Page 1
TM
Intel® Core
2 Duo processor
and Mobile Intel
Express Chipset
Development Kit User Manual
June 2007
®
GME965
Document Number: 316704-001
Page 2

INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL® PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT
AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY
WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL
PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY,
OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended
for use in medical, life saving, life sustaining, critical control or safety systems, or in nuclear facility applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
Intel Corporation may have patents or pending patent applications, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights
that relate to the presented subject matter. The furnishing of documents and other materials and information does not provide
any license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any such patents, trademarks, copyrights, or other intellectual
property rights.
Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked “reserved” or “undefined.” Intel
reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from
future changes to them.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor
family, not across different processor families. See http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number
The Intel
errata which may cause the product to deviate from published specifications. Current characterized errata are available on
request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature may be obtained
by calling 1-800-548-4725 or by visiting Intel's website at http://www.intel.com
BunnyPeople, Celeron, Celeron Inside, Centrino, Centrino logo, Core Inside, Dialogic, FlashFile, i960, InstantIP, Intel, Intel logo,
Intel386, Intel486, Intel740, IntelDX2, IntelDX4, IntelSX2, Intel Core, Intel Inside, Intel Inside logo, Intel. Leap ahead., Intel.
Leap ahead. logo, Intel NetBurst, Intel NetMerge, Intel NetStructure, Intel SingleDriver, Intel SpeedStep, Intel StrataFlash, Intel
Viiv, Intel vPro, Intel XScale, IPLink, Itanium, Itanium Inside, MCS, MMX, Oplus, OverDrive, PDCharm, Pentium, Pentium Inside,
skoool, Sound Mark, The Journey Inside, VTune, Xeon, and Xeon Inside are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel
Corporation or its subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2007, Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
®
CoreTM 2 Duo processor and Mobile Intel® GME965 Express Chipset may contain design defects or errors known as
.
for details.
2 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 3

Contents
1 About This Manual ............................................................................................6
1.1 Content Overview...................................................................................6
1.2 Text Conventions ...................................................................................6
1.3 Glossary of Terms and Acronyms..............................................................8
1.4 Support Options................................................................................... 13
1.4.1 Electronic Support Systems ......................................................13
1.4.2 Additional Technical Support ..................................................... 13
1.5 Product Literature.................................................................................13
1.6 Related Documents...............................................................................14
2 Getting Started............................................................................................... 15
2.1 Overview ............................................................................................15
2.1.1 Development Board Features ....................................................15
2.2 Included Hardware and Documentation ...................................................17
2.3 Software Key Features ..........................................................................17
2.3.1 AMI BIOS............................................................................... 18
2.4 Before You Begin.................................................................................. 18
2.5 Setting Up the Development Board ......................................................... 20
2.6 Configuring the BIOS ............................................................................22
3 Theory of Operation ........................................................................................24
3.1 Block Diagram ..................................................................................... 24
3.2 Mechanical Form Factor......................................................................... 24
3.3 Thermal Management ........................................................................... 25
3.4 System Features and Operation.............................................................. 25
3.4.1 Mobile Intel® GME965 GMCH..................................................... 25
3.4.2 ICH8-M..................................................................................27
3.4.3 POST Code Debugger...............................................................31
3.5 Clock Generation..................................................................................31
3.6 Power Management States.....................................................................31
3.7 Power Measurement Support..................................................................33
4 Hardware Reference ........................................................................................ 39
4.1 Primary Features..................................................................................39
4.2 Back Panel Connectors .......................................................................... 41
4.2.1 TV-Out D-Connector ................................................................ 42
4.3 Configuration Settings...........................................................................43
4.4 Power On and Reset Buttons .................................................................. 47
4.5 LEDs ..................................................................................................48
4.6 Other Headers, Slots and Sockets........................................................... 49
4.6.1 H8 Programming Headers......................................................... 49
4.6.2 Expansion Slots and Sockets.....................................................50
Appendix A . Heatsink Installation Instructions ....................................................................64
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 3
Page 4

Figures
Tables
Figure 1. Development Board Block Diagram.......................................................24
Figure 2. Development Board Component Locations ............................................. 39
Figure 3. Back Panel Connector Locations ........................................................... 42
Figure 4. D-Connector to Component Video Cable................................................ 43
Figure 5. D-Connector to Composite Video Cable .................................................43
Figure 6. D-Connector to S-Video Cable .............................................................43
Figure 7. Configuration Jumper and Switch Locations ...........................................44
Figure 8. LED Locations ...................................................................................48
Figure 9. Heatsink and Backplate ......................................................................64
Figure 10. Backplate Pins .................................................................................65
Figure 11. Applying the Thermal Grease.............................................................66
Figure 12. Squeezing Activation Arm..................................................................66
Figure 13. Installing the Heatsink......................................................................67
Figure 14. Plugging in the Fan ..........................................................................68
Figure 15. Completed Assembly ........................................................................68
Table 1. Text Conventions..................................................................................7
Table 2. Terms and Acronyms.............................................................................8
Table 3. Acronyms ......................................................................................... 10
Table 4. Intel Literature Centers........................................................................13
Table 5. Related Documents .............................................................................14
Table 6. Development Board feature Set Summary .............................................. 15
Table 7. BIOS Location Strapping Options...........................................................30
Table 8. Primary System Clocks ........................................................................31
Table 9. Power Management States ...................................................................32
Table 10. Power Management M-States..............................................................32
Table 11. Sleep Signals and M-State Definition....................................................33
Table 12. Development Board Voltage Rails ........................................................34
Table 13. Development Board Component Location Legend................................... 40
Table 14. Back Panel Connector Definitions.........................................................42
Table 15. Supported Configuration Jumper/Switch Settings................................... 44
Table 16. LED Functions...................................................................................48
Table 17. Expansion Slots and Sockets...............................................................50
Table 18. PCI Express* (x16) Pinout (J6B2)........................................................ 51
Table 19. ADD2 Slot (J6B2)..............................................................................54
Table 20. MEC Slot (J6B2)................................................................................ 57
Table 21. PCI Express* (x1) Pinout (J6B1, J7B1, J8B4).........................................60
Table 22. IDE Connector ..................................................................................60
Table 23. SATA Port 0 ‘Direct Connect’ Connector Pinout (J8J1) ............................. 61
Table 24. SATA Ports 1 and 2 ‘Cable Connect’ Connector Pinout (J7J3, J7H1)...........61
Table 25. SATA Power Connection (J7H2) ........................................................... 62
Table 26. Fan Connectors (J2B3, J2C1) .............................................................. 62
Table 27. Fan Connector (J2F1) ........................................................................62
Table 28. Front Panel Connector........................................................................62
Table 29. USB Headers ....................................................................................63
4 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 5

Revision History
Document
Number
316704 001 Initial public release. June 2007
Revision
Number
Description Revision Date
§
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 5
Page 6

1 About This Manual
This user’s manual describes the use of the Intel® CoreTM 2 Duo processor and Mobile
®
GME965 Express Chipset development kit. This manual has been written for
Intel
OEMs, system evaluators, and embedded system developers. This document defines
all jumpers, headers, LED functions, and their locations on the development board,
along with subsystem features and POST codes. This manual assumes basic familiarity
in the fundamental concepts involved with installing and configuring hardware for a
personal computer system.
®
For the latest information about the Intel
GME965 Express Chipset Development Kit, visit:
CoreTM 2 Duo processor and Mobile Intel®
About This Manual
http://developer.intel.com/design/intarch/devkits/index.htm
For design documents related to this platform please visit:
Processor: http://developer.intel.com/design/intarch/core2duo/tech_docs.htm
Chipset: http://www.intel.com/products/embedded/chipsets.htm
1.1 Content Overview
Chapter 1.0, “About This Manual” — This chapter contains a description of conventions
used in this manual. The last few sections explain how to obtain literature and contact
customer support.
Chapter 2.0, “Getting Started”— Provides complete instructions on how to configure
the development board and processor assembly by setting jumpers, connecting
peripherals and providing power.
Chapter 3.0, “Theory of Operation” — This chapter provides information on the system
design.
Chapter 4.0, “Hardware Reference”— This chapter provides a description of jumper
settings and functions, development board debug capabilities, and pinout information
for connectors.
Appendix A, “Heatsink Installation Instructions” gives detailed installation instructions
for the Intel
®
CoreTM 2 Duo processor heatsink.
1.2 Text Conventions
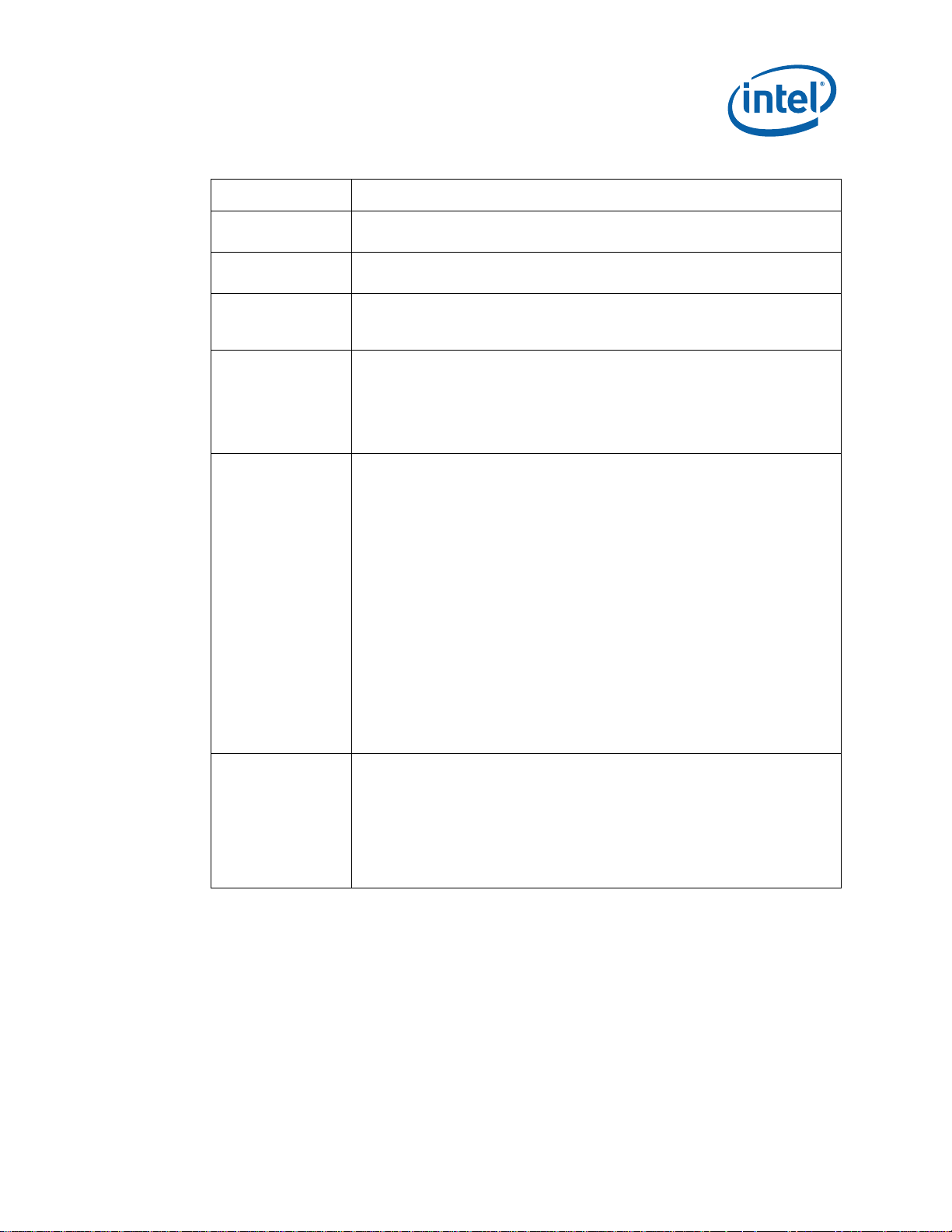
The notations listed in Table 1 may be used throughout this manual.
6 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 7
About This Manual
Table 1. Text Conventions
Notation Definition
# The pound symbol (#) appended to a signal name indicates that the signal
Variables Variables are shown in italics. Variables must be replaced with correct
Instructions Instruction mnemonics are shown in uppercase. When you are
Numbers Hexadecimal numbers are represented by a string of hexadecimal digits
Units of Measure
A
GByte
KByte
KΩ
mA
MByte
MHz
ms
mW
ns
pF
W
V
µA
µF
µs
µW
Signal Names Signal names are shown in uppercase. When several signals share a
is active low. (e.g., PRSNT1#)
values.
programming, instructions are not case-sensitive. You may use either
uppercase or lowercase.
followed by the character H. A zero prefix is added to numbers that begin
with A through F. (For example, FF is shown as 0FFH.) Decimal and binary
numbers are represented by their customary notations. (That is, 255 is a
decimal number and 1111 is a binary number. In some cases, the letter B
is added for clarity.)
The following abbreviations are used to represent units of measure:
amps, amperes
gigabytes
kilobytes
kilo-ohms
milliamps, milliamperes
megabytes
megahertz
milliseconds
milliwatts
nanoseconds
picofarads
watts
volts
microamps, microamperes
microfarads
microseconds
microwatts
common name, an individual signal is represented by the signal name
followed by a number, while the group is represented by the signal name
followed by a variable (n). For example, the lower chip-select signals are
named CS0#, CS1#, CS2#, and so on; they are collectively called CSn#.
A pound symbol (#) appended to a signal name identifies an active-low
signal. Port pins are represented by the port abbreviation, a period, and
the pin number (e.g., P1.0).
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 7
Page 8
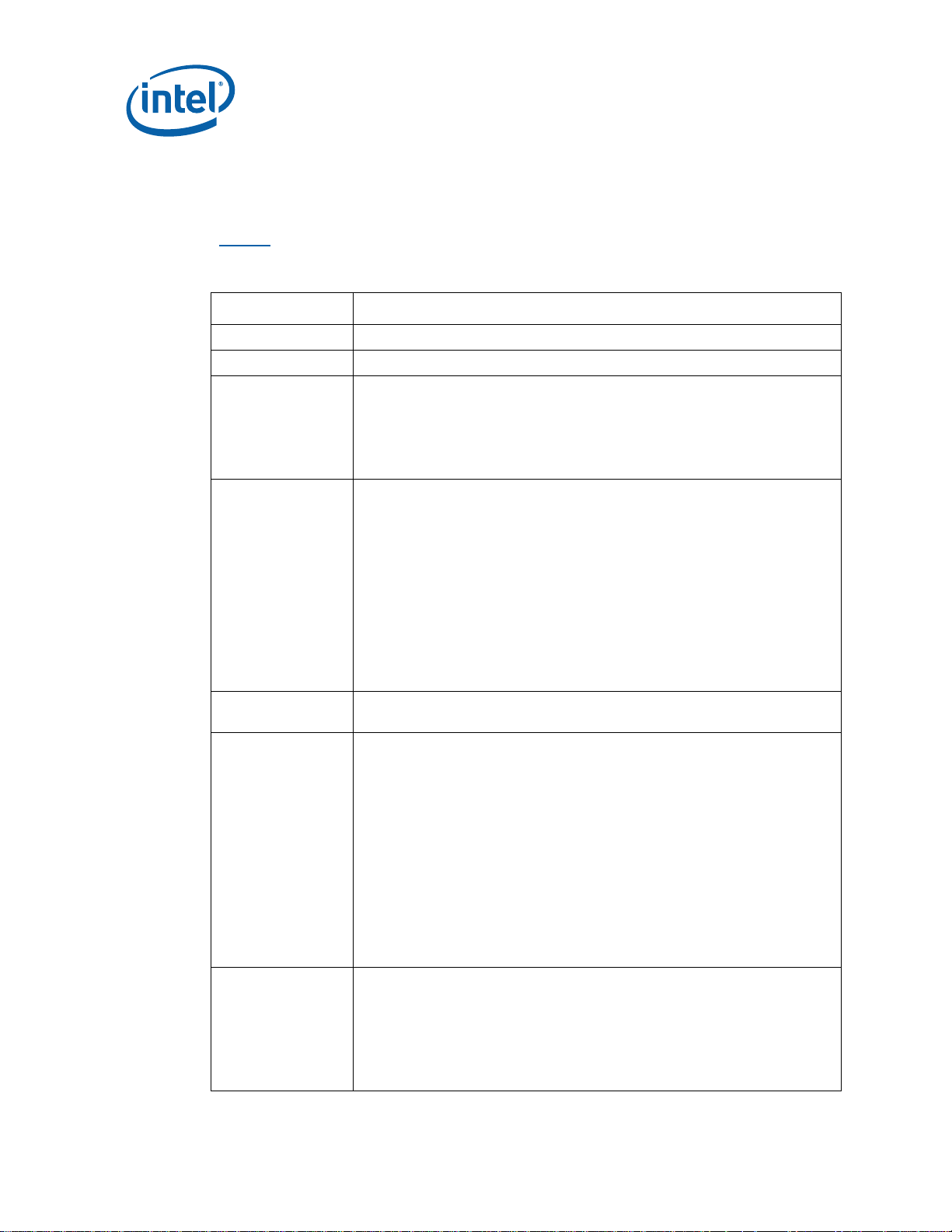
1.3 Glossary of Terms and Acronyms
Table 2 defines conventions and terminology used throughout this document.
Table 2. Terms and Acronyms
Term/Acronym Definition
Aggressor A network that transmits a coupled signal to another network.
Anti-etch Any plane-split, void or cutout in a VCC or GND plane.
Assisted Gunning
Transceiver Logic+
Asynchronous
GTL+
Bus Agent A component or group of components that, when combined, represent a
Crosstalk The reception on a victim network of a signal imposed by aggressor
Flight Time Flight time is a term in the timing equation that includes the signal
The front-side bus uses a bus technology called AGTL+, or Assisted
Gunning Transceiver Logic. AGTL+ buffers are open-drain, and require
pull-up resistors to provide the high logic level and termination. AGTL+
output buffers differ from GTL+ buffers with the addition of an active
pMOS pull-up transistor to assist the pull-up resistors during the first clock
of a low-to-high voltage transition.
The processor does not utilize CMOS voltage levels on any signals that
connect to the processor. As a result, legacy input signals such as A20M#,
IGNNE#, INIT#, LINT0/INTR, LINT1/NMI, PWRGOOD, SMI#, SLP#, and
STPCLK# utilize GTL+ input buffers. Legacy output signals (FERR# and
IERR#) and non-AGTL+ signals (THERMTRIP# and PROCHOT#) also
utilize GTL+ output buffers. All of these signals follow the same DC
requirements as AGTL+ signals, however the outputs are not actively
driven high (during a logical 0 to 1 transition) by the processor (the major
difference between GTL+ and AGTL+). These signals do not have setup or
hold time specifications in relation to BCLK[1:0], and are therefore
referred to as “Asynchronous GTL+ Signals”. However, all of the
Asynchronous GTL+ signals are required to be asserted for at least two
BCLKs in order for the processor to recognize them.
single load on the AGTL+ bus.
network(s) through inductive and capacitive coupling between the
networks.
Backward Crosstalk - Coupling that creates a signal in a victim network
that travels in the opposite direction as the aggressor’s signal.
Forward Crosstalk - Coupling that creates a signal in a victim network that
travels in the same direction as the aggressor’s signal.
Even Mode Crosstalk - Coupling from a signal or multiple aggressors when
all the aggressors switch in the same direction that the victim is switching.
Odd Mode Crosstalk - Coupling from a signal or multiple aggressors when
all the aggressors switch in the opposite direction that the victim is
switching.
propagation delay, any effects the system has on the T
clock-in to data-out) of the driver, plus any adjustments to the signal at
the receiver needed to ensure the setup time of the receiver. More
precisely, flight time is defined as:
The time difference between a signal at the input pin of a receiving agent
crossing the switching voltage (adjusted to meet the receiver
About This Manual
(time from
CO
8 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 9

