
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
CONTENTS PAGE
1. INTRODU CT IO N.................................................................................1
2. CONNECTING THE PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY VIA
GPIB INTER FA CE..............................................................................2
3. CONNECTING THE PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY VIA
RS232 INTE R FAC E.............................................................................5
4. INPUT AN D O UT PU T QU EUE..........................................................8
5. COMMANDS AND S YN TA X..............................................................9
6. DETAILS OF COM MAN D REF ERE NCE......................................21
7. STATUS A ND E RR OR R EP ORT IN G.............................................59
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
⎯ i ⎯
⎯ ii ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
1. INTRODUCTION
In the modern automatic measurement system, communication between
equipments and computers is essential. The measuring procedures can be
varied with users’ testing programs, therefore, the programmable power
supply can be operated remotely from an instrument controller or computer
through the RS232 interface (optional) or GPIB (optional).
Interface selection and setup
The GPIB address can be changed in normal operation condition. Press
[SHIFT] key and [LOCAL] key on the front panel, in which the last
transmitting interface settings will be displayed. Select interface and press
[ENTER], then select the baud rate (or GPIB address) and press [ENTER]
to confirm the setting by using the knobs.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
2. CONNECTING THE PROGRAMMABLE POWER
SUPPLY VIA GPIB INTERFACE
The GPIB interface capabilities:
The GPIB interface of the programmable power supply corr esponds to the
standard of IEEE488.1-1987, IEEE488.2-1 992 and SCPI-1994. The GPIB
interface functions are listed as follows:
SH1(Source Handshake) : The power supply can transmit multilane
messages through the GPIB.
AH1(Acceptor Handshake) : The power supply can receive multilane
messages across the GPIB.
T6(Talker) : Talker interface function includes basic
talker, serial poll, and unaddress if MLA
capabilities, without talk only mode
function.
L4 (Listener) : The power supply becomes a listener when
the controller sends its listen address with
the ATN (attention) line asserted. The
power supply does not have listen only
capability.
SR1 (Service Request) : The power supply asserts the SRQ (Service
request) line to notify the controller when
it requires service.
RL1 (Remote/Local) : The power supply responds to both the
GTL(Go to Local) and LLO(Local Lock
Out) interface messages.
PP0 (Parallel Poll) : The power supply has no Parallel Poll
interface function.
⎯ 1 ⎯
⎯ 2 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
DC1 (Device Clear) : The power supply has Device clear
capability to return the device to power on
status.
DT0 (Device Trigger) : The power supply has no Device Trigger
interface function.
C0 (Controller) : The power supply can not control other
devices.
Notes for GPIB installation
When the programmable power supply is set up with a GPIB system, please
check the following things:
z Only a maximum of 15 devices can be connected to a single GPIB bus.
z Do not use more than 20m of cable to connect devices to a bus.
z Connect one device for every 2m of cable used.
z Each device on the bus needs a unique device address. No two devices
can share the same devic e addres s.
z Turn on at least two-thirds of the devices on the GPIB system while
using the system.
z Do not use loop or parallel structure for the topology of GPI B system.
Computer’s Connection
A personal computer with a GPIB card is the essential facilities in order to
operate the programmable power supply via GPIB interfa ce.
The connections between power supply and co mputer are following :
I. Connect one end of a GPIB cab le to the compu ter.
II. Connect the other end of the GPIB cable to the GPIB port on the
programmable power supply.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
III. Turn on the programmable power supply.
IV. Turn on the computer.
The GPIB connection testing
If you want to test whether the GPIB connection is working or not, you can
send a GPIB command from compu ter. Fo r instan ce, the quer y comma nd
*idn?
should return the Manufacturer, model number, serial nu mber and firmware
version in the fol lowing forma t:
GW.Inc,PSM-2010,A000000,FW1.00
If you do not receive a proper response from the power supply, please
check if the power is on, the GPIB address is correct, and all cable
connections are active.
⎯ 3 ⎯
⎯ 4 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
3. CONNECTING THE PROGRAMMABLE POWER
SUPPLY VIA RS232 INTERFACE
The RS232 interface capabilities:
The RS232 interface provides a point-to-point connection between two
items of equipment such as a computer and the power supply. There are
some parameters you need to set on the both sides. Once you have set
these parameters, you can control the power supply through the RS232
interface.
z Baud rate: You can set rates of 1200, 2400, 4800 or 9600 baud.
z Parity bit: none.
z Data bit: 8 bits.
z Stop bit: 1 stop bit.
z Data flow control: none.
Notes for RS232 installation
The power supply is a DTE device with a 9-pin D-type shell RS232
connector located on the rear panel. Figure 1 shows the equipment of 9-pin
connector (male) with its pin number assignments. Figure 2 shows the
wiring configuration for DB9 to DB9. When the programmable power
supply is set up with a RS232 interface, please check the following points:
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
z Ensure that the chassis ground of the equipment is connected to the
chassis ground of the external device.
z Do not use more than 15m of cable to connect devices to a PC.
z Ensure the same baud rate is used on the device as the one used on PC
terminal.
z Ensure the connector for the both side of cable and the internal
connected line are met the demand of the instrument.
1. No connection
2. Receive Data(RxD) (input)
3. Transmit Data(TxD) (output)
4. No connection
5. Signal Ground(GND)
6. No connection
7. No connection
8. No connection
9. No connection
Figure 1 Pin assignments of the RS232 connector on the rear panel for DB-9-D
z Do not connect the output line of one DTE device to the output line of
the other.
z Many devices require a constant high signal on one or more input
pins.
z Ensure that the signal ground of the equipment is connected to the
signal ground of the external device.
⎯ 5 ⎯
⎯ 6 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
*idn?
EQUIPMENT
COMPUTER
should return the Manufacturer, model number, serial nu mber and firmware
version in the fol lowing forma t:
(DB9, DTE)
Pin2
(DB9, DTE)
Pin2
GW.Inc,PSM-2010,A000000,FW1.00
If you do not receive a proper response from the power supply, please
check if the power is on, the RS232 baud rate are the same on both sides,
and all cable connections are active.
Pin3
Pin5 Pin5
Pin3
4. INPUT AND OUTPUT QUEUE
Figure 2 Wiring configuration for DB9 to DB9
Computer’s Connection
A personal computer with a COM port is the essential facilities in order to
operate the programmable power supply via RS232 interface.
The connections between power supply and computer are as fo llows:
I. Connect one end of a RS232 cable to the computer.
The design of 128 bytes input queue and 128 bytes output queue for
storing the pending commands or return messages is to prevent the
transmitted commands of remote control and return messages from missing.
As the maximum stored capacity for Error/Event Queue is 20 groups of
messages, it should be noted that input data exceeding the capacity by using
these buffers will cause data missing.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
II. Connect the other end of the cable to the RS232 port on the
programmable power supply.
III. Turn on the programmable power supply.
IV. Turn on the computer.
The RS232 connection testing
If you want to test whether the RS232 connection is working or not, you
can send a command from computer. For instance, using a terminal
program send the query command.
⎯ 7 ⎯
⎯ 8 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
5. COMMANDS AND SYNTAX
The GPIB commands of the programmable power supply are compatible
with IEEE-488.2 and SCPI standards
SCPI
SCPI (Standard Commands for Programmable Instruments) is a standard
that created by an international consortium of the major test and
measurement equipment manufacturers. The IEEE-488.2
adopted by SCPI to provide common commands for the identical functions
of different programmable instruments.
Common Command & Queries
Syntax & Status Data Structure
SCPI
Interface Function
AABBCCDD
syntax has been
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
communication, which contain the <PROGRAM MESSAGE> (or simply
“commands”) and <RESPONSE MESSAGE>. The two kinds of messages
represent the syntax formation of device command and return value. The
data structure is the constitution of status reporting, which IEEE-488.2
standard have been defined.
The common commands and queries are included to layer C. Commands
and queries can be divided into two parts: mandatory and optional.
