PROFET® Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Smart Highside Power Switch
Reversave
•
Reverse battery protection by self turn on of
Product Summary
Operating voltage
V
bb(on)
power MOSFET
On-state resistance RON 16
Features
•
Short circuit protection
•
Current limitation
•
Overload protection
•
Thermal shutdown
•
Overvoltage protection (including load dump)
•
Loss of ground protection
•
Loss of V
charged inductive loads)
•
Very low standby current
•
Fast demagnetisation of inductive loads
•
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection
•
Optimized static electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
protection (with external diode for
bb
Load current (ISO) I
Current limitation
Package
TO-252-5-1
L(ISO)
I
L(SCr)
Diagnostic Function
•
Proportional load current sense (with defined fault signal during thermal shutdown)
Application
•
Power switch with current sense diagnostic feedback for 12V and 24 V DC grounded loads
•
All types of resistive, capacitive and inductive loads (no PWM with inductive loads)
•
Replaces electromechanical relays, fuses and discrete circuits
5.0 ... 36 V
mΩ
25 A
65 A
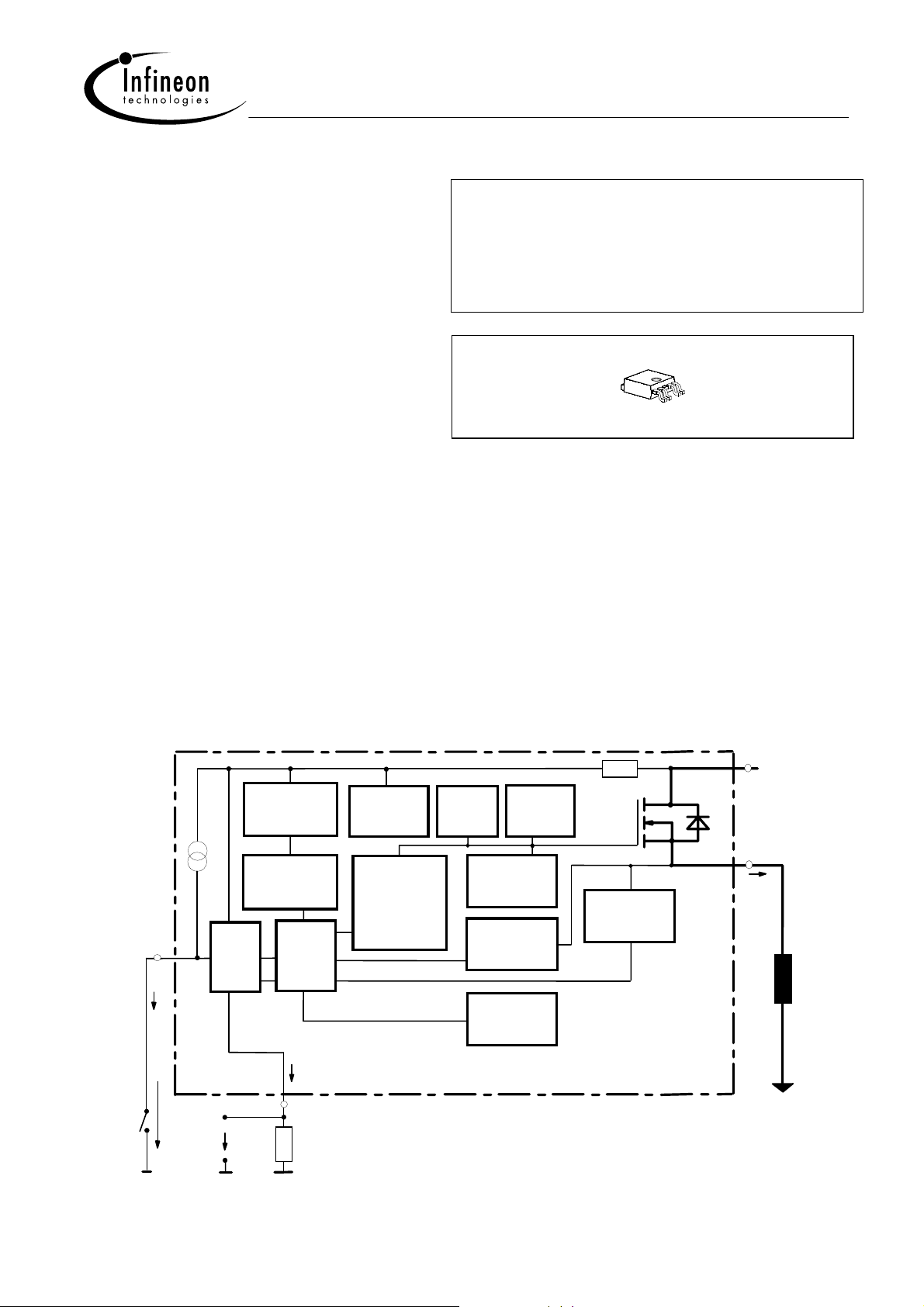
General Description
N channel vertical power FET with charge pump, current controlled input and diagnostic feedback with load
current sense, integrated in Smart SIPMOS
Voltage
source
Voltage
sensor
2
IN
ESD
I
IN
V
IN
V
IS
Logic
I
IS
IS
4
R
IS
chip on chip technology. Providing embedded protective functions.
3 & Tab
+ V
bb
OUT
1, 5
I
L
Load GND
Overvoltage
