
C505
C505C
Data Sheet, Dec. 2000
C505A
C505CA
8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
Microcontrollers
Never stop thinking.

Edition 2000-12
Published by Infineon Technologies AG,
St.-Martin-Strasse 53,
D-81541 München, Germany
© Infineon Technologies AG 2000.
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
The information herein is given to descr ibe certain components and shall not be considere d as warranted
characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
We hereby disclaim any and all warranties, including but not limited to warranties of non-infringement, regarding
circuits, descriptions and charts stated her ein.
Infineon Technologies is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Information
For further information on tech nology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your nearest
Infineon Technologies Office in Germany or our Infineon Technologies Representatives worldwide (see address
list).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements co mponents may contain dangerous substan ce s. For information on the t yp es in
question please contact your neares t Infineon Technologies Office.
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the express written
approval of Infineon T echnologies, if a f ailure of such components can reasonably be expected to cause the failure
of that lif e - su ppo rt de vi ce o r system, or to aff ec t th e sa fety or effectiveness of th a t d evice or system. L i fe support
devices or systems are inten ded to be implante d in the human body, or to support and/or maintain and sustain
and/or protect human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may
be endangered.

C505
C505C
Data Sheet, Dec. 2000
C505A
C505CA
8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
Microcontrollers
Never stop thinking.

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA Data Sheet
Revision History : Current Version : 2000-12
Previous Releases : 08.00, 06.00, 07.99, 12.97
Page
(in previous
version
24 24 Version register VR2 for C505A-4R/C505CA-4R BB step is updated.
Page
(in current
version)
Subjects (major changes since last revision)
Controller Area Network (CAN): License of Robert Bosch GmbH
We Listen to Your Comments
Any information within this document that you feel is wrong, unc lea r or missing at all?
Your feedback will help us to continuously improve the quality of this document.
Please send your proposal (including a reference to this document) to:
mcdocu.comments@infineon.com
8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
C500 Family
Advance Information
• Fully compatible to standard 8051 microcontroller
• Superset of the 8051 architecture with 8 datapointers
• Up to 20 MHz operating frequency
– 375 ns instruction cycle time @16 MHz
– 300 ns instruction cycle time @20 MHz (50 % duty cycle)
• On-chip program memory (with optional memory protection)
– C505(C)(A)-2R : 16K byte on-chip ROM
– C505A-4R/C505CA-4R: 32K byte on-chip ROM
– C505A-4E/C505CA-4E: 32K byte on-chip OTP
– alternatively up to 64k byte external program memory
• 256 byte on-chip RAM
• On-chip XRAM
– C505/C505C : 256 byte
– C505A/C505CA : 1K byte
(more features on next page)
C505/C505C/C505A/
C505CA
Oscillator
Watchdog
A/D Converter
C505/C505C : 8-bit
C505A/C505CA : 10-bit
Timer 2
Full-CAN Controller
C505C/C505CA only
Watchdog Timer
On-Chip Emulation Support Module
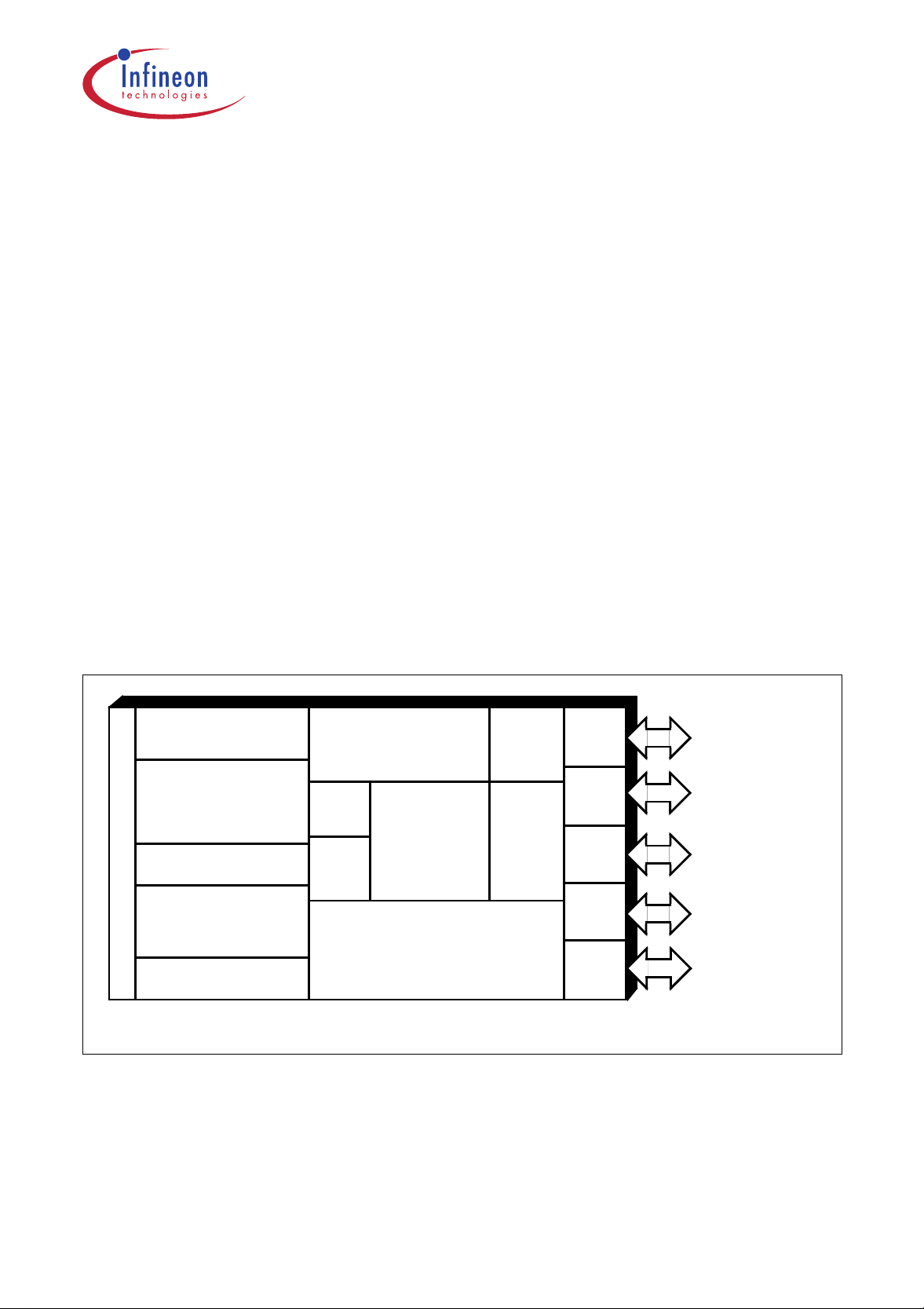
Figure 1
C505 Functional Units
XRAM
C505/C505C: 256 byte
C505A/C505CA: 1K byte
Timer
0
Timer
1
Program Memory
C505A-4R/C505CA -4R : 32K ROM
C505A-4E/C505CA-4E : 32K OTP
C500
Core
8 Datapointers
C505(C)(A)-2R : 16K ROM
RAM
256 byte
8-bit
USART
Port 0
Port 1
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
I/O
8 analog inputs /
8 digit. I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O (2-bit I/O port)
Data Sheet 1 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Features (continued) :
• 32 + 2 digital I/O lines
– Four 8-bit digital I/O ports
– One 2-bit digital I/O port (port 4)
– Port 1 with mixed analog/digital I/O capability
• Three 16-bit timers/counters
– Timer 0 / 1 (C501 compatible)
– Timer 2 with 4 channels for 16-bit capture/compare operation
• Full duplex serial interface with programmable baudrate generator (USART)
• Full CAN Module, version 2.0 B compliant (C505C and C505CA only)
– 256 register/data bytes located in external data memory area
– 1 MBaud CAN baudrate when operating frequency is equal to or above 8 MHz
– internal CAN clock prescaler when input frequency is over 10 MHz
• On-chip A/D Converter
– up to 8 analog inputs
– C505/C505C : 8-bit resolution
– C505A/C505CA: 10-bit resolution
• Twelve interrupt sources with four priority levels
• On-chip emulation support logic (Enhanced Hooks Technology
TM
)
• Programmable 15-bit watchdog timer
• Oscillator watchdog
• Fast power on reset
• Power Saving Modes
– Slow-down mode
– Idle mode (can be combined with slow-down mode)
– Software power-down mode with wake up capability through P3.2/INT0
or P4.1/RXDC pin
• P-MQFP-44 package
• Pin configuration is compatible to C501, C504, C511/C513-family
• Temperature ranges:
SAB-C505 versions T
SAF-C505 versions T
SAH-C505 versions T
SAK-C505 versions T
= 0 to 70 °C
A
= -40 to 85°C
A
= -40 to 110°C
A
= -40 to 125°C
A
Data Sheet 2 12.00
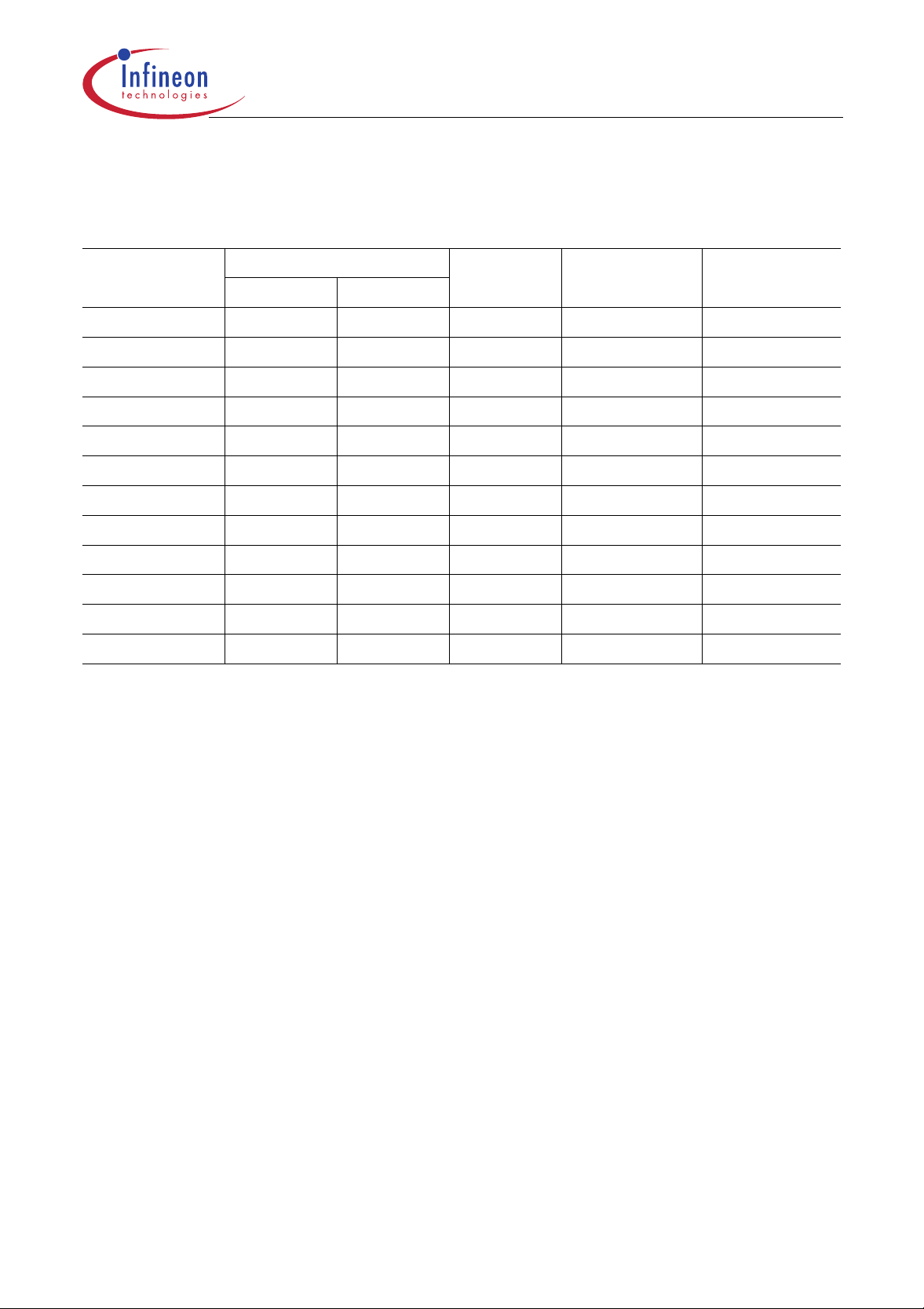
Table 1
Differences in Functionality of the C505 MCUs
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Device Internal Program Memory XRAM Size A/D Converter
ROM OTP
C505-2R 16K byte – 256 byte 8 Bit –
C505-L – – 256 byte 8 Bit –
C505C-2R 16K byte – 256 byte 8 Bit √
C505C-L – – 256 byte 8 Bit √
C505A-4R 32K byte – 1K byte 10 Bit –
C505A-2R 16K byte – 1K byte 10 Bit –
C505A-L – – 1K byte 10 Bit –
C505CA-4R 32K byte – 1K byte 10 Bit √
C505CA-2R 16K byte – 1K byte 10 Bit √
C505CA-L – – 1 K byte 10 Bit √
C505A-4E – 32K byte 1K byte 10 Bit –
C505CA-4E – 32K byte 1K byte 10 Bit √
Note: The term C505 refers to all versions described within this document unless otherwise noted.
However the term C505 may also be restricted by the context to refer to only CAN-less
derivatives with 8-Bit ADC which are C505-2R and C505-L in this document.
Resolution
CAN
Controller
Note: The term C505(C)(A)-2R, for simplicity, is used to stand for C505 16K byte ROM versions
within this document which are C505-2R, C505C-2R, C505A-2R and C505CA-2R.
Ordering Information
The ordering code for Infineon Technologies’ microcontrollers provides an exact reference to the
required product. This ordering code identifies:
• the derivative itself, i.e. its function set
• the specificed temperature rage
• the package and the type of delivery
For the available ordering codes for the C505 please refer to the “Product information
Microcontrollers”, which summarizes all available microcontroller variants.
Data Sheet 3 12.00
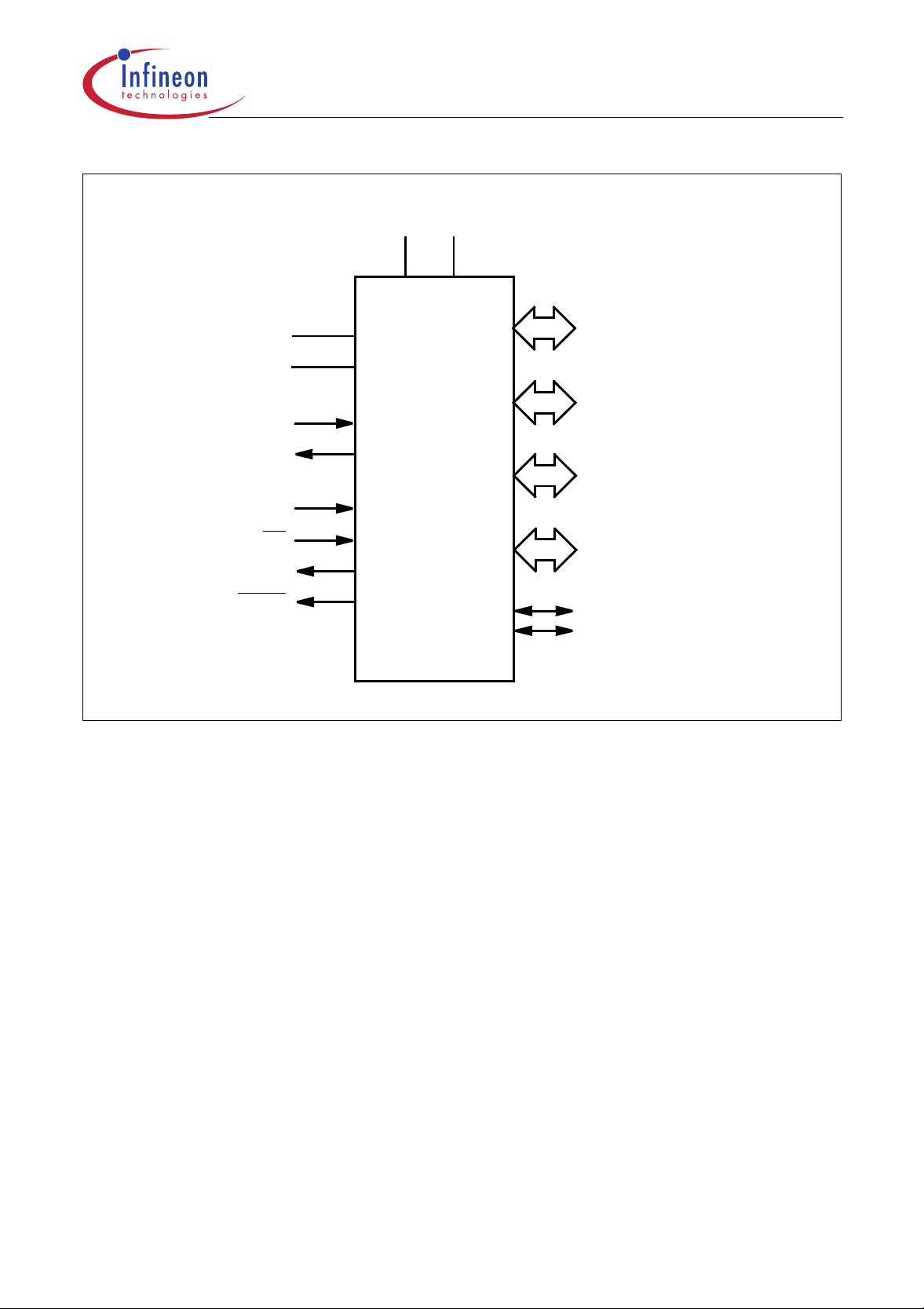
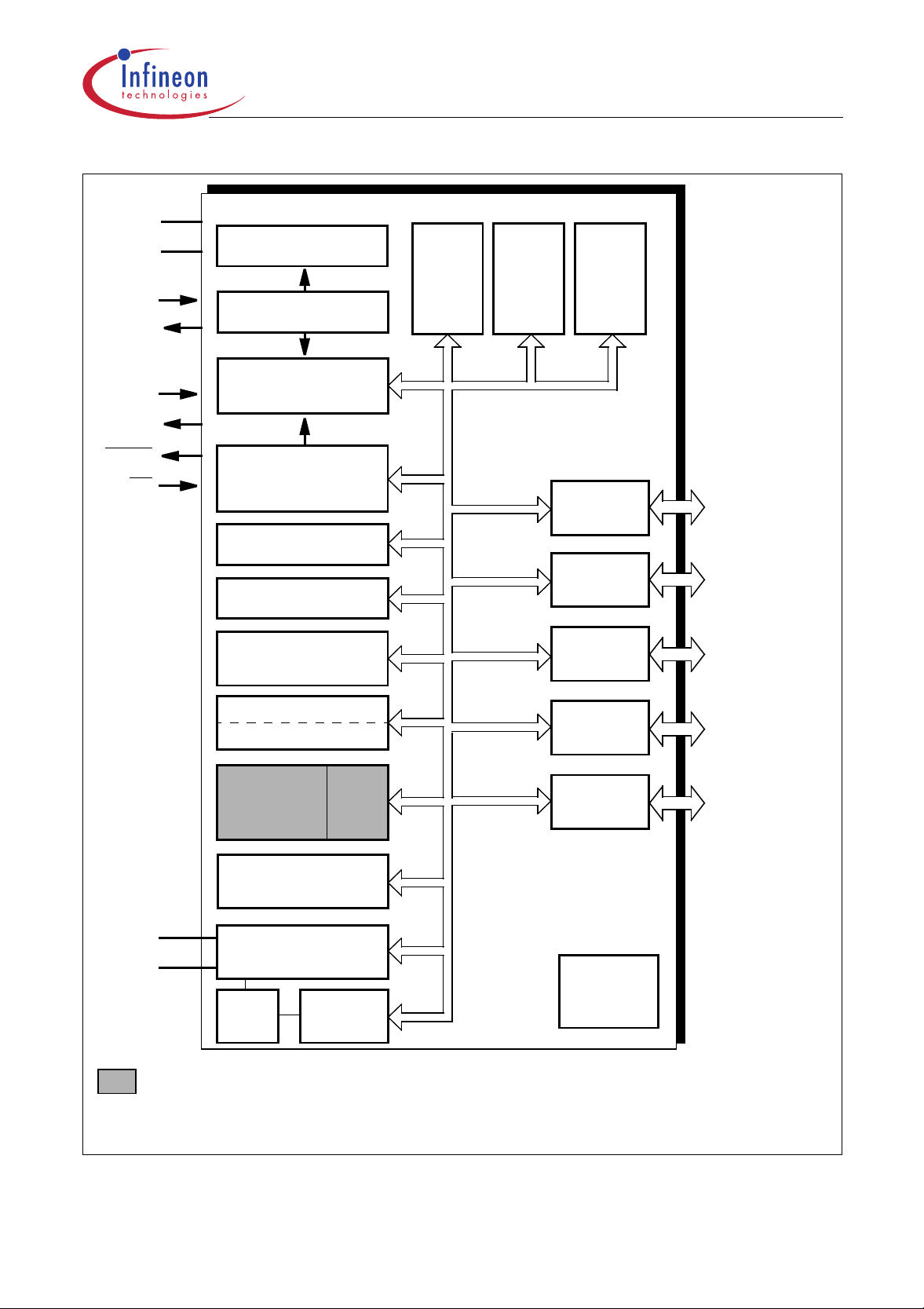
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
V
DDVSS
RESET
Figure 2
Logic Symbol
V
AREF
V
AGND
XTAL1
XTAL2
EA
ALE
PSEN
C505
C505C
C505A
C505CA
Port 0
8-bit Digital I/O
Port 1
8-bit Digital I/O /
8-bit Analog Inputs
Port 2
8-bit Digital I/O
Port 3
8-bit Digital I/O
Port 4
2-bit Digital I/O
Note: The ordering codes for the Mask-ROM versions are defined for each product after
verification of the respective ROM code.
