Page 1

Intel Express
220T and 210T
Stackable Hubs
User Guide
Page 2

Year 2000 Capable
An Intel product, when used in accordance with its associated documentation, is "Year 2000 Capable" when, upon
installation, it accurately stores, displays, processes, provides, and/or receives date data from, into, and between
the twentieth and twenty-first centuries, including leap year calculations, provided that all other technology used
in combination with said product properly exchanges date data with it.
Copyright © 1998, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel Corporation, 5200 NE Elam Young Parkway, Hillsboro OR 97124-6497
Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this manual. Nor does Intel make any commitment to update the
information contained herein.
* Other product and corporate names may be trademarks of other companies and are used only for explanation and
to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
First Edition May 1998 694466-001
Page 3
Contents
220T and 210T Overview .....................................................................2
Feature Comparison..............................................................................3
Understanding 220T Hubs.................................................................... 4
220T Port LEDs.............................................................................4
220T Hub LEDs ............................................................................5
Understanding 210T Hubs.................................................................... 6
210T Port LEDs.............................................................................6
210T Hub LEDs ............................................................................7
Connecting to Devices..........................................................................8
Connection Guidelines .................................................................. 8
Stacking Hubs.......................................................................................9
Why Stack? ................................................................................... 9
Bridging Segments ...............................................................................10
Bridging 220T Hubs...................................................................... 10
Bridging 210T Hubs...................................................................... 11
Cabling Devices....................................................................................12
Media Requirements ..................................................................... 12
Straight-through vs. Crossover Cables.......................................... 12
Frequently Asked Questions ................................................................. 14
Regulatory Information and Warnings .................................................16
Hardware W arranty...............................................................................18
Troubleshooting....................................................................................20
Intel Customer Support.........................................................................21
1
Page 4
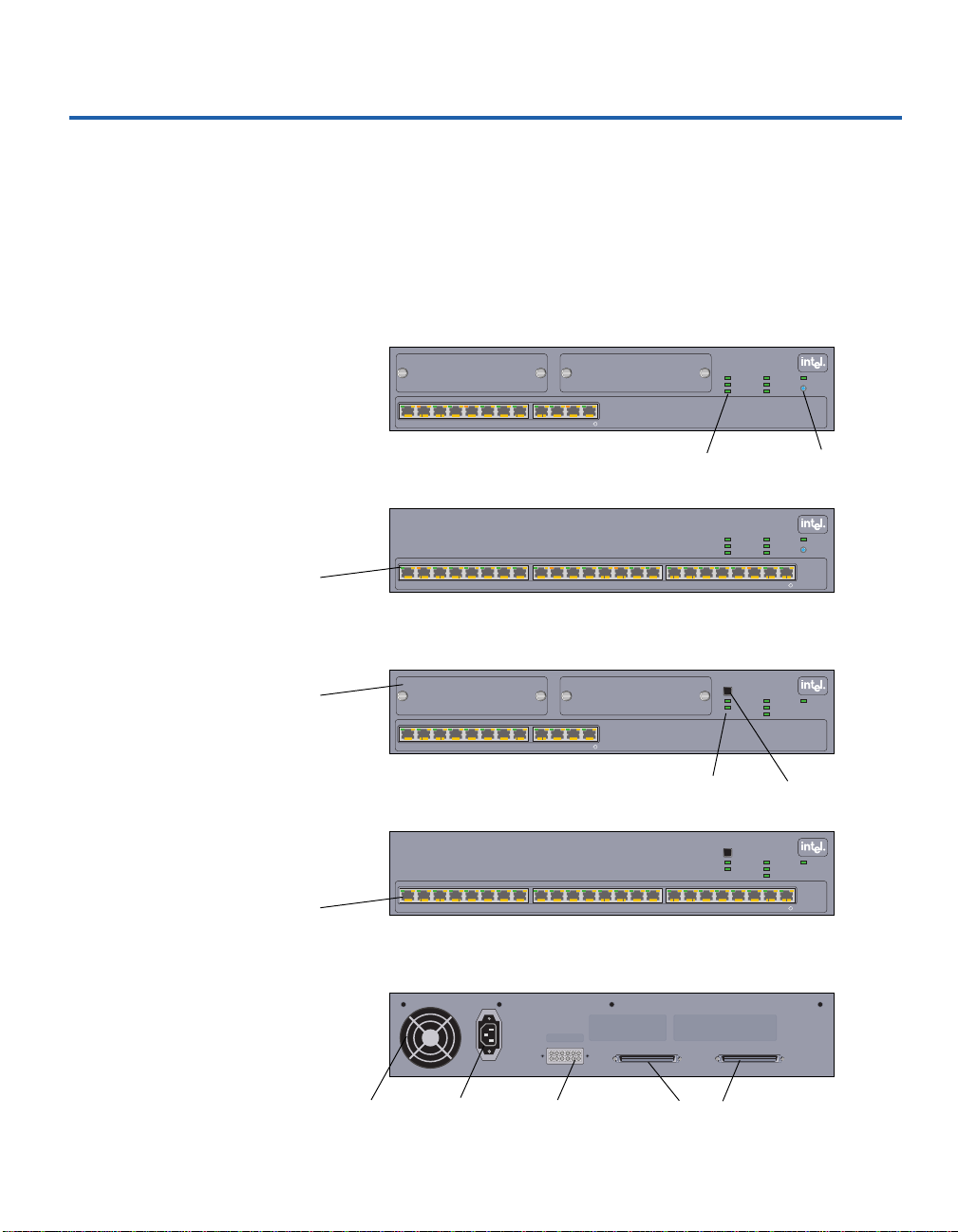
220T and 210T Overview
Features
This guide covers both the 12- and 24-port versions of the Intel® Express
220T Stackable Hub and the Express 210T Stackable Hub (formerly known
as the Express 10/100 Stackable Hub).
12-port 220T Hub
Intel Express 220T
Stackable Hub
Colls 10Mbps
Bridged
12345678 9101112
Class
I
Left (Orange/Green)
Orange = 10Mbps
Green = 100Mbps
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Colls 100Mbps
RPS
Managed
Status
Power
Enable/Disable
Bridging
Port LEDs
Expansion
Slot
Ports
24-port 220T Hub
12-port 210T Hub
12345678 9101112
24-port 210T Hub
Class
I
Left (Green)
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Hub LEDs
Hub LEDs
Intel Express 220T
Stackable Hub
Colls 10Mbps
Colls 100Mbps
Managed
Status
RPS
Intel Express 210T
Stackable Hub
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
Collision
100Base-TX
Managed
Status
Intel Express 210T
Stackable Hub
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
Collision
100Base-TX
Managed
Status
Bridging
Button
PowerBridged
Enable/Disable
