Page 1

Intel® Galileo
Board User Guide
March 2014
Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 2

Legal Lines and Disclaimers
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE , E XPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR
OTHERWISE, TO ANY INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS
OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELA TING
TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE,
MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
A "Mission Critical Application" is any application in which failure of the Intel Product could result, directly or indirectly, in personal injury or death.
SHOULD YOU PURCHASE OR USE INTEL'S PRODUCTS FOR ANY SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, YOU SHALL INDEMNIFY AND HOLD INTEL AND
ITS SUBSIDIARIES, SUBCONTRACTORS AND AFFILIATES, AND THE DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, AND EMPLOYEES OF EACH, HARMLESS AGAINST ALL
CLAIMS COSTS, DAMAGES, AND EXPENSES AND REASONABLE ATTORNEYS' FEES ARISING OUT OF , DIRECTL Y OR INDIRECTL Y, ANY CLAIM OF PRODUCT
LIABILITY, PERSONAL INJURY, OR DEATH ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF SUCH MISSION CRITICAL APPLICATION, WHETHER OR NOT INTEL OR ITS
SUBCONTRACTOR WAS NEGLIGENT IN THE DESIGN, MANUFACTURE, OR WARNING OF THE INTEL PRODUCT OR ANY OF ITS PARTS.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. Designers must not rely on the absence or characteristics
of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined". Intel reserves these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever
for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. The information here is subject to change without notice. Do not finalize a design
with this information.
The products described in this document may contain design defects or errors known as errata which may cause the product to deviate from published
specifications. Current characterized errata are available on request.
Contact your local Intel sales office or your distributor to obtain the latest specifications and before placing your product order.
Copies of documents which have an order number and are referenced in this document, or other Intel literature, may be obtained by calling 1-800-548-
4725, or go to: http://www.intel.com/design/literature.htm
Any software source code reprinted in this document is furnished for informational purposes only and may only be used or copied and no license, express
or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any of the reprinted source code is granted by this document.
Intel processor numbers are not a measure of performance. Processor numbers differentiate features within each processor family, not across different
processor families. Go to: http://www.intel.com/products/processor_number/
Code Names are only for use by Intel to identify products, platforms, programs, services, etc. (“products”) in development by Intel that have not been
made commercially available to the public, i.e., announced, launched or shipped. They are never to be used as “commercial” names for products. Also,
they are not intended to function as trademarks.
Intel and the Intel logo are trademarks of Intel Corporation in the U.S. and/or other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Copyright © 2014, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel® Galileo
Board User Guide March 2014
2 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 3

Revision History—Intel
®
Galileo Board
Revision History
Date Revision Description
March 2014 001 Initial release of document.
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 3
Intel® Galileo
Page 4

