaded by counting down to zero in periodic
mode, the xAPIC Timer may slip in its synchronization with the external clock. The
xAPIC timer may be shortened by up to one xAPIC timer tick.
Implication: When the xAPIC Timer is automatically reloaded by counting down to zero in periodic
mode, the xAPIC Timer may slip in its synchronization with the external clock. The
xAPIC timer may be shortened by up to one xAPIC timer tick.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
25
Page 26

AAU30. Reported Memory Type May Not Be Used to Access the VMCS and
Referenced Data Structures
Problem: Bits 53:50 of the IA32_VMX_BASIC MSR report the memory type that the processor
uses to access the VMCS and data structures referenced by pointers in the VMCS. Due
to this erratum, a VMX access to the VMCS or referenced data structures will instead
use the memory type that the MTRRs (memory-type range registers) specify for the
physical address of the access.
Implication: Bits 53:50 of the IA32_VMX_BASIC MSR report that the WB (write-back) memory type
will be used but the processor may use a different memory type.
Workaround: Software should ensure that the VMCS and referenced data structures are located at
physical addresses that are mapped to WB memory type by the MTRRs.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU31. Changing the Memory Type for an In-Use Page Translation May Lead
to Memory-Ordering Violations
Problem: Under complex microarchitectural conditions, if software changes the memory type for
data being actively used and shared by multiple threads without the use of semaphores
or barriers, software may see load operations execute out of order.
Implication: Memory ordering may be violated. Intel has not observed this erratum with any
commercially-available software.
Workaround: Software should ensure pages are not being actively used before requesting their
memory type be changed.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU32. Erratum AAU32 added to this specification Update in error; all erratum
details removed from the specification update document.
26
Specification Update
Page 27

AAU33. Delivery of Certain Events Immediately Following a VM Exit May Push
a Corrupted RIP onto the Stack
Problem: If any of the following events is delivered immediately following a VM exit to 64-bit
mode from outside 64-bit mode, bits 63:32 of the RIP value pushed on the stack may
be cleared to 0:
• A non-maskable interrupt (NMI);
• A machine-check exception (#MC);
• A page fault (#PF) during instruction fetch; or
• A general-protection exception (#GP) due to an attempt to decode an instruction
whose length is greater than 15 bytes.
Implication: Unexpected behavior may occur due to the incorrect value of the RIP on the stack.
Specifically , return from the event handler via IRET may encounter an unexpected page
fault or may begin fetching from an unexpected code address.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU34. Infinite Stream of Interrupts May Occur if an ExtINT Delivery Mode
Interrupt is Received while All Cores in C6
Problem: If all logical processors in a core are in C6, an ExtINT delivery mode interrupt is
pending in the xAPIC and interrupts are blocked with EFLAGS.IF=0, the interrupt will
be processed after C6 wakeup and after interrupts are re-enabled (EFLAGS.IF=1).
However, the pending interrupt event will not be cleared.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an infinite stream of interrupts will occur on the core servicing the
external interrupt. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially-av ailable
software/system.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU35. Two xAPIC Timer Event Interrupts May Unexpectedly Occur
Problem: If an xAPIC timer event is enabled and while counting down the current count reaches
1 at the same time that the processor thread begins a transition to a low power C-
state, the xAPIC may generate two interrupts instead of the expected one when the
processor returns to C0.
Implication: Due to this erratum, two interrupts may unexpectedly be generated by an xAPIC timer
event.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
27
Page 28

AAU36. EOI Transaction May Not be Sent if Software Enters Core C6 During an
Interrupt Service Routine
Problem: If core C6 is entered after the start of an interrupt service routine but before a write to
the APIC EOI (End of Interrupt) register, and the core is woken up by an event other
than a fixed interrupt source the core may drop the EOI tran saction the next time APIC
EOI register is written and further interrupts from the same or lower priority level will
be blocked.
Implication: EOI transactions and interrupts may be blocked when core C6 is used during interrupt
service routines. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially-available
software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU37. FR EEZE_WHILE_SMM Does Not Prevent Event From Pending PEBS
During SMM
Problem: In general, a PEBS record should be generated on the first count of the event after the
counter has overflowed. However, IA32_DEBUGCTL_MSR.FREEZE_WHILE_SMM (MSR
1D9H, bit [14]) prevents performance counters from counting during SMM (System
Management Mode). Due to this erratum, if
1. A performance counter overflowed before an SMI
2. A PEBS record has not yet been generated because another count of the ev ent has
not occurred
3. The monitored event occurs during SMM
then a PEBS record will be saved after the next RSM instruction.
When FREEZE_WHILE_SMM is set, a PEBS should not be generated until the event
occurs outside of SMM.
Implication: A PEBS record may be saved after an RSM instruction due to the associated
performance counter detecting the monitored event during SMM; even when
FREEZE_WHILE_SMM is set.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU38. AP IC Error “Received Illegal Vector” May be Lost
Problem: APIC (Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller) may not update the ESR (Error
Status Register) flag Received Illegal V ector bit [6] properly when an illegal vector error
is received on the same internal clock that the ESR is being written (as part of the
write-read ESR access flow). The corresponding error interrupt will also not be
generated for this case.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an incoming illegal vector error may not be logged into ESR
properly and may not generate an error interrupt.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
28
Specification Update
Page 29

AAU39. DR6 May Contain Incorrect Information When the First Instruction
After a MOV SS,r/m or POP SS is a Store
Problem: Normally, each instruction clears the changes in DR6 (Debug Status Re gister) caused
by the previous instruction. However, the instruction following a MOV SS,r/m (MOV to
the stack segment selector) or POP SS (POP stack segment selector) instruction will not
clear the changes in DR6 because data breakpoints are not taken immediately after a
MOV SS,r/m or POP SS instruction. Due to this erratum, any DR6 changes caused by a
MOV SS,r/m or POP SS instruction may be cleared if the following instruction is a store.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, incorrect information may exist in DR6. This erratum will not
be observed under normal usage of the MOV SS,r/m or POP SS instructions (i.e.,
following them with an instruction that writes [e/r]SP). When debugging or when
developing debuggers, this behavior should be noted.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU40. An Uncorrectable Error Logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS May Also
Result in a System Hang
Problem: Uncorrectable errors logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STATUS MSR (409H) may also result in a
system hang causing an Internal Timer Error (MCACOD = 0x0400h) to be logged in
another machine check bank (IA32_MCi_STATUS).
Implication: Uncorrectable errors logged in IA32_CR_MC2_STA TUS can further cause a system hang
and an Internal Timer Error to be logged.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU41. IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR May Be Incorrectly Initialized
Problem: The IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR (38FH) bits [34:32] may be incorrectly set to 7H
after reset; the correct value should be 0H.
Implication: The IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR bits [34:32] may be incorrect after reset
(EN_FIXED_CTR{0, 1, 2} may be enabled).
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU42. Performance Monitor Counter INST_RETIRED.STORES May Count
Higher than Expected
Problem: Performance Monitoring counter INST_RETIRED.STORES (Event: C0H) is used to track
retired instructions which contain a store operation. Due to this erratum, the processor
may also count other types of instructions including WRMSR and MFENCE.
Implication: Performance Monitoring counter INST_RETIRED.ST ORES may report counts higher than
expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
29
Page 30

