IMI Buschjost 84070 Series, Buschjost 84080N Series Operating Manual
Operation manual for indirect
controlled diaphragm valves
Document No. EN1377027BA Revision: 5
Keep documentation for future use!
P
A
A
Series
84070
84080
N
N
NPT thread
c
Contents
1 About this documentation 1
1.1 Documentation validity 1
1.2 Structure of safety instructions 1
1.3 Hazard classes (ANSI Z535.6) 1
1.4 Styles and symbols 1
1.5 Intended use 1
1.6 Improper use 2
1.7 Obligations of operator 2
1.8 Personnel qualification 2
1.9 Personal protection equipment 2
2 General safety instructions 2
3 Avoid damage to property 3
4 Identifying the valve 3
5 Transpor t and storage 3
6 Function 3
7 Mounting 4
7.1 Conditions of installation 4
7.2 Preparation 4
7.3 Mount valve to pipe line 4
8 Connect solenoid electrically 5
9 Operating conditions 5
10 Commissioning 5
10.1 Checking the switching function 5
10.2 Flooding the valve 5
11 Operation 6
12 Maintenance 6
12.1 Cleaning and visual inspection 6
12.2 Checking for tightness and strength 6
12.3 Preparing maintenance 6
12.4 Dismantling valve 6
12.5 Checking dismantled valve parts 7
12.6 Cleaning parts, checking valve seat 7
12.7 Replacing spare parts 7
12.8 Reassembling valve 7
12.9 Mounting solenoid 7
13 Re-commissioning 7
14 Decommissioning 7
15 Replacing complete valve 8
16 Trouble shooting 8
17 Return 8
18 Disposal 8
19 Directives and certificates 8
Translation of the original operating manual
Status as of October 2018
1
About this documentation
This operation manual guides you to guides
you to mount, operate and maintain indirect
controlled diaphragm valves safely.
1.1
Documentation validity
These mounting instructions applies to indirect
controlled diaphragm valves of series
•84070 (G thread)
•84080 (NPT thread)
in combination with these solenoid:
Series 9101 9104
84070 • •
N
84080
• •
This operation manual is intended for:
plant operators, installers, maintenance and
service technicians.
1.2
Structure of safety instructions
Safety instructions warn against dangerous
situations and must be observed in particular.
Safety instructions are structured as follows:
SIGNAL WORD
Type of hazard
Consequences of non-observance
→ Precautions necessary to avoid the hazard
1.3
Hazard classes (ANSI Z535.6)
! DANGER
Safety information indicates a hazardous situation
with high risk which, if not avoided, will certainly
result in death or (serious) injury.
! WARNING
Safety information indicates a hazardous situation
with moderate risk which, if not avoided, can cause
death or severe injury.
! CAUTION
Safety information indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or
moderate injury.
NOTICE
Information indicates a hazardous situation which, if
not avoided, could result damage to property.
1.4
Styles and symbols
This documentation uses the following styles
and symbols:
• list
→ instruction
1.
preset order of instructions
2.
1
part number (according to part list)
1 flexible part number (section)
replace spare part
q
! + DANGER / WARNING / CAUTION;
NOTICE: embedded safety message
given limits or fixed value
1.5
Intended use
The valve is solely intended to control or stop
a fluid flow within approved operating limits.
The fluid must only flow through the valve in
the determined flow direction.
You may only operate the valve with fluids that
will not cause any chemical reaction with the
valve’ materials or lead to abrasive effects.
10/2018
EN1377027BA
1

1.6
Improper use
Only operate the valve within approved operating limits.
In the following cases it is prohibited to operate the valve:
•The valve is not used for the designated
purpose.
•The valve is used beyond the permitted
operating limits. The permitted temperature
and pressure ranges are exceeded.
•Damages to the valve – e.g. cracks,
deformation – were detected but the valve
remains in operation.
•Malfunctions were detected but the valve
remains in operation.
