Page 1
Device manual
ProfiNet encoder
RM30xx
706354/00 06/2013
UK
Page 2

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
2
Contents
1 Preliminary note � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4
1�1 Symbols used� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4
1�2 Warning signs used � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4
1�3 Notes on this document � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4
2 Safety instructions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 4
3 General information � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
3�1 Absolute encoder � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
3�2 ProfiNet � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
4 Functions and features � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6
5 Electrical connection� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6
5�1 Ethernet and power supply� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6
5�2 Ethernet cables � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
5�2�1 RJ45 – M12 crossed � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
5�2�2 RJ45 – M12 straight� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
5�2�3 M12 – M12 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
6 LED indicators � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
6�1 Legend � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
6�2 Status LEDs � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
7 Installation� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 9
8 Device configuration � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
8�1 Standardisation � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
8�2 Encoder classes � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
8�3 Encoder functions� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
8�4 Signal list for cyclic data transmission � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
8�4�1 Format of position value� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
8�4�2 Encoder control word (STW2_ENC) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 13
8�4�3 Encoder status word (ZSW2_ENC) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 14
8�4�4 Encoder control word (G1_STW)� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 14
8�4�5 Encoder status word (G1_ZSW) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 15
8�5 Standard and vendor telegrams � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 15
9 Configuration principle � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 17
9�1 Overview of encoder functions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 17
9�2 Encoder functions – Data format � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 17
9�3 Parameters for acyclic data transmission� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 19
9�3�1 Standard parameters � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 20
9�3�2 Device parameters� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 20
9�3�3 Vendor parameters � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 20
9�4 Supported parameters � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 20
9�5 Encoder function description � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 22
9�5�1 Code sequence � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 23
9�5�2 Class 4 functionality � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 23
Page 3

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
3
9�5�3 Preset control for G1_XIST1 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 23
9�5�4 Scaling function control � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 23
9�5�5 Alarm channel control � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 24
9�5�6 Compatibility mode � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 24
9�5�7 Preset value � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 24
9�5�8 Offset value � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 27
9�5�9 Scaling parameters � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 27
9�5�10 Maximum master sign-of-life failures � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 27
9�5�11 Velocity measuring units� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 27
9�5�12 Velocity filter� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 28
9�5�13 Endless shaft (round axis) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 28
9�5�14 Encoder profile version � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 29
10 Configuring with STEP7 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 30
10�1 Installing the GSDML file � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 30
10�2 Adding an encoder to a STEP7 project � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 31
10�2�1 Standard encoder without PDEV � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 32
10�3 Module Access Point parameter setup: � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 37
Page 4

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
4
1 Preliminary note
1.1 Symbols used
► Instructions
> Reaction, result
[…] Designation of keys, buttons or indications
→ Cross-reference
Important note
Non-compliance can result in malfunction or interference�
Information
Supplementary note
1.2 Warning signs used
NOTE
Warning of damage to property�
1.3 Notes on this document
This document applies to encoders of the following type:
RM30xx (ProfiNet interface)
It is part of the device and contains information about the correct handling of the
product�
This document is intended for qualified electricians� These specialists are people
who are qualified by their training and their experience to recognise and to avoid
possible hazards that may be caused during operation of the device�
► Read this document before using the device�
► Keep this document during the service life of the device�
► Observe these operating instructions�
► Adhere to the warning notes�
2 Safety instructions
Non-observance of the instructions, operation which is not in accordance with use
as prescribed below, wrong installation or incorrect handling can affect the safety
of operators and machinery�
The installation and connection must comply with the applicable national and
international standards� Responsibility lies with the person installing the device�
Only the signals indicated in the technical data or on the device label may be
supplied to the connections or wires�
Page 5

