IFM Electronic AC1355, AC1356, AC1365, AC1366 Supplementary Device Manual
Supplementary device manual
AS-i controllere with Profibus DPV1
A
AC1355, AC1356
AC1365, AC1366
AS-i master profile: M4
Firmware: from version RTS 3.0 onwards
Target: from V.15 onwards
®
for CoDeSys
from version 2.3 onwards
7390702 / 01 08 / 2008
1

2
As on: 14 Aug. 2008
© All rights reserved by ifm electronic gmbh.
No part of this manual may be reproduced and used
without ifm electronic's consent.

Contents
1
On this manual .........................................................................................................................1-1
1.1 What do the symbols and formats stand for?................................................................ 1-1
1.2 What devices are described in this manual?................................................................. 1-2
1.3 How is this manual structured? ..................................................................................... 1-2
1.4 Overview: where is what? ............................................................................................. 1-3
2 Safety instructions................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1 General.......................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 What previous knowledge is required? ......................................................................... 2-1
2.3 Functions and features.................................................................................................. 2-1
3 System requirements............................................................................................................... 3-1
3.1 Information concerning the device ................................................................................ 3-1
3.2 Information concerning the software ............................................................................. 3-1
3.3 Required accessories.................................................................................................... 3-1
4 Getting started.......................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.1 Connection .................................................................................................................... 4-1
4.2 Set up the AS-i master .................................................................................................. 4-1
4.3 Set up Profibus DPV1 ................................................................................................... 4-1
5 Function.................................................................................................................................... 5-1
5.1 Data management......................................................................................................... 5-1
5.2 Status LED for the fieldbus............................................................................................ 5-2
5.3 Which operating modes are there for the PLC in the controllere? ................................ 5-2
6 Menu..........................................................................................................................................6-1
6.1 Main menu [Quick Setup] .............................................................................................. 6-1
6.2 Main menu [Fieldbus Setup].......................................................................................... 6-2
7 Set-up ........................................................................................................................................ 7-1
7.1 Parameter setting of the controllere.............................................................................. 7-1
7.1.1 Parameter setting of slaves in the controllere.................................................. 7-1
7.1.2 Set the parameters of the fieldbus interface in the controllere......................... 7-1
7.2 Connect the controllere to the Profibus host ................................................................. 7-2
7.3 Parameter setting of the Profibus host.......................................................................... 7-2
7.3.1 Assigning the addresses of the inputs/outputs to the host "locations"............. 7-4
7.3.2 Assign PLC addresses to the Profibus modules ............................................ 7-11
7.3.3 Define Profibus DP modules .......................................................................... 7-13
3

Device-specific Profibus DP parameters..................................................................... 7-25
7.4
7.4.1 Device-specific Profibus DP parameters (example)....................................... 7-25
7.4.2 Definitions in the GSD file............................................................................... 7-26
7.5 Finish set-up ................................................................................................................ 7-27
8 DP module 7: Command channel........................................................................................... 8-1
8.1 List of commands in module 7....................................................................................... 8-1
8.2 Module 7, command 1: read master flags.................................................................... 8-2
8.3 Module 7, command 2: change operating mode.......................................................... 8-3
8.4 Module 7, command 3: read current slave configuration ............................................. 8-4
8.5 Module 7, command 4: read projected slave configuration ......................................... 8-5
8.6 Module 7, command 5: change projected slave configuration..................................... 8-6
8.7 Module 7, command 6: read slave parameter.............................................................. 8-7
8.8 Module 7, command 7: change projected slave parameters ....................................... 8-8
8.9 Module 7, command 8: read LAS (list of active slaves) ............................................... 8-9
8.10 Module 7, command 9: read LDS (list of detected slaves) ........................................ 8-11
8.11 Module 7, command 10
8.12 Module 7, command 11
8.13 Module 7, command 13
8.14 Module 7, command 14
8.15 Module 7, command 15
8.16 Module 7, command 16
8.17 Module 7, command 19
8.18 Module 7, command 21
8.19 Module 7, command 22
8.20 Module 7, command 23
8.21 Module 7, command 62
8.22 Module 7, command 63
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
(0A
): read LPF (list of slaves with periphery fault)....... 8-12
hex
(0B
): read LPS (list of projected slaves) ...................... 8-13
hex
(0D
): read telegram error counter ................................ 8-14
hex
(0E
): read configuration error counter.......................... 8-15
hex
(0F
): read AS-i cycle counter ....................................... 8-16
hex
(10
): change current slave parameters........................ 8-17
hex
(13
): config. all ............................................................. 8-18
hex
(15
): save configuration in flash ................................... 8-19
hex
(16
): reset telegram error counter of a slave ............... 8-20
hex
(17
): address slave ...................................................... 8-21
hex
(3E
): operating mode "continuous command“ ............. 8-22
hex
(3F
): no operation command without function ............. 8-23
hex
9 DP module 12: Extended command channel ........................................................................ 9-1
9.1 List of extended commands in module 12..................................................................... 9-1
9.2 Data structure ................................................................................................................ 9-3
9.3 Error codes in the module 12 ........................................................................................ 9-5
9.4 CTT2 error code in module 12 ...................................................................................... 9-5
9.5 Module 12, extended command 0: no execution of a command ................................. 9-6
9.6 Module 12, extended command 1: write parameters to a connected AS-i slave......... 9-7
9.7 Module 12, extended command 3: adopt and store connected AS-i slaves in the
configuration ..................................................................................................................
9.8 Module 12, extended command 4: write LPS ............................................................ 9-11
9.9 Module 12, extended command 5: set the operating mode of the AS-i master......... 9-13
9.10 Module 12, extended command 6: readdress a connected AS-i slave...................... 9-15
9.11 Module 12, extended command 7: set the auto address mode of the AS-i master... 9-17
9.12 Module 12, extended command 9: change extended ID code 1 in the AS-i slave .... 9-18
4
9-9