Intel® Galileo Board—Contents
Contents
1.0 Overview .................................................................................................................. 5
1.1 Key Components ................................................................................................ 5
2.0 Details and Specifications ......................................................................................... 8
2.1 Physical Characteristics ....................................................................................... 8
2.2 Electrical Summary........................... ........................... .. ............................ .. ....... 8
2.3 Schematic and Reference Design .......................................................................... 8
2.4 Arduino Connector Pinout Details.......................................................................... 9
2.4.1 Properties of Pins Configured as OUTPUT ...................................................10
2.4.2 I/O Pin Mappings....................................................................................11
2.5 Jumpers...........................................................................................................12
2.5.1 IOREF Jumper........................................................................................13
2.5.2 I2C* Address Jumper..............................................................................13
2.5.3 VIN Jumper............................................................................................14
2.5.4 Force Recovery.......................................................................................14
2.6 Buttons ............................................................................................................15
3.0 Communication and Programming ...........................................................................16
3.1 Communication .................................................................................................16
3.2 Programming ....................................................................................................17
3.3 Automatic (Software) Reset .................................. .. .. ........................... ... .. ..........17
4.0 Related Documentation............................................................................................18
5.0 Galileo Disclaimer ....................................................................................................19
Figures
1 Galileo - Front and Back Views .................................................................................... 5
2 Key Components....................................... ........................... ..................................... 6
3 Galileo Board Connection Diagram............................................................................... 9
4 Jumper Locations .....................................................................................................13
5 Resistor Pin for Forcing Recovery ...............................................................................14
6 Reset Button and Reboot Button.......................... ............................ .. .. .......................15
Tables
1 Description of Key Components................................................................................... 6
2 Galileo I/O Mappings.................................................................................................11
3 Galileo I/O Function Multiplexing ................................................................................12
4 Related Documentation.............................................................................................18
§ §
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
4 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 5
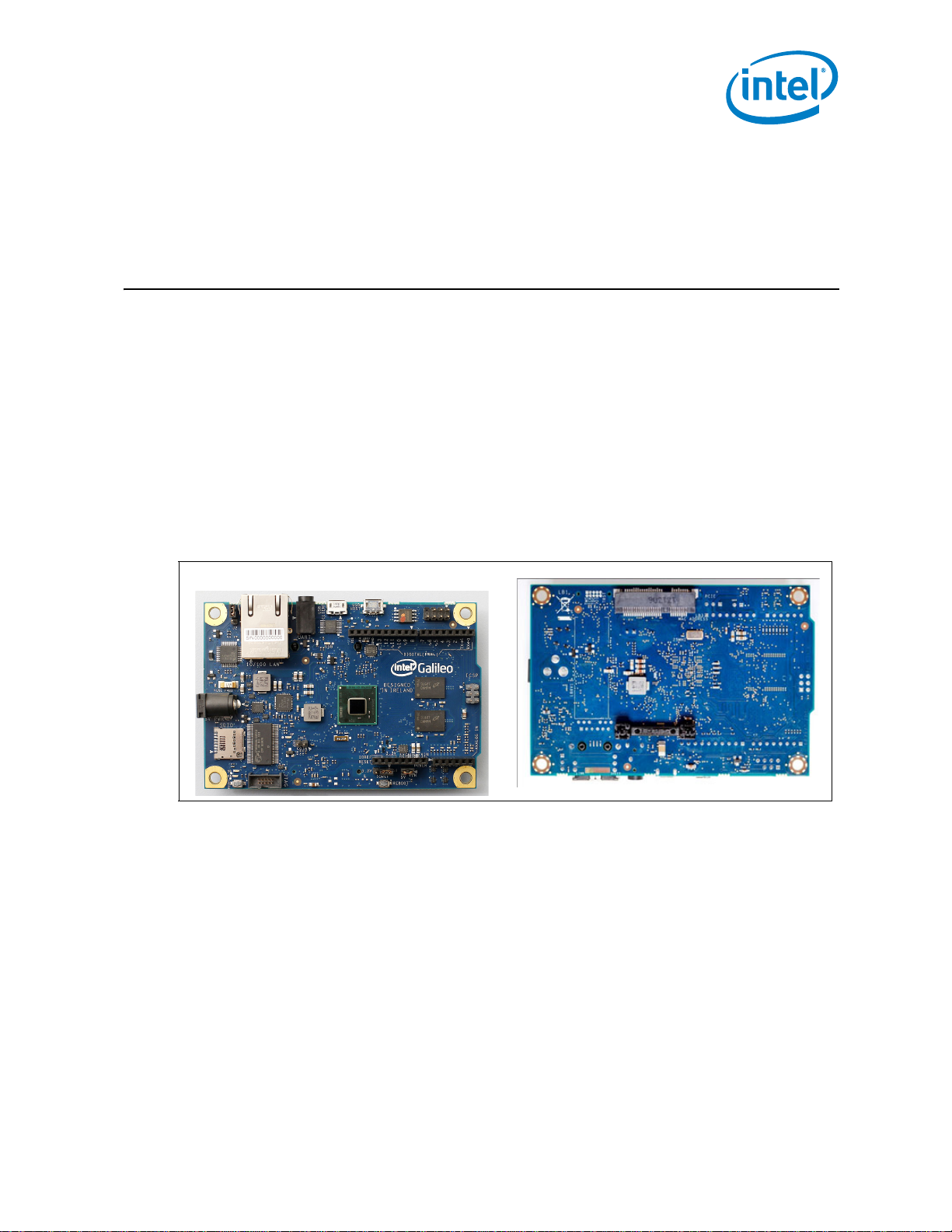
Overview—Intel
®
Galileo Board
1.0 Overview
The Intel® Galileo Board provides a programmable control PCB for the maker
community , students, and professional developers. It is based on the Intel
X1000 Application Processor, a 32-bit Intel Pentium-class system on a chip.
The Intel
®
Galileo Board is the first board based on Intel® architecture designed to be
hardware and software pin-compatible with Arduino shields designed for the Uno R3. It
is also software-compatible with the Arduino* Software Development Environment,
making usability and development a snap.
In addition to Arduino hardware and software compatibility, the Intel® Galileo Board
has several industry-standard I/O ports and features to expand native usage and
capabilities beyond the Arduino shield ecosystem, which are described in the next
section of this document.
Figure 1. Galileo - Front and Back Views
®
Quark SoC
1.1 Key Components
Figure 2 and Table 1 describe key components of the Intel® Galileo Board.
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 5
Intel® Galileo
Page 6
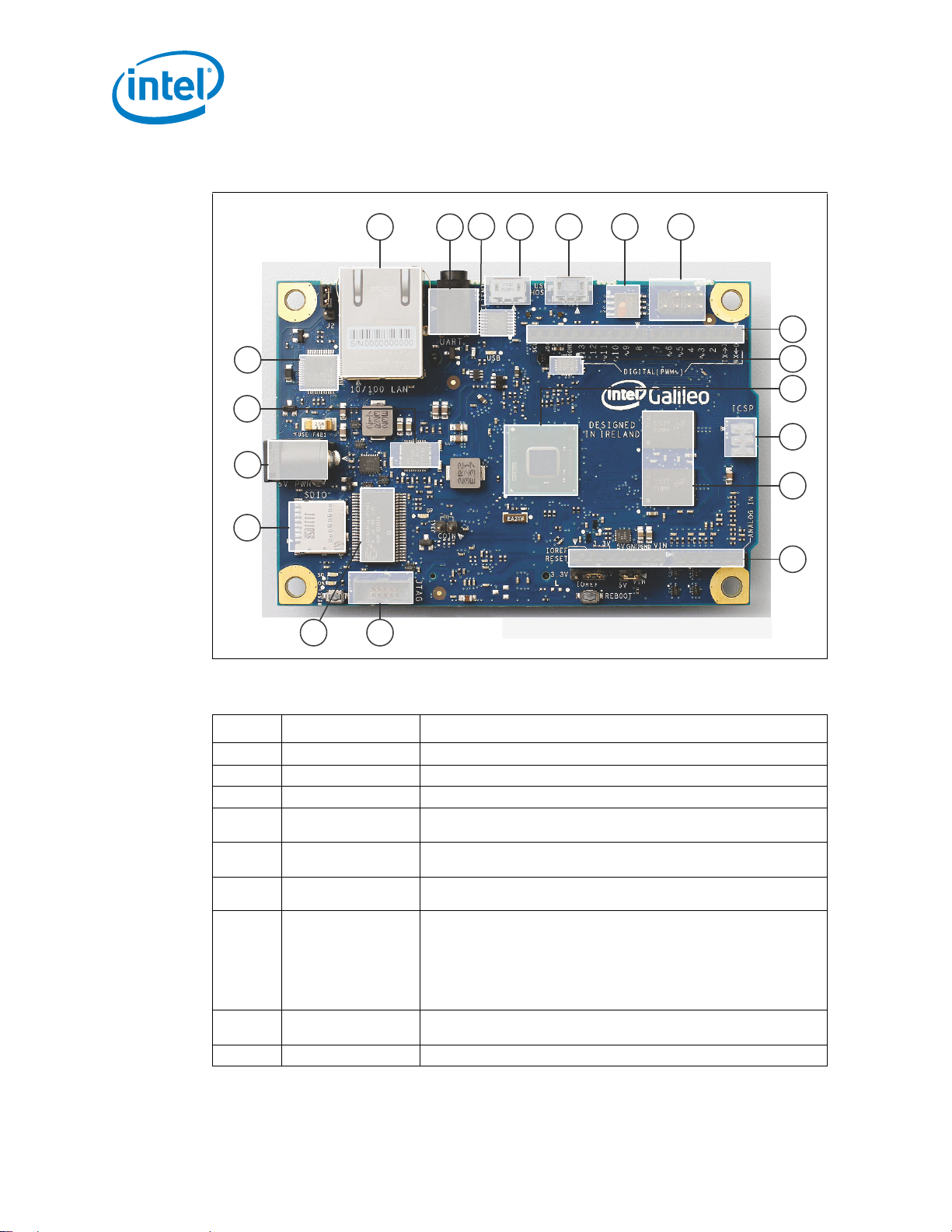
Figure 2. Key Components
,QWHO
4XDUN6R&
;
86%
&OLHQW
-7$*
'HEXJ3RUW
56
6HULDO
3RUW
(WKHUQHW
3RUW
9
3RZHU
86%
+RVW
0LFUR
6'VORW
63,)ODVK
3URJUDP
3RUW
$'&
3&,H*HQPLQLFDUGVORWRQEDFNRIERDUGÆ
$UGXLQR,QWHUIDFH
,&63
*3,2
([SDQGHU
(WK
3+<
0%
''5
5$0
9ROWDJH
5HJXODWRU
56
63,
)ODVK
$UGXLQR,QWHUIDFH
Intel® Galileo Board—Overview
Table 1. Description of Key Components (Sheet 1 of 2)
Number Component Description
1 Ethernet Port 10/100 Ethernet connector
2 RS-232 Serial Port 3-pin 3.5mm jack (not audio)
3 RS-232 RS-232 transceiver
4 USB 2.0 Client
5 USB 2.0 Host
6 SPI Flash
7 SPI Flash Program Port
8Shield Interface
9 ADC Analog to Digital converter
USB Client connector (Micro-USB Type B): a fully compliant USB 2.0
Device controller, typically used for programming
USB 2.0 Host connector (Micro-USB Type AB): supports up to 128 USB
end point devices
8 MByte Legacy SPI Flash to store the firmware (or bootloader) and the
latest sketch.
7-pin header for Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) programming
Defaults to 4 MHz to support Arduino Uno shields. Programmable up to
25 MHz.
Note: The board has a native SPI controller, however, it will act as a
master and not as an SPI slave. Therefore, it cannot be a SPI
slave to another SPI master. It can act, however, as a slave
device via the USB Client connector.
Complies with Arduino Uno Revision 3 shield pinout. See Section 2.4 for
details.
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
6 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 7

