Page 1

IP Gateway (Global Call)
Demo Guide
for Linux and Windows
Copyright © 2002-2005 Intel Corporation
05-1662-005
Page 2

COPYRIGHT NOTICE
INFORMATION IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED IN CONNECTION WITH INTEL®
PRODUCTS. NO LICENSE, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, BY ESTOPPEL OR OTHERWISE, TO ANY
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHTS IS GRANTED BY THIS DOCUMENT. EXCEPT AS
PROVIDED IN INTEL'S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE FOR SUCH PRODUCTS, INTEL
ASSUMES NO LIABILITY WHATSOEVER, AND INTEL DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTY, RELATING TO SALE AND/OR USE OF INTEL PRODUCTS
INCLUDING LIABILITY OR WARRANTIES RELATING TO FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE, MERCHANTABILITY, OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR
OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT. Intel products are not intended for use in medical,
life saving, or life sustaining applications.
Intel may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice.
This document as well as the software described in it is furnished under license and may only be used
or copied in accordance with the terms of the license. The information in this manual is furnished for
informational use only, is subject to change without notice, and should not be construed as a
commitment by Intel Corporation. Intel Corporation assumes no responsibility or liability for any
errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this document or any software that may be provided in
association with this document.
Except as permitted by such license, no part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval
system, or transmitted in any form or by any means without express written consent of Intel
Corporation.
Copyright © 2002-2005 Intel Corporation.
BunnyPeople, Celeron, Chips, Dialogic, EtherExpress, ETOX, FlashFile, i386, i486, i960, iCOMP,
InstantIP, Intel, Intel Centrino, Intel Centrino logo, Intel logo, Intel386, Intel486, Intel740, IntelDX2,
IntelDX4, IntelSX2, Intel Inside, Intel Inside logo, Intel NetBurst, Intel NetMerge, Intel NetStructure,
Intel SingleDriver, Intel SpeedStep, Intel StrataFlash, Intel Xeon, Intel XScale, IPLink, Itanium, MCS,
MMX, MMX logo, Optimizer logo, OverDrive, Paragon, PDCharm, Pentium, Pentium II Xeon,
Pentium III Xeon, Performance at Your Command, skoool, Sound Mark, The Computer Inside., The
Journey Inside, VTune, and Xircom are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its
subsidiaries in the United States and other countries.
*Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.
Publication Date: July, 2005
Intel Converged Communications, Inc.
1515 Route 10
Parsippany NJ 07054
For Technical Support, visit the Intel Telecom Support Resources website:
http://developer.intel.com/design/telecom/support/
For Products and Services Information, visit the Intel Telecom Products website:
http://www.intel.com/design/network/products/telecom
For Sales Offices, visit the Where to Buy Intel Telecom Products page:
http://www.intel.com/buy/networking/telecom.htm
Page 3

Table of Contents
1. About This Guide............................................................................................ 1
1.1. Purpose........................................................................................................... 1
1.2. Intended Audience ......................................................................................... 1
1.3. Related Documents ........................................................................................ 1
2. Demo Description............................................................................................ 3
2.1. About the Demo............................................................................................. 3
2.2. Choosing Channels ........................................................................................ 3
3. System Requirements ..................................................................................... 5
3.1. Hardware Requirements.................................................................................5
3.2. Software Requirements.................................................................................. 5
4. Preparing to Run the Demo ........................................................................... 7
4.1. Connecting to External Equipment............................................................... 7
4.2. Editing Configuration Files............................................................................9
4.2.1. Configuration File Location.................................................................. 9
4.2.2. Editing the gateway_r4.cfg File .......................................................... 10
5. Running the Demo ........................................................................................ 17
5.1. Starting the Demo ........................................................................................ 17
5.2. Demo Options .............................................................................................. 17
5.3. Using the Demo ........................................................................................... 20
5.4. Stopping the Demo....................................................................................... 20
6. Demo Details..................................................................................................21
6.1. Files Used by the Demo............................................................................... 21
6.1.1. Demo Source Files .............................................................................. 21
6.1.2. Utility Files.......................................................................................... 23
6.1.3. PDL Files............................................................................................. 24
6.2. Handling an Incoming Call.......................................................................... 25
6.2.1. Receiving a Call .................................................................................. 25
6.2.2. Handling a PSTN Call.........................................................................25
6.2.3. Handling an IP Call............................................................................. 26
6.3. Programming Model .................................................................................... 26
6.4. Initializations................................................................................................ 27
6.5. Event Mechanism ........................................................................................ 29
iii
Page 4

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
6.5.1. Handling Keyboard Input Events........................................................ 29
6.5.2. Handling SRL Events.......................................................................... 29
6.5.3. Handling Application Exit Events.......................................................30
6.6. Demo State Machine.................................................................................... 30
6.6.1. Call Establishment from IP ................................................................. 30
6.6.2. Call Establishment from PSTN ........................................................... 32
6.6.3. Call Teardown..................................................................................... 33
6.6.4. Glare Conditions ................................................................................. 34
Appendix A - Log File of IP Call Establishment............................................. 35
Appendix B - Log File of PSTN Call Establishment....................................... 39
Index....................................................................................................................45
iv
Page 5

List of Tables
Table 2. Command Line Switches ...................................................................... 18
Table 3. Runtime Keyboard Commands............................................................. 20
Table 4. Source Files Used by the IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo .................. 21
v
Page 6

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
vi
Page 7

List of Figures
Figure 1. Hardware Configuration with Onboard NIC and PSTN Front End....... 7
Figure 2. Hardware Configuration with Onboard NIC and separate PSTN
board..............................................................................................................8
Figure 3. Typical Topology .................................................................................. 9
Figure 4. Programming Model............................................................................ 26
Figure 5. Call Establishment from IP.................................................................. 31
Figure 6. Call Establishment from PSTN............................................................ 32
vii
Page 8

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
viii
Page 9

1. About This Guide
This section describes the purpose of this guide, the intended audience, and
references to other documents that may be useful to the user.
1.1. Purpose
This guide describes the operation of the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo.
1.2. Intended Audience
This guide is intended for application developers who will be developing a
PSTN-IP gateway application using the Global Call API.
Developers should be familiar with the C programming language and either the
Windows or Linux programming environment.
1.3. Related Documents
See the following for more information:
• The Release Update for your system release for information on problems
fixed, known problems, workarounds, compatibility issues, and last minute
updates not documented in the published information.
• The appropriate Configuration Guide for your hardware (Intel NetStructure
IPT Series or DM/IP Series board) and operating system
• Global Call API Software Reference Guide and the Global Call Application
Developer’s Guide
• Global Call IP Technology User’s Guide
• http://developer.intel.com/design/telecom/support/ (for technical support)
• http://www.intel.com/design/network/products/telecom (for product
information)
1
Page 10