Module 12, extended command 10...20
9.13
directly to / from 3 AS-i slaves in each case ...............................................................
(0A...14
dec
): force analogue data transfer
hex
9-20
9.14 Module 12, extended command 21
AS-i slave with the profile 7.4 ......................................................................................
9.15 Module 12, extended command 26
9.16 Module 12, extended command 28
changing to the protected mode..................................................................................
9.17 Module 12, extended command 31
"Extended safety monitor protocol" in the "Safety at work" monitor............................
9.18 Module 12, extended command 33
of an AS-i slave with the profile S-7.4 .........................................................................
9.19 Module 12, extended command 34
of an AS-i slave with the profile S-7.4 .........................................................................
9.20 Module 12, extended command 35
of an AS-i slave with the profile S-7.4 .........................................................................
9.21 Module 12, acyclic command 36
dec
with CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5) .........................................................
9.22 Module 12, acyclic command 37
dec
with CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5) .........................................................
9.23 Module 12, acyclic command 38
dec
of an AS-i slave with CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5) ...............................
9.24 Module 12, acyclic command 39
dec
of an AS-i slave with CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5) ...............................
(15
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
(24
(25
(26
(27
): read ID character string of an
hex
(1A
): read AS-i master version................... 9-28
hex
(1C
): deactivate the slave reset when
hex
(1F
): one-time execution of the
hex
(21
): read the diagnostic character string
hex
(22
): read parameter character string
hex
(23
): write parameter character string
hex
): standard read call of an AS-i slave
hex
): standard write call of an AS-i slave
hex
): manufacturer-specific read call
hex
): manufacturer-specific write call
hex
9-25
9-29
9-30
9-35
9-37
9-38
9-40
9-44
9-47
9-51
9.25 Module 12, extended command 50
of AS-i slaves 0(A)...15(A)...........................................................................................
9.26 Module 12, extended command 51
of AS-i slaves 16(A)...31(A).........................................................................................
9.27 Module 12, extended command 52
of the AS-i slaves 1B...15B..........................................................................................
9.28 Module 12, extended command 53
of the AS-i slaves 16B...31B........................................................................................
9.29 Module 12, extended command 54
connected AS-i slaves.................................................................................................
9.30 Module 12, extended command 55
9.31 Module 12, extended command 56
of the AS-i slaves 0(A)...15(A).....................................................................................
9.32 Module 12, extended command 57
of the AS-i slaves 16(A)...31(A)...................................................................................
9.33 Module 12, extended command 58
of the AS-i slaves 1B...15B..........................................................................................
9.34 Module 12, extended command 59
of the AS-i slaves 16B...31B........................................................................................
9.35 Module 12, extended command 96
flash memory of the controllere...................................................................................
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
(32
): read current configuration
hex
(33
): read current configuration
hex
(34
): read current configuration
hex
(35
): read current configuration
hex
(36
): read current parameters of the
hex
(37
): read current AS-i slave lists............... 9-61
hex
(38
): read projected configuration
hex
(39
): read projected configuration
hex
(3A
): read projected configuration
hex
(3B
): read projected configuration
hex
(60
): save data non-volatilely in the
hex
9-55
9-56
9-57
9-58
9-59
9-63
9-64
9-65
9-66
9-67
9.36 Module 12, extended command 97
controllere....................................................................................................................
9.37 Module 12, extended command 102
controllere display........................................................................................................
9.38 Module 12, extended command 105
of the controllere..........................................................................................................
dec
dec
dec
(61
): carry out various settings in the
hex
(66
): retrieve the status of the
hex
(69
): read the device properties
hex
9-68
9-69
9-71
5

Acyclic services for Profibus DPV1 ..................................................................................... 10-1
10
10.1 Description................................................................................................................... 10-1
10.2 Services for acyclic data transfer between DPM1 master and slave.......................... 10-2
10.3 Services for acyclic data transfer between DPM2 master and slave.......................... 10-2
10.4 DPV1 addresses in slot 0 for access via PLC............................................................. 10-3
10.5 Examples..................................................................................................................... 10-5
10.5.1 Examples DPV1 reading ................................................................................ 10-5
10.5.2 Examples DPV1 writing .................................................................................. 10-5
10.6 DPV1 error messages ................................................................................................. 10-5
10.6.1 DPV1 error code application........................................................................... 10-5
10.6.2 DPV1 error codes data access....................................................................... 10-5
10.6.3 DPV1 error codes device................................................................................ 10-6
10.6.4 DPV1 error codes application-specific ........................................................... 10-6
10.6.5 DPV1 function 58 "Reason codes" ................................................................. 10-6
11 The DPV1 command channel................................................................................................11-1
11.1 Overview of the commands in the DPV1 command channel...................................... 11-1
11.2 Syntax.......................................................................................................................... 11-2
11.3 DPV1 command 0
11.4 DPV1 command 1
11.5 DPV1 command 3
dec
dec
dec
(00
(01
(03
in the configuration ......................................................................................................
11.6 DPV1 command 4
11.7 DPV1 command 5
11.8 DPV1 command 6
11.9 DPV1 command 7
11.10 DPV1 command 9
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
(04
(05
(06
(07
(09
AS-i slave ..................................................................................................................
11.11 DPV1 command 10...20
to / from 3 AS-i slaves in each case ..........................................................................
11.12 DPV1 command 21
dec
(15
profile S-7.4 ...............................................................................................................
11.13 DPV1 command 28
dec
(1C
protected mode..........................................................................................................
11.14 DPV1 command 31
dec
(1F
protocol" in the "Safety at Work" monitor ..................................................................
11.15 DPV1 command 33
dec
(21
the profile S-7.4 .........................................................................................................
): no execution of a command.......................................... 11-4
hex
): write parameters to a connected AS-i slave ................. 11-5
hex
): adopt and store currently connected AS-i slaves
hex
): change the list of projected AS-i slaves (LPS)............. 11-9
hex
): set the operating mode of the AS-i master ................ 11-11
hex
): readdress a connected AS-i slave ............................. 11-13
hex
): set the auto address mode of the AS-i master .......... 11-15
hex
): change the extended ID code 1 in the connected
hex
(0A...14
dec
): read ID string of an AS-i slave with the
hex
): deactivate the slave reset when changing to the
hex
): one-time execution of the "Extended safety monitor
hex
): read diagnosis string of an AS-i slave with
hex
): force analogue data transfer directly
hex
11-7
11-16
11-18
11-23
11-26
11-27
11-32
11.16 DPV1 command 34
the profile S-7.4 .........................................................................................................
11.17 DPV1 command 35
the profile S-7.4 .........................................................................................................
11.18 DPV1 command 36
CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5)...............................................................
11.19 DPV1 command 37
CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5)...............................................................
6
dec
dec
dec
dec
(22
): read the parameter string of an AS-i slave with
hex
(23
): write parameter string of an AS-i slave with
hex
(24
): acyclic standard read call of an AS-i slave with
hex
(25
): acyclic standard write call of an AS-i slave with
hex
11-34
11-36
11-38
11-42

