Page 1
AL440LX
Motherboard
Product Guide
Order Number: 680701-001
Page 2

Revision History
Revision Revision History Date
-001 First release of the AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide. July 1997
Intel Corporation (Intel) makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this material, including, but not limited
to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Intel assumes no
responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document. Intel makes no commitment to update nor to
keep current the information contained in this document. No part of this document may be copied or
reproduced in any form or by any means without prior written consent of Intel.
†
Third-party brands and names are the property of their respective owners.
Copyright Intel Corporation, 1997. All Rights Reserved.
Page 3

Contents
1 Product Description
Features................................................................................................................................7
Components..........................................................................................................................8
Back Panel I/O Connectors...................................................................................................9
2 Installing the Motherboard
Before You Begin................................................................................................................11
Installing a Processor..........................................................................................................12
Installing the Retention Mechanism............................................................................12
Installing the Processor..............................................................................................13
Setting the Processor Speed......................................................................................14
Upgrading to a Boxed Pentium
Removing the Installed Processor ..............................................................................15
Removing the Heatsink Support Base........................................................................16
Upgrading the Processor............................................................................................18
Installing Memory................................................................................................................19
Removing Memory..............................................................................................................20
Replacing the Battery..........................................................................................................21
Installing and Removing the Motherboard ..........................................................................23
®
II Processor.....................................................................14
3 Configuring the Motherboard
Before You Begin................................................................................................................25
Configuration Modes...........................................................................................................26
Setting the Processor Speed..............................................................................................27
Clearing the Passwords......................................................................................................28
4 Using the Setup Program
Setup Menus.......................................................................................................................29
Function Keys.....................................................................................................................30
Maintenance Menu .............................................................................................................30
Main Menu..........................................................................................................................31
Floppy Options Submenu...........................................................................................32
IDE Device Configuration Submenus.........................................................................33
Advanced Menu..................................................................................................................34
Resource Configuration Submenu .............................................................................35
Peripheral Configuration Submenu ............................................................................36
Keyboard Features Submenu ....................................................................................37
Video Configuration Submenu ...................................................................................37
DMI Event Logging Submenu ....................................................................................37
Security Menu.....................................................................................................................38
Power Menu ........................................................................................................................38
Boot Menu ..........................................................................................................................39
Hard Drive Submenu..................................................................................................40
Removable Devices Submenu...................................................................................40
Exit Menu............................................................................................................................40
iii
Page 4

Contents
5 Upgrading the BIOS
Preparing for the Upgrade ..................................................................................................41
Obtaining the Upgrade Utility .....................................................................................41
Recording the Current BIOS Settings.........................................................................41
Creating a Bootable Floppy Diskette..........................................................................42
Creating the BIOS Upgrade Floppy Diskette..............................................................42
Upgrading the BIOS............................................................................................................42
Recovering the BIOS..........................................................................................................43
Changing the BIOS Language............................................................................................44
6 Technical Reference
Motherboard Connectors ....................................................................................................45
Front Panel Connectors......................................................................................................48
Motherboard Resources......................................................................................................49
Memory Map ..............................................................................................................49
DMA Channels...........................................................................................................49
I/O Map .....................................................................................................................50
PCI Configuration Space Map....................................................................................52
Interrupts....................................................................................................................52
A Error Messages
BIOS Beep Codes...............................................................................................................53
BIOS Error Messages.........................................................................................................53
B Regulatory and Integration Information
Regulatory Requirements ...................................................................................................55
Safety Standards........................................................................................................55
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Regulations.....................................................56
Product Certification Markings....................................................................................56
Installation Precautions.......................................................................................................57
Installation Instructions .......................................................................................................57
Ensure Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC).............................................................58
Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications....................................58
Prevent Power Supply Overload ................................................................................59
Place Battery Marking on the Computer.....................................................................59
Use Only for Intended Applications............................................................................59
iv
Page 5

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Figures
1. Motherboard Components............................................................................................8
2. Back Panel I/O Connectors..........................................................................................9
3. Installing the Processor Retention Mechanism ..........................................................12
4. Installing the Processor..............................................................................................13
5. Installing the Heatsink Support Top Bar.....................................................................14
6. Removing the Heatsink Support Top Bar and the Processor.....................................15
7. Removing the Heatsink Support Retention Pins ........................................................16
8. Placing the Heatsink Support Base Removal Tool on the Retention Pins..................17
9. Using the Heatsink Support Base Removal Tool .......................................................18
10. Location of DIMM Sockets .........................................................................................19
11. Installing a DIMM........................................................................................................20
12. Replacing the Battery.................................................................................................22
13. Mounting Screw Holes ...............................................................................................23
14. Configuration Header.................................................................................................26
15. Motherboard Connectors............................................................................................45
Tables
1. Jumper Settings for the Setup Program.....................................................................27
2. Setup Menu Bar.........................................................................................................29
3. Setup Function Keys..................................................................................................30
4. Maintenance Menu.....................................................................................................30
5. Main Menu .................................................................................................................31
6. Floppy Options Submenu...........................................................................................32
7. IDE Device Configuration Submenus.........................................................................33
8. Advanced Menu.........................................................................................................34
9. Resource Configuration Submenu.............................................................................35
10. Peripheral Configuration Submenu............................................................................36
11. Keyboard Features Submenu ....................................................................................37
12. Video Configuration Submenu ...................................................................................37
13. DMI Event Logging Submenu ....................................................................................37
14. Security Menu............................................................................................................38
15. Power Menu...............................................................................................................38
16. Boot Menu..................................................................................................................39
17. Hard Drive Submenu..................................................................................................40
18. Removable Devices Submenu...................................................................................40
19. Exit Menu...................................................................................................................40
20. Chassis Security Header (J2B1) ................................................................................45
21. Wake on LAN Header (J1C1).....................................................................................46
22. ATAPI CD Audio Connector (J1F1)............................................................................46
23. ATAPI Telephony Connector (J2F1) ..........................................................................46
24. ATAPI Line In Connector (J2F2)................................................................................46
25. Fan 1 Header (J8M1).................................................................................................46
26. Fan 2 Header (J3F1)..................................................................................................47
27. Fan 3 Header (J5L1) (Active Heatsink Fan)...............................................................47
28. SCSI Hard Drive LED Input Header (J8B1)................................................................47
29. Wake on Ring Header (J8A1) ....................................................................................47
v
Page 6

Contents
30. Front Panel Connectors .............................................................................................48
31. Memory Map ..............................................................................................................49
32. DMA Channels...........................................................................................................49
33. I/O Map ......................................................................................................................50
34. PCI Configuration Space Map....................................................................................52
35. Interrupts....................................................................................................................52
36. Beep Codes ...............................................................................................................53
37. BIOS Error Messages ................................................................................................53
vi
Page 7

1 Product Description
This chapter gives an overview of the AL440LX motherboard, including:
• Features
• Components
• Back panel I/O connectors
Features
The motherboard has these features:
®
• Support for one 233, 266, or 300 MHz Intel Pentium
cache integrated in the Single Edge Contact (S.E.C.) cartridge
• Support for up to 384 MB of 66 MHz synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) using three DIMM
sockets with 168-pin DIMM modules and 3.3 V memory
• Intel 440LX AGPset that includes a high-speed processor interface controller, a DRAM
controller, the Accelerated Graphics Port (A.G.P.) interface, a Universal Serial Bus (USB)
controller, a fully synchronous PCI bus interface, the real-time clock, and support for power
management and system management mode
• National Semiconductor PC97307 I/O component that includes the floppy-drive interface, one
multimode parallel port, two FIFO serial ports, keyboard and mouse controller, and an IrDA
compatible interface
• Intel/Phoenix BIOS that supports power management, Plug and Play, advanced IDE features,
and password security
†
• Five expansion slots: one 16-bit ISA/AT
slots, and one combination slot for either a PCI or an ISA card
• Two USB connectors
• Onboard connector that supports add-in A.G.P. boards
• Optional onboard audio subsystem based on the Yamaha OPL
controllers (YM 715)
• Optional onboard Yamaha YM 704 wavetable synthesizer
• Optional hardware monitor that integrates a temperature sensor, fan speed sensors, power
supply voltage monitor, support for Intel LANDesk
security
-compatible slot, three PCI-compatible expansion
II processor with a 512 KB second-level
†
family of single-chip audio
Client Manager, and support for chassis
†
-
NOTE
✏
Information about Intel motherboards including technical product specifications, BIOS upgrades,
and device drivers is available under “Product Info” at the Intel World Wide Web site:
http://www.intel.com/
7
Page 8
Product Description
Components
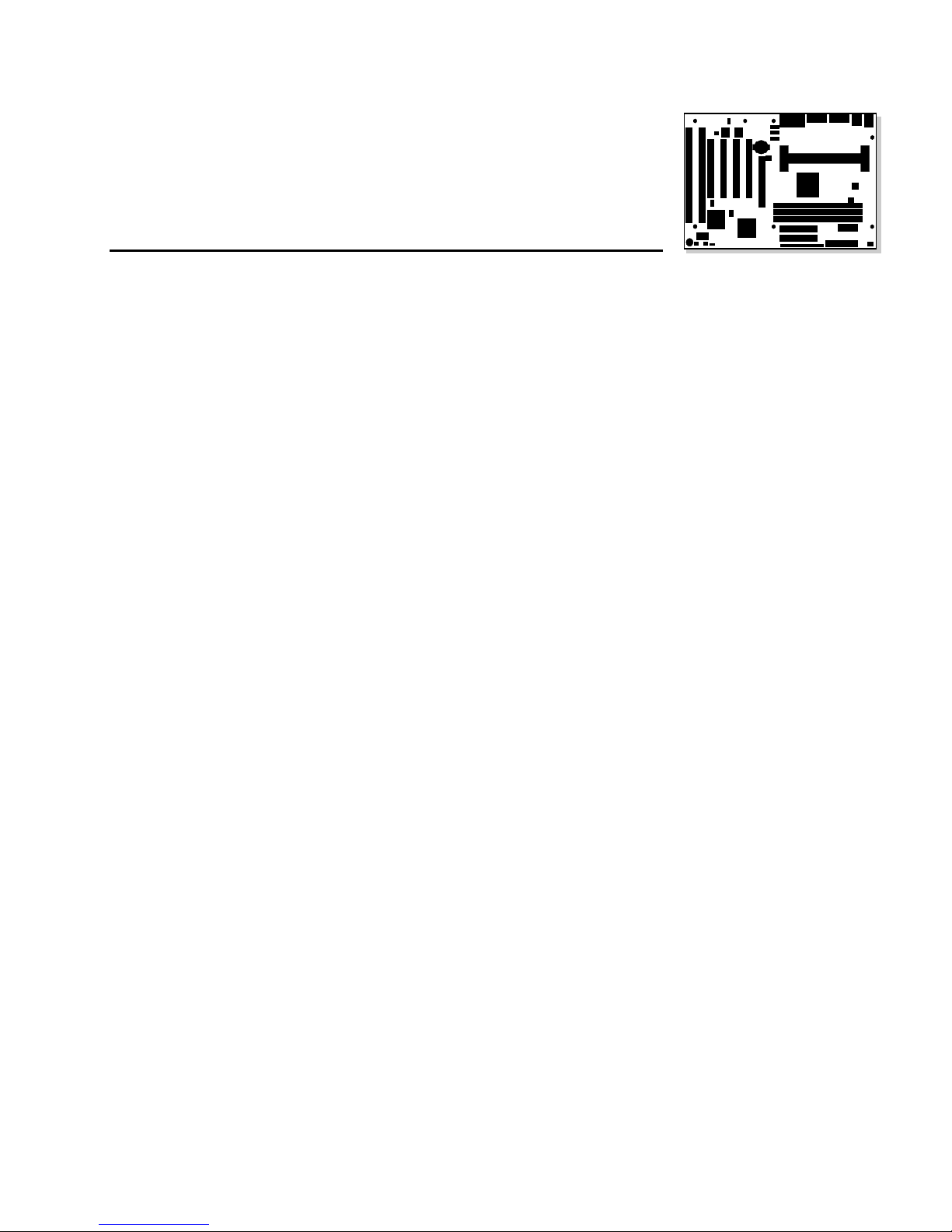
Figure 1 shows the components on the motherboard.
BCDFEGA
W
V
U
T
Q
MONSR P
H
I
J
K
L
OM06239
Figure 1. Motherboard Components
A Optional chassis security header M Floppy drive connector
†
B Optional Wake on LAN
C Battery O Front panel header
D Optional Line In connector P Accelerated Graphics Port (A.G.P.) connector
E Optional CD-ROM audio connector Q Configuration header
F Optional telephony connector R Optional SCSI hard disk LED header
G Back-panel I/O connectors S Wake on Ring header
H Slot 1 connector T Speaker
I Fan 3 header (for the active heatsink fan) U Fan 2 header
J DIMM sockets V PCI connectors
K Primary power connector W ISA connectors
L Fan 1 header
header N IDE connectors
NOTE
✏
Components labeled optional do not come on all AL440LX motherboards.
8
Page 9
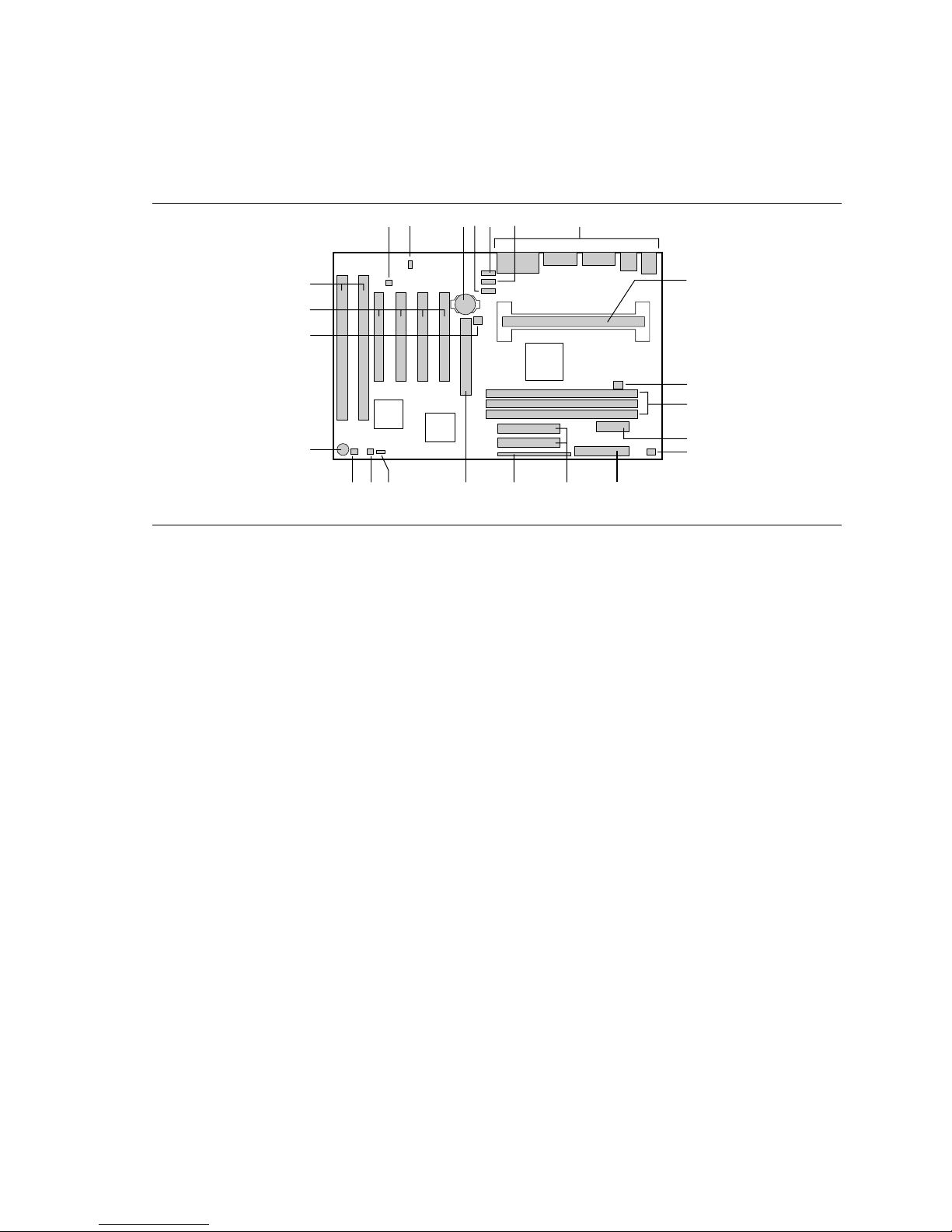
Back Panel I/O Connectors
Figure 2 shows the back panel connectors on the motherboard.
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
A
DF
E
B
G
C
H
J
I
OM06235
Figure 2. Back Panel I/O Connectors
A PS/2† connector (mouse or keyboard) F Serial port 1 connector
B Parallel port connector G Serial port 2 connector
C MIDI/game port connector (optional) H Audio Line Out jack (optional)
D PS/2 connector (mouse or keyboard) I Audio Line In jack (optional)
E USB connectors J Audio Mic In jack (optional)
9
Page 10

