Page 1

SeaI/O User Manual
www.sealevel.com PO Box 830 – Liberty, SC 29657 864.843.4343
Page 2

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION......................................................................................................................... 1
BEFORE YOU GET STARTED................................................................................................. 3
SEAI/O HARDWARE DESCRIPTION..................................................................................... 4
SEAI/O BASE AND EXPANSION MODULES.................................................................................... 4
SEAI/O MODULE COMMON FEATURES ........................................................................................ 5
SEAI/O CONFIGURATIONS & SPECIFICATIONS ............................................................................. 6
410 Series – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs......................................... 6
420 Series – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs................................................. 7
430 Series – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs............................................................................... 8
440 Series – 32 Reed Relay Outputs....................................................................................... 9
450 Series – 16 Form C Relay Outputs ................................................................................ 10
462 Series – 96 Channel TTL DB-78.................................................................................... 11
463 Series – 96 Channel TTL 50-Pin.................................................................................... 13
470 Series – 16 A/D, 2 D/A, 8 24V Outputs, 8 Isolated Inputs............................................. 16
520 Series – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs.......................... 17
POWER OPTIONS .................................................................................................................... 18
BASE MODULE POWER CONNECTION......................................................................................... 18
SEAI/O EXPANSION POWER CONNECTION ................................................................................. 18
SEAMAX APPLICATION SUITE........................................................................................... 20
SEAMAX OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................ 20
COMMUNICATING VIA MODBUS ................................................................................................ 21
SEAMAX SOFTWARE INSTALLATION ........................................................................................ 22
MAXSSD CONFIGURATION & DIAGNOSTICS UTILITY ............................................................... 23
TROUBLESHOOTING SEAMAX................................................................................................... 34
HARDWARE CONFIGURATION .......................................................................................... 36
ETTING DEVICE ADDRESS (SLAVE ID)..................................................................................... 36
S
CONFIGURING THE “BASE” SEAI/O MODULE............................................................................. 38
CONFIGURING N-SERIES EXPANSION MODULES........................................................................ 39
C
ONFIGURING A WIRELESS (W-SERIES) MODULE ..................................................................... 40
ONFIGURING AN ETHERNET (E-SERIES) MODULE.................................................................... 55
C
SEAI/O-463 RIBBON CABLE INSTALLATION .............................................................................. 58
SEAI/O-470 JUMPER AND DIPSWITCH SETTINGS........................................................................ 60
WIRING OPTIONS ................................................................................................................... 63
S
EAI/O PASS-THROUGH CONNECTOR........................................................................................ 63
I/O WIRING – SEAI/O-410, 420, 430, 440, AND 450 MODULES ................................................. 64
WIRING – SEAI/O-462 AND 463 MODULES.......................................................................... 65
I/O
I/O
WIRING – SEAI/O-470 MODULES ........................................................................................ 68
I/O WIRING – SEAI/O-520 MODULES ........................................................................................ 71
ONNECTOR PIN OUTS............................................................................................................... 72
C
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
SL9049 Revision 7/2008
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 3

MOUNTING OPTIONS............................................................................................................. 73
SEALATCH™ USB.................................................................................................................... 74
ACCESSORIES .......................................................................................................................... 76
APPENDIX A – HOW TO GET ASSISTANCE ..................................................................... 78
APPENDIX B – WIRELESS MODULE INFORMATION.................................................... 79
APPENDIX C – COMPLIANCE NOTICES........................................................................... 80
WARRANTY............................................................................................................................... 81
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
SL9049 Revision 7/2008
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 4

Introduction
Sealevel SeaI/O™ modules offer powerful data acquisition solutions that are perfect
for a wide range of applications and environments with easy interfacing to
computers, controllers, and PLCs. SeaI/O modules are available in various digital,
analog, and serial I/O configurations. Each SeaI/O model is designed for maximum
flexibility and easy field wiring.
Ordering options allow connection to the host device via Wireless 802.11b/g,
Ethernet, USB, RS-485, or RS-232. Up to 246 expansion modules can be daisy
chained together via RS-485 using convenient pass-through connectors.
For easy software integration, application programs or 3
Sealevel SeaMAX
and Modbus RTU (RS-232, RS-485, and USB) protocols.
Industry Segments
SeaI/O modules are perfect for a wide variety of applications and environments
including:
Process Control
Data Acquisition
Broadcast Automation
Security
Facility Management
rd
TM
library or industry standard Modbus TCP (Ethernet & Wireless)
party software can use the
Features
Choice of Connectivity:
o Wireless (802.11b/g)
o Ethernet
o USB
o RS-485
o RS-232
Supports Industry Standard Modbus TCP & RTU Protocols
Models Offering Choice of:
o Optically Isolated Inputs
o Reed Relay Outputs
o Form C Relay Outputs
o TTL Interfaces
o Analog A/D & D/A
Status Indicator LEDs for Communication, Fault, and Status
Field Removable Terminal Block Connectors (most models)
9-30VDC Power Input
Power Input via Terminal Block or DC Jack
Daisy Chain up to 247 Modules
Extended Temperature Range Available (-40°C to +85°C)
Rugged Metal Enclosure
Compact Size – 7.5"(L) x 5.1"(W) x 1.3"(H)
Din Rail or Table Mount
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 1 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 5

This manual covers the installation and operation of these SeaI/O products:
Wireless 802.11b & 802.11g
SeaI/O-410W – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-420W – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
SeaI/O-430W – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-440W – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-450W – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-462W – 96 Bit TTL I/O (DB-78)
SeaI/O-463W – 96 Bit TTL I/O (50-Pin IDC)
SeaI/O-470W – 8 Inputs/8 Outputs/2 D/A & 16 A/D
SeaI/O-520W – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
Ethernet 10/100 BaseT
SeaI/O-410E – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-420E – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
SeaI/O-430E – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-440E – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-450E – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-462E – 96 Bit TTL I/O (DB-78)
SeaI/O-463E – 96 Bit TTL I/O (50-Pin IDC)
SeaI/O-470E – 8 Inputs/8 Outputs/2 D/A & 16 A/D
SeaI/O-520E – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
USB
SeaI/O-410U – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-420U – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
SeaI/O-430U – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-440U – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-450U – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-462U – 96 Bit TTL I/O (DB-78)
SeaI/O-463U – 96 Bit TTL I/O (50-Pin IDC)
SeaI/O-470U – 8 Inputs/8 Outputs/2 D/A & 16 A/D
SeaI/O-520U – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
RS-485
SeaI/O-410M – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-420M – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
SeaI/O-430M – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-440M – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-450M – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-462M – 96 Bit TTL I/O (DB-78)
SeaI/O-463M – 96 Bit TTL I/O (50-Pin IDC)
SeaI/O-470M – 8 Inputs/8 Outputs/2 D/A & 16 A/D
SeaI/O-520M – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
RS-232
SeaI/O-410S – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-420S – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
SeaI/O-430S – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-440S – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-450S – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-462S – 96 Bit TTL I/O (DB-78)
SeaI/O-463S – 96 Bit TTL I/O (50-Pin IDC)
SeaI/O-470S – 8 Inputs/8 Outputs/2 D/A & 16 A/D
SeaI/O-520S – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
Expansion Units (Connect to Base Unit via RS-485)
SeaI/O-410N – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-420N – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
SeaI/O-430N – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-440N – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-450N – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-462N – 96 Bit TTL I/O (DB-78)
SeaI/O-463N – 96 Bit TTL I/O (50-Pin IDC)
SeaI/O-470N – 8 Inputs/8 Outputs/2 D/A & 16 A/D
SeaI/O-520N – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 2 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 6

Before You Get Started
What’s Included
All SeaI/O modules are shipped with the following items. If any of these items is
missing or damaged please contact Sealevel for a replacement.
SeaI/O Data Acquisition Module
Sealevel SeaMAX Software CD
Accessories (Model Dependent)
NOTE:
Depending on the interface type, your SeaI/O module may include
additional accessories. Included accessories are listed below.
Additional useful items can be found in the Accessories section of
this manual.
Included Communications and Expansion Accessories
SeaI/O modules are shipped with the following accessories:
W-Series (Wireless) Item# 930-033-R – Wireless antenna
E-Series (Ethernet) Item# CA246 – 1 x 7’ straight through Ethernet cable, for
connection to a network hub or switch (BLUE).
Item# CA251 – 1 x 7’ crossover cable, for direct connection to a
host computer’s Ethernet port (YELLOW).
DO NOT connect the yellow crossover cable to the RJ45 RS-485
pass-through connectors on the left side of the SeaI/O module!
U-Series (USB) Item# CA356 – 6’ Type A to SeaLATCH Type B USB cable.
M-Series (RS-485)
No cable is included. Use twisted-pair wiring connected to RS-485
signals via screw terminals on left side of SeaI/O module.
S-Series (RS-232) Item# KT119 – RS-232 DB9/RJ45 Kit, includes a DB9F to RJ45
adapter with RS-232 pinout (Item# DB109) and a 7’ CAT5 patch
cable (Item# CA246) for connecting SeaI/O modules to both
Sealevel and standard RS-232 serial ports.
N-Series (Expansion) KT122 – Expansion & Strap Kit, includes 5” CAT5 RS-485
interconnect cable, four metal straps, and four #4-40 metal screws,
for connecting two or more SeaI/O modules together in a “stack”.
All Models
Each SeaI/O unit is shipped with 4 adhesive rubber feet that can be
attached to the bottom of the enclosure to enhance stability in table
mount applications.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 3 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 7

SeaI/O Hardware Description
SeaI/O Base and Expansion Modules
Base Modules connect to the host via one of the following interfaces:
W-Series – Wireless Modbus TCP
E-Series - Ethernet Modbus TCP
U-Series - USB Modbus RTU
M-Series - RS-485 Modbus RTU
S-Series - RS-232 Modbus RTU
After the Base unit is installed, up to 246 additional SeaI/O N-Series Expansion
Units can be added to create an I/O network. These expansion modules interface via
RS-485 and can be located local to the Base SeaI/O device or remotely located up to
4000 feet away. Local installations should use the 5” CAT5 RS-485 pass-through
cable (Item number CA239) shipped with each N-series module to connect. Remote
expansion modules should use RS-485 twisted pair wiring from the Base unit
connected via the removable screw terminal connector.
For local installations power to the expansion modules is supplied from the Base unit
via the pass-through connectors. For remote devices, separate power is required at
each expansion unit. Refer to the Power Options section of this manual for more
information on SeaI/O power requirements and power supply sizing.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 4 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 8

SeaI/O Module Common Features
All SeaI/O modules include the same connectors and configuration options on the
side of the unit:
NOTE:
RS-485 networks should have termination enabled on each end of
the network. Pull-up and pull-down resistors should also be enabled
on the last device on the network.
The 9-30VDC input barrel connector is center positive.
Status LEDs are also included on the front of all SeaI/O modules to indicate the
following information:
Communication (Yellow) – Blinks when data is transmitted
Fault (Red) – Lights when there is a problem with the device
Status (Green) – See Device Address Configuration section of this manual
o Blinks when the rotary “ADDR” switch is set to “0” and the default
Slave ID is set to 247
o Lights steady when module is properly configured from the factory
defaults
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 5 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 9

SeaI/O Configurations & Specifications
410 Series – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/16 Reed Relay Outputs
SeaI/O-410 modules provide 16 optically isolated inputs and 16 Reed relay outputs.
Inputs can range from 5-30VDC, while the Reed relays provide long life switch
closures that are well suited for low current applications. Inputs and outputs are
grouped into four-bit segments. Each group shares a common for easy wiring via
removable 3.5mm terminal blocks.
Inputs
Type: 16 non-polarized optically isolated inputs
Voltage Range: 5-30VDC
Isolation: 300V
Input Resistance: 6.2K Ohms in series
Response Time: 4 microseconds
Outputs
Type: 16 SPST Form A Reed relays
Power: 10VA max.
Contact Voltage: 60VDC max.
Contact Current: 500mA max.
Operate Time: 0.5ms max.
Bounce Time: 0.5ms max.
Release Time: 0.2ms max.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 6 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 10

420 Series – 16 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 Form C Outputs
The SeaI/O-420 provides 16 optically isolated inputs and 8 SPDT Form C relay
outputs. Inputs can range from 5-30VDC and provide 300V isolation to ground. Each
output offers normally open and normally closed contact connections via 3.5mm field
removable terminal blocks.
Inputs
Type: 16 non-polarized optically isolated inputs
Voltage Range: 5-30VDC
Isolation: 300V
Input Resistance: 6.2K Ohms in series
Response Time: 4 microseconds
Outputs
Type: 8 SPDT Form C relays
Power: DC 30W/ AC 60 VA
Contact Voltage: 60VDC max.
Contact Current: 2A max.
Operate Time: 2ms max.
Bounce Time: 7ms max.
Release Time: 1ms max.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 7 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 11

430 Series – 32 Optically Isolated Inputs
SeaI/O-430 modules provide 32 optically isolated inputs with 300V external isolation
and high channel-to-channel isolation. Ideal for low voltage monitoring applications,
connection to real world signals is made via convenient 3.5mm field removable
screw terminal connectors.
Inputs
Type: 32 non-polarized optically isolated inputs
Voltage Range: 5-30VDC
Isolation: 300V
Input Resistance: 6.2K Ohms in series
Response Time: 4 microseconds
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 8 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 12