Bridging
Left (Orange/Green)
24232219 212016 17 1810 11 12 151413876549123
Orange = 10Mbps
Green = 100Mbps
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
I
Class
Blink = Wrong speed
Power
Change Speed
Button
Power
24232219 212016 17 1810 11 12 151413876549123
Left (Green)
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Class
I
Input
100-120VAC/2.5A
200-240VAC/1.5A
47Hz-63Hz
Redundant Power Supply (RPS)
Fan AC
Power
Plug
RPS
Connector
(220T Hubs only)
Cascade
Connectors
2
Page 5
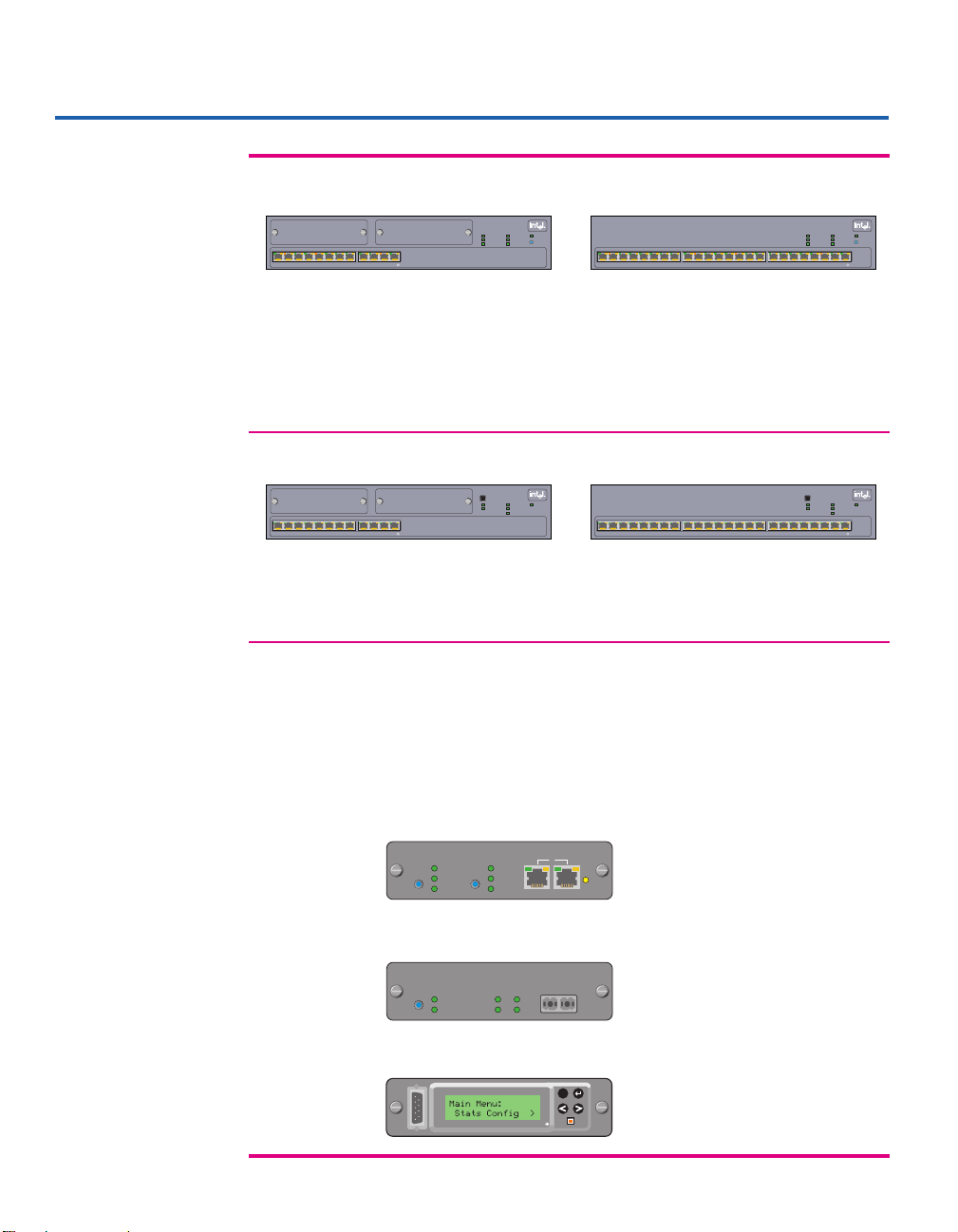
Feature Comparison
Change
duplex
Ethernet Module
MDI
MDI-X
Auto-negotiate
Full-duplex
Half-duplex
Change
duplex
Auto-negotiate
100 Mbps
10 Mbps
Coll
or
Xmt Link
Rcv Coll
TX RX
Fiber Module
Change
duplex
Half-duplex
Full-duplex
Express 220T (EE220TX12) Express 220T (EE220TX24)
Intel Express 220T
Stackable Hub
Colls 10Mbps
Bridged
Power
Colls 100Mbps
Managed
Enable/Disable
Bridging
Status
12345678 9101112
Left (Orange/Green)
Orange = 10Mbps
Green = 100Mbps
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
I
Class
Blink = Wrong speed
RPS
• 12 ports, autosensing 10Mbps or • 24 ports, autosensing 10Mbps or
100Mbps
per port
100Mbps
per port
• Bridges 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments • Bridges 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments
• Supports Redundant Power Supply (RPS) • Supports Redundant Power Supply (RPS)
• Two expansion slots for optional modules
Express 210T (EE210TX12) Express 210T (EE210TX24)
Intel Express 210T
Stackable Hub
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
Power
Collision
100Base-TX
Managed
12345678 9101112
•
All
12 ports operate at same •
Left (Green)
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Class I
Status
All
24 ports operate at same
speed (10 or 100Mbps) speed (10 or 100Mbps)
• Two expansion slots for optional modules
Intel Express 220T
Stackable Hub
Colls 10Mbps
Colls 100Mbps
RPS
Intel Express 210T
Stackable Hub
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
100Base-TX
PowerBridged
Managed
Enable/Disable
Bridging
Status
Left (Orange/Green)
24232219 212016 17 1810 11 12 151413876549123
Orange = 10Mbps
Green = 100Mbps
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
I
Class
Blink = Wrong speed
Power
Collision
Managed
Status
24232219 212016 17 1810 11 12 151413876549123
Left (Green)
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Class I
Common Features and Optional Modules
• Stack up to eight hubs (mixed 12- or 24-port)
• Compatible with Express 10/100 Stackable Hub
• Mix 220T, 210T, and Express 10/100 hubs in a stack
• Full-duplex support through the optional Ethernet Module.
• 100Base-FX support and full-duplex support through the optional Fiber Module.
• SNMP, RMON, and web-based management through the optional Management Module.
Management
Module
with RMON
Esc
Reset
3
Page 6
Understanding 220T Hubs
220T Port LEDs
The LEDs above each port provide information about the port’s
configuration and status.
Left side:
Orange/
Green
LED Status Meaning
Left Solid orange Device linked at 10Mbps.
Right Solid yellow Port disabled by management (not applicable
Solid green Device linked at 100Mbps.
Blinking orange Receive activity at 10Mbps.
Blinking green Receive activity at 100Mbps.
Off No link detected.
without optional Management Module).
Blinking yellow Speed mismatch (not applicable without
optional Management Module).
Erratic blinking yellow Port auto-disabled (partitioned). See below.
Blinking yellow and Out-of-specification cabling or port hardware
Status LED blinking problem. Try a different cable.
Right side:
Yellow
Partitioned ports
A port is automatically disabled (partitioned) by the hub when an invalid
condition occurs, such as too many consecutive collisions.
Once the hub sees a valid packet of data from the device or is able to
transmit data to the port, the hub automatically re-enables (unpartitions) the
port. Clients are usually not affected by a partitioned port because the port is
often unpartitioned very quickly.
Usually , a partitioned port indicates an overloaded network or a
malfunctioning device (like an adapter card) on the network. To alleviate an
overloaded network, segment so that fewer devices share the fixed amount
of bandwidth.
4
Page 7

