Page 1

ULTRA 485+2.PCI
USER MANUAL
TM
Sealevel Systems, Inc
P.O. Box 830
Liberty, SC 29657 USA
Part # 7204
Phone: (864) 843-4343
FAX: (864) 843-3067
www.sealevel.com
Page 2

Contents
INTRODUCTION ........................................................................ 1
OVERVIEW......................................................................................1
WHAT’S INCLUDED.........................................................................1
FACTORY DEFAULT SETTINGS ........................................................1
CARD SETUP ............................................................................ 2
RS-485 ENABLE MODES ................................................................2
Interface Mode Examples J1B and J2B (continued)...................4
ADDRESS AND IRQ SELECTION.......................................................4
LINE TERMINATION ........................................................................5
CLOCK MODES ...............................................................................6
BAUD RATES AND DIVISORS FOR THE ‘DIV1’ MODE .......................7
BAUD RATES AND DIVISORS FOR THE ‘DIV2’ MODE .......................8
INSTALLATION ......................................................................... 9
OPERATING SYSTEM INSTALLATION ...............................................9
For Windows Users.....................................................................9
Other Operating Systems ............................................................9
SYSTEM INSTALLATION ..................................................................9
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION .................................................... 10
INTERRUPTS..................................................................................10
WHY USE AN ISP? ........................................................................11
CONNECTOR PIN ASSIGNMENTS....................................................12
RS-422/485..................................................................................12
SPECIFICATIONS .................................................................... 13
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS ...............................................13
MANUFACTURING.........................................................................13
POWER CONSUMPTION .................................................................13
MEAN TIME BETWEEN FAILURES (MTBF) ...................................13
PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS.................................................................13
APPENDIX A - TROUBLESHOOTING....................................... 14
PCI COM NUMBER SELECTION IN WINDOWS 95..............15
APPENDIX B - HOW TO GET ASSISTANCE............................ 16
APPENDIX C - ELECTRICAL INTERFACE .............................. 17
RS-422.........................................................................................17
RS-485.........................................................................................17
PPENDIX D - ASYNCHRONOUS COMMUNICATIONS ............ 18
A
Page 3

APPENDIX E - SILK-SCREEN ................................................. 19
APPENDIX F - COMPLIANCE NOTICES .................................. 20
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION STATEMENT...............20
EMC DIRECTIVE STATEMENT ......................................................20
WARRANTY............................................................................ 21
Figures
Figure 1- Headers J1B and J2B, RS-422..................................................3
Figure 2 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘Auto’ Enabled, with
‘No Echo’ ....................................................................................................3
Figure 3 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘Auto’ Enabled, with
‘Echo’ ..........................................................................................................3
Figure 4 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘RTS’ Enabled, with
‘No Echo’ ....................................................................................................4
Figure 5 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘RTS’ Enabled, with
‘Echo’ ..........................................................................................................4
Figure 6 - Headers J1A and J2A, Line Termination...............................5
Figure 7- Clocking Mode 'Divide By 4' ....................................................6
Figure 8-Clocking Mode 'Divide By 2' .....................................................6
Figure 9-Clocking Mode 'Divide By 1 ......................................................6
Figure 10-Asynchronous Communications Bit Diagram......................18
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
SL9061 Revision 7/2006
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Page 4
Introduction
Introduction
Overview
The Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI is a two channel PCI Bus serial I/O
adapter for the PC and compatibles and features the 16850 advanced UART. It
provides two field selectable RS-422/485 serial ports supporting data rates up to
460.8K bps. The 16850 advanced UART provides a 128 byte FIFO that helps
reduce processor overhead by reducing the number of interrupts that need
servicing. Each port can be individually configured.
Choose the RS-422 mode for long distance device connections up to 4000ft.
where noise immunity and high data integrity are essential. Select RS-485 and
capture data from multiple peripherals in a RS-485 multidrop network. Up to 31
RS-485 devices can be connected to each port to automate your data collection.
You can even mix the ports in any of the interface combinations to provide
maximum flexibility to your application.
In RS-422 mode, the card works seamlessly with the standard operating system
serial driver. In RS-485 mode, our special auto-enable feature allows the RS-485
ports to be viewed by the operating system as a COM: port. This allows the
standard COM: driver to be utilized for RS-485 communications. Our on-board
hardware automatically handles the RS-485 driver enable.
What’s Included
The ULTRA 485+2.PCI is shipped with the following items. If any of these
items are missing or damaged, contact the supplier.
• ULTRA 485+2.PCI Serial I/O Adapter
• Serial Utility Software
• User Manual
Factory Default Settings
The ULTRA 485+2.PCI factory default settings are as follows:
Port # Electrical Specification
Port 1 RS-422
Port 2 RS-422
To install the ULTRA 485+2.PCI using factory default settings, refer to
Installation on page 9.
For your reference, record installed ULTRA 485+2.PCI settings below:
Port # Electrical Specification
Port 1
Port 2
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 1
Page 5

Card Setup
Card Setup
In all cases J1x refers to settings for the first port and J2x refer to settings
for the second port.
RS-485 Enable Modes
RS-485 is ideal for multi-drop or network environments. RS-485 requires a
tri-state driver that will allow the electrical presence of the driver to be removed
from the line. The driver is in a tri-state or high impedance condition when this
occurs. Only one driver may be active at a time and the other driver(s) must be
tri-stated. The output modem control signal Request To Send (RTS) is typically
used to control the state of the driver. Some communication software packages
refer to RS-485 as RTS enable or RTS block mode transfer.
One of the unique features of the ULTRA 485+2.PCI is the ability to be RS-485
compatible without the need for special software or drivers. This ability is
especially useful in Windows, Windows NT, and OS/2 environments where the
lower level I/O control is abstracted from the application program. This ability
means that the user can effectively use the ULTRA 485+2.PCI in a RS-485
application with existing (i.e. standard RS-232) software drivers.
Headers J1B and J2B are used to control the RS-485 mode functions for the
driver circuit. The selections are ‘RTS’ enable (silk-screen ‘RT’) or ‘Auto’
enable (silk-screen ‘AT’). The ‘Auto’ enable feature automatically
enables/disables the RS-485 interface. The ‘RTS’ mode uses the ‘RTS’ modem
control signal to enable the RS-485 interface and provides backward
compatibility with existing software products.
Position 3 (silk-screen ‘NE’) of J1B and J2B is used to control the RS-485
enable/disable functions for the receiver circuit and determine the state of the
RS-422/485 driver. The RS-485 ‘Echo’ is the result of connecting the receiver
inputs to the transmitter outputs. Every time a character is transmitted; it is also
received. This can be beneficial if the software can handle echoing (i.e. using
received characters to throttle the transmitter) or it can confuse the system if the
software does not. To select the ‘No Echo’ mode select silk-screen position
‘NE’.
