
iM871A Wireless M-Bus
User Manual
Document ID: 4100/6404/0048
IMST GmbH
Carl-Friedrich-Gauß-Str. 2-4
47475 KAMP-LINTFORT
GERMANY

User Manual
File name
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx
Created
2011-06-10
Total pages
32
Version
Note
0.8
Created, Preliminary Version
1.0
Added chapter USB-Stick
1.1
Added AES encryption
1.2
C-Mode added
iM871A Wireless M-Bus General Information
Document Information
Revision History
Aim of this Document
This document is intended to provide help using the iM871A Wireless M-Bus module. It gives an
overview about its features and the Wireless M-Bus Stack. It explains how to control the module
by a connected host controller.
This user manual includes the basic hardware specifications and describes how to put the
iM871A into operation with the Wireless M-Bus Starter Kit.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page i

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Table of Contents
Table of Contents
1. GENERAL 4
1.1 Key Features 4
1.2 Applications 5
2. GENERAL FEATURE OVERVIEW 6
3. MODULE FIRMWARE 9
3.1 Wireless M-Bus Stack 9
3.1.1 General 9
3.1.2 WM-Bus Modes 10
3.1.3 WM-Bus Telegrams 12
3.2 Serial Interface 14
3.2.1 Connection Settings 14
3.2.2 Host Controller Protocol 14
3.2.3 General Device Functions 14
3.2.4 Device Configuration 15
3.2.5 Operation Modes 16
3.2.6 Real Time Clock Support 16
3.2.7 AES-128 Encryption / Decryption 17
3.3 Low Power and Wake-up 17
3.3.1 Auto Power Saving 17
3.4 Port Pin Signaling 17
4. MODULE SPECIFICATION 18
4.1 General Radio Settings 18
4.1.1 Channel Setup 18
4.1.2 Power Level Setup 18
4.1.3 Data Rate Setup 19
4.2 System Timing 19
4.2.1 Wake-up after Low-Power-Mode 19
4.3 Current Consumption 21
5. WIRELESS M-BUS STARTER-KIT 22
5.1 Demo Board 22
5.1.1 Power Supply 23
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page ii

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Table of Contents
5.1.2 USB Interface 23
5.2 USB-Stick 24
5.2.1 USB Driver 24
5.3 Configuration with WM-Bus Studio 25
6. ORDERING INFORMATION 26
7. APPENDIX 27
7.1 List of Abbreviations 27
7.2 List of Figures 28
7.3 List of Tables 28
7.4 References 29
8. REGULATORY COMPLIANCE INFORMATION 30
9. IMPORTANT NOTICE 31
9.1 Disclaimer 31
9.2 Contact Information 31
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page iii

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus General
1. General
The iM871A is an ultra-low-power, high-performance, pre-certified Wireless M-Bus module
fully compliant with EN 13757 part 4, Wireless M-Bus standard.
The module offers a cost-effective wireless solution for smart metering applications
connecting water, heat, electricity and gas meters with data concentrators. It operates in the
868 MHz frequency band and it supports all unidirectional and bidirectional Wireless M-Bus
modes (S1, S1-m, S2, T1, T2, R2, C1 and C2).
With a standby current of less than 1 µA, the iM871A is well suited for battery powered
devices like water and gas meters. The pre-certified module provides a serial interface as well
as analog and digital inputs and outputs and can easily be integrated into a meter. With its
integrated Wireless M-Bus protocol stack it will reduce the development time and cost. The
iM871A can achieve a link budget up to 123 dB, resulting in exceptional RF range and
communication performance.
Figure 1-1: iM871A
1.1 Key Features
- Compact module 16.8 x 18.6 x 2 mm for SMD mounting
- Ultra low power modes for extended battery lifetime
- Communication/Configuration via UART, SPI and I²C interface
- Digital inputs and outputs
- Analog inputs
- Supply voltage range from 1.8 to 3.6 V
- RF interface matched to 50
- Output power level up to +14 dBm
- High link budget up to 123 dB
- Range up to 3000 m (line of sight)
- 64 kByte Flash + 4 kByte RAM Memory
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 4

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus General
1.2 Applications
The iM871A wireless M-Bus module offers a cost-effective RF solution for smart metering
applications connecting water, heat, electricity and gas meters with data concentrators in the
868 MHz frequency band.
- Electricity meters
- Gas, water and heat meters
- Data concentrators and readers
- Automatic meter reading (AMR)
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 5

