IDT IDT72T2098, IDT72T20108, IDT72T20118, IDT72T20128 User Manual
查询IDT72T20108供应商
2.5 VOLT HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATION
32,768 x 20/65,536 x 10, 65,536 x 20/131,072 x 10
131,072 x 20/262,144 x 10, 262,144 x 20/524,288 x 10
FEATURES:
••
• Choose among the following memory organizations:
••
IDT72T2098
IDT72T20108
IDT72T20118
IDT72T20128
• Up to 250MHz Operation of Clocks
- 4ns read/write cycle time, 3.2ns access time
• Users selectable input port to output port data rates, 500Mb/s
Data Rate
-DDR to DDR
-DDR to SDR
-SDR to DDR
-SDR to SDR
• User selectable HSTL or LVTTL I/Os
• Read Enable & Read Clock Echo outputs aid high speed operation
••
• 2.5V LVTTL or 1.8V, 1.5V HSTL Port Selectable Input/Ouput voltage
••
••
• 3.3V Input tolerant
••
• Mark & Retransmit, resets read pointer to user marked position
• Write Chip Select (WCS) input enables/disables Write
Operations
• Read Chip Select (RCS) synchronous to RCLK
32,768 x 20/65,536 x 10
65,536 x 20/131,072 x 10
131,072 x 20/262,144 x 10
262,144 x 20/524,288 x 10
IDT72T2098, IDT72T20108
IDT72T20118, IDT72T20128
• Programmable Almost-Empty and Almost-Full flags, each flag
can default to one of four preselected offsets
• Dedicated serial clock input for serial programming of flag offsets
• User selectable input and output port bus sizing
-x20 in to x20 out
-x20 in to x10 out
-x10 in to x20 out
-x10 in to x10 out
• Auto power down minimizes standby power consumption
• Master Reset clears entire FIFO
• Partial Reset clears data, but retains programmable settings
• Empty and Full flags signal FIFO status
• Select IDT Standard timing (using EF and FF flags) or First
Word Fall Through timing (using OR and IR flags)
• Output enable puts data outputs into High-Impedance state
• JTAG port, provided for Boundary Scan function
• 208 Ball Grid array (PBGA), 17mm x 17mm, 1mm pitch
• Easily expandable in depth and width
• Independent Read and Write Clocks (permit reading and writing
simultaneously)
• High-performance submicron CMOS technology
• Industrial temperature range (-40
°°
°C to +85
°°
°°
°C) is available
°°
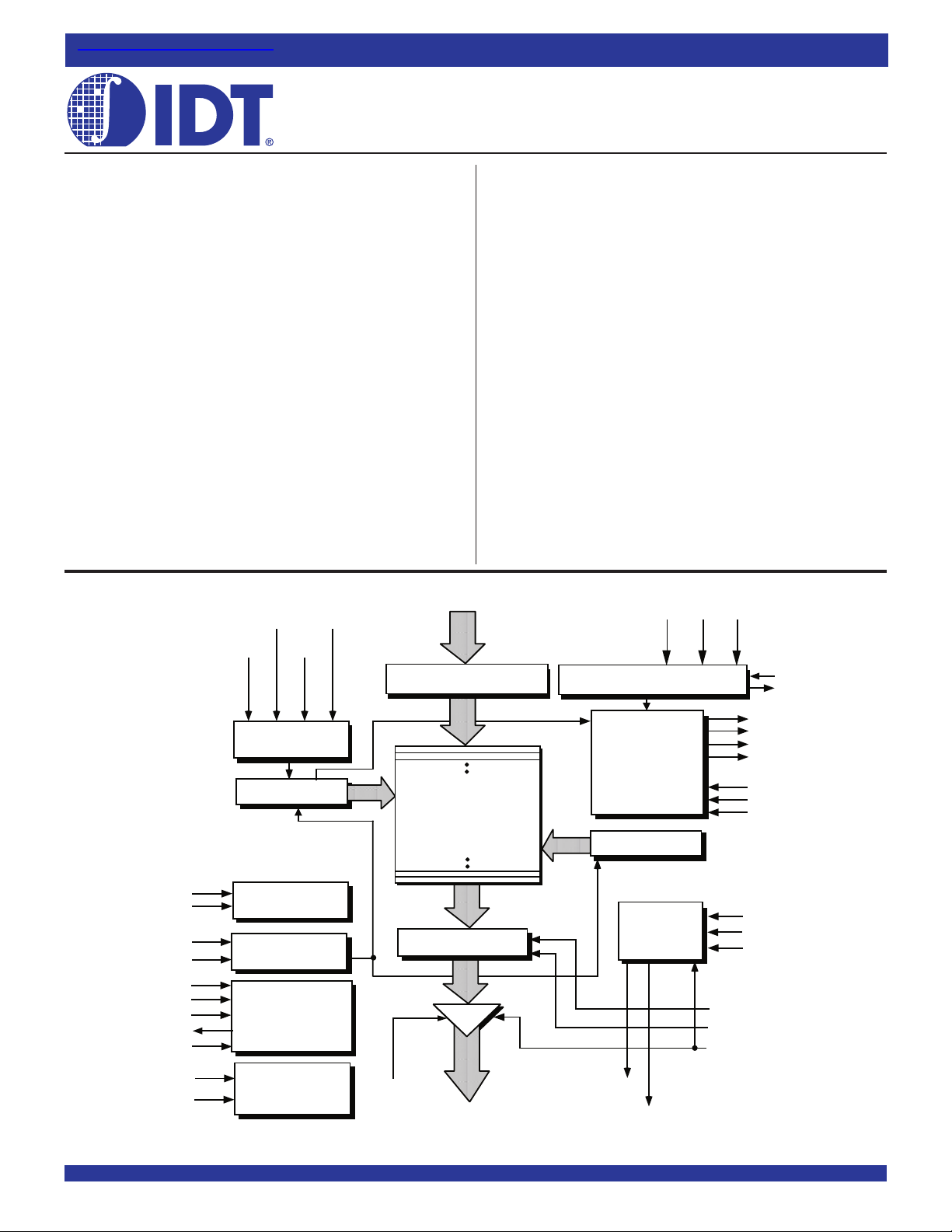
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
WCLK
WSDR
LOGIC
BUS
IW
OW
MRS
PRS
TCK
TRST
TMS
TDO
TDI
WEN
WCS
WRITE CONTROL
WRITE POINTER
CONFIGURATION
RESET
LOGIC
JTAG CONTROL
(BOUNDARY SCAN)
D0 -D
n
(x20, x10)
INPUT REGISTER
RAM ARRAY
32,768 x 20 or 65,536 x 10
65,536 x 20 or 131,072 x 10
131,072 x 20 or 262,144 x 10
262,144 x 20 or 524,288 x 10
OUTPUT REGISTER
SREN
SEN
OFFSET REGISTER
FLAG
LOGIC
READ POINTER
READ
CONTROL
LOGIC
SCLK
SI
SO
FF/IR
PAF
EF/OR
PAE
FWFT
FSEL0
FSEL1
RT
MARK
RSDR
RCLK
REN
RCS
Vref
HSTL
IDT and the IDT logo are registered trademarks of Integrated Device Technology, Inc. The TeraSync is a trademark of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
HSTL I/0
CONTROL
OE
Q0 -Qn (x20, x10)