Product Description
10
Page 11
2 Installing the Motherboard
This chapter describes the following:
• Installing a processor
• Preparing the motherboard for installing a boxed Pentium II processor
• Installing and removing memory
• Replacing the battery
• Installing and removing the motherboard
Before You Begin
CAUTION
Before you install this motherboard in a chassis, see Appendix B for regulatory requirements and
precautions.
• Always follow the steps in each procedure in the correct order.
• Set up a log to record information about your computer, such as model, serial numbers,
installed options, and configuration information.
• Use an antistatic wrist strap and a conductive foam pad when working on the motherboard.
WARNINGS
The procedures in this chapter assume familiarity with the general terminology associated with
personal computers and with the safety practices and regulatory compliance required for using
and modifying electronic equipment.
Disconnect the computer from its power source and from any telecommunications links,
networks, or modems before performing any of the procedures described in this chapter.
Failure to disconnect power, telecommunications links, networks, or modems before you open
the computer or perform any procedures can result in personal injury or equipment damage.
Some circuitry on the motherboard can continue to operate even though the front panel power
button is off.
CAUTION
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components. Perform the procedures described in this
chapter only at an ESD workstation. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD
protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the computer
chassis.
11
Page 12
Installing the Motherboard
Installing a Processor
To install a processor, you must:
1. Install the retention mechanism.
2. Install the processor.
3. Set the processor speed.
Detailed instructions for each of these procedures follow.
NOTE
✏
If you are installing a boxed Intel Pentium II processor, see the instructions on page 14.
Installing the Retention Mechanism
NOTE
✏
To install the retention mechanism, you need a Phillips (#2 bit) manual torque screwdriver
capable of a 6.0 in.-lb.
have a shaft longer than 2 inches.
1.0 in.-lb. (0.678 N-m ± 0.113 N-m) setting. The screwdriver also must
±
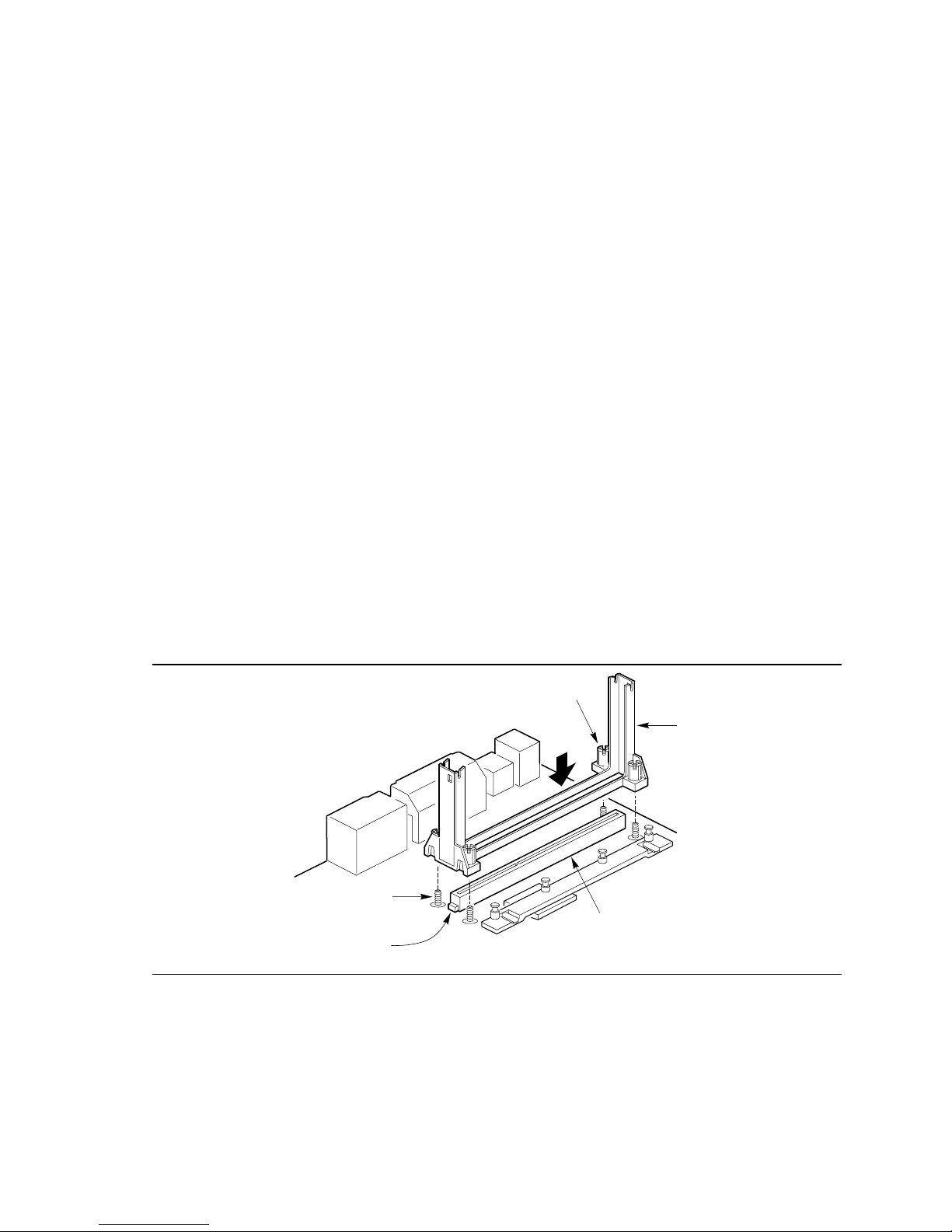
To install the retention mechanism, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” (see page 11).
2. Locate Slot 1 (A in Figure 3) and the four attachment studs (B) on the motherboard.
E
C
B
A
D
Figure 3. Installing the Processor Retention Mechanism
OM06225
3. To position the mechanism (C), orient it as shown in Figure 3. The tab (D) on the connector
fits into a notch in the base of the mechanism. When properly seated, the base of the
mechanism is flush with the motherboard.
12
Page 13
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
CAUTION
Overtightening the captive nuts on the retention mechanism can damage the motherboard. Tighten
the captive nuts (E in Figure 3) to no more than 6.0 in.-lb.
1.0 in.-lb. (0.678 N-m ± 0.113 N-m).
±
4. Finger tighten all four captive nuts to make sure they start correctly on the threads of the
attachment studs.
5. To secure the mechanism, tighten the captive nuts with the torque screwdriver to no more than
6.0 in.-lb. ± 1.0 in.-lb. (0.678 N-m ± 0.113 N-m).
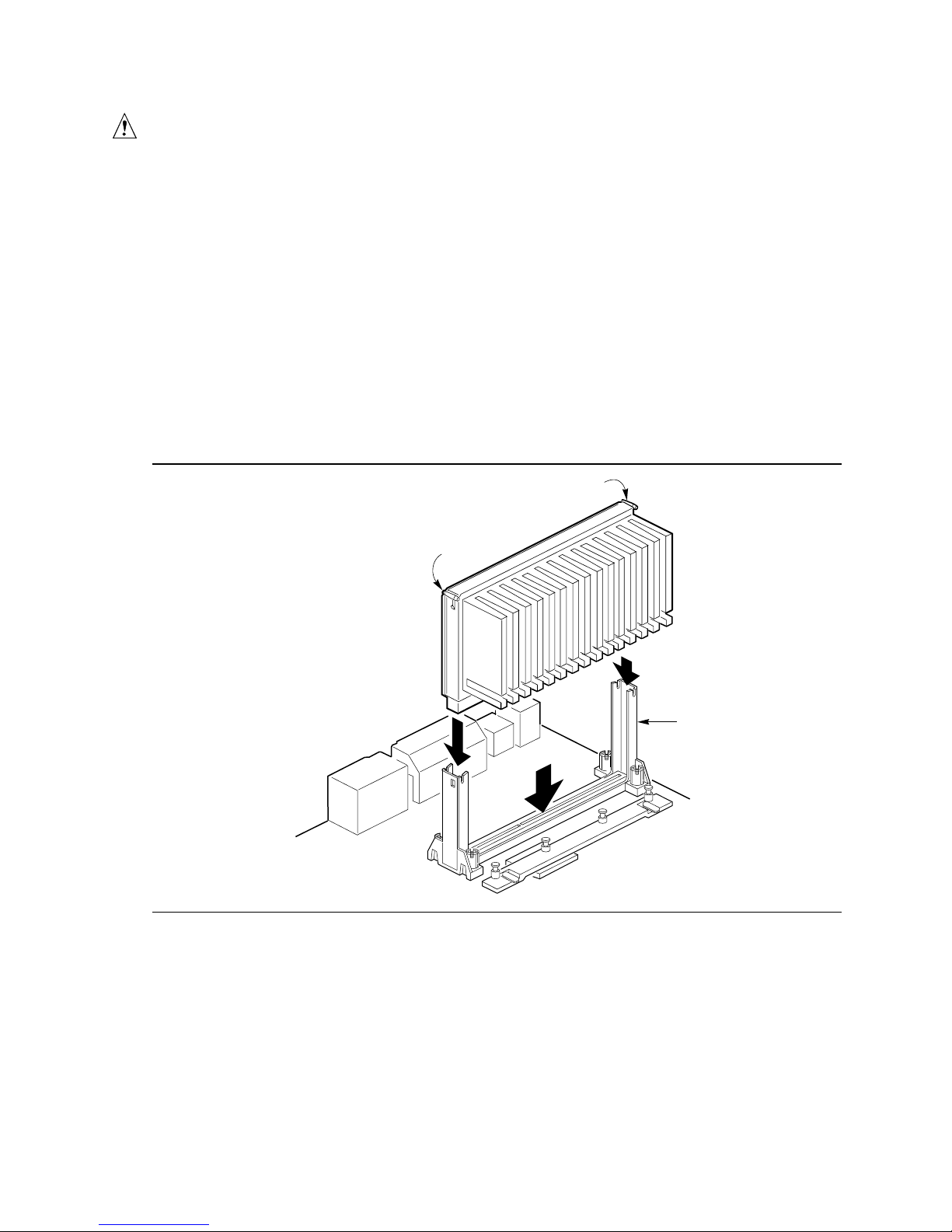
Installing the Processor
To install the processor, follow these steps:
1. Insert the processor in the retention mechanism (A in Figure 4).
2. Press down on the processor until it is firmly seated in the Slot 1 connector and the latches (B)
on the processor lock into place.
B
B
Figure 4. Installing the Processor
A
OM06228
13
Page 14
Installing the Motherboard
3. Slide the top heatsink support bar (A) onto the retaining pins (B) of the support’s base as
shown in Figure 5.
A
B
Figure 5. Installing the Heatsink Support Top Bar
OM06229
Setting the Processor Speed
After you install the processor and install the motherboard, set the processor speed by using the
Setup program. See Chapter 3 to set processor speed.
Upgrading to a Boxed Pentium® II Processor
Use the instructions in this section to prepare the motherboard for a boxed Pentium II processor
upgrade.
To prepare for a boxed Pentium II processor upgrade, you must:
1. Remove the heatsink support top bar and the installed processor.
2. Remove the heatsink support base.
3. Upgrade the processor.
Detailed instructions for each of these procedures follow.
14
Page 15
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
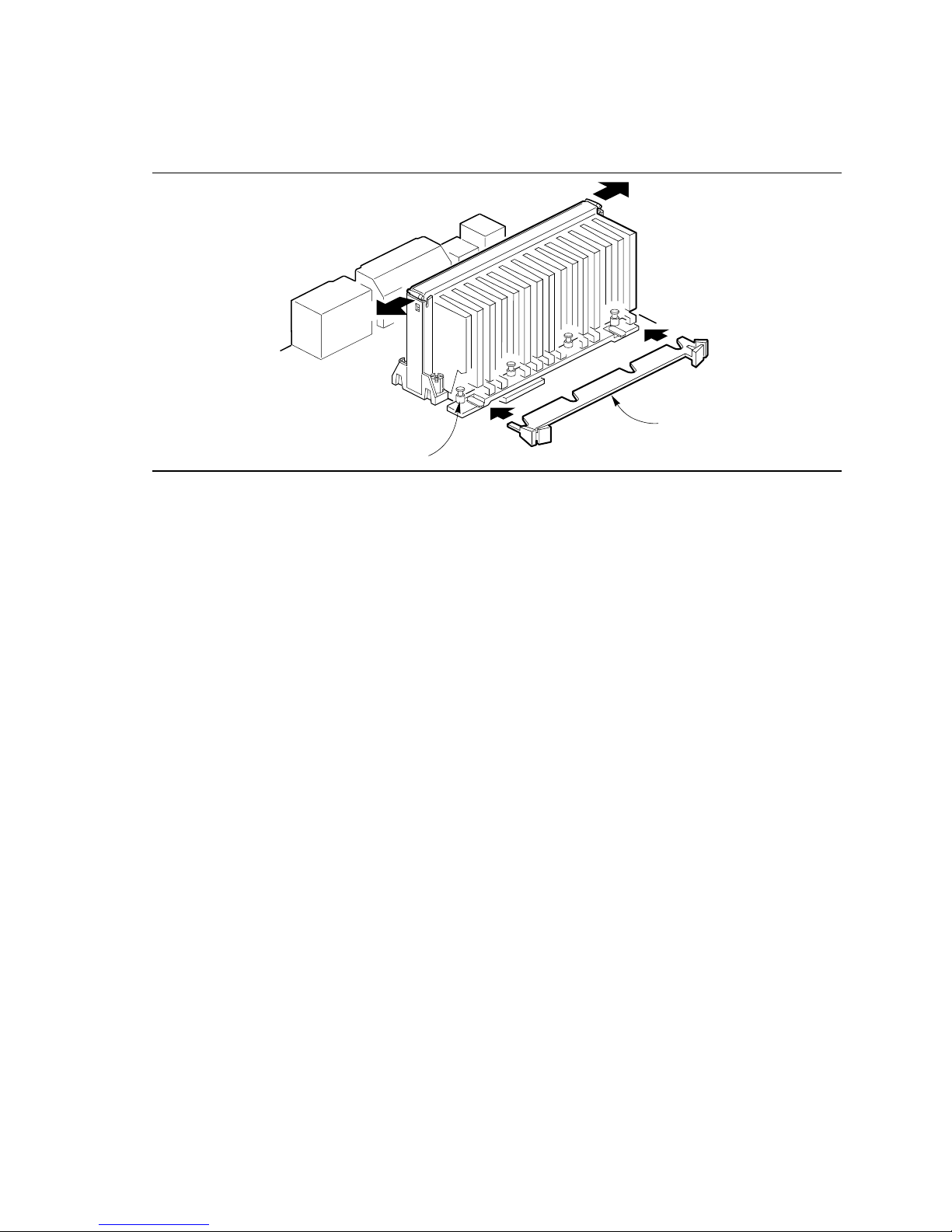
Removing the Installed Processor
To remove the installed processor, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” (see page 11).
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Remove the motherboard from the computer chassis. Refer to “ Installing and Removing the
