Page 1

Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device
User’s Guide
Page 2

Product Model
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device product models:
WUD2011BWW
WUD2011BSG
Copyright
Copyright © 2001, Intel Corporation. All rights reserved.
Intel Corporation, 5200 N.E. Elam Young Parkway, Hillsboro, OR 97124-6497
Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility for errors or omissions in this document. Nor does Intel make any commitment to update the
information contained herein.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
†Other product and corporate names mentioned herein may be trademarks of other companies and are used only for explanation and to the owners’
benefit, without intent to infringe.
Patents
This product is covered by one or more of the following U.S. and foreign patents:
U.S. Patent No.
4,360,798; 4,369,361; 4,387,297; 4,460,120; 4,496,831; 4,593,186; 4,603,262; 4,607,156; 4,652,750; 4,673,805; 4,736,095; 4,758,717; 4,816,660;
4,845,350; 4,896,026; 4,897,532; 4,923,281; 4,933,538; 4,992,717; 5,015,833; 5,017,765; 5,021,641; 5,029,183; 5,047,617; 5,103,461; 5,113,445;
5,130,520; 5,140,144; 5,142,550; 5,149,950; 5,157,687; 5,168,148; 5,168,149; 5,180,904; 5,216,232; 5,229,591; 5,230,088; 5,235,167; 5,243,655;
5,247,162; 5,250,791; 5,250,792; 5,260,553; 5,262,627; 5,262,628; 5,266,787; 5,278,398; 5,280,162; 5,280,163; 5,280,164; 5,280,498; 5,304,786;
5,304,788; 5,306,900; 5,321,246; 5,324,924; 5,337,361; 5,367,151; 5,373,148; 5,378,882; 5,396,053; 5,396,055; 5,399,846; 5,408,081; 5,410,139;
5,410,140; 5,412,198; 5,418,812; 5,420,411; 5,436,440; 5,444,231; 5,449,891; 5,449,893; 5,468,949; 5,471,042; 5,478,998; 5,479,000; 5,479,002;
5,479,441; 5,504,322; 5,519,577; 5,528,621; 5,532,469; 5,543,610; 5,545,889; 5,552,592; 5,557,093; 5,578,810; 5,581,070; 5,589,679; 5,589,680;
5,608,202; 5,612,531; 5,619,028; 5,627,359; 5,637,852; 5,664,229; 5,668,803; 5,675,139; 5,693,929; 5,698,835; 5,705,800; 5,714,746; 5,723,851;
5,734,152; 5,734,153; 5,742,043; 5,745,794; 5,754,587; 5,762,516; 5,763,863; 5,767,500; 5,789,728; 5,789,731; 5,808,287; 5,811,785; 5,811,787;
5,815,811; 5,821,519; 5,821,520; 5,823,812; 5,828,050; 5,850,078; 5,861,615; 5,874,720; 5,875,415; 5,900,617; 5,902,989; 5,907,146; 5,912,450;
5,914,478; 5,917,173; 5,920,059; 5,923,025; 5,929,420; 5,945,658; 5,945,659; 5,946,194; 5,959,285; D305,885; D341,584; D344,501; D359,483;
D362,453; D363,700; D363,918; D370,478; D383,124; D391,250; D405,077; D406,581; D414,171; D414,172
Invention No. 55,358; 62,539; 69,060; 69,187 (Taiwan); No. 1,601,796; 1,907,875; 1,955,269 (Japan);
European Patent 367,298; 367,299; 367,300; 414,281; UK 2,072,832; France 81/03938; Italy 1,138,713
A69522-002
ii Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide
Page 3

About This Document
Reference Documents
This reference guide refers to the following documents:
Part Number Document Title
A69587-002 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Quick Install Guide
Conventions
Keystrokes are indicated as follows:
ENTER identifies a key.
FUNC, CTRL, C identifies a key sequence. Press and release each key in turn.
Press A+B press the indicated keys simultaneously.
Hold A+B press and hold the indicated keys while performing or waiting for another
function. Used in combination with another keystroke.
Typeface conventions used include.
About This Document
<angles> indicates mandatory parameters in syntax.
[brackets] for command line, indicates available parameters; in configuration files,
brackets act as separators for options.
GUI Screen text
Italics indicates the first use of a term, book title, variable or menu title.
Bold indicates important user information, license provisions or warranty
Screen dialog
Screen text
Terminal text
Terminal text
Terminal textTerminal text
URL
indicates the name of a control in a GUI-based application.
conditions.
indicates screen dialog and user input options, and the exact syntax of items.
indicates text and data displayed in an application screen on a computer
monitor.
indicates text shown in a radio terminal LCD screen.
indicates a Uniform Resource Locator, such as a Web page address.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide iii
Page 4
About This Document
This document uses the following for certain conditions or information:
indicates tips or special requirements.
indicates conditions that can cause equipment damage or data loss.
indicates a potentially dangerous condition or procedure that only Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B
LAN USB Device-trained personnel should attempt to correct or perform.
iv Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide
Page 5

