Page 1

P
TM
C-ACB.MP
USER MANUAL
Sealevel Systems, Inc
P.O. Box 830
Liberty, SC 29657 USA
Part # 3612
Phone: (864) 843-4343
FAX: (864) 843-3067
www.sealevel.com
Page 2

Contents
INTRODUCTION.............................................................................................................................1
OVERVIEW ................................................................................................................................................... 1
WHAT’S INCLUDED......................................................................................................................................1
INSTALLATION..............................................................................................................................2
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION............................................................................................................3
FEATURES .................................................................................................................................................... 3
Internal Baud Rate Generator .................................................................................................................3
CONTROL AND STATUS REGISTERS DEFINITION...........................................................................................3
INTERFACE SELECTION.................................................................................................................................4
25 PIN CONNECTOR SIGNAL LAYOUTS (DB-25 MALE)................................................................................4
RS-232 Signals .......................................................................................................................................4
V.35 Signals............................................................................................................................................ 5
RS-530 (RS-422) ....................................................................................................................................5
RS-530A .................................................................................................................................................6
RS-485 or RS-485T................................................................................................................................ 6
SPECIFICATIONS ...........................................................................................................................7
ENVIRONMENTAL SPECIFICATIONS ..............................................................................................................7
POWER CONSUMPTION.................................................................................................................................7
MEAN TIME BETWEEN FAILURES (MTBF)...................................................................................................7
APPENDIX A - TROUBLESHOOTING..............................................................................................8
APPENDIX B - HOW TO GET ASSISTANCE ...................................................................................9
APPENDIX C - ELECTRICAL INTERFACE......................................................................................10
RS-232 ........................................................................................................................................................10
RS-422 ........................................................................................................................................................10
RS-485 ........................................................................................................................................................10
RS-530 / 530A.............................................................................................................................................10
V.35 ........................................................................................................................... .................................. 11
APPENDIX D - COMPLIANCE NOTICES.........................................................................................12
FEDERAL COMMUNICATIONS COMMISSION STATEMENT.............................................................................. 12
EMC DIRECTIVE STATEMENT......................................................................................................................12
ARRANTY...................................................................................................................................13
W
© Sealevel Systems Inc.
SL9115 Revision 12/2006
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Introduction
Introduction
Overview
In the last few years, the portable and notebook market has grown by leaps and bounds. Most early laptops and
notebooks handled I/O expansion through proprietary expansion slots. These slots provided limited expansion for
specific peripherals such as modems and FAX peripherals. Mass storage peripherals were factory installed and
could not be easily changed. Interconnectivity through local area networks offered limited performance through
slow parallel port network interfaces.
During this time period two standards organizations, JEIDA and PCMCIA, were working on the standardization of
memory IC cards. These cards were designed as strictly non-volatile silicon storage. JEIDA was the first to propose
the 68-pin connector standard for memory cards. In 1989, PCMCIA adopted the JEIDA 68 pin standard and worked
with JEIDA on further developments.
As the notebook market grew, the need for a standard I/O bus was seen. The PCMCIA groups saw an opportunity to
meet this need with an expanded version of the 68-pin interface. Further development occurred and within one year,
release 2.0 of the standard was completed. Release 2.0 was a major update to Release 1.0 and included full
hardware support for I/O devices. Release 2.0 coincided with JEIDA’s 4.1 release and is identical.
The PC-ACB.MP adapter provides your portable PC with a single channel multi-protocol serial interface utilizing
the Zilog Z85233 (ESCC™), which is suitable for the most popular communication protocols including
HDLC/SDLC, X.25, Bi-Sync, Mono-Sync, and asynchronous.
The PC-ACB.MP utilizes the Sipex-505 multi-protocol electrical interface chip that allows the PC-ACB.MP to be
compliant with EIA/TIA-530/530A, EIA/TIA-232E, EIA/TIA-485, and ITU V.35.
What’s Included
The PC-ACB.MP is shipped with the following items. If any of these items are missing or damaged, contact the
supplier.
• PC-ACB.MP PCMCIA Serial Interface Adapter
• DB-25 cable assembly
• Loopback Plug
• Impact Resistant Carrying Case (Jewel Case)
• Sealevel Software
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 1
Page 4