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
5
3 General information
3.1 Absolute encoder
The basic principle of an absolute encoder is the optical sampling of a transparent
code disc which is fixed with the shaft to be measured�
The absolute encoder has a resolution of 8,192 steps per resolution (13 bits) at
4,096 revolutions (12 bits)� This results in a maximum resolution of 33,554,432
steps (25 bits)�
For further information about the function principle and setup of a ProfiNet
network, please refer to
→ http://www.profibus.com/community/regional-pi-associations/germany
3.2 ProfiNet
ProfiNet is an industrial Ethernet standard merging plant automation with
enterprise IT resources� ProfiNet provides comparable functionality to PROFIBUS
with the additional possibility of firmware upgrades�
Established IT standards are employed as basis of communication:
UDP and IP� XML is used as description language for device profiles (GSDML
files)�
Two ways of using ProfiNet are available:
ProfiNet IO, similar to PROFIBUS DP as a distributed I/O system and ProfiNet
CBA as a modular component-based system for larger systems�
ProfiNet offers scalable communication for different applications in industrial
automation:
● ProfiNet NRT (Non Real Time) is suited for non-time-critical process
automation with clock rates of roughly 100 ms�
● ProfiNet RT (Real Time) offers a communication channel with optimised
performance (10 ms clock rate) for most factory automation tasks�
● ProfiNet IRT (Isochronous Real Rime) supports communication clock rates
around 1 ms and a jitter of less than 1 μs. This operating mode is mainly of use
for motion control applications�
ProfiNet IO uses a view of distributed controllers similar to PROFIBUS DP� IO
controllers (PLCs) run automation programs, IO devices (e�g� absolute encoders)
are remotely assigned field devices, and IO supervisors (e�g� programming
devices) are used for commissioning and diagnostics�
The setup of ProfiNet IO is done similar to PROFIBUS� The fieldbuses (e�g�
Ethernet topologies) are assigned to the control system during configuration� The
IO device is configured based on the GSDML contents�
After completion of the setup the configuration data are loaded into the IO
controller (PLC) and data exchange with the IO device takes place�
Page 6
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
6
An IO device is addressed within ProfiNet (and also possibly by external Ethernet
components) through its IP address�
Data can be transferred (process data) from the IO controller to the IO device (and
vice versa) cyclically� Apart from this, acyclic parameters can be exchanged during
setup of the IO device or by the use of PLC programming blocks during operation�
4 Functions and features
● Integrated bootloader for firmware upgrades
● Round axis functionality
● Neighbouring detection (when replacing the device)
● Device identification via LEDs
● Different filters for velocity
● ProfiNet encoder profile V4�0/V4�1
5 Electrical connection
► Disconnect power�
► Connect the device according to the indications on the type label�
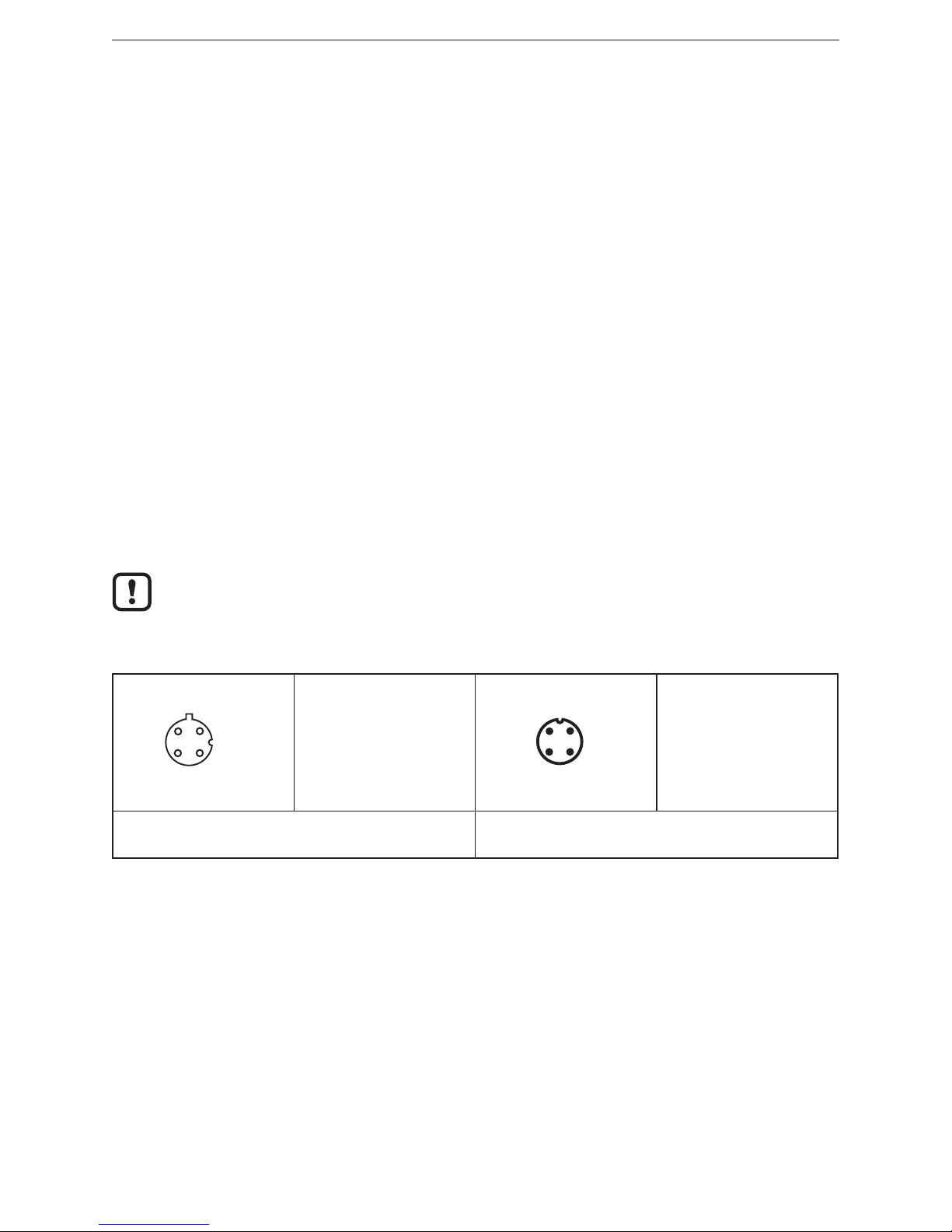
5.1 Ethernet and power supply
1
4
3
2
1: Tx +
2: Rx +
3: Tx -
4: Rx -
1: US (10 - 30 V DC)
2: not connected (n�c�)
3: GND (0 V)
4: not connected (n�c�)
Ethernet:
4 pin female, D-coded
Power supply:
4 pin male, A-coded
Page 7
UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
7
5.2 Ethernet cables
5.2.1 RJ45 – M12 crossed
Signal RJ45 M12
Tx + 1 2
Tx - 2 4
Rx + 3 1
Rx - 6 3
5.2.2 RJ45 – M12 straight
Signal RJ45 M12
Tx + 1 1
Tx - 2 3
Rx + 3 2
Rx - 6 4
5.2.3 M12 – M12
Signal M12 M12
Tx + 1 1
Tx - 2 2
Rx + 3 3
Rx - 4 4
6 LED indicators
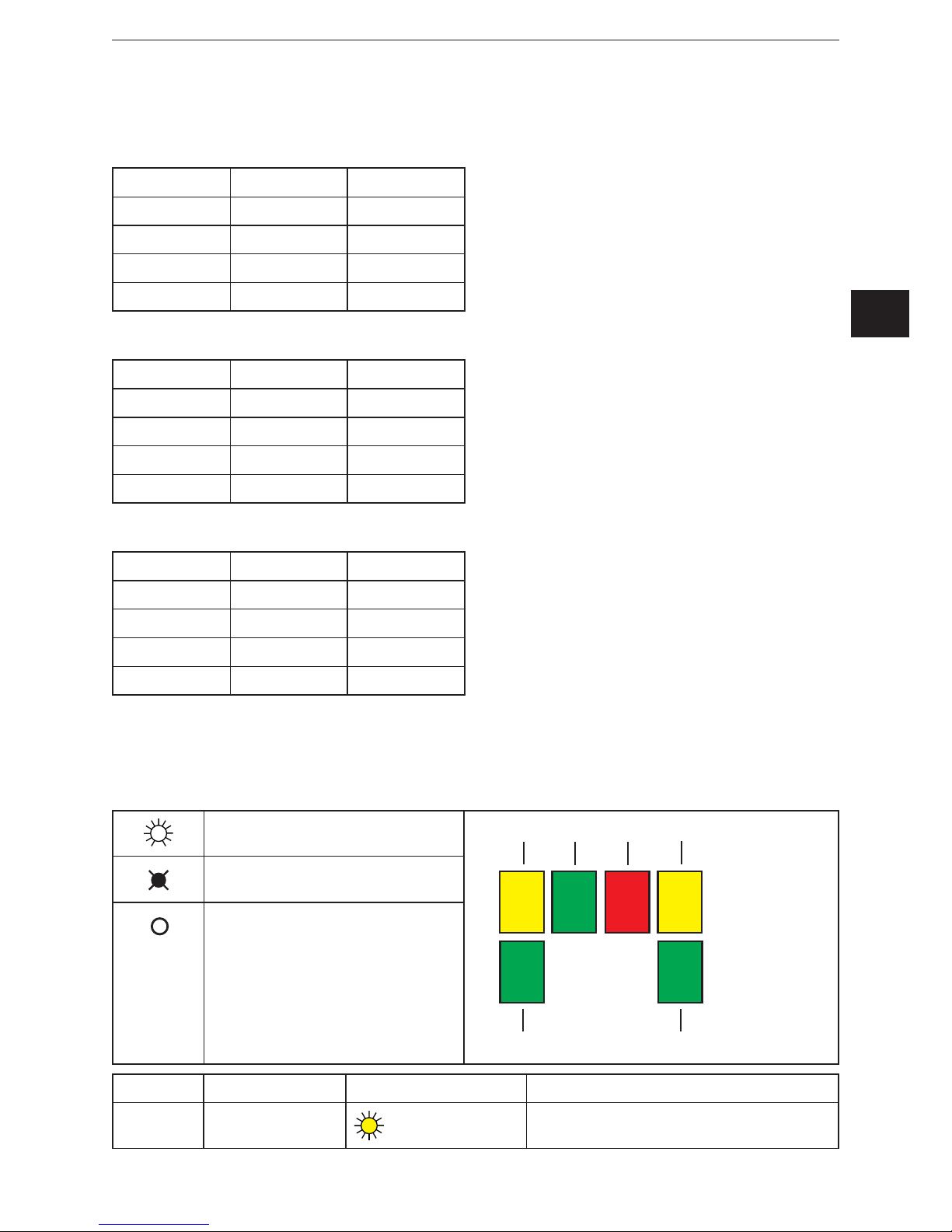
6.1 Legend
LED on / lit
Stat 1 Stat 2 Active 1
Active 2
Link 1Link 2
LED flashes
LED off
LED Colour Status / frequency Description
Active 1 Yellow
Data traffic on port 1
Page 8
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
8
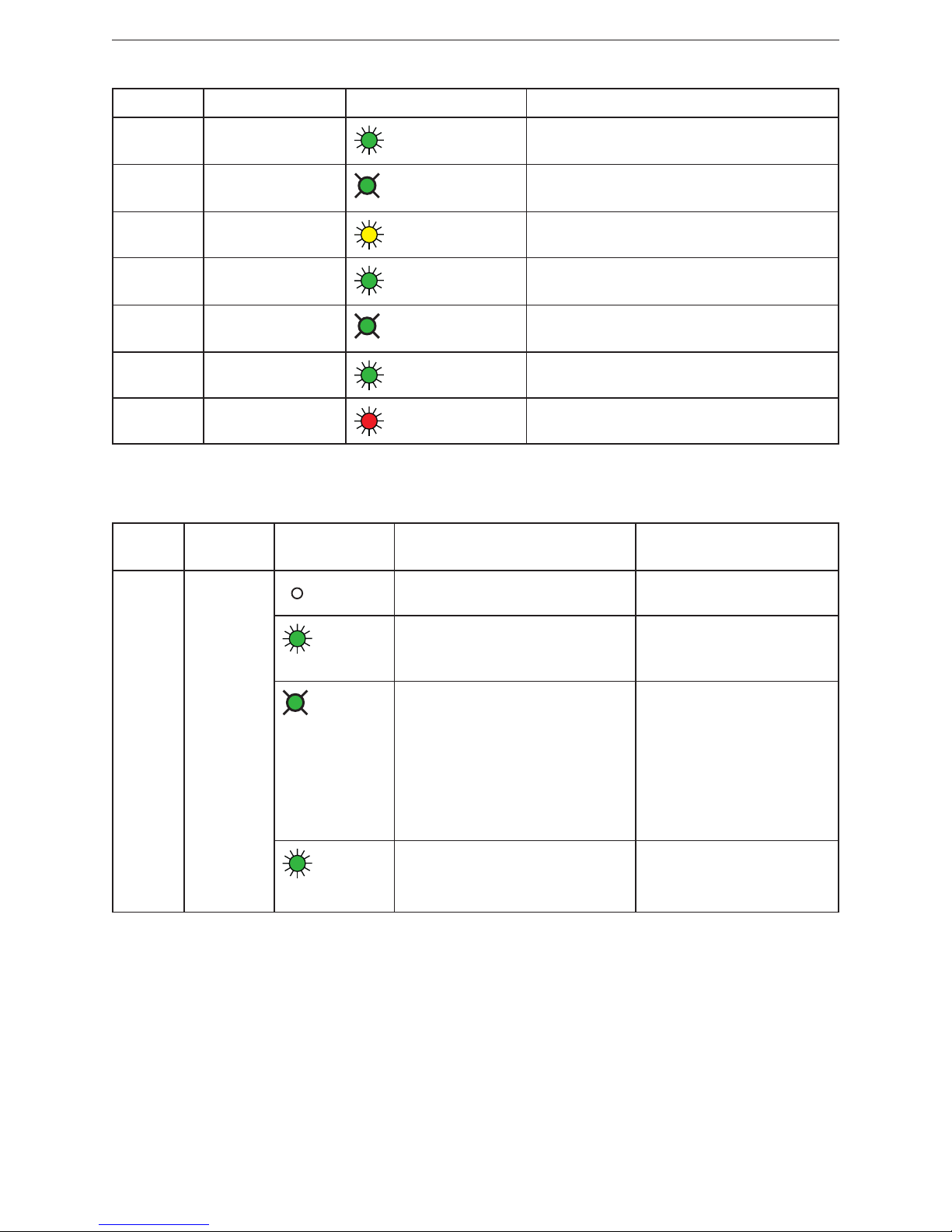
LED Colour Status / frequency Description
Link 1 Green
Active link to other Ethernet components
via port 1
Link 1 Green
2 Hz
Identification call is activated and link connection is available
Active 2 Yellow
Data traffic on port 2
Link 2 Green
Active link to other Ethernet components
via port 2
Link 2 Green
2 Hz
Identification call is activated and link connection is available
Stat 1 Green
Status 1, details → Status LEDs
Stat 2 Red
Status 2, details → Status LEDs
6.2 Status LEDs
LED Colour Status /
frequency
Description Cause
Status 1 Green
No power Fuse or cable defective
No connection to control unit
Criteria: no data exchange
– Bus disconnected
– IO controller not available
/ switched off
0�5 Hz
Parameterization fault, no data
exchange
Criteria: data exchange correct�
The slave did not switch to the
[data exchange] mode�
– Slave not configured yet
or wrong configuration
– Wrong station address
assigned (but not outside
the permitted range)
– Actual configuration of
the slave differs from the
desired configuration
Data exchange
Connected device and operation
OK�
Page 9
UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
9
LED Colour Status /
frequency
Description Cause
Status 1
(fault)
Red
No power Fuse or cable defective
No connection to control unit