DPV1 command 38
11.20
of an AS-i slave with CTT2 profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5) ..............................
dec
(26
): acyclic manufacturer-specific read call
hex
11-45
11.21 DPV1 command 39
of an AS-i slave with CTTS profile (S-7.5.5, S-7.A.5 or S-B.A.5)..............................
11.22 DPV1 command 50
AS-i slaves 0(A)...15(A).............................................................................................
11.23 DPV1 command 51
AS-i slaves 16(A)...31(A)...........................................................................................
11.24 DPV1 command 52
AS-i slaves 1B...15B..................................................................................................
11.25 DPV1 command 53
AS-i slaves 16B...31B................................................................................................
11.26 DPV1 command 54
a connected AS-i slave..............................................................................................
11.27 DPV1 command 55
11.28 DPV1 command 56
the AS-i slaves 1(A)...15(A).......................................................................................
11.29 DPV1 command 57
the AS-i slaves 16(A)...31(A).....................................................................................
11.30 DPV1 command 58
the AS-i slaves 1B…15B ...........................................................................................
11.31 DPV1 command 59
the AS-i slaves 16B…31B .........................................................................................
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
dec
(27
): acyclic manufacturer-specific write call
hex
(32
): read current configuration of
hex
(33
): Read current configuration of
hex
(34
): read current configuration of
hex
(35
): read current configuration of
hex
(36
): read current parameters of
hex
(37
): read current AS-i slave lists ..................................... 11-59
hex
(38
): projected configuration of
hex
(39
): read projected configuration of
hex
(3A
): read projected configuration of
hex
(3B
): read projected configuration of
hex
11-49
11-53
11-54
11-55
11-56
11-57
11-61
11-62
11-63
11-64
11.32 DPV1 command 96
of the controllere........................................................................................................
11.33 DPV1 command 97
11.34 DPV1 command 102
11.35 DPV1 command 105
dec
dec
dec
dec
(60
): save data non-volatilely in the flash memory
hex
(61
): carry out various settings in the controller
hex
(66
): retrieve the status of the controller
hex
(69
): read the device properties of the controller
hex
11-65
............. 11-66
e
display .......... 11-67
e
......... 11-69
e
12 Additional functions...............................................................................................................12-1
12.1 AS-i diagnosis via Profibus DP.................................................................................... 12-1
12.1.1 Digital inputs ................................................................................................... 12-1
12.1.2 Digital outputs................................................................................................. 12-1
12.1.3 Extended device-specific Profibus DP diagnosis ........................................... 12-2
12.1.4 Diagnostic master flags (byte 10 / byte 36) .................................................... 12-3
12.2 Set the Profibus DP address on the controllere.......................................................... 12-4
12.3 Read fieldbus parameters ........................................................................................... 12-6
12.4 Store system parameters .......................................................................................... 12-10
13 Technical data ........................................................................................................................ 13-1
13.1 Basic functions ............................................................................................................ 13-1
13.2 Profibus DP interface .................................................................................................. 13-1
14 Troubleshooting..................................................................................................................... 14-1
14.1 List of errors................................................................................................................. 14-1
14.2 Hardware error, exception error .................................................................................. 14-2
7

Terms, abbreviations.............................................................................................................15-1
15
16 Index........................................................................................................................................16-1
8
On this manual
What do the symbols and formats stand for?
1 On this manual
In this chapter you will find an overview of the following points:
• What do the symbols and formats stand for?
• What devices are described in this manual?
• How is this manual structured?
1.1 What do the symbols and formats stand for?
The following symbols or pictograms depict different kinds of remarks in this manual:
DANGER
Death or serious irreversible injuries are to be expected.
WARNING
Death or serious irreversible injuries may result.
CAUTION
Slight reversible injuries may result.
NOTICE
Property damage is to be expected or possible.
NOTE
The "i" in the square gives important information to help you handle the product or this manual
correctly.
► … Request for action
> … Reaction of device or software
→ ...
stands for "see"
abc Cross-reference (Link)
[…] [Designation] of key, signalling lamp, button, menu item ....
For several menu items to be selected consecutively we write:
[1st step] > [2nd step] > [3rd step]
ABC DESIGNATION of parameters (inputs, outputs, flags, function blocks)
Abc
● LED lit
○ LED off
✶
1-1
Designation of files and directories are written in monospace font
LED flashes