AAU43. Sleeping Cores May Not be Woken Up on Logical Cluster Mode
Broadcast IPI Using Destination Field Instead of Shorthand
Problem: If software sends a logical cluster broadcast IPI using a destination shorthand of 00B
(No Shorthand) and writes the cluster portion of the Destination Field of the Interrupt
Command Register to all ones while not using all 1s in the mask portion of the
Destination Field, target cores in a sleep state that are identified by the mask portion of
the Destination Field may not be woken up. This erratum does not occur if the
destination shorthand is set to 10B (All Including Self) or 11B (All Excluding Self).
Implication: When this erratum occurs, cores which are in a sleep state may not wake up to handle
the broadcast IPI. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially - available
software.
Workaround: Use destination shorthand of 10B or 11B to send broadcast IPIs.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU44. Faulting Executions of FXRSTOR May Update State Inconsistently
Problem: The state updated by a faulting FXRSTOR instruction may vary from one execution to
another.
Implication: Software that relies on x87 state or SSE state following a faulting execution of
FXRSTOR may behave inconsistently.
Workaround: Software handling a fault on an execution of FXRSTOR can compensate for execution
variability by correcting the cause of the fault and executing FXRSTOR again.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU45. Performance Monitor Event EPT.EPDPE_MISS May be Counted While
EPT is Disable
Problem: Performance monitor event EPT.EPDPE_MISS (Event: 4FH, Umask: 08H) is used to
count Page Directory Pointer table misses while EPT (extended page tables) is enabled.
Due to this erratum, the processor will count Page Directory Pointer table misses
regardless of whether EPT is enabled or not.
Implication: Due to this erratum, performance monitor ev ent EPT.EPDPE_MISS may report counts
higher than expected.
Workaround: Software should ensure this event is only enabled while in EPT mode.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU46. Memory Aliasing of Code Pages May Cause Unpredictable System
Behavior
Problem: The type of memory aliasing contributing to this erratum is the case where two
different logical processors have the same code page mapped with two different
memory types. Specifically, if one code page is mapped by one logical processor as
write-back and by another as uncachable and certain instruction fetch timing conditions
occur, the system may experience unpredictable behavior.
Implication: If this erratum occurs the system may have unpredictable behavior including a system
hang. The aliasing of memory regions, a condition necessary for this erratum to occur,
is documented as being unsupported in the Intel 64 and IA-32 Intel
Software Developer's Manual, Volume 3A, in the section titled Programming the PAT.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially-available software or
system.
Workaround: Code pages should not be mapped with uncacheable and cacheable memory types at
the same time.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
30
®
Architecture
Specification Update
Page 31

AAU47. Performance Monitor Counters May Count Incorrectly
Problem: Under certain circumstances, a general purpose performance counter, IA32_PMC0-4
(C1H - C4H), may count at core frequency or not count at all instead of counting the
programmed event.
Implication: The Performance Monitor Counter IA32_PMCx may not properly count the programmed
event. Due to the requirements of the workaround there may be an interruption in the
counting of a previously programmed event during the programming of a new event.
Workaround: Before programming the performance event select registers, IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSR
(186H - 189H), the internal monitoring hardware must be cleared. This is accomplished
by first disabling, saving valid events and clearing from the select registers, then
programming three event values 0x4300D2, 0x4300B1 and 0x4300B5 into the
IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSRs, and finally continuing with new event programming and
restoring previous programming if necessary. Each performance counter, IA32_PMCx,
must have its corresponding IA32_PREFEVTSELx MSR programmed with at least one of
the event values and must be enabled in IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR (38FH) bits
[3:0]. All three values must be written to either the same or different
IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSRs before programming the performance counters. Note that
the performance counter will not increment when its IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSR has a
value of 0x4300D2, 0x4300B1 or 0x4300B5 because those values have a zero UMASK
field (bits [15:8]).
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU48. Performance Monitor Event Offcore_response_0 (B7H) Does Not
Count NT Stores to Local DRAM Correctly
Problem: When a IA32_PERFEVTSELx MSR is programmed to count the Offcore_response_0
event (Event:B7H), selections in the OFFCORE_RSP_0 MSR (1A6H) determine what is
counted. The following two selections do not provide accurate counts when counting NT
(Non-Temporal) Stores:
• OFFCORE_RSP_0 MSR bit [14] is set to 1 (LOCAL_DRAM) and bit [7] is set to 1
(OTHER): NT Stores to Local DRAM are not counted when they should have been.
• OFFCORE_RSP_0 MSR bit [9] is set to (OTHER_CORE_HIT_SNOOP) and bit [7] is
set to 1 (OTHER): NT Stores to Local DRAM are counted when they should not have
been.
Implication: The counter for the Offcore_response_0 event may be incorrect for NT stores.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
31
Page 32