Commands modify control settings or tell the instrument to perform a
specific action. Queries cause the instrument to send data or status
information back to the computer. A question mark at the end of a
command identifies it as a query.
Layer D is interrelated with device information. Different devices have
different functions. SCPI command sets belong to this layer.
Command Syntax
If you want to transfer any ins tructions to an instrument, and comp ly with
SCPI, there are three basic elements must be included.
z Command header
z Parameter (if required)
z Message terminator or separator
SCPI
IEEE-488.2 IEEE-488.2
Figure 3 the relationship between IEEE-488.1, IEEE-488.2, and SCPI
SCPIIEEE-488.1
As shown in the figure 3, the IEEE-488.1 standard locates at layer A, th e
layer A belongs to the protocol of interface function on the GPIB bus. The
source handshake (SH), acceptor handshake (AH) and talker are included to
this layer (10 interface functions totally).
At layer B, the syntax and data structure could be the essence of entire
IEEE-488.2 standard. The syntax defines the function of message
⎯ 9 ⎯
⎯ 10 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
:
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Command Header
The command header has a hierarch ical st ructure th at can be repre sented b y
a command tree (Figure 4).
The top level of the tre e is the root level. A root node i s located at the root
level. A root node and one or more lower-level nodes form a header path to
the last node called the leaf node.
:ERRor
:SYSTem
:STATe
AUTO
:STARt
Root node
:CYCLe
Lower-level node
Leaf Node
Figure 4: Tree hierarchy
The command header is configured by header path and leaf node. Figure 5
shows the command header for the leaf node indicated in Figure 4.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Parameter
If the commands have parameters, the values have to be included. In this
manual, when we expressed the syntax of the command, the < > symbols
are used for enclosing th e parameter type. For instance, the synt ax of the
command in Figure 6 includes the Boolean parameter type.
NOTE: Do not include the <, >, or | symbols when entering the actual
value for a parameter.
Figure 6 Command Header with Parameter
Message Terminator and Message Separator
z GPIB message terminators
In accordance with IEEE 488.2 standard, any of the following message
terminators are acceptable:
^
z LF
END Line feed code (hexadecima l 0A) with END
message
z LF Line feed code
z <dab>
^
END Last data byte with END message
These terminators are compatible with most application programs. A
semicolon separates one command from another when the commands
appear on the same line.
Figure 5 Command Header
⎯ 11 ⎯
⎯ 12 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
z RS232 message terminators
As there is no signal of end message on RS232 bus, therefore, use LF as
message terminator. When a series of commands are sent to the instrument,
it must add a LF to be a judgment for message terminator. As for query
command, the return message of the instrument is also added a LF for PC to
judge message terminator.
Entering Commands
The standards that govern the command set for the programmable power
supply allow for a certain amount of flexibility when you enter commands.
For instance, you can abbreviate many commands or combine commands
into one message that you send to the programmable power supply. This
flexibility, called friendly listening, saves programming time and makes the
command set easier to remember and use.
Command Characters
The programmable power supplies are not sensitive to the case of
command characters. You can enter commands in either uppercase or
lowercase.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Combining Commands
You can use a semicolon (;) to combine commands. For example:
OUTP 1;MEAS:VOLT?;MEAS:CURR?------- ------- --
If the command that follows the s emicolon has a differ ent header pa th from
the root level, you must use a co lon to force a return to th e root l evel :
VOLT:PROT 20;:OUTP 1
If the command that follows the semicolon has the same header path, you
may omit the colon and the path and state only the new leaf node. For
example:
VOLT:PROT: LEV 12.34; VOLT:PROT:STAT 1
is equal to
VOLT:PROT:LEV 12.34; STAT 1
You can combine commands and queries into the same message. Note, for
example, the following combination:
VOLT 12.34;VOLT ?
You can execute any command with white space characters. You must,
however, use at least one space between the parameter and the command
header
Abbreviating Commands
Most commands have a long form and a short form. The listing for each
command in this section shows the abbreviations in uppercase. For
instance, you can enter the query :VOLTage 1.23 simply as :VOLT 1.23
Because the programmable power supply hypothesis that a command starts
from the root, you have the option of beginning the initial command header
with a colon (:).
⎯ 13 ⎯
Synopsis of Commands
The tables in this section summarize the command of the programmable
power supply. These tables divide the commands into three functional
classifications:
z General Setting Commands
z Trigger Commands
z Status Commands
z System Commands
z Calibration Commands
z RS232 Interface Commands
z IEEE-488.2 Common Commands
z Miscellaneous Commands
⎯ 14 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Note.
“ | ” It separates one of two or more alternative parameters.
“{}” It enclose parameters within a command string.
“[]” It indicate optional keywords or parameters.
“<>” It indicate to substitute a value or a code for the enclose parameters.
General Setting Commands
APPLy {<voltage>|DEF|MIN|MAX}[,{<current>|DEF|MIN|MAX}]
APPLy?
[SOURce:]CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude] {<current>|MIN|MAX|UP|DOWN}
[SOURce:]CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
[SOURce:]CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement] {<numeric value>|DEFault}
[SOURce:]CURRent[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement]? [DEFault]
[SOURce:]CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude] {<current>|MIN|MAX}
[SOURce:]CURRent[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel] {<current>|MIN|MAX}
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection[:LEVel]? [MIN|MAX]
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection:STATe?
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped?
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection:CLEar
[SOURce:]CURRent:PROTection:DELay {<numeric value> |MIN|MAX}
[SOURce:]VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude] {<voltage>|MIN|MAX|UP|DOWN}
[SOURce:]VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate][:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
[SOURce:]VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement] {<numeric value>|DEFault}
[SOURce:]VOLTage[:LEVel][:IMMediate]:STEP[:INCRement]? [DEFault]
[SOURce:]VOLTage[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude] {<current>|MIN|MAX}
**
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
[SOURce:]VOLTage[:LEVel]:TRIGgered[:AMPLitude]? [MIN|MAX]
[SOURce:]VOLTage:PROTection[:LEVel] {<current>|MIN|MAX}
[SOURce:]VOLTage:PROTection[:LEVel]? [MIN|MAX]
[SOURce:]VOLTage:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
[SOURce:]VOLTage:PROTection:STATe?
[SOURce:]VOLTage:PROTection:TRIPped?
[SOURce:]VOLTage:PROTection:CLEar
[SOURce:]VOLTage:RANGe {P8V|P20V|P15V|P30V|P60V|LOW|HIGH}*
[SOURce:]VOLTage:RANGe?
MEASure[:SCALar][:VOLTage][:DC] ?
MEASure[:SCALar]:CUR Rent[:DC] ?
OUTPut[:STATe]{0|1|OFF|ON}
OUTPut[:STATe]?
* P8V and P20V are for PSM-2010, P15V and P30V are for PSM-3004,
P30V and P60V are for PSM-6003.
** The range of the Delay time can be set at 0.0~10.0 sec.
z Trigger Commands
TRIGger[:SEQuence]:DELay {<seconds>|MIN|MAX}
TRIGger[:SEQuence]:DELay?
TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SOURce {BUS|IMMediate}
TRIGger[:SEQuence]:SOURce?
INITiate[:IMMediate]
*TRG
⎯ 15 ⎯
⎯ 16 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
z Status Commands
STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle {0|1}
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle?
STATus:QUEStionable[:EVENt]?
STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
STATus:OPERation:ENABle {0|1}
STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
STATus:OPERation[:EVENt]?
STATus:PRESet
z System Commands
*IDN?
*RST
*TST?
*SAV {0|1|2|…..|99}
*RCL {0|1|2|…..|99}
DISPlay:CONTrast {0|1|2|3|4}*
DISPlay:CONTrast?
DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe] {0|1|OFF|ON }
DISPlay[:WINDow][:STATe]?
DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA] <quoted string>
DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT[:DATA]?