For RS-422 compatibility remove the jumpers at J1B and J2B.
Examples on the following pages describe all of the valid settings for J1B and
J2B.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 2
Page 6
Card Setup
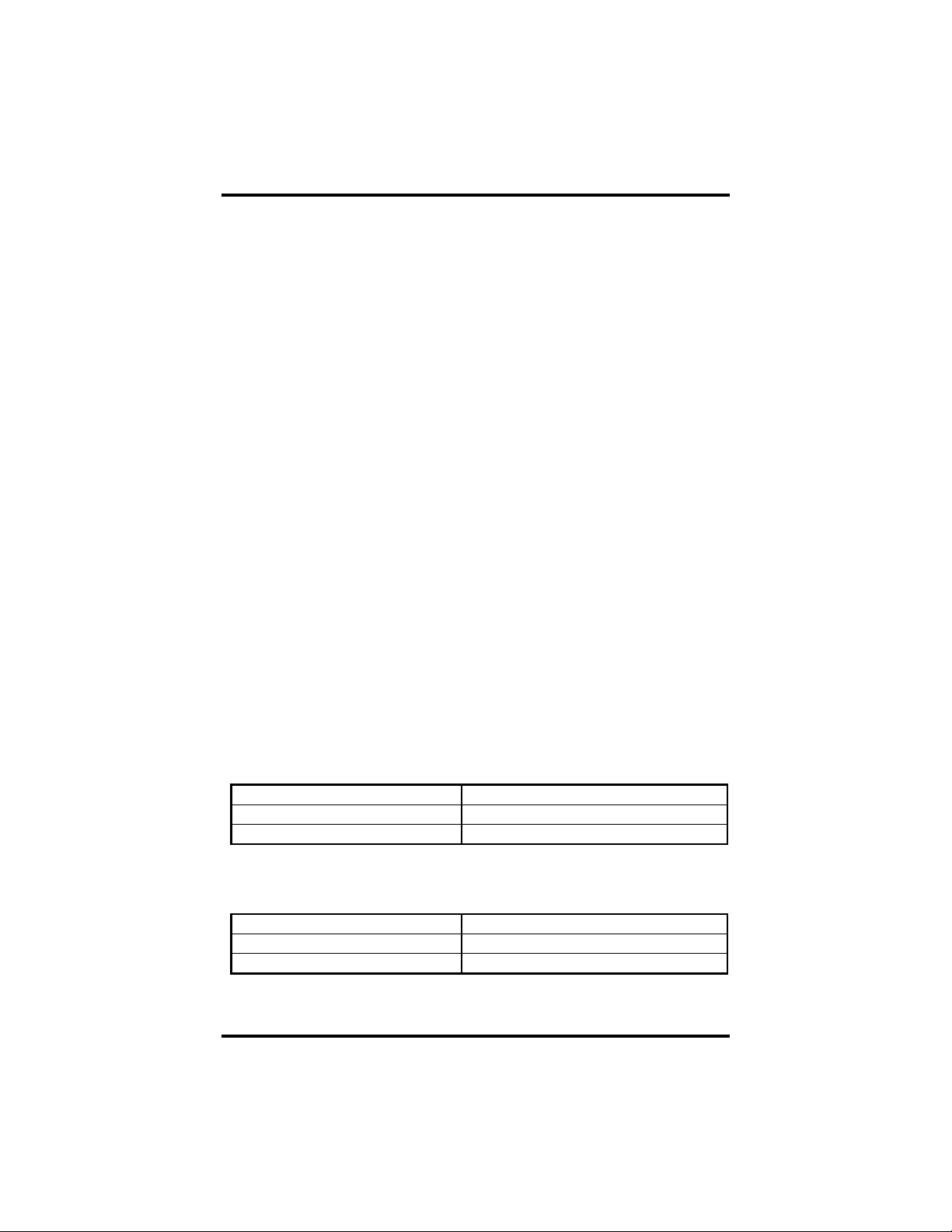
Interface Mode Examples J1B – J2B
ATRTNE
Figure 1- Headers J1B and J2B, RS-422
ATRTNE
Figure 2 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘Auto’ Enabled, with ‘No Echo’
ATRTNE
Figure 3 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘Auto’ Enabled, with ‘Echo’
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 3
Page 7
Card Setup
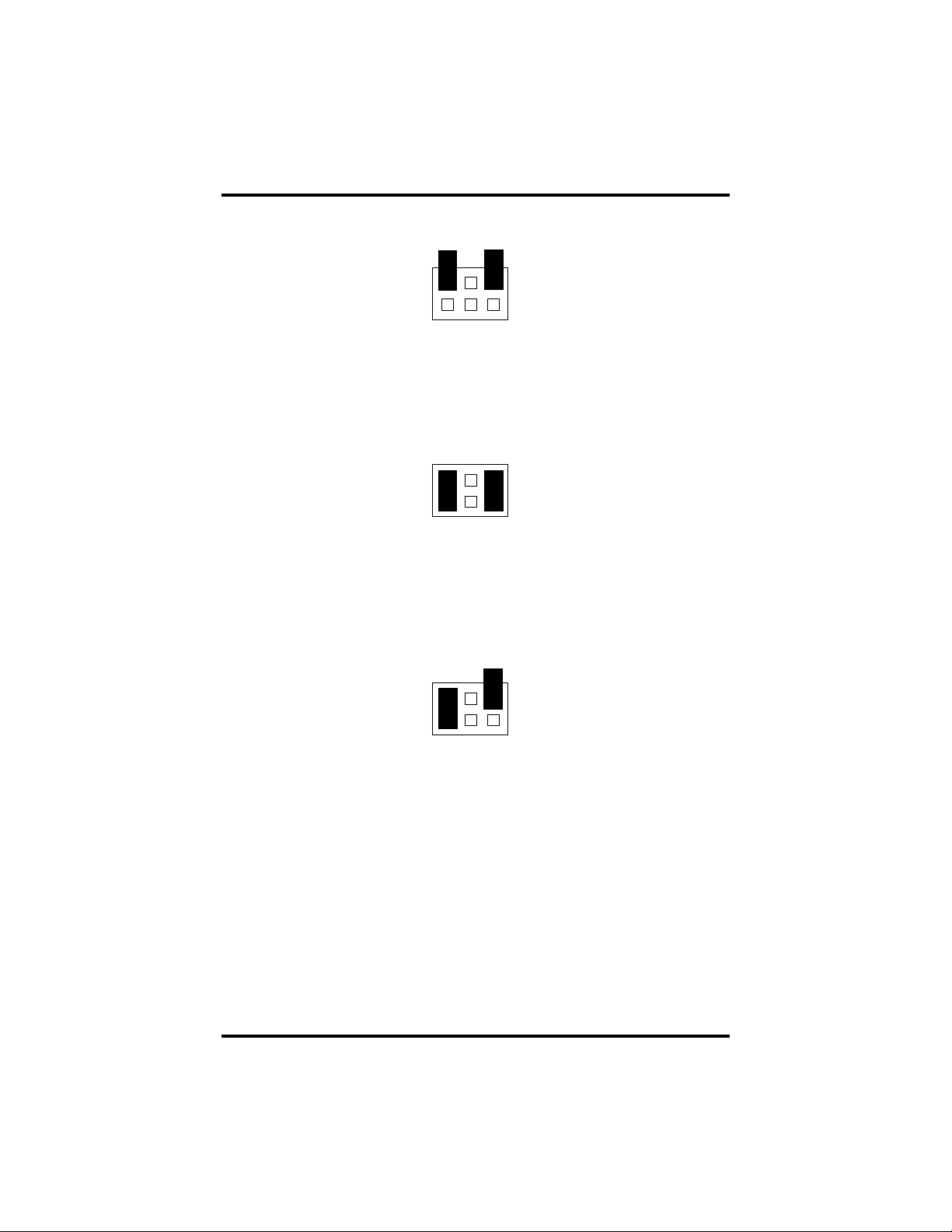
Interface Mode Examples J1B and J2B (continued)
ATRTNE
Figure 4 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘RTS’ Enabled, with ‘No Echo’
ATRTNE
Figure 5 - Headers J1B and J2B, RS-485 ‘RTS’ Enabled, with ‘Echo’
Address and IRQ selection
The ULTRA 485+2.PCI is automatically assigned I/O addresses and IRQs by
your motherboard BIOS. Only the I/O address may be modified by the user.
