Page 1

InfoPrint 6500 Line Matrix Printers
LQ-1600K Programmer’s Reference Manual
G550-1006-01
Page 2

Page 3

InfoPrint 6500 Line Matrix Printers
LQ1600-K Programmer’s Reference Manual
G550-1006-01
Page 4
Note!
Before using this information and the product it supports, read the information in “Notices” on
page 111.
Second Edition (January 2010)
This edition applies to the InfoPrint 6500-D Series Line Matrix Printer and replaces the following
publication:
G550-1006-00.
Visit our home page at: http://www.infoprint.com
You can send comments by e-mail to printpub@infoprint.com or by mail to:
InfoPrint Solutions Company, LLC
6300 Diagonal Hwy 002J
Boulder, CO 80301-9270
U.S.A.
This product is or contains commercial computer software and commercial computer software
documentation developed exclusively at private expense. As specified in Federal Acquisition
Regulation 12.212 in the case of civilian agencies and Defense Federal Acquisition Regulation
Supplement 227.7202 in the case of military agencies, use, duplication and disclosure by agencies
of the U.S. Government shall solely be in accordance with the accompanying International
Program License Agreement in case of software products and in accordance with the licensing
terms specified in the product’s documentation in the case of hardware products.
© Copyright InfoPrint Solutions Company 2008, 2010. All rights reserved.
InfoPrint 6500 Line Matrix Printers: LQ1600-K Programmer’s Reference Manual,
Internet
Page 5

Table of Contents
1 Introduction ........................................................... 9
About This Manual................................................................................. 9
Warnings and Special Information .................................................. 9
Related Product Information ........................................................... 9
Software Features ................................................................................. 9
2 LinePrinter Plus LQ-1600K Emulation ................ 11
LQ-1600K Emulation ........................................................................... 11
Exceptions And Differences .......................................................... 11
Default Values And States ............................................................ 12
Epson Character Sets ................................................................... 15
Escape Sequences ....................................................................... 16
FS Sequences............................................................................... 16
Super-Set Commands................................................................... 16
Set And Reset Codes.................................................................... 16
DBCS Mode .................................................................................. 17
Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes................. 17
Format For Control Code Descriptions.......................................... 17
Control Code Index ...................................................................... 18
Adjust Half-Width Characters To Fit Into DBCS Character
Spacing ......................................................................................... 21
Adjust Table Characters................................................................ 21
Align Two Half-Width Rotated Characters In DBCS Mode............ 22
Backspace..................................................................................... 23
Barcode Printing............................................................................ 24
Bell ................................................................................................ 27
Cancel Character Rotation ............................................................ 27
Cancel Line ................................................................................... 28
Cancel Spacing Adjustment .......................................................... 28
Carriage Return............................................................................. 28
CC DOS Control Code .................................................................. 29
Character Pitch 10 CPI ................................................................. 29
Character Pitch 12 CPI ................................................................. 29
Character Pitch 15 CPI ................................................................. 30
Condensed Print (Set/Reset) ........................................................ 30
DBCS Mode (Select) ..................................................................... 31
Page 6

Table of Contents
DBCS Mode (Cancel).................................................................... 31
DBCS Mode Underline .................................................................. 31
DBCS Superscript/Subscript Print (Set/Cancel)............................ 32
Define A Download Character (DBCS) ......................................... 32
Define Pattern For Special Printing Effect..................................... 33
Define User-Defined Character..................................................... 34
Delete Character ........................................................................... 35
Double High Print, Set/Reset ....................................................... 35
Double Strike (Select) ................................................................... 35
Double Strike (Cancel) .................................................................. 36
Double Wide Print ......................................................................... 36
Double Wide Print (One Line) ....................................................... 37
Double Wide Print (One Line), Cancel .......................................... 38
Double Wide Print (One Line) ...................................................... 38
Double Wide Print (One Line), Cancel .......................................... 38
Double Wide, Double High (2x2) Print .......................................... 39
Download Chinese Font (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................. 39
Emphasized Print (Select)............................................................. 39
Emphasized Print (Cancel) ........................................................... 40
Enable Printing Of Control Codes ................................................. 41
Font Expansion ............................................................................. 41
Form Feed..................................................................................... 42
Graphic Printing ............................................................................ 42
Graphics, Double Density ............................................................. 43
Graphics, Double Density, Double Speed..................................... 44
Graphics, Quadruple Density ........................................................ 45
Graphics, Standard Density .......................................................... 46
Half-Width Print ............................................................................. 47
Half-Width Print Cancel ................................................................. 47
Home Print Head........................................................................... 47
Horizontal Tab Execute ................................................................. 47
Horizontal Tab Set/Release .......................................................... 48
Initialize Printer.............................................................................. 49
Italic Printing (Select) .................................................................... 49
Italic Printing (Cancel) ................................................................... 49
Line Feed ...................................................................................... 50
Line Feed n/180 Inch .................................................................... 50
Line Spacing 1/6 Inch (6 lpi).......................................................... 51
Line Spacing 1/8 Inch (8 lpi).......................................................... 52
Line Spacing n/60 Inch.................................................................. 53
Line Spacing n/180 Inch................................................................ 54
Line Spacing n/360 Inch................................................................ 55
Page 7

Table of Contents
Make Hex 80-9F Control Codes.................................................... 56
Make Hex 80-9F Printable............................................................. 56
Master Print Select ........................................................................ 58
Master Print Select In DBCS Mode ............................................... 59
Master Select One-Line Attribute in DBCS Mode ......................... 60
Printer Deselect............................................................................. 60
Printer Select................................................................................. 61
Proportional Spacing, Select/Deselect ......................................... 61
Rotate Character 90 Degrees Counter-Clockwise ........................ 61
Select Autowrap Mode (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only) ................... 62
Select Bit Image ............................................................................ 62
Select DBCS ASCII Character Type ............................................. 63
Select DBCS Character Bitmap .................................................... 63
Select DBCS Character Font ........................................................ 63
Select DBCS Print Quality............................................................. 64
Select Graphics Mode................................................................... 65
Select Italic Character Set............................................................. 66
Select Print Quality........................................................................ 66
Select Special Printing Effect ........................................................ 67
Select Super/Subscript Printing (For Hanzi BIG5 Printer only) ..... 68
Select Typeface (For Hanzi BIG5 Printer only) ............................. 68
Select Underline Printing (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................ 68
Select Vertical Printing (for Hanzi BIG5 Printer only) .................... 69
Select Vertical Tab Channel.......................................................... 69
Set 0-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters................. 69
Set 3-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters................. 70
Set 6-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters................. 70
Set 12-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters............... 70
Set Absolute Horizontal Print Position In 1/60 Inch....................... 71
Set Chinese Font Rotate (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................ 71
Set Chinese Inner Code (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................. 72
Set Font/Line Gap (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only).......................... 72
Set Font Scale (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................................ 72
Set Form Length By Lines............................................................. 73
Set Form Length In Inches............................................................ 74
Set Font Pitch (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................................. 74
Set Intercharacter Spacing............................................................ 75
Set Intercharacter (One-Byte) Spacing In DBCS Mode ................ 75
Set Intercharacter (Two-Byte) Spacing In DBCS Mode ................ 76
Set International Character Set..................................................... 76
Set Left Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)............................... 78
Set Line Pitch (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................................. 78
Page 8

Table of Contents
Set Logic Right Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................... 78
Set Logical Left Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only) .................. 79
Set Margin (Left) ........................................................................... 79
Set Margin (Right) ......................................................................... 80
Set Paper Length (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only) ........................... 80
Set Relative Horizontal Print Position In 1/120 Inches.................. 81
Set Right Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only) ............................ 81
Set Vertical Tabs In Channels....................................................... 82
Skip Over Perforation.................................................................... 82
Skip Over Perforation Cancel ....................................................... 83
Static Barcode Function (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)................. 83
Superscript And Subscript Printing ............................................... 84
Superscript And Subscript Printing (Cancel)................................. 85
Turn On/Off Compress Mode ........................................................ 85
Turn On/Off OCRB Printing........................................................... 86
Underline....................................................................................... 86
Unidirectional Printing For One Line ............................................. 87
Unidirectional Printing, Set/Reset ................................................ 87
Vertical and Horizontal Extension ................................................. 87
Vertical Tab, Execute .................................................................... 88
Vertical Tab, Set/Clear .................................................................. 88
A Standard ASCII Character Set............................ 89
B Vertical Page Formatting..................................... 91
Overview.............................................................................................. 91
Executing Vertical Tabs ................................................................ 91
Vertical Tab Positions ................................................................... 92
C Graphics.............................................................. 93
Bit Image Graphics .............................................................................. 93
Designing a Bit Image Pattern ...................................................... 95
Bit Image Density .......................................................................... 95
Bit Image Programming Format .................................................... 96
Bit Image Sample .......................................................................... 97
Glossary .............................................................. 99
Notices .............................................................. 111
Product Recycling And Disposal........................................................ 114
Trademarks........................................................................................ 114
Communication Statements............................................................... 115
Page 9
1 Introduction
About This Manual
This manual is designed so you can quickly find the information you need to
use the LQ-1600K emulation.
This book does not explain how to operate the printer. For printer operation,
see the
Warnings and Special Information
Read and comply with all information highlighted under special headings:
InfoPrint 6500 Line Matrix Printers: User’s Manual.
WARNING
CAUTION
IMPORTANT
Conditions that could harm you as well as damage the equipment.
Conditions that could damage the printer or related equipment.
Information vital to proper operation of the printer.
NOTE: Information affecting printer operation.
Related Product Information
Refer to the following book for printer operation:
•
InfoPrint 6500 Line Matrix Printers: User’s Manual.
instructions and descriptions and troubleshooting guidelines.
Software Features
The LQ-1600K emulation software provides the following features:
• Graphics and print quality. You can enable graphics mode and specify a
density mode (dots per inch), for either 8-pin/24-pin images.
• Print Attributes. Characters can be bold, italic, double high, double wide,
etc.
• Page Formatting. Commands which allow you to set line spacing, page
length, and vertical tabbing.
Provides configuration
• Font Typefaces. Also referred to as print modes. There are six typefaces
that can print both SBCS and DBCS characters: LQ, Near LQ, Normal,
Hi-Speed, Super Hi-Speed, and Ultra Hi-Speed.
9
Page 10

