Industrial Fiber Optics ML 800 Series, ML 800, ML 810, ML 868, ML 869 Operator's Manual
...
IndustrIal FIber OptIcs
Model Numbers:
ML 800
ML 810
ML 868
ML 869
ML 869A
ML 800 Series Laser
Hard-Seal Helium Neon
Operator’s Manual

*
Copyright © 2016
Previous printings 2008, 2009 and 2013
by Industrial Fiber Optics, Inc.
Revision - H
Printed in the United States of America
* * *
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means
(electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise)
without prior written permission from Industrial Fiber Optics.
* * * * *

– i –
INTRODUCTION
This manual provides information about the family of Hard-Seal Helium Neon
Lasers that formerly were manufactured by Metrologic, Inc. It contains all the
information needed to set up and operate these lasers safely and knowledgeably,
even if you are a novice to laser technology. Please read the manual carefully
before operating the laser.
Industrial Fiber Optics makes every effort to incorporate state-of-the-art
technology, highest quality and dependability in its products. We constantly
explore new ideas and products to best serve the rapidly expanding needs of
industry and education. We encourage comments that you may have about our
products, and we welcome the opportunity to discuss new ideas that may better
serve your needs. For more information about our company and products refer to
www.i-beroptics.com on the Internet.
Thank you for selecting this Industrial Fiber Optics product. We hope it
meets your expectations and provides many hours of productive activity.
Sincerely,
The Industrial Fiber Optics Team

– ii –
.

– iii –
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction……………………….................…….....…………..…… i
LASER CLASSIFICATION.........….............................……..…...… iv
GENERAL…………................….............................……..…...…….. 1
SAFETY NOTES.............................................................................. 2
Laser Safety.................................................................................... 2
Electrical Safety.............................................................................. 3
CDRH Regulations.......................................................................... 3
OPERATING CONDITIONS…....................………..................……. 4
Input Voltage.................................................................................. 4
Environmental Limits...................................................................... 4
LASER SPECIFICATIONS.............................................................. 5
LASER OPERATION....................................................................... 6
Beam Controls............................................................................... 6
Power Controls.............................................................................. 6
Operating Instructions................................................................... 7