Adding or removing other hardware may change the assignment of I/O addresses
and IRQs.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 4
Page 8
Card Setup
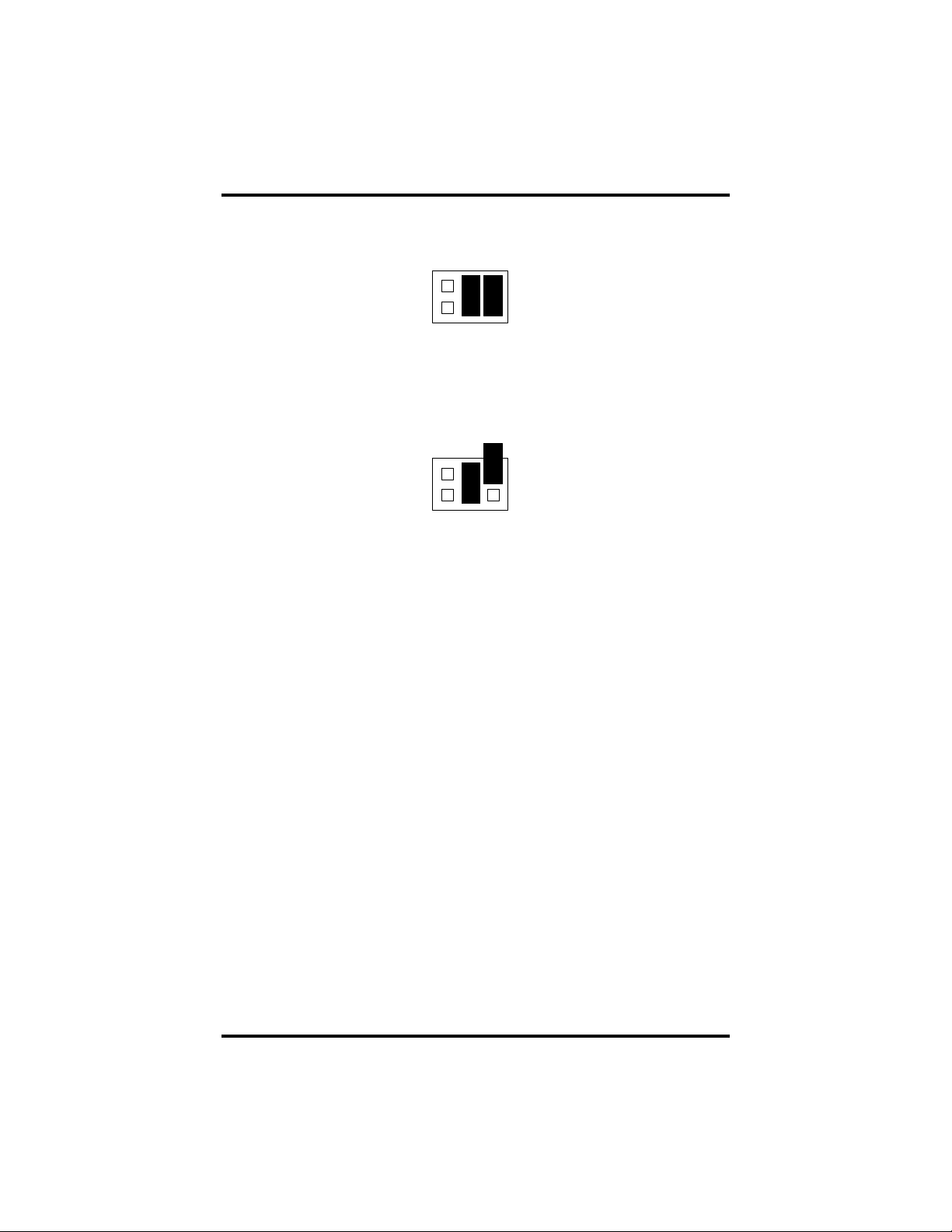
Line Termination
Typically, each end of the RS-485 bus must have line terminating resistors
(RS-422 terminates at the receive end only). A 120-ohm resistor is across each
RS-422/485 input in addition to a 1K ohm pull-up/pull-down combination that
biases the receiver inputs. Headers J1A and J2A allow the user to customize this
interface to their specific requirements. Each jumper position corresponds to a
specific portion of the interface. If multiple ULTRA 485+2.PCI adapters are
configured in a RS-485 network, only the boards on each end should have
jumpers T, P & P ON. Refer to the following table for each position’s operation:
Name Function
P Adds or removes the 1K ohm pull-down resistor in the
RS-422/RS-485 receiver circuit (Receive data only).
P Adds or removes the 1K ohm pull-up resistor in the RS-422/RS-
485 receiver circuit (Receive data only).
T Adds or removes the 120 ohm termination.
L Connects the TX+ to RX+ for RS-485 two wire operation.
L Connects the TX- to RX- for RS-485 two wire operation.