Chapter 1 Software Features
10
Page 11
2 LinePrinter Plus
LQ-1600K Emulation
LQ-1600K Emulation
“Emulation” refers to the ability of a printer to execute the commands of other
printer control languages. In LQ-1600K emulation mode, your printer prints
files coded for Epson LQ series printers, particularly the LQ-1600K.
Exceptions And Differences
Because Of Mechanical Differences Between Your Printer (A Line Matrix
Printer) And Moving Printhead Serial Matrix Printers, Some Features Are
Approximated Or Not Supported.
Commands not supported by our printer:
1. Control paper loading/ejecting (ESC EM n)
2. Select user-defined set (ESC % n)
3. Define user-defined characters (ESC k NUL
4. Copy ROM to RAM (ESC : NUL
5. Select justification (ESC
6. Set MSB to 1 (ESC >)
7. Set MSB to 0 (ESC =)
8. Cancel MSB Control (ESC #)
9. Reassign bit-image mode (ESC ?)
a n
n m
)
)
n m
)
11
Page 12
Chapter 2 LQ-1600K Emulation
Default Values And States
Your printer stores a set of typical operating states and conditions in the flash
memory. The first time you power up the printer, the factory settings in
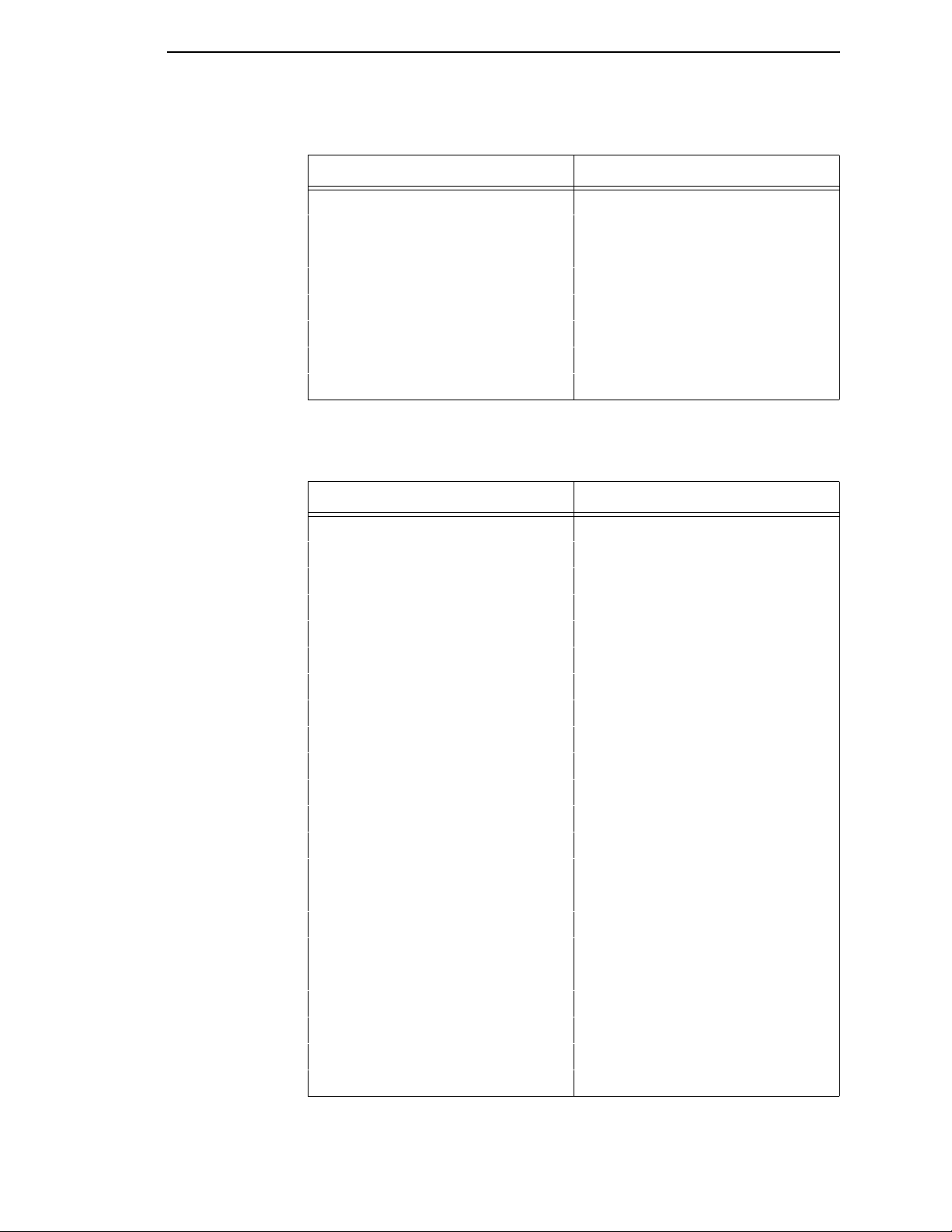
1 are automatically invoked.
Table 1. Factory Settings for Hanzi GB
Characteristic Default Setting
Select CPI 10.0
Select LPI 6.0
DBCS CPI 6.7
Host Command Ignore Unidir.
Typeface Near LQ
Styling Type SONG
High Density Disable
Proportional Spacing Disable
Table
Bold Print Disable
Italic Print Disable
Slashed Zero Disable
Text Position Bottom of Line
DBCS/ASCII Mode DBCS Mode
DBCS ASCII Style Normal
Compressed Mode Disable
DBCS Compressed Disable
Encoding Address Table
Taller 15 CPI Disable
Graphics Spd Up Normal
Left Margin 0 columns
Right Margin 0 columns
Bottom Margin 0 lines
Perforation Skip Disable
Form Length 11.0 inches
279.4 millimeters
66 lines
12
Form Width 13.6 inches
345.4 millimeters
136 characters
Reset Cmd CFG Ld Disable
Illegal Code Pt. Normal
Define CR Code CR = CR
Page 13
Default Values And States
Table 1. Factory Settings (continued) for Hanzi GB
Characteristic Default Setting
Auto LF Enable
Define LF Code LF = CR + LF
Printer Select Disable
Character Set Standard Sets (Epson Set; ASCII)
20 CPI Condensed Enable
Alt Set 80-9F Printable
Currency Sign RMB Select
AR3240 Compat. Disable
Table 2. Factory Settings for Hanzi Big5
Characteristic Default Setting
Select CPI 10.0
Select LPI 6.0
DBCS CPI 6.7
Host Command Ignore Unidir.
Typeface LQ
Styling Type MING
High Density Disable
Proportional Spacing Disable
Bold Print Disable
Italic Print Disable
Slashed Zero Disable
Text Position Bottom of Line
DBCS/ASCII Mode DBCS Mode
DBCS ASCII Style Normal
Compressed Mode Disable
DBCS Compressed Disable
Encoding Address Table
Taller 15 CPI Disable
Graphics Spd Up Normal
Left Margin 0 columns
Right Margin 0 columns
Bottom Margin 0 lines
13
Page 14
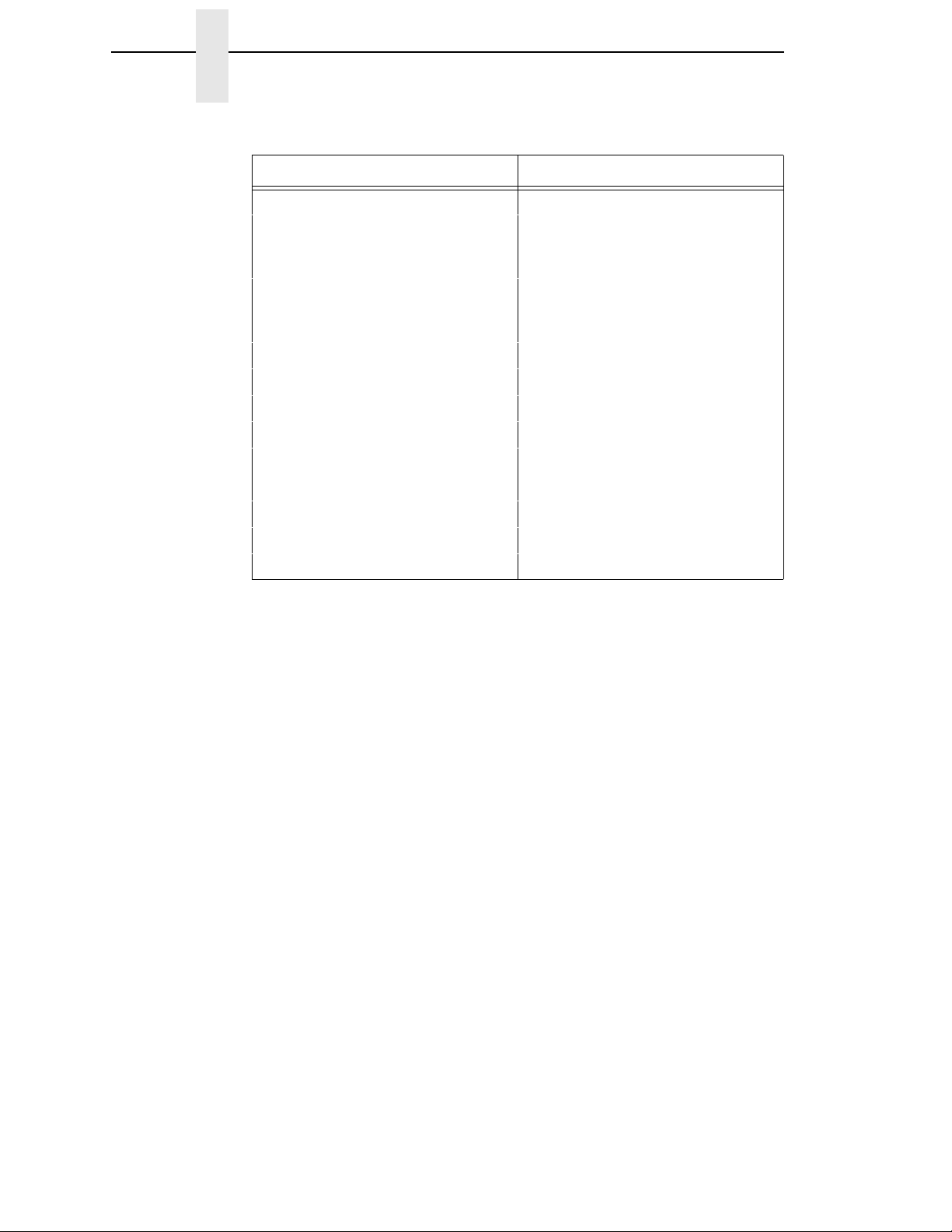
Chapter 2 LQ-1600K Emulation
Table 2. Factory Settings (continued) for Hanzi Big5
Characteristic Default Setting
Perforation Skip Disable
Form Length 11.0 inches
Form Width 13.6 inches
Reset Cmd CFG Ld Disable
Illegal Code Pt. Normal
Define CR Code CR = CR
Auto LF Enable
Define LF Code LF = CR + LF
Printer Select Disable
Character Set Standard Sets (Epson Set; ASCII)
279.4 millimeters
66 lines
345.4 millimeters
136 characters
20 CPI Condensed Enable
Alt Set 80-9F Printable
14
Page 15
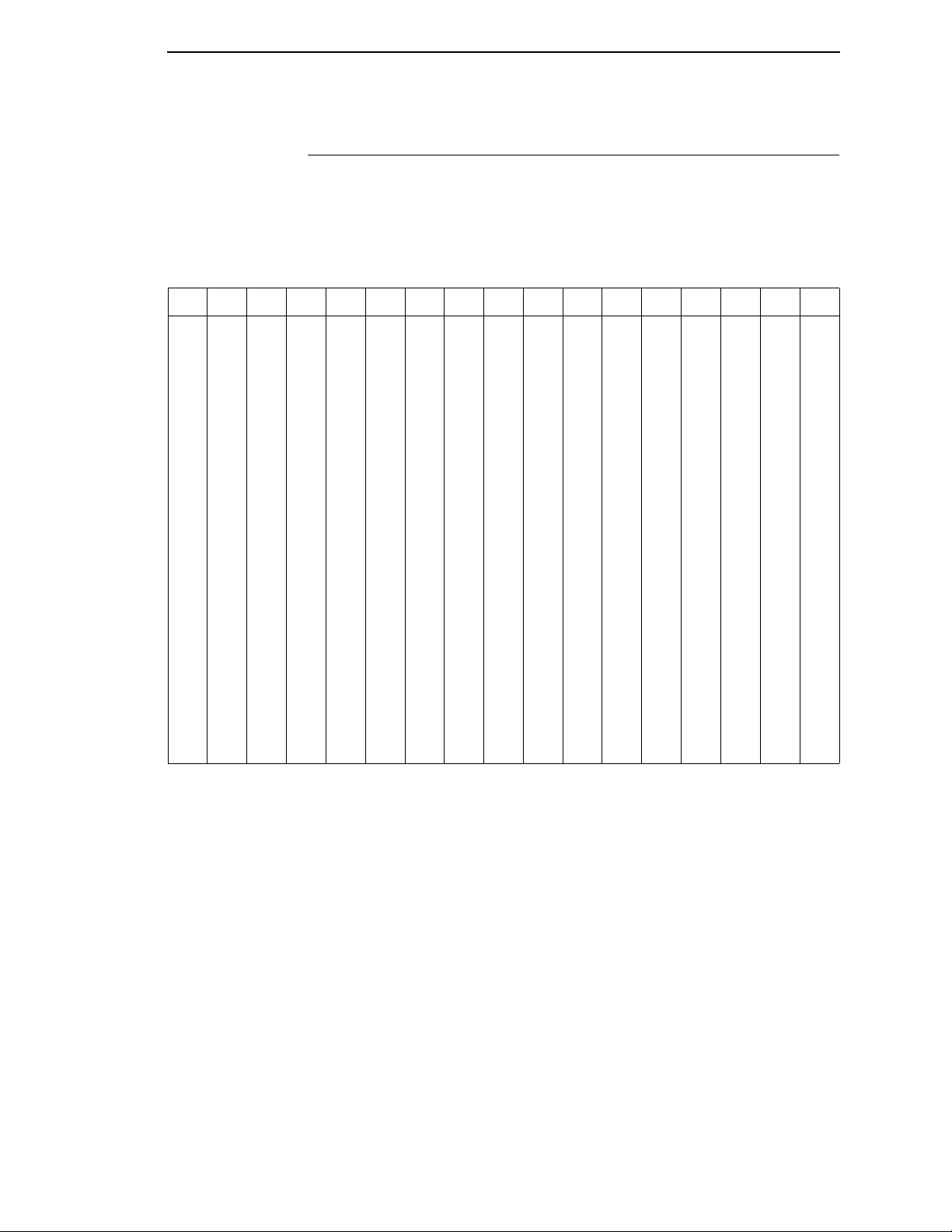
Epson Character Sets
Epson Character Sets
The LQ-1600K printer uses two character sets: the IBM PC set and the Epson
set. The Epson set is the ASCII character set with the upper,
non-ASCII set defined as italics and the usually unprintable codes designed
as international characters. (See
Table 3.)
Table 3. Epson Character Set
Hex 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
0 à § SP 0 @ P ‘ p
1 è ß ! 1 A Q a q
2 ù DC2 " 2 B R b r
3 ò DC3 # 3 C S c s
4 ì DC4 $ 4 D T d t
5 ° ø % 5 E U e u
6 £ ¨ & 6 F V f v
7 BEL Ä ‘ 7 G W g w
8 BS CAN ( 8 H X h x
9 HT Ü ) 9 I Y i y
A LF ä * : J Z j z
B VT ESC + ; K [ k {
C FF ü ’ < L \ l |
D CR É – = M ] m }
E SO é . > N ^ n ~
F SI ¥ / ? O _ o DEL
à § SP 0 @ P ‘ p
è ß ! 1 A Q a q
ù Æ " 2 B R b r
ò æ # 3 C S c s
ì ø $ 4 D T d t
° ø % 5 E U e u
£ ¨ & 6 F V f v
i Ä ’ 7 G W g w
¿ Ö ( 8 H X h x
Ñ Ü ) 9 I Y i y
ñ ä * : J Z j z
¤ ö + ; K [ k {
P
t
ü , < L \ l |
Å É – = M ] m }
å é . > N ^ n ~
Ç ¥ / ? O _ o ø
15
Page 16
Chapter 2 LQ-1600K Emulation
Escape Sequences
Some LQ-1600K control codes consisting of more than one character are
called escape sequences because the first character in the sequence is the
ASCII ESCape character. ESC alerts the printer that a special function
command—not printable characters—follows.
The format for an escape sequence is:
ESC (parameter 1)(parameter 2)...(parameter n)
For example, to select emphasized (offset) print, send the ESC character
immediately followed by the E character (do not add a space character):
ASCII: ESC E Hex: 1B 45Dec: 27 69
FS Sequences
Another type of control code which consists of more than one character is
called an “FS sequence,” because the first character is the ASCII FS
character. This control code is used when the printer is printing Double Byte
Character Set (DBCS) characters. The FS alerts the printer that a special
function command (not printable characters) follows. Most FS commands
work only on DBCS characters.
The format for an FS sequence is:
FS (parameter 1)(parameter 2)...(parameter n)
For example, to rotate DBCS characters by 90° counter-clockwise, send an
FS character immediately followed by the J character:
ASCII: FS J Hex: 1C 4ADec: 28 74
Super-Set Commands
The unique control code sequence for both SSCC and ASSC commands are
defined in the table below:
Control
Code
SSCC ESC | } ; 1B 7C 7D 3B 27 124 125 59
ASSC ESC | } ; q 1B 7C 7D 3B 71 27 124 125 59 113
ASCII Value Hex Value Dec Value
Set And Reset Codes
Set and reset are other ways of saying turn on and “turn off; select and
deselect; or enable” and disable.”
16
Some printer features are set and reset with an escape sequence and the
numbers 1 or 0. In those cases you can represent 1 and 0 as hexadecimal
codes 01 and 00 or as the ASCII codes for the numerals 1 and 0
(hexadecimal 31 and 30).
Page 17

DBCS Mode
DBCS Mode
When the printer is in DBCS mode, it can print double byte characters—
characters that require two bytes to define. It can also print a limited number
of single byte ASCII characters. If a form hex 0x20 through hex 0x7F is sent to
the printer, it will be printed as a standard ASCII character. If a character is
larger that 0x7F, it will be combined with the next character to produce one
DBCS character.
DBCS characters are only available in the LQ, Near LQ, Normal, Hi-Speed,
Super Hi-Speed, and Ultra Hi-Speed typefaces. The command to select
DBCS mode (FS &) switches the printer to one of these typefaces. Near LQ is
the default typeface, but if another print quality has been selected previously
through the FS x command, then that print quality is the DBCS typeface
selected.
The character printed when the printer combines two characters into one
double byte character depends on the character set of your particular printer.
Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
The remainder of this chapter describes the LQ-1600K printer control
language codes that may be sent from a host computer attached to the printer
in order to invoke and configure numerous LQ-1600K emulation functions.
Format For Control Code Descriptions
The following information is listed for each code (where applicable and
possible) in this chapter:
ASCII Mnemonic. The ASCII name for the control code.
Hex Code. The hexadecimal equivalent of the code. (For octal equivalents,
refer to Appendix A.)
Dec Code. The decimal equivalent of the code.
Purpose. The function(s) of the control code.
Expression. The control codes used in the BASIC programming language.
Comment. A description of exceptions or limitations to normal use.
Example. A sample expression written in the BASIC programming language
is provided for some control codes to illustrate how the code is used.
17
Page 18