TROUBLESHOOTING..................................................................... 7
MODULATED LASERS
(ML 868, ML 869, ML 869A).............................. 8
Connectors for Signal Input........................................................... 8
Modulation Characteristics............................................................ 8
Detectors....................................................................................... 8
Troubleshooting for Modulated Lasers.......................................... 9
APPLICATIONS AND DEMONSTRATIONS.................................... 10
Optical Galvanometer.................................................................... 10
Diffraction, Variable Slit................................................................. 10
Laser Light Show........................................................................... 11
Index of Refraction, Liquids........................................................... 11
Interference, Evaporation of Alcohol.............................................. 11
WARRANTY..................................................................................... 12
SHIPMENT DAMAGE CLAIMS....................................................... 13
SERVICE AND MAINTENANCE...................................................... 14
TABLE 1. COMMON ABBREVIATIONS.......................................... 15
– iv –
LASER CLASSIFICATIONS
All manufacturers of lasers used in the United States must conform to regulations
administered by the Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH), a branch of the
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. CDRH categorizes lasers as follows:
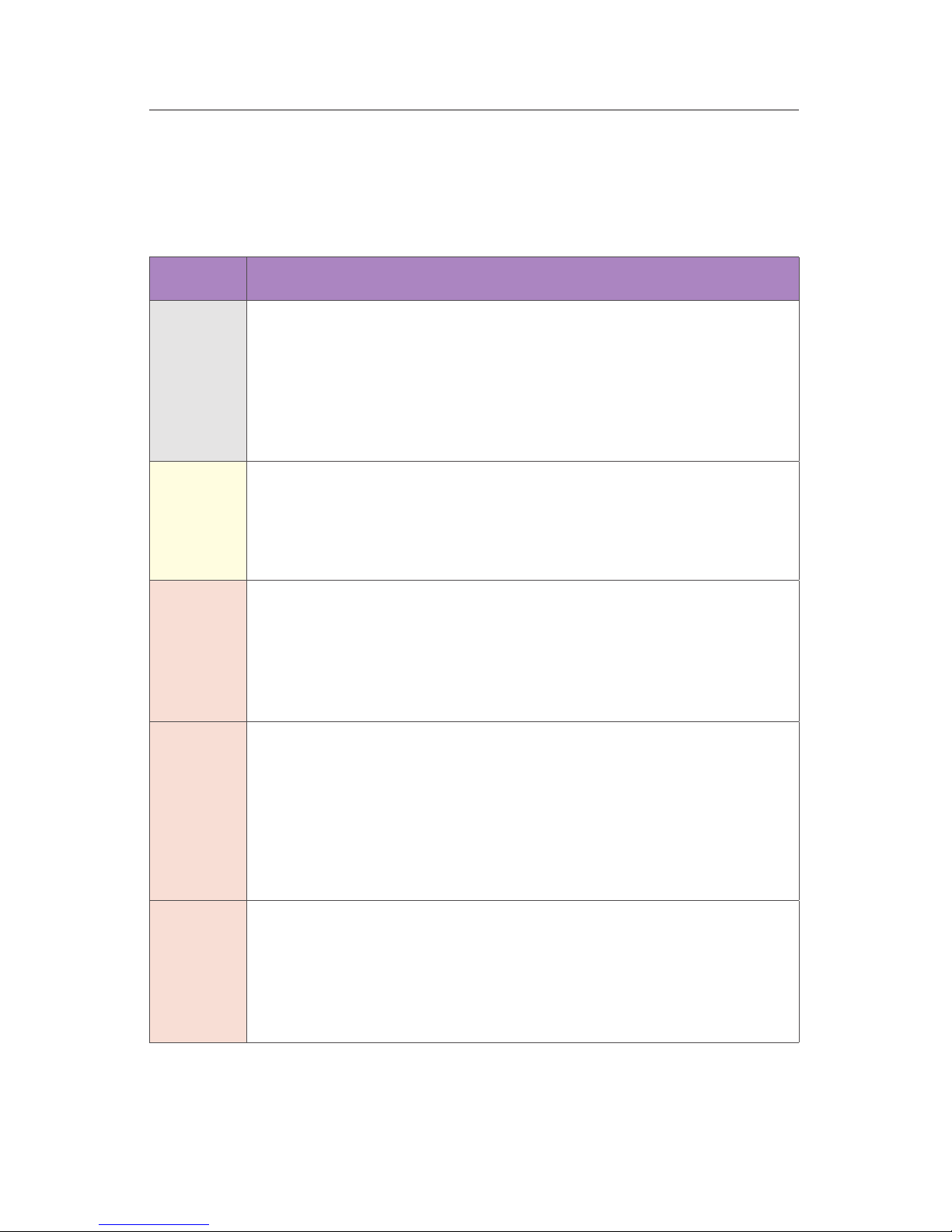
Class Description
I A laser or laser system, which does not present a hazard to skin
or eyes for any wavelength or exposure time. Exposure varies
with wavelength. For ultraviolet, 2 to 4 µm exposures is less than
from 8 nW to 8 µW. Visible light exposure varies from 4 µW to 200
µW, and for near-IR, the exposure is < 200 µW. Consult CDRH
regulations for specic information.
II Any visible laser with an output less than 1 mW of power. Warning
label requirements – yellow caution label stating maximum output
of 1 mW. Generally used as classroom lab lasers, supermarket
scanners and laser pointers
IIIa Any visible laser with an output over 1 mW of power with a
maximum output of 5 mW of power. Warning label requirements
– red danger label stating maximum output of 5 mW. Also used
as classroom lab lasers, in holography, laser pointers, leveling
instruments, measuring devices and alignment equipment.
IIIb Any laser with an output over 5 mW of power with a maximum
output of 500 mW of power and all invisible lasers with an output
up to 400 mW. Warning label requirements – red danger label
stating maximum output. These lasers also require a key switch
for operation and a 3.5-second delay when the laser is turned on.
