
Datasheet V4.5, Jan 2004
CoolSET™-F2
ICE2A0565/165/265/365
ICE2B0565/165/265/365
ICE2A0565Z
ICE2A180Z/280Z
ICE2A765I/2B765I
ICE2A765P2/ICE2B765P2
Off-Line SMPS Current Mode
Controller with integrated
650V/800V CoolMOS™
Power Management & Supply
Never stop thinking.
CoolSET™-F2
Revision History: 2004-01-28 Datasheet V4.5
Previous Version:
Page Subjects (major changes since last revision)
For questions on technology, delivery and prices please contact the Infineon Technologies Of fices in Germany or
the Infineon Technologies Companies and Representatives worldwide: see our webpage at http://
www.infineon.com.
CoolMOS™, CoolSET™ are trademarks of Infineon Technologies AG.
Edition 2004-01-28
Published by Infineon Technologies AG,
St.-Martin-Strasse 53,
D-81541 München
© Infineon Technologies AG 1999.
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
The information herein is given to describe certain components and shall not be considered as warr anted characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
We hereby disclaim any and all warranties, including but not limited to warranties of non-infringement, regarding
circuits, descriptions and charts stated herein.
Infineon Technologies is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your nearest
Infineon Technologies Office in Germany or our Infineon Technolog ies Representatives worldwide (see address
list).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in
question please contact your nearest Infineon Technologies Office.
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the ex press written
approval of Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasona bly be expe cted to cause the f ailure
of that life-support device or system, or to aff ect t he safety or effectiveness of that device or system. Life support
devices or systems are intended to be implanted in the human body, or to support and/or maintain and sustain
and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may
be endangered.
Off-Line SMPS Current Mode Controller
with integrated 650V/800V
CoolSET™-F2
Product Highlights
• Best in class in DIP8, DIP7, TO220 packages
• No heatsink required for DIP8, DIP7
• Lowest standby power dissipation
• Enhanced protection functions all with
Auto Restart Mode
• Isolated drain package for TO220
• Increased creepage distance for TO220 packages
Features
• 650V/800V avalanche rugged CoolMOS™
• Only few external components required
• Input Vcc Undervoltage Lockout
• 67kHz/100kHz switching frequency
• Max duty cycle 72%
• Low Power Standby Mode to meet
European Commission Requirements
• Thermal Shut Down with Auto Restart
• Overload and Open Loop Protection
• Overvoltage Protection during Auto Restart
• Adjustable Peak Current Limitation via
external resistor
• Overall tolerance of Current Limiting < ±5%
• Internal Leading Edge Blanking
• User defined Soft Start Soft Switching for low EMI
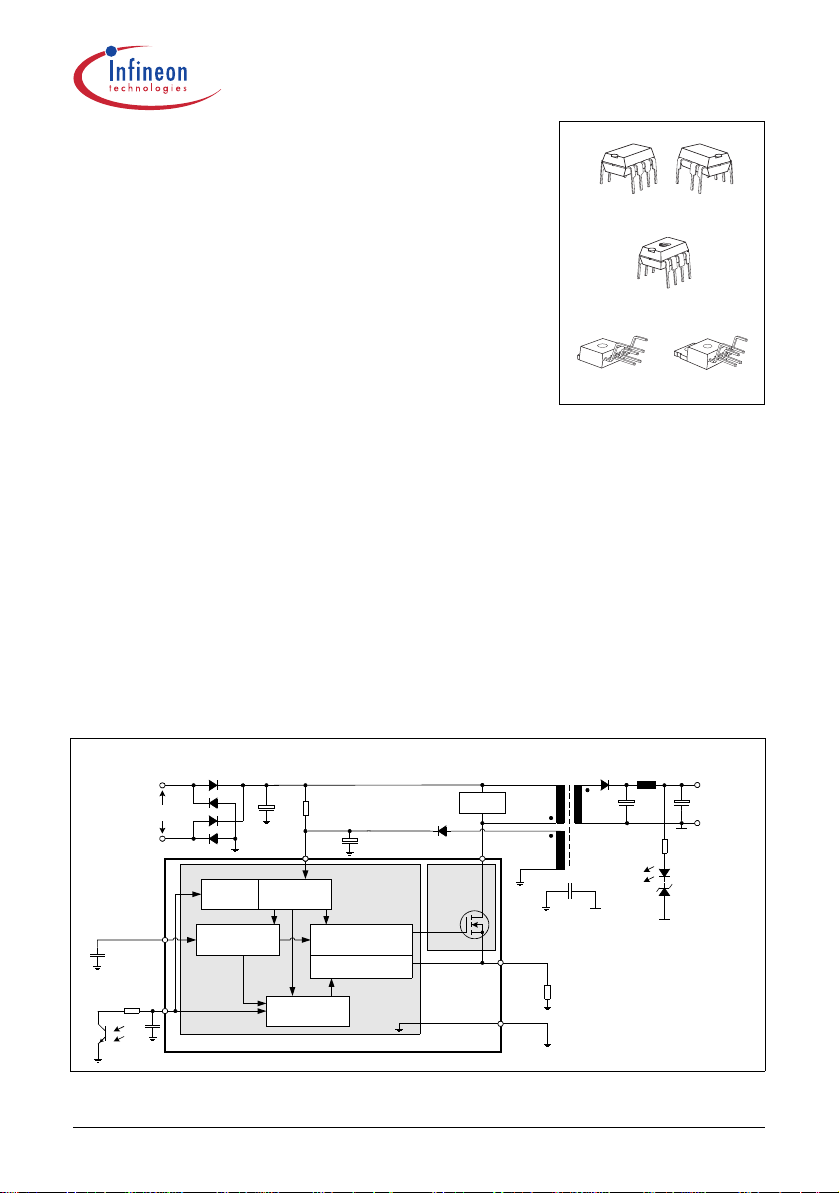
Typical Application
R
VCC
Power
Management
Protection Unit
Start-up
PWM Controller
Current Mode
Precise Low Tolerance
Peak Current Limitation
85 ... 270 VAC
SoftS
C
Soft Start
FB
Feedback
Low Power
StandBy
Soft-Start Control
PWM-Controller
CoolSET™-F2
Description
The second generation CoolSET™-F2 provides several
special enhancements to satisfy the needs for low power
standby and protection features. In standby mode
frequency reduction is used to lower the power
consumption and support a stable output voltage in this
mode. The frequency reduction is limited to 20kHz/21.5
kHz to avoid audible noise. In case of failure modes like
open loop, overvoltage or overload due to short circuit the
device switches in Auto Restart Mode which is controlled by
the internal protection unit. By means of the internal precise
peak current limitation the dimension of the transformer and
the secondary diode can be lower which leads to more cost
efficiency.
Snubber
C
VCC
Drain
CoolMOS™
Isense
GND
R
Sense
P-DIP-7-1
P-TO220-6-46
Feedback
P-DIP-7-1
P-DIP-8-6
P-DIP-8-4, -6
P-TO220-6-47P-TO220-6-46
P-TO220-6-47
+
Converter
DC Output
-
Datasheet V4.5 3 Jan 2004
CoolSET™-F2
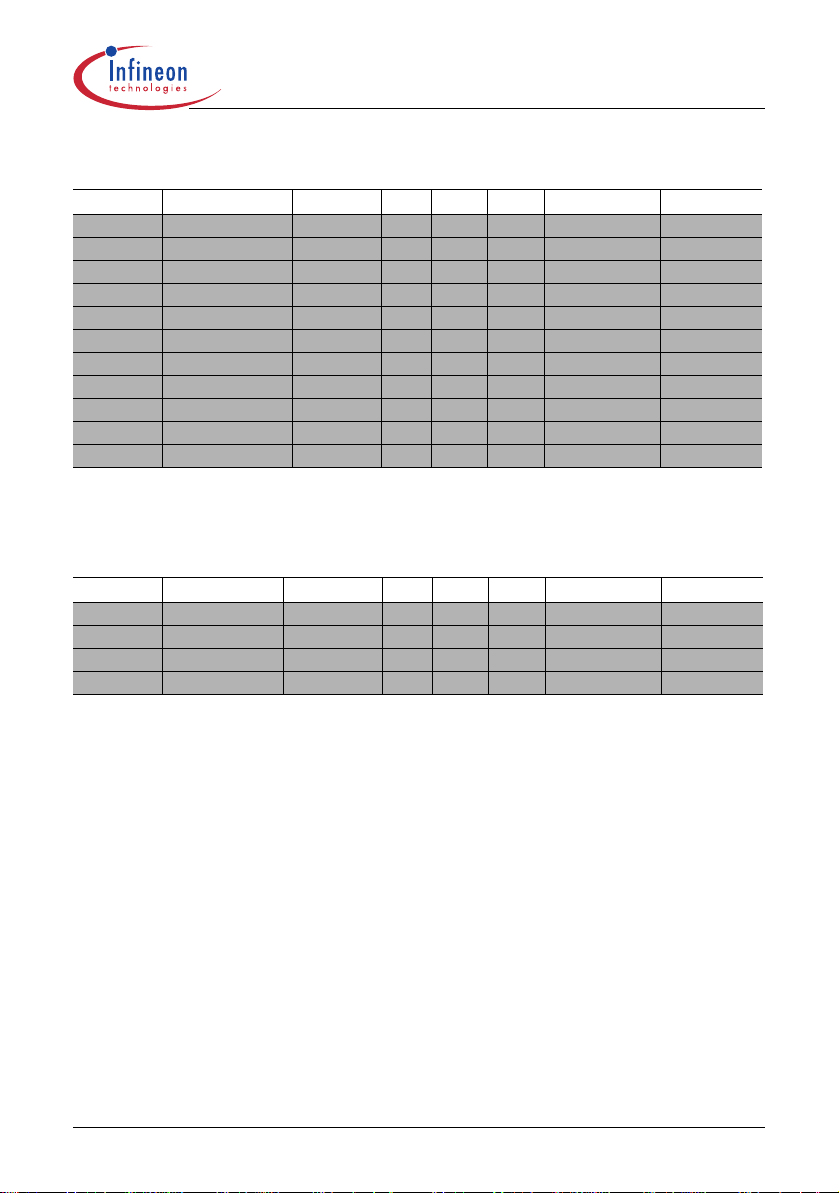
Ordering Codes
Type Ordering Code Package V
DSFOSCRDSon
1)
230VAC ±15%
ICE2A0565 Q67040-S4542 P-DIP-8-6 650V 100kHz 4.7Ω 23W 13W
ICE2A165 Q67040-S4426 P-DIP-8-6 650V 100kHz 3.0Ω 31W 18W
ICE2A265 Q67040-S4414 P-DIP-8-6 650V 100kHz 0.9Ω 52W 32W
ICE2A365 Q67040-S4415 P-DIP-8-6 650V 100kHz 0.45Ω 67W 45W
ICE2B0565 Q67040-S4540 P-DIP-8-6 650V 67kHz 4.7Ω 23W 13W
ICE2B165 Q67040-S4489 P-DIP-8-6 650V 67kHz 3.0Ω 31W 18W
ICE2B265 Q67040-S4478 P-DIP-8-6 650V 67kHz 0.9Ω 52W 32W
ICE2B365 Q67040-S4490 P-DIP-8-6 650V 67kHz 0.45Ω 67W 45W
ICE2A0565Z Q67040-S4541 P-DIP-7-1 650V 100kHz 4.7Ω 23W 13W
ICE2A180Z Q67040-S4546 P-DIP-7-1 800V 100kHz 3.0Ω 29W 17W
ICE2A280Z Q67040-84547 P-DIP-7-1 800V 100KHz 0.8Ω 50W 31W
1)
typ @ T=25°C
2)
Maximum power rating at Ta=75°C, Tj=125°C and with copper area on PCB = 6cm²
2)
85-265 VAC
2)
Type Ordering Code Package VDSF
OSCRDSon
1)
230VAC ±15%
2)
85-265 VAC
2)
ICE2A765I Q67040-S4609 P-TO-220-6-46 650V 100kHz 0.45Ω 240W 130W
ICE2B765I Q67040-S4607 P-TO-220-6-46 650V 67kHz 0.45Ω 240W 130W
ICE2A765P2 Q67040-S4610 P-TO-220-6-47 650V 100kHz 0.45Ω 240W 130W
ICE2B765P2 Q67040-S4608 P-TO-220-6-47 650V 67kHz 0.45Ω 240W 130W
1)
typ @ T=25°C
2)
Maximum practical continuous power in an open frame design at Ta=75°C, Tj=125°C and Rth=2.7K/W