440 Series – 32 Reed Relay Outputs
The SeaI/O-440 provides 32 SPST Form A dry-contact Reed relays. Reed relays
offer long life performance and fast response time. Convenient removable 3.5mm
screw terminal blocks compatible with 14-22 AWG wiring allow reliable connection
to real world I/O.
Outputs
Type: 32 SPST Form A Reed relays
Power: 10VA max.
Contact Voltage: 60VDC max.
Contact Current: 500mA max.
Operate Time: 0.5ms max.
Bounce Time: 0.5ms max.
Release Time: 0.2ms max.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 9 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 13

450 Series – 16 Form C Relay Outputs
Control a variety of low voltage, low current devices with the SeaI/O-450. The
module’s 16 channels of highly reliable SPDT Form C relay outputs are rated for up
to 60VDC @ 2A. Each output offers normally-open and normally-closed contact
connections via 3.5mm field removable terminal blocks.
Outputs
Type: 16 SPDT Form C relays
Power: DC 30W/ AC 60 VA
Contact Voltage: 60VDC max.
Contact Current: 2A max.
Operate Time: 2ms max.
Bounce Time: 7ms max.
Release Time: 1ms max.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 10 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 14

462 Series – 96 Channel TTL DB-78
Perfect for driving industry-standard solid-state relay (SSR) racks, the SeaI/O-462
provides 96 bits of buffered drive TTL I/O. Each DB-78 connector brings out 48 I/O
bits addressable as six, eight-bit ports. For easy connection to relay racks, Sealevel
offers a six-foot cable (Item# CA237) that terminates each DB-78 connector to two
industry standard 50-pin IDC connectors. Order part number 462x-KT and receive
two CA237 cables with each unit.
The SeaI/O-462 uses 74ABT245 octal bi-directional transceivers to provide TTL
input/output capabilities and can sink 64mA and source 32mA. Each bit is pulled to
+5V through a 10K ohm pull-up resistor to insure each bit is at a known state when
not driven.
Power Requirements
Max Output Power: +5VDC @ 1A (5W)
Inputs
Logic High: Max 0.8VDC
Logic Low: Min 2VDC
Outputs *
Logic High: Max 0.5VDC @ 64mA
Logic Low: Min 2VDC @ 32mA
NOTE:
The SeaI/O-462 modules are designed to work with industry
standard solid-state relay racks that expect negative logic to operate.
The SeaI/O-462 modules expect negative logic on the inputs.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 11 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 15
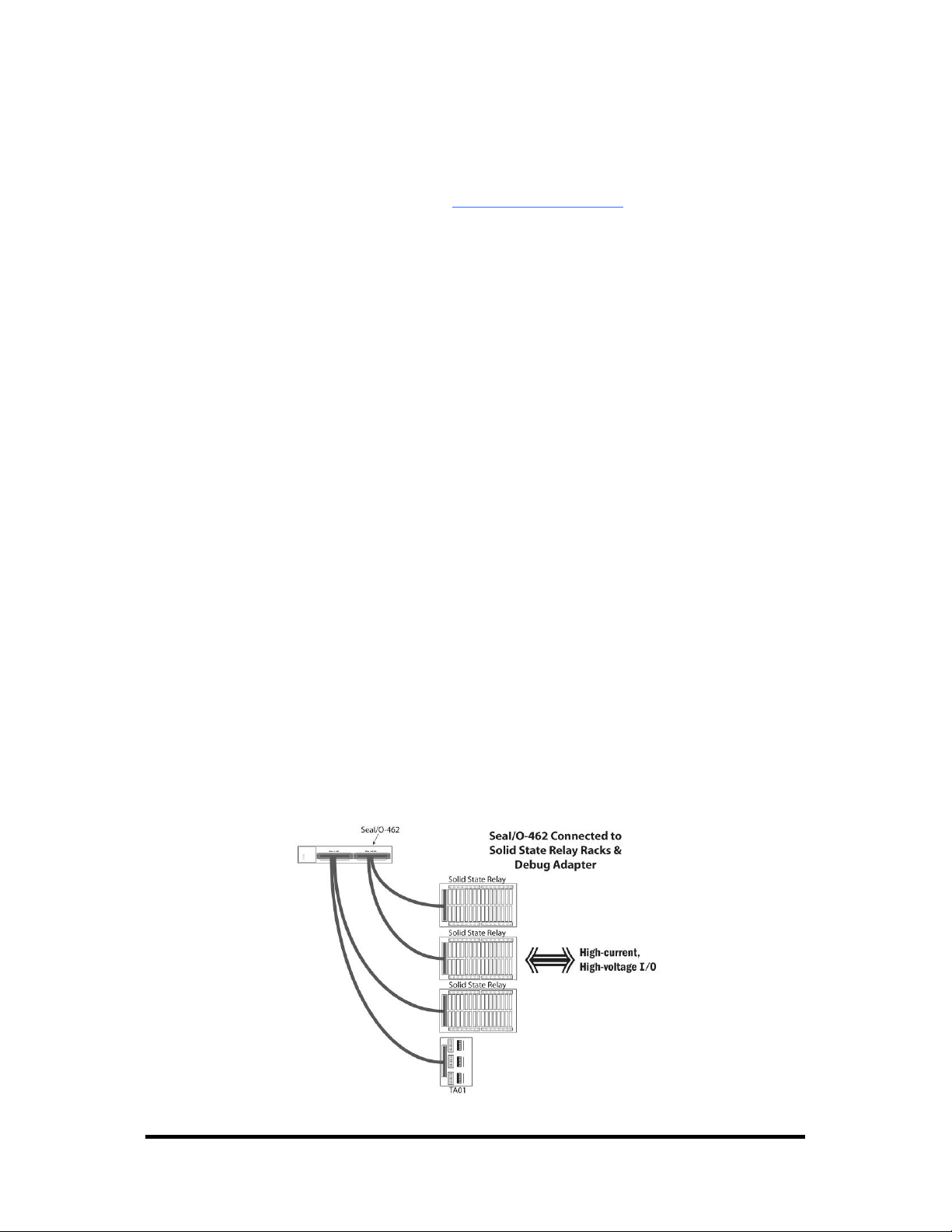
SeaI/O-462 Optional Items
Depending upon your application, you are likely to find one or more of the following
items useful for interfacing the SeaI/O-462 to real-world signals. All items can be
purchased from our website (http://www.sealevel.com
For high-current, high-voltage applications:
DB-78 to Dual IDC 50 Pin Ribbon Cable (Item Number CA237)
− 60” cable connects each SeaI/O-462’s DB-78 connectors to solid-state
relay racks equipped with 50-pin header interface.
Solid-State Relay Racks:
• Quad six position relay rack (Part Number PB24HQ)
− Relay rack can accept up to six QSSRs for a total of 24 channels.
Features a 50-pin header connector for easy interface via 50conductor ribbon cables.
• Quad four position relay rack (Part Number PB16HQ)
− Relay rack can accept up to four QSSRs for a total of 16 channels.
Features a 50-pin header connector for easy interface via 50conductor ribbon cables.
Quad Solid-State Relay Modules:
• AC Input (Part Number IA5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O
interface to monitor AC inputs up to 140V @ 10mA.
• DC Input (Part Number IB5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O
interface to monitor DC inputs from 3.3V to 32V.
• AC Output (Part Number OA5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O
interface to control AC outputs up to 140V @ 3A.
• DC Output (Part Number OB5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O
interface to control DC outputs up to 60V @ 3A.
Simulation/debug module (Part Number TA01)
− Module simulates the operation and load characteristics of a standard 24-
channel relay rack. An LED corresponding to each port bit illuminates to
indicate state. Eight position DIP-switches are used to generate input status
changes.
) or by calling 864-843-4343.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 12 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 16

463 Series – 96 Channel TTL 50-Pin
The SeaI/O-463 offers 96 bits of buffered drive TTL I/O via four internal industrystandard 50-pin header connectors. The interface module addresses the 96 channels
of I/O as 12 eight-bit ports, each programmable as input or output. Using standard
50-pin IDC ribbon cables, connect up to four industry standard relay racks for PC
based control and automation of equipment including sensors, switches, security
control systems, and other industrial automation systems. A metal strain relief
bracket is included to secure the cables after installation.
The SeaI/O-463 uses 74ABT245 octal bi-directional transceivers to provide TTL
input/output capabilities and can sink 64mA and source 32mA. Each bit is pulled to
+5V through a 10K ohm pull-up resistor to insure each bit is at a known state when
not driven.
Power Requirements
Max Output Power: +5VDC @ 1A (5W)
Inputs
Logic High: Max 0.8VDC
Logic Low: Min 2VDC
Outputs *
Logic High: Max 0.5VDC @ 64mA
Logic Low: Min 2VDC @ 32mA
NOTE:
The SeaI/O-463 modules are designed to work with industry
standard solid-state relay racks that expect negative logic to operate.
The SeaI/O-463 modules expect negative logic on the inputs.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 13 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 17

SeaI/O-463 Optional Items
Depending upon your application, you are likely to find one or more of the following
items useful for interfacing the SeaI/O-463 to real-world signals. All items can be
purchased from our website (http://www.sealevel.com
For TTL applications:
Terminal Block Kit - (Item# KT107)
− Kit includes the TB07 screw terminal block and CA167 ribbon cable for
connecting one of the SeaI/O-463’s 50-pin header connectors to your I/O.
6” Snap track and DIN rail clips are included for DIN rail mounting.
IDC 50 to IDC 50 Pin 40" Ribbon Cable (Item# CA167)
− Interfaces each of the SeaI/O-463’s 50-pin header connectors.
Simulation/debug module (Item# TA01)
− Module allows monitoring status of output pins and controlling state of
input pins. An LED corresponding to each port bit illuminates to indicate
state. Eight position DIP-switches are used to generate input status
changes.
) or by calling 864-843-4343.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 14 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 18
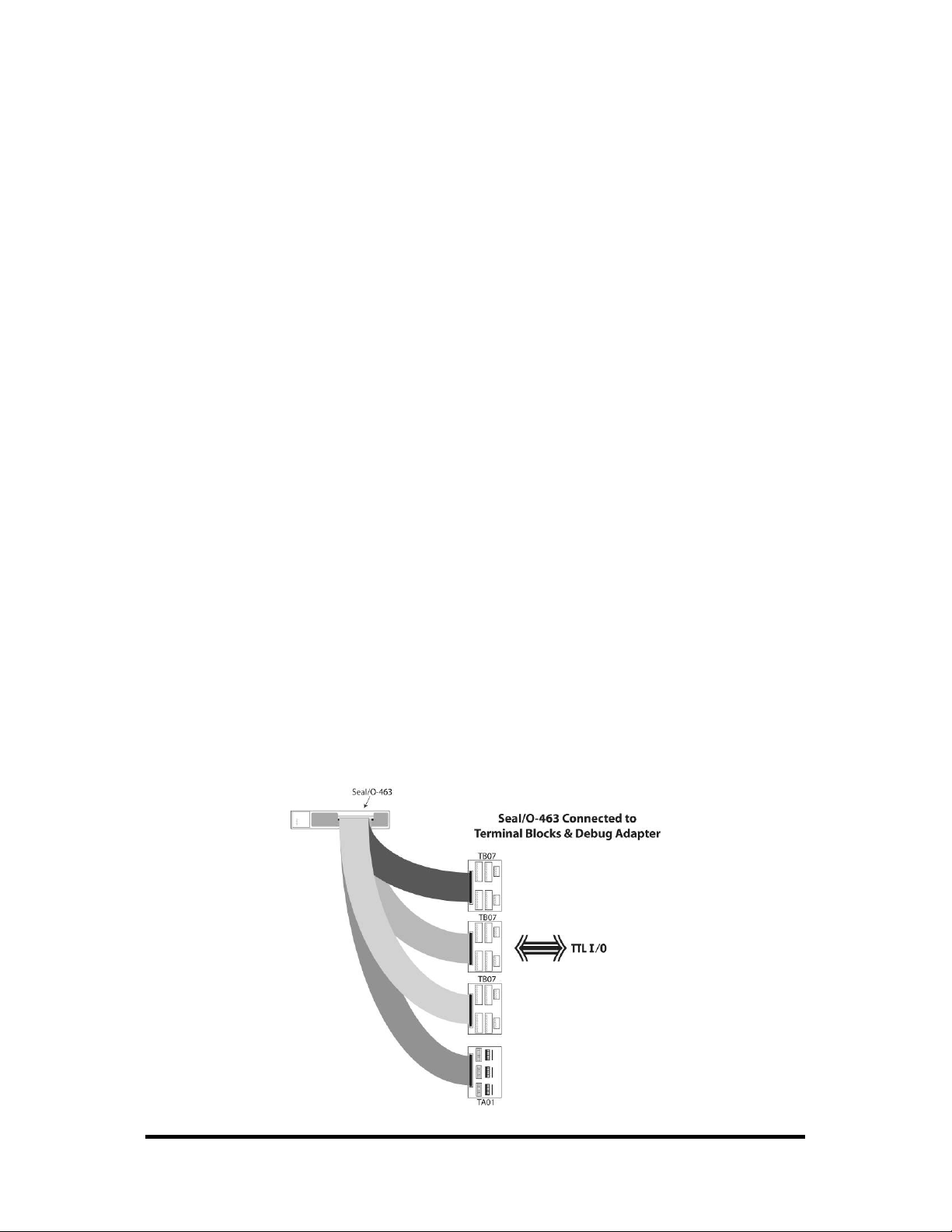
For high-current, high-voltage applications:
IDC 50 to IDC 50 Pin Ribbon Cable (Item# CA167)
− 40” cable connects the SeaI/O-463 to solid-state relay racks equipped with
50-pin header interface.
IDC 50 to IDC 50 Pin Ribbon Cable (Item# CA135)
− 40” cable connects the SeaI/O-463 to solid-state relay racks equipped with
50-pin edge connector.
Solid-State Relay Racks:
• Quad six position relay rack (Item# PB24HQ)
− Relay rack can accept up to six QSSRs for a total of 24 channels.
Features a 50-pin header connector for easy interface via 50conductor ribbon cables.
• Quad four position relay rack (Item# PB16HQ)
− Relay rack can accept up to four QSSRs for a total of 16 channels.
Features a 50-pin header connector for easy interface via 50conductor ribbon cables.
Quad Solid-State Relay Modules:
• AC Input (Item# IA5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O interface to
monitor AC inputs up to 140V @ 10mA.
• DC Input (Item# IB5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O interface to
monitor DC inputs from 3.3V to 32V.
• AC Output (Item# OA5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O interface to
control AC outputs up to 140V @ 3A.
• DC Output (Item# OB5Q) – Provides 4 channels of discrete I/O interface to
control DC outputs up to 60V @ 3A.
Simulation/debug module (Item# TA01)
− Module simulates the operation and load characteristics of a standard 24-
channel relay rack. An LED corresponding to each port bit illuminates to
indicate state. Eight position DIP-switches are used to generate input status
changes.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 15 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 19

