Page 1

ICE MAKER
POCKET GUIDE
“I” SERIES CUBE
ICE MAKERS
IMI CORNELIUS
One Cornelius Place
Anoka, MN 55303
1–800–238–3600
Rev 9/18/95
TD 2023/1/95
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
introduction 1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Original Owner, End-user responsibility 1. . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Plate Locations 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Model and Serial Number Defined 2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Number Defined After January 1, 1995 3. . . . . . . . . .
Electrical Specification 4-9. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Remote Condenser 10. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ICE CAPACITY INFORMATION 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ice Capacity 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ice Production Check 11. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
ADJUSTMENT OF ICE BRIDGE THICKNESS 12. . . . . . . .
Ice production capacities and charts 14-29. . . . . . . . . . . .
IAC322/IAC330 14. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IWC322/IWC330 15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IAC522/IAC530 16. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IWC522/IWC530 17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IAC630 18. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IWC630 19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IRC630 20. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IAC830 21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IWC830 22. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IRC830 23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IAC1230 24. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IWC1230 25. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IRC1230 26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IAC1448 27. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IWC1448 28. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
IRC1448 29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sequence of Operation 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Component Functions 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Board 30. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LED Indicators 31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
LED status indicator chart 32-34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reset Operation 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage Selector Switch 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Stacking Cable 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Test Plug 34. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Dump Cycle Options 35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Condenser Fan Cycling Control (Intergal Condenser) 36.
Harvest Safety Termination 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Circuit Board Diagnosis 36. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PAGE
i
TD 202
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS (CONT’D)
Sensors 37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sensor [Thermistor] Diagnosis 38. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Evaporator Switches 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Switch Notes 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Voltage Checks 39. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Water Regulating Valve 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
High Pressure Safety Switch 40. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Float Valve with Flow Washer 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Stem Valves 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Thermostatic Expansion Valves 41. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
diagnosis 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Starving TXV - Product Symptoms 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Flooding TXV - Product Symptoms 42. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Head Pressure Control Valve [Headmaster} Fan Cycle Switch
Contactor Compressor 44. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compressor & Starting Component Check-Out Procedure 45
Relay 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Capacitors 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Compressor 46. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Moisture Contamination 47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Wiring Diagrams 49-54. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Troubleshooting 55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cleaning Procedures 59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Prep – Cleaning 59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cleaning the Water System & Evaporator 59. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sanitizing Procedures 60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
(Remote Units Only) 43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Potential – 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Current – 45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PAGE
TD 202
ii
Page 4

introduction
This guide is published as an aid to the Service Technician. It is not
intended to replace the service manual. In it you will find useful information not found in the service manual. This information will
help you more quickly identify specific problems, however not all
problems or situations may be listed. We appreciate your comments
or suggestions, or if you have a specific problem not addressed in
this guide or service manual.
Please feel free to contact our service department at:
IMI CORNELIUS
One Cornelius Place
Anoka, MN 55303
1–800–554–3526
The warranty on Cornelius icemakers begins on the date of installation, as reported on the warranty registration card to the original
owner/user. If no warranty card is received by the factory, the date
of shipment from the factory will determine the start of the warranty.
Warranty labor will be paid per the labor rate guide and is subject to
change without notice. Call the Service Department for a copy of the
current Labor Rate Guide and/or applicable Warranty Document
Copy.
ORIGINAL OWNER, END-USER RESPONSIBILITY
1. To verify the equipment installation date by the return
of the warranty registration card to the factory within
five days of the installation.
2. To pay freight or handling charge.
3. To pay for service labor and/or parts required to correct improperly installed equipment. Installation must
comply with the installation instructions.
4. To pay for normal maintenance, adjustments and
cleaning.
5. To pay for service labor and/or parts required to correct unit modification or the use of non-approved remote condensers.
6. To pay for service labor and/or parts required because
of neglect, abuse, misuse, accident, fire, flood, freezing or any act of God.
7. To pay for mileage, truck charges, travel time, premium labor for holidays, weekends or after hours
work, flat rate service call charges, miscellaneous tool
charges, use of diagnostic meters or equipment and all
material not listed on the Warranty Time Rate Guide.
Rev 9/18/95
1 TD 2023/1/95
Page 5

Serial Plate Locations
Exterior: Left side, Lower Front corner.
Interior: Firewall, Front.
Model and Serial Number Defined
IAC 1230
IAC1230
Product
Identifica-
tion
94 A C E 0000
Year
(the first 2
digits
indicates
year of
produc-
tion)
Month of production code will be:
Note: The letter (I) is not used to avoid being confused with the
number(1)
Product Code:
A = Accessory* D = Dispenser (motel/hotel)
B = Bin (storage) E = External condenser (Remote)
C = Cuber F = Flaker
* Any accessory determined to be required to have a serial number.
A=Air
Cooled
Condenser
W=Water
Cooled
R=Remote
Month
Production
A = January G = July
B = February H = August
C = March J = September
D = April K = October
E = May L = November
F = June M = December
Cuber Series
Product
Code
Manufac-
turing
Tracking
Code
30” Wide
3
5
6
8
10
12
14
Cabinet
22 = 22”
Wide
48 = 48”
wide
Unit
Serial
Number
2TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 6