220T Hub LEDs
The hub LEDs on the 220T indicate these conditions: collisions, status of
internal bridging, if the hub is managed, and the condition of the hub’s
power supply.
Intel Express 220T
Stackable Hub
Colls 10Mbps
Colls 100Mbps
RPS
Bridged
Managed
Status
Power
Enable/Disable
Bridging
LED Status Meaning
Colls 10Mbps Blinking Collisions detected on 10Mbps segment.
Colls 100Mbps Blinking Collisions detected on 100Mbps segment.
RPS On (green) Optional RPS is present and on standby.
Off No RPS unit present.
On (red) RPS is active; hub power supply failed.
Bridged On 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments can
communicate.
Off No communication between segments.
Managed On Hub is managed by the optional
Management Module.
Off Hub is not managed.
Status On Hub is operating normally.
Blinking Hub has an internal hardware orsoftware
problem. See descriptions for the right
port LED on page 4.
Managed and Status Blinking Hub failed to load its internal software.
Power On Hub is receiving power.
Off Hub is not receiving power.
5
Page 8
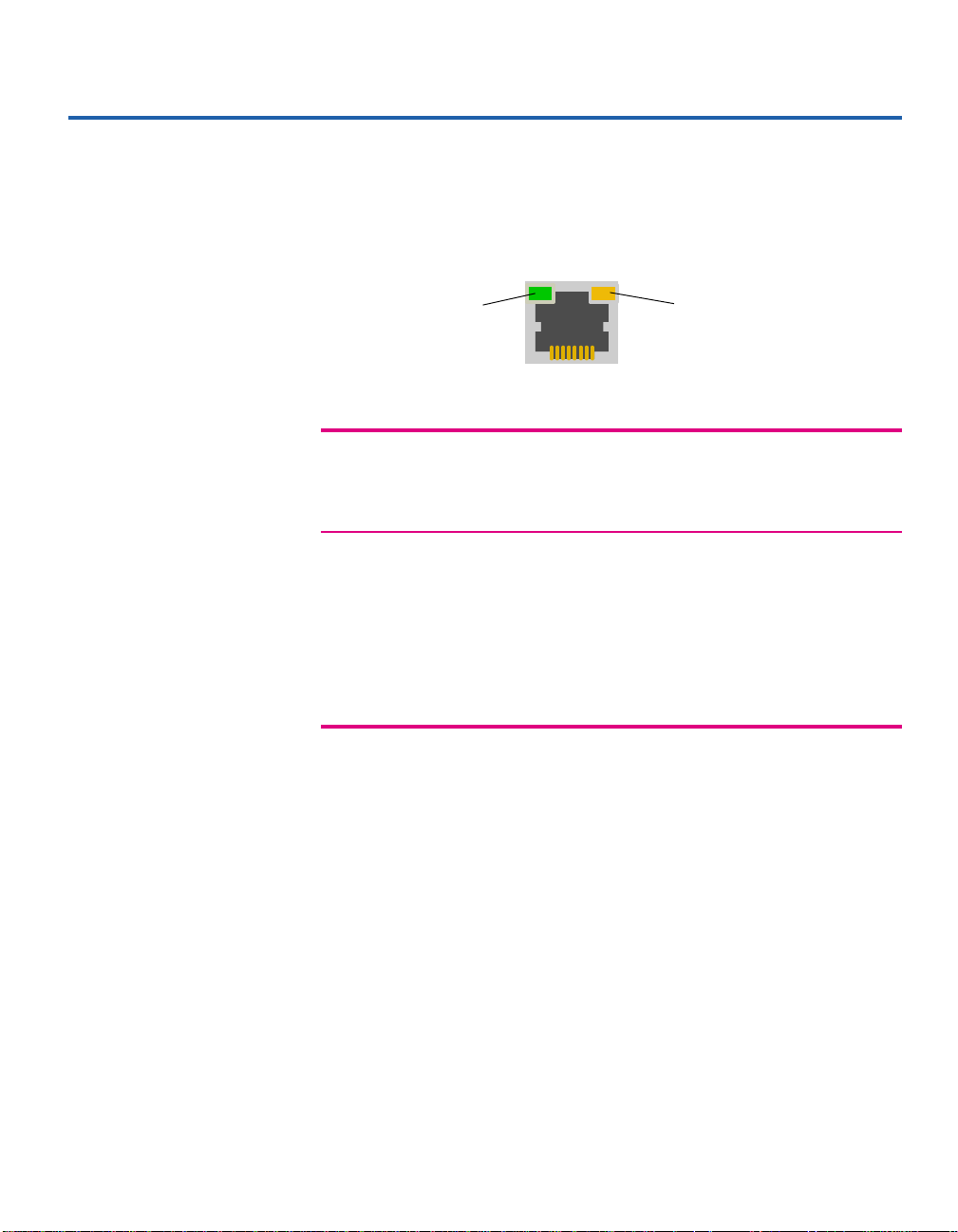
Understanding 210T Hubs
210T Port LEDs
The LEDs above each port provide information about the port’s
configuration and status.
Left side:
Green
LED Status Meaning
Left Solid green Port has a link.
Blinking green Receive activity at port.
Off No link detected.
Right Solid yellow Port disabled by management (not applicable
without optional Management Module).
Blinking yellow Speed mismatch. Check that device speed
and hub speed match.
Erratic blinking yellow Port auto-disabled (partitioned). See below.
Blinking yellow and Out-of-specification cabling or port hardware
Status LED blinking problem. Try a dif ferent cable.
Right side:
Yellow
Partitioned ports
A port is automatically disabled (partitioned off) by the hub when an invalid
condition occurs, such as too many consecutive collisions.
Once the hub sees a valid packet of data from the device, or is able to
transmit data to the port, the hub automatically re-enables (unpartitions) the
port. Clients are usually not affected by a partitioned port because the port is
often unpartitioned very quickly.
Usually , a partitioned port indicates an overloaded network or a
malfunctioning device (like an adapter card) on the network. To alleviate an
overloaded network, segment so that fewer devices share the fixed amount
of bandwidth.
6
Page 9

