INOVC IA80C152JA-PDW48I, IA80C152JA-PDW68I, IA80C152JA-PLC68I, IA80C152JB-PLC68C, IA80C152JB-PLC68I Datasheet
...
Page 1 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
FEATURES
• Form, Fit, and Function Compatible
with the Intel 80C152
• Packaging options available
− 48 Pin Plastic or Ceramic DIP
− 68 Pin Plastic or Ceramic LCC
• 8051 Core with:
− Direct Memory Access(DMA)
− Global Serial Channel (GSC)
− MCS- 51 Compatible UART
− Two Timers/Counters
− Maskable Interrupts
• Memory
− 256 Bytes Internal RAM
− 64K Bytes Program Memory
− 64K Bytes Data Memory
• 5 or 7 I/O Ports
• Up to 16.5 MHz Clock Frequency
• Two-Channel DMA With Multiple
Transfer Modes
• GSC Provides Support for Multiple
Protocols
− CSMA/CD
− SDLC/HDLC
− User Definable
• Separate Transmit & Receive FIFOs
• Special Protocol Features
− Up to 2.0625 Mbps Serial
Operation
− CSMA and SDLC Frame Formats
with CRC Checking
− Manchester, NRZ, & NRZI Data
Encoding
− Collision Detection & Resolution
in CSMA Mode
− Selectable Full/Half Duplex
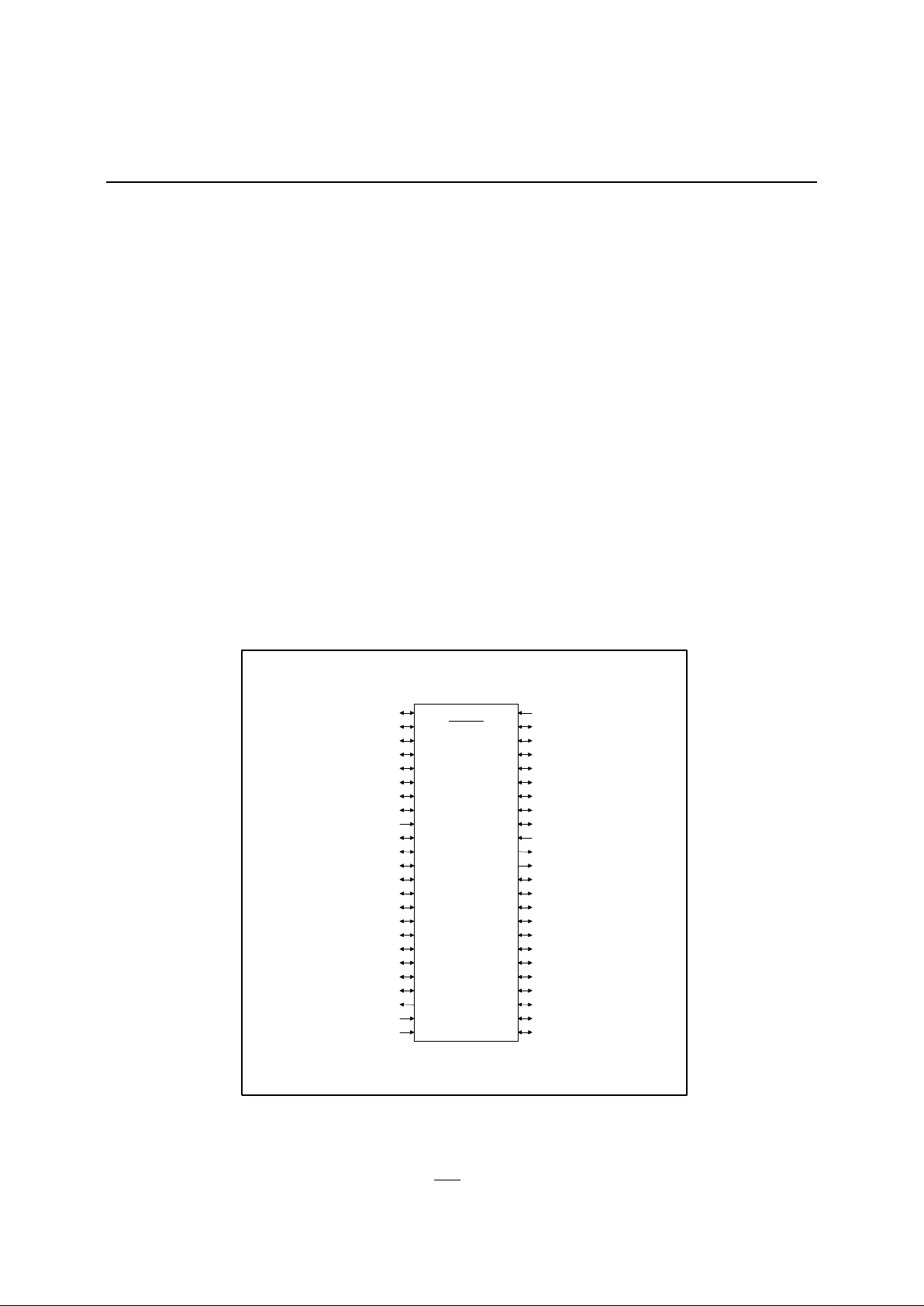
Figure 1 - 48 Pin DIP Pinout
(6)(HLDn) P1.5
(1)(GRXD) P1.0
(2)(GTXD) P1.1
(3)(DENn) P1.2
(4)(TXCn) P1.3
(5)(RXCn) P1.4
(7)(HLDAn) P1.6
(8)P1.7