Serial Number Defined
after January 1, 1995
AF 95 01 BC 0000
Eng
change
level
Engineering change level can be either 1 or 2 digits depending
on the revision level.
Month of production code will be:
01 = January 07 = July
02 = February 08 = August
03 = March 09 = September
04 = April 10 = October
05 = May 11 = November
06 = June 12 = December
Note: The Month must always be 2 digits.
Product Code:
BA = Accessory* BD = Dispenser (motel/hotel)
BB = Bin (storage) BE = External condenser (Remote)
BC = Cuber BF = Flaker
* Any accessory determined to be required to have a serial number.
year Month Product
Code
Unit
Serial
Number
Rev 9/18/95
3 TD 2023/1/95
Page 7
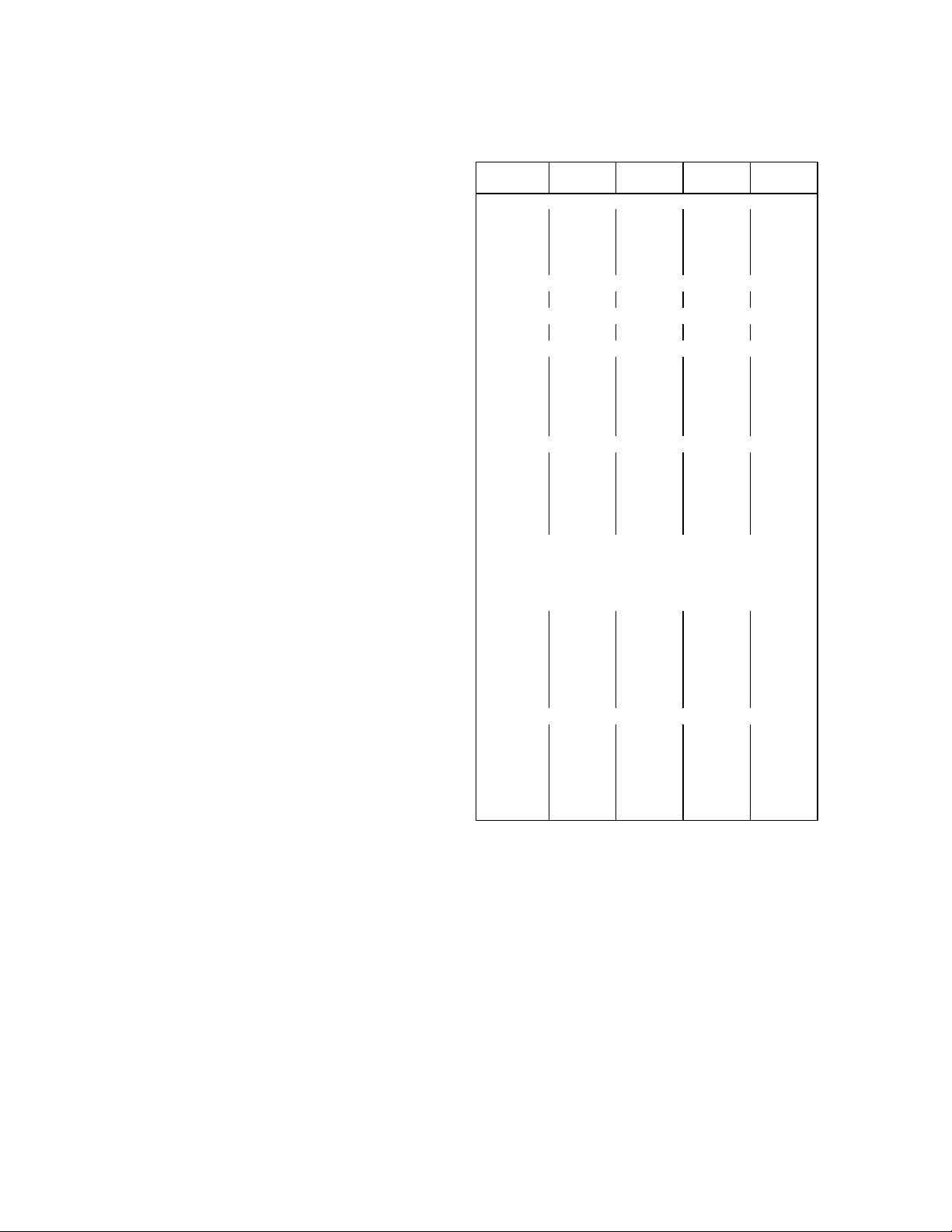
Electrical Specification
MODEL
UNIT
Volts 115 115 115 115
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
No. Wires 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground
MIN. CIRCUIT
Amps 20 20 20 20
MAX FUSE SIZE (HVAC CIRCUIT BREAKER REQ)
Amps 20 20 20 20
REFRIGERANT
Type
Weight
(oz)
Weight (g) 482 425 737 652
COMPRESSOR
Volts 115 115 115 115
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
LRA 51 51 59 59
RLA 11.5 11.5 11.6 11.6
CONDENSER FAN MOTOR (Air-Cooled System
Y OR
onl
AIR CIRCULATION FAN MOTOR (Water-Cooled
and Remote Systems only)
Volts 115 115 115 115
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
Amps
Running
Watts 50 6 50 6
WATER PUMP
Volts 115 115 115 115
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
Amps
Running
HP 1/40 1/40 1/40 1/40
IAC322/330IWC322/330IAC522/530IWC522/5
R404a
(HP62)
17 15 26 23
1.7 0.38 1.75 0.38
0.88 0.88 0.76 0.88
R404a
(HP62)
R404a
(HP62)
R404a
(HP 62)
30
4TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 8
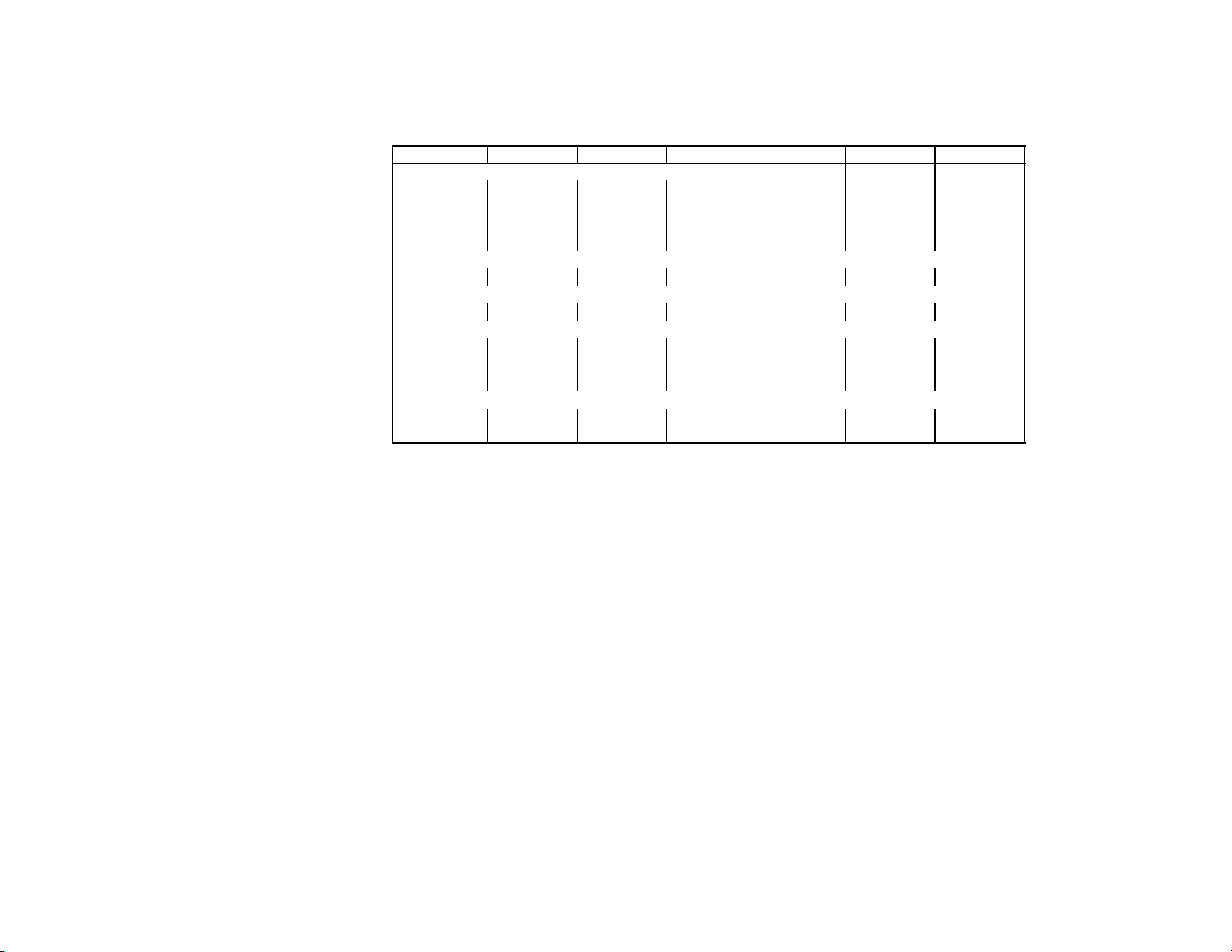
Rev 9/18/95
5 TD 2023/1/95
MODEL IAC630 IWC630 IRC630 IAC830 IWC830 IRC830
UNIT ELEC.
Volts 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
No. Wires 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground
MIN. CIRCUIT
Amps 20 20 20 20 20 20
MAX FUSE SIZE (HVAC CIRCUIT BREAKER REQUIRED)
Amps 20 20 20 20 20 20
REFRIGERANT
Type R404a(HP62) R404a(HP62) R404a(HP62) R404a(HP 62) R404a(HP 62) R404a(HP 62)
Weight (oz) 43 35 170 55 33 170
Weight (g) 1219 992 4820 1559 936 4820
COMPRESSOR
Volts 230 230 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Page 9
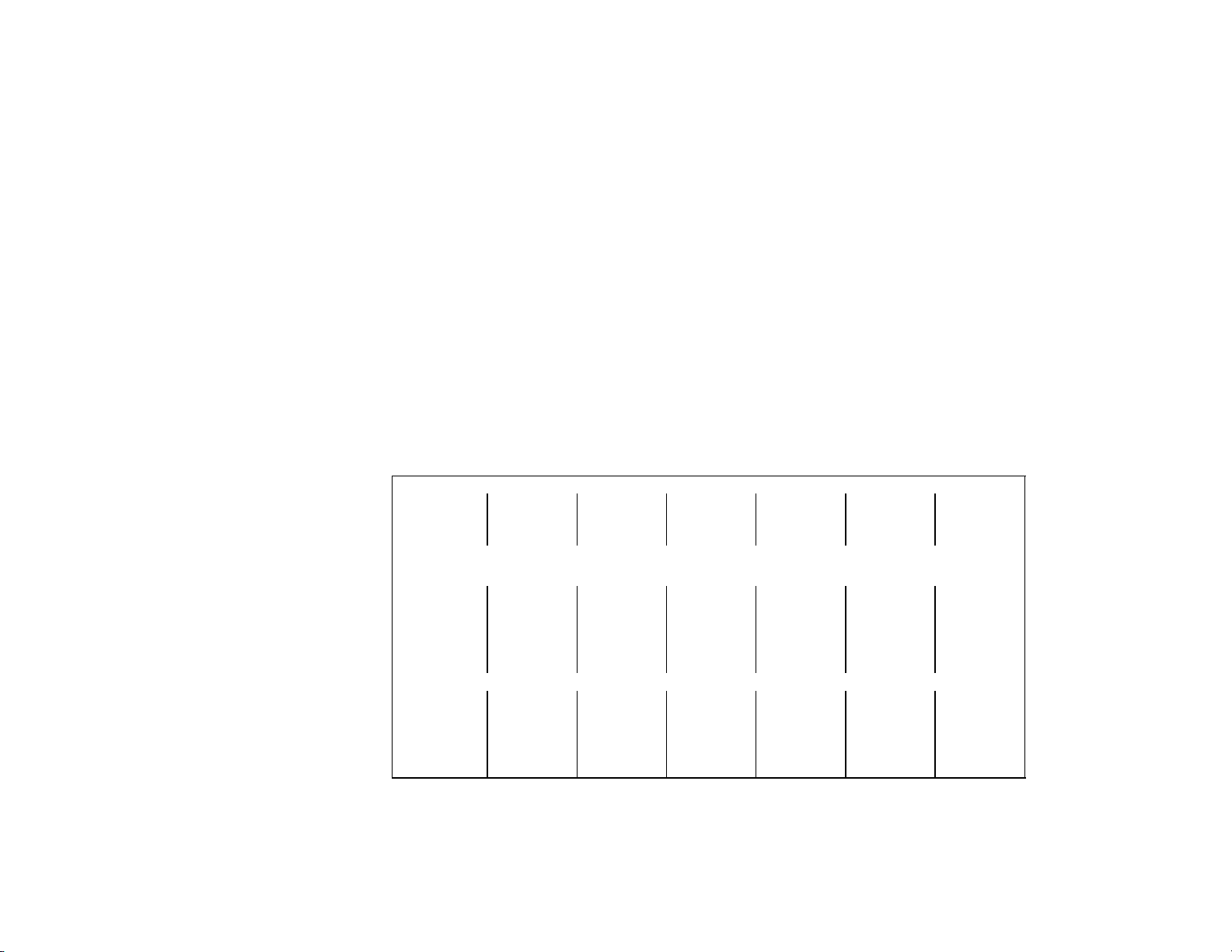
COMPRESSOR (CONT’D)
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
LRA 69 69 69 61 61 61
RLA 8.8 8.8 8.8 12.5 12.5 12.5
CONDENSER FAN MOTOR (Air-Cooled System only) or
AIR CIRCULATION FAN MOTOR (Water-Cooled and Remote Systems only)
Volts 230 230 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
6TD 202 3/1/95
Amps Running 1.09 0.36 0.36 1.09 0.36 0.36
Watts 75 6 6 75 6 6
WATER PUMP
Volts 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Rev 9/18/95
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
Amps Running 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5
HP 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30
All Product Supply Voltages Should Read 208/230 –5%, +10%
Page 10
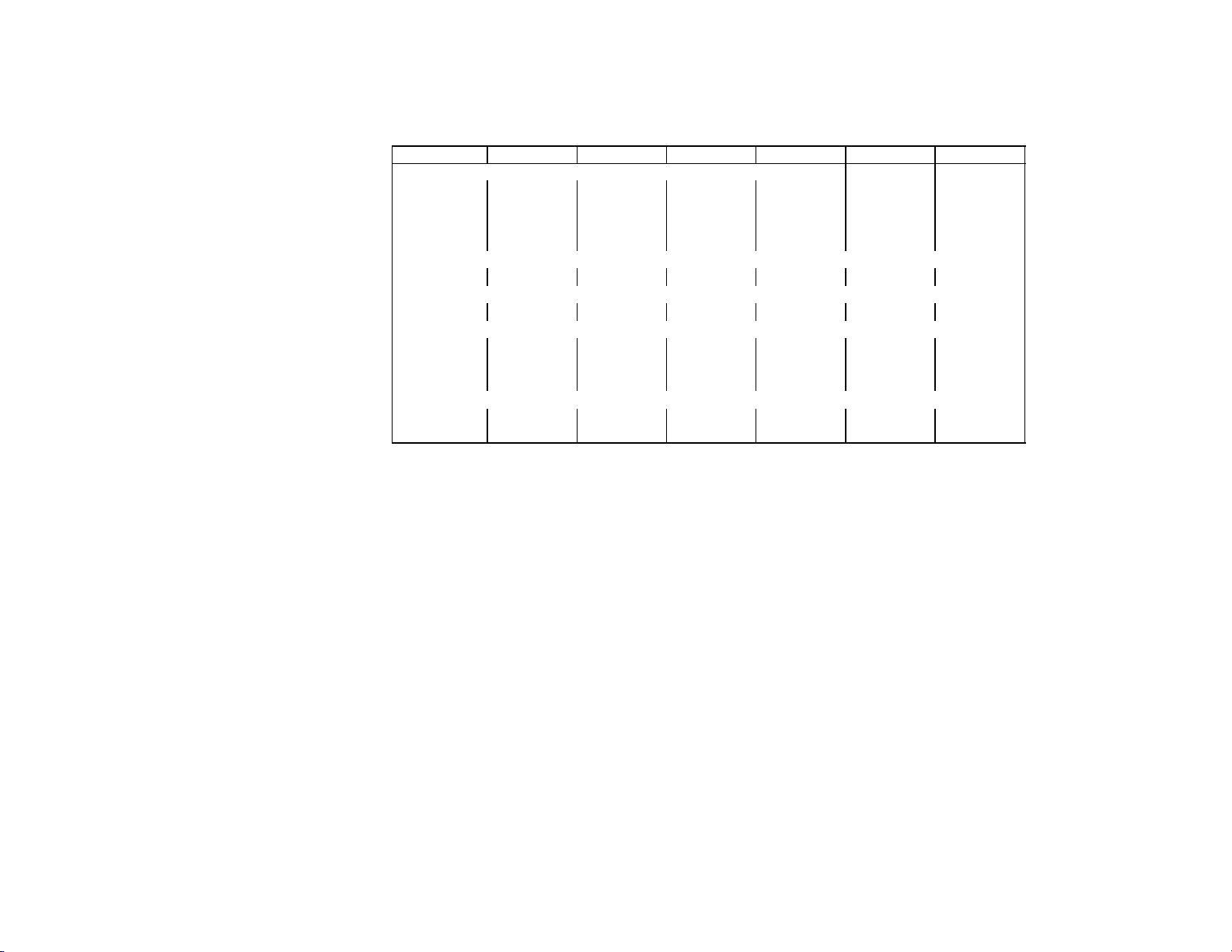
Rev 9/18/95
7 TD 2023/1/95
MODEL IAC1230 IWC1230 IRC1230 IAC1448 IWC1448 IRC1448
UNIT ELEC.
Volts 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
No. Wires 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground
MIN. CIRCUIT
Amps 20 20 20 25 25 25
MAX FUSE SIZE (HVAC CIRCUIT BREAKER REQUIRED)
Amps 20 20 20 25 25 25
REFRIGERANT
Type R404a(HP62) R404a(HP62) R404a(HP62) R404a(HP 62) R404a(HP 62) R404a(HP 62)
Weight (oz) 49 45 210 92 44 250
Weight (g) 1389 1276 5954 2608 1247 7088
COMPRESSOR
Volts 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Page 11
COMPRESSOR (CONT’D)
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
LRA 96 96 96 95.6 95.6 95.6
RLA 13.5 13.5 13.5 23.9 23.9 23.9
CONDENSER FAN MOTOR (Air-Cooled System only) or
AIR CIRCULATION FAN MOTOR (Water-Cooled and Remote Systems only)
Volts 230 230 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
8TD 202 3/1/95
Amps Running 0.89 X 2 0.36 0.36 0.4 0.36 0.36
Watts 50 W X 2 6 W 6 W 1/15 HP 6 W 6 W
WATER PUMP
Volts 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230 208/230
Phase 1 1 1 1 1 1
Rev 9/18/95
Hertz 60 60 60 60 60 60
Amps Running 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5
HP 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30
All Product Supply Voltages Should Read 208/230 –5%, +10%
Page 12
MODEL IRC630 IRC830. IRC1230 IRC1448
UNIT
Volts 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
No. Wires 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground 2+ground
MIN. CIRCUIT
Amps 20 20 20 25
MAX FUSE SIZE (HVAC CIRCUIT BREAKER REQUIRED)
Amps 20 20 20 25
REFRIGERANT
Type
Weight
(oz)
Weight (g) 4820 4820 5954 7088
COMPRESSOR
Volts 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
LRA 69 61 96 95.6
RLA 8.8 12.5 13.5 23.9
AIR CIRCULATION FAN MOTOR
Volts 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
Amps
Running
Watts 6 6 6 6
WATER PUMP
Volts 230 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60 60
Amps
Running
HP 1/30 1/30 1/30 1/30
R404a
(HP62)
170 170 210 250
0.36 0.36 0.36 0.36
0.5 0.5 0.5 0.5
R404a
(HP62)
R404a
(HP62)
R404a
(HP 62)
Rev 9/18/95
9 TD 2023/1/95
Page 13

Remote Condenser
MODEL CR800 CR1200 CR1400
Volts 230 230 230
Phase 1 1 1
Hertz 60 60 60
Amps 1.0 1.0 1.0
Output, HP 1/6 1/6 1/6
Max. fuse size, Amps (HVAC
circuit breaker
required)
20 20 20
10TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 14