DISPlay[:WINDow]:TEXT:CLEar
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
SYSTem:BEEPer:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON }
SYSTem:BEEPer::STATe?
SYSTem:BEEPer:[:IMMediate]
SYSTem:ERRor[:NEXT]?
SYSTem:VERSion?
SYSTem:MEMory?
*Arrange from dark to bright in the order of 0 ~ 4.
z Calibration Commands
CALibration:PASSword {password}*
CALibration:TYPe {0|1|2|3}**
CALibration:TYPe?
CALibration:VOLTage:MINimum {numeric value}
CALibration:VOLTage:MIDDle {numeric value}
CALibration:VOLTage:MAXimum {numeric value}
CALibration:VOLTage:PROTection
CALibration:CURRent:MINimum {numeric value}
CALibration:CURRent:MIDDle {numeric value}
CALibration:CURRent:MAXimum {numeric value}
CALibration:CURRent:PROTection
CALibration:SAVe
CALibration:END
* The cord number for PSM-2010 is 2010, for PSM-3004 is 3004 and for
PSM-6003 is 6003.
⎯ 17 ⎯
⎯ 18 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
* * 0: Voltage calibration, 1: OVP calibration, 2: Current calibration,
3: OCP calibration
z RS232 Interface Commands
SYSTem:LOCal
SYSTem:REMote
SYSTem:RWLock
z IEEE-488.2 Common Commands
*CLS
*ESE {enable value}
*ESE?
*ESR?
*IDN?
*OPC
*OPC?
*RCL {0|1|2|…..|99}
*RST
*SAV {0|1|2|…..|99}
*SRE {enable value}
*SRE?
*STB?
*TRG
*TST?
*WAI
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
z Miscellaneous Commands
SYSTem:AUTO[:STATe] {OFF|ON}
SYSTem:AUTO[:STATe]?
SYSTem:AUTO:STARt {0|1|2|…..|99}
SYSTem:AUTO:STARt?
SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe {0|1|2|…..|99}
SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe?
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe {0*|1| 2|…..|9999 9}
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe?
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay {0|1|2|…..|59999}**
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay?
* 0 : Auto, can proceed operation limitlessly (∞).
**Unit: 0.1second.
⎯ 19 ⎯
⎯ 20 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
6. DETAILS OF COMMAND REFERENCE
Each command in this chapter will give a detailed description. The
examples of each command will be provided and what query form might
return.
z IEEE-488.2 COMMON COMMANDS
*CLS
Function:
Clear all event status data register. This includes the Output Queue,
Operation Event Status Register, Questionable Event Status Register, and
Standard Event Status Register.
Syntax:
*CLS
Examples:
*CLS clears all event registers.
*ESE
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
value of the binary bits of the ESER.
Examples:
*ESE 65 sets the ESER to binary 0100 0001.
If the ESER contains the binary value 1000 0010, the *ESE? will return
the value of 130.
*ESR?
Function:
Return and clear the con ten ts of the Sta ndard Even t Sta tus Reg ist er ( SESR) .
Syntax:
*ESR?
Returns:
<Enable value> is a number from 0 to 255 that indicates the decimal
value of the binary bits of the ESER.
Examples:
If the ESER contains the binary value 1100 0110, the *ESR? will return
the value of 198.
Function:
Set or return the bits in the Event Status Enable Register (ESER). The
ESER enables the Standard Event Status Register (SESR) to be summarized
on bit 5 (ESB) of the Status Byte Register (SBR).
Syntax:
*ESE <Enable value>
*ESE?
<Enable value> is in the range from 0 through 255.
Returns:
<Enable value> is a number from 0 to 255 that indicates the decimal
⎯ 21 ⎯
*IDN?
Function:
Return the unique iden tifi catio n cod e of th e pow er suppl y.
Syntax:
*IDN?
Returns:
<string> includes Manufacturer, model number, serial number and
firmware version.
⎯ 22 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
*IDN? Returns
GW.Inc,PSM-2010,A1234567,FW1.00
*OPC
Function:
The command form (*OPC) sets the operation complete bit (bit 0) in the
Standard Event Status Register (SESR) when all pending operations are
finished.
The query form (*OPC?) tells the programmable power supply to place an
ASCII 1 in the Output Queue when the power supply completes all pending
operations.
Syntax:
*OPC
*OPC?
Returns:
1
*RCL
Function:
Recall the setting data from the memory saved previously.
Syntax:
*RCL <Integers>
<Integers> is in the range from 0 through 99.
Examples:
*RCL 12 recalls the setting data stored in memory location 12.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
*RST
Function:
Set all control settings of power supply to their default values but does not
purge stored setting. The equivalent panel control will be set as below:
Front Panel Control Default Setting
OUTPUT OFF
CURRENT SET
CURRENT TRIGGER
VOLTAGE SET
VOLTAGE TRIGGER
DELAY 0.1 sec
OCP DELAY 0 sec
AUTO SET OFF
RECALL (memory location) 00
OVP SET
OCP SET
STEP SET
RECALL RANGE
PSM-2010:20.000A
PSM-3004:7.000A
PSM-6003:6.000A
0
PSM-2010:22.000V
PSM-3004:32.000V
PSM-6003:65.000V
PSM-2010:22.000A
PSM-3004:7.700A
PSM-6003:6.600A
0.001V,0.001A
START 00
CEASE 99
CYCLE 2
⎯ 23 ⎯
⎯ 24 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Syntax:
*RST
*SAV
Function:
Save the setting data to a specific memory location.
Syntax:
*SAV <Integers>
<Integers> is in the range from 0 through 99.
Examples:
*SAV 01 saves the current setting data to memory location 1.
*SRE
Function:
Set the contents of the Service Request Enable Register (SRER). The query
form returns the contents of the SRER. Bit 6 of the SRER is always zero.
The bits on the SRER correspond to the bits on the SBR.
Syntax:
*SRE <Enable Value>
*SRE?
<Enable Value> is in the range from 0 through 255.
Returns:
<Integers> is in the range from 0 through 255.
Examples
*SRE 7 sets bits of the SRER to 0000 0111.
If the *SRE? returns 3, the SRER is set to 0000 0011.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
*STB?
Function:
The query of the Status Byte register (SBR) with *STB? will return a
decimal number represe ntin g the bits that ar e set ( true) in th e sta tus regis ter.
Syntax:
*STB?
Returns:
<Integers> is in the range from 0 through 255.
Examples:
*STB? returns 81, if SBR contains the binary value 0101 0001.
*TRG
Function:
When select bus as trigger source, this command will generates a trigger to
the trigger subs yste m.
Syntax:
*TRG
*PSC
Function:
Set or query the Power-on-Status-Clean-Flag.
Syntax:
*PSC {0|1}
*PSC?
Examples:
*When PSC 1 is turned on, the SESER,SRER,OSER and QSER will be
removed.
⎯ 25 ⎯
⎯ 26 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
*TST?
Function:
Self-test and test the RAM, ROM.
Syntax:
*TST?
Returns:
0|-300
Examples:
*TST? returns 0, if the test is successful.
*TST? returns –300, if the test i s unsuc cessfu l.
*WAI
Function:
WAI prevents the programming instrument from executing further
commands or queries until all pending operations are finish ed.
Syntax:
*WAI
z GENERAL SETTING COMMANDS
:APPLy
Function:
Set the output voltage and current value.
Syntax:
:APPLy {<Voltage>|DEF|MIN|MAX}[,{<Current>|DEF|MIN|MAX}]
:APPLy ?
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
:APPLy DEF, MAX
You can use DEF, MIN or MAX to replace voltage value <
current value
<Current>.
Voltage> or
1) When select DEF, the voltage value is at 0, and the current value is at
20A(PSM-2010). Please refer to Table1-1, Table1-2 and Table1-3.
2) When select MIN, both values of voltage and curr ent are a t 0.