Criteria: no data exchange
– Bus disconnected
– IO controller not available
/ switched off
0�5 Hz
Parameterization fault, no data
exchange
Criteria: data exchange correct�
The slave did not switch to the
[data exchange] mode�
– Slave not configured yet
or wrong configuration
– Wrong station address
assigned (but not outside
the permitted range)
– Actual configuration of
the slave differs from the
desired configuration
Data exchange
Connected device and operation
OK�
7 Installation
► Disconnect power�
► Ensure that the machine stands still�
► The drive must not be started during installation�
► Do not hit the shaft; do not use a file or similar tool on the shaft: Risk of
destruction!
This product is a precision measuring device� Therefore it has to be handled with care by trained
staff� The following warnings apply to influences outside the limit values indicated in the product data
sheet�
Damage to the product can be caused by:
● electrostatic discharge while touching the electronics
● too high forces on the shaft
● humidity and chemical liquids (do not connect any cables oriented upwards)
● extreme temperatures
● too high vibrations and shocks
● short circuit or too high an operating voltage
● impact, shock or any other physical forces
Page 10
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
10
8 Device configuration
8.1 Standardisation
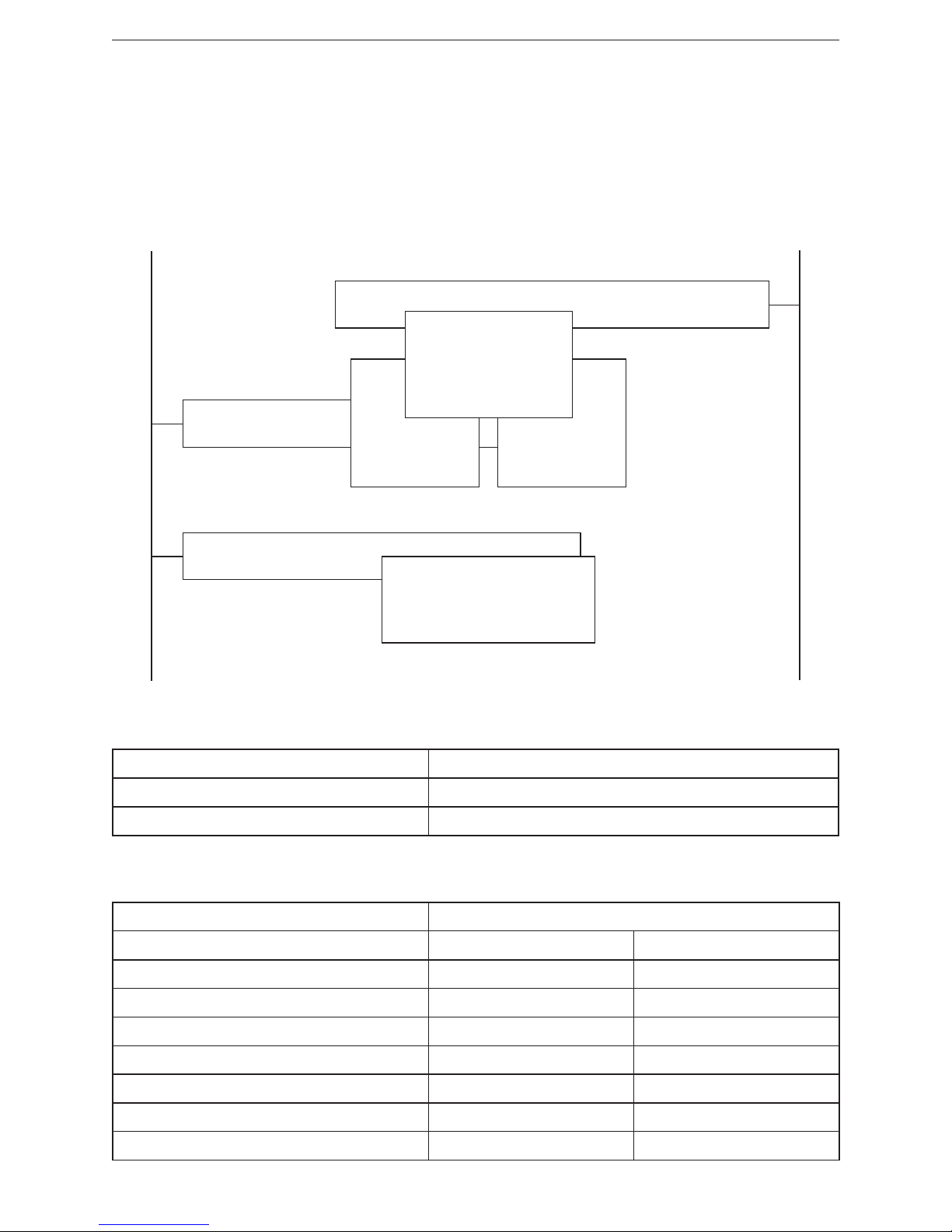
The current generation of ProfiNet encoders is based on the profile V4�0/V4�1
(PNO no� 3�162)� With this standardisation it is possible to substitute all products
that fulfil the specification�
PROFIBUS
Network
PROFINET
Network
PROFINET IO
PNO No. 2.332
PROFIBUS DP-V2
IEC 61158
PROFIDRIVE V4
PNO No. 3.172
I&M Functions
PNO No. 3.502
Encoder Profile V4
Class 3 and 4
PNO No. 3.162
Encoder Profile
Class 1 and 2
PNO No. 3.062
PROFIBUS DP
EN 50170
8.2 Encoder classes
Application class Description
3 Isochronous mode is not supported (RT)
4 Isochronous mode is supported (IRT)
8.3 Encoder functions
Implementation
Function Class 3 Class 4
Code sequence - / • * •
Class 4 functionality • •
G1_XIST1 preset control - / • * •
Scaling function control - / • * •
Alarm channel control • •
Preset value - / • * •
Preset value (64bit) - -
Page 11
UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
11
Implementation
Function Class 3 Class 4
Measuring units per revolution (32bit) - / • * •
Total resolution (32bit) - / • * •
Measuring units per revolution (64bit) - / • * •
Total resolution (64bit) - / • * •
Maximum master sign-of-life failures - / • * •
Velocity measuring unit - / • * •
Encoder profile version • •
Operating hours counter - -
Offset value - / • * •
Offset value at 64 bits - / • * •
Round axis function • •
Velocity filter • •
* If class 4 functionality is activated
8.4 Signal list for cyclic data transmission
Signal no. Meaning Abbreviation Length (bit) Sign
3 Master's sign-of-life counter STW2_ENC 16 -
4 Slave's sign-of-life counter ZSW2_ENC 16 -
6 Velocity value A NIST_A 16 •
8 Velocity value B NIST_B 32 •
9 Control word G1_STW 16 -
10 Status word G1_ZSW 16 -
11 Position value 1 G1_XIST1 32 -
12 Position value 2 G1_XIST2 32 -
13 Position value 3 G1_XIST3 64 -
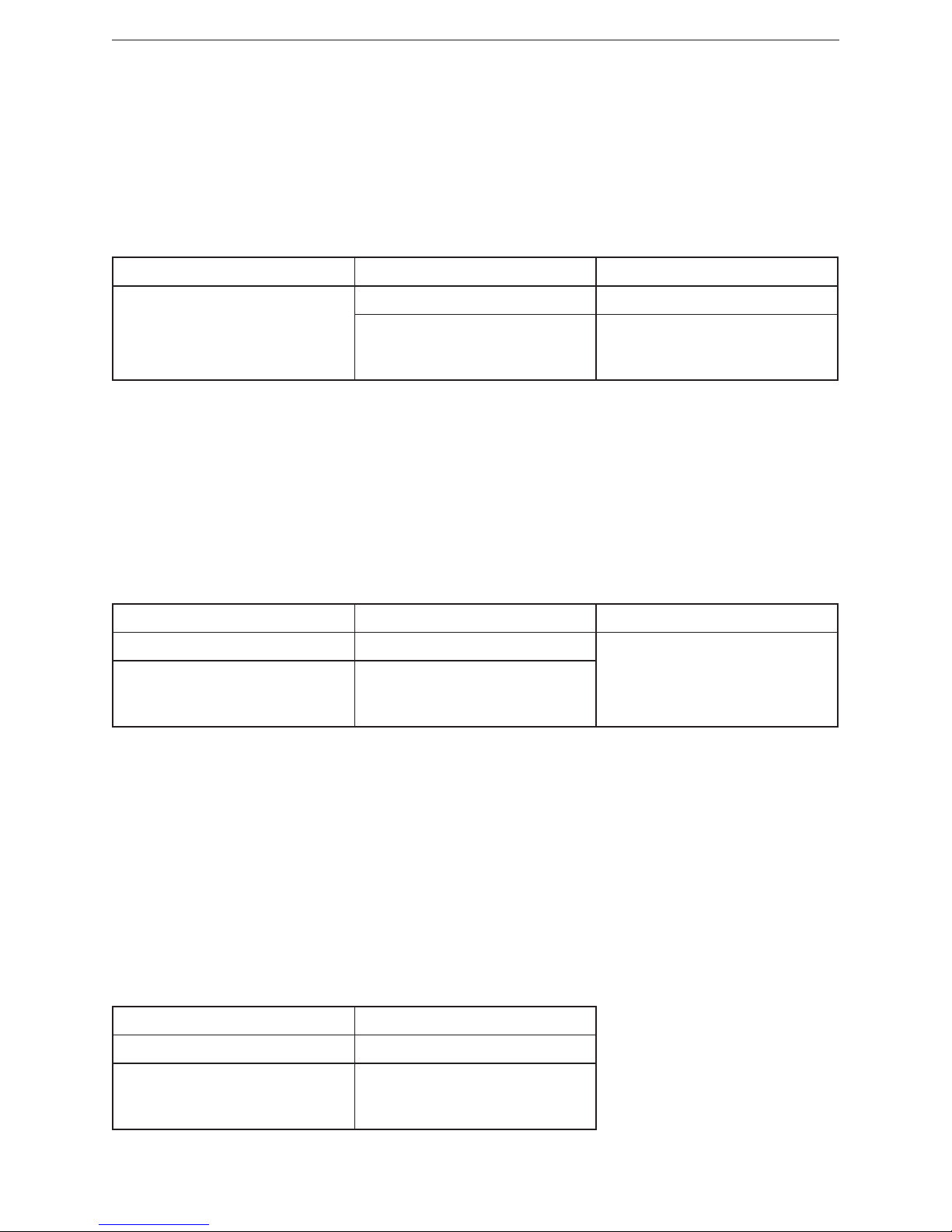
8.4.1 Format of position value
Note:
G1_XIST1 and G1_XIST2 are the actual position values in binary format� The
alignment in the data-frame (left or right-aligned) is considered for each individual
resolution� For absolute encoders an example is given below�
The alignment of the output format (left or right-aligned) remains constant and affects the actual
resolution� The number of bits provided changes depending on the resolution�
Example
25 bit multiturn absolute encoder (8,192 steps per revolution, 4,096 revolutions)�
Page 12
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
12
All values are presented in binary format� If an error occurs, G1_XIST2 displays
the error telegram instead of the right-aligned value�
The shifting factors in P979 "sensor format" display the current format� P979,
subindex 4 (shift factor for G1_XIST2) = 0� The settings in the encoder parameter
data affect the position value in both G1_XIST1 and G1_XIST2�
Absolute value in G1_XIST2
31���25 24���13 12���0
M S
Distinguishable
revolutions
(multiturn value)
Pulses
(singleturn steps
per revolution)
Setting: encoder profile 4.0*
● By default, G1_XIST1 is left-aligned�
● P979, subindex 3 (shift factor for G1_XIST1) = 32 – total resolution (next binary
value)
● G1_XIST1 transmits positions values independent of bit 10 in stw2 and bit 13 in
g1_stw1�
Absolute value in G1_XIST1 for encoder profile 4�0
31���20 19���7 6���0
M S
Distinguishable
revolutions
(multiturn value)
Pulses
(singleturn steps
per revolution)
Setting: encoder profile 4.1*
● By default, G1_XIST1 is right-aligned�
● A 32-bit counter starts with the absolute position value� After increasing to the
maximum counter value, start again with 0 or decreasing from the max� counter
value to 0�
● P979, subindex 3 (shift factor for G1_XIST1) = 0
● G1_XIST1 transmits positions values independent of bit 10 in stw2 and bit 13 in
g1_stw1�
Absolute value in G1_XIST1 for encoder profile 4�1
31���13 19���0
M S
Distinguishable
revolutions
(multiturn value)
Pulses
(singleturn steps
per revolution)
Page 13