Overview—Intel
®
Galileo Board
Table 1. Description of Key Components (Sheet 2 of 2)
Number Component Description
400 MHz 32-bit Intel
(ISA)-compatible processor
• 16 KByte L1 cache
10
Intel
X1000
®
Quark SoC
• 512 KBytes of on-die embedded SRAM
• Simple to program: Single thread, single core, constant speed
• ACPI compatible CPU sleep states supported
• An integrated Real Ti me Clock (R T C), with an optional 3V "coin cell"
battery for operation between turn on cycles.
11 ICSP
6-pin in-circuit serial programming (ICSP) header, located appropriately
to plug into existing shields. These pins support SPI communication
using the SPI library.
12 256 MB DDR3 RAM 256 MByte DRAM, enabled by the firmware by default.
13 Arduino Interface
Complies with Arduino Uno Revision 3 pinout. See Section 2.4 for
details.
14 JTAG Debug Port 10-pin standard JTAG header for debugging
15 GPIO Expander GPIO pulse width modulation provided by a single I
16 Micro SD slot (Optional) Supports micro SD card up to 32 GBytes
17 5V Power
18 Voltage Regulator
The board is powered via an AC-to-DC adapter , connected by plugging a
2.1 mm center-positive plug into the bo a rd's power jack. The
recommended output rating of the power adapter is 5V at up to 3A.
Generates 3.3 volt supply.
Maximum current draw to the shield is 800 mA.
19 Eth PHY Ethernet Physical layer transceiver
Full PCI Express* mini-card slot, with PCIe* 2.0 compliant features:
On back of board, see Figure 1.
• Works with half mini-PCIe* cards with optional converter plate
• Provides USB 2.0 Host Port at mini-PCIe* connector
®
Pentium instruction set architecture
2
C I/O expander
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 7
Intel® Galileo
Page 8

