IFM Electronic AL1000 Device Manual
Device manual
IO-Link master ProfiNet
AL1000
UK
7391030/00 02/2016

IO-Link master
Contents
1 Preliminary note � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 5
2 Safety instructions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 6
3 Documentation� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
4 Functions and features � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 7
5 Product description� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
5�1 DI (digital input) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
5�2 IOL (IO-Link port) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
5�3 Connections � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
5�4 Protection rating � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
6 Features � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 8
7 Scale drawings � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 9
7�1 Dimensions of the screw holes in the fixing clips � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 9
8 Structure of the device � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 9
8�1 Diagnostic and status indicators� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
8�1�1 Diagnostics � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
8�1�2 Status� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
9 Installation� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 10
9�1 Mechanical strain � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
9�2 Sources of interference � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
9�3 Cable routing in control cabinets � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
9�4 Cable routing in buildings � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �11
9�5 Cable routing outside buildings � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
9�6 Installing network/bus cables between buildings � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
9�6�1 Causes of surge voltages � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
9�6�2 Equipotential bonding line � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
9�6�3 Surge protective devices � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 12
9�7 Surge protection measures � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 13
9�8 Grounding concept � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 13
9�9 Installation instructions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 14
9�10 Mounting distances � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 14
9�11 Mounting dimensions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 14
10 Scale drawing � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 16
11 Electrical connection � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 16
11�1 Supply voltages U
11�2 Power supply U
11�3 Power supply U
and U
S
S � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �
A � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �
A� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �
16
17
17
12 Features � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 17
12�1 ProfiNet features � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 17
12�2 IO-Link features � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 18
12�3 General features� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 18
2

IO-Link master
13 Technical data� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 18
14 Connection options� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 22