Data Sheet 4 12.00
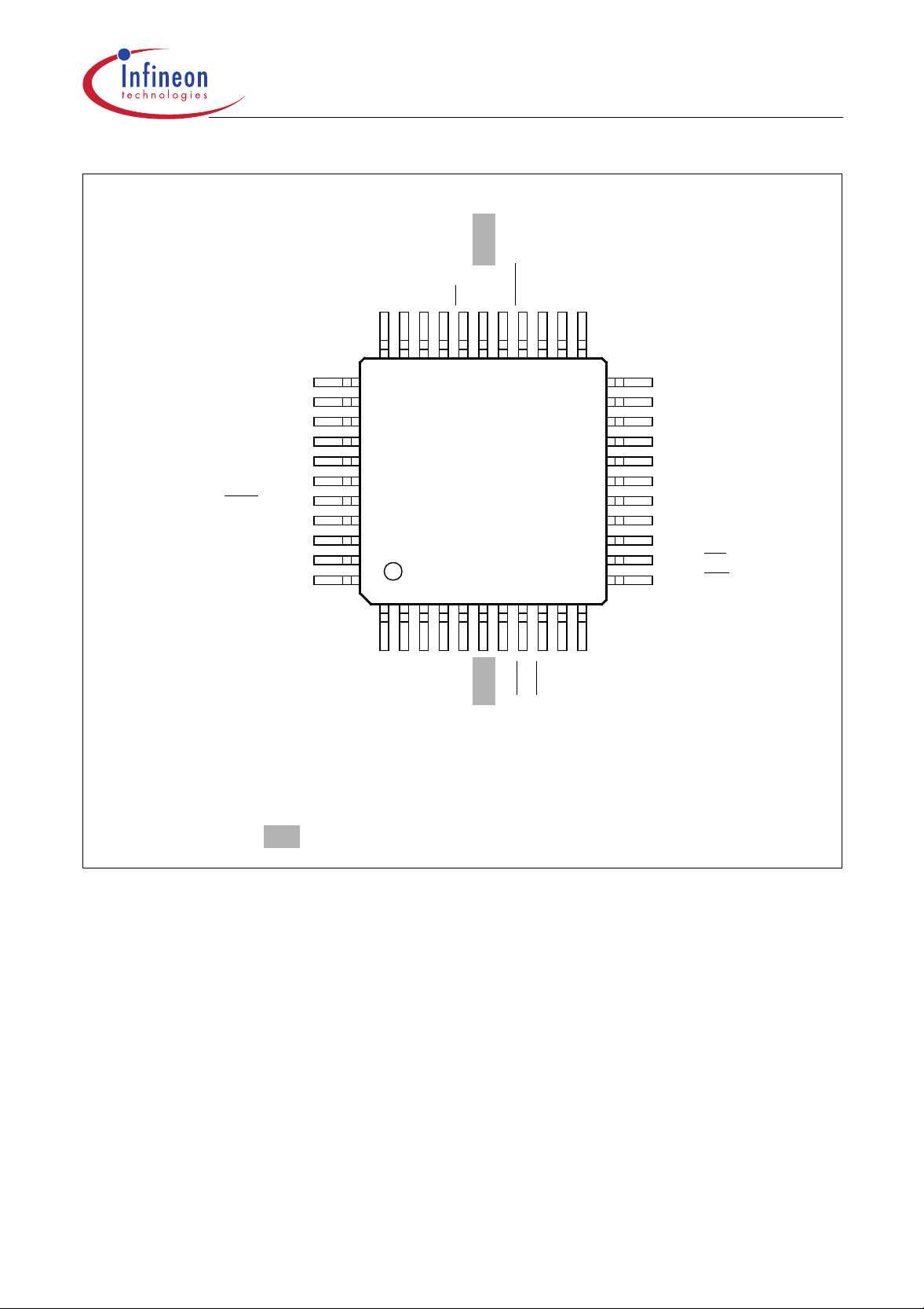
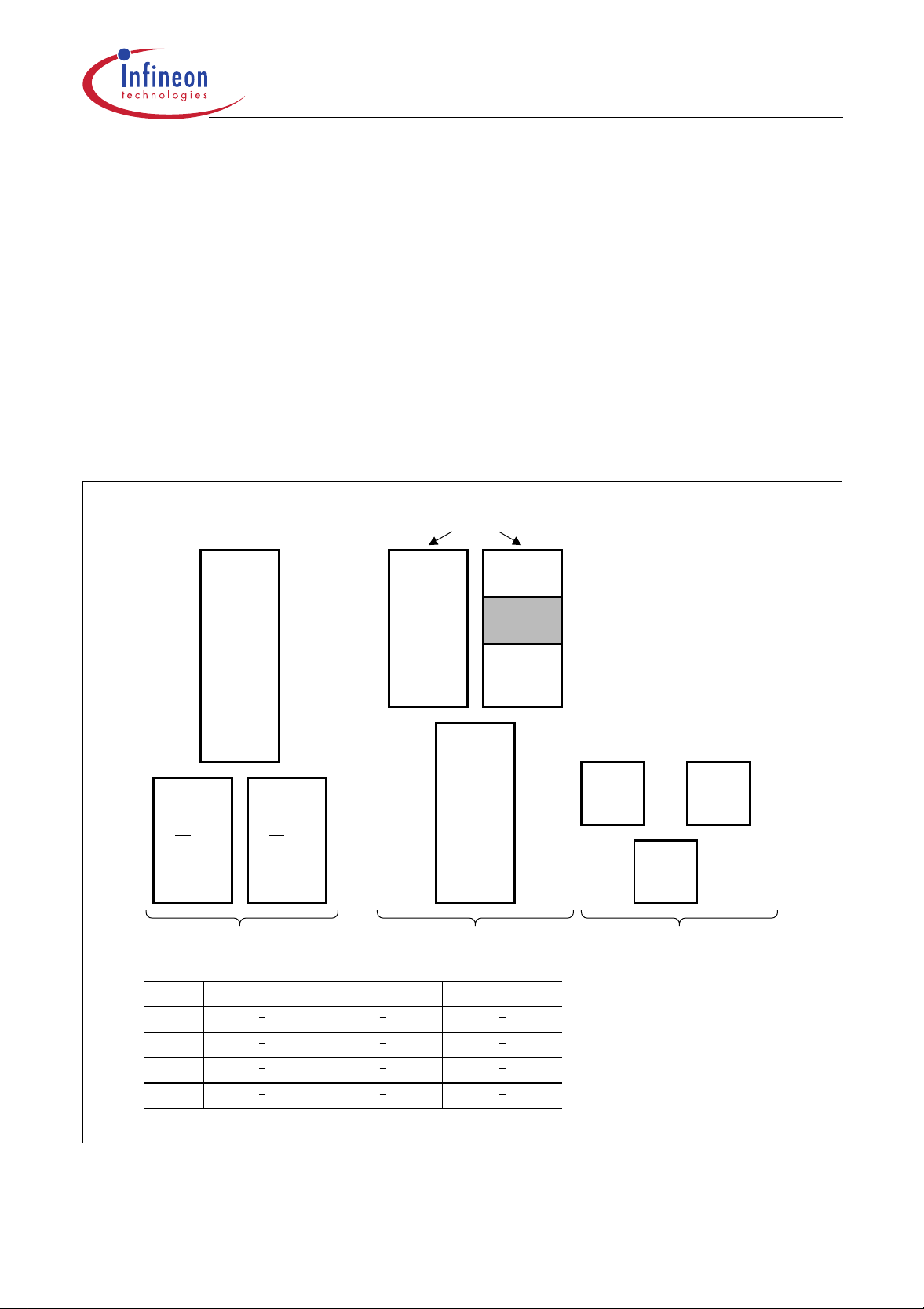
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
P0.4 / AD4
P0.5 / AD5
P0.6 / AD6
P0.3 / AD3
P0.2 / AD2
P0.1 / AD1
P0.0 / AD0
V
AREF
V
AGND
P1.0 / AN0 / INT3
/ CC0
P1.1 / AN1 / INT4 / CC1
P1.2 / AN2 / INT5 / CC2
P1.3 / AN3 / INT6 / CC3
P1.4 / AN4
P0.7 / AD7EAP4.1 / RXDC
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
123456789 10 11
C505C
C505A
C505CA
C505
ALE
PSEN
P2.5 / A13
P2.6 / A14
P2.7 / A15
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
P2.4 / A12
P2.3 / A11
P2.2 / A10
P2.1 / A9
P2.0 / A8
V
DD
V
SS
XTAL1
XTAL2
P3.7 / RD
P3.6 / WR
RESET
P3.1 / TxD
P3.0 / RxD
P3.2 / INT0
P4.0 / TXDC
P1.7 / AN7 / T2
P1.5 / AN5 / T2EX
P1.6 / AN6 / CLKOUT
This pin functionality is not ava ilable in the C505/C505A.
Figure 3
C505 Pin Configuration P-MQFP-44 Package (Top View)
P3.3 / INT1
P3.4 / T0
P3.5 / T1
Data Sheet 5 12.00
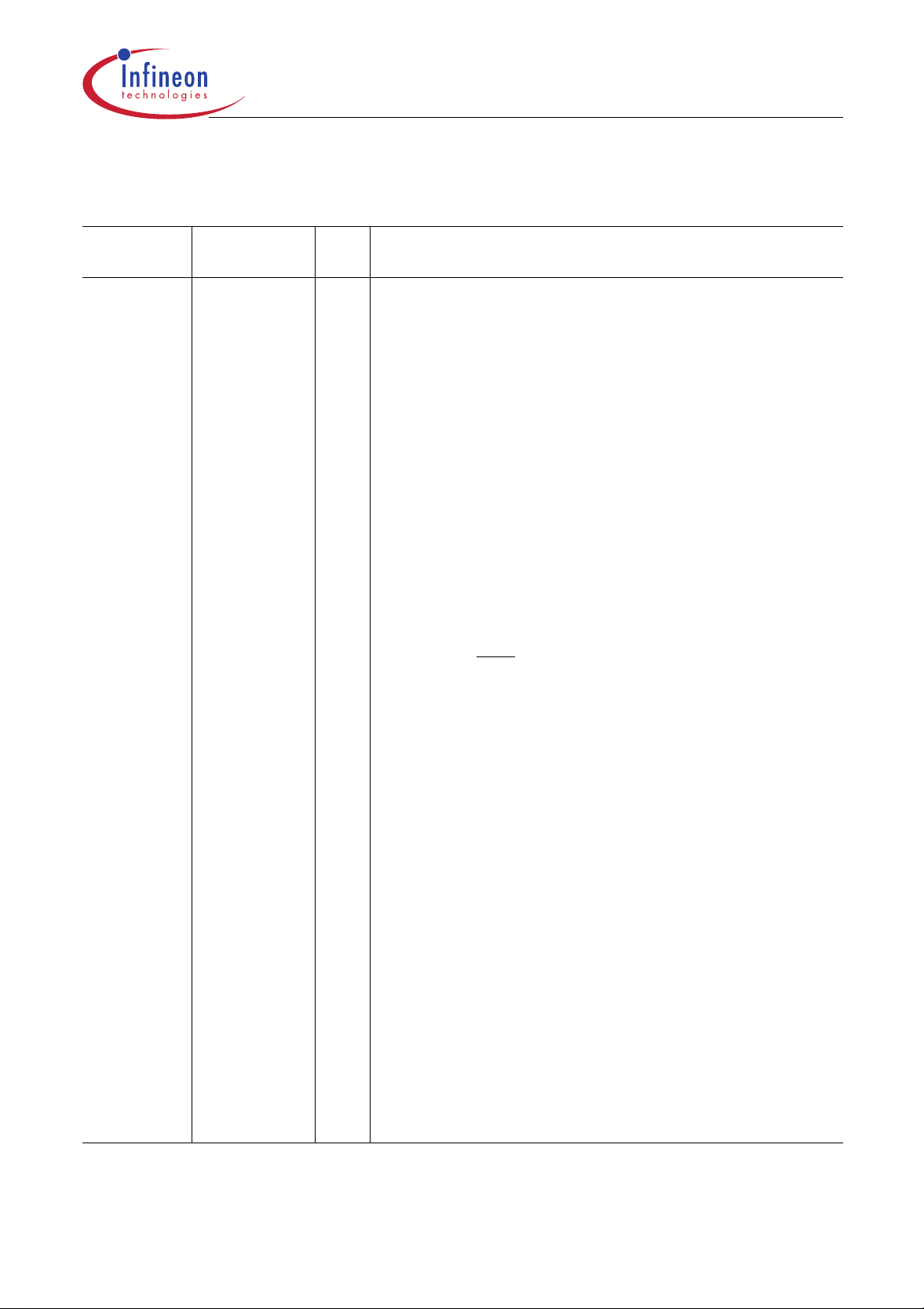
Table 2
Pin Definitions and Functions
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Symbol Pin Number I/O
*)
P1.0-P1.7 40-44,1-3
40
41
42
43
44
1
2
3
I/O Port 1
Function
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirecti onal port with internal pull-up
arrangement. Port 1 pins can be used for digital inpu t/output
or as analog inputs of the A/D converter. Port 1 pins that
have 1’s written to them are pulled high by internal pull-up
transistors and in that state can be used as inputs. As
inputs, port 1 pins being externally pulled low will source
current (I
internal pullup transistors. Port 1 pins are assigned to be
used as analog inputs via the register P1ANA.
As secondary digital functions, port 1 c ontains the i nterrupt,
timer, clock, capture and compare pins. The output latch
corresponding to a secondary function must be
programmed to a one (1) for that function to operate (except
for compare functions). The secondary functions are
assigned to the pins of port 1 as follows:
P1.0 / AN0 / INT3
P1.1 / AN1 / INT4 / CC1 Analog input channel 1/
P1.2 / AN2 / INT5 / CC2 Analog input channel 2 /
P1.3 / AN3 / INT6 / CC3 Analog input channel 3
P1.4 / AN4 Analog input channel 4
P1.5 / AN5 / T2EX Analog input channel 5 / Timer 2
P1.6 / AN6 / CLKOUT Analog input channel 6 /
P1.7 / AN7 / T2 Analog input channel 7 /
Port 1 is used for the low-order address byte during program
verification of the C505 ROM versions (i.e. C505(C)(A)-2R/
C505A-4R/C505CA-4R).
, in the DC characteristics) because of the
IL
/ CC0 Analog input channel 0
interrupt 3 input /
capture/compare channel 0 I/O
interrupt 4 input /
capture/compare channel 1 I/O
interrupt 5 input /
capture/compare channel 2 I/O
interrupt 6 input /
capture/compare channel 3 I/O
external reload / trigger input
system clock output
counter 2 input
*) I = Input
O=Output
Data Sheet 6 12.00
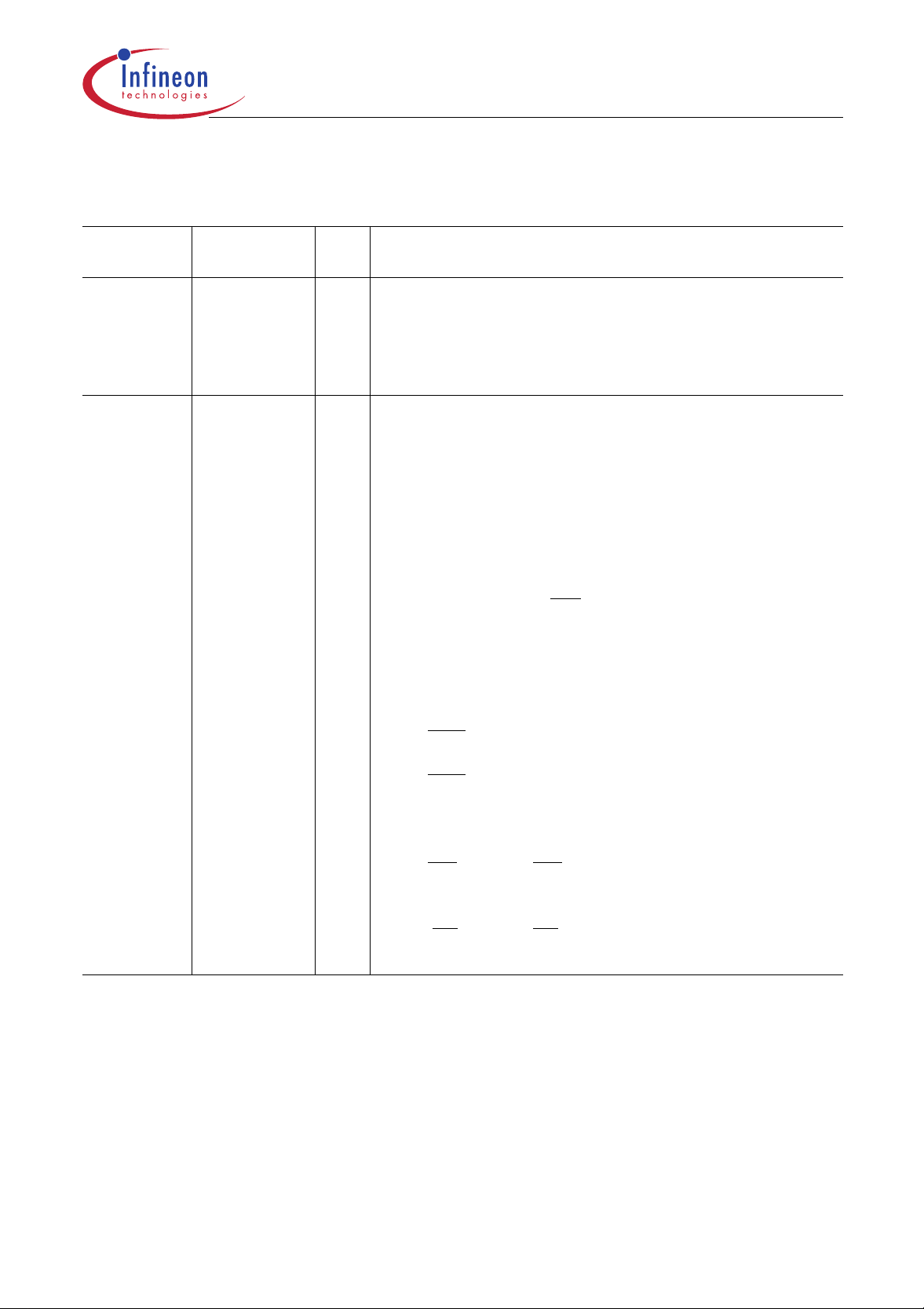
Table 2
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Symbol Pin Number I/O
Function
*)
RESET 4 I RESET
A high level on this pin for two machine cycle while the
oscillator is running resets the device. An internal diffused
resistor to V
external capacitor to V
P3.0-P3.7 5, 7-13
I/O Port 3
is an 8-bit quasi-bidirecti onal port with internal pull-up
arrangement. Port 3 pins that have 1’s written to them are
pulled high by t he internal pull-up tr ansistors and in tha t
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 3 pins being
externally pulled low will source current (I
characteristics) because of the internal pullup transistors.
The output latch corresponding to a secondary function
must be programmed to a one (1) for that function to operate
(except for TxD and WR
assigned to the pins of port 3 as follows:
5
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
P3.0 / RxD Receiver data input (asynch.) or data
P3.1 / TxD Transmitter data output (asynch.) or
P3.2 / INT0
P3.3 / INT1
P3.4 / T0 Timer 0 counter input
P3.5 / T1 Timer 1 counter input
P3.6 / WR
P3.7 / RD
permits power-on reset using only an
SS
.
DD
, in the DC
IL
). The secondary functio ns are
input/output (synch.) of serial interface
clock output (synch.) of serial interface
External interrupt 0 input / timer 0 gate
control input
External interrupt 1 input / timer 1 gate
control input
WR control output; latches the data
byte from port 0 into the external data
memory
RD control output; enables the external
data memory
*) I = Input
O=Output
Data Sheet 7 12.00
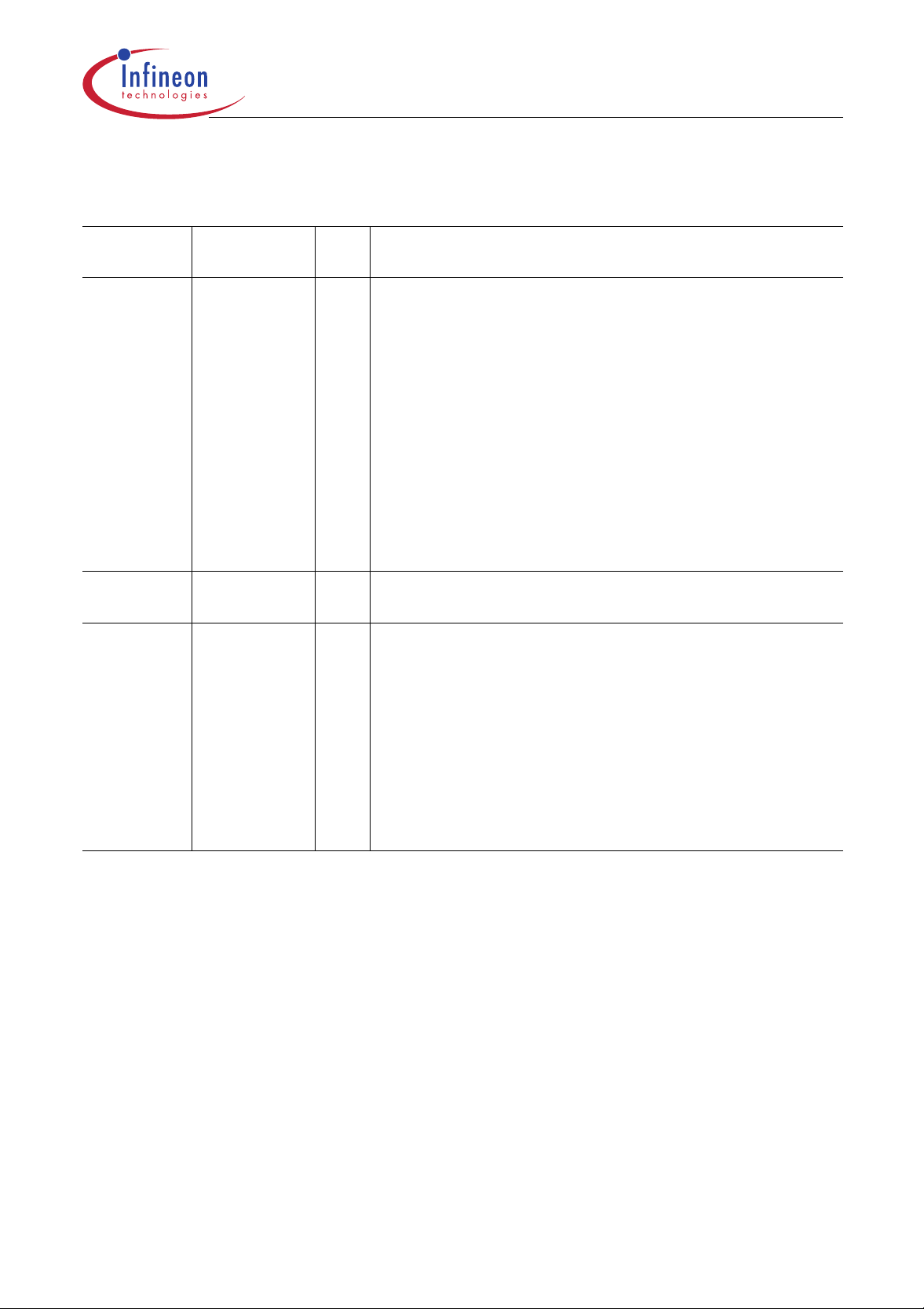
Table 2
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Symbol Pin Number I/O
*)
P4.0
P4.1
XTAL2 14 O XTAL2
XTAL1 15 I XTAL1
6
28
I/O
I/O
Function
Port 4
is a 2-bit quasi-bidirectional por t with internal pull-up
arrangement. Port 4 pins that have 1’s written to them are
pulled high by t he internal pull-up tr ansistors and in tha t
state can be used as inputs. As inputs, port 4 pins being
externally pulled low will source current (I
characteristics) because of the internal pullup transistors.
The output latch corresponding to the secondary function
RXDC must be programmed to a one (1) for that functi on to
operate. The secondary functions are assigned to the two
pins of port 4 as follows (C505C and C505CA only) :
P4.0 / TXDC Transmitter output of CAN controller
P4.1 / RXDC Receiver input of CAN controller
Output of the inverting oscillator amplifier.
Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the
internal clock generator circuits.
To drive the device from an external clock source, XTAL1
should be driven, while XTAL2 is left unconnected. To
operate above a frequency of 16 MHz, a duty cycle of the
etxernal clock signal of 50 % should be maintained.
Minimum and maximum high and low times as well as rise/
fall times specified in the AC character istics must be
observed.