protection
Charge pump
Level shifter
Rectifier
Current
limit
Gate
protection
Limit for
unclamped
ind. loads
Output
Voltage
detection
Temperature
sensor
R
bb
Current
Sense
PROFET
Load
Logic GND
Infineon Technologies AG Page 1 of 13 2003-Oct-01
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Pin Symbol Function
1 OUT O
2 IN I
Tab/(3) Vbb +
4 IS S
5 OUT O
*) Not shorting all outputs will considerably increase the on-state resistance, reduce the peak current capability
and decrease the current sense accuracy
Maximum Ratings at Tj = 25 °C unless otherwise specified
Parameter Symbol Values Unit
Supply voltage (overvoltage protection see page 4) Vbb 36 V
Supply voltage for full short circuit protection
(see also diagram on page 9) Tj=-40...150 °C:
Load dump protection V
LoadDump
RI= 2 Ω, RL= 2.7 Ω, td= 200 ms, IN= low or high
Load current (Short-circuit current, see page 4) IL self-limited A
Operating temperature range
Storage temperature range
Power dissipation (DC) TC ≤ 25°C P
Inductive load switch-off energy dissipation,
single pulse U=12V, I=10A, L=3mH Tj=150 °C: EAS 0.15 J
Electrostatic discharge capability (ESD)
(Human Body Model)
acc. ESD assn. std. S5.1-1993; R=1.5kΩ; C=100pF
Current through input pin (DC)
Current through current sense pin (DC)
see internal circuit diagrams page 7
Output to the load. The pin 1 and 5 must be shorted with each
other especially in high current applications!*)
Input, activates the power switch in case of short to ground
Positive power supply voltage, the tab is shorted to this pin.