EREN
ERCLK
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
2003 Integrated Device Technology, Inc. All rights reserved. Product specifications subject to change without notice.
1
5996 drw01
MARCH 2003
DSC-5996/7
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
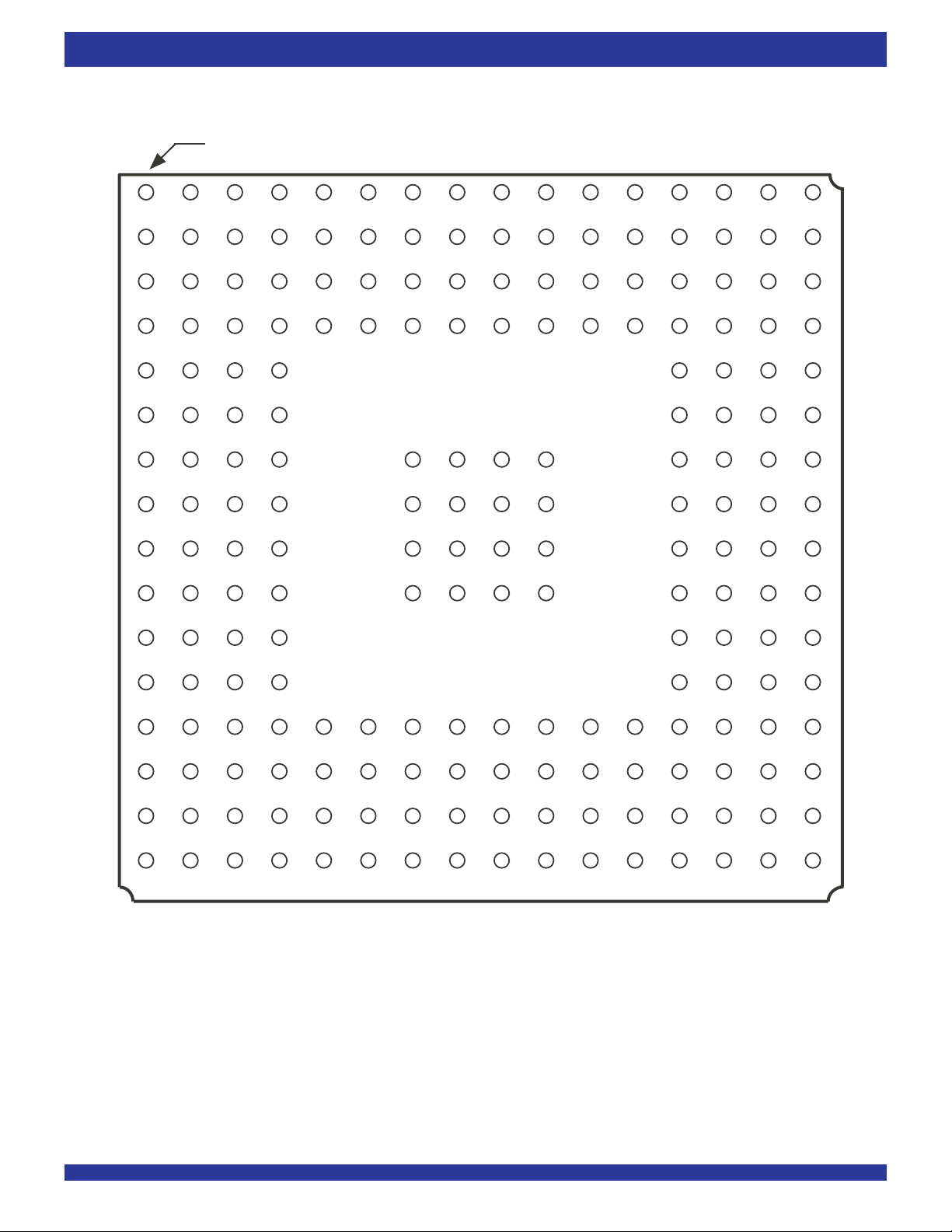
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
A1 BALL PAD CORNER
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
A
V
CC
DNC
V
CC
D4
D7
D9 GND
GND
Q1
Q3 V
Q7
Q5D1
Q9 V
DDQ
DDQ
B
DNC DNC D8
DNC
D2
HSTL GND
GNDD5
Q0
Q2
Q4
Q6 DNCQ8
DNC
C
DNC
DNC
D0
V
D3 V
D6 V
CC
CC
GND V
DDQ
GND DNCV
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DNCV
DNC
D
DNC
DNC
V
V
CC
V
V
CC
CC
CC
GND V
V
GND DNCV
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DDQ
DNCV
DNCDNC
E
DNC
TDI
TRST
GND
V
DDQ
MARK
DNC
DNC
F
TCK
TMS
TDO
V
DDQ
V
DDQ
RCS
RT
REN
G
WCLK
FWFT
PAF
V
DDQ
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
V
DDQ
OE
RCLK
H
WEN
WCS
FF/IR
V
DDQ
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
V
DDQ
SCLK
SI
J
SEN
MRS
FSEL1
FSEL0
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
V
DDQ
SREN
K
IW
DNC
PRS
V
CC
V
GND GND
GND
GND
GND
DDQ
SO
EREN
L
WSDR
RSDR
OW
V
CC
GND
V
DDQ
PAE
ERCLK
M
DNC
DNC
N
DNC
DNC
P
DNC
DNC
R
DNC
DNC
T
V
CCVCC
12 34 567 8 910111213141516
NOTE:
1. DNC - Do Not Connect.
DDQ
DDQ
V
V
V
DDQ
DDQ
Q13
DNC
DNC
V
V
CC
V
V
CC
GND V
D18
D19
D16 D12D14 Q19 Q15Q17 Q11 DNC
D17
REF
V
CC
V
CC
D15
V
V
D13
CC
CC
CC
GND V
CC
GND V
GND
D10
GND
D11
V
DDQ
GND V
GND V
DDQ
DDQ
V
DDQ
GND
GND
Q18 Q16 Q14 V
PBGA: 1mm pitch, 17mm x 17mm (BB208-1, order code: BB)
TOP VIEW
DDQ
EF
DNC
DNC
Q10Q12
/
OR
DNC
DNC
DNC
DDQ
DNC
DNC
DNC
DNC
DDQ
V
5996 drw02
2

IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
DESCRIPTION:
The IDT72T2098/72T20108/72T20118/72T20128 are exceptionally deep,
extremely high speed, CMOS First-In-First-Out (FIFO) memories with the ability
to read and write data on both rising and falling edges of clock. The device has
a flexible x20/x10 Bus-Matching mode and the option to select Single or Double
Data clock rates for input and output ports. These FIFOs offer several key user
benefits:
• Flexible x20/x10 Bus-Matching on both read and write ports
• Ability to read and write on both rising and falling edges of a clock
• User selectable Single or Double Data Rate of input and output ports
• A user selectable MARK location for retransmit
• User selectable I/O structure for HSTL or LVTTL
• The first word data latency period, from the time the first word is written to
an empty FIFO to the time it can be read, is fixed and short.
• High density offerings up to 5Mbit
• High speed operation of up to 250MHz
Bus-Matching Double Data Rate FIFOs are particularly appropriate for
network, video, telecommunications, data communications and other applications that require fast data transfer on both rising and falling edges of the clock.
This is a great alternative to increasing data rate without extending the width of
the bus or the speed of the device. They are also effective in applications that
need to buffer large amounts of data and match busses of unequal sizes.
Each FIFO has a data input port (Dn) and a data output port (Qn), both of
which can assume either a 20-bit or a 10-bit width as determined by the state
of external control pins Input Width (IW), Output Width (OW) during the Master
Reset cycle.
The input port is controlled by a Write Clock (WCLK) input and a Write Enable
(WEN) input. Data present on the Dn data inputs can be written into the FIFO
on every rising and falling edge of WCLK when WEN is asserted and Write
Single Data Rate (WSDR) pin held HIGH. Data can be selected to write only
on the rising edges of WCLK if WSDR is asserted. To guarantee functionality
of the device, WEN must be a controlled signal and not tied to ground. This is
important because WEN must be HIGH during the time when the Master Reset
(MRS) pulse is LOW. In addition, the WSDR pin must be tied HIGH or LOW.
It is not a controlled signal and cannot be changed during FIFO operation.
Write operations can be selected for either Single or Double Data Rate mode.
For Single Data Rate operation, writing into the FIFO requires the Write Single
Data Rate (WSDR) pin to be asserted. Data will be written into the FIFO on the
rising edge of WCLK when the Write Enable (WEN) is asserted. For Double
Data Rate operations, writing into the FIFO requires WSDR to be deasserted.
Data will be written into the FIFO on both rising and falling edge of WCLK when
WEN is asserted.
The output port is controlled by a Read Clock (RCLK) input and a Read
Enable (REN) input. Data is read from the FIFO on every rising and falling edge
of RCLK when REN is asserted and Read Single Data Rate (RSDR) pin held
HIGH. Data can be selected to read only on the rising edges of RCLK if RSDR
is asserted. To guarantee functionality of the device, REN must be a controlled
signal and not tied to ground. This is important because REN must be HIGH
during the time when the Master Reset (MRS) pulse is LOW. In addition, the
RSDR pin must be tied HIGH or LOW. It is not a controlled signal and cannot
be changed during FIFO operation.
Read operations can be selected for either Single or Double Data Rate mode.
Similar to the write operations, reading from the FIFO in single data rate requires
the Read Single Data Rate (RSDR) pin to be asserted. Data will be read from
the FIFO on the rising edge of RCLK when the Read Enable (REN) is asserted.
For Double Data Rate operations, reading into the FIFO requires RSDR to be
deasserted. Data will be read out of the FIFO on both rising and falling edge
of RCLK when and REN is asserted.
Both the input and output port can be selected for either 2.5V LVTTL or HSTL
operation. This can be achieved by tying the HSTL signal LOW for LVTTL or
HIGH for HSTL voltage operation. When the read port is setup for HSTL mode,
the Read Chip Select (RCS) input also has the benefit of disabling the read port
inputs, providing additional power savings.
