Page 1
查询IDT79RC64V474180DP供应商
RISController
64-bit Microprocessor, based on
RISCore4000
Features
Features
FeaturesFeatures
◆
High performance 64-bit microprocessor, based on the
RISCore4000
– Minimized branch and load delays, through streamlined
5-stage scalar pipeline.
– Single and double precision floating-point unit
– 125 peak MFLOP/s at 250 MHz
– 330 Dhrystone MIPS at 250 MHz
– Flexible RC4700-compatible MMU
– Joint TLB on-chip, for virtual-to-physical address mapping
◆
On-chip two-way set associative caches
– 16KB instruction cache (I-cache)
– 16KB data cache (D-cache)
◆
Optional I-cache and D-cache locking (per set), provides
improved real-time support
◆
Enhanced, flexible bus interface allows simple, low-cost
design
– 64-bit Bus Interface option, 1000MB/s bandwidth support
– 32-bit Bus Interface option, 500MB/s bandwidth support
– SDRAM timing protocol, through delayed data in write cycles
– RC4000/RC5000 family bus-protocol compatibility
– Bus runs at fraction of pipeline clock (1/2 to 1/8)
◆
Implements MIPS-III Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
◆
3.3V core with 3.3V I/O
TM
Embedded
TM
RC64474
RC64475
◆
Software compatible with entire RISController Series of
Embedded Microprocessors
◆
Industrial temperature range support
◆
Active power management
– Powers down inactive units, through sleep-mode feature
◆
100% pin compatibility between RC64574, RC64474 and
RC4640
◆
100% pin compatibility between RC64575, RC64475 and
RC4650
◆
RC64474 available in 128-pin QFP package, for 32-bit only
systems
◆
RC64475 available in 208-pin QFP package, for full 64/32 bit
systems
◆
Simplified board-level testing, throu gh full Joint T est Action
Group (JTAG) boundary scan
◆
Windows® CE compliant
™
™
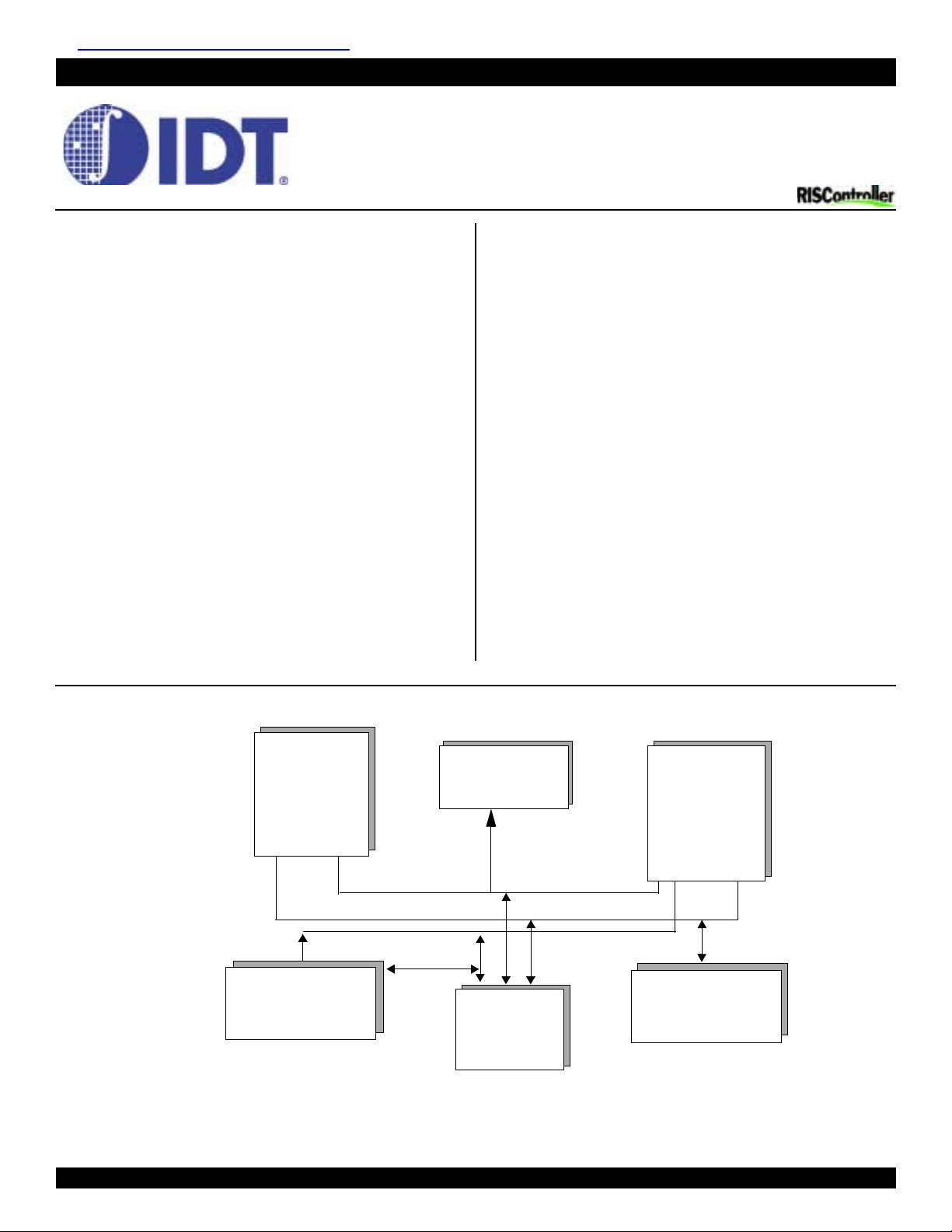
Block diagram
Block diagram
Block diagramBlock diagram
330 MIPS
64-bit
RISCore4000
CPU Core
Control Bus
Instruction Bus
16KB
Instruction Cache
(Lockable)
The IDT logo is a registered trademark and RC32134, RC32364, RC6414 5, RC64474, RC64475, RC4650, RC4640, RC4600,RC4700 RC3081, RC3052, RC3051, RC3041, RISController, and RISCore are trademarks of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
System Control
Coprocessor
(CP O )
32-/64-bit
Synchronized
System
Interface
125 MFLO PS
Single/Double
Precision
FPA
D a ta B u s
16KB
Data Cache
(Lockable)
2001 Integrated Device Technology, Inc .
1 of 25 April 10, 2001
DSC 4952
Page 2
RC64474™ RC64475™
Device Overview
Device Overview
Device OverviewDevice Overview
1111
Extending Integrated Device Technology’ s (IDT) RISCore4000 based
choices (see Table 1), the RC64474 and RC64475 are high performance 64-bit microprocessors targeted towards applications that require
high bandwidth, real-time response and rapid data processing and are
ideal for products ranging from internetworking equipment (switches,
routers) to multimedia systems such as web browsers, set-top boxes,
video games, and Windows
®
CE based products. These processors are
rated at 330 Dhrystone MIPS and 125 Million floating point operations
per second, at 250 MHz. The internal cache bandwidth for these devices
is over 3GB/second. The 64-bit external bus bandwidth is at more than
1000MB/s, and the 32-bit external bus bandwidth is at 500MB/s.
The RC64474 is packaged in a 128-pin QFP footprint package and
uses a 32-bit external bus, offering the ideal combination of 64-bit
processing power and 32-bit low-cost memory systems. The RC64475
is packaged in a 208-pin QFP footprint package and uses the full 64-bit
external bus. The RC64475 is ideal for applications requiring 64-bit
performance and 64-bit external bandwidth.
IDT’s RISCore4000 is a 250MHz 64-bit execution core that uses a
5-stage pipeline, eliminating the “issue restrictions” associated with
other more complex pipelines. The RISCore4000 implements the
MIPS-III Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) and is upwardly compatible
with applications that run on earlier generation parts.
Implementation of the MIPS-III architecture results in 64-bit operations, improved performance for commonly used code sequences in
1.
Detailed system operation information is provided in the RC64474/RC64475
user’s manual.
operating system kernels, and faster execution of floating-point intensive
applications.
The RISCore4000 integer unit implements a load/store architecture
with single cycle ALU operations (logical, shift, add, subtract) and an
autonomous multiply/divide unit. The ALU consists of the integer adder
and logic unit. The adder performs address calculations in addition to
arithmetic operations, and the logic unit performs all of the processor’s
logical and shift operations. Each unit is highly optimized and can
perform an operation in a single pipeline cycle. Both 32- and 64-bit data
operations are performed by the RISCore4000, utilizing 32 general
purpose 64-bit registers (GPR) that are used for integer operations and
address calculation. A complete on-chip floating-point co-processor
(CP1), which includes a floating-point register file and execution units,
forms a “seamless” interface, decoding and executing instructions in
parallel with the integer unit.
CP1’s floating-point execution units support both single and
double precision arithmetic—as specified in the IEEE Standard 754—
and are separated into a multiply unit and a combined add/convert/
divide/square root unit. Overlap of multiplies and add/subtract is
supported, and the multiplier is partially pipelined, allowing the initiation
of a new multiply instruction every fourth pipeline cycle.
The floating-point register file is made up of thirty-two 64-bit registers. The floating-point unit can take advantage of the 64-bit wide data
cache and issue a co-processor load or store doubleword instruction in
every cycle. The RISCore4000’s system control coprocessor (CP0)
registers are also incorporated on-chip and provide the path through
which the virtual memory system’s page mapping is examined and
changed, exceptions are handled, and any operating mode selections
are controlled.
RISCore4000/RISCore5000 Family of Socket Compatible Processors
RISCore4000/RISCore5000 Family of Socket Compatible Processors
RISCore4000/RISCore5000 Family of Socket Compatible ProcessorsRISCore4000/RISCore5000 Family of Socket Compatible Processors
32-bit Processors 64-bit Processors
RC4640 RC64474 RC64574 RC4650 RC64475 RC64575
CPU
Performance
FPA
Caches
External Bus
Voltage
Frequencies
Packages
MMU
Key Features
64-bit RISCore4000
w/ DSP extensions
>350MIPS >330MIPS >440MIPS >350MIPS >330MIPS >440MIPS
89 mflops, single pre-
cision only
8kB/8kB, 2-way, lock-
able by set
32-bit 32-bit, Super set pin
3.3V 3.3V 2.5V 3.3V 3.3V 2.5V
100-267 MHz 180-250 MHz 200-333 MHz 100-267 MHz 180-250 MHz 200-333 MHz
128 PQFP 128 QFP 128 QFP 208 QFP 208 QFP 208 QFP
Base-Bounds 96 page TLB 96 page TLB Base-Bounds 96 page TLB 96 page TLB
Cache locking, on-
chip MAC, 32-bit
external bus
64-bit RISCore4000 64-bit RISCore5000 w/
125 mflops, single and
double precision
16kB/16kB, 2-wa y,
lockable by set
compatible w/RC4640
Cache locking, JTAG,
syncDRAM mode, 32bit external bus
DSP extensions
666 mflops, single and
double precision
32kB/32kB, 2-way,
lockable by line
32-bit, Superset pin
compatible w/RC4640,
RC64474
Cache locking, JTAG,
syncDRAM mode, 32bit external bus
64-bit RISCore4000
w/ DSP extensions
89 mflops, single precision only
8kB/8kB, 2-way, lockable by set
32- or 64-bit 32-or 64-bit, Super-
Cache locking, onchip MAC, 32-bit & 64
bit bus option
Table 1 RISCore4000/RISCore5000 Processor Family
64-bit RISCore4000 64-bit RISCore5000
125 mflops, single
and double pr ecision
16kB/16kB, 2-way,
lockable by set
set pin compatible w/
RC4650
Cache locking, JTAG,
syncDRAM mode, 3264- bit bus option
w/ DSP extensions
666 mflops, single
and double precision
32kB/32kB, 2-way,
lockable by line
32-or 64-bit, Superset pin compati ble w/
RC4650, RC64475
Cache locking, JTAG,
syncDRAM mode, 3 264- bit bus option
2 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 3
RC64474™ RC64475™
A secure user processing environment is provided through the user,
supervisor, and kernel operating modes of virtual addressing to
system software. Bits in a status register determine which of these
modes is used.
If configured for 64-bit virtual addressing, the virtual address space
layout becomes an upwardly compatible extension of the 32-bit virtual
address space layout. Figure 1 is an illustration of the address space
layout for the 32-bit virtual address operation.
0xFFFFFFFF
0xE0000000
0xDFFFFFFF Supervisor virtual address space
0xC0000000
0xBFFFFFFF
0xA0000000
0x9FFFFFFF
0x80000000
0x7FFFFFFF
0x00000000
Figure 1 Kernel Mode Virtual Addressing (32-bit Mode)
Kernel virtual address space
(kseg3)
Mapped, 0.5GB
(sseg)
Mapped, 0.5GB
Uncached kernel physical address space
(kseg1)
Unmapped, 0.5GB
Cached kernel physical address space
(kseg0)
Unmapped, 0.5GB
User virtual address space
(useg)
Mapped, 2.0GB
The RC64474/RC64475’s Memory Management Unit (MMU)
controls the virtual memory system’s page mapping and consists of a
translation lookaside buffer (TLB) used for the virtual memory-mapping
subsystem.
This large, fully associative TLB maps 96 virtual pages to their
corresponding physical addresses. The TLB is organized as 48 pairs of
even-odd entries and maps a virtual address and address space identifier into the large, 64GB physical address space. To assist in controlling
the amount of mapped space and the replacement characteristics of
various memory regions, two mechanisms are provided. First, the page
size can be configured on a per-entry basis, to map a page size of 4KB
to 16MB (in increments of 4x).
The second mechanism controls the replacement algorithm, when a
TLB miss occurs. A random replacement algorithm is provided to select
a TLB entry to be written with a new mapping; however, the processor
provides a mechanism whereby a system specific number of mappings
can be locked into the TLB and avoid being randomly replaced, which
facilitates the design of real-time systems, by allowing deterministic
access to critical software.
The TLB also contains information to control the cache coherency
protocol, and cache management algorithm for each page. However,
hardware-based cache coherency is not supported.
The RC64474 and RC64475 enhance IDT’s entire RISCore4000
series through the implementation of features such as boundary scan, to
facilitate board level testing; enhanced support for SyncDRAM, to
simplify system implementation and improve performance.
The RC64474/475 processors offer a direct migration path for
designs based on IDT’s RC4640/RC4650 processors
2
, through full pin
and socket compatibility. Also, full 64-bit-family software and busprotocol compatibility ensures the RC64474/475 access to a robust
development tools infrastructure, allowing quicker time to market.
Deve lop m ent Tools
Deve lop m ent Tools
Deve lop m ent ToolsDeve lop m ent Tools
An array of hardware and software tools is available to assist system
designers in the rapid development of RC64474/475 based systems.
This accessibility allows a wide variety of customers to take full advantage of the device’s high-performance features while addressing today’s
aggressive time-to-market demands.
Cache Memory
Cache Memory
Cache MemoryCache Memory
To keep the RC64474 and RC64475’s high-performance pipeline full
and operating efficiently, on-chip instruction and data caches have been
incorporated. Each cache has its own data path and can be accessed in
the same single pipeline clock cycle.
The 16KB two-way set associative instruction cache (I-cache) is
virtually indexed, physically tagged, and word parity protected. Because
this cache is virtually indexed, the virtual-to-physical address translation
occurs in parallel with the cache access, further increasing performance
by allowing both operations to occur simultaneously. The instruction
cache provides a peak instruction bandwidth of 1000MB/sec at 250MHz.
The 16KB two-way set associative data cache (D-cache) is byte
parity protected and has a fixed 32-byte (eight words) line size. Its tag is
protected with a single parity bit. To allow simultaneous address translation and data cache access, the D-cache is virtually indexed and physically tagged. The data cache can provide 8 bytes each clock cycle, for a
peak bandwidth of 2GB/sec.
To lock critical sections of code and/or data into the caches for quick
access, a “cache locking” feature has been implemented. Once
enabled, a cache is said to be locked when a particular piece of code or
data is loaded into the cache and that cache location will not be selected
later for refill by other data. This feature locks a set (8KB) of Instructions
and/or Data.
Table 2 lists the RC64474/475 Instruction and data cache attributes.
2.
To ensure socket compatibility, refer to Table 8 and Table 9 at back of data
sheet.
3 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 4
RC64474™ RC64475™
Characteristics Instruction Data
Size 16KB 16KB
Organization 2-way set
associative
Line size 32B 32B
read unit 32-bits 64-bits
write policy na write-back, write-through
Line transfer order sub-block order,
for refill
Miss restart
after transfer of:
Parity per-word per-byte
Cache locking per set per set
Table 2 RC64474/RC64475 Instruction/Data Cache Attributes
System Interfaces
System Interfaces
System InterfacesSystem Interfaces
entire line miss word
2-way set
associative
with or without write-allocate
sub-block order, for load
sequential order, for store
The RC64475 supports a 64-bit system interface that is bus compatible with the RC4650 and RC64575 system interface. The system interface consists of a 64-bit Address/Data bus with 8 check bits and a 9-bit
command bus that is parity protected.
During 64-bit operation, RC64475 system address/data (SysAD)
transfers are protected with an 8-bit parity check bus, SysADC. When
initialized for 32-bit operation, the RC64475’s SysAD can be viewed as a
32-bit multiplexed bus that is protected by 4 parity check bits.
The RC64474 supports a 32-bit system interface that is bus compatible with the RC4640. During 32-bit operation, SysAD transfers are
performed on a 32-bit multiplexed bus (SysAD 31:0) that is protected by