ICE CAPACITY INFORMATION
Ice Capacity
Ice capacity of any ice maker is affected by many operating conditions, such as water and air temperature and location factors. Please
review the capacity tables in this manual for average 24–hour capacity under various conditions.
NOTE: All printed capacity ratings are 10% except 50 HZ
units these products have 12% increase in cycle time
and capacity decrease of approximately 17%.All
printed capacity ratings are 10% except 50 HZ
units these products have 12% increase in cycle time
and capacity decrease of approximately 17%.
Ice Production Check
If air cooled, take air temperature at the intake of the condenser, 2I
from the condenser fins.. Incoming water temperature at the outlet
of the “float” valve.*
Cycle time (CT) = freeze time plus harvest time, in minutes and seconds. 1440 divided by CT = number of cycles per 24 hours.
Measure weight of ice from one cycle in pounds and fractions of a
pound.
Example: Weight/cycle x cycles/day = total production/24 hrs.
* If water cooled be certain water regulator valve is set to maintain
300/310 PSI head pressure.
Compare to the production tables.
Rev 9/18/95
11 TD 2023/1/95
Page 15
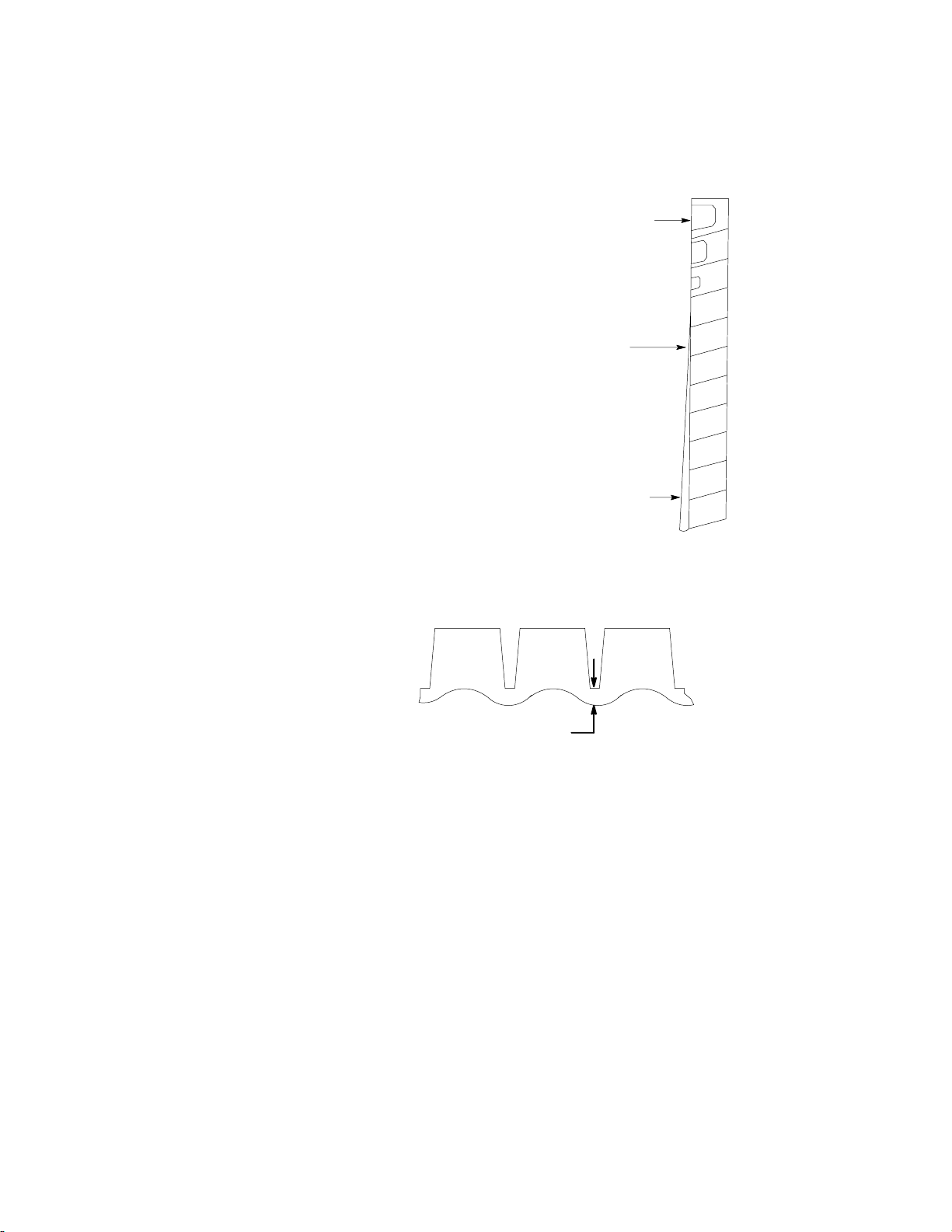
ADJUSTMENT OF ICE BRIDGE
THICKNESS
TOP ROW
3/8” - 5/8” DIM-
PLE
CENTER
1/8” BRIDGE
BOTTOM 2
ROWS
3/16” - 1/4”
BRIDGE
For optimum ice production and maximum cube separation, the ice
connecting the individual cubes should be a minimum of 1/8”
(.32cm) thick at the center area of the ice waffle.
BRIDGE 1/8I (0.32 CM)
It is normal for the ice slab to be slightly thicker at the bottom and
taper off in a slight wedge pattern at the top. The top row of cubes
must have a complete pattern of ice on all four sides and the back
wall. Remember, when you operate the product with the panels off
during testing the additional heat at the top of the evaporator will
cause thinner ice at the top than when the panels are in place.
12TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 16

Should a different thickness of the bridge be desired, it will be required to adjust the ice thickness “POT”, located on the circuit
board, as follows:
1. Thinner Bridge – turn the ice thickness “pot” adjustment screw CW one full turn. Allow two cycles
before determining if additional adjustments are required.
2. Thicker Bridge – turn the ice thickness “pot” adjusting
screw CCW one full turn. Allow two cycles before
determining if additional adjustments are required.
NOTE: Never judge the thickness of the ice from the first
batch of the ice produced – the first cycle is a bal-
ance cycle. Always wait for the second cycle before
making any adjustments.
Rev 9/18/95
13 TD 2023/1/95
Page 17

IAC322/IAC330
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
70 50 200 39 9:5 150 105 1:1 2.4 325
80 70 228 42 12:4 160 110 0:9 2.4 260
14TD 202 3/1/95
90 70 267 44 14:3 183 133 0:7 2.5 240
90 80 270 45 15.1 181 130 0.7 2.4 220
100 70 299 47 19:8 199 142 0:6 2.8 200
Rev 9/18/95
WATER
TEMP
_F
ICE PRODUCTION CAPACITIES AND CHARTS
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 18

IWC322/IWC330
Rev 9/18/95
15 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 300 40 12:1 143 103 0:9 2.8 310
80 70 300 42 15:3 160 116 1:1 2.8 245
90 70 300 43 16:2 160 118 1:2 2.9 240
90 80 303 44 16.4 173 120 1.1 2.8 230
100 70 300 44 16:3 160 117 1:3 2.6 215
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 19

IAC522/IAC530
AMBIENT
TEMP
16TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 320 46 20:9 220 120 0:6 5.2 350
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 220 38 12:5 155 95 1.0 5.1 540
80 70 250 42 14:6 175 111 0:9 4.8 450
90 70 275 41 17:4 195 120 0:7 5.1 405
90 80 290 45 17.9 200 120 0.6 5.0 387
Page 20

IWC522/IWC530
Rev 9/18/95
17 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 323 44 11:3 156 106 1:3 4.3 490
80 70 327 45 13:7 168 115 1.2 4.4 425
90 70 326 45 13:8 173 117 1:1 4.3 420
90 80 328 47 15.2 184 127 1:1 4.3 384
100 70 327 45 13:9 175 119 1:1 4.3 415
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 21

IAC630
AMBIENT
TEMP
18TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 333 43 17:1 200 125 1:1 6.0 475
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 225 34 8:4 148 88 1:5 5.4 755
80 70 261 37 11:3 166 101 1.2 5.6 640
90 70 296 40 12:6 183 113 1:1 5.6 590
90 80 297 40 13:2 184 113 1:0 5.5 560
Page 22

IWC630
Rev 9/18/95
19 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 299 35 10:1 143 86 1:6 5.8 715
80 70 299 38 12:4 152 92 1.4 6.0 622
90 70 300 38 12:3 153 93 1:4 5.9 620
90 80 304 39 14:0 166 100 1:2 6.0 570
100 70 300 38 12:2 152 93 1:4 5.8 615
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 23

IRC630
AMBIENT
TEMP
20TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 333 43 17:1 200 125 1:1 6.0 475
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 225 34 8:4 148 88 1:5 5.2 755
80 70 261 37 11:3 166 101 1.2 5.6 640
90 70 296 40 12:6 183 113 1:1 5.6 590
90 80 297 40 13:2 184 113 1:0 5.5 560
Page 24

IAC830
Rev 9/18/95
21 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 253 29 7:6 163 83 1:5 5.3 840
80 70 293 33 9:0 187 97 1.0 5.2 745
90 70 335 36 11:5 210 111 0:9 5.8 680
90 80 339 37 12:0 209 111 0:9 5.8 645
100 70 379 40 13:8 232 126 0:8 6.0 595
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 25

IWC830
AMBIENT
TEMP
22TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 295 34 11:1 175 93 1:3 5.9 690
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 298 32 8:6 154 81 1:5 5.6 795
80 70 296 34 10:2 163 86 1.3 5.7 715
90 70 295 34 10:7 164 87 1:3 5.9 710
90 80 298 37 12:1 166 88 1:2 6.0 650
Page 26

IRC830
Rev 9/18/95
23 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 253 29 7:6 163 83 1:5 5.3 840
80 70 293 33 9:0 187 97 1.0 5.2 745
90 70 335 36 11:5 210 111 0:9 5.8 680
90 80 339 37 12:0 209 111 0:9 5.8 645
100 70 379 40 13:8 232 126 0:8 6.0 595
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 27

IAC1030
AMBIENT
TEMP
24TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 349 41 18.7 215 100 1.0 10.8 793
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 240 33 13.5 164 75 1.7 11.6 1101
80 70 276 36 14.2 177 83 1.4 10.5 969
90 70 312 38 15.9 196 91 1.1 10.5 890
90 80 313 38 16.8 198 91 1.1 10.5 840
Page 28

IWC1030
Rev 9/18/95
25 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 296 34 13.0 155 73 1.8 10.7 1046
80 70 297 36 15.3 161 75 1.7 10.9 925
90 70 297 36 15.7 161 77 1.5 11.0 920
90 80 300 36 17.9 175 81 1.4 11.0 823
100 70 297 41 15.8 164 77 1.5 11.0 915
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 29

IRC1030
AMBIENT
TEMP
26TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 349 41 18.7 215 100 1.0 10.8 793
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 240 33 13.5 164 75 1.7 1.6 1101
80 70 276 36 14.2 177 83 1.4 10.5 969
90 70 312 38 15.9 196 91 1.1 10.5 890
90 80 313 38 16.8 198 91 1.1 10.5 840
Page 30

IAC1230
Rev 9/18/95
27 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 231 30 8:8 175 75 1:5 8.9 1249
80 70 266 33 11:4 191 84 1.1 9.5 1090
90 70 296 35 13:6 211 95 1:0 10.1 1000
90 80 295 36 14:5 211 93 0:9 10.1 948
100 70 331 38 16:3 232 105 0:9 10.3 865
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 31

IWC1230
AMBIENT
TEMP
28TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 324 30 14:0 180 76 1:3 10.9 1025
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 336 30 10:1 187 73 1:4 9.8 1221
80 70 324 30 13:2 177 76 1.3 10.7 1065
90 70 330 33 14:0 180 76 1:3 10.9 1030
90 80 323 32 14:8 180 78 1:3 10.9 973
Page 32

IRC1230
Rev 9/18/95
29 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 231 30 8:8 175 75 1:5 8.9 1249
80 70 266 33 11:4 191 84 1.1 9.5 1090
90 70 296 35 13:6 211 95 1:0 10.1 1000
90 80 295 36 14:5 211 93 0:9 10.1 948
100 70 331 38 16:3 232 105 0:9 10.3 865
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 33

IAC1448
AMBIENT
TEMP
30TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 352 38 15:8 242 106 0:8 13.1 1140
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 246 31 10:1 185 79 1:3 12.1 1525
80 70 280 34 11:8 201 88 1.3 12.3 1355
90 70 315 35 13:2 220 97 1:1 12.6 1275
90 80 317 37 13:7 222 98 1:1 12.4 1205
Page 34

IWC1448
Rev 9/18/95
31 TD 2023/1/95
AMBIENT
TEMP
_F
WATER
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
70 50 316 32 9:9 180 73 1:7 12.1 1505
80 70 318 35 11:9 188 77 1.4 12.7 1370
90 70 318 36 12:2 190 78 1:3 12.8 1360
90 80 317 37 13:0 194 80 1:3 12.6 1270
100 70 316 36 12:7 189 77 1:4 13.1 1335
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
Page 35

IRC1448
AMBIENT
TEMP
32TD 202 3/1/95
100 70 352 38 15:8 242 106 0:8 13.3 1150
Rev 9/18/95
FREEZE CYCLE HARVEST CYCLE
WATER
_F
TEMP
_F
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
HEAD
PRESSURE
Psig
SUCTION
PRESSURE
Psig
CYCLE
TIME
Min:Sec
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/Cycle
AVERAGE
ICE
WEIGHT
lb/day
70 50 246 31 10:1 185 79 1:3 12.1 1535
80 70 280 34 11:8 201 88 1.3 12.4 1365
90 70 315 35 13:2 220 97 1:1 12.7 1285
90 80 317 37 13:7 222 98 1:1 12.5 1215
Page 36