Intel® Galileo Board—Details and Specifications
2.0 Details and Specifications
2.1 Physical Characteristics
The Intel® Galileo Board is 10 cm long and 7 cm wide respectively, with the USB
connectors, UART jack, Ethernet connector, and power jack extending beyond the
former dimension. Four screw holes (4 mm diameter) allow the board to be attached to
a surface or case.
Note: The distance between digital pins 7 and 8 is 160 mil (0.16"); it is not an even multiple
of the 100 mil spacing of the other pins.
2.2 Electrical Summary
The Intel® Galileo Board is powered via an AC-to-DC adapter, connected by plugging a
2.1 mm center-positive plug into the board's power jack. The recommended output
rating of the power adapter is 5V at up to 3A.
Input Voltage (recommended) 5V
Input Voltage (limits) 5V
Digital I/O Pins 14 (of which 6 provide PWM output)
Analog Input Pins 6
Total DC Output Current on all I/O lines 80 mA
DC Current for 3.3V Pin 800 mA
DC Current for 5V Pin 800 mA
2.3 Schematic and Reference Design
Figure 3 shows a connection diagram for the Intel® Galileo Board.
For complete board details, see:
• Galileo Schematic in PDF:
https://communities.intel.com/docs/DOC-21822
• Galileo Reference Design: zip file containing Allegro Board file
https://communities.intel.com/docs/DOC-21824
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
8 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 9

Details and Specifications—Intel
®
Galileo Board
Figure 3. Galileo Board Connection Diagram
2.4 Arduino Connector Pinout Details
The Intel® Galileo Board is designed to support shields that operate at either 3.3V or
5V. The core operating voltage of Intel
the board enables voltage translation to 5V at the I/O pins. See Section 2.5.3, “VIN
Jumper” on page 14 for details.
The Intel
®
Galileo Board complies with the Arduino Uno Revision 3 pinout as follows:
• 14 digital input/output pins (IO2-IO13, TX, RX):
— Each of the 14 digital pins on Galileo can be used as an input or output, using
pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions.
— The pins operate at 3.3 volts or 5 volts. Each pin can source a max of 10 mA or
sink a maximum of 25 mA and has an internal pull-up resistor (disconnected by
default) of 5.6 k to 10 kOhms.
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 9
®
Galileo Board is 3.3V; however, a jumper on
Intel® Galileo
Page 10