Motherboard” on page 23.
5. Place the motherboard on a flat work surface and remove any components that block access to
the installed processor.
6. Remove the top bar of the heatsink support from the base as shown in Figure 6. Press in on the
latches (A) to release the top bar.
B
B
A
OM06230
Figure 6. Removing the Heatsink Support Top Bar and the Processor
CAUTION
Pressing on the motherboard or components while removing the processor can cause damage. If
necessary, you can safely press on the motherboard’s plastic connectors to gain leverage while
removing the processor.
7. Remove the processor by pressing in on the latches (B) and pulling the processor straight up as
shown in Figure 6. Place the processor aside.
15
Page 16
Installing the Motherboard
Removing the Heatsink Support Base
NOTE
✏
To remove the heatsink support base from the motherboard, you need a special removal tool
(MID #58982) that is available from Dexter Design (call 503-648-7000 for ordering information).
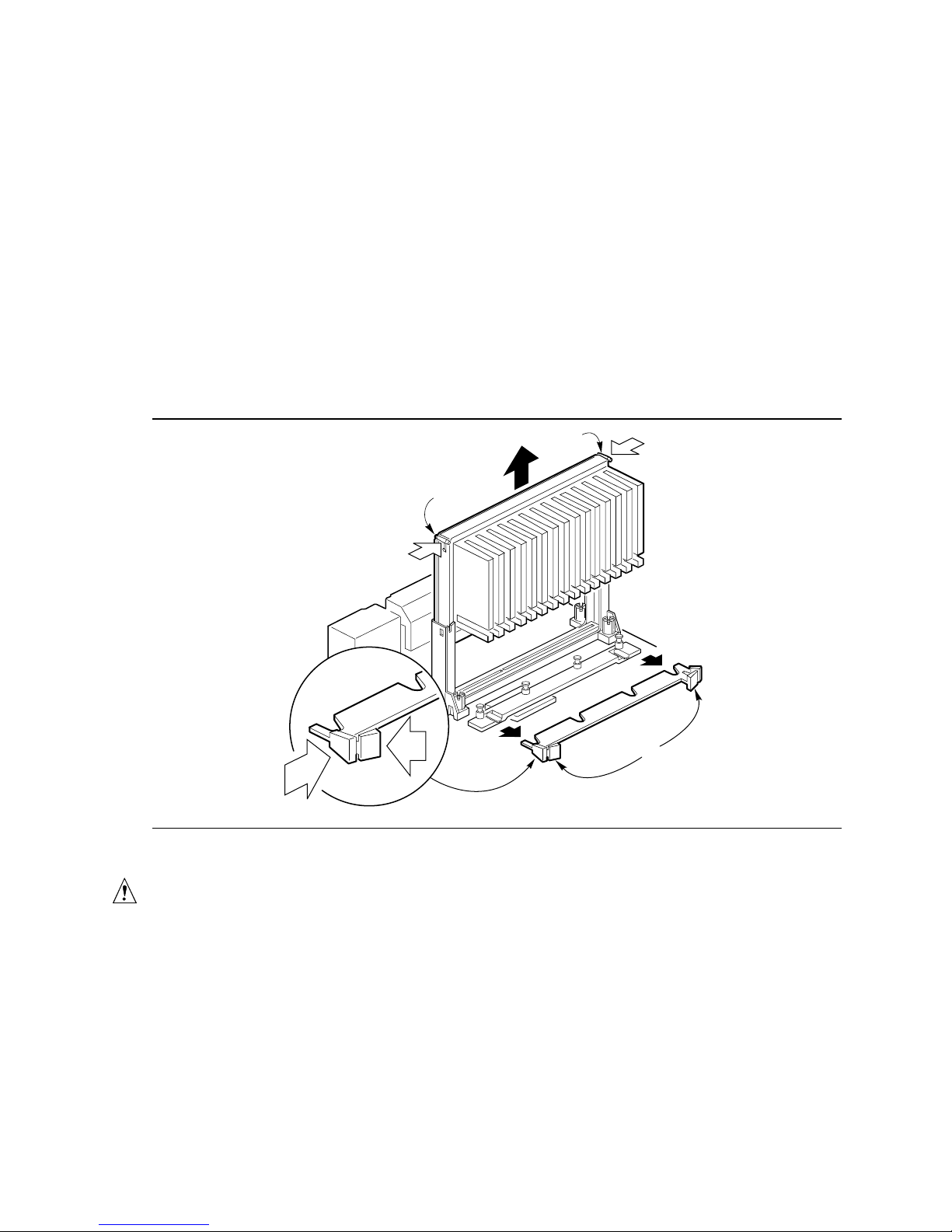
To remove the heatsink support base follow these steps:
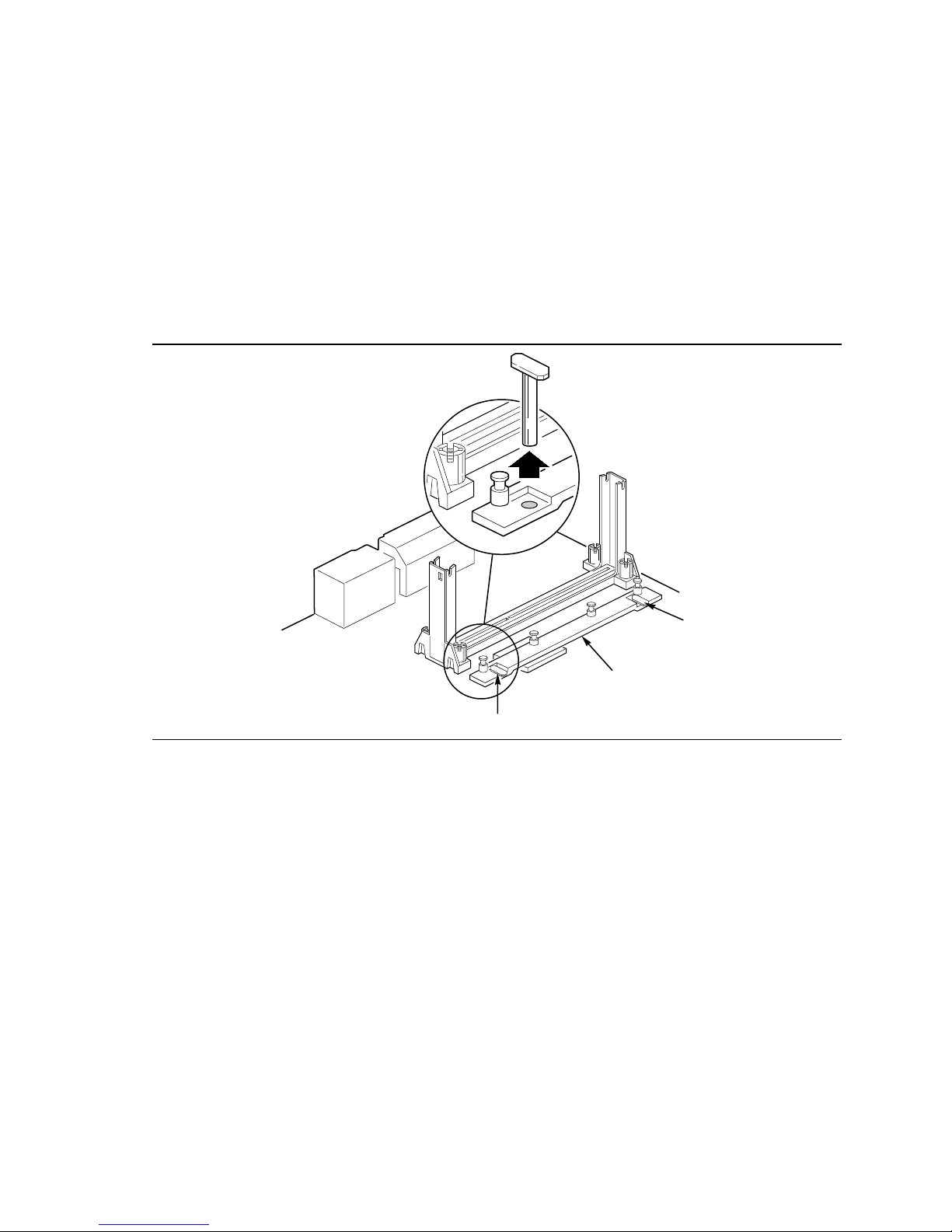
1. With your fingers, remove the two retention pins (A) from the heatsink support base (B) as
shown in Figure 7.
A
B
A
Figure 7. Removing the Heatsink Support Retention Pins
OM06231
16
Page 17
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
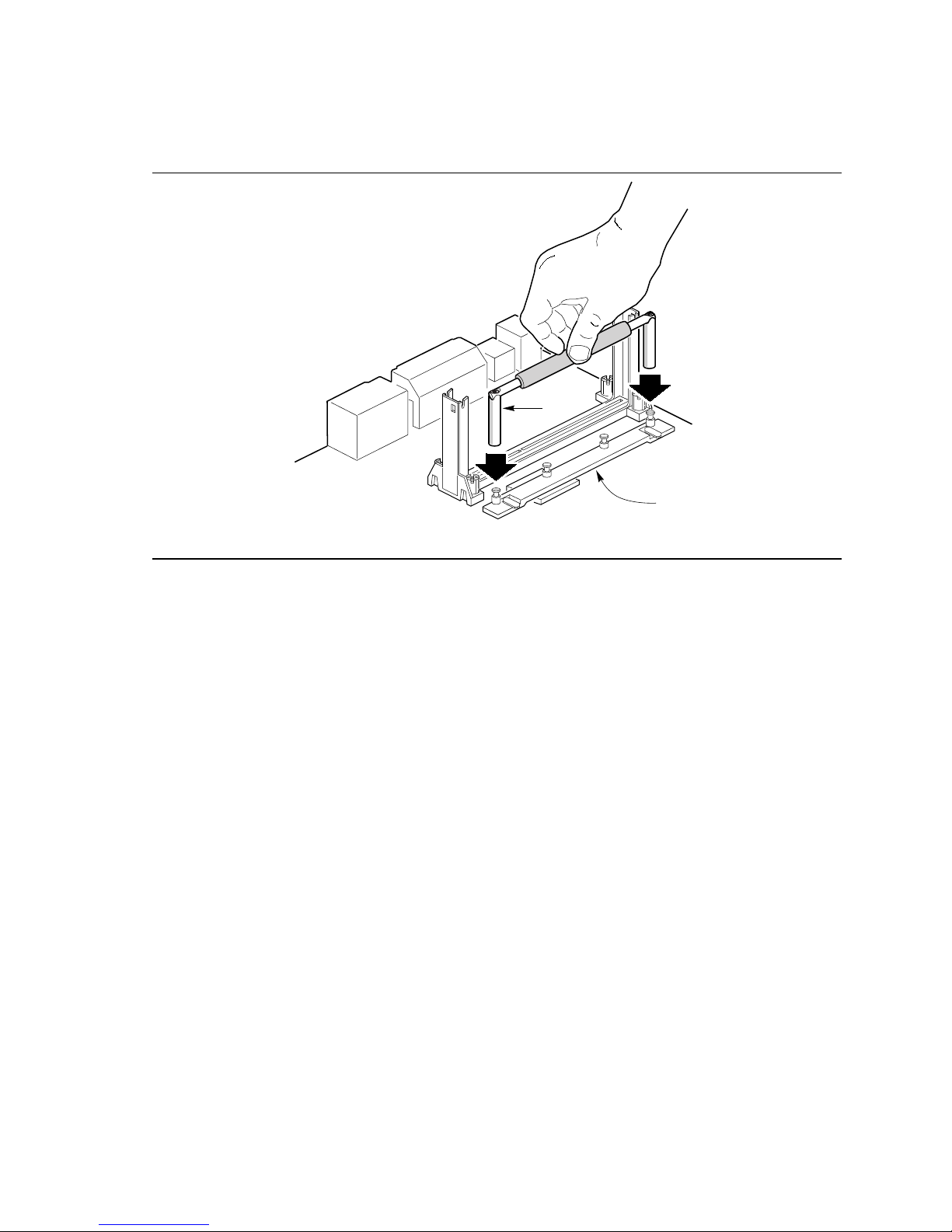
2. Place the heatsink support removal tool (A) over the two outside posts of the heatsink support
base (B) as shown in Figure 8. Make sure the tool completely engages the posts.
A
B
OM06232
Figure 8. Placing the Heatsink Support Base Removal Tool on the Retention Pins
17
Page 18
Installing the Motherboard
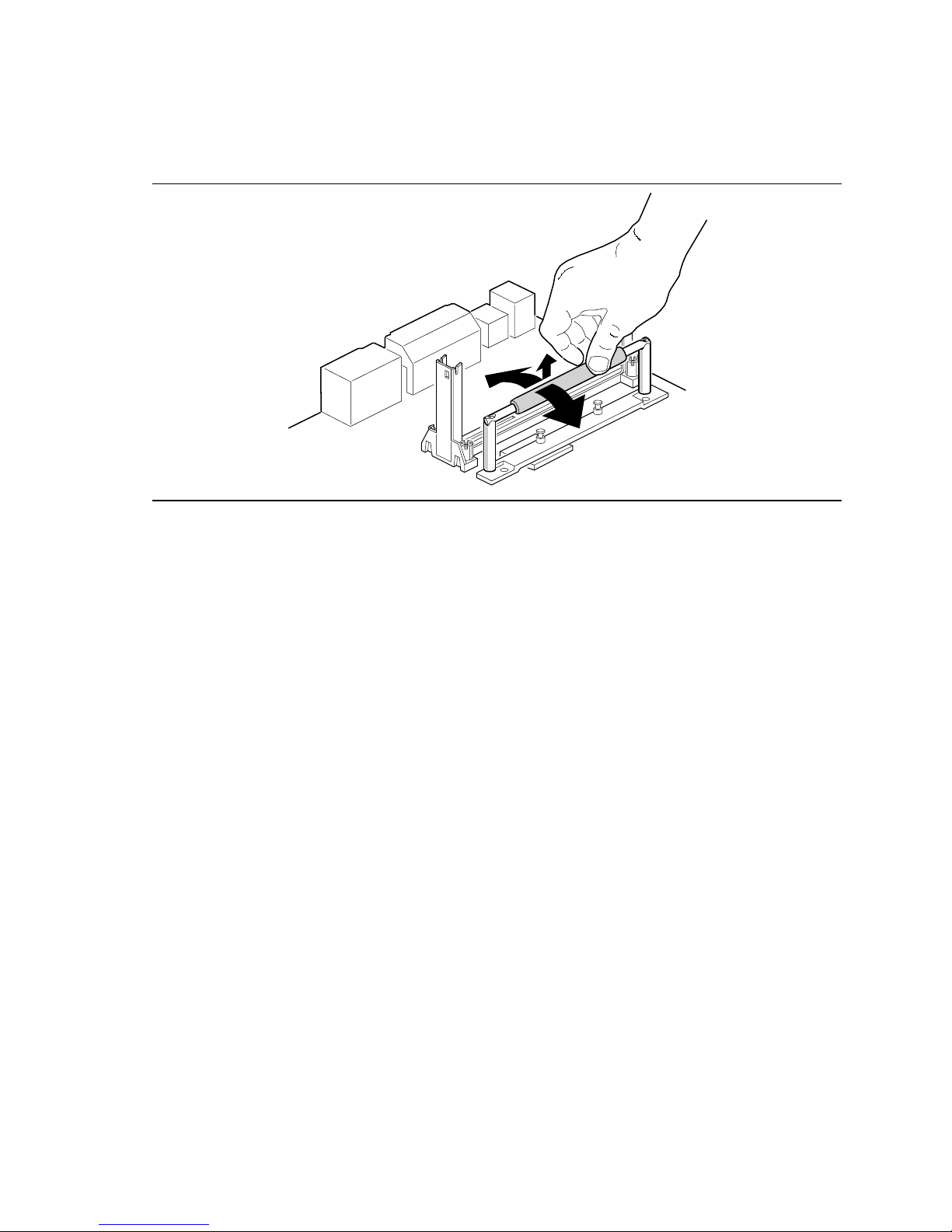
3. Carefully rock the tool back and forth until the heatsink support base disengages from the holes
in the motherboard (Figure 9). There is an audible click when the base disengages from the
motherboard.
OM06233
Figure 9. Using the Heatsink Support Base Removal Tool
4. Remove the tool and the heatsink support base from the motherboard.
Upgrading the Processor
Refer to the boxed Intel Pentium II processor documentation for installation instructions.
18
Page 19
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Installing Memory
You can install from 8 MB to 384 MB of memory in the motherboard DIMM sockets. The board
has DIMM sockets arranged as banks 0, 1, and 2. The motherboard supports the following
memory features:
• 168-pin 3.3 V DIMMs with gold-plated contacts
• 66 MHz unbuffered SDRAM
• Non-ECC (64-bit) or ECC (72-bit) memory
• 8 MB, 16 MB, 32 MB, 64 MB, and 128 MB modules
When adding memory, follow these guidelines:
• You can install DIMMs in any of the three banks.
• You can use different size DIMMs in different banks.
• The BIOS detects the size and type of installed memory.
• For ECC operation to be available, all installed memory must be ECC and you must enable the
ECC Configuration feature in the Setup program (see page 34).
NOTE
✏
DIMMs must meet the Intel specifications for either 64-bit or 72-bit SDRAM. For information
about vendors that support these specifications refer to the Intel World Wide Web site:
http://www.intel.com/
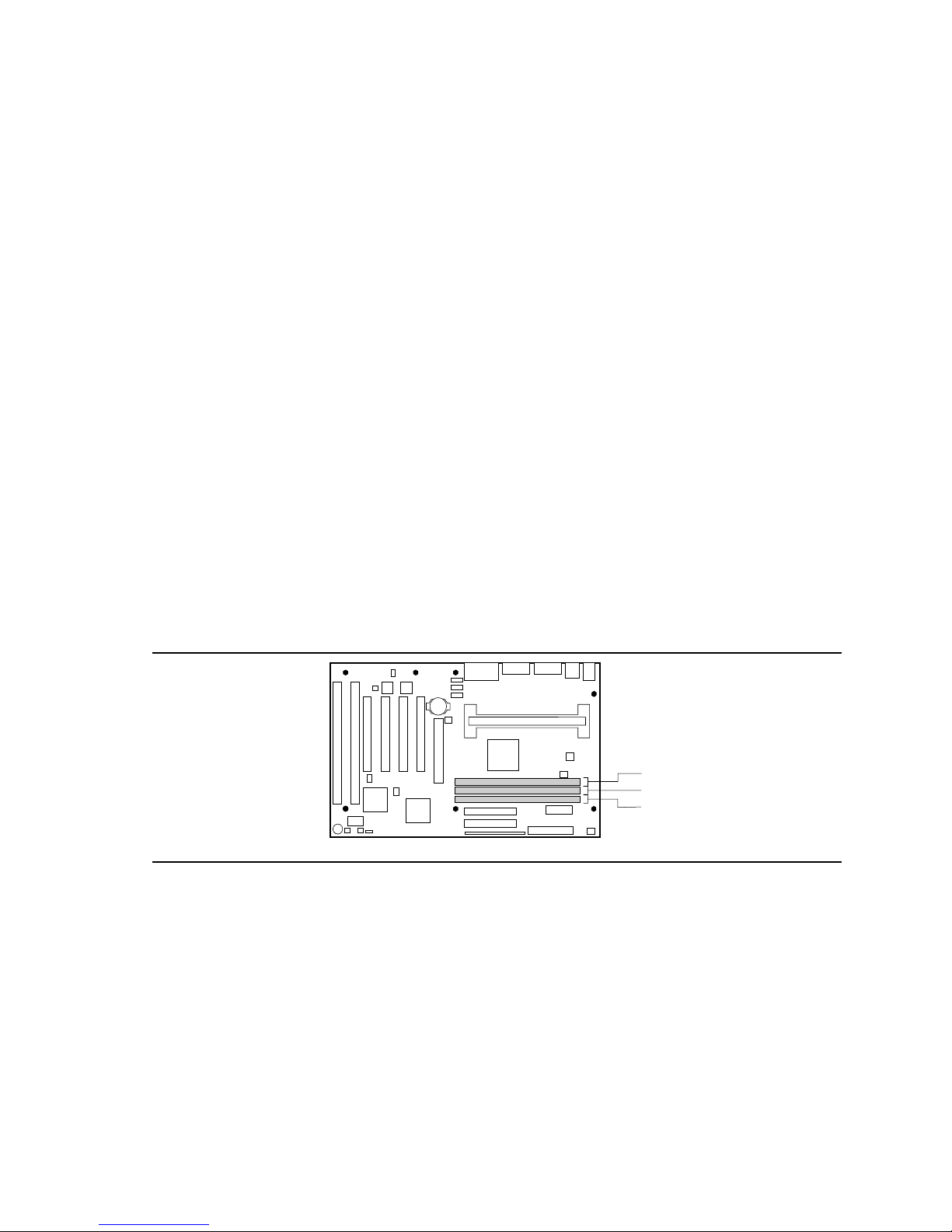
Figure 10 shows the location of the DIMM sockets.
2
1
0
Figure 10. Location of DIMM Sockets
To install DIMMs, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” (see page 11).
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the computer cover and locate the DIMM sockets.
4. Holding the DIMM by the edges, remove it from its antistatic package.
5. Make sure the clips at either end of the socket are pushed away from the socket.
19
Page 20
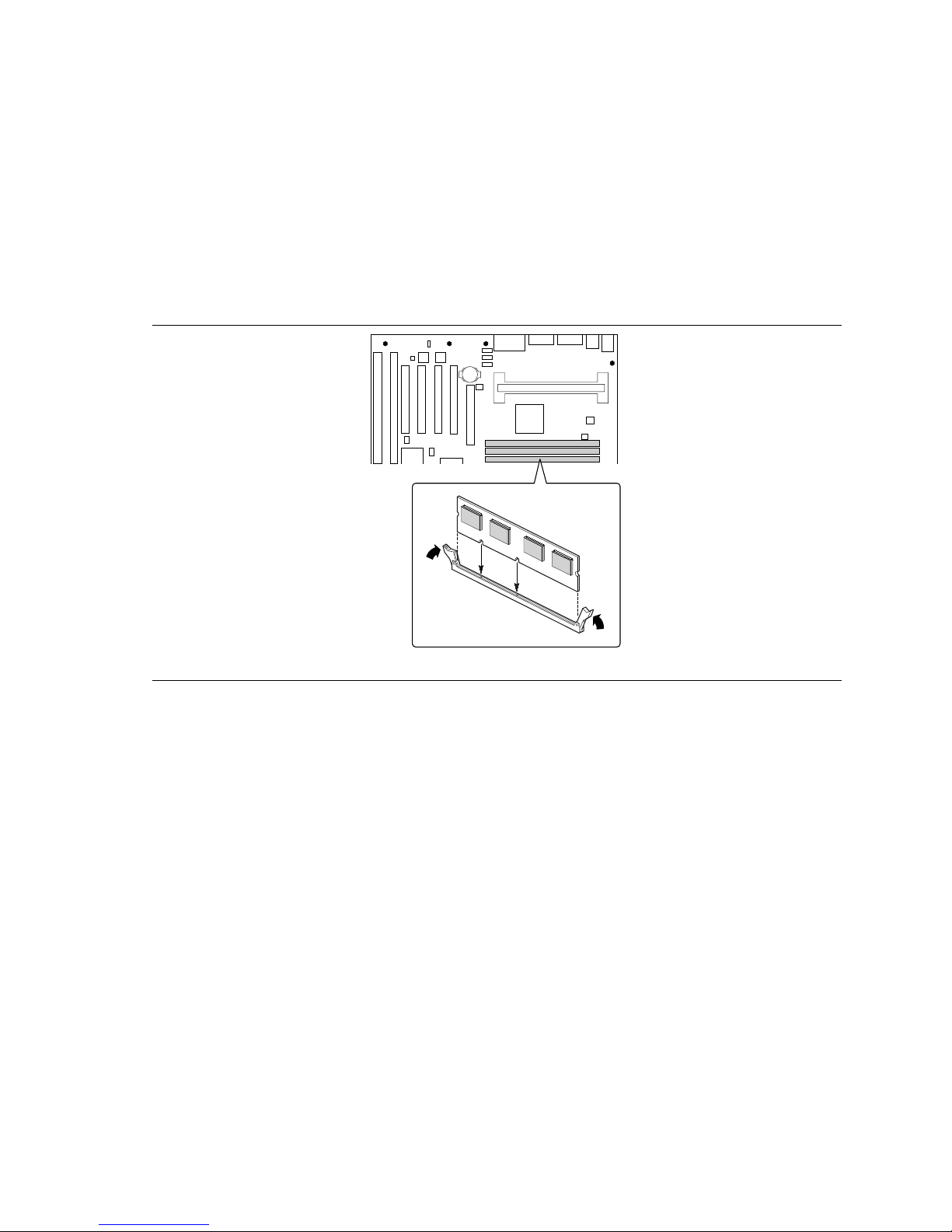
Installing the Motherboard
6. Position the DIMM above the socket. Align the two small notches in the bottom edge of the
DIMM with the keys in the socket.
7. Insert the bottom edge of the DIMM into the socket.
8. When the DIMM is seated, push down on the top edge of the DIMM until the retaining clips at
the ends of the socket snap into place. Make sure the clips are firmly in place.
9. Replace the computer cover.
10. If you installed a DIMM with ECC memory, start the computer and use the ECC Configuration
feature in Setup to enable the use of ECC.
OM06224
Figure 11. Installing a DIMM
Removing Memory
To remove a DIMM, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in "Before You Begin" (see page 11).
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Gently spread the retaining clips at each end of the socket. The DIMM pops out of the socket.
5. Hold the DIMM by the edges, lift it away from the socket, and store it in an antistatic package.
6. Reinstall and reconnect any parts you removed or disconnected to reach the DIMM sockets.
20
Page 21