About This Manual
Term/Acronym Definition
Media Expansion
manufacturer’s conditions required for AC timing specifications; i.e.,
ringback, etc.) and the output pin of the driving agent crossing the
switching voltage when the driver is driving a test load used to specify the
driver’s AC timings.
Maximum and Minimum Flight Time - Flight time variations are caused by
many different parameters. The more obvious causes include variation of
the board dielectric constant, changes in load condition, crosstalk, power
noise, variation in termination resistance, and differences in I/O buffer
performance as a function of temperature, voltage, and manufacturing
process. Some less obvious causes include effects of Simultaneous
Switching Output (SSO) and packaging effects.
Maximum flight time is the largest acceptable flight time a network will
experience under all conditions.
Minimum flight time is the smallest acceptable flight time a network will
experience under all conditions.
Infrared Data
Assoc.
IMVP6+ The Intel Mobile Voltage Positioning specification for the Intel® Core™ 2
Inter-Symbol
Interference
Card
Network The network is the trace of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) that completes
Overshoot The maximum voltage observed for a signal at the device pad, measured
Pad The electrical contact point of a semiconductor die to the package
Pin The contact point of a component package to the traces on a substrate,
Power-Good “Power-Good,” “PWRGOOD,” or “CPUPWRGOOD” (an active high signal)
Ringback The voltage to which a signal changes after reaching its maximum
The Infrared Data Association (IrDA) has outlined a specification for serial
communication between two devices via a bi-directional infrared data
port. The development board has such a port and it is located on the rear
of the platform between the two USB connectors.
Duo Processor. It is a DC-DC converter module that supplies the required
voltage and current to a single processor.
Inter-symbol interference is the effect of a previous signal (or transition)
on the interconnect delay. For example, when a signal is transmitted down
a line and the reflections due to the transition have not completely
dissipated, the following data transition launched onto the bus is affected.
ISI is dependent upon frequency, time delay of the line, and the reflection
coefficient at the driver and receiver. ISI may impact both timing and
signal integrity.
The Media Expansion Card (MEC) provides digital display options through
the SDVO interface. The MEC card also incorporates video-in via a x1 PCI
Express* port.
an electrical connection between two or more components.
with respect to VCC.
substrate. A pad is only observable in simulations.
such as the motherboard. Signal quality and timings may be measured at
the pin.
indicates that all of the system power supplies and clocks are stable.
PWRGOOD should go active at a predetermined time after system
voltages are stable and should go inactive as soon as any of these
voltages fail their specifications.
absolute value. Ringback may be caused by reflections, driver oscillations,
or other transmission line phenomena.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 9
Page 10
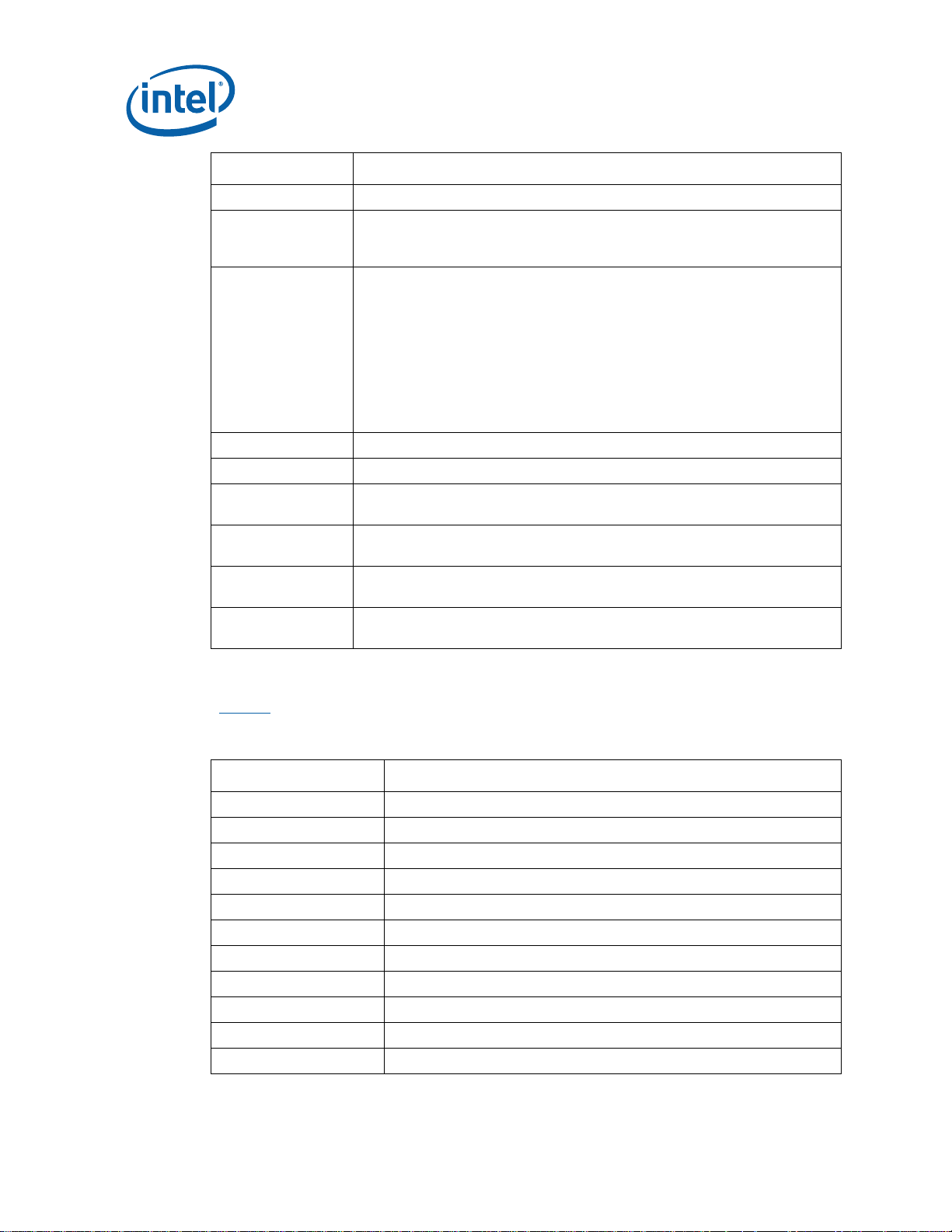
About This Manual
Term/Acronym Definition
System Bus The System Bus is the microprocessor bus of the processor.
Setup Window The time between the beginning of Setup to Clock (TSU_MIN) and the
arrival of a valid clock edge. This window may be different for each type of
bus agent in the system.
Simultaneous
Switching Output
Stub The branch from the bus trunk terminating at the pad of an agent.
Trunk The main connection, excluding interconnect branches, from one end.
System
Management Bus
Undershoot The minimum voltage extending below VSS observed for a signal at the
VCC (CPU core) VCC (CPU core) is the core power for the processor. The system bus is
Victim A network that receives a coupled crosstalk signal from another network is
Simultaneous Switching Output (SSO) effects are differences in electrical
timing parameters and degradation in signal quality caused by multiple
signal outputs simultaneously switching voltage levels in the opposite
direction from a single signal or in the same direction. These are called
odd mode and even mode switching, respectively. This simultaneous
switching of multiple outputs creates higher current swings that may
cause additional propagation delay (“push-out”) or a decrease in
propagation delay (“pull-in”). These SSO effects may impact the setup
and/or hold times and are not always taken into account by simulations.
System timing budgets should include margin for SSO effects.
A two-wire interface through which various system components may
communicate.
device pad.
terminated to VCC (CPU core).
called the victim network.
Table 3 defines the acronyms used throughout this document.
Table 3. Acronyms
Acronym Definition
AC Audio Codec
ACPI Advanced Configuration and Power Interface
ADD2 Advanced Digital Display 2
ADD2N Advanced Digital Display 2 Normal
AGTL Assisted Gunning Transceiver Logic
AMC Audio/Modem Codec.
ASF Alert Standard Format
AMI American Megatrends Inc. (BIOS developer)
ATA Advanced Technology Attachment (disk drive interface)
ATX Advance Technology Extended (motherboard form factor)
BGA Ball Grid Array
10 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 11
About This Manual
BIOS Basic Input/Output System
CK-SSCD Spread Spectrum Differential Clock
CMC Common Mode Choke
CMOS Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
CPU Central Processing Unit (processor)
DDR Double Data Rate
DMI Direct Memory Interface
ECC Error Correcting Code
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory
EHCI Enhanced Host Controller Interface
EMA Extended Media Access
EMI Electro Magnetic Interference
ESD Electrostatic Discharge
EV Engineering Validation
EVMC Electrical Validation Margining Card
FCBGA Flip Chip Ball Grid Array
FCPGA Flip Chip Pin Grid Array
FIFO First In First Out - describes a type of buffer
FS Full-speed. Refers to USB
FSB Front Side Bus
FWH Firmware Hub
GMCH Graphics Memory Controller Hub
HDA High Definition Audio
HDMI High Definition Media Interface
HS High-speed. Refers to USB
ICH I/O Controller Hub
IDE Integrated Drive Electronics
IMVP Intel Mobile Voltage Positioning
IP/IPv6 Internet Protocol/Internet Protocol version 6
IrDA Infrared Data Association
ISI Inter-Symbol Interference
KBC Keyboard Controller
LAI Logic Analyzer Interface
LAN Local Area Network
LED Light Emitting Diode
Acronym Definition
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 11
Page 12
About This Manual
Acronym Definition
LOM LAN on Motherboard
LPC Low Pin Count
LS Low-speed. Refers to USB
LVDS Low Voltage Differential Signaling
mBGA Mini Ball Grid Array
MC Modem Codec
MEC Media Expansion Card
MHz Mega-Hertz
OEM Original Equipment Manufacturer
PCIe PCI Express*
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
POST Power On Self Test
PLC Platform LAN Connect
RAID Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks
RTC Real Time Clock
SATA Serial ATA
SIO Super Input/Output
SKU StockKeeping Unit
SMBus System Management Bus
SODIMM Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module
SPD Serial Presence Detect
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface
SPWG Standard Panels Working Group - http://www.spwg.org/
SSO Simultaneous Switching Output
STR Suspend To RAM
TCO Total Cost of Ownership
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
TDM Time Division Multiplexed
TDR Time Domain Reflectometry
µBGA Micro Ball Grid Array
UDP User Datagram Protocol
UHCI Universal Host Controller Interface
USB Universal Serial Bus
VGA Video Graphics Adapter
VID Voltage Identification
12 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 13
About This Manual
Acronym Definition
VREG Voltage Regulator
XDP eXtended Debug Port
1.4 Support Options
1.4.1 Electronic Support Systems
Intel’s web site (http://www.intel.com/) provides up-to-date technical information and
product support. This information is available 24 hours per day, 7 days per week,
providing technical information whenever you need it.
1.4.2 Additional Technical Support
If you require additional technical support, please contact your Intel Representative or
local distributor.
1.5 Product Literature
In order to order hard copies of product literature the following instructions should be
followed:
1. Determine the SKU Number
If you do not know the SKU # of the document you are ordering, please select
the back button to view the document again. The SKU # is the first 6 digits of
the number on the PDF file, such as: 12345612.pdf or at the bottom of the
download page for that document.
2. Call, Mail or Email a request
Call: To place an order for a publication or text in hardcopy or CD form,
please contact our Intel® Literature Fulfillment Centers listed in Table 4
Table 4. Intel Literature Centers
Location Telephone Number
U.S. and Canada 1-800-548-4725
International 1-303-675-2148
Fax 1-303-675-2120
.
Mail a request to:
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 13
Page 14
Intel Literature Fulfilment Center
P.O. Box 5937
Denver, Colorado 80217-9808
USA
About This Manual
Email a request to: intelsupport@hibbertgroup.com
Please make sure to include in your mailed/emailed request:
SKU #
Company Name
Your Name (first, last)
Full mailing address
Daytime Phone Number in case of questions
Note: Please be aware not all documents are available in all media types. Some may only be
available as a download.
1.6 Related Documents
Table 5 provides a summary of publicly available documents related to this
development kit. For additional documentation, please contact your Intel
Representative.
Table 5. Related Documents
Document Title Location
Intel® Core™2 Duo Processor for Mobile
Intel® 965 Express Chipset Family
Datasheet
Mobile Intel® 965 Express Chipset Family
Datasheet
Intel® I/O Controller Hub 8 (ICH8) Family
Datasheet
Intel® Centrino® Pro processor technology
and Intel® Centrino® Duo processor
technology Design Guide For Intel®
Core™2 Duo Mobile Processor, Mobile
Intel® 965 Express Chipset Family and
Intel® 82801HBM ICH8M & Intel®
82801HEM ICH8M-E I/O Controller Hub
Based Systems
Intel® Core™2 Duo Mobile Processor,
Mobile Intel
and ICH8M I/O Controller Hub Schematics
®
965 Express Chipset Family
http://www.intel.com/design/mobile/datashts/316
745.htm
http://www.intel.com/design/mobile/datashts/316
273.htm
http://www.intel.com/design/chipsets/datashts/3
13056.htm
Contact your Intel representative for access to
this document
Contact your Intel representative for access to
this document
§
14 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 15
Getting Started
2 Getting Started
This chapter identifies the development kit’s key components, features and
specifications. It also details basic development board setup and operation.
2.1 Overview
The development board consists of a baseboard populated with the Intel® CoreTM 2
Duo processor, the Mobile Intel
®
GME965 Express Chipset, other system board
components and peripheral connectors.
Note: The development board is shipped as an open system allowing for maximum flexibility
in changing hardware configuration and peripherals. Since the board is not in a
protective chassis, take extra precaution when handling and operating the system.
2.1.1 Development Board Features
Features of the development board are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6. Development Board feature Set Summary
Development Board
Processor
F
Chipset
E
A
T
U
Memory
R
E
Video
PCI One 5V PCI slot PCI revision 2.3 compliant (33MHz)
Intel
4 MByte L2 Cache on 65nm process
FSB 533/667/800 MHz support
Mobile Intel® GME965 Express
Chipset (GMCH)
Intel
Enhanced (ICH8M-E)
Two DDR2 RAM SO-DIMM slots. Maximum 4GB of DDR2 Memory (RAM)
One PCI Express* Graphics Slot
One dual channel LVDS Connector
One VGA Connector
One TV D-Connector supporting SVideo, Composite video and
Component video
Implementation
®
CoreTM 2 Duo processor with
®
I/O Controller Hub 8-M
Comments
478 pin Flip Chip Pin Grid Array (MicroFCPGA) package
1299-pin Micro-FCBGA Package
676-pin BGA Package
using 1Gb technology and stacked SODIMMs.
Supports DDR2 frequency of 533 or
667MHz
The Mobile Intel
(GMCH) has 2 video pipes which allows
support of dual independent display.
18-bpp and 24-bpp LVDS panel support
Support for two SDVO channels via x16
PCIe connector (through ADD2 or MEC
cards)
®
GME965 Express Chipset
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 15
Page 16
Getting Started
Development Board
F
PCI Express*
E
A
T
On-Board LAN
U
R
SPI Two 16Mbit devices
E
ATA/Storage
USB
LPC One LPC slot Includes sideband headers
BIOS AMI BIOS installed in an 8Mb FWH 40-pin TSOP socket
SMC/KBC
Clocks
Three x1 connectors
One x16 connector
10/100/1000 Mbps connectivity
from the Intel® 82566MM Gigabit
Platform LAN Connect component
PATA 33/66/100 1 Channel
3 SATA Ports 2 Cable Connector and 1 Direct Connect
10 USB 2.0/1.1 Ports Five ports provided on rear-panel, four
Hitachi H8S/2104 micro-controller
Two PS/2 ports
One scan matrix keyboard
connector
CK-505 clock synthesizer and
DB800M clock buffer
Implementation
Revision 1.1 compliant
There are Five x1 PCI Express* slots but
slots 2 and 4 are not intended for use with
PCI Express* add-in cards. Only slots 1, 3
and 5 are supported.
The 82566MM is connected to the ICH via
the ICH’s GLCI and LCI interfaces.
Connector. RAID 0/1 support.
provided via headers (J6H3, J6H3) and
one via the PCI Express* docking
connector
ACPI compliant
Comments
Super I/O SMSC SIO1007-JV Supports IrDA and UART serial interfaces
RTC Battery-backed Real Time Clock
Thermal
Monitoring
Processor
Voltage
Regulator
Processor temperature sensor
IMVP-6+ for processor core
Desktop Mode ATX Power Supply
Power Supply
Debug
Interfaces
®
Intel
AMT
support
16 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Mobile Mode Battery Pack (smart battery support)
AC Mobile Brick
Port 80 display Through Add-in card. Four seven-segment
displays
Extended Debug Port (XDP) XDP connector
Intel® Active Management
Technology 2.5
Supported on the development board with
M0, M1, and M-off management states
Page 17
Getting Started
Development Board
ACPI Compliant S0 – Power On
Power
Management
Form Factor ATX 2.2 like form factor 10 layer board – 12” x 10.2”
Implementation
S3 – Suspend to RAM
S4 – Suspend to Disk
S5 – Soft Off
M0 – All Wells powered
M1 – Main Well down. Only ME power on
M-off – ME powered off
Note: Review the document provided with the Development Kit titled “Important Safety and
Regulatory Information”. This document contains safety warnings and cautions that
must be observed when using this development kit.
2.2 Included Hardware and Documentation
The following hardware and documentation is included in the development kit:
• One development board
®
• One Intel
the 478 pin Flip-Chip Pin Grid Array (Micro-FCPGA) package (Installed)
CoreTM 2 Duo processor with 4 MB L2 Cache on 65nm process in
Comments
• One Firmware Hub (FWH) (Installed)
• One GMCH (GME965) heatsink (Installed)
• One Type 2032, socketed 3 V lithium coin cell battery (Installed)
• One 256 MByte DDR2 SODIMM (200 Pin)
• One CPU thermal solution and CPU back plate (included in kit box – not
populated on board)
• One cable kit
• One Development Kit User’s Manual
• One Port 80 add-in card
2.3 Software Key Features
The driver CD included in the kit contains all of the software drivers necessary for
basic system functionality under the following operating systems: Windows* XP/XP
Embedded, Vista and Linux*.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 17
Page 18