Installation
Installation
Card and Socket Services must be loaded on the system prior to installing the PC-ACB.MP card. Card and Socket
Services are supplied by the PCMCIA slot provider (i.e. the computer manufacturer or the PC adapter
manufacturer). These may be in the form of a third party add-on Card and Socket service (e.g. CardSoft’s
CardWizard) or with your current operating system (e.g. Windows 95/98/NT/2000).
Socket Services are the lowest level of the PCMCIA Software hierarchy. Socket Services provide a standard
interface to the higher-level drivers and isolate the socket controller’s specific hardware details. Socket Services
provide the ‘BIOS’ interface to the socket controller hardware. Socket Services are typically hidden under Card
Services and are rarely directly accessible by application software.
Card Services provide the interface to application software and drivers. Card Services are responsible for allocating
card resources and ensuring that card resources do not interfere with other existing system resources. Card Services
are typically implemented as a driver. Almost all PCMCIA type cards require some sort of software driver. In the
case of the PC-ACB.MP, the generic Card Services driver supplied with the computer system should provide
adequate support for most applications.
Connecting the PC-ACB.MP to the computer requires no special technical skills. In fact it is usually done in as
simple as two steps:
1. Follow the directions given for your operating system found on the supplied software.
2. Simply slide the card into a PCMCIA Type II compliant slot on the personal computer. The PCMCIA slot
is keyed so that the PC-ACB.MP cannot be installed backwards or upside down. The card should install
with a minimal amount of pressure. Do not force the card into the slot. Forcing the card can result in
damage to the PC-ACB.MP or to the PCMCIA slot. After the card has been installed into the PCMCIA
slot, the I/O cable should be connected to the card. The cable is also keyed to prevent it from being
installed incorrectly.
3. For Windows users that are using Sealevel’s SeaMAC software please note that there is a different install
for this card than the normal SeaMAC software. When choosing to install the software from the CD scrool
down to the SeaMAC drivers. You should see:* Note: If you are installing Part# 3612 or 5102, click
here to install the Windows 2000 interrupt mode HDLC/SDLC driver. To install the Windows NT
interrupt mode Async driver and for all other ACB products, click the "install SeaMAC" button
below. Please be sure to follow these steps for a successful installation.
Installation is complete.
The PC-ACB.MP has a number of cabling options available. These options include:
• CA-103 - This cable provides a high quality shielded cable with th e V.35 mechanical specification met on one
end and a DB-25S (female) on the other end. V.35 has a mechanical specification that is impossible to place on
a PC bracket and requires this adapter cable.
• CA-104 - This cable provides a 6’ extension for use with RS-232, and RS-530/530A.
• CA-107 - RS-530 (DB-25P) to RS-449 (DB-37P) cabling adapter. RS-530 is replacing RS-449 in Telecom
applications, but there is still a very large base of installed equipment that uses the RS-449 pin-out. Both
standards use RS-422 to define the electrical specifications and are interchangeable via this adapter cable.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 2
Page 5
Technical Description
Technical Description
The PC-ACB.MP utilizes the Zilog 85233 Enhanced Serial Communications Controller (ESCC). This chip features
programmable baud rate, data format and interrupt control. Refer to the ESCC Users Manual for details on
programming the 85233 ESCC chip.
Features
• One channel of synchronous or asynchronous communications using the Zilog Z85233 chip
• Programmable electrical interface selection EIA/TIA-232/530/530A/485 and ITU V.35
• Programmable options for Transmit clock as input or output
• Software programmable baud rate
Internal Baud Rate Generator
The baud rate of the ESCC is programmed under software control.
Control and Status Registers Definition
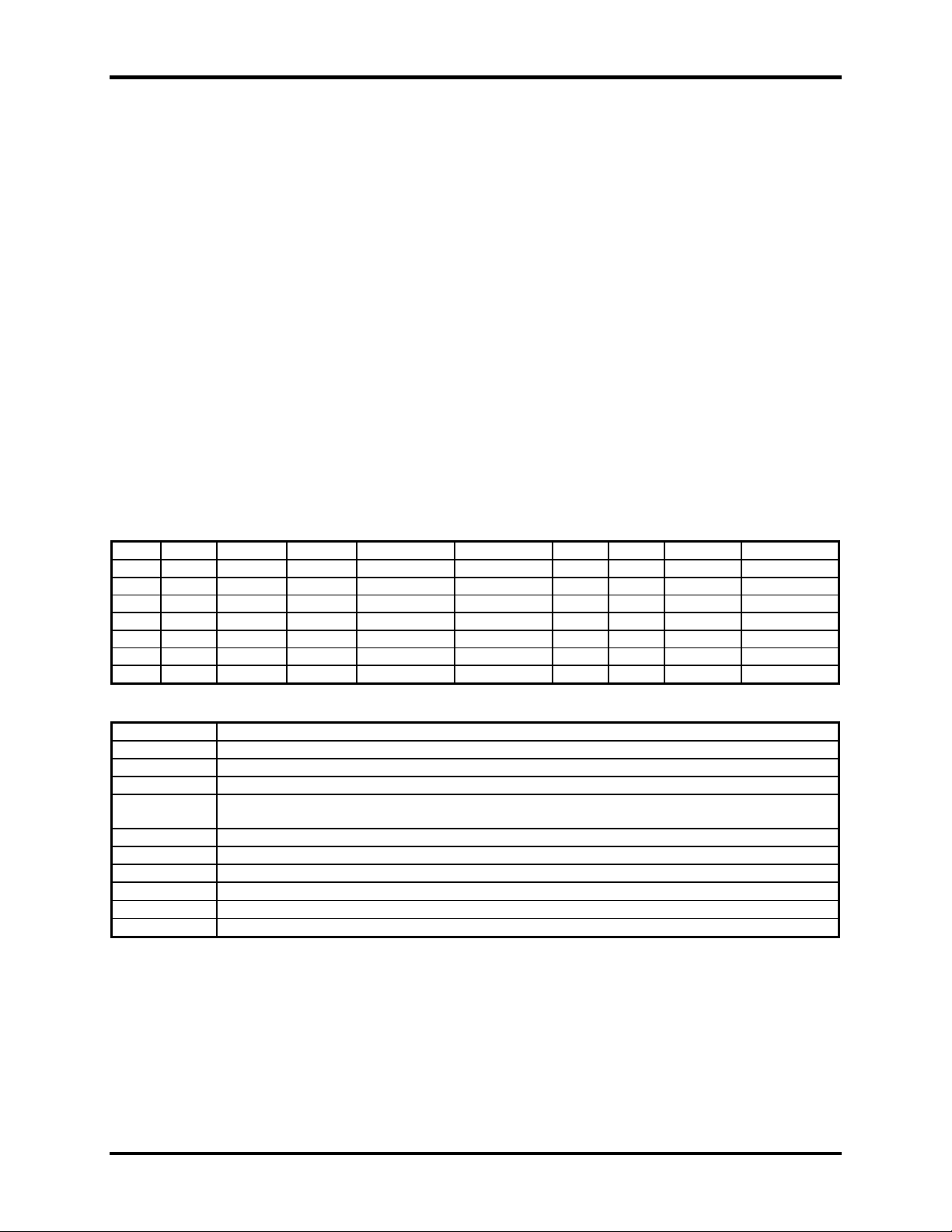
The control and status registers occupy 16 consecutive locations. The following tables provide a functional
description of the bit positions. X = do not care
Base Mode D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
+4
+4
+5
+5
+6
+6
+7
IRQST SCC interrupt status: 1 = No interrupt pending on ESCC 0 = Interrupt pending on ESCC.
DSRA DSRA: 1 = DSRA is not active 0 = DSRA is active
TSETSLA TSET clock source: 1 = Received TXC as source 0 = TRXCA as source
RXCOPTA RXCOPTA: 1 = Selects SCC PCLK for RTXCA 0 = Selects received RXC for
SYNCA_RTS SYNCA _RTS: 1 = SYNCA connected to RTS 0 = SYNCA is high
SYNCA_CTS SYNCA_CTS: 1 = SYNCA connected to CTS 0 = SYNCA is high
485CLK TSET switches with TXD 1 = clk switches 0 = no CLK switching
ECHOA ECHO enable: 1 = echo disabled 0 = echo enabled
AM0-AM3 I/O mode select. See table for valid interface options 0 = High Impedance
SD0-SD7 Optional security feature. Unique value per customer or application. Default value = FF
Note: Default values are listed in bold
RD 0 IRQST 0 0 0 0 0 DSRA
WR X X X X X X X X
RD 485CLK ECHOA SYNCA_RTS SYNCA_CTS AM3 AM2 AM1 AM0
WR 485CLK ECHOA SYNCA_RTS SYNCA_CTS AM3 AM2 AM1 AM0
RD 0 0 0 0 RLA LLA TSETSLA RXCOPTA
WR X X X X RLA LLA TSETSLA RXCOPTA
RD SD7 SD6 SD5 SD4 SD3 SD2 SD1 SD0
Field Description
RTXCA
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 3
Page 6