14�1 ProfiNet and voltage supply connection � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 22
14�2 ProfiNet pin connection � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 22
14�3 Pin connection voltage supply U
S/UA � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � �
22
14�4 Connection of IO Link ports and digital inputs � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 23
14�5 Pin connection of the inputs and IO-Link ports� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 23
15 Local status and diagnostic indicators � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 24
15�1 Indicators for Ethernet ports and voltage supply � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 24
15�2 Indicators for the IO-Link ports and inputs � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 26
16 ProfiNet data model � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 27
16�1 Status/control module� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 27
16�2 Flexible module configuration� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 30
17 I&M functions � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 33
UK
18 Set-up � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 36
18�1 On delivery/default settings � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 36
18�2 Restoring the default settings� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 36
18�3 Start of firmware � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 36
19 Parameterisation� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 37
20 LLDP - Link Layer Discovery Protocol � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 37
21 MRP - Media Redundancy Protocol � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 37
22 SNMP - Simple Network Management Protocol� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 38
23 FSU - Fast Start-Up � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 38
24 Shared Device � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 38
25 IO-Link master � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 38
26 WBM - Web-based management � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 38
26�1 Calling web-based management � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 38
27 Firmware update� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 39
28 Diagnostic alarms � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 39
29 Device replacement � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 39
30 Substitute value behaviour � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 40
31 Firmware Update ProfiNet � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 40
32 Firmware update� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 40
32�1 Access the FTP server � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 40
32�2 Upload � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 42
32�3 Firmware update � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 43
32�4 Access the web server � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 43
32�5 Setting the firmware update via FTP � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 44
3

IO-Link master
32�6 Perform the firmware update � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 45
32�7 Read out the firmware revision� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 46
33 Setup as per STEP 7 � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 47
33�1 Description of the setup of the device on a SIMATIC® S7 controller� � � 47