(9)RESETn
(10)(RXD) P3.0
(11)(TXD) P3.1
(12)(INT0n) P3.2
(13)(INT1n) P3.3
(14)(T0) P3.4
48 Pin DIP
JA/JC
IA80152
(48) VDD
(47)
(46)
(45)
(44)
(43)
(42)
(41)
(40) P4.7
(39) EA
(38) ALE
(37) PSENn
(36) P2.7 (A15)
(35) P2.6 (A14)
(20)(A / D2) P0.2
(15)(T1) P3.5
(16)(WRn) P3.6
(17)(RDn) P3.7
(18)(A / D0) P0.0
(19)(A / D1) P0.1
(21)(A / D3) P0.3
(22)XTAL2
(23)XTAL1
(24)Vss
(34)
(33)
(32)
(31)
(30)
(29)
(28)
(27)
(26)
(25)
P2.5 (A13)
P2.4 (A12)
P2.3 (A11)
P2.2 (A10)
P2.1 (A9)
P2.0 (A8)
P0.7 (A / D7)
P0.6 (A / D6)
P0.5 (A / D5)
P0.4 (A / D4)
P4.6
P4.5
P4.4
P4.3
P4.2
P4.1
P4.0
Page 2 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
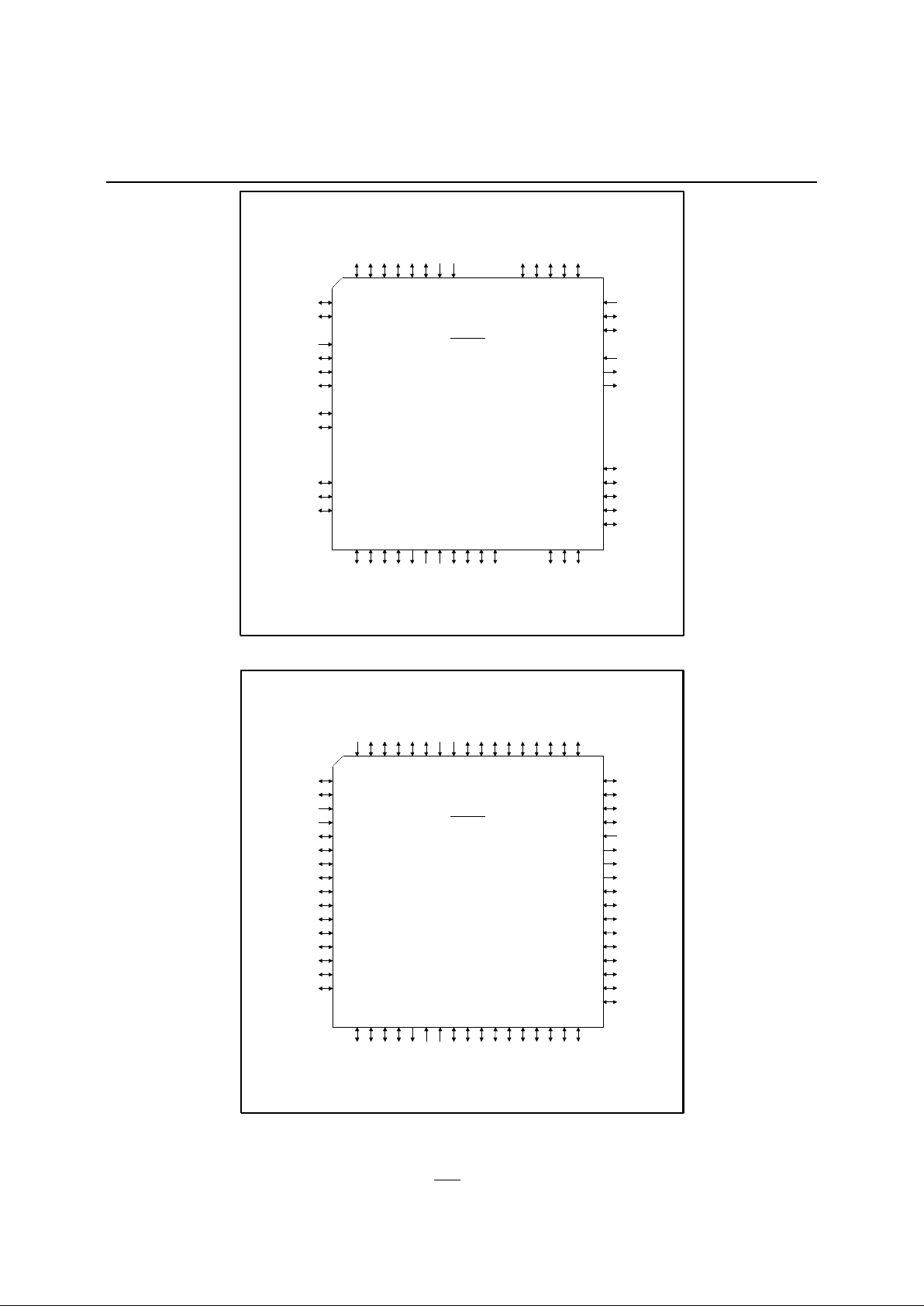
Figure 2 - 68 Lead LCC Pinout - JA/JC Versions
Figure 3 - 68 Lead LCC Pinout - JB/JD Versions
68 Pin LCC
JA/JC
IA82510
(15)(TXD) P3.1
(10)(HLDAn) P1.6
(11)P1.7
(12)N.C.
(13)RESETn
(14)(RXD) P3.0
(16)(INT0n) P3.2
(17)N.C.
(18)(INT1n) P3.3
(19)(T0) P3.4
(20)N.C.
(21)N.C.
(22)N.C.
(23)(T1) P3.5
(24)(WRn) P3.6
(25)(RDn) P3.7
(26)N.C.
(60) P4.5
(59)
(58)
(57)
(56)
(55)
(54)
(53)
(52) N.C.
(51) N.C.
(50) N.C.
(49) N.C.
(48) P2.7 (A15)
(47) P2.6 (A14)
(46)
(45)
(44)
P2.5 (A13)
P2.4 (A12)
P2.3 (A11)
N.C.
PSENn
ALE
EA
N.C.