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Control Code Index
The following index lists the control codes by function, ASCII mnemonic, and
page number. Some control code functions can also be selected at the control
panel.
FUNCTION ASCII CODE PAGE
Vertical Motion and Print Execution
Carriage Return CR 28
Form Feed FF 42
Line Feed LF 50
Line Feed n/180 Inch ESC J
Line Spacing 1/6 Inch (6 lpi) ESC 2 51
Line Spacing 1/8 Inch (8 lpi) ESC 0 52
Line Spacing n/60 Inch ESC A
Line Spacing n/180 Inch ESC 3
Line Spacing n/360 Inch ESC +
Select Vertical Tab Channel ESC /
Set Form Length by Lines ESC C
Set Form Length in Inches ESC C NUL
Set Vertical Tabs in Channels ESC b
Skip Over Perforation ESC N
Skip Over Perforation, Cancel ESC O 83
Vertical Tab, Execute VT 88
Vertical Tab Set/Clear ESC B
Horizontal Motion
Backspace BS 23
Carriage Return CR 28
Character Pitch 10 cpi ESC P 29
Character Pitch 12 cpi ESC M 29
Character Pitch 15 cpi ESC g 30
Horizontal Tab Execute HT 47
Horizontal Tab Set/Release ESC D
Proportional Spacing,
Select/Deselect ESC p
Set Absolute Horizontal Print
Position in 1/60” ESC $
Set Intercharacter Spacing ESC SP
Set Relative Horizontal Print
Position in 1/120” ESC \
Set Margin (Left) ESC l
Set Margin (Right) ESC Q
Emphasis
Condensed Print SI (or ESC SI) 30
Condensed Print Reset DC2 30
Define Pattern for Special
Printing Effect ESC ( X
Double High Print, Set/Reset ESC w
Double Strike (Select) ESC G 35
Double Strike (Cancel) ESC H 36
Double Wide Print ESC W
n
n
n
n
c
n
n
c n1 n2 n3...n16
n
n1 n2 n3...nk
n1...nk
NUL 48
n
n1 n2
n
n1 n2
n
n
n1 n2 a1 a2 a3
n
n
50
53
54
55
69
73
74
NUL 82
82
NUL 88
61
71
75
81
79
80
33
35
36
18
Page 19

Control Code Index
FUNCTION ASCII CODE PAGE
Double Wide Print (1 line) SO (or ESC SO) 37
Double Wide Print (1 line) Cancel DC4 38
Emphasized Print (Select) ESC E 39
Emphasized Print (Cancel) ESC F 40
Italic Printing, Select ESC 4 49
Italic Printing, Cancel ESC 5 49
Select Italic Character Set ESC t
Select Special Printing Effect ESC q
Superscript and Subscript Printing ESC S
Superscript and Subscript Printing,
Cancel ESC T 85
Underline ESC –
Print Quality Control
Master Print Select ESC !
Select Print Quality ESC x
Select Typeface (TW printer only) ESC k
Character Set Manipulation
Enable Printing of Control Codes ESC I
Make Hex 80-9F Printable ESC 6 56
Make Hex 80-9F Control Codes ESC 7 57
Set International Character Set ESC R
Data Manipulation
Cancel Line CAN 28
Delete Character DEL 35
Graphics
Graphics, Standard Density ESC K
Graphics, Double Density ESC L
Graphics, Double Density,
Double Speed ESC Y
Graphics, Quadruple Density ESC Z
Select Graphics Mode ESC *
Miscellaneous Printer Control
Bell BEL 27
Home Print Head ESC < 47
Initialize Printer ESC @ 49
Printer Select DC1 61
Printer Deselect DC3 60
Unidirectional Printing for One Line ESC < 87
Unidirectional Printing, Set/Reset ESC U
Superset Commands
Graphic Printing (Bit Image) SSCC * 62
Barcode Printing SSCC c 24
Select Vertical Printing SSCC +
Select Superscript/Subscript SSCC ~
Turn On/Off Compress Mode ASSC 0 x
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
m n1 n2
n
n
n
n
66
67
84
86
58
66
68
41
76
46
43
44
45
65
87
69
68
85
19
Page 20

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
FUNCTION ASCII CODE PAGE
Define User-Defined Character ASSC 0 2
Master Select One-line Attribute 60
in DBCS Mode ASSC 0 !
Turn On/Off OCRB Printing ASSC 0 z
AR3240 Commands (for GB and Kanji printer only)
Set 0-dot Intercharacter Spacing of
DBCS Characters SUB Q 69
Set 3-dot Intercharacter Spacing of
DBCS Characters SUB N 70
Set 6-dot Intercharacter Spacing of
DBCS Characters SUB E 70
Set 12-dot Intercharacter Spacing of
DBCS Characters SUB P 70
Select DBCS ASCII Character Type FS k
Select DBCS Character Font ESC u
Vertical and Horizontal Extension ESC e
Select DBCS Character Bitmap FS e
DBCS Command Set
Adjust Half-Width Characters to Fit
into DBCS character spacing FS U 21
Adjust Table Characters FS v
Align Two Half-Width Rotated
Characters in DBCS Mode FS D 22
Cancel Character Rotation FS K 27
Cancel Spacing Adjustment FS V 28
CC DOS Control Code ESC I
DBCS Mode (Select) FS & 31
DBCS Mode (Cancel) FS . 31
DBCS Mode Underline FS –
DBCS Superscript/Subscript Print
(Set/Cancel) FS r n 32
Define a Download Character
(DBCS) FS 2
Double Wide Print (1 line) FS SO 38
Double Wide Print (1 line),
Cancel FS DC4 38
Double Wide, Double High
(2x2) Print FS W
Half-Width Print FS SI 47
Half-Width Print Cancel FS DC2 47
Master Print Select in
DBCS Mode FS !
Rotate Character 90 degrees
Counter-Clockwise FS J 61
Select DBCS Print Quality FS x
Set Intercharacter Spacing (one-byte)
in DBCS Mode FS T
Set Intercharacter Spacing (two-byte)
in DBCS Mode FS S
n
n
n
n
n
n1 n2
n1 n2
n
n
n
n1 n2 n3...n74
n
n
n
n1 n2
n1 n2
34
86
63
63
87
63
21
29
31
32
39
59
64
75
76
20
Page 21

Adjust Half-Width Characters To Fit Into DBCS Character Spacing
Adjust Half-Width Characters To Fit Into DBCS
Character Spacing
ASCII Code FS U
Hex Code 1C 55
Dec Code 28 85
Purpose Aligns two half-width characters to fit the space normally
occupied by a single full-width DBCS character.
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Adjust Table Characters
ASCII Code FS v
Hex Code 1C 76
Dec Code 28 118
Purpose Extends the table (line draw) characters in the following ranges:
n
n
n
GB: A854~A870, A9A4~A9A7, A9B0~A9EF
BIG5: BIG5 A271~A275, A277~A278, A27A~A27E,
A2A1~A2A7, F9DD~F9FD
CNS A3B3~A3B7, A3B9~A3BA, A3BC~A3C7
TCA 8249~824D, 824F~8250, 8252~825A,
8261~8263
ETEN 8249~824D, 824F~8250, 8252~825A,
8261~8263
IBM5550 8A6E~8A72, 8A74~8A75, 8A77~8A7E,
8A80~8A83
TELETEXT NIL
WANG 8E58~8E5A, 8E61~8E62, 8E64~8E65,
8E67~8E72
BIG5+ A271~A275, A277~A278, A27A~A27E,
A2A1~A2A7, F9DD~F9FD
BIG5E A271~A275, A277~A278, A27A~A27E,
A2A1~A2A7, F9DD~F9FD
HKSCS-2001
A271~A275, A277~A278, A27A~A27E,
A2A1~A2A7, F9DD~F9FD
They are extended so they touch in both horizontal and vertical
directions.
Where:
n
= 0 to turn off this function
n
= 1 to turn on this function
21
Page 22

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Align Two Half-Width Rotated Characters In DBCS Mode
ASCII Code FS D
Hex Code 1C 44
Dec Code 28 68
Purpose Aligns two half-width rotated characters to fit the space
occupied by a normal size rotated character.
Comment Right after the control code sequence, two characters are
paired. The characters are not required to be half-width to be
aligned, because the command automatically takes care of
that. It is only necessary for the characters to be rotated in
order for the command to take effect. Only two characters are
combined at a time.
This command does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Example The following program demonstrates the function of the
command.
22
Page 23

Backspace
Backspace
ASCII Code BS
Hex Code 08
Dec Code 08
Purpose Moves the simulated print head to the left, one-byte space
toward the first character column. In DBCS mode, the
movement is two one-byte spaces.
Comment Moves the character position indicator one-byte space (two
one-byte spaces in DBCS mode) to the left at the current
character pitch setting. The code is ignored if the simulated
print head is positioned at the first character column.
Example Print and send two backspaces in ASCII and DBCS mode.
23
Page 24

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Barcode Printing
ASCII Code SSCC c
[; C ] [; H hh] [; D ] [; F
Hex Code SSCC 63
[; 50 p ] [; 43 ] [; 48 hh] [; 44 ] [; 46
Dec Code SSCC 99
[; 80 p ] [; 67 ] [; 72 hh] [; 68 ] [; 70
Where:
t
= type of Barcode
t (ASCII) t (hex) Selects Barcode
B 42 Codabar
C 43 Code 39
9 39 Code 93
D 44 Code 128
8 38 EAN-8
t; d data d
t; d data d
t; d data d
[; N n ;
[; 4E n ;
[; 78 n ;
xxxx ; yyyy
q data q
xxxx ; yyyy
xxxx ; yyyy
]
] [; X
] [; 58
q data q
] [; 88
q data q
mmmm
mmmm
]
mmmm
]
] [; P p ]
]
]
1 31 EAN-13
F 46 FIM
G 47 German I-2/5
I 49 Interleaved 2/5
M 4D MSI
4 34 PDF 417
O 4F PostBar
P 50 POSTNET
R 52 Royal Mail
T 54 Te l ep e n
V 56 UCC/EAN-128
A 41 UPC-A
E 45 UPC-E
S 53 UPC Shipping
U 55 UPS 11
24
Page 25
Where:
d
= barcode delimiter, which can be any character not used in
the barcode data field.
data
= variable length printable data field (PDF); character set
is Alphanumeric
The following parameters are optional:
where:
N = activates the offset
n
= the x and y coordinate unit system
n
(ASCII) Selects Value
0 Use current cpi and lpi values
1 Use 1/4 inch value
2 Use 1/2 centimeter value : 1/(2.54x2)
Barcode Printing
3 Use 1 mm value : 1/(25.4)
4 Use target barcode dot (refer to table immediately below)
when:
n
= 4
Front Panel Typeface X Offset Unit (Inch) Y Offset Unit (Inch)
LQ 1/180 1/180
Near LQ 1/120 1/120
Normal 1/180 1/144
Hi-Speed 1/180 1/120
Super Hi-Speed 1/180 1/90
Ultra Hi-Speed 1/180 1/90
25
Page 26

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Where:
xxxx
= 4-digit upper left corner x (horizontal axis)
yyyy
= 4-digit upper left corner y (vertical axis)
X = activates magnification
mmmm
The possible magnification is as follows:
Barcode Type Magnification
Code 39 X4 X3 X2 X1 X1.5 X1A X1B *X1C *X1D *X1E
Interleaved 2/5 X4 X3 X2 X2A X1 X1A X1B
German I-2/5 X4 X3 X2 X2A X1 X1A X1B
UPC Shipping X4 X3 X2 X1 X1.5 X1A X1B *X1C *X1D *X1E
Telepen X4 X3 X2 X1
= bar code magnification
X4 X3 X2 X2A X1 X1A X1B
X4 X3 X2 X1 X1.5
MSI X4 X3 X2 X1 X1.5
Code 128 X4 X3 X2 X1 X1.5
UCC/EAN-128 X4 X3 X2 X1 X1.5
Code 93 X2 X1
UPS 11 X2 X1
UPC-A X2 X1
UPC-E X2 X1
EAN 8 X4 X3 X2 X1
EAN 13 X1
Codabar X1 X1A
POSTNET X1 X1A
Royal Mail X1
Postbar X3 X2 X1
FIM
PDF 417
26
* The X1C, X1D, and X1E values can only be printed for a 180 dpi
horizontal barcode. If these values are sent for a 120 dpi horizontal
barcode, it will print as value X1.
Page 27

Bell
Where:
P = activates printable data field variable
p
= location of PDF (“A” {above}, “B” {below,default}, “N”
{none})
NOTE: FIM, Postbar, and PDF417 do not support this
parameter.
C = Calculate and plot check digit (if the check digit is optional)
H = activates the height variable
hh
= 2-digit barcode height in 1/10”
D = Dark barcode
(Note: This parameter does not take effect under any DBCS
typefaces.)
[;F
q data q
data field is only used to specify the barcode data when the
primary data field is empty (two delimiters without any data).
When the primary data field is not empty, the secondary data
field is ignored.
] = secondary data field (optional). The secondary
Bell
ASCII Code BEL
Hex Code 07
Dec Code 07
Purpose Sounds the printer's buzzer/beeper.
Comment The BEL function will sound the buzzer/beeper for 0.2 seconds
upon receipt of this command
Cancel Character Rotation
ASCII Code FS K
Hex Code 1C 4B
Dec Code 28 75
Purpose Cancels character rotation (horizontal printing mode).
Comment This command cancels the effect of FS J. This control code
does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
27
Page 28

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Cancel Line
ASCII Code CAN
Hex Code 18
Dec Code 24
Purpose Clears all data not yet printed from a line, but does not affect
control codes.
Comment You can use this control code to delete a line, but do so with
caution to avoid possible misprinting. This control code cancels
the double wide attribute set by SO. No other print attributes
are affected. The simulated print head goes to the print position
it had after the last CR or paper motion command.
Cancel Spacing Adjustment
ASCII Code FS V
Hex Code 1C 56
Dec Code 28 86
Purpose Cancels the spacing adjustment of half-width characters to fit
into the full-width DBCS character space.
Comment This command cancels the effect of FS U. This control code
does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Carriage Return
ASCII Code CR
Hex Code 0D
Dec Code 13
Purpose Returns the simulated print head to the left margin.
Comment The CR code may or may not cause printing or paper motion,
depending on the configuration as set from the control panel. If
CR=CR is set, the characters following the CR are printed over
the previous characters on the line. If CR=CR+LF is set, the
paper is also moved one line at the current line spacing. This
automatic LF will also cancel all single line print attributes.
28
Page 29

CC DOS Control Code
CC DOS Control Code
ASCII Code ESC I
Hex Code 1B 49
Dec Code 27 73
Value of
n
A Characters print normal size.
B Characters print double width, in both ASCII and Hanzi
C Characters print double height, only in Hanzi mode.
D Characters print double width and double height, but
n
n
n
Table 4. CC DOS Control Code Parameters
mode.
double height only prints in Hanzi mode.
Character Pitch 10 CPI
ASCII Code ESC P
Hex Code 1B 50
Function
Dec Code 27 80
Purpose Sets character pitch to 10 characters per inch (cpi).
Comment This command is available in all print modes except DBCS
mode. This command is normally used to cancel 12 cpi. This
command affects the front panel setting of cpi.
Character Pitch 12 CPI
ASCII Code ESC M
Hex Code 1B 4D
Dec Code 27 77
Purpose Sets character pitch to 12 characters per inch (cpi).
Comment This command is available in all print modes except DBCS
mode. This command affects the front panel setting of cpi.
29
Page 30

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Character Pitch 15 CPI
ASCII Code ESC g
Hex Code 1B 67
Dec Code 27 103
Purpose Sets character pitch to 15 characters per inch (cpi).
Comment This command is available in all print modes except DBCS
mode. This command affects the front panel setting of cpi.
Condensed Print (Set/Reset)
ASCII Code SI ESC SIDC2
Hex Code 0F 1B 0F18
Dec Code 15 27 1512
Purpose Condenses print pitch as close as possible to 60 percent of the
former character width.
Comment 10 cpi condenses to 17.1 cpi
12 cpi or 13.3 cpi condenses to 20 cpi
15 cpi will not have condense print
Control code SI affects all subsequent characters. After
receiving code SI, all characters are printed condensed until
the printer is reset by ESC M, ESC P, DC2, a printer reset, or a
new print mode control code. SI code (hex 0F) is equivalent to
the ESC SI code. If condensed print is not allowed in the
current font, this code is ignored. Proportional spacing
overrides condensed printing. This control code does not
function while in DBCS mode. 12 cpi will condense to 20 cpi
only
if the menu option “20 CPI Condensed” is enabled.
Example The program below shows condensed character printing and
reset.
30
Page 31