34 System requirements � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 47
34�1 Software � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 47
34�2 Hardware � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 47
35 Integrate ifm ProfiNet device in the S7 controller (STEP 7) � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 47
35�1 Creating/opening a project � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 47
35�2 Install the GSDML file� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 48
35�3 Inserting I/O devices in the hardware configurator� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 50
35�4 IO-Link devices� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 50
35�5 Assigning device names� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 51
35�6 Fast startup � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 54
35�7 Media Redundancy Protocol � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 56
35�8 Identification and maintenance� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 58
35�9 Diagnostic alarms� � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � � 60
4
IO-Link master
1 Preliminary note
This document applies to devices of the type "IO-Link master" (art� no� AL1000)�
This document is intended for specialists� These specialists are people who are
qualified by their appropriate training and their experience to see risks and to
avoid possible hazards that may be caused during operation or maintenance of
the device� The document contains information about the correct handling of the
device�
Read this document before use to familiarise yourself with operating conditions,
installation and operation� Keep this document during the entire duration of use of
the device�
Adhere to the safety instructions�
Symbols
► Instructions
UK
> Reaction, result
[…] Designation of keys, buttons or indications
→ Cross-reference
Important note
Non-compliance may result in malfunction or interference�
Information
Supplementary note
Warnings used
WARNING
Warning of serious personal injury�
Death or serious irreversible injuries may result�
CAUTION
Warning of personal injury�
Slight reversible injuries may result�
NOTE
Warning of damage to property�
5

IO-Link master
2 Safety instructions
These instructions contain texts and figures concerning the correct handling of the
device and must be read before installation or use�
Observe the operating instructions� Non-observance of the instructions, operation
which is not in accordance with use as prescribed below, wrong installation or
incorrect handling can seriously affect the safety of operators and machinery�
► Prepare installation
► Disconnect the power supply of the device�
► Ensure that devices cannot be accidentally restarted�
► Verify safe isolation from the supply�
► Earth and short circuit�
► Cover or enclose adjacent units that are live�
► Follow the specific mounting instructions of the device�
► Only suitably qualified personnel in accordance with EN 50 110-1/-2 (VDC 0105
part 100) is permitted to work on this device/system�
► Before installation and before touching the device ensure that you are free of
electrostatic charge�
► The functional earth (FE) must be connected to the protective earth (PE) or to
the potential equalisation� The system installer is responsible for implementing
this connection�
► Connection cables and signal lines must be installed in such a manner that
inductive and capacitive interference do not impair the automation functions�
► Install automation equipment and related operating elements in such a way that