210T Hub LEDs
The 210T hub LEDs indicate these conditions: hub speed, collisions in the
hub or stack of hubs, and whether the hub is managed.
Intel Express 210T
Stackable Hub
LED Status Meaning
10Base-T On Hub is operating at 10Mbps.
100Base-TX On Hub is operating at 100Mbps.
Collision Blinking Collisions detected on hub (or stack).
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
100Base-TX
Off No collisions detected.
Collision
Managed
Status
LED brightens as more collisions are
detected. Continuous blinking indicates
an overloaded network.
Power
Managed On Hub is managed by the optional
Management Module.
Off Hub is not managed.
Status On Hub is operating normally.
Blinking Hub has an internal hardware or software
problem. See descriptions for the right
port LED on page 6.
Managed and Status Blinking Hub failed to load its internal software
Power On Hub is receiving power.
Off Hub is not receiving power.
7
Page 10

Connecting to Devices
Connection Guidelines
General
• Ports on the 220T and 210T hubs are half-duplex. To connect to a device
at full-duplex, you must use the optional Ethernet or Fiber Modules.
• 220T ports are autonegotiating and can operate at 10Mbps or 100Mbps.
The hub matches the highest possible speed of an attached device.
• All ports on the 210T hub operate at the same speed, either 10Mbps or
100Mbps. The ports cannot autonegotiate speed.
• If the 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments are bridged externally (through a
switch or Ethernet Module), be sure to turn off the hub’s internal bridge
before connecting any devices.
Cabling
• Use Category 5 unshielded twisted-pair (CAT 5 UTP) cable when
connecting 100Mbps devices to the hub.
• Use Category 3, 4, or 5 unshielded twisted-pair (CAT 3, 4, 5 UTP) cable
when connecting 10Mbps devices to the hub.
• Limit the cable length between devices to 100 meters.
• Use a crossover cable to connect the hub to a switch.
• Use a straight-through cable to connect the hub to a server or
workstation. For more information on cabling, see pages 12-13.
Daisy-chaining Hubs
• Don’t daisy-chain two hubs operating at 100Mbps with UTP cabling
(this violates the IEEE 802.3u Fast Ethernet specification for Class I
hubs). You must use Intel Cascade Cables (EE200CC).
• Hubs can be daisy-chained only if they are operating at 10Mbps.
• When connecting 10Mbps hubs, please note the following diagram.
100m (max)
1010 10 10
500m (max)
8
Page 11

Stacking Hubs
Why Stack?
The Express 220T and 210T hubs use the same connectors so they can be
stacked together or stacked in combination with the Express 10/100
Stackable hub. By stacking Intel hubs you can:
• increase the number of available ports, yet still treat the stack as a
single repeater.
• use a single Management Module to manage all hubs in the stack.
• use the 220T’s internal bridge so 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments can
communicate.
Intel Express 220T
Stackable Hub
Power
Colls 10Mbps
Bridged
Colls 100Mbps
Managed
Enable/Disable
Bridging
RPS
12345678 9101112
Express 220T Hub
Left (Orange/Green)
Orange = 10Mbps
Green = 100Mbps
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Class
I
Guidelines
• You must use an Intel Cascade Cable to stack the hubs. Do not daisy-
Status
+
chain hubs operating at 100Mbps with UTP cable.
Intel Cascade
Cable
Can
stack
with
Intel Express 210T
Stackable Hub
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
Collision
100Base-TX
Managed
Intel Express
10/100 Stackable Hub
Change Hub Speed
10Base-T
100Base-TX
Status
Collision
Managed
Status
24232219 212016 17 1810 11 12 151413876549123
Class
I
12345678 9101112
Express 210T Stackable Hub and
Express 10/100 Stackable Hub
(12- or 24-port versions).
Left (Green)
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Yellow)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Class
I
Power
Power
Left (Green)
Solid = Link
Blink = Activity
Right (Amber)
Solid = Disabled
Blink = Wrong speed
Connect the Cacade
Cables to the hubs as
shown in the diagram.
• A stack can consist of any combination of 220T, 210T, or
Express 10/100 hubs (12- or 24-port versions).
• You can stack up to eight hubs.
• When cabled correctly, the top hub in a stack is numbered hub 1.
• If there is more than one 220T hub in a stack, only one bridge is active
at a time. The lowest numbered 220T hub is the active bridge.
• All devices at the same speed are in the same segment. For example, all
devices at 10Mbps are in one segment and all devices at 100Mbps are
in another.
Input
100-120VAC/2.5A
200-240VAC/1.5A
Hub 1
Hub 2
Hub 3
47Hz-63Hz
Input
100-120VAC/2.5A
200-240VAC/1.5A
47Hz-63Hz
Input
100-120VAC/2.5A
200-240VAC/1.5A
47Hz-63Hz
Redundant Power Supply (RPS)
Redundant Power Supply (RPS)
Redundant Power Supply (RPS)
Intel Cascade
Cable (EE200CC)
9
Page 12

Bridging Segments
Bridging 220T Hubs
A bridge allows two segments to communicate with each other. Typically, a
bridge connects segments operating at different speeds, but it can also
connect segments operating at the same speed. By default, the Express
220T’s internal bridge is active so 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments are
automatically bridged.
The 220T’s Enable/Disable bridging button allows the hub’s internal bridge
to be turned off. Disabling the internal bridge prevents a loopback error if
the 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments are bridged externally (through a
switch for example). Another reason to disable the bridge is to keep traffic
isolated on each segment.
Guidelines for bridging a stack of 220T hubs
• Only one bridge is active at a time. If that hub fails or is removed, the
next 220T automatically provides bridging for the stack.
• When active, the Bridged LED is illuminated on all hubs in the stack.
• Pressing the Enable/Disable Bridging button on any hub turns bridging
on or off for the entire stack.
10
• Disable the internal bridge if you are bridging segments externally
(through a switch) to prevent a loopback condition.
Example 1: 220T hubs stacked with 210T hubs
A quick way to bridge 210Ts or Express 10/100 hubs is to add a 220T to the
stack. The ports at 100Mbps on the 220T hubs will be in the same segment
as the 210T hub operating at 100Mbps; just as the ports at 10Mbps on the
220T hubs will be in the same segment as the 210T hub at 10Mbps.
All ports at 10Mbps
share the same
segment
220T (Hub 1)
210T (Hub 2)
220T (Hub 3)
210T (Hub 4)
10Mbps 100Mpbs
100Mbps
10Mbps 100Mpbs
Bridge
10Mbps
This 220T provides
bridging for all hubs
in the stack.
All ports at 100Mbps share
the same segment
Page 13