Diagnostic feedback providing a sense current proportional to the load
current; high current on failure (see Truth Table on page 6)
Output to the load. The pin 1 and 5 must be shorted with each
other especially in high current applications!*)
)
1
= UA + Vs, UA = 13.5 V
Vbb 24
2
V
Load dump
Tj
T
stg
42 W
tot
V
ESD
)
60 V
-40 ...+150
-55 ...+150
4.0
I
IN
IIS
+15, -100
+15, -100
V
°C
kV
mA
1 ) Short circuit is tested with 100mΩ and 20µH
2)
V
Load dump
is set-up without the DUT connected to the generator per ISO 7637-1 and DIN 40839
Infineon Technologies AG Page 2 of 13 2003-Oct-01
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Thermal Characteristics
Parameter and Conditions Symbol Values Unit
min typ max
3
)
Thermal resistance chip - case:
junction - ambient (free air): R
SMD version, device on PCB4):
R
thJC
thJA
-- -- 1.5
--
80 --
K/W
-- 45 --
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter and Conditions Symbol Values Unit
at Tj= -40°C...150°C, Vbb = 12 V unless otherwise specified
min typ max
Load Switching Capabilities and Characteristics
On-state resistance (pin 3 to pin 1,5)
VIN= 0, IL = 5 A Tj=25 °C:
Tj=150 °C:
Output voltage drop limitation at small load
currents (Tab to pin 1,5) Tj=-40...150 °C:
Nominal load current (Tab to pin 1,5)
ISO Proposal: TC=85°C, VON≤0.5V, T
≤150°C
j
SMD 4): TA=85°C, VON≤0.5V, Tj≤150°C
Turn-on time IIN to 90% V
Turn-off time IIN to 10% V
OUT
OUT
RL = 2,5Ω, Tj=-40...150 °C
Slew rate on
10 to 30% V
OUT
, R
= 2.5 Ω, Tj=-40...150 °C
L
Slew rate off
70 to 40% V
, RL = 2.5 Ω, Tj=-40...150 °C
OUT
:
:
RON
V
ON(NL)
I
L(ISO)
I
L(nom)
ton
t
off
dV /dt
-dV/dt
--
13
25
16
31
-- 50 -- mV
21
6.2
150
70
0.1 -- 1 V/µs
on
0.1 -- 1 V/µs
off
25
7.6
--
--
--
--
410
410
mΩ
A
µs
3)
Thermal resistance R
4)
Device on 50mm*50mm*1.5mm epoxy PCB FR4 with 6cm
connection. PCB is vertical without blown air.
case to heatsink (about 0.5 ... 0.9 K/W with silicone paste) not included!
thCH
2
(one layer, 70µm thick) copper area for Vbb
Infineon Technologies AG Page 3 of 13 2003-Oct-01
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Parameter and Conditions Symbol Values Unit
at Tj= -40°C...150°C, Vbb = 12 V unless otherwise specified
min typ max
Operating Parameters
Operating voltage (VIN=0V) V
Undervoltage shutdown 5) V
Undervoltage restart of charge pump (VIN=0V)
Overvoltage protection
Ibb=15 mA
Standby current Tj=-40...+25°C:
IIN=0 T
5.0 -- 36 V
bb(on)
1.5 3.0 4.5 V
bIN(u)
V
6)
V
3.0 4.5 6.0 V
bb(ucp)
61
Z,IN
I
--
bb(off)
=150°C:
j
--
68
2
4
Protection Functions 7)
Short circuit current limit (Tab to pin 1,5)
VON=8V, time until limitation max. 300µs
Repetitive short circuit current limit, T
Output clamp (inductive load switch off)
at V
I
= 40 mA
L
= Vbb - V
OUT
(e.g. overvoltage)
ON(CL)
)
8
=-40°C:
Tj
=25°C:
Tj
=+150°C:
Tj
j
= T
jt
I
I
35
L(SC)
35
35
-- 65 -- A
L(SCr)
V
ON(CL)
38
75
65
65
42 48 V
Thermal overload trip temperature Tjt 150 -- -- °C
Thermal hysteresis
∆
Tjt -- 10 -- K
Reverse Battery
-- V
5
8
110
110
125
µA
A
Reverse battery voltage -Vbb -- -- 20 V
On-state resistance (pin 1,5 to pin 3)
Vbb= - 8V, VIN= 0, IL = -5 A, RIS = 1 kΩ, Tj=25 °C:
Vbb= -12V, VIN= 0, IL = -5 A, RIS = 1 kΩ, Tj=25 °C:
Tj=150 °C:
R
ON(rev)
--
--
-16
25
22
mΩ
19
32
Integrated resistor in Vbb line Rbb -- 200 -- Ω
5)
VbIN=Vbb-VIN see diagram on page 11.