3) When select MAX, both values of voltage and current can be set at the
maximum value of the selected range. Please refer to Table1-1,
Table1-2 and Table1-3.
4) If only one parameter is specified, the power supply will regard it as
voltage value.
Ex
:APPLy 2.0
:APPLy ? This command returns present voltage and current setting
5)
values.
Voltage
Current
Programming Range 0V to 8.24V 0V to 20.6V
MAX Value 8.24V 20.6V
MIN Value 0V 0V
DEFault Value 0V 0V
*RST Value 0V
MAX Ovp Value 22V
MIN Ovp Value 0V
Programming Range 0A to 20.6A 0A to 10.3A
MAX Value 20.6A 10.3A
MIN Value 0A 0A
DEFault Value 20A 10A
*RST Value 20A
MAX Ocp Value 22A
MIN Ocp Value 0A
0-8V/20A Range 0-20V/10A Range
⎯ 27 ⎯
Table1-1. PSM-2010 Programming Ranges
⎯ 28 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
Voltage
Current
Voltage
Current
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Programming Range 0V to15.45V 0V to 30.9V
MAX Value 15.45V 30.9V
MIN Value 0V 0V
DEFault Value 0V 0V
*RST Value 0V
MAX Ovp Value 32V
MIN Ovp Value 0V
Programming Range 0A to 7.21A 0A to 4.12A
MAX Value 7.21A 4.12A
MIN Value 0A 0A
DEFault Value 7A 4A
*RST Value 7A
MAX Ocp Value 7.7A
MIN Ocp Value 0A
0-15V/7A Range 0-30V/4A Range
Table1-2. PSM-3004 Programming Ranges
Programming Range 0V to 30.9V 0V to 61.8V
MAX Value 30.9V 61.8V
MIN Value 0V 0V
DEFault Value 0V 0V
*RST Value 0V
MAX Ovp Value 65V
MIN Ovp Value 0V
Programming Range 0A to 6.18A 0A to 3.4A
MAX Value 6.18A 3.4A
MIN Value 0A 0A
DEFault Value 6A 3A
*RST Value 6A
MAX Ocp Value 6.6A
MIN Ocp Value 0A
0-30V/6A Range 0-60V/3A Range
Table1-3. PSM-6003 Programming Ranges
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
:CURRent
Function:
Set the output cur ren t valu e.
Syntax:
:CURRent {<current>|MIN|MAX|UP|DOWN}
1) <current> The range is from 0.0000 through 20.6000(PSM-2010
Please refer to Table1-1, Ta ble1-2 and Ta ble1-3.
2) MIN is for 0.0000 while MAX for 20 .6000(PSM-2010). Please refer to
Table1-1, Table1-2 and Table1-3.
3) Up is for the current with one value increasing while down for the
current with one value decr easing. The value is set by the co mmand of
CURRent:STEP.
Examples:
:CURRent 2.0 sets the current limit to 2.0000 amps(PSM-2010).
:CURRent MAX sets the current limit to 20.6000(PSM-2010) amps.
:CURRent:STEP 0.1;CURRent UP is for Current to increase 0.1 amps.
:CURRent?
Function:
Query the output current value.
Syntax:
:CURRent? [MIN|MAX]
Returns:
Scientific mark
⎯ 29 ⎯
⎯ 30 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
:CURRent? returns +1.20000000E-02 if the current limit setting is 0.0120
amps(PSM-2010).
:CURRent? MIN returns +0.00000000E+00(PSM-2010)..
:CURRent? MAX returns +2.06000000E+01 (PSM-2010).
:VOLTage
Function:
Set the output voltage value.
Syntax:
:VOLTage {<voltage>|MIN|MAX|UP|DOWN}
1) <voltage> the range is from 0.0000 through 20.6000 (PSM-2010).
Please refer to Table1-1, Ta ble1-2 and Ta ble1-3.
2) MIN is for 0.0000 while MAX for 20.6000(PSM-2010).
Table1-1, Table1-2 an d Ta ble1- 3.
3) UP is for the voltage with one value increasing while down for the
voltage with one value decreasing. The value is set by the command of
VOLTage:STEP.
Please refer to
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Syntax:
:VOLTage? [MIN|MAX]
Returns:
Scientific mark
Examples:
:VOLTage? returns +1.20000000E-02 if the voltage limit setting is 0.0120
volts(PSM-2010).
:VOLTage? MIN returns +0.00000000E+00(PSM-2010).
:VOLTage? MAX returns +2.06000000+01(PSM-2010).
:CURRent:STEP
Function:
Set or query the current step si ze.
Syntax:
:CURRent:STEP {<Decimal number>|DEFault}
:CURRent:STEP? [DEFault]
Examples:
Examples:
:VOLTage 2.0 sets the voltage limit to 2.0000 volts (PSM-2010).
:VOLTage MAX sets the voltage limit to 20.6000 volts (PSM-2010).
:VOLTage:STEP 0.1;VOLTage UP is for Voltage to increase 0.1 volts.
:VOLTage?
Function:
Query the output voltage value.
⎯ 31 ⎯
1) :CURRent:STEP 1.0 sets the step size to 1.0A for current
programming with the CURRent:UP and CURRent:DOWN
command .The immediate current level increases or decreases by the
value of the step size.
2) :CURRent:STEP DEF sets the step size to minimum resolution
0.5mA(PSM-2010).
3) :CURRent:STEP? returns the present current step size.
4) :CURRent:STEP? DEF returns the minimum resolution step size
0.5mA(PSM-2010).
⎯ 32 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
:VOLTage:STEP
Function:
Set or query the voltage step size.
Syntax:
:VOLTage:STEP {<Decimal number>|DEFault}
:VOLTage:STEP? [DEFault]
Examples:
1) :VOLTage:STEP 1.0 sets the step size to 1.0V for voltage
programming with the VOLTage:UP and VOLTage:DOWN
command .The immediate voltage level increases or decreases by the
value of the step size.
2) :VOLTage:STEP DEF sets the step size to minimum resolution
0.5mV(PSM-2010).
3) :VOLTage:STEP? returns the present voltage step size.
4) :VOLTage:STEP? DEF returns the minimum resolution step size
0.5mV(PSM-2010).
:CURRent:TRIGgered
Function:
Set or query the triggered current level.
Syntax:
:CURRent:TRIGgered {<Decimal number>|MIN|MAX}
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
2) :CURRent:TRIGgered MAX sets the triggered current to the highest
programmable triggered current levels.
3) :CURRent:TRIGgered MIN sets the triggered current to
0.0000A(PSM-2010).
4) :CURRent:TRIGgered? returns the pre sen t trigg ered curr ent lev el.
5) :CURRent:TRIGgered? MAX returns the highest programmable
triggered current level.
6) :CURRent:TRIGgered? MIN returns the lowest programmable
triggered current level.
:VOLTage:TRIGgered
Function:
Set or query the triggered voltage level.
Syntax:
:VOLTage:TRIGgered {<Decimal number>|MIN|MAX}
:VOLTage:TRIGgered? [MIN|MAX]
Examples:
1) :VOLTage:TRIGgered 1.0 sets the triggered voltage to
1.0000V(PSM-2010).
2) :VOLTage:TRIGgered MAX sets the triggered voltage to the highest
programmable triggered voltage levels.
:CURRent:TRIGgered? [MIN|MAX]
Examples:
1) :CURRent:TRIGgered 1.0 sets the triggered current to
1.0000A(PSM-2010).
⎯ 33 ⎯
3) :VOLTage:TRIGgered MIN sets the triggered voltage to
0.0000V(PSM-2010).
4) :VOLTage:TRIGgered? returns the pr esen t trig ger ed vo ltag e lev el.
5) :VOLTage:TRIGgered? MAX returns the highest programmable
triggered voltage level.
⎯ 34 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
6) :VOLTage:TRIGgered? MIN returns the lowest programmable
triggered voltage level.
:MEASure:CURRent?
Function:
Read the actual output current.