User Manual
MeteringHardware
Host-Controller
• Metering Application
• WM-Bus Application
Layer
• Interface Driver
UART
iM871A
• Wireless M-Bus Stack
• Host Controller Interface
• LINK Layer
• PHY Layer
Metering
Hardware
iM871A
• Metering Application
• WM-Bus Application Layer
• Wireless M-Bus Stack LINK/PHY
iM871A Wireless M-Bus General Feature Overview
2. General Feature Overview
The iM871A Wireless M-Bus module offers lots of features which gives the user the possibility
to save implementing functionalities on the host controller side. With the PC Application
Wireless M-Bus Studio the features can easily be explored. The module can either be used as
WM-Bus modem or can be taken as stand-alone solution (on request).
Figure 2-1: iM871A Metering Application Example with Host Controller
Figure 2-2: iM871A Metering Application Example Stand-Alone
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 6

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus General Feature Overview
iM871A Features
Host Controller Interface
With a message based serial protocol the user is able to connect the iM871A radio module
to a host system. It can be used for configuration, data exchange and device control. Each
message to or from the radio module is embedded in a specific message frame. For
Windows PC applications a library (DLL) can be used. To connect the radio module to
embedded systems example code is available.
Power Management
The iM871A radio module provides two different power saving modes to operate best in
battery driven applications:
Low Power Mode (with RTC running)
Low Power Mode (with RTC off)
These modes can be called via the Host Controller Interface (HCI). The wakeup can also be
done over the serial interface.
Moreover the iM871A provides the opportunity to enter one of the power save modes
automatically after a successful WM-Bus packet transmission.
Supported Device Modes
The iM871A is designed for metering applications (Meter-Mode), but it also can operate in
Other-Mode (Concentrator, Data Collector, etc.).
Operation- and State-Indication
When using the iM871A together with WiMOD Demoboard there is the option to indicate the
internal states of the module by LEDs.
TX Indicator LED: a WM-Bus packet is transmitted successfully
RX Indicator LED: a WM-Bus packet was received successfully
Alive Indicator LED: The module is awake and ready for operation
The LED indication can be disabled by configuration.
Real Time Clock
The iM871A provides an embedded RTC which can be used for timer controlled operations
e.g. automatic transmission of WM-Bus messages at specific times or with a configurable
interval (on inquiry).
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 7

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus General Feature Overview
AES Encryption
The iM871A supports automatic AES-128 encryption and decryption of radio link messages.
Hardware Test
Opportunity to generate a continuous wave signal on all supported channels.
Features in combination with the WM-Bus Studio
Packet Sniffer
With the Wireless M-Bus Studio a packet sniffer functionality for Wireless M-Bus packets is
given. An optional data logger can store the air traffic into a log file.
Radio Link Test
The iM871A offers the possibility to evaluate the radio link quality between two devices with
the Radio Link Test.
During this test a configurable number of packets including a TX packet counter is sent from
a local device which is connected to the WM-Bus Studio to a peer device. The peer device
returns the number of received packets back to the sender.
Wireless M-Bus Message Generator
The Message Generator offers the possibility to simulate real Wireless M-Bus packets. The
format is conform to the EN13757-4 standard. The content of these packets can be changed.
With this function the users is able to test the iM871A radio module against other Wireless MBus devices.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 8

User Manual
Host Controller
Interface driver
Application
HCI
LINK
PHY
iM871A
EN 13757-3
EN 60870-5-2
EN 13757-4
Transceiver
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
3. Module Firmware
3.1 Wireless M-Bus Stack
3.1.1 General
The Wireless M-Bus protocol stack implemented on iM871A is compliant the European
standard 13757 part 4: "Communication systems for meters and remote reading of meters"
[1]. It describes the wireless communication of water, heat, electricity and gas meters with
data concentrators. For sake of convenience in this manual such meter devices are called
"meter", the communications partner devices like concentrators are called "other".
Figure 3-1: iM871A WM-Bus Stack
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 9