“I” SERIES
SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
When the on off clean switch is pushed to the on position the compressor will start after a 2 second delay. The fan motor and pump are
delayed. The condenser fan motor on integral air cooled unites will
start when the condenser temperature rises to approximately 100° F.
The water pump will start when the suction line temperature reaches
approximately 25°F. Temperature information is transmitted to the
control board thru thermistor sensors. The unit is now in the freeze
cycle. If after approximately 6 minutes of operation the suction line
temperature is not below 40°F, the unit will shut down and show an
error light on the control board. When the harvesting set point temperature is reached, the circuit board will switch to the harvest cycle.
At the start of the harvest cycle the condenser fan motor will shut off
and the Dump Valve and Hot Gas Valve will open. The Water Pump
will shut down in approximately 15 seconds. Harvest will continue
for approximately 90 seconds. when the Ice is harvested the evaporator curtain opens and closes breaking a magnetic field of the evaporator proximity switch which signals the circuit board to switch
back to the Freeze Cycle.
When the Evaporator Curtain is held open, in the freeze cycle,
breaking the Evaporator Switch Magnetic Field for 5 to 8 seconds,
the circuit board is signaled that a full bin condition has been
reached , and shuts down the unit.
COMPONENT FUNCTIONS
Circuit Board
The circuit board controls the operation of the Ice Maker through information it receives from Thermistor Sensors and Proximity (magnetic) Switches.
Rev 9/18/95
33 TD 2023/1/95
Page 37
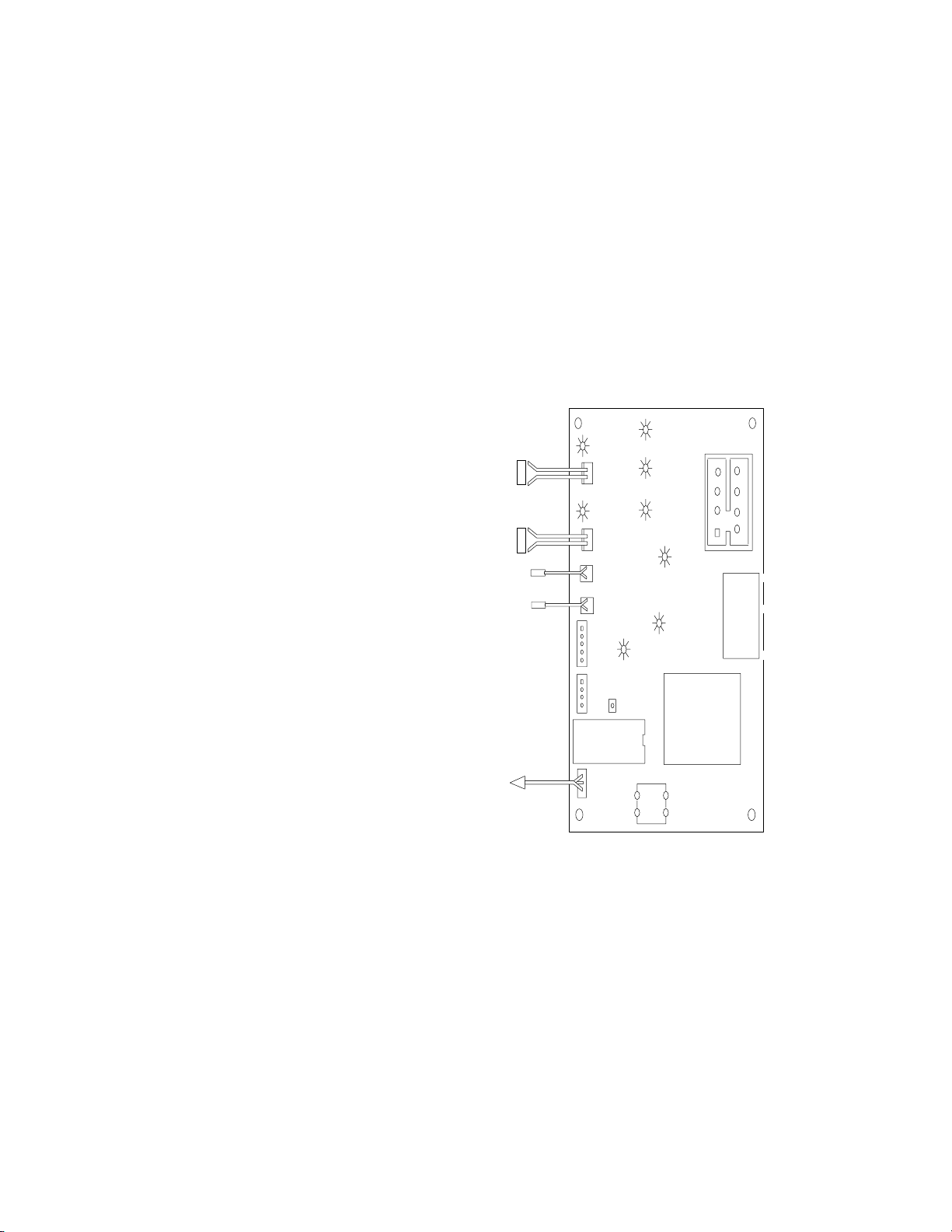
LED Indicators
The LEDs are board circuit indicators. If the LED in the functional
board circuit is complete, check component.
Example: Contactor does not energize and LED is “ON”, board cir-
cuit is OK. Check contactor, coil, leads, & connections.
Yellow;
S Evaporator switch(s) (proximity)
Green;
S D15 Water dump valve
S D14 Compressor contactor
S D12 Water Pump
S D11 Hot Gas Valve
S D6 Condenser Fan (cycles on &
off with fan)
Red D5;
Error in system operation. Product shut down.
Water
DĆ15
RH Evap. Switch
N
S
LH Evap. Switch
N
S
Condenser Sensor
Suction Line Sensor
white
Brown
DĆ13
YL
YL
DĆ10
Condenser
plug
Suction plug
Test
Plug
Options
Plug
RH Evap.
LH Evap.
DĆ14
DĆ12
RD
DĆ5
Error
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
Dump
Valve
Contactor
GR
DĆ11
Fan
GR
Water
Pump
DĆ6
Hot Gas
Transformer
7
8
5
6
3
4
2
1
230v
Voltage
neutral
Selector
Switch
115v
To Stacked
(if required)
Micro Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
Unit
Manual
Harvest
Switch
34TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 38

LED STATUS INDICATOR CHART
D6 Green LED Condenser Fan
D10 Yellow LED Left Water Curtain
D11 Green LED Hot Gas Valve
D12 Green LED Water Pump
D13 Yellow LED Right Water Curtain
D14 Green LED Compressor Contactor
D5 Red LED Error
D15 Green LED Dump Valve
Curtain Open
Yellow LED
D13
D10
D6
D14
D13
D10
D6
D12
D14
D13
D10
Yellow LED
Green LED
Green LED
Yellow LED
Yellow LED
Green LED
Green LED
Green LED
Yellow LED
Yellow LED
Off Right evaporator curtain
open
Off Left evaporator curtain open
Pre-Chill Mode
(on or
Condenser fan cycles on &
off)
off depending upon conĆ
denser temperature
(on) Compressor contactor acĆ
tive - Compressor running
(on) Right evaporator curtain
closed
(on) Left evaporator curtain
closed (only if unit has two
evaporators)
Ice Making Mode
(on or
Condenser fan cycles on
off)
and off depending upon
condenser temperature
(on) Water pump active
(on) Compressor contactor acĆ
tive - compressor running
(on) Right evaporator curtain
closed
(on) Left evaporator curtain
closed (only if unit has two
evaporators)
Table continued on page. 36
Rev 9/18/95
35 TD 2023/1/95
Page 39

D11
D12
D14
D15
D13
D10
D5
D5
D5
Green LED
Green LED
Green LED
Green LED
Yellow LED
Yellow LED
Red LED
Red LED
Red LED
Harvest Mode
(on) Three seconds after water
dump valve becomes acĆ
tive, the hot gas valve beĆ
comes active
(on)
Fifteen seconds after water
15
dump valve becomes acĆ
sec.
tive, the water pump deactiĆ
vates
(on) Compressor contactor acĆ
tive - compressor running
(on)
Water dump valve becomes
15
active at the start of harvest.
sec.
Water dump valve is active
for 15 seconds
(on) Right evaporator curtain
closed. When the ice falls
and the curtain opens the
LED will turn off.
(on) Same as D13 if there is a
second (left) evaporator
Error LED
(on) EVAPORATOR OPEN
THERMISTOR CIRCUIT Ć
thermistor open / broken
wire / poor connection. Ice
maker is SHUT DOWN.
Consult service manual
(Diagnostic Section) for
trouble shooting guide.
(on) EVAPORATOR HIGH TEMP.
ERROR: Six minutes into the
Freeze cycle the suction line
temperature failed to reach
40°F or below. Ice Maker is
SHUT DOWN. Consult serĆ
vice manual (Diagnostic
Section) for trouble shooting
guide.
(on) TWO REPEATED FAILED
HARVEST CYCLES Ć No ice
drop.
Table continued on page .37
36TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 40

Error LED (cont’d)
Red LED
D5
D5
D5
Red LED
Red LED
FlashĆ
CONDENSER OPEN
ing,
THERMISTOR CIRCUIT (Air
1/sec
Cooled only) Ć Thermistor
open / broken wire / poor
connection. Ice Maker is
SHUT DOWN. Consult serĆ
vice manual (Diagnostic
Section) for trouble shooting
guide.
FlashĆ
CONDENSER LOW TEMĆ
ing,
PERATURE CONDITION. Ć
1/sec
Condenser midpoint reachĆ
es 36°F Ć Ice Maker is SHUT
DOWN.
FlashĆ
CONDENSER HIGH TEMĆ
ing,
PERATURE SAFETY SHUT
1/sec
DOWN
Reset Operation
When Cuber is functionally shut down and red “Error LED” is op-
erational, the Cuber power switch must be turned off for 5 seconds
and returned to the on position to reset the circuit board and allow
the Cuber to restart operation.
Voltage Selector Switch
1. Selector bar in center position, switch is open. Product
is inoperative
2. Selector bar in down position, selection is for 115
VAC.
3. Selector bar in up position, selection is for 230 VAC.
Stacking Cable
When stacking the “I” series cuber the connecting cable (connecting
the two (2) circuit boards) will allow: When the bottom product
shuts off on the full bin signal (or any error code) the top product will
finish the cycle it is in and will also shut down. The “I” series should
never be stacked more than two high.
Test Plug
Board manufactures check point.
DO NOT ATTEMPT ANY VOLTAGE CHECKS AT THESE PINS.
Rev 9/18/95
37 TD 2023/1/95
Page 41

Dump Cycle Options
You have the option of selecting dump cycle intervals of:
S every cycle; (Standard setting from
factory)
S every 3rd cycle;
S every 5th cycle;
S every 7th cycle.
Remember, the higher the mineral content in the water supply the
more often it will be required to dump the water and/or clean the
product if proper water treatment is not used.
Water
DĆ15
RH Evap. Switch
N
S
LH Evap. Switch
N
S
Condenser Sensor
Suction Line Sensor
To Stacked
(if required)
Brown
Unit
white
DĆ13
YL
RH Evap.
YL
DĆ10
LH Evap.
Condenser
plug
Suction plug
Test
Plug
Options
Plug
Micro Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
DĆ14
DĆ12
RD
DĆ5
Error
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
Manual
Harvest
Switch
GR
Dump
Valve
Contactor
Water
Pump
DĆ11
Fan
GR
DĆ6
Hot Gas
Transformer
7
8
5
6
3
4
2
1
230v
Voltage
neutral
Selector
Switch
115v
Sleeve Connector
Dump
Every
Cycle
Options Plug
Dump
Dump
Every
Cycle
Dump
Every
5th
7th
Cycle
Rev 9/18/95
Every
3rd
Cycle
38TD 202 3/1/95
Page 42