On this manual
What devices are described in this manual?
1.2 What devices are described in this manual?
This manual describes the AS-i device family controller
of ifm electronic gmbh.
e
• with AS-i master profile M4
• with AS-i version 3.0 masters
• with a firmware from version RTS 2.2 onwards
• with the target from V.15 onwards.
In the "programming manual CoDeSys
®
2.3" more information about the use of the programming
system "CoDeSys for Automation Alliance" is given. This manual can be downloaded free of charge
from ifm's website at:
www.ifm.com> Select country/language > [Service] > [Download] > [Bus system AS-interface]
→
Description of the Ethernet programming interface
→ Separate supplement to this device manual.
1.3 How is this manual structured?
This manual is a combination of different instruction types. It is for beginners and also a reference for
advanced users.
How to use this manual:
• To find a certain subject straight away, please use the table of contents at the beginning of this
manual.
• Using the table of keywords at the end of the manual you can quickly find the term you are
looking for.
• At the beginning of a chapter we will give you a brief overview of its contents.
• You can find the title of the current chapter in bold in the header of each page. Below is the
current title of the second order.
• You can find the chapter-related number of the page in the footer of each page.
Abbreviations and technical terms
→ Chapter
Terms, abbreviations at the end of the manual.
We reserve the right to make alterations which can result in a change of contents of the manual. You
can find the current version on ifm's website at:
www.ifm.com > Select country/language > [Service] > [Download] > [Bus system AS-interface]
→
Nobody is perfect. Send us your suggestions for improvements to this manual and you will receive a
little gift from us to thank you.
© All rights reserved by ifm electronic gmbh. No part of this manual may be reproduced and used
without ifm electronic's consent.
1-2
On this manual
Overview: where is what?
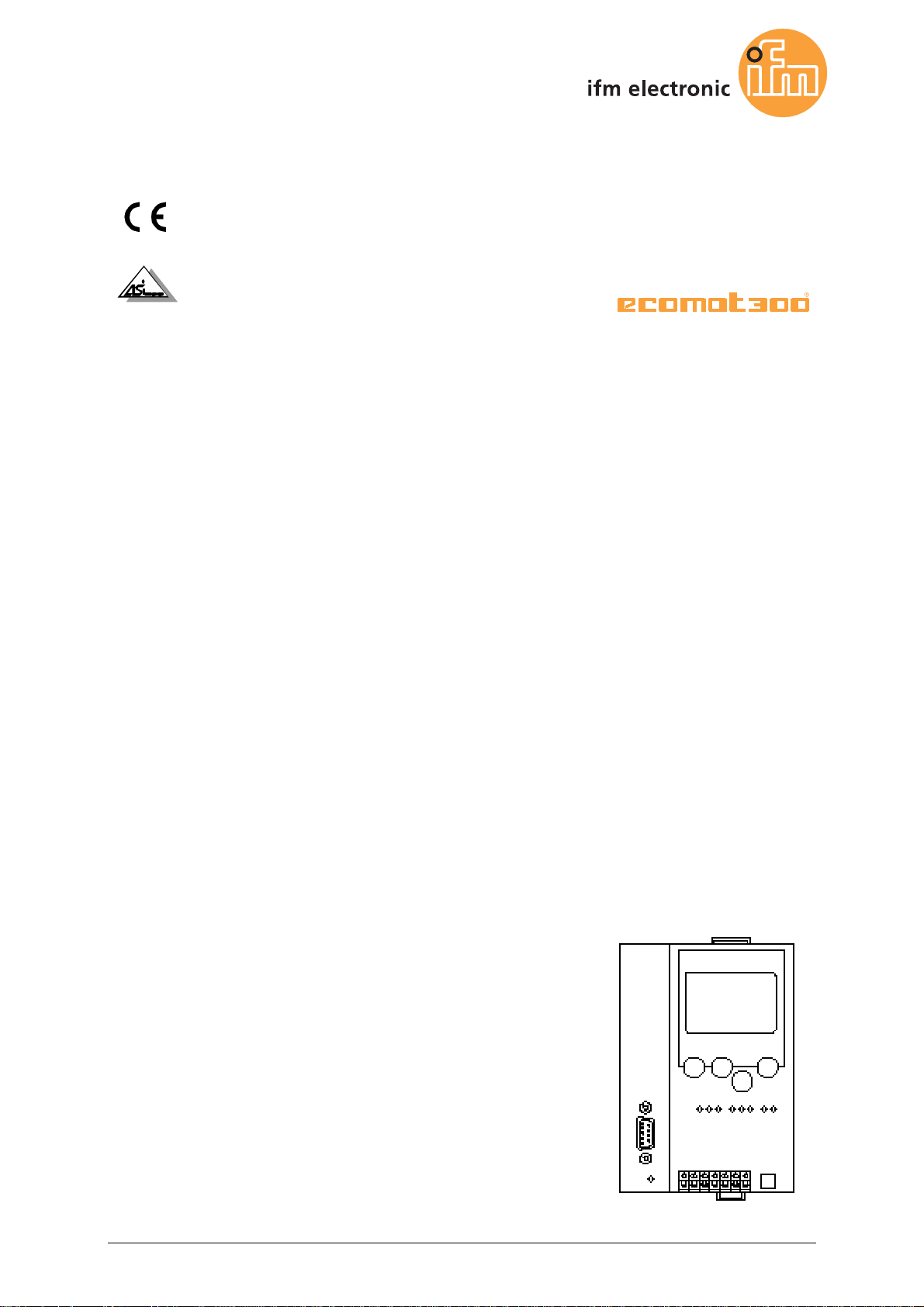
1.4 Overview: where is what?
metal housing IP20 key to unlock the device from a rail
status LEDs of the fieldbus
interface
(option)
text/graphics display
4 pushbuttons
option: fieldbus interface
(here: Ethernet)
terminals for the voltage supply
24 V, AS-i interface(s) and
protective wire
Figure: overview controllere
Option:
Ethernet programming
interface
status LEDs
6-pole RJ11 socket of RS-232C
as programming interface
1-3

On this manual
Overview: where is what?
1-4

Safety instructions
General
2 Safety instructions
In this chapter you will find general safety instructions such as:
• General rules
• Required previous knowledge
• Safety instructions for mounting and installation
• When are you allowed to use this device and when not?
2.1 General
→ separate basic instructions of the device manual
No characteristics are warranted with the information, notes and examples provided in this manual.
The drawings, representations and examples imply no responsibility for the system and no applicationspecific particularities.
The manufacturer of the machine/equipment is responsible for ensuring the safety of the
machine/equipment.
WARNING
Property damage or bodily injury possible when the notes in this manual are not adhered to!
ifm electronic assumes no liability for this.
► The acting person must have read and understood the safety instructions and the corresponding
chapters of this manual before performing any work on or with this device.
► The acting person must be authorised to work on the machine/equipment.
2.2 What previous knowledge is required?
This manual is for persons with knowledge of control technology and PLC programming with IEC
61131-3 as well as the CoDeSys
Knowledge of the fieldbus Profibus DPV1 is a prerequisite.
Profibus user organisation →
Connection and parameter settings of the Profibus host → its manuals.
The manual is intended for persons authorised to install, connect and set up the controllere according
to the EMC and low voltage directives. The controllers must be installed and put into operation by a
qualified electrician.
In case of malfunctions or uncertainties please contact the manufacturer.
®
software.
http://www.profibus.com/
2.3 Functions and features
→ basic instructions of the device manual
2-1

Safety instructions
Functions and features
2-2

System requirements
Information concerning the device
3 System requirements
3.1 Information concerning the device
→ separate basic instructions of the device manual
3.2 Information concerning the software
→ separate basic instructions of the device manual
3.3 Required accessories
Basic functions → separate basic instructions of the device manual
For configuration and programming you also need:
• the software "CoDeSys for Automation Alliance ™" version 2.3 or higher (→ CD)
• in case of direct connection of the controllere to a PC with Ethernet interface (LAN):
a cross-over CAT5 Ethernet patch cable with RJ45 plug on both sides:
2 m art. no. EC2080
5 m art. no. E30112
• In case of connection of the controllere to a PC with Ethernet interface (LAN) via a hub or switch:
a common CAT5 Ethernet patch cable with RJ45 plug on both sides
• In case of direct connection of the controllere to a PC with serial interface:
Programming cable art. no. E70320
3-1