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
13
* Profile 4.0 is realised with GSDML-V2.2-IFM-RM30xx+RN30xx-20130802, profile
4�1 with newer data�
G1_XIST3
For 64-bit position values G1_XIST3 is available� The binary value is output rightaligned and without shifting factor�
IO data (DWord) 1 2 3 4
Format 64-bit position value
8.4.2 Encoder control word (STW2_ENC)
4-bit counter, left-aligned� The master application starts the sign-of-life counter with
any value between 1 and 15� The master increases the counter in every cycle of
the master application�
Valid values for the master's sign-of-life counter are 1 to 15� "0" indicates an error
and is left out in normal operation�
Implementation
Bit Function Class 3 Class 4
0���9 Reserved,
currently not used
- -
10 Control by PLC • •
11 Reserved,
currently not used
- -
12���15 Sign-of-life status indication - -
Bit Value Meaning Comments
10 1 Control by PLC Control via interface,
IO data is valid
0 No control via PLC IO data is not valid, except sign-
of-life
12���15 Controller sign-of-life Continuously sends
counting values from 0 to 15
Page 14

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
14
8.4.3 Encoder status word (ZSW2_ENC)
4-bit counter, left-aligned� The slave application starts the sign-of-life counter with
any value between 1 and 15 after successful synchronisation to the clock pulse�
The counter is increased in every DP cycle of the slave application� Valid values
for the slave's sign-of-life counter are 1 to 15, "0" indicates an error and is left out
in normal operation�
Implementation
Bit Function Class 3 Class 4
0���8 Reserved,
currently not used
- -
9 Control requested Mandatory Mandatory
10���11 Reserved,
currently not used
- -
12���15 Encoder sign-of-life counter - Mandatory
Bit Value Meaning Comments
9 1 Control requested Control via interface,
IO data is valid
0 No control via PLC IO data is not valid, except sign-
of-life
12���15 Encoder
Sign-of-life counter
Continuously sends
counting values from 0 to 15
8.4.4 Encoder control word (G1_STW)
Bit Value Function Comments
0���10 Reserved,
currently not used
11 0/1 "Home position" mode Specifies if the position value
shall be set to a previously
programmed absolute value or
shifted by this value�
0: set home position / preset
(absolute)
1: shift home position / preset
(relative = offset)
12 1 Set preset /
shift request
Preset (shift) is set when changing this bit to "1" (rising edge)�
Default preset value:
(shift): 0
Warning:
After setting the preset the offset
will be saved in the EEPROM� In
these 5-10 ms the encoder will
not send position values�
Page 15