they are protected against unintentional operation�
► Suitable safety hardware and software measures should be implemented for
the I/O interface so that a line or wire breakage on the signal side does not
result in undefined states in the automation device�
► Ensure a reliable electrical isolation of the low voltage for the 24 V supply�
Only use power supplies compliant with IEC 60 364-4-41 or HD 384�4�41 S2
(VDE 0100 part 410)�
► Fluctuations or deviations of the mains voltage from the rated value must not
exceed the tolerance limits specified in the technical data; otherwise this may
cause malfunction and dangerous operation�
► E-stop devices to IEC/EN 60 204-1 must be effective in all operating modes of
the automation device� Unlatching the e-stop devices must not cause restart�
6

IO-Link master
► Devices that are designed for mounting in housings or control cabinets must
only be operated and controlled after they have been installed with the housing
closed� Desktop or portable units must only be operated and controlled in
enclosed housings�
► Measures should be taken to ensure the proper restart of programs interrupted
after a voltage dip or failure� This should not cause dangerous operating states
even for a short time� If necessary, an emergency stop must be carried out�
► Wherever faults in the automation system may cause personal injuries or
damage to property, external measures must be implemented to ensure a safe
operating state in the event of a fault or malfunction (e�g� by means of separate
limit switches, mechanical interlocks etc�)
► The electrical installation must be carried out in accordance with the relevant
regulations (e�g� with regard to cable cross-sections, fuses, PE)�
► All work relating to transport, installation, commissioning and maintenance
must only be carried out by qualified personnel� (IEC 60 364 or HD 384 or
DIN VDE 0100 and national work safety regulations have to be observed)�
UK
► All shrouds and doors must be kept closed during operation�
3 Documentation
This documentation relates to the hardware and firmware status at the time of
editing this manual� The features of the devices are continuously developed further
and improved�
4 Functions and features
The devices have been designed for use in applications described in this manual
and the device-specific data sheets�
Adhere to the data indicated in the data sheets and in the manual� If the handling
specifications and safety instructions for configuration, installation and operation
indicated in the documentation are adhered to, the devices normally do not lead to
a danger for persons and objects�
The input and output devices of the IO-Link master have been designed for
automation tasks in harsh environmental conditions� The devices meet the
requirements of IP65/67 protection rating� They enable direct connection of
sensors and actuators in an environment close to the station�
The devices are available with M12 connection technology�
The devices cannot be extended and have a directly integrated fieldbus
connection and I/O level� They are used for distribution in the field when only a few
digital or analogue I/O points are required�
7

IO-Link master
5 Product description
5.1 DI (digital input)
The digital inputs receive the digital control signals from the process level� These
signals are transferred to the higher-level automation device via the network/bus�
The signal status is indicated via LEDs� The sensors are connected via M12 screw
connectors� The sensors are supplied from the sensor voltage US�
5.2 IOL (IO-Link port)
These devices have IO-Link ports for communication-capable sensors so that the
automation device can make dynamic changes to the sensor parameters directly�
The IO-Link ports can be operated in the following operating modes:
– DI (behaves like a digital input supplied via U
– DO (behaves like a digital output supplied via U
– IO-Link (IOL sensor supplied via U
/ IOL actuator supplied via US and UA)
S
)
S
)
S
5.3 Connections
The bus, I/O devices and supply are connected via M12 screw connections� Each
device is connected directly to the network/bus system�
5.4 Protection rating
The devices have IP65/67 protection rating� To ensure IP65 / IP67 protection,
cover unused sockets with protective caps�
6 Features
The devices have been designed for use without a control cabinet in plant
construction� The fixing clips are firmly mounted�
The housing dimensions of the Profibus devices differ from the housing
dimensions of the Ethernet versions with regard to the depth at socket X21�
8
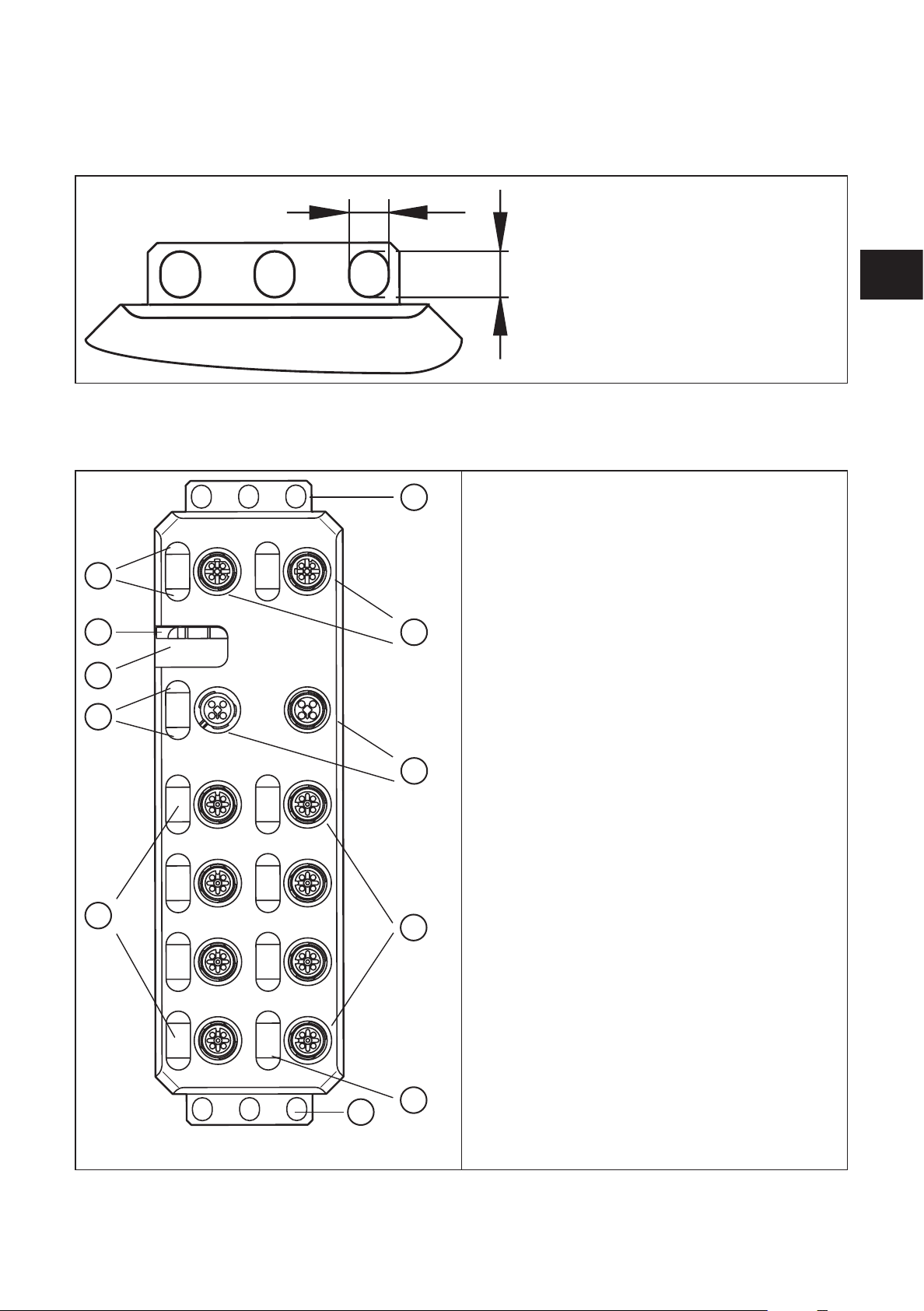
7 Scale drawings
6,3
7.1 Dimensions of the screw holes in the fixing clips
IO-Link master
8 Structure of the device
10
9
8
7
7,3
1
2
1� Fixing clips ( FE connection)
2� Network or bus connection (IN, OUT)
3� Connections for the supply voltages
4� Connections for inputs/outputs or IO-Link ports
5� Markers for labelling
6� Status indicators of the inputs/outputs or the
IO-Link ports
7� Diagnostics and status indication for the supply
voltages
8� Rotary coding switch (no function for ProfiNet)
9� Diagnostics and status indicators for the network
/ bus system
10� Diagnostics and status indicators for the net-
work (not for Profibus)
UK
3
6
1
4
5
9
IO-Link master
8.1 Diagnostic and status indicators
8.1.1 Diagnostics
The diagnostic indicators (green/yellow/red) indicate whether an error is present
or not� In case of an error, they indicate the error type and location� The device is
operating correctly if all green indicators are on�
8.1.2 Status
The status indicators (yellow) indicate the signal state of the corresponding input/
output or of the IO-Link port� If the yellow status indicators are on, this indicates
signal state “1” of the input/output signal�
The devices have three main areas for diagnostics and status indicators�
● Indicators for the network/bus system (network/bus-specific) - Data
● Indicators for the power supplies - Power
● Indicators for the inputs and outputs and the IO-Link ports (device-specific) -
Signal
Data
Power
Signal
9 Installation
When preparing for cable installation, the local conditions and the corresponding
mounting regulations are very important� Cables can be installed, for example, in
cable ducts or on cable bridges�
10

IO-Link master
Data corruption and loss
A minimum distance between the cabling and possible sources of interference (e�g�, machines, wel
ding equipment, power lines) is defined in the applicable regulations and standards� During system
planning and installation, these regulations and standards must be taken into account and observed�
Protect the bus cables from sources of electric/magnetic interference and mechanical strain�
Observe the following guidelines regarding “electromagnetic compatibility” (EMC) to keep mechanical
risks and interference to a minimum�
-
9.1 Mechanical strain
► Choose the correct cable type for the respective application (e�g�, indoor or
outdoor installation, drag chains)�
► Observe the minimum bending radius�
► Make sure that cables do not enter the shear area of moving machine parts�
► Do not install bus cables at right angles to driving routes and machine
movements�
► Use cable ducts and cable bridges�
► Observe the specifications of the cables used�
9.2 Sources of interference
Signal cables and power supply lines should not be installed in parallel�
► If necessary, metal isolating segments should be placed between the power
supply lines and signal cables�
UK
► Only use connectors with metal housing and connect as much of the shielding
as possible to the housing�
► For outdoor cables between buildings, make sure that grounding is carried out
in accordance with “Installing network/bus cables between buildings”�
► During installation, all connector locking mechanisms (screws, union nuts)
must be firmly tightened in order to ensure the best possible contact between
shielding and ground� Before initial startup, the ground or shielding connection
of cables must be checked for low-resistance continuity�
9.3 Cable routing in control cabinets
► Install network/bus cables in separate cable ducts or separate cable bundles�
► Where possible, do not install network/bus cables parallel to power supply
lines�
► Install network/bus cables at least 10 cm away from power lines�
9.4 Cable routing in buildings
► Where possible, use metal cable hangers�
11

IO-Link master
► Do not install network/bus cables together with or parallel to power supply
lines�
► Separate network/bus cables on cable bridges or in cable ducts from power
supply lines using isolating segments�
► Install network/bus cables as far away as possible from sources of interference,
such as motors and welding equipment�
► For long cable connections, install an additional equipotential bonding line
between the terminal points�
9.5 Cable routing outside buildings
► Install network/bus cables in metal pipes that are grounded on both sides or in
concrete cable ducts with continuous reinforcement�
► For long cable connections, install an additional equipotential bonding line
between the terminal points�
9.6 Installing network/bus cables between buildings
9.6.1 Causes of surge voltages
Surge voltages occur as a result of switching operations, electrostatic discharge,
and lightning discharge� Surge voltages can be inductively, capacitively or
galvanically coupled into electrical cables for mains supply, measured value
transmission, and data transmission� In this way, surge voltages reach the power
supply units and the interfaces of systems and devices�
9.6.2 Equipotential bonding line
Install an additional equipotential bonding line between the grounding points of
buildings, preferably in the form of
– a metal-reinforced concrete channel,
– an additional grounding cable or
– a metal pipe�
9.6.3 Surge protective devices
12
ifm recommends wiring all the wires of the cable to surge protective devices in order to protect the
devices against surge voltages�
Observe all national and international regulations when installing surge protective devices�
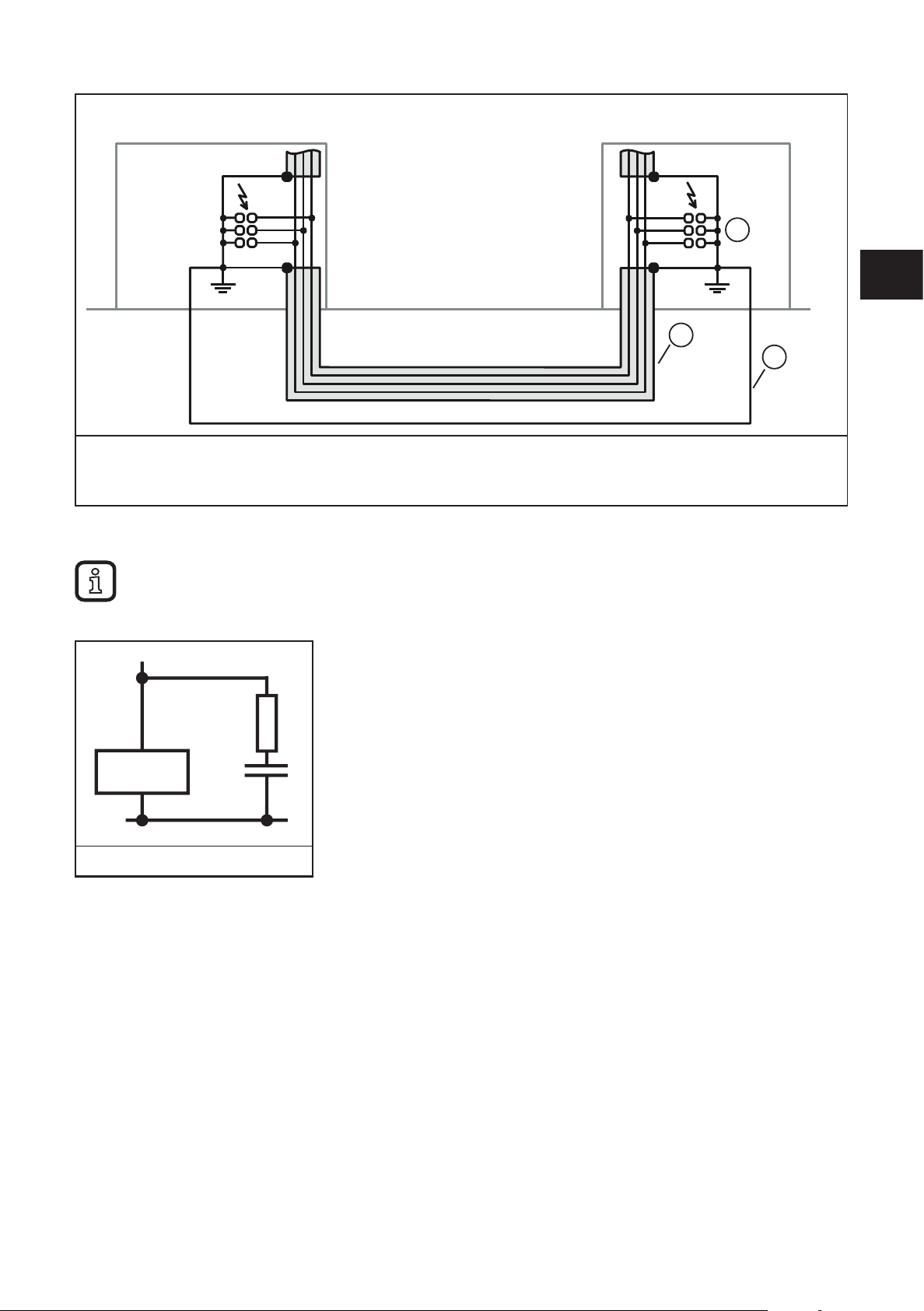
1� Surge protective devices
2� Cable shielding
3� Equipotential bonding line
IO-Link master
1
UK
2
3
9.7 Surge protection measures
ifm recommends wiring relay coils or motor coils to an RC element in order to protect the devices
against interference� Depending on the application, the delay time of the relay can be increased by
approximately 1 ms�
Relay coil with RC element
For the dimensioning of the RC element, the following values are recommended:
R = 100���200
Ω /
C = 220���470 nF
9.8 Grounding concept