Condenser Fan Cycling Control
(Intergal Condenser)
The condenser fan on air-cooled cubers is cycled by the circuit
board. The condenser sensor signals the circuit board when the condenser temperature reaches 100°F (38°C) the fan starts and contin-
ues to run until the temperature is reduced to 88°F (31°C).
NOTE: There is no pressure control used to cycle the fan
motor on Intergal Air Cooled Condenser Units.
Harvest Safety Termination
After 4 minutes in the harvest mode, the safety timer in the circuit
board will terminate the harvest mode and place the Cuber back into
a freeze mode. This safety cycle will protect the evaporator etc.
should the product fail to terminate the harvest mode for any reason.
Circuit Board Diagnosis
Turn the power switch off, center position. Disconnect the proximity switches and thermistors from the circuit board. Remove a sleeve
jumper from the options terminal and place it on terminals 4 and 5
(bottom 2 pins) of the test plug. (See Illustration on page 40) Turn
the power switch to the “on” position and immediately remove the
sleeve jumper from terminals 4 and 5. The LED indicators will cycle
“on” for approximately 2 seconds each in the following sequence.
1. Red D-5 (error)*
*Will only cycle if ice thickness
(pot) is within factory setting
2. Green D-6 (Condenser fan)
3. Green D-11 (hot gas valve)
4. Green D-12 (water pump)
5. Green D-14 (relay-contractor)
6. Green D-15 (dump valve)
Failure of the LED’s to cycle in this sequence will signal a defective
circuit board.
Rev 9/18/95
39 TD 2023/1/95
Page 43
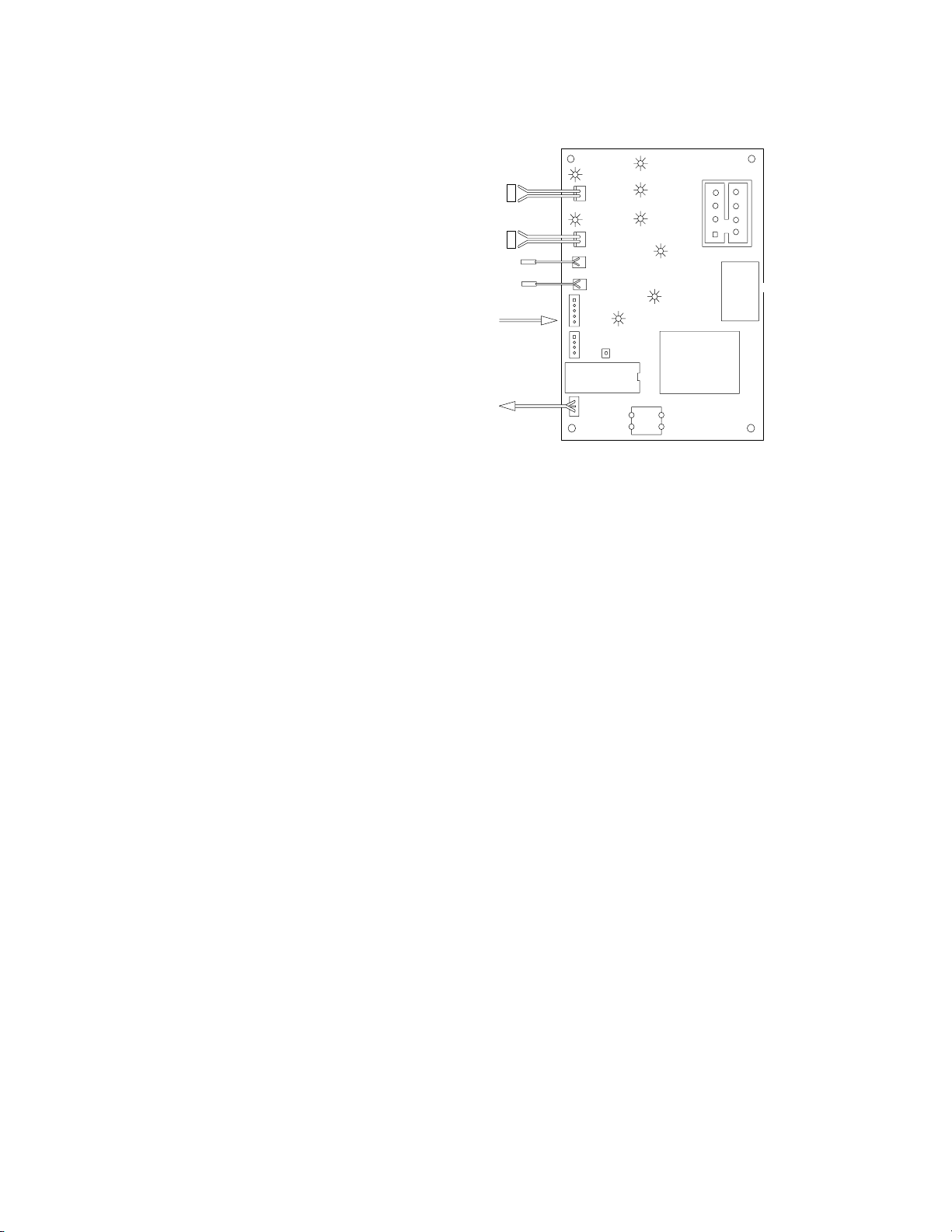
DĆ15
RH Evap. Switch
N
S
LH Evap. Switch
N
S
Condenser Sensor
Suction Line Sensor
To Stacked
(if required)
DĆ13
YL
RH Evap.
YL
DĆ10
LH Evap.
white
Brown
Unit
Condenser
plug
Suction plug
Test
Plug
Options
Plug
Micro Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
DĆ14
DĆ12
RD
DĆ5
Error
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
Manual
Harvest
Switch
GR
Water
Dump
Valve
Contactor
Water
Pump
DĆ11
Fan
GR
DĆ6
Hot Gas
Transformer
7
8
5
6
3
4
2
1
230v
Voltage
neutral
Selector
Switch
115v
Sensors
Condenser sensor (white) and suction line sensor (brown) are
thermistors rated 1k ohm at room temperature.
S Condenser sensor signals the circuit
board for fan cycling and also serves
as the high temperature safety shut
down. The red “Error LED” will flash
on and off every second, during high
temperature safety shut down. Product is functionally shut down. Reset
procedure must be performed to restart product operation.
S Suction line sensor signals the circuit
board the suction line temperature, to
control ice bridge thickness. Also the
sensor serves as suction line high
temperature signal (Cuber has 6 minutes to reduce suction line temperature to 40°F (4.4°C) in the freeze
mode). The red “Error LED” will be
steady on ...should this time frame not
be met, product is functionally inoperative during this safety shut down.
Reset procedure must be performed
to restart product operation.
40TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 44

Sensor [Thermistor] Diagnosis
Sensors
Condenser or suction line – Turn Cuber power switch OFF. Disconnect sensor plug from board. Use digital multimeter set for D.C.
Voltage. Turn power switch ON connect leads of meter across the
two pins of the sensor being checked, meter should read 2.5
VDC0.2 output voltage from the board. If voltage is not correct,
replace the circuit board.
Should the cuber operation indicate there may be a fault
in the sensor [thermistor] or the control board circuit proceed as follows.
1. Using a good multimeter check the control board sensor output voltage.
2. Voltage checks are correct proceed:
a. Disconnect the suction line sensor (brown lead)
from the control board.
b. Install the special test cord* to the control board
and reinstall the sensor to the test cord terminals.
c. Connect the multi-meter (set on VDC - milli-
volts) to the test cord leads.
d. Operate the cuber in the freeze cycle.
3. As the suction line temperature decreases the Millivolt reading will increase.
4. Sensor Shorted - milli-volt reading will cease to increase and will remain steady indicating a shorted sensor.
5. Sensor Open - The voltage reading will indicate the
control board output voltage of 2.5 VDC.
6. Should either “4.” or “5.” happen during this test, the
sensor will require replacement.
* Special test cord, part # 164984009, may be ordered
through the Service Department.
7. Condenser Sensor (white leads) - self-contained air
cooled only - water cooled and remote systems use a
resistor plug on the control board.
Complete the sensor and multi-meter connections as
described in
2- b.,c.,d..
8. Shorted sensor - a steady low milli-volt reading will
be recorded. The reading will not change.
9. Open sensor - the multi-meter will record control
board output voltage of 2.5 VDC.
Rev 9/18/95
41 TD 2023/1/95
Page 45

10. Should sensor (thermistor) pass the voltage test proceed to the control board diagnosis for LED sequence
(see page 39).
NOTE: The sensor controls the condenser fan cycling from
88/100 degree Fahrenheit. Thus any defects in the
condenser circuit will effect the fan cycling rate.
Evaporator Switches
Proximity Switches are half mounted to the water curtain, and the
other half mounted to the evaporator side rail. They provide signals
to the control board to allow the board to change cycles from harves
to freeze as well as shut down of the unit in a full bin condition.
Switch Notes
1. Manually holding the curtain open during freeze
mode, will shut the Cuber down in 5 seconds.
2. During harvest cycle, if curtain is open for 10 seconds,
the water pump will stop. The compressor will operate
for 20 additional seconds before Cuber shut down
takes place. When the water curtain closed, the Cuber
will begin the normal start-up process.
3. In single evaporator machines, the proximity switch
connection must be on the top (RH) connection on the
circuit board.
4. In dual evaporator machines, both RH and LH
switches must open and reset to start the next freeze
mode.
Voltage Checks
Turn Cuber power switch Off. Disconnect proximity switch plug(s)
from the circuit board. Use a digital multimeter set for D.C. Voltage;
turn power switch ON, connect leads of meter across the top two terminal pins on the board, (for the switch being tested), meter should
read 5 VDC ± 0.2 output voltage. If not, replace the circuit board.
42TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 46

Water Regulating Valve
The water regulating valve is used on water–cooled cubers only. The
valve is installed in the condenser outlet water line. It’s function is
to control the proper operating head pressure by regulating the
amount of water flowing through the condenser. The valve is adjustable and factory set to maintain condenser discharge water temperature @ 108/112_F (42-44_C). Setting the water regulating valve to
maintain discharge water temperature eliminates the need to enter
the sealed refrigeration system. When checking the valve, the water
temperature should be taken as close to the condenser discharged as
possible. The water temperature will equate to operating head pressure of approximately 310 PSI (21.1 BAR).
Should adjustment be required, the valve has an adjustment stem on
the top of the valve. After allowing the cuber to operate for 10 minutes in the ice making mode to balance the system, turning the adjusting stem CW will increase the discharge water temperature,
and CCW will decrease the discharge water temperature.
The water regulating valve must close off condenser water flow
completely during the “hot gas” harvest cycle. There should be no
discharge water flowing out of the condenser during the harvest
cycle. Should the valve fail to close during the harvest mode, the
condenser will continue to condense the compressor discharge vapor needed for the harvest cycle and this will result in long harvest
times.
Leaking (by–passing) water regulating valves are normally the result of scale build–up on the valve diaphragm and the valve should
be flushed, not replaced. To flush the valve, open the adjusting stem
wide open CCW (or force the valve spring up with a screwdriver),
open and close the water supply to the condenser resulting in the
flushing action. Should this not correct the problem replace the
valve diaphragm. This can be done without entering the sealed refrigeration system.
Damage to the water regulating valve may also be caused by water
hammer. Water hammer will result from the condenser inlet and outlet water lines being reversed or defective valve stops in the water
supply line. Proper installation of water cooled equipment should always include an anti–water hammer standpipe in the supply inlet
line as close to the cuber as possible.
High Pressure Safety Switch
All water-cooled and remote products contain a high pressure safety
cut-out switch. The function of this switch is to shut down the cuber
should excessive pressure develop in the high side of the refrigeration system. This switch will open the power supply at 450 PSI
(30.61 BAR) high side pressure. Should this control open, it must be
reset manually and the cause for the increase in pressure determined.
Rev 9/18/95
43 TD 2023/1/95
Page 47

Float Valve with Flow Washer
The Float Valve Maintains the proper water level in the water reservoir.
There is a flow washer in the inlet side of the float assembly that will
control inlet water pressure from 20/120 PSI (1.37/8.16 Bars). This
will prevent float flutter. In low water pressure conditions, 20 PSI
(1.37 Bars) or less, the flow washer may have to be removed from
the float assembly for proper volume.
Flow control washer flat side up
Service Stem Valves
When closing the service stem valves to remove your gauge and
manifold set always close the high side stem valve first. Following
this procedure will allow the system to “PULL” the refrigerant vapor
from your manifold set to reduce refrigerant loss. When the pressure
has been reduced, close the low side stem valve.
Thermostatic Expansion Valves
The following suggestions for diagnosis of automatic Thermostatic
Expansion Valve (TXV) are given with the understanding the following have been checked and are correct and/or have been corrected prior to proceeding.
1. The condenser and fan blade are clean and have proper operating conditions.
2. Water supply to the product is correct and flow over
the evaporator is correct.
3. Cuber refrigerant charge is correct.
4. TXV sensing bulb is properly located and secured to
the suction line and correctly insulated.
5. Hot gas valve(s) are not leaking and/or weeping
through.
44TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 48