AAU49. EFLAGS Discrepancy on Page Faults and on EPT-Induced VM Exits
after a Translation Change
Problem: This erratum is regarding the case where paging structures are modified to change a
linear address from writable to non-writable without software performing an
appropriate TLB invalidation. When a subsequent access to that address by a specific
instruction (ADD, AND, BTC, BTR, BTS, CMPXCHG, DEC, INC, NEG, NOT, OR, ROL/ROR,
SAL/SAR/SHL/SHR, SHLD, SHRD, SUB, XOR, and XADD) causes a page fault or an EPTinduced VM exit, the value saved for EFLAGS may incorrectly contain the arithmetic flag
values that the EFLAGS register would have held had the instruction completed without
fault or VM exit. For page faults, this can occur even if the fault causes a VM exit or if
its delivery causes a nested fault.
Implication: None identified. Although the EFLAGS value saved by an affected event (a page fault or
an EPT-induced VM exit) may contain incorrect arithmetic flag values, Intel has not
identified software that is affected by this erratum. This erratum will have no further
effects once the original instruction is restarted because the instruction will produce the
same results as if it had initially completed without fault or VM exit.
Workaround: If the handler of the affected events inspects the arithmetic portion of the saved
EFLAGS value, then system software should perform a synchronized paging structure
modification and TLB invalidation.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU50. Back to Back Uncorrected Machine Check Errors May Overwrite
IA32_MC3_STATUS.MSCOD
Problem: When back-to-back uncorrected machine check errors occur that would both be logged
in the IA32_MC3_STATUS MSR (40CH), the IA32_MC3_STATUS.MSCOD (bits [31:16])
field may reflect the status of the most recent error and not the first error. The rest of
the IA32_MC3_STATUS MSR contains the information from the first error.
Implication: Software should not rely on the value of IA32_MC3_STATUS.MSCOD if
IA32_MC3_STATUS.OVER (bit [62]) is set.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU51. Corrected Errors With a Yellow Error Indication May be Overwritten by
Other Corrected Errors
Problem: A corrected cache hierarchy data or tag error that is reported with
IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD (bits [15:0]) with value of 000x_0001_xxxx_xx01 (where
x stands for zero or one) and a yellow threshold-based error status indication (bits
[54:53] equal to 10B) may be overwritten by a corrected error with a no tracking
indication (00B) or green indication (01B).
Implication: Corrected errors with a yellow threshold-based error status indication may be
overwritten by a corrected error without a yellow indication.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
32
Specification Update
Page 33

AAU52. Performance Monitor Events DCACHE_CACHE_LD and
DCACHE_CACHE_ST May Overcount
Problem: The performance monitor events DCACHE_CACHE_LD (Event 40H) and
DCACHE_CACHE_ST (Event 41H) count cacheable loads and stores that hit the L1
cache. Due to this erratum, in addition to counting the completed loads and stores, the
counter will incorrectly count speculative loads and stores that were aborted prior to
completion.
Implication: The performance monitor events DCACHE_CACHE_LD and DCACHE_CACHE_ST may
reflect a count higher than the actual number of events.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU53. Rapid Core C3/C6 Transitions May Cause Unpredictable System
Behavior
Problem: Under a complex set of internal conditions, cores rapidly performing C3/C6 transitions
in a system with Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology enabled may cause a machine
check error (IA32_MCi_STATUS.MCACOD = 0x0106), system hang or unpredictable
system behavior.
Implication: This erratum may cause a machine check error, system hang or unpredictable system
behavior.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU54. APIC Timer CCR May Report 0 in Periodic Mode
Problem: In periodic mode the APIC timer CCR (current-count register) is supposed to be
automatically reloaded from the initial-count register when the count reaches 0,
consequently software would never be able to observe a value of 0. Due to this
erratum, software may read 0 from the CCR when the timer has counted down and is in
the process of re-arming.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an unexpected value of 0 may be read from the APIC timer CCR
when in periodic mode.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU55. Performance Monitor Events INSTR_RETIRED and
MEM_INST_RETIRED May Count Inaccurately
Problem: The performance monitor event INSTR_RETIRED (Event C0H) should count the n umber
of instructions retired, and MEM_INST_ RETIRED (Event 0BH) should count the number
of load or store instructions retired. However, due to this erratum, they may
undercount.
Implication: The performance monitor event INSTR_RETIRED and MEM_INST_RETIRED may reflect
a count lower than the actual number of events.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
33
Page 34

AAU56. A Page Fault May Not be Generated When the PS bit is set to "1" in a
PML4E or PDPTE
Problem: On processors supporting Intel® 64 architecture, the PS bit (Page Size, bit 7) is
reserved in PML4Es and PDPTEs. If the translation of the linear address of a memory
access encounters a PML4E or a PDPTE with PS set to 1, a page fault should occur . Due
to this erratum, PS of such an entry is ignored and no page fault will occur due to its
being set.
Implication: Software may not operate properly if it relies on the processor to deliver page faults
when reserved bits are set in paging-structure entries.
Workaround: Software should not set Bit 7 in any PML4E or PDPTE that has Present Bit (Bit 0) set to
"1".
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU57. BIST Results May be Additionally Reported After a GETSEC[WAKEUP]
or INIT-SIPI Sequence
Problem: BIST results should only be reported in EAX the first time a logical processor wakes up
from the Wait-For-SIPI state. Due to this erratum, BIST results may be additionally
reported after INIT-SIPI sequences and when waking up RLP's from the SENTER sleep
state using the GETSEC[WAKEUP] command.
Implication: An INIT-SIPI sequence may show a non-zero value in EAX upon wakeup when a zero
value is expected. RLP's waking up for the SENTER sleep state using the
GETSEC[WAKEUP] command may show a different value in EAX upon wakeup than
before going into the SENTER sleep state.
Workaround: If necessary software may save the value in EAX prior to launching into the secure
environment and restore upon wakeup and/or clear EAX after the INIT-SIPI sequence.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU58. Pending x87 FPU Exceptions (#MF) May be Signaled Earlier Than
Expected
Problem: x87 instructions that trigger #MF normally service interrupts before the #MF. Due to
this erratum, if an instruction that triggers #MF is executed while Enhanced Intel
SpeedStep
Thermal Monitor events occur, the pending #MF may be signaled before pending
interrupts are serviced.
Implication: Software may observe #MF being signaled before pending interrupts are serviced.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
®
Technology transitions, Intel® Turbo Boost Technology transitions, or
34
Specification Update
Page 35