Contents
Contents
Product Model............................................................................................................................ ii
Copyright ................................................................................................................................... ii
Patents ........................................................................................................................................ ii
About This Document............................................................................................ iii
Reference Documents ............................................................................................................... iii
Conventions .............................................................................................................................. iii
Contents ...................................................................................................................v
Chapter 1. Introduction to wireless networking .......................................................................................1
1.1 Infrastructure Mode: A WLAN with Access Points.............................................................1
1.2 Peer-to-Peer Mode: A WLAN without Access Points..........................................................1
1.3 Identifying a WLAN.............................................................................................................2
1.4 Identifying Devices on a WLAN ..........................................................................................2
1.5 Wireless Security ..................................................................................................................2
1.6 Radio Basics..........................................................................................................................2
1.7 Intel® PRO/Wireless LAN USB Software...........................................................................3
Chapter 2. Using the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility ..................................................................4
2.1 Viewing the Status Icon........................................................................................................4
2.2 Viewing Information about the Network Connection...........................................................5
2.3 Changing Network Settings..................................................................................................6
2.4 Implementing Security..........................................................................................................8
2.5 Viewing Driver and Firmware Information..........................................................................9
2.6 Downloading Drivers and Firmware.....................................................................................9
Chapter 3. Troubleshooting..........................................................................................................................10
Chapter 4. Customer Support.......................................................................................................................12
4.1 Intel Automated Customer Support ....................................................................................12
4.1.1 User Guide on Your Product CD-ROM ...................................................................12
4.1.2 Web and Internet Sites..............................................................................................12
4.1.3 Customer Support Technicians.................................................................................12
4.2 Intel Software License Agreement......................................................................................13
4.3 Limited Hardware Warranty...............................................................................................15
Returning a Defective Product...................................................................................................15
4.3.1 Limitation of Liability and Remedies.......................................................................16
4.4 Product Registration............................................................................................................16
Chapter 5. Regulatory Compliance Information....................................................................................17
Index............................................................................................................................................................................19
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide v
Page 6