DIAGNOSIS
Starving TXV - Product Symptoms
1. Suction pressure lower than normal for the operating
conditions.
2. Ice production lower than normal and/or none.
3. Ice pattern on evaporator (if any) thin at top and thick
at bottom.
Flooding TXV - Product Symptoms
1. Ice production lower than normal and/or none.
2. Suction pressure stabilizes at higher than normal pressure for operating conditions. Suction pressure does
not modulate and may start to slowly rise.
3. Ice pattern will be very heavy at the bottom and thin at
the top of the evaporator. Product may not enter harvest cycle because of higher than normal suction line
temperature.
Important: Frost on the suction line may be normal on me-
dium temperature refrigeration equipment. Frost
should be considered a red flag, long run times
will normally produce some type of frost pattern..
Before checking the sealed refrigeration system,
the external conditions that could lead to frost
follow:
1. Dirty condenser
2. Dirty condenser fan blade
3. Improper air clearance around Cuber
4. Loose TXV bulb mount
5. Poor water flow over evaporator
6. Ventilation problems
The expansion valves used on Cornelius “I” series ice equipment
have special super heat settings and bulb charge designed from the
product load and HP 62 refrigerant. Should the need arise to replace
this or any refrigerant components, be certain to use only components recommended by Cornelius for the model of the Cuber being
serviced. Use of nonapproved components will compound system
difficulties and may void product warranty.
Rev 9/18/95
45 TD 2023/1/95
Page 49
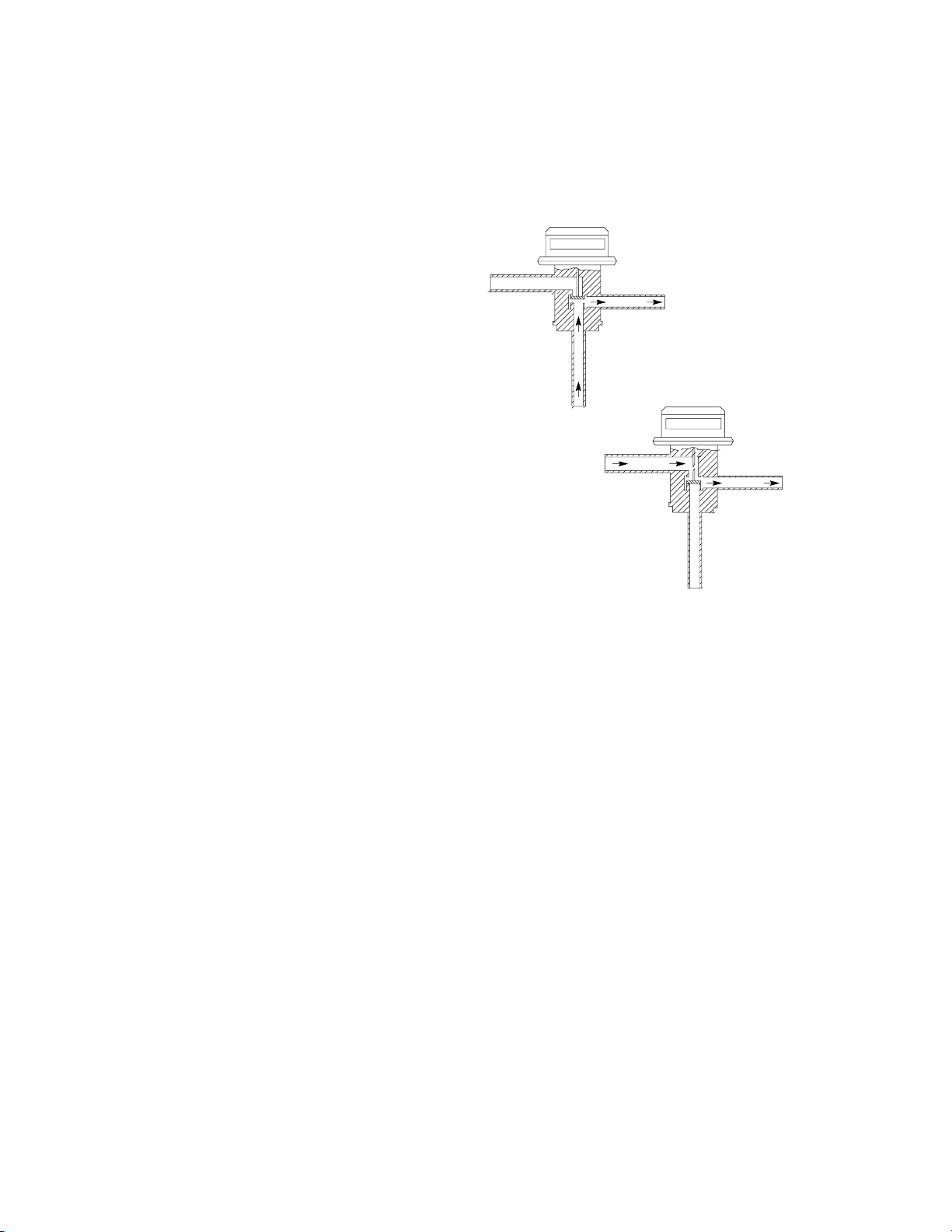
Head Pressure Control Valve
[Headmaster]/Fan Cycle Switch
(Remote Units Only)
condenser
receiver
dis-
charge
receiver
condenser
below 70°F by-pass
discharge
above 70°F
normal
The Cornelius “I” series remote systems use an Alco Head Pressure
Control, normally referred to as a headmaster. This control is
mounted in the remote condenser with a fan cycling control switch.
Using both these controls gives the system positive operation under
a wide range of condensing temperatures.
The fan cycling switch starts the fan at 270 PSI and stop it at 205 PSI
allowing a positive efficient operation at the high temperature operating ranges.
The headmaster controls the operation when the condensing temperature drops below 70°F. The “I” series refrigerant charge is
HP - 62 [R - 404A] and the headmaster dome charge setting is 200
PSI of nitrogen pressure making it stable under the low temperature
operating range down to - 20°F. (Continued on page 46)
The normal flow pattern through the headmaster is from the condenser port to the receiver port. When this flow pattern is unable to
46TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 50

maintain a receiver outlet pressure equal to or above the dome pressure setting of the valve the dome pressure will force the valve portage to change closing the condenser port and opening the bypass
port from the compressor discharge line. This allow the high pressure vapor from the discharge port to “buck” the receiver pressure
back up. With the condenser port closed, the refrigerant is backed up
in the condenser, basically reducing the condenser size, assisting in
maintaining the discharge portage flow and increasing the head
pressure.
Remember, sense of touch to the lines of the headmaster will determine the flow path the headmaster is in, condenser to receive or bypass to receiver.
High side gauge installed at the receiver outlet valve will determine
if the headmaster is functioning to maintain the proper operating
pressure.
In the event the control appears to be “stuck in bypass”, the pressure
drop across the headmaster must be measured. With a gauge
installed at the receiver outlet valve and the high side service valve,
the pressure difference at these two points must be less the 15 PSI.
Three most common causes of an excessive pressure drop are shortage of refrigerant, kinked remote lines, and excessive line length.
Eliminate refrigerant shortage first. Add refrigerant in two pound increments (not to exceed six pounds) to determine if it corrects the
pressure drop. If pressure drop is not corrected, inspect line set for
sharp bends or kinks, correct as required. If adding refrigerant does
not correct continued (bypass) condition and line set is not damaged, replace headmaster.
Contactor Compressor
The contactor serves as the voltage supply switch for the compressor circuit. Voltage to the coil of the contactor is supplied by the circuit board.
Check Out:
The two (2)* line supply screws of the contactor should always have
supply voltage present when voltage is on to the product.
The other two (2)* screws (load) should have line voltage when the
contactor is energized. The contactor coil receives its supply voltage
from the circuit board. Should the contactor fail to energize:
Check for supply voltage from circuit board, lead connections to
contactor coil, and ohms value of coil.
* (3) if the product is 3 phase
Compressor & Starting Component
Check-Out Procedure
When compressors fail to start or run properly, it is normally the external electrical supply or the compressor start components that are
defective. The overload protector, start and/or run capacitor, relay,
circuit board, safety controls, etc.
Rev 9/18/95
47 TD 2023/1/95
Page 51

1. Check voltage at compressor terminals. NO voltage
will require checking the electrical circuit working
back from the compressor to determine where the voltage supply is interrupted and correct as required. The
load voltage, while compressor is trying to start,
should not be less than 90% of rated required voltage.
Line voltage and wire size effect the life expectancy of the electrical
components, compressor, motor winding, solenoid coils, etc.
Poor line quality voltage will cause many erratic electrical problems. Remember every electrical product, ice machine, dispenser,
walk–in, reach–in, air conditioner, etc. required proper power supply to operate. Be certain when voltage checks are performed that
you are measuring load voltage, not line voltage.
2. A defective capacitor or start relay may prevent the
compressor from starting. Should the compressor attempt to start, but is unable to do so, or if the compressor hums or trips off on the over protector, check the
following:
NOTE: For 50 HZ application on dual rated 50/60 HZ mod-
els, load voltage while compressor is starting must
not be less than 90% of 50 HZ rating.
Relay
Potential –
For the potential type, contacts are normally closed. The start contacts open by C.E.M.F. generated by the compressor at approximately 80% of the normal operating speed. As the contacts open, only the
start capacitor is removed from the start circuit. Both the start and
run winding and the run capacitor remain in the circuit. This relay
may or may not be directional in mounting.
Current –
For the current type, contacts are normally open. The start contacts
close by the high current draw from the locked rotor condition with
only the run winding in the circuit. As the contacts close, the start
capacitor and the start winding is energized and the compressor
starts. At approximately 80% of its operating speed the current draw
drops off, the relay contacts open removing the start winding and
start capacitor from the circuit. Remember, current relays are directional in their mounting to allow contacts to lift and close.
Capacitors
A quick check is to replace suspected defective capacitors with
known good capacitors being careful to stay within the range for
substitute values. Should those values be unknown, a basic rule for
capacity is: for start capacitors 10% and run capacitors 5% of
the rating on the defective original capacitor being replaced. Voltage
should always try and be matched, if it cannot be it is acceptable to
48TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 52

increase up to 10% higher than the voltage listed on the capacitor being replaced. NEVER put a capacitor on a product with a voltage
rating lower than the original being replaced. If a capacitor analyzer
is not available, an ohm meter may be used to check a capacitor for
short or open circuits. Set the ohm meter to its highest scale and connect its leads to the capacitor terminals.
1. With a capacitor, without plate defect, the indicator
should first move to zero (0) and then gradually increase to infinity.
2. If there is no movement of the ohm meter indicator, an
open circuit is indicated.
3. If the ohm meter indicator moves to zero (0) and remains there, or on a low resistance reading, a short
circuit is indicated.
4. Please note this check does not determine if the capacitor will deliver the proper rated MFD/UFD required, it
only shows if the capacitor has shorted or open circuits.
5. Capacitors that show any signs of leakage of electrolyte, or damage of the can, should be replaced. DO
NOT TEST!
Compressor
1. Using an ohm meter, check for continuity from compressor terminal C to R and C to S. If the compressor
is hot, wait one (1) hour for compressor to cool and
recheck. An open internal overload protector can
cause a lack of continuity. If continuity cannot be measured through all windings, the compressor must be
replaced.
2. To check the compressor motor for accidental ground,
perform a continuity check between terminals C, R
and S to the compressor shell or a copper line of the
refrigeration system (do not use a painted surface).
Continuity present, the compressor windings are
grounded and the compressor must be replaced.
If the compressor starts, but trips repeatedly on the overload protector, remember that the overload is both temperature and current activated. Be sure to check; (Continued on page 49)
S Low voltage
S Undersized supply lines
S High head pressure
S High suction pressure
S Defective capacitors
S Compressor mechanical problems
S Low Refrigerant Charge
Rev 9/18/95
49 TD 2023/1/95
Page 53

Moisture Contamination
With the major changes in refrigerants in today’s marketplace and
the use of hydroscopic oils the control of moisture and contaminates
have become more critical to safeguard against than ever before in
the history of mechanical refrigeration.
Contaminates are also the most difficult of all problems to determine. A Meg–Ohm meter “Megger” can be a valuable tool to aid in
the analysis of this problem. A Meg–Ohm reading log may be
started any time after 90 days of operation of the product. To perform the test, proceed as listed.
Disconnect all three (3) compressor leads, take a Meg-Ohm meter
reading from each compressor terminal to a good chassis ground.
Compare reading to chart below:
Meter
Reading
Meg-Ohm
100 - ∞
50 to 100 Moisture present Replace drier.
20 to 50 Severe moisture &
.5 to 20 System has severe
(Continued on page 51)
Compressor
Condition
Okay None needed.
possible contaminated
oil with acid present
contamination
Maintenance Required
Replace drier with acid
hold type. Run 24
hours, change to regular drier.
Remove compressor
oil and refrigerant
charge. Evacuate,
install liquid and suction line driers (acid
hold type). Recharge
with new oil and refrigerant. Run 24
hours. Discharge system, discard suction
line drier, replace the
liquid line drier. Evacuate and recharge.
50TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 54