4 parity check bits (SysADC 6:0).
Writes to external memory—whether they are cache miss writebacks, stores to uncached or write-through addresses—use the on-chip
write buffer. The write buffer holds a maximum of four 64-bit addresses
and 64-bit data pairs. The entire buffer is used for a data cache writeback and allows the processor to proceed in parallel with memory
updates.
A boot-time mode control interface initializes fundamental
processor modes. The boot-time mode control interface is a serial interface that operates at a very low frequency (MasterClock divided by
256). This low-frequency operation allows the initialization information to
be kept in a low-cost EPROM; alternatively, the twenty-or-so bits could
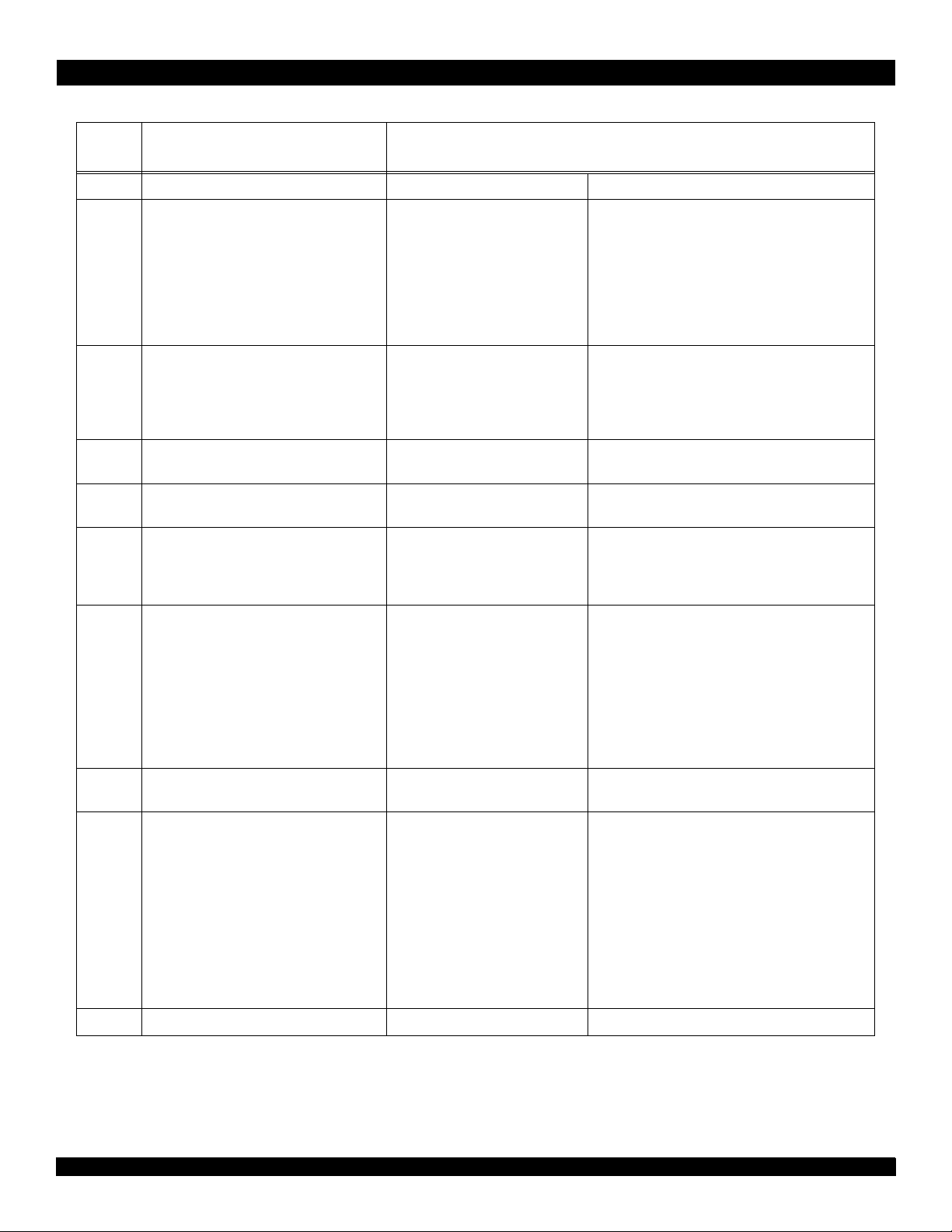
be generated by the system interface ASIC or a simple PAL. The boottime serial stream and configuration options are listed in Table 3.
The clocking interface allows the CPU to be easily mated with
external reference clocks. The CPU input clock is the bus reference
clock and can be between 25 and 125MHz. An on-chip phase-locked-
loop (PLL) generates the pipeline clock (PClock) through multiplication
of the system interface clock by values of 2,3,4,5,6,7 or 8, as defined at
system reset. This allows the pipeline clock to be implemented at a
significantly higher frequency than the system interface clock. The
RC64474/475 support single data (one to eight bytes) and 8-word block
transfers on the SysAD bus.
The RC64474/475 implement additional write protocols that
double the effective write bandwidth. The write re-issue has a repeat
rate of 2 cycles per write. Pipelined writes have the same 2-cycle per
write repeat rate, but can issue an additional write after WrRdy* deasserts.
Choosing a 32- or 64-bit wide system interface dictates whether a
cache line block transaction requires 4 double word data cycles or 8
single word cycles as well as whether a single data transfer—larger than
4 bytes—must be divided into two smaller transfers.
Board-level testing during Run-Time mode is facilitated through the
full JTAG boundary scan facility . Six pins—TDI, TDO, TMS, TCK, TRST*
and JTAG32*—have been incorporated to support the standard JTAG
interface.
System Enhancement
System Enhancement
System EnhancementSystem Enhancement
To facilitate discrete interface to SDRAM, the RC64474/475 bus
interface is enhanced during write cycles with a programmable delay
that is inserted between the write address and the write data (for both
block and non-block writes).
The bus delay can be defined as 0 to 7 MasterClock cycles and is
activated and controlled through mode bit (17:15) settings selected
during the reset initialization sequence. The ‘000’ setting provides the
same write operations timing protocol as the RC4640, RC4650, and
RC5000 processors.
Included in the system interface are six handshake signals:
RdRdy*, WrRdy*, ExtRqst*, Release*, ValidOut*, and ValidIn*; six inter-
rupt inputs, and a simple timing specification that is capable of transferring data between the processor and memory at a peak rate of
1000MB/sec. A boot-time selectable option to run the system interface
as 32-bits wide—using basically the same protocols as the 64-bit
system—is also supported.
4 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 5
RC64474™ RC64475™
Serial
Bit
255:18 Reserved Must be 0
17:15 WAdrWData_Del
Write address to write data delay in MasterClock cycles.®
14:13 Drv_Out
output dri ver sl ew ra te con trol . Bit 14 is MSB.
Affects only non-clock outputs.
12 System interface bus width 0 → 64-bit system interface
11 TmrIntEn
Disables the timer interrupt on Int*[5]
10:9 Non-block write
Selects non-block write type. Bit 10 is MSB.
Description Value & Mode Setting
000 → 0 cycles
001 → 1 cycle
010 → 2 cycles
011 → 3 cycles
100 → 4 cycles
101 → 5 cycles
110 → 6 cycles
111 → 7 cycles
Output driver strength:
10 → 100% strength (fastest)
11 → 83% strength
00 → 67% strength
01 → 50% strength (slowest)
1 → 32-bit system interface
0 → Enabled Timer Interrupt
1 → Disabled Timer Interrupt
00 → RC4x00 compatible
01 → Reserved
10 → Pipelined writes
11 → Write re-issue
7:5 Clock
Multiplier
MasterClock is multiplied internally to generate PClock
8EndBit
Specifies byte ordering
4:1 Writeback data rate
System interface data rate for block writes
only: bit 4 is MSB
0 Reserved Must be zero
Clock multiplier:
0 Multiply by 2
1 Multiply by 3
2 Multiply by 4
3 Multiply by 5
4 Multiply by 6
5 Multiply by 7
6 Multiply by 8
7 Reserved
0 → Little endian
1 → Big endian
64-bit:
9:15 Reserved
8 → dxxxdxxxdxxxdxxx
7 → ddxxxxxxddxxxxxx
6 → dxxdxxdxxdxx
5 → ddxxxxddxxxx
4 → ddxxxddxxx
3 → dxdxdxdx
2 → ddxxddxx
1 → ddxddx
0 → dddd
Table 3 Boot-tim e Mode Stream
32-bit:
9:15 Reserved
8 → wxxxwxxxwxxxwxxxwxxxwxxxwxxxwxxx
7 → wwxxxxxxwwxxxxxxwwxxxxxxwwxxxxxx
6 → wxxwxxwxxwxxwxxwxxwxxwxx
5 → wwxxxxwwxxxxwwxxxxwwxxxx
4 → wwxxxwwxxxwwxxxwwxxx
3 → wxwxwxwxwxwxwxwx
2 → wwxxwwxxwwxxwwxx
1 → wwxwwxwwxwwx
0 →Æ wwwwwwww
5 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 6
RC64474™ RC64475™
Power Management
Power Management
Power ManagementPower Management
Executing the WAIT instruction enables the processor to enter
Standby mode. The internal clocks will shut down, thus freezing the
pipeline. The PLL, internal timer, and some of the input pins (Int[5:0]*,
NMI*, ExtReq*, Reset*, and ColdReset*) will continue to run. Once the
CPU is in Standby Mode, any interrupt, including the internally generated timer interrupt, will cause the CPU to exit Standby Mode.
Thermal Considerations
Thermal Considerations
Thermal ConsiderationsThermal Considerations
The RC64474/475 come in a QFP with a drop-in heat spreader and
are guaranteed in a case temperature range of 0° to +85° C, for
commercial temperature devices; - 40° to +85° for industrial temperature devices. The type of package, speed (power) of the device, and
airflow conditions affect the equivalent ambient temperature conditions
that will meet this specification.
The equivalent allowable ambient temperature, T
using the thermal resistance from case to ambient (∅
, can be calculated
A
) of the given
CA
package. The following equation relates ambient and case temperatures:
T
A = TC
- P * ∅CA
where P is the maximum power consumption at hot temperature,
calculated by using the maximum I
Typical values for ∅
at various airflows are shown in Table 4. Note
CA
specification for the device.
CC
that the RC64474/475 processors implement advanced power management, which substantially reduces the typical power dissipation of the
device.
January 17, 2000: Added “with DSP extensions” in the CPU row
under RC64574 and RC64575 columns in Table 1. Added “lockable by
line” in the Caches row under RC64574 and RC64575 columns in Table
1. Revised Data Output and Data Output Hold rows in System Interface
Parameters table.
February 10, 2000: Revised values in Table 4, Thermal Resistance.
Old values were:
∅∅∅∅
CA
Airflow (ft/min) 0 200 400 600 800 1000
128 QFP 20 12 9 8 7 6
208 QFP 20 12 9 8 7 6
March 13, 2000: Replaced existing figure in Mode Configuration
Interface Reset Sequence section with 3 reset figures.
March 28, 2000: Removed the symbol t
April 17, 2000: Changed V
.
0.7V
CC
value in 200MHz column from 2.0V to
IH
from Figure 3.
DZ
April 10, 2001: In the Data Output and Data Output Hold categories
of the System Interface Parameters table, changed values in the Min
column for all speeds from 1.0 to 0. Deleted Output for Loading AC
Testing diagram and added Output Loading for AC Timing diagram
(Figure 8).
∅∅∅∅
CA
Airflow (ft/min) 0 200 400 600 800 1000
128 QFP 16 10 9 7 6 5
208 QFP 20 13 10 9 8 7
Table 4 Thermal Resistance (∅∅∅∅CA) at Various Airflows
Data Sheet Revision History
Data Sheet Revision History
Data Sheet Revision HistoryData Sheet Revision History
December 1998: Changed ordering code on 128-pin package from
DQ / DQI (Industrial) to DZ / DZI (Industrial).
January 1999: Removed 5V tolerance capability and deleted 5V
tolerant pin.
February 1999: Changed the package drawings to reflect the new
208-pin DP (DPI) and 128-pin DZ (DZI) packages.
May 1999: Removed “Preliminary” status from data sheet.
Changes in DC Electrical Characteristics table. Changes in Pin
Description table. Changes in Clock Parameters table. Changes in
System Interface Parameters table.
September 1999: Updated Revision History section.
6 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 7
RC64474™ RC64475™
Pin Description Table
Pin Description Table
Pin Description TablePin Description Table
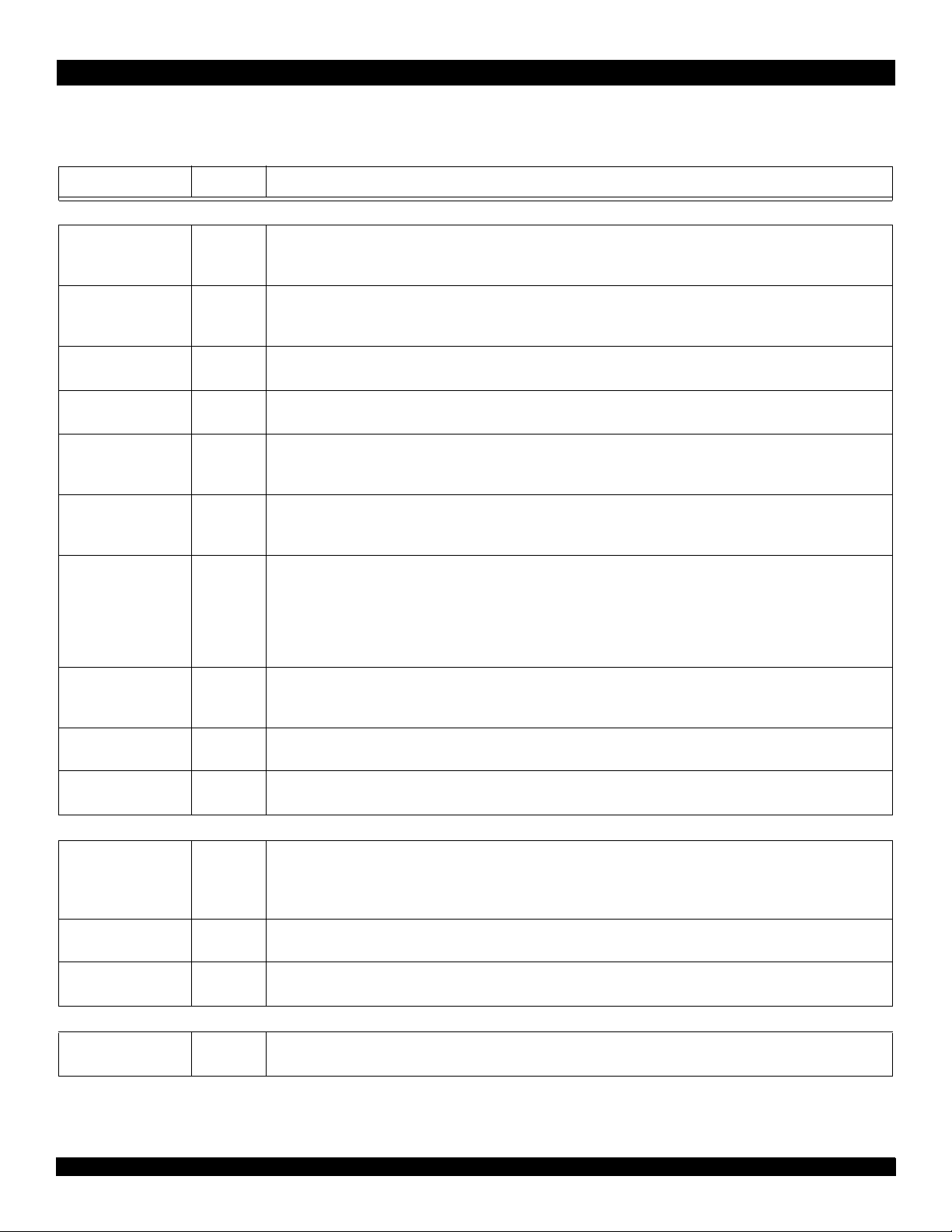
The following is a list of system interface pins available on the RC64474/475. Pin names ending with an asterisk (*) are active when low.
Pin Name Type Description
System Interface
ExtRqst* I External request
An external agent asserts ExtRqst* to request use of the System interface. The processor grants the request by asserting
Release*.
Release* O Release interface
In response to the assertion of ExtRqst* or a CPU read request, the processor asserts Release* and signals to the requesting device that the system interface is available.
RdRdy* I Read Ready
The external agent asserts RdRdy* to indicate that it can accept a processor read request.
WrRdy* I Write Ready
An external agent asserts WrRdy* when it can now accept a processor write request.
ValidIn* I Valid Input
Signals that an external agent is now driving a valid address or data on the SysAD bus and a valid command or data identifier on the SysCmd bus.
ValidOut* O Valid output
Signals that the processor is now driving a valid address or data on the SysAD bus and a valid command or data identifier
on the SysCmd bus.
SysAD(63:0) I/O System address/data bus
A 64-bit address and data bus for communication between the processor and an external agent. During address phases
only, SysAd(35:0) contains valid address information. The remaining SysAD(63:36) pins are not used. The whole 64-bit
SysAD(63:0) may be used during the data transfer phase.
In 32-bit mode and in the RC64474, SysAD(63:32) is not used, regardless of Endianness. A 32-bit address and data communication between processor and external agent is performed via SysAD(31:0).
SysADC(7:0) I/O System address/data check bus
An 8-bit bus containing parity check bits for the SysAD bus during data bus cycles.
In 32-bit mode and in the RC64474, SysADC(7:4) is not used. The SysADC(3:0) contains check bits for SysAD(31:0).
SysCmd(8:0) I/O System command/data identifier bus
A 9-bit bus for command and data identifier transmission between the processor and an external agent.
SysCmdP I/O System Command Parity
A single, even-parity bit for the Syscmd bus. This signal is always driven low.
Clock/Control Interface
MasterClock I Master Clock
Master clock input establishes the processor and bus operating frequency. It is multiplied internally by 2,3,4,5,6,7,8 to gen-
erate the pipeline clock (PClock). This clock must be driven by 3.3V (Vcc) clock signals, regardless of the 5V tolerant pin
setting.
P I Quiet VCC for PLL
CC
V
for the internal phase locked loop.
CC
Quiet V
V
PIQuiet VSS for PLL
SS
Quiet V
Interrupt Interface
Int*(5:0) I Interrupt
Six general processor interrupts, bit-wise ORed with bits 5:0 of the interrupt register.
for the internal phase locked loop.
SS
Table 5 Pin Descriptions (Page 1 of 2)
7 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 8
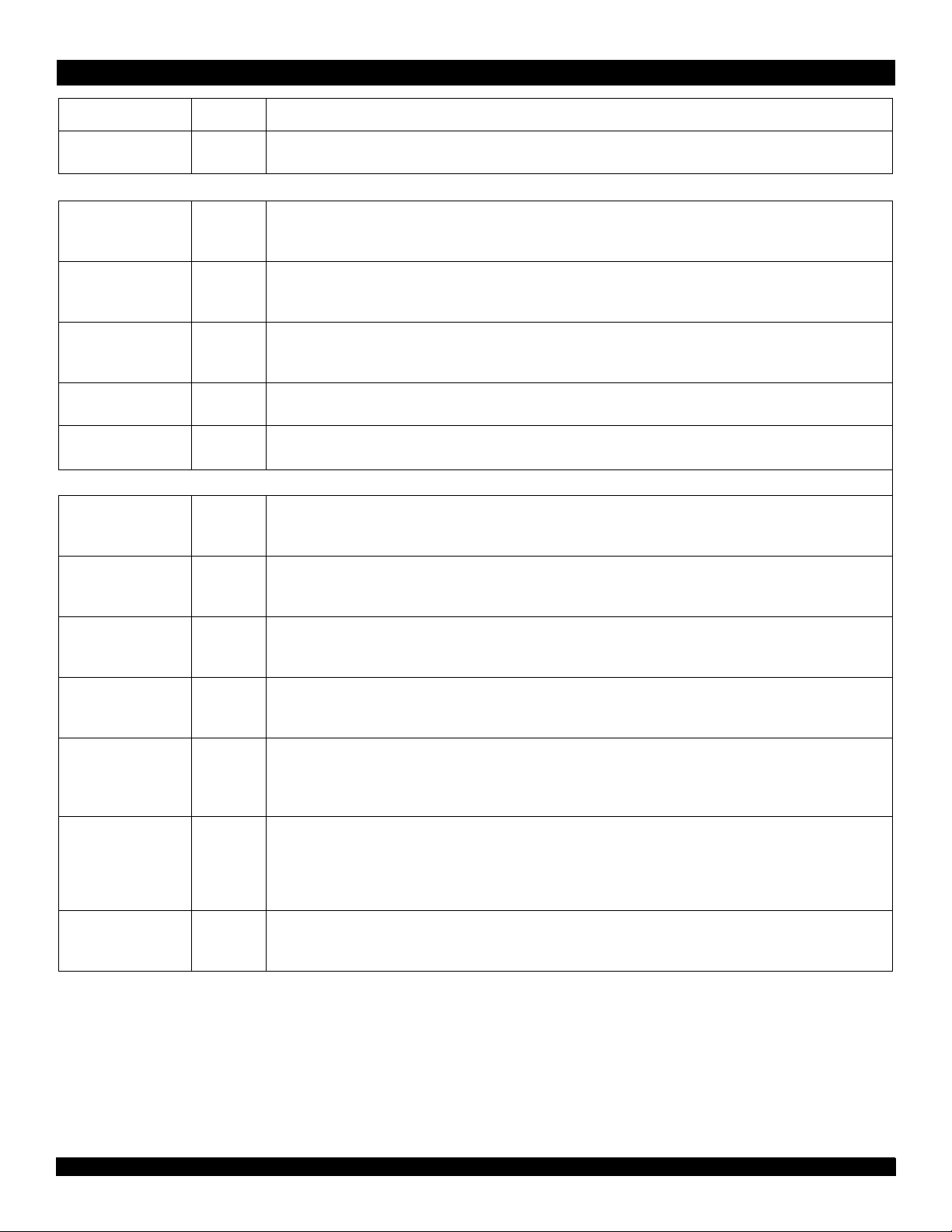
RC64474™ RC64475™
Pin Name Type Description
NMI* I Non-maskable interrupt
Non-maskable interrupt, ORed with bit 6 of the interrupt register.
Initialization Interface
kIV
O
V
CC
CC
is OK
When asserted, this signal indicates to the processor that the power supply has been above the Vcc minimum for more
than 100 milliseconds and will remain stable. The assertion of V
ColdReset* I Cold reset
This signal must be asserted for a power on reset or a cold reset. ColdReset must be de-asserted synchronously with Mas-
terClock.
Reset* I Reset
This signal must be asserted for any reset sequence. It can be asserted synchronously or asynchronously for a cold reset,
or synchronously to initiate a warm reset. Reset must be de-asserted synchronously with MasterClock.
ModeClock O Boot-mode clock
Serial boot-mode data clock output at the system clock frequency divided by two hundred fifty-six.
ModeIn I Boot-mode data in
Serial boot-mode data input.
JTAG Interface
TDI I JTAG Data In
On the rising edge of TCK, serial input data are shifted into either the Instruction register or Data register, depending on the
TAP controller state.
k initiates the initialization sequence.
CCO
TDO O JTAG Data Out
On the falling edge of TCK, the TDO is serial data shifted out from either the instruction or data register. When no data is
shifted out, the TDO is tri-stated (high impedance).
TCK I JTAG Clock Input
An input test clock used to shift into or out of the boundary-scan register cells. TCK is independent of the system and pro-
cessor clock with nominal 40-60% duty cycle.
TMS I JTAG Command Select
The logic signal received at the TMS input is decoded by the TAP controller to control test operation. TMS is sampled on
the rising edge of TCK.
TRST* I JTAG Reset
The TRST* pin is an active-low signal used for asynchronous reset of the debug unit, independent of the processor logic.
During normal CPU operation, the JTAG controller will be held in the reset mode, asserting this active low pin.
When asserted low, this pin will also tristate the TDO pin.
JTAG32* I JTAG 32-bit scan
This pin is used to control length of the scan chain for SYsAD (32-bit or 64-bit) for the JTAG mode. When set to Vss, 32-bit
bus mode is selected. In this mode, only SysAD(31:0) are part of the scan chain. When set to Vcc, 64-bit bus mode is
selected. In this mode, SysAD(63:0) are part of the scan chain. This pin has a built-in pull-down device to guarantee 32-bit
scan, if it is left uncovered.
JR_Vcc I JTAG VCC
This pin has an internal pull-down to continuously reset the JTAG controller (if left unconnected) bypassing the TRst* pin.
When supplied with Vcc, the TRst* pin will be the primary control for the JTAG reset.
Table 5 Pin Descriptions (Page 2 of 2)
8 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 9