Contents
vi Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide
Page 7
Chapter 1. Introduction to wireless networking
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device is an 802.11b wireless networking device that
connects to a USB port on your computer. Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN network products are
based on the IEEE 802.11b standard and connect computers together to form a wireless local area
network (WLAN).
All Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN products interoperate with other IEEE 802.11b compliant
wireless devices from other vendors. The WiFi certification logo indicates that the wireless device
is 802.11b compliant.
The Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device operates in either infrastructure mode or peerto-peer mode.
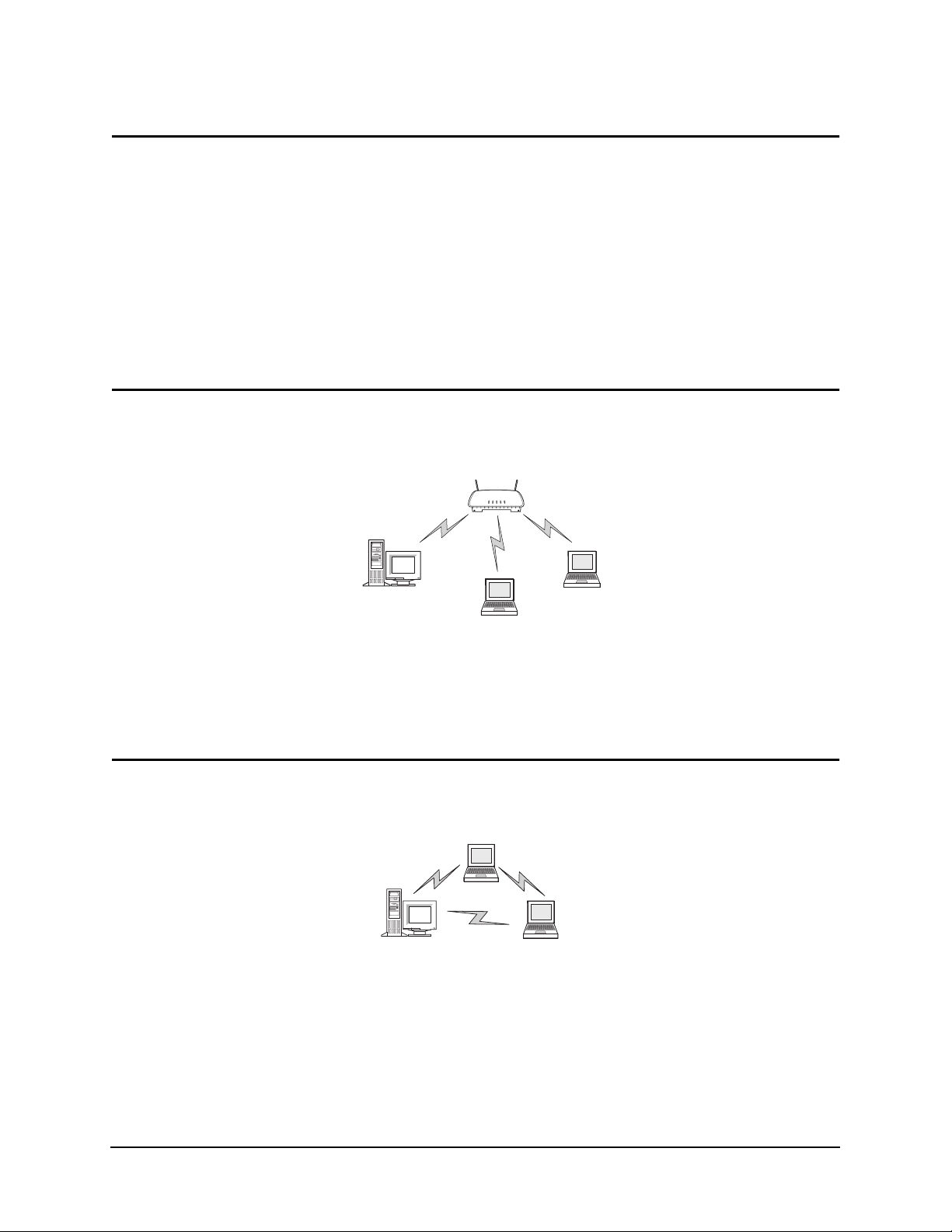
1.1 Infrastructure Mode: A WLAN with Access Points
In infrastructure mode, wireless clients send and receive information through access points. When a
wireless client communicates with another, it transmits to the access point. The access point
receives the information and rebroadcasts it. Then the other device receives the information.
Access points are strategically located within an area to provide optimal coverage for wireless
clients. A large WLAN uses multiple access points to provide coverage over a wide area. Access
points can connect to a LAN through a wired Ethernet connection. Access points send and receive
information from the LAN through this wired connection.
1.2 Peer-to-Peer Mode: A WLAN without Access Points
In peer-to-peer mode, also called Ad Hoc Mode, wireless clients send and receive information to
other wireless clients without using an access point. In contrast to infrastructure mode, this type of
WLAN only contains wireless clients.
You can use peer-to-peer mode to network computers in a home or small office, or to set up a
temporary wireless network for a meeting.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 1
Page 8
Chapter 1. Introduction to wireless networking
1.3 Identifying a WLAN
All the devices on a WLAN use a Network Name, or Service Set Identifier (SSID) to identify the
WLAN. In peer-to-peer mode, an Independent Basic Service Set Identifier (IBSSID) identifies a
WLAN. In infrastructure mode, an Extended Service Set Identifier (ESSID) identifies a WLAN.
This guide uses SSID as a general term for both ESSID and IBSSID. All the devices on a WLAN
must use the same SSID to communicate with other wireless devices. When installing an access
point or wireless device in a wireless client, the software asks you to specify an SSID.
1.4 Identifying Devices on a WLAN
A Basic Service Set Identifier (BSSID) uniquely defines each wireless device. The BSSID is the
Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) address of the wireless device installed in the wireless
client. The MAC address is permanently set when the device is manufactured. MAC addresses
determine the device sending or receiving data. A MAC address is a 48-bit number written as six
hexadecimal bytes separated by colons. For example:
00:A0:F8:24:9A:C8
To view the MAC address of an Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB device, see the label on the
back of the device.
1.5 Wireless Security
Wireless networking devices transmit information through the air. Without implementing security,
it is easy for an unauthorized person to intercept the information.
A common way of implementing security and protecting information is encryption. Before sending
information, the wireless client or access point encrypts or scrambles information using an
encryption key. The device receiving the information uses the same key to decrypt or unscramble
the information. The information is only readable to wireless devices that have the correct
encryption key.
The IEEE 802.11 wireless LAN standard specifies the Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) encryption
and decryption algorithm. The standard includes two levels of security, using a 40-bit key or a 128bit key. To implement WEP, use either one of these methods. For better security, use a 128-bit key.
A 128-bit key has several trillion times as many possible combinations as a 40-bit key. For added
security, change your keys often. Some vendors refer to 40-bit encryption as 64-bit. These are
identical. A wireless device that claims to have 40-bit encryption interoperates with a device that
claims to have 64-bit encryption.
The same device, host computer or front-end processor usually performs both encryption and
decryption. The algorithm, like the pattern of a lock, is standardized and may be used by anyone,
but the encrypted data is unreadable without the appropriate key, which is known only by the
sender and receiver of the transmitted data. You should change your keys often for added security.
1.6 Radio Basics
IEEE 802.11 networking devices transmit and receive radio signals. Users communicate with the
network by establishing radio links between mobile devices and access points, or between each
other.
2 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 9

IEEE 802.11 devices use frequency modulation (FM) to transmit digital data from one device to
another. The radio signal propagates into the air as electromagnetic waves. The receiving device
demodulates the signal, which results in the original digital data. The radio devices transmit in the
2.4 to 2.5 gigahertz frequency range, a license-free range throughout most of the world. The actual
range is country-dependent.
1.7 Intel® PRO/Wireless LAN USB Software
Intel® PRO/Wireless LAN USB software consists of the Windows device drivers for the USB
Device and the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility. The configuration utility allows you to
evaluate device performance and display and modify the wireless LAN settings for the Intel®
PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device. Settings include the operating mode, the SSID,
transmission rate, and encryption keys used for wireless network communication.
For the network device to function in a wireless LAN, you must change the settings to match the
settings of other wireless devices in your network.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 3
Page 10

Chapter 2. Using the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility
Chapter 2. Using the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility
The Wireless LAN Configuration Utility allows you to configure wireless clients, evaluate
performance, and display the current status of a wireless network device.
2.1 Viewing the Status Icon
The Wireless LAN Configuration Utility starts automatically and places a status icon on the
Windows taskbar when Windows starts. The status icon is shown below.
If the status icon is not present do the following:
1. Click the Windows Start menu and click Programs.
2. Click the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB software menu.
3. Click the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility.
The following colors on the taskbar icon show the status of the wireless device:
Color Infrastructure mode Ad hoc mode
Green Communicating successfully with an access
point.
Yellow Communicating with an access point but the
signal strength and quality are not optimal.
Red Searching for a new access point because it is:
• out of range of an access point.
• connected to an access point, but
attempting to find an access point with a
better signal.
Connected to another
wireless client.
Yellow is not used in
this mode.
Red is not used in this
mode.
4 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 11

