Ingersoll-Rand PP20A-XXX-XXX User Manual
OPERATOR’S MANUAL PP20A-XXX-XXX
INCLUDING: OPERATION, INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE
2" DRY POWDER DIAPHRAGM PUMP
1:1 RATIO (METALLIC)
READ THIS MANUAL CAREFULLY BEFORE INSTALLING,
OPERATING OR SERVICING THIS EQUIPMENT.
It is the responsibility of the employer to place this information in the hands of the operator. Keep for future reference.
RELEASED: 6-2-05
REVISED: 6(REV. 0
4)
21-10
SERVICE KITS
Refer to Model Description Chart to match the pump mate-
rial options.
7102 valve kit for repair of H254PS control valve.
4255 for repair of P29122-100 lter / regulator.
10
118597-002 spool kit for repair of A212PD 4-way alpha valve.
637309-XX for uid section repair (see page 6). NOTE: This kit
also contains several air motor seals which will need to be
replaced.
637421 for air section repair (see page 8).
PUMP DATA
Models . . . . . . . . . . . . . see Model Description Chart for “-XXX”
Pump Type . . . . . . . . . Metallic, Dry Powder, Diaphragm Pump
Material . . . . . . . . . . . . see Model Description Chart
Speci c Application for pumping powders up to 50 lb. / ft
Weight . . . PP20A-XAX-XXX . . . . . . . . . . 99.4 lbs (45.1 kgs)
PP20A-XSX-XXX . . . . . . . . . . 157.8 lbs (71.6 kgs)
Maximum Air Inlet Pressure . . . . . . . . 50 p.s.i.g. (3.4 bar)
Maximum Fluidizing Pressure . . . . . . 100 p.s.i.g. (6.9 bar)
Maximum Particle Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1/4” dia. (6.4 mm)
Maximum Temperature Limits (diaphragm / ball / seal
materials)
Nitrile . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10° to 180° F (-12° to 82° C)
Santoprene® . . . . . . . . . . . . . . -40° to 225° F (-40° to 107° C)
Dimensional Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . see page 12
Mounting Dimension . 9-1/16” x 10-1/16” (230 mm x 256 mm)
Noise Level @ 70 p.s.i., 50 c.p.m. . . . . 83.0 db(A)
Tested with 94085 mu er assembly installed.