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
2
Page 11

2. Demo Description
2.1. About the Demo
The IP Gateway (Global Call) demo is a host-based application that demonstrates
using the Global Call API to build a PSTN−IP gateway. The demo source code
can be used as sample code for those who want to begin developing an
application from a working application. The demo is not designed to implement a
complete gateway, lacking features such as least-cost routing, etc.
The IP Gateway (Global Call) demo is a cross-OS demo, running under the
Windows* or Linux* environments. Most of the differences in the environments
are handled directly by the programming interface and are transparent to the user.
Other differences, due to inherent differences in the operating systems, are
handled by the Platform Dependency Library (PDL).
For more information about the PDL refer to the source code in the pdl_win or
pdl_linux directories.
2.2. Choosing Channels
When a call comes from the PSTN, the call is answered by a PSTN line device.
During initialization, the PSTN channel was associated with a specific IP line
device, so the call is connected to the IP line device that is associated with this
PSTN line device.
When a call arrives from the IP network, there is no direct association of a
channel, since there are no individual physical connections for the IP channels.
The call is answered by a line device. During initialization, the line device was
associated with a specific PSTN line device. The Global Call API tells the IP
Gateway (Global Call) demo which PSTN channel is associated with this IP
channel. The application then connects the IP call to the appropriate PSTN
channel.
3
Page 12

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
4
Page 13

3. System Requirements
This chapter discusses the system requirement for running the IP Gateway
(Global Call) demo. It contains the following topics:
• Hardware Requirements
• Software Requirements
3.1. Hardware Requirements
To run the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo, you need:
• One of the following:
• Intel NetStructure® DM/IP Series board
• Intel NetStructure® IPT Series board
• an IPT Series board also requires an Intel NetStructure® DM/V-A
series board for PSTN connection
• IP Network cable
For other hardware requirements, such as memory requirements, see the Release
Guide for your system release.
3.2. Software Requirements
To run the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo, you need the Intel® Dialogic®
System Release 6.x for the Linux* or Windows* Operating Systems on Intel
Architecture. For a list of operating system requirements and supported compilers
see the Release Guide for your system release.
5
Page 14

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
6
Page 15
4. Preparing to Run the Demo
This chapter discusses how to prepare to run the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo.
It provides information about the following topics:
• Connecting to External Equipment
• Editing Configuration Files
4.1. Connecting to External Equipment
There are two possible hardware configurations for the IP Gateway (Global Call)
demo:
• Intel NetStructure® DM/IP series board(s) with on-board NIC and a PSTN
connection on the front end
• Intel NetStructure® IPT series board(s) with on-board NIC connected to an
Intel NetStructure® DM/V-A series board as the PSTN interface
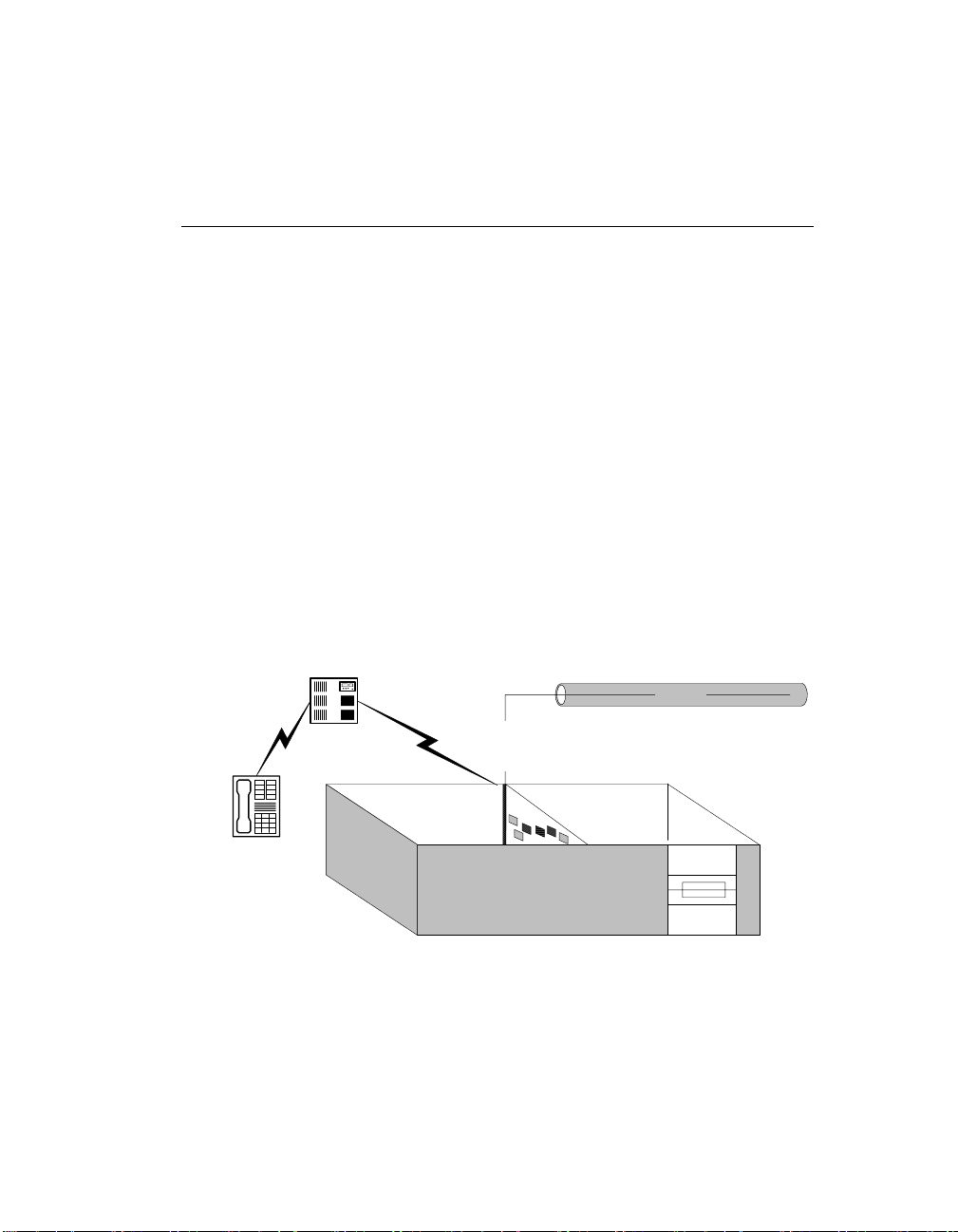
The following diagrams illustrate the possible hardware configurations.
Ethernet
PBX
Telephone
Intel NetStructure® IP board
with on-board NIC and a
PSTN connection on the front end
Figure 1. Hardware Configuration with Onboard NIC and PSTN Front
End
7
Page 16