P P T L L
Figure 6 - Headers J1A and J2A, Line Termination
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 5
Page 9

Card Setup
Clock Modes
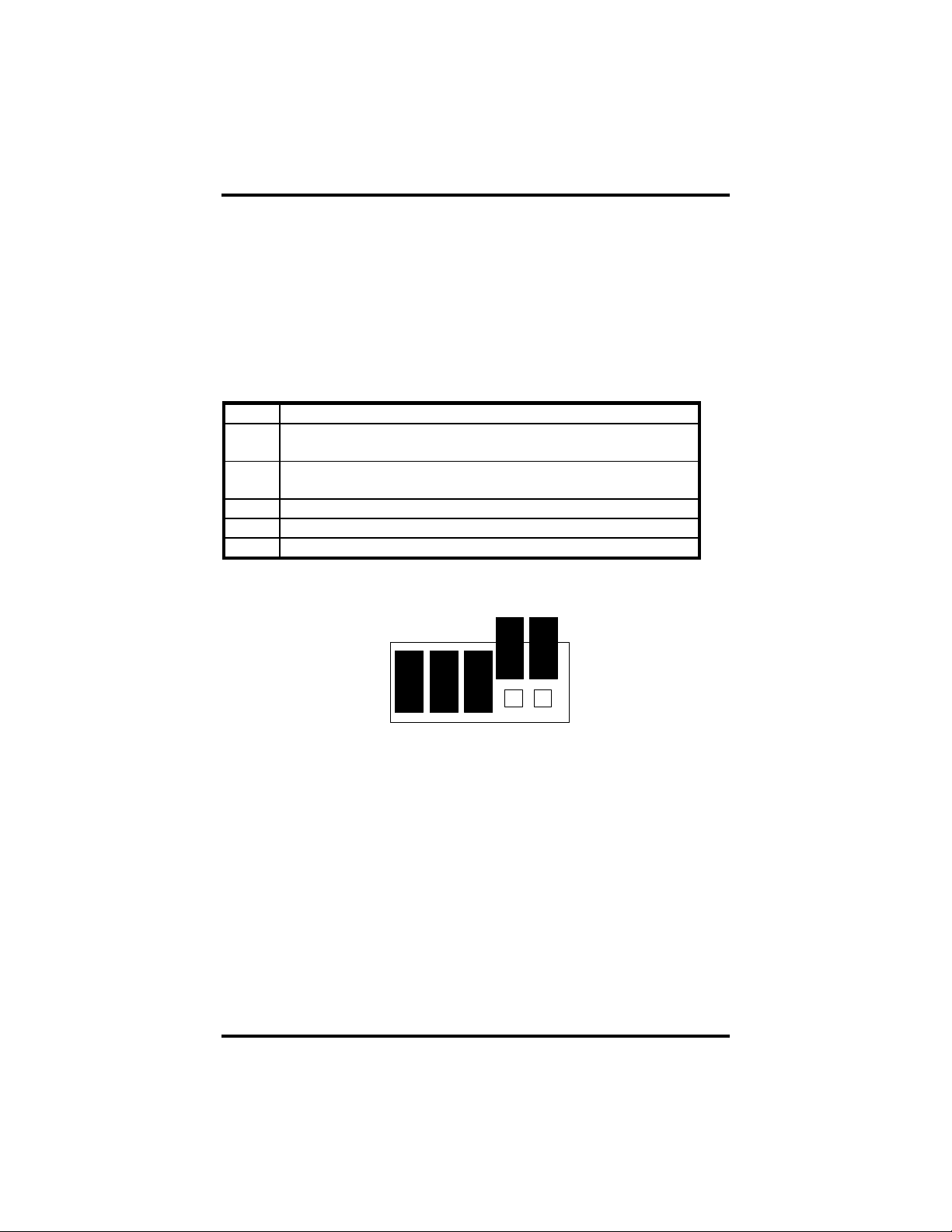
The ULTRA 485+2.PCI employs a unique clocking option that allows the end
user to select from divide by 4, divide by 2 and divide by 1 clocking modes.
These modes are selected at Headers J1C through J4C.
To select the Baud rates commonly associated with COM: ports (i.e. 2400,
4800, 9600, 19.2, … 115.2K Bps ) place the jumper in the divide by 4 mode
(silk-screen DIV4).
DIV1
DIV2
DIV4
Figure 7- Clocking Mode 'Divide By 4'
To double these rates up to a maximum rate for 230.4K bps place the jumper in
the divide by 2 (silk-screen DIV2) position.
DIV1
DIV2
DIV4
Figure 8-Clocking Mode 'Divide By 2'
To select the maximum data rate (460.8K bps) place the jumper in the divide by
1 (silk-screen DIV1) position.
DIV1
DIV2
DIV4
Figure 9-Clocking Mode 'Divide By 1
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 6
Page 10
Card Setup
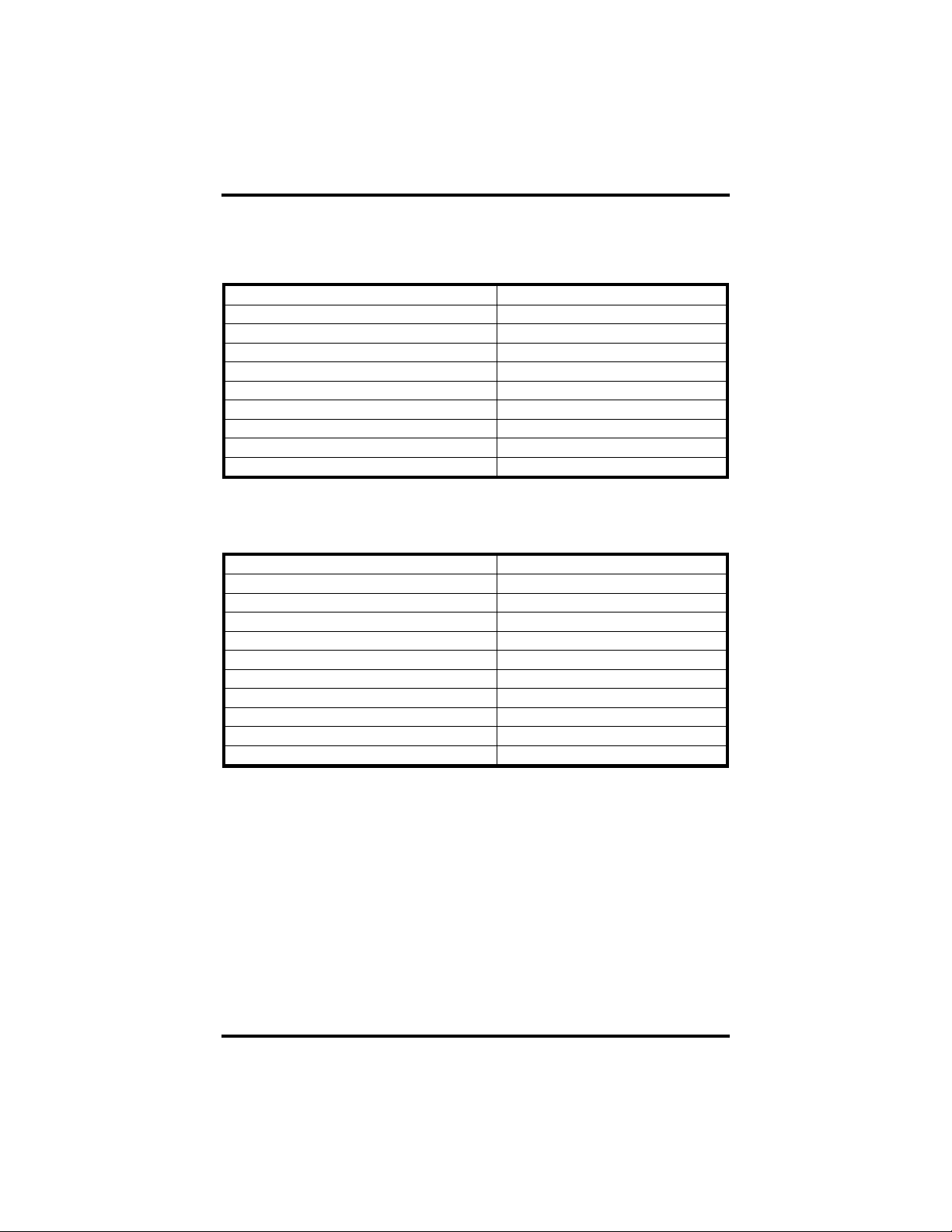
Baud Rates and Divisors for the ‘Div1’ mode
The following table shows some common data rates and the rates you should
choose to match them if using the adapter in the ‘Div1’ mode.