Intel® Galileo Board—Details and Specifications
— 6 digital pins can be used as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) outputs; they are
labeled with the ~ symbol. See Section 2.4.2, “I/O Pin Mappings” on page 11
for details.
— The RX and TX pins control the programmable speed UART port.
• SCL and SDA pins control the I2C* bus.
TWI: A4 or SDA pin and A5 or SCL pin. TWI communication is supported via the
Arduino Wire library.
• AREF is unused. Providing an external reference voltage for the analog inputs is not
supported.
®
Note: It is not possible on the Intel
Galileo Board to change the upper end of the
analog input range using the AREF pin and the analogReference() function.
• 6 analog input pins (A0-A5):
— Each one of the 6 analog input pins provides 12 bits of resolution (that is, 4096
different values). By default, they measure from ground to 5 volts.
•7 power pins:
— IOREF: The IOREF pin allows an attached shield with the proper configuration
to adapt to the voltage provided by the board. The IOREF pin voltage is
controlled by a jumper on the board, i.e., a selection jumper on the board is
used to select between 3.3 V and 5 V shield operation.
— RESET button/pin: Bring this line LOW to reset the sketch. T ypically used to add
a reset button to shields that block the one on the board.
— 3.3V output pin: A 3.3 Volt supply generated by the on-board regulator.
Maximum current draw to the shield is 800 mA.
— 5V output pin: This pin outputs 5 V from the external source or the USB
connector. Maximum current draw to the shield is 800 mA.
— GND (2 pins): Ground pins.
®
— VIN: The input voltage to the Intel
Galileo Board when it is using an external
power source (as opposed to 5 Volts from the regulated power supply
connected at the power jack). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if
supplying voltage via the power jack, access it through this pin.
Note: The voltage applied to this pin must be a regulated 5 V supply , otherwise it
could damage the Intel
®
Galileo Board or cause incorrect operation.
2.4.1 Properties of Pins Configured as OUTPUT
Pins configured as OUTPUT with pinMode() are said to be in a low-impedance state. On
the Intel
provided via an I
A0 to A5 can be configured as OUTPUT pins on the Intel
The I/O expander’s pins, when configured as OUTPUT, can source (provide positive
current) up to 10 mA (milliamps) and can sink (provide negative current) up to 25 mA
of current to other devices/circuits. The individual per pin current sourcing capability of
10 mA is subject to an overall limit of 80 mA combined between all OUTPUT pins. The
per pin capability current sinking capability is subject to an overall limit of 200 mA. The
table below provides a breakdown of the overall OUTPUT capabilities of the pins.
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
10 Order Number: 330237-001US
®
Galileo Board, when a pin is configured as OUTPUT, the functionality is
2
C*-based Cypress I/O expander. Digital pins 0 to 13 and Analog pins
®
Galileo Board.
Page 11

Details and Specifications—Intel
®
Galileo Board
Current Source
(mA)
Per Pin Capability 10 25
Digital Pins 3,5,9,10,12, 13 Combined 40 100
Digital Pins 0,1,2,4,6,7,8,11 and
Analog Pins A0,A1,A2,A3,A4, A5 Combined
Digital Pins 0-13 and Analog Pins A0-A5 Combined 80 200
40 100
Current Sink
(mA)
2.4.2 I/O Pin Mappings
Table 2. Galileo I/O Mappings
Arduino
IDE ID
IO0 Cypr GPORT4_BIT6_PWM2 50 N/A - BI UART0_RXD I w/ pullup off
IO1 Cypr GPORT4_BIT7_PWM0 51 N/A - BI UART0_TXD I w/ pullup off
IO2
IO3
IO4 Cypr GPORT1_BIT4_PWM6 28 - BI - I w/ pullup off
IO5 Cypr GPORT0_BIT1_PWM5 17 5 - BI (PWM) I w/ pullup off
IO6 Cypr GPORT1_BIT0_PWM6 24 6 - BI (PWM) I w/ pullup off
IO7 Cypr GPORT1_BIT3_PWM0 27 - BI - I w/ pullup off
IO8 Cypr GPORT1_BIT2_PWM2 26 - BI - I w/ pullup off
IO9 Cypr GPORT0_BIT3_PWM1 19 1 - BI (PWM) I w/ pullup off
IO10 Cypr GPORT0_BIT0_PWM7 16 7 - BI
IO11 Cypr GPORT1_BIT1_PWM4 25 4 - BI
IO12 Cypr GPORT3_BIT2_PWM3 38 - BI SPI1_MISO I w/ pullup off
IO13 Cypr GPORT3_BIT3_PWM1 39 - BI SPI1_SCK I w/ pullup off
IO14 Cypr GPORT4_BIT0_PWM6 44 - BI AD7298:VIN0 I w/ pullup off
IO15 Cypr GPORT4_BIT1_PWM4 45 - BI AD7298:VIN1 I w/ pullup off
IO16 Cypr GPORT4_BIT2_PWM2 46 - BI AD7298:VIN2 I w/ pullup off
IO17 Cypr GPORT4_BIT3_PWM0 47 - BI AD7298:VIN3 I w/ pullup off
IO18 Cypr GPORT4_BIT4_PWM6 48 - BI AD7298:VIN4 I w/ pullup off
IO19 Cypr GPORT4_BIT5_PWM4 49 - BI AD7298:VIN5 I w/ pullup off
Source Pin Linux Linux
SoC
(Cypr)
SoC
(Cypr)
GPIO<6>
(GPORT2_BIT0_PWM6_A3)14(32*)
GPIO<7>
(GPORT0_BIT2_PWM3)
GPIO PWM
- 0 BI - I w/ pullup off
15
(18*)
3 1 BI (PWM) I w/ pullup off
Int Dir Muxed with Initial Setup
(PWM)
SPI1_SS_B
(PWM)
SPI1_MOSI
I w/ pullup off
I w/ pullup off
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 11
Intel® Galileo
Page 12