Chapter 2. Using the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility
2.2 Viewing Information about the Network Connection
To view detailed status about your wireless network connection, double-click the status icon on the
Windows Taskbar. This information can help you troubleshoot problems and adjust the placement
of clients, access points, or antennas.
State: Shows the current status of your wireless network:
• Associated – The access point’s Ethernet Address (Media Access Controller ID). This access
point is the one your wireless client is communicating with.
• Scanning – The wireless client is searching for a wireless network. The scanning status also
occurs while the client is roaming between access points.
• Disconnected – The client is not connected to the wireless network.
Rescan button: Click to re-establish a connection with a wireless network. When you click this
button, the wireless client is briefly disconnected from the network and begins searching for an
access point with a stronger signal in the specified wireless network.
Current Channel: Displays the channel currently used for receiving and transmitting wireless data
communication.
Current Tx Rate: Shows the maximum achievable data rate allowed for this location. The data
transmit rate is automatically negotiated between wireless clients and access points, and changes
dynamically depending on signal strength and link quality. The data rates automatically shift
among 11Mbps, 5.5Mpbs, 2Mbps and 1Mbps.
Throughput (Bytes/sec): The Tx (transmit) and Rx (receive) throughput fields display the current
number of data packets that are transferred or received by the wireless client. This information is
updated every two seconds.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 5
Page 12

Chapter 2. Using the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility
Link Quality: A measure of the data quality. Both low signal strength and interference can
adversely affect the data quality.
Signal strength: The power of the received signal.
2.3 Changing Network Settings
The Configuration tab allows you to change the device’s network settings
You can configure the wireless device to communicate with an access point or directly with other
wireless computers.
Mode: This field indicates what kind of wireless network the device is connected to. Infrastructure
mode indicates that the device is communicating with an access point. Ad Hoc mode indicates that
the device is communicating directly with other computers without using an access point.
SSID: The SSID, also referred to as Network Name or Network ID, is the specific wireless network
the device is part of.
Tx Rate: Shows the maximum achievable data rate allowed for this location. The data transmit rate
is automatically negotiated between wireless clients and access points, and changes dynamically
depending on signal strength and link quality. The data rates automatically shift among 11Mbps,
5.5Mpbs, 2Mbps and 1Mbps.
PS Mode: This setting does not apply to the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device.
Channel: Indicates what channel the device is using to communicate with the access point or other
computers. If you are in Infrastructure mode, the access point and device must use the same
channel. In Ad Hoc mode, all wireless devices in the wireless network must use the same channel.
6 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 13