The pump sound pressure levels published here have been updated to
an Equivalent Continuous Sound Level (L
S1.13-1971, CAGI-PNEUROP S5.1 using four microphone locations.
NOTICE: All possible options are shown in the chart, however, certain
combinations may not be recommended. Consult a representative or
the factory if you have questions concerning availability.
) to meet the intent of ANSI
Aeq
3
Fluid Connection
A - 2 - 11-1/2 N.P.T.F. - 1
B - 2 - 11 BSP
C - 2-1/2” Tri-Clamp
Fluid Cap & Manifold Material
A - Aluminum
S - Stainless Steel
Hardware Material
P - Plated Steel
S - Stainless Steel
Seat Material
A - Santoprene
S - Stainless Steel
Ball Material
A - Santoprene
M - Medical Grade Santoprene
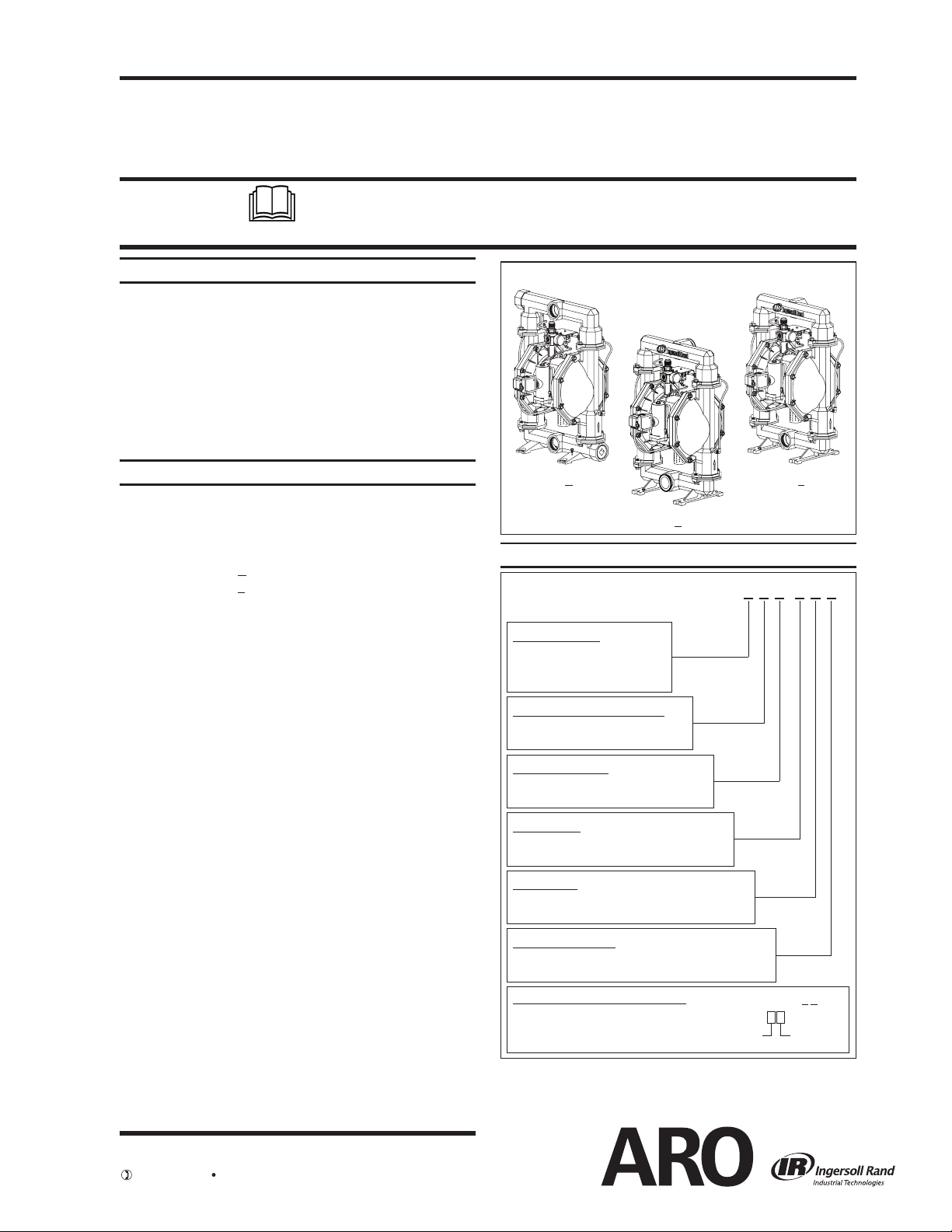
PP20A-XXX-XXX Powder Pump
PP20A-XAX-XXX PP20A-XSX-XXX
PP20A-CXX-XXX
Figure 1
MODEL DESCRIPTION CHART
PP20A - X X X - X X X
INGERSOLL RAND COMPANY LTD
209 NORTH MAIN STREET – BRYAN, OHIO 43506
(800) 495-0276 FAX(800) 892-6276
www.ingersollrandproducts.com
© 2010
CCN 15235526
Diaphragm Material
A - Santoprene
M - Medical Grade Santoprene
Fluid Section Service Kit Selection
EXAMPLE: Model #PP20A-AAS-AAA
Fluid Section Service Kit # 637309-AA
PP20A - XXX - X X X
637309 - X X
Ball Diaphragm

OPERATING AND SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
READ, UNDERSTAND AND FOLLOW THIS INFORMATION TO AVOID INJURY AND PROPERTY DAMAGE.
EXCESSIVE AIR PRESSURE
STATIC SPARK
WARNING
EXCESSIVE AIR PRESSURE. Can cause personal injury, pump damage or property damage.
Do not exceed the maximum inlet air pressure as
stated on the pump model plate.
Be sure material hoses and other components are able
to withstand uid pressures developed by this pump.
Check all hoses for damage or wear. Be certain dispensing device is clean and in proper working condition.
WARNING
STATIC SPARK. Can cause explosion resulting in severe injury or death. Ground pump and
pumping system.