System requirements
Required accessories
3-2

Getting started
Connection
4 Getting started
4.1 Connection
► Connect the functional earth
► Connect the yellow AS-i cable for every master
► Connect the 24 V supply
► Connect the Profibus cable to the fieldbus master
4.2 Set up the AS-i master
► Connect the addressed AS-i slaves to the yellow AS-i cable
► Apply voltage
► If correctly addressed slaves are connected:
controllere menu [Config All] (→ basic manual)
► If no slave is connected:
controllere menu [Easy Startup](→ basic manual)
4.3 Set up Profibus DPV1
► Controllere menu "Fieldbus Setup": set the Profibus address
(→ page
► Copy the GSD file from the ifm CD (folder "gateway") to the suitable directory of the
corresponding fieldbus configuration program
► Define the I/O areas and the system behaviour in the fieldbus configuration program
► Save the configuration
► Transfer the configuration to the DPV1 master
► Start the DPV1 master
7-1, chapter ‘Set the parameters of the fieldbus interface in the controllere’)
4-1

Getting started
Set up Profibus DPV1
4-2
Function
Data management
5 Function
Basic functions → separate basic instructions of the device manual
Ethernet programming interface → separate complementary device manual
5.1 Data management
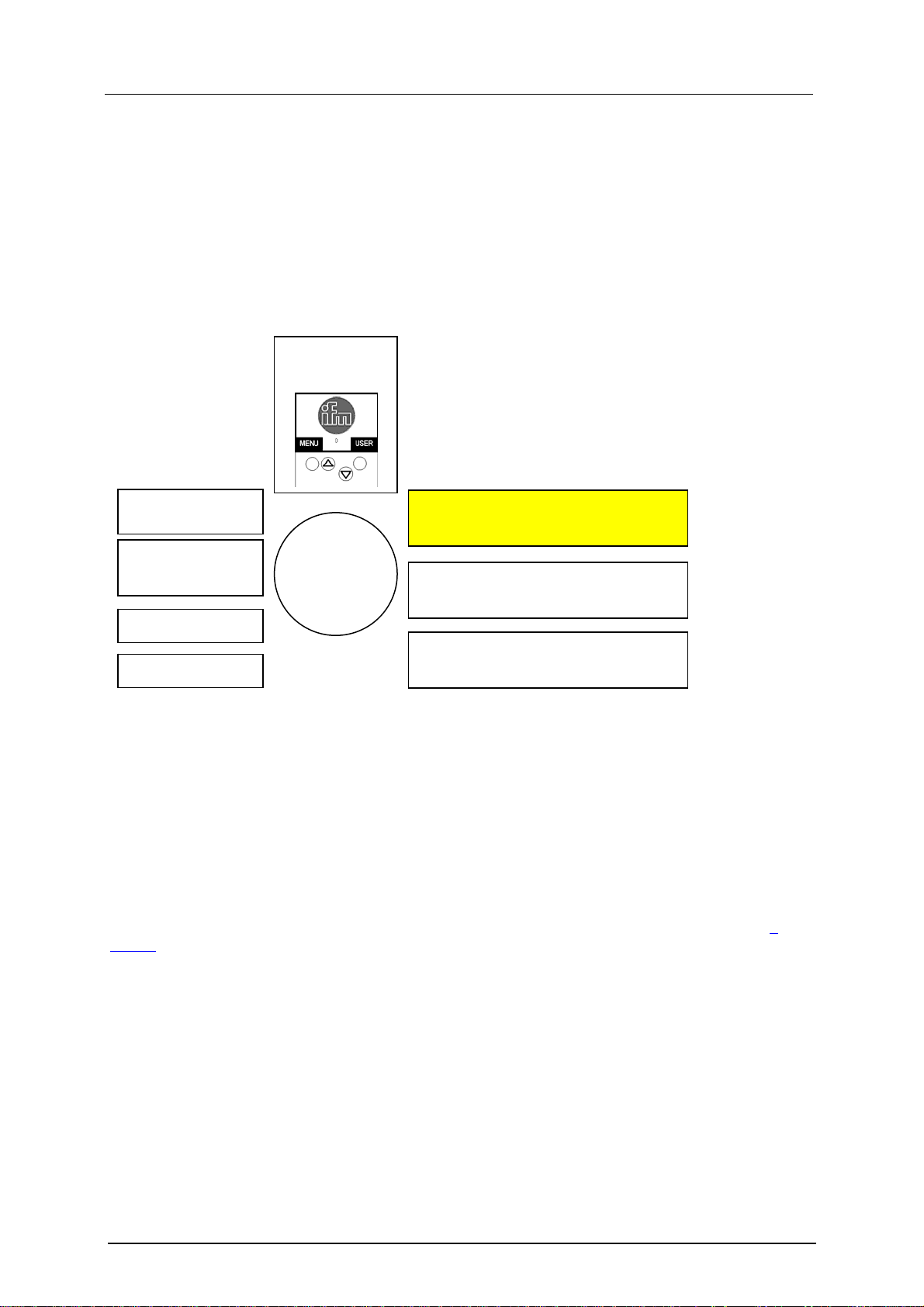
The controllere consists of different units:
AS-i master 1
text/graphics
display
fieldbus interface
Profibus DPV1
AS-i master 2
(optional)
CPU
PLC
Ethernet programming interface
(optional)
SRAM memory
RS-232C
flash memory
programming interface
This manual exclusively describes the following subject:
• The optional fieldbus interface Profibus DP operates independently and exchanges data with the
central system via a "Dual port RAM" interface .
For the AS-i controllers with Profibus interface the data management of Profibus DP is handled in the
operating system (firmware) of the device. A special driver in the PLC user program in the controllere
is not required. In the mode Run/Stop the digital and analogue output data is not transferred to the
outputs of the AS-i slaves. Therefore this data must be recopied in the PLC user program of the
controllere.
More information concerning the addresses and assignment to the Profibus modules → chapter
7,
Set-up.
5-1
Function
Status LED for the fieldbus
5.2 Status LED for the fieldbus
For Profibus DP there is only one red LED [Bus Failure].
LED Description
● lights
○ off
✶
flashes 2 Hz
When response monitoring (watchdog) active:
no Profibus connection
When response monitoring (watchdog) active:
Profibus connection ok
OR: master switched off
OR: response monitoring (watchdog) deactivated
device error → message text in text/graphics display
5.3 Which operating modes are there for the PLC in the controllere?
Operating mode Description Behaviour via DPV1 / fieldbus
Run PLC program start
> The PLC program stored in the
controllere is processed.
> LED [PLC RUN] lit
Stop PLC program stop
> The PLC program stored in the
controllere is stopped.
> LED [PLC RUN] flashes
Via DPV1, data can be written to AS-i
slaves in the controllere application
program:
Mapping of the PLC address ranges
%IB4.512…%IB4.639
%IW4.320…%IW4.639
Gateway Controllere as gateway
> LED [PLC RUN] goes out
Fieldbus has exclusive write access for
the AS-i outputs.
DPV1 has no access here!
The timeouts for the analogue and
digital AS-i outputs only work in the
operating mode gateway. There is no
timeout monitoring for the other data
areas written via DPV1.
NOTE
During changes to the PLC program or to the slaves the PLC program should be stopped to avoid
malfunctions.
NOTE
In devices with Profibus and Ethernet programming interface, DPV1 is not considered as fieldbus but
as interface for operation and configuration.
5-2