Datasheet V4.5 4 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Table of Contents Page
1 Pin Configuration and Functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.1 Pin Configuration with P-DIP-8-6 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.2 Pin Configuration with P-DIP-7-1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
1.3 Pin Configuration with P-TO220-6-46/47 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
1.4 Pin Functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
2 Representative Blockdiagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
3 Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3.1 Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3.2 Improved Current Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3.2.1 PWM-OP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
3.2.2 PWM-Comparator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
3.3 Soft-Start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
3.4 Oscillator and Frequency Reduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.4.1 Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.4.2 Frequency Reduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.5 Current Limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.5.1 Leading Edge Blanking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
3.5.2 Propagation Delay Compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.6 PWM-Latch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.7 Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
3.8 Protection Unit (Auto Restart Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
3.8.1 Overload / Open Loop with Normal Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
3.8.2 Overvoltage due to Open Loop with No Load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
3.8.3 Thermal Shut Down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
4 Electrical Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
4.2 Thermal Impedance (ICE2X765I and ICE2X765P2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
4.3 Operating Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
4.4 Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
4.4.1 Supply Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
4.4.2 Internal Voltage Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
4.4.3 Control Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
4.4.4 Protection Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
4.4.5 Current Limiting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
4.4.6 CoolMOS™ Section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .22
5 Typical Performance Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .24
6 Layout Recommendation for C
7 Outline Dimension . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
18
Datasheet V4.5 5 Jan 2004
Pin Configuration and Functionality
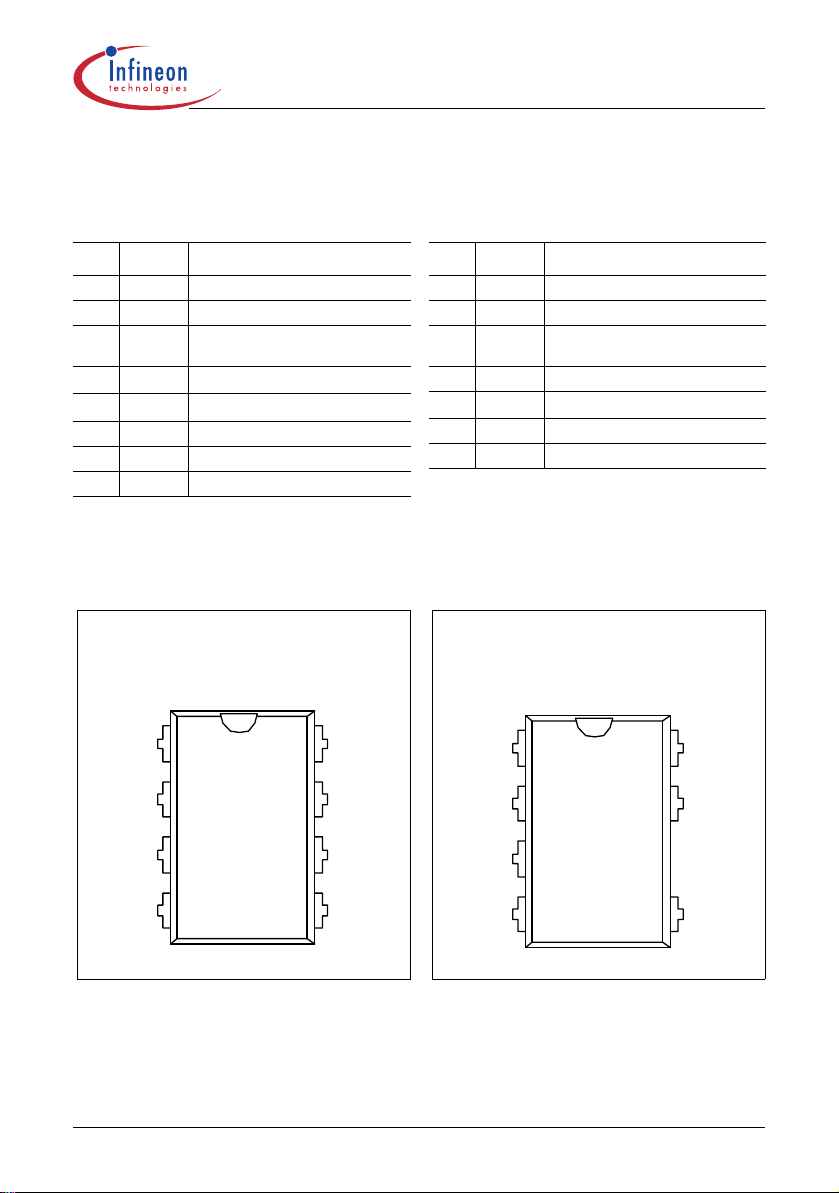
1 Pin Configuration and Functionality
1.1 Pin Configuration with P-DIP-8-6
1.2 Pin Configuration with P-DIP-7-1
CoolSET™-F2
Pin Symbol Function
1 SoftS Soft-Start
2 FB Feedback
3 Isense Controller Current Sense Input,
4 Drain
5 Drain
6 N.C Not connected
7 VCC Controller Supply Voltage
8 GND Controller Ground
1)
at Tj = 110°C
2)
at Tj = 25°C
CoolMOS™ Source Output
650V1)/800V2) CoolMOS™ Drain
650V1)/800V2) CoolMOS™ Drain
Package P-DIP-8-6
Sof tS
1
2
GND
8
7
VCCFB
Pin Symbol Function
1 SoftS Soft-Start
2 FB Feedback
3 Isense Controller Current Sense Input,
4 N.C. Not connected
5 Drain
7 VCC Controller Supply Voltage
8 GND Controller Ground
1)
at Tj = 110°C
2)
at Tj = 25°C
CoolMOS™ Source Output
650V1)/800V2) CoolMOS™ Drain
Package P-DIP-7-1
Sof tS
1
2
GND
8
7
VCCFB
Is ens e
Dr ai n
Figure 1 Pin Configuration (top view)
Datasheet V4.5 6 Jan 2004
3
4
6
N.C
5
Dr ain
Isense
Figure 2 Pin Configuration (top view)
n.c.
3
4
5
Dr ai n
1.3 Pin Conuration with P-TO220-6-46/47
CoolSET™-F2
Pin Configuration and Functionality
1.4 Pin Functionality
Pin Symbol Function
1 Drain
3 Isense
4 GND Controller Ground
5 VCC Controller Supply Voltage
6 SoftS Soft-Start
7 FB Feedback
1)
at Tj = 110°C
650V1) CoolMOS™ Drain
650V1) CoolMOS™ Source
Package P-TO220-6-46/47
1
234567
SoftS (Soft Start & Auto Restart Control)
This pin combines the function of Soft Start in case of
Start Up and Auto Restart Mode and the controlling of
the Auto Restart Mode in case of an error detection.
FB (Feedback)
The information about the regulation is provided by the
FB Pin to the internal Protection Unit and to t he internal
PWM-Comparator to control the duty cycle.
Isense (Current Sense)
The Current Sense pin senses the voltage developed
on the series resistor inserted in the source of the
integrated CoolMOS™. When Isense reaches the
internal threshold of the Current Limit Comparator, the
Driver output is disabled. By this means the Over
Current Detection is realized.
Furthermore the current information is provided for the
PWM-Comparator to realize the Current Mode.
Drain (Drain of integrated CoolMOS™)
Pin Drain is the connection to the Drain of the internal
CoolMOS
VCC (Power supply)
This pin is the positiv supply of the IC. The operating
range is between 8.5V and 21V.
To provide overvoltage protection the driver gets
disabled when the voltage becomes higher than 16.5V
during Start Up Phase.
GND (Ground)
This pin is the ground of the primary side of the SMPS.
TM
.