Getting Started
Note: While every care was taken to ensure the latest versions of drivers were provided on
the enclosed CD at time of publication, newer revisions may be available. Updated
drivers for Intel components can be found at:
http://developer.intel.com/design/intarch/software/index.htm
For all third-party components, please contact the appropriate vendor for updated
drivers.
Note: Software in the kit is provided free by the vendor and is only licensed for evaluation
purposes. Refer to the documentation in your evaluation kit for further details on any
terms and conditions that may be applicable to the granted licenses. Customers using
the tools that work with Microsoft* products must license those products. Any targets
created by those tools should also have appropriate licenses. Software included in the
kit is subject to change.
Refer to http://developer.intel.com/design/intarch/devkits
software from other third-party vendors.
2.3.1 AMI BIOS
This development kit ships with AMI* BIOS pre-boot firmware from AMI* preinstalled. AMI* BIOS provides an industry-standard BIOS platform to run most
standard operating systems, including Windows* XP/XP Embedded, Linux*, and
others.
The AMI* BIOS Application Kit (available through AMI*) includes complete source
code, a reference manual, and a Windows-based expert system, BIOStart*, to enable
easy and rapid configuration of customized firmware for your system.
The following features of AMI* BIOS are enabled in the development board:
• DDR2 SDRAM detection, configuration, and initialization
• Mobile Intel
• POST codes displayed to port 80h
• PCI/PCI Express* device enumeration and configuration
• Integrated video configuration and initialization
• Super I/O configuration
®
GME965 Express Chipset configuration
for details on additional
• CPU microcode update
• Active Management Technology
• RAID 0/1 Support
2.4 Before You Begin
The following additional hardware may be necessary to successfully set up and
operate the development board.
18 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 19

Getting Started
Note: The enclosed driver CD includes drivers necessary for LAN, Integrated graphics, and
VGA Monitor: Any standard VGA or multi-resolution monitor may be used. The setup
instructions in this chapter assume the use of a standard VGA monitor, TV, or flat
panel monitor.
Keyboard: The development board can support either a PS/2 or USB style keyboard.
Mouse: The development board can support either a PS/2 or USB style mouse.
Hard Drives and Optical Disc Drives: Up to Three SATA drives and two IDE devices
(master and slave) may be connected to the development board. An optical disc drive
may be used to load the OS. All these storage devices may be attached to the board
simultaneously.
Video Adapter: Integrated video is output from the VGA connector on the back panel
of the development board. Alternately, a standard PCI Express* video adapter, ADD2
card or MEC video adapter may be used for additional display flexibility. Please contact
the respective vendors for drivers and necessary software for adapters not provided
with this development kit. Check the BIOS and the graphics driver, where appropriate,
for the proper video output settings.
system INF utilities.
Network Adapter: A Gigabit network interface is provided on the development
board. The network interface will not be operational until after all the necessary
drivers have been installed. A standard PCI/PCI Express* adapter may be used in
conjunction with, or in place of, the onboard network adapter. Please contact the
respective vendors for drivers and necessary software for adapters not provided with
this development kit.
You must supply appropriate network cables to utilize the LAN connector or any other
installed network cards.
Power Supply: The development board has the option to be powered from two
different power sources: an ATX power supply or AC to DC adapter. The development
board contains all of the voltage regulators necessary to power the system.
There are two main supported power supply configurations, Desktop and Mobile. The
Desktop solution consists of only using the ATX power supply. The Mobile solution
consists of only using the AC to DC adapter.
Warning: The power supply cord is the main disconnect device to mains (AC power). The socket
outlet shall be installed near the equipment and shall be readily accessible.
Note: Desktop peripherals, including add-in cards, will not work in mobile power mode. If
desktop peripherals are used, the development board must be powered using desktop
power mode.
If using an ATX power supply, select a power supply that complies with the "ATX12V"
1.1 specification. For more information, refer to http://www.formfactors.org
.
Note: If the power button on the ATX power supply is used to shut down the system, wait at
least five seconds before turning the system on again to avoid damaging the system.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 19
Page 20
Other Devices and Adapters: The development board functions much like a
standard desktop computer motherboard. Most PC-compatible peripherals can be
attached and configured to work with the development board.
2.5 Setting Up the Development Board
Once the necessary hardware (described in Section 2.4) has been gathered, follow the
steps below to set up the development board.
Getting Started
Note: To locate items discussed in the procedure below, please refer to Chapter
1. Create a safe work environment.
Ensure a static-free work environment before removing any components from
their anti-static packaging. The development board is susceptible to
electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, and such damage may cause product
failure or unpredictable operation. A flame retardant work surface must also
be used.
Caution: It is recommended that an ESD wrist strap be used when handling the
development board.
2. Inspect the contents of your kit.
Check for damage that may have occurred during shipment. Contact your
sales representative if any items are missing or damaged.
Caution: Since the development board is not in a protective chassis, use caution
when connecting cables to this product.
Caution: Standby voltage is constantly applied to the development board. Remove
power before any hardware (peripherals, keyboards, mice, monitors,
accessories, add-in cards, etc) is added or removed from the board.
Note: The development board is a standard ATX form factor. An ATX chassis may
be used if a protected environment is desired. If a chassis is not used,
standoffs must be used to elevate the development board off the working
surface to protect the memory and board components from any
accidental contact to metal objects.
3. Check the jumper default position setting. Refer to Figure 7
for jumper location.
Jumper J5H2 is used to clear the CMOS memory. Make sure this jumper is set to
1-x for normal operation.
4. Be sure to populate the following hardware on your development board:
®
• One Intel
CoreTM 2 Duo processor
4.
• One processor thermal solution
• One 256 MByte DDR2 667 SODIMM (200-pin) into connector J5P1.
20 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 21

