Integrated Device Technology Inc IDT79R3052E20J, IDT79R305240MJ, IDT79R305240J, IDT79R305233MJ, IDT79R305233J Datasheet
...
COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE SEPTEMBER 1995
1995 Integrated Device Technology, Inc. 5.3 DSC-3000/5
IDT79R3051/79R3052
RISControllers
IDT79R3051, 79R3051E
IDT79R3052
, 79R3052E
FEATURES:
• Instruction set compatible with IDT79R3000A and
IDT79R3001 MIPS RISC CPUs
• High level of integration minimizes system cost, power
consumption
— IDT79R3000A /IDT79R3001 RISC Integer CPU
— R3051 features 4KB of Instruction Cache
— R3052 features 8KB of Instruction Cache
— All devices feature 2kB of Data Cache
— “E” Versions (Extended Architecture) feature full
function Memory Management Unit, including 64-
entry Translation Lookaside Buffer (TLB)
— 4-deep write buffer eliminates memory write stalls
— 4-deep read buffer supports burst refill from slow
memory devices
— On-chip DMA arbiter
— Bus Interface minimizes design complexity
• Single clock input with 40%-60% duty cycle
• 35 MIPS, over 64,000 Dhrystones at 40MHz
• Low-cost 84-pin PLCC packaging that's pin-/packagecompatible with thermally enhanced 84-pin MQUAD.
• Flexible bus interface allows simple, low-cost designs
• 20, 25, 33, and 40MHz operation
• Complete software support
— Optimizing compilers
— Real-time operating systems
— Monitors/debuggers
— Floating Point Software
— Page Description Languages
1
Clock
Generator
Unit
Master Pipeline Control
System Control
Coprocessor
Integer
CPU Core
Exception/Control
Registers
Memory Management
Registers
Translation
Lookaside Buffer
(64 entries)
General Registers
(32 x 32)
ALU
Shifter
Mult/Div Unit
Address Adder
PC Control
Virtual Address
Data
Cache
(2kB)
Instruction
Cache
(8kB/4kB)
Physical Address Bus
BIU
Control
DMA
Arbiter
4-deep
Read
Buffer
4-deep
Write
Buffer
Clk2xIn
Int(5:0)
32
32
BrCond(3:0)
Data Bus
Bus Interface Unit
Address/
Data
DMA
Ctrl
Rd/Wr
Ctrl
SysClk
2874 drw 01
The IDT logo is a registered trademark, and RISChipset, RISController, R3041, R3051, R3052, R3071, R3081, R3720, R4400 and R4600 are trademarks of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
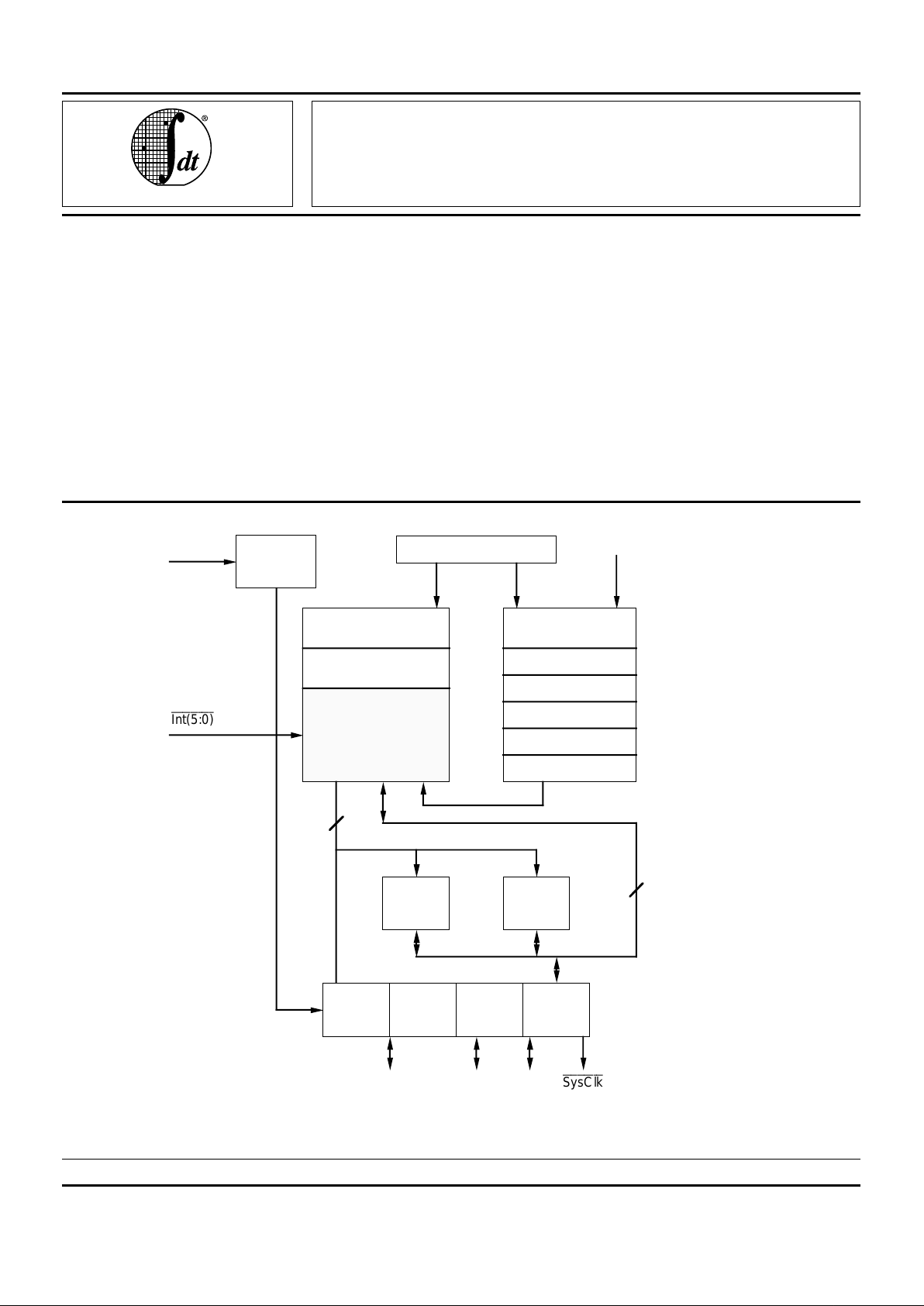
Figure 1. R3051 Family Block Diagram
Integrated Device Technology, Inc.

5.3 2
IDT79R3051/79R3052 INTEGRATED RISControllers COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
INTRODUCTION
The IDT IDT79R3051 family is a series of high-performance 32-bit microprocessors featuring a high level of integration which are targeted to high-performance, but costsensitive embedded processing applications. The IDT79R3051