For this Data Rate Choose this Data Rate
1200 bps 300 bps
2400 bps 600 bps
4800 bps 1200 bps
9600 bps 2400 bps
19.2K bps 4800 bps
57.6 K bps 14.4K bps
115.2 K bps 28.8K bps
230.4K bps 57.6 K bps
460.8K bps 115.2 K bps
If your communications package allows the use of Baud rate divisors, choose the
appropriate divisor from the following table:
For this Data Rate Choose this Divisor
1200 bps 384
2400 bps 192
4800 bps 96
9600 bps 48
19.2K bps 24
38.4K bps 12
57.6K bps 8
115.2K bps 4
230.4K bps 2
460.8K bps 1
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 7
Page 11

Card Setup
Baud Rates and Divisors for the ‘Div2’ mode
The following table shows some common data rates and the rates you should
choose to match them if using the adapter in the ‘Div2’ mode.
For this Data Rate Choose this Data Rate
1200 bps 600 bps
2400 bps 1200 bps
4800 bps 2400bps
9600 bps 4800 bps
19.2K bps 9600 bps
38.4K bps 19.2K bps
57.6 K bps 28.8K bps
115.2 K bps 57.6 K bps
230.4 K bps 115.2 K bps
If your communications package allows the use of Baud rate divisors, choose the
appropriate divisor from the following table:
For this Data Rate Choose this Divisor
1200 bps 192
2400 bps 96
4800 bps 48
9600 bps 24
19.2K bps 12
38.4K bps 8
57.6K bps 4
115.2K bps 2
230.4K bps 1
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 8
Page 12

Installation
Installation
Operating System Installation
For Windows Users
Start by choosing Install Software at the beginning of the CD. Choose
Asynchronous COM: Port Software, SeaCOM.
Other Operating Systems
Refer to the appropriate section of the Serial Utilities Software.System
Installation
System Installation
The ULTRA 485+2.PCI can be installed in any of the PCI expansion slots and
contains several jumper straps for each port that must be set for proper
operation.
1. Turn off PC power. Disconnect the power cord.
2. Remove the PC case cover.
3. Locate an available PCI slot and remove the blank metal slot cover.
4. Gently insert the ULTRA 485+2.PCI into the slot. Make sure that the
adapter is seated properly.
5. Replace the screw.
6. Replace the cover.
7. Connect the power cord.
Installation is complete.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 9
Page 13

Technical Description
Technical Description
The Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI provides a PCI interface adapter with
2 asynchronous, field selectable, RS-422/485 serial ports for industrial
automation and control applications.
The ULTRA 485+2.PCI uses the 16850 advanced UART. This chip features
programmable baud rates, data format, interrupt control and a 128-byte input and
output FIFO.
Interrupts
A good description of an interrupt and its importance to the IBM PC can be
found in the book ‘Peter Norton’s Inside the PC, Premier Edition’.
A good analogy of a PC interrupt would be the phone ringing. The phone ‘bell’
is a request for us to stop what we are currently doing and take up another task
(speak to the person on the other end of the line). This is the same process the
PC uses to alert the CPU that a task must be preformed. The CPU upon receiving
an interrupt makes a record of what the processor was doing at the time and
stores this information on the ‘stack’; this allows the processor to resume its
predefined duties after the interrupt is handled, exactly where it left off. Every
main sub-system in the PC has it’s own interrupt, frequently called an IRQ (short
for Interrupt ReQuest). The following IRQ table will define the system IRQs as
well as show typically free IRQs.
In these early days of PC’s Sealevel Systems decided that the ability to share
IRQs was an important feature for any add-in I/O card. Consider that in the IBM
XT the available IRQs were IRQ0 through IRQ7. Of these interrupts only IRQ25 and IRQ7 were actually available for use. This made the IRQ a very valuable
system resource. To make the maximum use of these system resources Sealevel
Systems devised an IRQ sharing circuit that allowed more than one port to use a
selected IRQ. This worked fine as a hardware solution but presented the software
designer with a challenge to identify the source of the interrupt. The software
designer frequently used a technique referred to as ‘round robin polling’. This
method required the interrupt service routine to ‘poll’ or interrogate each UART
as to its interrupt pending status. This method of polling was sufficient for use
with slower speed communications, but as modems increased their through put
abilities this method of servicing shared IRQs became inefficient.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 10
Page 14
Technical Description
Why use an ISP?
The answer to the polling inefficiency was the Interrupt Status Port (ISP). The
ISP is a read only 8-bit register that sets a corresponding bit when an interrupt is
pending. Port 1 interrupt line corresponds with Bit D0 of the status port, Port 2
with D1 etc. The use of this port means that the software designer now only has
to poll a single port to determine if an interrupt is pending.
The ISP is at Base+7 on each port (Example: Base = 280 Hex, Status Port = 287,
28F… etc.). The ULTRA 485+2.PCI will allow any one of the available
locations to be read to obtain the value in the status register. Both status ports on
the ULTRA 485+2.PCI are identical, so any one can be read.