Table 3. Galileo I/O Function Multiplexing
Intel® Galileo Board—Details and Specifications
Mux Selector
01
UART0_RXD IO0 GPORT3_BIT4_PWM7 40 O unknown
UART0_TXD IO1 GPORT3_BIT5_PWM5 41 O unknown
SPI1_SS_B IO10 GPORT3_BIT6_PWM3 42 O unknown
SPI1_MOSI IO11 GPORT3_BIT7_PWM1 43 O unknown
SPI1_MISO IO12 GPORT5_BIT2_PWM3 54 O unknown
SPI1_SCK IO13 GPORT5_BIT3_PWM1 55 O unknown
AD7298:VIN0 IO14 GPORT3_BIT1_PWM5 37 O 0
AD7298:VIN1 IO15 GPORT3_BIT0_PWM7 36 O 0
AD7298:VIN2 IO16 GPORT0_BIT7_PWM1 23 O 0
AD7298:VIN3 IO17 GPORT0_BIT6_PWM3 22 O 0
AD7298:VIN4 IO18 GPORT0_BIT5_PWM5 21 O 0
AD7298:VIN5 IO19 GPORT0_BIT4_PWM7 20 O 0
IO2 via SoC GPIO<6>
IO3 via SoC GPIO<7>
I2C
IO2 via Cypress
GPORT2_BIT0_PWM6
IO3 via Cypress
GPORT0_BIT2_PWM3
(AD7298:VIN4 or IO18) and
(AD7298:VIN5 or IO19)
Cypress GPIO Pin
GPORT1_BIT7_PWM0 31 O unknown
GPORT1_BIT6_PWM2 30 O unknown
GPORT1_BIT5_PWM4 29 O 1
Linux
GPIO ID
Dir Initial Setup
2.5 Jumpers
This section describes the jumpers on Galileo that are used to vary the configuration of
the board.
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
12 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 13

Details and Specifications—Intel
®
Galileo Board
Figure 4. Jumper Locations
2.5.1 IOREF Jumper
T o support both 3.3 V and 5 V shields, the external operating voltage is controlled via a
jumper.
• When the jumper is connected to 5 V , the board is configured to be compatible with
5 V shields and IOREF is set to 5 V.
• When the jumper is connected to 3.3 V, the board is configured to be compatible
with 3.3 V shields and IOREF is set to 3.3 V.
The input range of the Analog pins is also controlled by the IOREF jumper and must not
exceed the chosen oper ating vol tage. Howeve r, the resolution of AnalogR ead() remain s
at 5 V/1024 units for the default 10-bit resolution or, 0.0049 V (4. 9 mV) per unit
regardless of IOREF jumper setting.
Warning: The IOREF jumper should be used to match the board and shield operating voltages.
Incorrectly setting the voltage could damage the board or the shield.
2.5.2 I2C* Address Jumper
To prevent a clash between the I2C* Slave address of the on board I/O expander and
EEPROM with any external I
address of the on-board devices.
With J2 connected to pin 1 (marked with white triangle), the 7-bit I/O Expander
address is 0100001 and the 7-bit EEPROM address is 1010001.
Changing the jumper position changes the I/O Expander address to 0100000 and the
EEPROM address to 1010000.
2
C* Slave devices, jumper J2 can be used to vary the I2C*
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 13
Intel® Galileo
Page 14