P4.7
P4.6
(32)XTAL1
(27)(A / D0) P0.0
(28)(A / D1) P0.1
(29)(A / D2) P0.2
(30)(A / D3) P0.3
(31)XTAL2
(33)Vss
(34)(A / D4) P0.4
(35)(A / D5) P0.5
(36)(A / D6) P0.6
(37)(A / D7) P0.7
(38)N.C.
(39)N.C.
(40)N.C.
(41)(A8) P2.0
(42)(A9) P2.1
(43)(A10) P2.2
(9) P1.5 (HLDn)
(8)
(7)
(6)
(5)
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1) N.C.
(68) N.C.
(67) N.C.
(66) N.C.
(65) P4.0
(64) P4.1
(63)
(62)
(61)
P4.2
P4.3
P4.4
VDD
Vss
P1.0 (GRXD)
P1.1 (GTXD)
P1.2 (DENn)
P1.3 (TXCn)
P1.4 (RXCn)
68 Pin LCC
JB/JD
IA82510
(15)(TXD) P3.1
(10)(HLDAn) P1.6
(11)P1.7
(12)EBEN
(13)RESETn
(14)(RXD) P3.0
(16)(INT0n) P3.2
(17)P5.0
(18)(INT1n) P3.3
(19)(T0) P3.4
(20)P5.1
(21)P5.2
(22)P5.3
(23)(T1) P3.5
(24)(WRn) P3.6
(25)(RDn) P3.7
(26)
N.C.
(60) P4.5
(59)
(58)
(57)
(56)
(55)
(54)
(53)
(52) P6.2
(51) P6.7
(50) P6.4
(49) P5.7
(48) P2.7 (A15)
(47) P2.6 (A14)
(46)
(45)
(44)
P2.5 (A13)
P2.4 (A12)
P2.3 (A11)
EPSENn
PSENn
ALE
EA
P6.3
P4.7
P4.6
(32)XTAL1
(27)(A / D0) P0.0
(28)(A / D1) P0.1
(29)(A / D2) P0.2
(30)(A / D3) P0.3
(31)XTAL2
(33)Vss
(34)(A / D4) P0.4
(35)(A / D5) P0.5
(36)(A / D6) P0.6
(37)(A / D7) P0.7
(38)P5.4
(39)P5.5
(40)P5.6
(41)(A8) P2.0
(42)(A9) P2.1
(43)(A10) P2.2
(9) P1.5 (HLDn)
(8)
(7)
(6)
(5)
(4)
(3)
(2)
(1) P6.6
(68) P6.5
(67) P6.0
(66) P6.1
(65) P4.0
(64) P4.1
(63)
(62)
(61)
P4.2
P4.3
P4.4
VDD
Vss
P1.0 (GRXD)
P1.1 (GTXD)
P1.2 (DENn)
P1.3 (TXCn)
P1.4 (RXCn)
Page 3 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
The IA80C152 is a "plug-and-play" drop-in replacement for the original IC. innovASIC produces
replacement ICs using its MILESTM, or Managed IC Lifetime Extension System, cloning technology.
This technology produces replacement ICs far more complex than "emulation" while ensuring they
are compatible with the original IC. MILESTM captures the design of a clone so it can be produced
even as silicon technology advances. MILESTM also verifies the clone against the original IC so that
even the "undocumented features" are duplicated. This data sheet documents all necessary
engineering information about the IA80C152 including functional and I/O descriptions, electrical
characteristics, and applicable timing.
INTEL is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation
DESCRIPTION
The IA80C152 is a Universal Communications Controller (UCC) that is pin-for-pin compatible
with the Intel 80C152. This version of the UCC is a ROMless version. The ROM version is
identified as the 83C152 and can be easily derived from the 80C152 using a customer furnished
ROM program. The IA80C152 can be programmed with the same software development tools and
can transmit and receive using the same communication protocols as the Intel 80C152 making the
IA80C152 a drop-in replacement. Table 1 below cross-references IA80C152 versions with
protocol, package, and I/O Port capability. Pinout diagrams are provided in figures 1, 2, and 3.
Table 1 - IC Version Differences
innovASIC
Part Number
CSMA/CD,
SDLC/HDLC,
User-Defined
5 I/O
Ports
7 I/O
Ports 48 Pin DIP 68 Lead LCC
IA80C152JA
√ √ √ √
IA80C152JB
√ √ √
IA80C152JC
√ √ √ √
IA80C152JD
√ √ √
The only difference between The innovASIC 80C152 and the Intel 80C152 is that all protocols
are available in all IC versions. Originally, the Intel 80C152 JC and JD versions were limited to
SDLC/HDLC only. Also, innovASIC will support a ROM version (83152) in any of the JA, JB, JC,
or JD versions.
The IA80C152 is partitioned into three major functional units identified as the C8051, the Direct
Memory Access (DMA) Controller, and the Global Serial Channel (GSC). The C8051 is
implemented using a CAST, Inc. Intellectual Property (IP) core. This core is instruction set
compatible with the 80C51BH, and contains compatible peripherals including a UART interface
and timers. The special function registers (SFRs) and interrupts are modified from the original
8051BH to accommodate the additional DMA controller and GSC peripherals.
The DMA Controller is a 2 channel, 8-bit device that is 16-bit addressable. Either channel can
access any combination of reads and writes to external memory, internal memory, or the SFR's.
Various modes allow the DMA to access the UART, GSC, SFRs, and internal and external memory
as well as provide for external control. Since there is only 1 data/program memory bus, only one
DMA channel or the microcontroller can have control at any give time. Arbitration within the
device makes this control transparent to the programmer.
Page 4 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
The GSC is a serial interface that can be programmed to support CSMA/CD, SDLC, user definable
protocols, and limited HDLC. Protocol specific features are supported in hardware such as address
recognition, collision resolution, CRC generation and errors, automatic re-transmission, and
hardware acknowledge. The CSMA/CD protocol meets the requirements of ISO/IEC 8802-3 and
ANSI/IEEE Std 802.3 to the extent implemented in the original IC. The SDLC protocol meets
the requirements of IBM GA27-3093-04 to the extent implemented in the original IC.