There is the option of selecting different data rates on the input and output ports
of the device. There are a total of four combinations to choose from, Double Data
Rate to Double Data Rate (DDR to DDR), DDR to Single Data Rate (DDR to
SDR), SDR to DDR, and SDR to SDR. The clocking can be set up using the
WSDR and RSDR pins. For example, to set up the input to output combination
of DDR to SDR, WSDR will be HIGH and RSDR will be LOW. Read and write
operations are initiated on the rising edge of RCLK and WCLK respectively,
never on the falling edge. If REN or WEN is asserted after a rising edge of clock,
no read or write operations will be possible on the falling edge of that same pulse.
An Output Enable (OE) input is provided for high-impedance control of the
outputs. A read Chip Select (RCS) input is also provided for synchronous
enable/disable of the read port control input, REN. The RCS input is synchronized to the read clock, and also provides high-impedance controls to the Qn
data outputs. When RCS is disabled, REN will be disabled internally and the
data outputs will be in High-Impedance. Unlike the Read Chip Select signal
however, OE is not synchronous to RCLK. Outputs are high-impedance shortly
after a delay time when the OE transitions from LOW to HIGH.
The Echo Read Enable (EREN) and Echo Read Clock (ERCLK) outputs
are used to provide tighter synchronization between the data being transmitted
from the Qn outputs and the data being received by the input device. These
output signals from the read port are required for high-speed data communications. Data read from the read port is available on the output bus with respect
to EREN and ERCLK, which is useful when data is being read at high-speed
operations where synchronization is important.
The frequencies of both the RCLK and WCLK signals may vary from 0 to fMAX
with complete independence. There are no restrictions on the frequency of one
clock input with respect to another.
There are two possible timing modes of operation with these devices: IDT
Standard mode and First Word Fall Through (FWFT) mode.
In IDT Standard mode, the first word written to an empty FIFO will not appear
on the data output lines unless a specific read operation is performed. A read
operation, which consists of activating REN and enabling a rising RCLK edge,
will shift the word from internal memory to the data output lines. Be aware that
in Double Data Rate (DDR) mode only the IDT Standard mode is available.
In FWFT mode, the first word written to an empty FIFO is clocked directly to
the data output lines after three transitions of RCLK. A read operation does not
have to be performed to access the first word written to the FIFO. However,
subsequent words written to the FIFO do require a LOW on REN for access.
The state of the FWFT input during Master Reset determines the timing mode
in use.
For applications requiring more data storage capacity than a single FIFO can
provide, the FWFT timing mode permits depth expansion by chaining FIFOs
in series (i.e. the data outputs of one FIFO are connected to the corresponding
data inputs of the next). No external logic is required.
These FIFOs have four flag pins, EF/OR (Empty Flag or Output Ready), FF/
IR (Full Flag or Input Ready), PAE (Programmable Almost-Empty flag), and
PAF (Programmable Almost-Full flag). The EF and FF functions are selected
in IDT Standard mode. The IR and OR functions are selected in FWFT mode.
PAE and PAF are always available for use, irrespective of timing mode.
PAE and PAF flags can be programmed independently to switch at any point
in memory. Programmable offsets mark the location within the internal memory
that activates the PAE and PAF flags and can only be programmed serially. To
program the offsets, set SEN active and data can be loaded via the Serial Input
3

IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
DESCRIPTION (CONTINUED)
(SI) pin at the rising edge of SCLK. To read out the offset registers serially, set
SREN active and data can be read out via the Serial Output (SO) pin at the rising
edge of SCLK. Four default offset settings are also provided, so that PAE can
be marked at a predefined number of locations from the empty boundary and
the PAF threshold can also be marked at similar predefined values from the full
boundary. The default offset values are set during Master Reset by the state
of the FSEL0 and FSEL1 pins.
During Master Reset (MRS), the following events occur: the read and write
pointers are set to the first location of the internal FIFO memory, the FWFT pin
selects IDT Standard mode or FWFT mode, the bus width configuration of the
read and write port is determined by the state of IW and OW, and the default offset
values for the programmable flags are set.
The Partial Reset (PRS) also sets the read and write pointers to the first
location of the memory. However, the timing mode and the values stored in the
programmable offset registers before Partial Reset remain unchanged. The
flags are updated according to the timing mode and offsets in effect. PRS is useful
for resetting a device in mid-operation, when reprogramming programmable
flags would be undesirable.
The timing of the PAE and PAF flags are synchronous to RCLK and WCLK,
respectively. The PAE flag is asserted upon the rising edge of RCLK only and
not WCLK. Similarly the PAF is asserted and updated on the rising edge of
WCLK only and not RCLK.
This device includes a Retransmit from Mark feature that utilizes two control
inputs, MARK and RT (Retransmit). If the MARK input is enabled with respect
to the RCLK, the memory location being read at the point will be marked. Any
subsequent retransmit operation (when RT goes LOW), will reset the read
pointer to this “marked” location.
The device can be configured with different input and output bus widths as
previously stated. These rates are: x20 to x20, x20 to x10, x10 to x20 and x10
to x10.
If, at any time, the FIFO is not actively performing an operation, the chip will
automatically power down. Once in the power down state, the standby supply
current consumption is minimized. Initiating any operation (by activating control
inputs) will immediately take the device out of the power down state.
A JTAG test port is provided, here the FIFO has fully functional boundary
Scan feature, compliant with IEEE 1449.1 Standard Test Access Port and
Boundary Scan Architecture.
The Double Data Rate FIFO has the capability of operating in either LVTTL
or HSTL mode. HSTL mode can be selected by enabling the HSTL pin. Both
input and output ports will operate in either HSTL or LVTTL mode, but cannot
be selected independent of one another.
The IDT72T2098/72T20108/72T20118/72T20128 are fabricated using
IDT’s high-speed submicron CMOS technology.