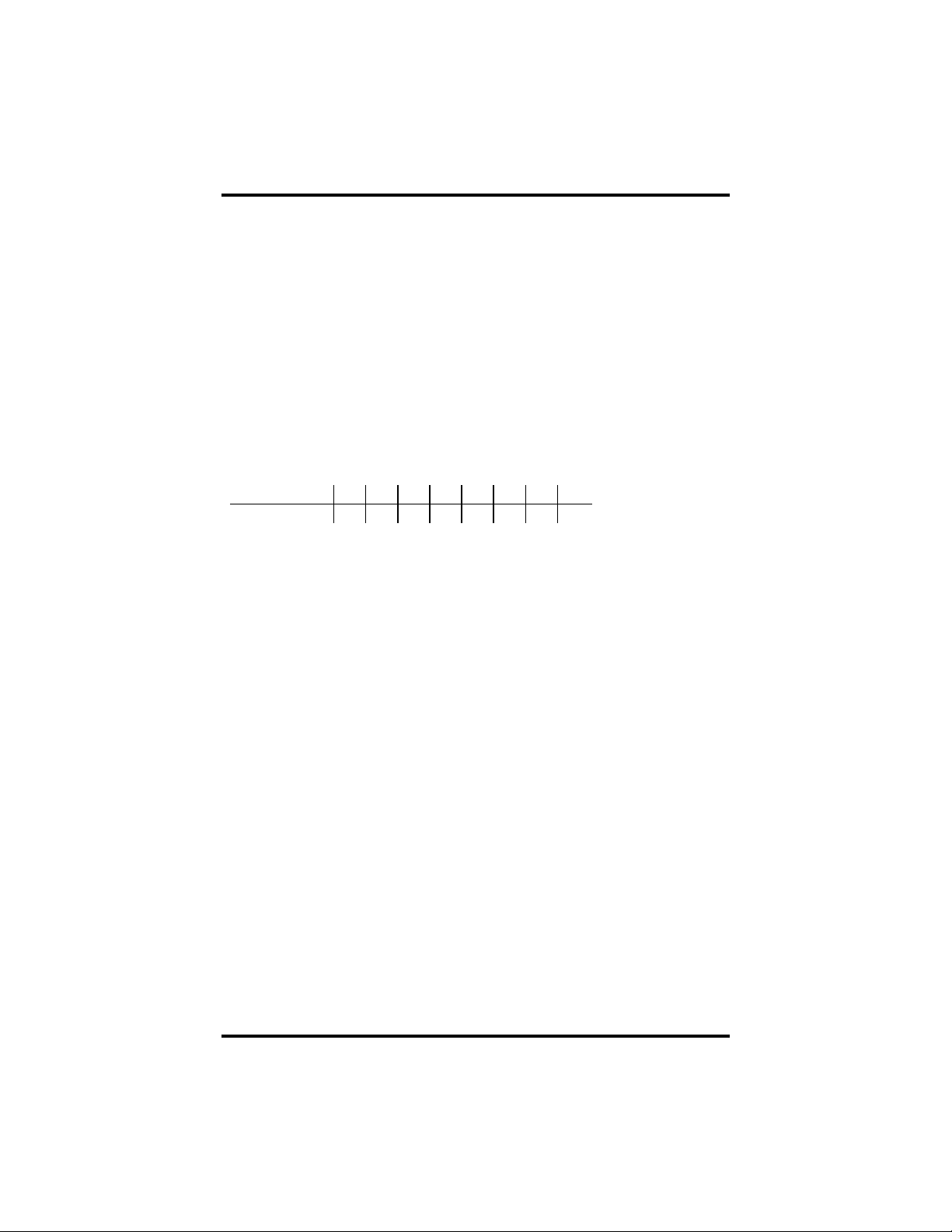
Example: This indicates that Channel 2 has an interrupt pending.
Bit Position: 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Value Read: 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
1
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 11
Page 15

Technical Description
Connector Pin Assignments
RS-422/485
Signal Name Pin # Mode
GND Ground 5
TX + Transmit Data Positive 4 Output
TX- Transmit Data Negative 3 Output
RTS+ Request To Send Positive 6 Output
RTS- Request To Send Negative 7 Output
RX+ Receive Data Positive 1 Input
RX- Receive Data Negative 2 Input
CTS+ Clear To Send Positive 9 Input
CTS- Clear To Send Negative 8 Input
Technical Note
common way to do this is connect RTS+ to CTS+ and RTS- to CTS-. Terminating these pins, if
not used, will help insure you get the best performance from your adapter.
: Please terminate any control signals that are not going to be used. The most
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 12
Page 16

Specifications
Specifications
Environmental Specifications
Specification Operating Storage
Temperature
Range
Humidity Range
0º to 50º C
(32º to 122º F)
10 to 90% R.H.
Non-Condensing
Manufacturing
• All Sealevel Systems Printed Circuit boards are built to U. L. 94V0 rating
and are 100% electrically tested. These printed circuit boards are solder
mask over bare copper or solder mask over tin nickel.
Power Consumption
-20º to 70º C
(-4º to 158º F)
10 to 90% R.H.
Non-Condensing
Supply line
Rating
+12VDC -12VDC +5 VDC
50 mA 50 mA 480 mA
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Greater than 150,000 hours. (Calculated)
Physical Dimensions
Board length 5.0 inches (12.7 cm)
Board Height including Goldfingers 4.2 inches (10.66 cm)
Board Height excluding Goldfingers 3.875 inches (9.841 cm)
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 13
Page 17

Appendix A - Troubleshooting
Appendix A - Troubleshooting
A Serial Utility Diskette is supplied with the Sealevel Systems adapter and will
be used in the troubleshooting procedures. By using this diskette and following
these simple steps, most common problems can be eliminated without the need
to call Technical Support.
1. Identify all I/O adapters currently installed in your system. This includes
your on-board serial ports, controller cards, sound cards etc. The I/O
addresses used by these adapters, as well as the IRQ (if any) should be
identified.
2. Configure your Sealevel Systems adapter so that there is no conflict with
currently installed adapters. No two adapters can occupy the same I/O
address.
3. Make sure the Sealevel Systems adapter is using a unique IRQ. While the
Sealevel Systems adapter does allow the sharing of IRQs, many other
adapters (i.e. SCSI adapters & on-board serial ports) do not
typically selected via an on-board header block. Refer to the section on Card
Setup for help in choosing an I/O address and IRQ.
4. Make sure the Sealevel Systems adapter is securely installed in a
motherboard slot.
. The IRQ is
5. When running DOS or Windows 3.x refer to the Serial Utilities disk 1 and
the User Manual to verify that the Sealevel Systems adapter is configured
correctly. The supplied diskette contains a diagnostic program ‘SSD’ that
will verify if an adapter is configured properly. This diagnostic program is
written with the user in mind and is easy to use. Refer to the ‘README’ file
on the supplied diskette for detailed instructions on using ‘SSD’.