We do not accept any liability for damages
caused by improper use.
Our guarantee expires in the following cases:
•Undue intervention and altering are done to
the valve.
•This documentation or the operating limits as
shown in the data sheet are not observed.
1.7
Obligations of operator
Product
→ Over the entire life cycle of the valve all
applicable regulations must be observed.
The instructions of this operation manual
must be observed and followed.
→ Initiate a risk assessment of the overall
installation, to detect potential dangers that
may occur in combination of the valve with
other components.
Persons
→ Initiate the instruction of each person who
is working with the valve.
Applicable regulations about occupational safety ad safety engineering must be
known and applied.
Documentation
→ This documentation must be fully read and
understood.
→ The instructions given in this operation
manual must be put into practice.
→ This documentation must be available at
any time.
Markings at the operating site
→ Ensure adequate warning of the risks linked
to the valve. Use in the area of the installed
valve the following warning and prohibition
sings in compliance with EN ISO 7010 and
BGV A8 (VBG125):
Warning sign to indicate risk of
burns at the solenoid
Warning sign to indicate electrical hazards at the solenoid
Prohibition sign to
prevent people from entering
hazardous areas
1.8
Personnel qualification
→ Ensure as operator that persons who work
on or with the valve are sufficient qualified
for this job.
→ Comprehensively train the operating per-
sonnel in terms of safety.
→ Only allow trained specialists to perform
electric connections, commissioning, maintenance and trouble shooting
Demands
Operating personnel must be instructed on
operational sequences and procedures.
Operating personnel must know its responsibilities regarding the work to be performed.
Trained specialists must possess profound
knowledge in mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, hydraulic und pneumatic.
Trained specialists must be authorized to
commission, ground and designate devices,
systems and power circuits according to the
standards of safety technology.
Trained specialists must possess profound
knowledge about design and principle of operation of the valves and the plant.
1.9
Personal protection equipment
→ Wear appropriate protection equipment.
Observe the personal protection equipment
as requested in “residual risks” (refer to
chapter
2 ).
Protective eye glasses
to protect from escaping fluids or
exhausting compressed air
Protective gloves
Resistance to cutting to pro-
tect from sharp edges or ridges;
resistance to acids to protect from
hazardous fluids
Protective footwear
to protect from parts or tools falling
down
2
General safety instructions
These safety instructions are only related to
the single valve. In combination with other
plant components there may be other potential
dangers, which must be taken into account by
carrying out a risk analysis for the system.
→ Compare the details on the rating plate and
data sheet to the operating data. The particular application must not exceed the given
limits (e.g. pressure, temperatures).
→ You must depressurize the pipe system and
de-energize the solenoid prior to perform
mounting and maintenance works.
→ Prime the valve slowly when commissio-
ning. Fast pressurizing will cause the valve
to open briefly.
→ Strength tests with the valve seat open are
permitted maximum up to 1.5 times of the
nominal pressure rating (PN) at room temperature. Do not operate valve during test.
!DANGER
Hazardous electrical voltage
(>25V AC; >60V DC)
There are risks from electrical
voltage during assembly and
maintenance.
→ The electrical connection of the solenoid
must be carried out only by a qualified
electrician.
→ You may only plug the device socket in
de-energized state.
→ Disconnect the power supply off the sole-
noid prior to assembly or dismantling.
! WARNING
Danger from pressurized
pipelines
Pressurized pipelines may burst
resulting in injuries.
→ Depressurize pipe system and block the
fluid stream prior to opening or unmounting the valve.
! CAUTION
Risk of burns at the solenoid
Solenoid is heating up during
operation. Touching the solenoid
leads to risk of burns.
→ Leave the solenoid to cool down before
working at the valve.
Residual risks
Weight of the valve
Phases: transport, storage, assembly,
kg
maintenance, disposal
Risk: falling off, tipping over
Personal protection equipment
(PPE): Protective footwear
Potentially explosive atmosphere
Risk: danger of explosion
! WARNING: Use solenoids and
device sockets with Ex-protection.