6)
see also V
7)
Integrated protection functions are designed to prevent IC destruction under fault condition described in the
data sheet. Fault conditions are considered as “outside” normal operating range. Protection functions are not
for continuous repetitive operation.
8) see also page 12.
in circuit diagram on page 7.
ON(CL)
Infineon Technologies AG Page 4 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Diagnostic Characteristics
Current sense ratio, static on-condition
k
= IL : IIS
ILIS
VON<1.5 V, VIS<V
OUT-
5 V, V
>4.5 V 9)
bIN
IL = 20A, Tj = -40°C:
Tj = +25°C:
Tj = +150°C:
IL = 5A, Tj = -40°C:
Tj = +25°C:
Tj = +150°C:
IL = 2.5A, Tj = -40°C:
Tj = +25°C:
Tj = +150°C:
IL = 1A, Tj = -40°C:
Tj = +25°C:
Tj = +150°C:
IIN = 0 (e.g. during de-energising of inductive loads):
Sense current under fault conditions;
VDS>1.5V, typ. Tj= -40...+150°C: I
k
--
ILIS
8200 --
7400
7500
7500
6800
7200
7200
6800
6800
6800
6800
6800
6800
8300
8300
8200
8300
8300
8200
8500
8500
8100
8600
8600
8600
9100
9100
8800
9700
9300
9000
10000
9800
9200
10500
10500
10500
-- n.a. --
IS,fault
2.5
4 -- mA
Fault-Sense signal delay after negative input slope t
Current sense leakage current
I
= 0:
IN
V
= 0, IL = 0:
IN
Current sense settling time to I
IS static
positive input slope, IL = 0 20 A
±10% after
10)
delay(fault)
I
IS(LL)
I
IS(LH)
t
son(IS)
0.8 ms
--
--
--
Tj= -40...+150°C:
61
68 -- V
Overvoltage protection
= 15 mA Tj = -40...+150°C: V
I
bb
Input
Required current capability of input switch
T
=-40..+150°C:
j
Maximum input current for turn-off Tj =-40..+150°C: I
I
bIS(Z)
-- 0.7 1.2 mA
IN(on)
-- -- 50 µA
IN(off)
-4
0.5
12
-- 400
µA
µs
9)
If VON is higher, the sense current is no longer proportional to the load current due to sense current
saturation.
10
) not subject to production test, specified by design
Infineon Technologies AG Page 5 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Truth Table
Input
Current
level
Normal
operation
Overload
L
H
L
H
Short circuit to GND
L
H
Overtemperature
L
H
Short circuit to Vbb
L
H
Open load
L
H
L = "Low" Level Z = high impedance, potential depends on external circuit
H = "High" Level
Output
level
L
H
L
H
L
L
L
L
H
H
Z
H
Current
Sense
I
IS
0
nominal
0
I
ISfault
0
I
ISfault
0
I
ISfault
0
<nominal
0
0
11
Terms
I
bb
V
bIN
V
bb
V
IN
2
R
IN
I
IN
Two or more devices can easily be connected in
parallel to increase load current capability.
3
V
bb
I
IN
PROFET
IS
bIS
V
4
IS
V
OUT
I
IS
D
S
R
IS
1,5
V
ON
L
V
OUT
11)
Low ohmic short to
V
may reduce the output current IL and therefore also the sense current IIS.
bb
Infineon Technologies AG Page 6 of 13 2003-Oct-01

−
Input circuit (ESD protection)
V
Z,IN
V
bIN
IN
I
V
IN
ZD
IN
ESD-Zener diode: 68 V typ., max 15 mA;
Current sense output
Normal operation
V
bb
R
bb
I
IS,fault
I
ZD
IS
V
Z,IS
IS
R
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Inductive and overvoltage output clamp
+ V
V
OUT
bb
ON
V
bb
R
bb
V
Z1
PROFET
VON is clamped to V
ON(Cl)
= 42 V typ.