6. For Windows 95 and Windows NT, the diagnostic tool ‘WinSSD’ is
installed in the Sealevel folder on the Start Menu during the setup process.
First find the ports using the Device Manager, then use ‘WinSSD’ to verify
that the ports are functional.
7. Always use the Sealevel Systems diagnostic software when troubleshooting
a problem. This will eliminate any software issues from the equation.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 14
Page 18

Appendix A - Troubleshooting
PCI COM NUMBER SELECTION IN WINDOWS 95
When installing a multi-port PCI card in Windows 95 the default starting COM:
number assigned to the first port will be COM:5 if no COM:5 exists. If there is a
COM: 5, 6, etc., the next available COM: number will be assigned to the first
port with all additional ports following in ascending order.
To change the first two ports so that Windows assigns them COM: 3 and COM:
4 port enumeration double click the Systems icon in control panel or right click
on My Computer and choose properties which will bring you to System
Properties. Choose the Device Manager tab and double click on the MultiFunction Adapter heading. This will show all the information concerning the
Sealevel adapter. Choose the Resources tab, which will show all resources
assigned to the multi-function adapter. Uncheck the Use Automatic Settings box.
Notice that with a two port card there will be three input/output, (I/O), ranges
listed. With a four port card there will be five input/output, (I/O), ranges listed.
The first I/O range is for the PCI bus and should not be changed. The second and
third I/O ranges are the ones that need to be changed in order to have those ports
enumerated as COM: 3 and COM: 4. Double click on the second I/O range
which will allow you to change the address. Highlight the entire I/O range and
type: 03e8–03ef for COM: 3. Click OK. Windows will inform you that you have
made modifications that may affect other devices. Click OK. Next double click
on the third I/O range. Highlight the entire I/O range and type: 02e8–02ef for
COM: 4. Again Windows will inform you that you have made modifications
that may affect other devices. Click OK.
Following these steps will change the COM: number assignments on the first two
ports to
COM: 3 and 4.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 15
Page 19
Appendix B - How To Get Assistance
Appendix B - How To Get Assistance
1. Begin by reading through the Trouble Shooting Guide in Appendix
A. If assistance is still needed please see below.
2. When calling for technical assistance, please have your user
manual and current adapter settings. If possible, please have the
adapter installed in a computer ready to run diagnostics.
3. Sealevel Systems provides an FAQ section on its web site. Please
refer to this for many commonly asked questions. This section can
be found at http://www.sealevel.com/faq.htm
.
4. Visit Sealevel’s website at www.sealevel.com
software updates and newest manuals.
5. Technical support is available Monday to Friday from 8:00 a.m. to
5:00 p.m. eastern time. Technical support can be reached at (864)
843-4343.
RETURN AUTHORIZATION MUST BE OBTAINED FROM SEALEVEL
SYSTEMS BEFORE RETURNED MERCHANDISE WILL BE
ACCEPTED. AUTHORIZATION CAN BE OBTAINED BY CALLING
SEALEVEL SYSTEMS AND REQUESTING A RETURN
MERCHANDISE AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER.
for the latest
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 16
Page 20

Appendix C – Electrical Interface
Appendix C - Electrical Interface
RS-422
The RS-422 specification defines the electrical characteristics of balanced
voltage digital interface circuits. RS-422 is a differential interface that defines
voltage levels and driver/receiver electrical specifications. On a differential
interface, logic levels are defined by the difference in voltage between a pair of
outputs or inputs. In contrast, a single ended interface, for example RS-232,
defines the logic levels as the difference in voltage between a single signal and a
common ground connection. Differential interfaces are typically more immune to
noise or voltage spikes that may occur on the communication lines. Differential
interfaces also have greater drive capabilities that allow for longer cable lengths.
RS-422 is rated up to 10 Megabits per second and can have cabling 4000 feet
long. RS-422 also defines driver and receiver electrical characteristics that will
allow 1 driver and up to 32 receivers on the line at once. RS-422 signal levels
range from 0 to +5 volts. RS-422 does not define a physical connector.
RS-485
RS-485 is backwardly compatible with RS-422; however, it is optimized for
partyline or multi-drop applications. The output of the RS-422/485 driver is
capable of being Active (enabled) or Tri-State (disabled). This capability allows
multiple ports to be connected in a multi-drop bus and selectively polled.
RS-485 allows cable lengths up to 4000 feet and data rates up to 10 Megabits
per second. The signal levels for RS-485 are the same as those defined by
RS-422. RS-485 has electrical characteristics that allow for 32 drivers and 32
receivers to be connected to one line. This interface is ideal for multi-drop or
network environments. RS-485 tri-state driver (not dual-state) will allow the
electrical presence of the driver to be removed from the line. Only one driver
may be active at a time and the other driver(s) must be tri-stated. RS-485 can be
cabled in two ways, two wire and four wire mode. Two wire mode does not
allow for full duplex communication, and requires that data be transferred in
only one direction at a time. For half-duplex operation, the two transmit pins
should be connected to the two receive pins (Tx+ to Rx+ and Tx- to Rx-). Four
wire mode allows full duplex data transfers. RS-485 does not define a connector
pin-out or a set of modem control signals. RS-485 does not define a physical
connector.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 17
Page 21

Appendix D - Asynchronous Communications
r
Appendix D - Asynchronous Communications
Serial data communications implies that individual bits of a character are
transmitted consecutively to a receiver that assembles the bits back into a
character. Data rate, error checking, handshaking, and character framing
(start/stop bits) are pre-defined and must correspond at both the transmitting and
receiving ends.
Asynchronous communications is the standard means of serial data
communication for PC compatibles and PS/2 computers. The original PC was
equipped with a communication or COM: port that was designed around an 8250
Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter (UART). This device allows
asynchronous serial data to be transferred through a simple and straightforward
programming interface. A start bit, followed by a pre-defined number of data bits
(5, 6, 7, or 8) defines character boundaries for asynchronous communications.
The end of the character is defined by the transmission of a pre-defined number
of stop bits (usually 1, 1.5 or 2). An extra bit used for error detection is often
appended before the stop bits.
Idle state of
line
1
0
5 to 8 Data Bits
Figure 10-Asynchronous Communications Bit Diagram
Odd, Even
or
Unused
P
BIT
STOP
Remain Idle o
next start bit
1
1.5
2
This special bit is called the parity bit. Parity is a simple method of determining
if a data bit has been lost or corrupted during transmission. There are several
methods for implementing a parity check to guard against data corruption.
Common methods are called (E)ven Parity or (O)dd Parity. Sometimes parity is
not used to detect errors on the data stream. This is refereed to as (N)o parity.