Technical Description
Interface Selection
The PC-ACB.MP supports a variety of electrical interfaces. Refer to the Control and Status Register Definitions
found in the Technical Description section of this manual for this bit description. There is line termination on
RXD, RXC, and TXC in the following modes: RS-530, RS-530A, RS-485T, and V.35.
HEX M3 M2 M1 M0 Interface Mode
0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 * not supported *
2 0 0 1 0
3 0 0 1 1 * not supported *
4 0 1 0 0
5 0 1 0 1
6,7,8,9 0 1 1 0 * not supported *
A 1 0 1 0
B 1 0 1 1
C 1 1 0 0 * not supported *
D 1 1 0 1
E 1 1 1 0
F 1 1 1 1
All signals are high impedance
RS-232
RS-485T with 120 ohm termination
RS-485 without termination
single ended loop-back
differential loop-back
RS-530
V.35
RS-530A
25 Pin Connector Signal Layouts (DB-25 Male)
RS-232 Signals
Base+5, M3-M0=2, 0010
Signal Name Pin # Mode
GND Ground 7
RD Receive Data 3 Input
CTS Clear To Send 5 Input
DSR Data Set Ready 6 Input
DCD Data Carrier Detect 8 Input
TM Test Mode 25 Input
TXC Transmit Clock 15 Input
RXC Receive Clock 17 Input
TSET Transmit Signal Element Timing 24 Output
DTR Data Terminal Ready 20 Output
TD Transmit Data 2 Output
RTS Request To Send 4 Output
Technical Note: Please terminate any control signals that are not going to be used. The most common way to do this
is connect RTS to CTS and RI. Also, con nect DCD to DTR and DSR. Terminating these pins, if no t used, will help
insure you get the best performance from your adapter.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 4
Page 7