, in the DC
IL
*) I = Input
O=Output
Data Sheet 8 12.00
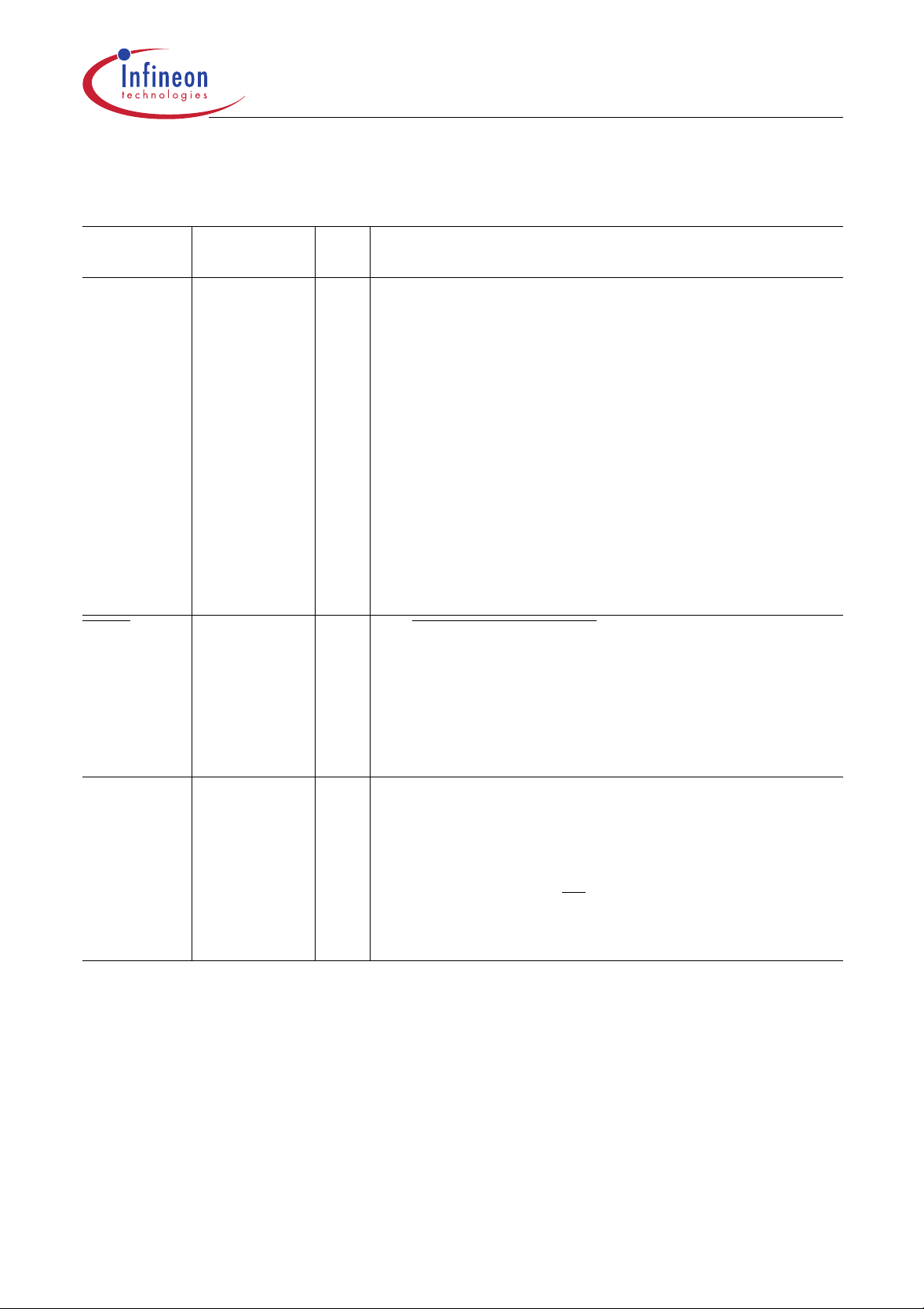
Table 2
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Symbol Pin Number I/O
*)
P2.0-P2.7 18-25 I/O Port 2
PSEN
26 O The Program Store Enable
Function
is a an 8-bit quasi-bidirectional I/O port with internal pullup
resistors. Port 2 pins that have 1’s written to them a re pulled
high by the internal pullup res istors, and in that st ate can be
used as inputs. As inputs, port 2 pins being e xternally pulled
low will source current (I
because of the internal pullup resistors. Port 2 emits the
high-order ad dress byte during fetches from ex ternal
program memor y and during accesses to external data
memory that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this
application it uses strong internal pullup transistors when
issuing 1s. During accesses to external data memory that
use 8-bit addresses (M OVX @Ri), port 2 issues the
contents of the P2 special function register and uses only
the internal pullup resistors.
output is a control signal that enables the external program
memory to the bus during extern al fetch operations. It is
activated every three oscillator periods except during
external data m emory accesses. Remains high dur ing
internal prog ram execution. This pin should n ot be driven
during reset operation.
, in the DC characteristics)
IL
ALE 27 O The Address Latch Enable
output is used for latching the low-byte of the address into
external memory during normal operation. It is activated
every three oscillator periods exc ept during an external data
memory access. When instructions are executed from
internal ROM or OTP (EA
disabled by bit EALE in SFR SYSCON.
ALE should not be driven during reset operation.
*) I = Input
O=Output
=1) the ALE generation can be
Data Sheet 9 12.00
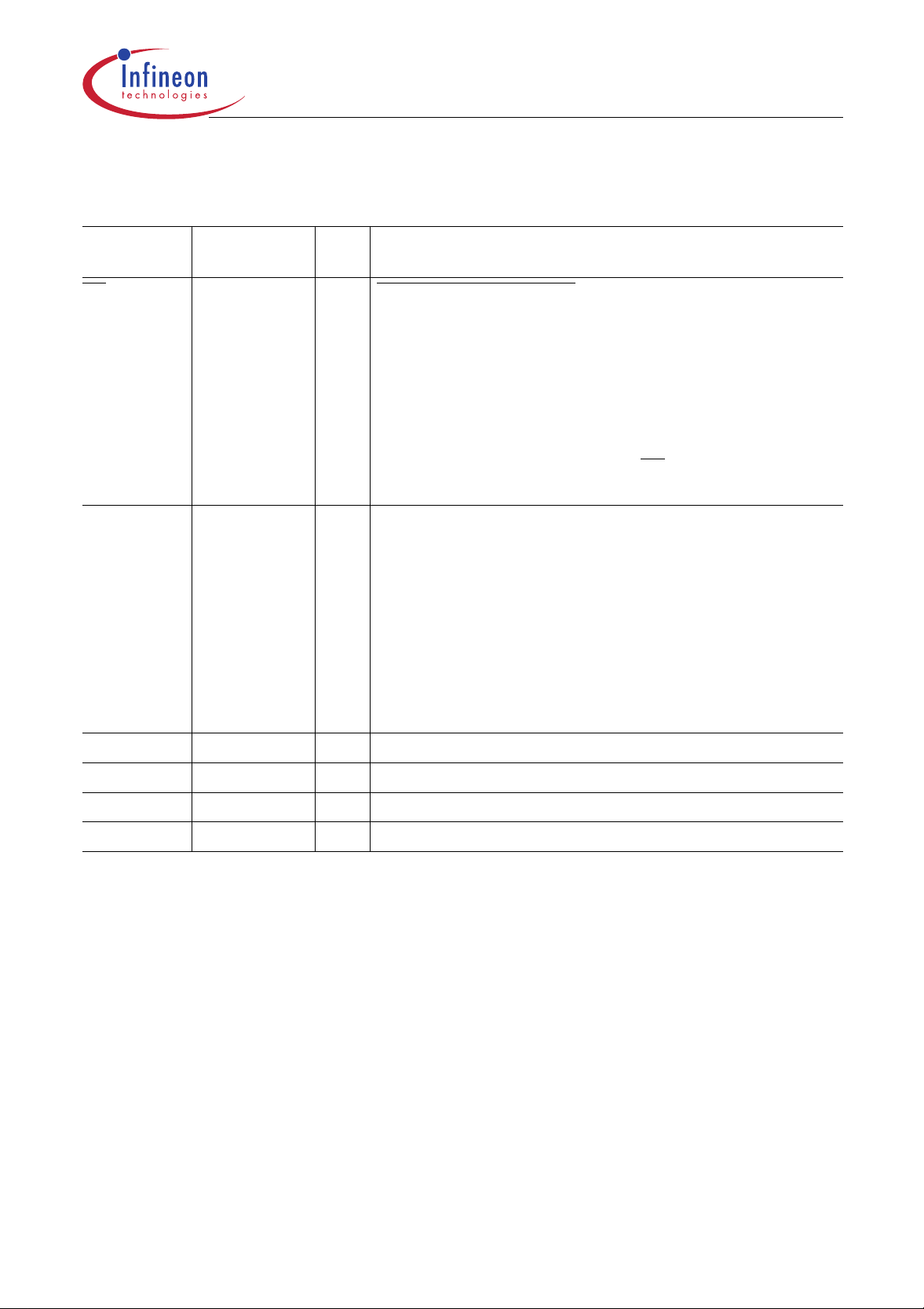
Table 2
Pin Definitions and Functions (cont’d)
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Symbol Pin Number I/O
Function
*)
EA 29 I External Access Enable
When held at high level, instructions are fetched from th e
internal program memory when the PC is less than 4000
(C505(C)(A)-2R) or 8000
4E/C505CA-4E). When held at low level, the C505 fetches
all instructions from external program memory.
For the C505 romless versions (i.e. C505-L, C505C-L,
C505A-L and C505CA-L) this pin must be tied low.
For the ROM protection version EA
reset.
P0.0-P0.7 37-30 I/O Port 0
is an 8-bit open-drain bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that
have 1’s written to them float, and in that state can be used
as high-impendance in puts. Port 0 is also the multiplexe d
low-order address and data bus during accesses to external
program or data memory. In this application it uses strong
internal pullup transistors when issuing 1’s.
Port 0 also outputs the code bytes during program
verification in the C505 ROM versions. External pullup
resistors are required during program verification.
(C505A-4R/C505CA-4R/C505A-
H
pin is latched during
H
V
AREF
V
AGND
V
SS
V
DD
*) I = Input
O=Output
38 – Reference voltage for the A/D converter.
39 – Reference ground for the A/D converter.
16 – Ground (0V)
17 – Power Supply (+5V)
Data Sheet 10 12.00
a
XTAL1
XTAL2
RESET
PSEN
V
DD
Vss
ALE
EA
Oscillator Watchdog
OSC & Timing
CPU
8 datapointers
Programmable
Watchdog Timer
XRAM
1)
256 Byte
or 1K Byte
RAM
256 Byte
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
ROM/
OTP
1)
16K or 32K
Byte
Port 0
Port 0
8-bit digit. I/O
V
V
AREF
AGND
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 2
USART
Baudrate generator
Full-CAN
Controller
Interrupt Unit
A/D Converter
8-/10-Bit
S&H
1)
MUX
Port 1
Port 1
8-bit digit. I/O /
8-bit analog In
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
256 Byte
Reg./Dat
Port 2
8-bit digit. I/O
Port 3
8-bit digit. I/O
Port 4
2-bit digit. I/O
Emulation
Support
Logic
C505C/C505CA only.
1) Please refer to Table 1 for device specific configuration.
Figure 4
Block Diagram of the C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Data Sheet 11 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
CPU
The C505 is efficient both as a controller and as an arithmetic processor. It has extensive facilities
for binary and BCD arithmetic and excels in its bit-handling capabilities. Efficient use of program
memory results from an instruction s et consisting of 44 % one-byte, 41 % two-byte , and 15% threebyte instructions. With a 16 MHz crystal, 58% of the instructions are executed in 375 ns (20MHz:
300 ns).
Special Function Register PSW (Address D0H) Reset Value : 00H
Bit No. MSB LSB
H
D7
CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 PD0
H
D6
H
D5
H
D4
Bit Function
CY Carry Flag
Used by arithmetic instruction.
AC Auxiliary Carry Flag
Used by instructions which execute BCD operations.
F0 General Purpose Flag
RS1
RS0
Register Bank Select Control Bits
These bits are used to select one of the four register banks.
RS1 RS0 Function
0 0 Bank 0 selected, data address 00H-07
0 1 Bank 1 selected, data address 08H-0F
1 0 Bank 2 selected, data address 10H-17
1 1 Bank 3 selected, data address 18H-1F
H
D3
H
D2
H
D1
H
D0
H
PSW
H
H
H
H
OV Overflow Flag
Used by arithmetic instruction.
F1 General Purpose Flag
P Parity Flag
Set/cleared by hardware after each instruction to indicate an odd/even
number of "one" bits in the accumulator, i.e. even parity.
Data Sheet 12 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Memory Organization
The C505 CPU manipulates operands in the following four address spaces:
– On-chip program memory :16K byte ROM (C505(C)(A)-2R) or
32K byte ROM (C505A-4R/C505CA-4R) or
32K byte OTP (C505A-4E/C505CA-4E)
– Totally up to 64K byte internal/external program memory
– up to 64 Kbyte of external data memory
– 256 bytes of internal data memory
– Internal XRAM data memory :256 byte (C505/C505C)
1K byte (C505A/C505CA)
– a 128 byte special function register area
Figure 5 illustrates the memory address spaces of the C505 versions.
Alternatively
FFFF
H
Ext.
4000 /
H
8000
H
3FFF /
7FFF
Int.
(EA = 1)
Ext.
(EA = 0)
0000
"Code Space" "Data Space" "Internal Data Space"
"Data Space" F700 to FFFF :
Device
C505
C505C
C505A
C505CA
HH
CAN Area
F700 F7FF
HH
F700 F7FF
HH
Unused Area
F700 FEFF
F800 FEFF
F700 FBFF
F800 FBFF
Ext.
Data
Memory
H
H
Ext.
Data
Memory
H
XRAM Area
HH
HH
H
H
FF00 FFFF
FF00 FFFF
FC00 FFFF
H
FC00 FFFF
H
FFFF
Internal
XRAM
Unused
Area
Int. CAN
H
See table below
for detailed
Data Memory
partitioning
Contr.
(256 Byte)
F6FF
H
F700
Indirect
H
Addr.
Internal
RAM
0000
H
HH
HH
HH
HH
FF
H
80
H
Internal
RAM
Direct
Addr.
Special
Function
Regs.
7F
H
00
H
MCB03632
FF
80
H
H
Figure 5
C505 Memory Map Memory Map
Data Sheet 13 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
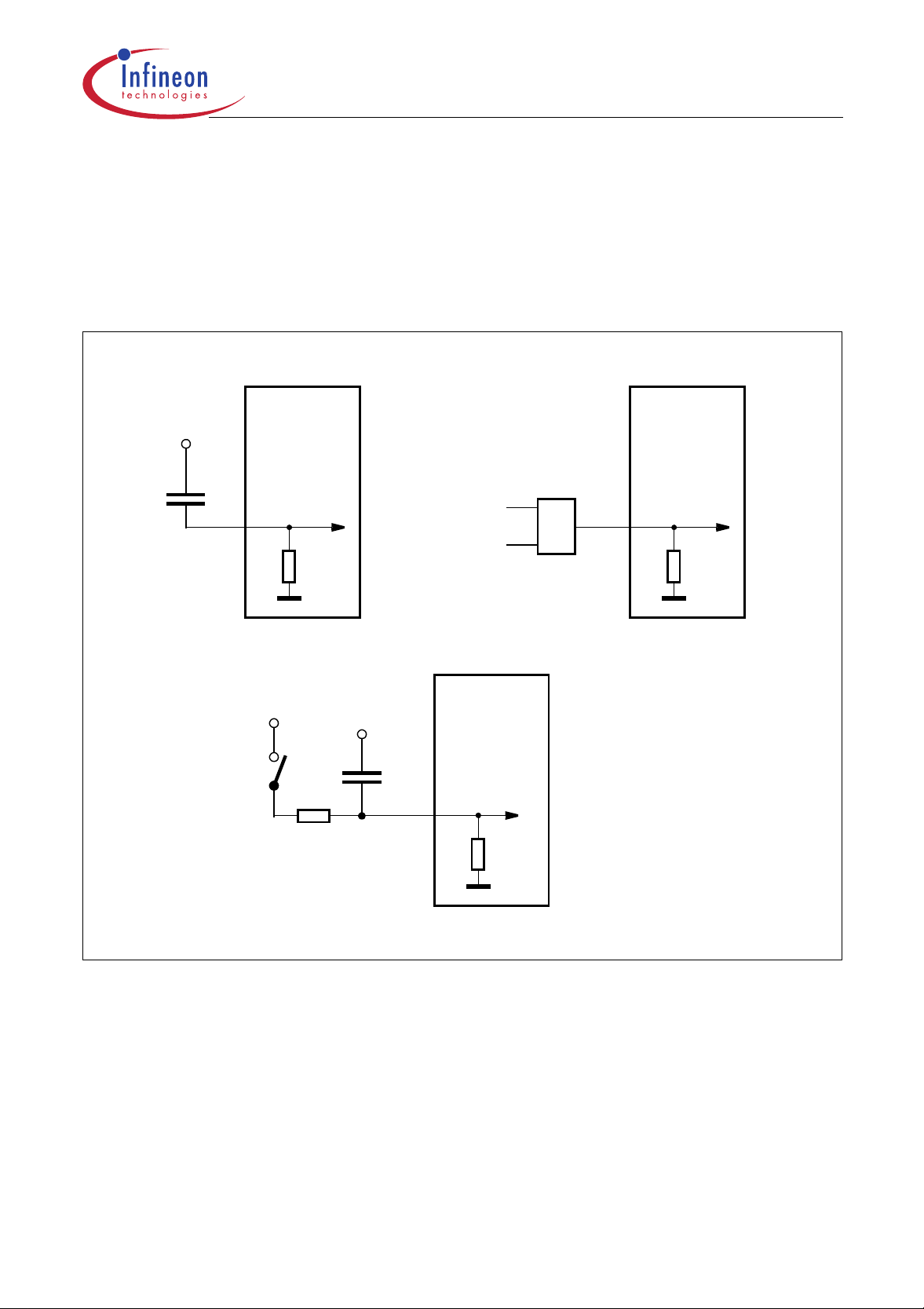
Reset and System Clock
The reset input is an active high input at pin RESET. Since the reset is synchronized internally, the
RESET pin must be held high for at least two machine cycles (12 oscillator periods) while the
oscillator is running. A pulldown resist or is internally connected to
an external capacitor only. An automatic reset can be obtained when
the RESET pin to
V
via a capacitor. Figure 6 shows the possible reset circuitries.
DD
V
to allow a power-up reset with
SS
V
is applied by connecting
DD
a)
C505
V
DD
C505C
C505A
C505CA
b)
C505
C505C
C505A
C505CA
+
RESET
RESET
&
c)
V
DD
V
DD
C505
C505C
C505A
+
C505CA
RESET
Figure 6
Reset Circuitries
Data Sheet 14 12.00
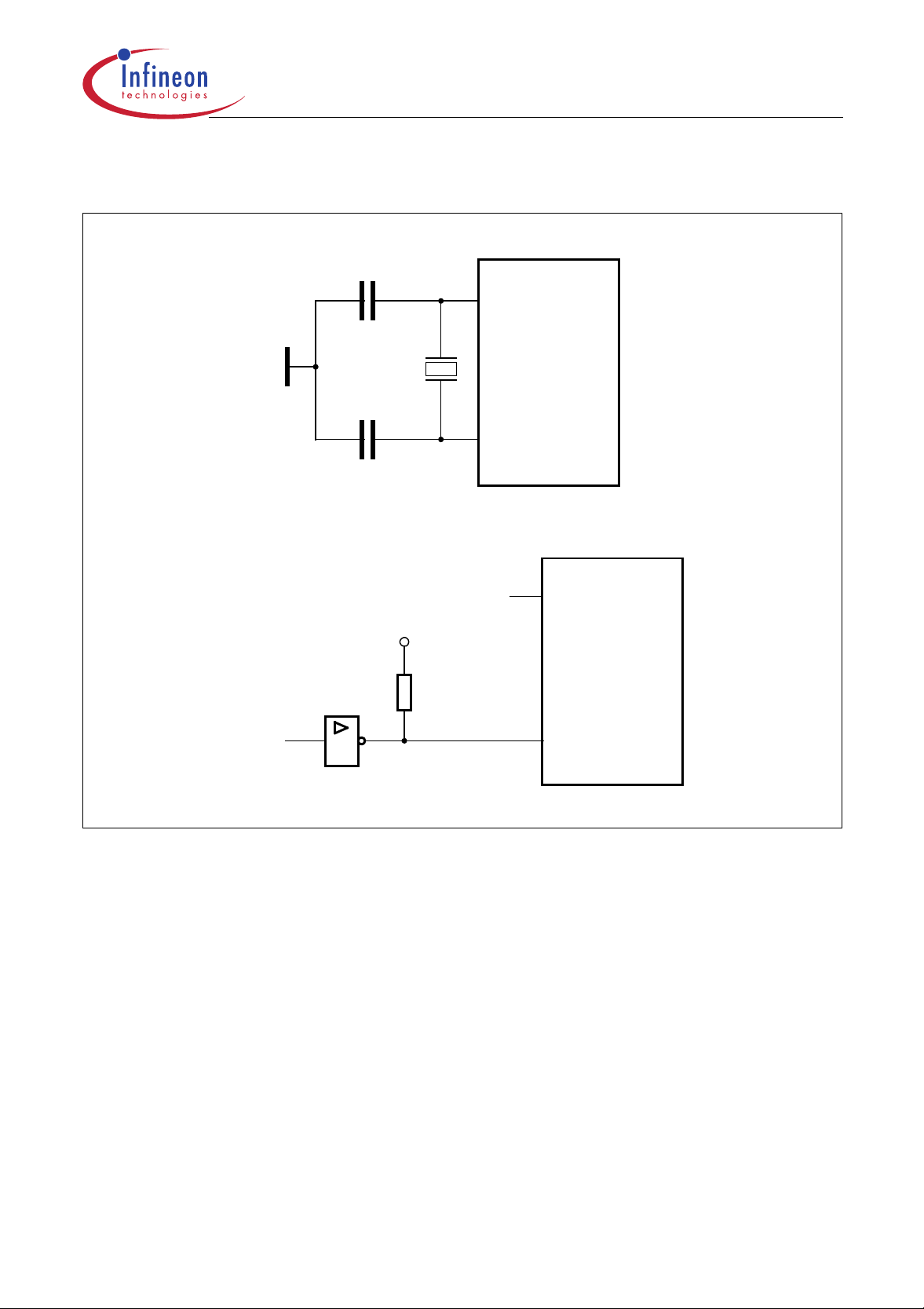
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Figure 7 shows the recommended oscillator circuits for crystal and external clock operation.
C
XTAL2
C505
2-20
MHz
C
C = 20pF ± 10pF for crystal operation
C = 20 pF ± 10pF for crystal operation
C505C
C505A
C505CA
XTAL1
V
External
Clock
Signal
Figure 7
Recommended Oscillator Circuitries
DD
N.C.
XTAL2
C505
C505C
C505A
C505CA
XTAL1
Data Sheet 15 12.00
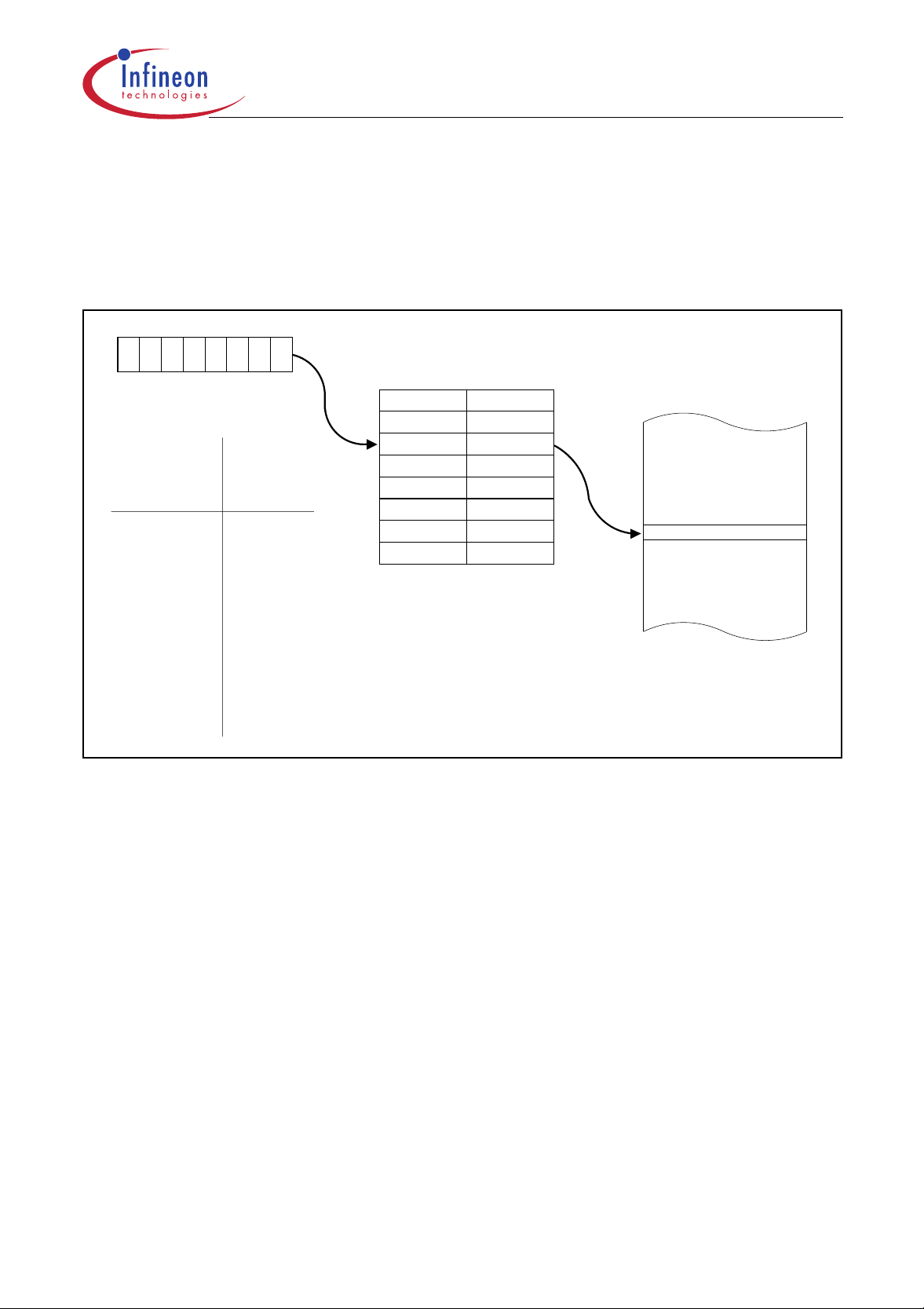
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Multiple Datapointers
As a functional enhancement to the standard 8051 architecture, the C505 contains eight 16-bit
datapointers instead of only one datapointer. The in struction set uses just one of these datapointers
at a time. The selection of the actual datapointer is done in the special function regsiter DPSEL.