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
Intel NetStructure®
DM/V-A series board
CTbus
cable
PSTN
line
Intel NetStructure®
IPT board
Internet/
Intranet line
Figure 2. Hardware Configuration with Onboard NIC and separate
PSTN board
The IP Gateway (Global Call) demo allows you to connect to gateways on an IP
network and establish voice calls via the IP network. It also allows you to
connect to H.323 terminals on the IP network and connect a call from the
terminal to a telephone via one of the gateways. Figure 3 shows a typical
topology for demonstrating the capabilities of the IP Gateway (Global Call)
demo. Note that the two PBXs that are shown can be a single PBX. Also note that
more than one PSTN line can be connected to a single gateway.
8
Page 17
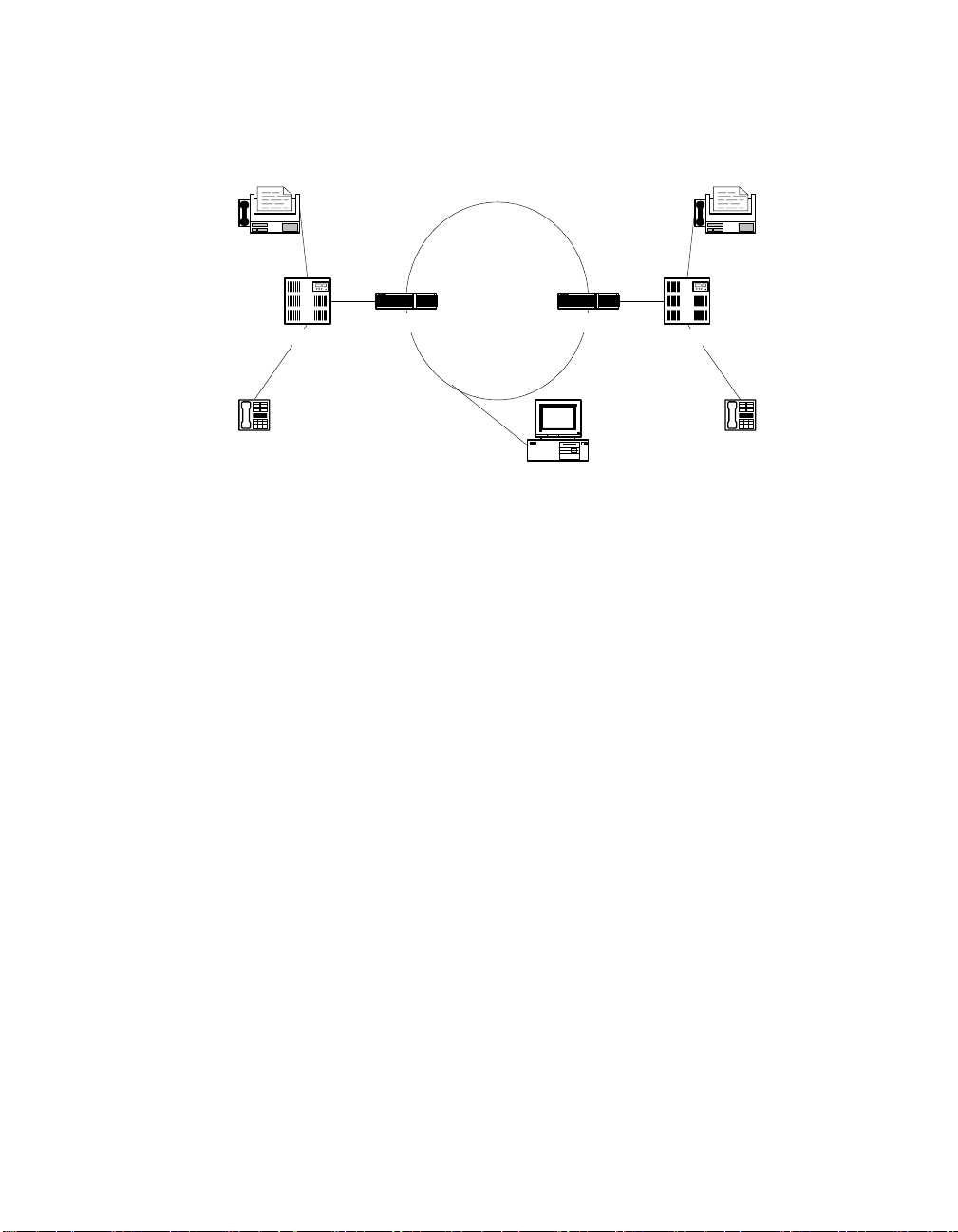
PBX
IP Gateway
IP Network
4. Preparing to Run the Demo
FaxFax
IP Gateway
PBX
Telephone
H.323 Terminal
Telephone
Figure 3. Typical Topology
4.2. Editing Configuration Files
This section discusses how to configure the demo for your system. It contains the
following topics:
• Configuration file location
• Editing the gateway_r4.cfg File
4.2.1. Configuration File Location
Before running the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo, modify the gateway_r4.cfg
file to reflect your system environment. Use a text editor and open the file from:
• Windows:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\samples\ipt_demos\gateway_r4\Release
• Linux:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/ipt_demos/gateway_r4/Release
where $(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR) identifies the base directory where the Intel
Dialogic System Release was installed.
9
Page 18

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
4.2.2. Editing the gateway_r4.cfg File
Below is an example of the gateway_r4.cfg file. Update the following
information:
ipProtocol
The IP Protocol used for opening the IP Line devices, values: H323, SIP,
both
Channel
Channels defined by this section of the file - may be individual channel or a
range of channels
Source
Source address
Destination
Destination address
RemotePhoneNumber
Destination phone number to call. Transferred during call establishment to
target gateway.
LocalPhoneNumber
The number used for PSTN calls
pstnProtocol
PSTN protocol to use
DTMFmode
One of the following: OutOfBand, inband, rfc2833
AudioRxCodecs
Capability for receive audio codecs. The following capabilities are defined:
• CoderType - preferred coder. Recognized coders are:
• g711Alaw
• g711Mulaw
• gsm
• gsmEFR
• g723_5_3k
• g723_6_3k
• g729a
• g729ab
10
Page 19

4. Preparing to Run the Demo
• CoderFramesPerPkt - frames per packet for the selected coder
• CoderVAD - Voice Activity Detection on/off
AudioTxCodecs
Capability for transmit audio codecs. See AudioRxCodecs for a complete
description.
DataCodecs
Capability for fax codecs. The demo currently support T38 only.
MediaAlarmLostPackets
Indicates that the percentage of packets lost during a call exceeded its
threshold value
• Threshold - defines when a Quality of Service (QoS) parameter is in a
fault condition. A fault occurs when the result of a measurement of a
QoS parameter crossed the Threshold value. Default = 20.
• DebounceOn - the time during which faults are measured (in msec., must
be a multiple of Interval). Default = 10000.
• DebounceOff - the dime during which successes are measured (in mesc.,
must be a multiple of Interval). Default = 10000.
• Interval - the amount of time between two QoS parameter measurements
(in multiples of 100 msec). Default = 1000.
• PercentSuccess - the threshold of successes during the DebounceOn time
(expressed as a percentage of successes). Default = 60.
• PercentFail - the threshold of failures during the DebounceOn time
(expressed as a percentage of failures). Default = 40.
MediaAlarmJitter
Indicates that the jitter (as defined in RFC 1889) exceeded its threshold value
• Threshold - Default = 60.
• DebounceOn - Default = 20000.
• DebounceOff - Default = 60000.
• Interval - Default = 5000.
• PercentSuccess - Default = 60.
• PercentFail - Default = 40.
Display
Display information passed to destination gateway during call establishment
IPT_UUI
User to User Information string. Information sent before Connected state.
11
Page 20