Menu
Main menu [Quick Setup]
6 Menu
NOTE
In this manual the menu texts are all in English.
Basic functions → separate basic instructions of the device manual
6.1 Main menu [Quick Setup]
Quick setting of the AS-i and fieldbus parameters, reading of the parameter data (password level 1
required). Details → page
Menu tree Explanation
12-6, chapter Read fieldbus parameters
Quick Setup
Fieldbus Setup
> Display of the current fieldbus address
► Change of the fieldbus address using the buttons [▲] or
[▼]
► After pressing [OK]:
> Controllere is set to the baud rate set in the Profibus DP
master.
► Always after pressing [OK]:
> Display of the data stored in the fieldbus master via the
data packets for communication with the AS-i controllere:
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of single or A slaves
on AS-i master 1
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master to single or A slaves
on AS-i 1
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of single or A slaves
on AS-i master 2
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master to single or A slaves
on AS-i 2
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of B slaves on AS-i
master 1
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master to B slaves on AS-i 1
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of B slaves on AS-i
master 2
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of B slaves on AS-i
master 2
• Analogue multiplex inputs in the fieldbus master
• Analogue multiplex outputs in the fieldbus master
• Fieldbus data command channel
• Fieldbus data PLC inputs in the fieldbus master
• Fieldbus data PLC outputs in the fieldbus master
• Analogue inputs in the fieldbus master of AS-i master 1
• Analogue outputs in the fieldbus master on AS-i master 1
• Analogue inputs in the fieldbus master of AS-i master 2
6-1

Menu
Main menu [Fieldbus Setup]
Menu tree Explanation
• Analogue outputs in the fieldbus master on AS-i master 2
• Fieldbus data diagnosis
• Fieldbus master command channel
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of single or A slaves
on AS-i master 1
(cycle starts again)
► Cancel with [ESC]
6.2 Main menu [Fieldbus Setup]
Setting of fieldbus parameters, reading of parameter data (password level 1 required).
Details → page
Menu tree Explanation
Fieldbus Setup > Display of the current fieldbus address
12-6, chapter Read fieldbus parameters
► Change of the fieldbus address using the keys [▲] / [▼]
► After pressing [OK]:
> Controllere is set to the baud rate set in the Profibus DP
master.
► Always after pressing [OK]:
> Display of the data stored in the fieldbus master via the
data packets for communication with the AS-i controllere:
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of single or A slaves
on AS-i master 1
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master on single or A slaves
on AS-i master 1
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of single or A slaves
on AS-i master 2
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master on single or A slaves
on AS-i master 2
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of B slaves on AS-i
master 1
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master on B slaves on AS-i
master 1
6-2
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of B slaves on AS-i
master 2
• Digital outputs in the fieldbus master on B slaves on AS-i
master 2
• Analogue multiplex inputs in the fieldbus master
• Analogue multiplex outputs in the fieldbus master
• Fieldbus data command channel
• Fieldbus data PLC inputs in the fieldbus master
• Fieldbus data PLC outputs in the fieldbus master
• Analogue inputs in the fieldbus master of AS-i master 1

Menu
Main menu [Fieldbus Setup]
Menu tree Explanation
• Analogue outputs in the fieldbus master on AS-i master 1
• Analogue inputs in the fieldbus master on AS-i master 2
• Analogue outputs in the fieldbus master on AS-i master 2
• Fieldbus data diagnosis
• Fieldbus master command channel
• Digital inputs in the fieldbus master of single or A slaves
on AS-i master 1
(cycle starts again)
► Cancel with [ESC]
6-3