Use the pump grounding screw terminal provided.
Use ARO® part no. 94829 ground kit or connect a suitable ground wire (12 ga. minimum) to a good earth
ground source.
Secure pump, connections and all contact points to
avoid vibration and generation of contact or static
spark.
Consult local building codes and electrical codes for
speci c grounding requirements.
After grounding, periodically verify continuity of
electrical path to ground. Test with an ohmmeter
from each component (e.g., hoses, pump, clamps, container, spray gun, etc.) to ground to insure continuity.
Ohmmeter should show 0.1 ohms or less.
Submerse the outlet hose end, dispensing valve or
device in the material being dispensed if possible.
(Avoid free streaming of material being dispensed.)
Use hoses incorporating a static wire.
Use proper ventilation.
Keep in ammables away from heat, open ames and
sparks.
Keep containers closed when not in use.
WARNING
Pump exhaust may contain contaminants.
Can cause severe injury. Pipe exhaust away from work
area and personnel.
In the event of a diaphragm rupture, material can be
forced out of the air exhaust mu er.
Pipe the exhaust to a safe remote location when
pumping hazardous or in ammable materials.
Use a grounded 1” minimum i.d. hose between the
pump and the mu er.
WARNING
HAZARDOUS PRESSURE. Can result in serious injury or property damage. Do not service or
clean pump, hoses or dispensing valve while the system is pressurized.
Disconnect air supply line and relieve pressure from
the system by opening dispensing valve or device and
/ or carefully and slowly loosening and removing outlet hose or piping from pump.
WARNING
HAZARDOUS MATERIALS. Can cause serious
injury or property damage. Do not attempt to return
a pump to the factory or service center that contains
hazardous material. Safe handling practices must
comply with local and national laws and safety code
requirements.
HAZARDOUS MATERIALS
HAZARDOUS PRESSURE
Obtain Material Safety Data Sheets on all materials
from the supplier for proper handling instructions.
WARNING
EXPLOSION HAZARD. Models containing aluminum wetted parts cannot be used with 1,1,1-trichloroethane, methylene chloride or other halogenated
hydrocarbon solvents which may react and explode.
Check pump motor section, uid caps, manifolds and
all wetted parts to assure compatibility before using
with solvents of this type.
WARNING
MISAPPLICATION HAZARD. Do not use models containing aluminum wetted parts with food products for human consumption. Plated parts can contain
trace amounts of lead.
CAUTION
Verify the chemical compatibility of the
pump wetted parts and the substance being pumped,
flushed or recirculated. Chemical compatibility may
change with temperature and concentration of the
chemical(s) within the substances being pumped,
ushed or circulated. For speci c uid compatibility,
consult the chemical manufacturer.
CAUTION
Maximum temperatures are based on
mechanical stress only. Certain chemicals will signi cantly reduce maximum safe operating temperature.
Consult the chemical manufacturer for chemical compatibility and temperature limits. Refer to PUMP DATA
on page 1 of this manual.
CAUTION
Be certain all operators of this equipment
have been trained for safe working practices, understand it’s limitations, and wear safety goggles / equipment when required.
CAUTION
Do not use the pump for the structural support of the piping system. Be certain the system components are properly supported to prevent stress on
the pump parts.
Suction and discharge connections should be flex-
ible connections (such as hose), not rigid piped,
and should be compatible with the substance being
pumped.
CAUTION
Prevent unnecessary damage to the pump.
Do not allow pump to operate when out of material
for long periods of time.
Disconnect air line from pump when system sits idle
for long periods of time.
CAUTION
Use only genuine ARO replacement parts to
assure compatible pressure rating and longest service
life.
NOTICE
Replacement warning labels are available
upon request: “Static Spark & Diaphragm Rupture” pn
\ 94080.
WARNING
= Hazards or unsafe practices which
could result in severe personal injury,
death or substantial property damage.
CAUTION
= Hazards or unsafe practices which
could result in minor personal injury,
product or property damage.
NOTICE
= Important installation, operation or
maintenance information.
Page 2 of 12 PP20A-XXX-XXX (en)

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The ARO diaphragm pump o ers high volume delivery even
at low air pressure and a broad range of material compatibility options available. Refer to the model and option chart.