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
UII
User Input Indication string to send
NonStdParm
Non-standard parameter data to send
NonStdCmd
Non-standard command string to send
ObjId
Object ID
Q931Facility
Facility data to send on the Q.931 channel
DTMF
DTMF mode. Possible options: OutOfBand, inband, rfc2833
enableRegestration
Register with gatekeeper
TTL
Time-to-live parameter (in seconds)
Protocol
Call control protocol. Possible values: h323, SIP, both
max_hops
Maximum number of router hops
regServerAddress
Gatekeeper IP address. Use 0.0.0.0 as the default address for discovering the
GK
NonStdRasCmd
Non-standard RAS command string to send
RasObjId
RAS object ID
Alias
Possible alias types: 1 = string, 2 = IP address, 3 = H323 ID, 4 = phone, 5 =
URL, 6 = EMail
12
Page 21

4. Preparing to Run the Demo
The following is an example of a configuration file.
########################################################################################
# Telephony Protocol :
# For ANAPI(Analog Front End) use the root file name of the analog protocol file for
your country or telephone network)
# For ICAPI (Digital Front End) use the root file name of the country dependent
parameter <.cdp> file
# IP Protocol :
# The IP Protocol used for opening the IP Line devices, values: H323, SIP, both
#
# DTMFmode
# possible options:
# OutOfBand, inband, rfc2833
#
#
# Capability for audio codecs:
# g711Alaw
# g711Mulaw
# gsm
# gsmEFR
# g723_5_3k
# g723_6_3k
# g729a
# g729ab
#
# Capability for data codecs:
# t38
#
# Note: if you want to run the demo with coder g729 use:
# g729a for running with VAD disable
# and 729ab for running with VAD enable
#
# Caution:
# If capability is g711Alaw /Mulaw ==> FramesPerPkt = 10,20,30.
# G711 frame per packet defines the packet
size in milliseconds
# If capability is g723_5_3k / 6_3k ==> FramesPerPkt = 1, 2, 3 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 30ms.
# If capability is gsm ==> FramesPerPkt = 1, 2, 3 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 20ms.
# If capability is gsmEFR ==> FramesPerPkt = 1, 2, 3 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 20ms.
# If capability is g729a ==> FramesPerPkt = 3, 4 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 10ms.
# VAD disable, the VAD parameter is ignored
# If capability is g729ab ==>FramesPerPkt = 3, 4 .
# FrameSize isn't needed, default= 10ms.
# VAD enable, the VAD parameter is ignored
#
########################################################################################
ipProtocol = H323
Channel = 1-120
{
Source = NAME:Intel Corp.
Destination = 0.0.0.0
RemotePhoneNumber = 23
LocalPhoneNumber = 26
pstnProtocol = isdn
13
Page 22

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
DTMFmode = OutOfBand
AudioRxCodecs
{
}
AudioTxCodecs
{
}
DataCodecs
{
}
MediaAlarmLostPackets
{
DebounceOn = 10000 # Threshold debounce ON
DebounceOff = 10000 # Threshold debounce OFF
Interval = 1000 # Threshold Time Interval (ms)
PercentSuccess = 60 # Threshold Success Percent
PercentFail = 40 # Threshold Fail Percent
}
MediaAlarmJitter
{
Threshold = 60 # Threshold value
DebounceOn = 20000 # Threshold debounce ON
DebounceOff = 60000 # Threshold debounce OFF
Interval = 5000 # Threshold Time Interval (ms)
PercentSuccess = 60 # Threshold Success Percent
PercentFail = 40 # Threshold Fail Percent
}
# MediaAlarmResetAlarmState = 0
Display = GATEWAY_Chan1
IPT_UUI = User_to_User_1
UII = 12345
NonStdParm = NSP_Chan1
NonStdCmd = NSC_Chan1
ObjId = 2 16 840 1 113741
Q931Facility = facility 01
DTMF = 1
}
#values - 1 -to enable board regestration , 0 not enabling board regestration
enableRegestration = 0
board = 1-1
{
CoderType = g711Mulaw
CoderFramesPerPkt = 30
CoderVAD = 0
CoderType = g711Mulaw
CoderFramesPerPkt = 30
CoderVAD = 0
CoderType = t38
Threshold = 20 # Threshold value
# time to live in seconds
TTL = 60
# possible values: h323, SIP, both
Protocol = h323
max_hops = 20
14
Page 23

4. Preparing to Run the Demo
# use 0.0.0.0 as the default address for descovering the GK
regServerAddress = 10.242.214.45
NonStdRasCmd = NSC_Chan1
RasObjId = Intel
# possible alias types: 1 = string, 2 = IP address, 3 = H323 ID, 4 = phone, 5 =
URL, 6 = EMail
Alias = 1
{
AliasType = 3
AliasName = intel
}
Alias = 2
{
AliasType = 4
AliasName = 1111
}
Prefix = 1
{
PrefixType = 3
PrefixName = pmac
}
Alias = 3
{
AliasType = 4
AliasName = 2222
}
}
15
Page 24

Page 25

5. Running the Demo
This chapter discusses how to run the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo. It contains
the following topics:
• Starting the Demo
• Demo Options
• Using the Demo
• Stopping the Demo
5.1. Starting the Demo
Windows
From a command prompt, change directories to:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\samples\\ipt_demos\gateway_r4\Release
Type gateway_r4 at the command prompt to run the IP Gateway (Global Call)
demo using the default settings.
Linux
Change directory to:
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\ipt_demos\gateway_r4/Release
Type gateway_r4 to run the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo using the default
settings.
5.2. Demo Options
To specify certain options at run-time, launch the demo from a command line,
using any of the switches listed in Table 1. Command Line Switches.
17
Page 26

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
Table 1. Command Line Switches
Switch Action Default
-c <filename> Configuration file name gateway_r4.cfg
-d Sets Debug Level (0-4):
0-FATAL: used when one or more
channels are deadlocked.
1-ERROR: used when the application
receives a failure which doesn’t cause the
channel to be deadlocked.
2-WARNING used when some problem
or failure occurred without affecting the
channel’s usual action.
3-TRACE used at the start of the
application entrance or the start of any
function.
4-INFO prints data related to a specific
action.
NOTE: Debug level is inclusive; higher
levels include all lower levels.
-f Identifies the front end:
0 = analog
1 = digital T-1
2 = digital E-1
0 - FATAL
0
-h or ? Prints the command syntax to the screen Off
18
Page 27