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
15
Bit Value Function Comments
13 1 Request absolute value cyclically Request of additional cyclic trans-
mission of the absolute actual
position in G1_XIST2� If no other
data needs to be transferred
due to commands or errors the
absolute position value will be
transmitted automatically�
14 1 "Parking sensor" activated If the "parking sensor" bit is
activated, the encoder transmits
no error messages�
15 1 Acknowledgement of a sensor
error
Request to acknowledge / reset a
sensor error
8.4.5 Encoder status word (G1_ZSW)
Bit Value Function Comments
0���10 Reserved,
currently not used
11 Acknowledgement of a sensor
error in process
Is set if the reset of a sensor error
takes longer than one bus cycle�
12 1 Set preset value /
shift reference point executed
Acknowledgement for "set preset
/ shift reference point"
13 1 Transmit absolute value cycli-
cally
Acknowledgement for "request
absolute value cyclically"
14 1 "Parking sensor" activated If the "parking sensor" bit is
activated, the encoder transmits
no error messages�
15 1 Acknowledgement of a sensor
error
Indicates a sensor error�
A device specific error code is
shown in G1_XIST2�
8.5 Standard and vendor telegrams
Standard telegram 81
IO data
(DWord)
1 2
Setpoint STW2_ENC * G1_STW1 *
IO data
(DWord)
1 2 3 4 5 6
Actual value ZSW2_ENC* G1_ZSW1* G1_XIST1* G1_XIST2*
Standard telegram 82
IO data
(DWord)
1 2
Setpoint STW2_ENC* G1_STW1 *
Page 16