ARO pumps feature stall resistant design, modular air motor
/ uid sections.
Air operated double diaphragm pumps utilize a pressure differential in the air chambers to alternately create suction and
positive fluid pressure in the fluid chambers, valve checks
insure a positive ow of uid.
This diaphragm pump was developed to address the unique
problems associated with pumping dry powders, which can
“pack out” inside the pump fluid chambers, if not kept in a
semi- uid state.
This system incorporates the use of special valves to introduce air or inert gas* into the uid chambers simultaneously
to a pumping cycle in a timed sequence which keeps the
powder in a uidized state during the transfer process.
THEORY OF OPERATION
The main air distribution valve (252) is a double pilot actuated four-way valve. It is a slave to the pump major air valve.
The distribution valve recognizes the signal from two pump
major air valve (259) ports (air dumps). These signals are converted into alternating output pressure distributions, which
are injected into the uid chambers during the pumping cycle to uidize the powder as the diaphragm moves through
the discharge stroke.
The ow of air supplied to the uid chamber is controlled by
the (248) filter / regulator. Under normal operating conditions, this is the primary control.
When air is supplied to the filter / regulator (248), the distribution valve directs the ow of air into the uid chamber
that will dispense rst for 3 to 8 seconds. The time delay then
supplies the start signal to open the main pump air supply
valve. When the pump diaphragm reaches the end of the
discharge stroke, it reverses direction. The distribution valve
then shifts and shuts off the fluidizing air to the first fluid
chamber as it applies a burst of air to the second uid chamber and uidizes the powder in the second chamber.
The air induction ori ce (76) increases the air velocity prior
to injection point because of the ori ce and it prevents clogging of the injector feed line.
NOTE: The restart valve (258) is a bleed valve which will stop
the pump and then restart the pump by re-initiating the time
delay cycle.
*NOTE: Use of other gases: Using only a gas to operate a 2”
pump can be rather expensive because of the high volume
needed. Separate air / gas inputs allow the uidizing feature
of this pump to utilize special inert gas, such as Nitrogen or
Argon (air), if necessary and still allow use of standard compressed shop air for the pumping function.
The ability to introduce special gas also means special materials could be injected through the fluidization lines. Applications may include such materials as colorants, foaming
agents, additives, neutralizers, etc.
AIR AND LUBE REQUIREMENTS
WARNING
damage, personal injury or property damage. The
pump air supply must be limited to 50 p.s.i.g. (3.4 bar)
maximum inlet air pressure.
The air supply line or hose to the pump should be ad-
equately sized to carry a sufficient volume of air to the
pump. The material inlet supply tubing should not be too
EXCESSIVE AIR PRESSURE. Can cause pump
small or restrictive, which will inhibit material flow. The
outlet material volume is governed not only by the air
supply, but also by the material volume available at the
inlet.
Air supply provided should be filtered to provide clean,
dry air. A filter capable of filtering out particles larger
than 40 microns should be used on the air supply. There
is no lubrication required other than the “O” ring lubricant
which is applied during assembly or repair.
If lubricated air is present, make sure that it is compatible
with the Nitrile “O” rings in the air motor section of the
pump.
NOTE: When using air for powder uidization, make sure
it is ltered and very dry.
INSTALLATION
WARNING
ED TO PREVENT STATIC DISCHARGE. THIS INCLUDES
THE PUMP AND ALL INPUT AND OUTPUT SUPPLY
LINES AND RELATED SYSTEM DEVICES AND ACCESSORIES. FAILURE TO DO SO CAN RESULT IN EXPLOSION
AND SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURY.
SYSTEM GROUNDING
Consult local building codes and electrical codes for
speci c requirements.
Must comply with all applicable Local and National
codes for such applications.
Grounding is accomplished through the ground lug
and strap provided on the pump. Keep the grounding
strap as short as possible.
Safe operating conditions are the responsibility of the
installer and operator.
Secure the diaphragm pump legs to a suitable surface
to avoid damage by excessive vibration.
THE PUMPING SYSTEM MUST BE GROUND-
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
START-UP
NOTE: PRIOR TO START-UP, MAKE SURE THE GROUNDING
INSTRUCTIONS WERE FOLLOWED.