RC64474™ RC64475™
Logic Diagram — RC64474/RC64475
Logic Diagram — RC64474/RC64475
Logic Diagram — RC64474/RC64475Logic Diagram — RC64474/RC64475
Figure 2 illustrates the direction and functional groupings for the processor signals.
MasterClock
V
P
CC
V
P
SS
Clock/Control Interface
TDI
TDO
TMS
Interface
TRST*
JTAG
TCK
JTag32*
JR_Vcc
RdRdy*
WrRdy*
ExtRqst*
Release*
RC64474/
RC64475
Logic
Symbol
64
8
9
SysAD(63:0)
SysADC(7:0)
SysCmd(8:0)
System Interface
SysCmdP
VCCOK
ColdReset*
Reset*
ModeClock
Interface
Initialization
ModeIn
NMI
*
6
Int*(5:0)
Interrupt
Interface
Signals
Handshake
ValidIn*
ValidOut*
Figure 2 Logic Diagram for RC64474/RC64475
9 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 10

RC64474™ RC64475™
RC64475 208-pin QFP Package Pin-out
RC64475 208-pin QFP Package Pin-out
RC64475 208-pin QFP Package Pin-out RC64475 208-pin QFP Package Pin-out
Pin names followed by an asterisk (*) are active when low. For maximum flexibility and compatibility with future designs, N.C. pins should be left
floating.
Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function
1 N.C. 53 JTAG32* 105 N.C. 157 N.C.
2 N.C. 54 N.C. 106 N.C. 158 N.C.
3 N.C. 55 N.C. 107 N.C. 159 SysAD59
4 N.C. 56 N.C. 108 N.C. 160 ColdReset*
5 N.C. 57 SysCmd2 109 N.C. 161 SysAD28
6 N.C. 58 SysAD36 110 N.C. 162 VCC
7 N.C. 59 SysAD4 111 N.C. 163 V
SS
8 N.C. 60 SysCmd1 112 N.C. 164 SysAD60
9N.C. 61V
10 SysAD11 62 V
11 V
12 V
SS
cc
63 SysAD35 115 ExtRqst* 167 SysAD61
64 SysAD3 116 V
SS
cc
13 SysCmd8 65 SysCmd0 117 V
14 SysAD42 66 SysAD34 118 SysAD21 170 V
15 SysAD10 67 V
16 SysCmd7 68 V
17 V
18 V
SS
cc
69 SysAD2 121 Modein 173 SysAD63
70 Int5* 122 SysAD22 174 V
SS
cc
19 SysAD41 71 SysAD33 123 SysAD54 175 V
20 SysAD9 72 SysAD1 124 V
21 SysCmd6 73 V
22 SysAD40 74 V
23 V
24 V
SS
cc
75 Int4* 127 SysAD23 179 N.C.
76 SysAD32 128 SysAD55 180 TDI
SS
cc
113 N.C. 165 Reset*
114 SysAD52 166 SysAD29
cc
SS
168 SysAD30
169 V
cc
SS
119 SysAD53 171 SysAD62
120 RdRdy* 172 SysAD31
cc
SS
125 V
cc
SS
176
177 SysADC3
OK
V
cc
126 Release* 178 SysADC7
25 SysAD8 77 SysAD0 129 NMI* 181 TRst*
26 SysCmd5 78 Int3* 130 V
27 SysADC4 79 V
28 SysADC0 80 V
29 V
30 V
SS
cc
81 Int2* 133 SysADC6 185
82 SysAD16 134 SysAD24 186
SS
cc
131 V
132 SysADC2 184 TDO
31 SysCmd4 83 SysAD48 135 V
32 SysAD39 84 Int1* 136 V
33 SysAD7 85 V
SS
137 SysAD56 189 V
cc
SS
cc
SS
182 TCK
183 TMS
P
V
cc
P
V
SS
187 MasterClock
188 V
cc
SS
Table 6 RC64475 208-pin QFP Package Pin-Out (Page 1 of 2)
10 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 11