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Replacing the Battery
When your computer is turned off, a lithium battery keeps the time-of-day clock and the values in
CMOS RAM current. Figure 12 shows the location of the battery.
The battery should last about seven years. When the battery begins to die, it loses voltage; when
the voltage drops below a certain level, the Setup program settings stored in CMOS RAM (for
example, the date and time) might not be accurate. Replace the battery with an equivalent one.
If your local ordinances permit, you may dispose of individual batteries as normal trash. Do not
expose batteries to excessive heat or fire. Keep all batteries away from children.
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if the battery is incorrectly replaced. Replace only with the same or
equivalent type recommended by the equipment manufacturer. Discard used batteries according to
manufacturer’s instructions.
ATTENTION
Il y a danger d’explosion s’il y a remplacement incorrect de la batterie. Remplacer uniquement
avec une batterie du méme type ou d’un type recommandé par le constructeur. Mettre au rébut les
batteries usagées conformément aux instructions du fabricant.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering. Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri af
samme fabrikat og type. Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Lithiumbatteri - Eksplosjonsfare. Ved utskifting benyttes kun batteri som anbefalt av
apparatfabrikanten. Brukt batteri returneres apparatleverandøren.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte. Använd samma batterityp eller en ekvivalent typ som
rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren. Kassera använt batteri enligt fabrikantens instruktion.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu. Vaihda paristo ainoastaan laitevalmistajan
suosittelemaan tyyppiin. Hävitä käjtetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
21
Page 22
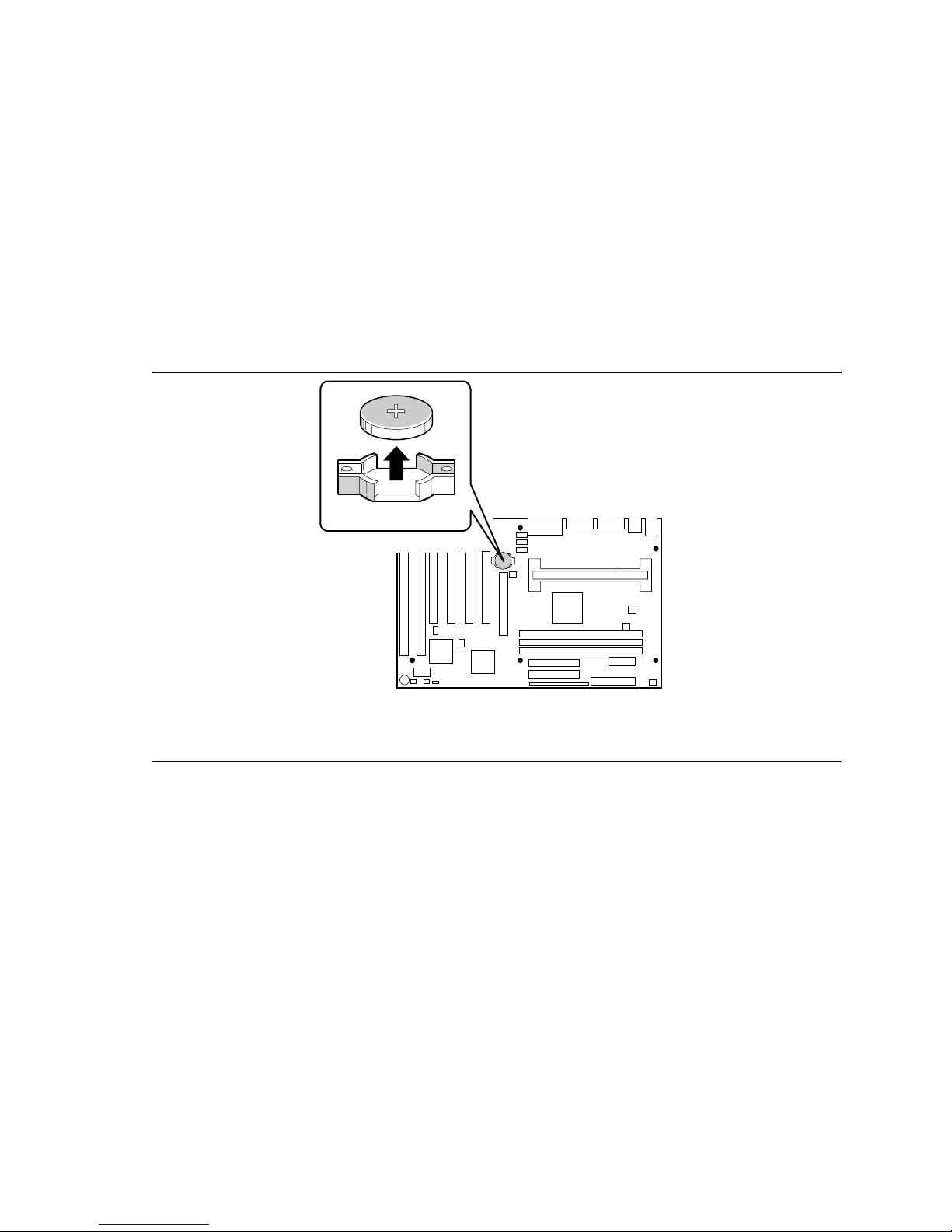
Installing the Motherboard
To replace the battery, follow these steps:
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” (see page 11).
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Locate the battery on the motherboard (see Figure 12).
5. With your fingers, gently pry the battery free from its socket. Note the orientation of the “+”
and “-” on the battery.
6. Install the new battery in the socket, orienting the “+” and “-” correctly.
7. Replace the computer cover.
22
OM06221
Figure 12. Replacing the Battery
Page 23
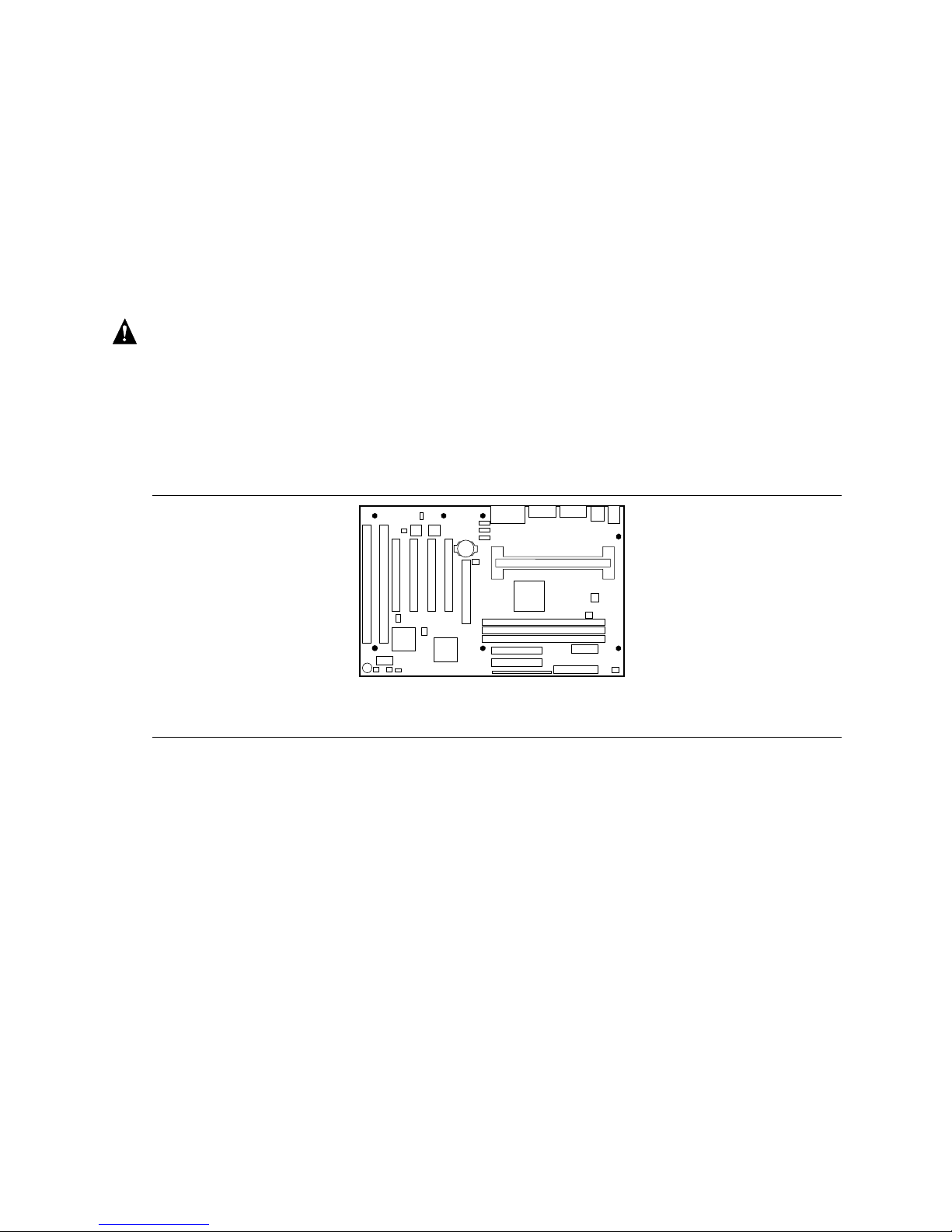
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Installing and Removing the Motherboard
Refer to your chassis manual for instructions on installing and removing the motherboard.
NOTES
✏
You will need a Phillips (#2 bit) screwdriver.
Refer to Appendix B for regulatory requirements and installation instructions and precautions.
WARNING
This procedure should be done only by qualified technical personnel. Disconnect the computer
from its power source before doing the procedures described here. Failure to disconnect the
power before you open the computer can result in personal injury or equipment damage.
The motherboard is secured to the chassis by seven screws. Figure 13 shows the locations of the
mounting screw holes.
OM06220
Figure 13. Mounting Screw Holes
23
Page 24