Readings in the range listed below 100 Meg–Ohm would be an indicator that the system being tested may have a contamination problem. Where does the problem come from? As an example, the filter
drier may become saturated and hold large percentages of moisture
and the system function without a problem until such time as the
product operating conditions change. Should the room temperature
increase, or the condenser plug–up etc., the higher operating pressures and temperatures may cause the drier filter to release a portion
of it’s held moisture. It is also imperative to avoid opening the sealed
refrigeration system whenever possible and when it is done to be
certain the true problem is correctly diagnosed and repaired. Remember, service gauge sets should only be installed after all external
checks have been performed.
Caution: Megger checks should NEVER be performed
on any compressor that is under a vacuum.
Rev 9/18/95
51 TD 2023/1/95
Page 55
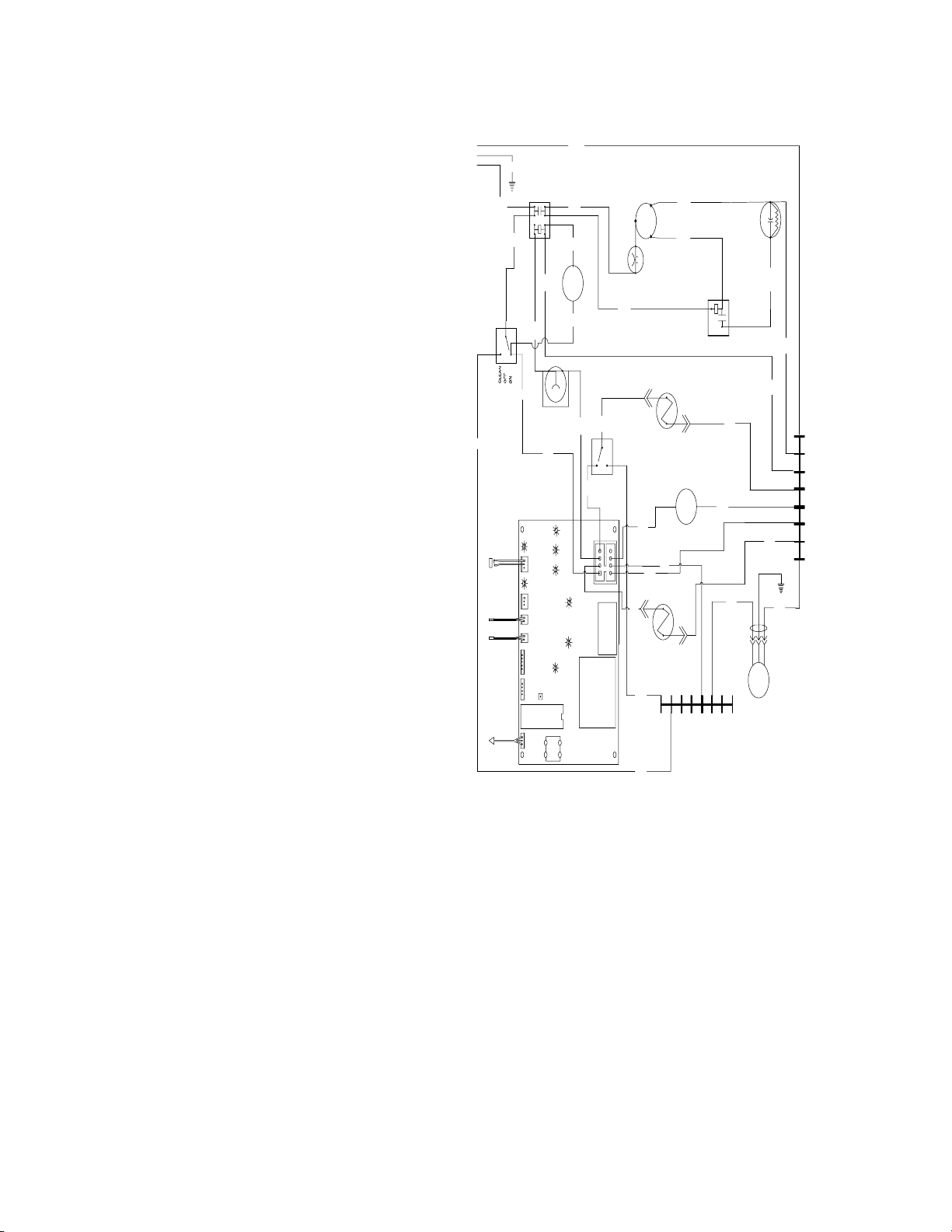
WH
GR
CONTACTOR
UNIT
SWITCH
BL
BK
BK
1
2
3
BR
BL
WH
CO
450 PSIG
BR
BR
BK
M
BK
CONDENSATION
FAN (W/C ONLY)
MANUAL RESET
HIGH PRESSURE
CONTROL(W/C ONLY)
BK
BL
3
1
YL
Water
D-15
Dump
GR
Valve
D-13
D-14
YL
RH Evap.
Switch
N
S
(White Lead)
Condenser
Sensor
See note 1
Suction Line
Sensor
(Brown Lead)
To Stacked
Unit
(if required)
NOTE 1: CONDENSER SENSOR USED ONLY ON A/C UNITS.
Relay
RH Evap.
YL
D-10
LH Evap.
Condenser
Plug
Suction
Plug
Test
Plug
Options
Plug
Micro
Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
GR
GR
D-12
Error
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
7
5
Water
3
Pump
1
D-11
Hot Gas
Valve
GR
GR
RD
D-6
D-5
Condenser
Manual
Harvest
Switch
Fan
Transformer
Voltage
Selector
Switch
230V
115V
1.8K ohm RESISTOR USED ONLY ON W/C UNITS.
COMPRESSOR
BR
WATER DUMP
SWITCH
2
8
6
4
2
C
BK
WH
RD
BL
BL
R
S
EXTERNAL
COMPRESSOR
OVERLOAD
POTENTIAL
START RELAY
BL
HOT GAS
SOLENOID
RD
YL
WATER DUMP
VALVE
CONDENSER
FAN MOTOR
(A/C ONLY)
M
IAC 322 & IWC 322
IAC 330 & IWC 330
243-292 mfd
2
5
1
WH
BK
COMPRESSOR
115 VAC
WH
PUMP
CORD
WATER PUMP
START
CAPACITOR
OR
WH
WH
WH
M
WH
52TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 56

WH
GR
CONTACTOR
BR
BK
M
WH
BK
CONDENSATION
BL
FAN (W/C ONLY)
MANUAL RESET
HIGH PRESSURE
CO
450 PSIG
BR
CONTROL(W/C ONLY)
BK
BL
WATER DUMP
1
SWITCH
3
2
BR
UNIT
SWITCH
BL
BK
BK
1
2
3
YL
Water
D-15
Dump
GR
Valve
D-13
D-14
YL
RH Evap.
Switch
N
S
(White Lead)
Condenser
Sensor
See note 1
Suction Line
Sensor
(Brown Lead)
To Stacked
Unit
(if required)
Relay
GR
RH Evap.
Water
GR
Pump
D-12
YL
D-10
LH Evap.
GR
Condenser
Plug
Suction
Plug
GR
Test
RD
Plug
Error
Options
Plug
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
Micro
Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
NOTE 1: CONDENSER SENSOR USED ONLY ON A/C UNITS.
1.8K ohm RESISTOR USED ONLY ON W/C UNITS.
D-11
D-6
D-5
Hot Gas
Condenser
Manual
Harvest
Switch
Valve
Voltage
Selector
Switch
Fan
Transformer
8
7
6
5
4
3
1
2
230V
115V
COMPRESSOR
R
C
S
COMPRESSOR
BR
BK
WH
RD
BL
BL
440 VAC
EXTERNAL
OVERLOAD
POTENTIAL
START RELAY
WATER DUMP
BL
HOT GAS
SOLENOID
COMPRESSOR
CAPACITOR
RD
30 mfd
YL
VALVE
CONDENSER
FAN MOTOR
(A/C ONLY)
M
IAC 522 & IWC 522
IAC 530 & IWC 530
RUN
5
1
BK
YL
2
WH
WH
PUMP
CORD
COMPRESSOR
START
CAPACITOR
RD
72-86 mfd
330 VAC
OR
WH
WH
M
WATER PUMP
WH
WH
Rev 9/18/95
53 TD 2023/1/95
Page 57

BK
RD
RD
SWITCH
BL
(White Lead)
Condenser
Sensor
See note 1
Suction Line
Sensor
(Brown Lead)
To Stacked
(if required)
RD
CRANKCASE
HEATER
(RC ONLY)
UNIT
RH Evap.
Switch
N
S
LH Evap.
Switch
N
S
Unit
GR
BK
BR
D-13
LIQUID LINE
SOLENOID
(R/C ONLY)
CONTACTOR
RD
BK
BL
450 PSIG
BR
D-15
GR
D-14
YL
GR
RH Evap.
GR
D-10
D-12
YL
LH Evap.
Suction
Plug
Test
Plug
Options
Plug
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
Micro
Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
RD
BR
BK
BK
M
BK
CONDENSATION FAN
(W/C & R/C ONLY)
HIGH PRESSURE CONTROL
(W/C & RC ONLY)
CO
BL
BR
YL
Water
Dump
Valve
Relay
Water
Pump
D-11
Hot Gas
GR
Valve
Condenser
Plug
D-6
Condenser
GR
Fan
RD
D-5
Error
Transformer
Manual
Harvest
Switch
BK
BR
MANUAL RESET
BK
WATER DUMP
1
SWITCH
3
2
7
8
6
5
4
3
2
1
230V
Voltage
Selector
Switch
115V
RD
COMPRESSOR
R
C
S
EXTERNAL
COMPRESSOR
OVERLOAD
BK
RD
RD
HOT GAS
SOLENOID
BL
BL
RD
COMPRESSOR
RD
YL
POTENTIAL
START RELAY
WATER DUMP
VALVE
M
CONDENSOR
FAN MOTOR
(A/C ONLY)
BL
IAC 830, IWC 830 & IRC 830
IAC 630, IWC 630 & IRC 630
RUN
CAPACITOR
YL
2
5
1
RD
See note 2
35 mfd
370 VAC
WH
BK
WH
PUMP
CORD
WATER PUMP
COMPRESSOR
START
CAPACITOR
145-174 mfd
250 VAC
OR
RD
WH
WH
M
RD
NOTE 1: CONDENSER SENSOR USED ONLY ON A/C UNITS.
1.8K ohm RESISTER USED ONLY ON W/C & R/C UNITS.
NOTE 2: CAPACITORS USED ON 630 BRISTOL COMPRESSOR:
RUN CAP, 25mfd 440 VAC
START CAP. 161-193mfd 250 VAC
54TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 58