Syntax:
:MEASure:CURRent?
Returns:
Scientific mark
Examples:
:MEASure:CURRent? might return +1.23400000E+00 to indicate that
the load is drawing 1.2340 A(PSM-2010).
:MEASure?
Function:
Read the actual output voltage.
Syntax:
:MEASure?
Returns:
Scientific mark
Examples:
:MEASure? might return +1.15500000E+01 to indicate the voltage output
is 11.5500V(PSM-2010).
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
:CURRent:PROTection
Function:
Set the overcurrent protection value.
Syntax:
:PROTection:CURRent {<Decimal numbers>|MIN|MAX}
Examples:
:CURRent:PROTection 10 sets the overcurrent protection value to
10.000A(PSM-2010).
:CURRent:PROTection MIN sets the overcurrent protection value to
0.000A(PSM-2010).
:CURRent:PROTection MAX sets the overcurrent protection value to
22.000A(PSM-2010). Please refer to Table1-1, Table1-2 and Table1-3.
:CURRent:PROTection?
Function:
Query the overcurr ent pro tec tion valu e.
Syntax:
:CURRent:PROTection? [MIN|MAX]
Returns:
Scientific mark
Examples:
:CURRent:PROTection? will return the overcurrent protection value.
:CURRent:PROTection? MIN will return 0.
:CURRent:PROTection? M AX will return the hi ghest programmable current
values. Please refer to Table1-1, Table1-2 and Tabl e1-3.
⎯ 35 ⎯
⎯ 36 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
:CURRent:PROTection:STATe
Function:
Set or query the overcurrent pro tec tion status.
Syntax:
:CURRent:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
:CURRent:PROTection?
Examples:
:CURRent:PROTection:STATe 0 sets the over-current protection off.
If the overcurrent protection setting is on, the command of
CURRent:PROTection? will return the value of 1.
:CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped?
Function:
Query if the overcurrent protection circuit is tripped.
Syntax:
:CURRent:PROTection:TRIPped?
Returns:
0|1
Examples:
This command will returns “1” if the overcurrent protection is tripped and
not cleared or “0” if not tripped.
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay
Function:
Set the OCP delay value.
Syntax:
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay{<Decimal number>|MIN|MAX}
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay 3 sets the OCP delay va lu e to 3 s ec.
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay MIN sets the OCP delay value to 0.1
sec.
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay MAX sets the OCP delay value to 10 .0
sec.
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay?
Function:
Query the OCP delay value.
Syntax:
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay?[MIN|MAX]
Return:
<Decimal number>
Examples:
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay? will return the OCP value.
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay? MIN will return 0.1 sec.
:CURRent:PROTection:DELay? MAX will return 10.1 sec.
:VOLTage:PROTection
Function:
Set the overvoltage protection value.
Syntax:
:PROTection:VOLTage {<Decimal numbers>|MIN|MAX}
Examples:
:VOLTage:PROTection 10 sets the overvoltage protection value to
10.000V(PSM-2010).
:VOLTage:PROTection MIN sets the overvoltage protection value to
0.000V(PSM-2010).
⎯ 37 ⎯
⎯ 38 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
:VOLTage:PROTection MAX sets the overvoltage protection value to
22.000V(PSM-2010). Please refer to Table1-1, Table1-2 and Table1-3.
:VOLTage:PROTection?
Function:
Query the overvoltage protection value.
Syntax:
:VOLTage:PROTection? [MIN|MAX]
Returns:
Scientific Mark
Examples:
:VOLTage:PROTection? will return the overvoltage protection value.
:VOLTage:PROTection? MIN will return 0.
:VOLTage:PROTection? MAX will return the highest programmable
overvoltage values. Plea se ref er to Ta ble1-1 , T abl e1- 2 a nd T abl e1 -3.
:VOLTage:PROTection:STATe
Function:
Set or query the overvoltage protection status.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
:VOLTage:PROTection:TRIPped?
Function:
Query if the overvoltage protection circuit is tripped.
Syntax:
:VOLTage:PROTection:TRIPped?
Returns:
0|1
Examples:
This command will returns “1” if the overvoltage protection is tripped and
not cleared or “0” if not tripped.
:CURRent:PROTection:CLEar
Function:
Clear OCP status.
Syntax:
:CURRent:PROTection:CLEar
When the panel displays the protective message, no further setting can be
accepted by the device. Uses this command to clear the displayed messages
in order to execute further setting.
Syntax:
:VOLTage:PROTection:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
:VOLTage:PROTection?
Examples:
:VOLTage:PROTection:STATe 0 sets the overvoltage protection off.
If the overvoltage protection setting is on, the command of
VOLTage:PROTection? will return the value of 1.
⎯ 39 ⎯
Examples:
:CURRent:PROTection:CLEar
:VOLTage:PROTection:CLEar
Function:
Clear OVP status.
Syntax:
:VOLTage:PROTection:CLEar
⎯ 40 ⎯
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
When the panel displays the protective message, no further setting can be
accepted by the device. Uses this command to clear the displayed messages
in order to execute further setting.
Examples:
:VOLTage:PROTection:CLEar
:VOLTage:RANGe
Function:
Set output range..
Syntax:
:VOLTage:RANGe {P8V|P20V|LOW|HIGH} (for PSM-2010)
:VOLTage:RANGe {P15V|P30V|LOW|HIGH} (for PSM-3004)
:VOLTage:RANGe {P30V|P60V|LOW|HIGH} (for PSM-6003)
Examples:
:VOLTage:RANGe P8V set the range to 8V/20A(PSM-2010)
:VOLTage:RANGe HIGH set the range to 20V/10A(PSM-2010)
When set to 8V/20A range (or any other range), the maximum
programmable voltage and current are limited to a specific value (Please
refer to Table1-1, Table1-2 and Table1-3). “P8V” or “LOW” is for the
range of 8V/20A while “P20V” or ”HIGH” for the ran ge of 2 0V/10 A.
:VOLTage:RANGe?
Function:
Query output range..
Syntax:
:VOLTage:RANGe?
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
:VOLTage:RANGe? returns the currently selected ran ge.
The returned parameter for the PSM-2010 will be “P8V” or “P20V”.
The returned parameter for the PSM-3004 will be “P15V” or “P30V”.
The returned parameter for the PSM-6003 will be “P30V” or “P60V”.
:OUTPut
Function:
Set or query the output state.
Syntax:
OUTPut:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
OUTPut:STATe?
Examples:
OUTPut:STATe 1(or “ON”) enable s th e power supp ly ou tpu t.
If the power supply output is disabled, OUTPut:STATe? will return 0 .
z STATUS COMMANDS
STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
Function:
Return the contents of the OPERation register. The programmable power
supplies, however, do not use the OPERation register to report any
conditions.
Syntax:
STATus:OPERation:CONDition?
⎯ 41 ⎯
⎯ 42 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Returns
<Integers>
Examples:
STATus:OPERation:CONDition? returns 0.
STATus:OPERation:ENABle
Function:
Set or query the enable mask that allows the masked conditions in the event
register to be reported in the summary bit . If a bit is 1 (true) in the enable
register and its associated event bit changes to 1 (true), the associated
summary bit will change to 1 (true). Even though this is a 16-bit register,
only 15 bits (bit 0 through bit 14) are used. Bit 15 always reads 0.
Syntax
STATus:OPERation:ENABle <Enable Value>
STATus:OPERation:ENABle?
<Enable Value> is an integer from 0 to 32767.
Returns
<Integers>
Examples
STATus:OPERation:ENABle 32767 sets all 15 bits of the register to 1.
If the STATus:OPERation:ENABle? returns 0, all 15 bits of the
register are 0.
STATus:OPERation?
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Syntax:
STATus:OPERation?
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
STATus:OPERation? returns 0.
STATus:PRESet
Function:
Set the OPERation and QUESTionable enable reg isters to ze ros.