RC64474™ RC64475™
Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function
34 SysCmd3 86 V
35 V
36 V
SS
cc
87 SysAD17 139 SysAD57 191 SysADC1
88 SysAD49 140 N.C. 192 V
cc
37 SysAD38 89 Int0* 141 V
138 SysAD25 190 SysADC5
cc
SS
193 V
SS
38 SysAD6 90 SysAD18 142 N.C 194 SysAD47
39 ModeClock 91 V
40 WrRdy* 92 V
SS
cc
41 SysAD37 93 SysAD50 145 N.C. 197 V
42 SysAD5 94 ValidIn* 146 V
43 V
44 V
SS
cc
45 N.C. 97 V
46 N.C. 98 V
95 SysAD19 147 V
96 SysAD51 148 SysAD27 200 SysAD45
SS
cc
47 N.C. 99 ValidOut* 151 N.C. 203 V
48 N.C. 100 SysAD20 152 N.C. 204 V
143 SysAD26 195 SysAD15
144 SysAD58 196 SysAD46
cc
cc
SS
198 V
SS
199 SysAD14
149 N.C. 201 SysAD13
150 JR_
V
cc
202 SysAD44
SS
cc
49 N.C. 101 N.C. 153 N.C. 205 SysAD12
50 N.C. 102 N.C. 154 N.C. 206 SysCmdP
51 N.C. 103 N.C. 155 N.C. 207 SysAD43
52 N.C. 104 N.C. 156 N.C. 208 N.C.
Table 6 RC64475 208-pin QFP Package Pin-Out (Page 2 of 2)
RC64474 128-pin QFP Package Pin-out
RC64474 128-pin QFP Package Pin-out
RC64474 128-pin QFP Package Pin-out RC64474 128-pin QFP Package Pin-out
Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function
1 JTAG32* 33 V
cc
2 SysCmd2 34 Vss 66 SysAD28 98 Vss
3 Vcc 35 SysAD13 67 ColdReset* 99 SysAD19
4 Vss 36 SysAD14 68 SysAD27 100 ValidIn*
5 SysAD5 37 Vss 69 Vss 101 Vcc
6 WrRdy* 38 Vcc 70 Vcc 102 Vss
7 ModeClock 39 SysAD15 71 JR_Vcc 103 SysAD18
8 SysAD6 40 Vss 72 SysAD26 104 Int0*
9 Vcc 41 Vcc 73 N.C. 105 SysAD17
10 Vss 42 SysADC1 74 Vss 106 Vcc
11 SysCmd3 43 Vss 75 N.C. 107 Vss
12 SysAd7 44 Vcc 76 SysAD25 108 Int1*
13 SysCmd4 45 MasterClock 77 Vss 109 SysAD16
65 V
cc
97 Vcc
Table 7 RC64474 128-pin QFP Package Pin-out (Page 1 of 2)
11 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 12