Figure 8 illustrates the datapointer addressing mechanism.
Datapointer
DPTR 0000
.0.1.2
DPTR7
DPTR0
DPH(83 ) DPL(82 )
HH
-----
DPSEL(92 )
DPSEL Selected
.2 .1 .0
0 0 1 DPTR 1
0 1 0 DPTR 2
0 1 1 DPTR 3
1 0 0 DPTR 4
1 0 1 DPTR 5
1 1 0 DPTR 6
1 1 1 DPTR 7
H
Figure 8
External Data Memory Addressing using Multiple Datapointers
External Data Memory
MCD00779
Data Sheet 16 12.00
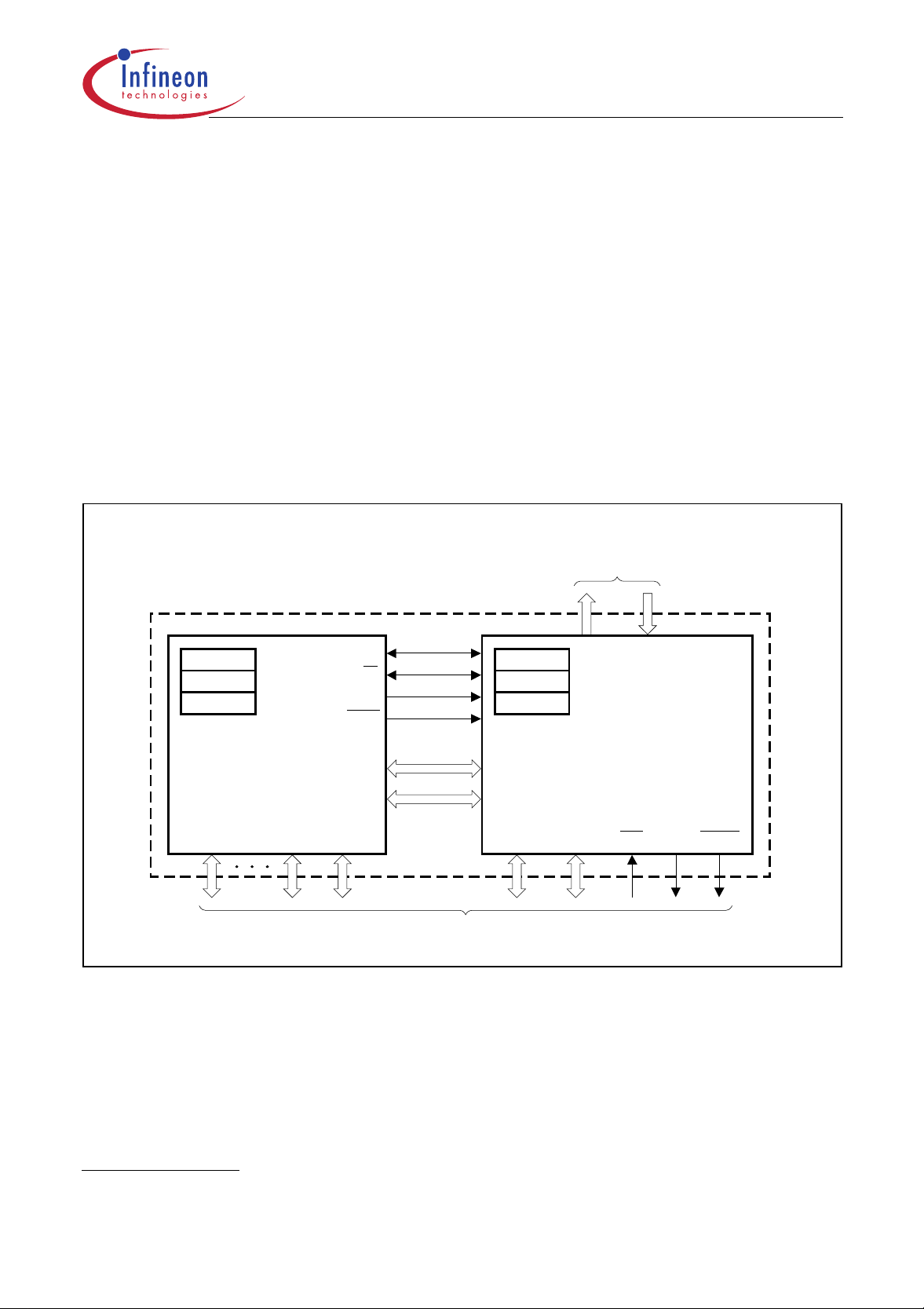
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept
The Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept of the C500 microcontroller family is a new, innovative
way to control the execution of C500 MCUs and to gain extensive information on the internal
operation of the controllers. Emulation of on-chip ROM based programs is possible, too.
Each production chip has built-in logic for the supprt of the Enhanced Hooks Emulation Concept.
Therefore, no costly bond-out chips are necessary for emulation. This also ensure that emulation
and production chips are identical.
1)
TM
The Enhanced Hooks Technology
together with an EH-IC to function similar to a bond-ou t chip. This simpli fies the design and redu ces
costs of an ICE-system. ICE-systems using an EH-IC and a compatible C500 are able to emulate
all operating modes of the different versions of the C500 microcontrollers. This includes emulation
of ROM, ROM with code rollover and ROMless modes of operation. It is also able to operate in
single step mode and to read the SFRs after a break.
, which requires embedded logic in the C500 allows the C500
to Emulation Hardware
SYSCON
PCON
TCON
RESET
EA
ALE
PSEN
RSYSCON
RPCON
RTCON
C500
MCU Interface Circuit
Optional
I/O Ports
Figure 9
Basic C500 MCU Enhanced Hooks Concept Configuration
Port 3 Port 1
Port 0
Port 2
Target System Interface
ICE-System Interface
EH-IC
Enhanced Hooks
RPort 0RPort 2
TEA TALE TPSEN
MCS02647
Port 0, port 2 and some of the control lines of the C500 based MCU are used by Enhanced Hooks
Emulation Concept to control the operation of the device during emulation and to transfer
informations about the programm execution and data transfer between the external emulation
hardware (ICE-system) and the C500 MCU.
1)
“Enhanced Hooks Technology“ is a trademark and patent of Metalink Corporation licensed to Infineon
Technologies.
Data Sheet 17 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Special Function Registers
The registers, except the program counter and the four general purpose register banks, reside in
the special function register area. The special function register area consists of two portions : the
standard special function register area and the mapp ed spec ial func tion regi ster area. Fiv e spec ial
function register of the C505 (PCON1,P1ANA, VR0, VR1, VR2) are located in the mapped special
function register area. For accessing the mapped special function regi ster area, bit RMAP in special
function register SYSCON must be set. All other special function registers are located in the
standard special function register area which is accessed when RMAP is cleared (“0“).
The registers and data locations of the CAN controller (CAN-SFRs) are located in the external data
memory area at addresses F700H to F7FFH..
Special Function Register SYSCON (Address B1H) Reset Value : XX100X01
(C505CA only) Reset Value : XX100001
Bit No. MSB LSB
76543210
B1
H
Bit Function
RMAP Special function register map bit
CSWO CAN Controller switch-off bit
––
The functions of the shaded bits are not described here.
1) This bit is only available in the C505CA.
RMAP = 0 : The access to the non-mapped (standard) special function register
RMAP = 1 : The access to the mapped special function register area is enabled.
CSWO = 0 : CAN Controller is enabled (default after reset).
CSWO = 1 : CAN Controller is switched off.
EALE RMAP CMOD
area is enabled.
CSWO
1)
XMAP1
XMAP0
SYSCON
B
B
As long as bit RMAP is set, mapped special function register area can be accessed. This bit is not
cleared by hardware automatically. Thus, when non-mapped/mapped regist ers are to be accessed,
the bit RMAP must be cleared/set respectively by software.
All SFRs with addresses where address bits 0-2 are 0 (e.g. 80H, 88H, 90H, 98H, ..., F8H, FFH) are
bitaddressable.
The 52 special function registers (SFRs) in the standard and mapped SFR area include pointers
and registers that provide an interface between the CPU and the other on-chip peripherals. The
SFRs of the C505 are listed in Table 3 and Table 4. In Table 3 they are organized in groups which
refer to the functional blocks of the C505. The CAN-SFRs (applicable for the C505C and C505CA
only) are also included in Table 3. Table 4 illustrates the contents of the SFRs in numeric order of
their addresses. Table 5 list the CAN-SFRs in numeric order of their addresses.
Data Sheet 18 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 3
Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks
Block Symbol Name Address Contents after
Reset
CPU ACC
B
DPH
DPL
DPSEL
PSW
SP
SYSCON
VR0
VR1
VR2
A/DConverter
ADCON0
ADCON1
ADDAT
ADST
ADDATH
4)
4)
Accumulator
B-Register
Data Pointer, High Byte
Data Pointer, Low Byte
Data Pointer Select Register
Program Status Word Register
Stack Pointer
2)
System Control Register
Version Register 0
Version Register 1
4)
Version Register 2
2)
A/D Converter Control Register 0
A/D Converter Control Register 1
A/D Converter Data Reg. (C505/C505C)
A/D Converter Start Reg. (C505/C505C)
A/D Converter High Byte Data Register
E0
F0
83
82
92
D0
81
B1
FC
FD
FE
D8
DC
D9
DA
D9
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
1)
1)
1)
H
H
1)
H
H
(C505A/C505CA)
ADDATL
A/D Converter Low Byte Data Register
DA
H
(C505A/C505CA)
P1ANA
Interrupt
System
IEN0
IEN1
IP0
IP1
TCON
T2CON
SCON
IRCON
XRAM XPAGE
2) 4)
Port 1 Analog Input Selection Register
2)
2)
2)
Interrupt Enable Register 0
Interrupt Enable Register 1
Interrupt Priority Register 0
Interrupt Priority Register 1
2)
Timer Control Register
2)
Timer 2 Control Register
2)
Serial Channel Control Register
Interrupt Request Control Register
Page Address Register for Extended on-chip
90
A8
B8
A9
B9
88
C8
98
C0
91
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
XRAM and CAN Controller
SYSCON
1) Bit-addressable special fun ction registers
2) This special function register is listed repeatedly since some bits of it also belong to other functional blocks.
3) “X“ means that the value is undefined and the location is reserved
4) This SFR is a mapped SFR. For ac ce ssing this SFR, bit RMAP in SFR SYSCON must be set.
5) The content of this SFR varies with t he ac t ual s t ep of the C505 (eg. 01
6) C505 / C505A/C505C only
7) C505CA only
2)
System Control Register
B1
H
for the first step)
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
XXXXX000
00
H
07
H
XX100X01
XX100001
C5
H
05
H
5)
00X00000
01XXX000
00
H
3)
XX
H
00
H
00XXXXXX
FF
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
XX000000
00
H
00X00000
00
H
00
H
00
H
XX100X01
XX100001
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
3) 7)
B
3)
3) 7)
3)
3) 6)
3)
3)
3)
3) 6)
Data Sheet 19 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 3
Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks (cont’d)
Block Symbol Name Address Contents after
Reset
Ports P0
P1
P1ANA
P2
P3
P4
Serial
Channel
ADCON0
PCON
2)
SBUF
SCON
SRELL
SRELH
Timer 0/
Timer 1
TCON
TH0
TH1
TL0
TL1
TMOD
Compare/
Capture
Unit /
Timer 2
CCEN
CCH1
CCH2
CCH3
CCL1
CCL2
CCL3
CRCH
CRCL
TH2
TL2
T2CON
2)
IEN0
2)
IEN1
Watchdog WDTREL
2)
IEN0
2)
IEN1
2)
IP0
Pow. Save
Modes
1) Bit-addressable special function registers
2) This special function register is listed repeatedly since some bits of it also belong to other functional blocks.
3) “X“ means that the value is undefined and the location is reserved
4) SFR is located in the mapped SFR area. For accessing this SFR, bit RMAP in SFR SYSCON must be set.
PCON
PCON1
2)
Port 0
Port 1
2) 4)
Port 1 Analog Input Selection Register
Port 2
Port 3
Port 4
2)
A/D Converter Control Register 0
Power Control Register
Serial Channel Buffer Register
Serial Channel Control Register
Serial Channel Reload Register, low byte
Serial Channel Reload Register, high byte
Timer 0/1 Control Register
Timer 0, High Byte
Timer 1, High Byte
Timer 0, Low Byte
Timer 1, Low Byte
Timer Mode Register
Comp./Capture Enable Reg.
Comp./Capture Reg. 1, High Byte
Comp./Capture Reg. 2, High Byte
Comp./Capture Reg. 3, High Byte
Comp./Capture Reg. 1, Low Byte
Comp./Capture Reg. 2, Low Byte
Comp./Capture Reg. 3, Low Byte
Reload Register High Byte
Reload Register Low Byte
Timer 2, High Byte
Timer 2, Low Byte
Timer 2 Control Register
Interrupt Enable Register 0
Interrupt Enable Register 1
Watchdog Timer Reload Register
Interrupt Enable Register 0
Interrupt Enable Register 1
Interrupt Priority Register 0
Power Control Register
4)
Power Control Register 1
80
H
90
H
90
H
A0
H
B0
H
E8H
D8
H
87
H
99
H
98
H
AA
H
BA
H
88
H
8C
H
8D
H
8A
H
8B
H
89
H
C1
H
C3
H
C5
H
C7
H
C2
H
C4
H
C6
H
CB
H
CA
H
CD
H
CC
H
C8
H
A8
H
B8
H
86
H
A8
H
B8
H
A9
H
87
H
88
H
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
1)
FF
H
FF
H
FF
H
FF
H
FF
1)
H
XXXXXX11
00X00000
00
H
3)
XX
H
00
H
D9
H
XXXXXX11
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
3)
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00X00000
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
00
H
0XX0XXXX
B
B
B
3)
3)
B
3)
3)
B
Data Sheet 20 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 3
Special Function Registers - Functional Blocks (cont’d)
Block Symbol Name Address Contents after
Reset
CAN
Controller
(C505C/
C505CA
only)
CR
SR
IR
BTR0
BTR1
GMS0
GMS1
UGML0
UGML1
LGML0
LGML1
UMLM0
UMLM1
LMLM0
LMLM1
Control Register
Status Register
Interrupt Register
Bit Timing Register Low
Bit Timing Register High
Global Mask Short Register Low
Global Mask Short Register High
Upper Global Mask Long Register Low
Upper Global Mask Long Register High
Lower Global Mask Long Register Low
Lower Global Mask Long Register High
Upper Mask of Last Message Register Low
Upper Mask of Last Message Register High
Lower Mask of Last Message Register Low
Lower Mask of Last Message Register High
F700
F701
F702
F704
F705
F706
F707
F708
F709
F70A
F70B
F70C
F70D
F70E
F70F
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
01
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
UU
H
0UUUUUUU
3)
UU
H
UUU11111
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
UUUUU000
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
UUUUU000
B
B
B
B
Message Object Registers :
MCR0
MCR1
UAR0
UAR1
LAR0
LAR1
MCFG
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DB6
DB7
1) Bit-addressable special fun ction registers
2) This special function register is listed repeatedly since some bits of it also belong to other functional blocks.
3) “X“ means that the value is undefined and the location is reserved. “U“ means that the value is unchanged by
a reset operation. “U“ values are undefined (as “X“) after a power-on reset operation
4) SFR is located in the mapped SFR area. For accessing this SFR, bit RM AP in SFR SYSCON must be set.
5) The notation “n“ (n= 1 to F) in the me ssage object address definition def ines the number of the related
message object.
Message Control Register Low
Message Control Register High
Upper Arbitration Register Low
Upper Arbitration Register High
Lower Arbitration Register Low
Lower Arbitration Register High
Message Configuration Register
Message Data Byte 0
Message Data Byte 1
Message Data Byte 2
Message Data Byte 3
Message Data Byte 4
Message Data Byte 5
Message Data Byte 6
Message Data Byte 7
F7n0
F7n1
F7n2
F7n3
F7n4
F7n5
F7n6
F7n7
F7n8
F7n9
F7nA
F7nB
F7nC
F7nD
F7nE
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
5)
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
3)
UU
H
UUUUU000
UUUUUU00
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
3)
XX
H
B
B
3)
3)
3)
3)
3)
3)
Data Sheet 21 12.00
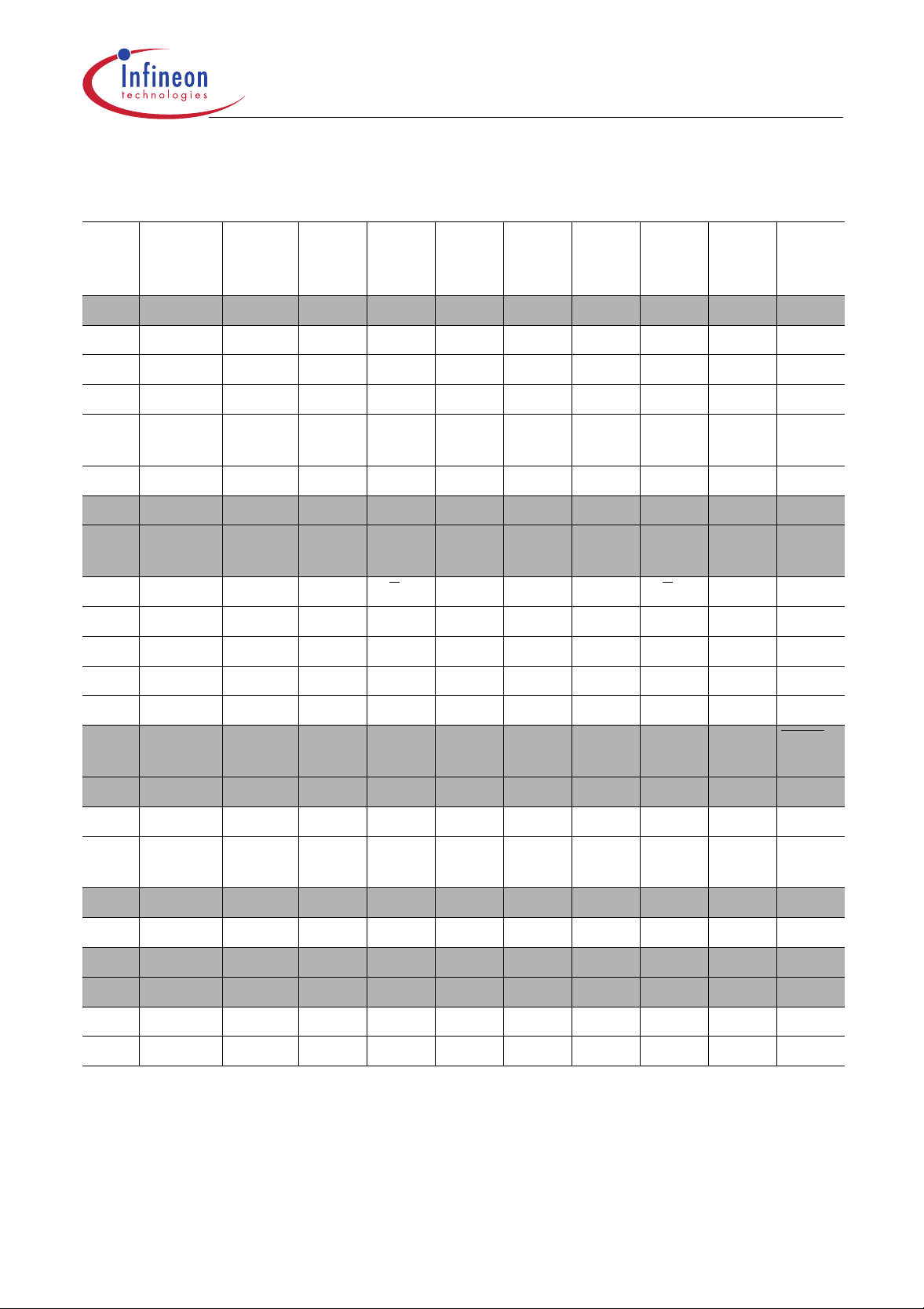
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 4
Contents of the SFRs, SFRs in numeric order of their addresses
Addr Register Content
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
after
80
81
82
83
86
2)
P0 FF
H
SP 07
H
DPL 00
H
DPH 00
H
WDTREL 00
H
Reset
H
H
H
H
H
1)
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
WDT
.6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
PSEL
87
88
88
89
8A
8B
8C
8D
90
PCON 00
H
2)
TCON 00
H
3)
PCON1 0XX0-
H
TMOD 00
H
TL0 00
H
TL1 00
H
TH0 00
H
TH1 00
H
2)
P1 FF
H
H
H
XXXX
H
H
H
H
H
H
SMOD PDS IDLS SD GF1 GF0 PDE IDLE
TF1 TR1 TF0 TR0 IE1 IT1 IE0 IT0
EWPD – – WS – – – –
B
GATE C/T
M1 M0 GATE C/T M1 M0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
T2 CLK-
T2EX .4 INT6 INT5 INT4 .INT3
OUT
3)
90
91
92
98
99
A0
A8
A9
AA
1) X means that the value is undefined and the location is reserved
2) Bit-addressable special function registers
3) SFR is located in the mapped SF R ar ea. Fo r ac ce s sin g th is SF R, bit RMAP in SFR SYSCON must be set.