DBCS Mode (Select)
DBCS Mode (Select)
ASCII Code FS &
Hex Code 1C 26
Dec Code 28 38
Purpose Places the printer in DBCS mode.
Comment All data received by the printer with the MSB set will be paired
with the next character which may or may not be a DBCS
character. If the pair constitutes a 2-byte code which falls within
the defined DBCS character set range, a DBCS character will
be printed. Otherwise, the characters will be treated individually
and printed accordingly. Control codes which normally can be
applied to a non-DBCS mode typeface will not have an effect.
This command will set the DBCS/ASCII mode in the front panel
to DBCS mode.
DBCS Mode (Cancel)
ASCII Code FS .
Hex Code 1C 2E
Dec Code 28 46
Purpose Cancels the effect of the FS & command and places the printer
in single-byte character mode (ASCII). The typeface will remain
the same.
Comment Control codes which are not valid for DBCS mode but sent
while in DBCS mode will take effect after the changeover.
This command will set the DBCS/ASCII mode in the front panel
to ASCII mode.
DBCS Mode Underline
ASCII Code FS –
Hex Code 1C 2D
Dec Code 28 45
Purpose Turns automatic underlining on and off.
n
n
n
Where:
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) to turn off underlining
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) to turn on single underlining
n
= STX (hex 02) or 2 (hex 32) to turn on double underlining
(only in DBCS 24 and Draft 24 mode)
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
DBCS Superscript/Subscript Print (Set/Cancel)
ASCII Code FS r
Hex Code 1C 72
Dec Code 28 114
Purpose Selects superscript/subscript printing in DBCS mode.
Comment This command is canceled by FS DC2. This control code does
n
n
n
Where:
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) to enable superscript printing
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) to enable subscript printing
not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Define A Download Character (DBCS)
ASCII Code FS 2
Hex Code 1C 32
Dec Code 28 50
Purpose Defines a DBCS character for downloading. The control code
a1 a2 n1...n72
a1 a2 n1...n72
a1 a2 n1...n72
should be followed by 72 bytes of data.
define the code point of the download character where
high byte and
The character can then be printed by sending
printer. The character can print in all the DBCS typefaces. It will
be available until the printer power is recycled.
The download ranges are different for different types of
printers:
a2
is the low byte.
a1
and a2 together
a1 a2
a1
is the
to the
32
GB: AAA1~AFFE, F8A1~FEFE, A140~A7A0, FF40~FF7E,
FF80~FFFE
BIG5: BIG5 8140~A07E, 81A1~A0FE, C840~C87E,
C8A1~C8FE, FA40~FE7E, FAA1~FEFE,
8100~FE3F, A180~FEAD
CNS AAA1~C1FE, C3A1~C3FE, F321~FE7E
TCA DF30~FC39, DF61~FC7A, DF80~FCFD,
DF41~FC5A
ETEN 8D30~9039, 8D41~905A, 8D61~907A,
8D80~90FD
IMB5550
D240~E87E, D280~E8FC, F940~FB7E,
F980~FBFC
TELETEXT
F7A1~FEFE
WANG DBA0~F4EE, F9A0~FBEE
BIG5+ NIL
Page 33

Define Pattern For Special Printing Effect
BIG5E 8840~8D7E, 88A1~8DFE, FA40~FE7E,
FAA1~FEFE
HKSCS-2001
8140~877E, 81A1~87FE
UTF8 E000~F8FF
Multiple characters from these ranges can be defined as long
as the printer does not run out of memory.
Define Pattern For Special Printing Effect
ASCII Code ESC ( X
Hex Code 1B 28 58
Dec Code 27 40 88
Purpose Defines the pattern to be used in conjunction with outlined
characters.
Where:
n1
a1
0 ≤ a2
a3
Where:
a1
a1
a2
a2
a2
a2
a2
Comment This command will not take effect unless the characters printed
are outlined, as set by the ESC q control code.
n1 n2 a1 a2 a3
n1 n2 a1 a2 a3
n1 n2 a1 a2 a3
=3 (default),
=0, 1
≤ 4
=0 (default)
=0 background
=1 fill pattern
=0 black on white, normal
=1 white on black
=2 dotted
=3 slashed
=4 meshed
n2
=0 (default)
33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Example The following program demonstrates the function of the
command.
Define User-Defined Character
ASCII Code ASSC 0 2
Hex Code ASSC 30 32
Dec Code ASSC 48 50
Purpose Sets the ASCII format data for a user-defined character. The
user-defined characters can be printed by sending
printer.
Where:
a1
= high byte code point
a2 = low byte code point
d1...d144
Comment This command takes effect only in DBCS mode.
a1 a2 d1...d144
a1 a2 d1...d144
a1 a2 d1...d144
= 144 bytes ASCII format data
a1 a2
to the
34
Page 35

Delete Character
Delete Character
ASCII Code DEL
Hex Code 7F
Dec Code 127
Purpose Deletes the previous character on a line.
Comment This command is ignored if it occurs immediately after a CR or
a paper motion command. Characters truncated due to line
length restrictions are not affected by this code.
Double High Print, Set/Reset
ASCII Code ESC w
Hex Code 1B 77
Dec Code 27 119
Purpose Turns double high character printing on and off. Double high
characters are standard width but twice as high.
Where:
n
n
Comment This control code does not function while in DBCS mode.
n
n
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) turns double high printing on
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) turns double high printing off
Double Strike (Select)
ASCII Code ESC G
Hex Code 1B 47
Dec Code 27 71
Purpose Makes text bolder by printing each dot twice.
Comment This command makes text bolder by printing each dot twice,
the second dot offset to the right of the first by a distance equal
to 1/2 the width of a dot, the same as with ESC E.
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Double Strike (Cancel)
ASCII Code ESC H
Hex Code 1B 48
Dec Code 27 72
Purpose Turns off the double strike printing set by ESC G or ESC !.
Comment This control code resets only the double strike print attribute.
Other print attributes, such as double wide printing, are not
affected.
Example The following program illustrates double strike character
printing.
Double Wide Print
ASCII Code ESC W
Hex Code 1B 57
Dec Code 27 87
Purpose Turns double wide print on and off.
Where:
n
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) turns double wide print off
Comment When ESC W is received, all characters are printed twice as
wide until reset. This command overrides SO, ESC SO, and
DC4.
n
n
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) turns double wide print on
36
Page 37

Double Wide Print (One Line)
Example The following program illustrates double wide character
printing.
Double Wide Print (One Line)
ASCII Code SO ESC SO
Hex Code 0E 1B 0E
Dec Code 14 27 14
Purpose Selects double wide print for one line only.
Comment This control code is a line-by-line print attribute. When SO or
ESC SO is received, the characters on the current line print
twice as wide and then reset automatically.
This control code is cancelled by the DC4 or FS DC4 codes, by
a paper motion control code (LF, VT, etc.), or by CR.
Example The following program illustrates double wide print for one line
only.
37
Page 38

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Double Wide Print (One Line), Cancel
ASCII Code DC4
Hex Code 14
Dec Code 20
Purpose Cancels the double wide print for one line only selected by SO,
ESC SO, or FS SO.
Comment This command cancels the double wide print selected by SO,
ESC SO, or FS SO, but does not cancel double wide printing
selected by ESC W or ESC !.
Double Wide Print (One Line)
ASCII Code FS SO
Hex Code 1C 0E
Dec Code 28 14
Purpose Selects double wide print for one line only.
Comment This control code is a line-by-line print attribute. When FS SO is
received, the characters on the current line print twice as wide
and then reset automatically.
This control code is cancelled by the DC4 or FS DC4 codes, by
a paper motion control code (LF, VT, etc.), or by CR.
NOTE: This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Double Wide Print (One Line), Cancel
ASCII Code FS DC4
Hex Code 1C 14
Dec Code 28 20
Purpose Cancels the double wide print for one line only selected by
FS SO.
Comment This command cancels the double wide print selected by SO,
ESC SO, or FS SO, but does not cancel double wide printing
selected by ESC W or ESC !.
NOTE: This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
38
Page 39

Double Wide, Double High (2x2) Print
Double Wide, Double High (2x2) Print
ASCII Code FS W
Hex Code 1C 57
Dec Code 28 87
Purpose Turns on double wide, double high (2x2) printing in DBCS
Comment In a non-DBCS mode, this command will function like ESC W.
n
n
n
mode.
Download Chinese Font (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T 2 [X] 0 [c1]c2c3 data
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 32 [X] 30 [c1]c2c3 data
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 50 [X] 48 [c1]c2c3 data
Purpose To download the user defined characters with 24x24 cell size.
Where
• [X] is an optional parameter:
without X: the data is 72 byte binary data
with X: the data is 144 byte ASCII data
• [c1]c2c3 is code point:
c2c3 is 2 byte code point in normal code page
c1c2c3 is byte code point in UTF8 code page
• data: download data in 72/144 byte which is arranged in
horizontal sequence.
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Emphasized Print (Select)
ASCII Code ESC E
Hex Code 1B 45
Dec Code 27 69
Purpose Selects emphasized character print format.
Comment Emphasized print makes text bolder by printing each dot twice,
the second dot offset to the right of the first by a distance equal
to 1/2 the width of a dot.
39
Page 40

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Example The following program illustrates emphasized character
printing.
Emphasized Print (Cancel)
ASCII Code ESC F
Hex Code 1B 46
Dec Code 27 70
Purpose Cancels emphasized character printing selected by ESC E or
ESC !.
40
Page 41

Enable Printing Of Control Codes
Enable Printing Of Control Codes
ASCII Code ESC I
Hex Code 1B 49
Dec Code 27 73
Purpose Tells the printer to treat codes 0x00 through 0x1F and 0x80
Comment This command has no effect when the italic character table is
n
n
n
through 0x9F as either printable characters or control codes.
Where:
n
= 1, codes 0x00 through 0x1F and 0x80 through 0x9F are
treated as printable characters
n
= 0, codes 0x00 through 0x1F and 0x80 through 0x9F are
treated as control codes
selected; no characters are defined for these codes in the italic
character table.
Font Expansion
ASCII Code ASSC 0 e n1 n2
Hex Code ASSC 30 65 n1 n2
Dec Code ASSC 48 101 n1 n2
Purpose Expand the DBCS characters up to the size of 72.
For this command to work, n1 must be the same value as n2
(i.e. n1=n2). When n1 and n2 = 25 to 72, this set font expansion
mode is ON. The value of n1 and n2 determines the bitmap
size. For example, if the size of n1 is 50, then the size of the
bitmap will be set to 50x50. For n1 and n2 = 24, the font
expansion mode resets to OFF and the bitmap size reverts to
the default, 24x24.
Inter-line spacing and inter-character spacing calculations are
based on standard setting as if the bitmap is 24x24. This
command only increases the size of the bitmap and does not
affect the inter-character spacing or inter-line spacing. For
example, if inter-line spacing is 6 dot rows, when the bitmap is
expanded from 24x24 to 72x72, the inter-line spacing still
remains as 6 dot rows. The same is true for inter-character
spacing.
Other commands, such as double height, double width, 2x2
times, left/right margin etc., will not function when the font
expansion mode is set on. For different typefaces, the
characters will expand based on the appropriate typeface
resolution. All commands affecting LPI and CPI still takes effect
and is set as if the bitmap is 24x24 as mentioned above.
Where
n1 = 24 - 71
n2 = 24 - 72
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
41
Page 42
Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Form Feed
ASCII Code FF
Hex Code 0C
Dec Code 12
Purpose Prints the data in the buffer, if any, then moves the paper to the
top of the next form.
Comment The simulated print head moves to the left margin. This code
cancels all single line print attributes.
Graphic Printing
ASCII Code ASSC 0 * m nL nH d1...dk
Hex Code ASSC 30 2A m nL nH d1...dk
Dec Code ASSC 48 42 m nN nH d1...dk
Purpose Prints dot-grphics in 16 or 24-dot columns, depending on the
following parameters:
Where:
m specifies the dot density
nL, nH specifies the total number of columns or graphics data
that follow (number of dot columns) = ((nHx256) + nL)
d1...dk specifies bytes of graphics data; k is determined by
multiplying the total number of columns times the number of
bytes required for each column.
Parameter
m is ASSC*
0 180 180 24 3
1 90 180 24 3
2 120 120 16 2
3 90 144 24 3
4 90 120 16 2
5 90 90 16 2
Horizontal
Density (dpi)
Vertic al
Density (dpi)
Dots Per
Column
Bytes Per
Column
42
Page 43

Graphics, Double Density
Graphics, Double Density
ASCII Code ESC L
Hex Code 1B 4C
Dec Code 27 76
Purpose Selects double density bit image graphics of 120 dpi
horizontally and 72 dpi vertically.
Expression CHR$(27);“L”;CHR$(n1);CHR$(n2);“
Where:
n1
n2
n1
d1 d2...dk
NOTE:
Comment Double density printing reduces print speed.
Example The following example produces double density bit-image
d1 d2...dk (DATA
top and “1” bits producing dots. (0 < =
graphics of the pattern used in the standard density bit-image
mode example. The amount of data must be doubled for double
density (the data is used 54 times rather than 27).
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
DATA
”
= 0 through 255
= 0 through 31
+ (256 x n2) defines the number of data bytes to follow.
= ASCII characters for the dot pattern bytes.
) consists of 8-bit dot columns, with the MSB at the
d
< = 255)
43
Page 44

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Graphics, Double Density, Double Speed
ASCII Code ESC Y
Hex Code 1B 59
Dec Code 27 89
Purpose Selects double density, double speed bit-image graphics of 120
dpi horizontally and 72 dpi vertically.
Expression CHR$(27);“Y”;CHR$(n1);CHR$(n2);“
Where:
n1
n2
n1
d1 d2...dk
NOTE:
Comment This mode prints double density with no adjacent dots. It is
Example The following example produces a double density, double
d1 d2...dk (DATA
top and “1” bits producing dots. (0 < =
similar to ESC L, except that if the graphics data contain
horizontally adjacent dots, the data may print incorrectly. This
feature is widely used to move the print head precisely by
printing blank dot columns.
speed graphic image of the pattern used in the standard
density example. The amount of data must be doubled for
double density (the data is used 54 times rather than 27).
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
= 0 through 255
= 0 through 31
+ (256 x
n2
) defines the number of data bytes to follow.
= ASCII characters for the dot pattern bytes.
) consists of 8-bit dot columns, with the MSB at the
DATA
d
< = 255)
”
44
Page 45