4
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
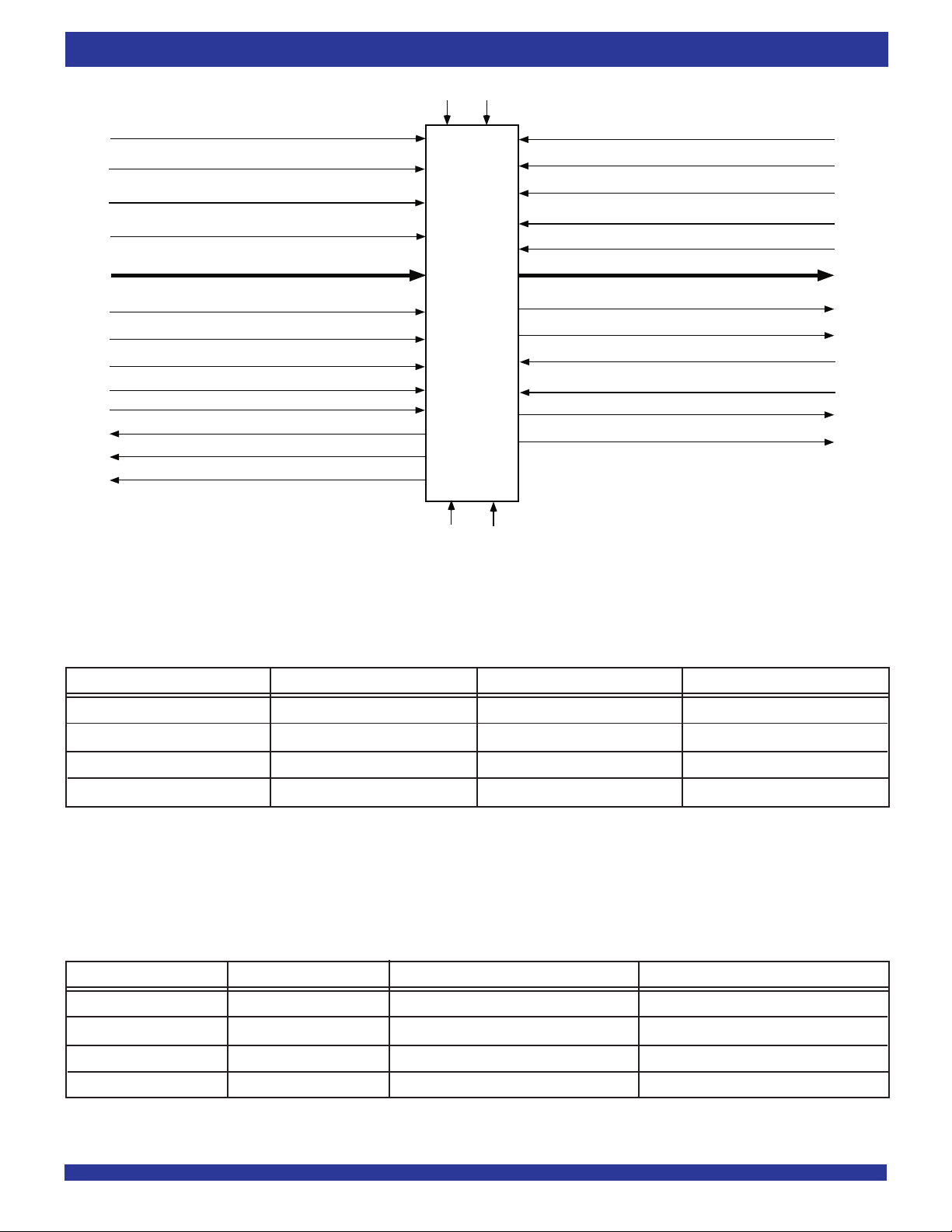
PARTIAL RESET (PRS)
WRITE CLOCK (WCLK)
WRITE ENABLE (WEN)
WRITE CHIP SELECT (WCS)
WRITE SINGLE DATA RATE (WSDR)
SERIAL CLOCK (SCLK)
SERIAL ENABLE(SEN)
SERIAL READ ENABLE(SREN)
FIRST WORD FALL THROUGH (FWFT)
SERIAL INPUT (SI)
SERIAL OUTPUT (SO)
FULL FLAG/INPUT READY (FF/IR)
PROGRAMMABLE ALMOST-FULL (PAF)
INPUT WIDTH (IW)
MASTER RESET (MRS)
READ CLOCK (RCLK)
READ ENABLE (REN)
OUTPUT ENABLE (OE)
IDT
72T2098
72T20108
72T20118
72T20128
READ CHIP SELECT (RCS)
READ SINGLE DATA RATE (RSDR)
(x20, x10) DATA OUT (Q0 - Qn)(x20, x10) DATA IN (D0 - Dn)
RCLK ECHO (ERCLK)
REN ECHO (EREN)
MARK
RETRANSMIT (RT)
EMPTY FLAG/OUTPUT READY (EF/OR)
PROGRAMMABLE ALMOST-EMPTY (PAE)
OUTPUT WIDTH (OW)
5996 drw03
Figure 1. Single Device Configuration Signal Flow Diagram
TABLE 1 — BUS-MATCHING CONFIGURATION MODES
I W OW Write Port Width Read Port Width
L L x20 x20
L H x20 x10
H L x10 x20
H H x10 x10
NOTE:
1. Pin status during Master Reset.
TABLE 2 — DATA RATE-MATCHING CONFIGURATION MODES
WSDR RSDR Write Port Width Read Port Width
H H Double Data Rate Double Data Rate
H L Double Data Rate Single Data Rate
L H Single Data Rate Double Data Rate
L L Single Data Rate Single Data Rate
NOTE:
1. Pin status during Master Reset.
2. Data Rate Matching can be used in conjunction with Bus-Matching modes.
5
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
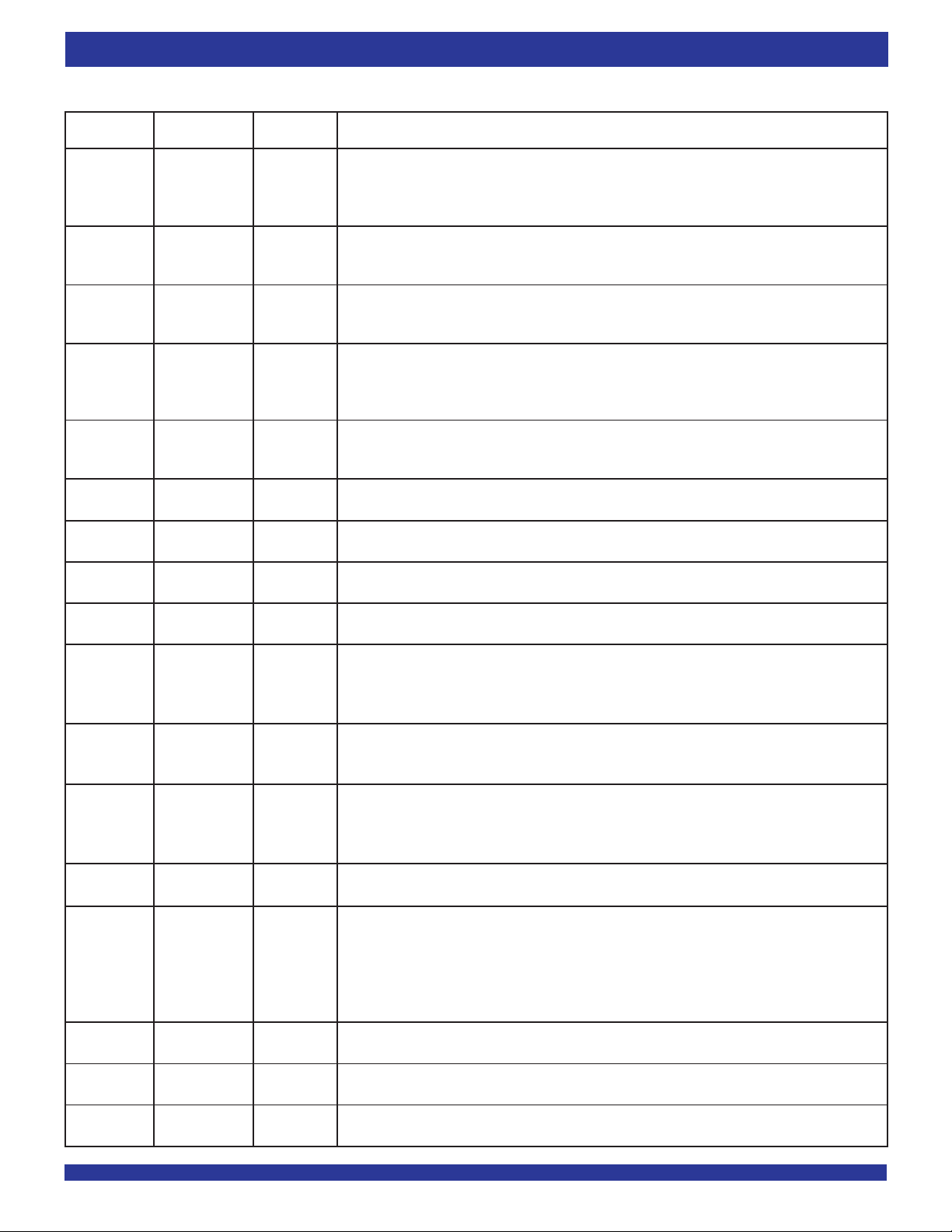
PIN DESCRIPTION
Symbol & Name I/O TYPE Description
Pin No.
D0-D19 Data Inputs HSTL-LVTTL Data inputs for a 20-, or 10-bit bus. When using 10- bit mode, the unused input pins are in a don’t care
(See Pin No. INPUT state. The data bus is sampled on both rising and falling edges of WCLK when WEN is enabled and DDR
table for details) Mode is enabled or on the rising edges of WCLK only in SDR Mode.
EF/OR Empty Flag/ HSTL-LVTTL In the IDT Standard mode, the EF function is selected. EF indicates whether or not the FIFO memory is
(M14) Output Ready OUTPUT empty. In FWFT mode, the OR function is selected. OR indicates whether or not there is valid data available
at the outputs.
ERCLK Echo Read HSTL-LVTTL Read Clock Echo output, must be equal to or faster than the Qn data outputs.
(L16) Clock OUTPUT
EREN Echo Read HSTL-LVTTL Read Enable Echo output, used in conjunction with ERCLK.
(K16) Enable OUTPUT
FF/IR Full Flag/ HSTL-LVTTL In the IDT Standard mode, the FF function is selected. FF indicates whether or not the FIFO memory is
(H3) Input Ready OUTPUT empty. In FWFT mode, the IR function is selected. IR indicates whether or not there is space available
for writing to the FIFO memory.
(1)
FSEL0
(J3) INPUT flags PAE and PAF. There are four possible settings available.
(1)
FSEL1
(J2) INPUT flags PAE and PAF. There are four possible settings available.
FWFT First Word Fall LVTTL During Master reset, selects First Word Fall Through or IDT Standard mode. FWFT is not available in
(G2) Through INPUT DDR mode. In SDR mode, the first word will always fall through on the rising edge.
(1)
HSTL
(B7) INPUT input must be tied HIGH, otherwise it should be tied LOW.
(1)
IW
(K1) INPUT
MARK Mark Read HSTL-LVTTL When this pin is asserted the current location of the read pointer will be marked. Any subsequent Retransmit
(E14) Pointer for INPUT operation will reset the read pointer to this position. There is an unlimited number to times to set the mark
MRS Master Reset HSTL-LVTTL MRS initializes the read and write pointers to zero and sets the output registers to all zeros. During Master
(J1) INPUT Reset, the FIFO is configured for either FWFT or IDT Standard mode, Bus-Matching configurations,
OE Output Enable HSTL-LVTTL When HIGH, data outputs Q
(G15) INPUT No other outputs are affected by OE.