1.
Connect air supply to (263) main air supply control valve
(30 - 40 p.s.i. / 2.1 - 2.8 bar).
2.
Turn the air on.
3.
Attach air (or gas) to (248) lter / regulator. CAUTION: Do
not apply excessive Fluidization Gas* Pressure (refer to
note under “General Description”).
.
4
At (248), turn on air (or inert gas) supply. There will be a
3 to 8 second time delay, during which the pump will be
fluidizing any powder left in the pump from an earlier
dispense. This time delay will occur on all start-ups.
OPERATION AND ADJUSTMENT
NOTE: Powder type materials can vary in ow-ability and the
same settings may not work universally. Factors such as density and humidity can require changing the mixture of ow
rate and uidization air and some experimenting should be
expected.
IMPORTANT: DO NOT TURN FILTER / REGULATOR (248) OFF.
Positive air (or gas) pressure must be supplied to the lter /
regulator to allow the pump to function. Powder will accumulate in the uid caps if the pump is not allowed to expel
excess material before the pump shuts down. Restart can
PP20A-XXX-XXX (en) Page 3 of 12
compress some powders to a solid that may cause the pump
to fail. The pump should cycle until most of the powder has
been purged before it is shut down.
Calibration procedure on initial start-up:
NOTE: Once these parameters are established for your speci c application, they should not need to be changed.
1.
Turn the ow and pressure on the (248) lter / regulator
all the way up.
2.
Slowly decrease pressure and ow until pump begins to
labor (work harder).
3.
Increase pressure and flow back to a point where the
pump begins to run smoothly. This will optimize the airto-powder mix and will help to establish the most efficient working parameters.
If the pump should begin to cycle slowly (bog down), the
powder can be purged by depressing restart button. This will
stop the pump and restart the aeration cycle and allow time
to increase air ow to the aeration ports for proper material
movement.
IMPORTANT
SHUT DOWN PROCEDURE - TO HELP PREVENT PACK-OUT
It is good operating practice to dry cycle the pump 5 - 10
seconds at the end of each dispense cycle. This can be accomplished by closing o the powder source at the suction
of the pump or pull wand from material. This will help clear
the pump chambers of any residual powder.
NOTICE: Failure to insure proper uidization can result in
internal parts breakage and pump failure.
MAINTENANCE
Refer to the part views and descriptions as provided on page
6 through 11 for parts identi cation and Service Kit information.
Keep good records of service activity and include pump
in preventive maintenance program.
Certain ARO “Smart Parts” are indicated which should be
available for fast repair and reduction of down time.
Service kits are divided to service two separate dia-
phragm pump functions: 1. AIR SECTION, 2. FLUID SECTION. The FLUID SECTION is divided further to match
typical part MATERIAL OPTIONS.
Provide a clean work surface to protect sensitive internal
moving parts from contamination from dirt and foreign
matter during service disassembly and reassembly.
Before disassembling, empty captured material in the
outlet manifold by turning the pump upside down to
drain material from the pump.