AAU59. VM Exits Due to "NMI-Window Exiting" Ma y Be Delayed by One
Instruction
Problem: If VM entry is executed with the "NMI-window exiting" VM-execution control set to 1, a
VM exit with exit reason "NMI window" should occur before execution of any instruction
if there is no virtual-NMI blocking, no blocking of events by MOV SS, and no blocking of
events by STI. If VM entry is made with no virtual-NMI blocking but with blocking of
events by either MOV SS or STI, such a VM exit should occur after execution of one
instruction in VMX non-root operation. Due to this erratum, the VM exit may be delayed
by one additional instruction.
Implication: VMM software using "NMI-window exiting" for NMI virtualization should generally be
unaffected, as the erratum causes at most a one-instruction delay in the injection of a
virtual NMI, which is virtually asynchronous. The erratum may affect VMMs relying on
deterministic delivery of the affected VM exits.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU60. The Memory Controller tTHROT_OPREF Timings May be Violated
During Self Refresh Entry
Problem: During self refresh entry, the memory controller may issue more refreshes than
permitted by tTHROT_OPREF (bits 29:19 in MC_CHANNEL_{0,1}_REFRESH_TIMING
CSR).
Implication: The intention of tTHROT_OPREF is to limit current. Since current supply conditions near
self refresh entry are not critical, there is no measurable impact due to this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU61. VM Exits Due to EPT Violations Do Not Record Information About Pre-
IRET NMI Blocking
Problem: With certain settings of the VM-execution controls VM exits due to EPT violations set bit
12 of the exit qualification if the EPT violation was a result of an execution of the IRET
instruction that commenced with non-maskable interrupts (NMIs) blocked. Due to this
erratum, such VM exits will instead clear this bit.
Implication: Due to this erratum, a virtual-machine monitor that relies on the proper setting of bit
12 of the exit qualification may deliver NMIs to guest software prematurely.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU62. Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of
IA32_FIXED_CTR2
Problem: When multiple performance counters are set to gener ate interrupts on an ov erflow and
more than one counter overflows at the same time, only one interrupt should be
generated. However, if one of the counters set to generate an interrupt on overflow is
the IA32_FIXED_CTR2 (MSR 30BH) counter, multiple interrupts may be generated
when the IA32_FIXED_CTR2 overflows at the same time as any of the other
performance counters.
Implication: Multiple counter overflow interrupts may be unexpectedly generated.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
35
Page 36

AAU63. LBRs May Not be Initialized During Power-On Reset of the Processor
Problem: If a second reset is initiated during the power-on processor reset cycle, the LBRs (Last
Branch Records) may not be properly initialized.
Implication: Due to this erratum, debug software may not be able to rely on the LBRs out of power-
on reset.
Workaround: Ensure that the processor has completed its power-on reset cycle prior to initiating a
second reset.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU64. LBR, BTM or BTS Records May have Incorrect Branch From
Information After an EIST Transition, T-states, C1E, or Adaptive
Thermal Throttling
Problem: The "From" address associated with the LBR (Last Branch Record), BTM (Branch Trace
Message) or BTS (Branch Trace Store) may be incorrect for the first branch after an
EIST (Enhanced Intel
®
SpeedStep Technology) transition, T-states, C1E (C1
Enhanced), or Adaptive Thermal Throttling.
Implication: When the LBRs, BTM or BTS are enabled, some records may have incorrect branch
"From" addresses for the first branch after an EIST transition, T-states, C1E, or
Adaptive Thermal Throttling.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU65. VMX-Preemption Timer Does Not Count Down at the Rate Specified
Problem: The VMX-preemption timer should count down by 1 every time a specific bit in the TSC
(Time Stamp Counter) changes. (This specific bit is indicated by IA32_VMX_MISC bits
[4:0] (0x485h) and has a value of 5 on the affected processors.) Due to this erratum,
the VMX-preemption timer may instead count down at a different rate and may do so
only intermittently.
Implication: The VMX-preemption timer may cause VM exits at a rate different from that expected
by software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
36
Specification Update
Page 37

AAU66. Multiple Performance Monitor Interrupts are Possible on Overflow of
Fixed Counter 0
Problem: The processor can be configured to issue a PMI (performance monitor interrupt) upon
overflow of the IA32_FIXED_CTR0 MSR (309H). A single PMI should be observed on
overflow of IA32_FIXED_CTR0, however multiple PMIs are observed when this erratum
occurs.
This erratum only occurs when IA32_FIXED_CTR0 overflows and the processor and
counter are configured as follows:
®
•Intel
Hyper-Threading Technology is enabled
• IA32_FIXED_CTR0 local and global controls are enabled
• IA32_FIXED_CTR0 is set to count events only on its own thread
(IA32_FIXED_CTR_CTRL MSR (38DH) bit [2] = ‘0)
• PMIs are enabled on IA32_FIXED_CTR0 (IA32_FIXED_CTR_CTRL MSR bit [3] = ‘1)
• Freeze_on_PMI feature is enabled (IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H) bit [12] = ‘1)
Implication: When this erratum occurs there may be multiple PMIs observed when
IA32_FIXED_CTR0 overflows
Workaround: Disable the FREEZE_PERFMON_ON_PMI feature in IA32_DEBUGCTL MSR (1D9H) bit
[12].
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU67. VM Exits Due to LIDT/LGD T/SIDT/SGDT Do Not Report Correct
Operand Size
Problem: When a VM exit occurs due to a LIDT, LGDT, SIDT, or SGDT instruction with a 32-bit
operand, bit 11 of the VM-exit instruction information field should be set to 1. Due to
this erratum, this bit is instead cleared to 0 (indicating a 16-bit operand).
Implication: Virtual-machine monitors cannot rely on bit 11 of the VM-exit instruction information
field to determine the operand size of the instruction causing the VM exit.
Workaround: Virtual Machine Monitor software may decode the instruction to determine operand
size.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU68. Performance Monitoring Events STORE_BLOCKS.NOT_STA and
STORE_BLOCKS.STA May Not Count Events Correctly
Problem: Performance Monitor Events STORE_BLOCKS.NOT_STA and STORE_BLOCKS.STA
should only increment the count when a load is blocked by a store. Due to this erratum,
the count will be incremented whenever a load hits a store, whether it is blocked or can
forward. In addition this event does not count for specific threads correctly.
Implication: If Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology is disabled, the Performance Monitor events
STORE_BLOCKS.NOT_STA and STORE_BLOCKS.STA may indicate a higher occurrence
of loads blocked by stores than have actually occurred. If Intel Hyper-Threading
Technology is enabled, the counts of loads blocked by stores may be unpredictable and
they could be higher or lower than the correct count.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
37
Page 38