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
16
IO data
(DWord)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Actual value ZSW2_ENC* G1_ZSW1* G1_XIST1* G1_XIST2* NIST_A*
Standard telegram 83
IO data
(DWord)
1 2
Setpoint STW2_ENC* G1_STW1 *
IO data
(DWord)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Actual value ZSW2_ENC* G1_ZSW1* G1_XIST1* G1_XIST2* NIST_B*
Standard telegram 84
IO data
(DWord)
1 2
Setpoint STW2_ENC* G1_STW1 *
IO data
(DWord)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Actual value ZSW2_ENC* G1_ZSW1* G1_XIST3* G1_XIST2* NIST_B*
* Details on the variables → chapter 3.4
Vendor telegram 860
With this telegram it is not necessary to set special bits for a cyclic data
transmission� In its functionality, it is similar to PROFIBUS and provides for easy
configuration of the preset value during PLC operation� The velocity value uses the
format that is defined in the velocity measuring unit�
If bit 31 is set to "1", the preset value will be adopted immediately� A further preset
value can only be set if bit 31 is reset to "0"�
● No control word
● No status word
● No status indication
● Output: 32 bit-unsigned preset value (bit 31 preset control, must be less than
total resolution)
● Input: 32 bit-unsigned preset value + 32 bit-integer velocity value
Data input (from encoder to controller): 8 bytes
Position value - 32-bit unsigned Velocity value - 32-bit signed
Page 17

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
17
Byte 0 Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3 Byte 4 Byte 5 Byte 6 Byte 7
MSB LSB MSB LSB
Data output (from controller to encoder): 4 bytes
Preset - 32-bit unsigned
Bit 31 Bit 30 ���������������������������������������������������������������������������������bit 0
Preset control Preset value < Total resolution
9 Configuration principle
Encoders with ProfiNet interface can be programmed according to the needs of
the user�
► The GSDML file of the encoder has to be installed in the PLC software tool�
9.1 Overview of encoder functions
Function Communication channel
Position value Cyclic input (IO device -> IO controller)
Preset Cyclic output (IO controller -> IO device)
Code sequence Acyclic input/output
Scaling function Acyclic input/output
9.2 Encoder functions – Data format
ProfiNet IO devices are set up in modules� Each module can be assigned to slot�
One sub slot can contain several cyclic input/output channels as well as acyclic
record channels (required for parameters)�
There are PLC versions from different manufacturers available� Some of them
support only one sub slot� Others, e�g� S7 400, support several sub slots� To work
with all PLCs there are two directories in the GSDML file: standard (for IRT) and
"no PDEV"�
ifm encoders offer for the standard profile one slot with one sub slot for all old
PLCs that do not support several sub slots�
Device parameters are systematically grouped together in a table� The following
tables give an overview of the ifm encoder functions�
Page 18

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
18
EncoderGSDML file
ControllerSPS project tool
1 2
1: Acyclic data transmission (parameters)
2: Cyclic data transmission (process data)
Page 19

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
19
9.3 Parameters for acyclic data transmission
In the start-up phase the user parameters are sent to the encoder as data record
object for mapping of the different encoder functions in the user data section (data
record 0xBF00)� In addition to the parameter "data configuration" the encoder
supports a number of PROFIdrive parameters and encoder specific parameters via
the acyclic data exchange service�
With GSDML version GSDML-V2�2-IFM-RM30xx+RN30xx-20130802, it is
possible to change the telegram type without changing the MAP parameters�
MAP
Parameter
Access
Encoder
Functions
Parameter
Manager
Parameter
Data Base
Standard
Telegram 81.
82, 83 or 84
Sub 1Sub 2
Sub 2Sub 0
Slot 1 Standard Telegrams
Sub 0
Slot 0
Page 20

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
20
9.3.1 Standard parameters
Function Slot Sub slot Index Offset Length IO
Code sequence 1 1 0xBF00 0�0 1 bit -
Class 4 functionality 1 1 0xBF00 0�1 1 bit -
G1_XIST1 preset control 1 1 0xBF00 0�2 1 bit -
Scaling function control 1 1 0xBF00 0�3 1 bit -
Alarm channel control 1 1 0xBF00 0�4 1 bit -
Compatibility mode 1 1 0xBF00 0�5 1 bit -
Measuring units per revolution 1 1 0xBF00 1 8 bytes -
Total resolution 1 1 0xBF00 9 8 bytes -
Maximum master
sign-of-life failures
1 1 0xBF00 17 1 byte -
Velocity unit 1 1 0xBF00 18 1 byte -
9.3.2 Device parameters
Function Slot Sub slot Index Offset Length IO
Preset value 1 1 0xB02E via parameter no�
65000
-
9.3.3 Vendor parameters
Function Slot Sub slot Index Offset Length IO
Preset value 1 1 0x1000 0 1 byte -
9.4 Supported parameters
Number Parameter Read only Read/Write
922 Telegram selection • -
925 Number of tolerated sign-of-life failures - •
964 Device identification • -
965 Profile identification number • -
971 Transfer into EEPROM - •
975 DO identification • -
979 Sensor format • -
980 List of defined parameters • -
65000 Preset - •
65001 Operating status • -
Page 21