Technical Description
V.35 Signals
Base+5, M3-M0=E, 1110
Signal Name DB-25 V.35 Mode
GND Ground 7 B
RDB RX+ Receive Positive 16 T Input
RDA RX- Receive Negative 3 R Input
TXCB TXC+ Transmit Clock Positive 12 AA Input
TXCA TXC- Transmit Clock Negative 15 Y Input
RXCB RXC+ Receive Clock Positive 9 X Input
RXCA RXC- Receive Clock Negative 17 V Input
TDB TX+ Transmit Positive 14 S Output
TDA TX- Transmit Negative 2 P Output
TSETB TSET+ Transmit Signal Element Timing + 11 W Output
TSETA TSET- Transmit Signal Element Timing - 24 U Output
CTS Clear To Send 5 D Input *
DSR Data Set Ready 6 E Input *
DCD Data Carrier Detect 8 F Input *
DTR Data Terminal Ready 20 H Output *
RTS Request To Send 4 C Output *
• Note: All modem control signals are single ended (un-balanced) with RS-232 signal levels.
RS-530 (RS-422)
Base+5, M3-M0=D, 1101
Signal Name Pin # Mode
GND Ground 7
RDB RX+ Receive Positive 16 Input
RDA RX- Receive Negative 3 Input
CTSB CTS+ Clear To Send Positive 13 Input
CTSA CTS- Clear To Send Negative 5 Input
DCDB DCD+ Data Carrier Detect Positive 10 Input
DCDA DCD- Data Carrier Detect Negative 8 Input
TXCB TXC+ Transmit Clock Positive 12 Input
TXCA TXC- Transmit Clock Negative 15 Input
RXCB RXC+ Receive Clock Positive 9 Input
RXCA RXC- Receive Clock Negative 17 Input
TDB TX+ Transmit Positive 14 Output
TDA TX- Transmit Negative 2 Output
RTSB RTS+ Request To Send Positive 19 Output
RTSA RTS- Request To Send Negative 4 Output
DTRB DTR+ Data Terminal Ready Positive 23 Output
DTRA DTR- Data Terminal Ready Negative 20 Output
TSETB TSET+ Transmit Signal Element Timing Positive 11 Output
TSETA TSET- Transmit Signal Element Timing Negative 24 Output
DSRB DSR+ Data Set Ready Positive 22 Input
DSRA DSR- Data Set Ready Negative 6 Input
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 5
Page 8