Drain
Isense
GND
VCC
SoftS
FB
Figure 3 Pin Configuration (top view)
Datasheet V4.5 7 Jan 2004
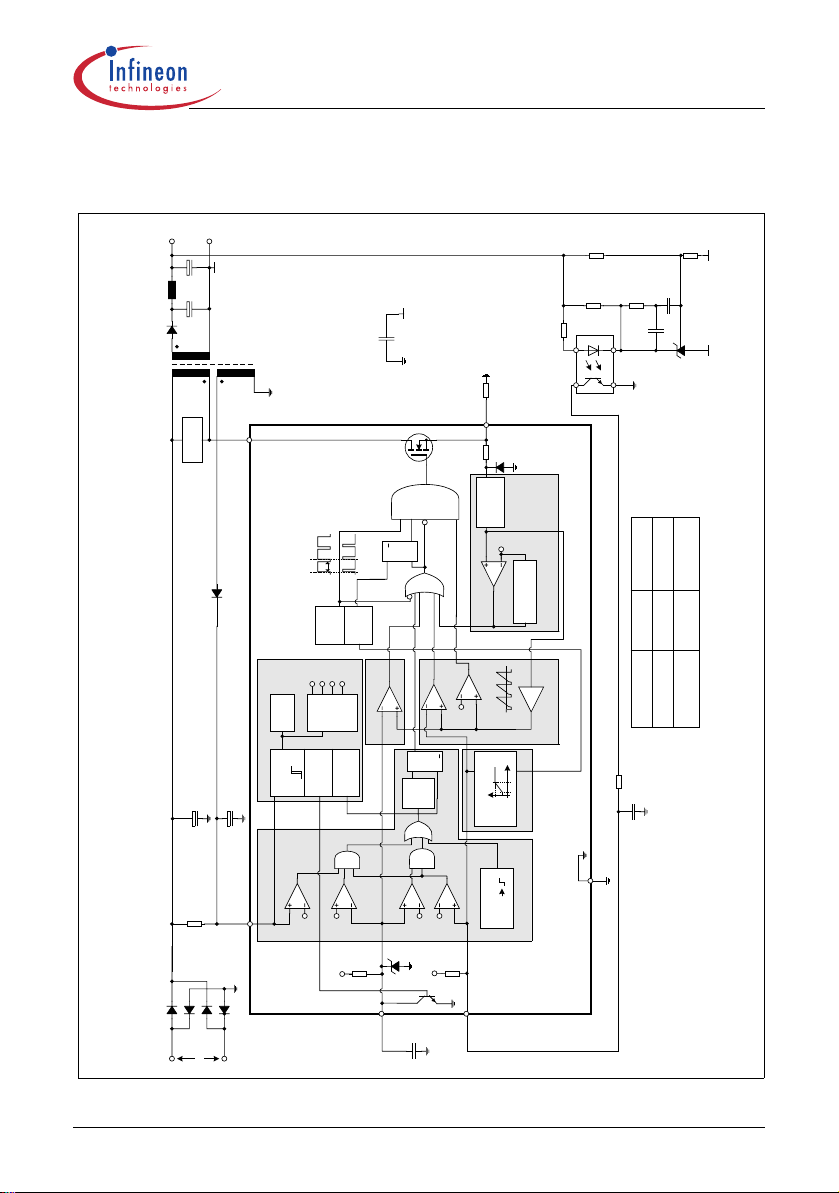
2 Representative Blockdiagram
OUT
-
+
V
Converter
DC Output
Snubber
Drain
CoolMOS™
Gate
Driver
Q
Q
S
Clock
Reset
R
PWM-Latch
G4
norm
-f
standby
f
Spike
SQ
Blanking
G3
PWM
Comparator
Q
R
Error-Latch
s
5
G2
Soft-Start
Soft Start
Comparator
0.72
Duty Cycle Max
max
Duty Cycle
Oscillator
6.5V
4.8V
5.3V
4.0V
Voltage
Reference
Internal Bias
Power Management
13.5V
Reset
Lockout
Power-Down
Line
C
Undervoltage
VCC
C
Power-Up
8.5V
G1
CoolSET™-F2
Representative Blockdiagram
Sense
R
Isense
D1
10k
220ns
Blanking
Leading Edge
csth
V
Comparator
Current-Limit
C5
0.3V
osc
f
norm
f
f
Optocoupler
ICE2Bxxxx
Compensation
Propagation-Delay
Current Limiting
ICE2Axxxx
x3.65
0.8V
Improved Current Mode
PWM OP
FB
U
standby
Standby Unit
67kHz
20kHz
100kHz
21.5kHz
norm
standby
f
f
Start-up
R
85 ... 270 VAC
VCC
C1
4.0V
16.5V
6.5V
C4
C3
>140°C
j
T
Thermal Shutdown
4.8V
5.3V
5.6V
Soft-Start
R
SoftS
FB
R
6.5V
T1
Soft-Start
C
Protection Unit
FB
GND
CoolSET™-F2
C2
Figure 4 Representative Blockdiagram
Datasheet V4.5 8 Jan 2004
3 Functional Description
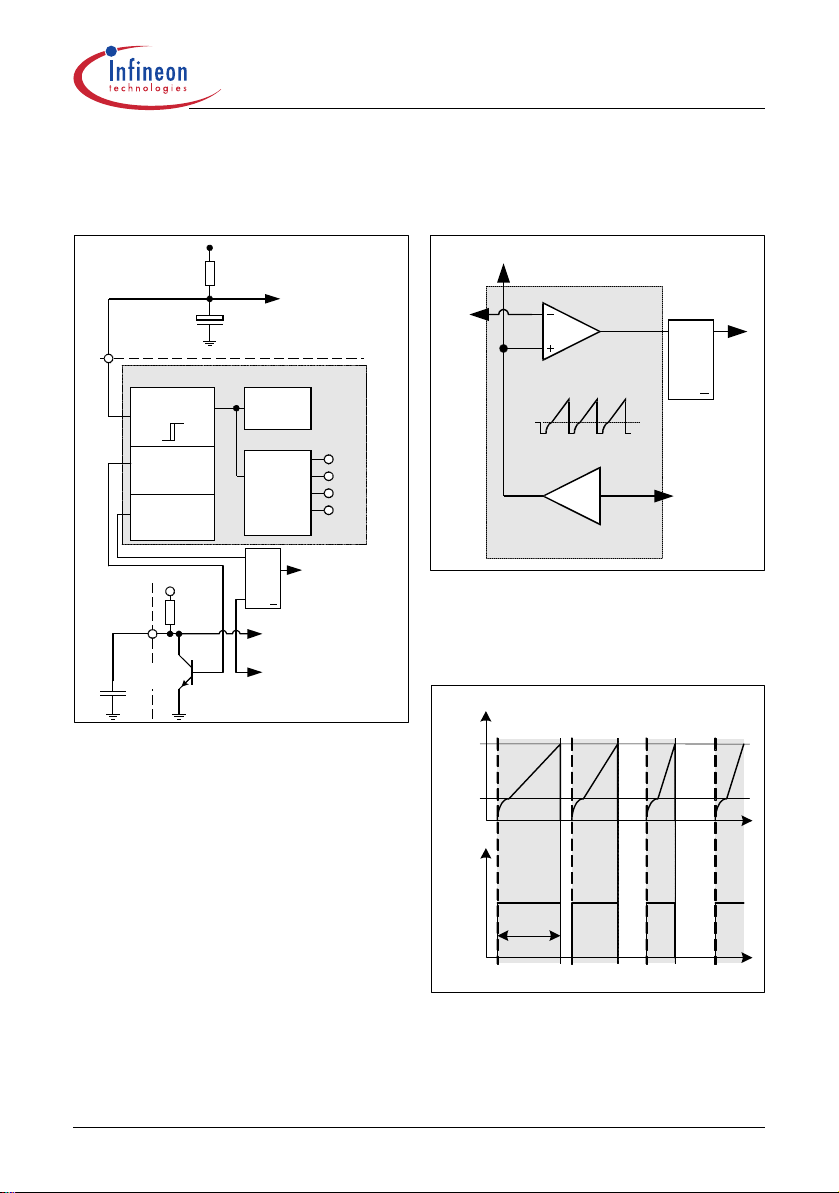
3.1 Power Management
CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
3.2 Improved Current Mode
Main Line (100V-380V)
R
Start-Up
Primary Winding
C
VCC
VCC
Power Management
SoftS
C
Soft-Start
Undervoltage
Lockout
8.5V
Pow er-D own
Reset
Power-Up
Reset
R
T1
13.5V
6.5V
Soft-S ta rt
Intern al
Bias
Voltage
Reference
RSQ
Q
Error-Latch
Soft-S ta rt C o m para to r
Error-D ete ction
6.5V
5.3V
4.8V
4.0V
PWM-Latch
Figure 5 Power Management
The Undervoltage Lockout monitors the external
supply voltage V
current consumption is max. 55µA. When the SMPS is
plugged to the main line the current through R
charges the external Capacitor C
exceeds the on-threshold V
circuit and the voltage reference are switched on. After
that the internal bandgap generates a reference
voltage V
avoid uncontrolled ringing at switch-on a hysteresis is
implemented which means that switch-off is only after
active mode when Vcc falls below 8.5V.
In case of switch-on a Power Up Reset is done by
reseting the internal error-latch in the protection unit.
When V
internal reference is switched off and the Power Down
reset let T1 discharging the soft-start capaci tor C
at pin SoftS. Thus it is ensu re d th at at ev ery s wi tch- on
the voltage ramp at pin SoftS starts at zero.
REF
falls below the off-threshold V
VCC
. In case the IC is inactive the
VCC
Start-up
. When V
VCC
=13.5V the internal bias
CCon
VCC
=6.5V to supply the internal circuits. To
=8.5V the
CCoff
Soft-Start
Soft-Start Com parator
FB
PW M-Latch
RSQ
Driver
PW M Com parator
Q
0.8V
PWM OP
x3.65
Isense
Improved
Current Mode
Figure 6 Current Mode
Current Mode means that the duty cycle is controlled
by the slope of the primary current. This is done by
comparison the FB signal with the amplified current
sense signal.
Amplified Current Signal
FB
0.8V
Driver
T
on
t
t
Figure 7 Pulse Width Modulation
In case the amplified current sense signal exceeds the
FB signal the on-time T
reseting the PWM-Latch (see Figure 7).