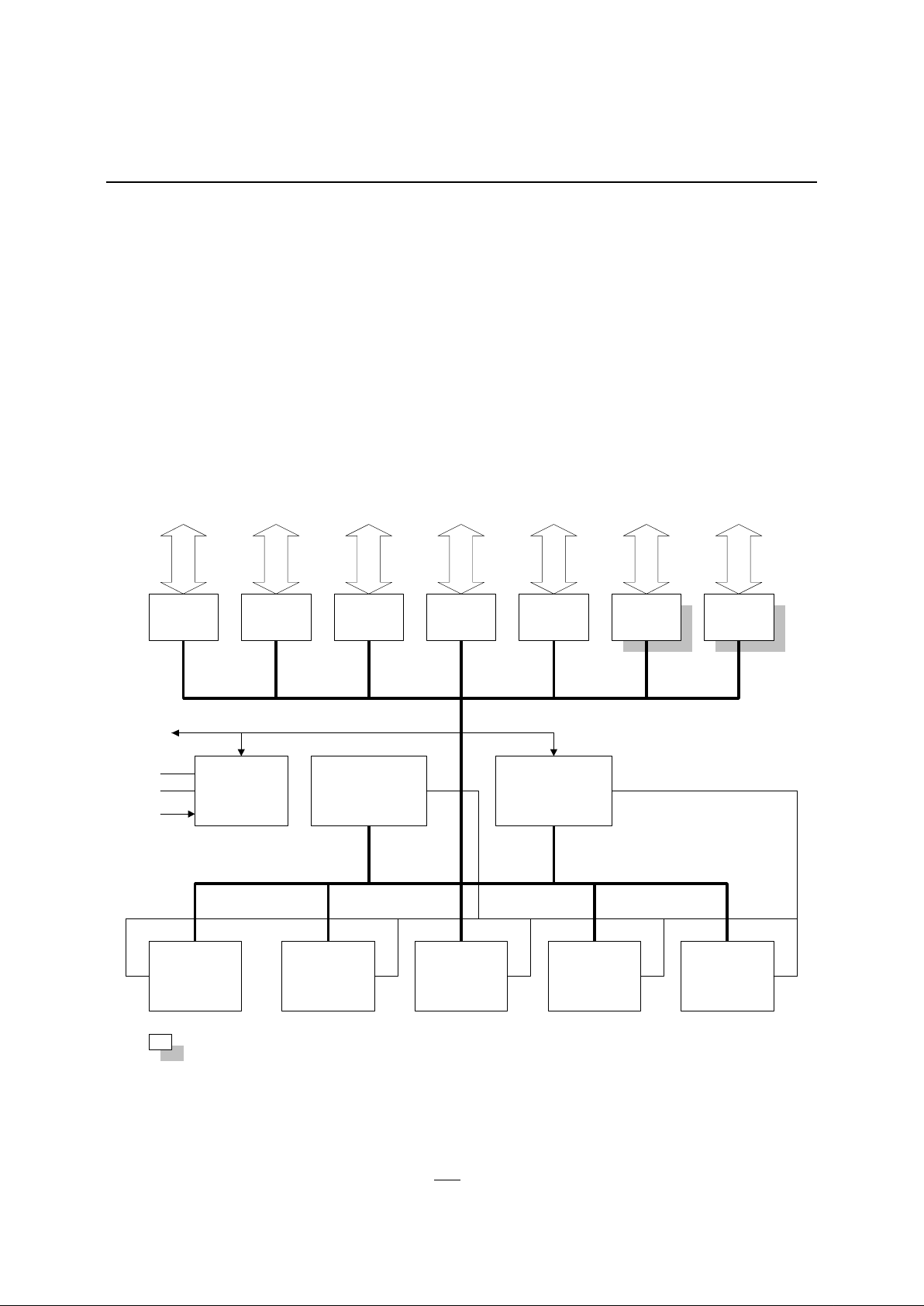
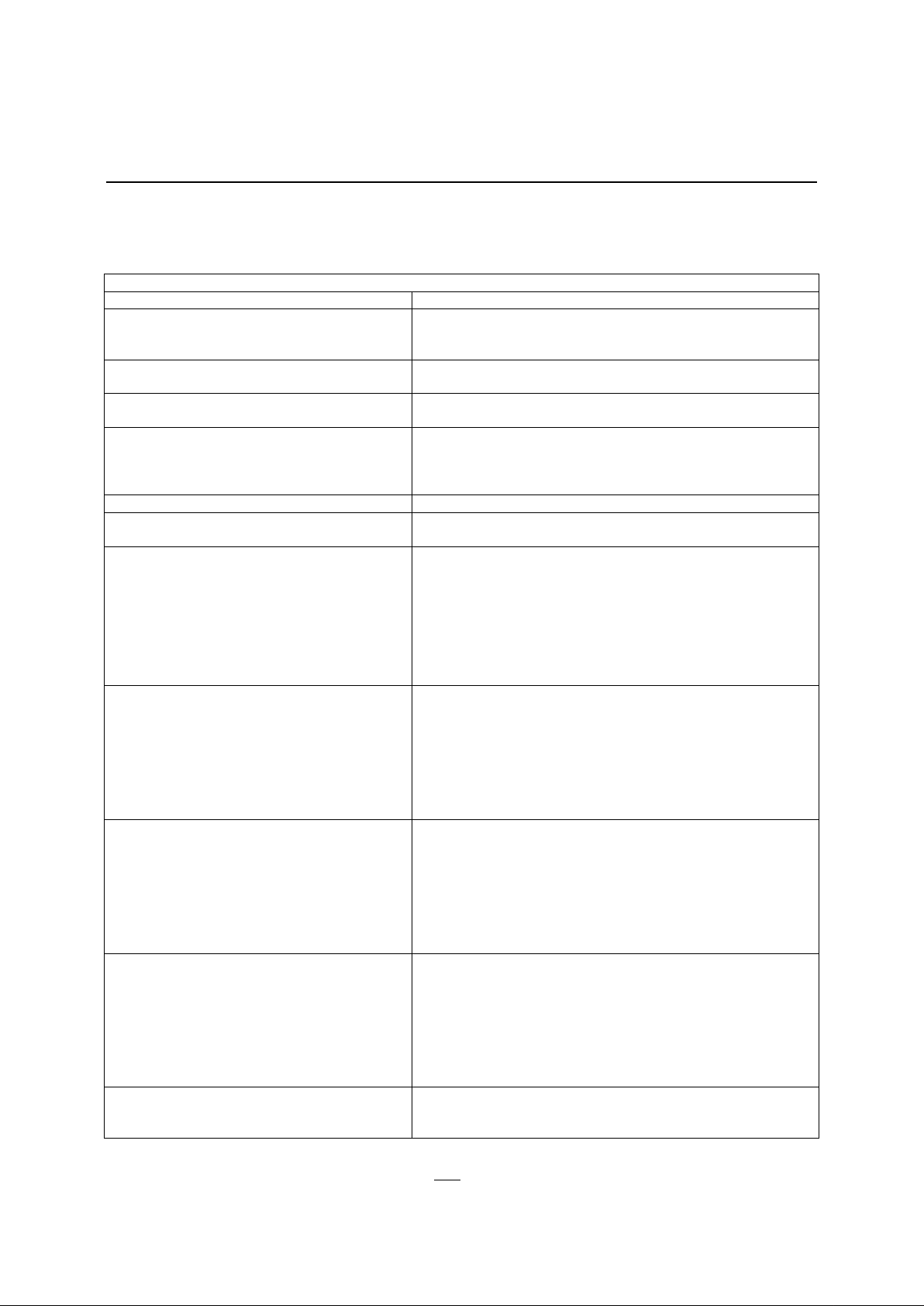
Functional Block Diagram
Figure 4 shows the major functional blocks of the IA80C152. Each version of the IA80C152
function identically to each other with the exception of the 2 additional I/O ports (Port 5 and
Port 6) in the JB and JD versions.
Figure 4 - Functional Block Diagram
256x8 RAM
C8051
CPU
UART DMA GSC
Port 0 Port 1 Port 2 Port 4Port 3 Port 5 Port 6
Interrupts Timers
Control
Address/Data
Clock Gen.
& Timing
XTAL
Reset
Memory
Control
I/O for Memory, GSC, DMA, UART, Interrupts, Timers
= JB and JD Versions Only
Page 5 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
I/O Signal Description
Table 2 below describes the I/O characteristics for each signal on the IC. The signal names
correspond to the signal names on the pinout diagrams provided above. (!) Denotes active Low.
Table 2 - I/O Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Description
!EA External Access enable. Since there is no internal ROM in the
80C152, this signal has no function in the JA and JC versions. For
the JB and JD versions, controls program memory fetch locations.
!EPSEN E-bus Program Store ENable. When EBEN is 1, this signal is the
read strobe for external program memory.
!PSEN Program Store ENable. When EBEN is 0, this signal is the read
strobe for external program memory.
!RESET Reset. When this signal is low for 3 machine cycles, the device is put
into reset. The GSC may continue transmitting after reset is applied.
An internal pull-up allow the use of an external capacitor to generate
a power-on reset.
ALE Address Latch Enable. Latches the low-byte of external memory.
EBEN E-Bus ENable. In conjunction with EA, EBEN designates program
memory fetches from either Port 0,2 or Port 5,6.
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
P0.3
P0.4
P0.5
P0.6
P0.7
Port 0 - open drain 8-bit bi-directional port that bit addressable and
can drive up to 8 LS TTL inputs. The port signals can be used as