The devices operate in the low-level signal voltage range� In the case of low-level
signal devices, interference is discharged via functional earth (FE)� Functional
earth (FE) is only used to discharge interference� It does not provide shock
protection for people�
Functional grounding
The devices are designed to be screwed onto a flat mounting surface�
► Ground the devices by means of the mounting screws of the fixing clips�
13

IO-Link master
9.9 Installation instructions
Electrostatic discharge
The device contains components that can be damaged or destroyed by
electrostatic discharge� When handling the device, observe the necessary safety
precautions against electrostatic discharge (ESD) according to EN 61340-5-1 and
IEC 61340-5-1�
Damage to the electronics
► The device may only be installed and removed by qualified electricians in accordance with the
ESD regulations�
► Implement the FE connection using mounting screws, in order to ensure immunity to interference�
► To ensure IP65/IP67 protection, cover unused connections with protective caps�
► Only supply the sensors with the voltage U
► Avoid polarity reversal of supply voltages US and UA�
Data corruption or loss
► Implement the FE connection using mounting screws, in order to ensure immunity to interference�
which is provided at the terminal points�
S
9.10 Mounting distances
No specific distances are required between devices or between a device and a
cabinet door or cover� Mounting distances are determined solely by the plugs used
and the bending radii of the cables�
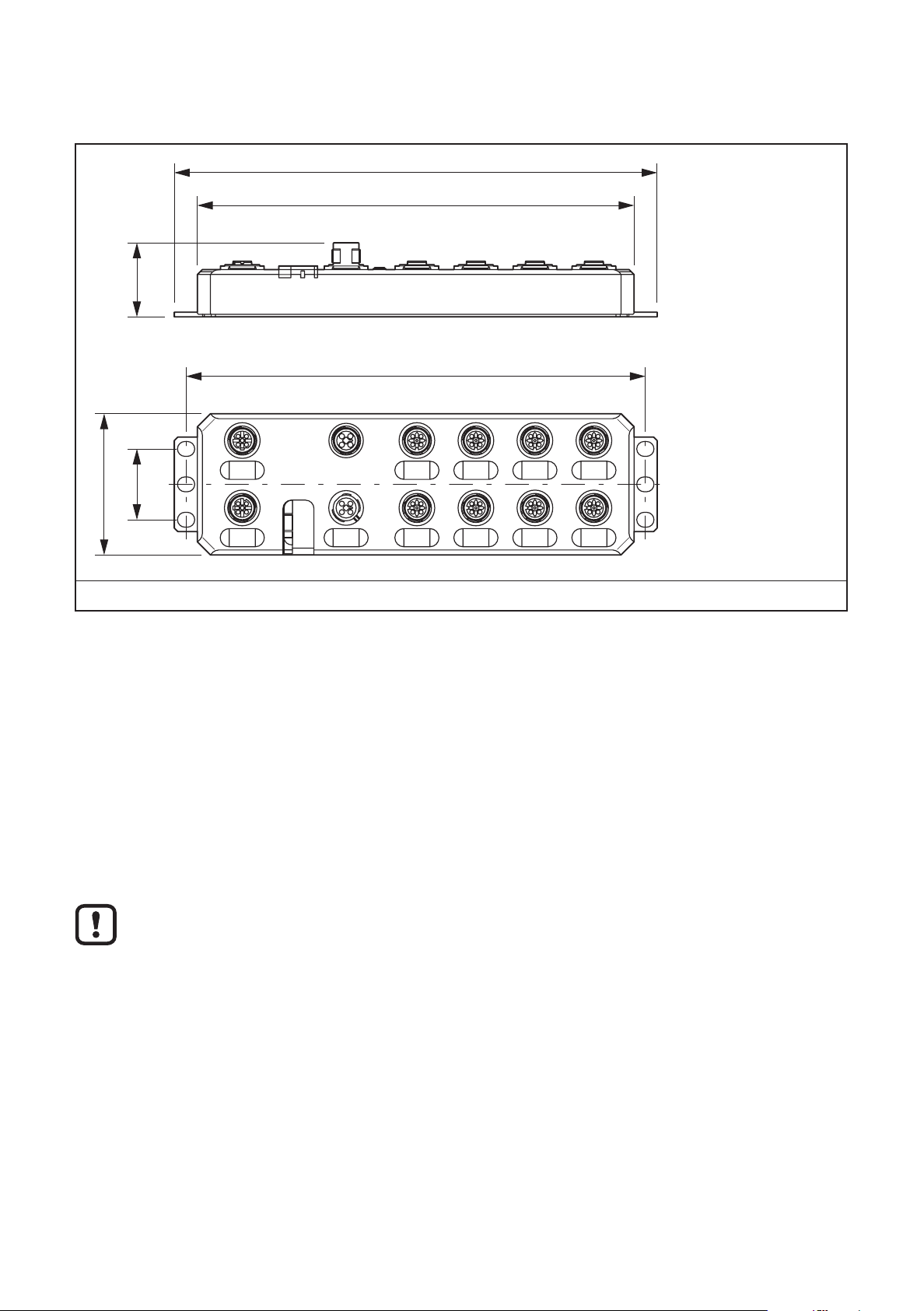
9.11 Mounting dimensions
► Screw the device directly onto the flat mounting surface using the drill holes (1)
of the fixing clips�
14
IO-Link master
30
1
UK
198,5
1
► Use standard M5 screws with toothed lock washer and self-locking nuts�
► Observe the maximum torque of the screws�
Functional grounding
► Functional grounding is crucial for interference-free operation� Ground the device by means of the
mounting screws of the fixing clips�
15
IO-Link master
212
60
10 Scale drawing
30,5
185
198,5
30
X21
Scale drawing AL1000
11 Electrical connection
For the devices, a distinction is made between two voltages:
– U
to supply the communications power and the sensors (always required),
S
– U
for supplying the actuators, only required for devices with fixed outputs or
A
for additional devices�
All supply voltages are connected via M12 connectors�
Damage to the electronics
► Connect both supply voltages completely (to +24 V and GND)�
Do not connect several supply voltages via one GND, as this will exceed the current rating of the
contacts�
11.1 Supply voltages US and U
A
The voltages US and UA are fed in at connection X31�
Power supply U
is required to supply the communications power of the device
S
electronics and to supply the sensors� It must be connected to every device� If this
supply voltage is disconnected, the device will not work�
► Install the power supply for the device electronics independently of the power
supply for the actuators�
16

IO-Link master
► Protect the power supplies independently�
> This means that the bus can continue running even if some I/O devices are
switched off�
11.2 Power supply U
S
► Connect power supply Usfor the logic and sensors to socket X31�
► To supply additional devices, connect the cable for the outgoing supply voltage
to socket X32�
Damage to the electronics
The current rating of the M12 connectors is 12 A per contact�
Make sure that this value is not exceeded� Please note that the connection for the outgoing supply