AAU69. Storage of PEBS Record Delayed Following Execution of MOV SS or STI
Problem: When a performance monitoring counter is configured for PEBS (Precise Event Based
Sampling), overflow of the counter results in storage of a PEBS record in the PEBS
buffer. The information in the PEBS record represents the state of the next instruction
to be executed following the counter overflow. Due to this erratum, if the counter
overflow occurs after execution of either MOV SS or STI, storage of the PEBS record is
delayed by one instruction.
Implication: When this erratum occurs, software may observe storage of the PEBS record being
delayed by one instruction following execution of MOV SS or STI. The state information
in the PEBS record will also reflect the one instruction delay.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU70. Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX May Not
Count Some Transitions
Problem: Performance Monitor Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX (Event CCH, Umask 01H) counts
transitions from x87 Floating Point (FP) to MMX™ instructions. Due to this erratum, if
only a small number of MMX instructions (including EMMS) are executed immediately
after the last FP instruction, a FP to MMX transition may not be counted.
Implication: The count value for Performance Monitoring Event FP_MMX_TRANS_TO_MMX may be
lower than expected. The degree of undercounting is dependent on the occurrences of
the erratum condition while the counter is active. Intel has not observed this erratum
with any commercially-available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU71. INVLPG Following INVEPT or INVVPID May Fail to Flush All
Translations for a Large Page
Problem: This erratum applies if the address of the memory operand of an INVEPT or INVVPID
instruction resides on a page larger than 4KBytes and either (1) that page includes the
low 1 MBytes of physical memory; or (2) the physical address of the memory operand
matches an MTRR that covers less than 4 MBytes. A subsequent execution of INVLPG
that targets the large page and that occurs before the next VM-entry instruction may
fail to flush all TLB entries for the page. Such entries may persist in the TLB until the
next VM-entry instruction.
Implication: Accesses to the large page between INVLPG and the next VM-entry instruction may
incorrectly use translations that are inconsistent with the in-memory page tables.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
38
Specification Update
Page 39

AAU72. Logical Processor May Use Incorrect VPID after VM Entry That Returns
From SMM
Problem: A logical processor in VMX root operation should use VPID 0000H. Due to this erratum,
a logical processor may instead use VPID 1FB3H if VMX root operation was entered
using a VM entry that returns from SMM.
Implication: After a VM entry that sets the "enable VPID" VM-execution control and that establishes
VPID 1FB3H, the logical processor may erroneously use TLB entries that were cached in
VMX root operation.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU73. The Memory Controller May Hang Due to Uncorrectable ECC Errors or
Parity Errors Occurring on Both Channels in Mirror Channel Mode
Problem: If an uncorrectable ECC or parity error occurs on the mirrored channel before an
uncorrectable ECC or parity error on the other channel can be resolved, the Memory
Controller may hang without an uncorrectable ECC or parity error being logged.
Implication: The processor may hang and not report the error when uncorrectable ECC or parity
errors occur in close proximity on both channels in a mirrored channel pair. No
uncorrectable ECC or parity error will be logged in the machine check banks.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU74. MSR_TURBO_RATIO_LIMIT MSR May Return Intel® Turbo Boost
Technology Core Ratio Multipliers for Non-Existent Core
Configurations
Problem: MSR_TURBO_RATIO_LIMIT MSR (1ADH) is designed to describe the maximum Intel
Turbo Boost Technology potential of the processor. On some processors, a non-zero
Intel Tu rbo Boost Technology value will be returned for non-existent core
configurations.
Implication: Due to this erratum, software using the MSR_TURBO_RA TIO_LIMIT MSR to report Intel
Turbo Boost Technology processor capabilities may report erroneous results.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU75. Internal Parity Error May Be Incorrectly Signaled during C6 Exit
Problem: In a complex set of internal conditions an internal parity error may occur during a Core
C6 exit.
Implication: Due to this erratum, an uncorrected error may be reported and a machine check
exception may be triggered.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
39
Page 40

AAU76. PMIs during Core C6 Transitions May Cause the System to Hang
Problem: If a performance monitoring counter overflows and causes a PMI (Performance
Monitoring Interrupt) at the same time that the core enters C6, then this may cause
the system to hang.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may hang when a PMI coincides with core C6 entry.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU77. 2MB Page Split Lock Accesses Combined With Complex Internal
Events May Cause Unpredictable System Behavior
Problem: A 2MB Page Split Lock (a locked access that spans two 2MB large pages) coincident
with additional requests that have particular address relationships in combination with
a timing sensitive sequence of complex internal conditions may cause unpredictable
system behavior.
Implication: This erratum may cause unpredictable system behavior. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU78. If the APIC timer Divide Configuration Register (Offset 03E0H) is
written at the same time that the APIC timer Current Count Register
(Offset 0390H) reads 1H, it is possible that the APIC timer will deliver
two interrupts.
Problem: If the APIC timer Divide Configuration Register (Offset 03E0H) is written at the same
time that the APIC timer Current Count Register (Offset 0390H) reads 1H, it is possible
that the APIC timer will deliver two interrupts.
Implication: Due to this erratum, two interrupts may unexpectedly be generated by an APIC timer
event.
Workaround: Software should reprogram the Divide Configuration Register only when the APIC timer
interrupt is disarmed.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU79. TXT.PUBLIC.KEY is Not Reliable
Problem: On Intel® TXT (Intel® Trusted Execution Technology) capable processors, the
TXT.PUBLIC.KEY value (Intel TXT registers FED3_0400H to FED3_041FH) is not
reliable.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the TXT.PUBLIC.KEY value should not be relied on or used for
retrieving the hash of the TXT public key for the platform.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
40
Specification Update
Page 41

AAU80. 8259 Virtual Wire B Mode Interrupt May Be Dropped When it Collides
With Interrupt Acknowledge Cycle From the Preceding Interrupt
Problem: If an un-serviced 8259 Virtual Wire B Mode (8259 connected to IOA PIC) External
Interrupt is pending in the APIC and a second 8259 Virtual Wire B Mode External
Interrupt arrives, the processor may incorrectly drop the second 8259 Virtual Wire B
Mode External Interrupt request. This occurs when both the new External Interrupt and
Interrupt Acknowledge for the previous External Interrupt arrive at the APIC at the
same time.
Implication: to this erratum, any further 8259 Virtual Wire B Mode External Interrupts will
subsequently be ignored.
Workaround: Do not use 8259 Virtual Wire B mode when using the 8259 to deliver interrupts.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU82. The APIC Timer Current Count Register May Prematurely Read 0x0
While the Timer is Still Running
Problem: The APIC Timer Current Counter Register may prematurely read 0x00000000 while the
timer is still running. This problem occurs when a core frequency or C-state transition
occurs while the APIC timer countdown is in progress.
Implication: Due to this erratum, certain software may incorrectly assess that the APIC timer
countdown is complete when it is actually still running. This erratum does not affect the
delivery of the timer interrupt.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU83. Secondary PCIe Port May Not Train After A Warm Reset
Problem: In a dual PCIe port configuration, the secondary PCIe port may not train after a warm
reset.
Implication: The second PCIe port and therefore any device connected to the PCIe bus instantiated
by that PCIe port may not be functional after a warm reset. Intel has not observed this
erratum with any commercially available system.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
Specification Update
41
Page 42