Bridging 210T Hubs
100Mbps
10Mbps
10Mbps
100Mbps
Ethernet
Module
All ports on the Express 210T hub operate at the same speed (10Mbps or
100Mbps) so the hub belongs to only one segment at a time. The 210T hub
doesn’t contain an internal bridge. To communicate, the segments must be
bridged by a 220T hub or by an external device (like a 10/100 switch).
Example 2: Bridging with a 10/100 switch
In a stack of 210T and Express 10/100 hubs, the hubs at 10Mbps can
communicate and the hubs at 100Mbps can communicate. However, hubs at
10Mbps can’t communicate with hubs at 100Mbps. You can use a switch
with individual ports that can operate at 10Mbps or 100Mbps to bridge hubs.
Use a crossover
cable to connect
210T (Hub 1)
210T (Hub 2)
100Mbps
10Mbps
Cascade
Cable
the hub to the
switch.
10/100 (Hub 3)
10/100 (Hub 4)
100Mbps
10Mbps
10/100 switch
Example 3: Bridging with an Ethernet Module
Another way to bridge segments is to use an Ethernet Module. Plug the
module into the expansion port of a 12-port hub operating at either 10Mbps
or 100Mbps. Next, use UTP cable to connect the module to a hub operating
at the other speed. Since the Ethernet Module is a switched port, it bridges
the two segments.
Use a UTP cable
210T (Hub 1)
210T (Hub 2)
10/100 (Hub 3)
10/100 (Hub 4)
Cascade
Cable
to connect from
a port on the
module to a port
on the hub.
11
Page 14

Cabling Devices
1
8
Media Requirements
Incorrect cabling is often the cause of network configuration problems.
Read the next two pages if you’re unsure of your requirements.
100Base-TX
The 100Base-TX Fast Ethernet specification requires that you use
CAT 5 UTP cabling to operate at 100Mbps. If you use lower grade cabling
(CAT 3 or CAT 4), you may get a connection, but will soon experience data
loss or slow performance. You’re limited to 100 meters between any two
devices.
10Base-T
The 10Base-T Ethernet specification allows you to use CAT 3, CAT 4, or
CAT 5 UTP cabling. You’re limited to 100 meters between any two devices.
100Base-FX
The optional Fiber Module lets you connect to a switch, bridge, or router up
to 160 meters away at half-duplex or up to 2 km at full-duplex. Use 62.5/
125µ multimode fiber optic cable with an SC-type fiber optic connector.
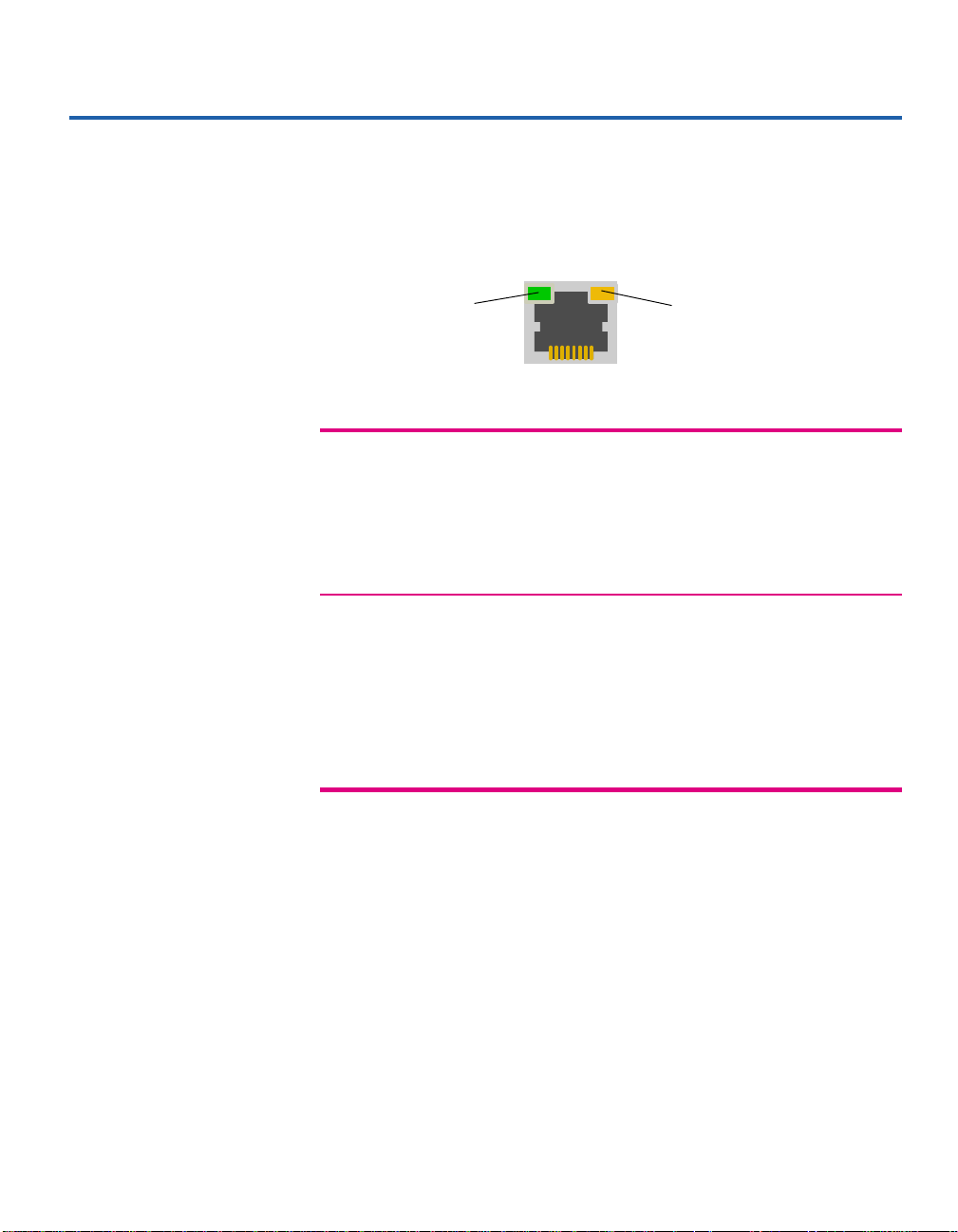
Straight-through vs. crossover cables
Hub ports are wired MDI-X, so use a straight-through cable when
connecting to a workstation or server (network adapter cards are wired
MDI). For direct connection to another MDI-X port, use a crossover cable.
Here are the pin arrangements for the hub’s ethernet jack and the typical
RJ-45 connector.
Clip
12
Pin 8 Pin 1
Page 15