Overvoltage protection of logic part
+ V
bb
V
V
Z,IN
Z,IS
R
IN
IN
V
IS
IS
IS
Logic
R
bb
PROFET
V
OUT
= 68 V (typ.), R
V
Z,IS
devices are connected in parallel). I
= 1 kΩ nominal (or 1 kΩ /n, if n
IS
= IL/k
S
can be
ilis
only driven by the internal circuit as long as
V
- VIS > 5V. If you want to measure load currents
out
VV/5
up to I
, RIS should be less than
L(M)
Note: For large values of R
almost V
. See also overvoltage protection.
bb
the voltage VIS can reach
IS
bb
KI
ilisML
)(
If you don't use the current sense output in your
application, you can leave it open.
= 200 Ω typ., V
R
bb
R
IS
Signal GND
Z,IN
R
= V
V
V
= 68 V typ., R
Z,IS
Z,VIS
IS
= 1 kΩ
nominal. Note that when overvoltage exceeds 73 V typ.
a voltage above 5V can occur between IS and GND, if
.
R
, V
V
are not used.
Z,VIS
Infineon Technologies AG Page 7 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Reversave (Reverse battery protection)
V
bb
-
R
bb
IN
OUT
R
IN
1
=
V
Power
Transistor
R
L
Power
for reverse
above 16V;
bb
−
bb
and R
IS
V.
A
,05.0
VV
12||
≥1kΩ, R
R
V
R
IN
Logic
IS
R
D
Signal
= 1 kΩ nominal. Add R
IS
R
IS
V
battery protection in applications with V
1
recommended value:
R
1
+
+
R
IN
IS
To minimise power dissipation at reverse battery
operation, the summarised current into the IN and IS
pin should be about 50mA. The current can be
provided by using a small signal diode D in parallel to
the input switch, by using a MOSFET input switch or by
proper adjusting the current through R
Since the current through Rbb generates additional
heat in the device, this has to be taken into account in
the overall thermal considerations.
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Version b:
V
PROFET
V
bb
IS
bb
OUT
IS
, VZb.
ZL
R
L
OUT
V
bb
IN
V
Zb
Note that there is no reverse battery protection when
using a diode without additional Z-diode V
Version c:
Sometimes a necessary voltage clamp is given by non
inductive loads R
connected to the same switch and
L
eliminates the need of clamping circuit:
V
bb
IN
PROFET
Vbb disconnect with energised inductive
load
Provide a current path with load current capability by
using a diode, a Z-diode, or a varistor. (V
V
< 30 V if RIN=0). For higher clamp voltages
Zb
currents at IN and IS have to be limited to
Version a:
V
bb
IN
V
bb
PROFET
IS
OUT
< 73 V or
ZL
250 mA.
V
ZL
Infineon Technologies AG Page 8 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Inductive load switch-off energy
dissipation
E
bb
E
AS
V
bb
i (t)
Z
{
L
L
L
R
L
(t) dt,
V
bb
PROFET
IN
IS
I
IN
OUT
R
IS
Energy stored in load inductance:
/
·L·I
2
2
L
1
=
E
L
While demagnetising load inductance, the energy
dissipated in PROFET is
= Ebb + EL - ER= V
E
AS
ON(CL)·iL
E
E
E
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Maximum allowable load inductance for
a single switch off
Load
L
R
L = f (I
L[mH]
100
10
1
0.1
L
); T
j,start
150°C, V
=
= 12 V, RL = 0 Ω
bb
with an approximate solution for RL > 0
· L
I
AS
=
L
(V
+ |V
OUT(CL)
bb
·R
2
L
|) ln (1+
E
Ω:
|V
·R
I
L
L
OUT(CL)
)
|
The device is not suitable for permanent PWM with
inductive loads if active clamping occurs every cycle.