P1ANA FF
H
XPAGE 00
H
DPSEL XXXX-
H
2)
SCON 00
H
SBUF XX
H
2)
P2 FF
H
2)
IEN0 00
H
IP0 00
H
SRELL D9
H
H
H
X000
H
H
H
H
H
H
EAN7 EAN6 EAN5 EAN4 EAN3 EAN2 EAN1 EAN0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
–––––.2 .1 .0
B
SM0 SM1 SM2 REN TB8 RB8 TI RI
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
EA WDT ET2 ES ET1 EX1 ET0 EX0
OWDS WDTS .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
Data Sheet 22 12.00
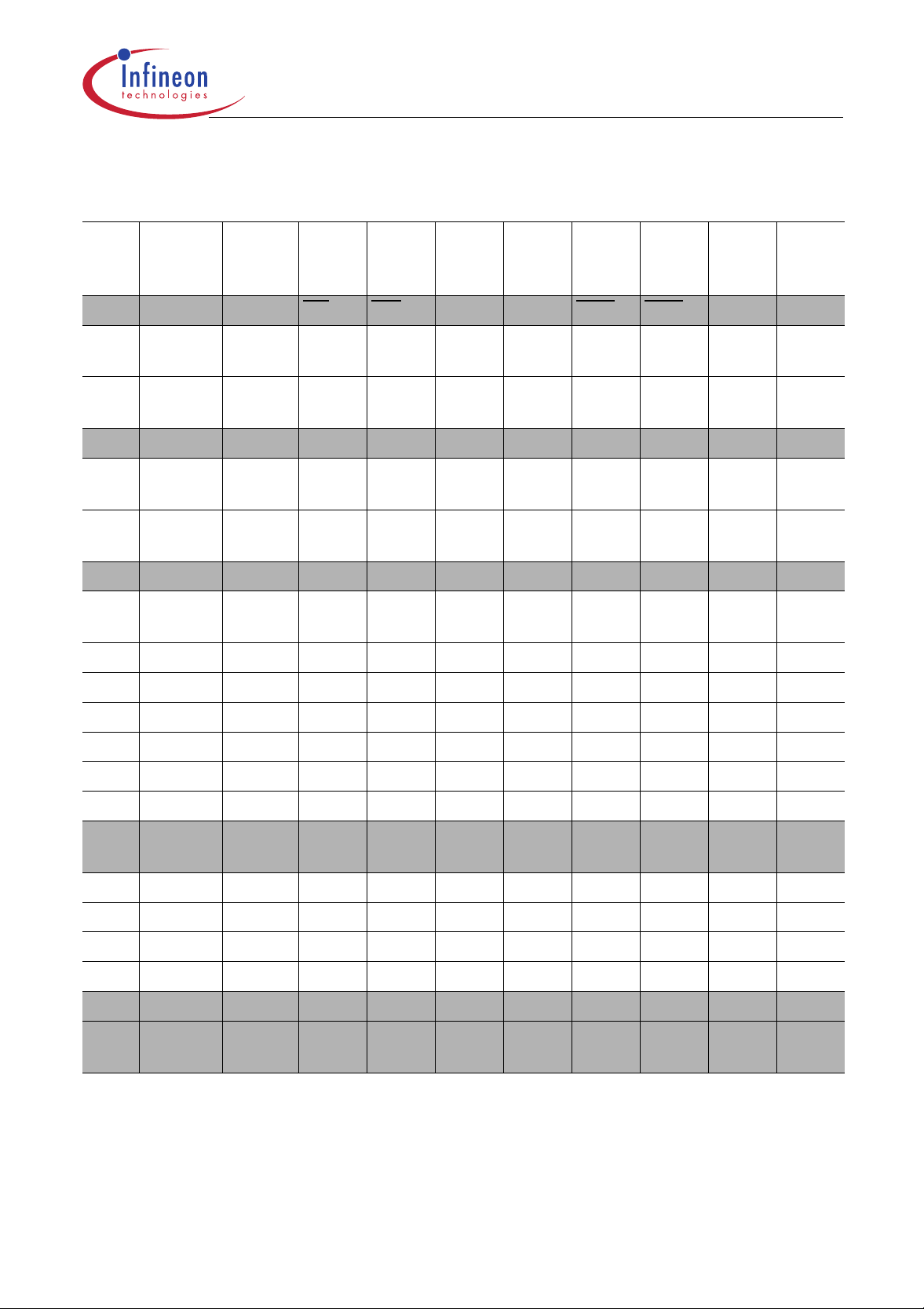
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 4
Contents of the SFRs, SFRs in numeric order of their addresses (cont’d)
Addr Register Content
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
after
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
1)
RD WR T1 T0 INT1 INT0 TxD RxD
––EALE RMAP CMOD – XMAP1 XMAP0
B
––EALE RMAP CMOD CSWO XMAP1 XMAP0
B
EXEN2 SWDT EX6 EX5 EX4 EX3 ECAN EADC
––.5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
B
––––––.1 .0
B
EXF2 TF2 IEX6 IEX5 IEX4 IEX3 SWI IADC
COCAH3COCAL3COCAH2COCAL2COCAH1COCAL1COCAH0COCAL
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
T2PS I3FR – T2R1 T2R0 T2CM T2I1 T2I0
B
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
CY AC F0 RS1 RS0 OV F1 P
BD CLK – BSY ADM MX2 MX1 MX0
B
Reset
2)
B0
B1
B1
B8
B9
P3 FF
H
SYSCON
H
3)
SYSCON
H
4)
2)
IEN1 00
H
IP1 XX00-
H
XX100X01
XX100001
0000
BA
SRELH XXXX-
H
XX11
2)
C0
C1
C2
C3
C4
C5
C6
C7
C8
IRCON 00
H
CCEN 00
H
CCL1 00
H
CCH1 00
H
CCL2 00
H
CCH2 00
H
CCL3 00
H
CCH3 00
H
2)
T2CON 00X0-
H
0000
CA
CB
CC
CD
D0
D8
CRCL 00
H
CRCH 00
H
TL2 00
H
TH2 00
H
2)
PSW 00
H
2)
ADCON0 00X0-
H
0000
1) X means that the value is undefined and the location is reserved
2) Bit-addressable special function registers
3) C505 /C505C/C505A only
4) C505CA only
0
Data Sheet 23 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 4
Contents of the SFRs, SFRs in numeric order of their addresses (cont’d)
Addr Register Content
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
after
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
1)
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.9 .8 .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2
––––––––
B
.1 .0 ––––––
B
ADCL1 ADCL0 –––MX2 MX1 MX0
B
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
– – – – – – RXDC TXDC
B
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
11000101
00000101
8)
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
9)
10)
for the AA step)
H
for the BA step)
H
H
or 11
H
or 21
for the first step)
H
Reset
6)
6)
00
00
XXXX-
D9
D9
DA
H
H
H
ADDAT
ADDATH
7)
ADST
XXXX
DA
DC
ADDATL
H
7)
ADCON1 01XX-
H
00XX-
XXXX
X000
2)
E0
E8
ACC 00
H
2)
P4 XXXX-
H
XX11
2)
F0
FC
FD
FE
B 00
H
3)4)
VR0 C5
H
3)4)
VR1 05
H
3)4)
VR2
H
5)
01
12
33
1) X means that the value is undefined and the location is reserved
2) Bit-addressable special function registers
3) SFR is located in the mapped SF R ar ea. Fo r ac ce s sin g th is SF R, bit RMAP in SFR SYSCON must be set.
4) These are read-only registers
5) The content of this SFR varies with the actual of the step C505 (eg. 01
6) C505 / C505C only
7) C505A / C505CA only
8) C505 / C505C AB step only
9) C505A-4E / C505CA-4E BA step only (11
10) C505A-4R / C505CA-4R BB step only (32
Data Sheet 24 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 5
Contents of the CAN Registers in numeric order of their addresses
(C505C/C505CA only)
Addr.
n=1-F
1)
F700
F701
F702
F704
F705
Register Content
H
CR 01
H
SR XX
H
IR XX
H
BTR0 UU
H
BTR1 0UUU.
H
after
Reset
H
H
H
H
UUUU
F706
F707
F708
F709
F70AHLGML0 UU
GMS0 UU
H
GMS1 UUU1.
H
UGML0 UU
H
UGML1 UU
H
H
1111
H
H
H
B
F70BHLGML1 UUUU.
U000
B
F70CHUMLM0 UU
F70DHUMLM1 UU
F70EHLMLM0 UU
F70F
F7n0
F7n1
LMLM1 UUUU.
H
MCR0 UU
H
MCR1 UU
H
H
H
H
U000
H
H
B
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
2)
TEST CCE 0 0 EIE SIE IE INIT
BOFF EWRN – RXOK TXOK LEC2 LEC1 LEC0
INTID
SJW BRP
0 TSEG2 TSEG1
B
ID28-21
ID20-18 11111
ID28-21
ID20-13
ID12-5
ID4-0 000
ID28-21
ID20-18 ID17-13
ID12-5
ID4-0 000
MSGVAL TXIE RXIE INTPND
RMTPND TXRQ MSGLST
NEWDAT
CPUUPD
F7n2
F7n3
F7n4
F7n5
1) The notation “n“ (n= 1 to F) in the address definition defines the num ber of the related message objec t.
2) “X“ means that the v alue is und efined and t he loc atio n is r eserv ed. “U“ mea ns t hat the valu e is uncha nge d
UAR0 UU
H
UAR1 UU
H
LAR0 UU
H
LAR1 UUUU.
H
by a reset operation. “U“ values are undefined (as “X“) after a power-on reset operation
H
H
H
U000
ID20-18 ID17-13
ID4-0 000
B
ID28-21
ID12-5
Data Sheet 25 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 5
Contents of the CAN Registers in numeric order of their addresses (cont’d)
(C505C/C505CA only)
Addr.
n=1-F
1)
F7n6
Register Content
H
MCFG UUUU.
H
after
Reset
UU00
F7n7
F7n8
F7n9
F7nAHDB3 XX
F7nBHDB4 XX
F7nCHDB5 XX
F7nDHDB6 XX
F7nEHDB7 XX
1) The notation “n“ (n= 1 to F) in the address definition defines the num ber of the related message objec t.
2) “X“ means that the v alue is und efined and t he loc atio n is r eserv ed. “U“ mea ns t hat the valu e is uncha nge d
DB0 XX
H
DB1 XX
H
DB2 XX
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
by a reset operation. “U“ values are undefined (as “X“) after a power-on reset operation
Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
2)
DLC DIR XTD 0 0
B
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
.7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
Data Sheet 26 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
I/O Ports
The C505 has four 8-bit I/O ports and one 2-bit I/O port. Port 0 is an open-drain bidirectional I/O
port, while ports 1 to 4 are quasi-bidirectional I/O ports with internal pullup resistors. That means,
when configured as inputs, ports 1 to 4 will be pulled high and will source current when externally
pulled low. Port 0 will float when configured as input.
The output drivers of port 0 and 2 and the input buffers of port 0 are also used for accessing external
memory. In this application, port 0 outputs the low byte of the external memory address, time
multiplexed with the byte being written or read. Port 2 outputs the h igh byte of t he external m emory
address when the address is 16 bits wide. Otherwise, the port 2 pins continue emitting the P2 SFR
contents. In this function, port 0 is not an open-drain port, but uses a strong internal pullup FET .
Port 4 is 2-bit I/O port with CAN controller specific alternate functions. The eight analog input lines
are realized as mixed digital/analog inputs. The 8 analog inputs, AN0-AN7, are located at the port
1 pins P1.0 to P1.7. After reset, all analog inputs are disabled and the related pins of port 1 are
configured as digital inputs. The analog function of a specific port 1 pin is enabled by bits in the SFR
P1ANA. Writing a 0 to a bit position of P1ANA assigns the corresponding pin to operate as analog
input.
Note : P1ANA is a mapped SFR and can be only accessed if bit RMAP in SFR SYSCON is set.
Data Sheet 27 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Timer / Counter 0 and 1
Timer/Counter 0 and 1 can be used in four operating modes as listed in Table 6 :
Table 6
Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Operating Modes
Mode Description TMOD Input Clock
M1 M0 internal external (max)
f
0 8-bit timer/counter with a
00
divide-by-32 prescaler
1 16-bit timer/counter 0 1
/6x32 f
OSC
OSC
/12x32
2 8-bit timer/counter with
10
8-bit autoreload
3 Timer/counter 0 used as one
11
/6 f
OSC
OSC
/12
f
8-bit timer/counter and one
8-bit timer
Timer 1 stops
In the “timer” function (C/T
count rate is
f
OSC
/6.
= ‘0’) the register is incremented every machine cycle. Therefore the
In the “counter” function the register is incremented in response to a 1-to-0 transition at its
corresponding external input pin (P3.4/T0, P3.5/T1). Since it takes two machine cycles to detect a
falling edge the max. count rate is
f
/12. External inputs INT0 and INT1 (P3.2, P3.3) can be
OSC
programmed to function as a gate to facilitate pulse width measurem ents. Figure 10 illustrates the
input clock logic.
P3.4/T0
P3.5/T1
OSC
÷
6
C/T = 0
C/T = 1
Control
f
/6
OSC
Timer 0/1
Input Clock
Gate
(TMOD)
P3.2/INT0
P3.3/INT1
=1
TR0
TR1
_
<
1
&
MCS03117
Figure 10
Timer/Counter 0 and 1 Input Clock Logic
Data Sheet 28 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Timer/Counter 2 with Compare/Capture/Reload
The timer 2 of the C505 provides additional compare/capture/reload features. which allow the
selection of the following operating modes:
– Compare : up to 4 PWM signals with 16-bit/300 ns resolution (@ 20 MHz clock)
– Capture : up to 4 high speed capture inputs with 300 ns resolution
– Reload : modulation of timer 2 cycle time
The block diagram in Figure 11 shows the general configuration of timer 2 with the additional
compare/capture/reload registers. The I/O pins which can used for timer 2 control are located as
multifunctional port functions at port 1.
P1.5/
T2EX
P1.7/
T2
OSC
Sync.
T2I0
T2I1
Sync.
&
÷6
f
OSC
÷12
T2PS
Bit16 16 Bit 16 Bit 16 Bit
Comparator
Comparator
Comparator
EXEN2
Reload
EXF2
Reload
Timer 2
TH2TL2
Compare
Comparator
Capture
_
<
1
TF2
Input/
Output
Control
Interrupt
Request
P1.0/
INT3/
CC0
P1.1/
INT4/
CC1
P1.2/
INT5/
CC2
P1.2/
INT6/
CCL3/CCH3
CCL2/CCH2
CCL1/CCH1
CRCL/CRCH
CC3
MCB02730
Figure 11
Timer 2 Block Diagram
Data Sheet 29 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Timer 2 Operating Modes
The timer 2, which is a 16-bit-wide register, can operate as timer, event counter, or gated timer. A
roll-over of the count value in TL2/TH2 from all 1’s to a ll 0’s sets the timer overflow flag TF2 in SFR
IRCON, which can generate an interrupt. The bits in register T2CON are used to control the timer
2 operation.
Timer Mode :
offers the possibility of selecting a count rate of 1/6 or 1/12 of the oscillator frequency.
Gated Timer Mode :
the input of timer 2. lf T2 is high, the internal clock input is gated to the timer. T2 = 0 stops the
counting procedure. This facilitates pu lse width measurements. The external gate signal is sampled
once every machine cycle.
Event Counter Mode :
to-0 transition at its corresponding ex ternal input pin T2 (P1.7). In this func tion, the ex ternal input is
sampled every machine cycle. Since it tak es two machine cycles (12 oscillator periods) to recogn ize
a 1-to-0 transition, the maximum count rate is 1/6 of the oscillator frequency. There are no
restrictions on the duty cycle of the exte rnal input signal, but to en sure that a given level i s sampled
at least once before it changes, it must be held for at least one full machine cycle.
Reload of Timer 2 :
In mode 0, when timer 2 rolls over fro m all 1’s to all 0’s, it not only sets TF2 but also causes the timer
2 registers to be loaded with the 16-bit value in the CRC register, which is preset by software.
In mode 1, a 16-bit reload from the CRC register is caused by a negative transition at the corresponding input pin P1.5/T2EX. This transition will also set flag EXF2 if bit EXEN2 i n SFR IEN1 has been
set.
In timer function, the count rate is derived from the oscillator frequency. A prescaler
In gated timer function, the external input pin T2 (P1.7) functions as a gate to
In the event counter function. the timer 2 is incremented in response to a 1-
Two reload modes are selectable:
Data Sheet 30 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Timer 2 Compare Modes
The compare function of a timer/register combination operates as follows : the 16-bit value stored
in a compare or compare/capture registe r is com pared with the c ontents of t he tim er regi ster; i f the
count value in the timer reg ister matches the stored value, an appropriate out put signal is generated
at a corresponding port pin and an interrupt can be generated.
Compare Mode 0
In compare mode 0, upon matching the timer and compare register contents, the output signal
changes from low to high. lt goes back to a low level on timer overflow. As long as compare mode
0 is enabled, the appropriate output pin is controlled by the timer circuit only and writing to the port
will have no effect. Figure 12 shows a functional diagram of a port circuit when used in compare
mode 0. The port latch is directly controlled by the timer overflow and compare match signals. The
input line from the internal bus and the write-to-latch line of the port latch are disconnected when
compare mode 0 is enabled.
Compare Register
Circuit
Compare Reg.
16 Bit
Comparator
Bit16
Timer Register
Timer Circuit
Compare
Match
Timer
Overflow
Figure 12
Port Latch in Compare Mode 0
Port Circuit
Internal
Bus
Write to
Latch
S
D
CLK
R
Port
Latch
Read Latch
Q
Q
Read Pin
V
DD
Port
Pin
MCS02661
Data Sheet 31 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Compare Mode 1
If compare mode 1 is enabled and the software writes to the appropriate output latch at the port, the
new value will not appear at the output pin until the next compare match occurs. Thus, it can be
choosen whether the output signal has to make a new transition (1-to-0 or 0-to -1, depending on the
actual pin-level) or should keep its old value at the time when the timer value matches the stored
compare value.
In compare mode 1 (see Figure 13) the port cir cuit consists of two separat e latches. One latch
(which acts as a "shadow latch") can be written under software control, but its value will only be
transferred to the port latch (and thus to the port pin) when a compare match occurs.
Port Circuit
Compare Register
Circuit
Compare Reg.
Internal
16 Bit
Comparator
16 Bit
Timer Register
Timer Circuit
Compare
Match
Bus
Write to
Latch
Figure 13
Compare Function in Compare Mode 1
Timer 2 Capture Modes
D
Shadow
Latch
CLK
Read Latch
Q
D
Port
Latch
Read Pin
Q
QCLK
V
DD
Port
Pin
MCS02662
Each of the compare/capture registers CC1 to CC3 and the CRC register can be used to latch the
current 16-bit value of the timer 2 registers TL 2 and TH2. Two different m odes are provi ded for this
function.
In mode 0
, the external event causing a capture is :
– for CC registers 1 to 3: a positive transition at pins CC1 to CC3 of port 1
– for the CRC register: a positive or negative transition at the corresponding pin, depending
on the status of the bit I3FR in SFR T2CON.
In mode 1
a capture occurs in response to a write instruction to the low order byte of a capture
register. The write-to-register signal (e.g. write-to-CRCL) is used to initiate a capture. The timer 2
contents will be latched into the appropriate capture register in the cycle following the write
instruction. In this mode no interrupt request will be generated.
Data Sheet 32 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Serial Interface (USART)
The serial port is full duplex and can operate in four modes (one synchronous mode, three
asynchronous modes) as illustrated in Table 7.
Table 7
USART Operating Modes
Mode
0 0 0 Shift register mode, fixed baud rate
1 0 1 8-bit UART, variable baud rate
2 1 0 9-bit UART, fixed baud rate
3 1 1 9-bit UART, variable baud rate
For clarification some terms regarding the difference between "baud rate clock" and "baud rate"
should be mentioned. In the asynchronous modes
16 times the baud rate for internal synchronization. Therefore, the baud rate generators/timers have
to provide a "baud rate clock" (output si gnal in Figure 14 to the serial interface which - there divided
by 16 - results in the actual "baud rate". Further, the abbrevation f
frequency (crystal or external clock operation).
The variable baud rates for modes 1 and 3 of the serial interfac e can be derive d either from timer 1
or from a decdicated baud rate generator (see Figure 14).
SCON Description
SM0 SM1
Serial data enters and exits through R×D; T×D outputs th e shift
clock; 8-bit are transmitted/received (LSB first)
10 bits are transmitted (through T×D) or received (at R×D)
11 bits are transmitted (through T×D) or received (at R×D)
Like mode 2
the serial interfaces require a clock rate which is
refers to the oscillator
OSC
Data Sheet 33 12.00

Timer 1
Overflow
f
OSC
Baud
Rate
Generator
(SRELH
SRELL)
6÷÷
ADCON0.7
(BD)
0
1
Mode 2
Mode 0
Mode 1
Mode 3
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
SCON.7
SCON.6
(SM0/
SM1)
Only one mode
can be selected
PCON.7
2
(SMOD)
0
1
Baud
Rate
Clock
Note: The switch configuration shows the reset state.
MCS02733
Figure 14
Block Diagram of Baud Rate Generation for the Serial Interface
Table 8 below lists the values/formulas for the baud rate calculation of the serial interface with its
dependencies of the control bits BD and SMOD.
Table 8
Serial Interface - Baud Rate Dependencies
Serial Interface
Operating Modes
Mode 0 (Shift Register) ––
Mode 1 (8-bit UART)
Mode 3 (9-bit UART)
Active Control Bits Baud Rate Calculation
BD SMOD
f
/ 6
OSC
0 X Controlled by timer 1 overflow :
SMOD
(2
× timer 1 overflow rate) / 32
1 X Controlled by baud rate generator
SMOD
× f
(2
OSC
) /
(32 × baud rate generator overflow rate)
Mode 2 (9-bit UART) – 0
1
f
f
OSC
OSC
/ 32
/ 16
Data Sheet 34 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
CAN Controller (C505C and C505CA only)
The on-chip CAN controller, compliant to version 2.0B, is the functional heart which provides all
resources that are required to run the standard CAN protocol (11-bit identifiers) as well as the
extended CAN protocol (29-bit identifiers). It provides a sophisticated object layer to relieve the
CPU of as much overhead as possible when controll ing many different m essage objects (up to 15).
This includes bus arbitration, resending of garbled messages, error handling, interrupt generation,
etc. In order to implement the physical layer, external components have to be connected to the
C505C/C505CA.
The internal bus interface connects the on-chip CAN controller to the internal bus of the
microcontroller. The registers and data loc ations of the CAN interface are mapped to a specific 256
byte wide address range of the external data memory area (F700H to F7FFH) and can be accessed
using MOVX instructions. Figure 15 shows a block diagram of the on-chip CAN controller.
The TX/RX Shift Register holds the destuffed bit stream from the bus line to allow the parallel
access to the whole data or remo te frame for the acc eptance mat ch test and the para llel trans fer of
the frame to and from the Intelligent Memory.
The Bit Stream Processor (BSP) is a sequencer controlling the sequential data stream between
the TX/RX Shift Register, the CRC Register, and the bus line. The BSP also controls the EML and
the parallel data stream between the TX/RX Shift Register a nd the Intelligent Me mory such that the
processes of reception, arbitration, transmission, and error signalling are performed according to
the CAN protocol. Note that the automatic retransmission of mes sages which have been c orrupted
by noise or other external error conditions on the bus line is handled by the BSP.
The Cyclic Redundancy Check Register (CRC) generates the Cyclic Redundancy Check code to
be transmitted after the data bytes and checks the CRC code of incoming messages. This is done
by dividing the data stream by the code generator polynomial.
The Error Management Logic (EML) is responsible for the fault confinement of the CAN device. Its
counters, the Receive Error Counter and the Transmit Error Counter, are incremented and
decremented by commands from the Bit Stream Processor. According to the values of the error
counters, the CAN controller is set into the states error active, error passive and busoff.
The Bit Timing Logic (BTL) monitors the busline input RXDC and handles the busline related bit
timing according to the CAN protocol. The BTL synchronizes on a recessive to dominant busline
transition at Start of Frame (hard synchronization) and on any further recessive to dominant busline
transition, if the CAN controller itself does n ot transmit a dominant bi t (resynchroni zation). The BTL
also provides programmable time segments to compensate for the propagation delay time and for
phase shifts and to define the position of the Sample Point in the bit time. The programming of the
BTL depends on the baudrate and on external physical delay times.
The Intelligent Memory (CAM/RAM array) provides storage for up to 15 message objects of
maximum 8 data bytes length. Each of these objects has a unique identifier and its own set of
control and status bits. After the initial configuration, the Intelligent Memory can handle the
reception and transmission of data without further microcontroller actions.
Data Sheet 35 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
TXDC RXDC
Messages
Handlers
BTL-Configuration
TX/RX Shift Register
Intelligent
Memory
Interrupt
Register
CRC
Gen./Check
Messages
Bit
Timing
Logic
Timing
Generator
Clocks
(to all)
Control
Status +
Control
Status
Register
to internal Bus
Figure 15
CAN Controller Block Diagram
Bit
Stream
Processor
Error
Management
Logic
MCB02736
Data Sheet 36 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
CAN Controller Software Initialization
The very first step of the initialization is the CAN controller input clock selection. A divide-by-2
prescaler is enabled by default after res et (Figure 16). Setting bit CMOD (SYSCON.3) disables the
prescaler. The purpose of the prescaler selection is:
– to ensure that the CAN controller is operable when f
– to achieve the maximum CAN baudrate of 1 Mbaud when f
SYSCON.3
(CMOD)
f
OSC
2
1
0
f
CAN
is over 10 MHz (bit CMOD =0)
osc
is 8 MHz (bit CMOD=1)
osc
Full-CAN
Module
Condition: CMOD = 0, when > 10 MHz
f
OSC
Frequency (MHz) CMOD
f
OSC
f
CAN
8 8 1 000000
8 4 0 000000
16 8 0 000000
Note : The switch configuration s hows the reset state of bit CMOD.