Installing the Motherboard
24
Page 25

3 Configuring the Motherboard
This chapter describes how to configure the motherboard using the Setup program. Refer to
Chapter 4 for more information about Setup.
Before You Begin
CAUTION
If you are installing this motherboard in a chassis, see Appendix B for regulatory requirements
and precautions.
• Always follow the steps in each procedure in the correct order.
• Set up a log to record information about your computer, such as model, serial numbers,
installed options, and configuration information.
• Use an antistatic wrist strap and a conductive foam pad when working on the motherboard.
WARNINGS
The procedures in this chapter assume familiarity with the general terminology associated with
personal computers and with the safety practices and regulatory compliance required for using
and modifying electronic equipment.
Disconnect the computer from its power source and from any telecommunications links,
networks, or modems before performing any of the procedures described in this chapter.
Failure to disconnect power, telecommunications links, networks, or modems before you open
the computer or perform any procedures can result in personal injury or equipment damage.
Some circuitry on the motherboard may continue to operate even though the front panel power
button is off.
CAUTION
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage components. Perform the procedures described in this
chapter only at an ESD workstation. If such a station is not available, you can provide some ESD
protection by wearing an antistatic wrist strap and attaching it to a metal part of the computer
chassis.
25
Page 26

Configuring the Motherboard
Configuration Modes
The Setup program has three configuration modes:
• Normal mode for normal operations
• Configure mode for configuring the processor speed and clearing passwords
• Recovery mode for recovering the BIOS data
Figure 14 shows the location of the configuration header on the motherboard. The jumper is
usually set to normal mode at the factory.
1
3
Configuration Jumper
✏
J8B2
Figure 14. Configuration Header
NOTE
OM06055
A jumper is a small plastic conductor that slips over two header pins. To change a setting, remove
the jumper from the pins and slide it onto the new pins for the desired setting.
CAUTION
To avoid bending or breaking pins, use caution when removing or installing a jumper.
26
Page 27

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Table 1 shows jumper settings for the different Setup modes. These modes configure Setup for
normal operations, maintenance options, or recovering the BIOS.
Table 1. Jumper Settings for the Setup Program
Jumper
Function
Normal 1-2 BIOS uses current configuration and passwords for booting.
Configure 2-3 After the POST runs, Setup starts and displays the Maintenance menu. This menu
Recovery None BIOS recovers data from a recovery diskette. Refer to Chapter 5 for information on
(J8B2) Description
displays options for setting the processor speed and clearing passwords. Refer to
Chapter 4 for information on the Maintenance menu.
recovering the BIOS data during an upgrade.
Setting the Processor Speed
Set the processor speed after you have installed or upgraded the processor. This procedure assumes
that the motherboard is installed in the computer and the configuration header (J8B2) has the
jumper set on pins 1-2 for normal mode.
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” (see page 11).
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Locate the configuration header (Figure 14; J8B2 on the motherboard).
5. On the header, move the jumper to pins 2-3 as shown below to set configure mode.
1
3
J8B2
OM06240B
6. Replace the cover, turn on the computer, and allow it to boot.
7. The computer starts the Setup program. Setup displays the Maintenance menu.
8. Use the arrow keys to select the Processor Speed feature and press <Enter>. Setup displays a
popup screen with the available processor speeds.
9. Use the arrow keys to select the processor speed. For example, select 266 for a 266 MHz
Pentium II processor. Press <Enter> to confirm the speed. This Maintenance menu reappears
again.
10. Press <F10> to save the current values and exit Setup.
11. Turn off the computer.
12. Remove the computer cover.
27
Page 28