10/2018
EN1377027BA
2
Hazardous fluids
7
Phases: assembly, operation, maintenance, disposal
Risk: skin contact, eye contact,
breathing vapors
PPE: protective gloves, protective eye
glasses, breathing protection
Sharp threads and edges
Phases: transport, assembly, main-
tenance, disposal
Risk: risk of cuts
PPE: protective gloves
3
Avoid damage to property
NOTICE
Deposits and dirt lead to malfunctions
If the control bores are clogged or the
core is blocked by soil the valve no longer
closes or opens.
→ Install a strainer (mesh size≤0,25mm) in
front of the valve inlet if necessary.
Damages through accumulation of heat
The solenoid will overheat during continuous duty if the heat can not be radiated. This may shorten the solenoid coil’s
product life cycle.
→ You must not cover the solenoid with paint.
→ You must not encase the solenoid in a
tight housing or in a thermal insulation.
Residual risks
Pressure against valve outlet
Valve only firmly closes in flow
direction.
Fluid freezing
The valve is not designed to withstand the fluid freezing.
4
Identifying the valve
The rating plate is situated on the solenoid
body.
Made in Germany
Buschjost GmbH
D-32545 Bad Oeynhausen
1
Part no./Bestell-Nr.
2
3
8407382.9104.23049
VHz
230
PA
www.imi-precision.com
40-60
9VA/9VA
0,3–10,5
use -plug only
bar
XXXX
Rating plate (example)
Order number
1
Operating voltage
2
Frequency of voltage
3
Power consumption inrush/hold
4
Operating pressure range
5
Date of manufacture (week /year)
6
if this marking is shown on the rating plate:
7
use device socket with rectifier
5
Transport and storage
NOTICE
Damage of the valve
Valve may be damaged if foreign particles
get into the valve.
→ Only transport and store valve in its deli-
very packaging.
→ Take valve out of the packaging immedia-
tely prior to assembly.
prolonged storage at −10°C to +20°C
Avoid during transport:
mechanical loads: falling off, tipping over
damages to the electrical terminal elements
Avoid during storage:
thermal stress: permanently increased storage
temperatures; distance to heating devices < 1m
chemical load:at the storing site through sol-
4
3
vents, chemicals, acids, fuels and similar
Weather conditions: at construction sites strong,
4
5
6
watertight containers are necessary
Unfavourable storing conditions may reduce
the service life of the sealing materials
6
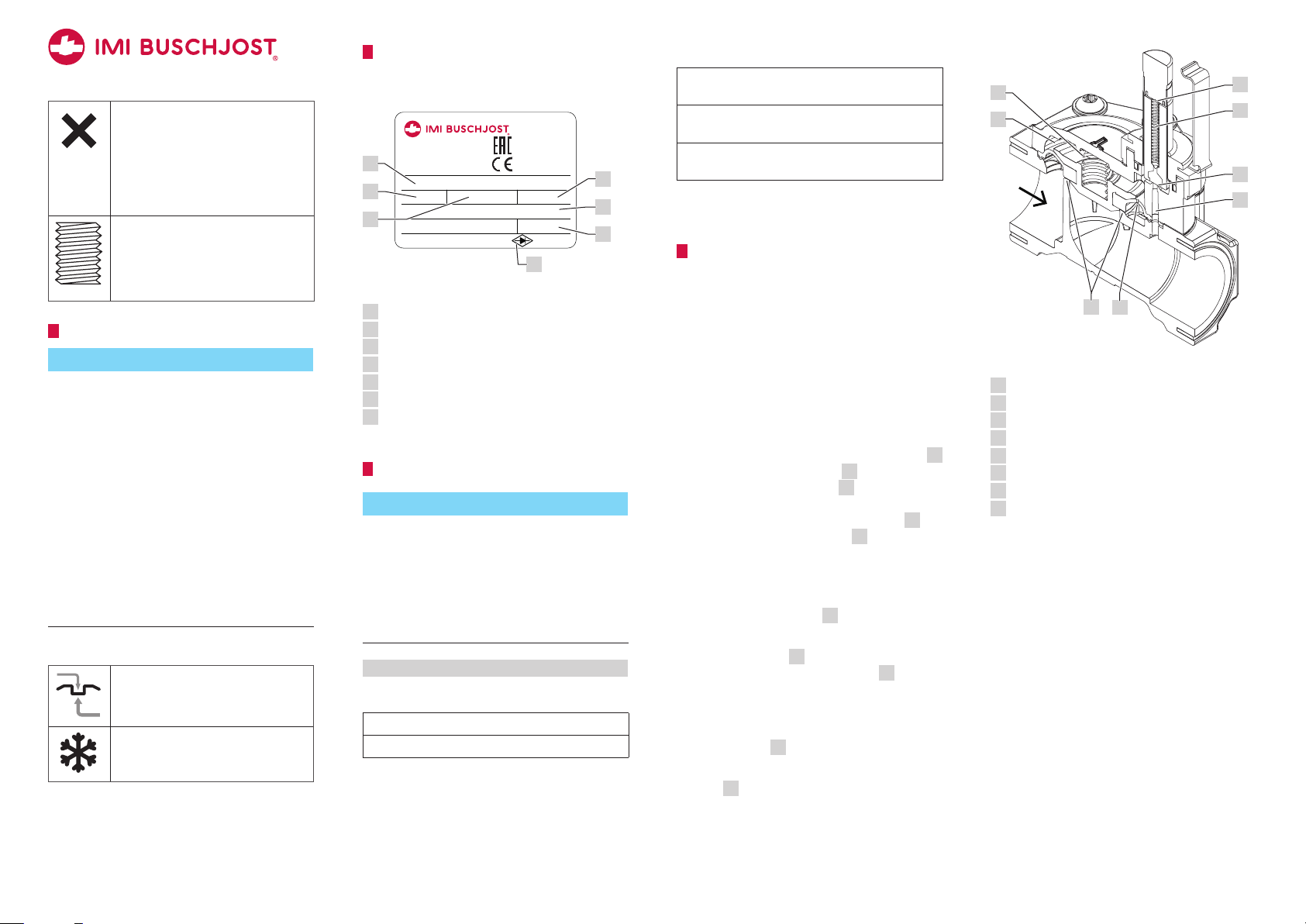
Function
P
Design
Through-way valve as seat valve with diaphragm as sealing device.
1
2
Operation
The valve is electromagnetic indirectly-controlled. The switching function needs a pressure
difference between valve inlet P and valve
outlet A.
Normal position: closed
Due to the effect of the compression spring 7
inside the core the pilot seat
compression spring presses
6 is closed. A
4 the diaphragm
sealingly to the main valve seat. The operating fluid flows through the control bore
the diaphragm to the chamber
3 above the
2 in
Sectional view without solenoid
Main valve seat
1
Control bore of diaphragm (pressure build-up)
2
Control space
3
Compression spring above diaphragm
4
Control bore in valve (pressure reduction)
5
Pilot seat
6
Compression spring inside core
7
Magnet face of core tube
8
8
7
6
5
A
diaphragm and increases the closing force.
Switching position: open
The magnetic force lifts the core towards the
magnet face of core tube
8 when the sole-
noid is energized.
Since the pilot seat
pressure is reducing from chamber
6 is open the fluid
3 towards
valve outlet.
More fluid is flowing off via the pilot seat to
the chamber than the amount flowing in via
the control bore
4 in the diaphragm.
The differential pressure lifts up the diaphragm
1 and opens the main valve seat.
10/2018
EN1377027BA
3
 Loading...
Loading...