Getting Started
Note: Ensure that the processor has been locked into the socket by turning the
socket screw fully clockwise.
Note: For proper installation of the CPU thermal solution, please refer
to
5. Connect a SATA or IDE hard disk drive.
6. Connect any additional storage devices to the development board.
7. Connect the keyboard and mouse.
Connect a PS/2-style or USB mouse and keyboard (see Figure 3 on page 38
for connector locations).
Note: J1A1 (on the baseboard) is a stacked PS/2 connector. The bottom
connector is for the keyboard and the top is for the mouse.
8. Connect an Ethernet cable (optional).
9. Connect the monitor through the VGA connector.
10. Connect the power supply.
Connect an appropriate power supply to the development board. Make sure
the power supply is not plugged into an electrical outlet (turned off). After
connecting the power supply board connectors, plug the power supply cord
into an electrical outlet.
11. Power up the development board.
Power and Reset are implemented on the development board through buttons
located on SW1C1 and SW1C2, respectively. See Figure 7
Turn on the power to the monitor and development board. Ensure that the
fansink on the processor is operating.
Appendix A
for switch locations.
Note: The power button may have to be pressed twice to turn the power on.
12. Install operating system and necessary drivers.
Depending on the operating system chosen, all necessary drivers for
components included in this development kit can be found on the enclosed
CD. Please see Section
2.3 for information on obtaining updated drivers.
2.6 Configuring the BIOS
AMI* BIOS is pre-loaded on the development board. The default BIOS settings may
need to be modified to enable/disable various features of the development board. The
BIOS settings are configured through a menu-driven user interface which is accessible
during the Power On Self Test (POST). The Delete key on the attached keyboard
should be pressed during POST to enter the interface. For AMI BIOS POST codes, visit:
http://www.ami.com
For BIOS Updates please contact your Intel Sales Representative.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 21
§
Page 22

3 Theory of Operation
3.1 Block Diagram
Figure 1. Development Board Block Diagram
Theory of Operation
3.2 Mechanical Form Factor
The development board conforms to the ATX form factor. For extra protection in a
development environment, you may want to install the development board in an ATX
22 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 23

Theory of Operation
chassis. Internal and rear panel system I/O connectors are described in Section 3.4.
An overview of connector and slot locations is provided in Chapter 4.
3.3 Thermal Management
The objective of thermal management is to ensure that the temperature of each
component is maintained within specified functional limits. The functional temperature
limit is the range within which the electrical circuits can be expected to meet their
specified performance requirements. Operation outside the functional limit can
degrade system performance and cause reliability problems.
The development kit is shipped with a heatsink thermal solution for installation on the
processor. This thermal solution has been tested in an open-air environment at room
temperature and is sufficient for development purposes. The designer must ensure
that adequate thermal management is provided for if the system is used in other
environments or enclosures.
3.4 System Features and Operation
The following section provide a detailed view of the system features and operation of
the development board.
3.4.1 Mobile Intel® GME965 GMCH
The Mobile Intel® GME965 Express Chipset GMCH provides the processor interface
optimized for Intel
internal graphics. It provides flexibility and scalability in graphics and memory
subsystem performance. The following list describes the development board’s
implementation of the Mobile Intel
A list of features follows:
• 1299-ball Micro-FCBGA package
• 533/667/800 MHz Front Side Bus
• 36-bit host bus addressing
• System memory controller (DDR2 implemented)
o Supports Dual Channel and Single Channel operation
o Two 200-pin SODIMM slots
o DDR2 533/667
®
CoreTM 2 Duo processors, system memory interface, DMI and
®
GME965 Express Chipset GMCH features.
• Direct Media Interface (DMI)
• Integrated graphics based on the Intel Graphics Media Accelerator X3100
o Directly supports on-board VGA, TV D-Connector and LVDS interfaces.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 23
Page 24

Theory of Operation
• SDVO interface via PCI Express* x16 connector provides maximum display
flexibility
o Can drive up to two display outputs
3.4.1.1 System Memory
The development board supports DDR2 533/667 main memory. Two 200-pin SODIMM
connectors (one per channel) on the development board support unbuffered, non-ECC,
single and double-sided DDR2 533/667 MHz SODIMMs. These SODIMMs provide the
ability to use up to 1 Gbit technology for a maximum of 4 GBytes system memory.
Note: Memory that utilizes 128 MBit technology is not supported on the Mobile Intel
GME965 Express Chipset.
Note: The SODIMM connectors are on the back side of the development board.
Caution: Standby voltage may be applied to the SODIMM sockets when the system is in the
S3, S4 and S5 states. Therefore, do not insert or remove SODIMMs unless the
system is unplugged.
®
3.4.1.2 DMI
The Mobile Intel® GME965 Express Chipset GMCH’s Direct Media Interface (DMI)
provides high-speed bi-directional chip-to-chip interconnect for communication with
the ICH8-M.
3.4.1.3 Advanced Graphics and Display Interfaces
The development board has five options for displaying video: VGA, LVDS, TV-Out,
SDVO, or PCI Express* Graphics. SDVO and PCI Express* Graphics are multiplexed on
the same pins within the Mobile Intel
board contains one SDVO/PCI Express* Graphics Slot (J6B2) for a PCI Express*
compatible graphics card or an SDVO compatible graphics card, one LVDS connector
(J6F1), one TV-Out connector (J2A1), and one 15-pin VGA connector (J2A2).
3.4.1.3.1 VGA Connector
A standard 15 pin D-Sub connector on the rear panel provides access to the analog
output of the Mobile Intel
capable analog CRT or flat panel display with compatible input.
When used in conjunction with the other display options, the displays can operate in
Dual Independent mode. This allows unique content to appear on each display at
unique refresh rates and timings.
®
GME965 Express Chipset. This can be connected to any
®
GME965 Express Chipset. The development
3.4.1.3.2 LVDS Flat Panel Interface
The development board provides one 50-pin LVDS video interface connector. The
interface is compliant with the SPWG 3.5 (for 18-bpp panels) and proposed SPWG 4.0
(for 24-bpp panels) standards.
24 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 25

Theory of Operation
3.4.1.4 PCI Express x16 Slot
The development board provides access to one x16 PCI Express* connector. Any
industry standard x1 or x16 PCI Express* video adapter may be used with this
interface. Additionally, any industry standard non-graphics x1, x4 or x8 adapter may
also be used. x2 adapters are not part of the PCI Express* specification but x2 nongraphics devices are also supported.
Note: The AMI BIOS that is included with the development board is configured to allow x2,
x4 and x8 non-graphics support through the x16 PCI Express* connector. If the user
wishes to use another BIOS on the development board then the BIOS may need to be
modified to support this feature.
3.4.2 ICH8-M
The ICH8-M is a highly integrated multifunctional I/O controller hub that provides the
interface to the system peripherals and integrates many of the functions needed in
today’s PC platforms. The following sections describe the development board
implementation of the ICH8-M features, which are listed below:
• Three PCI Express* (x1) connectors
• One PCI connectors
• LPC interface
• System Bus Management
• ACPI* 3.0 compliant
• Real Time Clock
• 676-ball mBGA package
• Three SATA drive connectors
• One IDE connector
• Ten Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 ports (five ports provided on rear-panel,
four provided via headers (J6H3, J6H4) and one on the docking connector.
3.4.2.1 PCI Express* Slots
The development board has three x1 PCI Express* slots for add-in cards. The PCI
Express* interface is compliant to the PCI Express* Rev. 1.1 Specification.
Note: There are actually Five x1 PCI Express* slots but slots 2 and 4 are not intended for
use with PCI Express* add-in cards. Only slots 1, 3 and 5 are supported.
3.4.2.2 PCI Slots
The development board has one 5V PCI slot for add-in cards. The PCI bus is compliant
to the PCI Rev. 2.3 Specification at 32-bit/33 MHz
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 25
Page 26

3.4.2.3 On-Board LAN
The development board has one RJ-45 interface – at connector J5A1 - through which
10/100/1000 ethernet is available. The ethernet MAC is located in the ICH8-M and the
PHY is located externally in the 82566MM LAN Connect Interface (LCI) device. The
82566MM is connected to the ICH8-M via two interfaces: LCI for 10/100 Mbps traffic
and GLCI (Gigabit LCI) for 1000Mbps traffic. Intel
optionally supported through these components.
Information on Intel
http://www.intel.com/technology/manage/iamt/
Theory of Operation
®
Active Management Technology is
®
Active Management Technology can be found at:
Note: Further details on the location of the RJ-45 interface can be found in Section
3.4.2.4 High Definition Audio
Intel® High Definition Audio is not supported on the development board.
3.4.2.5 ATA/ Storage
The development board has one parallel ATA IDE connector and three serial ATA
connectors.
The parallel ATA IDE Connector is a standard 40-pin connector at J7J4. This connector
supports up to two Ultra ATA/100 hard drives; one master and one slave.
There are three SATA connectors on the development board – one ‘Direct Connect’
connector and two ‘Cable Connect’ connectors. The ‘Direct Connect’ connector, located
at J8J1, provides both signaling and power while the ‘Cable Connect’ connectors,
located at J7H1 and J7J3, only provides signals (the user typically uses an ATX power
supply for the drive power). A green LED at location CR6J1 indicates activity on the
ATA channel.
The development board also supports ‘ATA swap’ capability for both the parallel IDE
channel and the serial ATA channels. A device can be powered down by software and
the port can then be disabled, allowing removal and insertion of a new device. The
parallel IDE device should be powered from the power connector, J4J2, on the
development board to utilize the hot swap feature. This feature requires customerdeveloped software support.
4.2.
Note: Desktop hard drives must be powered using the external ATX power supply, not the
onboard power supply.
®
The Mobile Intel
providing greater performance and reliability through features such as Native
Command Queuing (NCQ) and RAID 0/1. For more information about Intel
GME965 Express Chipset includes Intel® Matrix Storage Technology,
®
Matrix
Storage Technology, refer to Intel’s website at:
http://www.intel.com/design/chipsets/matrixstorage_sb.htm
3.4.2.6 USB Connectors
The ICH8-M provides a total of ten USB 2.0 ports. Three ports are routed to a triplestack USB connector at J3A1. Two ports are routed to a combination RJ-45/dual USB
26 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 27

Theory of Operation
connector at J5A1. Four ports are routed to USB front panel headers at J6H3 and
J6H4. The last is routed to the PCI-Express* docking connector at J9C1.
There are Five UHCI Host Controllers and two EHCI Host Controllers. Each UHCI Host
Controller includes a root hub with two separate USB ports each, for a total of ten
legacy USB ports. The first EHCI Host Controller includes a root hub that supports up
to six USB 2.0 ports and the second EHCI Host Controller includes a root hub that
supports up to four USB 2.0 ports.
The connection to either the UHCI or EHCI controllers is dynamic and dependant on
the particular USB device. As such, all ports support High Speed, Full Speed, and Low
Speed (HS/FS/LS).
3.4.2.7 LPC Super I/O (SIO)/LPC Slot
An SMSC SIO1007-JV serves as the SIO on the development board. Shunting the
jumper at J7D1 to the 2-3 positions can disable the SIO by holding it in reset. This
allows other SIO solutions to be tested in the LPC slot at J8E1. A sideband header is
provided at J9G1 for this purpose. This sideband header also has signals for LPC
power management. Information on this header is on sheet 44 of the development
board schematics.
3.4.2.8 Serial, IrDA
The SMSC SIO incorporates a serial port, and IrDA (Infrared), as well as general
purpose IOs (GPIO). The Serial Port connector is provided at J2A2, and the IrDA
transceiver is located at U4A1. The IrDA transceiver on the development board
supports SIR (slow IR), FIR (Fast IR) and CIR (Consumer IR). The option to select
between these is supported through software.
3.4.2.9 BIOS Firmware Hub (FWH)
An 8-Mbit Flash device used on the development board to store system and video. The
reference designator location of the FWH device is U8G1. The BIOS can be upgraded
using an MS-DOS* based utility called FWHFlash and is addressable on the LPC bus off
of the ICH8-M. FWHFlash is available on request from your Intel representative.
3.4.2.10 SPI
The Serial Peripheral Interface on ICH8-M is used to support two compatible flash
devices at locations U7E1 and U6D2. By default, the SPI flash is used to store
configuration data for the LAN controller. Optionally it may be used for BIOS and AMT
firmware storage.
It is necessary to set certain strapping options to enable either a FWH-based or SPIbased BIOS. Optionally, it is also possible to direct BIOS access to the PCI interface.
Table 7
describes these strapping options.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 27
Page 28

Table 7. BIOS Location Strapping Options
Theory of Operation
ICH8-M Signal
GNT#0 SPI_CS1# BIOS Location
0 1 SPI
1 0 PCI
1 1 LPC (Default)
Note: GNT#0 is configurable via jumper J8E2. Further details on its location can be found in
Section 4.3. SPI_CS1# is configurable via stuffing option R7U12. By default R7U12 is
not stuffed resulting in a SPI_CS1# strapping value of 1.
3.4.2.11 System Management Controller (SMC)/Keyboard Controller
The Hitachi* H8S/2104RV serves as both SMC and KBC for the development board.
The SMC/KBC controller supports two PS/2 ports, battery monitoring and charging,
EMA support, wake/runtime SCI events, and power sequencing control. The two PS/2
ports on the development board are for legacy keyboard and mouse. The keyboard
plugs into the bottom jack and the mouse plugs into the top jack at J1A1. Scan matrix
keyboards can be supported via an optional connector at J9E1.
3.4.2.12 Clocks
The development board uses a CK-505 clock synthesizer and DB800 clock buffer
compatible solution. The FSB frequency is determined from decoding the processor
BSEL[2:0] pin settings. This pin settings may be strapped using the jumpers at J1G2,
J1G5 and J1G8. Refer to Figure 7
jumpers.
and Table 15 for further information on these
3.4.2.13 Real Time Clock
An on-board battery at BT5H1 maintains power to the real time clock (RTC) when in a
mechanical off state. A CR2032 battery is installed on the development board.
Warning: Risk of explosion if the lithium battery is replaced by an incorrect type. Dispose of
used batteries according to the vendor's instructions.
3.4.2.14 Thermal Monitoring
The processor has a thermal diode for temperature monitoring. The SMC throttles the
processor if it becomes hot. If the temperature of the processor rises too high, the
SMC alternately blinks the CAPS lock and NUM lock LEDs on the development board,
and the development board shuts down.
A 3-pin fan header J3C1 is provided to support Tachometer output measurement for
GMCH. The development board supports PWM based speed control. As part of the
thermal measurement, the speed of the fan is varied based on the temperature
measurement.
28 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 29