RC64474™ RC64475™
Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function Pin Function
14 Vcc 46 VssP 78 Vcc 110 Int2*
15 Vss 47 VccP 79 SysAD24 111 Vcc
16 SysAdC0 48 TDO 80 SysADC2 112 Vss
17 SysCmd5 49 TMS 81 Vss 113 Int3*
18 SysAD8 50 TCK 82 Vcc 114 SysAD0
19 Vcc 51 TRst* 83 NMI* 115 Int4*
20 Vss 52 TDI 84 SysAD23 116 Vcc
21 SysCmd6 53 Vss 85 Release* 117 Vss
22 SysAD9 54 SysADC3 86 Vss 118 SysAD1
23 Vcc 55 VccOK 87 Vcc 119 Int5*
24 Vss 56 Vss 88 SysAD22 120 SysAD2
25 SysCCmd7 57 Vcc 89 Modein 121 Vcc
26 SysAD10 58 SysAD31 90 RdRdy* 122 Vss
27 SysCmd8 59 Vss 91 SysAD21 123 SysCmd0
28 Vcc 60 Vcc 92 Vss 124 SysAd3
29 Vss 61 SysAD30 93 Vcc 125 Vcc
30 SysAD11 62 SysAD29 94 ExtRqst* 126 Vss
31 SysCmdP 63 Reset* 95 SysAD20 127 SysCmd1
32 SysAD12 64 Vss 96 ValidOut* 128 SysAD4
Table 7 RC64474 128-pin QFP Package Pin-out (Page 2 of 2)
Socket Compatibility—RC64474 & RC4640
Socket Compatibility—RC64474 & RC4640
Socket Compatibility—RC64474 & RC4640 Socket Compatibility—RC64474 & RC4640
To ensure socket compatibility between the RC4640 and the RC64474 devices, several pin changes are required, as shown below.
Pin RC4640
1 N.C JTAG32* Yes. Pin has an internal pull-down, to enable 32-bit scan.
48 V
49 V
50 V
51 V
52 V
71 N.C. JR_V
ss
ss
ss
ss
ss
RC64574/
RC64474
TDO Yes. Can be driven with Vss, if JTAG is not needed. Is tristated when TRst* is low.
TMS Yes. Can be driven with Vss if JTAG is not needed.
TCK Yes. Can be driven with Vss if JTAG is not needed.
TRst* Yes. Can be driven with Vss if JTAG is not needed.
TDI Yes. Can be driven with Vss if JTAG is not needed.
cc
Compatible to
RV4640?
Can also be left a N.C.
Yes. Can be left N.C. in RC64474, if JTAG is not need. If JTAG is needed, it must
be driven to V
Table 8 RC64574 Socket Compatibility to RC64474 and R4640
.
cc
Comments
12 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 13