Syntax:
STATus:PRESet
STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Function:
Return the contents of the QUEStionable register. Reading the condition
register is non-destructive.
Syntax:
STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition?
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
Function:
Returns and clears the contents of the OPERation register.
⎯ 43 ⎯
STATus:QUEStionable:CONDition? returns 0.
⎯ 44 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle
Function:
Set or query the enable mask that allows the masked conditions in the event
register to be reported in the summary bit . If a bit is 1 (true) in the enable
register and its associated event bit changes to 1 (true), the associated
summary bit will change to 1 (true). Even though this is a 16-bit register,
only 15 bits (bit 0 through bit 14) are used. Bit 15 always reads 0.
Syntax:
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle <Enable Value>
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle?
<Enable Value> is an integer from 0 to 32767.
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle 32767 sets all 15 bits of the register
to 1.
If the STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle? returns 0, all 15 bits of the
register are 0.
STATus:QUEStionable?
Function:
Return and clear the contents of the QUEStionable register. The response is
a decimal value that summarizes the binary values of the set bits.
Syntax:
STATus:QUEStionable?
Returns:
<Integers>
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
STATus:QUEStionable? returns 0.
z
MISCELLANEOUS COMMANDS
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe
Function:
Set or query the number of times of execution.
Syntax:
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe <Integers>
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe?
<Integers> is in the range from 0 through 99999 or infinite.
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe 8 sets auto cycle on to repeat the setting 8 times.
SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe 0 sets auto cycle on to repe at th e set ting infin ite.
If the command SYSTem:AUTO:CYCLe? Returns 0, means infinite.
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay
Function:
Set the delay time under the current responding memory status
Syntax:
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay <Integers>
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay?
<Integers> is in the range from 1 through 59999, its unit is 100ms.
.
⎯ 45 ⎯
⎯ 46 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay 1 sets auto delay time at 100ms for the memory of
the specific section.
SYSTem:AUTO:DELay 1000 sets auto delay time at 100 seconds for the
memory of the specific section, no further setting of auto delay will be done
on next memory section until the previous auto delay is fulfilled. If the
command SYSTem:AUTO:DELay? Returns 5, means d elay 500ms at the
current memory section that displayed on the panel.
SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe
Function:
Set the end memory section for auto execute continuously
Syntax:
SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe <Integers>
SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe?
<Integers> is in the range from 0 through 99 and must be large or equal
to the value of S TART .
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe 8 sets auto end on from the memory of location 8
of the current device.
If the command SYSTem:AUTO:CEASe? Returns 99, means set the
section 99 as the end.
.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
SYSTem:AUTO:STARt
Function:
Set the start memory section for auto execute continuously
.
Syntax:
SYSTem:AUTO:STARt <Integers>
SYSTem:AUTO:STARt?
< Integers> is in the range from 0 through 99 and must be small or equal
to the value of CE ASE .
Returns:
<Integers>
Examples:
SYSTem:AUTO:STARt 0 sets auto start on from the memory of location 0
of the current device.
If the command SYSTem:ATUO:STARt? Returns 2, means set the section
2 as the start.
SYSTem:AUTO
Function:
Set or return automatic sequence setting
Syntax:
SYSTem:AUTO:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
SYSTem:AUTO:STATe?
Returns:
0|1
Examples:
SYSTem:AUTO:STATe 1 sets auto sequence on.
.
⎯ 47 ⎯
⎯ 48 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
z SYSTEM COMMANDS
SYSTem:ERRor?
Function:
Query the next error me ssage from the Error/Event qu eue. The result o f the
query is the error number followed by the error tex t.
Syntax:
SYSTem:ERRor?
Returns:
<string>
Examples:
SYSTem:ERRor? returns 0, “No error”
SYSTem:MEMory?
Function:
Read the current memory section number displayed on the panel
Syntax:
SYSTem:MEMory?
Returns:
<Integers> The range is from 0 through 99.
.
SYSTem:VERSion?
Function:
Return the SCPI v ersio n o f the dev ice .
Syntax:
SYSTem:VERSion?
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Returns:
1994.0
SYSTem:BEEPer:STATe
Function:
Set or query the currently b eeper sta te.
Syntax:
SYSTem:BEEPer:STATe {0|1|OFF|ON}
SYSTem:BEEPer:STATe?
Examples:
SYSTem:BEEPer:STATe ON set beeper state on.
SYSTem:BEEPer
Function:
To issue a single beep immedia tely.
Syntax:
SYSTem:BEEPer
z RS-232 INTERFACE COMMANDS
SYSTem:LOCal
Function:
This command is to set the power supply to the local mode. During the
operation of RS-232, all control knobs on the front panel are enabled.
Syntax:
⎯ 49 ⎯
SYSTem:LOCal
⎯ 50 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
SYSTem:REMote
Function:
This command is to set the power supply to the remote mode. During the
operation of RS-232, all control knobs on the front panel are disabled
except the “Local” key.
Note: Under the operation of RS-232, it needs to send SYSTem:REMote
in order to set the power supply to the remote mode, otherwise, an
unexpectable result will be occurred.
Syntax:
SYSTem:REMote
SYSTem:RWLock
Function:
This command is the same as SYSTem:REMote, except all control knobs
including “Local” key are disabled.
Syntax:
SYSTem:RWLock
z SYSTEM COMMANDS
DISPlay
Function:
Set or query the front panel display off or on.
Syntax:
DISPlay {0|1|OFF|ON}
DISPlay?
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Examples:
DISPlay ON turns on front panel display.
If display is turned off , all annunciators are disabled except ERROR.
And the display will turned on when return to local mode.
DISPlay:TEXT
Function:
To display a message on the front panel.
Syntax:
DISPlay:TEXT <quoted string>
DISPlay:TEXT?
Examples:
DISPlay:TEXT “ABCD” will display “ABCD” on the front panel.
DISPlay:TEXT? will return “ABCD”.
DISPlay:TEXT:CLEar
Function:
To clear the message displayed on the front panel.
Syntax:
DISPlay:TEXT:CLEar
DISPlay:CONTrast
Function:
Change the brightness of the display on the front panel.
⎯ 51 ⎯
⎯ 52 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Syntax:
DISPlay:CONTrast {0|1|2|3|4}according to the sequence of 0 to 4
from dark to bright.
z TRIGGER COMMANDS
The power supply’s triggering system allows a change in voltage and
current when receiving a trigger, to select a trigger source, and to insert a
trigger. Triggering the power supply is a multi-step process.
z First, you must specify the source from which the power supply will
accept the trigger. The power supply will accept a bus (software)
trigger or an immediate trigger from the remote interface.
z Then, you can set the time delay between the detection of the trigger
on the specific trigger source and the start of any corresponding
output change.
Notice that the time delay is valid for only the bus trigger source.
z Finally, you must provide an INITiate command. If the IMMediate
source is selected, the selected output is set to the triggered level
immediately. But if the trigger source is the bus, the power supply is
set to the triggered level after receiving the Group Execute Trigger
(GET) or *TRG command.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
TRIGger:SOURce? Returns “BUS” or “IMM”.
TRIGger:DELay
Function:
Set or query the currently trigger delay.
Syntax:
TRIGger:DELay {<Integers>|MIN|MAX}
TRIGger:DELay?
<Integers> the range is within 0~3600s.
MIN is for 0 while MAX for 3600.
INITiate
Function:
To cause the trigger system to initiate.
Syntax:
INITiate
Examples:
TRIG:SOUR IMM
z TRIGGER COMANDS
TRIGger:SOURce
Function:
Set or query the currently trigger source.
Syntax:
TRIGger:SOURce {BUS|IMMediate}
⎯ 53 ⎯
VOLT:TRIG 5.0
CURR:TRIG 3.0
INIT
After proceeding above program, the output will be change to 5V/3A
immediately.