Theory of Operation
3.4.3 POST Code Debugger
A Port 80-83 Add-in card can be plugged into to the development board at the TPM
header (J9A1). This card decodes the LPC bus BIOS POST codes and displays them on
four 7-segment LED displays.
For AMI* BIOS POST codes, please visit: http://www.ami.com
3.5 Clock Generation
The development board uses a CK-505 and DB800 compatible solution. The FSB
frequency is determined from decoding the processor BSEL[2:0] pin settings.
The clock generator provides Processor, GMCH, ICH8-M, PCI, PCI Express*, SATA, and
USB reference clocks. Clocking for DDR2 is provided by the GMCH.
Table 8. Primary System Clocks
Clock Name Speed
CPU 133 MHz @ 533 FSB Speed
DDR2 133 MHz @ 533 Memory Speed
PCI Express* and DMI 100 MHz
SATA 100MHz
PCI 33MHz
USB 48MHz
Super I/O 14MHz
166 MHz @ 667 FSB Speed
200 MHz @ 800 FSB Speed
166 MHz @ 667 Memory Speed
3.6 Power Management States
Table 9 and Table 10 lists the power management states that have been defined for
the baseboard.
The Manageability Engine (ME) operates at various power levels, called M-states. M0
is the highest power state, followed by M1 and M-off. The Manageability Engine
provides some of the functionality required to implement Intel
Technology (iAMT) on the development board. Further information on iAMT can be
found here: http://www.intel.com/technology/manage/iamt/
Table 9. Power Management States
State Description
G0/S0/C0 Full on
G0/S0/C2 STPCLK# signal active
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 29
®
Active Management
Page 30

State Description
G0/S0/C3 Deep Sleep: DPSLP# signal active
G0/S0/C4 Deeper Sleep: DPRSLP# signal active
G1/S3 Suspend To RAM (all switched rails are turned off)
G1/S4 Suspend To Disk
G2/S5 Soft Off
G3 Mechanical Off
Table 10. Power Management M-States
Theory of Operation
M-
State
M0 Full on. All
M1 Manageability
M-off Manageability is
NOTES:
1. Memory subsystem is the memory and memory-related power supplies to the MCH.
2. Manageability Subsystem includes manageability functions in the chipset, SPI flash, and
3. In M1 the clock is powered, however only the BCLK pair to the MCH is active.
Description Main
manageability
functions
supported
functions that only
require memory
are supported
disabled
LAN devices.
Everything besides the PLL in the clock chip is disabled and powered down.
System
Powered Powered and
Off Powered - Self
Off Off Off Off
Memory
Subsystem1
active
refresh.
Manageability
Subsystem2
Powered Powered
Powered Only
Clocks
BCLK pair
to MCH is
3
active
Note: While in an M-state other than M-off, the traditional hardware definition of the S-State
as defined by the SLP signals is overridden by the ICH8M. This allows devices
controlled by SLP_S3# and SLP_S4#, such as system memory, to be available to the
Manageability system as needed. Even though the SLP signals may be driven
differently in M-States, the S-State information is retained in the ICH8M for transition
to M-off. S4_STATE# is the new signal to indicate S4 transition.
Table 11
provides a truth table of the SLP signals in various system states and M-
States. The ICH8M provides all of the SLP signals shown in the table below.
30 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 31

R
Theory of Operation
Table 11. Sleep Signals and M-State Definition
S0/M0
S3/M1
S4/M1
S5/M1
S3/M-off
S4/M-off
State
S5/M-off
S0 (Non-AMT)
S3 (Non-AMT)
S4 (Non-AMT)
S5 (Non-AMT)
Signal
SLP_S3# SLP_S4# SLP_S5# S4_STATE# SLP_M#
High High High High High
Low High High High High
Low High High Low High
Low High Low Low High
Low High High High Low
Low Low High Low Low
Low Low Low Low Low
High High High High High
Low High High High Low
Low Low High Low Low
Low Low Low Low Low
3.7 Power Measurement Support
Power measurement resistors are provided on the development board to measure the
power of most subsystems. All power measurement resistors have a tolerance of 1%.
The value of these power measurement resistors are 0.002Ω by default. Power on a
particular subsystem is calculated using the following formula:
2
V
P
=
R = value of the sense resistor (typically 0.002Ω)
V = the voltage difference measured across the sense resistor
Use of an oscilloscope or high precision digital multi-meter tool such as the Agilent*
34401A digital multi-meter is recommended. Meters such as this have 6½ digits of
accuracy and can provide a much greater accuracy in power measurement than a
common 3½ digit multi-meter.
Table 12
development board. All resistors are 0.002 Ω unless otherwise noted. Reference
designators marked with an asterisk are “not stuffed” on the development board.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 31
summarizes all the power measurement resistors located on the
Page 32

Table 12. Development Board Voltage Rails
Theory of Operation
Component
/ Interface
CPU VR 5V +V5S +V5S_IMVP6 R1B1
CPU VR Battery +VBAT +VDC_PHASE R2P12
CPU VR Variable 6208_1_PHASE_LOUT +VCC_CORE R3D1
CPU VR Variable 6208_2_PHASE_LOUT +VCC_CORE R2D1
CPU VR Variable 6208_3_PHASE_LOUT +VCC_CORE R2D2
CPU 1.05V +V1.05S +V1.05S_CPU R3T2* and R3R7*
CPU 1.5V +V1.5S +VCCA_PROC R3U1 (0.01Ω)
GMCH VR Battery +VBATA 1.5S_VIN R5V3
GMCH VR Battery +VBATA VGMCH_IN R5F16
GMCH VR 5 V +V5S +V5S_GVR R3F12
GMCH VR Battery +VBAT GVR_VBAT R3V2
GMCH VR 3.3V V3.3S_TVDAC_R2 +V3.3S_TVDAC R3E2 (0.01Ω)
GMCH VR Battery +VBATA V1.25M_VIN R4V4
GMCH VR 1.05 V +V1.05OUT +V1.05M R4F13 (0.01Ω)
GMCH 1.05V +V1.05S +VCC_GMCH R6E1
GMCH VCCP
GMCH 1.05V +V1.05S +VCC_PEG R6T14
GMCH 1.25S +V1.25S +VCC_PEG R6T13*
GMCH 1.05V +V1.05S +VCC_DMI R6T11
GMCH 1.25S +V1.25S +VCC_DMI R6E2*
GMCH 1.05V +V1.05M +VCC_AXM R6R1
GMCH V_GFX
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25S +V1.25S_PEGPLL R5E3
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25M +V1.25M_A_SM_CK R5P5
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25S +V1.25S_DMI R6D5
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25S +V1.25S_MCH_PLL R5U24
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25M V1.25M_MCH_PLL2 R4D6
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25M +V1.25M_A_SM R4R2
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25M +V1.25M_AXD R4C27
GMCH 1.25V +V1.25S +V1.25S_AXF R4F9
GMCH 1.5V +V1.5S TVDAC_FB R5U8
Voltage
Plane
(1.05V)
(1.05S)
Supply Rail Reference
+V1.05S +VCCP_GMCH R5U26
+VCC_GFXCORE +VCC_GFX R3F8
Designator
32 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 33

Theory of Operation
Component
/ Interface
GMCH 1.8V +V1.8 +V1.8_GMCH R5D1
GMCH 1.8V +V1.8_GMCH +V1.8_SM_CK R5D2
GMCH 1.8V +V1.8 +V1.8_TXLVDS R5U25
GMCH 1.8V +V1.8 +V1.8_DLVDS R5E5
GMCH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_HV R5U2
GMCH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_SYNC R5F9
GMCH 3.3V +VCCA_TVDAC +V3.3S_DAC_BG R5U19 (0.03Ω)
GMCH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PEG_BG R6E3
PCI-E Gfx 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PEG R6C1
PCI-E Gfx 3.3V +V3.3 +V3.3S_PEG R6P2*
PCI-E Gfx Battery +VBATS +V12S_PEG R6N9
PCI-E Gfx Battery +VBAT_S4 +V12S_PEG R6N5*
ICH 1.05V +V1.05S +V1.05S_ICH R7F12
ICH 1.05V +V1.05S +V1.05S_ICH_IO R6V11
ICH 1.25V +V1.25S +V1.25S_DMI_ICH R6G3
ICH 1.5V +V1.5S +V1.5S_PCIE_ICH R6F13
ICH 1.5V +V1.5S +V1.5S_SATA_ICH R8G2
ICH 1.5V +V1.5S +V1.5S_USB_ICH R8F7
ICH 1.5V +V1.5S +V1.5S_APLL_ICH R8G2
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_DMI_ICH R6G4
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_GLAN_ICH R6F2
ICH 3.3V +V3.3M +V3.3M_ICH R7U3
ICH 3.3V +V3.3A +V3.3A_ICH R6V12
ICH 3.3V +V3.3A +V3.3A_USB_ICH R8F4
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_IDE_ICH R8G1
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_VCCPCORE_ICH R8V14
ICH 3.3V +V3.3M +V3.3M_VCCPAUX R7F1
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCI_ICH R8F5
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_SATA_ICH R8G7
ICH 3.3V +V3.3S_1.5S_HDA_IO +V3.3S_1.5S_HDA_IO_IC
Memory Battery +VBATA 1.8_VIN R5N13
Memory 0.9 V +V0.9 +V0.9_R R4B13
Memory 1.8V +V1.8 +V1.8_DIMM0 R5C2
Voltage
Plane
Supply Rail Reference
H
Designator
R7V4 (0.022Ω)
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 33
Page 34

Theory of Operation
Component
/ Interface
Memory 1.8V +V1.8 +V1.8_DIMM1 R5B10
Memory 3.3V +V3.3M +V3.3M_DIMM0 R4C1 (0.022Ω)
Memory 3.3V +V3.3M +V3.3M_DIMM1 R4B26 (0.022Ω)
LAN 3.3V +V3.3M_LAN_SW +V3.3M_LAN R6A23
LAN 1.8V +V1.8_LAN +V1.8_LAN_M R6M1
LAN 1V +V1.0_LAN_M +V1.0_LAN_M_IN R6M3
PCI 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCI R9D2
PCI 3.3V +V3.3 +V3.3_PCISLT3 R8C5*
PCI 3.3V +V3.3S_PCI +V3.3_PCISLT3 R9D3
PCI 5V +V5S +V5S_PCI R9B1
PCI 5V +V5 +V5_PCISLT3 R8B3*
PCI 5V +V5S_PCI +V5_PCISLT3 R9B2
PCI 5V +V5 +V5_PCI R9A11*
PCI 12V +V12S +V12S_PCI R8B1
PCI-E 12V +V12S +V12S_PCIESLOT1 R7N11
PCI-E 12V +V12S +V12S_PCIESLOT2 R7C20
PCI-E 12V +V12S +V12S_PCIESLOT3 R8B2
PCI-E 12V +V12S +V12S_PCIESLOT4 R8C7
PCI-E 12V +V12S +V12S_PCIESLOT5 R7N9
Voltage
Plane
Supply Rail Reference
Designator
PCI-E 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCIESLOT1 R7N10
PCI-E 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCIESLOT2 R7R1
PCI-E 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCIESLOT3 R7N5
PCI-E 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCIESLOT4 R8D2
PCI-E 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_PCIESLOT5 R7N8
Audio 3.3 V +V3.3S +V3.3S_1.5S_HDA_IO R7W5
Audio 1.5 V +V1.5S +V3.3S_1.5S_HDA_IO R7H6*
Audio 1.5 V +V1.5A_HDA_IO +V3.3A_1.5A_HDA_IO R8E8*
Audio 3.3 V +V3.3A +V3.3A_1.5A_HDA_IO R8E7
Panel Bklt 5V +V5S +V5S_LVDS_BKLT R6U8
Panel Bklt Battery +VBAT +VCC_LVDS_BKLT R6F1
Panel LVDS 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_L R6U13
Panel LVDS 5V +V5S +V3.3S_L R6U16*
Panel LVDS 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_LVDS_DDC R6F9
34 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 35

Theory of Operation
Component
/ Interface
Panel LVDS 5V +V5S +V3.3S_LVDS_DDC R6U9*
CK505 3.3V +V3.3M_CK505 VDD_CK505 R5G11
CK505 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_DB800 R7C10
CK505 0.9V IO_VOUT_D +VDDIO_CLK R5V11
LPC 3.3V +V3.3 +V3.3_LPCSLOT R8F2
LPC 5V +V5 +V5_LPCSLOT R8E2
TPM 5V +V5 V5_R1_TPM R9M7
TPM 3.3V +V3.3S V3.3S_R1_TPM R9M8
TPM 3.3V +V3.3A V3.3A_R1_TPM R9A8
SMC 3.3V +V3.3A +V3.3A_KBC R8H1
PS2 5V +V5 +V5_PS2 R1A1
SIO 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_SIO R7E1
IR 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_IR R4M3
FWH 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_FWH R8V17
USB 5V +V5A +V5A_USBPWR_IN1 R5W9
USB 5V +V5A +V5A_USBPWR_IN2 R7H7
USB 5V +V5A +V5A_USBPWR_IN3 R3B5
IDE 5V +V5S +V5S_PATA R5Y6
IDE 12V +V12S +V12S_PATA R3Y2
SPI 3.3V +V3.3M +V3.3M_SPI R6D8
SATA 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_SATA_P0 R8Y2
SATA 5V +V5S +V5S_SATA_P0 R8H6
SATA 12V +V12S +V12S_SATA_P0 R8W11
SATA 3.3V +V3.3S +V3.3S_SATA_P1 R7H9
SATA 5V +V5S +V5S_SATA_P1 R8H7
SATA 12V +V12S +V12S_SATA_P1 R8H2
System Battery +VCHGR_OUT +VBS R1W15 (0.02Ω)
System Battery +V_BC_OUT +VBS R2H5 (0.005Ω)
System Battery +VBATA 51120DRVH1_+VBATA R3H20
System Battery +VBATA 51120DRVH2_+VBATA_Q R3H5
System 3.3V 51120VBST2_LR +V3.3A_MBL R3G3
System 5V ‘51120_+V5A_MBL_QL +V5A_MBL R3J1
System 1.25V +V1.25M_OUT +V1.25M R4V2
System 1.5V +V1.5S +V1.5S_SW R5G23
Voltage
Plane
Supply Rail Reference
Designator
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 35
Page 36