Technical Description
RS-530A
Base+5, M3-M0=F, 1111
Signal Name Pin # Mode
GND Ground 7
RDB RX+ Receive Positive 16 Input
RDA RX- Receive Negative 3 Input
CTSA CTS- Clear To Send Negative 5 Input
DCDA DCD- Data Carrier Detect Negative 8 Input
TXCB TXC+ Transmit Clock Positive 12 Input
TXCA TXC- Transmit Clock Negative 15 Input
RXCB RXC+ Receive Clock Positive 9 Input
RXCA RXC- Receive Clock Negative 17 Input
TDB TX+ Transmit Positive 14 Output
TDA TX- Transmit Negative 2 Output
RTSA RTS- Request To Send Negative 4 Output
DTRA DTR- Data Terminal Ready Negative 20 Output
TSETB TSET+ Transmit Signal Element Timing Positive 11 Output
TSETA TSET- Transmit Signal Element Timing Negative 24 Output
RS-485 or RS-485T
Base+5, M3-M0=4, 0100 (With termination)
Base+5, M3-M0=5, 0101 (Without termination)
Signal Name Pin # Mode
GND Ground 7
RDB RX+ Receive Positive 16 Input
RDA RX- Receive Negative 3 Input
TXCB TXC+ Transmit Clock Positive 12 Input
TXCA TXC- Transmit Clock Negative 15 Input
RXCB RXC+ Receive Clock Positive 9 Input
RXCA RXC- Receive Clock Negative 17 Input
TDB TX+ Transmit Positive 14 Output
TDA TX- Transmit Negative 2 Output
TSETB TSET+ Transmit Signal Element Timing Positive 11 Output
TSETA TSET- Transmit Signal Element Timing Negative 24 Output
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 6
Page 9

Specifications
Specifications
Environmental Specifications
Specification Operating Storage
Temperature Range
Humidity Range
Power Consumption
0 to 50 º C
(32 to 122 º F)
10 - 90% R.H. Non Condensing 10 - 90% R.H. Non Condensing
-20 to 70 º C
(-4 to 158 ºF)
Supply line
Rating
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Greater than 150,000 hours. (Calculated)
+5 VDC
170 mA
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 7
Page 10

Appendix A - Troubleshooting
Appendix A - T roubleshooting
The Developers Toolkit Software is supplied with the Sealevel Systems adapter and will be used in the
troubleshooting procedures. Using this software and following these simple steps can eliminate most common
problems without the need to call Technical Support.
1. Identify all I/O adapters currently installed in your system. This includes your on-board serial ports, controller
cards, sound cards etc. The I/O addresses used by these adapters, as well as the IRQ (if any) should be
identified.
2. Make sure the Sealevel Systems adapter is securely installed in a PCMCIA slot.
3. Use the supplied software and User Manual to verify that the Sealevel Systems adapter is configured correctly.
The supplied software contains a diagnostic program “SSDMP” that will verify if an adapter is configured
properly. This diagnostic program is written with the user in mind and is easy to use.
4. Windows users can use the installed programs in the SeaMAC folder to verify operation.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 8
Page 11