Figure 16
CAN controller Input Clock Selection
(SYSCON.3)
BRP
(BTR0.0-5)
B
B
B
MCS03296
CAN
baudrate
(Mbaud/sec)
1
0.5
1
Data Sheet 37 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
8-Bit A/D Converter (C505 and C505C only)
The C505/C505C includes a high performance / high speed 8-bit A/D conv erter (ADC) with 8 analog
input channels. It operates with a successive approximation technique and provides the following
features:
– 8 multiplexed input channels (port 1), which can also be used as digital outputs/inputs
– 8-bit resolution
– Internal start-of-conversion trigger
– Interrupt request generation after each conversion
– Single or continuous conversion mode
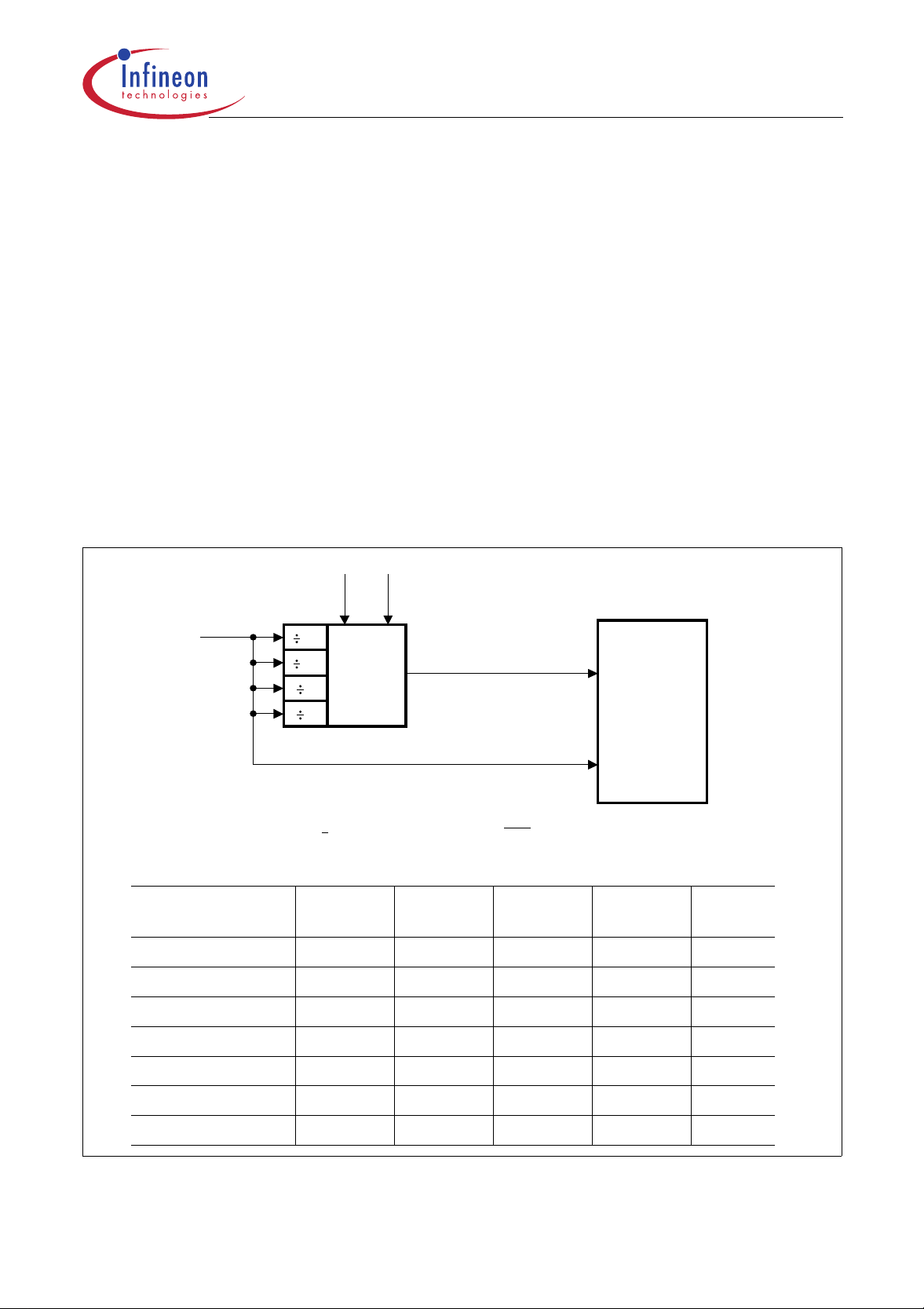
The 8-bit ADC uses two clock signals for operation : the conversion clock f
input clock f
(1/tIN). f
IN
is derived from the C505 system cloc k f
ADC
which is applied at the XTAL
OSC
ADC
(=1/t
pins via the ADC clock presca ler as shown in Figure 17. The input clock is equal to f
conversion clock f
is limited to a maximum frequency of 1.25 MHz. Therefore, the ADC clock
ADC
ADC
) and the
. The
OSC
prescaler must be programmed to a value which assures that the c onversion clock does not exceed
1.25 MHz. The prescaler ratio is selected by the bits ADCL1 and ADCL0 of SFR ADCON1.
ADCL0
Conversion Clock
Input Clock
f
OSC
=
=
f
IN
1
CLP
f
ADC
A / D
Converter
f
IN
MCS03299
f
OSC
Condition:
ADCL1
32
16
8
4
Clock Prescaler
f
ADC max
< 1.25 MHz
MUX
MCU System Clock
Rate (f
OSC
)
f
IN
[MHz]
Prescaler
Ratio
f
ADC
[MHz]
ADCL1 ADCL0
2 MHz 2 ÷ 4 0.5 0 0
5 MHz 5 ÷ 4 1.25 0 0
6 MHz 6 ÷ 8 0.75 0 1
10 MHz 10 ÷ 8 1.25 0 1
12 MHz 12 ÷ 16 0.75 1 0
16 MHz 16 ÷ 16110
20 MHz 20 ÷ 16 1.25 1 0
Figure 17
8-Bit A/D Converter Clock Selection
Data Sheet 38 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Internal
IEN1 (B8 )
H
Bus
Port 1
f
OSC
V
AREF
EXEN2
IRCON (C0 )
SWDT
H
TF2EXF2
P1ANA (90 )
EAN7
ADCON1 (DC )
H
EAN6
H
ADCL1HADCL0
ADCON0 (D8 )
BD
CLK
MUX
Conversion
Clock
Prescaler
EAN5
Input Clock f
EX5EX6
IEX5IEX6
EAN4
BSY
S&H
fConversion Clock
IN
EX4
IEX4
EAN3
ADM MX2
ADC
EX3
IEX3
EAN2
MX2
ECAN
SWI
EAN1
MX1
MX1
Single /
Continuous Mode
A / D
Converter
EADC
IADC
EAN0
MX0
MX0
ADDAT
(D9 )
H
LSB
.1
.2
.3
.4
.5
.6
MSB
ADST
(DA )
H
V
AGND
Start of
conversion
Internal
Bus
Shaded Bit locations are not used in ADC-functions.
Write to ADST
MCB03298
Figure 18
Block Diagram of the 8-Bit A/D Converter
Data Sheet 39 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
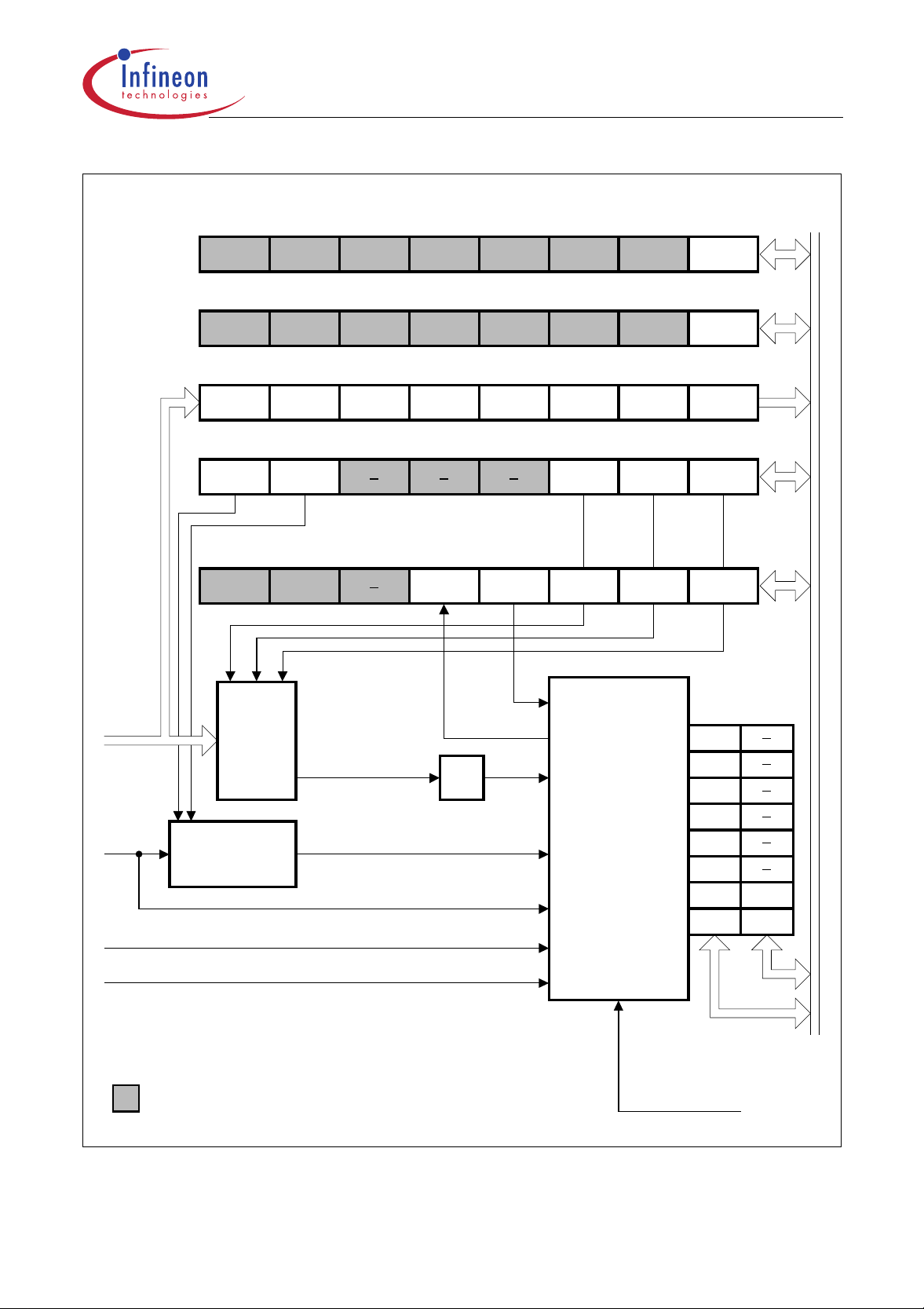
10-Bit A/D Converter (C505A and C505CA only)
The C505A/C505CA includes a high performance / high speed 10-bit A/D-Converter (ADC) with 8
analog input channels. It operates with a successive approximation technique and uses self
calibration mechanisms for reduction and compensation of offset and linearity errors. The A/D
converter provides the following features:
– 8 multiplexed input channels (port 1), which can also be used as digital inputs/outputs
– 10-bit resolution
– Single or continuous conversion mode
– Internal start-of-conversion trigger capability
– Interrupt request generation after each conversion
– Using successive approximation conversion technique via a capacitor array
– Built-in hidden calibration of offset and linearity errors
The 10-bit ADC uses two clock signals for op eration : the c onve rsion cloc k f
input clock f
(=1/tIN). f
IN
XTAL pins. The input clock f
is derived from the C505 system clock f
ADC
is equal to f
IN
The conversion f
OSC
OSC
clock is limited to a maximum
ADC
(=1/t
ADC
which is applied at the
ADC
) and the
frequency of 2 MHz. Therefore, the ADC clock prescaler must be pr ogrammed to a value which
assures that the conversion clock does not exceed 2 MHz. The prescaler ratio is selected by the
bits ADCL1 and ADCL0 of SFR ADCON1.
f
OSC
Condition:
ADCL1
32
16
8
4
Clock Prescaler
f
ADC max
< 2 MHz
MUX
ADCL0
Conversion Clock
Input Clock
f
OSC
=
=
f
IN
1
CLP
f
ADC
A / D
Converter
f
IN
MCS03635
MCU System Clock
Rate (f
OSC
)
f
IN
[MHz]
Prescaler
Ratio
f
ADC
[MHz]
ADCL1 ADCL0
2 MHz 2 ÷ 4 0.5 0 0
6 MHz 6 ÷ 4 1.5 0 0
8 MHz 8 ÷ 4200
12 MHz 12 ÷ 8 1.5 0 1
16 MHz 16 ÷ 8201
20 MHz 20 ÷ 16 1.25 1 0
Figure 19
10-Bit A/D Converter Clock Selection
Data Sheet 40 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Internal
IEN1 (B8 )
H
Bus
Port 1
f
OSC
V
AREF
EXEN2
IRCON (C0 )
EXF2
P1ANA (90 )
EAN7
ADCON1 (DC )
SWDT
H
TF2
H
EAN6
H
ADCL1HADCL0
ADCON0 (D8 )
BD
CLK
MUX
Conversion
Clock
Prescaler
EX6
IEX6
EAN5
Input Clock f
EX5
IEX5
EAN4
BSY
S&H
fConversion Clock
IN
EX4
IEX4
EAN3
ADM MX2
ADC
EX3
IEX3
EAN2
MX2
ECAN
SWI
EAN1
MX1
MX1
Single /
Continuous Mode
A / D
Converter
EADC
IADC
EAN0
MX0
MX0
ADDAT
ADDATH
(D9 )
H
)
(D9
H
.2
.3
.4
.5
.6
.7
.8
MSB
ADST
ADDATL
(DA )
H
(DAH)
LSB
.1
V
AGND
Start of
conversion
Internal
Bus
Shaded Bit locations are not used in ADC-functions.
Write to ADDATL
MCB03636
Figure 20
Block Diagram of the 10-Bit A/D Converter
Data Sheet 41 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
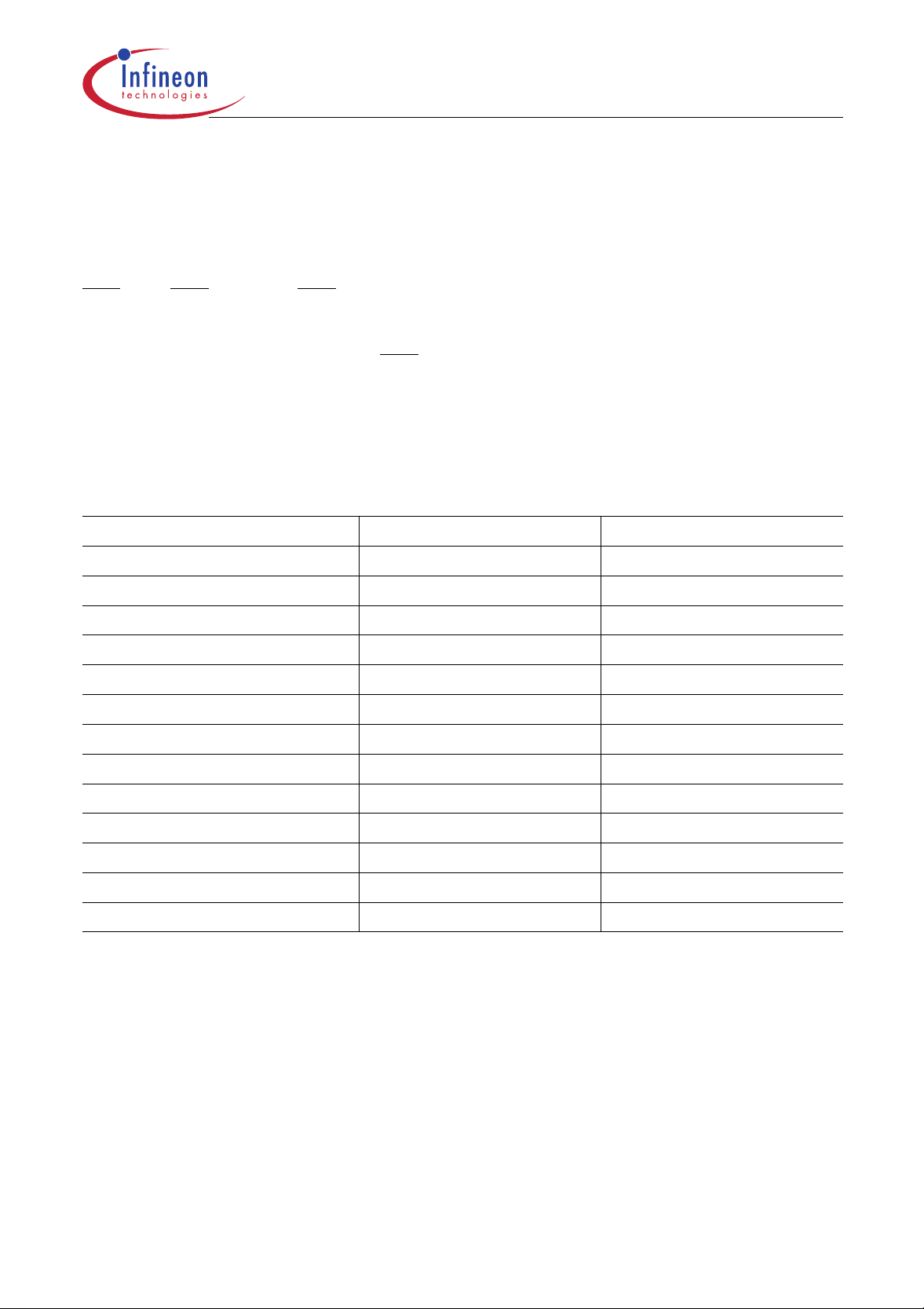
Interrupt System
The C505 provides 12 interrupt vectors with four priority levels. Five interrupt requests can be
generated by the on-chip peripherals (timer 0, timer 1, timer 2, serial interface, A/D converter). One
interrupt can be generated by the CAN controller (C505C an d C505CA only) or by a software setting
and in this case the interrupt vector is the same. Six interrupts may be triggered externally (P3.2/
, P3.3/INT1, P1.0/AN0/INT3/CC0, P1.1/AN1/INT4/CC1, P1.2/AN2/INT5/CC2, P1.3/AN3/INT6/
INT0
CC3). Additionally, the P1.5/AN5/T2EX can trigger an interrupt. The wake-up from power-down
mode interrupt has a special functi onali ty whic h a llows to exit from the software power-down mode
by a short low pulse at either pin P3.2/INT0
Figure 21 to Figure 23 give a general overview of the interrupt sources and illustrate the request
and the control flags which are described in the next secti ons. Table 9 lists all interrupt sources with
their request flags and interrupt vector addresses.
Table 9
Interrupt Source and Vectors
or the pin P4.1/RXDC.
Interrupt Source Interrupt Vector Address Interrupt Request Flags
External Interrupt 0 0003
Timer 0 Overflow 000B
External Interrupt 1 0013
Timer 1 Overflow 001B
Serial Channel 0023
Timer 2 Overflow / Ext. Reload 002B
A/D Converter 0043
CAN Controller / Software Interrupt 004B
External interrupt 3 0053
External Interrupt 4 005B
External Interrupt 5 0063
External interrupt 6 006B
Wake-up from power-down mode 007B
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
IE0
TF0
IE1
TF1
RI / TI
TF2 / EXF2
IADC
– / SWI
IEX3
IEX4
IEX5
IEX6
–
Data Sheet 42 12.00
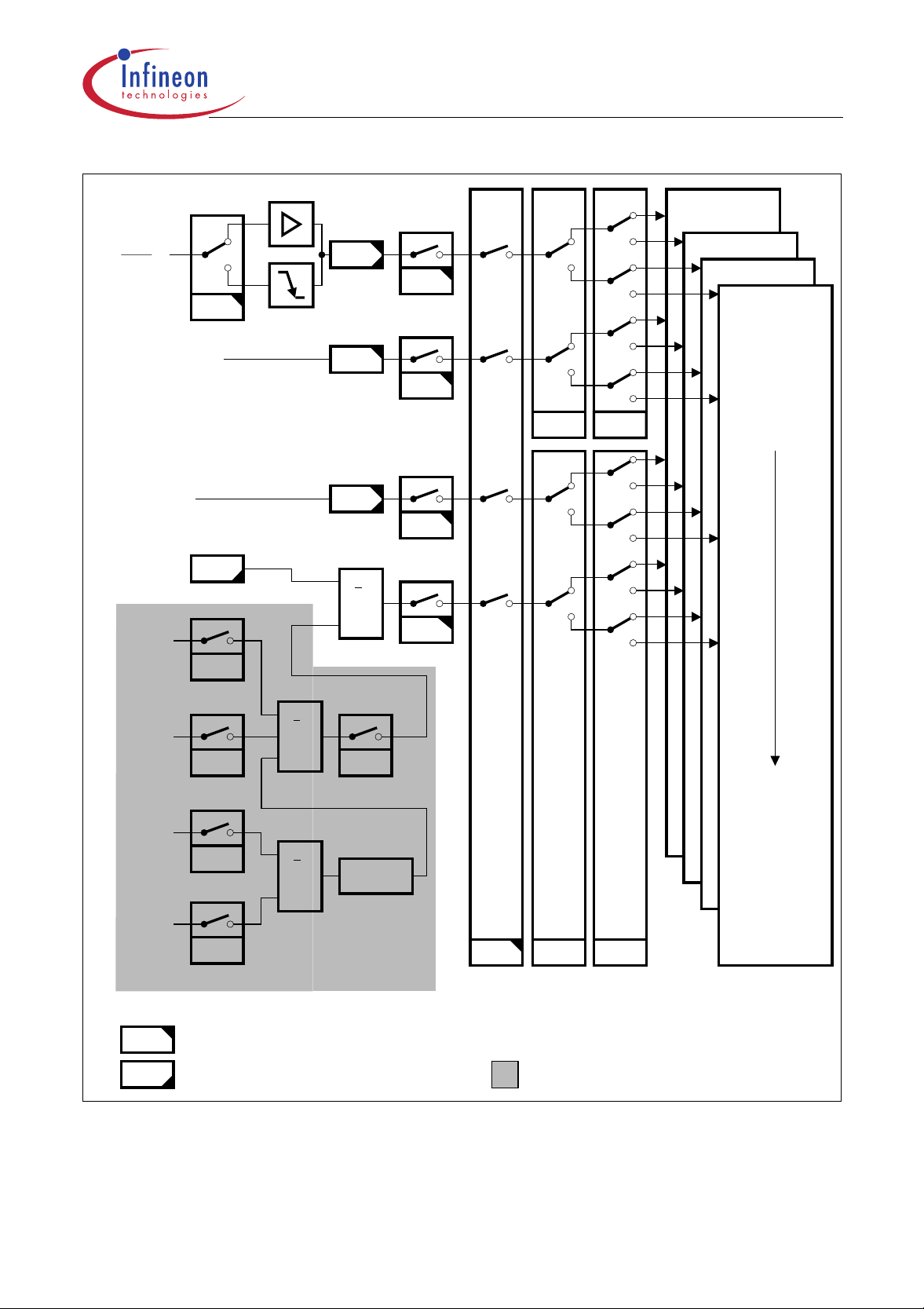
P3.2 /
INT0
A / D Converter
Timer 0
Overflow
Status
Error
IT0
TCON.0
SWI
IRCON.1
SIE
CR.2
EIE
>1
IE0
TCON.1
IADC
IRCON.0
TF0
TCON.5
>1
IE
CR.1CR.3
EX0
IEN0.0
EADC
IEN1.0
ET0
IEN0.1
ECAN
ECAN
IEN1.1
0003
0043
000B
004B
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Highest
Priority Level
H
Lowest
Priority Level
H
IP1.0 IP0.0
H
H
P
o
l
l
i
n
g
S
e
q
u
e
n
c
e
Message
Transmit
TXIE
MCR0.5 / 4
CAN Controller Interrupt Sources
Message
>1
INTPND
MCR0.0 / 1
Receive
RXIE
MCR0.3 / 2
EA
IEN0.7
IP1.1
IP0.1
Bit addressable
Request flag is cleared by hardware
C505C and C505CA Only
MCB03303
Figure 21
Interrupt Structure, Overview Part 1
Note: Each of the 15 CAN controller message objects (C505C and C505CA only), shown in the
shaded area of Figure 21 provides the bits/flags.