Theory of Operation
Component
/ Interface
System ATX +V5A +V5_ATX R4J1*
System ATX +V3.3A +V3.3_ATX R4W23*
System ATX +V12_ATX +VBATA R4Y1
System ATX -V12_ATX -V12A R4Y2
System ATX +V5SB_ATX +V5SB_ATXA R5H17
System +VAC_B
Voltage
Plane
RCK
Supply Rail Reference
+VAC_BRCK_IN NEG_SENSE R1G8
Designator
§
36 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 37

Hardware Reference
4 Hardware Reference
This section provides reference information on the hardware, including locations of
development board components, connector pinout information and jumper settings.
4.1 Primary Features
Figure 2 shows the major components of the development board and Table 13 gives a
brief description of each component.
Figure 2. Development Board Component Locations
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 37
Page 38

Table 13. Development Board Component Location Legend
Hardware Reference
Reference
Designator
BT5H1 CMOS Battery
J1C1 Reserved
J1D1 XDP Connector
J1F4 CPU FSB Sideband Signals
J1G1 Reserved
J1G3 Reserved
J1G4 Reserved
J1G6 AC Brick Connector
J1G7 Battery Connector B
J1H1 Battery Connector A
J2B3 CPU Fan Connector
J2F1 Reserved
J2F2 Reserved
J2G2 Reserved
J3C1 GMCH Fan Connector
J3J4 Reserved
J4J1 ATX Power Connector
J4J2 PATA Power Connector
J6B1 PCI Express Slot 1
J6B2 PCI Express x16 Graphics Port
J6C2 HDA Header for External HDMI Support
J6C3 Reserved
J6F1 LVDS Connector
J6H3 USB Ports 7 and 8
J6H4 USB Ports 2 and 4
J6H5 Front Panel Header
J6J1 Reserved
J7B1 PCI Express Slot 5
J7D2 Reserved
J7H1 SATA Port 2, Cable Connect
J7H2 SATA Power Connector
J7J3 SATA Port 1, Cable Connect
Function
38 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 39

Hardware Reference
Reference
Designator
J7J4 PATA Connector
J8A1 Reserved
J8A2 Reserved
J8B3 PCI Slot 3
J8B4 PCI Express Slot 3
J8D1 PCI Express Slot 4
J8E1 LPC Slot
J8G2 Extended Mobile Access Header
J8J1 SATA Port 0, Direct Connect
J9A1 Trusted Platform Module Header
J9C1 PCI Express Docking Interface
J9E1 Scan Matrix Key Board Connector
J9E2 HDA Header for MDC Interposer
J9E3 LPC Hot Docking Connector
J9E4 HDA Header for MDC Interposer
J9G1 LPC Side Band Header
S9B1 PCI-Edge Connector
U2E1 Intel® CoreTM 2 Duo processor
U5E1 Mobile Intel® GME965 Express Graphics Memory Controller Hub
U6A1 82566MM Gigabit Ethernet Phy
U6D2 16Mb SPI Flash
U6H2 CK505 Clock Synthesizer
U7C2 DB800 Clock Buffer
U7E1 16Mb SPI Flash
U7E6 Super I/O
U7F1 Intel® I/O Controller Hub 8-M (ICH8-M)
U8G1 Firmware Hub
U9G2 H8S/2104 KSC
Function
4.2 Back Panel Connectors
This section describes the panel connectors on the development board. Figure 3 shows
these connectors.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 39
Page 40

Figure 3. Back Panel Connector Locations
n o p q r
s t u
Table 14. Back Panel Connector Definitions
Hardware Reference
Item Description Ref
1 PS/2 Mouse J1A1 5 RJ-45 LAN J5A1
2 TV-Out D-Connector J2A1 6 PS/2 Keyboard J1A1
3 Serial Port J2A2 7 VGA J2A2
4 3 USB Ports J3A1 8 2 USB Ports J5A1
4.2.1 TV-Out D-Connector
The TV-Out D-connector supplies the necessary signals to support the Composite, SVideo, and Component TV standards. Component video (Figure 4
video (Figure 5
Component Video cable (with three RCA receptacles at one end and D-mating
connector on other end). S-video (Figure 6
D-connector to S-Video cable (with 4-pin DIN connector one end and D-mating
connector on other end).
) is connected to the development board using D-connector to
Des
Item Description Ref Des
) and Composite
) is connected to development board using
40 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 41
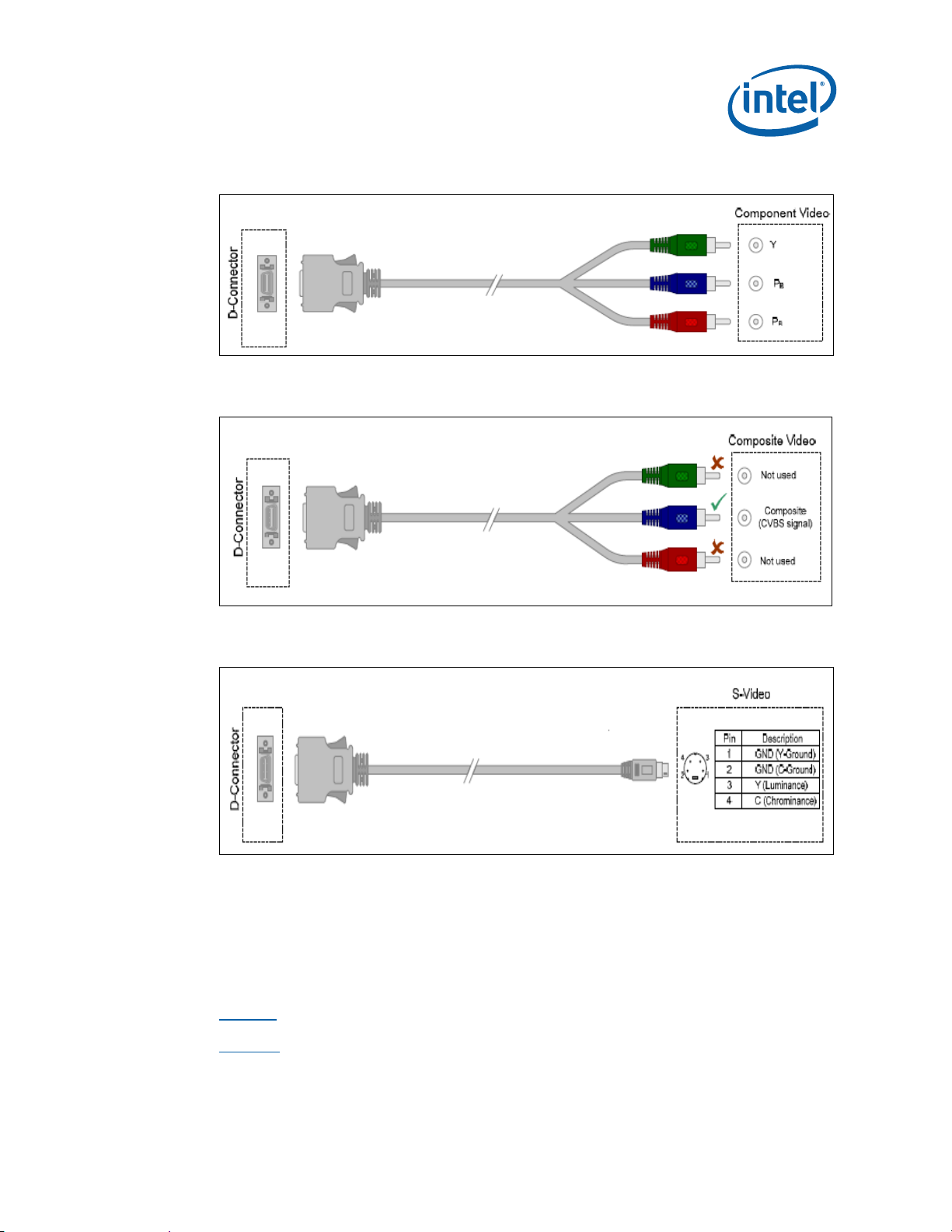
Hardware Reference
Figure 4. D-Connector to Component Video Cable
Figure 5. D-Connector to Composite Video Cable
Figure 6. D-Connector to S-Video Cable
4.3 Configuration Settings
Note: Do not move jumpers with the power on. Always turn off the power and unplug the
power cord from the computer before changing jumper settings. Failure to do so may
cause damage to the development board.
Figure 7
Table 15 summarizes the jumpers and switches and gives their default and optional
settings.
shows the location of the configuration jumpers and switches.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 41
Page 42

The unsupported jumpers must remain in their default position or the operation of the
development board is unpredictable. The development board is shipped with the
jumpers and switches shunted in the default locations.
Figure 7. Configuration Jumper and Switch Locations
Hardware Reference
Table 15. Supported Configuration Jumper/Switch Settings
Reference
Designator
J1G2 BSEL0
J1G5 BSEL1
J1G8 BSEL2
J1J1 Reserved OUT
J1J2 Reserved OUT
J2B2 CPU VID Code OUT 15-16: Activate Override
42 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Function Default Setti ng Optional Setting
1-2: Processor BSEL Select
1-2: Processor BSEL Select
1-2: Processor BSEL Select
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
2-3: Tied to logic high
Empty: Tied to logic low
2-3: Tied to logic low
Empty: Tied to logic high
2-3: Tied to logic low
Empty: Tied to logic high
Page 43

Hardware Reference
Reference
Designator
J2F3 Reserved OUT
J2G1 GFX VID Code
J2H1 Force
J2H2 Reserved OUT
J2H3 Reserved OUT
J2J1 Reserved OUT
J2J2 Reserved OUT
J2J3 Reserved OUT
J2J4 Reserved OUT
J2J5 Reserved OUT
J2J6 Reserved OUT
J3B2 Thermal
J3G1 Power On
Function Default Setti ng Optional Setting
Override
Override
Shutdown
Diode
Connection
Latch
Do not alter jumper setting
OUT 1-2: Activate Override
OUT: Normal Operation IN: Force the board to shutdown
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
1-2 and 3-4: Normal operation OUT: Disconnect CPU thermal
OUT: Normal operation IN: Latch the power on
For each VID signal
IN: Tied to logic low
OUT: Tied to logic high
13 and 14 = VID0
11 and 12 = VID1
9 and 10 = VID2
7 and 8 = VID3
5 and 6 = VID4
3 and 4 = VID5
1 and 2 = VID6
For each VID signal
IN: Tied to logic low
OUT: Tied to logic high
3 and 4 = VID0
5 and 6 = VID1
7 and 8 = VID2
9 and 10 = VID3
11 and 12 = VID4
13 and 14 = VR_ENABLE
15 and 16 = No Function
diode from thermal sensor
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 43
Page 44

Hardware Reference
Reference
Designator
J3J1 Reserved OUT
J3J2 Reserved OUT
J3J3 Reserved OUT
J4H1 ME G3 to M1 OUT: Normal operation IN: Jump power state from G3 to M1
J5H1 Reserved OUT
J5H2 Clear CMOS OUT: Normal operation IN: Clear CMOS
J6G1 Reserved OUT
J6H2 Reserved IN
J7D1 Super IO
J7J1 Reserved OUT
J7J2 SATA Power
J8B1 Remote H8
J8B2 Remote H8
J8E2 Boot BIOS
J8F1 Reserved OUT
J8F2 BIOS
J8G1 Reserved OUT
J9F1 H8 Reset 1-2: Normal operation 2-3: Hold H8 in reset
J9F2 LAN Enable 1-2: LAN Enable 2-3: LAN Disable
J9G2 Boot Block
J9H1 Virtual
J9H2
Function Default Setti ng Optional Setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
Do not alter jumper setting
1-2: Normal operation 2-3: Hold Super IO in reset
Reset
Do not alter jumper setting
IN: (SATA Port-1) Hot
Enable
Programming
Programming
Location
Recovery
Programming
Docking
1Hz clock and OUT: Normal operation, clock IN: Clock disabled, enable H8
Plug/Removal Supported
(SATA Port -2) Device not
connected through cable
1-2: Normal operation 2-3: Program H8
1-2: Normal operation 2-3: Program H8
OUT: Normal operation.
Boot through LPC (If
R7U12 is NO STUFF)
Do not alter jumper setting
OUT: Normal operation IN: BIOS recovery
Do not alter jumper setting
IN: Normal operation OUT: Program H8
OUT: Normal operation IN: Virtual docking enabled
OUT: (SATA Port-1) Hot
Plug/Removal not Supported
(SATA Port -2) Device
connected through cable
IN: PCI or SPI (Depends on
R7U12 stuffing)
44 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 45

Hardware Reference
Reference
Designator
J9H3 KBC Disable OUT: Normal operation,
J9H4 SMC MD0 IN: Normal operation.
J9H5 SATA Device
J9H6 SMC MD2 OUT: Normal operation IN: Advanced single chip mode
J9H7 SMC MD1 IN: Normal operation.
J9H8 Lid Position OUT: Lid Open IN: Lid Closed
J9H9 Virtual
SW1C1 Power Button N/A N/A
SW1C2 Reset Button N/A N/A
SW8E1 Net Detect N/A N/A
SW9H1 Virtual
SW9H2 Virtual
SW9J1 Lid Position OUT: Lid Open IN: Lid Closed
Function Default Setti ng Optional Setting
H8
Programming
NMI
External programming
IN: SATA device present OUT: SATA device not present
Detect
External programming
OUT: Normal operation IN: Virtual battery mode
Battery
1-2: Normal operation 2-3: Virtual docking enabled
Docking
1-2: Normal operation 2-3: Virtual battery mode
Battery
enabled programming
IN: Keyboard Controller
Keyboard Controller
enabled
OUT: No external programming
allowed
OUT: No external programming
allowed
disabled
Note: A jumper consists of two or more pins mounted on the motherboard. When a jumper
cap is placed over two pins, it is designated as IN. When there are more than two
pins on the jumper, the pins to be shorted are indicated as 1-2 (to short pin 1 to pin
2), or 2-3 (to short pin 2 to pin 3). When no jumper cap is to be placed on the
jumper, it is designated as OUT. When a switch is designated as 1-2 the switch slide
is positioned such that pins 1 and 2 are shorted together.
4.4 Power On and Reset Buttons
The development board has two push buttons that implement POWER and RESET
functionality. The POWER button releases power to the entire development board,
causing the board to boot. The RESET button will force all systems to warm reset. The
two buttons are located near the CPU close to the edge of the development board. The
POWER button is located at SW1C1 and the RESET button is located at SW1C2.
Note: If the development board is powered from an external ATX power supply (not a power
brick), the Power button may need to be pressed twice to turn on the system.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 45
Page 46