To configure the Device to communicate with an access point
1. In the Mode field, select Infrastructure.
2. In the SSID field, enter the SSID. The SSID is case sensitive and must not exceed 30
characters. This entry must be the same as the SSID set on the access point.
To configure the Device to communicate directly with other computers
3. In the Mode field, select Ad Hoc.
4. In the SSID field, enter the SSID. The SSID is case sensitive and must not exceed 30
characters. This SSID must be the same as the SSID assigned to all other computers in your
wireless network.
5. Select a channel you want to use for receiving and transmitting wireless data communication.
Wireless clients using the same channel communicate with each other.
If you set the transmission rate to 1, 2, 5.5, or 11 Mbps, configure all other wireless clients in the
peer-to-peer network to use the same transmission rate.
Restore the Default Settings
To restore all values on the screen to the original default values, click Restore Defaults.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 7
Page 14
Chapter 2. Using the Wireless LAN Configuration Utility
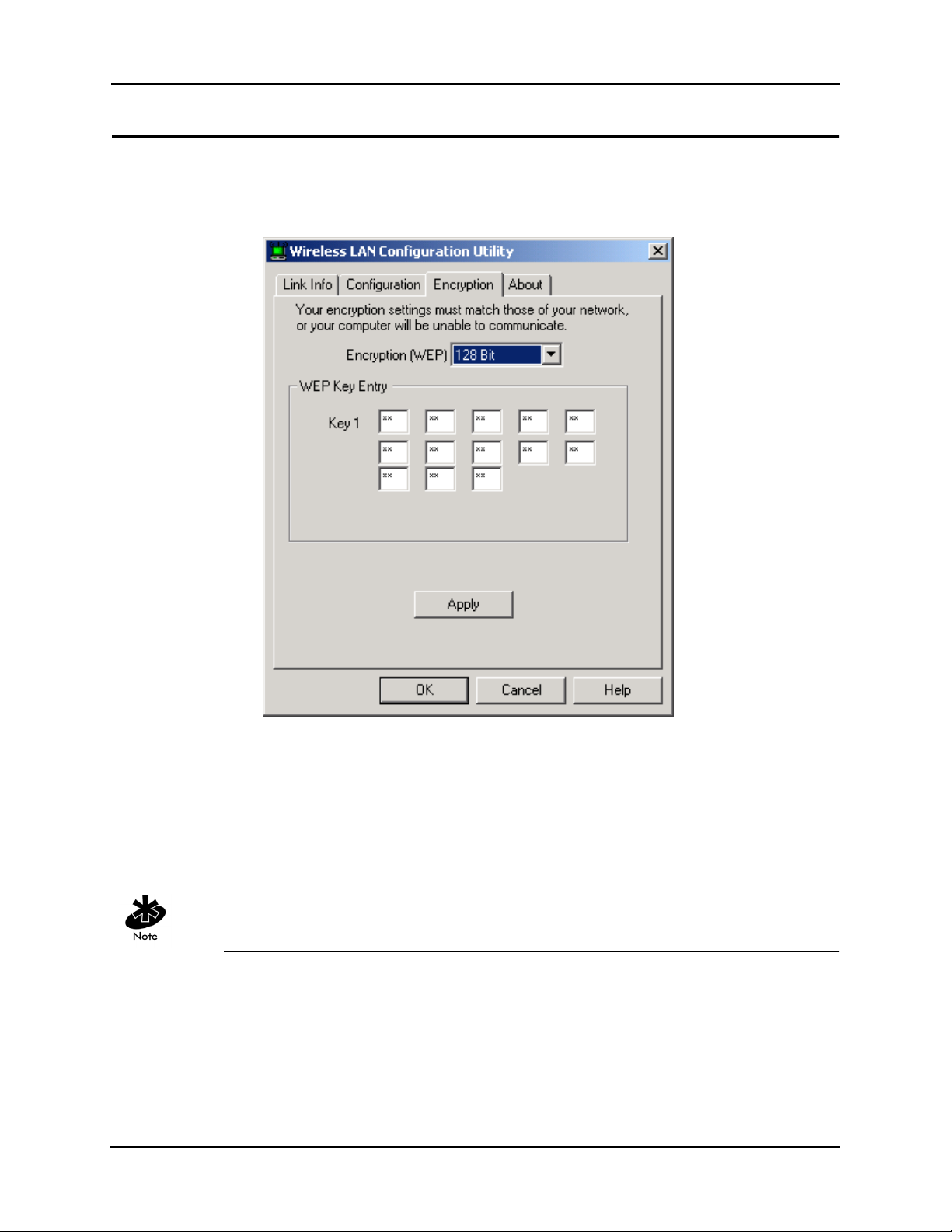
2.4 Implementing Security
The Encryption tab allows you to set up WEP encryption to protect your wireless network. WEP
encryption uses either a 64-bit key or 128-bit key to provide security during every data
transmission.
Each wireless device on your network must use the same encryption method and keys.
Choose one of the following settings from the Encryption(WEP) drop down box:
• Disabled: Data is not encrypted.
• 64-bit: All communication is encrypted with a 64-bit key.
• 128-bit: All communication is encrypted with a 128-bit key. This setting gives you the best
security, but network performance is slightly less.
For security purposes, the utility displays asterisks for the encryption key every time the Wireless
LAN Configuration Utility window is closed and then re-opened.
To use 64-bit WEP Encryption
1. Select 64-bit from the Encryption (WEP) drop down box.
2. Enter a key. The WEP key values are hexadecimal and can only contain the numbers 0 through
9 and the letters a through f.
8 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 15

To use 128-bit WEP Encryption
1. Select 128-bit from the Encryption (WEP) drop down box.
2. Enter a key. The WEP key values are hexadecimal and can only contain the numbers 0 through
9 and the letters a through f.
Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) Connection
For added security, use a VPN. For more information, consult the documentation regarding VPN
software.
2.5 Viewing Driver and Firmware Information
The About tab allows you to view driver, firmware, and software versions.
2.6 Downloading Drivers and Firmware
To download the latest drivers and firmware for this product, go to the Intel support web site:
http://www.intel.com/support
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 9
Page 16

Chapter 3. Troubleshooting
Chapter 3. Troubleshooting
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device is similar to a wired network adapter except that the
connection is wireless. The troubleshooting techniques that apply to a wired network adapter also
apply to this wireless device.
To see if the wireless device is working, note the color of the device icon on the right side of the
Windows taskbar:
Green indicates that the device is communicating. Double-click the icon for more status
information. For more information, see Chapter 2.
The light on the front of the device indicates the following:
• Off: no power
• Blink: looking for association
• On: associated or in Ad Hoc mode
Unable to communicate with an access point or other wireless computers
For the wireless device to communicate with an access point or otherwireless computers::
• The Network Name (SSID) of all wireless devices must match.
• If the WEP encryption option is enabled, all wireless devices must use the same encryption
level and key.
• The preamble settings of the device must be the same as the settings for other wireless devices.
If the access point or other devices use long preamble headers, your device must also use long
preamble headers. To check or change the preamble settings:
1. Double-click
2. Double-click
– Windows 2000: Right-click the
2011B LAN USB Device and click
– Windows ME, 98, and 95: Select Intel(R) PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device
and click
3. Click the
My Computer, and then double-click Control Panel.
Network.
Local Area Connection for the Intel(R) PRO/Wireless
Properties.
Properties.
Advanced tab and select Preamble Mode.
Degraded performance detected
• Place the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device in an open area and as high as
possible. Metal objects and fluorescent lights can adversely affect performance.
Windows 98 Troubleshooting Tips
• Windows 98 does not recognize the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device when
installed.
— Verify the computer has a Plug and Play BIOS.
• The driver fails to load.
— A resource conflict could exist. Use the
Select the
System applet from the Control Panel. Select the Device Manager tab.
Device Manager to resolve resource conflicts.
• Network drive mappings disappear when the laptop suspends or the device is removed then
reinserted. Windows 98 does not restore network drive mappings under these conditions.
— Log out and log in again, or restart the computer to restore the connections.
10 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 17