Data Sheet 43 12.00
P3.3 /
INT1
P1.0 /
AN0 /
INT3 /
CC0
IT1
TCON.2
I3FR
T2CON.6
IE1
TCON.3
IEX3
IRCON.2
EX1
IEN0.2
EX3
IEN1.2
0013
0053
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Highest
Priority Level
H
Lowest
Priority Level
P
H
IP1.2
IP0.2
o
l
l
i
n
g
Timer 1
Overflow
TF1
TCON.7
P1.1 /
AN1 /
INT4 /
CC1
IEX4
IRCON.3
Bit addressable
Request flag is cleared by hardware
Figure 22
Interrupt Structure, Overview Part 2
ET1
IEN0.3
EX4
IEN1.3
001B
H
005B
H
EA
IEN0.7
S
e
q
u
e
n
c
e
IP0.3IP1.3
MCB03304
Data Sheet 44 12.00

USART
P1.2 /
AN2 /
INT5 /
CC2
Timer 2
Overflow
P1.5 /
AN5 /
T2EX
P1.3 /
INT6 /
CC3
RI
SCON.0
TI
SCON.1
EXEN2
IEN1.7
Bit addressable
IRCON.4
TF2
IRCON.6
EXF2
IRCON.7
IRCON.5
>1
IEX5
>1
IEX6
ES
IEN0.4
EX5
IEN1.4
ET2
IEN0.5
EX6
IEN1.5
0023
H
0063
H
002B
H
006B
H
EA
IEN0.7
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Highest
Priority Level
Lowest
Priority Level
P
o
l
IP1.4
IP0.4
IP0.5IP1.5
l
i
n
g
S
e
q
u
e
n
c
e
Request flag is cleared by hardware
Figure 23
Interrupt Structure, Overview Part 3
MCB03305
Data Sheet 45 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Fail Save Mechanisms
The C505 offers enhanced fail s afe mechanisms , which all ow an automati c recovery from soft ware
upset or hardware failure :
– a programmable watchdog timer (WDT), with variable time-out period from 192 µs up to
approx. 393.2 ms at 16 MHz (314.5 ms at 20 MHz).
– an oscillator watchdog (OWD) which monitors the on-chip oscillator and forces the
microcontroller into reset state in case the on-chip oscill ator fails; it also provides the clock for
a fast internal reset after power-on.
The watchdog timer in the C505 is a 15-bit timer, which is incremented by a count rate of
upto
f
/192. The system clock of the C505 is divided by two prescalers, a divide-by-two and a
OSC
f
OSC
/12
divide-by-16 prescaler. For programmi ng of the watchdog timer o verflow rate, the upper 7 bits of the
watchdog timer can be written. Figure 24 shows the block diagram of the watchdog timer unit.
07
f
/ 6
OSC
2
16
14
WDTL
8
WDT Reset - Request
WDTH
IP0 (A9 )
H
OWDS
WDTS
WDTPSEL
External HW Reset
670
WDTREL (86 )
H
Control Logic
WDT
SWDT
IEN0 (A8 )
IEN1 (B8 )
H
H
MCB03306
Figure 24
Block Diagram of the Programmable Watchdog Timer
The watchdog timer can be started by software (bit SWDT in SFR IEN1) but it cannot be stopped
during active mo de of the device. I f the software fails t o refresh the runni ng watchdog timer a n
internal reset will be initiated on watchdog timer overflow. For refreshing of the watchdog timer the
content of the SFR WDTREL is transfered to the upper 7-bit of the watchdog timer. The refresh
sequence consists of two consequtive instructions which set the bits WDT and SWDT each. The
reset cause (external reset or reset caused by the watchdog) can be examined by software (flag
WDTS). It must b e noted, however, tha t the watchdog time r is halted during the idle mode and
power down mode of the processor.
Data Sheet 46 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Oscillator Watchdog
The oscillator watchdog unit serves for three functions:
– Monitoring of the on-chip oscillator's function
The watchdog supervises the on-chip oscillator's frequency; if it is lower than the frequency
of the auxiliary RC oscillator in the watchdog unit, the internal clock is supplied by the RC
oscillator and the device is brought into reset; if the failure condition disappears (i.e. the onchip oscillator has a higher frequency than the RC oscillator), the part, in order to allow the
oscillator to stabilize, executes a final reset phase of typ. 1 ms; then the oscillator watchdog
reset is released and the part starts program execution from address 0000H again.
– Fast internal reset after power-on
The oscillator watchdog unit provides a clock s upply for the reset before the on -chip oscillator
has started. The oscillator watchdog unit also works identically to the monitoring function.
– Control of external wake-up from software power-down mode
When the power-down mode is left by a low level at the P3.2/INT0
the oscillator watchdog unit assures that the microco ntrolle r resumes operatio n (exec ution of
the power-down wake-up interrupt) with the nominal clock rate. In the power-down mode the
RC oscillator and the on-chip oscillator are stopped. Both oscillators are started again when
power-down mode is released. When the on-chip oscillator has a higher frequency than the
RC oscillator, the microcontr oller starts program execution by process ing a power down
interrupt after a final delay of typ. 1 ms in order to allow the on-chip oscillator to stabilize.
pin or the P4.1/RXDC pin,
Data Sheet 47 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
EWPD
P4.1 / RXDC
P3.2 / INT0
XTAL1
XTAL2
Control
Logic
RC
Oscillator
On-Chip
Oscillator
WS
(PCON1.4)(PCON1.7)
Start /
Stop
f
RC
3 MHz
Start /
Stop
Power - Down
Mode Activated
f
10
1
f
2
OWDS
Frequency
Comparator
Power-Down Mode
Wake - Up Interrupt
Control
Logic
<
f
f
2
1
Delay
Internal Reset
>1
IP0 (A9 )
H
Int. Clock
MCB03308
Figure 25
Functional Block Diagram of the Oscillator Watchdog
Data Sheet 48 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Power Saving Modes
The C505 provides two basic power saving modes, the idle mode and the power down mode.
Additionally, a slow down mode is available. This power saving mod e reduces the internal clock rate
in normal operating mode and it can be also used for further power reduction in idle mode.
– Idle mode
In the idle mode the main oscillator of the C505 continues to run, but the CPU is gated off from
the clock signal. All peripheral units are further provided with the clock. The CPU status is
preserved in its entirety. The idle mode can be terminate d by any enabled interrupt of a
peripheral unit or by a hardware reset.
– Power down mode
The operation of the C505 is completely stopped a nd the oscill ator is turned off. Th is mode is
used to save the contents of the internal RAM with a very low standby current. Power down
mode is entered by software and can be left by reset or by a short low pulse at pin P3.2/
.or P4.1/RXDC.
INT0
– Slow down mode
The controller keeps up the fu ll operating functionality, but its n ormal clock frequency is
internally divided by 32. T his slows down all parts of the controller, the CP U and all
peripherals, to 1/32-th of their norma l operating frequency. Slo wing down the frequen cy
significantly reduces power consumption.
V
In the power down mode of operation,
V
be ensured, however, that
is not reduced before the power down mode is invoked, and that V
DD
can be reduced to minimize power consumpti on. It must
DD
DD
is restored to its normal operating level, before the power down mode is terminat ed. Table 10 gives
a general overview of the entry and exit procedures of the power saving modes.
Table 10
Power Saving Modes Overview
Mode Entering
Leaving by Remarks
(Instruction
Example)
Idle Mode ORL PCON, #01H
ORL PCON, #20H
Ocurrence of an
interrupt from a
peripheral unit
Hardware Reset
CPU clock is stopped;
CPU maintains their data;
peripheral units are active (if
enabled) and provided with
clock
Power Down Mode ORL PCON, #02H
ORL PCON, #40H
Hardware Reset Oscillator is stopped;
Short low pulse at
pin P3.2/INT0
or
contents of on-chip RAM and
SFR’s are maintained;
P4.1/RXDC
Slow Down Mode ORL PCON,#10H ANL PCON,#0EFH
or
Hardware Reset
Oscillator frequency is
reduced to 1/32 of its nominal
frequency
Data Sheet 49 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
OTP Memory Operation (C505A-4E and C505CA-4E only)
The C505A-4E/C505CA-4E contains a 32K byte one-time programmable (OTP) program me mory.
With the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E fast programming cycles are achieved (1 byte in 100
several levels of OTP memory protection can be selected.
For programming of the device, the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E must be put into the programming
mode. This typically is done not in-system but in a special programming hardware. In the
programming mode the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E operates as a slave device similar as an EPROM
standalone memory device and mus t be controlled wi th address/data informatio n, control lines, and
an external 11.5V programming voltage. Figure 26 shows the pins of the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E
which are required for controlling of the OTP programming mode.
µsec). Also
A0-A7 /
A8-A14
PALE
PMSEL0
PMSEL1
XTAL1
XTAL2
Figure 26
Programming Mode Configuration
V
DD
Port 2
C505A-4E
C505CA-4E
V
SS
Port 0
D0-D7
EA
/V
PP
PROG
PRD
RESET
PSEN
PSEL
Data Sheet 50 12.00

Pin Configuration in Programming Mode
D4D5D6D7EA
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23
33
D3
D2
D1
D0
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
123456789 10 11
C505A-4E
C505CA-4E
/ V
PP
N.C.
PROG
PSEN
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
A5 / A13
A6 / A14
A7
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
A4 / A12
A3 / A11
A2 / A10
A1 / A9
A0 / A8
V
DD
V
SS
XTAL1
XTAL2
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
N.C.
RESET
PMSEL0
N.C.
PSEL
PMSEL1
N.C.
PRD
PALE
Figure 27
P-MQFP-44 Pin Configuration of the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E in Programming Mode (Top View)
Data Sheet 51 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
The following Table 11 contains the functional description of all C505A-4E/C505CA-4E pins which
are required for OTP memory programming.
Table 11
Pin Definitions and Functions in Programming Mode
Symbol
Pin Number
I/O*)Function
RESET 4 I Reset
This input must be at static “1“ (active) level during the whole
programming mode.
PMSEL0
PMSEL157
I
I
Programming mode selection pins
These pins are used to select the different access modes in
programming mode. PMSEL1,0 must satisfy a setup time to the
rising edge of PALE. When the logic level of PMSEL1,0 is
changed, PALE must be at low level.
PMSEL1 PMSEL0 Access Mode
00Reserved
0 1 Read version bytes
1 0 Program/read lock bits
1 1 Program/read OTP memory byte
PSEL
8IBasic programming mode select
This input is used for the basic programming mode selection
and must be switched according Figure 28.
PRD
9IProgramming mode read strobe
This input is used for read access c ontrol for OTP memory read,
Version Register read, and lock bit read operations.
PALE 10 I Programming address latch enable
PALE is used to latch the high a ddress lines. The high address
lines must satisfy a setup a nd hold time to/from the falling edge
of PALE. PALE must be at low level when the logic level of
PMSEL1,0 is changed.
XTAL2 14 O XTAL2
Output of the inverting oscillator amplifier.
XTAL1 15 I XTAL1
Input to the oscillator amplifier.
V
SS
16 – Circuit ground potential
must be applied in programming mode.
V
DD
17 – Power supply terminal
must be applied in programming mode.
*) I = Input
O=Output
Data Sheet 52 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Table 11
Pin Definitions and Functions in Programming Mode (cont’d)
Symbol
Pin Number
I/O*)Function
P2.0-7 18-25 I Address lines
P2.0-7 are used as multiplexed address input lines A0-A7 and
A8-A14. A8-A14 must be latched with PALE.
PSEN
26 I Program store enable
This input must be at static “0“ level during the whole
programming mode.
PROG
27 I Programming mode write strobe
This input is used in programming mode as a write strobe for
OTP memory program, and lock bit write operations During
basic programming mode selection a lo w level must be appli ed
.
EA
/V
PP
to PROG
29 – External Access / Programming voltage
This pin must be at 11.5V (V
programming of an OTP memory byte or lock bit. During an
OTP memory read operation this pin must be at V
This pin is also used for basic programming mode selectio n. At
basic programming mode selection a lo w level must be appli ed
/VPP.
to EA
) voltage level during
PP
high level.
IH
D7-0 30-37 I/O Data lines 0-7
During programming mode, data bytes are transferred via the
bidirectional port 0 data lines.
N.C. 1-3, 6, 11-13,
28, 38-44
– Not Connected
These pins should not be connected in programming mode.
*) I = Input
O=Output
Data Sheet 53 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Basic Programming Mode Selection
The basic programming mode selection scheme is shown in Figure 2 8 .
V
DD
Clock
(XTAL1/XTAL2)
RESET
PSEN
PMSEL1,0
PROG
PRD
PSEL
PALE
5V
stable
“1“
“0“
0,1
“0“
“1“
“0“
EA/V
PP
During this period signals
are not actively driven
Figure 28
Basic Programming Mode Selection
0V
V
PP
V
IH
Ready for access
mode selection
Data Sheet 54 12.00

Table 12
Access Modes Selection
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Access Mode
V
Program OTP memory byte V
Read OTP memory byte V
Program OTP lock bits V
Read OTP lock bits V
Read OTP version byte V
EA
/
PROG PRD
PP
PP
IH
PP
IH
IH
H
H
H L H Byte addr.
HH H A0-7
HH L – D1,D0 see
PMSEL Address
10
(Port 2)
A8-14
Data
(Port 0)
D0-7
Table 13
D0-7
of sign. byte
Lock Bits Programming / Read
The C505A-4E/C505CA-4E has two programmable lock bits which, when programmed according
to Table 13, provide four levels of protection for the on-chip OTP code memory. The state of the
lock bits can also be read.
Table 13
Lock Bit Protection Types
Lock Bits at D1,D0 Protection
D1 D0
Level
Protection Type
1 1 Level 0 The OTP lock feature is disabled. During normal operation of
the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E, the state of the EA
pin is not
latched on reset.
1 0 Level 1 During normal operation of the C505A-4E/C505CA-4E, MOVC
instructions executed from external program memory are
disabled from fetching code bytes from internal me mory. EA
is
sampled and latched on reset. An OTP memory read ope ration
is only possible using the ROM/OTP verification mode 2 for
protection level 1. Further programming of the OTP memory is
disabled (reprogramming security).
0 1 Level 2 Same as level 1, but also OTP memory read operation using
OTP verification mode is disabled.
0 0 Level 3 Same as level 2; but additionally external code execution by
setting EA
=low during normal operation of the C505A-4E/
C505CA-4E is no more possible.
External code execution, which is initiated by an internal
program (e.g. by an internal jump instruction above the ROM
boundary), is still possible.
Data Sheet 55 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Notes
min. max.
Storage temperature
Voltage on V
to ground (
pins with respect
DD
V
)
SS
Voltage on any pin with respect
to ground (
V
)
SS
Input current on any pin during
T
ST
V
DD
V
IN
– 65 150 ° C –
– 0.5 6.5 V –
– 0.5 VDD + 0.5 V –
– 10 10 mA –
overload condition
Absolute sum of all input currents
| 100 mA | mA –
during overload condition
Power dissipation
P
DISS
1W–
Note: Stresses above those listed under “Absolute Maximum Ratings” may cause permanent
damage of the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the device at
these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this
specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for longer
periods may affect device reliability. During absolute maximum rating overload conditions
> VDD or VIN< VSS) the voltage on VDD pins with respect to ground (VSS) must not
(V
IN
exceed the values defined by the absolute maximum ratings.
Data Sheet 56 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Operating Conditions
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Notes
min. max.
Supply voltage V
DD
4.25 5.5 V Active mode,
f
osc max
= 20 MHz
2 5.5 V PowerDown mode
Ground voltage V
Ambient temperature
SAB-C505 T
SAF-C505 T
SAH-C505 T
SAK-C505 T
Analog reference
V
SS
A
A
A
A
AREF
0 V Reference voltage
°C –
070
-40 85
-40 110
-40 125
4 V
+ 0.1 V –
DD
voltage
Analog ground voltage
Analog input voltage
XTAL clock f
V
V
osc
AGND
AIN
V
– 0.1 V
SS
V
-0.2 V
AGND
+ 0.2 V –
SS
+0.2 V –
AREF
220
MHz
1)
(with 50% duty
cycle)
1) For the extended temperature range -40 °C to 110 °C (SAH) and -40 °C to 125 °C (SAK), the
devices C505-2R, C505-L, C505C-2R and C505C-L have the max. operating frequency of
16MHz with 50% clock duty cycle.
Parameter Interpretation
The parameters listed in the following partly represent the characteristi cs of the C505 and partly its
demands on the system. To aid in interpreting the parameters right, when evaluating them for a
design, they are marked in column “Symbol”:
CC (Controller Characteristics):
The logic of the C505 will provide signals with the respective characteristics.
SR (System Requirement):
The external system must provide signals with the respective characteristics to the C505.
Data Sheet 57 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
DC Characteristics
(Operating Conditions apply)
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. max.
Input low voltages
all except EA
pin
EA
RESET pin
Input high voltages
all except XTAL1, RESET
XTAL1 pin
RESET pin
Output low voltages
Ports 1, 2, 3, 4
Port 0, ALE, PSEN
Output high voltages
Ports 1, 2, 3, 4
Port 0 in external bus mode,
ALE, PSEN
Logic 0 input current
Ports 1, 2, 3, 4
Logical 1-to-0 transition current
Ports 1, 2, 3, 4
, RESET
V
IL
V
IL1
V
IL2
V
IH
V
IH1
V
IH2
V
OL
V
OL1
V
OH
V
OH2
I
IL
I
TL
– 0.5
– 0.5
– 0.5
0.2 VDD+0.9
0.7
V
DD
0.6 V
DD
–
–
2.4
V
0.9
DD
2.4
V
0.9
DD
0.2
0.2
0.2
V
DD
V
DD
V
DD
0.45
0.45
–
–
–
–
V
- 0.1
DD
V
- 0.3
DD
V
+ 0.1
DD
+ 0.5
+ 0.5
+ 0.5
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
V
–
–
–
–
–
–
I
= 1.6 mA
OL
I
= 3.2 mA
OL
I
= – 80 µA
OH
I
= – 10 µA
OH
I
= – 800 µA
OH
I
= – 80 µA
OH
– 10 – 70 µA VIN=0.45V
– 65 – 650 µA VIN=2V
1)
1)
2)
Input leakage current
Port 0, AN0-7 (Port 1), EA
Input high current to RESET
Pin capacitance C
Overload current
Programming voltage V
Supply current at EA/V
PP
I
LI
I
IH
IO
I
OV
PP
– ± 1 µA0.45<VIN< V
14)
5100µA
0.6 V
DD <VIN<VDD
– 10 pF fc=1MHz,
T
=25°C
A
– ± 5mA
3) 4)
10.9 12.1 V 11.5 V ± 5%
30 mA
6)
DD
5)
Notes see Page 60
Data Sheet 58 12.00

Power Supply Currents
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
C505 /
C505C
C505A-4E
/C505CA-4E
C505A-4R /
C505CA-4R
/C505A-2R /
C505CA-2R
/C505A-L /
C505CA-L
Active Mode 12 MHz
Idle Mode 12 MHz
Active Mode with
slow-down enabled
Idle Mode with
slow-down enabled
Power down mode I
Active Mode 16 MHz
Idle Mode 16 MHz
Active Mode with
slow-down enabled
Idle Mode with
slow-down enabled
Power down mode I
Active Mode 16 MHz
Idle Mode 16 MHz
Active Mode with
slow-down enabled
Idle Mode with
slow-down enabled
Power down mode I
20 MHz
20 MHz
12 MHz
20 MHz
12 MHz
20 MHz
20 MHz
20 MHz
16 MHz
20 MHz
16 MHz
20 MHz
20 MHz
20 MHz
16 MHz
20 MHz
16 MHz
20 MHz
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
12)
typ.
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
PD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
PD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
I
DD
PD
19.3
31.3
10.3
16.2
3.9
4.8
3.2
4.0
10 50 µA VDD= 2..5.5 V
28.7
35.2
14.9
17.7
9.9
12.3
5.1
6.3
5.6 20 µA VDD= 2..5.5 V
22.8
27.6
12.7
15.0
6.6
7.3
5.0
5.3
5.3 30 µA VDD= 2..5.5 V
13)
max.
27.039mA
13.0
21.0
5.5
7.5
5.0
7.0
30.7
37.6
15.9
18.9
12.8
15.6
5.6
6.8
29.2
35.3
16.3
19.3
8.2
9.3
5.9
6.5
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
7)
8)
9)
10)
11)
Notes see Page 60
Data Sheet 59 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Note:
1) Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may c ause spurious noise puls es t o be superimposed on th e VOL of ALE
and port 3. The noise is due to external bus capacitance discharging into the port 0 and port 2 pins when these
pins make 1-to-0 t ransitions during b us opera tion. In the wo rst case (c apacitiv e loading > 100 pF), the noise
pulse on ALE line may exceed 0.8 V. In such cases it may be desira ble to qualify ALE with a schmitt-trigge r,
or use an address latch with a schm it t- trig ger strobe input.
2) Capacitive loading on ports 0 and 2 may cause the
V
0.9
specification when the address lines are stabilizing.
DD
V
on ALE and PSEN to mom entarily fall below the
OH
3) Overload conditions under operating conditions occur if the voltage on the respective pin exceeds the specified
operating range (i.e.
pins may not exceed 50 mA. T he s upply voltage
V
> VDD+0.5V or VOV< VSS- 0.5 V). The absolute sum of input currents on all po rt
OV
V
and VSS must remain within the specified limits.
DD
4) Not 100% tested, gua rant eed by design characterizatio n.
5) Only valid for C505A-4E and C505CA-4E.
6) Only valid for C505A-4E and C505CA-4E in programming mode.
7)
I
(active mode) is measured with:
DD
XTAL1 driven with
=Port 0=RESET=VDD; all other pins are disconnected.
EA
8)
I
(idle mode) is measured with all output pins disconnected and with all peripherals disabled;
DD
XTAL1 driven with
RESET = EA
t
, tF= 5 ns, 50% duty cycle , VIL= VSS+0.5V, VIH= VDD– 0.5 V; XTAL2 = N.C.;
R
t
, tF= 5 ns, 50% duty cycle, VIL= VSS+0.5V, VIH= VDD– 0.5 V; XTAL2 = N.C.;
R
= VSS; Port0 = VDD; all other pins are disconnected; the microcontroller is put into idle mode by
software;
9)
I
(active mode with slow-down mode) is measured with all output pins disconnected and with all peripherals
DD
disabled;
XTAL1 driven with
RESET = EA
t
, tF= 5 ns, 50% duty cycle, VIL= VSS+0.5V, VIH= VDD– 0.5 V; XTAL2 = N.C.;
R
= VSS; all other pins are disconnected; the microcontroller is put into slow-down mode by
software;
10)
I
(idle mode with slow -dow n m ode) is me asure d with all outpu t pin s disc onnec ted and w ith a ll perip hera ls
DD
disabled;
t
XTAL1 driven with
RESET = EA
= VSS; Port0 = VDD; all other pins are disconnected ; the microcontro ller is put in to idle mode
, tF= 5 ns, 50% duty cycle, VIL= VSS+0.5V, VIH= VDD– 0.5 V; XTAL2 = N.C.;
R
with slow-down enabled by so ftw are;
11)
I
(power-down mode) is meas ured under following conditions :
PD
Port 0 = E
A = VDD; RESET =VSS; XTAL2 = N.C.; XTAL1 = VSS; V
AGND
= VSS; V
AREF
= VDD;
all other pins are disconnected.
12) The typi c al
13) The max im um
I
values are periodically measured at T
DD
I
values are measured under worst case conditions (T
DD
= +25 °C but not 100% tested.
A
= 0 °C or -40 °C an d V
A
=5.5V)
DD
14) The values are valid for C505C A-4R, C505CA-2R, C505CA-L, C5 05A-4R, C505A-2R and C505A -L only.