Appendix B - How To Get Assistance
Appendix B - How To Get Assistance
Please refer to Troubleshooting Guide prior to calling Technical Support.
1. Begin by reading through the Trouble Shooting Guide in Appendix A. If assistance is still needed
please see below.
2. When calling for technical assistance, please have your user manual and current adapter settings. If
possible, please have the adapter installed in a computer ready to run diagnostics.
3. Sealevel Systems provides an FAQ section on its web site. Please refer to this to answer many
common questions. This section can be found at http://www.sealevel.com/faq.htm
4. Sealevel Systems maintains a Home page on the Internet. Our home page address is
www.sealevel.com
that can be accessed from our home page.
5. Technical support is available Monday to Friday from 8:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. eastern time. Technical
support can be reached at (864) 843-4343.
RETURN AUTHORIZATION MUST BE OBTAINED FROM SEALEVEL SYSTEMS BEFORE
RETURNED MERCHANDISE WILL BE ACCEPTED. AUTHORIZATION CAN BE OBTAINED BY
CALLING SEALEVEL SYSTEMS AND REQUESTING A RETURN MERCHANDISE
AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER.
. The latest software updates, and newest manuals are available via our FTP site
.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 9
Page 12

Appendix C - Electrical Interface
Appendix C - Electrical Interface
RS-232
Quite possibly the most widely used communication standard is RS-232. This implementation has been defined and
revised several times and is often referred to as RS-232 or EIA/TIA-232. It is defined by the EIA as the Interface
between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit- Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data
Interchange. The mechanical implementation of RS-232 is on a 25 pin D sub connector. RS-232 is capable of
operating at data rates up to 20 Kbps at distances less than 50 ft. The absolute maximum data rate may vary due to
line conditions and cable lengths. RS-232 often operates at 38.4 Kbps over very short distances. The voltage levels
defined by RS-232 range from -12 to +12 volts. RS-232 is a single ended or unbalanced interface, meaning that a
single electrical signal is compared to a common signal (ground) to determine binary logic states. A voltage of +12
volts (usually +3 to +10 volts) represents a binary 0 (space) and -12 volts (-3 to -10 volts) denotes a binary 1 (mark).
The RS-232 and the EIA/TIA-574 specification defines two type of interface circuits, Data Terminal Equipment
(DTE) and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment (DCE). The Sealevel Systems adapter is a DTE interface.
RS-422
The RS-422 specification defines the electrical characteristics of balanced voltage digital interface circuits. RS-422
is a differential interface that defines voltage levels and driver/receiver electrical specifications. On a differential
interface, logic levels are defined by the difference in voltage between a pair of outputs or inputs. In contrast, a
single ended interface, for example RS-232, defines the logic levels as the difference in voltage between a single
signal and a common ground connection. Differential interfaces are typically more immune to noise or voltage
spikes that may occur on the communication lines. Differential interfaces also have greater drive capabilities that
allow for longer cable lengths. RS-422 is rated up to 10 Megabits per second and can have cabling 4000 feet long.
RS-422 also defines driver and receiver electrical characteristics that will allow 1 driver and up to 32 receivers on
the line at once. RS-422 signal levels range from 0 to +5 volts. RS-422 does not define a physical connector.
RS-485
RS-485 is backwardly compatible with RS-422; however, it is optimized for party line or multi-drop applications.
The output of the RS-422/485 driver is capable of being Active (enabled) or Tri-State (disabled). This capability
allows multiple ports to be connected in a multi-drop bus and selectively polled. RS-485 allows cable lengths up to
4000 feet and data rates up to 10 Megabits per second. The signal levels for RS-485 are the same as those defined
by RS-422. RS-485 has electrical characteristics that allow for 32 drivers and 32 receivers to be connected to one
line. This interface is ideal for multi-drop or network environments. RS-485 tri-state driver (not dual-state) will
allow the electrical presence of the driver to be removed from the line. Only one driver may be active at a time and
the other driver(s) must be tri-stated. RS-485 can be cabled in two ways, two wire and four wire mode. Two-wire
mode does not allow for full duplex communication, and requires that data be transferred in only one direction at a
time. For half-duplex operation, the two transmit pins should be connected to the two receive pins (Tx+ to Rx+ and
Tx- to Rx-). Four wire mode allows full duplex data transfers. RS-485 does not define a connector pin-out or a set
of modem control signals. RS-485 does not define a physical connector.
RS-530 / 530A
RS-530 (a.k.a. EIA-530) compatibility means that RS-422 signal levels are met, and the pin-out for the DB-25
connector is specified. The EIA (Electronic Industry Association) created the RS-530 specification to detail the
pin-out, and define a full set of modem control signals that can be used for regulating flow control and line status.
The major difference between RS-530 and RS-530A lies in the modem control interface signals. In RS-530 all
signals are differential, in RS-530A signals DTR, DSR, DCD are single ended. The RS-530 specification defines
two types of interface circuits, Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment (DCE).
The Sealevel Systems adapter is a DTE interface.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 10
Page 13