Configuring the Motherboard
13. On the header (J8B2), move the jumper back to pins 1-2 to restore normal operation as shown
below.
1
3
J8B2
OM06240A
14. Replace the cover and turn on the computer.
15. Verify the processor speed in the startup information the BIOS displays.
Clearing the Passwords
This procedure assumes that the motherboard is installed in the computer and the configuration
header (J8B2) has the jumper set on pins 1-2 for normal mode.
1. Observe the precautions in “Before You Begin” (see page 11).
2. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
3. Remove the computer cover.
4. Locate the configuration header (Figure 14; J8B2 on the motherboard).
5. On the header (J8B2), move the jumper to pins 2-3 as shown below to set configure mode.
1
3
J8B2
OM06240B
6. Replace the cover, turn on the computer, and allow it to boot.
7. The computer starts the Setup program. Setup displays the Maintenance menu.
8. Use the arrow keys to select Clear Passwords. Press <Enter> and Setup displays a pop-up
screen requesting that you confirm clearing the password. Select Yes and press <Enter>.
Setup displays the Maintenance menu again.
9. Press <F10> to save the current values and exit Setup.
10. Turn off the computer.
11. Remove the computer cover.
12. On the header (J8B2), move the jumper back to pins 1-2 to restore normal operation as shown
below.
1
3
J8B2
OM06240A
13. Replace the cover and turn on the computer.
28
Page 29

4 Using the Setup Program
This chapter provides an overview of the Setup program. You can use the Setup program to
change the configuration information and boot sequence for the computer.
NOTE
✏
For reference purposes, you should write down the current Setup settings. When you make
changes to the settings, update this record.
Setup Menus
To enter the Setup program, turn the computer on and press <F2> when you see the message:
Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
Table 2 is an overview of the menu screens in the Setup program.
Table 2. Setup Menu Bar
Setup Menu Screen Description
Maintenance Specifies the processor speed and clears the Setup passwords. This is
only available in configure mode. Refer to Chapter 3 for information
about configure mode.
Main Allocates resources for hardware components.
Advanced Specifies advanced features available through the chipset.
Security Specifies passwords and security features.
Power Specifies power management features.
Boot Specifies boot options and power supply controls.
Exit Saves or discards changes to the Setup program options.
29
Page 30

Using the Setup Program
Function Keys
Table 3 shows the function keys available for menu screens.
Table 3. Setup Function Keys
Setup Key Description
<F1> or <Alt-H> Brings up a help screen for the current item.
<Esc> Exits the menu.
<←> or <→>
Selects a different menu screen.
<↑> or <↓>
<Home> or <End> Moves cursor to top or bottom of the window.
<PgUp> or <PgDn> Moves cursor to top or bottom of the window.
<F5> or <-> Selects the previous value for a field.
<F6> or <+> or <Space> Selects the next value for a field.
<F9> Load the default configuration values for the current menu.
<F10> Save the current values and exit Setup.
<Enter> Executes command or selects the submenu.
Moves cursor up or down.
Maintenance Menu
Use this menu to specify the processor speed and clear the Setup passwords. Setup only displays
this menu in configure mode (see page 26).
Table 4. Maintenance Menu
Feature Options Description
Processor Speed
Clear All Passwords No options Clears the user and supervisor passwords.
• 200
• 233
• 266
• 300
Specifies the processor speed in megahertz.
30
Page 31

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Main Menu
This menu reports processor and memory information. Use it to configure the system date, system
time, floppy options, and IDE devices.
Table 5. Main Menu
Feature Options Description
Processor Type No options Displays processor type.
Processor Speed No options Displays processor speed.
Cache RAM No options Displays size of second-level cache.
Total Memory No options Displays the total amount of RAM on the motherboard.
BIOS Version No options Displays the version of the BIOS.
Language English (US) Selects the default language used by the BIOS.
System Time Hour, minute,
and second
System Date Month, day, and
year
Floppy Options,
submenu
Primary IDE Master,
submenu
Primary IDE Slave,
submenu
Secondary IDE
Master, submenu
Secondary IDE
Slave, submenu
No options When selected, displays the Floppy Options submenu.
No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected, displays
No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected, displays
No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected, displays
No options Reports type of connected IDE device. When selected, displays
Specifies the current time.
Specifies the current date.
the Primary IDE Master submenu.
the Primary IDE Slave submenu.
the Secondary IDE Master submenu.
the Secondary IDE Slave submenu.
31
Page 32
Using the Setup Program
Floppy Options Submenu
Use this submenu to configure floppy drives.
Table 6. Floppy Options Submenu
Feature Options Description
Diskette A:
Diskette B:
Floppy Write Protect
• Disabled
• 360 KB, 5¼″
• 1.2 MB, 5¼″
• 720 KB, 3½″
• 1.44/1.25 MB, 3½″ (default)
• 2.88 MB, 3½″
• Disabled (default)
• 360 KB, 5¼″
• 1.2 MB, 5¼″
• 720 KB, 3½″
• 1.44/1.25 MB, 3½″
• 2.88 MB, 3½″
• Disabled (default)
• Enabled
Specifies the capacity and physical size
of diskette drive A.
Specifies the capacity and physical size
of diskette drive B.
Disables or enables write protect for the
diskette drive(s).
32
Page 33
IDE Device Configuration Submenus
Use this submenu to configure IDE devices, including:
• Primary IDE master
• Primary IDE slave
• Secondary IDE master
• Secondary IDE slave
Table 7. IDE Device Configuration Submenus
Feature Options Description
Type
Cylinders 1 to
Heads 1 to 16 Specifies number of disk heads.
Sectors 1 to 64 Specifies number of disk sectors.
Maximum Capacity No options Reports the maximum capacity for the hard disk.
Multi-Sector Transfers
LBA Mode Control
None
•
ATAPI Removable
•
CD-ROM
•
User
•
Auto (default)
•
XXXX
Disabled
•
2 Sectors
•
4 Sectors
•
8 Sectors
•
16 Sectors (default)
•
Disabled
•
Enabled (default)
•
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Specifies the IDE configuration mode for IDE
devices.
User allows the cylinders, heads, and sectors
fields to be changed.
Auto automatically fills in the values for the
cylinders, heads, and sectors fields.
Specifies number of disk cylinders.
Value calculated from number of cylinders, heads,
and sectors.
Specifies number of sectors per block for
transfers from the hard drive to memory.
Check the hard drive’s specifications for optimum
setting.
Enables or disables logical block addressing (LBA)
in place of the Cylinders, Heads, and Sectors
fields.
Transfer Mode
Ultra DMA
Standard
•
Fast PIO 1
•
Fast PIO 2
•
Fast PIO 3
•
Fast PIO 4 (default)
•
Disabled (default)
•
Mode 0
•
Mode 1
•
Mode 2
•
CAUTION
Changing the LBA Mode Control after a hard
drive has been formatted can corrupt data on
the drive.
Specifies method for transferring data between
the hard drive and system memory.
Specifies the ultra DMA mode for the hard drive.
33
Page 34
Using the Setup Program
Advanced Menu
Use this menu to set advanced features that are available through the chipset.
Table 8. Advanced Menu
Feature Options Description
Plug & Play O/S
Reset Configuration Data
Memory Cache
ECC Configuration
Resource Configuration,
submenu
Peripheral Configuration,
submenu
Keyboard Features,
submenu
Video Configuration,
submenu
DMI Events Logging,
submenu
• No
• Yes (default)
• No (default)
• Yes
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Non-ECC
(default)
• ECC
No options Configures memory blocks and IRQs for legacy ISA
No options Configures peripheral ports and devices. When
No options Configures keyboard features. When selected,
No options Configures video features. When selected, displays
No options Configures DMI Events Logging. When selected,
Specifies if a Plug and Play operating system is being
used.
No lets the BIOS configure all devices.
Yes lets the operating system configure Plug and
Play devices. Not required with a Plug and Play
operating system.
Clears the BIOS configuration data on the next boot.
Enables or disables the memory cache.
Specifies ECC memory operation.
devices. When selected, displays the Resource
Configuration submenu.
selected, displays the Peripheral Configuration
submenu.
displays the Keyboard Features submenu.
the Video Configuration submenu.
displays the DMI Events Logging submenu.
34
Page 35
Resource Configuration Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the memory and interrupts.
Table 9. Resource Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Memory
Reservation
IRQ
Reservation
• C800 - CBFF Available (default) | Reserved
• CC00- CFFF Available (default) | Reserved
• D000 - D3FF Available (default) | Reserved
• D400 - D7FF Available (default) | Reserved
• D800 - DBFF Available (default) | Reserved
• DC00 - DFFF Available (default) | Reserved
• Memory hole Disabled (default) | Conventional | Extended
• IRQ3 Available (default) | Reserved
• IRQ4 Available (default) | Reserved
• IRQ5 Available (default) | Reserved
• IRQ7 Available (default) | Reserved
• IRQ10 Available (default) | Reserved
• IRQ11 Available (default) | Reserved
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Reserves specific
upper memory blocks
for use by legacy ISA
devices.
Memory hole frees
address space in RAM
for an legacy ISA
boards.
Reserves specific
IRQs for use by
legacy ISA devices.
An * (asterisk)
displayed next to an
IRQ indicates an IRQ
conflict.
35
Page 36
Using the Setup Program
Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the computer peripherals.
Table 10. Peripheral Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Serial port A
Serial port B
Mode
Parallel port
Mode
Floppy disk
controller
IDE controller
Audio
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
• Normal (default)
• IrDA
• ASK-IR
• Disabled
• Enabled
• Auto (default)
• Output Only
• Bi-directional (default)
• EPP
• ECP
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Disabled
• Primary
• Secondary
• Both (default)
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Configures serial port A.
Auto assigns the first free COM port, normally COM1,
the address 3F8h and the interrupt IRQ4.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
Configures serial port B.
Auto assigns the first free COM port, normally COM2,
the address 2F8h and the interrupt IRQ3.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
If either serial port address is set, that address will not
appear in the list of options for the other serial port.
ATI mach32
If an
active as an add-in card, the COM4, 2E8h address will
not appear in the list of options for either serial port.
Specifies the mode for Serial Port B for normal (COM 2)
or infrared applications.
Configures the parallel port.
Auto assigns LPT1 the address 378h and the interrupt
IRQ7.
An * (asterisk) displayed next to an address indicates a
conflict with another device.
Selects the mode for the parallel port.
Output Only operates in AT-compatible mode.
Bi-directional operates in bidirectional PS/2-compatible
mode.
EPP is Extended Parallel Port mode, a high-speed
bidirectional mode.
ECP is Enhanced Capabilities Port mode, a high-speed
bidirectional mode.
Configures the floppy disk controller.
Configures the IDE controller.
Both specifies both the primary and secondary the
primary and secondary channel are used.
Enables or disables the onboard audio subsystem.
†
or an
ATI mach64
†
video controller is
36
Page 37
Keyboard Features Submenu
Use this submenu to set keyboard features.
Table 11. Keyboard Features Submenu
Feature Options Description
Numlock
Key Click
Keyboard auto-repeat rate
Keyboard auto-repeat delay
• Auto (default)
• On
• Off
• Disabled (default)
• Enabled
• 30/sec (default)
• 26.7/sec
• 21.8/sec
• 18.5/sec
• 13.3/sec
• 10/sec
• 6/sec
• 2/sec
• ¼ sec
• ½ sec (default)
• ¾ sec
• 1 sec
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Specifies the power on state of the Numlock
feature on the numeric keypad of the keyboard.
Enables the key click option.
Selects the key repeat rate.
Selects the delay before key repeat.
Video Configuration Submenu
Use this submenu to configure video features.
Table 12. Video Configuration Submenu
Feature Options Description
Palette Snooping
• Disabled (default)
• Enabled
DMI Event Logging Submenu
Use this submenu to set keyboard features.
Table 13. DMI Event Logging Submenu
Feature Options Description
Event log capacity No options Indicates if there is space available in the event log.
Event log validity No options Indicates if the contents of the event log are valid.
View DMI event log No options Enables viewing of DMI event log.
Clear all DMI event logs
Event Logging
ECC Event Logging
Mark DMI events as read No options Marks all DMI events as read.
• No (default)
• Yes
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Disabled (default)
• Enabled
Controls the ability of a primary PCI graphics controller to
share a common palette with an ISA add-in video card.
Clears the DMI Event Log after rebooting.
Enables logging of DMI events.
Enables logging of ECC events.
37
Page 38
Using the Setup Program
Security Menu
Use this menu to set passwords and security features.
Table 14. Security Menu
Feature Options Description
User Password Is No options Reports if there is a user password set.
Supervisor Password Is No options Reports if there is a supervisor password set.
Set User Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
Set Supervisor Password Password can be up to seven
alphanumeric characters.
Unattended Start
• Disabled (default)
• Enabled
Specifies the user password.
Specifies the supervisor password.
Enables the unattended start feature. When
enabled, the computer boots, but the keyboard
is locked. The user must enter a password to
unlock the computer or boot from a floppy
diskette.
Power Menu
Use this menu to set power management features.
Table 15. Power Menu
Feature Options Description
Power Management
Inactivity Timer
Hard Drive
VESA† Video Power Down
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Off (default)
• 1 Minute
• 2 Minutes
• 4 Minutes
• 6 Minutes
• 8 Minutes
• 12 Minutes
• 16 Minutes
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
• Disabled
• Enabled (default)
Enables or disables the BIOS power
management feature.
Specifies the amount of time before the
computer enters standby mode.
Enables power management for hard disks
during standby and suspend modes.
Enables power management for video during
standby and suspend modes.
38
Page 39
Boot Menu
Use this menu to specify the boot features and the boot sequence.
Table 16. Boot Menu
Feature Options Description
Restore on
AC/Power Loss
On Modem Ring
On LAN
On PME
QuickBoot Mode
Scan User Flash
Area
First Boot Device
Second Boot Device
Third Boot Device
Fourth Boot Device
Hard Drive, submenu No options Lists available hard drives. When selected, displays the
Removable Devices,
submenu
• Stay Off
• Last State
(default)
• Power On
• Stay Off
• Power On (default)
• Stay Off
• Power On (default)
• Stay Off
• Power On (default)
• Enabled
• Disabled (default)
• Enabled (default)
• Disabled
• Removable devices
• Hard Drive
• ATAPI CD-ROM
Drive
• Network boot
No options Lists available removable devices. When selected,
Specifies how the computer responds following a power
failure.
Stay Off keeps power off until power button pressed.
Last State restores previous power state before a power
failure.
Power On restores power without restoring previous
power state.
Specifies how the computer responds to an incoming call
on an installed modem when the power is off.
Specifies how the computer responds to a LAN wakeup
event when the power is off.
Specifies how the computer responds to a PCI power
management enable event when the power is off.
Enables the computer to boot without running certain
POST tests.
Enables the BIOS to scan the flash memory for user
binary files that are executed at boot time.
Specifies the boot sequence from the available devices.
To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <+> to move the device up the list or <-> to
move the device down the list.
The operating system assigns a drive letter to each boot
device in the order listed. Changing the order of the
devices changes the drive lettering.
Hard Drive submenu.
displays the Removable Devices submenu.
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
39
Page 40
Using the Setup Program
Hard Drive Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the boot sequence for hard drives.
Table 17. Hard Drive Submenu
Options Description
• Installed hard drive
• Bootable ISA Cards
Specifies the boot sequence for the hard drives attached to the computer. To
specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <+> to move the device up the list or <-> to move the device down
the list.
The operating system assigns a drive letter to each device in the order listed.
Changing the order of the devices changes the drive lettering.
Removable Devices Submenu
Use this submenu to configure the boot sequence for removable devices.
Table 18. Removable Devices Submenu
Options Description
• Legacy Floppy Drives
Specifies the boot sequence for the removable hard drives attached to the
computer. To specify boot sequence:
1. Select the boot device with <↑> or <↓>.
2. Press <+> to move the device up the list or <-> to move the device down
the list.
The operating system assigns a drive letter to each device in the order listed.
Changing the order of the devices changes the drive lettering.
Exit Menu
Use this menu to exit the Setup program, save changes, load defaults, and save defaults.
Table 19. Exit Menu
Feature Description
Exit Saving Changes Exits and saves the changes in CMOS RAM.
Exit Discarding Changes Exits without saving any changes made in Setup.
Load Setup Defaults Loads the default values for all the Setup options.
Load Custom Defaults Loads the custom defaults for Setup options.
Save Custom Defaults Saves the current values as custom defaults. Normally, the BIOS reads the
Setup values from flash memory. If this memory is corrupted, the BIOS reads
the custom defaults. If no custom defaults are set, the BIOS reads the factory
defaults.
Discard Changes Discards changes without exiting Setup. The option values present when the
computer was turned on are used.
40
Page 41