Straight-through UTP cable
Hub (MDI-X) Adapter (MDI)
100
1 (RX+) 1 (TX+)
2 (RX-) 2 (TX-)
3 (TX+) 3 (RX+)
6 (TX-) 6 (RX-)
4 Not used 4 Not used
5 Not used 5 Not used
7 Not used 7 Not used
8 Not used 8 Not used
Crossover UTP cable
Hub (MDI-X) Switch (MDI-X)
100
1 (RX+) 1 (RX+)
2 (RX-) 2 (RX-)
3 (TX+) 3 (TX+)
6 (TX-) 6 (TX-)
4 Not used 4 Not used
5 Not used 5 Not used
7 Not used 7 Not used
8 Not used 8 Not used
13
Page 16

Frequently Asked Questions
Can I stack Intel Express 220T Stackable Hubs with Intel
Express 210T Stackable Hubs or Intel Express 10/100 Stackable
Hubs?
Yes. These hubs use the same Intel Cascade Cable and connectors.
Can I stack Intel Express 220T or 210T Stackable Hubs with Intel
Express 100Base-TX Stackable Hubs?
No. The hubs use a different Cascade Cable and connectors. However ,
both are 100Base-TX compliant and can exist in the same network.
How do I get devices running at 10Mbps to talk to devices
running at 100Mbps?
The 220T hub’s internal bridge allows 10Mbps and 100Mbps segments
to communicate with each other. By default the 220T’s internal bridge is
active. If the segments aren’t communicating, press the Enable/Disable
Bridging button on the front panel to toggle the feature.
The 210T hubs operate at either 10Mbps or 100Mbps and can exist in the
same stack. However, the hubs operating at 10Mbps and the hubs
operating at 100Mbps are on separate network segments. To enable the
segments to communicate, add a 220T hub to the stack or use another
device to bridge the segments, such as a switch or an optional Ethernet
Module. See pages 10-11 for more information
14
Can I set the speed on individual ports?
On the 220T hub all ports are autosensing and operate at either 10Mbps
or 100Mbps, depending on the speed of the attached device. To force port
speed on the 220T, you must purchase the optional Management Module
(EE200MM).
On the 210T hub, all ports operate at the same speed (10Mbps or
100Mbps). Individual port speed cannot be set.
Can I configure a full-duplex link from the 220T or 210T hubs to
another device?
Not directly, because the ports on the 220T and 210T hubs are capable of
only half-duplex. However, you can configure a full-duplex link through
the optional Ethernet Module or Fiber Module. The external ports on
these modules are switched ports and are capable of full-duplex.
Page 17

Can I daisy-chain a 100Mbps hub to the 220T hub with UTP
cabling?
No. Only hubs operating at 10Mbps can be daisy-chained to the 220T.
You must use an Intel Cascade Cable to connect Intel hubs operating at
100Mbps.
Can I daisy-chain 210T hubs together with UTP cabling?
Only if the hubs are operating at 10Mbps. You must use an Intel Cascade
Cable to connect hubs at 100Mbps. Also, daisy-chained hubs cannot be
managed as a single stack.
I have a 210T hub at 10Mbps and another 210T at 100Mbps
connected with an Intel Cascade Cable. Can they talk to each
other?
No. All 210T hubs operating at 100Mbps are in one segment (or collision
domain) and all 210T hubs at 10Mbps are in a separate segment. For
more information, see page 10.
Why would I stack hubs operating at 10Mbps to hubs at
100Mbps?
By putting hubs running at 10Mbps and 100Mbps in the same stack, you
need only one Management Module to control the entire stack. This
simplifies the network management configuration. Remember to connect
the hubs with an Intel Cascade Cable, not UTP cabling.
15
Page 18

Regulatory Information and Warnings
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is
likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
The user is cautioned that changes and modifications made to the equipment without approval of the manufacturer could void the user’s
authority to operate this equipment.
Manufacturer Declaration
This certifies that the Intel Express 220T Stackable Hub and Intel Express 210T Stackable Hub complies with the EU Directive 89/336/
EEC, using the EMC standards EN55022 (Class A) and EN50082-1. These products also meet or exceed EN 60950 (safety)
requirements. These products have been tested and verified to meet CISPR 22 Class A requirements.
WARNING
This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required
to take adequate measures.
Internal access to Intel Express Stackable Hubs is intended only for qualified service personnel. Do not remove any covers except
Expansion Slot covers when optional modules are being installed.
WARNING
The system is designed to operate in a typical office environment. Choose a site that is:
Do not attempt to modify or use the supplied AC power cord if it is not the exact type required.
Ensure that the system is disconnected from its power source and from all telecommunications links, networks, or modems lines
whenever the chassis cover is to be removed. Do not operate the system with the cover removed.
· Clean and free of airborne particles (other than normal room dust).
· Well ventilated and away from sources of heat including direct sunlight.
· Away from sources of vibration or physical shock.
· Isolated from strong electromagnetic fields produced by electrical devices.
· In regions that are susceptible to electrical storms, we recommend you plug your system into a surge suppressor and
disconnect telecommunication lines to your modem during an electrical storm.
· Provided with a properly grounded wall outlet.
AVERTISSEMENT
Le système a été conçu pour fonctionner dans un cadre de travail normal. L’emplacement choisi doit être:
Ne pas utiliser ni modifier le câble d’alimentation C. A. fourni, s’il ne correspond pas exactement au type requis.
Assurez vous que le système soit débranché de son alimentation ainsi que de toutes les liaisons de télécomunication, des réseaux, et des
lignes de modem avant d’enlever le capot. Ne pas utiliser le système quand le capot est enlevé.
· Propre et dépourvu de poussière en suspension (sauf la poussière normale).
· Bien aéré et loin des sources de chaleur, y compris du soleil direct.
· A l’abri des chocs et des sources de ibrations.
· Isolé de forts champs magnétiques géenérés par des appareils électriques.
· Dans les régions sujettes aux orages magnétiques il est recomandé de brancher votre système à un supresseur de surtension,
et de débrancher toutes les lignes de télécommunications de votre modem durant un orage.
· Muni d’une prise murale correctement mise à la terre.
16
Page 19