Menu
Main menu [Fieldbus Setup]
6-4
Set-up
Parameter setting of the controllere
7 Set-up
This chapter shows you how to get the Profibus interface started quickly.
7.1 Parameter setting of the controllere
7.1.1 Parameter setting of slaves in the controllere
Set the parameters of the slaves in the AS-i controllere as described in the basic device manual.
7.1.2 Set the parameters of the fieldbus interface in the controllere
[Menu] > [Fieldbus Setup] > Choose address > [OK]
1.
MMEENNUU
Quick Setup
2.
PLC Setup
Slave Lists
OOKK
Diagnostics
3.
Master Setup
Fieldbus Setup
OOKK
0
1
▲ ▼
1
▲ ▼
UUSSEERR
EESSCC
EESSCC
► Press [MENU]
► Scroll to [Fieldbus Setup] with [▼]
► Select [Fieldbus Setup] with [OK].
7-1
Set-up
Connect the controllere to the Profibus host
Fieldbus Address
4.
0
OOKK
Fieldbus Address
5.
OOKK
Fieldbus Baudrate
6.
#### KBaud
OOKK
87
▲ ▼
32
87
▲ ▼
88
▲ ▼
► Scroll to the requested address with [▲] / [▼].
EESSCC
► Save the fieldbus address with [OK].
EESSCC
> If there is communication with the fieldbus master:
display of negotiated baud rate
► Acknowledge with [OK].
EESSCC
> If there is no communication with the fieldbus master:
display value not defined
► Cancel with [ESC].
7.2 Connect the controllere to the Profibus host
► Connect the Profibus cable to the controllere.
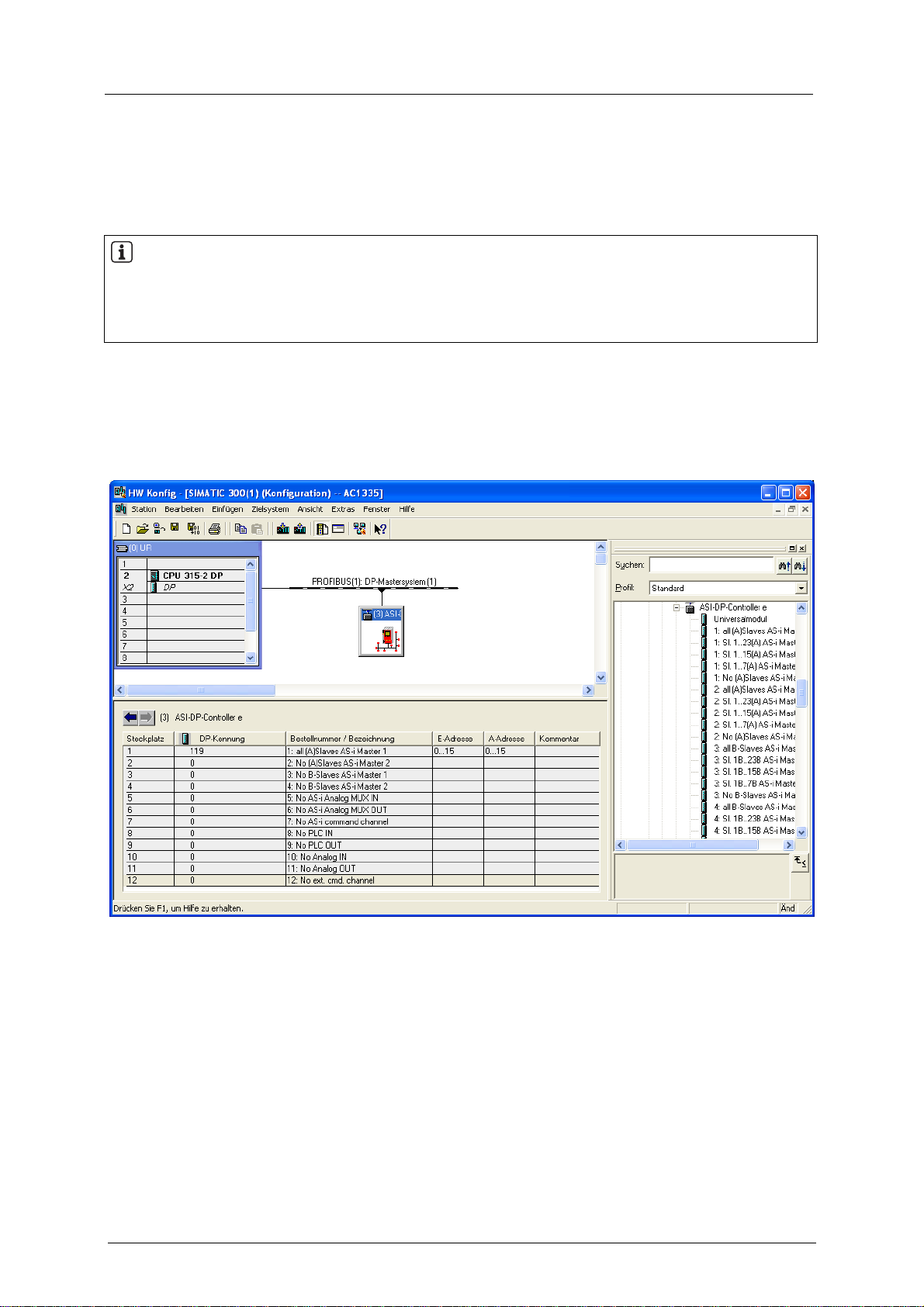
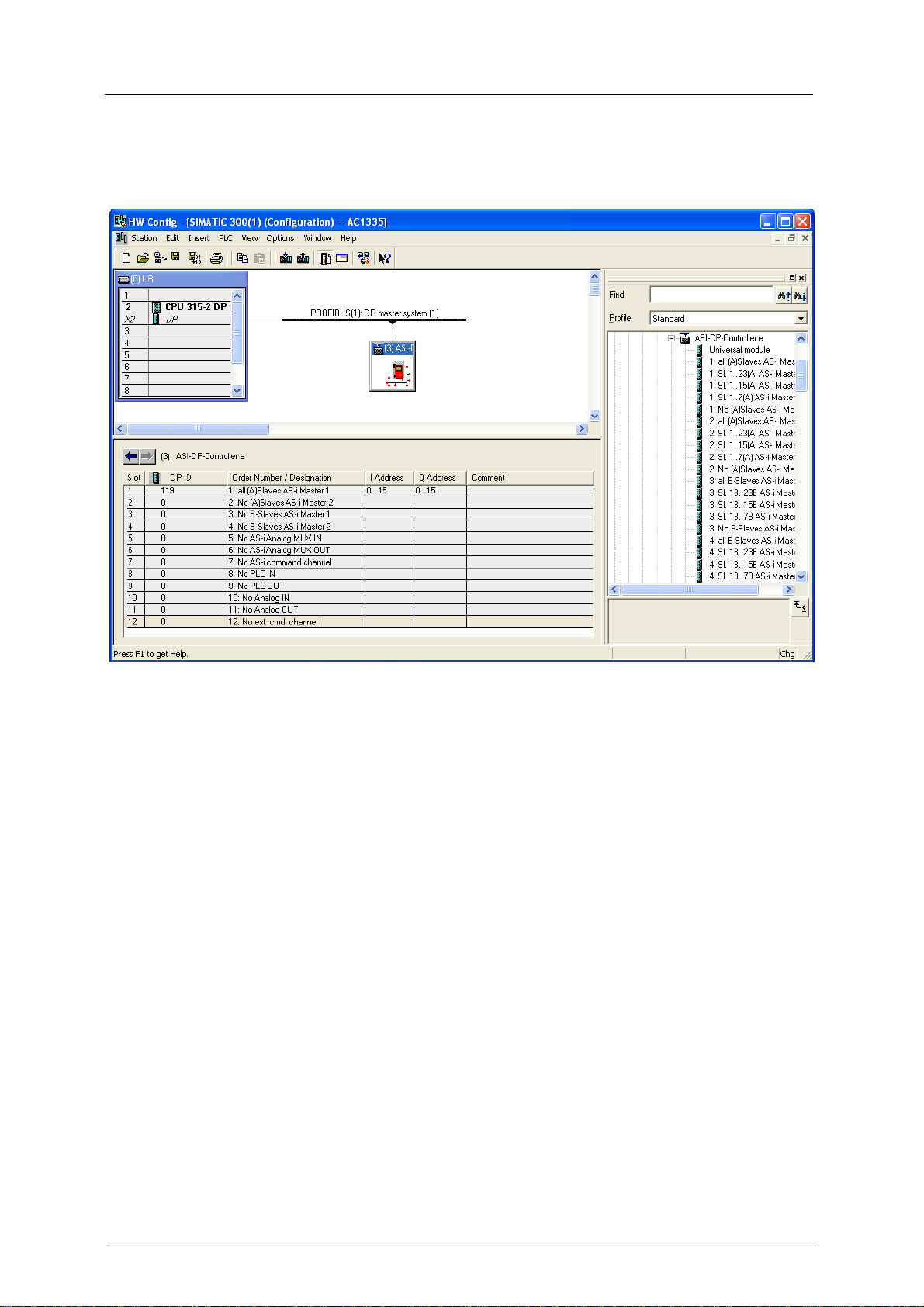
7.3 Parameter setting of the Profibus host
NOTE
Refer to the description of the Profibus interface on the host
(host = fieldbus master = in most cases higher-level PLC)
GSD file
(GSD = General Station Description) The GSD file ifm604D8.gsd on the ifm CD contains different
possible definitions (indications of lengths) for each of the 12 modules, adapted to the controllere. →
Hardware catalogue of the Profibus configuration software in the gateway folder.
► Copy this file to the suitable directory of the corresponding fieldbus configuration program (→ its
description).
7-2