RC64474™ RC64475™
Socket Compatibility—RC64475 & RC4650
Socket Compatibility—RC64475 & RC4650
Socket Compatibility—RC64475 & RC4650Socket Compatibility—RC64475 & RC4650
Pin
RV4650
32-bit
RC64575
32-bit
RC64475
32-bit
RV4650
64-bit
RC64575
64-bit
RC64475
64-bit
Compatible
to RV4650?
Comments
53 N.C. JTAG32* No Connect JTAG32* Yes In 32-bit, this pin can be left unconnected
because of internal pull-down.
In 64-bit, this assumes that JTAG will not be
used. If using JTAG, this pin must be at V
150 N.C. JR_V
cc
No Connect JR_V
cc
Yes In RC64475, can be left a N.C, if JTAG is not
need. If JTAG is needed, it must be driven to
Vcc.
180 N.C. TDI No Connect TDO Yes If JTAG is not needed, can be left a N.C.
181 N.C. TRsT* No Connect TRsT* Yes If JTAG is not needed, can be left a N.C.
182 N.C. TCK No Connect TCK Yes If JTAG is not needed, can be left a N.C.
183 N.C. TMS No Connect TMS Yes If JTAG is not needed, can be left a N.C.
184 N.C. TDO No Connect TDIO Yes If JTAG is not needed, can be left a N.C.
Table 9 RC64575 Socket Compatibility to RC64475 & RC4650
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute Maximum RatingsAbsolute Maximum Ratings
Note:
Stresses greater than those listed under ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional
operation of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum
rating conditions for extended periods may affect reliability.
.
cc
RC64474/475
Symbol Rating
3.3V±5%
Commercial Industrial
V
TERM
T
C
T
BIAS
T
STG
I
IN
I
OUT
1.
VIN minimum = –2.0V for pulse width less than 15ns. VIN should not exceed V
2.
When VIN < 0V or VIN > V
3.
Not more than one output should be shorted at a time. Duration of the short should not exceed 30 seconds.
Recommended Operation Temperature and Supply Voltage
Recommended Operation Temperature and Supply Voltage
Recommended Operation Temperature and Supply VoltageRecommended Operation Temperature and Supply Voltage
Terminal Voltage with respect to GND –0.51 to +4.6
Operating Temperature(case) 0 to +85 -40 to +85 °C
Case Temperature Under Bias –55 to +125 –55 to +125 °C
Storage Temperature –55 to +125 –55 to +125 °C
DC Input Current 20
DC Output Current 50
CC
2
3
+0.5 Volts.
CC
Grade Temperature Gnd
Commercial 0°C to +85°C (Case) 0V 3.3V±5%
Industrial -40 + 85°C (Case) 0V 3.3V±5%
RC64474/475
3.3V±5%
1
–0.5
2
20
3
50
RC64474/475
V
CC
Unit
to +4.6 V
mA
mA
13 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 14