Graphics, Quadruple Density
Graphics, Quadruple Density
ASCII Code ESC Z
Hex Code 1B 5A
Dec Code 27 90
Purpose Selects Quadruple Density Bit Image graphics of 240 dpi
horizontally and 72 dpi vertically.
Expression CHR$(27);“Z”;CHR$(n1);CHR$(n2);“
Where:
n1
n2
n1
d1 d2...dk
NOTE:
Comment This mode is similar to ESC L, except that four dot columns are
Example The following example produces quadruple density graphics of
d1 d2...dk (DATA
top and “1” bits producing dots. (0 < =
printed in the space normally taken by two columns.
the pattern used in the standard density example. The amount
of data must be quadrupled for quadruple density (the data is
used 108 times rather than 27).
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
DATA
”
= 0 through 255
= 0 through 31
+ (256 x n2) defines the number of data bytes to follow.
= ASCII characters for the dot pattern bytes.
) consists of 8-bit dot columns, with the MSB at the
d
< = 255)
45
Page 46

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Graphics, Standard Density
ASCII Code ESC K
Hex Code 1B 4B
Dec Code 27 75
Purpose Selects normal density bit image graphics of 60 dpi horizontally
and 72 dpi vertically.
Expression CHR$(27);“K”;CHR$(n1);CHR$(n2);“
Where:
n1
n2
n1
d1 d2...dk
NOTE:
Example The following example produces a pattern of standard density
d1 d2...dk (DATA
top and “1” bits producing dots. (0 < =
bit image graphics. The 9 data-bit pattern is repeated 27 times.
Compare this example to the double density and quadruple
density examples.
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
n1 n2 d1 d2...dk
DATA
”
= 0 through 255
= 0 through 31
+ (256 x n2) defines the number of data bytes to follow.
= ASCII characters for the dot pattern bytes.
) consists of 8-bit dot columns, with the MSB at the
d
< = 255)
46
Page 47

Half-Width Print
Half-Width Print
ASCII Code FS SI
Hex Code 1C 0F
Dec Code 28 15
Purpose Sets the printing of DBCS characters as half-width. SBCS
characters maintain at their normal width.
Comment This command takes effect only for DBCS characters and is
canceled by FS DC2.
Half-Width Print Cancel
ASCII Code FS DC2
Hex Code 1C 12
Dec Code 28 18
Purpose Resets half-width/superscript/subscript printing of DBCS
characters to normal size.
Comment This command cancels the effect of FS SI and FS r.
Home Print Head
ASCII Code ESC <
Hex Code 1B 3C
Dec Code 27 60
Purpose Moves the print head to the extreme left position so the next
line prints left to right.
Horizontal Tab Execute
ASCII Code HT
Hex Code 09
Dec Code 09
Purpose Moves the simulated print head to the next horizontal tab stop.
Comment Power-on default horizontal tabs are set at every eighth
character at the current character spacing. Tab positions are
not affected by a change of font or character width. Underline
will not be printed between the current print position and the
next tab position.
47
Page 48

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Horizontal Tab Set/Release
ASCII Code ESC D
Hex Code 1B 44
Dec Code 27 68
Purpose Sets up to 32 horizontal tab positions.
Expression CHR$(27);“D”;CHR$(n1);...CHR$(
n
Where:
n1
positions. NUL is the sequence terminator. ESC D NUL clears
all tabs.
Comment The values of n must be listed in ascending order or they are
ignored. Tabs greater than 32 or those positioned beyond the
right margin are ignored. The physical tab position is the
product of
double wide.
After tabs are set, HT moves the simulated print head to the
next tab stop. Sending ESC @ initializes the printer and resets
the tabs to every eighth character column (which is the default).
In proportional mode, the size of 10 CPI characters determines
tab positions.
Example The following example illustrates how to set horizontal tabs.
n1...nk
n1...nk
n1...nk
= 1-255; k = 1-32
through
NUL
00
0
n32
specify the character column of the tab
n
and the current cell width (1/pitch), excluding
n32
);CHR$(0);
48
Page 49

Initialize Printer
Initialize Printer
ASCII Code ESC @
Hex Code 1B 40
Dec Code 27 64
Purpose Resets all print-related parameters to the power-up
configuration values.
Comment Restores the power-up configuration. The print buffer is cleared
of printable data on the line preceding the command. Current
position is set as top-of-form.
All settings, such as font, international language selection, etc.,
are reset to the power-up default values. Character-bycharacter and line-by-line attributes are canceled. All channels
of the vertical format unit are cleared. This command resets the
horizontal tabs to every eighth character column. Interface
parameters and printer protocol selection are
not
affected.
Italic Printing (Select)
ASCII Code ESC 4
Hex Code 1B 34
Dec Code 27 52
Purpose Turns on italic character printing.
Comment Character graphics (IBM graphic set hex B0 through DF)
cannot be italicized. Italic printing will reduce throughput.
Italic Printing (Cancel)
ASCII Code ESC 5
Hex Code 1B 35
Dec Code 27 53
Purpose Turns off italic character printing.
49
Page 50

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Line Feed
ASCII Code LF
Hex Code 0A
Dec Code 10
Purpose Prints the data in the buffer (if any) and advances the vertical
character position a distance of one line at the current line
spacing.
Comment If configured for LF equals newline (LF=CR+LF), the simulated
print head is moved to the left margin, otherwise it is not moved
from its current position. The current line is printed, and the
simulated printhead moves down a distance equal to the
current line spacing. If there are no dots, the paper is moved
but no printing occurs. When possible, successive line feeds
are accumulated and moved at once. The amount of paper
advanced by the LF code can be set by any of the line spacing
control codes: ESC 0, ESC 2, ESC 3, ESC A, or ESC +.
This code cancels all single line print attributes such as double
high and double wide characters.
Line Feed n/180 Inch
ASCII Code ESC J
Hex Code 1B 4A
Dec Code 27 74
Purpose Immediately advances the paper n/180 inch.
Where:
n
Comment
Example The following example illustrates n/180-inch line spacing.
n
feed but does not affect line spacing or produce a carriage
return. Any one-line-only print attributes in effect are canceled.
Small values of n may result in overlapping lines. Overlapping
lines may also occur if print attributes such as double high,
superscript, or subscript characters are used on the same line.
n
n
n
= 0 through 255
= 0 is ignored. This command produces an immediate line
50
Page 51

Line Spacing 1/6 Inch (6 lpi)
Line Spacing 1/6 Inch (6 lpi)
ASCII Code ESC 2
Hex Code 1B 32
Dec Code 27 50
Purpose Sets the line spacing to 1/6 inch (6 lpi) for subsequent line
feeds.
Comment The 2 is ASCII character 2, not hex 2. When ESC 2 is received,
all lines are printed at 6 lpi until a new line spacing is selected
or the printer is reset.
This control code overrides line spacing set at the control
panel.
Example The following example illustrates 1/6-inch line spacing.
51
Page 52

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Line Spacing 1/8 Inch (8 lpi)
ASCII Code ESC 0
Hex Code 1B 30
Dec Code 27 48
Purpose Sets the line spacing to 1/8 inch (8 lpi) for subsequent line
feeds.
Comment The 0 is ASCII character 0, not hex 0. When ESC 0 is received,
all lines are printed at 8 lpi until a new line spacing is selected
or the printer is reset. This control code overrides line spacing
set at the control panel.
Example The following example illustrates 1/8-inch line spacing.
52
Page 53

Line Spacing n/60 Inch
Line Spacing n/60 Inch
ASCII Code ESC A
Hex Code 1B 41
Dec Code 27 65
Purpose Sets a line spacing of n/60 inch for subsequent line feeds.
Where:
n =
Comment When this control sequence is received, all subsequent line
feeds are
printer is reset. This setting overrides line spacing set at the
control panel. When
Small values of n may result in overlapping lines. Overlapping
lines may also occur if print attributes such as Elongated
(Double High), Superscript, or Subscript characters are used
on the same line. If lines overlap, printing speed is reduced.
Any values set by ESC 3 (line spacing
replaced.
Example The following example illustrates 20/60-inch line spacing.
n
n
n
0 through 85 (all other values are ignored)
n
/60-inch until a new line spacing is selected or the
n
= 0, the current line spacing is printed.
n
/180 inch) are
53
Page 54

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Line Spacing n/180 Inch
ASCII Code ESC 3
Hex Code 1B 33
Dec Code 27 51
Purpose Specifies the line spacing at n/180-inch increments.
Comment The 3 is an ASCII character 3, not hex 3. All line feeds following
Example The following example illustrates n/180-inch line spacing.
n
n
n
Where:
n
= 0 through 255
receipt of this code are at
line spacing is selected or the printer is reset. Line spacing set
by this control code overrides the line spacing setting set at the
control panel. When
If the vertical distance to move is other than a multiple of the n/
180 inch, the remainder is added to the next paper motion
command.
Use caution when combining this control code with other print
attributes such as Elongated (Double High), Superscript, or
Subscript, because overlapping lines may occur. Print speed is
reduced if lines overlap.
n
/180-inch line spacing until a new
n
= 0, the current line spacing is printed.
54
Page 55

Line Spacing n/360 Inch
Line Spacing n/360 Inch
ASCII Code ESC +
Hex Code 1B 2B
Dec Code 27 43
Purpose Specifies the line spacing at n/360-inch increments.
Comment All line feeds following receipt of this code are at n/360-inch line
Example The following example illustrates n/360-inch line spacing.
n
n
n
Where:
n
= 0 through 255
spacing until a new line spacing is selected or the printer is
reset. Line spacing set by this control code overrides line
spacing set at the control panel. When
spacing is printed.
If the vertical distance to move is other than a multiple of n/360
inch, the remainder is added to the next paper motion
command.
Use caution when combining this control code with other print
attributes such as Elongated (Double High), Superscript, or
Subscript, because overlapping lines may occur. Print speed is
reduced if lines overlap.
n
= 0, the current line
55
Page 56

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Make Hex 80-9F Control Codes
ASCII Code ESC 7
Hex Code 1B 37
Dec Code 27 55
Purpose Makes codes hex 80-9F control codes.
Comment This is the default when the Epson italic character set is
selected as the default set at the control panel.
Make Hex 80-9F Printable
ASCII Code ESC 6
Hex Code 1B 36
Dec Code 27 54
Purpose Makes codes hex 80-9F printable characters.
Comment The 6 is an ASCII character 6, not hex 6. This is the default
when the IBM PC graphics character set (Code Page 437) is
selected as the default set at the control panel.
The characters printable in the Epson italic character set are
shown in
Figure 1.
56
Page 57

Make Hex 80-9F Printable
B7
BITS
B4 B2B3 B1
10 1 1
B8
B7
BITS
B4 B2B3 B1
0000
00 10
001 0
001 1
010 0
010 1
011 0
011 1
1000
100 1
101 0
101 1
110 0
110 1
111 0
111 1
B6
B6
0
0
B5
ESC
B5
ROW
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
33
27
1B
11
00
0
0
COLUMN
89
200
128
à
80
201
129
è
81
202
130
ù
82
203
131
ò
83
204
132
ì
84
205
o
133
85
206
134
£
86
207
135
¡
87
210
136
¿
88
211
137
Ñ
89
212
138
ñ
8A
213
139
¤
8B
214
P
t
140
8C
215
141
Å
8D
216
142
å
8E
217
143
ç
8F
KEY
OCTAL
DECIMAL
HEX
CHARACTER
0
1
220
144
§
90
221
145
ß
91
222
146
Æ
92
223
147
æ
93
224
148
Ø
94
225
149
ø
95
226
150
¨
96
227
151
Ä
97
230
152
Ö
98
231
153
Ü
99
232
154
ä
9A
233
155
ö
9B
234
156
ü
9C
235
157
É
9D
236
158
é
9E
237
159
¥
9F
Figure 1. LQ-1600K Printable Codes (Hex 80-9F)
57
Page 58
Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Master Print Select
ASCII Code ESC !
Hex Code 1B 21
Dec Code 27 33
Purpose Selects or changes print attributes in a single command.
Table 5. Master Print Select Bit Values
Bit No. Bit = 0 Bit = 1
0 10 cpi 12 cpi
1 Monospaced Proportional
2 Normal Condensed
3 Normal Emphasized
4 Normal *Double Strike
5 Normal Double Wide
6 Normal Italic
n
n
n
Where:
n
= an 8-bit number with the bits set to specify print attributes,
as shown in
Table 5. (0 < = n < = 255)
7 Normal Underlined
For example, to specify 10 cpi, proportional spacing, and italics,
n
= 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
Where:
bit 0 = 0 (10 cpi)
bit 1 = 1 (proportional)
bit 2, 3, 4, 5 = 0 (normal)
bit 6 = 1 (italic)
bit 7 = 0 (normal)
n
= a binary number (0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0), which equals hex 42.
The hex command sequence is 1B 21 42.
Comment Emphasized is substituted for double strike.
58
Page 59

Master Print Select In DBCS Mode
Master Print Select In DBCS Mode
ASCII Code FS !
Hex Code 1C 21
Dec Code 28 33
Purpose Selects or changes DBCS print attributes in a single command.
Bit No. Bit = 0 Bit = 1
0 Normal Vertical print (rotated)
1 Normal Half-width
2 Normal Double width
3 Normal Double height
4 Normal 1/4 size
5 Superscript Subscript
6 - -
n
n
n
Where:
n
= an 8-bit number with the bits set to specify print attributes,
as shown below.
Table 6. Master Print Select Bit Values
(0 < = n < = 255)
7 Normal Underlined
59
Page 60
Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Master Select One-Line Attribute in DBCS Mode
ASCII Code ASSC 0 !
Hex Code ASSC 30 21
Dec Code ASSC 48 33
Purpose Where:
0 < = n < = 255
Select any combination of several one-line attributes by setting
or clearing the appropriate bit in the
Table 7.
Bit On/Off Hex Dec Function
2 Off
On
3 Off
On
Comment These attributes are canceled when the printer receives the
following commands: LF, FF, VT, and CR.
This command takes effect only in DBCS mode.
00
04
00
08
n
n
n
Table 7
0
4
0
8
n
parameter, as shown in
Cancel double width
Select double width
Cancel double height
Select double height
Printer Deselect
ASCII Code DC3
Hex Code 13
Dec Code 19
Purpose Places printer in the deselected state.
Comment The configuration parameter Printer Select must be set to
Enable.
When the printer receives this command, it ignores data until a
DC1 (Printer Select) command is received.
60
Page 61

Printer Select
Printer Select
ASCII Code DC1
Hex Code 11
Dec Code 17
Purpose Places printer in the selected state.
Comment The configuration parameter Printer Select must be set to
Enable.
This control code allows the printer to receive and print data
from the host if it was deselected by DC3. If the printer was not
deselected by DC3, this code is ignored.
Proportional Spacing, Select/Deselect
ASCII Code ESC p
Hex Code 1B 70
Dec Code 27 112
Where:
n
n
Purpose Turns proportional mode on and off.
Comment This command only affects the character printing in ASCII
mode. This command affects the “Prop. Spacing” setting in the
front panel.
n
n
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) turns proportional mode off
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) turns proportional mode on
Rotate Character 90 Degrees Counter-Clockwise
ASCII Code FS J
Hex Code 1C 4A
Dec Code 28 74
Purpose Rotates characters while in DBCS mode (vertical printing
mode).
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
61
Page 62