Windows ME Installation
Step 1 - Install the software
1. Insert the Intel® PRO/Wireless LAN USB Software CD into your CD-ROM drive and wait for
your computer to display the following:
2. Click Install Software and follow the instructions in the installation program.
Step 2 - Install the hardware
1. Place the wireless device in an open area as high as possible and away from metal objects or
florescent lights.
2. Plug the cable from the USB device into a USB port in your computer.
Step 3 - Install the driver
1. After you connect the USB cable, Windows starts the New Hardware Wizard.
2. Click Next and follow the steps in the Wizard. Make sure that you click Specify the location
of the driver and select Search for the best driver for your device.
3. Finish the wizard and restart your computer if prompted.
Step 4 - Configure the device
1. Double click the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device icon on the right side of the
Windows taskbar:
Chapter 3. Troubleshooting
2. If the icon is missing from the taskbar, click Start, Programs, Intel(R) Wireless LAN,
Wireless LAN Utilities, and then Configuration Utility.
3. Click the Configuration tab and set the following:
– Mode: If you have a wireless access point, select Infrastructure. If you are
connecting directly to other wireless computers, select Ad Hoc.
– Network Name (SSID): Type the same name used by other wireless devices on your
network. For information about these settings, click the Help button.
4. If you use encryption to protect your wireless network, click the Encryption tab and type
settings that match the other wireless devices on your network
5. Click OK and restart your computer for these settings to take effect.
Step 5 - Check the device
To see if the wireless device is working, note the color of the device icon on the right side of the
Windows taskbar:
Green indicates that the device is communicating. Double-click the icon for more status
information. For more information, see Chapter 2.
The light on the front of the device indicates the following:
• Off: no power
• Blink: looking for association
• On: associated or in Ad Hoc mode
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 11
Page 18

Chapter 4. Customer Support
Chapter 4. Customer Support
4.1 Intel Automated Customer Support
You can reach Intel automated support services 24 hours a day, every day at no charge. The services
contain the most up-to-date information about Intel products. You can access installation
instructions, troubleshooting information, and product information.
4.1.1 User Guide on Your Product CD-ROM
For more information about installing drivers or troubleshooting other topics, see the online User
Guide. To view the guide, insert the Intel CD in your drive and wait for the Autorun to display.
Click the
guide.
4.1.2 Web and Internet Sites
• Support: http://support.intel.com
• Network Products: http://www.intel.com/network
• Corporate: http://www.intel.com
• Newsgroups: news://cs.intel.com
•FTP Host: ftp://download.intel.com
• FTP Directory: /support/network/<device>/
User Guide button to view the guide. Note that a web browser is required to view the
4.1.3 Customer Support Technicians
U.S. and Canada
For customer support, please call +1 916-377-7000 (7:00 – 17:00 M–F Pacific Time). You can also
visit the Intel customer support web site
(http://support.intel.com
Worldwide Access
Intel has technical support centers worldwide. Many of the centers are staffed by technicians who
speak the local languages. For a list of all Intel support centers, the telephone numbers, and the
times they are open, refer to the Customer Support Phone Numbers web site
(http://www.intel.com/support/9089.htm
).
).
12 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 19

Chapter 4. Customer Support
4.2 Intel Software License Agreement
IMPORTANT - READ CAREFULLY BEFORE COPYING, INSTALLING OR USING.
Do not use or load this software and any associated materials (collectively, the “Software”)
until you have carefully read the following terms and conditions. By loading or using the
Software, you agree to the terms of this Agreement. If you do not wish to so agree, do not
install or use the Software.
LICENSES
• If you are a network administrator, the “Site License” below shall apply to you.
• If you are an end user, the “Single User License” shall apply to you.
Single User License
You may copy the Software onto a single computer for your personal, noncommercial use, and you
may make one back-up copy of the Software, subject to these conditions:
1. This Software is licensed for use only in conjunction with Intel component products. Use
of the Software with non-Intel component products is not licensed hereunder.
2. You may not copy, modify, rent, sell, distribute or transfer any part of the Software except as
provided in this Agreement, and you agree to prevent unauthorized copying of the Software.
3. You may not reverse engineer, decompile, or disassemble the Software.
4. You may not sublicense or permit simultaneous use of the Software by more than one user.
5. The Software may include portions offered on terms in addition to those set out here, as set out
in a license accompanying those portions.
OWNERSHIP OF SOFTWARE AND COPYRIGHTS
Title to all copies of the Software remains with Intel or its suppliers. The Software is copyrighted
and protected by the laws of the United States and other countries, and international treaty
provisions. You may not remove any copyright notices from the Software. Intel may make changes
to the Software, or to items referenced therein, at any time without notice, but is not obligated to
support or update the Software. Except as otherwise expressly provided, Intel grants no express or
implied right under Intel patents, copyrights, trademarks, or other intellectual property rights. You
may transfer the Software only if the recipient agrees to be fully bound by these terms and if you
retain no copies of the Software.
LIMITED MEDIA WARRANTY
If the Software has been delivered by Intel on physical media, Intel warrants the media to be free
from material physical defects for a period of ninety days after delivery by Intel. If such a defect is
found, return the media to Intel for replacement or alternate delivery of the Software as Intel may
select.
EXCLUSION OF OTHER WARRANTIES
EXCEPT AS PROVIDED ABOVE, THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS” WITHOUT
ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY OF ANY KIND INCLUDING WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY, NONINFRINGEMENT, OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE. Intel does not warrant or assume responsibility for the accuracy or completeness of
any information, text, graphics, links or other items contained within the Software.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 13
Page 20