family is designed to bring the high-performance inherent in
the MIPS RISC architecture into low-cost, simplified, powersensitive applications.
Functional units were integrated onto the CPU core in order
to reduce the total system cost, without significantly degrading
system performance. Thus, the IDT79R3051 family is able to
offer 35MIPS of integer performance at 40MHz without requiring external SRAM or caches.
Furthermore, the IDT79R3051 family brings dramatic power
reduction to these embedded applications, allowing the use of
low-cost packaging for devices up to 25 MHz. The IDT79R3051
family allows customer applications to bring maximum performance at minimum cost.
Figure 1 shows a block-level representation of the functional units within the IDT79R3051 family. The IDT79R3051
family could be viewed as the embodiment of a discrete
solution built around the IDT79R3000A or IDT79R3001.
However, by integrating this functionality on a single chip,
dramatic cost and power reductions are achieved.
Currently, there are four members of the IDT79R3051
family. All devices are pin- and software-compatible: the
differences lie in the amount of instruction cache, and in the
memory management capabilities of the processor:
• The IDT79R3052"E” incorporates 8kB of Instruction Cache,
and features a full-function Memory Management Unit
(MMU), including a 64-entry fully-associative Translation
Lookaside Buffer (TLB). This is the same MMU incorporated
into the IDT79R3000A and IDT79R3001.
• The IDT79R3052 also incorporates 8kB of Instruction Cache.
However, the MMU is a much simpler subset of the capabilities of the enhanced versions of the architecture, and in fact
does not use a TLB.
• The IDT79R3051"E” incorporates 4KB of Instruction Cache.
Additionally, this device features the same full-function
MMU (including TLB file) as the IDT79R3052"E”, and
IDT79R3000A.
• The IDT79R3051 incorporates 4KB of Instruction Cache,
and uses the simpler memory management model of the
IDT79R3052.
An overview of the functional blocks incorporated in these
devices follows.
CPU Core
The CPU core is a full 32-bit RISC integer execution
engine, capable of sustaining close-to single cycle execution
rate. The CPU core contains a five stage pipeline and 32
orthogonal 32-bit registers. The IDT79R3051 family implements the MIPS ISA. In fact, the execution engine of the
IDT79R3051 family is the same as the execution engine of the
IDT79R3000A (and IDT79R3001). Thus the IDT79R3051
family is binary-compatible with those CPU engines.