of the driver is finished by
on
Datasheet V4.5 9 Jan 2004
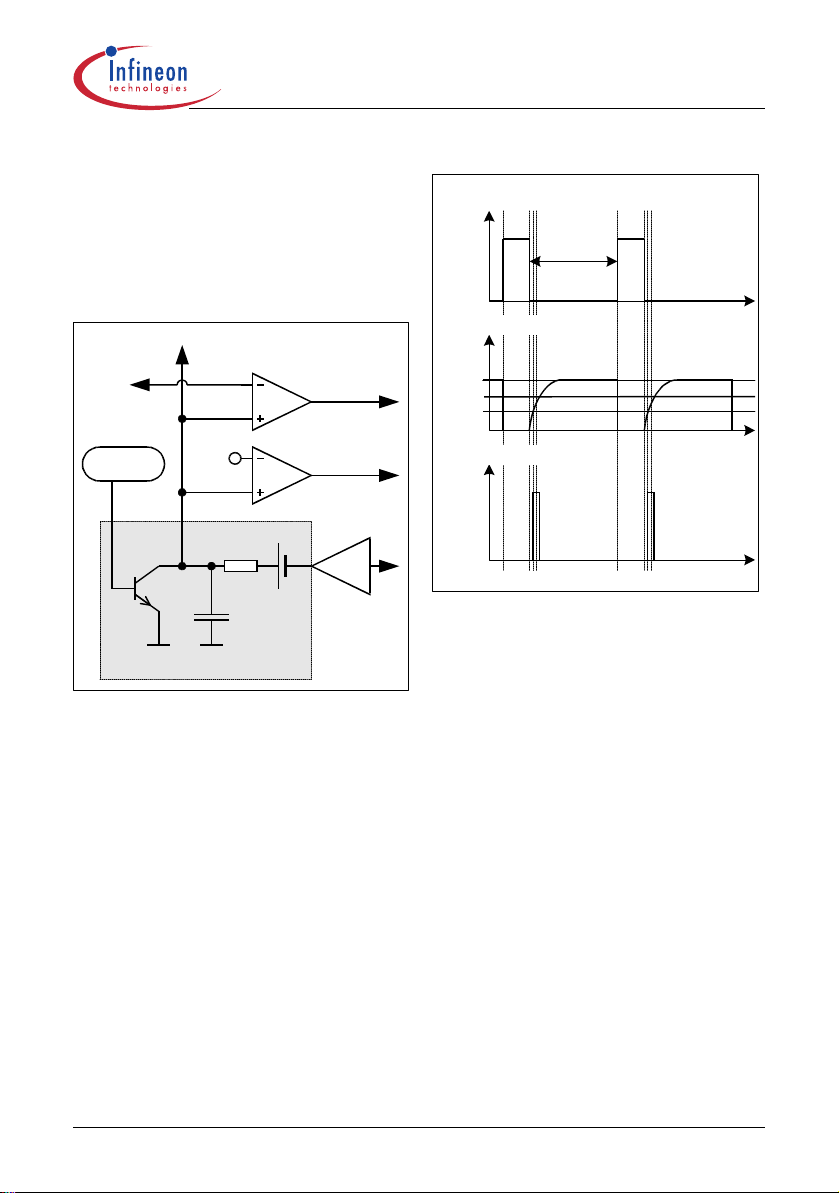
The primary current is sensed by the external series
resistor R
CoolMOS™. By means of Current Mode the regulation
of the secondary voltage is insensitive on line
variations. Line variation causes varition of the
increasing current slope which controls the duty cycle.
The external R
the maximum source current of the integrated
inserted in the source of the integrated
Sense
allows an individual adjustment of
Sense
CoolMOS™.
Soft-Start Com parator
PWM Comparator
FB
PW M-Latch
OSC
0.3V
C5
G a te Drive r
O scillato r
V
0.8V
10k
Ω
x3.65
T
2
R
1
V
1
C
20pF
1
PWM O P
Voltage Ramp
Figure 8 Improved Current Mode
To improve the Current Mode during light load
conditions the amplified current ramp of the PWM-OP
is superimposed on a voltage ramp, which is built by
the switch T
low pass filter composed of R
Figure 9). Every time the oscillator shuts down for max.
duty cycle limitation the switch T2 is closed by V
When the oscillator triggers the Gate Driver T2 is
opened so that the voltage ramp can start.
In case of light load the amplified current ramp is to
small to ensure a stable regulation. In that case the
Voltage Ramp is a well defined signal for the
comparison with the FB-signal. The duty cycle is then
controlled by the slope of the Voltage Ramp.
By means of the Compa rator C5, the Gate Driver is
switched-off until the voltage ramp exceeds 0.3V. It
allows the duty cycle to be reduced continously till 0%
by decreasing V
, the voltage source V1 and the 1st order
2
below that threshold.
FB
and C1(see Figure 8,
1
OSC
.
CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
V
OSC
max.
Duty Cycle
Voltage Ramp
0.8V
FB
0.3V
Gate Driver
Figure 9 Light Load Conditions
3.2.1 PWM-OP
The input of the PWM-OP is applied over the internal
leading edge blanking to the external sense resistor
connected to pin ISense. R
R
Sense
source current into a sense voltage. The sense voltage
is amplified with a gain of 3.65 by PWM OP. The output
of the PWM-OP is connected to the voltage source V1.
The voltage ramp with the superimposed amplified
current singal is fed into the positive inputs of the PWMComparator, C5 and the Soft-Start-Comparator.
Sense
3.2.2 PWM-Comparator
The PWM-Comparator compares the sensed current
signal of the integrated C oolMOS
signal V
external optocoupler or external transistor in
combination with the internal pullup resistor R
provides the load information of the feedback circuitry.
When the amplified current signal of the integrated
CoolMOS™ exceeds the signal V
(see Figure 10). VFB is created by an
FB
Comparator switches off the Gate Driver.
TM
with the feedback
FB
t
t
t
converts the
and
FB
the PWM-
Datasheet V4.5 10 Jan 2004
6.5V
R
FB
FB
Soft-Start Com parator
PW M-Latch
PW M Com parator
0.8V
Optocoupler
PWM OP
Ise n s e
x3.65
Improved
Current Mode
Figure 10 PWM Controlling
3.3 Soft-Start
V
So ftS
5.6V
5.3V
T
So ft-Start
G a te Drive r
t
t
Figure 11 Soft-Start Phase
The Soft-Start is realized by the internal pullup resistor
and the external Capacitor C
R
Soft-Start
Figure 2). The Soft-Start voltage V
charging the external capacitor C
is generated by
SoftS
Soft-Start
(see
Soft-Start
by the internal
CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
pullup resistor R
compares the voltage at pin SoftS at the negative input
with the ramp signal of the PWM-OP at the positive
input. When Soft-Start voltage V
Feedback voltage V
the pulse width by reseting the PWM-Latch (see Figure
11). In addition to Start-Up, Soft-Start is also activated
at each restart attempt during Auto Restart. By means
of the above mentioned C
defined by the user. The Soft-Start is finished when
exceeds 5.3V. At that time the Protection Unit is
V
SoftS
activated by Comparator C4 and senses the FB by
Comparator C3 wether the voltage is below 4.8V which
means that the voltage on the secondary side of the
SMPS is settled. The internal Zener Diode at SoftS with
breaktrough voltage of 5.6V is to prevent the internal
circuit from saturation (see Figure 12).
6.5V
5.6V
So ftS
6.5V
5.3V
4.8V
R
FB
FB
Figure 12 Activation of Protection Unit
The Start-Up time T
voltage V
Start Phase T
C
Soft Start–
By means of Soft-Start there is an effective
minimization of current and voltage stresses on the
integrated CoolMOS™, the clamp circuit and the output
overshoot and prevents saturation of the transformer
during Start-Up.
is settled must be shorter than the Soft-
OUT
Soft-Start
. The Soft-Start-Comparator
Soft-Start
the Soft-Start-Comparator limits
FB
SoftS
the Soft-Start can be
Soft-Start
Power-Up Reset
R
Sof t-S ta rt
C4
Erro r-L atc h
G2
C3
Clock
PWM-Latch
within the converter output
Start-Up
(see Figure 13).
T
Soft Start–
------------------------------------- -=
R
Soft Start–
1.69×
is less than
RSQ
Q
RSQ
Gate
Driver
Q
Datasheet V4.5 11 Jan 2004
CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
V
SoftS
5.3V
T
So ft-S tart
V
FB
t
4.8V
V
OUT
V
OUT
T
Start-Up
t
t
Figure 13 Start Up Phase
3.4 Oscillator and Frequency Reduction
3.4.1 Oscillator
The oscillator generates a frequency f
100kHz. A resistor, a capacitor and a current source
and current sink which determine the frequency are
integrated. The charging and discharging current of the
implemented oscillator capacitor are internally
trimmed, in order to achieve a very accurate switching
frequency. The ratio of controlled charge to discharge
current is adjusted to reach a max. duty cycle limitation
of D
=0.72.
max
switch
= 67kHz/
3.4.2 Frequency Reduction
The frequency of the oscillator is depending on the
voltage at pin FB. The dependence is shown in Figure
14. This feature allows a power supply to operate at
lower frequency at light loads thus lowering the
switching losses while maintaining good cross
regulation performance and low output ripple. In case
of low power the power consumption of the whole
SMPS can now be reduced very effective. The minimal
reachable frequency is limited to 20kHz/21.5 kHz to
avoid audible noise in any case.
kHz
100
65
OSC
f
21.5
1.0
1.1 1. 2 1.3 1.4 1. 5 1.6 1.7 1.8 1. 9 2.0
f
norm
f
standby
21.5kHz
67kHz
20kHz
ICE2BxxxxICE2Axxxx
100kHz
V
FB
V
Figure 14 Frequency Dependence
3.5 Current Limiting
There is a cycle by cycle current limiting realised by the
Current-Limit Comparator to provide an overcurrent
detection. The source current of the integrated
CoolMOS
R
transformed to a sense voltage V
voltage V
V
off the gate drive. To prevent the Current Limiting from
distortions caused by leading edge spikes a Leading
Edge Blanking is integrated at the Current Sense.
Furthermore a Propagation Delay Compensation is
added to support the immedeate shut down of the
CoolMOS™ in case of overcurrent.
TM
is sensed via an external sense resistor
. By means of R
Sense
exceeds the internal threshold voltage
Sense
the Current-Limit-Comparator immediately turns
csth
the source current is
Sense
. When the
Sense
3.5.1 Leading Edge Blanking
V
Sense
V
csth
t
= 220ns
LEB
t
Figure 15 Leading Edge Blanking
Each time when CoolMOS™ is switched on a leading
spike is generated due to the primary-side
capacitances and secondary-side rectifier reverse
recovery time. To avoid a premature termination of the
switching pulse this spike is blanked out with a time
constant of t
= 220ns. During that time the output of
LEB
Datasheet V4.5 12 Jan 2004

the Current-Limit Comparator cannot switch off the
gate drive.