TRIG:SOUR BUS
VOLT:TRIG 5.0
⎯ 54 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
CURR:TRIG 3.0
TRIG:DEL 3.0
INIT
*TRG
After proceeding above program, the output will be change to 5V/3A
immediately.
z
CALIBRATION COMMANDS
CALibration:PASSword
Function:
Input Password to enter calibration mode.
Syntax:
CALibration:PASSword <password>
The Password for PSM-2010 is 2010.
The Password for PSM-3004 is 3004.
The Password for PSM-6003 is 6003.
Examples:
CALibration:PASSword 2010 for PSM-2010 to enter calibration
mode
CALibration:TYPe
Function:
Select calibration mode.
Syntax:
CALibration:TYPe {0|1|2|3}
0:Voltage, 1:OVP , 2:Current 3:Ocp
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
CALibration:VOLTage:MINimum
CALibration:VOLTage:MIDDle
CALibration:VOLTage:MAXimum
Function:
Input the voltage value separately.
Syntax:
CALibration:VOLTage:MINimum <Decimal numbers>
CALibration:VOLTage:MIDDle <Decimal numbers>
CALibration:VOLTage:MAXimum <Decimal numbers>
CALibration:VOLTage:PROTection
Function:
Auto calibrate OVP.
Syntax:
CALibration:VOLTage:PROTection
CALibration:CURRent:MINimum
CALibration:CURRent:MIDDle
CALibration:CURRent:MAXimum
Function:
Input current value separ atel y.
⎯ 55 ⎯
⎯ 56 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Syntax:
CALibration:CURRent:MINimum <Decimal numbers>
CALibration:CURRent:MIDDle <Decimal numbers>
CALibration:CURRent:MAXimum <Decimal numbers>
CALibration:CURRent:PROTection
Function:
Auto calibrate OCP.
Syntax:
CALibration:CURRent:PROTection
CALibration:SAVe
Function:
To leave calibration mode after sav e.
Syntax:
CALibration:SAVe
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
voltage meter, use the commands of
CALibration:VOLTage:MINimum<measured value>,
CALibration:VOLTage:MIDDle < measured value >,
CALibration:VOLTage:MAXimum < measured value >
in sequence to complete the voltage calibration, then the program will
select type 1 automatically, therefore, just send the command
CALibration:VOLTage:PROTection directly, the OVP calibration
will be done
The current and OCP calibration method is the same as above
procedure. After calibration, se nd the co mmand CALibration:SAVe to
save the calibration value, then exit the calibration mode, or send the
command CALibration:end not to save the calibration value and exit
the calibration mode.
2) During calibrating, use the command CALibration:TYPe to select the
calibration type, the same type can be calibrated repeatedly.
automatically.
CALibration:END
Function:
To leave calibration mode without saving.
Syntax:
CALibration:END
Note:
1) General calibration procedure:
Input Password to enter calibration mode, send command
CALibration:TYPe 0, then according to the value measured with
⎯ 57 ⎯
⎯ 58 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
7. STATUS AND ERROR REPORTING
A set of status registers allows the user to quickly determine the power
supply’s internal processing status. The status register, as well as the status
and event reporting system, adhere to SCPI recommendations.
Structure of System
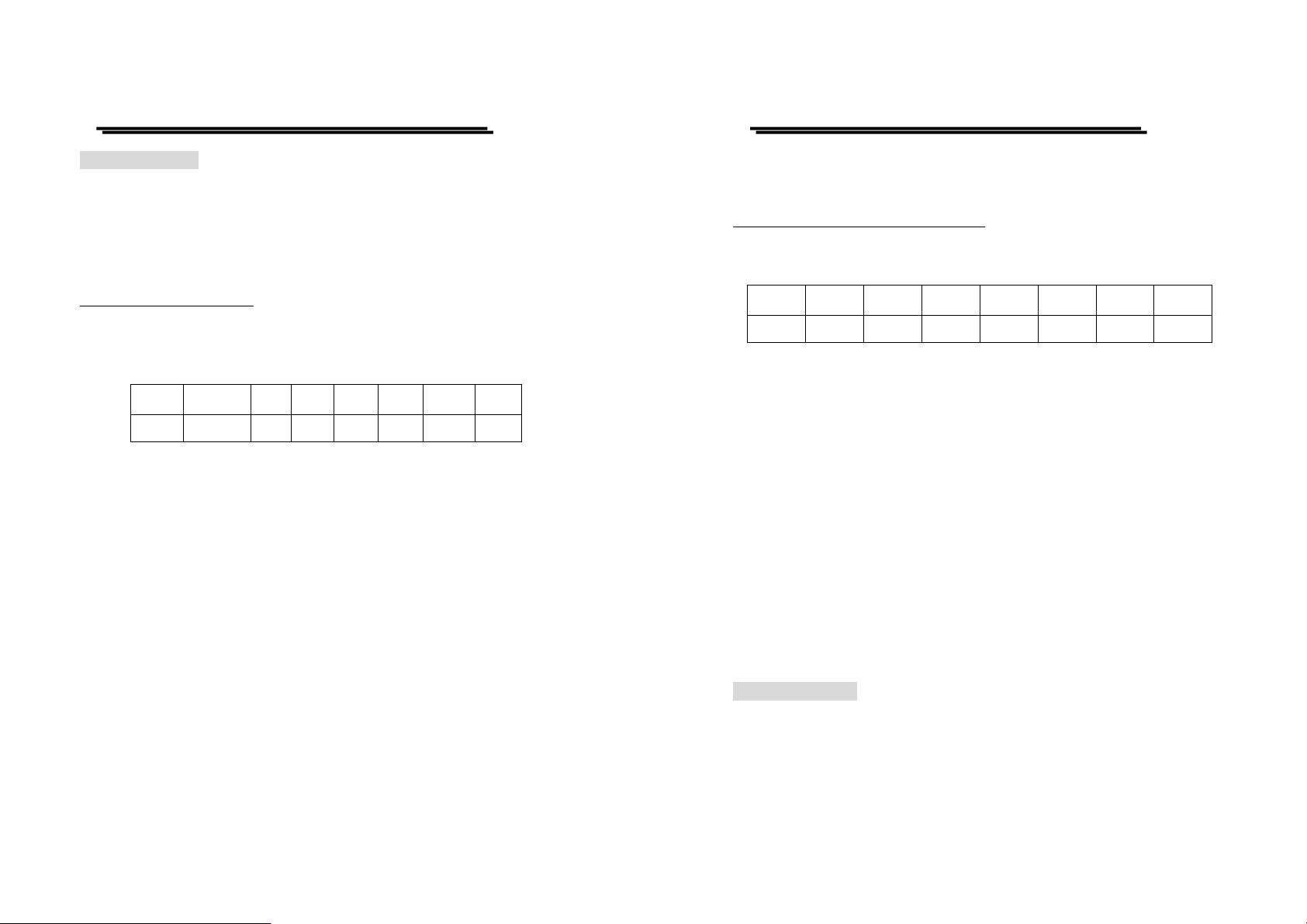
The sketch of the status and event reporting system is showed as figur e
7. Each component of the sketch represents a set of registers and queues
that can read, report, or ena ble the occurrence of certain events with in the
system.
If a specific event in the power supply sets a bit in a status register, reading
which can tell you what types of events have occurred.
Each bit in the status register corresponds to a bit in an enable register; the
enable bit must be high for the event to be reported to the Status Byte
Register.
A Service Request (SRQ) is the last event to occur. The SRQ requests an
interrupt on the GPIB to report events to the system controller.
Status Registers
There are two kinds of status registers are included to the programmable
power supplies.
z OPERation Status Registers ( CONDition, EVENt, and ENABle)
z QUEStionable Status Registers (CONDition, EVENt, and ENABle)
The lower level nodes: QUEStionable and OPERation each have three 16
bits registers: CONDition, EVENt, and ENABle. Figure 8 shows the
sequential relationship between these three types of registers and the
commands that relate to each regis ter.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
QUEStionable
Summary Voltage
Summary Current
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Summary OVP
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
Status
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
OPERation
Status
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Error/Ev e nt Q u eue
Output Queue
Figure 7. A graphic representation of the status registers and their connections.