Data Sheet 60 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
I
DD
[mA]
40
35
30
25
20
15
e
d
o
M
e
v
i
t
c
A
c
A
e
d
o
M
e
v
i
t
ode
e M
l
Id
d
I
e
d
o
M
e
l
C505
C505C
I
DD
max
I
DD
typ
10
ive
t
c
A
5
12842016
+S
e
d
o
M
e
d
o
M
e
l
d
I
wn
o
d
-
w
lo
n
w
o
d
-
w
o
l
S
+
Figure 29
I
Diagram of C505 and C505C
DD
C505/C505C : Power Supply Current Calculation Formulas
Parameter Symbol Formula
Active mode
Idle mode
Active mode with
slow-down enabled
Idle mode with
slow-down enabled
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
1.5 * f
f
1.5
*
0.74 * f
f
1.0
*
0.11 * f
0.25
*
0.1 * f
0.25
*
OSC
OSC
OSC
f
OSC
f
+ 1.3
+ 9.0
OSC
+ 1.0
OSC
OSC
+ 2.0
OSC
+ 1.4
+ 2.6
+ 2.5
+ 2.0
f
OSC
[MHz]
Note:
f
is the oscillator frequency in MHz. IDD values are given in mA.
osc
Data Sheet 61 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
I
DD
[mA]
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
C505A-4E
C505CA-4E
e
d
o
M
e
v
i
t
c
A
d
I
e
v
i
t
c
A
12842016
e
d
o
M
e
l
n
w
o
d
-
w
o
l
S
+
e
d
o
M
n
w
do
-
ow
l
S
e+
od
M
e
l
d
I
f
OSC
[MHz]
I
DD
max
I
DD
typ
Figure 30
Diagram of C505A-4E and C505CA-4E
I
DD
C505A-4E/C505CA-4E : Power Supply Current Calculation Formulas
Parameter Symbol Formula
Active mode
Idle mode
Active mode with
slow-down enabled
Idle mode with
slow-down enabled
f
Note:
is the oscillator frequency in MHz. IDD values are given in mA.
osc
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
1.63 * f
1.74
*
0.69 * f
0.74
*
0.6 * f
f
0.7
*
0.3 * f
f
0.3
*
f
f
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
+ 0.3
+ 1.6
+ 0.3
+ 0.8
+ 2.6
+ 2.8
+ 3.9
+ 4.1
Data Sheet 62 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
I
DD
[mA]
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
C505A-4R
C505A-2R
C505A-L
C505CA-4R
C505CA-2R
C505CA-L
I
DD
max
e
d
o
M
e
v
i
t
c
A
A
e
l
I
d
12842016
d
I
d
o
M
e
v
i
t
c
S
+
e
d
o
M
e
d
o
M
e
l
n
w
o
d
-
w
o
l
S
+
e
n
w
o
d
-
w
o
l
f
OSC
[MHz]
I
DD
typ
Figure 31
Diagram of C505A-4R/C505A-2R/C505A-L/C505CA-4R/C505CA-2R/C505CA-L
I
DD
C505A-4R/C505A-2R/C505A-L/C505CA-4R/C505CA-2R/C505CA-L :
Power Supply Current Calculation Formulas
Parameter Symbol Formula
Active mode
Idle mode
Active mode with
slow-down enabled
Idle mode with
slow-down enabled
f
Note:
is the oscillator frequency in MHz. IDD values are given in mA.
osc
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
I
DD typ
I
DD max
1.19 * f
1.54
*
0.57 * f
0.75
*
0.18 * f
0.28
*
0.07 * f
0.14
*
f
f
f
f
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
OSC
+ 3.77
+ 4.47
+ 3.55
+ 4.26
+ 3.74
+ 3.67
+ 3.91
+ 3.64
Data Sheet 63 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
A/D Converter Characteristics of C505 and C505C
(Operating Conditions apply)
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. max.
Analog input voltage
V
AIN
V
AGND
0.2
-
V
+
AREF
V
0.2
1)
Sample time t
Conversion cycle time t
Total unadjusted error T
Internal resistance of
R
reference voltage source
Internal resistance of
R
analog source
ADC input capacitance C
Notes see next page.
Clock calculation table :
Clock Prescaler
ADCL1, 0 t
Ratio
S
ADCC
UE
AREF
ASRC
AIN
t
ADC
– 64 x t
32 x t
16 x t
8 x t
– 320 x t
160 x t
80 x tIN
40 x t
– ± 2LSBV
– t
ADC
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
IN
/ 500
ns Prescaler ÷ 32
Prescaler
Prescaler
Prescaler
ns Prescaler ÷ 32
Prescaler
Prescaler
kΩ
Prescaler
+0.5V ≤ V
SS
t
in [ns]
ADC
- 1
t
– tS / 500
kΩ
in [ns]
S
- 1
– 50 pF
t
S
ADCC
6)
÷ 16
÷ 8
÷ 4
÷ 16
÷ 8
÷ 4
5) 6)
2) 6)
2)
3)
≤ VDD-0.5V
AIN
4)
÷ 32 1 1 32 x t
÷ 16 1 0 16 x t
÷ 8 0 1 8 x t
÷ 4 0 0 4 x t
Further timing conditions : t
min = 800 ns
ADC
= 1 / f
t
IN
64 x tIN 320 x tIN
IN
32 x tIN 160 x tIN
IN
16 x tIN 80 x tIN
IN
8 x tIN 40 x tIN
IN
= t
OSC
CLP
Data Sheet 64 12.00

Note:
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
1) V
2) During the samp le time the in put c apac itance C
3) This parameter includes the sample time t
4) T
may exeed V
AIN
these cases will be 00
or V
AGND
H
AREF
or FFH, respectively.
up to the absolute maximum ratings. However, the conversion result in
must be charged/dis charg ed by the e xternal so urce. T he
AIN
internal resistance of the analog source must allow the capacitanc e to reac h th eir fi nal v olt age level within t
After the end of the sample time t
conversion clock t
(max.) is te sted at –40 ≤ TA ≤= 125 °C ; VDD ≤ 5.5 V; V
UE
depend on programming and can be taken from the table on the previous page.
ADC
, changes of the analog input voltage have no effect on the conversion result.
S
, the time for determining the digital result. Values for the
S
≤ VDD + 0.1 V and VSS= ≤ V
AREF
AGND
. It is
S
guaranteed by design characterization for all other voltages within the defined voltage range.
If an overload condition occurs on maximum 2 unused analog input pins and the absolute sum of input overload
currents on all analog input pins does not excee d 10 mA, an additional conversion error of 1/2 LSB is
permissible.
5) During the conversion the ADC’s capacitance must be repeatedly charged or discharged. The internal
resistance of the reference source must allow the capacitance to reach their final voltage level within the
indicated time. The maxim um int ernal resistance results from the programmed conversion timin g.
6) Not 100% tested, but guaranteed by design characteriz at ion.
.
Data Sheet 65 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
A/D Converter Characteristics of C505A and C505CA
(Operating Conditions apply)
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit Test Condition
min. max.
Analog input voltage
V
Sample time t
Conversion cycle time t
Total unadjusted error T
Internal resistance of
R
reference voltage source
Internal resistance of
R
analog source
ADC input capacitance C
AIN
S
ADCC
UE
AREF
ASRC
AIN
V
AGND
– 64 x t
– 384 x t
V
AREF
32 x t
16 x t
8 x t
192 x t
V
ns Prescaler ÷ 32
IN
IN
IN
IN
ns Prescaler ÷ 32
IN
IN
96 x tIN
48 x t
– ± 2LSBV
– ± 4LSBV
– t
ADC
- 0.25
– tS / 500
- 0.25
– 50 pF
IN
/ 250
kΩ
kΩ
1)
Prescaler
Prescaler
Prescaler
Prescaler
Prescaler
Prescaler
+0.5V ≤ V
SS
< V
SS
V
t
ADC
t
S
6)
AIN
- 0.5 V < V
DD
in [ns]
in [ns]
÷ 16
÷ 8
÷ 4
÷ 16
÷ 8
÷ 4
AIN
< VDD+0.5V
5) 6)
2) 6)
2)
3)
≤ VDD-0.5V
< VDD
AIN
4)
4)
Notes see next page.
Clock calculation table :
Clock Prescaler
ADCL1, 0 t
ADC
Ratio
÷ 32 1 1 32 x t
÷ 16 1 0 16 x t
÷ 8 0 1 8 x t
÷ 4 0 0 4 x t
Further timing conditions : t
min = 500 ns
ADC
= 1 / f
t
IN
t
IN
IN
IN
IN
OSC
t
S
ADCC
64 x tIN 384 x tIN
32 x tIN 192 x tIN
16 x tIN 96 x tIN
8 x tIN 48 x tIN
= t
CLP
Data Sheet 66 12.00

Note:
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
1) V
2) During the samp le time the in put c apac itance C
3) This parameter incl udes the sample time t
may exeed V
AIN
these cases will be X000
AGND
or V
or X3FFH, respecti vely.
H
up to the absolute maximum ratings. However, the conversion result in
AREF
must be charged/dis charg ed by the e xternal so urce. T he
AIN
internal resistance of the analog source must allow the capacitanc e to reac h th eir fi nal v olt age level within t
After the end of the sample time t
calibration. Values for the conversion clock t
, changes of the analog input voltage have no effect on the conversion result.
S
, the time for determinin g the digital result and the tim e for the
S
depend on programming and can be taken from the table on
ADC
S
the previo us page.
4) T
is tested at V
UE
AREF
= 5.0 V, V
= 0 V, VDD = 4.9 V. It is guaranteed by design characterization for all
AGND
other voltages within the defined voltage range.
If an overload condition occurs on maximum 2 unused analog input pins and the absolute sum of input overload
currents on all analog input pins does not excee d 10 mA, an additional conversion error of 1/2 LSB is
permissible.
5) During the conversion the ADC’s capacitance must be repeatedly charged or discharged. The internal
resistance of the reference source must allow the capacitance to reach their final voltage level within the
indicated time. The maxim um int ernal resistance results from the programmed conversion timin g.
6) Not 100% tested, but guaranteed by design characteriz at ion.
.
Data Sheet 67 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
AC Characteristics (16 MHz, 0.4 to 0.6 Duty Cycle)
(Operating Conditions apply)
(
C
for port 0, ALE and PSEN outputs = 100 pF; CL for all other outputs = 80 pF)
L
Program Memory Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
ALE pulse width
Address setup to ALE
Address hold after ALE
ALE to valid instruction in
ALE to PSEN
PSEN
pulse width t
PSEN
to valid instruction in t
Input instruction hold after PSEN
Input instruction float after PSEN
Address valid after PSEN
Address to valid instruction in
Address float to PSEN
t
LHLL
t
AVLL
t
LLAX
t
LLIV
t
LLPL
PLPH
PLIV
t
PXIX
t
PXIZ
t
PXAV
t
AVIV
t
AZPL
16-MHz clock
Duty Cycle
Variable Clock
1/CLP= 2 MHz to 16 MHz
0.4 to 0.6
min. max. min. max.
48 – CLP - 15 – ns
10 – TCL
10 – TCL
-15 – ns
Hmin
-15 – ns
Hmin
– 75 – 2 CLP - 50 ns
10 – TCL
73 – CLP+
TCL
– 38 – CLP+
-15 – ns
Lmin
– ns
-15
Hmin
TCL
Hmin
ns
- 50
0 – 0 – ns
*)
– 15 – TCL
*)
20 – TCL
- 5 – ns
Lmin
– 95 – 2 CLP +
TCL
Lmin
Hmin
-10 ns
ns
-55
-5 – -5 – ns
*)
Interfacing the C505 to devices with float times up to 20 ns is permissible. Th is lim it ed bus contention will not
cause any damage to port 0 driv ers.
Data Sheet 68 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
AC Characteristics (16 MHz, 0.4 to 0.6 Duty Cycle, cont’d)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
pulse width
RD
WR
pulse width
Address hold after ALE
RD
to valid data in
Data hold after RD
Data float after RD
ALE to valid data in
Address to valid data in
ALE to WR
or RD
Address valid to WR
or RD high to ALE high
WR
Data valid to WR
transition
Data setup before WR
Data hold after WR
Address float after RD
t
RLRH
t
WLWH
t
LLAX2
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
LLDV
t
AVDV
t
LLWL
t
AVWL
t
WHLH
t
QVWX
t
QVWH
t
WHQX
t
RLAZ
16-MHz clock
Duty Cycle
Variable Clock
1/CLP= 2 MHz to 16 MHz
0.4 to 0.6
min. max. min. max.
158 – 3 CLP - 30 – ns
158 – 3 CLP - 30 – ns
48 – CLP - 15 – ns
– 100 – 2 CLP+
TCL
Hmin
- 50
ns
0 – 0 – ns
– 51 – CLP - 12 ns
– 200 – 4 CLP - 50 ns
– 200 – 4 CLP +
TCL
Hmin
73 103 CLP +
TCL
Lmin
- 15
CLP+
TCL
Lmin
-75
+ 15
ns
ns
95 – 2 CLP - 30 – ns
10 40 TCL
5 – TCL
163 – 3 CLP +
TCL
5 – TCL
- 15 TCL
Hmin
- 20 – ns
Lmin
Hmin
+ 15 ns
– ns
- 50
Lmin
- 20 – ns
Hmin
– 0 – 0ns
Data Sheet 69 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
AC Characteristics (16 MHz, 0.4 to 0.6 Duty Cycle, cont’d)
External Clock Drive Characteristics
Parameter Symbol CPU Clock = 16 MHz
Duty Cycle 0.4 to 0.6
Variable CPU Clock
1/CLP = 2 to 16 MHz
Unit
min. max. min. max.
Oscillator period CLP 62.5 62.5 62.5 500 ns
High time TCL
Low time TCL
Rise time
Fall time
t
R
t
F
H
L
25 – 25 CLP - TCL
25 – 25 CLP - TCL
ns
L
ns
H
– 10 – 10 ns
– 10 – 10 ns
Oscillator duty cycle DC 0.4 0.6 25 / CLP 1 - 25 / CLP –
Clock cycle TCL 25 37.5 CLP * DC
min
CLP * DC
max
ns
Note: The 16 MHz values in the tables are given as an example for a typical duty cycle variation of
the oscillator clock from 0.4 to 0.6.
Data Sheet 70 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
AC Characteristics (20 MHz, 0.5 Duty Cycle)
(Operating Conditions apply)
(
C
for port 0, ALE and PSEN outputs = 100 pF; CL for all other outputs = 80 pF)
L
Program Memory Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
ALE pulse width
Address setup to ALE
Address hold after ALE
ALE to valid instruction in
ALE to PSEN
PSEN
pulse width t
PSEN
to valid instruction in t
Input instruction hold after PSEN
Input instruction float after PSEN
Address valid after PSEN
Address to valid instruction in
t
LHLL
t
AVLL
t
LLAX
t
LLIV
t
LLPL
PLPH
PLIV
t
PXIX
t
PXIZ
t
PXAV
t
AVIV
20 MHz clock
0.5 Duty Cycle
Variable Clock
1/CLP = 2 MHz to 20 MHz
min. max. min. max.
35 – CLP - 15 – ns
10 – CLP/2 - 15 – ns
10 – CLP/2 - 15 – ns
– 55 – 2 CLP - 45 ns
10 – CLP/2 - 15 – ns
60 – 3/2 CLP
– ns
- 15
– 25 – 3/2 CLP
ns
- 50
0 – 0 – ns
*)
– 20 – CLP/2 - 5 ns
*)
20 – CLP/2 - 5 – ns
– 65 – 5/2 CLP
ns
- 60
Address float to PSEN
*)
Interfacing the C505 to devices with float times up to 20 ns is permissible. Th is lim it ed bus contention will not
cause any damage to port 0 driv ers.
t
AZPL
- 5 – - 5 – ns
Data Sheet 71 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
AC Characteristics (20 MHz, 0.5 Duty Cycle, cont’d)
External Data Memory Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
pulse width
RD
pulse width
WR
Address hold after ALE
to valid data in
RD
Data hold after RD
Data float after RD
ALE to valid data in
Address to valid data in
ALE to WR
or RD
Address valid to WR
WR
or RD high to ALE high
Data valid to WR
transition
Data setup before WR
Data hold after WR
Address float after RD
t
RLRH
t
WLWH
t
LLAX2
t
RLDV
t
RHDX
t
RHDZ
t
LLDV
t
AVDV
t
LLWL
t
AVWL
t
WHLH
t
QVWX
t
QVWH
t
WHQX
t
RLAZ
20 MHz clock
0.5 Duty Cycle
Variable Clock
1/CLP = 2 MHz to 20 MHz
min. max. min. max.
120 – 3 CLP - 30 – ns
120 – 3 CLP - 30 – ns
35 – CLP - 15 – ns
– 75 – 5/2 CLP- 50 ns
0 – 0 – ns
– 38 – CLP - 12 ns
– 150 – 4 CLP - 50 ns
– 150 – 9/2 CLP - 75 ns
60 90 3/2 CLP - 15 3/2 CLP + 15 ns
70 – 2 CLP - 30 – ns
10 40 CLP/2 - 15 CLP/2 + 15 ns
5 – CLP/2 - 20 – ns
125 – 7/2 CLP - 50 – ns
5 – CLP/2 - 20 – ns
– 0 – 0ns
External Clock Drive Characteristics
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
Variable Clock
Freq. = 2 MHz to 20 MHz
min. max.
Oscillator period CLP 50 500 ns
High time
TCL
Low time TCL
Rise time t
Fall time t
R
F
15 CLP-TCL
H
15 CLP-TCL
L
L
H
– 10 ns
– 10 ns
ns
ns
Oscillator duty cycle DC 0.5 0.5 –
Data Sheet 72 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
t
LHLL
ALE
PSEN
Port 0
Port 2
t
AVLL
A0 - A7
t
PLPH
t
LLPL
t
LLIV
t
PLIV
t
t
AVIV
t
AZPL
LLAX
t
Instr.IN
t
PXAV
t
PXIZ
PXIX
A0 - A7
A8 - A15 A8 - A15
Figure 32
Program Memory Read Cycle
MCT00096
Data Sheet 73 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
t
WHLH
ALE
PSEN
t
LLDV
RD
t
LLWL
t
RLDV
t
RLRH
t
AVLL
Port 0
A0 - A7 from
Ri or DPL from PCL
t
AVWL
Port 2
Figure 33
Data Memory Read Cycle
t
LLAX2
t
AVDV
t
RLAZ
Data IN
t
RHDZ
t
RHDX
A0 - A7 Instr.
A8 - A15 from PCHP2.0 - P2.7 or A8 - A15 from DPH
IN
MCT00097
Data Sheet 74 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
t
WHLH
ALE
PSEN
WR
t
AVLL
t
Port 0
A0 - A7 from
Ri or DPL from PCL
t
AVWL
Port 2
Figure 34
Data Memory Write Cycle
t
LLWL
LLAX2
t
QVWX
t
WLWH
t
QVWH
Data OUT
t
WHQX
A0 - A7
A8 - A15 from PCHP2.0 - P2.7 or A8 - A15 from DPH
Instr.IN
MCT00098
CLP
t
R
t
F
0.7V
0.7
V
DD
DD
0.2V
0.2
- 0.1
DD
- 0.1
V
DD
MCT03310
XTAL1
TCL
H
TCL
L
Figure 35
External Clock Drive on XTAL1
Data Sheet 75 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
AC Characteristics of Programming Mode (C505A-4E and C505CA-4E only)
V
= 5 V ± 10 %; VPP = 11.5 V ± 5%; TA = 25 °C ± 10 °C
DD
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
min. max.
PALE pulse width
PMSEL setup to PALE rising edge
Address setup to PALE, PROG
, or PRD
falling edge
Address hold after PALE, PROG
, or PRD
falling edge
Address, data setup to PROG
Address, data hold after PROG
PMSEL setup to PROG
or PRD t
PMSEL hold after PROG
PROG
PRD
pulse width t
pulse width t
or PRD t
or PRD t
or PRD t
Address to valid data out
to valid data out t
PRD
Data hold after PRD
Data float after PRD
PROG
high between two consecutive PROG
low puls es
t
PAW
t
PMS
t
PAS
t
PAH
PCS
PCH
PMS
PMH
PWW
PRW
t
PAD
PRD
t
PDH
t
PDF
t
PWH1
35 – ns
10 –
10 – ns
10 – ns
100 – ns
0 – ns
10 – ns
10 – ns
100 – µs
100 – ns
– 75 ns
– 20 ns
0 – ns
– 20 ns
1 – µs
PRD
high between two consecutive PRD low
t
PWH2
100 ns
pulses
XTAL clock period
t
CLKP
83.3 500 ns
Data Sheet 76 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
t
PAW
PALE
t
PMS
PMSEL1,0
t
PAH
Port 2
t
PAS
A8-A14 A0-A7
Port 0
PROG
t
PCS
Notes: PRD must be high during a programming write cycle.
Figure 36
Programming Code Byte - Write Cycle Timing
H, H
t
D0-D7
PWW
t
PCH
t
PWH
MCT03642
Data Sheet 77 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
t
PAW
PALE
t
PMS
PMSEL1,0
t
PAH
t
PAD
Port 2
t
PAS
A8-A14 A0-A7
Port 0
PRD
t
PCS
PROG must be high during a programming read cycle.Notes:
Figure 37
Verify Code Byte - Read Cycle Timing
H, H
t
PDH
D0-D7
t
t
PRW
t
t
PDFPRD
PCH
t
PWH
MCT03643
Data Sheet 78 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
PMSEL1,0
Port 0
t
PMS
PROG
PRD
PALE should be low during a lock bit read / write cycle.Note:
Figure 38
Lock Bit Access Timing
H, L H, L
D0, D1 D0, D1
t
PCS
t
PWW
t
PCH
t
PMH
t
PMStPRD
t
PRW
t
PDH
t
PDF
t
PMH
MCT03644
PMSEL1,0
Port 2
Port 0
PRD
PROG must be high during a programming read cycle.Note:
t
t
PMS
PCS
L, H
e. g. FD
D0-7
t
PRD
t
PRW
H
t
PCH
t
PDH
t
PDF
t
PMH
MCT03645
Figure 39
Version Byte Read Timing
Data Sheet 79 12.00
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
ROM/OTP Verification Characteristics for C505
ROM Verification Mode 1 (C505(C)(A)-2R and C505(C)A-4R only)
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
min. max.
Address to valid data
P1.0 - P1.7
P2.0 - P2.6
Port 0
Address: P1.0 - P1.7 = A0 - A7
Data: P0.0 - P0.7 = D0 - D7
Note: P2.6 should be connected to V
Figure 40
ROM Verification Mode 1
t
AVQV
P2.6
P2.0 - P2.5 = A8 - A14
– 5 CLP ns
Address
t
AVQV
Data OUT
Inputs:
Inputs: P2.6, P2.7, PSEN =
SS
P2.7, PSEN = V
ALE, EA = V
ALE, EA =
RESET = V
RESET =
for C505(C)(A)-2R
V
IH
IH2
V
IH2
V
SS
SS
IH
MCT03693
Data Sheet 80 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
ROM/OTP Verification Characteristics for C505 (cont’d)
ROM/OTP Verification Mode 2
Parameter Symbol Limit Values Unit
min. typ max.
ALE pulse width
ALE period
Data valid after ALE
Data stable after ALE
P3.5 setup to ALE low
t
AWD
t
ACY
t
DVA
t
DSA
t
AS
– CLP – ns
– 6 CLP – ns
––2 CLP ns
4 CLP ––ns
– t
CL
– ns
Oscillator frequency 1/ CLP 4 – 6MHz
t
ACY
t
AWD
ALE
t
DSA
t
DVA
Port 0
t
AS
Data Valid
P3.5
MCT02613
Figure 41
ROM/OTP Verification Mode 2
Data Sheet 81 12.00

C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
VDD-0.5 V
0.45 V
V
+0.90.2
DD
VDD0.2 -0.1
Test Points
MCT00039
AC Inputs during testing are driven at VDD- 0.5 V for a logic ’1’ and 0 .45 V for a logi c ’0’.
Timing measurements are made at
for a logic ’1’ and V
IHmin
for a logic ’0’.
ILmax
V
Figure 42
AC Testing: Input, Output Waveforms
V
OH
V
OL
-0.1 V
+0.1 V
V
Load
V
V
Load
Load
+0.1 V
Timing Reference
Points
-0.1 V
MCT00038
For timing purposes a port pin is no longer floating when a 100 mV change from load voltage
occurs and begins to float when a 100 mV change from the loaded
I
OL/IOH
≥±20 mA
V
OH/VOL
level occurs.
Figure 43
AC Testing : Float Waveforms
Crystal Oscillator Mode Driving from External Source
C
XTAL2
N.C.
XTAL2
2 - 20
MHz
External Oscillator
Signal
C
XTAL1
XTAL1
Crystal Mode: C = 20 pF 10 pF (incl. stray capacitance)
MCS03311
Figure 44
Recommended Oscillator Circuits for Crystal Oscillator
Data Sheet 82 12.00

P-MQFP-44-2 (SMD)
(Plastic Metric Quad Flat Package)
C505/C505C/C505A/C505CA
Figure 45
P-MQFP-44 Package Outline
Sorts of Packing
Package outlines for tubes, trays etc. are contained in our
Data Book “Package Information”
SMD = Surface Mounted Device
GPM05622
Dimensions in mm
Data Sheet 83 12.00

Infineon goes for Business Excellence
“Business excellence means intelligent approaches and clearly
defined processes, which are both constantly under review and
ultimately lead to good operating results.
Better operating results and business excellence mean less
idleness and wastefulness for all of us, more professional
success, more accurate information, a bet ter overview and,
thereby, less frustration and more satisfaction.”
Dr. Ulrich Schumacher
http://www.infineon.com
Published by Infineon Technologies AG
 Loading...
Loading...