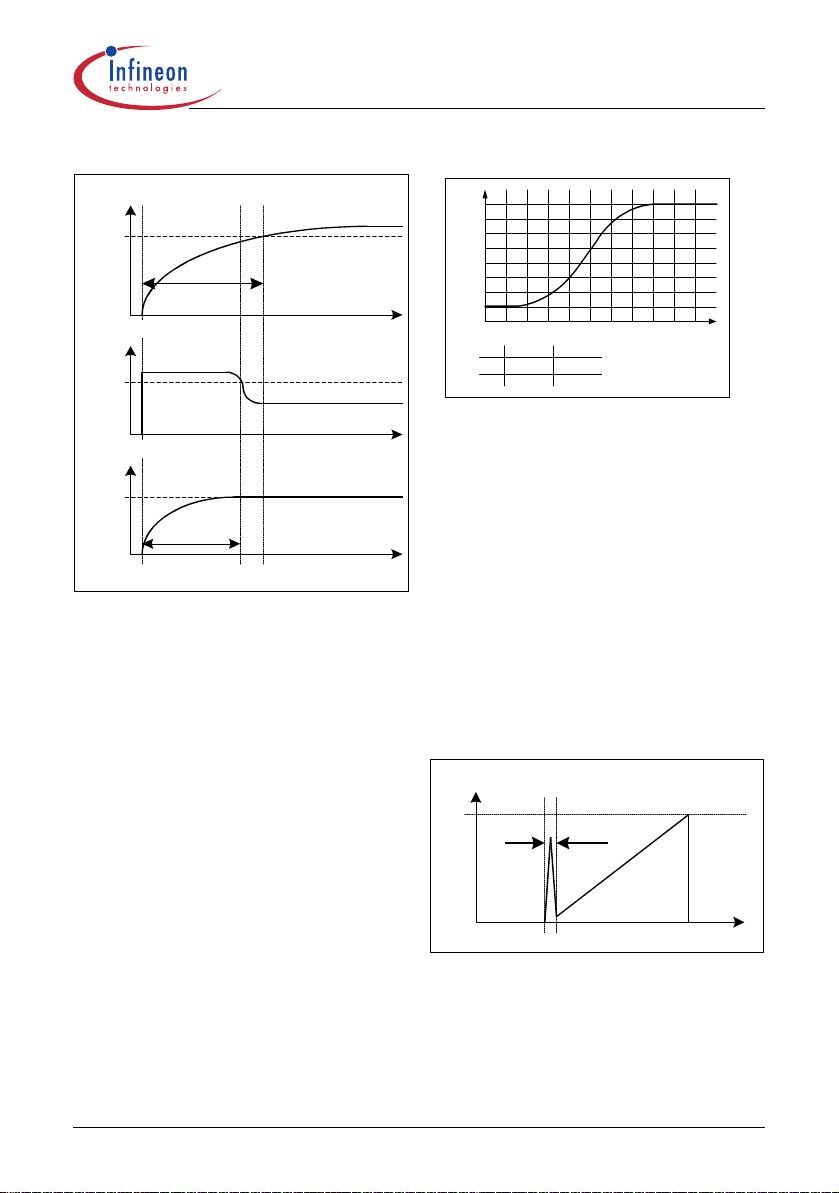
3.5.2 Propagation Delay Compensation
In case of overcurrent detection by I
of CoolMOS™ is delayed due to the propagation delay
of the circuit. This delay causes an overshoot of the
peak current I
the peak current (see Figure 16).
which depends on the ratio of dI/dt of
peak
.
the shut down
Limit
Signal2Signal1
I
peak2
I
peak1
I
Limit
I
Sense
I
Overs hoot2
t
Propagation Delay
I
Overshoot1
t
Figure 16 Current Limiting
The overshoot of Signal2 is bigger than of Signal1 due
to the steeper rising waveform.
A propagation delay compensation is integrated to
bound the overshoot dependent on dI/dt of the rising
primary current. That means the propagation delay
time between exceeding the current sense threshold
and the switch off of CoolMOS™ is compensated
V
csth
over temperature within a range of at least.
0 R
≤≤
So current limiting is n ow capable in a very accura te
way (see Figure 18).
V
V
OSC
Sense
V
Sense
csth
dI
peak
------------
×
dt
max. Duty Cycle
dV
Sense
---------------
dt
off time
t
Propagation Del ay
t
Signal1 Signal 2
Figure 17 Dynamic Voltage Threshold V
csth
CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
The propagation delay compensation is done by
means of a dynamic threshold voltage V
17). In case of a steeper slope the switch off of the
driver is earlier to compensate the delay.
E.g. I
= 0.5A with R
peak
delay compensation the current sense threshold is set
to a static voltage level V
dI/dt = 0.4A/µs, that means dV
propagation delay time of i.e. t
leads then to a I
propagation delay compensation the overshoot is only
about 2% (see Figure 18).
V
1.3
1.25
1.2
1.15
1.1
Sense
V
1.05
1
0.95
0.9
peak
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2
= 2 . Without propagation
Sense
=1V. A current ramp of
csth
Sense
overshoot of 12%. By means of
dV
dt
without compensation
Sense
with compensation
Figure 18 Overcurrent Shutdown
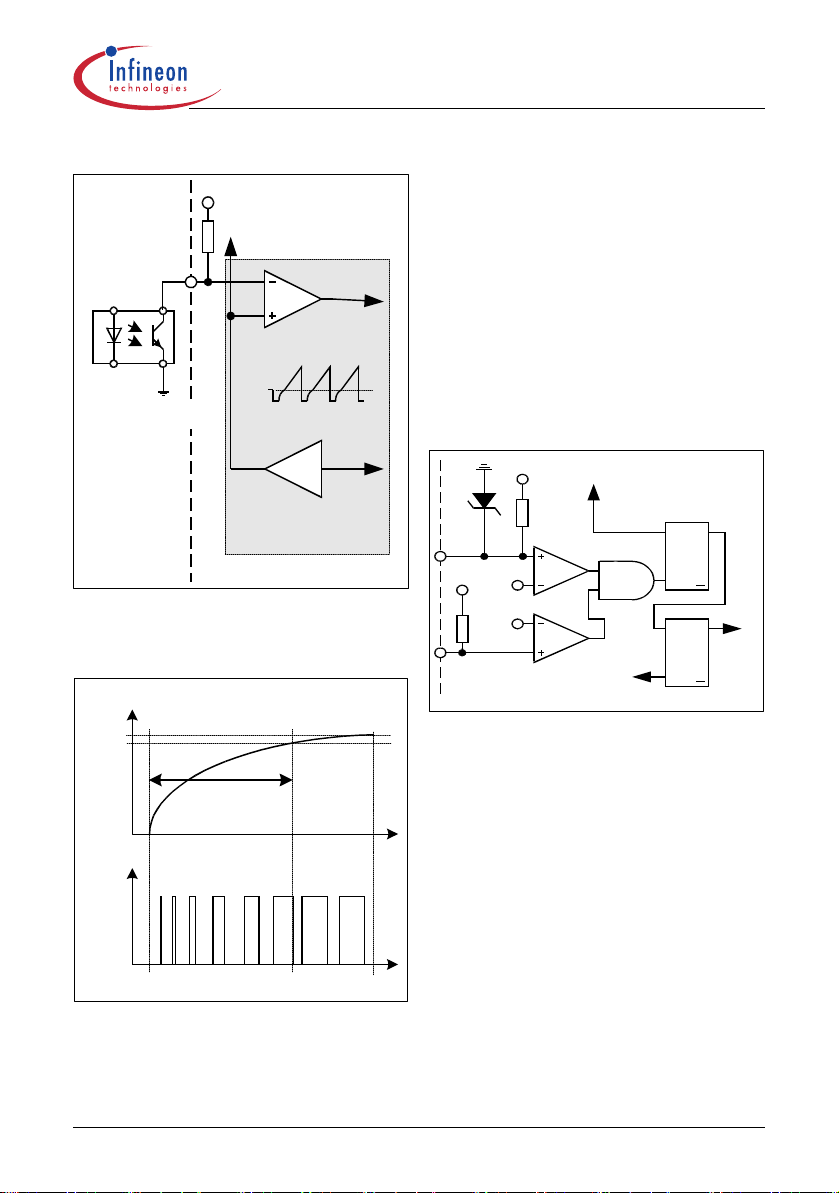
3.6 PWM-Latch
The oscillator clock output applies a set pulse to the
PWM-Latch when initiating CoolMOS™ conduction.
After setting the PWM-Latch can be reset by the PWMOP, the Soft-Start-Comparator, the Current-LimitComparator, Comparator C3 or the Error-Latch of the
Protection Unit. In case of reseting the driver is shut
down immediately.
3.7 Driver
The driver-stage drives the gate of the CoolMOS™
and is optimized to minimize EMI and to provide high
circuit efficiency. This is done by reducing the switch on
slope when reaching the CoolMOS™ threshold. This is
achieved by a slope control of the rising edge at the
driver’s output (see Figure 19).
Thus the leading switch on spike is minimized. When
CoolMOS™ is switched off, the falling shape of the
driver is slowed down when reaching 2V to prevent an
overshoot below ground. Furthermore the driver circuit
is designed to eliminate cross conduction of the output
stage. At voltages below the undervoltage lockout
threshold V
the gate drive is active low.
VCCoff
(see Figure
csth
/dt = 0.8V/µs, and a
Propagation Delay
=180ns
V/us
Datasheet V4.5 13 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
ca. t = 130ns
V
Gate
5V
t
Figure 19 Gate Rising Slope
3.8 Protection Unit (Auto Restart Mode)
An overload, open loop and overvoltage detection is
integrated within the Protection Unit. These three
failure modes are latched by an Error-Latch. Ad ditiona l
thermal shutdown is latched by the Error-Latch. In case
of those failure modes the Error-Latch is set after a
blanking time of 5µs and the CoolMOS™ is shut down.
That blanking prevents the Error-Latch f rom distor tions
caused by spikes during operation mode.
3.8.1 Overload / Open L oop with Normal Load
Figure 20 shows the Auto Restart Mode in case of
overload or open loop with normal load. The detection
of open loop or overload is provided by the Comparator
C3, C4 and the AND-gate G2 (see Figure 21). The
detection is activated by C4 when the voltage at pin
SoftS exceeds 5.3V. Till this time the IC operates in the
Soft-Start Phase. After this phase the comparator C3
can set the Error-Latch in case of open loop or ove rload
which leads the feedback voltage V
threshold of 4.8V. After latching VCC decreases till
8.5V and inactivates the IC. At this time the external
Soft-Start capacitor is discharged by the internal
transistor T1 due to Power Down Reset. When the IC
is inactive V
the Capacitor C
R
Start-Up
Reset and the external Soft-Start capacitor C
charged by the internal pullup resistor R
the Soft-Start Phase which ends when the voltage at
pin SoftS exceeds 5.3V the detection of overload and
open loop by C3 and G2 is inactive. In this way the Start
Up Phase is not detected as an overload.
increases till V
VCC
by means of the Start-Up Resistor
VCC
. Then the Error-Latch is reset by Power Up
CCon
to exceed the
FB
= 13.5V by charging
is
Soft-Start
. During
Soft-Start
Overload / Open Loop wi th Normal Load
5µs Blanking
FB
4.8V
Soft S
5.3V
Dri ver
VCC
13.5V
8.5V
Fail ure
Dete cti on
Soft-St art Phase
T
Burst1
Figure 20 Auto Restart Mode
So ftS
FB
C
6.5V
Soft-S ta rt
R
Soft-S ta rt
T1
R
FB
6.5V
Power Up Reset
C4
5.3V
4.8V
C3
T
Restar t
t
t
t
t
Error-L a tch
G2
Figure 21 FB-Detection
Datasheet V4.5 14 Jan 2004

But the Soft-Start Phase must be finished within the
Start Up Phase to force the voltage at pin FB below the
failure detection threshold of 4.8V.