Figure 2. R3051 Family 5-Stage Pipeline
The execution engine of the IDT79R3051 family uses a
five-stage pipeline to achieve close-to single cycle execution.
A new instruction can be started in every clock cycle; the
execution engine actually processes five instructions concurrently (in various pipeline stages). Figure 2 shows the
concurrency achieved by the IDT79R3051 family pipeline.
IF
Current
CPU
Cycle
I#1 ALURD MEM WB
IFI#2 ALURD MEM WB
IFI#3 ALURD MEM WB
IFI#4 ALURD MEM WB
IFI#5 ALURD MEM WB
2874 drw 02
System Control Co-Processor
The R3051 family also integrates on-chip the System
Control Co-processor, CP0. CP0 manages both the exception handling capability of the IDT79R3051 family, as well as
the virtual to physical mapping of the IDT79R3051 family.
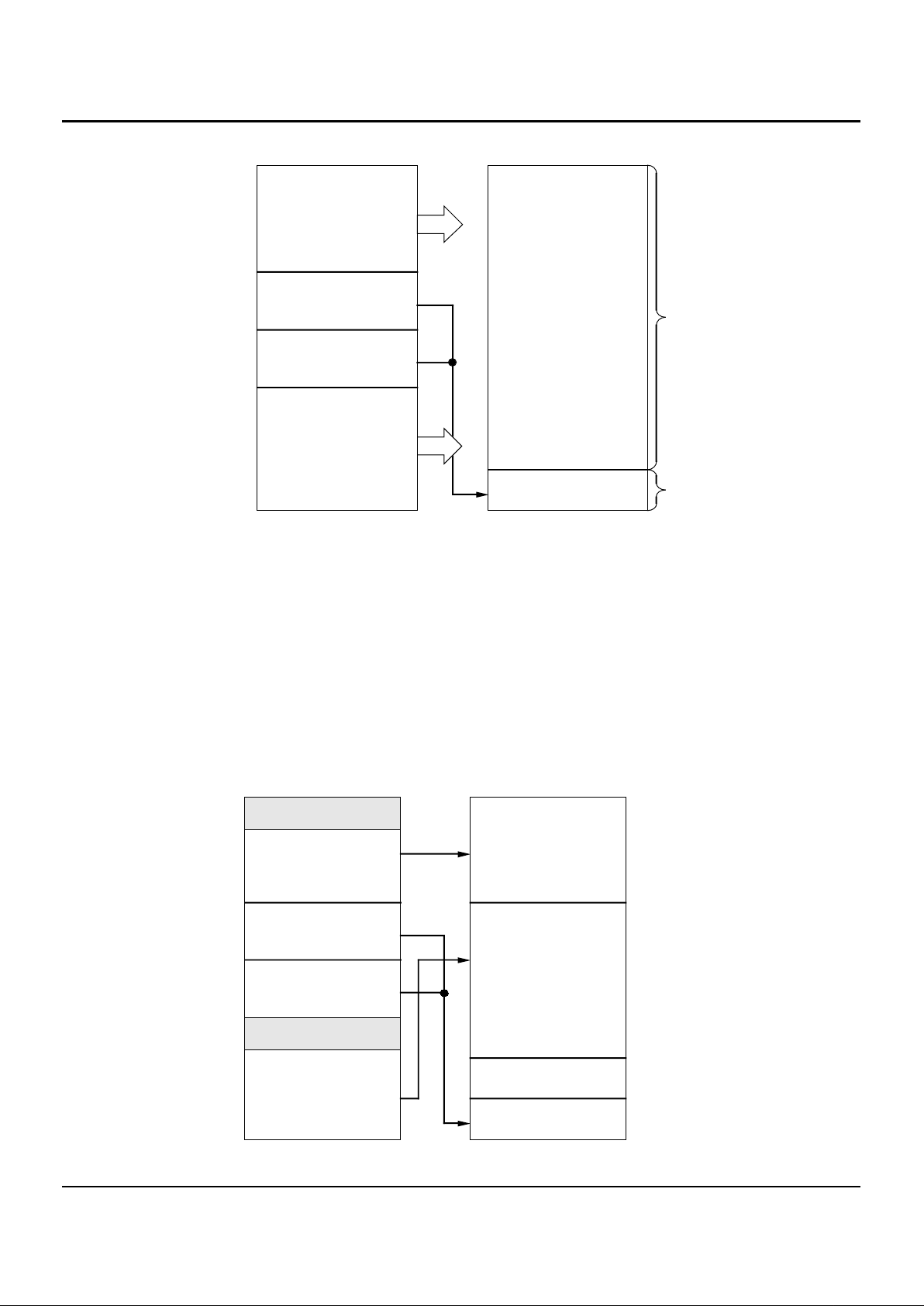
There are two versions of the IDT79R3051 family architecture: the Extended Architecture Versions (the IDT79R3051E
and IDT79R3052E) contain a fully associative 64-entry TLB
which maps 4KB virtual pages into the physical address
space. The virtual to physical mapping thus includes kernel
segments which are hard mapped to physical addresses, and
kernel and user segments which are mapped on a page basis
by the TLB into anywhere within the 4GB physical address
space. In this TLB, 8-page translations can be “locked” by the
kernel to insure deterministic response in real-time applications. These versions thus use the same MMU structure as
that found in the IDT79R3000A and IDT79R3001. Figure 3
shows the virtual-to-physical address mapping found in the
Extended Architecture versions of the processor family.