4.5 LEDs
The development board has a number of LEDs. These LEDs provide status for various
functions on the development board. Figure 8
Table 16
Figure 8. LED Locations
Hardware Reference
indicates the location of the LEDs and
describes their function.
Table 16. LED Functions
Function Reference
Keyboard Number Lock CR9G1
Keyboard Scroll Lock CR9G2
Keyboard Caps Lock CR9G3
System State S0 CR5H5
System State S3 CR3G2
System State S4 CR5H3
System State S5 CR5H4
ATA Activity CR6J1
46 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Designator
Page 47

Hardware Reference
Function Reference
VID 0 CR1B1
VID 1 CR1B2
VID 2 CR1B3
VID 3 CR1B4
VID 4 CR1B5
VID 5 CR1B6
VID 6 CR1B7
M0/M1 CR4H1
System Power Good CR5J1
Reserved CR8G1
Designator
4.6 Other Headers, Slots and Sockets
4.6.1 H8 Programming Headers
The microcontroller firmware for system management/keyboard/mouse control can be
upgraded in two ways. The user can either use a special DOS* utility known as
KSCFlash (in-circuit) or use an external computer connected (remote) to the system
via the serial port on the development board. KSCFlash is available on request from
your Intel representative.
If the user chooses to use an external computer connected to the system via the serial
port, there are four jumpers that must be set correctly first. Please refer to Table 15
for a summary of these jumpers and refer to Figure 7
for the location of each jumper.
Required Hardware: one Null Modem Cable and a Host Unit with a serial COM port
(System used to flash the development board)
Here is the sequence of events necessary to program the H8 via the serial port.
1. Extract all files (keep them in the same folder) to a single directory of your
choice on the host machine or on a floppy disk.
2. Connect a NULL modem cable to the serial ports of each platform (host and
unit to be flashed).
3. With the development board powered off, move the following jumpers to the
programming stuffing option.
a. J9G2 (remove) (default: 1-2), Sets SMC_INIT_CLK high.
b. J8B1 (2-3) (default: 1-2), link the Host Unit to on-board H8.
c. J8B2 (2-3) (default: 1-2), link the Host Unit to on-board H8.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 47
Page 48

d. J9H2 (1-2) (default: 1-X), disable 1 Hz Clock.
4. Attach an ATX power supply or AC to DC adapter to the system and power up
the development board.
5. From the directory where you extracted the files, run the “kscflash ksc.bin /
remote” command to program the H8 via the serial port.
6. Follow the instructions the flash utility provides.
7. With the development board powered off, return the jumpers to their default
setting.
Note: Make sure the development board is not powered on, and the power supply is
disconnected before moving any of the jumpers.
4.6.2 Expansion Slots and Sockets
Following is a list of the slots and sockets available for attaching additional devices.
Refer to Figure 2
for locations.
Hardware Reference
Table 17. Expansion Slots and Sockets
Reference
Designator
U2E1 478 Pin Grid Array (Micro-FCPGA) Processor Socket
J5P1 DDR2 - Channel 0 - SODIMM slot
J5N1 DDR2 - Channel 1 - SODIMM slot
J8F1 LVDS Graphics Interface
J6B2 PCI Express* (x16) Table 18
J6B2 ADD2 Slot Table 19
J6B2 Media Expansion Card Slot Table 20
J8B4 PCI Express* (x1) Slot 3 Table 21
J7B1 PCI Express* (x1) Slot 5 Table 21
J6B1 PCI Express* (x1) Slot 1 Table 21
J8B3 PCI 2.3 Slot 3
J7J4 IDE Interface Connector Table 22
J8J1 SATA ‘Direct Connect’ Connector Table 23
J7J3, J7H1 SATA ‘Cable Connect’ Connector Table 24
J6H3 SATA Desk Top Power Connector Table 25
U8G1 Intel Firmware Hub Socket
BT5H1 Battery
J2B3, J2C1 Fan Connectors Table 26
J2F1 Fan Connector Table 27
Slot/Socket Description Detail
48 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 49

Hardware Reference
Reference
Designator
J6H5 Front Panel Header Table 28
J6H3, J6H4 USB Header Table 29
Slot/Socket Description Detail
4.6.2.1 478 Pin Grid Array (Micro-FCPGA) Socket
The pin locking mechanism on the CPU socket is released by rotating the screw on the
socket 180 degrees counter-clockwise. CPU pins are keyed so as to only allow
insertion in one orientation. DO NOT FORCE CPU into socket. Once the CPU is properly
seated into the socket, turn the screw 180 degrees clock-wise to secure the CPU in the
socket. Note that the slot on the screw aligns with the lock and unlock legend on the
case of the CPU socket.
Caution: Please refer to the heatsink installation instructions in Appendix A prior to inserting
the heatsink as the CPU and socket can be easily damaged.
®
Caution: Only insert Intel
with the Mobile Intel
These processors have a pinout known as Socket-P. Earlier Intel
Mobile processors that have a pinout known as Socket-M are mechanically
compatible with the processor socket but not electrically compatible. Insertion of
these processors will cause damage to the processor and the development board.
CoreTM 2 Duo Mobile processors that are intended for operation
®
965 Express Chipset Family into the development board.
®
CoreTM 2 Duo
4.6.2.2 PCI Express* (x16)
The development board has one x16 lane PCI Express* Graphics slot and supports
either x1, x2, x4, x8 or x16 modes. The slot is wired “lane reversed” which connects
the Mobile Intel
on the slot. The Mobile Intel
wiring since its CFG9 power-on strap is tied low.
Table 18. PCI Express* (x16) Pinout (J6B2)
Pin Description Pin Description
A1 PRSNT1# B1 +12V
A2 +12V B2 +12V
A3 +12V B3 +12V
A4 GND B4 GND
A5 JTAG2 (TCK) B5 SMCLK
A6 JTAG3 (TDI) B6 SMDAT
A7 JTAG4 (TDO) B7 GND
A8 JTAG5 (TMS) B8 +3.3V
A9 +3.3V B9 JTAG1 (TRST#)
A10 +3.3V B10 +3.3VAUX
®
GME965 Express Chipset lanes 0 through 15 to lanes 15 through 0
®
GME965 Express Chipset will internally un-reverse this
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 49
Page 50

Pin Description Pin Description
A11 PERST# B11 WAKE#
Key
A12 GND B12 RSVD
A13 REFCLK+ B13 GND
A14 REFCLK- B14 LANE 0 (T+)
A15 GND B15 LANE 0 (T-)
A16 LANE 0 (R+) B16 GND
A17 LANE 0 (R-) B17 PRSNT2*
A18 GND B18 GND
End of x1 Connector
A19 RSVD B19 LANE 1 (T+)
A20 GND B20 LANE 1 (T-)
A21 LANE 1 (R+) B21 GND
A22 LANE 1 (R-) B22 GND
A23 GND B23 LANE 2 (T+)
A24 GND B24 LANE 2 (T-)
A25 LANE 2 (R+) B25 GND
A26 LANE 2 (R-) B26 GND
A27 GND B27 LANE 3 (T+)
A28 GND B28 LANE 3 (T-)
A29 LANE 3 (R+) B29 GND
A30 LANE 3 (R-) B30 RSVD
A31 GND B31 PRSNT2#
A32 RSVD B32 GND
End of x4 Connector
A33 RSVD B33 LANE 4 (T+)
A34 GND B34 LANE 4 (T-)
A35 LANE 4 (R+) B35 GND
A36 LANE 4 (R-) B36 GND
A37 GND B37 LANE 5 (T+)
A38 GND B38 LANE 5 (T-)
A39 LANE 5 (R+) B39 GND
A40 LANE 5 (R-) B40 GND
A41 GND B41 LANE 6 (T+)
A42 GND B42 LANE 6 (T-)
Hardware Reference
50 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 51

Hardware Reference
Pin Description Pin Description
A43 LANE 6 (R+) B43 GND
A44 LANE 6 (R-) B44 GND
A45 GND B45 LANE 7 (T+)
A46 GND B46 LANE 7 (T-)
A47 LANE 7 (R+) B47 GND
A48 LANE 7 (R-) B48 PRSNT#2
A49 GND B49 GND
A50 RSVD B50 LANE 8 (T+)
A51 GND B51 LANE 8 (T-)
A52 LANE 8 (R+) B52 GND
A53 LANE 8 (R-) B53 GND
A54 GND B54 LANE 9 (T+)
A55 GND B55 LANE 9 (T-)
A56 LANE 9 (R+) B56 GND
A57 LANE 9 (R-) B57 GND
A58 GND B58 LANE 10 (T+)
A59 GND B59 LANE 10 (T-)
A60 LANE 10 (R+) B60 GND
A61 LANE 10 (R-) B61 GND
A62 GND B62 LANE 11 (T+)
A63 GND B63 LANE 11 (T-)
A64 LANE 11 (R+) B64 GND
A65 LANE 11 (R-) B65 GND
A66 GND B66 LANE 12 (T+)
A67 GND B67 LANE 12 (T-)
A68 LANE 12 (R+) B68 GND
A69 LANE 12 (R-) B69 GND
A70 GND B70 LANE 13 (T+)
A71 GND B71 LANE 13 (T-)
A72 LANE 13 (R+) B72 GND
A73 LANE 13 (R-) B73 GND
A74 GND B74 LANE 14 (T+)
A75 GND B75 LANE 14 (T-)
A76 LANE 14 (R+) B76 GND
End of x8 Connector
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 51
Page 52

Pin Description Pin Description
A77 LANE 14 (R-) B77 GND
A78 GND B78 LANE 15 (T+)
A79 GND B79 LANE 15 (T-)
A80 LANE 15 (R+) B80 GND
A81 LANE 15 (R-) B81 PRST2#
A82 GND B82 RSVD
4.6.2.3 ADD2/Media Expansion Card (MEC) Slot
When not being used for PCI Express*, the x16 slot can be used for Serial Digital
Video Out (SDVO). An ADD2N card can be inserted into the SDVO slot to enable the
use of third party vendor transmitters to output video formats such as DVI, TV, LVDS
and HDMI. Table 19
The SDVO interface will also support a Media Expansion Card (MEC), which provide TV
Capture over the PCI Express* x1 port in addition to the standard ADD2 card video
out capabilities. Table 20
describes the ADD2N interface pin-out.
describes the MEC interface pin-out.
Hardware Reference
Table 19. ADD2 Slot (J6B2)
Pin Description Pin Description
A1 N/C B1 12 V
A2 12 V B2 12 V
A3 12 V B3 Reserved
A4 GND B4 GND
A5 N/C B5 N/C
A6 TDI B6 N/C
A7 TDO B7 GND
A8 N/C B8 3.3 V
A9 3.3 V B9 N/C
A10 3.3 V B10 N/C
A11 RESET B11 N/C
A12 GND B12 Reserved
A13 N/C B13 GND
A14 N/C B14 SDVOB_Red+
A15 GND B15 SDVOB_Red-
A16 SDVO_TVClkIn+ B16 GND
A17 SDVO_TVClkIn- B17 SDVO_CtrlClk
Key
52 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 53

Hardware Reference
Pin Description Pin Description
A18 GND B18 GND
A19 Reserved B19 SDVO_Green+
A20 GND B20 SDVO_Green-
A21 SDVOB_Int+ B21 GND
A22 SDVOB_Int- B22 GND
A23 GND B23 SDVOB_Blue+
A24 GND B24 SDVOB_Blue-
A25 SDVO_Stall+ B25 GND
A26 SDVO_Stall- B26 GND
A27 GND B27 SDVOB_Clk+
A28 GND B28 SDVOB_Clk-
A29 N/C B29 GND
A30 N/C B30 Reserved
A31 GND B31 SDVO_CtrlData
A32 Reserved B32 GND
A33 Reserved B33 SDVOC_Red+
A34 GND B34 SDVOC_Red-
A35 N/C B35 GND
A36 N/C B36 GND
A37 GND B37 SDVOC_Green+
A38 GND B38 SDVOC_Green-
A39 SDVOC_Int+ B39 GND
A40 SDVOC_Int- B40 GND
A41 GND B41 SDVOC_Blue+
A42 GND B42 SDVOC_Blue-
A43 N/C B43 GND
A44 N/C B44 GND
A45 GND B45 SDVOC_Clk+
A46 GND B46 SDVOC_Clk-
A47 N/C B47 GND
A48 N/C B48 N/C
A49 GND B49 GND
End of x1 Connector
End of x4 Connector
End of x8 Connector
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 53
Page 54

Pin Description Pin Description
A50 Reserved B50 N/C
A51 GND B51 N/C
A52 N/C B52 GND
A53 N/C B53 GND
A54 GND B54 N/C
A55 GND B55 N/C
A56 N/C B56 GND
A57 N/C B57 GND
A58 GND B58 N/C
A59 GND B59 N/C
A60 N/C B60 GND
A61 N/C B61 GND
A62 GND B62 N/C
A63 GND B63 N/C
A64 N/C B64 GND
A65 N/C B65 GND
A66 GND B66 N/C
A67 GND B67 N/C
A68 N/C B68 GND
A69 N/C B69 GND
A70 GND B70 N/C
A71 GND B71 N/C
A72 N/C B72 GND
A73 N/C B73 GND
A74 GND B74 N/C
A75 GND B75 N/C
A76 N/C B76 GND
A77 N/C B77 GND
A78 GND B78 N/C
A79 GND B79 N/C
A80 N/C B80 GND
A81 N/C B81 N/C
A82 GND B82 Reserved
Hardware Reference
54 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 55