AAU84. The PECI Bus May Be Tri-stated after System Reset
Problem: During power-up, the processor may improperly assert the PECI (Platform Environment
Control Interface) pin. This condition is cleared as soon as Bus Clock starts toggling.
However, if the PECI host (also referred to as the master or originator) incorrectly
determines this asserted state as another PECI host initiating a transaction, it may
release control of the bus resulting in a permanent tri-state condition.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the PECI host may incorrectly determine that it is not the bus
master and consequently PECI commands initiated by the PECI software layer may
receive incorrect/invalid responses.
Workaround: To workaround this erratum the PECI host should pull the PECI bus low to initiate a
PECI transaction.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU85. The Combination of a Page-Split Lock Access And Data Accesses That
Are Split Across Cacheline Boundaries May Lead to Processor Livelock
Problem: Under certain complex micro-architectural conditions, the simultaneous occurrence of a
page-split lock and several data accesses that are split across cacheline boundaries
may lead to processor livelock.
Implication: Due to this erratum, a livelock may occur that can only be terminated by a processor
reset. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU86. Processor Hangs on Package C6 State Exit
Problem: An internal timing condition in the processor power management logic will result in
processor hangs upon a Package C6 state exit.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor will hang during Package C6 state exit.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU87. A Synchrono us SMI May be Delayed
Problem: A synchronous SMI (System Management Interrupt) occurs as a result of an SMI
generating I/O Write instruction and should be handled prior to the next instruction
executing. Due to this erratum, the processor may not observe the synchronous SMI
prior to execution of the next instruction.
Implication: Due to this erratum, instructions after the I/O Write instruction, which triggered the
SMI, may be allowed to execute before the SMI handler. Delayed delivery of the SMI
may make it difficult for an SMI Handler to determine the source of the SMI. Software
that relies on the IO_SMI bit in SMM save state or synchronous SMI behavior may not
function as expected.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
42
Specification Update
Page 43

AAU88. FP Data Operand Pointer May Be Incorrectly Calculated After an FP
Access Which Wraps a 4-Gbyte Boundary in Code That Uses 32-Bit
Address Size in 64-bit Mode
Problem: The FP (Floating Point) Data Operand Pointer is the effective address of the operand
associated with the last non-control FP instruction executed by the processor. If an 80bit FP access (load or store) uses a 32-bit address size in 64-bit mode and the memory
access wraps a 4-Gbyte boundary and the FP environment is subsequently saved, the
value contained in the FP Data Operand Pointer may be incorrect.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the FP Data Operand Pointer may be incorrect. W rapping an 80-bit
FP load around a 4-Gbyte boundary in this way is not a normal programming practice.
Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: If the FP Data Operand Pointer is used in a 64-bit operating system which may run code
accessing 32-bit addresses, care must be taken to ensure that no 80-bit FP accesses
are wrapped around a 4-Gbyte boundary.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU89. PCI Express x16 Port Links May Fail to Dynamically Switch From
5.0GT/s to 2.5GT/s
Problem: If an endpoint device initiates a PCI Express speed change from 5.0 GT/s to 2.5 GT/s,
the link may incorrectly go into Recovery.Idle rather than the expected Recovery.Speed
state. This may cause the link to lose sync, eventually resulting in a link down. The link
will recover and re-train to the L0 state, however any outstanding packets queued
during the speed change may be lost.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the link may lose sync resulting in link down with queued packet
being lost. No known failures have been observed on systems using production PCI
Express graphics cards. This erratum has only been observed in a synthetic test
environment.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU90. PCI Express Cards May Not Train to x16 Link Width
Problem: The Maximum Link Width field in the Link Capabilities register (LCAP; Bus 0; Device 1;
Function 0; offset 0xAC; bits [9:4]) may limit the width of the PCI Express link to x8,
even though the processor may actually be capable of supporting the full x16 width.
Implication: PCI Express x16 Graphics Cards used in normal operation and PCI Express CLB
(Compliance Load Board) Cards used during PCI Express Compliance mode testing may
only train to x8 link width.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU91. Unexpected Graphics VID Transition During Warm Reset May Cause
the System to Hang
Problem: During a warm reset to the processor, the graphics VID (Voltage ID) may transition to
an unexpected value that may cause the voltage regulator to shut off.
Implication: The processor may hang during integrated graphics initialization. Cold boots and
platforms using discrete graphics are not affected by this issue.
Workaround: A BIOS code change has been identified and may be implemented as a workaround for
this erratum.
Specification Update
43
Page 44

Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU92. IO_SMI Indication in SMRA M State Save Area May Be Lost
Problem: The IO_SMI bit (bit 0) in the IO state field at SMRAM offset 7FA4H is set to "1" by the
processor to indicate a System Management Interrupt (SMI) is either taken
immediately after a successful I/O instruction or is taken after a successful iteration of
a REP I/O instruction. Due to this erratum, the setting of the IO_SMI bit may be lost.
This may happen under a complex set of internal conditions with Intel® Hyper-
Threading Technology enabled and has not been observed with commercially available
software.
Implication: Due to this erratum, SMI handlers may not be able to identify the occurrence of I/O
SMIs.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU93. VM Entry to 64-Bit Mode May Fail if Bits 48 And 47 of Guest RIP A re
Different
Problem: VM entry to 64-bit mode should allow any value for bits [47:0] of the RIP field in the
guest-state area as long as bits 63:48 are identical. Due to this erratum, such a VM
entry may fail if bit 47 of the field has a value different from that of bit 48.
Implication: It is not possible to perform VM entry to a 64-bit guest that has made a transition to a
non-canonical instruction pointer.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU94. VM Entry Loading an Unusable SS Might Not Set SS.B to 1
Problem: If the unusable bit (bit 16) is 1 in the guest SS (Stack Segment) access-rights field, VM
entry should set the B bit (default stack-pointer size) in the SS (stack segment)
register to 1. Due to this erratum, VM entry may instead load SS.B from bit 14 of the
guest SS access-rights field, potentially clearing SS.B to 0.
Implication: This erratum can affect software only if a far RET instruction is executed after a VM
entry that erroneously clears the B bit and only if the following other three conditions
are also true: (1) the SS register is not loaded between VM entry and far RET; (2) the
far RET instruction is executed in 64-bit mode with an immediate operand; (3) the far
RET instruction makes a transition to compatibility mode without changing CPL
(Current Privilege Level). Due to the far RET being executed with an immediate
operand, an adjustment is made to the stack pointer. Normally, when SS is unusable
the SS.B bit is 1 and the adjustment will be to the 32-bit ESP register. Due to this
erratum, the adjustment will incorrectly be made to the 16-bit SP register. Intel has not
observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU95. FSW May Be Corrupted If an x87 Store Instruction Causes a Page Fault
in VMX Non-Root Operation
Problem: The X87 FSW (FPU Status Word) may be corrupted if execution of a floating-point store
instruction (FST, FSTP, FIST, FISTP, FISTTP) causes a page fault in VMX non-root
operation.
44
Specification Update
Page 45

Implication: This erratum may result in unexpected behavior of software that uses x87 FPU
instructions.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: None identified.
AAU96. Under Certain Low Temperature Conditions, Some Uncore
Performance Monitoring Events May Report Incorrect Results
Problem: Due to this erratum, under certain low operating temperatures, a small number of Last
Level Cache and external bus performance monitoring events in the uncore report
incorrect counts. This erratum may affect event codes in the ranges 00H to 0CH and
40H to 43H.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the count value for some uncore Performance Monitoring Events
may be inaccurate. The degree of under or over counting is dependent on the
occurrences of the erratum condition while the counter is active. Intel has not
observedthis erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU97. CKE May go Low Within tRFC(min) After a PD Exit
Problem: After a refresh command is issued, followed by an early PD(Power Down) Entry and
Exit, the CKE (Clock Enable) signal may be asserted low prior to tRFC(min), the
Minimum Refresh Cycle timing. This additional instance of CKE being low causes the
processor not to meet the JEDEC DDR3 DRAM specification requirement (Section
4.17.4 Power-Down clarifications - Case 3).
Implication: Due to this erratum, the processor may not meet the JEDEC DDR3 DRAM specification
requirement that states: “CKE cannot be registered low twice within a tRFC(min)
window”. Intel has not observed any functional failure due to this erratum.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU98. Erratum AAU98 added to this specification Update in error; all erratum
details removed from the specification update document.
AAU99. Performance Monitor Events for Hardware Prefetches Which Miss The
L1 Data Cache May be Over-Counted
Problem: Hardware prefetches that miss the L1 data cache but cannot be processed immediately
due to resource conflicts will count and then retry. This may lead to incorrectly
incrementing the L1D_PREFETCH.MISS (event 4EH, umask 02H) event multiple times
for a single miss.
Implication: The count reported by the L1D_PREFETCH.MISS event may be higher than expected.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU100. VM Exit May Incorrectly Clear IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL [34:32]
Problem: If the “load IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL” VM-exit control is 1, a VM exit should load the
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR (38FH) from the IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL field in the
guest-state area of the VMCS. Due to this erratum, such a VM exit may instead clear
bits 34:32 of the MSR, loading only bits 31:0 from the VMCS.
Specification Update
45
Page 46

Implication: All fixed-function performance counters will be disabled after an affected VM exit, even
if the VM exit should have enabled them based on the IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL field
in the guest-state area of the VMCS.
Workaround: A VM monitor that wants the fixed-function performance counters to be enabled after a
VM exit may do one of two things: (1) clear the “load IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL” VMexit control; or (2) include an entry for the IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL MSR in the VMexit MSR-load list.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU101. Correctable and Uncorrectable Cache Errors May be Reported Until the
First Core C6 Transition
Problem: On a subset of processors it is possible that correctable/uncorrectable cache errors may
be logged and/or a machine check exception may occur prior to the first core C6
transition. The errors will be logged in IA32_MC5_STATUS MSR (415H) with the
MCACOD (Machine Check Architecture Error Code) bits [15:0] indicating a Cache
Hierarchy Error of the form 000F 0001 RRRR TTLL.
Implication: Due to this erratum, correctable/uncorrectable cache error may be logged or signaled.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU102. Accesses to a VMCS May Not Operate Correctly If CR0.CD is Set on Any
Logical Processor of a Core
Problem: The VMX (virtual-machine extensions) are controlled by the VMCS (virtual-machine
control structure). If CR0.CD is set on any logical processor of a core, operations using
the VMCS may not function correctly. Such operations include the VMREAD and
VMWRITE instructions as well as VM entries and VM exits.
Implication: If CR0.CD is set on either logical processor in a core, the VMWRITE instruction may not
correctly update the VMCS and the VMREAD instruction may not return correct data.
VM entries may not load state properly and may not establish VMX controls properly.
VM exits may not save or load state properly.
Workaround: VMMs (Virtual-machine monitors) should ensure that CR0.CD is clear on all logical
processors of a core before entering VMX operation on any logical processor. Software
should not set CR0.CD on a logical processor if any logical processor of the same core is
in VMX operation. VMM software should prevent guest software from setting CR0.CD by
setting bit 30 in the CR0 guest/host mask field in every VMCS.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU103. PCIe Port’s LTSSM May Not Transition Properly in the Presence of TS1
or TS2 Ordered Sets That Have Unexpected Symbol s Within those Sets
Problem: When a PCIe p ort re ceives TS1 and/or TS2 ordered sets with unexpecte d symb ols (p er
the PCIe Base Specification), the port’s LTSSM (Link Training State Machine) might not
transition according to the PCIe Base Specification requirements. The LTSSM may
incorrectly stay in its current state, or transition to an incorrect state. If the unexpected
symbols are sporadic in nature the link will recover and go to the proper state.
Implication: PCIe Port’s LTSMM may not transition according to PCIe Base Specification as described
above. This problem has not been seen in real system testing, but was discovered by
synthetic tests designed to check for illegal conditions.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
46
Specification Update
Page 47