The Extended Architecture devices allow the system
designer to implement kernel software to dynamically manage
User task utilization of memory resources, and also allow the
Kernel to effectively “protect” certain resources from user
tasks. These capabilities are important in a number of
embedded applications, from process control (where resource
protection may be extremely important) to X-Window display
systems (where virtual memory management is extremely
important), and can also be used to simplify system debugging.
5.3 3
IDT79R3051/79R3052 INTEGRATED RISControllers COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
Figure 3. Virtual-to-Physical Mapping of Extended Architecture Versions
Kernel Mapped
(kseg2)
Kernel Uncached
(kseg1)
Kernel Cached
(kseg0)
User Mapped
Cacheable
(kuseg)
Physical
Memory
Memory
0xffffffff
0xc0000000
0xa0000000
0x80000000
0x00000000
3548MB
512MB
Any
Any
VIRTUAL PHYSICAL
2874 drw 03
Figure 4. Virtual-to-Physical Mapping of Base Architecture Versions
1MB Kernel Rsvd
Kernel Cacheable
Tasks
Kernel/User
Cacheable
Tasks
Inaccessible
Kernel Boot
and I/O
0xffffffff
0xc0000000
0xa0000000
0x80000000
0x00000000
1024MB
2048MB
512MB
512MB
VIRTUAL PHYSICAL
Kernel Cached
(kseg2)
Kernel Uncached
(kseg1)
Kernel Cached
(kseg0)
User
Cached
(kuseg)
1MB User Rsvd
2874 drw 04
The base versions of the architecture (the IDT79R3051
and IDT79R3052) remove the TLB and institute a fixed
address mapping for the various segments of the virtual
address space. The base processors support distinct kernel
and user mode operation without requiring page management
software, leading to a simpler software model. The memory
mapping used by these devices is illustrated in Figure 4. Note
that the reserved address spaces shown are for compatibility
with future family members; in the current family members,
references to these addresses are translated in the same
fashion as their respective segments, with no traps or exceptions taken.
When using the base versions of the architecture, the
system designer can implement a distinction between the
user tasks and the kernel tasks, without having to execute
page management software. This distinction can take the
form of physical memory protection, accomplished by address decoding, or in other forms. In systems which do not
wish to implement memory protection, and wish to have the
kernel and user tasks operate out of a single unified memory
space, upper address lines can be ignored by the address
decoder, and thus all references will be seen in the lower
gigabyte of the physical address space.

5.3 4
IDT79R3051/79R3052 INTEGRATED RISControllers COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
Clock Generation Unit
The IDT79R3051 family is driven from a single input clock,
capable of operating in a range of 40%-60% duty cycle. On
chip, the clock generator unit is responsible for managing the
interaction of the CPU core, caches, and bus interface. The
clock generator unit replaces the external delay line required
in IDT79R3000A and IDT79R3001 based applications.
Instruction Cache
The current family includes two different instruction cache
sizes: the IDT79R3051 family (the IDT79R3051 and
IDT79R3051E) feature 4KB of instruction cache, and the
IDT79R3052 and IDT79R3052E each incorporate 8KB of
Instruction Cache. For all four devices, the instruction cache
is organized as a line size of 16 bytes (four words). This
relatively large cache achieves a hit rate well in excess of 95%
in most applications, and substantially contributes to the
performance inherent in the IDT79R3051 family. The cache is
implemented as a direct mapped cache, and is capable of
caching instructions from anywhere within the 4GB physical
address space. The cache is implemented using physical
addresses (rather than virtual addresses), and thus does not
require flushing on context switch.