470 Series – 16 A/D, 2 D/A, 8 24V Outputs, 8 Isolated Inputs
Designed using the Maxim MAX197 successive approximation-type A/D chip, the
SeaI/O-470 provides eight differential or 16 single-ended 12-bit inputs. The A/D
inputs can be individually configured for sensing 4-20mA current loop signals.
Additionally, the module provides two 12-bit D/A output channels, eight optically
isolated inputs, and eight open collector outputs, ideal for driving 24V devices
commonly found in industrial environments. Perfect for a variety of data
acquisition/control and test & measurement applications, the SeaI/O-470 includes
removable screw terminals, which simplify field-wiring connections.
Optically Isolated Inputs
Input Range: 5-30VDC
Open Collector Outputs
Output Voltage: Max. 30VDC
Output Current: Max. 500mA (single output)
Output Current: Max. 580mA (all outputs)
A/D Inputs
Number of Channels: 8 differential or 16 single-ended
Resolution: 12-bits
Sampling Rate: 100K/s
A/D Input Range
Software Selectable: 0-5V, 0-10V, +/-5V, +/-10V
Hardware Selectable: 0-20mA current loop (for 4-20mA devices)
D/A Outputs
Number of Channels: 2 single-ended
Resolution: 12-bits
Output Range: 0-5V, 0-10V
Load Resistance: Min. 2K
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 16 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 20

520 Series – 8 Optically Isolated Inputs/8 High-Current Form C Outputs
The SeaI/O-520 provides 8 optically isolated inputs and 8 SPDT high-current Form C
relay outputs. Inputs can range from 5-30VDC and provide 300V isolation to ground.
Each output offers normally open and normally closed contact connections via
3.5mm field removable terminal blocks.
Inputs
Type: 8 non-polarized optically isolated inputs
Voltage Range: 5-30VDC
Isolation: 300V
Input Resistance: 6.2K Ohms in series
Response Time: 4 microseconds
Outputs
Type: 8 SPDT High-Current Form C relays
Contact Voltage: 250VAC/60VDC max.
Contact Current (AC): 6A max.
Contact Current (DC): <30 VDC @5A max. / >30 VDC @500mA max.
Switching Capacity: 5 VDC @ 100mA min.
Operate Time: 10ms max.
Release Time: 10ms max.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 17 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 21

Power Options
Base Module Power Connection
Base modules are powered from a 9-30VDC source using either the DC jack or screw
terminals on the side of the unit. Sealevel offers several power supply choices to
make connection easy (see the Accessories chapter at the end of this document).
SeaI/O Expansion Power Connection
Each SeaI/O product, including the expansion modules, contains an onboard
switching regulator power supply rated for 9-30VDC. For local installations (less
than 10’ apart), expansion unit power is usually supplied from the Base unit via the
pass-through connectors. The number of expansion modules that can be driven from
the Base unit depends on the power source and number/type of expansion units.
Refer to the chart below for power requirements. For expansion modules mounted
remotely (greater than 10’ apart), separate power is required at each expansion unit.
SeaI/O Max Power Requirements
SeaI/O-410 3.4W 2.9W 1.7W 1.4W 1.6W 1.4W
SeaI/O-420 4.0W 3.5W 2.3W 2.0W 2.2W 2.0W
SeaI/O-430 2.4W 1.9W 0.7W 0.4W 0.6W 0.4W
SeaI/O-440 4.5W 4.0W 2.8W 2.5W 2.7W 2.5W
SeaI/O-450 5.8W 5.3W 4.1W 3.8W 4.0W 3.8W
SeaI/O-470 3.5W 3.0W 1.8W 1.5W 1.7W 1.5W
SeaI/O-520 5.5W 5.0W 3.8W 3.5W 3.7W 3.5W
TTL Power Requirements
SeaI/O-462 2.5W 2.0W 0.8W 0.5W 0.7W 0.5W
SeaI/O-463 2.5W 2.0W 0.8W 0.5W 0.7W 0.5W
W-Series E-Series U-Series M-Series S-Series N-Series
W-Series E-Series U-Series M-Series S-Series N-Series
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 18 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 22
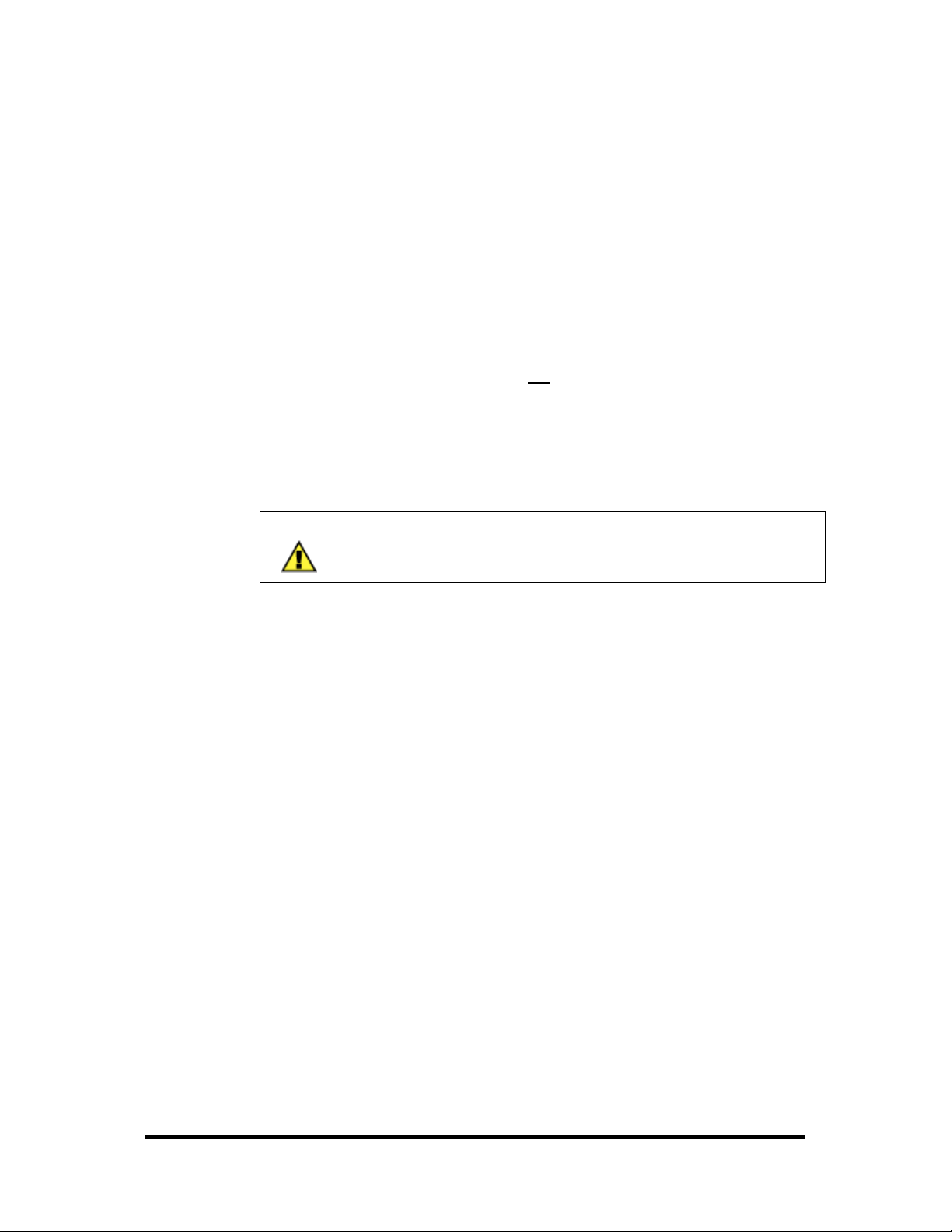
Sample Power Calculation
A typical application for SeaI/O products would use one Base module and several Nseries units in a local expansion configuration. In this arrangement, with power
applied to the Base module through either the DC jack or screw terminal connector
and passed-through to the expansion units, attention should be given to ensure the
input power to the Base module is adequate.
Example:
Power (W)
Base Unit: SeaI/O-430U 0.7
Expansion 1: SeaI/O-410N 1.4
Expansion 2: SeaI/O-440N 2.5
4.6W Power Required
In this application, the Sealevel Item# TR112 “wall wart” power supply is a good
choice since it is low-cost and supplies 24VDC @ 250mA (6W).
NOTE:
A complete listing of recommended power supplies is provided in
the Accessories section of this manual.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 19 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 23

SeaMAX Application Suite
SeaMAX Overview
The SeaMAX Suite is a collection of software libraries, and configuration and
diagnostic utilities that facilitates rapid application development. The following
libraries and utilities are included in the SeaMAX Suite and are covered in this
chapter:
MaxSSD Configuration & Diagnostics utility
Ethernet Config utility
SeaMAX API
Sealevel digital and analog I/O modules supported by SeaMAX software are
designed to work with third party applications via the SeaMAX API. To help
simplify application development, the complete API documentation and code
samples are automatically installed with the SeaMAX Suite and can be found in
Windows by clicking Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ Documentation.
Additional SeaMAX documentation is available online that completely details the
functions of the SeaMAX API. Example code is included for several popular
languages and compilers. The interactive online documentation is located on the
Sealevel website at:
http://www.sealevel.com/software/SeaMAX/
Please contact Sealevel technical support with any questions regarding SeaMAX
documentation:
Phone: (864) 843-4343
Email: support@sealevel.com
.
NOTE:
This chapter covers all SeaMAX supported devices.
Not all features are applicable to all devices.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 20 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 24
Communicating Via Modbus
Sealevel SeaI/O and SeaDAC modules are designed to integrate seamlessly into
existing Modbus networks. The supported command set will vary depending on the
SeaI/O model number used. Specialized diagnostic commands and other RTU
specific codes are not supported. An overview of the Modbus specification for both
RTU and TCP connections is covered in detail in the interactive documentation
located on the Sealevel website at:
http://www.sealevel.com/software/SeaMAX/
The official Modbus specification can be found at:
http://www.modbus.org
NOTE:
SeaDAC Lite modules do not currently support Modbus commands.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 21 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 25
SeaMAX Software Installation
Proceed with installing the SeaMAX Software Suite using the software CD that was
included with your Sealevel I/O module. Software drivers are also available on the
product webpage on the Sealevel website at www.sealevel.com
Windows 2000/XP/Vista™ Operating Systems
.
NOTE:
Important! Do not connect the I/O module to the host until the
software is installed.
1. Start Windows.
2. Insert the Sealevel Software CD in to your CD drive.
3. If ‘Auto-Start’ is enabled the installation window will automatically appear.
Otherwise, navigate to the root directory of your CD drive and double-click
the ‘autorun.exe’ application to launch the installation window.
4. Select ‘Install Software’.
5. Select the Part Number for your device from the listing.
6. The setup file will automatically detect the operating environment and install
the proper components. Follow the information presented on the installation
screens that follow.
7. A screen may appear with the declaration: “The publisher cannot be
determined due to the problems below: Authenticode signature not found.”
Please select the ‘Yes’ button and proceed with the installation. This
declaration simply means that the Operating System is not aware of the
driver being loaded. It will not cause any harm to your system.
8. During setup, you may specify installation directories and other preferred
configurations. This program also adds entries to the system registry that are
necessary for specifying the operating parameters for each driver. An
uninstall option is included to remove the driver and all registry/INI file
entries from your system.
9. Proceed with configuring your Sealevel I/O module using the MaxSSD
utility detailed on the following pages.
NOTE:
If you are using a Wireless (W-series) or Ethernet (E-series) SeaI/O
module, skip ahead to either the Configuring a Wireless Module
or Configuring an Ethernet Module sections of this manual,
before using MaxSSD.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 22 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 26