AAU104. NTB/RP Link Will Send Extra TS2 Ordered Set During Link Training
Problem: The NTB (Non-Transparent Bridge) when operating in NTB/RP (Root Port) mode will
send a superfluous TS2 ordered set after transitioning to the CONFIGURATION.IDLE
state during link training. This TS2 ordered set may contain invalid capability data.
Implication: NTB/RP Link will transmit a TS2 ordered set after transitioning to the
CONFIGURATION.IDLE state. No impact expected for specification compliant PCIe
partners. Specification compliant PCIe link partners will have transitioned to
CONFIGURATION.IDLE before this ordered set is sent and will ignore it.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU105. PCIe Ports May Not Enter Slave Loopback Mode From the
Configuration LTSSM State
Problem: If a PCIe port’s LTSSM (Link Training State Machine) is in the
CONFIG.LINK_WIDTH_START state, it may not enter slave loopback mode when
requested to do so by the link partner. If the request is missed the link will continue to
train and enter the Slave loopback mode after it first transitions through the L0 and
RECOVERY LTSSM states.
Implication: Due to this erratum, PCIe ports may be delayed in entering the slave loopback mode.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU106. USB Devices May Not Function Properly With Integrated Graphics
While Running Targeted Stress Graphics Workloads With Non-
Matching Memory Configurations
Problem: When the integrated graphics engine continuously generates a large stream of writes to
system memory, and Intel Flex Memory Technology is enabled, with a different amount
of memory in each channel, the memory arbiter may temporarily stop servicing other
device-initiated traffic. In some cases this can cause certain USB devices, such as
keyboard and mouse, to become unresponsive. Intel has only observed this erratum
with targeted stress content. This erratum is not seen when the platform is configured
with single channel or dual channel symmetric memory and is not dependent on the
memory frequency.
Implication: Due to this erratum, certain USB devices may become unresponsive.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU107. VM Entry May Omit Consistency Checks Related to Bit 14 (BS) of the
Pending Debug Exception Field in Guest-State Area of the VMCS
Problem: Section “Checks on Guest Non-Register State” of Volume 3B specifies consistency
checks that VM entry should perform for bit 14 (BS, indicating a pending single-step
exception) of the pending debug exception field in guest-state area of the VMCS. These
checks enforce the consistency of that bit with other fields in the guest-state area. Due
to this erratum, VM entry may fail to perform these checks.
Implication: A logical processor may enter VMX non-root operation with a pending single-step
debug exception that not consistent other register state; this may result in unexpected
behavior. Intel has not observed this erratum with any commercially available software.
Workaround: When using VMWRITE to write to a field in th e guest -state area, softw are should ensure
that the value written is consistent with the state of other guest-state fields.
Specification Update
47
Page 48

Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU108. Intel Turbo Boost Technology Ratio Changes May Cause Unpredictable
System Behavior
Problem: When Intel Turbo Boost Technology is enabled as determined by the
TURBO_MODE_DISABLE bit being “0” in the IA32_MISC_ENABLES MSR (1A0H), the
process of locking to new ratio may cause the processor to run with incorrect ratio
settings. The result of this erratum may be unpredictable system behavior.
Implication: Due to this erratum, unpredictable system behavior may be observed.
Workaround: It is possible for the BIOS to contain a workaround for this erratum.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU109. Execution of VMPTRLD May Corrupt Memory If Current-VMCS Pointer
is Invalid
Problem: If the VMCLEAR instruction is executed with a pointer to the current-VMCS
(virtualmachine control structure), the current-VMCS pointer becomes invalid as
expected. A subsequent execution of the VMPTRLD (Load Pointer to Virtual-Machine
Control Structure) instruction may erroneously overwrite the four bytes at physical
address 0000008FH.
Implication: Due to this erratum, the four bytes in system memory at physical address 0000008FH
may be corrupted.
Workaround: None identified.
Status: For the steppings affected, see the Summary Tables of Changes.
AAU110. PerfMon Overflow Status Can Not be Cleared After Certain Conditions
Have Occurred
Problem: Under very specific timing conditions, if software tries to disable a PerfMon counter
through MSR IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_CTRL (0x38F) or through the per-counter
eventselect (e.g. MSR 0x186) and the counter reached its overflow state very close to
that time, then due to this erratum the overflow status indication in MSR
IA32_PERF_GLOBAL_STAT (0x38E) may be left set with no way for software to clear it.
Implication: Due to this erratum, software may be unable to clear the PerfMon counter overflow
status indication.
Workaround: Software may avoid this erratum by clearing the PerfMon counter value prior to
disabling it and then clearing the overflow status indication bit.
48
Specification Update
Page 49

Specification Changes
The Specification Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
•Intel
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
There are no new Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium®
Processor G6950 Datasheet - Volumes 1 and 2
Architecture
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
System Programming Guide
System Programming Guide
Specification Update
49
Page 50

Specification Clarifications
The Specification Clarifications listed in this section may apply to the following
documents:
•Intel® Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium®
Processor G6950 Datasheet - Volumes 1 and 2
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
Architecture
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
System Programming Guide
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
System Programming Guide
There are no new Specification Changes in this Specification Update revision.
50
Specification Update
Page 51

Documentation Changes
The Documentation Changes listed in this section apply to the following documents:
®
•Intel
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 1: Basic
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2A:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 2B:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3A:
•Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architectures Software Developer’s Manual, Volume 3B:
All Documentation Changes will be incorporated into a future version of the appropriate
Processor documentation.
Note: Documentation changes for Intel
Developer's Manual volumes 1, 2A, 2B, 3A, and 3B will be posted in a separate
document, Intel® 64 and IA-32 Architecture Software Developer's Manual
Documentation Changes. Follow the link below to become familiar with this file.
Core™ i5-600, i3-500 Desktop Processor Series and Intel® Pentium®
Processor G6950 Datasheet - Volumes 1 and 2
Architecture
Instruction Set Reference Manual A-M
Instruction Set Reference Manual N-Z
System Programming Guide
System Programming Guide
®
64 and IA-32 Architecture Software
http://developer.intel.com/products/processor/manuals/index.htm
There are no new Documentation Changes in this Specification Update revision.
Specification Update
51
 Loading...
Loading...