Intel® Galileo Board—Details and Specifications
2.5.3 VIN Jumper
The VIN pin can be used to supply 5 V from the regulated power supply connected at
the power jack to attached shields or devices. If there is a need to supply more than
5 V to a shield using VIN, then the VIN jumper should be removed from the board to
break the connection between the on-board 5 V supply and the VIN connection on the
board header.
Warning: If the VIN jumper is not removed and more than 5 V is connected to VIN, it may
damage the board or lead to unreliable operation.
2.5.4 Force Recovery
If your Intel® Galileo Board is in an unbootable state, you can force recovery to recover
the contents of the SPI flash. For example, if power was lost during a normal firmware
update, the board would be unbootable and this procedure would be necessary. You will
need to ground a resistor pin as described below.
Figure 5. Resistor Pin for Forcing Recovery
Boot the firmware in recovery mode by performing the following steps:
1. Copy a SPI Flash recovery file (the FVMAIN.fv file described in the [Build Guide]) to
the root directory of a USB key. Insert the USB key into the board.
2. Connect the serial cable between the computer and the board’s RS-232 serial port
(see Figure 2). Set up a serial console session (for example, PuTTY) and connect to
the board’s COM port at 115200 baud rate.
3. Remove power from the board.
4. Make a connection from ground to the resistor pin shown in Figure 5 (resistor
R2B16).
5. Connect power to the board.
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
14 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 15
Details and Specifications—Intel
®
Galileo Board
6. The serial console displays a list of Quark platforms. Select Galileo.
7. The serial console displays a user action menu. Disconnect the resistor pin shown
in Figure 5 from ground. Select the system recovery option.
The recovery procedure begins and the SPI flash is reprogrammed. This will take
about 5 minutes. The recovery completes with a system reboot.
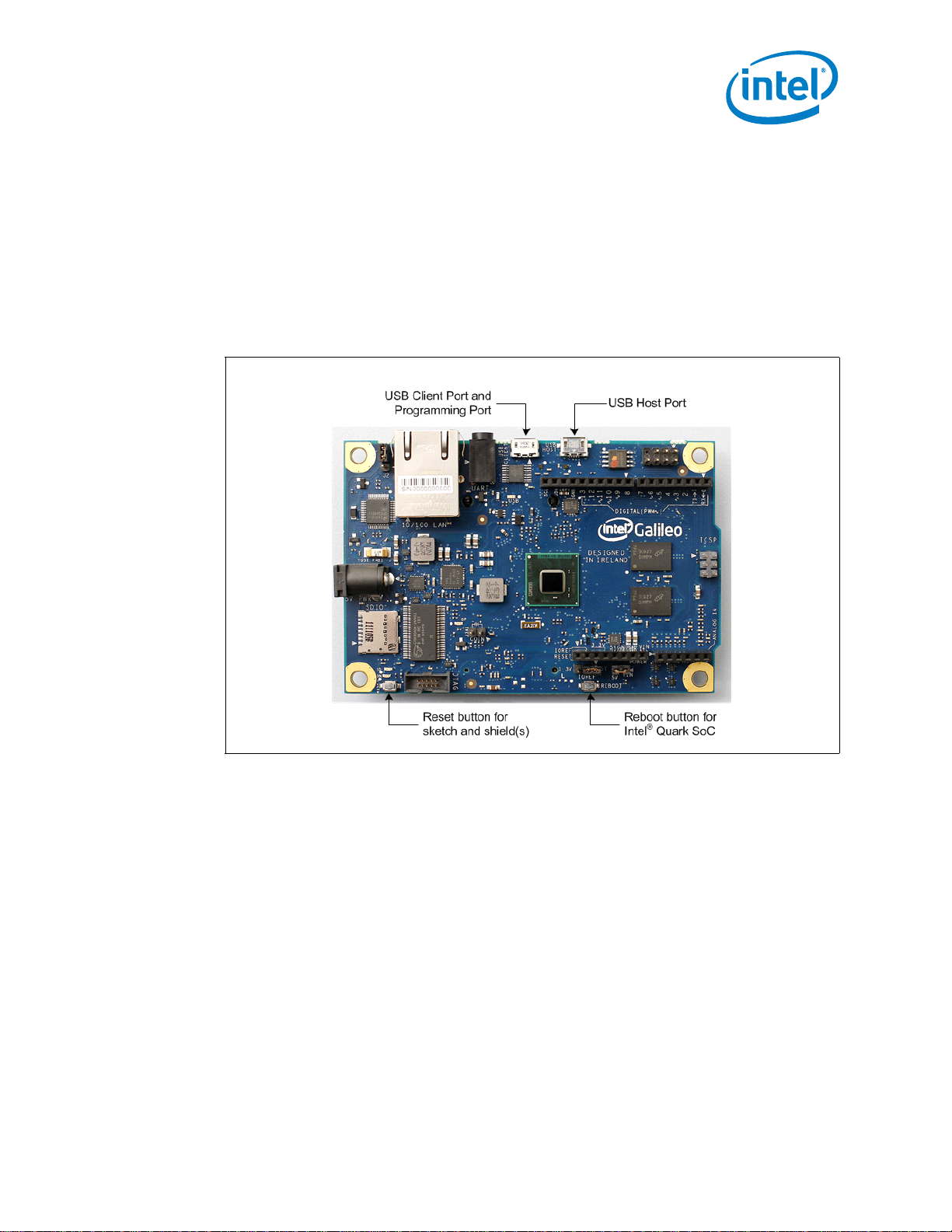
2.6 Buttons
There are two buttons on the Intel® Galileo Board, shown in Figure 6.
Figure 6. Reset Button and Reboot Button
• Reset button:
To reset the currently running Arduino* sketch and any connected shield(s), press
the button marked Reset.
You can also reset the board in software (recommended for faster rebooting).
• Reboot button:
To reset the entire board, you can trigger a reboot of the Intel
®
Quark SoC X1000
by pressing the button marked Reboot. See the Note below.
Note: Using Reset versus Reboot
On an Arduino Uno, pressing the reset button resets the microcontroller and any
attached shields. This also resets the currently running sketch. On the Intel
Galileo Board, you don’t need to reboot the Intel
®
Quark SoC X1000 to reset the
®
sketch or any attached shields. If the SoC is rebooted each time a sketch is reset or
a new sketch is uploaded, it causes a full (and usually unnecessary) reboot of the
Linux operating system.
Instead, the Intel
the sketch and any attached shields without triggering a reboot of the Intel
®
Galileo Board provides a Reset button that can be used to reset
®
Quark
SoC X1000. If the SoC needs to be rebooted, you can do this by pressing the
Reboot button on the board.
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 15
Intel® Galileo
Page 16