5. Running the Demo
Switch Action Default
-l <n,…> Printouts will be printed into channel log
Disabled
files.
If ‘all’ follows the –l, log files will be
created for all available channels.
If a list of channels in the following
format: C1-C2, C3-C4, C5 (e.g., 110,112-150,314) follows the –l, log files
are created for the channel ranges or
specific channels specified in the list.
If “–l” option is not used all prints go to
the stdout, for the first 2 channels only (to
keep from overloading the CPU, and
more convenient for viewing printouts).
-n Sets the number of channels The lesser of
PSTN Devices
and IP Devices
-p 0-Disable dialing
-p1
1-Enable dialing
Used for testing purposes, or if running
the demo on a machine that does not have
all of the necessary external connections
-q Enables the Quality of Service feature Disabled
-r Sets the number of rings before
2
answering the call on the PSTN
-s 0-Disable DNIS
0
1-Enable DNIS
Used for testing purposes, or if running
the demo on a machine that does not have
all of the necessary external connections
19
Page 28

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
5.3. Using the Demo
The demo always waits for input from the keyboard. While the demo is running,
you can enter any of the following commands:
Table 2. Runtime Keyboard Commands
Command Function
c or C Print channel information
d<n> or D<n> Change debug level during runtime
f or F Send Q.931 facility information
n or N Send non-standard command
q or Q Terminates the application
r or R Sends non-standard RAS
s or S Unregister with a Gatekeeper
t or T Sends DTMF
u or U Sends UII (User Input Indication)
5.4. Stopping the Demo
The IP Gateway (Global Call) demo runs until it is terminated. Press “q” or “Q”
to terminate the demo application.
20
Page 29

6. Demo Details
This chapter discusses the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo in more detail. It
contains the following topics:
• Files Used by the Demo
• Handling an Incoming Call
• Programming Model
• Initializations
• Event Handling
• Demo State Machine
6.1. Files Used by the Demo
6.1.1. Demo Source Files
In Windows the following files are located in
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\samples\ipt_demos\gateway_r4.
In Linux the following files are located in
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/ipt_demos/gateway_r4.
Table 3. Source Files Used by the IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo
Filename Description OS
gatedefs.h Gateway definitions Both
gateip.c IP communication functions Both
gateip.h Function prototype for gateip.c Both
gatemain.c Main file (including MAIN loop) Both
21
Page 30

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
Filename Description OS
gatepars.c The demo configuration file
Both
parsing functions
gatepars.h Function prototype for gatepars.c Both
gatepstn.c PSTN-specific functions Both
gatepstn.h Function prototype for gatepstn.c Both
gatestate.c State machine functions Both
gatestate.h Function prototype for gatestat.c Both
gatestrc.h Demo structure (including Main
Both
Structure Session)
gatevars.h Global variables Both
gateway_r4 Linux executable Linux
gateway_r4.cfg Config file Linux
gateway_r4.dsp Visual C++ project file Windows
gateway_r4.dsw Visual C++ project workspace Windows
gateway_r4_
Demo version information Both
version.c
incfile.h Function prototype for Global Call
Both
and R4 functions.
main.h Function prototype for gatemain.c Both
makefile Linux compilation file Linux
mediaalarms.c QoS functions Both
mediaalarms.h Function prototype for
Both
mediaalarms.c
register.c RAS functions Both
22
Page 31

Filename Description OS
register.h Function prototype for register.c Both
6. Demo Details
Release\
Demo configuration file Windows
gateway_r4.cfg
Release/
Demo configuration file Linux
gateway_r4.cfg
Release\
Executable Windows
gateway_r4.exe
Release/
Executable Linux
gateway_r4.exe
6.1.2. Utility Files
In Windows the following files are located
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\samples\ipt_demos\Shared
In Linux the following files are located in
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/ipt_demosShared.
Filename Description OS
libdbg.c Debugging functions Both
libdbg.h Function prototype for libdbg.c Both
libdefs.h #DEFINE inclusions Both
Release/libutil.a Compiled Utility library Linux
Makefile Compilation file Linux
util.dsp Utility library Visual C project file Windows
util.dsw Utility library Visual C workspace Windows
util_version.c Utility library version information Both
23
Page 32

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
Filename Description OS
Release\util.lib Compiled Utility library Windows
6.1.3. PDL Files
In Windows the following files are located in
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)\samples\ipt_demosShared
In Linux the following files are located in
$(INTEL_DIALOGIC_DIR)/ipt_demos/Shared
Filename Description OS
pdl_win\iptransport.cpp PDL IP transport functions Windows
pdl_win\iptransport.h Function prototype for
Windows
iptransport.cpp
pdl_win\pdl.c Platform dependency functions Windows
pdl_win\pdl.h Function prototype for pdl.c Windows
pdl_win\pdl_version.c PDL version information Windows
pdl_win\pdl_win.dsp PDL Visual C project file Windows
pdl_win\pdl_win.dsw PDL Visual C workspace Windows
pdl_win\Release\
Compiled PDL library Windows
pdl_win.lib
/pdl_linux/
PDL IP transport functions Linux
iptransport.cpp
/pdl_linux/iptransport.h Function prototype for
Linux
iptransport.cpp
/pdl_linux/libpdl.a Compiled PDL library Linux
/pdl_linux/makefile.pdl Compilation file Linux
24
Page 33

6. Demo Details
Filename Description OS
/pdl_linux/pdl.c Platform dependency functions Linux
/pdl_linux/pdl.h Function prototype for pdl.c Linux
/pdl_linux/
PDL version information Linux
pdl_linux_version.c
6.2. Handling an Incoming Call
This section discusses how the demo application handles incoming calls. It
contains the following topics:
• Receiving a Call
• Handling a PSTN Call
• Handling an IP Call
6.2.1. Receiving a Call
The demo can receive calls from either the PSTN or the IP network. The demo
uses a configuration file (gateway_r4.cfg) to determine parameters that are
associated with a particular call. The configuration file allows you to configure
different channels with different properties. See Section 4.2. Editing
Configuration File for a more detailed description of the gateway_r4.cfg file, as
well as a description of the different configuration properties.
6.2.2. Handling a PSTN Call
A call that arrives from the PSTN needs to be routed to either a destination PSTN
number (via another gateway) or to an H.323 terminal. The demo uses the
gateway_r4.cfg file to determine the destination IP address as well as the
(optional) destination PSTN number (remote phone number). The IP Gateway
(Global Call) demo initiates an IP (H.323) call to the destination IP address. If the
configuration file indicates a PSTN destination number then that number is
passed to the destination gateway during the call establishment procedure.
25
Page 34

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
Once the destination gateway has answered the H.323 call, the IP Gateway
(Global Call) demo connects the PSTN call to the IP call. An audio path is now
established between the PSTN call and the destination IP station. For more details
see section 6.5. Event Mechanism .
6.2.3. Handling an IP Call
A call that arrives from the IP network needs to be routed to a PSTN number.
That number may arrive as part of the call establishment procedure (if the call
was originated by another IP Gateway for example). If the destination number
arrived during call establishment, then the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo uses
that number to call the PSTN. If no destination number was included in the call
establishment procedure, then the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo uses the
gateway_r4.cfg file to determine the destination number to call (local phone
number). Once the IP Gateway (Global Call) demo answers and connects the call
on the IP network, it initiates (dial out) a call on the PSTN line and connects the
two calls. This allows the calling party to hear the call progress tones on the local
PSTN. For more details see section 6.5. Event Mechanism .
6.3. Programming Model
The IP Gateway (Global Call) Object Oriented demo operates with two threads,
as shown in Figure 4.
Keyboard
R4/GC
IP
SRL
Main Thread
Sub-Thread
Figure 4. Programming Model
26
Page 35