3.8.2 Overvoltage due to Open Loop with No Load
Open loop & no load condition
5µs Blanking
FB
4.8V
Failure
Detection
CoolSET™-F2
Functional Description
normal operation mode is prevented from overvoltage
detection due to varying of VCC concerning the
regulation of the converter output. When the voltage
is above 4.0V the overvoltage detection by C1 is
V
SoftS
deactivated.
VCC
So ftS
6.5V
16.5V
R
Soft-Start
4.0V
C1
C2
G1
Error L a tch
So ftS
5.3V
4.0V
Driver
VCC
16.5V
13.5V
8.5V
Soft- S ta rt P h a s e
Overvoltage
Detection Phase
Overvoltage D etection
T
Burst2
T
t
t
Restart
t
t
Figure 22 Auto Restart Mode
Figure 22 shows the Auto Restart Mode for open loop
and no load condition. In case of this failure mode the
converter output voltage increases and also VCC. An
additional protection by the comparators C1, C2 and
the AND-gate G1 is implemented to consider this
failure mode (see Figure 23).The overvoltage detection
is provided by Comparator C1 only in the first time
during the Soft-Start Phase till the Soft-Start voltage
exceeds the threshold of the Comparator C2 at 4.0V
and the voltage at pin FB is above 4.8V. When VCC
exceeds 16.5V during the overvoltage detect ion pha se
C1 can set the Error-Latch and the Burst Phase during
Auto Restart Mode is finished earlier. In that case
is shorter than T
T
Burst2
. By means of C2 the
Soft-Start
C
So ft-S tart
T1
Power Up Reset
Figure 23 Overvoltage Detection
3.8.3 Thermal Shut Down
Thermal Shut Down is latched by the Error-Latch when
junction temperature T
exceeding an internal threshold of 140°C. In that case
the IC switches in Auto Restart Mode.
Note: All the values which are mentioned in the
functional description are typical. Please refer
to Electrical Characteristics for min/max limit
values.
of the pwm controller is
j
Datasheet V4.5 15 Jan 2004
CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
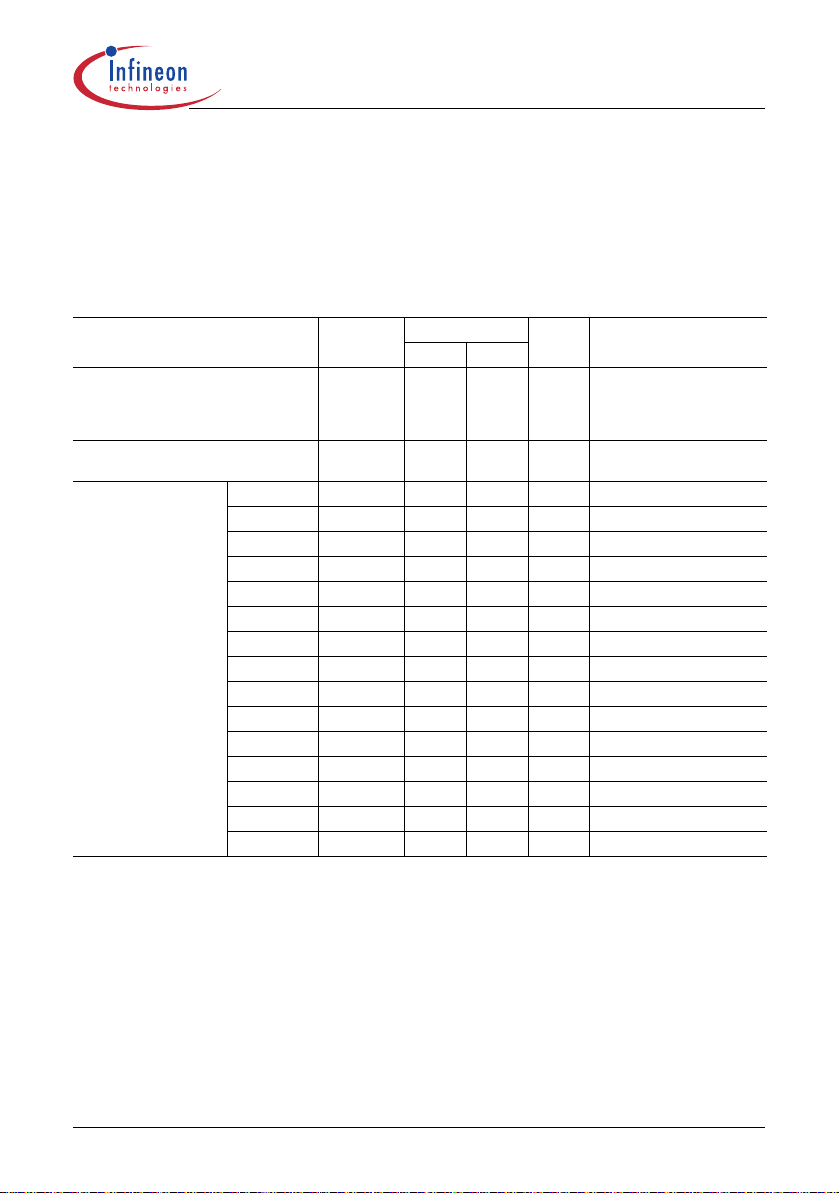
4 Electrical Characteristics
4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Note: Absolute maximum ratings are defined as ratings, which when being exceeded may lead to destruction
of the integrated circuit. For the same reason make sure, that any capacitor that will be connected to pin
(VCC) is discharged before assembling the application circuit.
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Remarks
min. max.
Drain Source Voltage
ICE2A0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2B0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2A0565Z
Drain Source Voltage
ICE2A180Z/280Z
Avalanche energy,
repetitive t
max. T
AR
=150°C
j
limited by
1)
ICE2A0565 E
ICE2A165 E
ICE2A265 E
ICE2A365 E
ICE2B0565 E
ICE2B165 E
ICE2B265 E
ICE2B365 E
ICE2A0565Z E
ICE2A180Z E
ICE2A280Z E
ICE2A765I E
ICE2B765I E
ICE2A765P2 E
ICE2B765P2 E
1)
Repetitive avalanche causes additional power losses that can be calculated as PAV=EAR* f
V
DS
V
DS
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
AR8
AR9
AR10
AR11
AR12
AR13
AR14
AR15
- 650 V Tj = 110°C
- 800 V Tj = 25°C
- 0.01 mJ
- 0.07 mJ
- 0.40 mJ
- 0.50 mJ
- 0.01 mJ
- 0.07 mJ
- 0.40 mJ
- 0.50 mJ
- 0.01 mJ
- 0.07 mJ
- 0.40 mJ
- 0.50 mJ
- 0.50 mJ
- 0.50 mJ
- 0.50 mJ
6
Datasheet V4.5 16 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Remarks
min. max.
Avalanche current,
repetitive tAR limited by
max. T
=150°C
j
VCC Supply Voltage V
FB Voltage V
SoftS Voltage V
I
Sense
Junction Temperature T
Storage Temperature T
Thermal Resistance
Junction-Ambient
ESD Robustness1)
1)
Equivalent to discharging a 100pF capacitor through a 1.5 kΩ series resistor
2)
1kV at pin drain of ICE2x0565, ICE2A0565Z
ICE2A0565 I
ICE2A165 I
ICE2A265 I
ICE2A365 I
ICE2B0565 I
ICE2B165 I
ICE2B265 I
ICE2B365 I
ICE2A0565Z I
ICE2A180Z I
ICE2A280Z I
ICE2A765I I
ICE2B765I I
ICE2A765P2 I
ICE2B765P2 I
AR1
AR2
AR3
AR4
AR5
AR6
AR7
AR8
AR9
AR10
AR11
AR12
AR13
AR14
AR15
I
Sense
R
R
V
CC
FB
SoftS
j
S
thJA1
thJA2
ESD
- 0.5 A
- 1 A
- 2 A
- 3 A
- 0.5 A
- 1 A
- 2 A
- 3 A
- 0.5 A
- 1 A
- 2 A
- 7 A
- 7 A
- 7 A
- 7 A
-0.3 22 V
-0.3 6.5 V
-0.3 6.5 V
-0.3 3 V
-40 150 °C Cont roller & CoolMOS™
-50 150 °C
- 90 K/W P-DIP-8-6
- 96 K/W P-DIP-7-1
- 2
2)
kV Human Body Model
Datasheet V4.5 17 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
4.2 Thermal Impedance (ICE2X765I and ICE2X765P2)
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Remarks
min. max.
Thermal Resistance
Junction-Ambient
Junction-Case ICE2A765I
4.3 Operating Range
Note: Within the operating range the IC operates as described in the functional description.
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Remarks
VCC Supply Voltage V
Junction Temperature of
Controller
Junction Temperature of
CoolMOS™
ICE2A765I
ICE2B765I
ICE2A765P2
ICE2B765P2
ICE2B765I
ICE2A765P2
ICE2B765P2
CC
T
JCon
T
JCoolMOS
R
thJA3
R
thJC
- 74 K/W Free standing with no heatsink
- 2.5 K/W
min. max.
V
CCoff
21 V
-25 130 ° C Limited due to thermal shut down
of controller
-25 150 ° C
Datasheet V4.5 18 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
4.4 Characteristics
Note: The electrical characteristics involve the spread of values given within the specified supply voltage and
junction temperature range T
are related to 25°C. If not otherwise stated, a supply voltage of V
4.4.1 Supply Section
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
Start Up Current I
Supply Current with Inactive
Gate
Supply Current
with Active Gate
Supply Current
with Activ Gate
VCC Turn-On Threshold
VCC Turn-Off Threshold
VCC Turn-On/Off Hysteresis
ICE2A0565 I
ICE2A165 I
ICE2A265 I
ICE2A365 I
ICE2B0565 I
ICE2B165 I
ICE2B265 I
ICE2B365 I
ICE2A0565Z I
ICE2A180Z I
ICE2A280Z I
ICE2A765I I
ICE2B765I I
ICE2A765P2 I
ICE2B765P2 I
from – 25 °C to 125 °C.Typical values represent the median values, which
J
= 15 V is assumed.
CC
min. typ. max.
VCC1
I
VCC2
VCC3
VCC4
VCC5
VCC6
VCC7
VCC8
VCC9
VCC10
VCC11
VCC12
VCC13
VCC14
VCC15
VCC16
VCC17
VCCon
VCCoff
VCCHY
- 27 55 µA VCC=V
- 5.0 6.6 mA V
IFB = 0
- 5.3 6.7 mA V
- 6.5 7.8 mA V
IFB = 0
IFB = 0
- 6.7 8.0 mA V
IFB = 0
- 8.5 9.8 mA V
- 5.2 6.7 mA V
IFB = 0
IFB = 0
- 5.5 7.0 mA V
IFB = 0
- 6.1 7.3 mA V
IFB = 0
- 7.1 8.3 mA V
- 5.3 6.7 mA V
IFB = 0
IFB = 0
- 6.5 7.8 mA V
IFB = 0
- 7.7 9.0 mA V
- 8.5 9.8 mA V
IFB = 0
IFB = 0
- 7.1 8.3 mA V
IFB = 0
- 8.5 9.8 mA V
- 7.1 8.3 mA V
13
-
4.5
13.5
8.5
5
14
-
5.5
V
V
V
IFB = 0
IFB = 0
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
SoftS
CCon
= 0
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
= 5V
-0.1V
Datasheet V4.5 19 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
4.4.2 Internal Voltage Reference
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. typ. max.