Appendix C - Electrical Interface
V.35
V.35 is a standard defined by ITU (formerly CCITT) that specifies an electrical, mechanical, and physical interface
that is used extensively by high-speed digital carriers such as AT&T Dataphone Digital Service (DDS). ITU V.35 is
an international standard that is often refereed to as Data Transmission at 48 Kbps Using 60 - 108 KHz Group-Band
Circuits. ITU V.35 electrical characteristics are a combination of unbalanced voltage and balanced current mode
signals. Data and clock signals are balanced current mode circuits. These circuits typically have voltage levels from
0.5 Volts to -0.5 Volts (1 Volt differential). The modem control signals are unbalanced signals and are compatible
with RS-232. The physical connector is a 34-pin connector that supports 24 data, clock and control signals. The
physical connector is defined in the ISO-2593 standard. ITU V.35 specification defines two types of interface
circuits, Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment (DCE). The Sealevel Systems
adapter is a DTE interface.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 11
Page 14

Appendix D – Compliance Notices
Appendix D - Compliance Notices
Federal Communications Commission Statement
FCC - This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for Class A digital device, pursuant to
Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in such case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own ex pense.
EMC Directive Statement
Products bearing the CE Label fulfill the requirements of the EMC directive (89/336/EEC) and of
the low-voltage directive (73/23/EEC) issued by the European Commission.
To obey these directives, the following European standards must be met:
• EN55022 Class A - “Limits and methods of measurement of radio interference characteristics of
information technology equipment”
• EN55024-‘Information technology equipment Immunity characteristics Limits and methods of
measurement.
• EN60950 (IEC950) - “Safety of information technology equipment, including electrical business
equipment”
Warning
This is a Class A Product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case
the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Always use cabling provided with this product if possible. If no cable is provided or if an alternate cable is required,
use high quality shielded cabling to maintain compliance with FCC/EMC directives.
U.S. Patent Nos. 4,603,320 4,686,506 4,972,470
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 12
Page 15

Warranty
Warranty
Sealevel Systems, Inc. provides a limited lifetime warranty. Should this product fail to be
in good working order at any time during this period, Sealevel Systems will, at it’s option,
replace or repair it at no additional charge except as set forth in the following terms. This
warranty does not apply to products damaged by misuse, modifications, accident or
disaster.
Sealevel Systems assumes no liability for any damages, lost profits, lost savings or any other incidental or
consequential damage resulting from the use, misuse of, or inability to use this product. Sealevel Systems will not
be liable for any claim made by any other related party.
RETURN AUTHORIZATION MUST BE OBTAINED FROM SEALEVEL SYSTEMS BEFORE
RETURNED MERCHANDISE WILL BE ACCEPTED. AUTHORIZATION CAN BE OBTAINED BY
CALLING SEALEVEL SYSTEMS AND REQUESTING A RETURN MERCHANDISE
AUTHORIZATION (RMA) NUMBER.
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated
2779 Greenville Highway
P.O. Box 830
Liberty, SC 29657 USA
(864) 843-4343 FAX:(864) 843-3067
www.sealevel.com
email: support@sealevel.com
Technical Support is available from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. Eastern time.
Monday - Friday
Trademarks
Sealevel Systems, Incorporated acknowledges that all trademarks referenced in this manual are the service mark,
trademark, or registered trademark of the respective company.
PC-ACB.MP is a trademark of Sealevel Systems, Incorporated.
Sealevel Systems PC-ACB.MP Page 13
 Loading...
Loading...