(1)
OW
(L3) INPUT
PAE Programmable HSTL-LVTTL PAE goes HIGH if the number of words in the FIFO memory is greater than or equal to offset n, which is
(L15) Almost-Empty OUTPUT stored in the Empty Offset register. PAE goes LOW if the number of words in the FIFO memory is less than
PAF Programmable HSTL-LVTTL PAF goes HIGH if the number of free locations in the FIFO memory is more than offset m, which is stored
(G3) Almost-Full Flag OUTPUT in the Full Offset register. PAF goes LOW if the number of free locations in the FIFO memory is less than
PRS Partial Reset HSTL-LVTTL PRS initializes the read and write pointers to zero and sets the output registers to all zeros. During Partial
(K3) INPUT Reset, the existing mode (IDT standard or FWFT) and programmable flag settings are not affected.
Q
0-Q19 Data Outputs HSTL-LVTTL Data output s for a 2 0-, or 1 0-bit bus. When in 10- bit mode, the unused output pins should not be connected.
(See Pin No. OUTPUT The output data is clocked on both rising and falling edges of RCLK when REN is enabled and DDR Mode
table for details) is enabled or on the rising edges of RCLK only in SDR Mode.
RCLK Read Clock HSTL-LVTTL Input clock when used in conjunction with REN for reading data from the FIFO memory and output
(G16) INPUT register.
Flag Select Bit 0 LVTTL During Master Reset, this input along with FSEL1 will select the default offset values for the programmable
Flag Select Bit 1 LVTTL During Master Reset, this input along with FSEL0 will select the default offset values for the programmable
HSTL Select LVTTL This input pin is used to select HSTL or 2.5V LVTTL device operation. If HSTL inputs are required, this
Input Width LVTTL During Master Reset, this pin, along with OW selects the bus width of the read and write port.
Retransmit location, but only the most recent location marked will be acknowledged.
programmable flag default settings, and single or double data clock mode.
0-Q19 are in high impedance. When LOW, the data outputs Q0-Q19 are enabled.
Output Width LVTTL During Master Reset, this pin along with IW selects the bus width of the read and write port.
Flag offset n.
or equal to m.
6
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
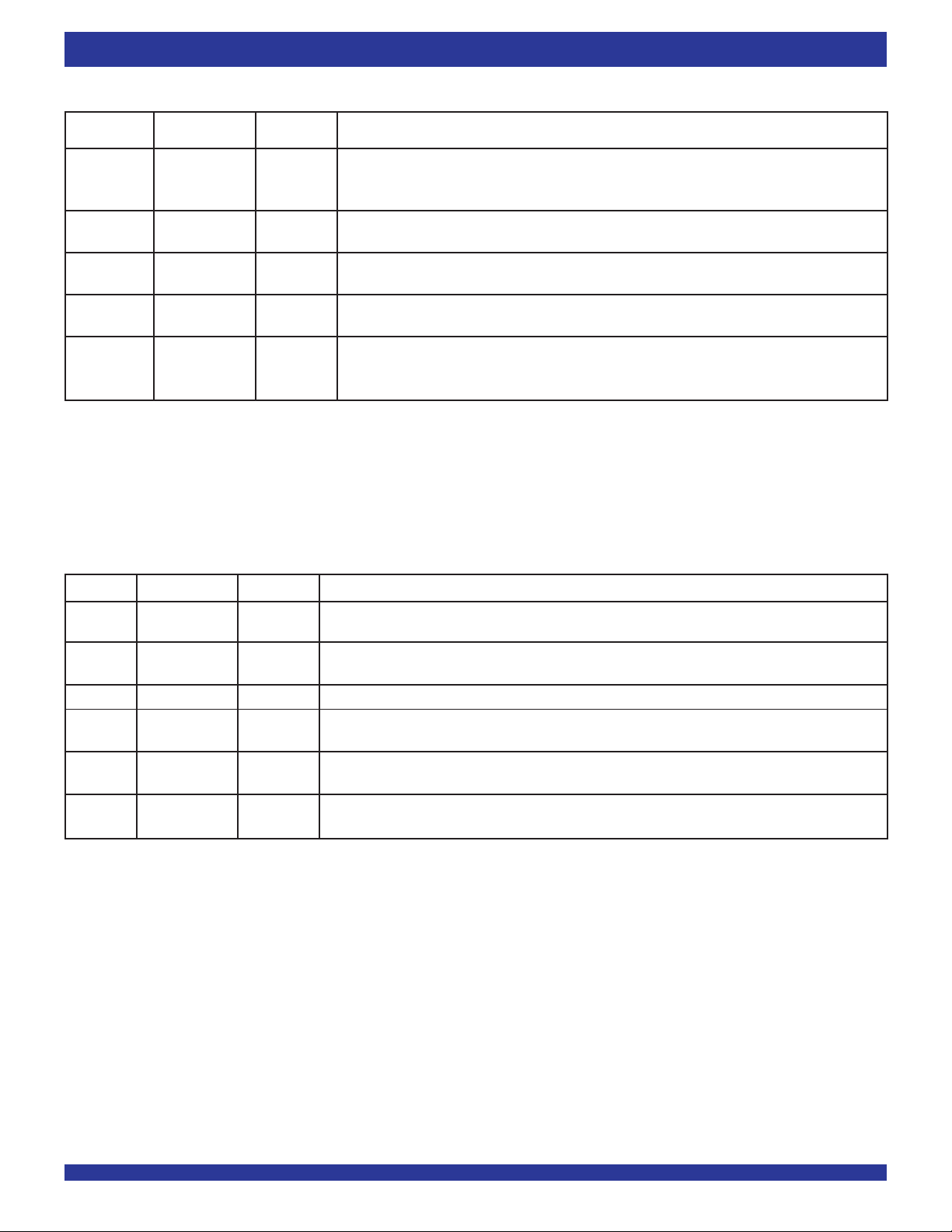
PIN DESCRIPTION (CONTINUED)
Symbol & Name I/O TYPE Description
Pin No.