User Manual
Mode
Direction
Data Rate
Coding
Frequency
Preamble +
Synchronization
S1
Meter => Other
32.768 kcps
Manchester
868.3 MHz
582 chips
S1-m
Meter => Other
32.768 kcps
Manchester
868.3 MHz
56 chips
S2
Meter => Other
32.768 kcps
Manchester
868.3 MHz
56 chips
Other => Meter
32.768 kcps
Manchester
868.3 MHz
56 chips
T1
Meter => Other
100 kcps
3 out of 6
868.95 MHz
56 chips
T2
Meter => Other
100 kcps
3 out of 6
868.95 MHz
56 chips
Other => Meter
32.768 kcps
Manchester
868.3 MHz
56 chips
R2
Meter => Other
4.8 kcps
Manchester
868.03 MHz + n*60
kHz
104 chips
Other => Meter
4.8 kcps
Manchester
868.33 MHz
104 chips
C1
Meter => Other
100 kcps
NRZ
868.95 MHz
64 chips
C2
Meter => Other
100 kcps
NRZ
868.95 MHz
64 chips
Other => Meter
50 kcps
NRZ
869.525 MHz
64 chips
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
3.1.2 WM-Bus Modes
The iM871A supports all link modes according to EN 13757-4: S (stationary), T (frequent
transmit), R (frequent receive) and C (compact operation). These four main modes are
divided into further sub-modes for dedicated applications. All modes are described from the
meters view. Table 3-1 gives an overview over all WM-Bus modes and their physical
parameters.
Table 3-1: Wireless M-Bus Modes
WM-Bus Mode S
Stationary mode
Mode S1 transmit only, unidirectional, long preamble
Mode S1-m unidirectional, transmission to mobile data collectors, short preamble
Mode S2 bidirectional, short preamble
Operation at 868.3 MHz, chip rate: 32.768 kcps, encoding: "Manchester"
Telegram Format A
WM-Bus Mode T
Frequent transmit mode
Mode T1 unidirectional, frequent operation
Mode T2 bidirectional, frequent operation
Transmission at 868.95 MHz, chip rate: 100 kcps, encoding: "3 out of 6"
Receiving (meter) at 868.3 MHz, chip rate: 32.768 kcps, decoding: "Manchester"
Telegram Format A
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 10

User Manual
Note: The iM871A can be used as RF-Adapter for Wireless M-Bus devices. It
provides the physical access to the Wireless M-Bus "Network". For complete
Wireless M-Bus protocol operation a host controller is needed which is able to
generate telegrams which meet the EN13757-3 requirements.
Some M-Bus modes require response times which cannot be fulfilled with an
external host controller due to long transmission times on the wired interface. For
these cases we can provide customized solutions.
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
WM-Bus Mode R2
Frequent receive mode
Mode R2 bidirectional, meter always available
Transmission at channel 0-9, chip rate: 4.8 kcps, encoding: "Manchester"
Receiving at 868.33 MHz (channel 5), chiprate 4.8 kcps, decoding: "Manchester"
Once a mode is configured the module firmware configures all required physical parameter
automatically according to EM 13757-4.
Telegram Format A
WM-Bus Mode C
Compact mode
Mode C1 unidirectional, compact operation
Mode C2 bidirectional, compact operation
Transmission at 868.95 MHz, chip rate: 100 kcps, encoding: "NRZ"
Receiving (meter) at 869,525 MHz, chip rate: 50 kcps, decoding: "NRZ"
Telegram Format A / Telegram Format B
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 11