0.01
0 25 50 75 100
IL [A]
Infineon Technologies AG Page 9 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Timing diagrams
Figure 1a: Switching a resistive load,
change of load current in on-condition:
I
IN
V
OUT
90%
10%
I
L
t
on
dV/dton
tt
slc(IS)
t
off
slc(IS)
dV/dtoff
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Figure 2a: Switching motors and lamps:
I
IN
V
OUT
I
IL
Load 1
I
IS
t
son(IS)
Load 2
t
soff(IS)
The sense signal is not valid during a settling time
after turn-on/off and after change of load current.
Figure 1b: typical behaviour of sense output:
I
S
I
IS,fault >= 2.5mA
I
L(lim) = 20A
I
IS
t
Sense current above I
IS,fault
can occur at very high
t
inrush currents.
Figure 2b: Switching an inductive load:
I
IN
V
OUT
I
L
I
L
I
IS
t
Infineon Technologies AG Page 10 of 13 2003-Oct-01

j
A
Figure 3a: Short circuit:
IN
I
L
I
L(SCp)
I
IS
I
ISfault
Figure 4a: Overtemperature
Reset if T
j<Tjt
I
L(SCr)
Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Figure 5a: Undervoltage restart of charge pump,
overvoltage clamp
V
12
OUT
10
8
6
dynamic, short
Undervoltage
4
2
t
0
V
024681012
bIN(u)
not below
V
bIN(u)
VIN= 0
V
bIN(ucp)
V
IIN= 0
ON(CL)
V
ON(CL)
V
bb
I
IN
I
IS
V
OUT
I
IS,fault
uto Restart
T
t
Infineon Technologies AG Page 11 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Figure 6a: Current sense versus load current:
[mA] I
IS
2.0
1.0
0
0 5 10 15 20
)
Figure 6b: Current sense ratio
12
:
k
ILIS
[A]
Figure 7a: Output voltage drop versus load current:
V
[V]
0.1
ON
V
ON(NL)
R
ON
0.05
I
L
I
L
0.0
012345678
[A]
8200
I
[A]
L
0
0 2.5 10 20
12
) This range for the current sense ratio refers to all
devices. The accuracy of the k
means of calibration the value of k
5
can be raised by
ILIS
for every
ILIS
single device.
Infineon Technologies AG Page 12 of 13 2003-Oct-01

Data Sheet BTS 443 P
Package and Ordering Code
All dimensions in mm
D-Pak-5 Pin: TO-252-5-1
Sales Code BTS443P
Ordering code Q67060-S7404-A 2
B
±0.1
1
0.51 min
2.3
+0.05
-0.10
0.9
0.5
GPT09161
+0.08
-0.04
+0.08
-0.04
0.1
+0.15
6.5
-0.10
±0.1
5.4
±0.1
1
-0.2
±0.5
(4.17)
6.22
9.9
0.15 max
per side
4.56
All metal surfaces tin plated, except area of cut.
±0.15
0.8
5x0.6
1.14
A
±0.1
0...0.15
M
B
A0.25
Published by
Infineon Technologies AG,
St.-Martin-Strasse 53,
D-81669 München
© Infineon Technologies AG 2001
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
The information herein is given to describe certain components and shall not be considered as a guarantee of
characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to technical change reserved.
We hereby disclaim any and all warranties, including but not limited to warranties of non-infringement, regarding circuits,
descriptions and charts stated herein.
Infineon Technologies is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Information
For further information on technology, delivery terms and conditions and prices please contact your nearest Infineon
Technologies Office in Germany or our Infineon Technologies Representatives worldwide (see address list).
Warnings
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types in question
please contact your nearest Infineon Technologies Office.
Infineon Technologies Components may only be used in life-support devices or systems with the express written approval
of Infineon Technologies, if a failure of such components can reasonably be expected to cause the failure of that lifesupport device or system, or to affect the safety or effectiveness of that device or system. Life support devices or systems
are intended to be implanted in the human body, or to support and/or maintain and sustain and/or protect human life. If they
fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the user or other persons may be endangered.
Infineon Technologies AG Page 13 of 13 2003-Oct-01
 Loading...
Loading...