RC64474™ RC64475™
DC Electrical Characteristics
DC Electrical Characteristics
DC Electrical CharacteristicsDC Electrical Characteristics
Commercial Temperature Range—RC64474/64475
= 3.3±5
(V
CC
%, T
= 0°C to +85°C)
CASE
RC64474/RC64475
Parameter
180MHz
Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum Minimum Maximum
V
OL
V
OH
V
OL
V
OH
V
IL
V
IH
I
IN
C
IN
C
OUT
I/O
LEAK
Power Consumption—RC64474
Power Consumption—RC64474
Power Consumption—RC64474Power Consumption—RC64474
.
— 0.1V — 0.1V — 0.1V |I
VCC - 0.1V — VCC - 0.1V — VCC - 0.1V —
— 0.4V — 0.4V — 0.4V |I
2.4V — 2.4V — 2.4V —
–0.5V 0.2V
2.0V VCC + 0.5V 0.7V
— ±10uA — ±10uA — ±10uA 0 ≤ VIN ≤ V
— 10pF — 10pF — 10pF —
— 10pF — 10pF — 10pF —
— 20uA — 20uA — 20uA Input/Output Leakage
RC64474 180MHz RC64474 200MHz RC64474 250MHz
Parameter
Typical
1
RC64474/RC64475
CC
–0.5V 0.2V
CC
Max Typical
RC64474/RC64475
200MHz
CC
–0.5V 0.2V
250MHz
VCC + 0.5V 2.0V VCC + 0.5V —
1
Max Typical
1
CC
Max
Conditions
|= 20uA
OUT
|= 4mA
OUT
—
Conditions
CC
System Condition: 180/90MHz 200/100MHz 250/125MHz —
standby — 60 mA
I
CC
— 110 mA
active 530 mA
2
2
2
630 mA
2
—60 mA
—110 mA
2
600mA
700 mA
2
2
2
— 100 mA
— 110 mA
2
700 mA
850mA
2
2
2
CL = 0pF
CL = 50pF
CL = 0pF
No SysAd activity
630mA
2
750 mA
2
700 mA
2
850 mA
2
850mA
2
1000mA
2
CL = 50pF
R4x00 compatible writes,
TC = 25oC
750 mA
2
1050 mA
4
850 mA
2
1200 mA
4
1000mA
2
1400mA
2
CL = 50pF
Pipelined writes or write
re-issue,
T
1.
Typical integer instruction mix and cache miss rates
2.
These are not tested. They are the results of engineering analysis and are provided for reference only
3.
Guaranteed by design.
4.
These are the specifications IDT tests to insure compliance.
= 25oC
C
3
3
3
14 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 15

RC64474™ RC64475™
Power Consumption—RC64475
Power Consumption—RC64475
Power Consumption—RC64475Power Consumption—RC64475
RC64475 180MHz RC64475 200MHz RC64475 250MHz
Parameter
Typical
1
Max Typical
1
Max Typical
1
Max
System Condition: 180/90MHz 200/100MHz 250/125MHz —
I
standby — 60 mA
CC
2
— 60 mA
— 110 m2A — 110 mA
2
active,
64-bit bus
option
1.
Typical integer instruction mix and cache miss rates
2.
These are not tested. They are the results of engineering analysis and are provided for reference only.
3.
Guaranteed by design.
4.
In 32-bit bus option, use RC64474 power consumption values.
5.
These are the specifications IDT tests to insure compliance.
720 mA
4
850 mA
1000 mA
2
2
850 mA
1000 mA
1200 mA
2
2
5
850 mA
1000 mA
1200 mA
2
2
2
2
1000 mA
1200 mA
1400 mA
1100 mA
1360mA
1600 mA
2
2
2
2
2
— 100 mA
2
2
2
5
— 110 mA
2
935 mA
2
1100mA
2
1360 mA
Conditions
CL = 0pF
3
CL = 50pF
CL = 0pF
No SysAd activity
3
CL = 50pF
R4x00 compatible writes,
TC = 25oC
CL = 50pF
Pipelined writes or write re-issue,
T
= 25oC
C
3
Timing Characteristics—RC64474/RC64475
Timing Characteristics—RC64474/RC64475
Timing Characteristics—RC64474/RC64475Timing Characteristics—RC64474/RC64475
Cycle
MasterClock
SysAD,SysCmd Driven
SysADC
SysAD,SysCmd Received
SysADC
Control Signal CPU driven
ValidOut*
Release*
Control Signal CPU received
RdRdy*
WrRdy*
ExtRqst*
ValidIn*
NMI*
Int*(5:0)
1 2 3 4
t
MCkHigh
t
MCkLow
D D D
t
DM
t
DO
D D D D
t
DS
t
DH
t
DO
t
DS
t
MCkP
t
DOH
t
DOH
t
DH
* = active low signal
Figure 3 System Clocks Data Setup, Output, and Hold Timing
15 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 16