User Manual
Preamble-
sequence
specified by mode 18 bytes
Block 1 Postamble
18 or less bytes
Block 2 Block n -1 Block n
Sync-
word
12 bytes 18 bytes max. 1 byte
L-Field
Address
Type
Version
1 byte
4 bytes 1 byte 1 byte
6 bytes1 byte
C-Field M-Field A-Field
2 bytes
CRC-Field
2 bytes
CI-Field
1 byte 15 bytes or, if last block, (((L-9) MOD 16) -1) bytes
Data-Field CRC-Field
2 bytes
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
3.1.3 WM-Bus Telegrams
In this section the message format on the air interface is described.
There are two different telegram formats specified in EN13757-4. Telegram Format A and
Telegram Format B. The operating modes S, T and R2 use Telegram Format A. The C-mode
supports both telegram formats.
Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A
Figure 3-2: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A
Every Wireless M-Bus telegram starts with a preamble sequence followed by a synchronization
word. The length of these fields is mode-dependent. The implementation is done according to
EN13757-4 [1]. The postamble contains normally 8 chips. Only for even packet sizes in T
mode (Meter) the postamble consists of four chips.
Block 1:
Figure 3-3: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A, block1 (header)
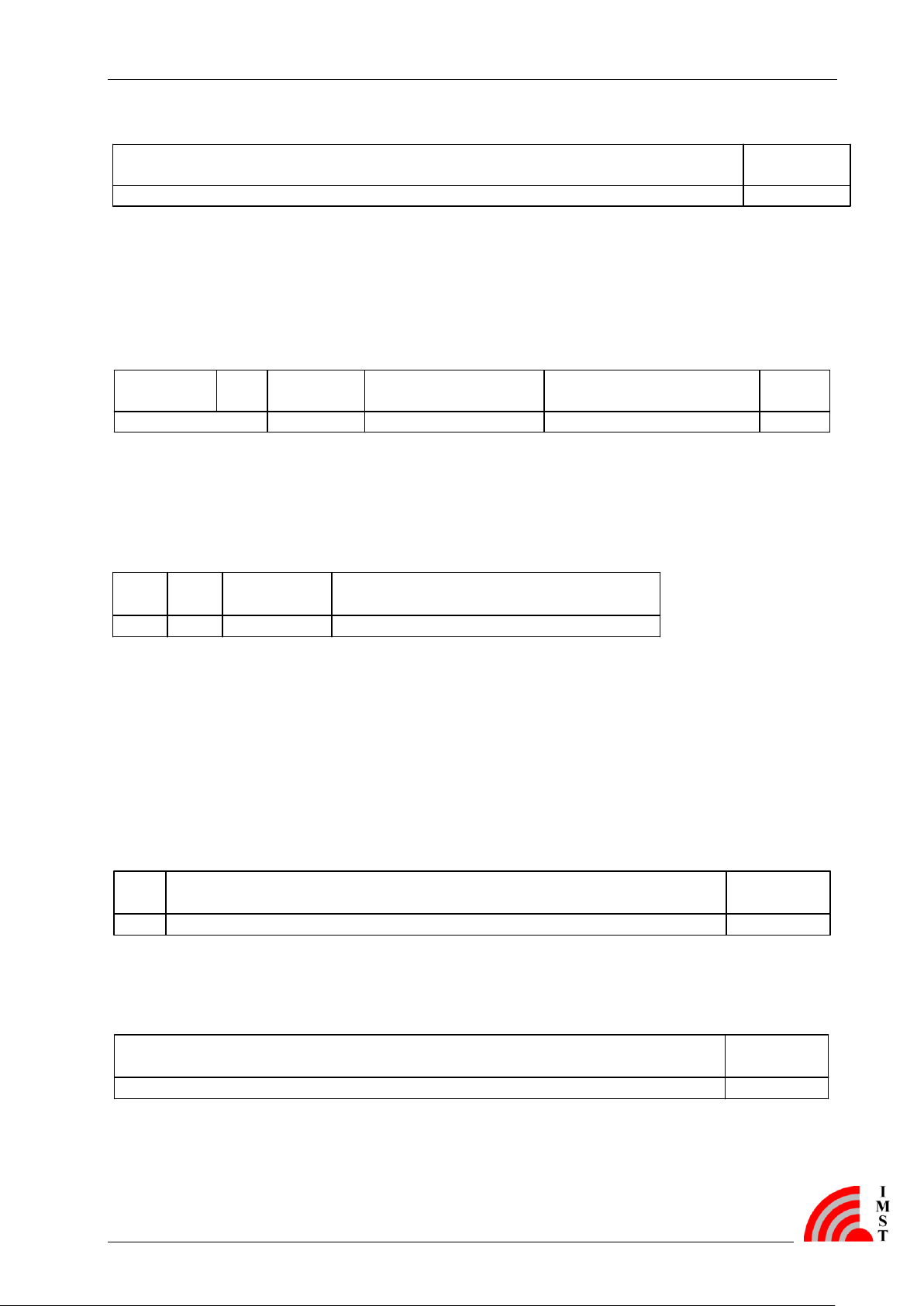
The first byte of block 1 is the length byte. It describes the number of the following user bytes
including C-Field-, M -Field- and A-Field-Data, but without any CRC byte.
C-Field, M-Field and A-fields can be pre-configured and stored in the non-volatile memory.
L-Field and CRC-fields are filled by the firmware at transmission.
Block 2:
Figure 3-4: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A, block2
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 12
User Manual
16 bytes or, if last block, ((L-9) MOD 16) bytes
Data-Field CRC-Field
2 bytes
Preamble-
sequence
specified by mode 115 bytes
Block 1
Postamble
Block 2
Sync-
word
10 bytes
max. 1 byte126 bytes
Block 3
L-Field
1 byte 6 bytes1 byte
C-Field M-Field A-Field
2 bytes
CI-Field
1 byte 115 bytes or, if last block, (L-12) bytes
Data-Field CRC-Field
2 bytes
(L-129) bytes
Data-Field CRC-Field
2 bytes
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
Block 3 to block n (optional blocks):
Figure 3-5: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A, block3 to block n
Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B
Figure 3-6: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B
Block 1:
Figure 3-7: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B, block1 (header)
The first byte of block 1 is the length byte. It describes the number of all following bytes
including the CRC bytes.
The block 1 in Telegram Format B is the same as in Telegram Format A, only the CRC Field
is missing.
Block 2:
Figure 3-8: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B, block2
Block 3 (optional block):
Figure 3-9: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B, block3
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 13