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Select Autowrap Mode (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T m n
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 6D n
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 109 n
Purpose To set Auto Line Feed
Where
n = 0x30: reset auto LF (default)
n = 0x31: set auto LF
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Select Bit Image
ASCII Code SSCC *
Hex Code SSCC 2A
Dec Code SSCC 42
Purpose Prints dot graphics in 12- or 16-dot columns, depending on the
following parameters:
Where:
0 < = nL < = 255
0 < = nH < = 31
m
= 30, 31, 32
m
specifies the dot density.
nL nH
that follow (number of dot columns) = (
d1...dk
the total number of columns times the number of bytes required
for each column.
Parameter
m
in ESC *
30 90 90 12 2
31 120 120 16 2
Horizontal
Density (dpi)
m nL nH d1...dk
m nL nH d1...dk
m nL nH d1...dk
specifies the total number of columns of graphics data
nH
x 256 + nL)
bytes of graphics data; k is determined by multiplying
Vertical
Density (dpi)
Dots per
Column
Bytes per
Column
62
32 90 90 16 2
Page 63

Select DBCS ASCII Character Type
Select DBCS ASCII Character Type
ASCII Code FS k
Hex Code 1C 6B
Dec Code 28 107
Purpose This selects a DBCS ASCII character:
n
= 0 or 40 Selects normal DBCS ASCII characters
n
= 1 or 49 Selects oversized DBCS ASCII characters.
Where
n
= 0, 1, 48, 49
The default is n = 0, normal DBCS ASCII character.
Comment This command affects the front panel setting of “DBCS ASCII
Style.”
n
n
n
Select DBCS Character Bitmap
ASCII Code FS e
Hex Code 1C 65
Dec Code 28 101
Purpose Sets the character bitmap to 24 x 24.
Where:
n1, n2
Comment The vertical cell size is n1 dots; the horizontal cell size is n2
dots.
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
= 0 or 8 < =
n1, n2
< = 232
Select DBCS Character Font
ASCII Code ESC u
Hex Code 1A 75
Dec Code 27 117
Purpose This selects a DBCS character font:
Where:
n
= 0 or 49 to select 24x24 DBCS character.
n
n
n
63
Page 64

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Select DBCS Print Quality
ASCII Code FS x
Hex Code 1C 78
Dec Code 28 120
Purpose Selects the typeface for printing in DBCS mode.
Comment This command overrides control panel print quality selections.
n
n
n
Where:
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) selects LQ print quality
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) selects Hi-Speed print quality
n
= STX (hex 02) or 2 (hex 32) selects Near LQ print quality
n
= ETX (hex 03) or 3 (hex 33) selects Super Hi-Speed print
quality
n
= EOT (hex 04) or 4 (hex 34) selects Normal print quality
n
= ENQ (hex 05) or 5 (hex 35) selects Ultra Hi-Speed print
quality
64
Page 65

Select Graphics Mode
Select Graphics Mode
ASCII Code ESC *
Hex Code 1B 2A
Dec Code 27 42
Purpose Turns on 8-pin/24-pin bit image graphics mode m. Table 8
Comment
Table 8. LQ-1600K Graphics Modes
m
0 Single density 60 8
1 Double density 120 8
2 Double density double speed 120 8
3 Quadruple density 240 8
Mode
m n1 n2
m n1 n2
m n1 n2
charts the graphics modes available.
n1
= 0 through 255;
n2
= 0 through 31;
n = n1
to follow.
For example, to specify 257 columns: 1 + (1 x 256) = 257.
+ (n2 x 256), the total number of columns or data bytes
Density*
(dots per inch)
Pins used
4 Monitor graphics I 80 8
6 Monitor graphics II 90 8
32 Single density 60 24
33 Double density 120 24
38 Monitor graphics III 90 24
39 Triple density 180 24
40 Sextuple density 360 24
65
Page 66

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Select Italic Character Set
ASCII Code ESC t
Hex Code 1B 74
Dec Code 27 116
Purpose Selects the italics character set from hex 80 through hex FF.
Comment The graphics character set is assumed to be the IBM Graphics
n
n
n
Where:
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) selects the graphics character
set
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) selects the italics character set
Code.
Select Print Quality
ASCII Code ESC x
Hex Code 1B 78
Dec Code 27 120
Purpose Selects print quality.
Where:
n
n
n
n
n
n
Comment This command overrides control panel print quality selections.
n
n
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) selects Hi-Speed
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) selects LQ
= STX (hex 02) or 2 (hex 32) selects Near LQ
= ETX (hex 03) or 3 (hex 33) selects Super Hi-Speed
= EOT (hex 04) or 4 (hex 34) selects Normal
= ENQ (hex 05) or 5 (hex 35) selects Ultra Hi-Speed
66
Page 67

Select Special Printing Effect
Select Special Printing Effect
ASCII Code ESC q
Hex Code 1B 71
Dec Code 27 113
Purpose Select the desired effect for printing.
Where:
n
n
n
n
Comment This command does not affect graphics characters.
Example The following program demonstrates the function of the
command.
n
n
n
=0 (normal)
=1 (outline)
=2 (shadow)
=3 (outline and shadow)
67
Page 68

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Select Super/Subscript Printing (For Hanzi BIG5 Printer only)
ASCII Code SSCC ~
Hex Code SSCC 7E
Dec Code SSCC 126
Purpose Prints characters that follow at about 1/2 their normal width and
1/2 their normal height; the printing location depends on the
value of
n
= 0 or 48 Upper part of the character space
n
= 1 or 49 Lower part of the character space
n
= 2 or 50 Normal character
Where:
n
= 0, 1, 2, 48, 49, 50
Comment Setting n =2 returns the character back to its normal height.
n
n
n
n
as follows:
Select Typeface (For Hanzi BIG5 Printer only)
ASCII Code ESC k
Hex Code 1B 6B
n
n
Dec Code 27 107
Purpose This is to select DBCS ASCII typeface:
n
n
Where:
n
Comment This command only takes effect in DCBS mode.
n
= 0 Normal
= 5 OCRB
= 0, 5
Select Underline Printing (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T - n
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 2D n
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 45 n
Purpose To set underline printing.
Where:
n = 0x30: reset (default)
n = 0x31: underline for all characters
n = 0x32: underline for all characters except space (0x20).
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
68
Page 69

Select Vertical Printing (for Hanzi BIG5 Printer only)
Select Vertical Printing (for Hanzi BIG5 Printer only)
ASCII Code SSCC +
Hex Code SSCC 2B
Dec Code SSCC 43
Purpose The character is printed with different degrees of rotation in the
counter-clockwise direction under DBCS mode.
n
= 0 or 48 90 degrees rotation
n
= 1 or 49 180 degree rotation
n
= 2 or 50 270 degree rotation
n
= 3 or 51 rotate DBCS full width character 90 degrees
n
= 4 or 52 normal character
Where:
n
= 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52
Comment The default value is n = 4, normal character.
NOTE: This command is only supported in the Hanzi TW printer.
n
n
n
Select Vertical Tab Channel
ASCII Code ESC /
Hex Code 1B 2F
Dec Code 27 47
Purpose Selects a vertical tab channel set by ESC b.
c
c
c
Where:
c
= 0 through 7
Comment Subsequent VT (hex 0B) commands use tab table specified by
c.
If no tab table is selected, table 0 is used.
Set 0-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters
ASCII Code SUB Q
Hex Code 1A 51
Dec Code 26 81
Purpose Sets 0-dot intercharacter spacing of DBCS characters.
Comment This command affects the front panel setting of “DBCS CPI.”
69
Page 70

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set 3-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters
ASCII Code SUB N
Hex Code 1A 4E
Dec Code 26 78
Purpose Sets 3-dot intercharacter spacing of DBCS characters. The left
intercharacter space is 0 dots; the right intercharacter space is
3 dots. The dot size is 1/180 inch.
Comment This command also affects an SBCS character if the character
is aligned with a DBCS character by an FS U command. If an
SBCS character is aligned with a DBCS character, the
intercharacter space of an SBCS character is half.
This command affects the front panel setting of “DBCS CPI.”
Set 6-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters
ASCII Code SUB E
Hex Code 1A 45
Dec Code 26 69
Purpose Sets 6-dot intercharacter spacing of DBCS characters. The left
intercharacter space is 3 dots; the right intercharacter space is
3 dots. The dot size is 1/180 inch.
Comment This command also affects an SBCS character if the character
is aligned with a DBCS character by an FS U command. If an
SBCS character is aligned with a DBCS character, the
intercharacter space of an SBCS character is half.
This command affects the front panel setting of “DBCS CPI.”
Set 12-dot Intercharacter Spacing of DBCS Characters
ASCII Code SUB P
Hex Code 1A 50
Dec Code 26 80
Purpose Sets 12-dot intercharacter spacing of DBCS characters. The
left intercharacter space is 6 dots; the right intercharacter
space is 6 dots. The dot size is 1/180 inch.
Comment This command also affects an SBCS character if the character
is aligned with a DBCS character by an FS U command. If an
SBCS character is aligned with a DBCS character, the
intercharacter space of an SBCS character is half.
70
This command affects the front panel setting of “DBCS CPI.”
Page 71

Set Absolute Horizontal Print Position In 1/60 Inch
Set Absolute Horizontal Print Position In 1/60 Inch
ASCII Code ESC $
Hex Code 1B 24
Dec Code 27 36
Purpose Moves the simulated print head to an absolute horizontal print
position using 1/60-inch increments.
Where:
n1
n2
(n1 + (n2 x 256)) / 60 = the unsigned distance in inches from
the left margin.
Comment If the distance goes beyond the right margin, the sequence is
ignored.
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
= 0 through 127
= 0 through 255
Set Chinese Font Rotate (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T + n
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 2B n
Decimal ASSC 48 84 43 n
Purpose Set rotation as:
n = 0x31: DBCS character in normal (do not rotate, default).
n = 0x32: DBCS character rotate 90 degrees counterclockwise.
n = 0x33: DBCS character rotate 270 degrees
counterclockwise.
n = 0x34: DBCS character rotate 180 degrees.
n = 0x35: ASCII character in normal (do not rotate).
n = 0x36: ASCII character rotate 90 degrees counterclockwise.
n = 0x37: ASCII character rotate 270 degrees
counterclockwise.
n = 0x38: ASCII character rotate 180 degrees.
Where
n = 0x31 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
71
Page 72

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set Chinese Inner Code (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T A n
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 41 n
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 65 n
Purpose Select code page as:
n = 0x30: Big5 (default)
n = 0x31: NS
n = 0x32: DCI
n = 0x36: IBM5550
n = 0x37: UTF8
Comment This control code does not function while in non DBCS mode.
Set Font/Line Gap (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T G m n1 n2 n3 n4
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 47 m n1 n2 n3 n4
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 71 m n1 n2 n3 n4
Purpose To set inter-character and inter-line spacing in dot by 300 dpi,
which will convert to dot by 180 dpi. The inter-char spacing is
set according to DBCS ASCII character.
Where
m = 0x30: set inter-char spacing
m = 0x31: set inter-line spacing
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Set Font Scale (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T W n1 n2
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 57 n1 n2
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 87 n1 n2
Purpose Character expands as: n1-vertical expand, n2-horizontal
expand
n1, n2 = 0x30: reset
n1, n2 = 0x31: normal (1x1)
n1, n2 = 0x32: expand twice (double height, double width)
When n1=0x32 (double height), the line spacing will double.
Where
n1, n2 = 0x30~0x32
72
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Page 73

Set Form Length By Lines
Set Form Length By Lines
ASCII Code ESC C
Hex Code 1B 43
Dec Code 27 67
Purpose Sets the form length by lines.
Where:
n
current line spacing. 0 <
inches.
Comment The current line becomes the first line of the form. The forms
length units are always defined in inches; therefore,
subsequent line spacing changes do not affect the result of this
command. Changing lpi does not change the forms length.
The forms length is set to the number of lines defined by the
quotient of
inches.
If the calculated forms length in lines is not an exact multiple of
the target machine dot size, the forms length value will be
adjusted down to the next possible multiple.
When forms length is set by an ESC C sequence, the skip-over
perforation set by ESC N is cancelled.
This command affects the front panel setting of “Funct. of
Lines.”
n
n
n
= 1 through 127 to specify the number of lines per form at the
n
x (current line spacing) < = 22
n
and the current line spacing so that the units are in
73
Page 74

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set Form Length In Inches
ASCII Code ESC C NUL
Hex Code 1B 43 00
Dec Code 27 67 0
Purpose Sets form length to n inches
Where:
n =
1 through 22 to specify the number of inches on a form.
Comment Upon receipt of this code, the current line becomes the first line
of the form, and the form length set becomes the current forms
length. Vertical tab positions set below the bottom of the form
are ignored. Forms length is defined in inches; therefore,
subsequent line spacing changes do not affect the result of this
command.
Values of n greater than 22 are ignored.
When forms length is set by an ESC C sequence, the skip-over
perforation set by ESC N is cancelled.
This control code overrides forms length set at the control
panel.
n
n
n
.
Set Font Pitch (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T P n1 n2 n3 n4
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 50 n1 n2 n3 n4
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 80 n1 n2 n3 n4
Purpose To set character spacing by dot in 300 dpi, which will convert to
180 dpi. The character spacing includes character width and
inter-character spacing. The character width refers to DBCS
single byte character width in normal mode.
Where
n1, n2, n3, n4 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control codes does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
74
Page 75

Set Intercharacter Spacing
Set Intercharacter Spacing
ASCII Code ESC SP
Hex Code 1B 20
Dec Code 27 32
Purpose Defines n dots for intercharacter spacing.
Comment The valid values of n = 0 through 127. This control code defines
the space to the right of the printed character in dot positions.
Each time a character is printed,
preceding the next character. For different print modes, the dot
resolution varies, e.g. DP=120 dpi, NLQ=180 dpi. If double
wide printing is enabled, the dot size adjusts accordingly. This
control code does not function while in DBCS mode.
Example The following program illustrates intercharacter space setting.
n
n
n
n
number of dots are left blank
Set Intercharacter (One-Byte) Spacing In DBCS Mode
ASCII Code FS T
Hex Code 1C 54
Dec Code 28 84
Purpose Defines preceding/succeeding dots for inter-character spacing.
Comment This control code defines the space to the left/right of the
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
printed character in dot positions. The dot size for
equal to 180 dpi. The default for n1=0 and n2=2. This control
code does not function while in non-DBCS mode and only for
one-byte characters in DBCS mode.
n1
and
n2 is
75
Page 76

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set Intercharacter (Two-Byte) Spacing In DBCS Mode
ASCII Code FS S
Hex Code 1C 53
Dec Code 28 83
Purpose Defines preceding/succeeding dots for intercharacter spacing.
Comment This control code defines the space to the left/right of the
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
printed character in dot positions. The dot size for
equal to 180 dpi. The default for n1=0 and n2=3. This control
code does not function while in non-DBCS mode and only for
two-byte characters in DBCS mode.
n1 and n2 is
Set International Character Set
ASCII Code ESC R
Hex Code 1B 52
Dec Code 27 82
Purpose Specifies a language overlay that prints the characters shown
in
Where:
n
in
n
n
n
Table 9 when the specified code is invoked.
= hex 0 through E to determine the language overlay shown
Table 9.
The real Epson only defines character sets through hex C.
76
Page 77

Set International Character Set
Table 9. Epson International Character Sets
(Hex) Hex Codes
If
n=
International
Character Set Is:
0
USA
1
French
2
German
3
English (UK)
4
Danish I
5
Swedish
6
Italian
7
Spanish I
8
Japanese
9
Norwegian
A
Danish II
B
Spanish II
C
Latin American I
French Canadian
D
Latin American II
E
23 24 40 5B 5C 5D 5E 60 7B 7C 7D 7E
Comment This control code setting overrides a character set selection
made at the control panel. Values of
n
not in Table 9 are
ignored. This control code does not function while in DBCS
mode.
Example The following example compares the Swedish character set to
the USA (ASCII) character set.
77
Page 78