Chapter 4. Customer Support
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY
IN NO EVENT SHALL INTEL OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES
WHATSOEVER (INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS, BUSINESS
INTERRUPTION, OR LOST INFORMATION) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OF OR
INABILITY TO USE THE SOFTWARE, EVEN IF INTEL HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE
POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. SOME JURISDICTIONS PROHIBIT EXCLUSION
OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR
CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY
NOT APPLY TO YOU. YOU MAY ALSO HAVE OTHER LEGAL RIGHTS THAT VARY
FROM JURISDICTION TO JURISDICTION.
TERMINATION OF THIS AGREEMENT
Intel may terminate this Agreement at any time if you violate its terms. Upon termination, you will
immediately destroy the Software or return all copies of the Software to Intel.
APPLICABLE LAWS
Claims arising under this Agreement shall be governed by the laws of California, excluding its
principles of conflict of laws and the United Nations Convention on Contracts for the Sale of
Goods. You may not export the Software in violation of applicable export laws and regulations.
Intel is not obligated under any other agreements unless they are in writing and signed by an
authorized representative of Intel.
GOVERNMENT RESTRICTED RIGHTS
The Software is provided with “RESTRICTED RIGHTS.” Use, duplication, or disclosure by the
Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in FAR52.227-14 and DFAR252.227-7013 et seq.
or its successor. Use of the Software by the Government constitutes acknowledgment of Intel’s
proprietary rights therein. Contractor or Manufacturer is Intel Corporation, 2200 Mission College
Blvd., Santa Clara, CA 95052.
14 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 21

4.3 Limited Hardware Warranty
Intel warrants to the original owner that the hardware product delivered in this package will be free
from defects in material and workmanship. This warranty does not cover the product if it is
damaged in the process of being installed. Intel recommends that you have the company from
whom you purchased this product install the product. Intel reserves the right to fill your order with
a product containing new or remanufactured components.
THE ABOVE WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ANY OTHER WARRANTY, WHETHER
EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO ANY
WARRANTY OF NON-INFRINGEMENT OF INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY,
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR ARISING OUT
OF ANY PROPOSAL, SPECIFICATION OR SAMPLE.
This warranty does not cover replacement of hardware products damaged by abuse, accident,
misuse, neglect, alteration, repair, disaster, improper installation or improper testing.
If the hardware product is found to be otherwise defective, Intel, at its option, will replace or repair
the hardware product at no charge except as set forth below, provided that you deliver the hardware
product along with a Return Material Authorization (RMA) number (see below) either to the
company from whom you purchased it or to Intel (North America only). If you ship the hardware
product, you must assume the risk of damage or loss in transit. You must use the original container
(or the equivalent) and pay the shipping charge.
Intel may replace or repair the hardware product with either new or remanufactured product or
parts, and the returned hardware product becomes Intel’s property. Repaired or replaced products
will be returned at the same revision level as received or higher, at Intel’s option. Intel reserves the
right to replace discontinued product with an equivalent current generation product.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may have other rights which vary from state
to state. All parts or components contained in this hardware product are covered by Intel’s limited
warranty for this product; the product may contain fully tested, recycled parts, warranted as if new.
For warranty information call one of the numbers below.
Returning a Defective Product
From North America
Before returning any hardware product, contact Intel Customer Support to obtain an RMA number
by calling +1 916-377-7000.
If the Customer Support Group verifies that the hardware product is defective, they will have the
Return Material Authorization Department issue you an RMA number to place on the outer
package of the hardware product. Intel cannot accept any product without an RMA number on the
package.
All Other Locations
Return the hardware product to the place of purchase for a refund or replacement.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 15
Page 22
Chapter 4. Customer Support
4.3.1 Limitation of Liability and Remedies
INTEL’S SOLE LIABILITY HEREUNDER SHALL BE LIMITED TO DIRECT,
OBJECTIVELY MEASURABLE DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT SHALL INTEL HAVE ANY
LIABILITY FOR ANY INDIRECT OR SPECULATIVE DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITING THE FOREGOING, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, AND
SPECIAL DAMAGES) INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, INFRINGEMENT OF
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY, REPROCUREMENT COSTS, LOSS OF USE, BUSINESS
INTERRUPTIONS, LOSS OF GOODWILL, AND LOSS OF PROFITS, WHETHER ANY
SUCH DAMAGES ARISE OUT OF CONTRACT, NEGLIGENCE, TORT OR UNDER
ANY WARRANTY, IRRESPECTIVE OF WHETHER INTEL HAS ADVANCE NOTICE
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF ANY SUCH DAMAGES. NOTWITHSTANDING THE
FOREGOING, INTEL’S TOTAL LIABILTIY FOR ALL CLAIMS UNDER THIS
AGREEMENT SHALL NOT EXCEED THE PRICE PAID FOR THE PRODUCT. THESE
LIMITATIONS ON POTENIAL LIABLITIES WERE AN ESSENTIAL ELEMENT IN
SETTING THE PRODUCT PRICE. INTEL NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES
ANYONE TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITIES.
Some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so the
above limitations may not apply to you.
Critical Control Applications
Intel specifically disclaims liability for use of the hardware product in critical control applications
(including, for example only, safety or health care control systems, nuclear energy control systems,
or air or ground traffic control systems) by you or your customers, and such use is entirely at the
user’s risk. You agree to defend, indemnify, and hold Intel harmless from and against any and all
claims arising out of use of the hardware product in such applications by you or your customers.
Software
Software provided with the hardware product is not covered under the hardware warranty described
above. See the applicable software license agreement which shipped with the hardware product for
details on any software warranty.
4.4 Product Registration
The Beginning of a Valuable Relationship…
Register Your Product Today!
As a registered customer, you stay connected and informed by receiving:
• Access to Intel’s outstanding technical support for optimum performance.
• Advance notice of product upgrades and new products to give you a competitive edge.
• Information updates to keep you current.
• Special offers for savings on products and evaluation units.
There are three easy ways to register:
• Browse the Intel product registration web site (http://www.intel.com/product/register
• Mail the attached postage prepaid registration card.
• Fax the attached registration card to +1 608-757-1727.
).
16 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 23