6. Demo Details
The threads are created as follows:
• The first (main) thread is created by the demo application to get the keyboard
input.
• The second thread is an SRL thread, created as a result of the demo
application calling sr_enblhdlr( ) in Windows. In Linux, the thread must be
explicitly created. All Global Call events are received through the SRL.
6.4. Initializations
The application main() function calls gateInitialize(), which does the following:
1. Calls checkArg( ) to check for command line parameters and handle them
accordingly.
2. Calls IPTResetSession() to reset the demo data structures and initialize all
channels’ states to INIT.
3. Calls ClearAllBoards() to reset the board structures to default values.
4. Calls gateConfiguration() to read information from the configuration file
(gateway_R4.cfg or other CFG file determined by the user) and update the
ConfigFileParm in the Session data structure.
5. Calls gc_Start( ) to open all configured, call control libraries.
6. Calls printAllLibs() to print library status (open or failed).
7. Sets-up the call-back handler, PDLsr_enbhdlr( ). The callback handler
handles events that it receives from the SRL library. For more details see
Section 6.5.2. Handling SRL Events.
8. Calls pstnGetVOXChannels( ) which checks how many available PSTN
voice channels there are by doing the following:
• Gets number of PSTN boards, by calling PDLsr_getboardcnt( ).
• For each board that was found:
• Calls dx_Open( ) to open an analog board, or dt_Open( ) to open a
digital board.
• Calls ATDV_SUBDEVS( ) to get the number of channels on the
board.
27
Page 36

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
• Calculates the logical board and channel and saves them into
Session.pstnParams
• Closes the board, by calling dx_Close( ) or dt_Close( ).
9. Call ipGetChannels( ) which checks how many available IP channels there
are by doing the following:
• Gets number of IP boards from #define MAX_IP_BOARDS in
gatedefs.h
• For each board that was found:
• Calls gc_OpenEx( ) to open the board
• Calls ATDV_SUBDEVS( ) to get the number of channels on the
board
• Calculates the logical board and channel and save them in
Session.ipParams
• Registers the board with the Gatekeeper by calling
boardRegistration( )
10. Calls getGateChannels( ) to find the demo MAX available channels (the
smaller of available IP or Voice Devices and the number of channels
specified with the –n command line option, if used).
11. Calls pstnOpenFrontEnd( ) which opens the PSTN channels by doing the
following. For each channel:
• Calls gc_OpenEx ( ), which returns the PSTN LineDevH, and saves it
in Session.pstnParams
• If the PSTN board is an analog board:
• Calls gc_LoadDxParm( )
• Calls gc_GetVoiceH( ), which returns the PSTN VoiceH, and saves
it in Session.pstnParams
• If the PSTN board is a digital board:
• Calls gc_OpenEx( ), which returns the PSTN LineDevH, and saves
it in the Session.pstnParams structure
• Calls gc_GetNetworkH( ), which returns the PSTN NetwH, and
saves it in Session.pstnParams
12. Calls ipOpenDevices( ) which opens the IP channels by doing the following:
28
Page 37

6. Demo Details
• Calls gc_OpenEx( ) which opens all IP devices, returns the IP
LineDevH, and saves it in Session.ipParams
• Saves the channel number in the global array HandleToChannel[ ]
according to the LineDevH handle
13. The application main() function calls waitForKey( ), to receive keyboard
input.
6.5. Event Mechanism
The IP Gateway (Global Call) demo uses the SRL mechanism to retrieve events.
When an event occurs, SRL calls event handlers automatically. All events are
received by the SRL and then passed to the callback_hdlr() function for
handling.
In the initialization phase of the demo the gateInitialize() function sets up the
call-back handler, by calling PDLsr_enbhdlr().
6.5.1. Handling Keyboard Input Events
There is an endless loop {while(1)} in the main() function in the Gatemain.c file.
In that loop, the application waits forever for a keyboard event by calling the
waitForKey() function. The event must be handled immediately and eventspecific information should be retrieved before the next call to waitForKey().
When the next event occurs or when a time-out is reached, the waitForKey()
returns and the call-back handler function is called automatically.
6.5.2. Handling SRL Events
When the R4/Global Call event is received, the callback_hdlr( ) function
performs the following:
1. Calls gc_GetMetaEvent( ) to get the event
2. If the event is for a board, the application calls rasProcessEvent( ) to
process it.
29
Page 38

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
3. Otherwise, the application calls gc_GetUsrAttr( ) and then calls either
ipGetEvent( ) to process the IP event, or pstnGetEvent( ) to process the
PSTN event.
6.5.3. Handling Application Exit Events
Normal application exit events don’t enter the SRL. The main() function calls
PDLSetApplicationExitPath() before initialization. In Linux, this function sets
the signals (SIGINT, SIGTERM, SIGABRT) for making the appropriate exit
from the application. In Windows, this function enables the detection of
CTRL_CLOSE_EVENT (closing the window).
6.6. Demo State Machine
The application waits for a GCEV_UNBLOCKED event in the GATE_INIT state.
Upon receiving this event, the application calls ag_getxmitslot() for an analog
PSTN board or dt_getxmitslot() for a digital PSTN board to get the transmit time
slot (Xmitslot) for the PSTN device and saves it in the session.PSTNParams
structure. The application then calls gc_GetXmitSlot(VoiceH) to get the transmit
time slot (Xmitslot) for the IP device and saves it in the session.IPParams
structure.
The application then calls gc_WaitCall() to set the conditions for processing an
inbound call.
If the application receives GCEV_TASKFAIL, GCEV_BLOCKED, or
GCEV_OPENEX_FAIL, it calls endApplication() to gracefully shut down the
application.
If the application receives GCEV_OPENEX, it does nothing to avoid causing an
error.
The state transitions to GATE_NULL.
6.6.1. Call Establishment from IP
This section describes what happens when a call is initiated from the IP network.
30
Page 39