User Manual
SOF
Control
Field
MsgID
Field
Length
Field
Payload
Field
CRC16
8 Bit
8 Bit 8 Bit 8 Bit
n * 8 Bit 16 Bit
Msg Header
Field
24 Bit
Note: In this chapter only a short summary of the serial interface commands is
given. For detailed information please refer please refer HCI specification [3].
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
3.2 Serial Interface
The iM871A can be controlled and configured via serial Interface (UART). On inquiry the
module can also be driven by Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI).
3.2.1 Connection Settings
The UART baud rate which is required for communication between host controller and radio
module is 57600 baud. Further 8 data bits, 1 stop bit and no parity bit have to be
configured.
3.2.2 Host Controller Protocol
The iM871A offers the user a host controller interface (HCI) and uses a specific host
controller message protocol With this message based serial protocol the user is able to
connect the iM871A radio module to a host system. It can be used for configuration, data
exchange and device control. Each message to or from the radio module is embedded in a
specific message frame.
Figure 3-10: Message format on serial interface
3.2.3 General Device Functions
Ping Request
This function can be used to check the wired communication interface (HCI) and if the
connected device is alive. If a “Ping Command” message is received the device answers
with a “Ping Response” message.
Reset Request
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 14
This function can be used to perform a software reset of the iM871A firmware.

User Manual
Parameter
Description
Default
Device Mode
Meter/Other Selection
Other
Link Mode
Wireless M-Bus Mode (S1, S1m, S2, ...)
S2
C-Field (Block 1)
1 byte Control Field
0x00
M-Field (Block 1)
2 byte Manufacturer ID
0x0CAE
2 byte Manufacturer ID (USB-Stick Variant)
0x25B3
Device ID (Block 1)
4 byte Device Identification (A-Field)
0x12345678
4 byte Device Identification (A-Field) (USB-Stick Variant)
preconfigured
address
Version (Block 1)
1 byte Version (A-Field)
0x01
Device Type (Block 1)
1 byte Device Type (A-Field)
0x00
Radio Channel
R-Mode channel
1
Radio Power Level
Transmission power
13
RX Window
Receive time after transmission in ms (Meter only)
50
Power Saving Mode
Enable / disable automatic power saving after transmission (Meter only)
Off
LED Control
LED indication for TX/RX/Alive
Off
RX Timestamp
Timestamp attachment on HCI message for received messages
Off
RSSI Attachment
RSSI attachment on HCI message for received messages
Off
Real Time Clock
Enable / disable Real Time Clock
Off
Encryption
Enable / disable encryption
Off
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
Get Device Info
For identification purpose the WM-Bus firmware provides a service to readout some
information elements e.g. Module Type, Firmware Version. This command returns the
basic device information block.
3.2.4 Device Configuration
The WM-Bus Firmware supports several kinds of configurable system parameters which can
be stored in a non-volatile parameter memory. The configuration parameters are readout
during start-up and used to configure the firmware components and the hardware units.
Table 3-2 gives an overview about all changeable parameters.
Table 3-2: Parameter Overview
When sending a WM-Bus message by HCI command the Block 1 parameters can either be
taken from the configuration or can individually be transferred with each message.
For reading and writing the parameters listed in Table 3-2 the following functions can be
used.
Get Device Configuration
This function can be used to readout all configuration parameters.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 15

User Manual
Note: The new configuration gets active after reboot.
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
Set Device Configuration
This function can be used to change several system parameters. The function allows to
change parameter directly and to save them in a non-volatile memory. Please get the list
of the configurable parameters from the HCI Specification.
Factory Reset Request
This function can be used to reset the WM-Bus device configuration to its default factory
settings.
3.2.5 Operation Modes
The WM-Bus firmware can operate in different kinds of System Operation Modes. The
operation modes enables the device to align its behaviour according to a given use case e.g.
test mode, application mode. The system operation mode is determined during firmware
start-up and requires a reset to get changed.
Get System Operation Mode
This function returns the current System Operation Mode.
Set System Operation Mode
The following System Operation Modes are supported:
- Application Mode
- Hardware Test Mode
3.2.6 Real Time Clock Support
The iM871A provides an embedded RTC which can be used for timer controlled operations
e.g. automatic transmission of WM-Bus messages at specific times or with a configurable
interval.
Get RTC Time
This function can be used to read the RTC time.
Set RTC Time
This function can be used to set the RTC time.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 16

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Firmware
3.2.7 AES-128 Encryption / Decryption
The iM871A supports automatic AES-128 encryption and decryption of radio link messages.
There is the chance to configure up to 16 decryption keys for 16 different devices. The keys
can be stored in a RAM table together with the complete WM-Bus device address. For
detailed information please refer the WM-Bus Studio User Manual [2].
3.3 Low Power and Wake-up
The Low Power Mode can be entered manually by sending a command via the serial
interface. The radio part is in shutdown state and the CPU is in sleep mode. Additionally the
Real Time Clock can be disabled to reduce the power consumption to the minimum. The
module can be woken up again by sending a new HCI command.
3.3.1 Auto Power Saving
For devices which are configured to operate in Meter mode the feature Auto Power Saving
can be enabled. Automatic Power Saving means, that the device enters the configured power
saving mode automatically when a WM-Bus message was sent. The next command on the
serial interface will wake-up the device.
For devices operation in Other mode power saving is not intended. Other devices are always
on and ready to receive Wireless M-Bus packets.
3.4 Port Pin Signaling
The embedded Firmware can be configured to use three port pins of the radio module as
follows:
Alive Indicator (module pin 1)
indicates if the module is active (pin 1 high) or sleeping (pin 1 low)
TX Indicator (module pin 3)
toggles every time a message was sent
RX Indicator (module pin 6)
toggles every time a message was received
When using the iM871A in Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit the indicator pins are connected to
LEDs of the Demo Board.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 17