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set Left Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T I n1 n2 n3
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 6C n1 n2 n3
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 108 n1 n2 n3
Purpose To set the left margin in 1/10 inch (10 CPI equivalent)
according to the number of half-width characters, that is in
n1n2n3 from the left most position.
Where
n1, n2, n3 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Set Line Pitch (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T 3 n1 n2 n3 n4
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 30 n1 n2 n3 n4
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 48 n1 n2 n3 n4
Purpose To set the line spacing by dot in 300 dpi, which will convert to
180 dpi. n1n2n3 is in ASCII value.
Where:
n1, n2, n3, n4 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
Set Logic Right Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T y n1n2n3n4
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 79 n1n2n3n4
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 121 n1n2n3n4
Purpose To set right margin by current right margin - n1n2n3n4.
n1n2n3n4 is dot in 300 dpi, and will be converted to 180 dpi
Where:
n1, n2, n3, n4 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
This will affect the Set Right Margin front panel setting.
78
Page 79

Set Logical Left Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
Set Logical Left Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T $ n1 n2 n3 n4
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 24 n1 n2 n3 n4
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 36 n1 n2 n3 n4
Purpose To set left margin by current left margin +n1n2n3n4. n1n2n3n4
is dot by 300 dpi, and will be converted in dot by 180 dpi.
Where:
n1, n2, n3, n4 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
This will affect the Left Margin front panel setting.
Set Margin (Left)
ASCII Code ESC l
Hex Code 1B 6C
Dec Code 27 108
Purpose Sets the left margin to n columns in the current font.
Comment Be sure to use the alphabetic lowercase “l” (as in “left”) rather
n
n
n
Where:
n
= 1 though 255; the number of columns from the left edge of
the physical page to the beginning of the print line.
than the capital letter “I” (as in “Island”) for this command. The
number of inches of margin does not vary if the font, character
width, or horizontal dot density changes. The smallest possible
space between the left and right margins is the width of one
double-wide, 10 cpi character. If a margin control code violates
this minimum distance, it is ignored. Settings in proportional
mode are treated as 10 CPI.
In DBCS mode, the right margin will be set according to the
width of DBCS characters.
This command affects the front panel setting of “Left Margin.”
79
Page 80

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set Margin (Right)
ASCII Code ESC Q
Hex Code 1B 51
Dec Code 27 81
Where:
n
physical page to the end of the print line.
Purpose Sets the right margin to n columns at the current character
width.
Comment The number of inches of margin does not vary if the font,
character width, or horizontal dot density changes. This
command automatically clears and resets horizontal tabs to
every eight characters, then performs a CAN operation. The
smallest possible space between the left and right margins is
the width of one double-wide 10 cpi character. If a margin
control code violates this minimum distance, it is ignored.
Settings in proportional mode are treated as 10 CPI.
In DBCS mode, the right margin will be set according to the
width of DBCS characters.
This command affects the front panel setting of “Right Margin.”
n
n
n
= 1 through 255; number of columns from the left edge of the
Set Paper Length (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T C n1 n2 n3
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 43 n1 n2 n3
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 67 n1 n2 n3
Purpose To set form length to 1/6 inches.
Where
n1, n2, n3 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non DBCS mode.
80
Page 81

Set Relative Horizontal Print Position In 1/120 Inches
Set Relative Horizontal Print Position In 1/120 Inches
ASCII Code ESC \
Hex Code 1B 5C
Dec Code 27 92
Purpose Moves the simulated print head to a relative horizontal print
Comment Adds (n1 + (n2 x 256)) dots to the horizontal position of the
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
position (in dots), using 1/120 inch increments in Near LQ
mode and 1/180 inch increments in all other modes.
Where:
n1
= 0 through 127
n2
= 0 through 255
simulated print head. The number sent is two's complement,
with negative numbers moving to the left. The command is
ignored if it would move the simulated print head beyond the
page margins.
Set Right Margin (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T Q n1 n2 n3
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 51 n1 n2 n3
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 81 n1 n2 n3
Purpose To set margin in 1/10 inches (10 CPI equivalent) according to
the number of half-width characters.
Where
n1, n2, n3 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
81
Page 82

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Set Vertical Tabs In Channels
ASCII Code ESC b
Hex Code 1B 62
Dec Code 27 98
Purpose Assigns vertical tabs to channels selected by ESC /.
Where:
c
n
n1
tab(s), up to a maximum of 16 tab positions in every channel,
with a maximum of eight channels. NUL must end the
sequence.
Comment Channels are selected by ESC /. The distance of each tab stop
from TOF is the current line spacing times the number of lines
given in
If paper movement is commanded to a value of n greater than
the page length, the paper movement command is ignored.
The values of
sequence up to and including the out of sequence number is
ignored. The rest of the load is processed, and skip over
perforation is ignored.
You can clear any channel by sending ESC b c NUL, where c is
the channel number.
c n1 n2 n3...n16
c n1 n2 n3...n16
c n1 n2 n3...n16
= 0 through 7
= 1 through 255
through
n16
specify the line numbers for each of the vertical
n.
n
must be in ascending order. If they are not, the
NUL
00
0
The values for n must be in ascending order; a value of n less
than the previous
n
ends tab setting (just like the NUL code).
Skip Over Perforation
ASCII Code ESC N
Hex Code 1B 4E
Dec Code 27 78
Purpose Selects the number of lines (at the current line spacing) for the
paper to skip at the bottom of the perforation.
Where:
n
Comment
n
one page and the first line on the next page. The actual
distance set is the product of
the value of
one line smaller than the form length or to 0, whichever is
greater.
Skip over perforation set by this command overrides control
panel settings. This feature is canceled by ESC O, ESC C, or
ESC C NUL.
n
n
n
= 1 through 127, n < n x (current line spacing) < page length.
is the number of lines skipped between the last line printed on
n
and the current line spacing. If
n
exceeds the current form length, the skip is set to
82
Page 83

Skip Over Perforation Cancel
Skip Over Perforation Cancel
ASCII Code ESC O
Hex Code 1B 4F
Dec Code 27 79
Purpose Cancels the skip over perforation set by ESC N and resets the
bottom margin to zero.
Comment O is ASCII uppercase o, not zero (0).
Static Barcode Function (For Hanzi Big5 Printer Only)
ASCII Code ASSC 0 T c t [;d data d] [;0 n1n2n3] [;#p]
Hex Code ASSC 30 54 63 t [;d data d] [;30 n1n2n3] [;23 p]
Dec Code ASSC 48 84 99 t [;d data d] [;48 n1n2n3] [;35 p]
Purpose To set various barcode types:
t = @: Interleaved 2/5
t = A: Code 39
t = B: Interleaved 2/5
t = C: Code 39
t = D: Interleaved 2/5
t = E: Codabar
t = F: EAN-13
t = G: EAN-8
t = H: Codabar
t = I: UPC_A
Where:
• 0: the height of the barcode
n1n2n3 is in ASCII value, the height is 300 dpi, and is
converted to dot by 180 dpi.
• #: PDF enable/disable
p = 0x30: disable
p = 0x31: enable
• t = barcode type
• n1, n2, n3 = 0x30 ~ 0x39
Comment This control code does not function while in non-DBCS mode.
The default barcode height is 1/3 inch.
83
Page 84

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Superscript And Subscript Printing
ASCII Code ESC S
Hex Code 1B 53
Dec Code 27 83
Purpose Selects superscript or subscript printing.
Where:
n
n
Comment Superscript prints full-sized characters with a baseline higher
than the normal characters. Subscript prints full-sized
characters with a baseline lower than the normal characters.
When the control code is received, all characters are
superscript or subscript until reset by ESC T or printer reset.
You can print both superscript and subscript characters in the
same character column by using the Backspace (BS) control
code, but these characters will not print when double high
printing is in effect.
Example The following program illustrates superscript and subscript
printing.
n
n
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) to enable superscript printing
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) to enable subscript printing
84
Page 85

Superscript And Subscript Printing (Cancel)
Superscript And Subscript Printing (Cancel)
ASCII Code ESC T
Hex Code 1B 54
Dec Code 27 84
Purpose Cancels superscript and/or subscript printing as set by ESC S
n.
Turn On/Off Compress Mode
ASCII Code ASSC 0 x
Hex Code ASSC 30 78
Dec Code ASSC 48 120
Where:
n
= 0, 1, 48, 49
The default is n = 0.
Purpose Turn on/off compress mode as follows:
n
= 0 or 48 - turns off compress mode
n
= 1 or 49 - turns on compress mode
NOTE: When compress mode is turned on, some features, such as double
height, double width, two-by-two, etc., are ignored.
Comment This command affects the front panel setting of “Compressed
Mode.”
n
n
n
85
Page 86

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Turn On/Off OCRB Printing
ASCII Code ASSC 0 z
Hex Code ASSC 30 7A
Dec Code ASSC 48 122
Where:
n
= 0, 1, 48, 49
The default is n = 0.
Purpose Turn on/off OCRB mode as follows:
n
= 0 or 48 - turns off OCRB mode
n
= 1 or 49 - turns on OCRB mode
NOTE: When OCRB is turned on, the OCRB character can be printed out.
Comment This command affects the front panel setting of “OCBR
Selection.”
This command only works in DBCS mode.
n
n
n
Underline
ASCII Code ESC –
Hex Code 1B 2D
Dec Code 27 45
Purpose Turns automatic underlining on and off.
n
n
n
Where:
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) to turn off underlining
n
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) to turn on underlining
Comment Spaces are underlined, but graphics and grey scale characters
are not. This control code does not function while in DBCS
mode.
Example The following program illustrates underlining.
86
Page 87

Unidirectional Printing For One Line
Unidirectional Printing For One Line
ASCII Code ESC <
Hex Code 1B 3C
Dec Code 27 60
Purpose Causes printing to occur from left to right for one line only.
Unidirectional Printing, Set/Reset
ASCII Code ESC U
Hex Code 1B 55
Dec Code 27 85
Purpose Causes printing to occur in only one direction of shuttle
movement (left to right).
Where:
n
n
Comment Printing normally occurs in both directions of shuttle movement.
Unidirectional printing slows the printer down approximately
50%, but it is sometimes used when very accurate dot
placement is desired in graphics.
n
n
n
= NUL (hex 00) or 0 (hex 30) turns unidirectional mode off
= SOH (hex 01) or 1 (hex 31) turns unidirectional mode on
Vertical and Horizontal Extension
ASCII Code ESC e
Hex Code 1A 65
Dec Code 27 101
Purpose Enables the extension of the character bitmap so that they
touch in both horizontal and vertical directions as follows:
n1 n2
n1 n2
n1 n2
•
n1
= 1 or 49, n2 = 1 or 49 Normal character
• 2 < =
•
• 2 < =
Where:
Comment The default is normal character.
n1
< = 4 or 50 < = n1 < = 52, n2 = 1 or 49 Double height
character (same with FS ! 8)
n1
= 1 or 49, 2 < = n2 < = 4 or 50 < = n2 < = 52 Double width
character (same with FS ! 4)
n1
< = 4 or 50 < = n1 < = 52, 2 < = n2 < = 4 or 50 <= n2
< = 52 Double width and double height character (same
with FS ! 12)
1 < = n1 < = 4 or 49 < = n1 < = 52
1 < = n2 < = 4 or 49 < = n2 < = 52
87
Page 88

Chapter 2 Configuring The LQ-1600K Emulation With Control Codes
Vertical Tab, Execute
ASCII Code VT
Hex Code 0B
Dec Code 11
Purpose Advances the simulated print head to the next vertical tab
position selected by ESC
Comment If no vertical channel was selected, channel 0 is used. If no
vertical tabs were set, the paper advances one line.
The simulated print head moves to the left margin. If a tab
position is on the current line, the paper is moved to the next
tab position. If there are no tab positions between the current
line and the end of the form, the paper is moved to the top of
the next form. If the printing crosses the page boundary, the VT
command causes the paper to move to the top of the next form.
This code cancels all single line print attributes.
/.
Vertical Tab, Set/Clear
ASCII Code ESC B
Hex Code 1B 42
Dec Code 27 66
Purpose Sets up to 16 vertical tab positions.
Where:
n
k
n1
to a maximum of 16 tab positions. NUL must end the sequence.
To clear the tab settings, send ESC B NUL (1B 42 00).
Expression CHR$(27);“B”;CHR$(n1);...CHR$(nk);CHR$(0);
Comment The values of n range from 1 through 255 and must be in
ascending order. The distance of each tab stop from TOF is the
current line spacing times the number of lines given in
value of
tab position are ignored.
If values of n are not in ascending order, the sequence up to
and including the out-of-sequence number is ignored, and the
rest of the load is processed. Skip over perforation is ignored.
n1 n2 n3...nk
n1 n2 n3...nk
n1 n2 n3...nk
= 1 through 255
= 1 through 16
through nk specify the line number for the vertical tab(s), up
n
exceeds the form length, commands to move to that
NUL
00
0
n
. If the
88
This command always sets channel 0. You can clear channel 0
by sending ESC B NUL. (See also the channel selection
command, ESC /, and the channel loading command, ESC b.)
Page 89

A Standard ASCII Character
Set
0
0
B5
ESC
1
33
27
1B
OCTAL
DECIMAL
HEX
KEY
B7
B6
BITS
B4 B2B3 B1
10 1 1
ASCII CHARACTER
B70000111 1
BITS
B4 B2B3 B1
0000
00 10
00 1 0
00 1 1
01 0 0
01 0 1
01 1 0
01 1 1
1000
10 0 1
10 1 0
10 1 1
11 0 0
11 0 1
11 1 0
11 1 1
B6 0
B5 0
COLUMN
ROW
NUL
0
SOH
1
2
STX
3
ETX
4
EOT
5
ENQ
6
ACK
7
BEL
8
BS
9
HT
10
LF
11
VT
12
FF
13
CR
14
SO
15
SI
01234567
0
0
0
1
1
1
2
2
2
3
3
3
4
4
4
5
5
5
6
6
6
7
7
7
10
8
8
11
9
9
12
10
0
13
11
0
14
12
0
15
13
0
16
14
0
17
15
0
0
20
16
DLE
10
21
DC1
17
(XON)
11
22
18
DC2
12
23
DC3
19
(XOFF)
13
24
DC4
20
14
EM
FS
GS
RS
US
25
21
15
26
22
16
27
23
17
30
24
18
31
25
19
32
26
1A
33
27
1B
34
28
1C
35
29
1D
36
30
1E
37
31
1F
NAK
SYN
ETB
CAN
SUB
A
ESC
B
C
D
E
F
1
1
SP
"
#
$
%
&
(
)
*
+
-
0
40
32
20
41
!
33
21
42
34
22
43
35
23
44
36
24
45
37
25
46
38
26
47
'
39
27
50
40
28
51
41
29
52
42
2A
53
43
2B
54
44
,
2C
55
45
2D
56
46
.
2E
57
47
/
2F
1
1
60
0
48
30
61
1
49
31
62
50
2
32
63
51
3
33
64
4
52
34
65
5
53
35
66
54
6
36
67
7
55
37
70
56
8
38
71
57
9
39
72
:
58
3A
73
;
59
3B
74
<
60
3C
75
=
61
3D
76
62
>
3E
77
63
?
3F
@
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
O
0
0
100
64
40
101
65
41
102
66
42
103
67
43
104
68
44
105
69
45
106
70
46
107
71
47
110
72
48
111
73
I
49
112
74
4A
113
75
4B
114
76
4C
115
77
4D
116
78
4E
117
79
4F
Q
W
^
0
120
P
80
50
121
81
51
122
82
R
52
123
83
S
53
124
T
84
54
125
U
85
55
126
86
V
56
127
87
57
130
88
X
58
131
89
Y
59
132
Z
90
5A
133
[
91
5B
134
\
92
5C
135
]
93
5D
136
94
5E
137
95
_
5F
1
1
m
0
140
96
60
141
a
97
61
142
98
b
62
143
99
c
63
144
d
100
64
145
e
101
65
146
102
f
66
147
g
103
67
150
104
h
68
151
105
i
69
152
j
106
6A
153
k
107
6B
154
l
108
6C
155
109
6D
156
110
n
6E
157
111
o
6F
p
q
r
s
t
u
v
w
x
y
z
{
|
}
~
DEL
1
1
160
112
70
161
113
71
162
114
72
163
115
73
164
116
74
165
117
75
166
118
76
167
119
77
170
120
78
171
121
79
172
122
7A
173
123
7B
174
124
7C
175
125
7D
176
126
7E
177
127
7F
89
Page 90