5 Upgrading the BIOS
This chapter describes how to upgrade the BIOS and how to recover the BIOS if an upgrade fails.
Preparing for the Upgrade
Before you upgrade the BIOS, prepare for the upgrade by recording the current BIOS settings,
obtaining the upgrade utility, and making a copy of the current BIOS.
Obtaining the Upgrade Utility
You can upgrade to a new version of the BIOS using the new BIOS files and the BIOS upgrade
utility, iFLASH.EXE. You can obtain the BIOS upgrade file and the iFLASH.EXE utility through
your computer supplier or from the Intel World Wide Web site:
http://www.intel.com.
NOTE
✏
Please review the instructions distributed with the upgrade utility before attempting a BIOS
upgrade.
This upgrade utility allows you to:
• Upgrade the BIOS in flash memory.
• Update the language section of the BIOS.
The following steps explain how to upgrade the BIOS.
Recording the Current BIOS Settings
1. Boot the computer and press
Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
NOTE
Do not skip step 2. You will need these settings to configure your computer at the end of the
procedure.
2. Write down the current settings in the BIOS Setup program.
when you see the message:
<F2>
41
Page 42

Upgrading the BIOS
Creating a Bootable Floppy Diskette
1. Use a DOS or Windows† 95 system to create the floppy disk.
2. Insert a floppy disk in floppy drive A.
3. At the C:\ prompt, for an unformatted floppy disk, type:
format a:/s
or, for a formatted floppy disk, type:
sys a:
4. Press
<Enter>
Creating the BIOS Upgrade Floppy Diskette
The BIOS upgrade file is a compressed self-extracting archive that contains the files you need to
upgrade the BIOS.
1. Copy the BIOS upgrade file to a temporary directory on your hard disk.
2. From the C:\ prompt, change to the temporary directory.
3. To extract the file, type the name of the BIOS upgrade file, for example:
10006BI1.EXE
4. Press
<Enter>
LICENSE.TXT
README.TXT
BIOS.EXE
5. Read the
README.TXT
6. Insert the bootable floppy disk into drive A.
7. To extract the
the
BIOS.EXE
BIOS A:
8. Press
<Enter>
9. The floppy disk now holds the BIOS upgrade and recovery files.
. The extracted file contains the following files:
LICENSE.TXT
file, which contains the software license agreement and the
file, which contains the instructions for the BIOS upgrade.
BIOS.EXE
file to the floppy disk, change to the temporary directory that holds
file and type:
.
Upgrading the BIOS
1. Boot the computer with the floppy disk in drive A. The BIOS upgrade utility screen appears.
2. Select
3. Select
4. Use the arrow keys to select the correct
5. When the utility asks for confirmation that you want to flash the new BIOS into memory,
6. When the utility displays the message
7. As the computer boots, check the BIOS identifier (version number) to make sure the upgrade
42
Update Flash Memory From a File
Update System BIOS
select
Continue with Programming
<Enter>
.
was successful.
. Press
.
file. Press
.bio
.
<Enter>
<Enter>
.
<Enter>
. Press
upgrade is complete
.
, remove the floppy disk. Press
Page 43

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
8. To enter the Setup program, press
Press <F2> Key if you want to run SETUP
when you see the message:
<F2>
9. For proper operation, load the Setup program defaults. To load the defaults, press
10. To accept the defaults, press
<Enter>
.
11. Set the options in the Setup program to the settings you wrote down before the BIOS upgrade.
12. To save the settings, press
13. To accept the settings, press
<F10>
<Enter>
.
.
14. Turn off the computer and reboot.
Recovering the BIOS
It is unlikely that anything will interrupt the BIOS upgrade; however, if an interruption occurs, the
BIOS could be damaged. The following steps explain how to recover the BIOS if an upgrade fails.
The following procedure use recovery mode for the Setup program. See Chapter 3 for more
information about Setup modes.
NOTE
Because of the small amount of code available in the non-erasable boot block area, there is no
video support. You will not see anything on the screen during the procedure. Monitor the
procedure by listening to the speaker and looking at the floppy drive LED.
<F9>
.
1. Turn off all peripheral devices connected to the computer. Turn off the computer.
2. Remove the computer cover.
3. Locate the configuration header (see Figure 14 on page 26; J8B2 on the motherboard).
4. On the header (J8B2), remove the jumper from all pins as shown below to set recovery mode for
Setup.
1
3
J8B2
OM06240
5. Insert the bootable BIOS upgrade floppy disk into floppy drive A.
6. Replace the cover, turn on the computer, and allow it to boot.
7. Reconnect the AC power cord and turn on the computer. The recovery process will take a few
minutes.
8. Listen to the speaker.
• Two beeps and the end of activity in drive A indicate successful BIOS recovery.
• A series of continuous beeps indicates failed BIOS recovery.
9. If recovery fails, return to step 1 and repeat the recovery process.
10. If recovery is successful, turn off the computer and disconnect the AC power cord from the
computer. Remove the computer cover and continue with the following steps.
43
Page 44

Upgrading the BIOS
11. On the header (J8B2), move the jumper back to pins 1-2 as shown below to set normal mode
for Setup.
1
3
J8B2
OM06240A
12. Replace the computer cover and reconnect the AC power cable; leave the upgrade disk in
drive A and turn on the computer.
13. Continue with the BIOS upgrade (see page 42).
Changing the BIOS Language
You can use the BIOS upgrade utility to change the language the BIOS uses for messages and the
Setup program. Use a bootable floppy disk containing the Intel flash utility and language files (see
page 42).
1. Boot the computer with the bootable floppy disk in drive A. The BIOS upgrade utility screen
appears.
2. Select
3. Select
Update Flash Memory From a File
Update Language Set
. Press
<Enter>
4. Select drive A and use the arrow keys to select the correct
5. When the utility asks for confirmation that you want to flash the new language into memory,
select
Continue with Programming
6. When the utility displays the message
<Enter>
.
. Press
upgrade is complete
7. The computer will reboot and the changes will take effect.
.
.
<Enter>
file. Press
.lng
<Enter>
.
, remove the floppy disk. Press
.
44
Page 45

6 Technical Reference
Motherboard Connectors
The following figure shows the location of the motherboard connectors.
1
Chassis
Security
J2B1
1
Fan 2
J3F1
1
2
Wake on Ring
J8A1
3
1
Wake on
LAN
J1C1
SCSI Hard
Drive LED
J8B1
1
Telephony
J2F1
41
CD-ROM Audio
J1F1
1
2
4
Slot 1
J4J1
1
Line In Audio
J2F2
1
31
Fan 1
J8M1
4
Fan 3
(Active
Heatsink
Fan)
J5L1
Table 20. Chassis Security Header (J2B1)
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 CHS_SEC
OM06236
Figure 15. Motherboard Connectors
45
Page 46

Technical Reference
Table 21. Wake on LAN Header (J1C1)
Pin Signal Name
1 +5 VSB
2 Ground
3 WOL
Table 22. ATAPI CD Audio Connector (J1F1)
Pin Signal Name
1 CD_IN-Left
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 CD_IN-Right
Table 23. ATAPI Telephony Connector
(J2F1)
Pin Signal Name
1 Audio Out (monaural)
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 Audio In (monaural)
Table 24. ATAPI Line In Connector (J2F2)
Pin Signal Name
1 Left Line In
2 Ground
3 Ground
4 Right Line In (monaural)
Table 25. Fan 1 Header (J8M1)
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 FAN_CTRL (+12 V)
3 FAN_SEN*
* If the optional management extension hardware is not available, pin 3 is ground.
46
Page 47

Table 26. Fan 2 Header (J3F1)
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 FAN_CTRL (+12 V)
3 FAN_SEN*
* If the optional management extension hardware is not available, pin 3 is ground.
Table 27. Fan 3 Header (J5L1) (Active
Heatsink Fan)
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 +12 V
3 Ground
Table 28. SCSI Hard Drive LED Input Header
(J8B1)
Pin Signal Name
1 DRV_ACT#
2 No connect
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Table 29. Wake on Ring Header (J8A1)
Pin Signal Name
1 Ground
2 RINGA
47
Page 48