Data Cache
All four devices incorporate an on-chip data cache of 2KB,
organized as a line size of 4 bytes (one word). This relatively
large data cache achieves hit rates well in excess of 90% in
most applications, and contributes substantially to the performance inherent in the IDT79R3051 family. As with the instruction cache, the data cache is implemented as a direct mapped
physical address cache. The cache is capable of mapping any
word within the 4GB physical address space.
The data cache is implemented as a write through cache,
to insure that main memory is always consistent with the
internal cache. In order to minimize processor stalls due to
data write operations, the bus interface unit incorporates a 4deep write buffer which captures address and data at the
processor execution rate, allowing it to be retired to main
memory at a much slower rate without impacting system
performance.
Bus Interface Unit
The IDT79R3051 family uses its large internal caches to
provide the majority of the bandwidth requirements of the
execution engine, and thus can utilize a simple bus interface
connected to slow memory devices.
The IDT79R3051 family bus interface utilizes a 32-bit
address and data bus multiplexed onto a single set of pins.
The bus interface unit also provides an ALE signal to demultiplex the A/D bus, and simple handshake signals to
process processor read and write requests. In addition to the
read and write interface, the IDT79R3051 family incorporates
a DMA arbiter, to allow an external master to control the
external bus.
The IDT79R3051 family incorporates a 4-deep write buffer
to decouple the speed of the execution engine from the speed
of the memory system. The write buffers capture and FIFO
processor address and data information in store operations,