MaxSSD Configuration & Diagnostics Utility
The Sealevel Systems configuration utility, MaxSSD, is designed to simplify the
installation, configuration, and diagnostics of Sealevel I/O modules. MaxSSD is a
Microsoft Windows application and has been tested with Windows 2000, XP, and
Vista.
Host PC Configuration Tab
The first time you run the MaxSSD utility (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel
SeaMAX Æ MaxSSD) it will default to the “Host PC Configuration” tab. This tab
allows the user to choose the initial communication settings for the connected I/O
device. The “COM Port” dropdown box allows the selection of a serial COM port
(from COM1 to COM256), Ethernet (for Ethernet SeaI/O modules), or SeaDAC Lite
(USB).
USB connected SeaI/O and SeaDAC modules are installed as virtual COM ports.
Using device manager, expand “Ports (COM & LPT)” by clicking on the ‘+’ next to
the category, and locate the COM port for your device and use it in the dropdown box
in MaxSSD.
Once a COM port is selected, the baud rate and parity can be selected.
NOTE:
The baud rate and parity of the PC must match the settings of the
Sealevel I/O module to be configured. The factory default settings
for all Sealevel I/O modules are 9600 baud and no parity.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 23 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 27

Host PC Configuration Tab (continued)
To communicate with a SeaDAC Lite module, select “SeaDAC Lite” from the “COM
Port” dropdown box. MAXSSD will search for any SeaDAC Lite modules
connected to a USB port and display them in a frame (as shown below). A new
“Digital I/O” tab will appear. If more than one SeaDAC Lite module is connected,
select the one you want to test from the list and click the “Digital I/O tab”. You can
use this new tab to test the functionality of inputs and relay outputs. The “Digital
I/O” tab is covered in detail on subsequent pages.
To communicate with a SeaI/O Ethernet or Wireless 802.11b/g module, select
“ETHERNET” from the “COM Port” dropdown box. When Ethernet is selected,
MaxSSD searches for any SeaI/O Ethernet or Wireless modules on the network and
displays their IP addresses in the “Available Ethernet Devices” list box (not shown).
When an IP address is selected from the list box, a socket is opened to the SeaI/O
module and it is ready for communication.
NOTE:
If no IP address is shown when using Ethernet modules, review the
previous Hardware Configuration section, or proceed to the
Troubleshooting section at the end of this manual.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 24 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 28

SeaI/O Configuration Tab
Once the host computer is configured correctly, the “SeaI/O Configuration” tab
becomes available. This tab only appears for SeaI/O and SeaDAC modules and will
not appear when using SeaDAC Lite modules.
Before communicating with a SeaI/O or SeaDAC module, the configuration utility
must determine if there is an I/O module at that slave ID address, and if so, what type
of module it is. This is the purpose of the Get operation.
To perform a Get operation, first select the slave ID to which the module is
configured. SeaI/O modules are shipped at hardware setting 0 (labeled “ADDR” on
the left side of the module) and slave ID 247 by default. All other slave ID addresses
(from 1 to 246) are available. However, each daisy chained SeaI/O module must have
a unique slave ID address - no duplicates are allowed.
SeaDAC modules are only available on slave ID 247, and this number cannot be
changed. To communicate with a different SeaDAC module, select a different COM
port. Use device manager, if necessary, to locate the proper COM port.
Once a slave ID is selected, click the “Get SeaIO Module Settings” button. After a
short delay, the information for that I/O module should be displayed. If no
information appears, verify the host settings and baud rates are correct and make
changes, if necessary. For SeaDAC modules, make sure the baud rate is set to
9600bps. For SeaI/O modules, check the hardware settings (on the left side of the
module) and try again.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 25 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 29

SeaI/O Configuration Tab (continued)
After the Get command is executed, the “Module Description” frame will display the
model type, description, interface, and I/O type. In the example shown, the module
found at slave ID 247 is a SeaI/O-410 module with an Ethernet (Modbus TCP)
interface. The “Set Settings” and “Change Slave ID” buttons will also be enabled for
this module.
After a successful Get operation, additional tabs may be displayed in MaxSSD,
depending on the found device model. These tabs display device I/O and allow easy
configuration for all SeaMAX supported devices.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 26 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 30

SeaI/O Configuration Tab (continued)
The “Broadcast to Multiple Modules” checkbox, along with the “Set Settings” button
can be used to change the baud rate and parity on multiple SeaI/O modules at once.
This function only works with SeaI/O modules connected together via the passthrough connectors. This function is disabled with SeaDAC and SeaDAC Lite
modules since these devices do not have pass-through connectors.
MaxSSD broadcasts a set data rate and set parity command to all devices on the RS485 bus, but only those modules listening at the current baud rate will be able to
receive and respond. For example, if you have five SeaI/O modules chained together
and two are set to 9600 bps and no parity and three are set to 115.2k bps and the PC
is set to 9600 bps, only the two modules set to 9600 bps will receive the broadcast set
data rate and parity message.
NOTE:
Important! Ethernet (E-series) and Wireless (W-series) modules
The broadcast feature sets the Ethernet SeaI/O (E-series) module’s
TCP/IP to RS-485 translation data rate independently of the SeaI/O
module itself. If you set the data rate to 115.2K bps via a MaxSSD
broadcast command, both the RS-485 port and the Ethernet port will
respond thereafter to 115.2K bps, as expected. However, if you reset
the SeaI/O module, by rotating the rotary switch clockwise one
complete revolution, the RS-485 port will reset to 9600 bps and no
parity, but the Ethernet port will remain unaffected. To restore
communications, broadcast another set data rate and parity
command (9600 and no parity) via MaxSSD.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 27 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 31

Digital I/O Tab
The “Digital IO” tab of MaxSSD is displayed when using Sealevel I/O devices
featuring discrete inputs and outputs. It displays the device’s current input and/or
output status in an intuitive and usable manner.
When displaying SeaI/O or SeaDAC modules (excluding SeaDAC Lite), the “Digital
IO” tab displays inputs and outputs in groupings (or banks) of eight. Therefore, a
Sealevel I/O device with 16 inputs and 8 outputs would show two banks of inputs and
one bank of outputs.
When banks of inputs are displayed, the status LEDs update on each of the banks
automatically. This allows you to actively monitor external signals.
With a bank of outputs, the output coils can be set using the buttons below each
output LED. As each coil is set, the I/O module is read. The corresponding status
LED in the “Digital IO” window indicates the state of the coil. In the example
below, a SeaI/O module with 16 Reed relays is shown.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 28 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 32

Digital I/O Tab (continued)
When displaying SeaDAC Lite modules, the “Digital IO” tab displays inputs and
outputs in groupings (or banks) of four. Therefore, a SeaDAC Lite module with four
inputs and four outputs would show only one bank of inputs and one bank of outputs.
When banks of inputs are displayed, the status LEDs update on each of the banks
automatically. This allows you to actively monitor external signals.
With a bank of outputs, the output coils can be set using the buttons below each
output LED. As each coil is set, the SeaDAC Lite module is read. The corresponding
status LED in the “Digital IO” window indicates the state of the coil. In the example
below, a SeaDAC Lite module with four inputs and four Form C relays is shown,
with the state of the relays showing either normally-open (NO) or normally-closed
(NC).
NOTE:
The “SeaI/O Configuration” tab does not appear in MaxSSD when
using SeaDAC Lite modules since they have no configurable
communication settings.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 29 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 33

Programmable I/O Tab
The “Programmable IO” tab of MaxSSD is displayed when using Sealevel I/O
devices featuring programmable inputs or outputs. This tab allows for bank
configuration, input/output configuration, as well as bit-level presets.
Each bank of programmable I/O can be set as either an 8-bit group of inputs or
outputs. By selecting “Bank 1” from the drop-box, clicking the “Bank functions as
Input” radio button, and then clicking the “Set Programmable IO Options” button, the
first 8 PIO bits on the device will now function as inputs. For ease of configuration,
an “All Banks of IO” option is available to configure all of the I/O at one time.
Inputs have no preset mode; therefore, the preset options are disabled for any bank of
inputs. Outputs; however, have bit-addressable presets. These presets are used
whenever the device is powered up or the bank direction changes from input to
output.
NOTE:
The output presets, will not lock the outputs into a specified on or
off state. They only set the state of the outputs on a power on or
bank direction change.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 30 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 34

A/D Inputs Tab
The “A/D Inputs” tab displays the current state of the analog-to-digital channels for
Sealevel I/O devices that feature A/D inputs. Settings are provided for both device
wide and per-channel configuration.
The “Device Configuration” selection drop-box adjusts the arrangement and function
of the A/D input channels. Input channels are displayed as banks (groups of eight).
Each channel is range configurable via the voltage range dropdown list. Both the
channel voltage range and device-wide configuration are set on a dropdown list.
There is no need to save your settings – they are automatically saved to the device as
you select the various configuration options.
“10x Hardware Gain Enabled” checkbox – Indicates whether or not the onboard
hardware gain jumper is currently set. This option is not user configurable – it only
reflects the status of the onboard hardware jumper settings. Set the hardware jumper
to enable this functionality, which allows smaller voltages to be measured more
accurately (e.g., a 0-1V input signal can be measured more accurately by enabling the
10x hardware gain jumper and setting the SeaI/O-470 A/D input channel for 0-10V
range).
“Show 12-Bit Hex Values” checkbox – Displays the values returned by the A/D
converter as a hexadecimal value without converting the values to engineering units
(i.e., Amps or Volts)
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 31 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 35

D/A Outputs Tab
The “D/A Outputs” tab is useful for manually setting the digital to analog output
voltages on applicable Sealevel I/O devices with D/A channels. A preliminary
diagnostics utility (see following page) has been provided to verify proper hardware
functionality.
The D/A outputs of the SeaI/O-470 and SeaDAC 8227 are factory set for 0-10V. To
configure the D/A outputs for 0-5V, you will need to open the enclosure and set the
correct jumpers. Refer to the Hardware Configuration section of this manual for
instructions on opening the enclosure and accessing the correct jumpers.
To adjust a particular channel’s output voltage, drag the slider until the desired
voltage is displayed in the window on the right side. Also, you may type the desired
voltage directly into the voltage display and then confirm your entry by pressing the
‘Enter’ key on your keyboard.
NOTE:
The output voltage will not change until the ‘Enter’ key is pressed
or you have clicked on the window anywhere outside of the text
entry field.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 32 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 36

A/D & D/A Diagnostics
To check basic functionality of both the A/D and D/A converters, press the
“Diagnostics Utility” button on the “D/A Outputs” tab (shown on the previous page)
and then press the “Start” button, as shown below. Any errors will be shown in the
“Results” pane. If any errors occur, please contact technical support for further help.
Converting A/D & D/A Values
To properly use the values returned from the SeaI/O-470 and SeaDAC 8227
module’s A/D channels, the application program must convert the returned values to
engineering units (voltage). Likewise, the application program must output the
correct value to the I/O module’s D/A outputs to generate the desired voltage.
The conversion formulas will vary depending on how the I/O module is configured.
The formulas and their uses are covered in detail in the interactive documentation
located on the Sealevel website at:
http://www.sealevel.com/software/SeaMAX/
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 33 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 37

Troubleshooting SeaMAX
Following these simple steps can eliminate most common problems.
1. Read this manual thoroughly before attempting to install the device in your system.
2. Uninstall any previous versions of the SeaMAX software before installing any new
versions.
3. Install SeaMAX software first, before connecting any Sealevel I/O devices.
Installing the software places the necessary files in the proper locations on your
system. After installing the software, proceed with adding the hardware.
4. When installing SeaI/O modules, connect them one at a time
. The “base” module
must be properly configured and communicating successfully with the host before
you can add additional expansion modules. Verify that each expansion module can
communicate before connecting additional expansion modules.
5. Confirm that all screw terminal connections are correct and secure and that the
correct cables are being used, including network cables (crossover vs. patch cables).
6. You can use standard network patch cables (straight-through cables) to connect
SeaI/O modules together via the pass-through connectors on the left side of the
module. Crossover cables should never be used to connect two or more SeaI/O
modules together. Crossover cables should only be used to connect an Ethernet
SeaI/O module to a host without going through an Ethernet hub or switch.
7. On SeaI/O modules, verify that the device address (slave ID) is properly set. Refer to
the Hardware Configuration section of this manual for instructions on setting the
device slave ID.
8. Use the MaxSSD utility, included on the software CD, to verify proper installation.
MaxSSD is designed to simplify the installation, configuration, and diagnostics of
Sealevel SeaI/O modules.
9. If the SeaI/O modules only sometimes respond to a Get operation or return invalid
data, you may have termination improperly set. Refer to the Hardware
Configuration section of this manual for instructions on properly setting line
termination and pull-up/pull-down resistors.
10. Refer to the Troubleshooting Ethernet & Wireless Modules section on the
following page for additional steps regarding Ethernet (E-series) SeaI/O modules.
11. If these steps do not solve your problem, please contact Sealevel Technical Support.
Our technical support is free and available from 8:00AM-5PM Eastern Time,
Monday through Friday. You can contact Technical Support via:
Phone: (864) 843-4343
Email: support@sealevel.com
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 34 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 38