Trimmed Reference Voltage V
REF
4.4.3 Control Section
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
Oscillator Frequency
ICE2A0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2A0565Z/180Z/280Z
Oscillator Frequency
ICE2B0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
Reduced Osc. Frequency
ICE2A0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2A0565Z/180Z/280Z
Reduced Osc. Frequency
ICE2B0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
Frequency Ratio f
ICE2A0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2A0565Z/180Z/280Z
Frequency Ratio f
ICE2B0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
Max Duty Cycle D
Min Duty Cycle D
PWM-OP Gain A
VFB Operating Range Min Level V
VFB Operating Range Max level V
Feedback Resistance R
Soft-Start Resistance R
osc1/fosc2
osc3/fosc4
6.37 6.50 6.63 V measured at pin FB
min. typ. max.
f
OSC1
f
OSC3
f
OSC2
f
OSC4
93 100 107 kHz VFB = 4V
62 67 72 kHz VFB = 4V
- 21.5 - kHz VFB = 1V
- 20 - kHz VFB = 1V
4.5 4.65 4.9
3.18 3.35 3.53
max
min
V
FBmin
FBmax
FB
Soft-Start
0.67 0.72 0.77
0 - - VFB < 0.3V
3.45 3.65 3.85
0.3 - - V
- - 4.6 V
3.0 3.7 4.9 kΩ
42 50 62 kΩ
Datasheet V4.5 20 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
4.4.4 Protection Unit
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. typ. max.
Over Load & Open Loop
Detection Limit
Activation Limit of Overload &
Open Loop Detection
Deactivation Limit of
Overvoltage Detection
Overvoltage Detection Limit V
Latched Thermal Shutdown T
Spike Blanking t
1)
The parameter is not subjec t to pr o duction test - varified by design/characterization
4.4.5 Current Limiting
Parameter Symbol Limit Valu es Unit Test Condition
Peak Current Limitation
(incl. Propagation Delay Time)
Leading Edge Blanking t
V
V
V
FB2
SoftS1
SoftS2
VCC1
jSD
Spike
V
LEB
csth
4.65 4.8 4.95 V V
SoftS
> 5.5V
5.15 5.3 5.46 V VFB > 5V
3.88 4.0 4.12 V VFB > 5V
VCC > 17.5V
16 16.5 17.2 V V
130 140 150 °C
< 3.8V
SoftS
VFB > 5V
1)
- 5 - µs
min. typ. max.
0.95 1.0 1.05 V dV
sense
- 220 - ns
/ dt = 0.6V/µs
Datasheet V4.5 21 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
4.4.6 CoolMOS™ Section
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. typ. max.
Drain Source Breakdown Voltage
ICE2A0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2B0565/165/265/365/765I/765P2
ICE2A0565Z
Drain Source Breakdown Voltage
ICE2A180Z/280Z
Drain Source
On-Resistance
ICE2A0565 R
ICE2A165 R
ICE2A265 R
ICE2A365 R
ICE2B0565 R
ICE2B165 R
ICE2B265 R
ICE2B365 R
ICE2A0565Z R
ICE2A180Z R
ICE2A280Z R
ICE2A765I R
ICE2B765I R
ICE2A765P2 R
ICE2B765P2 R
V
(BR)DSS
V
(BR)DSS
DSon1
DSon2
DSon3
DSon4
DSon5
DSon6
DSon7
DSon8
DSon9
DSon10
DSon11
DSon12
DSon13
DSon14
DSon15
600
650--
800
870--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
4.7
10.0
3
6.6
0.9
1.9
0.45
0.95
4.7
10.0
3
6.6
0.9
1.9
0.45
0.95
4.7
10.0
3
6.6
0.8
1.7
0.45
0.95
0.45
0.95
0.45
0.95
0.45
0.95
-
-
-
-
5.5
12.5ΩΩ
3.3
7.3
1.08
2.28ΩΩ
0.54
1.14ΩΩ
5.5
12.5ΩΩ
3.3
7.3
1.08
2.28ΩΩ
0.54
1.14ΩΩ
5.5
12.5ΩΩ
3.3
7.3
1.06
2.04ΩΩ
0.54
1.14ΩΩ
0.54
1.14ΩΩ
0.54
1.14ΩΩ
0.54
1.14ΩΩ
V
V
V
V
Ω
Ω
Tj=25°C
Tj=110°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=110°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Ω
Ω
Ω
Ω
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Tj=25°C
Tj=125°C
Datasheet V4.5 22 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. typ. max.
Effective output
capacitance,
energy related
Zero Gate Voltage Drain Current I
Rise Time t
Fall Time t
1)
Measured in a Typical Flyback Converter Application
ICE2A0565 C
ICE2A165 C
ICE2A265 C
ICE2A365 C
ICE2B0565 C
ICE2B165 C
ICE2B265 C
ICE2B365 C
ICE2A0565Z C
ICE2A180Z C
ICE2A280Z C
ICE2A765I C
ICE2B765I C
ICE2A765P2 C
ICE2B765P2 C
o(er)1
o(er)2
o(er)3
o(er)4
o(er)5
o(er)6
o(er)7
o(er)8
o(er)9
o(er)10
o(er)11
o(er)12
o(er)13
o(er)14
o(er)15
DSS
rise
fall
- 4.751 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 7 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 21 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 30 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 4.751 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 7 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 21 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 30 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 4.751 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 7 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 22 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 30 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 30 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 30 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 30 - pF VDS =0V to 480V
- 0.5 - µA V
- 30
- 30
1)
1)
- ns
- ns
VCC
=0V
Datasheet V4.5 23 Jan 2004

Typical Performance Charac t er is ti cs
5 Typical Performance Characteristics
CoolSET™-F2
40
38
36
[µA]
34
VCC1
32
30
28
26
Start Up Current I
24
22
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 24 Start Up Current I
5,9
5,7
5,5
[mA]
VCC2
5,3
5,1
4,9
Supply Current I
4,7
4,5
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 25 Static Supply Current I
8,8
8,4
8,0
7,6
[mA]
7,2
VCCi
6,8
6,4
6,0
5,6
5,2
4,8
Supply Current I
4,4
4,0
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 26 Supply Current I
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
VCC1
Junction Temperature [°C]
VCC2
ICE2A365
ICE2A165
ICE2A0565
/Z
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
VCCI
j
vs. T
j
j
ICE2A265
7,1
6,9
6,7
6,5
[mA]
6,3
VCCi
6,1
5,9
5,7
PI-001-190101
5,5
5,3
5,1
Supply Current I
4,9
4,7
4,5
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 27 Supply Current I
8,5
8,3
8,1
7,9
7,7
[mA]
7,5
7,3
VCCi
7,1
6,9
PI-003-190101
6,7
6,5
6,3
6,1
Supply Current I
5,9
5,7
5,5
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 28 Supply Current I
9,0
8,8
8,6
8,4
8,2
[mA]
8,0
VCCi
7,8
7,6
7,4
PI-002-190101
7,2
7,0
6,8
Supply Current I
6,6
6,4
6,2
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 29 Supply Current I
ICE2B365
ICE2B265
ICE2B165
ICE2B0565
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
VCCI
ICE2A180Z
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
VCCI
ICE2A765P2
ICE2B765P2
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
VCCI
PI-002-190101
j
ICE2A280Z
PI-002-190101
j
PI-002-190101
j
Datasheet V4.5 24 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Typical Performance Charac t er is ti cs
13,58
13,56
[V]
13,54
CCon
13,52
13,50
13,48
13,46
13,44
VCC Turn-On Threshold V
13,42
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 30 VCC Turn-On Threshold V
8,67
8,64
[V]
8,61
VCCoff
8,58
8,55
8,52
8,49
8,46
8,43
VCC Turn-Off Threshold V
8,40
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Figure 31 VCC Turn-Off Threshold V
5,10
[V]
5,07
CCHY
5,04
5,01
4,98
4,95
4,92
4,89
4,86
4,83
VCC Turn-On/Off Hysteresis V
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
VCCon
Junction Temperature [°C]
VCCoff
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 32 VCC Turn-On/Off HysteresisV
vs. T
vs. T
VCCHY
j
j
vs. T
6,510
[V]
6,505
REF
6,500
6,495
6,490
PI-004-190101
6,485
6,480
6,475
Trimmed Reference Voltage V
6,470
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 33 Trimmed Reference V
102,0
101,5
101,0
[kHz]
100,5
OSC1
100,0
99,5
PI-005-190101
99,0
98,5
98,0
97,5
Oscillator Frequency f
97,0
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 34 Oscillator Frequency f
70,0
69,5
69,0
[kHz]
68,5
68,0
OSC3
67,5
67,0
PI-006-190101
66,5
66,0
65,5
65,0
64,5
Oscillator Frequency f
64,0
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 35 Oscillator Frequency f
j
Junction Temperature [°C]
ICE2A0565
ICE2A165
ICE2A265
ICE2A365
ICE2A180Z
ICE2A280Z
ICE2A765P2
ICE2B0565
ICE2B165
ICE2B265
ICE2B365
ICE2B765P2
REF
/Z
OSC1
OSC3
vs. T
vs. T
vs. T
PI-007-190101
j
PI-008-190101
j
PI-008a-190101
j
Datasheet V4.5 25 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Typical Performance Charac t er is ti cs
22,0
21,8
[kHz]
21,6
OSC2
21,4
21,2
21,0
20,8
20,6
20,4
20,2
Reduced Osc. Frequency f
20,0
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
ICE2A0565
ICE2A165
ICE2A265
ICE2A365
ICE2A180Z
ICE2A280Z
ICE2A765P2
/Z
Figure 36 Reduced Osc. Frequency f
21,0
20,8
[kHz]
20,6
OSC4
20,4
20,2
20,0
19,8
19,6
19,4
19,2
Reduced Osc. Frequency f
19,0
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
ICE2B0565
ICE2B165
ICE2B265
ICE2B365
ICE2B765P2
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 37 Reduced Osc. Frequency f
4,75
4,73
4,71
OSC2
/f
4,69
OSC1
4,67
4,65
4,63
4,61
4,59
Frequency Ratio f
4,57
4,55
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 38 Frequency Ratio f