and presents it to the bus interface as write transactions at the
rate the memory system can accommodate.
The IDT79R3051/52 read interface performs both single
word reads and quad word reads. Single word reads work with
a simple handshake, and quad word reads can either utilize
the simple handshake (in lower performance, simple systems) or utilize a tighter timing mode when the memory system
can burst data at the processor clock rate. Thus, the system
designer can choose to utilize page or nibble mode DRAMs
(and possibly use interleaving), if desired, in high-performance systems, or use simpler techniques to reduce complexity.
In order to accommodate slower quad-word reads, the
IDT79R3051 family incorporates a 4-deep read buffer FIFO,
so that the external interface can queue up data within the
processor before releasing it to perform a burst fill of the
internal caches. Depending on the cost vs. performance
tradeoffs appropriate to a given application, the system design
engineer could include true burst support from the DRAM to
provide for high-performance cache miss processing, or utilize the read buffer to process quad word reads from slower
memory systems.
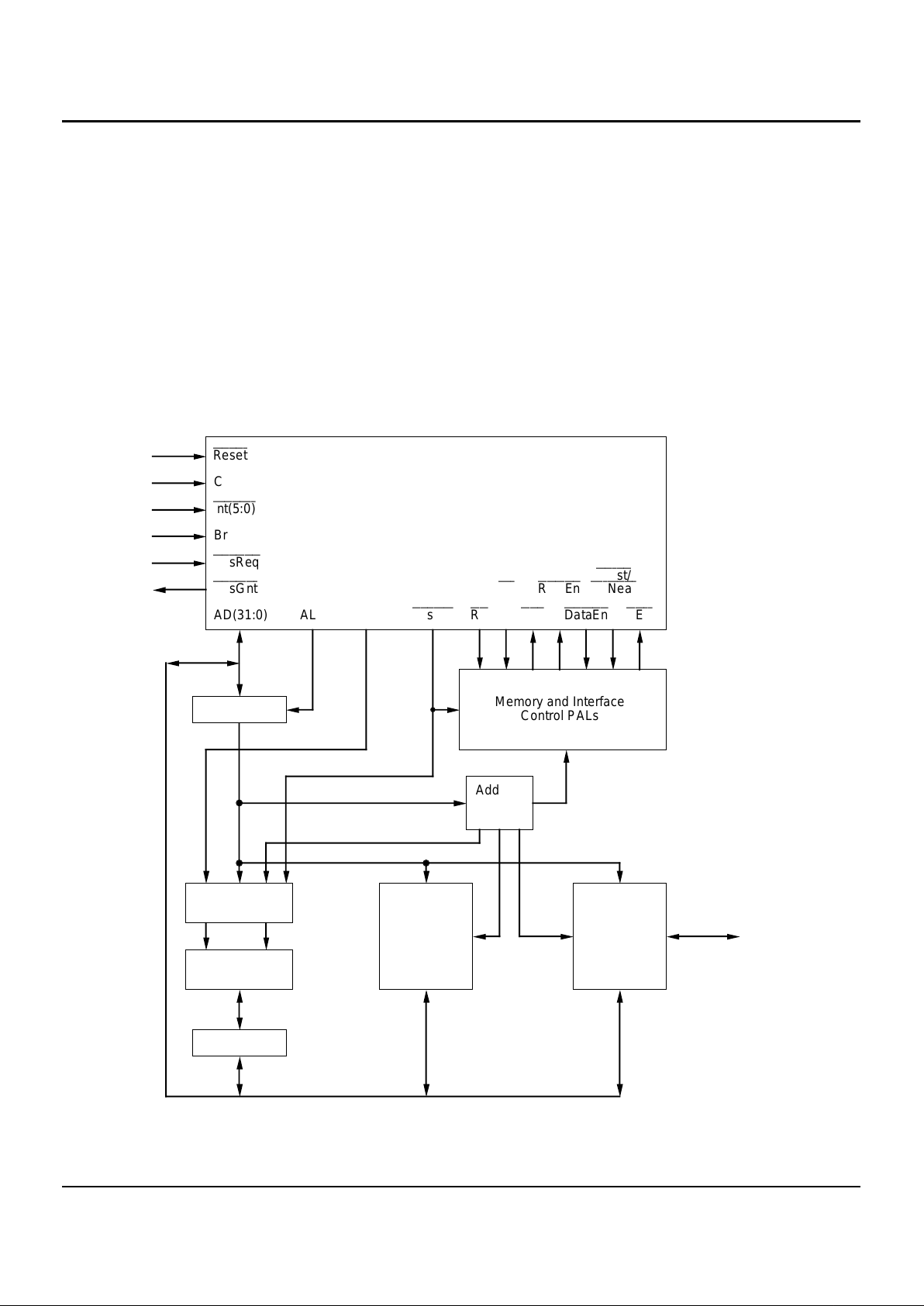
SYSTEM USAGE
The IDT79R3051 family has been specifically designed to
easily connect to low-cost memory systems. Typical low-cost
memory systems utilize slow EPROMs, DRAMs, and application-specific peripherals. These systems may also typically
contain large, slow Static RAMs, although the IDT79R3051
family has been designed to not specifically require the use of
external SRAMs.
Figure 5 shows a typical system block diagram. Transparent latches are used to de-multiplex the IDT79R3051/52
address and data busses from the A/D bus. The data paths