Standard Event Status Registers
Operation Complete
Device Dependent Error
Execution Error
Command Error
0
1
Not Used
Query Error
2
3
4
5
User Request
6
7
Power On
Summ ary of IEEE 488.2 Status Structure Registers
Status Byte Register
0
Not Used
1
Not Used
E/E
2
QUES
3
MAV
4
ESB
5
RQS/MSS
6
7
OPER
SRQ
⎯ 59 ⎯
⎯ 60 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Condition
Register
Event
Register
Enable
Register
To SBR
Figure 8: Status registers and related commands
The CONDition register is a read -only register which monitors th e present
state of the instrument. The CONDition register updates in real time and
the inputs are not latched or buffered. When a condition monitored by the
CONDition register becomes true, the bit for that condition also becomes
true (1). When the condition is false, the bit is 0.
The read-only EVENt register latch es any false-to- true change in condition.
Once the bit in the EVENt regis ter is set, it is no longer affe cted by change s
in the corresponding bit of the CONDition register. The bit remains set until
the controller reads it. The command *CLS (Clear Status) clears the EVENt
register.
QUEStionable Status Registers.
Table 4 shows the bit designations of the 16 bit QUEStionable Status
Register.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Table 4: QUEStionable Status Register
Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8
∗
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bi t 1 Bit 0
NU NU NU NU NU NU
NU NU NU NU NU Summary
OVP
Summar
y Current
NU
Summary
Voltage
The command STATus:QUEStionable:CONDtion? Reads the
QUEStionable CONDition register but dose not clear it.
The command STATus:QUEStionable:EVENt? Reads the
QUEStionable EVENt Status register and clears it.
OPERation Status Registers
Table 5 shows the bit designations of the 16 bit OPERation Status Register.
Table 5: OPERation Status Register
Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8
NU NU NU NU NU NU NU
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
NU NU NU NU NU NU NU NU
⎯ 61 ⎯
∗
NU: not used
⎯ 62 ⎯
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Status Registers
There are two status r egisters are included to the pow er supply defined by
IEEE-488.1 and IEEE-488.2 standards.
z Status Byte Register (SBR)
z Standard Event Status Register (SESR)
Status Byte Register (SBR)
: The SBR (Table 6) summarizes the status of all
other registers and queues.
Table 6: Status By te R egi ste r (S BR)
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
OPER RQS/MSS ESB MAV QUES E/E NU NU
The bit 0 and 1 are not u sed, so these bits are always zer o. The bit 2 (Error
and Event) indicates an error code is waiting to be read in the Error Event
Queue. The bit 3 (QUES, QUEStionable) is the summary bit for the QESR
(QUEStionable Event Status Register). When the bit is high it indicates that
status is enabled and present in the QUES. The bit 4 (MAV, Message
Available) indicates that output is available in the output queue. The bit 5
(ESB, Event Status Bit) is the summary bit for the Standard Event Status
Register (SESR). When the bit is high it indicates that status is enabled and
present in the SESR. The bit 6 (RQS, Request Service) is obtained from a
serial poll and shows that the power supp ly requests service from the GPIB
controller. The bit 7 (OPER, OPERation) is the summary bit for the OESR
(OPERation EVENt STATus Register).
Use the serial poll or the *STB? Query to read the contents of the SBR.
The bits in the SBR are set and cleared depending on the con tents of the
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Standard Event Status Register (SESR), the Standard Event Status Register
(SESR), and the Output Queue.
Standard Event Status Register (SESR)
: Table 7 shows the SESR
Table 7: Standard Event Status Register (SESR)
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PON URQ CME EXE DDE QYE NU OPC
The bit 0 (OPC, Operation Co mplet e) shows tha t the oper ation is co mpleted .
This bit is active when all pending operations are completed following an
*OPC command. The bit 1 is always zero. The bit 2 (QYE, Query Error)
indicates a command or query protocol error. The bit 3 (DDE, Device Error)
shows that a device error occurred. The bit 4 (EXE, Execution Error) shows
that an error occurred while the power supply was ex ecuting a command or
query. The bit 5 (CME, Command Error) shows that an error occurred
while the power supply was parsing a command or q uery. The bit 6 (USR,
User Request) indicates the LOCAL button was pushed. The bit 7 (PON,
Power On) shows that the power supply w as powered on.
Use the *ESR? Query to read the SESR. Read the SESR and clear the bits
of the registers so that the register can accumulate information about new
events.
Enable Registers
The enable registers determine whether certain events are reported to the
Status Byte Register and SRQ. The programmable power supply has the
following enable registers.
z Event Statu s Enable Register (ESER)
⎯ 63 ⎯
⎯ 64 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
z OPERation Enable Register
z QUEStionable Enable Register
z Service Request Enable Register (SRER)
When one of the bits of the enable register s is high and the corresponding
bit in the status register is high, the enable registers will perform a logical
OR function, the output that controls the set bit of the Status Byte Register
is high.
Various commands set the bits in the enable registers. The following
sections describe the enable r egis ters and the co mmand s that set the m.
Event Status Enable Register (ESER)
: The ESER controls which types of
events are summarized by the Event Status Bit (ESB) in the SBR. The bits
of the ESER correspond to the bits of the SESR.
Use the *ESE command to set the bits in ESER. Use the *ESE? query to
read it.
OPERation Enable Register
: Even though the OPE Ration Enable Register
is present in the programmable power supplies, the OPERation registers do
not report any conditions.
QUEStionable Enable Register
: The QUEStionable Enable Register
controls which types of events ar e summarized by the QUES status bit in
the SBR. Use th e STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle command to set the
bits in the QUEStionable Enable register. Use the
STATus:QUEStionable:ENABle? query to read it.
Service Request Enable Register (SRER)
: The SRER controls which bits in
the SBR generate a service request.
Use the *SRE command to set the SRE R. Use th e *SRE? query to read it.
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
Queues
The output queue is included to power supplies.
Output Queue
: The programmable power supplies store query responses in
the output queue by succeeding the IEEE 488.2 protocol. If the power
supply receives a new command or query message after a message
terminator, the power supply will clear and reset this queue each time. Th e
computer must read a query response before it sends the next command (or
query) or it loses response to earlier queries.
Error/Event Queues
When an error or event occurs, the output queue stores the message. The
output queue stores and reports the messages on a FIFO (first in first out)
state. The SYSTem:ERRor? query reads the next item from the output
queue. If output queue overflows, the error message is –350, “Queue
overflow”; the queue can’t store or report succeeding messages till it is
read or cleared.
Error Message5
-101 Invalid character
-102 Syntax error
-103 Invalid separator
-104 Data type error
-105 GET not allowed
-108 Parameter not allowed
-109 Missing parameter
-112 Program mnemonic too long
-113 Undefined header
-121 Invalid character in number
⎯ 65 ⎯
⎯ 66 ⎯

PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
PSM SERIES PROGRAMMABLE POWER SUPPLY
-123 Numeric overflow
-124 Too many digits
-128 Numeric data not allowed
-131 Invalid suffix
-134 Suffix too long
-138 Suffix not allowed
-141 Invalid character data
-144 Character data too long
-148 Character data not allowed
-151 Invalid string data
-158 String data not allowed
-160 to -168 Block data errors
-170 to -178 Expression errors
-211 Trigger ignored
-213 Init ignored
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
PROGRAMMER MANUAL
-430 Query DEADLOCKED
-440 Query UNTERMINATED after indefinite response
-221 Settings conflict
-222 Data out of range
-223 Too much data
-224 Illegal parameter value
-330 Self-test failed
-350 Too many errors
-410 Query INTERRUPTED
-420 Query UNTERMINATED
⎯ 67 ⎯
⎯ 68 ⎯
 Loading...
Loading...