Because each bit in asynchronous communications is sent consecutively, it is
easy to generalize asynchronous communications by stating that each character is
wrapped (framed) by pre-defined bits to mark the beginning and end of the serial
transmission of the character. The data rate and communication parameters for
asynchronous communications have to be the same at both the transmitting and
receiving ends. The communication parameters are baud rate, parity, number of
data bits per character, and stop bits (i.e. 9600,N,8,1).
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 18
Page 22
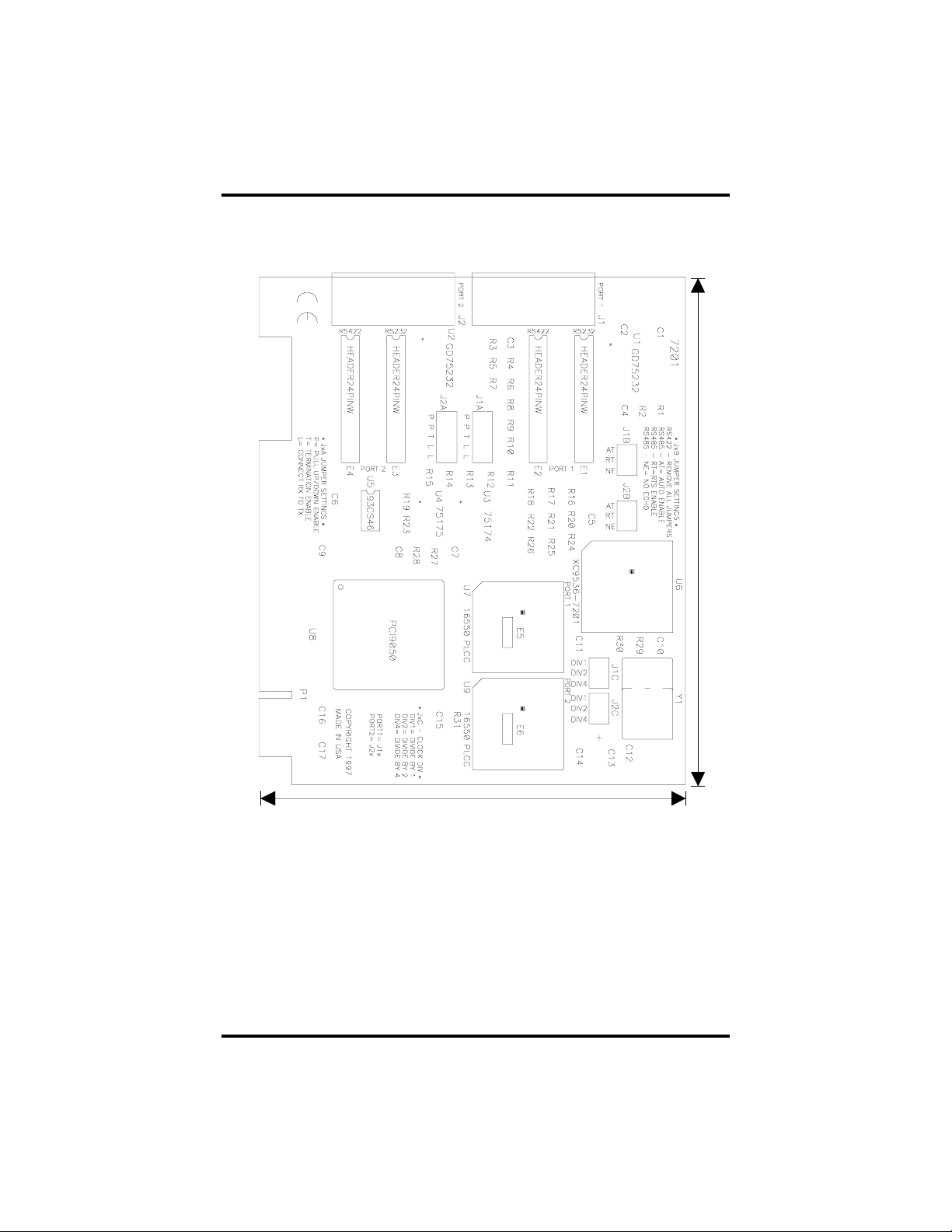
Appendix E - Silk-Screen
Appendix E - Silk-Screen
5.0"
4.2"
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 19
Page 23
Appendix F - Compliance Notices
Appendix F - Compliance Notices
Federal Communications Commission Statement
FCC - This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for
Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are
designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to
cause harmful interference in such case the user will be required to correct the
interference at his own expense.
EMC Directive Statement
Products bearing the CE Label fulfill the requirements of the
EMC directive (89/336/EEC) and of the low-voltage directive
(73/23/EEC) issued by the European Commission.
To obey these directives, the following European standards must be met:
• EN55022 Class A - “Limits and methods of measurement of radio
interference characteristics of information technology equipment”
• EN55024-‘Information technology equipment Immunity
characteristics Limits and methods of measurement.
• EN60950 (IEC950) - “Safety of information technology
equipment, including electrical business equipment”
Warning
This is a Class A Product. In a domestic environment this product may
cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take
adequate measures.
Always use cabling provided with this product if possible. If no cable is
provided or if an alternate cable is required, use high quality shielded cabling to
maintain compliance with FCC/EMC directives.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 20
Page 24
Warranty
Warranty
Sealevel Systems, Inc. provides a limited lifetime
warranty. Should this product fail to be in good
working order at any time during this period, Sealevel
Systems will, at it’s option, replace or repair it at no
additional charge except as set forth in the following
terms. This warranty does not apply to products damaged by misuse,
modifications, accident or disaster.
Sealevel Systems assumes no liability for any damages, lost profits, lost savings
or any other incidental or consequential damage resulting from the use, misuse
of, or inability to use this product. Sealevel Systems will not be liable for any
claim made by any other related party.
RETURN AUTHORIZATION MUST BE OBTAINED FROM SEALEVEL
SYSTEMS BEFORE RETURNED MERCHANDISE WILL BE
ACCEPTED. AUTHORIZATION CAN BE OBTAINED BY CALLING
SEALEVEL SYSTEMS AND REQUESTING A RETURN
MERCHANDISE AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER.
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated
2779 Greenville Highway
P.O. Box 830
Liberty, SC 29657 USA
(864) 843-4343 FAX:(864) 843-3067
www.sealevel.com
email: support@sealevel.com
Technical Support is available from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Eastern time.
Monday - Friday
Trademarks
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated acknowledges that all trademarks referenced in
this manual are the service mark, trademark, or registered trademark of the
respective company.
ULTRA 485+2.PCI is a trademark of Sealevel Systems, Incorporated.
Sealevel Systems ULTRA 485+2.PCI Page 21
 Loading...
Loading...