between the memory system elements and the R3051 family
A/D bus is managed by simple octal devices. A small set of
simple PALs can be used to control the various data path
elements, and to control the handshake between the memory
devices and the CPU.
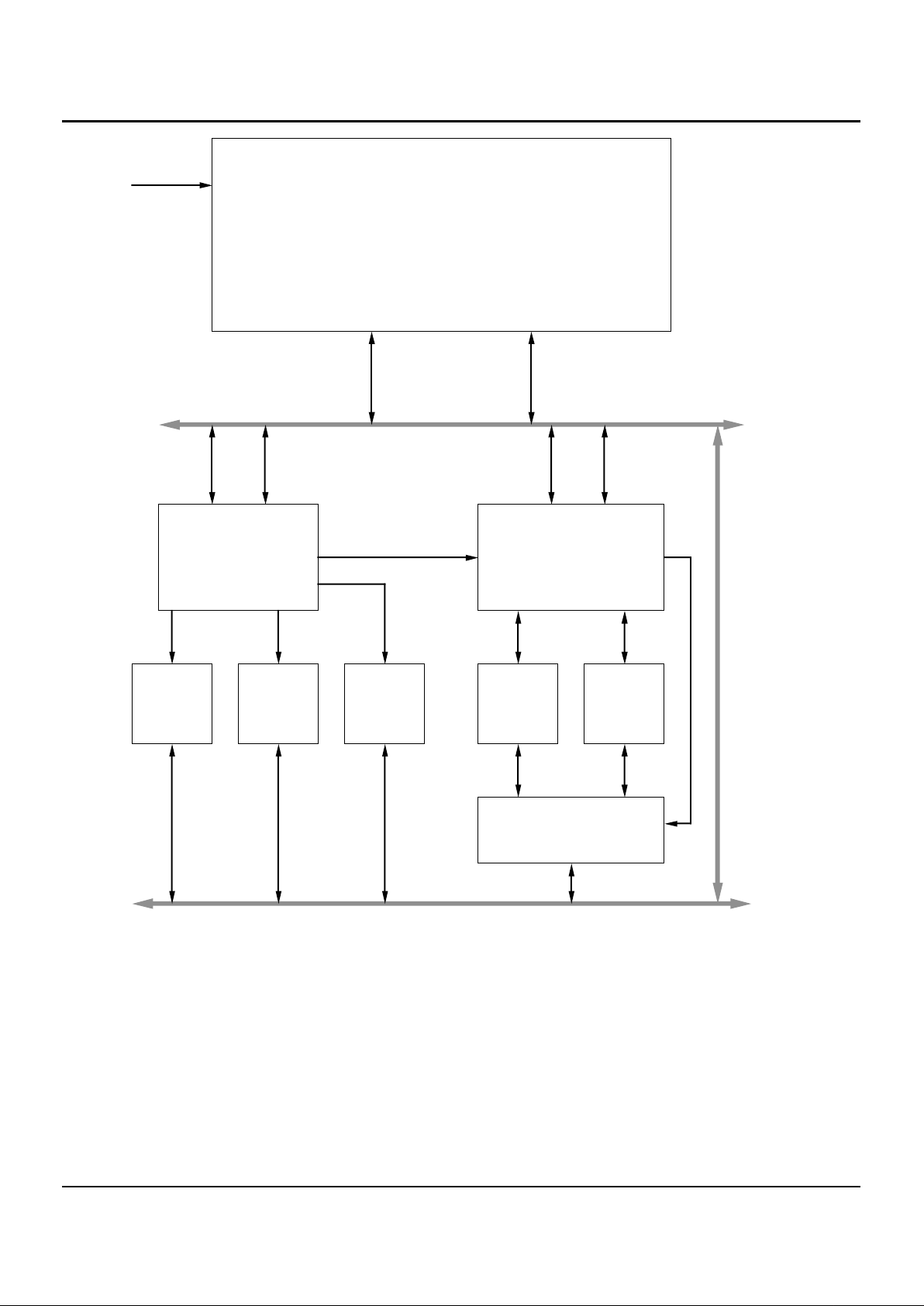
DEVELOPMENT SUPPORT
The IDT79R3051 family is supported by a rich set of
development tools, ranging from system simulation tools
through prom monitor support, logic analysis tools, and subsystem modules.
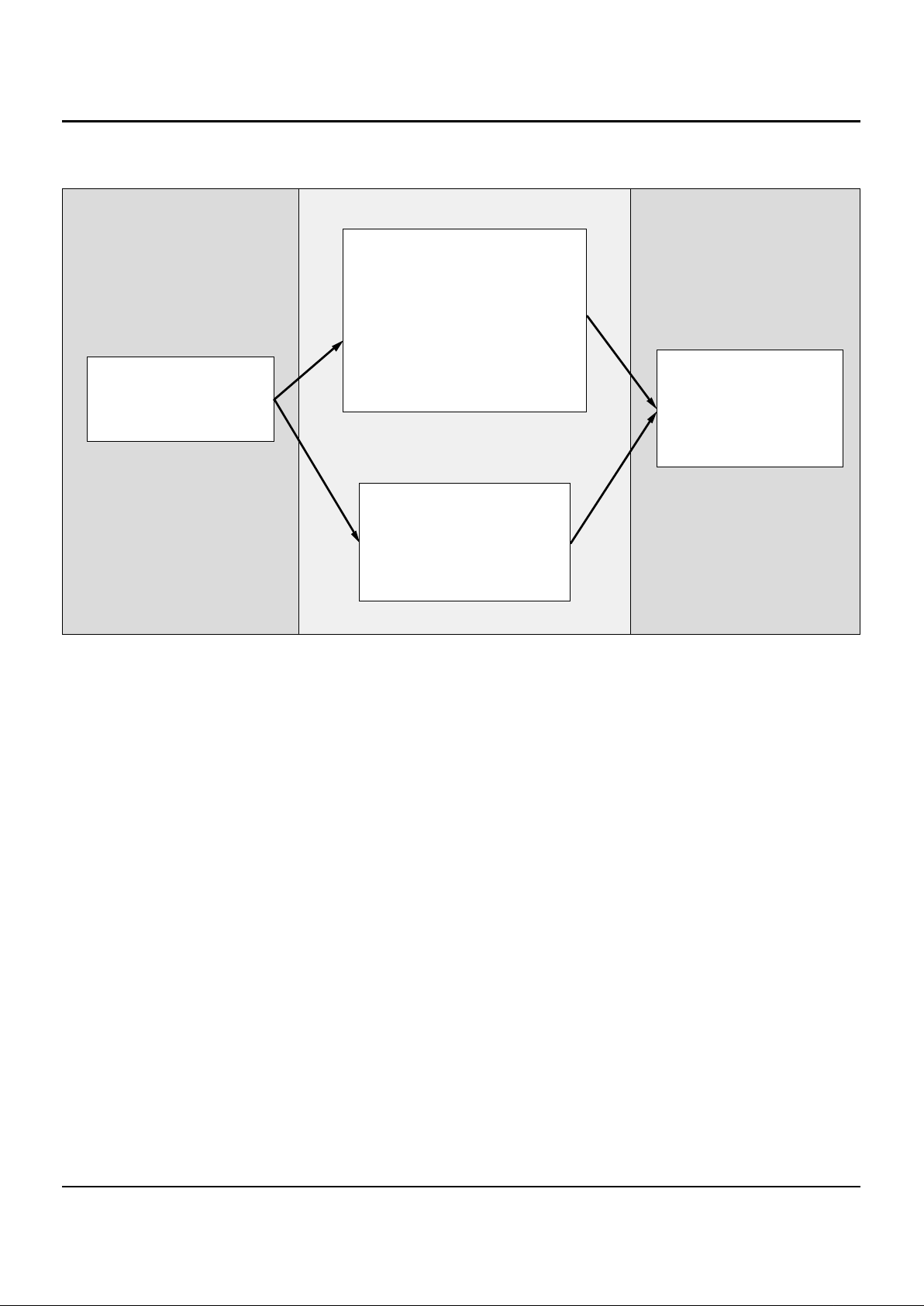
Figure 7 is an overview of the system development process
typically used when developing IDT79R3051 family-based
applications. The IDT79R3051 family is supported by powerful tools through all phases of project development. These
tools allow timely, parallel development of hardware and
software for IDT79R3051/52 based applications, and include
tools such as:
• A program, Cache-3051, which allows the performance of
an IDT79R3051 family based system to be modeled and
understood without requiring actual hardware.
5.3 5
IDT79R3051/79R3052 INTEGRATED RISControllers COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
• Sable, an instruction set simulator.
• Optimizing compilers from MIPS, the acknowledged leader
in optimizing compiler technology.
• IDT Cross development tools, available in a variety of
development environments.
• The high-performance IDT floating point library software,
which has been integrated into the compiler toolchain to
allow software floating point to replace hardware floating
point without modifying the original source code.
• The IDT Evaluation Board, which includes RAM, EPROM,
I/O, and the IDT Prom Monitor.
• The IDT Laser Printer System board, which directly drives
a low-cost print engine, and runs Microsoft TrueImage