Hardware Reference
Table 20. MEC Slot (J6B2)
Pin Description Pin Description
A1 N/C B1 12 V
A2 12 V B2 12 V
A3 12 V B3 Reserved
A4 GND B4 GND
A5 N/C B5 N/C
A6 N/C B6 N/C
A7 N/C B7 GND
A8 N/C B8 3.3 V
A9 3.3 V B9 N/C
A10 3.3 V B10 +3.3VA
A11 RESET B11 WAKE#
A12 GND B12 Reserved
A13 REFCLK+ B13 GND
A14 REFCLK- B14 Lane 0 (T+)
A15 GND B15 Lane 0 (T-)
A16 Lane 0 (R+) B16 GND
A17 Lane 0 (R-) B17 SDVO_CtrlClk
A18 GND B18 GND
A19 Reserved B19 N/C
A20 GND B20 N/C
A21 N/C B21 GND
A22 N/C B22 GND
A23 GND B23 N/C
A24 GND B24 N/C
A25 N/C B25 GND
A26 N/C B26 GND
A27 GND B27 N/C
A28 GND B28 N/C
A29 N/C B29 GND
A30 N/C B30 Reserved
A31 GND B31 SDVOB_CtrlData
A32 Reserved B32 GND
Key
End of x1 Connector
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 55
Page 56

Pin Description Pin Description
End of x4 Connector
A33 Reserved B33 N/C
A34 GND B34 N/C
A35 N/C B35 GND
A36 N/C B36 GND
A37 GND B37 N/C
A38 GND B38 N/C
A39 N/C B39 GND
A40 N/C B40 GND
A41 GND B41 N/C
A42 GND B42 N/C
A43 N/C B43 GND
A44 N/C B44 GND
A45 GND B45 N/C
A46 GND B46 N/C
A47 N/C B47 GND
A48 N/C B48 MEC_Enable
A49 GND B49 GND
End of x8 Connector
A50 Reserved B50 SDVOC_CLK+
A51 GND B51 SDVOC_CLK-
A52 N/C B52 GND
A53 N/C B53 GND
A54 GND B54 SDVOC_Blue+
A55 GND B55 SDVOC_Blue-
A56 N/C B56 GND
A57 N/C B57 GND
A58 GND B58 SDVOC_Green+
A59 GND B59 SDVOC_Green-
A60 SDVOC_Int+ B60 GND
A61 SDVOC_Int- B61 GND
A62 GND B62 SDVOC_Red+
A63 GND B63 SDVOC_Red-
A64 N/C B64 GND
A65 N/C B65 GND
Hardware Reference
56 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 57

Hardware Reference
Pin Description Pin Description
A66 GND B66 SDVOB_Clk+
A67 GND B67 SDVOB_Clk-
A68 N/C B68 GND
A69 N/C B69 GND
A70 GND B70 SDVOB_Blue+
A71 GND B71 SDVOB_Blue-
A72 SDVO_Stall+ B72 GND
A73 SDVO_Stall- B73 GND
A74 GND B74 SDVOB_Green+
A75 GND B75 SDVOB_Green-
A76 SDVOB_Int+ B76 GND
A77 SDVOB_Int- B77 GND
A78 GND B78 SDVOB_Red+
A79 GND B79 SDVOB_Red-
A80 SDVO_TVClkIn+ B80 GND
A81 SDVO_TVClkIn- B81 N/C
A82 GND B82 Reserved
4.6.2.4 PCI Express* (x1)
The three PCI Express* x1 connectors allow the use of any industry standard PCI
Express* device. The pin configuration of the connectors is given below.
Table 21. PCI Express* (x1) Pinout (J6B1, J7B1, J8B4)
Pin Description Pin Description
A1 PRSNT1# B1 +12V
A2 +12V B2 +12V
A3 +12V B3 +12V
A4 GND B4 GND
A5 JTAG2 (TCK) B5 SMCLK
A6 JTAG3 (TDI) B6 SMDAT
A7 JTAG4 (TDO) B7 GND
A8 JTAG5 (TMS) B8 +3.3V
A9 +3.3V B9 JTAG1 (TRST#)
A10 +3.3V B10 +3.3VAUX
A11 PERST# B11 WAKE#
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 57
Page 58

Pin Description Pin Description
A12 GND B12 RSVD
A13 REFCLK+ B13 GND
A14 REFCLK- B14 LANE 0 (T+)
A15 GND B15 LANE 0 (T-)
A16 LANE 0 (R+) B16 GND
A17 LANE 0 (R-) B17 PRSNT2*
A18 GND B18 GND
4.6.2.5 IDE Connector
The IDE interface can support up to two devices, a master and a slave. Ensure that
the jumpers on the devices are properly selected for the given configuration. Mobile
devices with an IDE interface will require an adapter to connect to this port.
Hardware Reference
Key
Table 22. IDE Connector
Pin Signal Pin Signal
1 Reset 2 Ground
3 Data 7 4 Data 8
5 Data 6 6 Data 9
7 Data 5 8 Data 10
9 Data 4 10 Data 11
11 Data 3 12 Data 12
13 Data 2 14 Data 13
15 Data 1 16 Data 14
17 Data 0 18 Data 15
19 Ground 20 Key
21 DDRQ 22 Ground
23 I/O Write 24 Ground
25 I/O Read 26 Ground
27 I/O HRDY 28 Cable Select
29 DDACK 30 Ground
31 IRQ 32 No Connect
33 Address 1 34 DMA66_Detect
35 Address 0 36 Address 2
37 Chip Select 1 38 Chip Select 3
39 Activity 40 Ground
58 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 59

Hardware Reference
4.6.2.6 SATA Pinout
Up to three SATA devices may be supported by the SATA connectors on the
development board. Table 23
describes the SATA ‘Cable Connect’ connectors.
24
Table 23. SATA Port 0 ‘Direct Connect’ Connector Pinout (J8J1)
Pin Signal
2 TX
3 TX#
5 RX#
6 RX
8, 9, 10 +3.3V
14, 15, 16 +5V
20, 21, 22 +12V
1, 4, 7, 11 GND
12, 13, 17, 19 GND
describes the SATA ‘Direct Connect’ connector and Table
Table 24. SATA Ports 1 and 2 ‘Cable Connect’ Connector Pinout (J7J3, J7H1)
Pin Signal
2 TX
3 TX#
5 RX#
6 RX
1, 4, 7 GND
Table 25. SATA Power Connection (J7H2)
Pin Signal
1, 3 +3.3V
3, 4 +5V
5 +12V
6, 7, 8, 9, 10 GND
4.6.2.7 Fan Connectors
The development board implements three fan connectors. The connectors at J2B3 and
J2C1 have a speed controlled power supply. The connector at J2F1 has a fixed power
supply.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 59
Page 60

Connector J2B3 is used to power the CPU fan. Connectors J2C1 and J2F1 are not used
in the default operation of the development board.
Table 26. Fan Connectors (J2B3, J2C1)
Pin Signal
1 +V
2 TACH
3 GND
Table 27. Fan Connector (J2F1)
Pin Signal
1 +5V
2 NC
3 GND
Hardware Reference
4.6.2.8 Front Panel Header (J6H5)
The front panel header allows connection of the LEDs and switches typically found in
an ATX chassis to the development board.
Table 28. Front Panel Connector
Pin Signal Definition
1 FRONT1 5 volt front panel LED supply
2 FRONT2 5 volt front panel LED supply
3 ATA_LED# Indicates PATA or SATA activity –
4 GND Ground
5 GND Ground
6 PWR_CONN_D System Power – Active Low
7 RST_PUSH#_D System Reset – Active Low
8 GND Ground
9 +V5 5 volt supply
10 N/C No Connect
11 N/C No Connect
12 GND Ground
13 GND Ground
14 N/C No Connect
15 Reserved
Active Low
60 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 61

Hardware Reference
16 +V5 5 volt supply
4.6.2.9 USB Headers (J6H3, J6H4)
The USB headers implement 4 additional USB ports on the development board.
Connector J6H3 implements ports 7 and 8 and connector J6H4 implements ports 2
and 4.
Table 29. USB Headers
Pin Signal Definition
1 +V5A_L_USBPWR 5 volt – Always On
2 +V5A_L_USBPWR 5 volt – Always On
3 USB_PNx Data- (USB Port x)
4 USB_PNy Data- (USB Port y)
5 USB_PPx Data+ (USB Port x)
6 USB_PPy Data+ (USB Port y)
7 GND Ground
8 GND Ground
9 N/C No Connect
10 N/C No Connect
§
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 61
Page 62

Hardware Reference
Appendix A . Heatsink Installation
Instructions
It is necessary for the Intel® CoreTM 2 Duo processor to have a thermal solution
attached to it in order to keep it within its operating temperature.
Caution: An ESD wrist strap must be used when handling the board and installing the
heatsink/fan assembly.
A heatsink is included in the kit. To install the heatsink:
1. Remove the heatsink from its package and separate the fan heatsink portion
from the heatsink backplate.
Figure 9. Heatsink and Backplate
2. Examine the base of the heatsink, where contact with the processor die is
made. This surface should be clean of all materials and greases. Wipe the
bottom surface clean with isopropyl alcohol.
3. Place the backplate on the underside of the development board so that the
pins protrude through the holes in the development board around the
processor.
62 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 63

Hardware Reference
Figure 10. Backplate Pins
4. Clean the die of the processor with isopropyl alcohol before the heatsink is
attached to the processor. This ensures that the surface of the die is clean.
5. Remove the tube of thermal grease from the package and use it to coat the
exposed die of the CPU with the thermal grease.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 63
Page 64

Figure 11. Applying the Thermal Grease
Hardware Reference
6. Pick up the heatsink and squeeze the activation arm until it comes in contact
with the base plate that is attached to the heatsink base. This will cause the
springs on the heatsink attachment mechanism to compress.
Figure 12. Squeezing Activation Arm
64 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
Page 65

Hardware Reference
7. While keeping the activation arm compressed, place the heatsink over the pins
of the heatsink backplate. Lower the heatsink until the lugs have inserted into
the base of the heatsink. Slide the heatsink over the lugs on the backplate
pins so that the base is directly over the processor die and the pins on the
backplate have travelled the entire length of the channel in the heatsink base.
Slowly let go of the activation arm until the base of the heatsink makes
contact with the processor die. The heatsink base should be flat on top of the
processor die.
Figure 13. Installing the Heatsink
8. Plug the fan connector for the heatsink onto the CPU fan header (J2B3) on the
motherboard.
Note: The CPU fan header (J2B3) is a 3-pin connector. This is a change from the Mobile
Intel® 945GM Express Chipset Development Kit which has a 2-pin CPU fan header. As
a result, it is not possible to use the heatsink from the Intel® 945GM Express Chipset
Development Kit even though the heatsink and backplate are mechanically
compatible.
316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual 65
Page 66
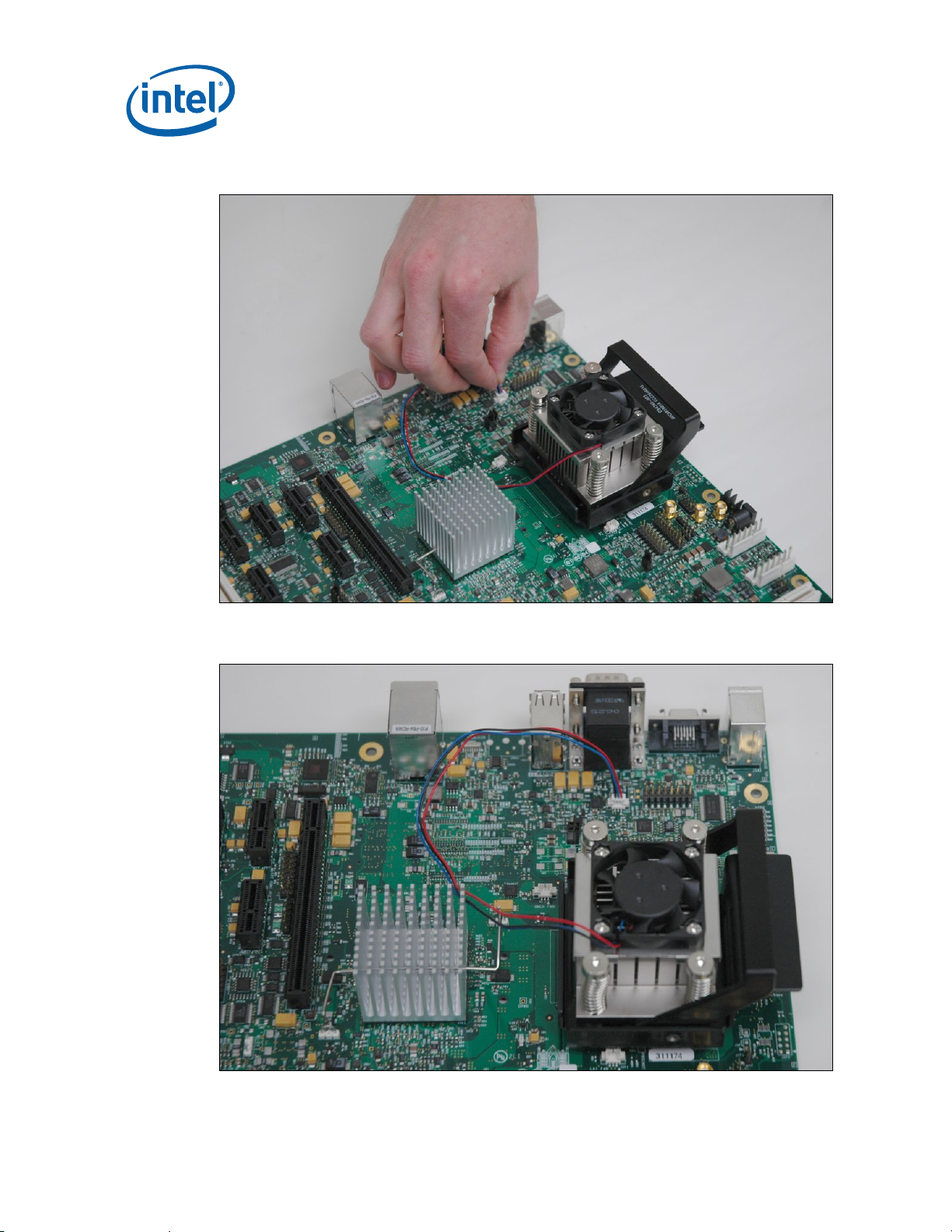
Figure 14. Plugging in the Fan
Hardware Reference
Figure 15. Completed Assembly
66 316704-001 / Development Kit User’s Manual
 Loading...
Loading...