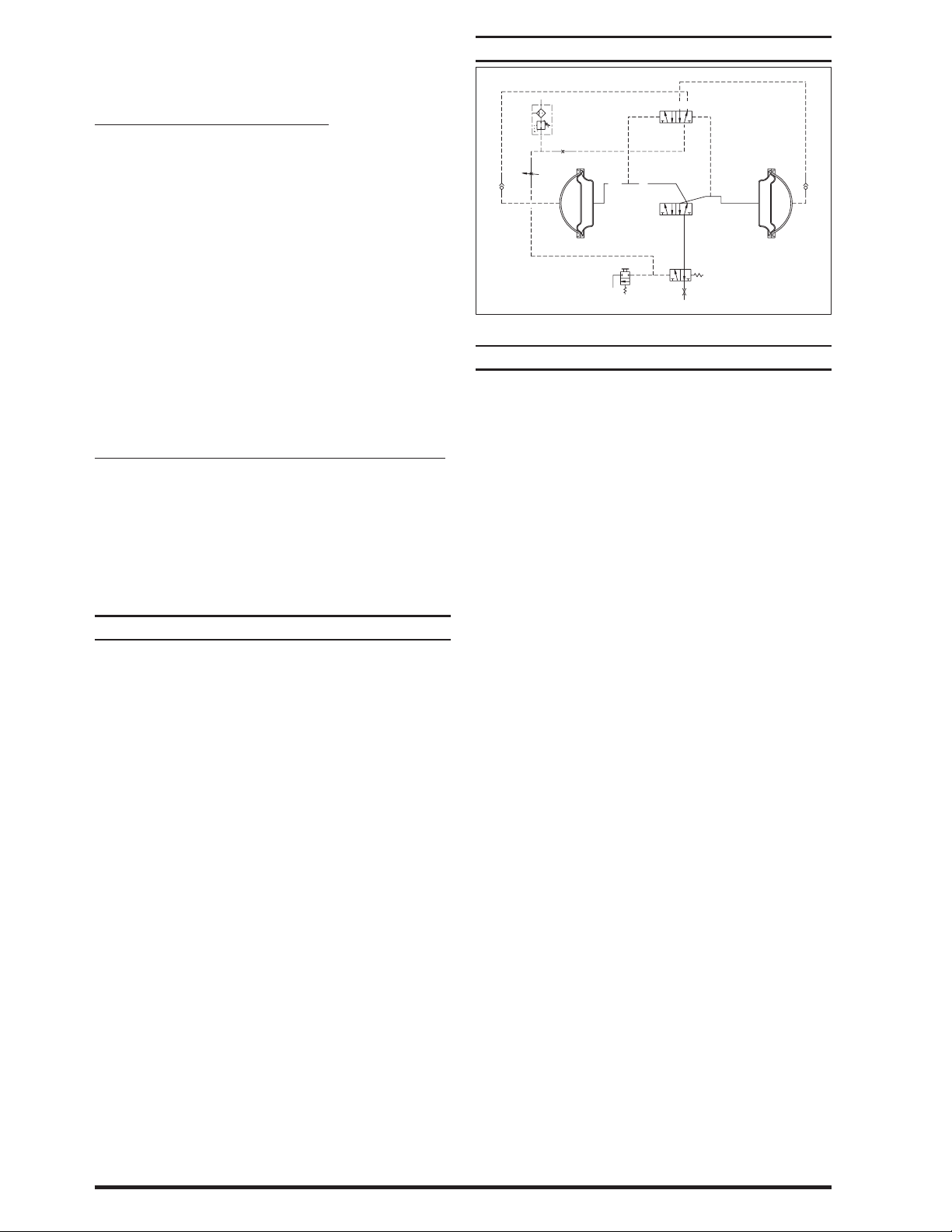
SCHEMATIC CIRCUIT
Air / Nitrogen
95077
119309-103
Left 2
Exh 24130
42
12 14
A212PD
2
4
1
2
1
94977
3
Right 4
H254PS
Figure 2
TROUBLE SHOOTING
Product discharged from exhaust outlet.
Check for diaphragm rupture.
Check tightness of (14) diaphragm screw.
Motor blows air or stalls.
Check (176) check valve for damage or wear.
Check for restrictions in valve / exhaust.
Low output volume, erratic ow, or no ow.
Check air supply.
Check for plugged outlet hose.
Check for kinked (restrictive) outlet material hose.
Check for kinked (restrictive) or collapsed inlet material
hose.
Suction hose must be a non-collapsing type, conductive
and capable of pulling a high vacuum (up to 30” mercury).
Check all joints on the inlet manifolds and suction con-
nections. Connection must be air tight.
Inspect the pump for solid objects lodged in the dia-
phragm chamber or the seat area.
CP10-BCP10-B
Loctite® and 242® are registered trademarks of Henkel Loctite Corporation ARO® is a registered trademark of Ingersoll-Rand Company
Santoprene® is a registered trademark of Monsanto Company, licensed to Advanced Elastomer Systems, L.P. 271™ is a trademark of Henkel Loctite Corporation
Page 4 of 12 PP20A-XXX-XXX (en)
Lubriplate® is a registered trademark of Lubriplate Division (Fiske Brothers Re ning Company)
 Loading...
Loading...