Chapter 5. Regulatory Compliance Information
Chapter 5. Regulatory Compliance Information
For U.S. and international regulatory compliance information for the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B
LAN USB Device, please see the Regulatory Specifications posted at the following web sites:
sDOC URL:
http://developer.intel.com/design/litcentr/ce_docs/
Regulatory document URL:
http://support.intel.com/support/network#Wireless_Ethernet_LAN
Important Regulatory Compliance Instructions
If your country is listed on the regulatory labels included with the Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B
LAN USB Device hardware, remove the label for your country and attach it to the bottom of the
device in the space provided. Failure to apply the label for the appropriate country constitutes a
breach of law.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: 1) this device may not cause harmful interference, and 2) this device must accept any
interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Any changes or modificaitons made by the user that are not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate the equipment.
Radio Frequency Interference Requirements – European Union
CE Marking & European Union Compliance
CE Marking and European Union compliance details are as follows:
Products intended for sale within the European Union are
marked with the Conformite Europeene (CE) Marking, which
indicates compliance with the applicable Directives and
European Normes, and amendments, identified below.
This equipment also carries the Class 2 identifier.
This equipment also carries the Class 2 identifier.
English
This product follows the provisions of the European Directive
1999/5/EC.
Danish
Dette produkt er i overensstemmelse med det europæiske direktiv 1999/5/EC
Dutch
Dit product is in navolging van de bepalingen van Europees Directief 1999/5/EC.
Finnish
Tämä tuote noudattaa EU-direktiivin 1999/5/EC määräyksiä.
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide 17
Page 24

Chapter 5. Regulatory Compliance Information
French
Ce produit est conforme aux exigences de la Directive Européenne 1999/5/EC.
German
Dieses Produkt entspricht den Bestimmungen der Europäischen Richtlinie 1999/5/EC.
Greek
Фп рспъьн бхфь рлзспЯ фйт рспвлЭшейт фзт ЕхсщрбъкЮт Пдзгйбт 1999/5/EC.
Icelandic
Þessi vara stenst reglugerð Evrópska Efnahags Bandalagsins númer 1999/5/EC.
Italian
Questo prodotto è conforme alla Direttiva Europea 1999/5/EC.
Norwegian
Dette produktet er i henhold til bestemmelsene i det europeiske direktivet 1999/5/EC.
Portuguese
Este produto cumpre com as normas da Diretiva Européia 1999/5/EC.
Spanish
Este producto cumple con las normas del Directivo Europeo
1999/5/EC.
Swedish
Denna produkt har tillverkats i enlighet med EG-direktiv 1999/5/EC.
18 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device Users Guide
Page 25

Index
Index
Numerics
128-bit WEP encryption, 9
64-bit WEP encryption, 8
A
Ad Hoc, 7
C
changing settings, 6
channel, 5
customer support, 12
D
data decryption, 2
WEP algorithm, 2
data encryption
WEP algorithm, 2
F
finding a stronger signal, 5
frequency, 3
frequency modulation, 3
frequency range, 3
I
IEEE address
MAC, 2
implementing security, 8
infrastructure, 7
Intel PRO/Wireless LAN
radio basics, 2
L
license agreement, 13
link quality, 6
N
network name, 6
P
product registration, 16
R
radio basics, 2
digital data, 3
electromagnetic waves, 2
radio links, 2
regulatory compliance, 17
rescanning, 5
restoring defaults, 7
S
security
decryption, 2
WEP algorithm, 2
selecting a channel, 6
signal strength, 6
SSID, 6
state, 5
status icon, 4
status information, 5
T
throughput, 5
transmission rate, 5
troubleshooting, 10
Tx rate, 6
V
viewing information, 5
VPN, 9
W
warranty, 15
WEP algorithm, 2
Wireless LAN Configuration Utility, 4
Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide 19
Page 26

Index
20 Intel® PRO/Wireless 2011B LAN USB Device User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...