Troubleshooting Ethernet & Wireless SeaI/O Modules
Problem: The SeaI/O module starts up with a strange IP address (i.e., 169.254.x.x)
All Ethernet (E-series) and Wireless (W-series) SeaI/O modules are shipped with
DHCP enabled. If no DHCP server is available or the DHCP server cannot be
reached, Ethernet SeaI/O modules default to a random IP address in the range
169.254.x.x. Wireless SeaI/O modules default to a random IP address in the range
192.168.0.x. Change the PC’s network settings to place both the SeaI/O module and
PC on the same subnet. Adjust the SeaI/O module’s IP address and Netmask using
the Ethernet Config utility (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ Ethernet
Config) installed with SeaMAX. Then restore the PC’s network settings.
Problem: The SeaI/O module is visible in Ethernet Config, but the network settings
cannot be changed
The SeaI/O module is most likely on a different subnet than the PC. The PC’s IP
address and Netmask must be altered to place both the SeaI/O module and the PC
within the same subnet. Contact your network administrator for assistance.
Problem: The SeaI/O module doesn’t show up in Ethernet Config
Ethernet and Wireless SeaI/O modules are discovered via a UDP broadcast. Verify
that any firewall software, such as Windows Firewall, ZoneAlarm, etc., or router
settings that would hinder UDP transmissions are disabled.
It is also possible that the SeaI/O module may not be discovered if the PC and
module are on separate subnets. This may occur if the module’s IP address is
configured outside the range of the PC’s subnet. It can also occur during a failed
DHCP discovery. In either case, the “Recover Module” button in Ethernet Config
utility may be used to recover the device. Refer to the Hardware Configuration
section of this manual for more information.
Problem: The rotary switch (ADDR) was used to reset an Ethernet (or Wireless)
SeaI/O module, but it no longer responds to a ‘Get’ operation.
If you reset the SeaI/O module by rotating the rotary switch clockwise one full
revolution, the RS-485 port will reset to 9600 bps and no parity, but the Ethernet port
will remain unaffected.
The broadcast feature in MaxSSD sets the SeaI/O module’s TCP/IP to RS-485
translation data rate independently of the SeaI/O module itself. Therefore, if you
have an Ethernet or Wireless SeaI/O module and you set the data rate to 115.2K bps
via a MaxSSD broadcast command, both the RS-485 port and the Ethernet port will
respond thereafter to 115.2K bps, as expected. Using the rotary switch will reset the
RS-485 port, but the Ethernet port will still try to communicate at 115.2k bps. To
restore communications, broadcast a set data rate and parity command (9600 and no
parity) via MaxSSD.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 35 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 39

Hardware Configuration
Setting Device Address (Slave ID)
Before configuring SeaI/O modules using MaxSSD, you must first select a device
addressing method. Next, you must properly set termination and pull-up/pull-down
resistors. Finally, you must configure the SeaI/O modules one at a time before
MaxSSD and any subsequent applications (using the SeaMAX API) will be able to
successfully communicate.
SeaI/O modules have a rotary switch, labeled “ADDR”, located on the left side of the
device that is used to set the device address (slave ID). The default position for all
SeaI/O modules is position “0” (zero). Each SeaI/O module must be set to a unique
slave ID in order to properly communicate with the host device, which can be a
computer or Modbus device. The slave ID can be set by hardware using the rotary
switch, which is recommended for most users. The slave ID can also be set in
software by leaving the rotary switch at position “0” and using MaxSSD to set the
slave ID. The rotary switch has three functions:
Set Address (slave ID) via Hardware – If the rotary switch is set to a position
between “1” and “15” (F). The SeaI/O module will then always respond to
commands issued at that slave ID. This is useful when there are fewer than 16
SeaI/O modules in a chain and the slave ID is not required to change. This
method is recommended for most users.
Set Address (slave ID) via Software – If the rotary switch is left in the “0”
(zero) position, the SeaI/O module uses a default slave ID of 247 for
communications. By using MaxSSD (or the SeaMAX libraries), it is possible to
set the slave ID to a software address between 1 and 247. This is useful when
there are more than 16 SeaI/O modules in a chain, or when the slave ID of a
module needs to be frequently changed.
Hardware Reset – If you have an existing SeaI/O module set to an unknown
slave ID or baud rate, you may wish to reset the device. If the rotary switch is
rotated clockwise one full revolution, the SeaI/O module will be reset to factory
defaults (slave ID 247, 9600 bps, and no parity).
NOTE:
A Hardware Reset will not reset the communication rate of Ethernet
(E-series) and Wireless (E-series) modules. Rotate the rotary switch
clockwise one full revolution, and then use the MaxSSD utility to
broadcast a set baud rate command to 9600 bps and no parity.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 36 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 40

Setting Termination & Pull-Up/Pull-Down Resistors
A “stack” or “chain” of SeaI/O modules, connected via the pass-through connectors
or screw terminals on the left side of the enclosure, communicates via an RS-485 bus,
which must be properly terminated to work correctly. A set of three dipswitches is
located on the left side of enclosure, next to the “ADDR” rotary switch. These
switches control line termination and the RS-485 pull-up and pull-down resistors.
The pull-up and pull-down resistors ensure that the input ports are at a known state
when not being driven by the RS-485 line. In most cases, all three of the dipswitches
on each SeaI/O module should be in the down position, except the two end modules.
The first and last SeaI/O modules in the chain should have all three dipswitches in the
up (enabled) position.
NOTE:
Make sure that only the first and last SeaI/O modules have line
termination enabled (up position). Improper termination settings
can result in invalid data or communication failures.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 37 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 41

Configuring the “Base” SeaI/O Module
Once the SeaMAX Software Suite has been installed successfully and you have
decided which address (slave ID) method you intend to use, start by connecting the
first SeaI/O module to your computer. This will be referred to as the “base” module.
If you are chaining multiple SeaI/O modules together, only one SeaI/O module in the
chain can be the “base”. All other SeaI/O modules connected to the “base” module
are referred to as expansion modules. Multiple “base” modules can be directly
connected to a host computer, but expansion modules must be connected (daisy
chained) to a “base” module.
NOTE:
If you are configuring an Ethernet (E-series) or Wireless (W-series)
SeaI/O module, skip ahead to the Configuring an Ethernet
Module or Configuring a Wireless Module sections for specific
information on installing those modules.
For all other SeaI/O modules (U-series, S-series, or M-series), locate the COM port
by expanding the ‘Ports’ list in Windows Device Manager.
Start MaxSSD (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ MaxSSD) and choose
the correct port (IP address or COM port) to communicate with the “base” module.
Ensure a successful Get operation (refer to the MaxSSD section on the following
pages for more information).
Set the slave ID of the “base” module using the rotary switch or software selection
method discussed in the Setting Device Address section on the previous pages. This
guarantees that any expansion modules connected next will not conflict with the
“base” module. Perform another Get operation to verify that you can communicate
with the “base” module at the new slave ID.
NOTE:
Configure SeaI/O modules one at a time. Set the address to a
hardware slave ID other than “0” or a software slave ID other than
247, which avoids device conflicts during setup.
After the “base” module is successfully communicating via MaxSSD, you can
proceed with adding SeaI/O expansion modules (N-series) one at a time
, as required.
NOTE:
If the “base” module doesn’t respond as expected, turn the rotary
switch (ADDR) clockwise one full revolution to reset. Configure the
PC to communicate at 9600 bps and no parity and then try again.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 38 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 42

Configuring N-Series Expansion Modules
Once you have successfully connected and communicated with a “base” module, you
can begin adding expansion modules (N-series). Connect a single expansion module
to the “base” module via the RJ45 pass-through connectors or screw terminals on the
left side of the enclosure. Expansion modules include a convenient 5” interconnect
cable (item# CA239) to simplify daisy-chaining SeaI/O modules together.
Alternately, you can use standard network patch cables to chain expansion modules
to a “base” module.
NOTE:
CAUTION! The RJ45 pass-through connectors on the left side of
SeaI/O modules are NOT Ethernet connectors. Do not connect the
ports to Ethernet enabled devices else damage to Ethernet devices
WILL result.
Ensure a successful Get operation (refer to the MaxSSD section on the following
pages for more information). Set the slave ID of the expansion module using the
rotary switch or software selection method discussed in the Setting Device Address
section on the preceding pages. Perform another Get operation to verify that you can
communicate with the expansion module at the new slave ID.
Continue adding expansion modules (N-series) one at a time
, until all modules have
been successfully daisy-chained together and respond to a Get operation in MaxSSD.
Once all SeaI/O modules are configured and communicating successfully, they are
ready to communicate with your application.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 39 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 43

Configuring a Wireless (W-Series) Module
NOTE:
This section applies only to Wireless (W-series) SeaI/O modules.
For all other SeaI/O modules, refer to the Configuring a “Base”
SeaI/O Module and Configuring Expansion Modules sections on
the previous pages.
Start by connecting power to the wireless SeaI/O module. The LEDs will blink to
confirm that the unit is powered up and is ready to be configured to work with your
wireless network.
The first time you power up the wireless SeaI/O module (and every time it is reset), it
will take 20 seconds to “boot up” before it appears on the wireless network.
The wireless SeaI/O module ships in Ad Hoc mode by default and should be
immediately visible with SSID of “SL_Recovery” to any computer equipped with a
wireless adapter.
Most wireless adapters include a utility that allows you to see the wireless devices on
your network. Please refer to the instructions included with your wireless adapter for
details on how to locate wireless devices on your network. If the wireless SeaI/O
module is not visible, you may need to adjust your security settings until you have
successfully configured the wireless SeaI/O module.
Once you have confirmed that the wireless SeaI/O module is visible to your network,
you can proceed with configuring the module. Instructions for configuring a SeaI/O
module using Windows XP are detailed on the following pages.
SeaI/O Wireless Default Configuration
SSID: SL_Recovery
Topology: Ad Hoc
Security: No Encryption
Channel: [Varies] *
NOTE:
* The channel number will increment each time a reset occurs. If
you reset the module and can’t see it on your wireless network, reset
it again to increment the channel number up by one.
To reset the unit to factory defaults and increment the channel, locate the Reset
button on the front of the module just above the antenna. Using a small rigid wire
(e.g., paperclip), depress and hold the reset button. Power cycle the module by
removing the barrel connector or terminal block supplying power to the unit, and
then reconnecting the barrel connector or terminal block. Release the reset button
and the SeaI/O module will be reset to the factory defaults and the channel number
will increment up by one. The LEDs will blink to confirm that the SeaI/O module
has been reset and is ready to be configured.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 40 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 44

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Verify that SeaMAX software has been installed successfully and that a wireless
SeaI/O module is connected to power and ready to be configured to communicate
with your wireless network. This module will become the “base” module.
NOTE:
To configure a wireless SeaI/O module, you must be using a laptop
or desktop computer with a wireless 802.11b/g compatible adapter.
The security settings on many wireless access points (WAP) prevent
you from seeing Ad Hoc devices by default. Therefore, configuring
a wireless SeaI/O module through a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
is not supported.
Wireless Configuration Overview
1. Using a wireless enabled computer, connect to the Ad Hoc network “SL_Recovery”.
2. Move your wireless adapter to subnet 192.168.0.x.
3. Use the Ethernet Config utility to configure the wireless SeaI/O module to work
with your wireless network (SSID, topology, channel, and security) settings.
4. Using the same wireless enabled computer, connect to your wireless network.
5. Use the Ethernet Config utility to configure the wireless SeaI/O module to use the
same subnet as your wireless network.
6. Move your wireless adapter back to your wireless network subnet.
7. Use MaxSSD to configure the Slave ID of the wireless SeaI/O module and test
settings.
The detailed configuration instructions that follow are for Windows XP. The basic
instructions for Windows 2000 are the same. If you have any questions, please
contact Sealevel technical support at support@sealevel.com
.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 41 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 45

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Start by opening the Windows Wireless Network Connection utility, which can be
found by clicking the Start button and hovering over My Network Places. Rightclick on My Network Places and then select Properties from the menu. You should
see a Wireless Network Connection listed in the new window that opens up.
Right-click on your wireless network connection and select ‘View Available
Wireless Networks’ from the menu.
The Wireless Network Connection window opens, as shown below, and you should
see the SeaI/O module listed with the SSID “SL_Recovery.” If not, reset the module
using the instructions on the previous page. Other nearby wireless networks will also
be listed here. Select the SSID “SL_Recovery” and click the Connect button.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 42 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 46

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
The Wireless Network Connection window will now display “Limited or no
connectivity” next to the “SL_Recovery” network connection. All wireless SeaI/O
modules are shipped with DHCP enabled. When you first connect a wireless SeaI/O
module to the network, the status LEDs on the front of the module will blink while it
searches for a DHCP server.
Since “SL_Recovery” is an Ad hoc point-to-point network and not on the same
network as any available DHCP servers, the SeaI/O module will not be able to
complete the connection.
Close the Wireless Network Connection utility (you will still be directly connected
to “SL_Recovery”).
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 43 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 47