User Manual
Channel
Frequency [MHz]
1
868.09
2
868.15
3
868.21
4
868.27
5
868.33
6
868.39
7
868.45
8
868.51
Power Level
TX power [dBm]
Description
0
-8
Minimum output power
1
-5
2
-2
3
+1
4
+4
5
+7
6
+10
7
+13
Maximum output power
Notes: The TX power values are dependent on the supply voltage of the radio module.
These values are valid for 3V supply voltage.
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Specification
4. Module Specification
4.1 General Radio Settings
In this chapter the possible radio configurations of the iM871A are described.
4.1.1 Channel Setup
Table 4-1 shows the RF channel setup. These channels are available in R-Mode for
transmissions from Meter to Other devices. The opposite direction is always done in 868.33
MHz (channel 5).
Table 4-1: Possible Frequency Channel Settings in R-Mode
4.1.2 Power Level Setup
Table 4-2 shows the possible power level setup relating to the 50 connector (pin ANT).
Table 4-2: Possible Output Power Settings
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 18

User Manual
RF data rate [kcps]
Description
4.8
chip rate, results in a data rate of 2.4 kbps (Manchester coding)
32.768
chip rate, results in a data rate of 16.384 kbps (Manchester coding)
50
chip rate = data rate (NRZ coding)
100
chip rate, results in a data rate of 66.66 kbps (3 out of 6 coding)
chip rate = data rate (NRZ coding)
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Specification
4.1.3 Data Rate Setup
Table 4-3 shows the used RF data rates setups. They are configured automatically by the
module firmware dependent on the selected Wireless M-Bus mode, the Device Mode and the
data direction.
Table 4-3: Possible RF Data Rates
4.2 System Timing
4.2.1 Wake-up after Low-Power-Mode
Figure 4-1 shows the timing diagram of the transmission of a 42 byte WM-Bus packet in SMode. The device is in Low Power Mode and is woken up by the edge of the first UART bit
that is received from the host controller. After successful RF transmission, the host controller is
informed with a status message. Hereafter the metering device is able to receive command
messages (e.g. from a data collector) for the configure RX Window (here: 10ms). If no
command is received the radio is shutdown and the module returns to Low Power Mode
again.
Figure 4-1 Packet Timing after Wake-up
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 19

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Specification
Figure 4-2 shows the time gap between the RX signal and the wake-up indication.
Figure 4-2: Packet Timing after Wake-up, detailed view
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 20

User Manual
µC
RX
T
X
~4mA
~21mA
~38mA
RX-Window
< 100nA
µC
RX
T
X
RX-Window
Low Power Mode (RTC off)
Low Power Mode (RTC off)
1s
2s 3s
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Module Specification
4.3 Current Consumption
Figure 4-3 shows schematically the current consumption of a meter device, that is triggered
by the host controller to transmit a Wireless M-Bus packet every 2 seconds. After transmission
the meter is able to receive commands from a master device (concentrator, data collector,
etc.). The rest of the time the meter remains in Low Power Mode.
Figure 4-3: Current Consumption
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 21

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit
5. Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit
To explore the features and capabilities of the iM871A Wireless M-Bus radio module a plug
& play Starter-Kit solution is available.
5.1 Demo Board
The Starter-Kit usually contains two Demo Boards where the iM871A modules can be
mounted on. The Demo Boards offer several often used peripherals like e.g. buttons and
LEDs. The module can easily be accessed via the on board FTDI RS232 to USB converter.
Figure 5-1 gives an overview of the Demo Board and its peripherals.
Figure 5-1: Demo Board
Using the Demo Board with the iM871A it must be soldered on its specific adapter board and
plugged into X1 and X2. Now all necessary module pins are available on X5, X6, and X7 of
the Demo Board.
Table 5-1 shows the used peripherals and its mapping to the radio module iM871A when
setting the corresponding jumper on X5, X6 and X7.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 22