Page Description Language on top of PeerlessPage Advanced Printer Controller BIOS.
• Adobe PostScript
Page Description Language, ported to
the R3000 instruction set, runs on the IDT79R3051 family.
• The IDT Prom Monitor, which implements a full prom
monitor (diagnostics, remote debug support, peek/poke,
etc.).
• An In-Circuit Emulator, developed and sold by Embedded
Performance, Inc.
Figure 5. Typical R3051 Family Based System
Reset
Clk2xIn
Int(5:0)
BrCond(3:0)
BusReq
BusGnt
AD(31:0) ALE Addr(3:2)
SysClk Rd
Wr
Ack
RdCEn
DataEn
Burst/
WrNear
BErr
Memory and Interface
Control PALs
Address
Decode
PAL
FCT373T
DRAM Control
PALs
DRAM
FCT245T
EPROM
I/O Devices/
Peripherals
System I/O
IDT R3051 Family
RISController
2874 drw 05
5.3 6
IDT79R3051/79R3052 INTEGRATED RISControllers COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
Figure 6. R3051 Family Chip Set Based System
Clk2xIn
IDT79R3051 Family
RISController
Address/
Data
Control
I/O Controller
DRAM
Controller
DRAM DRAMPROM I/O I/O
IDT73720
Bus Exchanger
R3051 Family
Local Bus
(2)
2874 drw 06
5.3 7
IDT79R3051/79R3052 INTEGRATED RISControllers COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
Figure 7. R3051 Family Development Toolchain
Cache-R305x
Benchmarks
Evaluation Board
Laser Printer System
SABLE Simulator
DBG Debugger
PIXIE Profiler
MIPS Compiler Suite
Stand-Alone Libraries
Floating Point Library
Cross Development Tools
Adobe PostScript
PDL
MicroSoft TrueImage
PDL
Ada
Cache-R305x
Hardware Models
General CAD Tools
RISC Sub-systems
Evaluation Board
Laser Printer System
Hardware
Software
Logic Analysis
Diagnostics
IDT PROM Monitor
Remote Debug
Real-Time OS
In-Circuit Emulator
System
Architecture
Evaluation
System
Development
Phase
System
Integration
and Verification
2874 drw 07
 Loading...
Loading...