WARNUNG
Das System wurde für den Betrieb in einer normalen Büroumgebung entwickelt. Der entwickelt. Der Standort sollte:
Versuchen Sie nicht, das mitgelieferte Netzkabel zu ändern oder zu verwenden, wenn es sich nicht um genau den erforderlichen Typ
handelt.
Das System darf weder an eine Stromquelle angeschlossen sein noch eine Verbindung mit einer Telekommunikationseinrichtung, einem
Netzwerk oder einer Modem-Leitung haben, wenn die Gehäuseabdeckung entfernt wird. Nehmen Sie das System nicht ohne die
Abdeckung in Betrieb.
· sauber und staubfrei sein (Hausstaub ausgenommen);
· gut gelüftet und keinen Heizquellen ausgesetzt sein (einschließlich direkter Sonneneinstrahlung);
· keinen Erschütterungen ausgesetzt sein;
· keine starken, von elektrischen Geräten erzeugten elektromagnetischen Felder aufweisen;
· in Regionen, in denen elektrische Stürme auftreten, mit einem Überspannungsschutzgerät verbunden sein; während eines
elektrischen Sturms sollte keine Verbindung der Telekommunikationsleitungen mit dem Modem bestehen;
· mit einer geerdeten Wechselstromsteckdose ausgerüstet sein.
AVVERTENZA
Il sistema è progettato per funzionare in un ambiente di lavoro tipico. Scegliere una postazione che sia:
· Pulita e libera da particelle in sospensione (a parte la normale polvere presente nell’ambiente).
· Ben ventilata e lontana da fonti di calore, compresa la luce solare diretta.
· Al riparo da urti e lontana da fonti divibrazione.
· Isolata dai forti campi magnetici prodotti da dispositivi elettrici.
· In aree soggette a temporali, è consigliabile collegare il sistema ad un limitatore di corrente. In caso di temporali, scollegare
le linee di comunicazione dal modem.
· Dotata di una presa a muro correttamente installata.
Non modificare o utilizzare il cavo di alimentazione in c. a. fornito dal produttore, se non corrisponde esattamente al tipo
richiesto.
Prima di rimuovere il coperchio del telaio, assicurarsi che il sistema sia scollegato dall’alimentazione, da tutti i collegamenti di
comunicazione, reti o linee di modem. Non avviare il sistema senza aver prima messo a posto il coperchio.
ADVERTENCIAS
El sistema está diseñado para funcionar en un entorno de trabajo normal. Escoja un lugar:
· Limpio y libre de partículas en suspensión (salvo el polvo normal)
· Bien ventilado y alejado de fuentes de calor, incluida la luz solar directa.
· Alejado de fuentes de vibración.
· Aislado de campos electromagnéticos fuertes producidos por dispositivos eléctricos.
· En regiones con frecuentes tormentas eléctricas, se recomienda conectar su sistema a un eliminador de sobrevoltage y
desconectar el módem de las líneas de telecomunicación durante las tormentas.
· Previsto de una toma de tierra correctamente instalada.
No intente modificar ni usar el cable de alimentación de corriente alterna, si no se corresponde exactamente con el tipo requerido.
Asegúrese de que cada vez que se quite la cubierta del chasis, el sistema haya sido desconectado de la red de alimentación y de todos lo
enlaces de telecomunicaciones, de red y de líneas de módem. No ponga en funcionamiento el sistema mientras la cubierta esté quitada.
17
Page 20

Hardware Warranty
Limited Hardware Warranty
Intel warrants to the original owner that the hardware product delivered in this package will be free from defects in material and workmanship for three (3)
years following the latter of: (i) the date of purchase only if you register by returning the registration card as indicated thereon with proof of purchase; or (ii)
the date of manufacture; or (iii) the registration date if by electronic means provided such registration occurs within thirty (30) days from purchase. This
warranty does not cover the product if it is damaged in the process of being installed. Intel recommends that you have the company from whom you
purchased this product install the product.
INTEL RESER VES THE RIGHT TO FILL YOUR ORDER WITH A PRODUCT CONTAINING NEW OR REMANUFACTURED COMPONENTS. THE
ABOVE WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTY, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, ANY WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR ANY WARRANTY ARISING OUT OF ANY PROPOSAL, SPECIFICATION, SAMPLE OR OTHERWISE.
This warranty does not cover replacement of products damaged by abuse, accident, misuse, neglect, alteration, repair, disaster, improper installation or
improper testing. If the product is found to be otherwise defective, Intel, at its option, will replace or repair the product at no charge except as set forth
below, provided that you deliver the product along with a return material authorization (RMA) number either to the company from whom you purchased it
or to Intel (North America only). If you ship the product, you must assume the risk of damage or loss in transit. You must use the original container (or the
equivalent) and pay the shipping charge. Intel may replace or repair the product with either new or remanufactured product or parts, and the returned product
becomes Intel’s property. Intel warrants the repaired or replaced product to be free from defects in material and workmanship for a period of the greater of:
(i) ninety (90) days from the return shipping date; or (ii) the period of time remaining on the original three (3) year warranty.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may have other rights which vary from state to state. All parts or components contained in this product
are covered by Intel’s limited warranty for this product; the product may contain fully tested, recycled parts, warranted as if new. For warranty information
call one of the numbers below.
Returning a Defective Product (RMA)
Before returning any product, contact an Intel Customer Support Group and obtain an RMA number by calling:
North America only: (916) 377-7000
Other locations: Return the product to the place of purchase.
If the Customer Support Group verifies that the product is defective, they will have the Return Material Authorization Department issue you an RMA
number to place on the outer package of the product. Intel cannot accept any product without an RMA number on the package.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY AND REMEDIES
INTEL SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY FOR ANY INDIRECT OR SPECULATIVE DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL AND SPECIAL DAMAGES) ARISING FROM THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT,
WHETHER ARISING OUT OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE, TORT, OR UNDER ANY WARRANTY, IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER INTEL HAS
ADVANCE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF ANY SUCH DAMAGES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF USE, INFRINGEMENT
OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, BUSINESS INTERRUPTIONS, AND LOSS OF PROFITS, NOTWITHSTANDING THE FOREGOING, INTEL’S
TOT AL LIABILITY FOR ALL CLAIMS UNDER THIS AGREEMENT SHALL NOT EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT. THESE
LIMITATIONS ON POTENTIAL LIABILITIES WERE AN ESSENTIAL ELEMENT IN SETTING THE PRODUCT PRICE. INTEL NEITHER
ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANYONE TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITIES.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the above limitations or exclusions may not apply to you.
Critical Control Applications: Intel specifically disclaims liability for use of the hardware product in critical control applications (including, for example
only, safety or health care control systems, nuclear energy control systems, or air or ground traffic control systems) by Licensee or Sublicensees, and such
use is entirely at the user’s risk. Licensee agrees to defend, indemnify, and hold Intel harmless from and against any and all claims arising out of use of the
hardware product in such applications by Licensee or Sublicensees.
Software: Software provided with the hardware product is not covered under the hardware warranty described above. See the applicable software license
agreement which shipped with the hardware product for details on any software warranty.
18
Page 21