ICE2A0565
ICE2A165
ICE2A265
ICE2A365
ICE2A180Z
ICE2A280Z
ICE2A765P2
OSC1
/Z
/ f
OSC2
OSC2
OSC4
vs. T
vs. T
vs. T
3,45
3,43
3,41
OSC4
/f
3,39
OSC3
3,37
3,35
PI-009-190101
3,33
3,31
3,29
Frequency Ratio f
3,27
3,25
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Figure 39 Frequency Ratio f
j
0,730
0,728
0,726
0,724
0,722
0,720
PI-009a-190101
0,718
0,716
Max. Duty Cycle
0,714
0,712
0,710
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Figure 40 Max. Duty Cycle vs. T
j
3,70
3,69
3,68
3,67
V
3,66
3,65
PI-010-190101
3,64
3,63
PWM-OP Gain A
3,62
3,61
3,60
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
j
Figure 41 PWM-OP Gain AV vs. T
Junction Temperature [°C]
Junction Temperature [°C]
Junction Temperature [°C]
ICE2B0565
ICE2B165
ICE2B265
ICE2B365
ICE2B765P2
OSC3
PI-010a-190101
/ f
vs. T
OSC4
j
PI-011-190101
j
PI-012-190101
j
Datasheet V4.5 26 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Typical Performance Charac t er is ti cs
4,00
3,95
3,90
[kOhm]
3,85
FB
3,80
3,75
3,70
3,65
3,60
3,55
Feedback Resistance R
3,50
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 42 Feedback Resistance RFB vs. T
58
56
[kOhm]
54
52
Soft-Start
50
48
46
44
42
40
Soft-Start Resistance R
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Figure 43 Soft-Start Resistance R
4,810
4,805
[V]
4,800
FB2
4,795
4,790
Detection Limit V
4,785
4,780
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 44 Detection Limit V
Junction Temperature [°C]
Soft-Start
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
FB2
j
j
vs. T
5,320
5,315
5,310
[V]
5,305
5,300
Soft-Start1
5,295
PI-013-190101
5,290
5,285
5,280
Detection Limit V
5,275
5,270
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 45 Detection Limit V
4,05
4,04
4,03
[V]
4,02
4,01
Soft-Start2
4,00
PI-014-190101
3,99
3,98
3,97
Detection Limit V
3,96
3,95
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
j
Figure 46 Detection Limit V
16,80
16,75
[V]
16,70
VCC1
16,65
16,60
16,55
16,50
PI-015-190101
16,45
16,40
16,35
16,30
16,25
16,20
Overvoltage Detection Limit V
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 47 Overvoltage Detection Limit V
Junction Temperature [°C]
Soft-Start1
Junction Temperature [°C]
Soft-Start2
Junction Temperature [°C]
vs. T
vs. T
j
j
VCC1
vs. T
PI-016-190101
PI-017-190101
PI-018-190101
j
Datasheet V4.5 27 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Typical Performance Charac t er is ti cs
1,010
1,008
[V]
1,006
csth
1,004
1,002
1,000
0,998
0,996
0,994
0,992
Peak Current Limitation V
0,990
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Figure 48 Peak Current Limitation V
280
270
[ns]
260
LEB
250
240
230
220
210
200
190
Leading Edge Blanking t
180
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Figure 49 Leading Edge Blanking V
1,0
0,9
0,8
[Ohm]
0,7
dson
0,6
0,5
0,4
On-Resistance R
0,3
0,2
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Junction Temperature [°C]
ICE2A365
ICE2B365
Junction Temperature [°C]
csth
VCC1
vs. T
Figure 50 Drain Source On-Resistance R
vs. T
DSon
j
j
vs. T
2,2
2,0
1,8
[Ohm]
1,6
dson
1,4
1,2
PI-019-190101
1,0
0,8
On-Resistance R
0,6
0,4
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
ICE2A265
ICE2B265
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 51 Drain Source On-Resistance R
9,5
8,5
7,5
[Ohm]
6,5
dson
5,5
PI-020-190101
4,5
3,5
On-Resistance R
2,5
1,5
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
ICE2A0565
/Z
ICE2B0565
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 52 Drain Source On-Resistance R
1,0
0,9
0,8
[Ohm]
0,7
dson
0,6
PI-022-190101
0,5
0,4
On-Resistance R
0,3
0,2
-25-15-5 5 152535455565758595105115125
Figure 53 Drain Source On-Resistance R
j
ICE2A765P2
ICE2B765P2
Junction Temperature [°C]
ICE2A280Z
ICE2A165
ICE2B165
ICE2A180Z
DSon
DSon
DSon
vs. T
vs. T
vs. T
PI-022-190101
j
PI-022-190101
j
PI-022-190101
j
Datasheet V4.5 28 Jan 2004

720
700
[V]
680
(BR)DSS
660
640
620
600
580
Breakdown Voltage V
560
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 54 Breakdown Voltage V
940
[V]
920
900
(BR)DSS
880
860
840
820
800
Breakdown Voltage V
780
-25 -15 -5 5 15 25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
Junction Temperature [°C]
Figure 55 Breakdown Voltage V
ICE2A0565
ICE2A165
ICE2A265
ICE2A365
ICE2B0565
ICE2B165
ICE2B265
ICE2B365
ICE2A765P2
ICE2B765P2
ICE2A180Z
ICE2A280Z
/Z
BR(DSS)
BR(DSS)
vs. T
vs. T
CoolSET™-F2
Typical Performance Charac t er is ti cs
PI-025-190101
j
PI-025-190101
j
Datasheet V4.5 29 Jan 2004

CoolSET™-F2
Layout Recommendation for C
6 Layout Recommendation for C
Note: Only for ICE2A765I/P2 and ICE2B765I/P2
18
Soft Start Capacitor Layout Recommendation in Detail
Detail X
Figure 56B Detail X, Soft Start Capacitor C18 Layout
Recommendation
Place Soft Start capacitor C18 in the same way as
shown in Detail X (blue mark).
18
Figure 56A Layout of Board EVALSF2_ICE2B765P2
To improve the startup behavior of the IC during
startup or auto restart mode, place the soft start
capacitor C
as close as possible to the soft start PIN 6 and
GND PIN 4. More details see Detail X in Figure
56B.
Figure 56 Layout Recommendation for ICE2A765I/P2 and ICE2B765I/P2
Datasheet V4.5 30 Jan 2004
(red section Detail X in Figure 56A)
18

7 Outline Dimension
P-DIP-8-6
(Plastic Dual In-line
Package)
Figure 57 P-DIP-8-6 (Plastic Dual In-line Package)
CoolSET™-F2
Outline Dimension
P-DIP-7-1
(Plastic Dual In-line
Package)
1.7 MAX.
4.37 MAX.
0.38 MIN.
2.54
±0.1
0.46
Index Marking
1)
Does not include plastic or metal protrusion of 0.25 max. per side
7
1
9.52
±0.25
0.35
7x
3.25 MIN.
5
4
1)
Figure 58 P-DIP-7-1 (Plastic Dual In-line Package)
Datasheet V4.5 31 Jan 2004
7.87
8.9
±0.38
±1
+0.1
0.25
1)
±0.25
6.35
Dimensions in mm

CoolSET™-F2
Outline Dimension
P-TO220-6-46
Isodrain Package
±0.3
±0.3
10.2
12.1
0...0.15
Figure 59 P-TO220-6-46 (Isodrain Package)
P-TO220-6-47
Isodrain Package
±0.3
±0.3
15.6
17.5
0...0.15
8
4 x 1.27
13
1.274 x
7.62
9.9
9.5
7.62
9.9
7.5
6.6
7.5
6.6
±0.2
±0.2
A
1.3
+0.1
-0.02
4.4
B
(0.8)
0.05
1)
±0.3
8.6
0.25 AMB
±0.1
6 x 0.6
1) Shear and punch direction no burrs this surface
Back side, heatsink contour
All metal surfaces tin plated, except area of cut.
A
±0.2
2.8
-0.15
3.7
±0.3
1.3
5.3
0.05
+0.1
-0.02
B
2.4
±0.3
±0.3
8.4
4.4
1)
8.6
6 x 0.6
0.25 AMB
±0.1
5.3
2.4
±0.3
8.4
±0.3
±0.2
9.2
±0.2
9.2
0.5
0.5
±0.1
±0.1
1) Shear and punch direction no burrs this surface
Back side, heatsink contour
All metal surfaces tin plated, except area of cut.
Figure 60 P-TO220-6-47 (Isodrain Package)
Dimensions in mm
Datasheet V4.5 32 Jan 2004

Total Quality Management
Qualität hat für uns eine umfassende
Bedeutung. Wir wollen allen Ihren
Ansprüchen in der bestmöglichen
Weise gerecht werden. Es geht uns also
nicht nur um die Produktqualität –
unsere Anstrengungen gelten
gleichermaßen der Lieferqualität und
Logistik, dem Service und Support
sowie allen sonstigen Beratungs- und
Betreuungsleistungen.
Dazu gehört eine bestimmte
Geisteshaltung unserer Mitarbeiter.
Total Quality im Denken und Handeln
gegenüber Kollegen, Lieferanten und
Ihnen, unserem Kunden. Unsere
Leitlinie ist jede Aufgabe mit „Null
Fehlern“ zu lösen – in offener
Sichtweise auch über den eigenen
Arbeitsplatz hinaus – und uns ständig
zu verbessern.
Unternehmensweit orientieren wir uns
dabei auch an „top“ (Time Optimized
Processes), um Ihnen durch größere
Schnelligkeit den entscheidenden
Wettbewerbsvorsprung zu verschaffen.
Geben Sie uns die Chance, hohe
Leistung durch umfassende Qualität zu
beweisen.
Wir werden Sie überzeugen.
Quality takes on an allencompassing
significance at Semiconductor Group.
For us it means living up to each and
every one of your demands in the best
possible way. So we are not only
concerned with product quality. We
direct our efforts equally at quality of
supply and logistics, service and
support, as well as all the other ways in
which we advise and attend to you.
Part of this is the very special attitude of
our staff. Total Quality in thought and
deed, towards co-workers, suppliers
and you, our customer. Ou r gui del ine i s
“do everything with zero defects”, in an
open manner that is demonstrated
beyond your immediate workplace, and
to constantly improve.
Throughout the corporation we also
think in terms of Time Optimized
Processes (top), greater speed on our
part to give you that decisive
competitive edge.
Give us the chance to prove the best of
performance through the best of quality
– you will be convinced.
http://www.infineon.com
Published by Infineon Technologies AG

This datasheet has been download from:
www.datasheetcatalog.com
Datasheets for electronics components.
 Loading...
Loading...