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Start the Ethernet Config utility (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ
Ethernet Config) installed with SeaMAX. In the ‘Available SeaI/O Devices’ pane,
you should see a “SeaIO Wireless” module listed under Model, as shown below.
If the module doesn’t show up, click the “Search for SeaI/O Devices” button. The
‘Available SeaI/O Devices’ pane should refresh with any Ethernet or Wireless SeaI/O
modules that are found on the network.
At this point, since no DHCP server is available, the wireless SeaI/O module will
default to a random IP address in the range 192.168.0.x.
Notice that the ‘Name’ is not displayed due to the wireless SeaI/O module residing
on a different subnet than your wireless adapter. Ethernet Config will mask the
‘Name’ of SeaI/O modules operating on a different subnet than the subnet you are
currently using.
Take note of the IP Address of the wireless SeaI/O module listed in the ‘Available
SeaI/O Devices’ pane. You will need this number in order to continue.
Also, make sure that the MAC Address shown matches the MAC Address on the
label on the bottom of the wireless SeaI/O module. If the MAC address doesn’t
match, contact technical support for further assistance.
Close Ethernet Config before continuing.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 44 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 48

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
You must now change the IP Address of your wireless adapter to match the subnet
(first 3 octets) of the wireless SeaI/O module listed in Ethernet Config.
You can change your wireless adapter's IP Address by going to the Properties dialog
for your wireless adapter (Start Æ Settings Æ Network Connections). Right-click on
your network adapter and then select Properties from the menu. This opens the
Wireless Network Connection Properties window.
On the General tab, select ‘Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’, leaving the box checked, and
then click the Properties button.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 45 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 49

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
NOTE:
Before you change any settings in the following window, make a
note of your original settings. You will need to revert back to your
original wireless adapter settings once you have successfully
configured the wireless SeaI/O module to work with your network.
In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, click the radio button for
‘Use the following IP Address’. The first 3 octets of the IP address must match the
IP address displayed for the wireless SeaI/O module. The last octet must be different
In this example, the last octet for the wireless SeaI/O module is 32 and we configured
the last octet for the wireless adapter to 55. Click the OK button in this window.
Click the OK button on the Wireless Network Connection Properties window.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 46 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 50

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
To confirm that the IP Address for your wireless adapter was changed successfully,
reopen Ethernet Config (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ Ethernet
Config).
You should now see the wireless SeaI/O module’s ‘Name’ listed (“DemoUnit” in this
example). This indicates that your wireless adapter and the wireless SeaI/O module
are on the same subnet and you are now able to communicate with the wireless
SeaI/O module.
NOTE:
IMPORTANT!
Do not make any changes to the ‘Device Network Settings’ at this
point. You must complete the Wireless Configuration first.
Verify that you can communicate with the wireless SeaI/O module by clicking the
“Wireless Configuration” button.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 47 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 51

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Now that you can communicate with the wireless SeaI/O module, the Wireless
Configuration settings window will open, as shown.
You can now change the Network SSID, Topology, Channel, and Security Settings to
match your wireless network. After making your changes and clicking OK, the
device will reboot and take 20 seconds to appear on the network using your new
settings. If you change the SSID and/or network Topology and/or Channel, you’ll
have to reconnect to the SeaI/O module. Close Ethernet Config for now.
The supported wireless configuration settings are detailed on the following page.
NOTE:
The Network SSID, wireless network channel, and security settings
are specific to your wireless network. Consult your IT department if
you are unsure of your wireless network settings.
NOTE:
IMPORTANT! Once you change the wireless configuration and
click the OK button, the wireless SeaI/O module will disappear
from the Ethernet Config window. The SeaI/O module will now be
configured to work with your wireless network, but will likely be on
a different subnet. You still need to configure the Device Network
Settings before the module will work with your wireless network.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 48 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 52

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
The following options are available in the Wireless Configuration window:
Wireless Configuration Default Settings Available Options
Network SSID SL_Recovery Alphanumeric
Case Sensitive
32 Characters
Topology Ad Hoc Ad Hoc
Infrastructure
Channel [Varies] 1 – 11 (US)
1 – 14 (Europe, Japan)
Security Settings
(Ad Hoc Mode)
No Security Enabled No Security Enabled
64-bit Open WEP
64-bit Shared WEP
128-bit Open WEP
128-bit Shared WEP
Security Settings
(Infrastructure Mode)
No Security Enabled No Security Enabled
64-bit Open WEP
64-bit Shared WEP
128-bit Open WEP
128-bit Shared WEP
WPA Encryption w/ TKIP
WPA2 Encryption w/ AES
Key Encoding Passphrase Passphrase
Hexadecimal Key
Network Key [None] [See Next Page]
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 49 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 53

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
This information explains the various configuration options available. Continue with
the wireless SeaI/O configuration on the following page.
The Network SSID (Service Set Identifier) is the name of the wireless network. The
SSID can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters and is case-sensitive. If you are using
the wireless SeaI/O module with a wireless access point (WAP), then the SSID
names must match.
The network Topology defaults to Ad Hoc mode and supports Infrastructure mode.
Ad Hoc mode is a point-to-point method used to communicate with other wireless
network clients, including laptop computers and desktop computers using a wireless
adapter. If you are using a WAP, select Infrastructure mode.
The network Channel will vary depending on the number of times the wireless
SeaI/O module is reset. Every time the wireless SeaI/O module is reset, the channel
will increment up by one. Since the wireless SeaI/O module supports channels 1-14,
there is a chance that a reset can put the wireless SeaI/O module on a channel not
compatible with your wireless adapter or access point. If you cannot see the wireless
SeaI/O module on your network, try resetting the module using the steps described at
the beginning of this section. Depending on the country used, it may take several
reset cycles to get the unit back to a channel valid for your region. Use the Wireless
Configuration window to change channels, if possible.
The Key Encoding method can be either a Passphrase or a Hexadecimal Key, if
using a WEP variant. If you are using a WPA variant, then the Key Encoding
method is Passphrase.
Different security encryption methods require different Network Key types and
lengths. The different key types and lengths are displayed below:
WEP 64-bit 10 character hexadecimal key or up to 32 character passphrase
WEP 128-bit 26 character hexadecimal key or up to 32 character passphrase
WPA up to 64 character passphrase
WPA2 up to 64 character passphrase
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 50 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 54

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Open the Wireless Network Connection utility again (Start Æ right-click on My
Network Places Æ select Properties from the menu. In the next window, right-click
on your wireless network connection Æ select ‘View Available Wireless Networks’
from the menu).
Select the SSID for your wireless network and click the “Connect” button. The
wireless SeaI/O module will no longer be visible since you configured it to work with
your wireless network in the previous step. You still need to configure the ‘Device
Network Settings’ in Ethernet Config to complete the configuration of the wireless
SeaI/O module.
Open Ethernet Config (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ Ethernet
Config). The wireless SeaI/O module should appear in the ‘Available SeaI/O
Devices’ pane. Click on the wireless SeaI/O module to select the device. The
current settings now appear in the ‘Device Network Settings’ area.
If your wireless network is set up to use DHCP, click the ‘enable DHCP
configuration’ checkbox and then click the ‘Apply Changes’ button.
Otherwise, set the IP Address, Network Mask, and Gateway to match the settings for
your wireless network. You can change the ‘Device Name’ to something appropriate
for your application. Click the ‘Apply Changes’ button. The wireless SeaI/O module
will again disappear, but is now fully configured to work with your wireless network.
Close the Ethernet Config utility.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 51 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 55

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
To complete the configuration, you need to change the IP Address of your wireless
adapter back to its original settings. Open the Network Connections utility (Start Æ
Settings Æ Network Connections). Right-click on your network adapter and select
Properties.
On the General tab, select ‘Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)’, leaving the box checked, and
then click the Properties button.
In the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties window, change the settings for your
wireless adapter back to the original settings you noted at the beginning on this
section. Click the OK button in this window. Click the OK button on the Wireless
Network Connection Properties window.
Your wireless adapter should now be configured for your wireless network and the
wireless SeaI/O module should now be properly configured to work with your
wireless network. You can open Ethernet Config to verify. If you have any
problems, please contact Sealevel technical support at support@sealevel.com
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 52 -
SeaI/O User Manual
.
Page 56

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Start MaxSSD (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ MaxSSD) and select
Ethernet in the drop down box. Verify that the IP Address for the wireless SeaI/O
module appears in the right hand pane.
Choose the correct IP Address (if more than one is listed) and click the “SeaI/O
Configuration” tab. Use the drop down box to select the appropriate Slave ID (default
is 247) and the click the “Get SeaI/O Module Settings” button. You will see the
description for the wireless SeaI/O module appear in the right hand frame.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 53 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 57

Configuring a Wireless Module (Continued)
Set the slave ID of the “base” wireless SeaI/O module using the rotary switch or
software selection method discussed in the Setting Device Address section
(MaxSSD chapter) of this manual. This guarantees that any expansion modules
connected next will not conflict with the “base” module. Perform another Get
operation to verify that you can communicate with the “base” wireless SeaI/O
module at the new slave ID.
NOTE:
Configure the SeaI/O modules one at a time. Set the address to a
hardware slave ID other than “0” or a software slave ID other than
247, to avoid device conflicts during setup.
After the “base” wireless SeaI/O module is successfully communicating via
MaxSSD, you can proceed with adding SeaI/O expansion modules (N-series). Refer
to the Configuring Expansion Modules section of this manual.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 54 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 58

Configuring an Ethernet (E-Series) Module
NOTE:
This section applies only to Ethernet (E-series) SeaI/O modules.
For all other SeaI/O modules, refer to the Configuring a “Base”
SeaI/O Module and Configuring Expansion Modules sections on
the previous pages.
Verify that SeaMAX software has been installed successfully and that an Ethernet
SeaI/O module is connected directly to your computer using the yellow crossover
cable supplied with your module. This module will become the “base” module.
All Ethernet SeaI/O modules are shipped with DHCP enabled. When you first
connect an Ethernet SeaI/O module to the network, the status LEDs on the front of
the module will blink while it searches for a DHCP server. Once it receives an IP
address, the status LEDs will remain on.
If no DHCP server is available, the Ethernet SeaI/O module will default to a random
IP address in the range 169.254.x.x. To discover the SeaI/O module’s IP address,
start the Ethernet Config utility (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ
Ethernet Config) installed with SeaMAX.
Click on the “Search for SeaI/O Devices” button and the ‘Available SeaI/O Devices’
pane should refresh with any Ethernet or Wireless SeaI/O modules that are found on
the network. Select one of the modules in the list by clicking on it. You can update
the settings in the Device Network Settings pane and then confirm these changes by
clicking the “Apply Changes” button. The module list should refresh, indicating that
your changes were successful.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 55 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 59

Configuring an Ethernet Module (Continued)
NOTE:
If the module does not change or respond, the PC and the module
may be on different subnets. Proceed to the Recover Module
section on the following page.
Start MaxSSD (Start Æ All Programs Æ Sealevel SeaMAX Æ MaxSSD) and choose
the correct IP address to communicate with the “base” Ethernet SeaI/O module.
Ensure a successful Get operation (refer to the MaxSSD section of this manual for
more information).
Set the slave ID of the “base” Ethernet SeaI/O module using the rotary switch or
software selection method discussed in the Setting Device Address section on the
previous pages. This guarantees that any expansion modules connected next will not
conflict with the “base” module. Perform another Get operation to verify that you
can communicate with the “base” Ethernet SeaI/O module at the new slave ID.
NOTE:
Configure the SeaI/O modules one at a time. Set the address to a
hardware slave ID other than “0” or a software slave ID other than
247, which avoids device conflicts during setup.
After the “base” Ethernet SeaI/O module is successfully communicating via
MaxSSD, you can proceed with adding SeaI/O expansion modules (N-series). Refer
to the Configuring Expansion Modules section on the previous pages.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 56 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 60

Resetting an Ethernet SeaI/O Module
An Ethernet SeaI/O module may become no longer visible in the module list in the
Ethernet Config utility if the Ethernet SeaI/O module has been configured to use a
different subnet than the host computer.
In other cases, the Ethernet SeaI/O module doesn’t appear in the module list due to a
DHCP discovery failure. In either case, clicking on the “Recover Module” button
(see image on previous page) in the Ethernet Config utility will bring up the
“Module Reset” window shown below.
Before recovery begins, make certain that the PC and Ethernet SeaI/O module are on
the same network segment – they should be connected with an Ethernet crossover
cable, through a hub, or through a non-routing switch. Ethernet SeaI/O modules are
shipped with both an Ethernet patch cable (blue) and an Ethernet crossover cable
(yellow).
Enter the MAC address found on the label on the bottom of the SeaI/O enclosure. A
MAC address is made up of six pairs of hex digits separated by dashes (i.e., xx-xxxx-xx-xx-xx). While entering the MAC address, the indicator to the right of the field
will turn red if the MAC address entered is invalid. Once a MAC address is
successfully entered, the indicator light will turn green and the “Network Settings”
options will be enabled.
Contact your network administrator if you are unsure of the proper network settings
to choose. If a DHCP server is available, select the “Enable DHCP Configuration”
checkbox. Otherwise, complete the network settings and click the “Recover Module”
button to complete the configuration changes.
Proceed with configuring expansion modules, explained in the previous section.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 57 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 61