Limited Hardware Warranty (Europe only)
Intel warrants to the original owner that the hardware product delivered in this package will be free from defects in material and workmanship for three (3)
years following the latter of: (i) the date of purchase only if you register by returning the registration card as indicated thereon with proof of purchase; or (ii)
the date of manufacture; or (iii) the registration date if by electronic means provided such registration occurs within thirty (30) days from purchase. This
warranty does not cover the product if it is damaged in the process of being installed. Intel recommends that you have the company from whom you
purchased this product install the product.
INTEL RESER VES THE RIGHT TO FILL YOUR ORDER WITH A PRODUCT CONTAINING NEW OR REMANUFACTURED COMPONENTS. THE
ABOVE WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTY, WHETHER EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, ANY WARRANTY OF NONINFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, SATISFACT ORY QUALITY, FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR ANY WARRANTY ARISING OUT OF ANY PROPOSAL, SPECIFICATION, SAMPLE OR OTHERWISE.
This warranty does not cover replacement of products damaged by abuse, accident, misuse, neglect, alteration, repair, disaster, improper installation or
improper testing. If the product is found to be otherwise defective, Intel, at its option, will replace or repair the product at no charge except as set forth
below, provided that you deliver the product along with a return material authorization (RMA) number either to (a) the company from whom you purchased
it or (b) to Intel, North America only (if purchased in Europe you must deliver the product to “(a)”. If you ship the product, you must assume the risk of
damage or loss in transit. You must use the original container (or the equivalent) and pay the shipping charge. Intel may replace or repair the product with
either new or remanufactured product or parts, and the returned product becomes Intel’s property. Intel warrants the repaired or replaced product to be free
from defects in material and workmanship for a period of the greater of: (i) ninety (90) days from the return shipping date; or (ii) the period of time
remaining on the original three (3) year warranty.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may have other rights which vary from state to state. All parts or components contained in this product
are covered by Intel’s limited warranty for this product; the product may contain fully tested, recycled parts, warranted as if new. For warranty information
call one of the numbers below.
Returning a Defective Product (RMA)
Before returning any product, contact an Intel Customer Support Group and obtain an RMA number by calling the non-toll free numbers below:
Country Number Language
France +44 1793 404988 French
Germany +44 1793 404777 German
Italy +44 1793 404141 Italian
UK +44 1793 404900 English
If the Customer Support Group verifies that the product is defective, they will have the Return Material Authorization Department issue you an RMA
number to place on the outer package of the product. Intel cannot accept any product without an RMA number on the package.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY AND REMEDIES
INTEL SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY FOR ANY INDIRECT OR SPECULATIVE DAMAGES (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL AND SPECIAL DAMAGES) ARISING FROM THE USE OF OR INABILITY TO USE THIS PRODUCT,
WHETHER ARISING OUT OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE, TORT, OR UNDER ANY WARRANTY, IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER INTEL HAS
ADVANCE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF ANY SUCH DAMAGES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF USE, INFRINGEMENT
OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, BUSINESS INTERRUPTIONS, AND LOSS OF PROFITS, NOTWITHSTANDING THE FOREGOING, INTEL’S
TOT AL LIABILITY FOR ALL CLAIMS UNDER THIS AGREEMENT SHALL NOT EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT. THESE
LIMITATIONS ON POTENTIAL LIABILITIES WERE AN ESSENTIAL ELEMENT IN SETTING THE PRODUCT PRICE. INTEL NEITHER
ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANYONE TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITIES.
Critical Control Applications: Intel specifically disclaims liability for use of the hardware product in critical control applications (including, for example
only, safety or health care control systems, nuclear energy control systems, or air or ground traffic control systems) by Licensee or Sublicensees, and such
use is entirely at the user’s risk. Licensee agrees to defend, indemnify, and hold Intel harmless from and against any and all claims arising out of use of the
hardware product in such applications by Licensee or Sublicensees.
Software: Software provided with the hardware product is not covered under the hardware warranty described above. See the applicable software license
agreement which shipped with the hardware product for details on any software warranty.
This limited hardware warranty shall be governed by and construed in accordance with the laws of England and Wales. The courts of England shall have
exclusive jurisdiction regarding any claim brought under this warranty.
19
Page 22

Troubleshooting
No link (left LED is off).
• Remove the cable and plug it in again. Wait up to six seconds for a link.
• Make sure you’re using the right type of cable (straight-through or
crossover) for the device you want to connect to. If you’re using the
wrong cable, the left LED above the port will not come on.
• Make sure the device you’ve connected to a port is a 10Base-T or
100Base-TX device. The Express 220T and 210T Stackable Hubs don’ t
support 100Base-T4 devices running at 100Mbps. However, they do
support T4 devices running at 10Mbps.
• Check the speed and duplex settings on the PC’s network adapter.
No link, yellow (right) LED above port is blinking slowly.
The hub’s speed setting doesn’ t match the attached device’s speed setting.
T o correct the problem, change either the hub or device speed setting so
they match.
Link, but yellow (right) LED above port is blinking erratically.
The port is partitioned (auto-disabled). This condition is usually caused by
a malfunctioning network adapter or an overloaded network segment. For
more information, see page 4.
20
Intermittent loss of link.
• You may be using the wrong grade of cable. The wrong cable grade can
cause erratic performance and you may eventually lose the connection
between the port and the attached device. For more information, see
page 12.
• If hubs are operating in a 100Mbps environment, make sure you use an
Intel Cascade Cable, not UTP cable, to connect the hubs.
• Make sure the device connected to the hub port is configured for
half-duplex operation. Hubs operate at half-duplex only.
• A cable segment somewhere in your collision domain is too long. Make
sure none of your UTP cabling is longer than 100 meters.
• Make sure your stack contains no more than eight hubs.
10Mbps or 100Mbps devices can’t communicate with each other.
Internal bridging might be disabled. Check to see if the Bridged LED on
the 220T hub is on. If it is not, press the Enable/Disable Bridging button.
Page 23

Intel Customer Support
Automated Support
You can reach Intel’s automated support services 24 hours a day, every day
at no charge. The services contain the most up-to-date information about
Intel products. You can access installation instructions, troubleshooting
information, and general product information.
World Wide Web & Internet FTP
Access Intel’s World Wide Web page or download information using anonymous FTP.
How to Access:
WWW
Customer Support:
News:
news://cs.intel.com
FTP
Host:
download.intel.com
http://support.intel.com
Customer Support Technicians
Free support for 90 days: You can speak with our technical support
professionals free of charge for 90 days after your initial call.
North America only: (916) 377-7000
Other support services: You can purchase a range of support services,
including 24 hour support, per incident support, on-site service, and
software and hardware maintenance agreements. For details about the Intel
Support Service options, go to our Web site at http://support.intel.com/
services and choose your geography.
Worldwide access: Intel has technical support centers worldwide. Many of
the centers are staffed by technicians who speak the local languages. Go to
our Web site at http://www.intel.com/intel/contact to find the Intel support
center for your geography.
Country Number Language
France +44 1793 404988 French
Germany +44 1793 404777 German
Italy +44 1793 404141 Italian
UK +44 1793 404900 English
If you don’t have access to automated services, contact your local dealer or
distributor. Or call +1-916-377-7000 from 07:00 to 17:00 Monday through
Friday , U.S. Pacific Time.
04/20/98
21
Page 24

694466-001
 Loading...
Loading...