User Manual
Peripheral on the
Demo Board
Jumper setting on
the Demo Board
Demo Board
X1/X2
iM871A pin
LED 1
X5.19 to X5.20
X2.4 1 LED 2
X6.3 to X6.4
X2.5
3
LED 3
X6.5 to X6.6
X2.6 6 LED 4
X6.7 to X6.8
X2.7
7
UART RxD
X7.13 to X7.14
X2.15
19
UART TxD
X7.19 to X7.20
X2.18
18
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit
Table 5-1: Pin mapping to important peripherals of the Demo Board
5.1.1 Power Supply
The Demo Board and the attached radio module may be powered from either two “AAA” size
batteries or from the USB bus when connected to a USB port on a PC. The sliding switch S1
toggles between these power sources and must be set according to what power source is
used. In position “USB” the USB bus voltage together with a voltage regulator (3 V) is used. In
position “BAT” the battery voltage is used directly. LED 6 is turned on when the iM871A is
powered on. Additionally LED 5 is turned on if a USB connection to a PC is established. It is
recommended either to use the battery or the USB power, thus S1 can be used as on-offswitch.
To supply the radio module with power jumper JP1 must be set.
Power supply of the iM871A (except the USB interface) and the attached radio module is
interrupted if push button B4 is pressed. Because the radio module has a Power-On-Reset
(POR) functionality B4 serves as the RESET button.
5.1.2 USB Interface
The USB interface of the Demo Board can be used for communication between the attached
radio module and a PC. The USB controller (FT232RQ) is turned on once the connection to
a PC is established. This is also signalized by LED 5. The USB interface supports ”USB 1.1“
and “USB 2.0 full speed“ modes.
Before the USB interface can be used for the first time, the desired hardware driver for the
USB controller must be installed on the PC. If the PC will detect the Demo Board as new
hardware please follow the given instructions to install the new virtual COM port.
For more information see http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 23

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit
5.2 USB-Stick
Figure 5-2: iM871A USB-Stick
For an easy use a compact iM871A USB adapter is available. It covers all the main
communication functionalities of the demo board and can be used with the Wireless M-Bus
Studio as well. With its internal antenna nothing more is needed as a free USB port on the
host system. The iM871A USB-Stick is not part of the Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit, it has to be
ordered separately.
5.2.1 USB Driver
Before the USB interface can be used for the first time, the desired hardware driver for the
USB controller must be installed on the PC. If the PC will detect the USB-Stick as new
hardware please follow the given instructions to install the new virtual COM port.
The USB-Stick contains the Silabs USB-to-UART-Bridge CP210x. Virtual Com Port (VCP)
drivers for Microsoft WindowsTM, WindowsCE and Linux available.
For more information see
http://www.silabs.com/products/mcu/Pages/USBtoUARTBridgeVCPDrivers.aspx
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 24

User Manual
Note: For detailed information please refer the WM-Bus Studio User Manual [2].
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Wireless M-Bus Starter-Kit
5.3 Configuration with WM-Bus Studio
The Wireless M-Bus Studio is a Windows tool which allows to explore the capabilities of the
iM871A. The GUI offers a comfortable way to configure and control some features of the
embedded Wireless M-Bus Stack like:
• Wireless M-Bus Modes
• RF Message Header Configuration
• Radio Configuration
• Automatic Power Saving
• Embedded Radio Link Test
• RF Message Generator
• Real Time Clock Support
• AES Keys
Figure 5-3: Wireless M-Bus Studio
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 25

User Manual
Ordering Part
Number
Description
Distributor
iM871A
Radio module iM871A
wimod@imst.de
SK – iM871A
Starter Kit for the iM871A. See Notes.
wimod@imst.de
AB – iM871A
2x Adapter Board with iM871A
wimod@imst.de
iM871A – USB
USB Stick with module iM871A
wimod@imst.de
Notes:
The Starter Kit contains two Demo Boards, two Adapter Boards with iM871A, two antennas, batteries, and a CD
with documentation.
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Ordering information
6. Ordering information
Table 6-1: Ordering Information
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 26

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Appendix
7. Appendix
7.1 List of Abbreviations
ADC = Analog-to-Digital Converter
AMR = Automatic Meter Reading
DIO = Digital Input/Output
DLL = Dynamic Link Library
GUI = Graphical User Interface
HCI = Host Controller Interface
MCU = Microcontroller Unit
PCB = Printed Circuit Board
PER = Packet Error Rate
RAM = Random Access Memory
RF = Radio Frequency
RSSI = Received Signal Strength Indication
RTC = Real Time Clock
SMD = Surface-mounted device
SPI = Serial Peripheral Interface
SRD = Short Range Devices
UART = Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter
USB = Universal Serial Bus
WM-Bus = Wireless M-Bus
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 27