high impedance inputs.
This port also provides the low-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
P1.0 - GRXD, GSC Receive
P1.1 - GTXD, GSC Transmit
P1.2 - !DEN, Driver Enable
P1.3 - !TXC, External Transmit Clock
P1.4 - !RXC, External Receive Clock
P1.5 - !HLD, DMA Hold
P1.6 - !HLDA, DMA Hold Acknowledge
P1.7
Port 1 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
Port signals in this port also serve as I/O for 80C152 functions.
These I/O signals are defined next to the port name.
P2.0
P2.1
P2.2
P2.3
P2.4
P2.5
P2.6
P2.7
Port 2 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
This port also provides the high-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
P3.0 - RXD, UART Receive
P3.1 - TXD, UART Transmit
P3.2 - !INT0, External Interrupt 0
P3.3 - !INT1, External Interrupt 1
P3.4 - T0, Timer 0 External Input
P3.5 - T1, Timer 1 External Input
P3.6 - !WR, External Data Memory Write Strobe
P3.7 - !RD, External Data Memory Read Strobe
Port 3 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
Port signals in this port also serve as I/O for 80C152 functions.
These I/O signals are defined next to the port name.
P4.0
P4.1
P4.2
Port 4 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is bit addressable. To use a port
signal as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups pull
the input high and source current when the input is driven low. To
Page 6 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 2 - I/O Signal Descriptions
Signal Name Description
P4.3
P4.4
P4.5
P4.6
P4.7
use a port signal as an output, a 1 or 0 written to the port location is
presented at the output.
P5.0
P5.1
P5.2
P5.3
P5.4
P5.5
P5.6
P5.7
Port 5 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is NOT bit addressable. To use
the port as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups
pull the input high and source current when the input is driven low.
To use the port as an output, 1s or 0s written to the port are
presented at the output.