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
21
Parameter model
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Request Reference Request ReferenceResponse ID Request ID
DO-ID No of Parameters DO-IDNo of Parameters
Parameter
response
Parameter
request
ParameterResponse
Data Record
0xB02E (READ)
Data Record
0xB02E (WRITE)
Controller/Supersivor
PROFIdrive
Base Mode
Parameter
response
PROFIdrive
Base Mode
Parameter
request
write
Data Record
0xB02E
read
Data Record
0xB02E
error: 1)
ErrorCode = 0xDE
ErrorDecode = 0x80
ErrorCode 1 = 0xB5
ErrorCode 2 = 0
ParameterRequest
error: 3)
ErrorCode = 0xDF
ErrorDecode = 0x80
ErrorCode 1 = 0xB5
ErrorCode 2 = 0
request
accepted
error “state
conflict”, request
not accepted
readout of
parameter
response
error “state conflict”,
no response
available
ok
ok
transfer
response to
Data Record
transfer
request to
Parameter
Manager
BlockHeader;
ParameterRequest
BlockHeader;
ParameterResponse
Parameter
Manager 2)
Parameter
Data Base
Drive / DO
PROFIdrive
Base Mode Parameter
request
PROFIdrive
Base Mode Parameter
response
Request Reference Request ReferenceResponse ID Request ID
DO-ID No of Parameters DO-IDNo of Parameters
Page 22

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
22
Example of configuration according encoder profile V4�1
9.5 Encoder function description
Implementation Description
chapter
Function Class 3 Class 4
Code sequence - / • * • 9�5�1
Class 4 functionality • • 9�5�2
G1_XIST1 preset control - / • * • 9�5�3
Scaling function control - / • * • 9�5�4
Alarm channel control • • 9�5�5
Compatibility mode • • 9�5�6
Preset value - / • * • 9�5�7
Preset value (64 bits) - - -
Measuring units per revolution (32 bits) - / • * • 9�5�9
Total measuring range (32 bits) - / • * • 9�5�9
Measuring units per revolution (64 bits) - / • * • -
Total measuring range (64 bits) - / • * • -
Maximum master sign-of-life failures - / • * • 9�5�10
Velocity unit - / • * • 9�5�11
Encoder profile version • • 9�5�14
Operating hours counter - - -
Offset value - / • * • 9�5�8
Offset value 64 bits - / • * • -
Page 23

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
23
Implementation Description
chapter
Function Class 3 Class 4
Round axis functionality • • 9�5�13
Velocity filter • • 9�5�12
* If class 4 functionality is activated
9.5.1 Code sequence
The parameter "code sequence" defines the counting direction of the position
value� The value increases when the shaft is rotating clockwise (CW) or counterclockwise (CCW) (view onto the shaft)�
Code sequence Direction of rotation when viewing the shaft Code sequence
922 Clockwise (CW) Increasing
925 Counter-clockwise (CCW) Decreasing
9.5.2 Class 4 functionality
The parameter "class 4 functionality" defines that scaling, preset and code
sequence affect the position value in G1_XIST1, G1_XIST2 and G1_XIST3�
Class 4 control Class 4 function
0 (standard) Deactivated (disable)
1 Activated (enable)
9.5.3 Preset control for G1_XIST1
The parameter "preset control" defines the preset function� If parameter class 4
is activated and preset control is deactivated, then the preset value will not be
affected in G1_XIST1�
Preset control Preset function
0 (standard) Preset does not affect G1_XIST1
1 Preset affects G1_XIST1
9.5.4 Scaling function control
The parameter "scaling function control" activates / deactivates the scaling
function� If it is not activated, the physical position value is returned by the
encoder� Scaling function control is only available when class 4 control is
activated�
Scaling function control Scaling function
0 (standard) Deactivated
Page 24

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
24
Scaling function control Scaling function
1 Activated
9.5.5 Alarm channel control
The parameter "alarm channel control" defines the length of the diagnostic
telegram� If the alarm channel is deactivated, then only the first 6 bytes of the
diagnosis will be transmitted�
Alarm monitoring Alarm function
0 (standard) Deactivated
1 Activated
9.5.6 Compatibility mode
This parameter defines if the encoder should be executed in a mode compatible to
version 3�1�
Overview of functions when compatibility mode is disabled
Compatibility mode Compatibility function Meaning
0 Activated Compatible to encoder profile
V3�1
1 (standard) Deactivated No downward compatibility
Function Compatibility mode
Active (=0)
Compatibility mode
Active (=1)
Control by PLC
(STW2_ENC)
Ignored; the control word (G1_STW)
and setpoint values are always valid�
Control request
(ZSW2_ENC) is not supported and
is set to 0
Supported
User parameter
"maximum master sign-oflife failures"
Supported Not supported; one sign-of-life failure
is tolerated, P925 can optionally moni-
tor the sign-of-life counter�
User parameter "alarm
channel"
Supported Not supported; the alarm channel
function is active and
monitored by PROFIdrive parameters�
P965 - profile version 31 (V3�1) 41 (V4�1)
9.5.7 Preset value
With the preset value it is possible to adapt the encoder zero point to the zero
point of the application� When using this function the current encoder position
value is set to the desired preset value� The integrated microcontroller calculates
the internal zero point shift� It is stored in the EEPROM (~ 10 ms)�
Page 25

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
25
Set preset only in standstill�
There is no preset activated when the preset value is written to the encoder�
The preset function is controlled by the bits in sensor control and status words
(G1_STW and G1_ZSW)� The preset value is used when a preset is requested by
bit 12 of the sensor control (G1_STW)�
Class 4 functionality must be enabled�
If the preset value is greater than the total resolution, then the error message 0x02
(lower or higher limit value exceeded) appears in the parameter response in base
mode�
Parameter Meaning Data type
Preset value Preset value is defined via asynchronous
data exchange�
Default value = 0
Integer 32
Page 26

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
26
Example of parameter order for preset with record read-write for SIMATIC CPU300
RecordWriteData] = {
0x00,0x02,0x00,0x01, // Header
0x10,0x00,0xFD,0xE8,0x00,0x00, // Parameter address (preset)
0x43,0x01,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x64 // Parameter value (preset value=100=0x64h)
};
Meaning:
0x00,0x02,0x00,0x01,
| | | |------- Number of parameters = 1
| | |------------- Axis no�/DO-ID = 0
| |------------------ Request ID = 2 Change value
|---------------------- Request reference
0x10,0x00,0xFD,0xE8,0x00,0x00, // Parameter address (preset)
| | | | | |--- Subindex LOW byte
| | | | |------- Subindex HIGH byte
| | | |------------ Parameter number (PNU) LOW byte
| | |----------------- Parameter number (PNU) HIGH byte
| |---------------------- Number of elements
|-------------------------- Attributes
0x01,0x00,0x00,0x00,0x64 // Parameter value (preset value=100=0x64h)
| | | | | |--- Preset value LSB
| | | | |------- Preset value
| | | |------------ Preset value
| | |----------------- Preset value MSB
| |---------------------- Number of values =1
|-------------------------- Format: 0x43= DWord or integer 32bit
SIMATIC S7:
-SFB53
-FC x:
CALL "WRREC", DB53
REQ :=M41�7 // activate sfb request
ID :=DW#16#0 // logical slot address -> adapt
INDEX :=W#16#B02E // record index number
LEN := 16 // data length in byte size of (RecordWriteData[])
DONE :=M41�1 // request finished
BUSY :=M41�2 // busy bit
ERROR :=M41�3 // error bit
STATUS:=MD46 // error number, if error bit = 1
RECORD:= RecordWriteData // record buffer address -> adapt
Page 27