6. Demo Details
IP: GCEV_EXTENSION
IP: gc_SetUserInfo( )
IP: gc_AnswerCall( )
IP_OFFERED
IP: GCEV_ANSWERED
IP: gc_Listen( )
PSTN: gc_MakeCall( )
GATE_NULL
IP: GCEV_OFFERED
IP: gc_Extension( )
IP_CONNECTED
IP, PSTN: GCEV_RELEASECALL
IP, PSTN: IPTResetSession( )
GATE_RELEASE
IP: GCEV_EXTENSIONCMPLT
IP, PSTN: gc_ReleaseCallEx( )
IP, PSTN: GCEV_DISCONNECTED
pstnUnListen( )
IP, PSTN: gc_DropCall( )
GATE_CONNECTED
PSTN: GCEV_CONNECTED
PSTN: ag_Listen( )
or dt_Listen( )
IP, PSTN: GCEV_DROPCALL
IP: gc_Extension( )
GATE_DROP
Figure 5. Call Establishment from IP
1. In GATE_NULL, the application receives GCEV_OFFERED from the IP
side.
The application checks if there is a conflict with PSTN side. If there is no
conflict, the application calls gc_Extension( ) to get coder and telephone
number information from the IP side.
The state transitions to IP_OFFERED.
2. In IP_OFFERED, the application waits for GCEV_EXTENSION which
contains the coder and telephone number information.
The application then calls gc_SetUserInfo( ) and gc_AnswerCall( ).
When the application receives GCEV_ANSWERED from the IP side, the
application calls gc_Listen( ), to tell the IP line device to listen to the PSTN
time slot. The application calls gc_MakeCall( ) for the PSTN side to set up
the call on the PSTN side.
The state transitions to IP_CONNECTED.
31
Page 40

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
3. In IP_CONNECTED, when the application receives GCEV_CONNECTED
from the PSTN side, the application calls pstnListen( ), which in turn calls
ag_Listen( ) or dt_Listen( ) (ag for analog; dt for digital) to tell the PSTN
line device to listen to the IP time slot
The state transitions to GATE_CONNECTED
6.6.2. Call Establishment from PSTN
This section describes what happens when a call is initiated from the PSTN
network.
GATE_NULL
PSTN: GCEV_OFFERED
PSTN: gc_AcceptCall( )
IP: gc_MakeCall( )
IP, PSTN: GCEV_RELEASECALL
IPTResetSession( )
GATE_RELEASE
IP, PSTN: GCEV_DROPCALL
IP: gc_Extension( )
PSTN: GCEV_ACCEPT
PSTN_OFFERED
IP: GCEV_CONNECTED
IP: gc_Extension( )
PSTN: dt_Listen( ) or ag_Listen( )
IP: gc_Listen( )
PSTN: gc_AnswerCall( )
PSTN: GCEV_ACCEPT PSTN: GCEV_EXTENSION
IP_CONNECTED
IP: GCEV_EXTENSIONCMPLT
IP, PSTN: gc_ReleaseCallEx( )
GATE_DROP
IP, PSTN: GCEV_DISCONNECTED
IP, PSTN: gc_unlisten( )
IP, PSTN: gc_dropCall( )
GATE_CONNECTED
PSTN: GCEV_ANSWERED
Figure 6. Call Establishment from PSTN
1. In GATE_NULL, when the application receives GCEV_OFFERED from the
PSTN side, the application calls gc_AcceptCall( ) for the PSTN and
gc_MakeCall( ) for the IP side.
The state transitions to PSTN_OFFERED
32
Page 41

6. Demo Details
2. In PSTN_OFFERED the application waits for GCEV_CONNECTED from
the IP side.
When the application receives GCEV_CONNECTED it calls:
• gc_Extension( ) to get the call information from the IP side
• gc_Listen( ) to tell the IP line device to listen to the PSTN time slot
• pstnListen( ) which calls ag_Listen( ) or dt_Listen( ) (ag for analog; dt for
digital) to tell the PSTN line device to listen to the IP time slot
• gc_AnswerCall( ) to answer the call on the PSTN
The state transitions to IP_CONNECTED.
3. In IP_CONNECTED, when the application receives GCEV_ANSWERED
from the PSTN the state transitions to GATE_CONNECTED.
6.6.3. Call Teardown
1. When either side (PSTN or IP) sends a GCEV_DISCONNECTED event in
any state except for IP_OFFERED, the application calls gc_Unlisten( ) for
the IP side and ag_Unlisten( ) or dt_Unlisten( ) for the PSTN side. The
application also calls gc_DropCall( ) for both sides of the call to disconnect
the call.
The state transitions to GATE_DROP.
2. When the application receives GCEV_DROPCALL from both sides the
application calls gc_Extension( ) to get RTCP information for the call.
When the application receives GCEV_EXTENSION with the RTCP
information it calls gc_ReleaseCall( ) to release the call.
The state then transitions to GATE_RELEASE.
3. When the application receives a GCEV_RELEASECALL event it sends
IPTResetSession() and the call state transitions to GATE_NULL.
If a GCEV_DISCONNECTED event is received from the IP side when the state is
IP_OFFERED:
1. The application calls gc_DropCall( ) for the IP side and the state transitions
to IP_DROP.
33
Page 42

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
2. When the application receives GCEV_DROPCALL from the IP side, it calls
gc_Extension( ) to get the RTCP information.
When the application receives GCEV_EXTENSION the application calls
gc_ReleaseCall( )and the state transitions to GATE_NULL.
6.6.4. Glare Conditions
Glare conditions occur when a call is being initiated from both sides at the same
time. If such a condition is discovered, the state transitions directly to
GATE_DROP and proceeds with call teardown.
34
Page 43

Appendix A
Log File of IP Call Establishment
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:20
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 189
End of pstnOpenFrontEnd function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 99
Start ipOpenDevices function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 116
End of ipOpenDevices function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 57
In GATE_INIT State on channel 14
got Event GCEV_UNBLOCKED (0x833) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 57
In GATE_INIT State on channel 14
got Event GCEV_UNBLOCKED (0x833) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:49:21
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 129
In GATE_NULL State on channel (0xe)
got event GCEV_OFFERED (0x824) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
35
Page 44

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 227
Start OnExtension function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 250
Got extension data display:
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 262
Got extension data phone list:
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 336
Got extension data H221NONSTANDARD: country_code 181,extension 11,
manufacturer_code 11
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 342
Got extension data IPPARM_VENDOR_PRODUCT_ID IPLink
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 348
Got extension data IPPARM_VENDOR_VERSION_ID Dialogic Corp.
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 291
Got extension data IPPARM_CONFERENCE_GOAL
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 298
Got extension data IP_CONF
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 362
End of OnExtension function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 357
In IP_OFFERED State on channel (0xe)
got event GCEV_EXTENSION (0x868) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:00
ERENCEGOAL_ID A&ö= V4444ï
36
Page 45

TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:01
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:01
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 357
In IP_OFFERED State on channel (0xe)
got event GCEV_ANSWERED (0x802) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:01
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:01
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 654
In IP_CONNECTED State on channel 14
got event GCEV_CONNECTED (0x822) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:01
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 232
In pstnListen function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:53:01
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 275
End of pstnListen function on channel 14
Appendix A
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 436
Got GCEV_DISCONNECTED. Reason: Remote Termination
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 797
In GATE_CONNECTED State on channel 14
got event GCEV_DISCONNECTED (0x826) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 296
In pstnUnListen function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 348
End of pstnUnListen function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
37
Page 46