This port also provides the low-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
P6.0
P6.1
P6.2
P6.3
P6.4
P6.5
P6.6
P6.7
Port 6 - 8-bit bi-directional port that is NOT bit addressable. To use
the port as an input, write a 1 to the port location. Internal pull-ups
pull the input high and source current when the input is driven low.
To use the port as an output, 1s or 0s written to the port are
presented at the output.
This port also provides the high-byte of the multiplexed address and
data bus depending on the state of !EBEN.
VCC Supply Voltage
VSS Device Ground
XTAL1 Input to the internal clock generator
XTAL2 Output from the internal oscillator amplifier
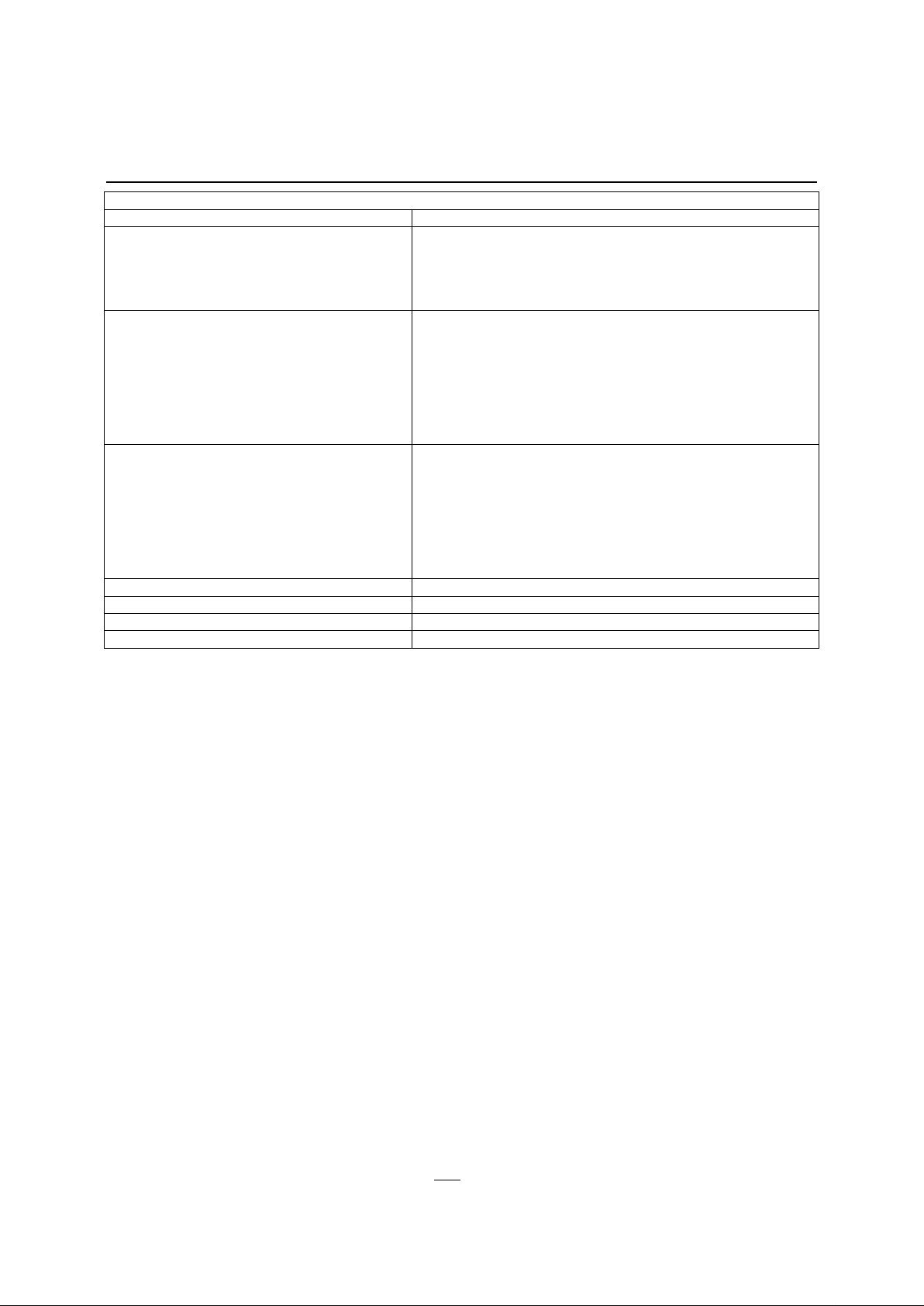
Memory Space
Memory space is divided up into program and data memory. Program memory is all external to the
IA80C152. Data memory is divided up into external and internal data memory. There can be up to
64K bytes of external program and data memory. Internal data memory is 256 bytes that is
mapped between RAM, SFRs, and Register Banks. Figure 5 diagrams the organization of the
IA80C152 memory space. See the C8051 section for further details.
Program memory is accessed using control signals and ports. On the JA and JC versions of the
IA80C152 this access is performed through ports P0 and P2. Further, since there is no internal
ROM, the entire program memory space is accessed via ports P0 and P2. On the JB and JD
version of the IA80C152, program memory access can be through either ports P0 and P2, or ports
P5 and P6. Which set of ports program memory fetches are made is controlled by the input signals
!EA and !EBEN. Table 3 summarizes the IA80C152 versions and the relationship to program
memory fetches.

Page 7 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Figure 5 - Memory Space
Table 3 - Summary of Program Memory Fetches
Fetch Control Fetch Signal
Version
EBEN EA
Fetch Ports
PSEN EPSEN
Memory Space
JA, JC N/A 0 or 1 P0, P2 Active - 0h - FFFFh
0 0 P0, P2 Active - 0h - FFFFh
1 0 P5, P6 - Active 0h - FFFFh
P5, P6 - Active 0h - 1FFFh
JB, JD
1 1
P0, P2 Active - 2000h - FFFFh
Summary of the 80C152 Registers and Interrupts
The 80C152 combines the register set of the 8051BH and additional SFRs for the DMA and GSC
functions. Likewise, the 80C152 combines the interrupts of the 8051BH and the interrupts
required by the DMA and GSC. Table 4 contains a summary of the 80C152 registers, and table 5
contains a summary of the 80C152 interrupts.