Intel® Galileo Board—Communication and Programming
3.0 Communication and Programming
3.1 Communication
The Intel® Galileo Board has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer,
another Arduino board, or other microcontrollers.
UART
The board provides UART TTL (5 V/3.3 V) serial communication, which is available
on digital pin 0 (RX) and 1 (TX). In addition, a second UART provides RS-232
support and is connected via a 3.5 mm jack.
USB Client Ports
The USB Client ports allows for serial (CDC-ACM) communications over USB. This
provides a serial connection to the Serial Monitor or other applications on your
computer. It is also used to upload sketches to the board.
USB Host Port
The USB Host port allows the board to act as a USB Host for connected peripherals
such as mice, keyboards, and smartphones.
mini PCI Express* (mPCIe*)
The Intel
®
Galileo Board is the first Arduino board to provide a mini PCI Express*
(mPCIe*) slot. This slot allows full size and half size (with adapter) mPCIe*
modules to be connected to the board and also provides an additional USB Host
port via the mPCIe* slot. Any standard mPCIe* module can be connected and used
to provide applications such as WiFi, Bluetooth or Cellular connectivity. Initially, the
mPCie* slot provides support for the WiFi Library. For additional information, see
the Intel
®
Galileo Board Getting Started Guide ([GSG] in Table 4).
Ethernet RJ45
An Ethernet RJ45 Connector is provided to allow the board to connect to wired
networks. Full support of on-board Ethernet interface is fully supported and does
not require the use of the SPI interface like existing Arduino shields.
microSD card reader
The onboard microSD card reader is accessible through the Arduino SD Library.
The communication between the board and the SD card is provided by an
integrated SD controller and does not require the use of the SPI interface like other
Arduino boards. The native SD interface runs at up to 50 MHz depending on the
class of card used.
2
TWI/I
C*
The Arduino software includes a Wire library to simplify use of the TWI/I
2
C* bus;
see the Arduino documentation for details.
SPI
For SPI communication, use the Arduino SPI library.
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
16 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 17

Communication and Programming—Intel
3.2 Programming
®
Galileo Board
Use the Arduino Software Development Environment to create programs, called
sketches, for the Intel
®
Galileo Board. To run a sketch on the board:
1. Connect a power supply.
2. Connect the board’s USB client port to a computer.
3. Upload the sketch using the IDE interface.
®
The sketch runs on the Intel
in the board’s firmware using the Arduino I/O adapter. For complete details on
programming your board, see the Intel
Galileo Board and communicates with the Linux* kernel
®
When the board boots up, two scenarios are possible:
• If a sketch is present in persistent storage, it is executed.
• If no sketch present, the board waits for upload commands from the IDE.
If a sketch is executing, you can upload from the IDE without having to press the reset
button on the board. The sketch is stopped; the IDE waits for the upload state, and
then starts the newly uploaded sketch.
Pressing the reset button on the board restarts a sketch if it is executing and resets any
attached shields.
3.3 Automatic (Software) Reset
Rather than requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the Intel®
Galileo Board is designed in a way that allows it to be reset by software running on a
connected computer. USB CDC-ACM control signals are used to transition the board
from run-time to bootloader mode. The Arduino software uses this capability to allow
you to upload code by simply pressing the upload button in the Arduino environment.
For details, see the Intel
®
Galileo Board Getting Started Guide (Table 4).
Galileo Board Getting Started Guide (Table 4).
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 17
Intel® Galileo
Page 18

4.0 Related Documentation
Table 4. Related Documentation
Title Number Reference
®
Intel
Galileo Board Getting Started Guide
https://communities.intel.com/docs/DOC-22204
®
Galileo Software Release Notes
Intel
https://communities.intel.com/docs/DOC-21837
Galileo Schematic
https://communities.intel.com/docs/DOC-21822
Galileo Reference Design
https://communities.intel.com/docs/DOC-21824
®
Quark SoC X1000 Board Support Package (BSP) Build and Software
Intel
User Guide
Intel® Galileo Board—Related Documentation
329685 [GSG]
328686 [Gal RN]
n/a [Schematic]
n/a [Ref Design]
329687 [Build Guide]
®
Galileo
Intel
Board User Guide March 2014
18 Order Number: 330237-001US
Page 19

Galileo Disclaimer—Intel
®
Galileo Board
5.0 Galileo Disclaimer
Intel® Galileo Design Document
This Intel® Galileo design document is licensed by Intel under the terms of the
Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike License (ver. 3), subject to the following
terms and conditions. The Intel® Galileo design document IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND
"WITH ALL FAUL TS." Intel DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
REGARDING THE GALILEO DESIGN OR THIS GALILEO DESIGN DOCUMENT INCLUDING,
BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Intel® may make changes to the specifications, schematics and product descriptions at
any time, without notice. The Customer must not rely on the absence or characteristics
of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Intel® reserves these
for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or
incompatibilities arising from future changes to them. ENJOY!
§ §
March 2014 Board User Guide
Order Number: 330237-001US 19
Intel® Galileo
 Loading...
Loading...