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 841
Drop call on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 880
In GATE_DROP State on channel 14
got event GCEV_DROPCALL (0x805) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 880
In GATE_DROP State on channel 14
got event GCEV_DROPCALL (0x805) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 227
Start OnExtension function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 272
Got extension data RTCP info:timestamp 644440,tx_packets 1948,tx_octets 490896
send_indication 1
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 362
End of OnExtension function on channel 14
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:54:24
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 880
In GATE_DROP State on channel 14
got event GCEV_EXTENSION (0x868) from IP
38
Page 47

Appendix B
Log File of PSTN Call Establishment
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:55
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 189
End of pstnOpenFrontEnd function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:56
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 99
Start ipOpenDevices function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:56
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 116
End of ipOpenDevices function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:57
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:57
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 57
In GATE_INIT State on channel 10
got Event GCEV_UNBLOCKED (0x833) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:57
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:57
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 57
In GATE_INIT State on channel 10
got Event GCEV_UNBLOCKED (0x833) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:57:57
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:37
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:37
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 129
In GATE_NULL State on channel (0xa)
got event GCEV_OFFERED (0x824) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:37
39
Page 48

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 140
Start ipMakeCall function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:37
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 205
End of ipMakeCall function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:37
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:37
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 511
In PSTN_OFFERED State on channel (0xa)
got event GCEV_ACCEPT (0x804) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 511
In PSTN_OFFERED State on channel (0xa)
got event GCEV_PROCEEDING (0x827) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 511
In PSTN_OFFERED State on channel (0xa)
got event GCEV_CONNECTED (0x822) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 232
In pstnListen function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 275
End of pstnListen function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 10
40
Page 49

DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 227
Start OnExtension function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 250
Got extension data display: target
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 362
End of OnExtension function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 654
In IP_CONNECTED State on channel 10
got event GCEV_EXTENSION (0x868) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 10
Appendix B
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 10:58:38
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 654
In IP_CONNECTED State on channel 10
got event GCEV_ANSWERED (0x802) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 416
Got GCEV_DISCONNECTED. Reason: Normal clearing
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 797
In GATE_CONNECTED State on channel 10
got event GCEV_DISCONNECTED (0x826) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 296
In pstnUnListen function on channel 10
41
Page 50

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 348
End of pstnUnListen function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 841
Drop call on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatepstn.c Line: 369
In pstnGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:03
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 880
In GATE_DROP State on channel 10
got event GCEV_DROPCALL (0x805) from PSTN
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 880
In GATE_DROP State on channel 10
got event GCEV_DROPCALL (0x805) from IP
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 385
In ipGetEvent function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 227
Start OnExtension function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
INFO: File: gateip.c Line: 272
Got extension data RTCP info:timestamp 649480,tx_packets 7971,tx_octets 733332
send_indication 1
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 362
End of OnExtension function on channel 10
DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gatestate.c Line: 880
In GATE_DROP State on channel 10
got event GCEV_EXTENSION (0x868) from IP
42
Page 51

DATE: 08/16/01 TIME: 11:00:05
TRACE: File: gateip.c Line: 466
End of ipGetEvent function on channel 10
Appendix B
43
Page 52

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
44
Page 53

Index
A
ag_Listen( ), 32, 33
ag_Unlisten( ), 33
APPMAIN.C, 29
ATDV_SUBDEVS( ), 27
C
Call connection, 3
Call establishment, 25
Call progress tones, 26
Call state
GATE_CONNECTED, 32, 33
GATE_DROP, 33
GATE_NULL, 30
IP_CONNECTED, 31, 33
IP_DROP, 33
IP_OFFERED, 31, 33
PSTN_OFFERED, 32
Call Teardown, 33
checkArg( ), 27
Command Line Switches, 18
ConfigFileParm, 27
Configuration file, 23, 25
D
Debug Level, 18
dt_Listen( ), 32, 33
dt_Unlisten( ), 33
G
GATE_CONNECTED, 32, 33
GATE_DROP, 33
GATE_NULL, 30
gatedefs.h, 21
gateip.c, 21
gateip.h, 21
gatemain.c, 21
gatepars.c, 22
gatepars.h, 22
gatepstn.c, 22
gatepstn.h, 22
gatestate.c, 22
gatestate.h, 22
gatestrc.h, 22
gatevars.h, 22
gateway_r4
executable, 22
gateway_r4.cfg, 9, 22, 25
gateway_r4.dsp, 22
gateway_r4.dsw, 22
gateway_r4.exe, 23
gateway_r4.ver, 22
gc_AcceptCall( ), 32
gc_AnswerCall( ), 31, 33
gc_Close( ), 27
45
Page 54

IP Gateway (Global Call) Demo Guide for Linux and Windows
gc_DropCall( ), 33
gc_Extension( ), 31, 33
gc_GetNetworkH( ), 28
gc_GetVoiceH( ), 28
gc_GetXmitSlot(), 30
gc_Listen( ), 31, 33
gc_MakeCall( ), 31, 32
gc_Open( ), 27
gc_OpenEx( ), 28
gc_OpenEx( ) , 28
gc_ReleaseCall( ), 33
gc_SetUserInfo( ), 31
gc_Start( ), 27
gc_Unlisten( ), 33
GCEV_ANSWERED, 31, 33
GCEV_CONNECTED, 32, 33
GCEV_DISCONNECTED, 33
GCEV_DROPCALL, 33
GCEV_EXTENSION, 31, 33
GCEV_OFFERED, 31, 32
Glare Conditions, 34
H
H.323 terminal, 25
HandleToChannel[ ], 28
I
incfile.h, 22
IP
State Diagram, 31
IP address, 25
IP, Log File, 35
IP_CONNECTED, 31, 33
IP_DROP, 33
IP_OFFERED, 31, 33
ipGetChannels( ), 27
ipOpenDevices( ), 28
IPTMail_R4.cfg, 27
K
Keyboard Commands, 20
L
libdbg.c, 23
libdbg.h, 23
libdefs.h, 23
libpdl.a, 24
libutil.a, 23
line device, 3
LineDevH, 28
local phone number, 26
Log File, IP, 35
Log File, PSTN, 39
M
main(), 29
main.h, 22
makefile, 22
makefile.util, 23
46
Page 55

Index
N
NetwH, 28
P
PDL, 3
pdl.c, 24
PDLsr_enbhdlr( ), 27
PDLsr_getboardcnt( ), 27
Platform Dependency Library, 3
PSTN
State Diagram, 32
PSTN channel, 3
PSTN, Log File, 39
PSTN_OFFERED, 32
pstnGetVOXChannels( ), 27
pstnOpenFrontEnd( ), 28
R
remote phone number, 25
Routing, 25
T
Teardown, 33
U
util.dsp, 23
util.dsw, 23
util.lib, 23
util.ver, 23
V
VoiceH, 28
S
Session.ipParams, 28
Session.pstnParams, 27, 28
sr_enbhdlr( ), 29
SRL mechanism, 29
State Diagram
IP, 31
PSTN, 32
State machine, 22
Switches
Command Line, 18
47
Page 56

48
 Loading...
Loading...