SeaI/O-463 Ribbon Cable Installation
A copy of these instructions is included with the SeaI/O-463 module and can also be
downloaded from the SeaI/O-463 product page on the Sealevel website.
NOTE:
Do not perform these instructions with the power connected. Be
sure to follow proper ESD procedures by grounding yourself and the
SeaI/O module.
What you will need:
SeaI/O-463 module
Phillips head screwdriver
Slotted screwdriver
50-pin IDC ribbon cable* (up to four)
*Ribbon cable accessories available:
• CA167 – 40” IDC 50-pin to IDC 50-pin ribbon cable
• CA197 – 18” IDC 50-pin to IDC 50-pin ribbon cable
• CA135 – 40” IDC 50-pin to 50-pin edge connector ribbon cable
Step 1
Remove the terminal block from the left side and
then remove the two black screws from each side
of the module as shown in the image.
Step 2
On the front right side of the module, wedge a
slotted screwdriver between the top and bottom
halves as shown. Pry upwards – a pem in the top
half must clear the metal lip in the bottom half of
the enclosure.
Step 3
Remove the two screws from the metal strain
relief, as shown.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 58 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 62

Step 4
Remove the three screws from the bottom of the
module and remove the front plate.
Step 5
Install up to four industry standard ribbon cables
in the 50-pin header connectors. A list of optional
cable part numbers is listed on the previous page.
Step 6
Replace the front plate and install the three screws
in the bottom of the module as shown.
Step 7
Replace the metal strain relief. Start both screws
and tighten only until snug. Do not over-tighten.
Step 8
Replace the top half by starting it on the left side
over the connectors and then snapping the right
side down into place. Be careful not to pinch
fingers. Replace both screws on each side and
then replace the terminal block on the left side.
Step 9
Continue with the installation of the SeaI/O-463
module. The SeaI/O Hardware Description
section of this manual contains information on
TTL applications and optional accessories. The
SeaMAX Application Suite section walks you
through setting up the hardware address (Slave ID)
and software installation.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 59 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 63

SeaI/O-470 Jumper and Dipswitch Settings
The SeaI/O-470 module ships factory configured with the D/A outputs set for 0-10V
and current loop mode on the A/D inputs disabled. If you need to enable current loop
mode or set the D/A outputs to 0-5V, you will need to open the enclosure and access
the jumpers (shown on the next page).
NOTE:
Do not perform these instructions with the power connected. Be
sure to follow proper ESD procedures by grounding yourself and the
SeaI/O module.
What you will need:
SeaI/O-470 module
Phillips head screwdriver
Slotted screwdriver
Step 1
Remove the terminal block from the left side and
then remove the two black screws from each side
of the module as shown in the image.
Step 2
On the front right side of the module, wedge a
slotted screwdriver between the top and bottom
halves as shown. Pry upwards – a pem in the top
half must clear the metal lip in the bottom half of
the enclosure.
Jumpers and dipswitch locations are shown on the
following page.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 60 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 64

SeaI/O-470 Jumper Locations
This detail image of the right side of the SeaI/O-470 circuit board shows the locations
of the user configurable jumpers and dipswitches. Refer to the following pages for
instructions on properly configuring the jumpers and switches. The colored boxes
are shown here for clarity and are not visible on the actual circuit board.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 61 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 65

D/A Settings
The (E1) and (E2) jumpers (shown in the orange boxes on the previous page)
configure the D/A outputs for 0-5V or 0-10V. Both channels can be configured
independently. The D/A outputs do not support negative voltages. You must also set
the correct output voltage in your application or MaxSSD. Refer to the SeaMAX
Application Suite section of this manual for help configuring software to work with
the SeaI/O-470.
A/D 10X Gain
The A/D 10X gain (E3) jumper (shown in the green box on the previous page) is
disabled at the factory. Position the hardware jumper on both pins to enable this
functionality, which allows smaller voltages to be measured more accurately (e.g., a
0-1V input signal can be measured more accurately by enabling the 10x hardware
gain jumper and setting the SeaI/O-470 A/D input channel for 0-10V range). You
can also set the A/D input channel for 0-5V to sense voltages smaller than 0.5V.
When the jumper is enabled, the “10X Hardware Gain” checkbox will also be
enabled on the A/D Inputs tab in MaxSSD. Refer to the SeaMAX Application Suite
section of this manual for information on using MaxSSD.
A/D and Current Loop Dipswitches
The (SW3) and (SW4) dipswitches (shown in the yellow box on the previous page)
configure the A/D inputs for current loop mode and are disabled at the factory. Since
current loop mode is differential, the corresponding dipswitch on both (SW3) and
(SW4) should be properly set (e.g., ‘CH1’ on both dipswitches needs to be set to
‘ON’ to enable current loop mode).
SW3 – enables the current-loop sensing resistor
SW4 – ties the other half of connection to ground
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 62 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 66

Wiring Options
SeaI/O Pass-Through Connector
All SeaI/O modules include two RS-485 pass-through connectors on the left side of
the unit that are internally connected to the same pins on the screw terminals. This
offers two convenient options for adding additional expansion modules.
For connecting several SeaI/O modules together in a “stack”, all N-series expansion
modules ship with an expansion and strap kit (item# KT122) that includes four metal
straps, four #4-40 screws, and a 5” RJ45 RS-485 interconnect cable (item# CA239).
The metal straps allow you to securely connect multiple SeaI/O modules together.
The interconnect cable can be used to connect SeaI/O modules together via the RJ45
pass-through connectors, providing an easy method to cascade RS-485 signals and
power from one module to the next.
For expansion modules that are less than ten feet from a base unit, a standard RJ45
CAT5 patch cable (“straight-through”) may be used. For SeaI/O modules greater
than ten feet apart, use twisted-pair cable connecting the data lines to the screw
terminals instead. If RJ45 connectors are preferred, be sure to connect only the data
lines (pins 4 & 5).
NOTE:
NOTE:
When using standard CAT5 patch cables to connect modules less
than ten feet apart, ensure the cables are wired “straight-through.”
DO NOT connect network crossover cables to the pass-through
connectors, else damage to equipment may result.
Modules greater than ten feet apart must have separate power
supplies. Refer to the Power Options section of this manual for
recommendations.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 63 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 67

I/O Wiring – SeaI/O-410, 420, 430, 440, and 450 Modules
Optically isolated inputs are arranged such that each group of four shares a single
common. The four I/O points and shared common are connected via a five-position
removable screw terminal. Input voltage range is 5-30VDC. Like the inputs, each
group of four Reed relays also shares a single common and connects via a fiveposition removable screw terminal. Form C Relay outputs are arranged such that each
group of two relays shares a common. The NC and NO contacts of each relay along
with the common are brought out via a five-position removable screw terminal.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 64 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 68

I/O Wiring – SeaI/O-462 and 463 Modules
The SeaI/O-462 and SeaI/O-463 use 74ABT245 octal bi-directional transceivers to
provide TTL input/output capabilities and can sink 64mA and source 32mA. Each
bit is pulled to +5V through a 10K ohm pull-up resistor to insure each bit is at a
known state when not driven. The maximum output power is +5V @ 1A (5W).
SeaI/O-462 DB-78F Connectors
The SeaI/O-462’s 96 digital I/O channels are brought out to two DB-78 Female
connectors on the front of the enclosure (pinout shown below). Each connector
provides 48 bits of digital I/O divided into six eight-bit ports. Each port may be
individually configured via software command as an input or an output.
Bits A1 B1 C1 A2 B2 C2
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
Bits A3 B3 C3 A4 B4 C4
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
+5V
Commons 41 – 58, 64 – 73
75 38 18 10 30 2
76 37 17 9 29 1
77 36 16 8 28 22
78 35 15 7 27 21
59 34 14 6 26 40
39 33 13 5 25 60
20 32 12 4 24 61
19 31 11 3 23 62
75 38 18 10 30 2
76 37 17 9 29 1
77 36 16 8 28 22
78 35 15 7 27 21
59 34 14 6 26 40
39 33 13 5 25 60
20 32 12 4 24 61
19 31 11 3 23 62
Power & Commons
63, 74
Bits 1-48
Bits 49-96
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 65 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 69

SeaI/O-462 Optional Cable (Item# CA237) Pinout
For easy connection to industry-standard solid-state relay racks, Sealevel
manufactures a 6’ cable, Item# CA237, that terminates the DB-78 to two industry
standard 50-pin header connectors. Two cables and a SeaI/O unit can be order
together as a kit using Item# 462x-KT. The pinout for the two 50-pin headers is
shown below.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 66 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 70

SeaI/O-463 50-Pin Header Connectors
The SeaI/O-463’s 96 digital I/O channels are accessed via four industry-standard 50pin header connectors. Each header provides 24 bits of digital I/O divided into three
eight-bit ports. Each port may be individually configured via software command as
an input or an output.
You will need to open the SeaI/O-463’s enclosure to access the four header
connectors: P2, P3, P4, and P5. The connector designators are silk-screened onto the
PCB for easy identification. Once cables are connected to the headers, route them
through the opening in the front of the enclosure, attach the included strain-relief
bracket to secure the cables and reassemble the enclosure. Refer to the ribbon cable
installation instructions included with the SeaI/O-463.
Each of the four 50-pin connectors has the following pinout, which is compatible
with a wide variety of industry-standard solid-state relay racks:
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 67 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 71

I/O Wiring – SeaI/O-470 Modules
A/D Wiring Connections
The SeaI/O-470 supports single-ended, differential, and current loop A/D inputs.
Single-ended and differential modes can be configured in software. Current loop
mode requires configuring dipswitches inside the enclosure. Refer to the Hardware
Configuration section of this manual for instructions on configuring the current loop
dipswitches.
The SeaI/O-470 can be configured for up to sixteen 12-bit single-ended A/D inputs.
Each input is referenced to a common ground. The user selectable voltage ranges are
0-5V, 0-10V, +/-5V, and +/-10V.
The SeaI/O-470 can be configured for up to eight 12-bit differential A/D inputs. The
inputs are not referenced to ground. The user selectable voltage ranges are 0-5V, 010V, +/-5V, and +/-10V.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 68 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 72

The SeaI/O-470’s A/D channels can also be configured to provide up to eight 12-bit
current loop inputs. Each input has two terminals – one positive and one negative.
The input current range is 0-20mA for interfacing commonly used 4-20mA devices.
The dipswitches inside the enclosure must be properly configured for each current
loop input.
D/A Wiring Connections
The SeaI/O-470 provides two 12-bit D/A output channels, configured for 0-10V.
0-5V mode requires different jumper settings inside the enclosure. Refer to the
Hardware Configuration section of this manual for instructions on configuring the
D/A jumpers.
The SeaI/O-470 module’s D/A output channels can be independently configured for
0-5V or 0-10V. The D/A outputs do not support negative voltages.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 69 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 73

Digital I/O Wiring Connections
The SeaI/O-470 modules include eight optically isolated inputs that are arranged such
that each group of four inputs shares a single common. The four I/O points and
shared common are connected via a five-position removable screw terminal.
The SeaI/O-470 modules provide eight open-collector digital outputs. The outputs
do not source any current and must be connected to an external power source, max
30VDC. The outputs act as a switch and the circuit is open until energized. When
the output circuit is energized in software, the output sinks the current to ground,
closing the circuit.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 70 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 74

I/O Wiring – SeaI/O-520 Modules
Optically isolated inputs are arranged such that each group of two shares a single
common. The four I/O points and shared common are connected via a six-position
removable screw terminal. Input voltage range is 5-30VDC. Like the inputs, each
group of two Form C relays also shares a single common. The NC and NO contacts
of each relay along with the commons are brought out via a six-position removable
screw terminal.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 71 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 75

Connector Pin Outs
SeaI/O (RS-232) S-Series Modules
SeaI/O S-Series (RS-232) modules have an RJ45 connector on the face of the
enclosure. Each S-series module includes a kit (item# KT119) to convert the RJ45
RS-232 pin out to a standard DB9 RS-232 pin out. The kit ships with a DB-9F to
RJ45 modular adapter (item# DB109) with RS-232 pin out and a standard 7' CAT5
patch cable (item# CA246). This kit allows SeaI/O S-series modules to be easily
connected to a standard DB9 RS-232 serial port. For other interfacing options, the
RJ45 serial pin out is shown below.
NOTE:
For SeaI/O S-series modules, pin 4 of the RJ45 connector outputs
5VDC @300mA. This is useful for powering the wireless
Bluetooth adapter (Sealevel Item# BT-SD100). This allows any
Bluetooth capable host to access a SeaI/O module as easily as
communicating with a standard RS-232 serial port.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 72 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 76

Mounting Options
SeaI/O Mounting Kit
Expanding your I/O count is as simple as adding
N-Series expansion units to the Base SeaI/O
module (or other N-series modules). Each NSeries module includes an expansion and strap kit
(Item# KT122), which includes a 5” CAT5
interconnect cable, four metal straps, and four #440 metal screws. The image shows a SeaI/O stack
configuration using the expansion kit.
DIN Rail Mounting
All SeaI/O modules are available with a factoryinstalled DIN-rail mounting clip. Alternatively
DIN-rail mounting clips can be ordered as a field
upgrade kit (Item# DR104). The bracket with clip
is easily attached using two included #4-40
Phillips head machine screws.
Table/Wall Mounting
The flush mount bracket kit (Item# KT123) is
extremely versatile and can be used to mount
SeaI/O modules from the top, bottom, or back
edge. Individual modules or a stack of SeaI/O
modules can be mounted flat to a tabletop,
underneath a counter, or inside an enclosure. The
kit can be used to mount SeaI/O modules flat to a
wall, or along the back edge, similar to DIN-rail
mounting options.
Universal Mounting Bracket
The universal mounting bracket (Item# KT125)
can be used as a “backpack” to mount power
supplies and other devices to SeaI/O modules. The
bracket has holes for both 75mm and 100mm
VESA mounting options. The universal
arrangement of slots and holes accept bolt sizes to
M4 and can be used for virtually any mounting
configuration.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 73 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 77