Appendix A
90
Page 91

B Vertical Page Formatting
Overview
Rapid vertical paper movement is called slewing. You can enable the printer
to slew paper to preset locations on a page by loading the vertical tab table.
The vertical tab table is a set of programmed vertical tabs. Various lines of the
form are assigned vertical tabs, which are then accessed by control codes for
rapid paper advancement to the tab position.
Two control codes are used for vertical tabbing: ESC B sets single channel
vertical tabs, and VT executes a vertical tab. These codes are described in
Chapter 3. The Epson emulation also has ESC / to select one of eight tab
channels and ESC b to set the tabs in a particular channel.
Executing Vertical Tabs
The vertical tab execute code is VT (hex 0B). It prints the contents of the print
buffer (if data are in the buffer) and causes paper movement to the next
predefined vertical tab position. If a tab position is not defined, the paper is
moved to the next line at the current line spacing. If a tab position is at the
current line, the paper is moved to the next tab position. If no tab positions are
defined between the current line and the end of the form, the paper moves to
the next TOF.
91
Page 92

Appendix B Overview
Vertical Tab Positions
Vertical tab positions are set by line number. A maximum of 16 vertical tab
positions can be set on the form. A sample format is shown in
The first vertical tab is set at line 6 for part number data, a second tab is set at
line 8 for part name data, and a third tab is set at line 14 for quantity data. The
ESC B code assigns the vertical tabs to the lines of the form. Once the tab
positions are set, sending the vertical tab execute code (VT) causes the paper
(currently at the top-of-form position) to advance to the first tab position for
PART NUMBER data. Sending another VT moves the paper to the second
tab position for PART NAME, followed by a third VT to access the third tab
position for QUANTITY data.
Figure 2.
Form Data
PART NUMBER
PART NAME
QUANTITY
Form Line Number
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
20
Vertical Tabs
Top of Form
Tab 1
Tab 2
Tab 3
92
Figure 2. Example of Vertical Tab Positions
Page 93
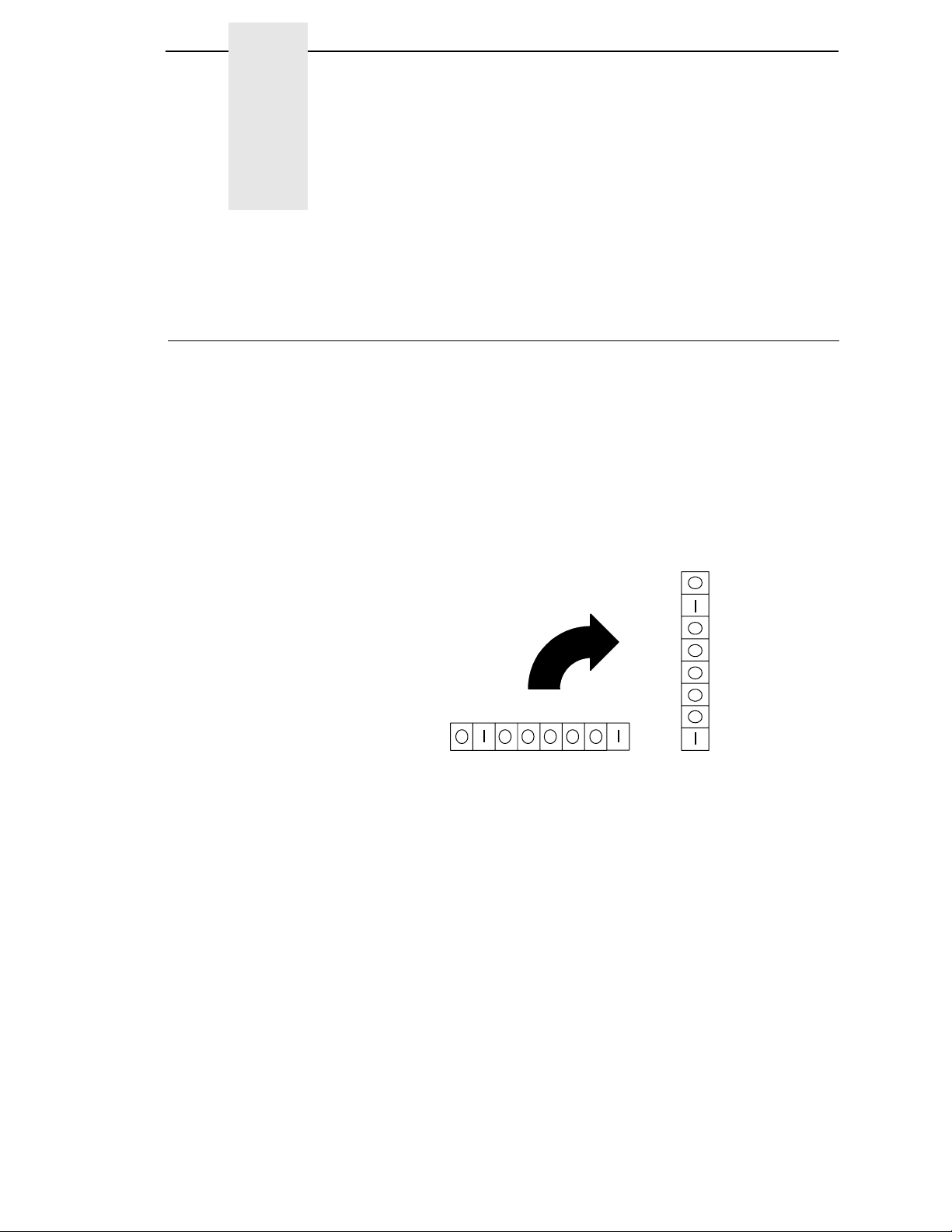
C Graphics
Bit Image Graphics
Bit image graphics are created by vertically printing the bit pattern of a series
of data bytes. For example, the bit pattern of the ASCII character A (hex 41,
decimal 65) is shown in
clockwise, we have a vertical data byte with the most significant bit (MSB) at
the top. If we then print each 1 (true) bit as a dot, the result is a “bit image” plot
of the ASCII character A.
Figure 3. If we rotate this data byte 90 degrees
ASCII character A = Hex 41 = Binary 01000001
MSB : Most Significant Bit
MSB
876 54321
Figure 3. Vertical Data Byte Pattern
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
MSB
93
Page 94

Appendix C Bit Image Graphics
The relationship between the ASCII character, its decimal value, and its bit
image plot is shown in
but some fonts have taller and shorter characters. (You may have to adjust
the line spacing in order to print without horizontal gaps.) Data bytes are
identified by their binary, octal, hexadecimal, or decimal equivalents. These
numeric equivalents are combined in data streams to form graphic patterns
such as the one illustrated in
Figure 4. All 8 bits of the data byte are used in all fonts,
Figure 5.
ASCII
Character
Decimal
Value
Binary
Code
Equivalent
128
to
Vertically
Rotated Data
Byte
MSB
Printed
Bit Image
64
32
16
=A65=
8
=
4
2
1
Figure 4. Bit Image Pattern from an ASCII Character
Bit image plotting is not limited to printable ASCII characters. You can print bit
image patterns for any 8-bit data byte with decimal values ranging from 0
through 255 (hex 00 through hex FF). (The ASCII character set is charted in
Appendix A.)
94
Page 95

Designing a Bit Image Pattern
Designing a Bit Image Pattern
A bit image pattern is produced in four steps:
1. On a quadrille pad or graph paper, lay out the graphic pattern you want to
print. (See
2. Determine the decimal equivalent of each vertical data byte in your
pattern. (The sum of the decimal equivalent of each true bit in the vertical
data byte is the decimal equivalent of the data byte.)
3. Write a program to generate the pattern.
4. Enter and run the program on the host computer.
Figure 5.)
1st Bit Image Data Byte
Decimal
Weights
MSB
LSB
128
64
32
16
8
4
2
1
73
146
2nd Bit Image Data Byte
36
255
36
146
73
7th Bit Image Date Byte
Decimal
Equivalents
Figure 5. Bit Image Pattern Plan
Bit Image Density
You can print bit image graphics in different dot densities. Select dot densities
by sending a control code in the data stream.
NOTE: Every line of graphics data must include the necessary bit image
command so the printer can perform the chosen graphics functions.
Single Density Mode: ESC K
Single density mode selects normal density bit image graphics of 60 dpi
horizontally and 72 dpi vertically.
95
Page 96

Appendix C Bit Image Graphics
Double Density Mode: ESC L
Double density mode prints up to twice the number of dots per inch
horizontally in the same space used for single density. The vertical dot density
remains the same as in single density mode. Double horizontal density
requires twice the number of input data bytes to print the same length line as
single density. Printing double density reduces the printing speed by half.
Double Speed-Double Density Mode: ESC Y
When the double density-double speed control code is received, data bytes
print at double the current horizontal dot density, but adjacent dots are not
printed. Since double density graphics are printed at half speed, double
speed-double density graphics are printed at the same speed as single
density graphics. This mode is often used to position a simulated print head
precisely by sending blank dot columns.
Quadruple Density Mode: ESC Z
When printing quadruple density graphics, the printer combines adjacent
quadruple density bit image bytes. The compounded data are then printed in
double density mode.
Bit Image Programming Format
The bit image command format is:
ESC CC (n1) (n2)
where:
ESCthe escape sequence control code
CC
K, L, Y or Z to select dot density
(K=single, L=double, Y=double density-double speed,
Z=quadruple density)
n1
(Number of DATA bytes) - 256(n2)
(remainder of division of number of DATA bytes by 256,
sometimes referred to as MOD 256)
n2
(Number of DATA bytes) / 256 (quotient of division)
DATA
the dot pattern bytes
The syntax of the bit image expression must be correct.
The number of data bytes and the n1,
Any characters following
the
n1, n2
definition is satisfied.
If
n1 = n2 =
The maximum number of data bytes that can be included in the DATA portion
of the program statement (when using 132 column paper) varies according to
the dot density:
0, then control codes K, L, Y, or Z are ignored.
At 60 dpi, single density = 792 bytes
double density = 1584 bytes
quadruple density = 3168 bytes
n1
DATA
and
n2
definition must be equal.
n2
are interpreted and plotted as data until
96
Page 97

Bit Image Sample
Data that go past the right margin are discarded if automatic line feed is
disabled. If automatic line feed is enabled, data that go past the right margin
trigger an automatic line feed (LF) and are printed on the next line.
Bit Image Sample
The sample below shows the single density bit image pattern shown in Figure
5. The 7-byte pattern is repeated 40 times.
10 WIDTH “LPT1:”, 255
20 LPRINT “Single Density Bit Image Graphics”
30 LPRINT CHR$(27);”K”;CHR$(24);CHR$(1);
40 FOR N=1 TO 40
50 RESTORE
60 FOR I=1 TO 7
70 READ R
80 LPRINT CHR$(R);
90 NEXT I
100 NEXT N
110 DATA 73,146,36,255,36,146,73
120 LPRINT
Figure 6. Sample Single-Density Bit Image Graphics
97
Page 98

Appendix C Bit Image Graphics
98
Page 99

Glossary
A
A to D Analog to Digital.
ACK Acknowledge character. A transmission control character
transmitted by the printer as an affirmative response to
an inquiry from the host.
active column The horizontal location on the paper where the next
character will print.
active line The vertical location on the paper where the next
character will print.
active position The position on the paper where the next character will
print. The intersection of the active column and the active
line.
ASCII
attributes, print Operations performed on text that alter its appearance
Abbrev. for
Interchange. A standard character encoding scheme
introduced in 1963 and used widely on many computers
and printers. It is a 7-bit code with 128 different bit
patterns. There is no parity recommendation.
but do not change the font. Examples: underlining,
superscripting, bold, etc.
American Standard Code for Information
B
bar code A printed code consisting of parallel bars of varied width
and spacing and designed to be read by a onedimensional scanning device.
baud A unit of speed that measures the rate at which
information is transferred. Baud rate is the reciprocal of
the length in seconds of the shortest pulse used to carry
data. For example, a system in which the shortest pulse
is 1/1200 second operates at 1200 baud. On RS-232
serial lines, the baud rate equals the data flow rate in bits
per second (bps). To communicate properly, a printer
must be configured to operate at the same baud rate as
its host computer.
99
Page 100

Glossary
bit
bold A print attribute specifying text of a heavy line thickness.
Boot-up The start-up procedure which causes a computer
buffer A reserved area in memory that data is written to and
bus A circuit for the transfer of data or electrical signals
byte A group of consecutive bits forming a unit of storage in a
Contraction of
system, represented by a 0 or a 1. A bit is the smallest
unit of storage in a digital computer, where 0 and 1 are
represented by different voltages. Groups of bits form
other units of storage called nibbles, bytes, and words.
See also
operating system to be loaded into main memory.
read from during data transfers.
between two devices.
digital computer and used to represent one alphanumeric
character. A byte usually consists of 8 bits, but may
contain more or fewer bits, depending on the computer or
protocol.
binary digit. A digit in the binary number
character weight.
C
character cell The invisible rectangular space occupied by a character,
including the white space around the character. The
height of a cell remains constant even with changes to
the current line spacing, and the width is equal to the
current character spacing. Used as a unit of spacing.
character proportionThe ratio of character height to character width.
See also
character set A set of codes, each of which represents a control or
printable character, including symbols, punctuation,
numbers, diacritical markings, and alphabet characters.
Each character is assigned a unique address in memory.
character weight The degree of lightness and thickness of printed text. For
example: “Bold” refers to a heavy or thick character
weight. “Medium,” “normal,” or “book weight” refer to the
character weight used in this sentence.
checksum A value used to verify microcode correctness.
command An operating instruction (e.g., form feed, or FF) sent from
a computer to the printer. Also called a control code or
non-printable character. Commands are opposed to
data, which is printed.
command delimiter An ASCII character used to begin a command string.
Commonly used command delimiters are ESC (hex 1B)
and SOH (hex 01).
compressed and expanded.
100
 Loading...
Loading...