Used in many of the same applications as the Class IIIa when
more power is required.
IV Any laser with an output over 500 mW of power. Warning label
requirements – red danger label stating maximum output. These
lasers are primarily used in industrial applications such as tooling,
machining, cutting and welding. Most medical laser applications
also require these high-powered lasers.

– 1 –
GENERAL
In the ML 800 Series, Industrial Fiber Optics offers lasers in a range of power, size and
price. The helium neon tubes used in these lasers have a shelf life of at least 10 years, and
a lifespan of at least 20,000 hours of continuous operation.
Recommended uses of the different lasers are listed below:
ML 800
Student Use, Demonstrations
ML 810 Student Use, Holography
ML 868 Lecture Demos, Modulation, Voice or Video Communication
ML 869 Lecture Demos, Modulation, Voice or Video Communication,
Holography, Research
ML 869A
Lecture Demos, Modulation, Voice Communication,
Holography, Research
This manual contains information on laser specification, operation, safety and troubleshooting. The manual includes experiments that can be conducted with the laser.
Many ideas for additional activities and investigations can be found on our website,
www.i-fiberoptics.com. Look for the Laser Teaching Supplements on the website.
Additionally, the following complete projects/labs (and many others) can be purchased
from Industrial Fiber Optics for use with the laser:
Laser Optics Lab
This lab contains more than 30 optical parts and
accessories. These tools can be used to demonstrate the
principles of optics in a basic course of physics or physical
science.
Physical Optics Lab
With this lab, image processing and Fourier transforms
of optical formations can be practical studies for high
schools and undergraduate physics classes.
Michelson Interferometer
This is a classic device for splitting a beam of
monochromatic light into two parts that travel along
different optical paths and then merge again to produce
interference fringes.
Modern Laser Optics Kit
This innovative collection of nine unique optical mounts
offers endless possibilities for exploring the many aspects
of modern optical technology.
Laser Audio Receiver
This lab contains a microphone and audio receiver, along
with the instructions needed to turn your modulated
laser into a free-air voice communication link.
Check the website www.i-fiberoptics.com for details.
45-600
45-688
45-940
IF 535
IF LSL2
– 2 –
SAFETY NOTES
Laser Safety
Lasers are valuable sources of light for conducting exciting demonstrations and laboratory
experiments in schools.
Industrial Fiber Optics lasers emit a beam of visible light. However, they do not
emit invisible, exotic, or otherwise harmful radiations. See page iv for LASER
CLASSIFICATIONS.
Industrial Fiber Optics lasers are low-power lasers. The light output is only a few milliwatts,
i.e., a few thousandths of a watt. These lasers should not be confused with the powerful
lasers intended for burning, cutting and drilling.
Although the power of Industrial Fiber Optics lasers is low, treat all laser beams with
caution and common sense because they are intense and concentrated. The greatest
potential for harm with Industrial Fiber Optics lasers is to the eyes. Just as no one should
stare at the sun or arc lamps, no one should look directly into the laser beam or stare at its
bright reflections.
The United States Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) regulates
manufacturers of lasers to ensure that users are not endangered. The federal government
classifies lasers according to their power levels and specifies appropriate safety features for
each level. Demonstration lasers fall into Class II and they can be identified by a yellow
“Caution” label that contains the warning, “Do not stare into beam.” Class II lasers have a
maximum power of 0.95 milliwatt, i.e., 1/1000th of a watt. They conclude that the power
is eye-safe, except possibly in the case of deliberate, long-term direct staring into the beam.
Safety features include a pilot lamp, which glows when the electrical power is on, and a
mechanical beam stop, which can block the beam when the power is on.