RC64474™ RC64475™
t
TCK
TCK
TDI/
TMS
TDO
Notes to diagram:
t1 = t
TCKlow
t2 = t
TCKHIGH
t
t3 =
t4 = T
t5 = t
AC Electrical Characteristics
AC Electrical Characteristics
AC Electrical CharacteristicsAC Electrical Characteristics
TCKFALL
(reset pulse width)
RST
TCKRise
TRST*
Commercial Temperature Range RC64474/RC64475
=3.3V ± 5%; T
(V
CC
Clock Parameters
Clock Parameters
Clock Parameters Cloc k Parameters
= 0×C to +85°C)
CASE
t3
t1
t
DS
TDO
t
DO
t4
> = 25 ns
Figure 4 Standard JTAG timing
t5
TDO
t2
t
DH
Parameter
Pipeline clock
1
Symbol
PClk 80 180 80 200 80 250 MHz
Test
Conditions
Frequency
MasterClock HIGH t
MasterClock LOW t
MasterClock
MCHIGH
MCLOW
—
Transition ≤ 3ns 3 — 3 — 2.5 — ns
Transition ≤ 3ns 3 — 3 — 2.5 — ns
— 10 90 10 100 10 125 MHz
Frequency
MasterClock Period t
Clock Jitter for
MCP
t
JitterIn
— 11.1 100 10 100 8 100 ns
— — ±250 — ±250 — ±250 ps
MasterClock
MasterClock Rise Time t
MasterClock Fall Time t
ModeClock Period
JTAG Clock Input t
JTAG Clock HIGH t
JTAG Clock Low t
JTAG Clock Rise Time t
JTAG Clock Fall Time t
1.
Timings are measured from 1.5V of the clock to 1.5V of the signal.
MCRise
MCFall
t
ModeCKP — — 256*
TCK
TCKHIGH
TCKLOW
TCKRise
TCKFall
——2.5—2—2ns
——2.5—2—2ns
— 100 — 100 — 100 — ns
— 40 — 40 — 40 — ns
— 40 — 40 — 40 — ns
——5—5—5ns
——5—5—5ns
RC64474/ RC64475
180MHz
RC64474/ RC64475
200MHz
RC64474/ RC64475
250MHz
Min Max Min Max Min Max
t
MCP
— 256*
t
MCP
— 256*
t
MCP
Units
ns
16 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 17

RC64474™ RC64475™
Capacitive Load Deration—RC64474/RC64475
Capacitive Load Deration—RC64474/RC64475
Capacitive Load Deration—RC64474/RC64475Capacitive Load Deration—RC64474/RC64475
Parameter Symbol
Load Derate C
System Interface Parameters
System Interface Parameters
System Interface Parameters System Interface Parameters
LD
Note: Operation of the RC64474/RC64475 is only guaranteed with the Phase Lock Loop enabled.
1
Parameter
Data Output
2
Data Output Hold t
Input Data Setup t
Input Data Hold t
1.
Timings are measured from 1.5V of the clock to 1.5V of the signal.
2.
Capacitive load for all output timings is 50pF.
3.
Guaranteed by design.
4.
50pf loading on external output signals, fastest settings. Also applies to JTAG signals (TRST*,TDO,TDI,TMS)
Symbol Test Conditions
tDM= Min
= Max
t
DO
4
DOH
DS
DH
Test
Conditions
180MHz 200MHz† 250MHz†
Min Max Min Max Min Max
— — 2 — 2 — 2 ns/25pF
RC64474/
RC64475
180MHz
RC64474/
RC64475
200MHz
RC64474/
RC64475
250MHz
Min Max Min Max Min Max
mode
mode
mode
mode
mode
mode
mode
mode
t
rise
t
fall
= 10 0
14..13
= 11 0
14..13
= 00 —9—9—7ns
14..13
= 01 —9—9—7ns
14..13
= 10 0
14..13
= 11 0
14..13
= 00 0
14..13
= 01 0
14..13
= 5ns
= 5ns
3
3
3
3
3
3
6035034.7 ns
6035034.7 ns
—03—03—ns
—03—03—ns
—03—03—ns
—03—03—ns
2—2—2—ns
1.0—1.0—1.0—ns
Units
Units
Boot-Time Interface Parameters
Boot-Time Interface Parameters
Boot-Time Interface ParametersBoot-Time Interface Parameters
RC64474/
RC64475
Parameter Symbol
180 MHz
Min Max Min Max Min Max
Mode Data Setup t
Mode Data Hold t
DS
DH
3 — 3 — 3 — Master Clock C ycle
0 — 0 — 0 — Master Clock C ycle
RC64474/
RC64475
200 MHz
RC64474/
RC64475
250MHz
Units
17 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 18

RC64474™ RC64475™
Mode Configuration Interface Reset Se quence
Mode Configuration Interface Reset Se quence
Mode Configuration Interface Reset Se quenceMode Configuration Interface Reset Se quence
Vcc
MasterClock
(MClk)
VCCOK
ModeClock
> 100ms
TDS
256 MClk cycles
TMDS
ModeIn
TDS
ColdReset*
TDS
Reset*
Figure 5 Power-on Reset
Vcc
Master
Clock
(MClk)
VCCOK
TDS
> 100ms
TDS
256 MClk cycles
256
MClk
cycles
Bit 1
Bit 0
64K MClk cycles
>
256
256
MClk
MClk
cycles
cycles
TMDH
Bit
255
TDS
64 MClk cycles
>
TDS
2.3V
2.3V
ModeClock
ModeIn
ColdReset*
Reset*
Vcc
Master
Clock
(MClk)
VCCOK
ModeClock
ModeIn
ColdReset*
Reset*
TDS
TDS
256 MClk cycles
TMDS
Bit
Bit
1
0
>
64K MClk cycles
Figure 6 Cold Reset
> 64 MClk cycles
TMDH
Bit
255
TDS
64 MClk cycles
>
TDSTDS
TDS
Figure 7 Warm Reset
18 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 19

RC64474™ RC64475™
1.5V
50 Ω
RC64474/RC64475
Output
.
Signal
All Signals 25 pF
Figure 8 Output Loading for AC Timing
50 Ω
Equivalent Limp
Capacitance
19 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 20

RC64474™ RC64475™
RC64475 Physical Specifications
RC64475 Physical Specifications
RC64475 Physical Specifications RC64475 Physical Specifications
The RC64475 is available in a 208-pin power quad (PQUAD) package.
20 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 21

RC64474™ RC64475™
RC64475 208-p i n Package (page 2)
RC64475 208-p i n Package (page 2)
RC64475 208-p i n Package (page 2)RC64475 208-p i n Package (page 2)
21 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 22

RC64474™ RC64475™
RC64474 128-Pin Package (Page 1 of 3)
RC64474 128-Pin Package (Page 1 of 3)
RC64474 128-Pin Package (Page 1 of 3)RC64474 128-Pin Package (Page 1 of 3)
22 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 23

RC64474™ RC64475™
RC64474 128-pin Package (page 2 of 3)
RC64474 128-pin Package (page 2 of 3)
RC64474 128-pin Package (page 2 of 3)RC64474 128-pin Package (page 2 of 3)
23 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 24

RC64474™ RC64475™
RC64474 128-pin Package (Page 3 of 3)
RC64474 128-pin Package (Page 3 of 3)
RC64474 128-pin Package (Page 3 of 3)RC64474 128-pin Package (Page 3 of 3)
24 of 25 April 10, 2001
Page 25

RC64474™ RC64475™
Ordering Information
Ordering Information
Ordering InformationOrdering Information
IDT79RCXX
Product
Type
YY XXXX
Operating
Voltage
Device
Type
999 A
Speed
Package
A
Temp range/
Process
Blank
I
DZ
DP
180
200
250
474
475
Commercial Temperature
(0°C to +85°C Case)
Industrial Temperature
(-40°C to +85°C Case)
128-pin QFP
208-pin QFP
180 MHz PClk
200 MHz PClk
250 MHz PClk
Embedded Processor
Val id combinations
Val id combinations
Val id combinationsValid co mb inations
IDT79RC64V474 - 180, 200, 250 DZ 128-pin QFP package, Commercial Temperature
IDT79RC64V475 - 180, 200, 250 DP 208-pin QFP package, Commercial Temperature
IDT79RC64V474 - 180, 200, 250 DZI 128-pin QFP package, Industrial Temperature
IDT79RC64V475 - 180, 200, 250 DPI 208-pin QFP package, Industrial Temperature
CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS
2975 Stender Way
Santa Clara, CA 95054
The IDT logo is a registered trademark of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
25 of 25 April 10, 2001
V
79RC64
for SALES:
800-345-7015 or 408-727-6116
fax: 408-330-1748
www.idt.com
3.3V +/-5%
64-bit Embedded
Microprocessor
for Tech Support:
email: rischelp@idt.com
phone: 408-492-8208
 Loading...
Loading...