External RAM
00H
FFFFH
0000H
Internal RAM
7FH
8000H
4000H
C000H
80H
FFH
Lower 128
Bytes
Upper 128
Bytes
SFR Space
Page 8 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 4 - SFR Summary
Item
Register
Name
Register
Address
Functional
Block Description
Initial
Value
1. A 0E0h C8051 Accumulator 00h
2. ADR0 095h GSC Address Match 0 00h
3. ADR1 0A5h GSC Address Match 1 00h
4. ADR2 0B5h GSC Address Match 2 00h
5. ADR3 0C5h GSC Address Match 3 00h
6. AMSK0 0D5h GSC Address Mask 0 00h
7. AMSK1 0E5h GSC Address Mask 1 00h
8. B 0F0h C8051 B Register 00h
9. BAUD 094h GSC Baud Rate 00h
10. BCRL0 0E2h DMA Byte Count Register (Low) 0 X
11. BCRH0 0E3h DMA Byte Count Register (High) 0 X
12. BCRL1 0F2h DMA Byte Count Register (Low) 1 X
13. BCRH1 0F3h DMA Byte Count Register (High) 1 X
14. BKOFF 0C4h GSC Backoff Timer X
15. DARL0 0C2h DMA Destination Address Register (Low) 0 X
16. DARH0 0C3h DMA Destination Address Register (High) 0 X
17. DARL1 0D2h DMA Destination Address Register (Low) 1 X
18. DARH1 0D3h DMA Destination Address Register (High) 1 X
19. DCON0 092h DMA DMA Control 0 00h
20. DCON1 093h DMA DMA Control 1 00h
21. DPH 083h C8051 Data Pointer High 00h
22. DPL 082h C8051 Data Pointer Low 00h
23. GMOD 084h GSC GSC Mode X0000000b
24. IE 0A8h C8051 Interrupt Enable 0XX00000b
25. IEN1 0C8h DMA, GSC Interrupt Enable 1 XX000000b
26. IFS 0A4h GSC Interframe Space 00h
27. IP 0B8h C8051 Interrupt Priority XXX00000b
28. IPN1 0F8h DMA, GSC Interrupt Priority 1 XX000000b
29. MYSLOT 0F5h GSC GSC Slot Address 00h
30. P0 080h C8051 Port 0 0FFh
31. P1 090h C8051 Port 1 0FFh
32. P2 0A0h C8051 Port 2 0FFh
33. P3 0B0h C8051 Port 3 0FFh
34. P4 0C0h C8051 Port 4 0FFh
35. P5 091h C8051 Port 5 0FFh
36. P6 0A1h C8051 Port 6 0FFh
37. PCON 087h C8051 Power Control 0XXX0000b
38. PRBS 0E4h GSC Pseudo-Random Sequence 00h
39. PSW 0D0h C8051 Program Status Word 00h
40. RFIFO 0F4h GSC Receive FIFO X
41. RSTAT 0E8h GSC Receive Status 00h
42. SARL0 0A2h DMA Source Address Register (Low) 0 X
43. SARH0 0A3h DMA Source Address Register (High) 0 X
44. SARL1 0B2h DMA Source Address Register (Low) 1 X
45. SARH1 0B3h DMA Source Address Register (High) 1 X
46. SBUF 099h C8051 Serial Channel Buffer (UART) X
47. SCON 098h C8051 Serial Channel Control (UART) 00h
48. SLOTTM 0B4h GSC GSC Slot Time 00h
49. SP 081h C8051 Stack Pointer 07h
50. TCDCNT 0D4h GSC Transmit Collision Counter X
51. TCON 088h C8051 Timer Control 00h
Page 9 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
Table 4 - SFR Summary
Item
Register
Name
Register
Address
Functional
Block Description
Initial
Value
52. TFIFO 085h GSC Transmit FIFO X
53. TH0 08Ch C8051 Timer (High) 0 00h
54. TH1 08Dh C8051 Timer (High) 1 00h
55. TL0 08Ah C8051 Timer (Low) 0 00h
56. TL1 08Bh C8051 Timer (Low) 1 00h
57. TMOD 089h C8051 Timer Mode 00h
58. TSTAT 0D8h GSC Transmit Status XX000100b
Table 5 - Interrupt Summary
Interrupt
Priority
Interrupt
Name
Priority
Symbol
Name
Enable
Symbol
Name
Priority
Address
Enable
Address
Vector
Address
- Enable All Interrupts - EA - 0AFh 1 External Interrupt 0 PX0 EX0 0B8h 0A8h 03h
2 GSC Receive Valid PGSRV EGSRV 0F8h 0C8h 2Bh
3 Timer 0 Overflow PT0 ET0 0B9h 0A9h 0Bh
4 GSC Receive Error PGSRE EGSRE 0F9h 0C9h 33h
5 DMA Channel 0 Done PDMA0 EDMA0 0FAh 0CAh 3Bh
6 External Interrupt 1 PX1 EX1 0BAh 0AAh 13h
7 GSC Transmit Valid PGSTV EGSTV 0FBh 0CBh 43h
8 DMA Channel 1 Done PDMA1 EDMA1 0FCh 0CCh 53h
9 Timer 1 Overflow PT1 ET1 0BBh 0ABh 1Bh
10 GSC Transmit Error PGSRE EGSRE 0FDh 0CDh 4Bh
11 UART Transmit/Receive PS ES 0BCh 0ACh 23h
Power Conservation Modes
There are 2 power conservation modes identified as Idle Mode and Power Down Mode. The
IA80C152 pins will have values according to the Table 6 below.