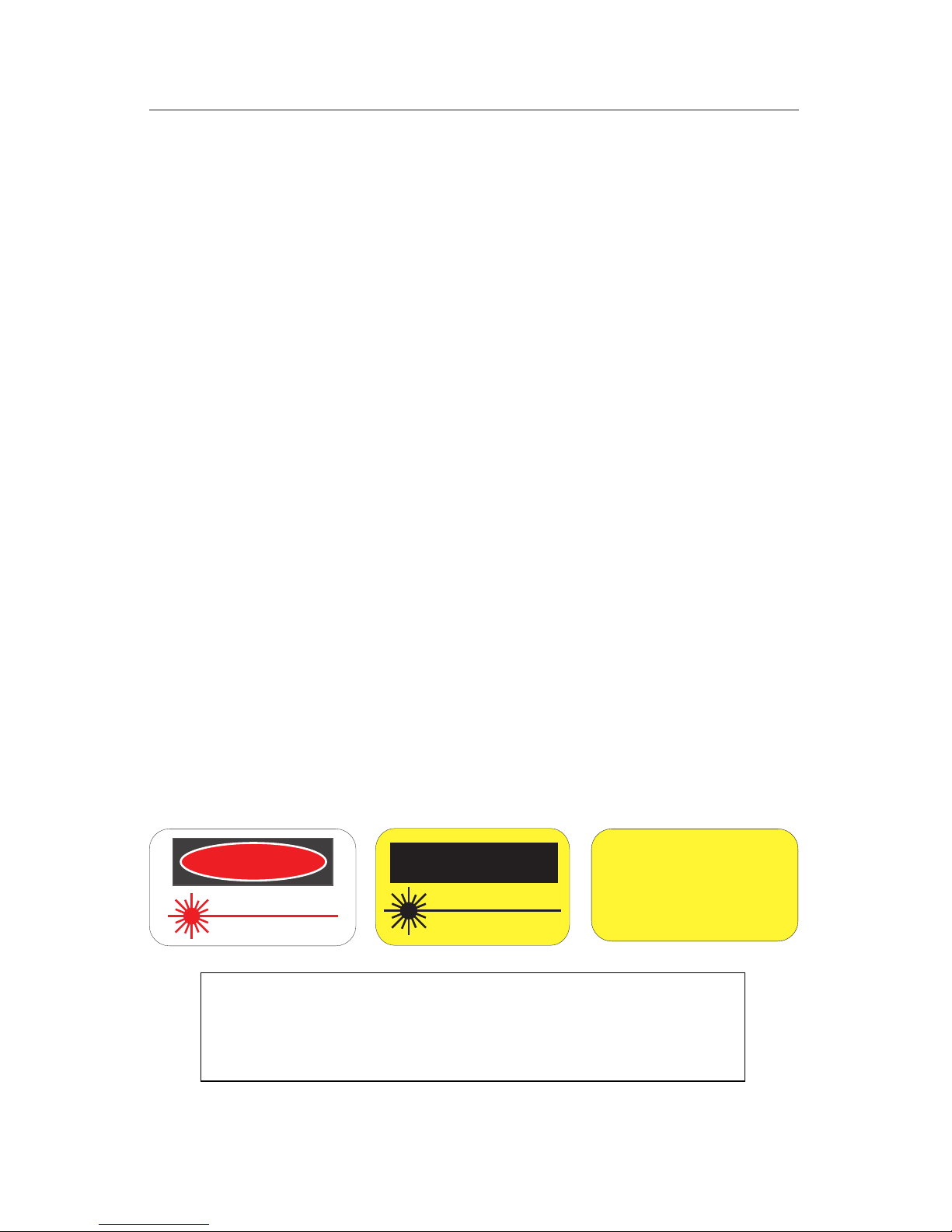
The following are labels located on helium-neon lasers:
Hard-Seal Laser
Periodic operation not required
Figure 1. Laser labels.
CAUTION
LASER RADIATION
DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM
PEAK POWER 1 mW
WAVELENGTH 600 - 700 nm
Class II Laser Product
1189.eps
LASER RADIATION
DO NOT STARE INTO BEAM
PEAK POWER 5 mW
WAVELENGTH 600 - 700 nm
Class IIIa Laser Product
DANGER
1190.eps
CAUTION!
Plug laser only into
grounded outlets
1533.eps
 Loading...
Loading...