SeaLATCH™ USB
SeaI/O USB modules integrate a patent-pending SeaLATCH USB port, which is
fully compatible with standard USB cables. When used with the included USB cable
(Item# CA356) with a SeaLATCH USB type B connector, the metal thumbscrew
provides a secure metal-to-metal connection to the module and prevents accidental
cable disconnection.
Sealevel incorporates SeaLATCH locking USB ports on many USB hubs and I/O
devices. Accidental cable disconnection is the most common point of failure with
USB industrial I/O devices and SeaLATCH cables and connectors prevents that
while being fully compatible with standard USB cables.
Examples of the isolated 7-port USB hub (Item# SeaI/O-270U) with SeaLATCH
equipped Sealevel I/O devices are shown below.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 74 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 78

SeaLATCH Locking USB Cables
SeaLATCH USB Connectors
SeaLATCH locking USB cables
integrate a small thumbscrew into
each USB connector. SeaLATCH
USB cables are fully interchangeable
with standard USB cables. The
thumbscrew provides a secure metalto-metal connection preventing
accidental disconnection. SeaLATCH
USB cables are available in three
configurations.
Item# CA356
The CA356 is a 72” USB cable with a
SeaLATCH type B connector and a
standard USB type A connector. This
cable provides a secure connection
between Sealevel products with a
SeaLATCH type B port and legacy
USB type A ports. The CA356 is
included with Sealevel devices with a
SeaLATCH type B port.
Item# CA332
The CA332 is a 72” cable with both
SeaLATCH type A and B connectors.
This cable secures both ends of the
cable to devices with SeaLATCH
USB ports and offers complete
protection against accidental cable
disconnection.
Item# CA355
The CA355 is a 72” cable with a
standard USB type B and a
SeaLATCH type A connector. This
cable provides a secure connection
between legacy USB devices and
Sealevel products with a SeaLATCH
type A port, such as the isolated USB
hub (Item# 270U).
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 75 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 79

Accessories
Power Supplies
US Options
TR112 – 120VAC to 24VDC 250mA “Wall Wart” Power Supply with 1.3mm Plug
(for single SeaI/O module)
TR109 – 120VAC to 24VDC 500mA “Wall Wart” Power Supply with 1.3mm Plug
(for multiple SeaI/O modules)
TR108-US – 100-250VAC to 24VDC 36W 1.5A “Desktop” Power Supply with
1.3mm Plug, includes (CA248) Nema 5-15P 6’ US Power Cord
PS101 – 100-240VAC to 24VDC 7.5W 300mA DIN Rail Mount Power Supply
(connects via screw terminals, no wire included)
PS103 – 100-240VAC to 24VDC 50W 2.1A DIN Rail Mount Power Supply
(connects via screw terminals, no wire included)
International Options
TR108-AU - 100-250VAC to 24VDC 36W 1.5A “Desktop” Power Supply with
1.3mm Plug, includes (CA187) “AS 3112” 6’ Australian Power Cord
TR108-EC - 100-250VAC to 24VDC 36W 1.5A “Desktop” Power Supply with
1.3mm Plug, includes (CA188) “Schuko” 6’ Continental European Power Cord
TR108-UK - 100-250VAC to 24VDC 36W 1.5A “Desktop” Power Supply with
1.3mm Plug, includes (CA189) “BS 1363” 6’ UK Power Cord
TR108 – 100-250VAC to 24VDC 36W 1.5A “Desktop” Power Supply with 1.3mm
Plug, requires IEC country-specific Power Cord
Mounting Options
KT122 – Expansion & Strap Kit. Includes 5” RS-485 Interconnect Cable (item#
CA239), four metal straps, and four #4-40 metal screws, for connecting two SeaI/O
modules together in a “stack”
KT123 – Flush Mount Bracket Kit. Includes two metal brackets and four #4-40
metal screws, for mounting SeaI/O modules or stacks in a variety of positions and
locations
KT125 – Universal Mounting Bracket. Includes metal mounting bracket and four
#4-40 metal screws, for mounting devices to SeaI/O modules or mounting SeaI/O
modules to VESA mounts and other devices.
DR104 – DIN Rail Mounting Assembly. Connects to the back edge of SeaI/O
modules to facilitate an easy DIN rail mounting option and a cleaner installation
RK1U – 1U 19” Rack Tray
RK2U – 2U 19” Rack Tray
RK-CLAMP – Securely holds SeaI/O modules to rack trays
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 76 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 80

Cabling Options
CA239 – 5” CAT5 RS-485 Interconnect Cable, used to connect SeaI/O modules
together in a stack (included in 4xxN SeaI/O expansion modules)
CA246 – 7’ Blue Ethernet Patch Cable. Can be used to connect SeaI/O Ethernet
modules to a hub (included with 4xxE SeaI/O Ethernet modules). Can be used to
connect SeaI/O RS-232 modules to both Sealevel and standard RS-232 serial ports
(included with 4xxS SeaI/O RS-232 modules as part of p/n: KT119). Optionally, it
can be used as an RS-485 interconnect cable to cascade additional SeaI/O modules
via the RS-485 In/Out ports on the side of SeaI/O modules
CA251 – 7’ Yellow Crossover Cable. Used to connect SeaI/O Ethernet modules
directly to a computer’s Ethernet port without having to go through a hub or switch
CA247 – 10’ Blue Ethernet Patch Cable. Can be used to connect SeaI/O Ethernet
modules to a hub, or can be used as an RS-485 interconnect cable to cascade SeaI/O
modules via the RS-485 In/Out ports
CA179 – Standard USB type A to USB type B Device Cable, 6’ in length
CA332 – SeaLATCH locking USB type A to SeaLATCH locking USB type B
Device Cable, 6’ in length
CA356 – USB type A to SeaLATCH locking USB type B Device Cable, 6’ in length
(included with SeaI/O USB modules)
CA355 – SeaLATCH locking USB type A to USB type B Device Cable, 6’ in length
KT119 – RS-232 DB9/RJ45 Kit, includes (DB109) DB9F to RJ45 adapter with RS-
232 pinout, and (CA246) 7’ CAT5 patch cable. For connecting SeaI/O modules to
both Sealevel and standard RS-232 serial ports (included with 4xxS SeaI/O RS-232
modules)
KT120 – RS-422 DB9/RJ45 Kit, includes (DB110) DB9F to RJ45 adapter with RS422 pinout, and (CA246) 7’ CAT5 patch cable. Optional accessory for connecting
SeaI/O modules to Sealevel RS-422 serial port products
KT121 – RS-485 DB9/RJ45 Kit, includes (DB111) DB9F to RJ45 adapter with RS485 pinout, and (CA246) 7’ CAT5 patch cable. Optional accessory for connecting
SeaI/O modules to Sealevel RS-485 serial port products
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 77 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 81

Appendix A – How to Get Assistance
When calling for technical assistance, please have your user manual and current
device settings ready. If possible, please have the device installed and ready to run
diagnostics.
Sealevel Systems maintains a website on the Internet. Our homepage address is
http://www.sealevel.com
available via our FTP site that can be accessed from our home page. Manuals and
software can also be downloaded from the product page for your device.
Sealevel Systems provides an FAQ section on our website. Please refer to this to
answer many common questions. This section can be found at
http://www.sealevel.com/faq.asp
Technical support is available Monday to Friday from 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. Eastern
Standard Time. You can contact Technical Support via:
Phone: (864) 843-4343
. The latest software updates and newest manuals are
Email: support@sealevel.com
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 78 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 82

Appendix B – Wireless Module Information
SeaI/O wireless (W-series) modules are compatible with 802.11b and 802.11g
wireless networking equipment operating in the 2.4GHz frequency spectrum. The
wireless modules can operate over any of the 14 available channels, defined by the
IEEE 802.11 specification, listed by country below. These regulations are subject to
change at any time. Please consult your local regulatory authority for current
information.
Wireless Specifications
Standards: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11i
Channels: 1-14
Frequency Range: 2.412 – 2.484 GHz
Wireless Output Power: 14 dBm +1.5/-1.0 dBm
Data Rates: 54Mbps Max, 1Mbps Min
Range: 328’ (Indoors)
Frequency
Channel
1 2.412 OK OK OK
2 2.417 OK OK OK
3 2.422 OK OK OK
4 2.427 OK OK OK
5 2.432 OK OK OK
6 2.437 OK OK OK
7 2.442 OK OK OK
8 2.447 OK OK OK
9 2.452 OK OK OK
10 2.457 OK OK OK OK OK
11 2.462 OK OK OK OK OK
12 2.467
13 2.472
14 2.484
This device contains an FCC approved RF module.
The transmitter carries FCC ID: R68WIPORTG.
RSS-GEN Sections 7.1.4 and 7.1.5 Statement for Devices with Detachable Antennas
This device has been designed to operate with the antennas listed in the Certificate, and
having a maximum gain of 5 dB. Antennas not included in this list or having a gain greater
than 5 dB are strictly prohibited for use with this device. The required antenna impedance is
50 ohms.
(GHz)
North
America
No
No
No No
Europe Japan France Spain
OK OK OK
OK OK OK
802.11b
No No
No No
No No
No No
No No
No No
No No
No No
No No
No
No
No No
To reduce potential radio interference to other users, the antenna type and its gain should be
so chosen that the equivalent isotropically radiated power (EIRP) is not more than that
required for successful communication.
Note:
a) This module is authorized under limited module approval specified to mobile host
equipment. So, the antenna must be installed such that 20cm is maintained between the
antenna and users.
b) The transmitter module may not be co-located with any other transmitter or antenna.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 79 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 83

Appendix C – Compliance Notices
Federal Communications Commission Statement
FCC - This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class
A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in such case the user will be required to correct the interference at the
user’s expense.
EMC Directive Statement
Products bearing the CE Label fulfill the requirements of the EMC directive
(89/336/EEC) and of the low-voltage directive (73/23/EEC) issued by the European
Commission.
To obey these directives, the following European standards must be met:
EN55022 Class A - “Limits and methods of measurement of radio interference
characteristics of information technology equipment”
EN55024 – “Information technology equipment Immunity characteristics Limits and
methods of measurement”.
EN60950 (IEC950) - “Safety of information technology equipment, including
electrical business equipment”
Warning
This is a Class A Product. In a domestic environment, this product may cause
radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures to prevent or correct the interference.
Always use cabling provided with this product if possible. If no cable is provided or
if an alternate cable is required, use high quality shielded cabling to maintain
compliance with FCC/EMC directives.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 80 -
SeaI/O User Manual
Page 84

Warranty
Sealevel's commitment to providing the best I/O solutions is reflected in the Lifetime
Warranty that is standard on all Sealevel manufactured products. We are able to
offer this warranty due to our control of manufacturing quality and the historically
high reliability of our products in the field. Sealevel products are designed and
manufactured at its Liberty, South Carolina facility, allowing direct control over
product development, production, burn-in and testing.
Sealevel Systems, Inc. (hereafter "Sealevel") warrants that the Product shall conform
to and perform in accordance with published technical specifications and shall be free
of defects in materials and workmanship for life. In the event of failure, Sealevel will
repair or replace the product at Sealevel's sole discretion. Failures resulting from
misapplication or misuse of the Product, failure to adhere to any specifications or
instructions, or failure resulting from neglect or abuse are not covered under this
warranty. Warranty service is obtained by delivering the Product to Sealevel and
providing proof of purchase.
NOTE:
Return authorization must be obtained from Sealevel Systems
before returned merchandise will be accepted. Authorization is
obtained by calling Sealevel Systems and requesting a Return
Merchandise Authorization (RMA) number.
The Customer agrees to insure the Product or assume the risk of loss or damage in
transit, to prepay shipping charges to Sealevel, and to use the original shipping
container or equivalent. Warranty is valid only for original purchaser and is not
transferable.
Sealevel Systems assumes no liability for any damages, lost profits, lost savings or
any other incidental or consequential damage resulting from the use, misuse of, or
inability to use this product. Sealevel Systems will not be liable for any claim made
by any other related party.
This warranty applies to Sealevel manufactured Product. Product purchased through
Sealevel but manufactured by a third party will retain the original manufacturer's
warranty.
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated
2779 Greenville Highway
P.O. Box 830
Liberty, SC 29657 USA
(864) 843-4343 FAX: (864) 843-3067
www.sealevel.com
email: support@sealevel.com
Technical Support is available Monday - Friday from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Eastern time.
Trademarks
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated acknowledges that all trademarks referenced in this
manual are the service mark, trademark, or registered trademark of the respective
company.
© Sealevel Systems, Inc.
- 81 -
SeaI/O User Manual
 Loading...
Loading...