Idle Mode is entered through software control of the PCON register. Idle halts processor
execution and the DMA. The GSC continue to operate to the extent that it can without the
processor or DMA servicing its requests. Idle mode is exited upon receipt of any enabled interrupt
or invoking a hardware reset.
Power Down Mode is entered through software control of the PCON register. Power Down
disables the oscillator causing all functions to stop. RAM data is maintained since power is not
removed from the device. The only way to exit power down mode is to invoke a hardware reset.
Page 10 of 32
IA80C152 Preliminary Data Sheet
UNIVERSAL COMMUNICATIONS CONTROLLER
Copyright 2000
innovASIC
[_________The End of Obsolescence
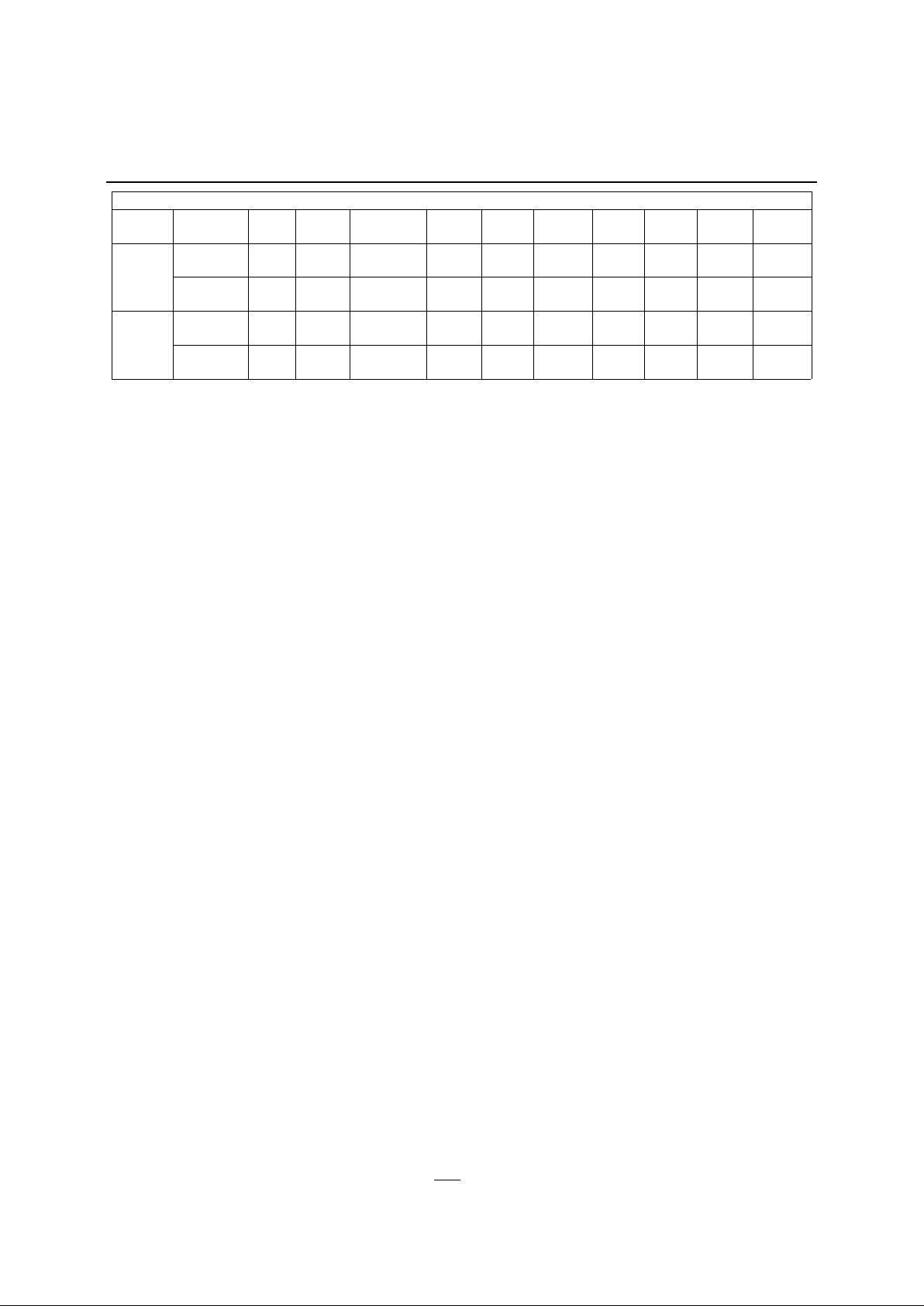
Table 6 - Power Conservation Modes
Mode
Program
Fetch ALE PSEN EPSEN*
Port0Port1Port2Port3Port4Port
5*
Port
6*
P0, P2 1 1 1 Float Data Addr. Data Data 0FFh 0FFhIdle
P5, P6* 1 1 1 Data Data Data Data Data 0FFh Addr.
P0, P2 0 0 1 Float Data Data Data Data 0FFh 0FFhPower
Down
P5, P6* 0 1 0 Data Data Data Data Data 0FFh 0FFh
*JB and JD Versions Only
Oscillator Pins
There are 2 methods for providing a clock to the 80C152. One method is to provide a crystal
oscillator and the other method is to provide an external clock source. When providing a crystal
oscillator, the XTAL1 pin is the input and XTAL2 is the output. The min and max crystal
frequencies are 3.5 MHz and 16.5 MHz, respectively.
When providing an external clock source, XTAL1 is the input and XTAL has no connection. Duty
cycle does not matter to the device, however, the external clock source requires a minimum pulse
width of 20 ns.
Summary of the 8051 Instruction Set
Table 7 provides a summary of the instruction set organized by hexadecimal opcode. Please refer
to the original Intel Data Book for individual instruction set details.
 Loading...
Loading...