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Appendix
7.2 List of Figures
Figure 1-1: iM871A ..................................................................................................... 4
Figure 2-1: iM871A Metering Application Example with Host Controller ............................. 6
Figure 2-2: iM871A Metering Application Example Stand-Alone ....................................... 6
Figure 3-1: iM871A WM-Bus Stack ............................................................................... 9
Figure 3-2: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A ............................................................. 12
Figure 3-3: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A, block1 (header) ..................................... 12
Figure 3-4: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A, block2 .................................................. 12
Figure 3-5: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format A, block3 to block n .................................. 13
Figure 3-6: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B ............................................................. 13
Figure 3-7: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B, block1 (header) ..................................... 13
Figure 3-8: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B, block2 .................................................. 13
Figure 3-9: Wireless M-Bus Telegram Format B, block3 .................................................. 13
Figure 3-10: Message format on serial interface ............................................................ 14
Figure 4-1 Packet Timing after Wake-up ....................................................................... 19
Figure 4-2: Packet Timing after Wake-up, detailed view .................................................. 20
Figure 4-3: Current Consumption ................................................................................. 21
Figure 5-1: Demo Board.............................................................................................. 22
Figure 5-2: iM871A USB-Stick ..................................................................................... 24
Figure 5-3: Wireless M-Bus Studio ............................................................................... 25
7.3 List of Tables
Table 3-1: Wireless M-Bus Modes ................................................................................ 10
Table 3-2: Parameter Overview .................................................................................... 15
Table 4-1: Possible Frequency Channel Settings in R-Mode ............................................. 18
Table 4-2: Possible Output Power Settings ..................................................................... 18
Table 4-3: Possible RF Data Rates ................................................................................ 19
Table 5-1: Pin mapping to important peripherals of the Demo Board ............................... 23
Table 6-1: Ordering Information .................................................................................. 26
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 28

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Appendix
7.4 References
[1] EN13575-4 : 2011
Communication systems for meters and remote reading of meters
[2] WM-Bus Studio User Manual
[3] iM871A HCI Specification
[4] iM871A Datasheet
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 29

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Regulatory Compliance Information
8. Regulatory Compliance Information
The use of radio frequencies is limited by national regulations. The radio module has been
designed to comply with the European Union’s R&TTE (Radio & Telecommunications Terminal
Equipment) directive 1999/5/EC and can be used free of charge within the European Union.
Nevertheless, restrictions in terms of maximum allowed RF power or duty cycle may apply.
The radio module has been designed to be embedded into other products (referred as “final
products”). According to the R&TTE directive, the declaration of compliance with essential
requirements of the R&TTE directive is within the responsibility of the manufacturer of the final
product. A declaration of conformity for the radio module is available from IMST GmbH on
request.
The applicable regulation requirements are subject to change. IMST GmbH does not take
any responsibility for the correctness and accuracy of the aforementioned information.
National laws and regulations, as well as their interpretation can vary with the country. In
case of uncertainty, it is recommended to contact either IMST’s accredited Test Center or to
consult the local authorities of the relevant countries.
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 30

User Manual
iM871A Wireless M-Bus Important Notice
9. Important Notice
9.1 Disclaimer
IMST GmbH points out that all information in this document is given on an “as is” basis. No
guarantee, neither explicit nor implicit is given for the correctness at the time of publication.
IMST GmbH reserves all rights to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, and other
changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service
without prior notice. It is recommended for customers to refer to the latest relevant
information before placing orders and to verify that such information is current and complete.
All products are sold and delivered subject to “General Terms and Conditions” of IMST
GmbH, supplied at the time of order acknowledgment.
IMST GmbH assumes no liability for the use of its products and does not grant any licenses
for its patent rights or for any other of its intellectual property rights or third-party rights. It is
the customer’s duty to bear responsibility for compliance of systems or units in which products
from IMST GmbH are integrated with applicable legal regulations. Customers should provide
adequate design and operating safeguards to minimize the risks associated with customer
products and applications. The products are not approved for use in life supporting systems
or other systems whose malfunction could result in personal injury to the user. Customers
using the products within such applications do so at their own risk.
Any reproduction of information in datasheets of IMST GmbH is permissible only if
reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied by all given associated warranties,
conditions, limitations, and notices. Any resale of IMST GmbH products or services with
statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by IMST GmbH for that
product/solution or service is not allowed and voids all express and any implied warranties.
The limitations on liability in favor of IMST GmbH shall also affect its employees, executive
personnel and bodies in the same way. IMST GmbH is not responsible or liable for any such
wrong statements.
Copyright © 2011, IMST GmbH
9.2 Contact Information
IMST GmbH
Carl-Friedrich-Gauss-Str. 2-4
47475 Kamp-Lintfort
Germany
T +49 2842 981 0
F +49 2842 981 299
E wimod@imst.de
I www.wireless-solutions.de
iM871A_WMBus_UserManual.docx, Wireless Solutions, v1.2 Page 31
 Loading...
Loading...