Set-up
Parameter setting of the Profibus host
Programming software
The data of the controllere or the connected AS-i systems to be transferred can be defined (by
indicating the length of up to 12 modules) in the programming software for the Profibus DP master
system (host).
You can select from these definitions for parameter setting in the host:
Example for module 1:
There is a choice of 5 entries:
• all single and A slaves on AS-i master 1
(length = 16 bytes)
• single and A slaves with the addresses
1(A)...23(A) on AS-i master 1
(length = 12 bytes)
• single and A slaves with the addresses
1(A)...15(A) on AS-i master 1
(length = 8 bytes)
• single and A slaves with the addresses
1(A)...7(A) on AS-i master 1
(length = 4 bytes)
• no single or A slaves on AS-i master 1
(length = 0 bytes)
If the parameters for a smaller number of slaves than indicated in the selection point are to be set, you
have created free reserve in the host.
Example:
5 single and/or A slaves are connected to the AS-i master 1.
You have selected on the host:
"single and A slaves with the addresses 1(A)...7(A) on AS-i master 1"
You have then created an address area reserve of 1 byte in the host which is not used for the time being. The first 3 bytes of the
reserved address area are used to exchange data.
7-3
Set-up
Parameter setting of the Profibus host
7.3.1 Assigning the addresses of the inputs/outputs to the host "locations"
For Profibus DP, virtual locations in the host are assigned to the inputs/outputs addressed via AS-i.
NOTE
Addressing of CTT2 and CTT3 slaves → separate basic instructions of the device manual
and there → chapter "Use of analogue channels in the controllere depending on the slave profile"
and → chapter "Data distribution of slaves to the M4 controllere"
Digital inputs / outputs
st
example:
1
Siemens S7 with AS-i controllere as gateway. The digital inputs/outputs on the AS-i controllere are
assigned to the host as bytes 0...15.
In this constellation, how are the IEC addresses distributed to the inputs and outputs of the slaves? →
next page
7-4
Set-up
Parameter setting of the Profibus host
Digital inputs and outputs of the slaves at start address 0
Start address Bits 7...4 Bits 3...0
(Slave 0) reserved for master flags Slave 1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Reserved Conf.
Err.
0 .7 0 .6 0 .5 0 .4 0 .3 0 .2 0 .1 0 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
1 .7 1 .6 1 .5 1 .4 1 .3 1 .2 1 .1 1 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
2 .7 2 .6 2 .5 2 .4 2 .3 2 .2 2 .1 2 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
3 .7 3 .6 3 .5 3 .4 3 .3 3 .2 3 .1 3 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
4 .7 4 .6 4 .5 4 .4 4 .3 4 .2 4 .1 4 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
5 .7 5 .6 5 .5 5 .4 5 .3 5 .2 5 .1 5 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
6 .7 6 .6 6 .5 6 .4 6 .3 6 .2 6 .1 6 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
7 .7 7 .6 7 .5 7 .4 7 .3 7 .2 7 .1 7 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
8 .7 8 .6 8 .5 8 .4 8 .3 8 .2 8 .1 8 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
9 .7 9 .6 9 .5 9 .4 9 .3 9 .2 9 .1 9 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
10 .7 10 .6 10 .5 10 .4 10 .3 10 .2 10 .1 10 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
11 .7 11 .6 11 .5 11 .4 11 .3 11 .2 11 .1 11 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
12 .7 12 .6 12 .5 12 .4 12 .3 12 .2 12 .1 12 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
13 .7 13 .6 13 .5 13 .4 13 .3 13 .2 13 .1 13 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
14 .7 14 .6 14 .5 14 .4 14 .3 14 .2 14 .1 14 .0
D3 D2 D1 D0 D3 D2 D1 D0
15 .7 15 .6 15 .5 15 .4 15 .3 15 .2 15 .1 15 .0
No Slave PF.Err D3 D2 D1 D0
Slave 2 Slave 3
Slave 4 Slave 5
Slave 6 Slave 7
Slave 8 Slave 9
Slave 10 Slave 11
Slave 12 Slave 13
Slave 14 Slave 15
Slave 16 Slave 17
Slave 18 Slave 19
Slave 20 Slave 21
Slave 22 Slave 23
Slave 24 Slave 25
Slave 26 Slave 27
Slave 28 Slave 29
Slave 30 Slave 31
7-5
Set-up
Parameter setting of the Profibus host
nd
example:
2
Siemens S7 with AS-i controllere as gateway. The digital inputs/outputs on the AS-i controllere are
assigned to the host as bytes 65...80.
In this constellation, how are the IEC addresses distributed to the inputs and outputs of the slaves? →
next page
7-6
 Loading...
Loading...