Technical Reference
Front Panel Connectors
The motherboard has connectors for controls and indicators typically located on the front panel of
the computer.
AB C D E FG
27
Table 30. Front Panel Connectors
Connector Pin Signal Name
A. Speaker* 27 SPKR_HDR
26 PIEZO_IN
25 Key
24 Ground
B. Reset switch 23 SW_RST
22 Ground
Key
C. Power LED 20 +5 V
19 Key
18 Ground
Key
D. Hard drive LED 16 +5 V
15 HD Active#
14 Key
13 +5 V
Key
E. Infrared 11 CONIR (consumer IR)
10 IrTX (transmit)
9 Ground
8 IrRX (receive)
7 Key
6 +5 V
Key
F. Sleep switch 4 +5 V
3 SLEEP
G. Power switch 2 Ground
1 SW_ON#
* A jumper on pins 26-27 enables the onboard speaker.
J9D1
1
24611162024 22
OM05705
48
Page 49
Motherboard Resources
Memory Map
Table 31. Memory Map
Address Range (decimal) Address Range (hex) Size Description
1024 K - 393216 K 100000 - 18000000 383 MB Extended memory
1008 K - 1024 K FC000 - FFFFF 16 KB Boot block
1000 K - 1008 K FA000 - FBFFF 8 KB ESCD (Plug and Play configuration and DMI)
996 K - 1000 K F9000 - F9FFF 4 KB Reserved for BIOS
992 K - 996 K F8000 - F8FFF 4 KB OEM Logo or Scan User Flash
928 K - 992 K E8000 - F7FFF 64 KB POST BIOS
896 K - 928 K E0000 - E7FFF 32 KB POST BIOS (Available as UMB)
800 K - 896 K C8000 - DFFFF 96 KB Available high DOS memory (open to ISA
640 K - 800 K A0000 - C7FFF 160 KB Video memory and BIOS
639 K - 640 K 9FC00 - 9FFFF 1 KB Extended BIOS data (movable by memory
512 K - 639 K 80000 - 9FBFF 127 KB Extended conventional memory
0 K - 512 K 00000 - 7FFFF 512 KB Conventional memory
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
and PCI bus)
manager software)
DMA Channels
Table 32. DMA Channels
DMA Channel Number Data Width System Resource
0 8- or 16-bits Audio
1 8- or 16-bits Audio / parallel port
2 8- or 16-bits Floppy drive
3 8- or 16-bits Parallel port (for ECP)/audio
4 Reserved - cascade channel
5 16-bits Open
6 16-bits Open
7 16-bits Open
49
Page 50
Technical Reference
I/O Map
Table 33. I/O Map
Address (hex) Size Description
0000 - 000F 16 bytes PIIX4- DMA 1
0020 - 0021 2 bytes PIIX4 - interrupt controller 1
002E - 002F 2 bytes Super I/O controller configuration registers
0040 - 0043 4 bytes PIIX4 - Counter/Timer 1
0048 - 004B 4 bytes PIIX4- Counter/Timer 2
0060 1 byte Keyboard Controller Byte - Reset IRQ
0061 1 byte PIIX4 - NMI, Speaker Control
0064 1 byte Keyboard controller, CMD/STAT Byte
0070, bit 7 1 bit PIIX4 - enable NMI
0070, bits 6:0 7 bits PIIX4 - real time clock, address
0071 1 byte PIIX4 - real time clock, data
0078 1 byte Reserved - motherboard configuration
0079 1 byte Reserved - motherboard configuration
0080 - 008F 16 bytes PIIX4 - DMA page registers
00A0 - 00A1 2 bytes PIIX4 - interrupt controller 2
00B2 - 00B3 2 bytes APM control
00C0 - 00DE 31 bytes PIIX4 - DMA 2
00F0 1 byte Reset numeric error
0170 - 0177 8 bytes Secondary IDE channel
01F0 - 01F7 8 bytes Primary IDE channel
0201 1 byte Audio / game port
0220 - 022F 16 bytes Audio (Sound Blaster† compatible)
0228 - 022F 8 bytes LPT3
0240 - 024F 16 bytes Audio (Sound Blaster compatible)
0278 - 027F 8 bytes LPT2
0290 - 0297 8 bytes Management extension hardware
02E8 - 02EF 8 bytes COM4/Video (8514A)
02F8 - 02FF 8 bytes COM2
0300 - 0301 2 bytes MPU-401 (MIDI)
0330 - 0331 2 bytes MPU-401 (MIDI)
0332 - 0333 2 bytes MPU-401 (MIDI)
0334 - 0335 2 bytes MPU-401 (MIDI)
0376 1 byte Secondary IDE channel command port
0377 1 byte Floppy channel 2 command
0377, bit 7 1 bit Floppy disk change, channel 2
0377, bits 6:0 7 bits Secondary IDE channel status port
50
continued ☛
Page 51
AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Table 33. I/O Map
Address (hex) Size Description
0378 - 037F 8 bytes LPT1
0388- 038D 6 bytes AdLib (FM synthesizer)
03B4 - 03B5 2 bytes Video (VGA†)
03BA 1 byte Video (VGA)
03C0 - 03CA 11 bytes Video (VGA)
03CC 1 byte Video (VGA)
03CE - 03CF 2 bytes Video (VGA)
03D4 - 03D5 2 bytes Video (VGA)
03DA 1 byte Video (VGA)
03E8 - 03EF 8 bytes COM3
03F0 - 03F5 6 bytes Floppy Channel 1
03F6 1 byte Primary IDE channel command port
03F7 (Write) 1 byte Floppy channel 1 command
03F7, bit 7 1 bit Floppy disk change channel 1
03F7, bits 6:0 7 bits Primary IDE channel status port
03F8 - 03FF 8 bytes COM1
04D0 - 04D1 2 bytes Edge/level triggered PIC
0530 - 0537 8 bytes Windows Sound System
0604 - 060B 8 bytes Windows Sound System
LPTn + 400h 8 bytes ECP port, LPTn base address + 400h
0CF8 - 0CFB* 4 bytes PCI configuration address register
0CF9** 1 byte Turbo and reset control register
0CFC - 0CFF 4 bytes PCI configuration data register
0E80 - 0E87 8 bytes Windows Sound System
0F40- 0F47 8 bytes Windows Sound System
0F86 - 0F87 2 bytes Yamaha OPL3-SA configuration
FF00 - FF07 8 bytes IDE bus master register
FFA0 - FFA7 8 bytes Primary bus master IDE registers
FFA8 - FFAF 8 bytes Secondary bus master IDE registers
(continued)
* DWORD access only
** Byte access only
NOTE
✏
This table does not list I/O addresses that may be used by add-in cards in the system.
51
Page 52
Technical Reference
PCI Configuration Space Map
Table 34. PCI Configuration Space Map
Bus
Number (hex)
00 00 00 Intel 82440LX (PAC)
00 01 00 Intel 82371AB (PIIX4 ) A.G.P. bus
00 07 00 Intel 82371AB (PIIX4 ) PCI/ISA bridge
00 07 01 Intel 82371AB (PIIX4 ) IDE bus master
00 07 02 Intel 82371AB (PIIX4 ) USB
00 07 03 Intel 82371AB (PIIX4 ) power management
00 0D 00 PCI expansion slot 1 (J4D2)
00 0E 00 PCI expansion slot 2 (J4D1)
00 0F 00 PCI expansion slot 3 (J4C1)
00 10 00 PCI expansion slot 4 (J4B1)
Device
Number (hex)
Interrupts
Table 35. Interrupts
IRQ System Resource
NMI I/O channel check
0 Reserved, interval timer
1 Reserved, keyboard buffer full
2 Reserved, cascade interrupt from slave PIC
3 COM2*
4 COM1*
5 LPT2 (Plug and Play option) / audio / user available
6 Floppy drive
7 LPT1*
8 Real time clock
9 Reserved
10 User available
11 Windows Sound System* / user available
12 Onboard mouse port (if present, else user available)
13 Reserved, math coprocessor
14 Primary IDE (if present, else user available)
15 Secondary IDE (if present, else user available)
* Default, but can be changed to another IRQ
Function
Number (hex) Description
52
Page 53
A Error Messages
BIOS Beep Codes
One long beep followed by several short beeps indicates a video problem.
Table 36. Beep Codes
Beeps 80h Code Description
1 B4h One short beep before boot
1-2 98h Search for option ROMs
1-2-2-3 16h BIOS ROM checksum
1-3-1-1 20h Test DRAM refresh
1-3-1-3 22h Test keyboard controller
1-3-4-1 2Ch RAM failure on address line
1-3-4-3 2Eh RAM failure on data bits
1-4-1-1 30h RAM failure on data bits
2-1-2-3 46h Check ROM copyright notice
2-2-3-1 58h Test for unexpected interrupts
xxxx
*
xxxx
* of low byte of memory bus
xxxx
* of high byte of memory bus
BIOS Error Messages
Table 37. BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
Diskette drive A error or
Diskette drive B error
Extended RAM Failed at offset:
nnnn
Failing Bits:
Fixed Disk 0 Failure or
Fixed Disk 1 Failure or
Fixed Disk Controller Failure
Incorrect Drive A type - run
SETUP
nnnn
Drive A: or B: is present but fails the POST diskette tests. Check that the
drive is defined with the proper diskette type in Setup and that the
diskette drive is installed correctly.
Extended memory not working or not configured properly at offset
The hex number nnnn is a map of the bits at the RAM address (System,
Extended, or Shadow memory) that failed the memory test. Each 1 in the
map indicates a failed bit.
Fixed disk is not working or not configured properly. Check to see if fixed
disk is installed properly. Run Setup be sure the fixed-disk type is
correctly identified.
Type of floppy drive for drive A: not correctly identified in Setup.
nnnn
continued
.
☛
53
Page 54
Error Messages
Table 37. BIOS Error Messages
Error Message Explanation
Invalid NVRAM media type Problem with NVRAM (CMOS) access.
Keyboard controller error The keyboard controller failed test. Try replacing the keyboard.
Keyboard error Keyboard not working.
Keyboard error nn BIOS discovered a stuck key and displays the scan code nn for the stuck
Keyboard locked - Unlock key
switch
Monitor type does not match
CMOS - Run SETUP
Operating system not found Operating system cannot be located on either drive A: or drive C:. Enter
Parity Check 1 Parity error found in the system bus. BIOS attempts to locate the
Parity Check 2 Parity error found in the I/O bus. BIOS attempts to locate the address
Press <F1> to resume, <F2> to
Setup
Real time clock error Real-time clock fails BIOS test. May require motherboard repair.
Shadow RAM Failed at offset:
nnnn
System battery is dead Replace and run SETUP
System cache error - Cache
disabled
System CMOS checksum bad run SETUP
System RAM Failed at offset:
nnnn
System timer error The timer test failed. Requires repair of system motherboard.
(continued)
key.
Unlock the system to proceed.
Monitor type not correctly identified in Setup.
Setup and see if fixed disk and drive A: are properly identified.
address and display it on the screen. If it cannot locate the address, it
displays ????.
and display it on the screen. If it cannot locate the address, it displays
????.
Displayed after any recoverable error message. Press <F1> to start the
boot process or <F2> to enter Setup and change any settings.
Shadow RAM failed at offset
was detected.
The CMOS clock battery indicator shows the battery is dead. Replace
the battery and run Setup to reconfigure the system.
RAM cache failed the BIOS test. BIOS disabled the cache.
System CMOS RAM has been corrupted or modified incorrectly, perhaps
by an application program that changes data stored in CMOS. Run Setup
and reconfigure the system either by getting the default values and/or
making your own selections.
System RAM failed at offset
was detected.
nnnn
of the 64 KB block at which the error
nnnn
of the 64 KB block at which the error
54
Page 55

B Regulatory and Integration Information
This appendix contains:
• Safety standards, electromagnetic compatibility regulations, and product certification markings
for this motherboard
• Instructions and precautions for integrators who are installing this motherboard in a chassis
Regulatory Requirements
This printed circuit assembly meets the following safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
regulations when correctly installed in a compatible host computer.
Safety Standards
UL 1950 - CSA 950-95, 3rd edition, 28 July 1995
The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including Electrical Business
Equipment. (USA and Canada)
CSA C22.2 No. 950-95, 3rd Edition
The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including Electrical Business
Equipment. (Canada)
EN 60 950, 2nd Edition, 1992 (with Amendments 1, 2, and 3)
The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including Electrical Business
Equipment. (European Union)
IEC 950, 2nd edition, 1991 (with Amendments 1, 2, and 3)
The Standard for Safety of Information Technology Equipment including Electrical Business
Equipment. (International)
EMKO-TSE (74-SEC) 207/94
Summary of Nordic deviations to EN 60 950. (Norway, Sweden, Denmark, and Finland)
55
Page 56

Regulatory and Integration Information
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Regulations
CISPR 22, 2nd Edition, 1993
Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of Information
Technology Equipment. (International)
EN 55 022, 1995
Limits and methods of measurement of Radio Interference Characteristics of Information
Technology Equipment. (Europe)
EN 50 082-1, 1992
Generic Immunity Standard. Currently compliance is determined via testing to
IEC 801-2, -3 and -4. (Europe)
VCCI Class 2 (ITE)
Implementation Regulations for Voluntary Control of Radio Interference by Data Processing
Equipment and Electronic Office Machines. (Japan)
ICES-003, Issue 2
Interference-Causing Equipment Standard, Digital Apparatus. (Canada)
Product Certification Markings
This printed circuit assembly has the following product certification markings:
• European CE Mark
Marking on the board or shipping container.
• UL Recognition Mark
Marking is the UL File No. E139761 on the component side of the board and the PB No.
on the solder side of the board. Board material flammability is 94V-1 or -0.
• Canadian Compliance Mark
Marking is a small c followed by a stylized backward UR on the component side of the
board.
56
Page 57

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Installation Precautions
When you install and test the motherboard, observe all warnings and cautions in the installation
instructions.
To avoid injury, be careful of:
• Sharp pins on connectors
• Sharp pins on printed circuit assemblies
• Rough edges and sharp corners on the chassis
• Hot components (like processors, voltage regulators, and heat sinks)
• Damage to wires that could cause a short circuit
Observe all warnings and cautions that instruct you to refer computer servicing to qualified
technical personnel.
WARNING
Do not open the power supply. Risk of electric shock and burns from high voltage and rapid
overheating. Refer servicing of the power supply to qualified technical personnel.
Installation Instructions
CAUTION
Follow these guidelines to meet safety and regulatory requirements when installing this board
assembly.
Read and adhere to all of these instructions and the instructions supplied with the host computer
and associated modules. If the instructions for the host computer are inconsistent with these
instructions or the instructions for associated modules, contact the supplier’s technical support to
find out how you can ensure that your computer meets safety and regulatory requirements. If you
do not follow these instructions and the instructions provided by host computer and module
suppliers, you increase safety risk and the possibility of noncompliance with regional laws and
regulations.
57
Page 58

Regulatory and Integration Information
Ensure Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
Before computer integration, make sure that the host chassis, power supply, and other modules
have passed EMC testing using a motherboard with a microprocessor from the same family (or
higher) and operating at the same (or higher) speed as the microprocessor on this motherboard.
In the installation instructions for the host chassis, power supply, and other modules pay close
attention to the following:
• Certifications (see page 75)
• External I/O cable shielding and filtering
• Mounting, grounding, and bonding requirements
• Keying connectors when mismating of connectors could be hazardous
If the host chassis, power supply, and other modules have not passed applicable EMC testing
before integration, EMC testing must be conducted on a representative sample of the newly
completed computer.
Ensure Host Computer and Accessory Module Certifications
Make sure that the host computer, any added subassembly, such as a board or drive assembly, and
internal or external wiring, are certified for the region(s) where the end-product will be used.
Marks on the product are proof of certification. Certification marks are as follows:
In Europe
The CE marking signifies compliance with all relevant European requirements. If the host
computer does not bear the CE marking, obtain a supplier’s Declaration of Conformity to the
appropriate standards required by the European EMC Directive and Low Voltage Directive. Other
directives, such as the Machinery and Telecommunications Directives, may also apply depending
on the type of product. No regulatory assessment is necessary for low voltage DC wiring used
internally or wiring used externally when provided with appropriate overcurrent protection.
Appropriate protection is provided by a maximum 8-Amp current limiting circuit or a maximum 5Amp fuse or positive temperature coefficient (PTC) resistor. All Intel motherboards now have
PTCs on all external ports that provide DC power externally.
In the United States
A certification mark by a Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory (NRTL) such as UL, CSA, or
ETL signifies compliance with safety requirements. External wiring must be UL Listed and
suitable for the intended use. Internal wiring must be UL Listed or Recognized and rated for
applicable voltages and temperatures. The FCC mark (Class A for commercial or industrial only
or Class B for residential) signifies compliance with electromagnetic interference requirements.
In Canada
A nationally recognized certification mark such as CSA or cUL signifies compliance with safety
requirements. No regulatory assessment is necessary for low voltage DC wiring used internally or
wiring used externally when provided with appropriate overcurrent protection. Appropriate
protection is provided by a maximum 8-Amp current limiting circuit or a maximum 5-Amp fuse or
positive temperature coefficient (PTC) resistor. All Intel motherboards now have PTCs on all
external ports that provide DC power externally.
58
Page 59

AL440LX Motherboard Product Guide
Prevent Power Supply Overload
Unless the power supply has inherent overcurrent protection, do not overload the power supply
output. To avoid overloading the power supply, make sure that the calculated total current load of
all the modules within the computer is less than the output current rating of the power supply. If
you do not do this, the power supply could overheat, catch fire, or damage the insulation that
separates hazardous AC line circuitry from low-voltage user accessible circuitry. If the load drawn
by a module cannot be determined by the markings and instructions supplied with the module,
contact the module supplier’s technical support.
Place Battery Marking on the Computer
There is insufficient space on this motherboard to provide instructions for replacing and disposing
of the battery. The following warning must be placed permanently and legibly on the host
computer as near as possible to the battery.
WARNING
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace with only the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Dispose of
used batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Use Only for Intended Applications
This product was evaluated for use in computers that will be installed in offices, homes, schools,
computer rooms, and similar locations. The suitability of this product for other applications, (such
as medical, industrial, alarm systems, and test equipment) may require further evaluation.
59
Page 60

Regulatory and Integration Information
60
 Loading...
Loading...