LIQUID LINE
RD
SOLENOID
(R/C ONLY)
RD
BK
CRANKCASE
HEATER
(RC ONLY)
GR
BK
BK
CONTACTOR
RD
BR
BK
M
RD
BK
BL
BK
CO
450 PSIG
Water
Dump
GR
Valve
D-14
Relay
GR
Water
GR
Pump
D-12
D-11
GR
D-6
GR
RD
D-5
Error
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
HIGH PRESSURE
BL
BR
Hot Gas
Valve
Condenser
Fan
Transformer
Manual
Harvest
Switch
YL
BK
BR
UNIT
RD
SWITCH
BL
(White Lead)
Suction Line
(Brown Lead)
(if required)
NOTE 1: CONDENSER SENSOR USED ONLY ON A/C UNITS.
D-15
D-13
YL
RH Evap.
Switch
N
RH Evap.
S
D-10
YL
LH Evap.
Switch
N
LH Evap.
S
Condenser Sensor
Condenser
Plug
See note 1
Suction
Plug
Sensor
Test
Plug
Options
Plug
To Stacked
Micro
Processor
Unit
Stacking
Cable
Plug
1.8K ohm RESISTER USED ONLY ON W/C & R/C UNITS.
2: Capacitors used on 103 Compressor
RUN CAP. 37 mfd 370V
START CAP. 145-174 MFD 250v
RD
BK
COMPRESSOR
BR
CONDENSATION
FAN (W/C & R/C)
MANUAL RESET
CONTROL(W/C & R\C)
BK
WATER DUMP
1
SWITCH
3
2
8
7
6
5
43
21
RD
230V
Voltage
Selector
Switch
115V
BL
BL
RD
RD
R
C
S
YL
EXTERNAL
COMPRESSOR
OVERLOAD
POTENTIAL
START RELAY
WATER DUMP
M
BK
M
BL
RD
HOT GAS
SOLENOID
IAC 1230, IWC 1230 & IRC 1230
IAC 1030 IWC 1030 & IRC 1030
COMPRESSOR
CAPACITOR
5
VALVE
CONDENSOR
FAN MOTORS
(A/C ONLY)
RUN
YL
2
1
WH
RD
See note 2
40 mfd
370 VAC
BK
BK
WH
PUMP
CORD
WATER PUMP
COMPRESSOR
START
CAPACITOR
189-227 mfd
330 VAC
OR
RD
WH
WH
M
RD
Rev 9/18/95
55 TD 2023/1/95
Page 59
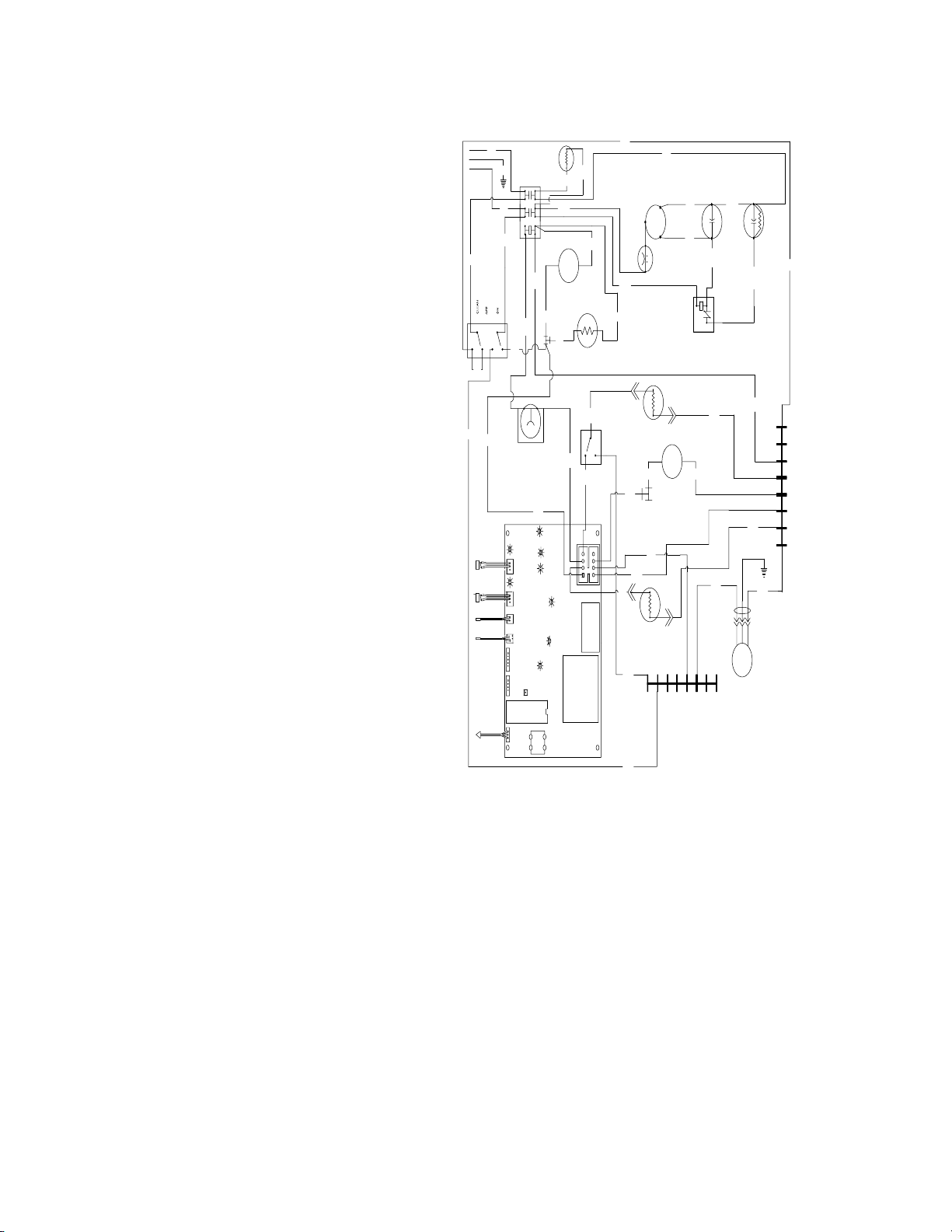
RD
RD
UNIT
SWITCH
RD
BL
BR
HIGH PRESSURE
RH Evap.
Switch
N
S
LH Evap.
Switch
N
S
(White
Lead)
Condenser Sensor
See note 1
Suction Line
Sensor
(Brown
Lead)
To Stacked
Unit
(if required)
LIQUID LINE
SOLENOID
(R/C ONLY)
GR
CONTACTOR
BK
BK
RD
BK
BL
BR
CO
450 PSIG
MANUAL RESET
CONTROL(W/C & R/C)
BR
D-15
Water
Dump
GR
Valve
D-13
D-14
YL
GR
Relay
RH Evap.
Water
GR
Pump
YL
D-12
D-10
D-11
LH Evap.
GR
Condenser
Plug
D-6
Suction
Plug
GR
Test
RD
Plug
D-5
Error
Options
Plug
Adjustable Ice
Thickness Pot.
Micro
Processor
Stacking
Cable
Plug
BK
RD
BR
BK
M
CONDENSATION
FAN (W/C & R/C)
BK
CRANKCASE HEATER
(A/C & R/C ONLY)
BK
1
3
BL
YL
7
5
Hot Gas
Valve
230V
Voltage
Selector
Switch
Condenser
Fan
115V
Transformer
Manual
Harvest
Switch
BK
WATER DUMP
SWITCH
2
8
6
43
21
RD
BR
RD
BK
RD
HOT GAS
SOLENOID
BL
BL
RD
COMPRESSOR
R
C
S
EXTERNAL
COMPRESSOR
OVERLOAD
POTENTIAL
START RELAY
WATER DUMP
VALVE
M
BK
CONDENSOR
FAN MOTOR
(A/C ONLY)
BL
IAC 1448, IWC 1448 & IRC 1448
COMPRESSOR
RUN
CAPACITOR
RD
YL
YL
5
1
WH
40 mfd
440 VAC
2
WH
WH
PUMP
CORD
WATER PUMP
COMPRESSOR
START
CAPACITOR
RD
OR
WH
M
189-227 mfd
330 VAC
RD
WH
RD
NOTE 1: CONDENSER SENSOR USED ONLY ON A/C UNITS.
1.8K ohm RESISTER USED ONLY ON W/C & R/C UNITS.
56TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 60
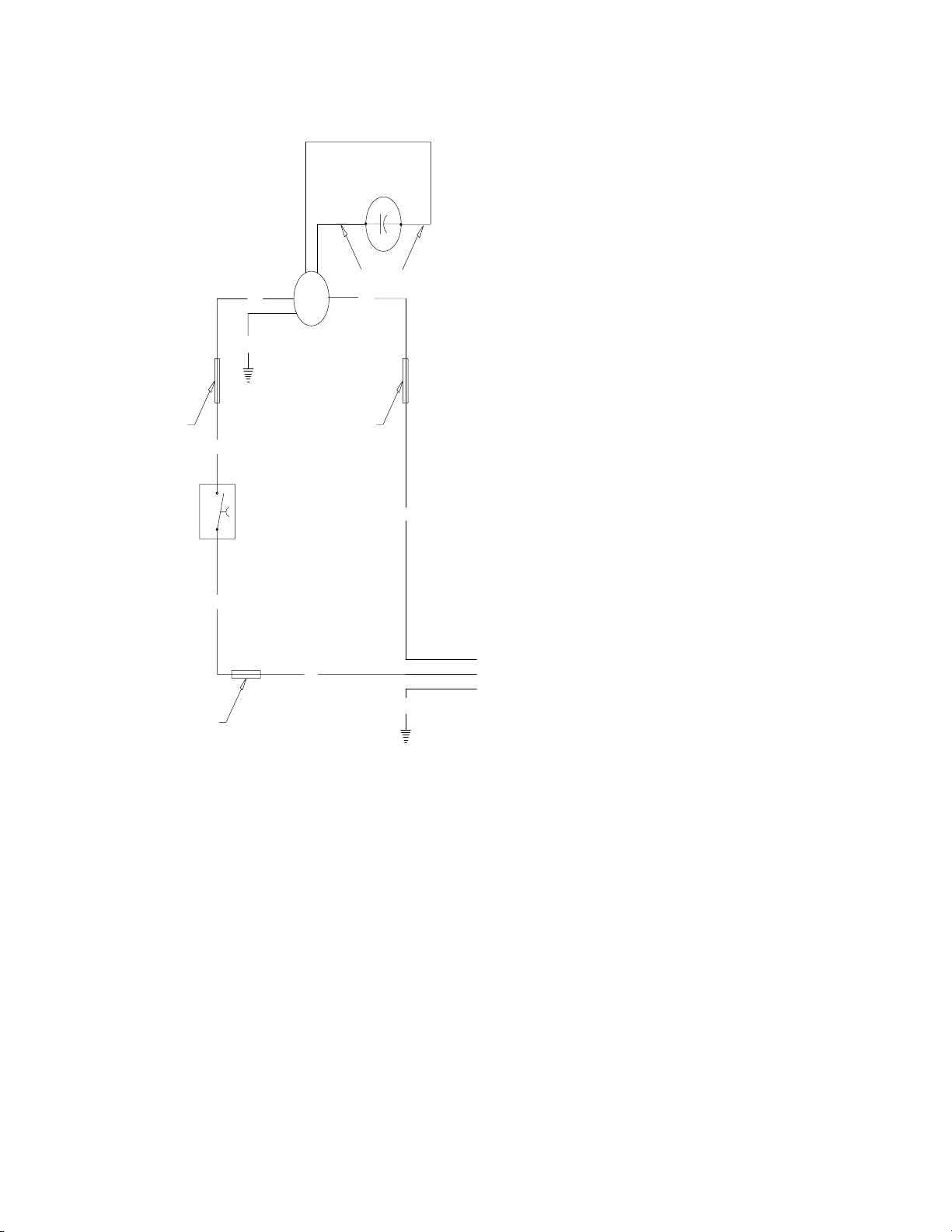
CAPACITOR
2 mfd 440 VAC
RED
COL-
ORED
BK
GR
M
CONDENSOR
FAN MOTOR
BAND
BK
HEAT
SHRINK
TAPE
HEAT SHRINK TAPE
Rev 9/18/95
HEAT SHRINK TAPE
RD
FAN CYCLING
SWITCH
RD
RD
CR800, CR1200, & CR1400 REMOTE CONDENSERS
208/230 VOLTS 60 HZ
57 TD 2023/1/95
BK
GR
Page 61

TROUBLESHOOTING
IMPORTANT: Only qualified personnel should service internal components or electrical wiring.
Trouble Probable Cause Remedy
CUBER NOT
OPERATING
CUBER NOT
OPERATING
INDICATOR
LIGHTS “OFF”,
NO POWER TO
CIRCUIT
BOARD
A. Power
switch in
center “OFF”
position.
A. Test power
switch and
leads.
B. High
pressure
cut-out
open. (water
cooled or
remote
systems)
A. Place switch in
“ON” position.
A. If defective,
replace.
B. Press manual
reset.
Determine
cause:
Water supply
shut off; water
pressure too
low; water valve
defective or out
of adjustment;
water condenser
dirty or corroded;
unit
over-charged;
water inlet
pressure too
high. Replace
defective
component as
needed.
58TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 62

Trouble RemedyProbable Cause
CUBER NOT
OPERATING
INDICATOR
LIGHTS “OFF”,
POWER TO
THE CIRCUIT
BOARD
COMPRESSOR
DOES NOT
RUN, CIRCUIT
BOARD
INDICATOR
LIGHTS “ON”
A. Magnet not
in proximity
switch field.
B. No curtain
movement.
C. Faulty
proximity
switch.
D. Unit “OFF”
due to bin
full.
A. Check
contactor
and leads.
B. Compressor
overload
“open”.
C. Check
compressor
and start
components.
A. Water curtain
drifting out of
switch range.
Reduce
clearance
between curtain
and proximity
switch.
B. Adjust proximity
switch.
C. Replace
proximity switch.
D. Remove ice from
curtain.
Eliminate curtain
restriction.
A. Replace if
defective.
B. Permit overload
to cool and reset
or replace.
C. Replace as
needed.
Rev 9/18/95
59 TD 2023/1/95
Page 63

Trouble RemedyProbable Cause
COMPRESSOR
RUNS BUT
DOES NOT
COOL, CIRCUIT
BOARD
INDICATOR
LIGHTS “ON”
A. Low charge. A. Leak check –
Recharge.
CUBER
REMAINS IN
THE FREEZE
CYCLE
B. Hot gas
solenoid
leaking.
C. Defective
expansion
valve.
D. Inefficient
compressor.
E. Internal
by-pass
open,
compressor
noisy.
A. Check
suction line
thermistor
(sensor)
lead wire
connection
at the circuit
board.
B. Evaporator
thermistor
shorted.
C. Check
thermistor
(1K ohm).
D. Ice bridge
setting too
low.
B. Replace.
C. Replace.
D. Replace.
E. Permit pressures
to equalize.
A. Tighten,
reattach.
B. Replace.
C. Replace if out of
range.
D. Adjust per bridge
adjustment
instructions.
60TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 64

Trouble RemedyProbable Cause
E. Expansion
valve failure
(will not pull
down).
CUBER
REMAINS IN
THE HARVEST
CYCLE
SUCTION LINE THERMISTOR OPEN
(STARTS IN HARVEST)
A. Loose
connection
at the circuit
board.
B. Test
thermistor.
PROXIMITY SWITCH LIGHT “OUT”
C. Loose wire
connection
at circuit
board.
D. Proximity
switch
defective,
see
check-out
procedure.
E. Tighten bulb,
replace as
needed, See
check-out
procedure.
A. Tighten or
reconnect.
B. Replace if out of
range.
C. Tighten, reattach
wire.
D. Replace as
needed.
Rev 9/18/95
E. Water
curtain
stuck,
curtain
frozen to ice
on
evaporator.
Curtain hung
on water
pan,
proximity
switch out of
range.
PROXIMITY SWITCH LIGHT “ON”
61 TD 2023/1/95
E. Check and
adjust as
needed.
Page 65

Cleaning Procedures
Approved ice machine cleaners by brand names:
S Lime-A-Way
S Calgon Nickel Safe (green color
only)
NOTE: All ice machine cleaners labeled safe for nickel ARE
NOT the brand CALGON NICKEL SAFE.
Caution: Ice machine cleaners are acidic-based chemi-
cals. Before begnning any cleaning of the cuber, the ice in the storage bin or dispenser must
be removed.
Caution: When using any chemical, rubber gloves and
eye protection should be worn.
Prep – Cleaning
Use full-strength ice machine cleaner on a coarse-surface cloth material (such as terry cloth) and wipe down the inside wall of the evaporator area, the water pan, the water curtain and evaporator plastic
extrusions. If the water distributor tube has heavy scale build–up, remove and soak it in full-strength ice machine cleaner (or exchange
the tube and clean the scaled tube at a later date).
Cleaning the Water System &
Evaporator
Power Switch
1. Set the switch to Clean and allow any ice on the evap-
orator to release and melt away.
2. Remove all ice from the storage bin.
3. Remove the water curtain(s), pour 1/2 oz. of ice machine cleaner down the rear key-slot openings. The
cleaner will drain into the water pan.
62TD 202 3/1/95
Rev 9/18/95
Page 66

4. Return the water curtain(s) to their proper operating
position.
5. Add 3 oz. for a single evaporator, or 5 oz. for a dual
evaporator of “Calgon Nickel-Safe” or “Lime-A-
Away” ice machine cleaner directly into the water pan
the float will balance with inlet water. Set switch to
CLEAN, circulate for a maximum of 15 minutes.
6. Depress and hold the dump switch to allow the cleaner
to drain away.
7. Fill the water pan with clean fresh water, circulate for
approximately 3 minutes. Depress and hold the DUMP
switch and allow the water to drain away. Repeat the
procedure 3 times.
8. After third rinse cycle, place product power switch in
ice position. Allow Cuber to produce one slab of ice –
DISCARD THE ICE.
9. When the clean cycle is complete, return cuber to normal operating mode.
NOTE: Please Take Note of the Following:
S Ice machines should only be
cleaned when needed, not by a
timed schedule of every 60
days, etc.
S Should your ice machine re-
quire cleaning more than twice
a year, consult your distributor
or dealer about proper water
treatment.
Sanitizing Procedures
NOTE: To be performed only after cleaning the ice ma-
chine:
1. Add 1/4 ounce sodium hypochlorite solution (common liquid laundry bleach) to the water pan and allow
the pump to circulate the solution for 5 minutes. You
may also use a commercial sanitizer such as Calgon
Ice Machine Sanitizer following the directions on the
product label.
2. Turn the Cuber power switch off and depress and hold
the dump switch to drain the water pan.
3. To sanitize the bin and other surface areas, use 1
ounce of liquid bleach per gallon of water and wipe all
areas with the solution. Or use a commercial sanitizer.
4. Place the Cuber power switch in the ice position. Discard the first batch of ice produced.
5. Cleaning and sanitizing are now complete. Cuber may
be returned to normal service.
Rev 9/18/95
63 TD 2023/1/95
 Loading...
Loading...