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
27
9.5.8 Offset value
The offset value is calculated in the preset function and exchanges the position
value for the calculated value�
9.5.9 Scaling parameters
The scaling parameters are used to change the resolution� This parameter only
refers to the output values if the scaling function is enabled�
Parameter Meaning Data type
Measuring units
per revolution
Singleturn resolution in steps Unsigned 32
Total measuring range
in measuring units
Total measuring range Unsigned 32
If the resolution per revolution is reduced, a skip in the position value may occur when crossing the
physical zero point�
Reason: The position values exceed the real total resolution�
Use the formula below to avoid this problem:
Total resolution = desired measuring steps / revolution x revolutions
9.5.10 Maximum master sign-of-life failures
With this parameter the number of allowed failures of the master's sign of life is
defined�
Parameter Meaning Value
Maximum master sign-oflife failures
Number of permissible failures
of the sign-of-life counter
0 … 255
Standard =1
9.5.11 Velocity measuring units
This parameter defines the coding of velocity measuring unit used to configure the
values NIST_A and NIST_B� Only telegrams 82-84 use the velocity outputs�
Velocity unit Value
Steps / s 0
Steps / 100 ms 1
Steps / 10 ms 2
RPM 3
N2/N4 4
Page 28

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
28
N2/N4: Velocity scaling used for PROFIdrive telegrams
The current velocity value in NIST is the share in per cent of the reference value�
The reference value can be programmed with parameter P2000�
● N2 (NIST_A), 4000 hex corresponds to a value of 100% of the reference value
● N4 (NIST_B), 4000 0000 hex corresponds to a value of 100% of the reference
value
● The value range is between -200% and +200%
MSB = 1 corresponds to a negative sign
MSB = 0 corresponds to a positive sign
9.5.12 Velocity lter
The velocity value can be used with three different exponential moving average
filter types�
Parameter Meaning Data type
Velocity filter Parameter selection: fine, normal, coarse Integer 32
Ratio between old and current velocity:
– Fine: 7:3
– Normal: 96:4
– Coarse: 996:4
9.5.13 Endless shaft (round axis)
Normally the "total resolution" / "measuring units per revolution" must be an
integer and the total resolution must fit an integer number of times into 8192 for an
encoder with 13 bits per revolution� This means that e�g� 100 or 325 revolutions
could cause troubles�
So the following equation must apply:
(4096 x measuring units per revolution) / total resolution = integer
But the ProfiNet encoder solves this problem automatically� The encoder checks
whether the parameters need the endless shaft and activates this functionality
independently�
The internal software routine only works if the encoder is in operation� If it is necessary to turn the
encoder shaft more than 1,024 revolutions without power supply this can lead to problems (the
internal routine will not work without power supply)� With this function there will be saved additional
values in the internal EEPROM�
Page 29

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
29
9.5.14 Encoder prole version
The encoder profile version is implemented in the encoder� This parameter is not
affected by the compatibility settings�
Bits Meaning
0���7 Profile version, least significant number (value range: 0…99), decimal coding
8���15 Profile version, most significant number (value range: 0…99), decimal coding
16���31 Reserved
Page 30

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
30
10 Configuring with STEP7
In the following chapter the configuration of the ifm encoder with the configuration
tool Hardwaremanager STEP 7 is shown exemplarily�
In this example STEP7 version 5�4 SP4 and the CPU 315-2PN/DP or Simotion
Scout with single axis controller D410 (integrated ProfiNet controller) are used�
10.1 Installing the GSDML file
Prior to initial configuration of the system in the hardware configurator of the
software, the GSD files of the encoder must be imported into the software�
Start the software and proceed as follows to import the above GSx files:
► Open new or existing project�
► Open hardware configurator�
Copy the required GSx file to the software via menu item [Options] → [Install GSD
Files���]�
Importing a GSD file
The GSDML file is supplied by ifm (free of charge on www�ifm�com)�
In order to display the encoder as a bitmap in STEP7 the file will be installed
automatically with the GSDML file – both files must be in the same directory� The
main software release number in the GSDML file and the firmware must be the
same, e�g� 4�xx�
► Select the GSD file from the according source directory�
Page 31

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
31
Selecting the GSD file from the directory
After correct import and an update of the hardware catalogue via [Options] →
[Update catalog] the modules will be displayed as separate entries in the hardware
catalogue�
The exact configuration procedure can be found in the operating manual which is supplied together
with the software�
10.2 Adding an encoder to a STEP7 project
To add an encoder to a project, drag the device [OCD-ENCODER] to an existing
ProfiNet Ethernet network (or choose the network and double-click the [OCDEncoder] icon)�
► Move the telegram to the free slot�
Encoder selection
– Standard encoder with PDEV (asynchronous + RT + IRT)
– Standard encoder without PDEV (asynchronous + RT)
Page 32

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
32
10.2.1 Standard encoder without PDEV
Asynchronous + RT communication for controllers which do not support IRT
functionality�
Standard encoder without ohne PDEV
Page 33

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
33
Encoder name and IP address
Double-click the encoder icon to set the PLC communication parameters�
► Set a device name and the IP address of the encoder�
Set device name
► Click [Ethernet]�
► Also, under the [IO cycle] tab, set the desired update time�
► The device name and IP address have to be set directly in the encoder�
► Connect the PLC and the encoder to Ethernet and switch them on�
Page 34

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
34
► Click [Target system] -> [Ethernet] -> [Edit Ethernet node] and then [Browse]�
Edit Ethernet node
> A new window with the Ethernet nodes is opened�
> STEP7 will scan for devices on Ethernet and will display them in the window�
> The encoder is displayed under [IFM OCD]�
► Select this entry and click [Flash]�
> The link LEDs flash with 2 Hz�
► Click [OK] �
> The MAC address is transferred to a new window�
► Click [Use IP parameters]�
► Enter the IP address and subnet mask of the encoder�
► Click [Assign IP configuration]�
► Enter the name of the device in the text field [Device name]�
Page 35

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
35
► Click [Assign name]�
If more than one encoder is used in the same ProfiNet network, each encoder must be assigned a
different name�
Browse network
Page 36

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
36
Encoder name and IP address
► Double-click the encoder icon to set the PLC communication parameters�
► Assign device name�
► Click [Ethernet] and set the IP address of the encoder�
► Set the desired update time under the [IO cycle] tab�
IO cycle
Page 37

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
37
10.3 Module Access Point parameter setup:
► Double-click on the menu item [Module Access Point]�
Module Access Point
> The window with the list of parameters is opened�
Page 38

Encoder with ProfiNet interface
38
These parameters will be transmitted to the encoder on each start of the PLC�
Parameter settings
Page 39

UK
Encoder with ProfiNet interface
39
 Loading...
Loading...