voltage is not monitored for overload� If the permissible current rating is exceeded, this may result in
damage to the connectors�
11.3 Power supply U
A
The voltage supply UA is only required for the supply of the IO-Link actuators� IOLink port in the operating mode DO is supplied via US�
Damage to the electronics
Power supplies U
and UA should only be supplied with SELV�
S
UK
12 Features
The device is designed for use within a ProfiNet network�It enables the operation
of up to eight IO-Link sensors/actuators and is also used to acquire digital signals�
12.1 ProfiNet features
● Connection to the ProfiNet network using M12 connectors (D-coded)
● Transmission speed 100 Mbps
● Two Ethernet ports (with integrated switch)
● ProfiNet RT
● Supported protocols: SNMP, LLDP, MRP, DCP
● ProfiNet features:
– FSU, Shared Device, I&M functions
● Device description using GSDML file
● Firmware can be updated
● Integrated web server for web-based management
12.2 IO-Link features
● Connection of eight IO-Link devices
17
IO-Link master
– 4 type A ports with an additional digital input
– 4 type B ports with an additional voltage supply
● Connection of IO-Link ports using M12 connectors (A-coded, 5 poles)
● Parameter data storage on the master
● Parameterisable process data width
● Supporting the IOL_CALL function module
● IO-Link specification v1�1
12.3 General features
● Diagnostic and status indicators
● Short-circuit and overload protection of the sensor supply
● IP65/67 protection rating
13 Technical data
General data
Housing material Pocan
Weight [kg] 0�48
Ambient temperature (operation) [°C] -25 ���60
Ambient temperature (storage/transport) [°C] -25���85
Permissible humidity (operation) [%] 5���95
Air pressure (operation) [kPa] 70���106 (up to 3000 m above sea
level)
Air pressure (storage/transport) [kPa] 70���106 (up to 3000 m above sea
level)
Protection rating IP65 / IP67
Protection class III, IEC 61140, EN 61140, VDE
0140-1
Connection data
Connection method M12 connector
Interface ProfiNet
Number 2
Connection method M12 connector, D-coded
Designation connection point copper cable
Number of poles 4
Transmission speed [Mbps] 100 (with auto-negotiation)
ProfiNet
Equipment type ProfiNet Device
18
IO-Link master
Conformance class B
Update rate [ms] 1
Number of supported application relationships (AR) 2
Additional protocols SNMP v1, HTTP, TFTP, FTP
ProfiNet protocols LLDP, MRP client, DCP, DCE-RPC
Supply of the module electronics and sensors
Connection method M12 connector (T-coded)
Number of poles 4
UK
Designation U
S
Supply voltage [V] 24 DC
Nominal supply voltage range [V] 18���31�2 DC
(including all tolerances, including
ripple)
Typical current consumption [mA] 180 ± 15 % at 24 V DC
Maximum current consumption [A] 12
Supply of the actuators
Connection method M12 connector (T-coded)
Number of poles 4
Designation U
A
Supply voltage [V] 24 DC
Nominal supply voltage range [V] 19���31�2 DC
(including all tolerances, including
ripple)
Typical current consumption [mA] 28 ± 15 % at 24 V DC
Max� current consumption [A] 12
Supply of the IO-Link ports
I/O supply voltage [V] 24 DC
Nominal current for each IO-Link port [mA] 200
Nominal current for each device [A] 1�6
Overload protection electronic
Permissible cable length to the sensor [m] < 20
IO-Link ports in the mode digital input (DI)
Number of inputs max� 8 (EN 61131-2 type 1)
Connection method M12 connector, X01 ��� X04 with
two configurations
Connection method 2, 3 wires
Nominal input voltage [V] 24 DC
Nominal input current [mA] typ� 3
19
 Loading...
Loading...