RCS Read Chip HSTL-LVTTL RCS provides synchronous enable/disable control of the read port and High-Impedance control of the
(F14) Select INPUT Qn data outputs, synchronous to RCLK. When using RCS the OE pin must be tied LOW. During Master
or Partial Reset the RCS input is don’t care, if OE is LOW the data outputs will be Low-Impedance regardless
of RCS.
REN Read Enable HSTL-LVTTL When LOW and in DDR mode, REN along with a rising and falling edge of RCLK will send data in FIFO
(F16) INPUT memory to the output register and read the current data in output register. In SDR mode data will only
be read on the rising edge of RCLK only.
(1)
RSDR
(L2) Data Rate INPUT operate in Double Data Clock mode. This pin must be tied either HIGH or LOW and cannot toggle during
RT Retransmit HSTL-LVTTL RT asserted on the rising edge of RCLK initializes the read pointer to the first location in memory. EF flag
(F15) INPUT is set to LOW (OR to HIGH in FWFT mode). The write pointer, offset registers, and flag settings are not
SCLK Serial Clock LVTTL A rising edge of SCLK will clock the serial data present on the SI input into the offset registers provided
(H15) INPUT that SEN is enabled. A rising edge of SCLK will also read data out of the offset registers provided that SREN
SEN Serial Input HSTL-LVTTL SEN used in conjunction with SI and SCLK enables serial loading of the programmable flag offsets.
(J15) Enable INPUT
SREN Serial Read HSTL-LVTTL SREN used in conjunction with SO and SCLK enables serial reading of the programmable flag offsets.
(J16) Enable INPUT
SI Serial Input HSTL-LVTTL This input pin is used to load serial data into the programmable flag offsets. Used in conjunction with SEN
(H16) INPUT and SCLK.
SO Serial Output HSTL-LVTTL This output pin is used to read data from the programmable flag offsets. Used in conjunction with SREN
(K15) OUTPUT and SCLK.
(2)
TCK
(F1) INPUT operations of the device are synchronous to TCK. Data from TMS and TDI are sampled on the rising edge
(2)
TDI
(E2) Input INPUT operation, test data serially loaded via the TDI on the rising edge of TCK to either the Instruction Register,
(2)
TDO
(F3) Output OUTPUT operation, test data serially loaded output via the TDO on the falling edge of TCK from either the Instruction
(2)
TMS
(F2) Select INPUT the device through its TAP controller states. An internal pull-up resistor forces TMS HIGH if left unconnected.
(2)
TRST
(E3) INPUT automatically reset upon power-up, thus it must be reset by either this signal or by setting TMS= HIGH
WCLK Write Clock HSTL-LVTTL Input clock when used in conjunction with WEN for writing data into the FIFO memory.
(G1) INPUT
WCS Write Chip Select HSTL-LVTTL The WCS pin an be regarded as a second WEN input, enabling/disabling write operations.
(H2) INPUT
WEN Write Enable HSTL-LVTTL When LOW and in DDR mode, WEN along with a rising and falling edge of WCLK will write data into the
(H1) INPUT FIFO memory. In SDR mode data will only be read on the rising edge of RCLK only.
Read Single LVTTL When LOW, this input pin sets the read port to Single Data Clock mode. When HIGH, the read port will
operation.
affected. If a mark has been set via the MARK input pin, then the read pointer will initialize to the mark location
when RT is asserted.
is enabled.
JTAG Clock HSTL-LVTTL Clock input for JTAG function. One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. Test
of TCK and outputs change on the falling edge of TCK. If the JTAG function is not used this signal needs
to be tied to GND.
JTAG Test Data HSTL-LVTTL One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. During the JTAG boundary scan
ID Register and Bypass Register. An internal pull-up resistor forces TDI HIGH if left unconnected.
JTAG Test Data HSTL-LVTTL One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. During the JTAG boundary scan
Register, ID Register and Bypass Register. This output is high impedance except when shifting, while in
SHIFT-DR and SHIFT-IR controller states.
JTAG Mode HSTL-LVTTL TMS is a serial input pin. One of four terminals required by IEEE Standard 1149.1-1990. TMS directs the
JTAG Reset HSTL-LVTTL TRST is an asynchronous reset pin for the JTAG controller. The JTAG TAP controller does not
for five TCK cycles. If the TAP controller is not properly reset then the FIFO outputs will always be in highimpedance. If the JTAG function is used but the user does not want to use TRST, then TRST can be tied
with MRS to ensure proper FIFO operation. If the JTAG function is not used then this signal needs to be
tied to GND. An internal pull-up resistor forces TRST HIGH if left unconnected.
7
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
PIN DESCRIPTION (CONTINUED)
Symbol & Name I/O TYPE Description
Pin No.
(1)
WSDR
(L1) Rate INPUT operate in Double Data Clock mode. This pin must be tied either HIGH or LOW and cannot toggle during
V
CC +2.5V Supply INPUT There are VCC supply inputs and must be connected to the 2.5V supply rail.
(See below)
V
DDQ O/P Rail Voltage INPUT This pin should be tied to the desired voltage rail for providing power to the output drivers. Nominally 1.5V
(See below) or 1.8V for HSTL, 2.5V for LVTTL.
GND Ground Pin INPUT These are Ground pins are for the core device and must be connected to the GND rail.
(See below)
Vref Reference INPUT This is a Voltage Reference input and must be connected to a voltage level determined in the Recommended
(T3) Voltage DC Operating Conditions section. This provides the reference voltage when using HSTL class inputs.
NOTES:
1. Inputs should not change state after Master Reset.
2. These pins are for the JTAG port. Please refer to pages 24-27 and Figures 5-7.
Write Single Data LVTTL When LOW, this input pin sets the write port to Single Data Clock mode. When HIGH, the write port will
operation.
If HSTL class inputs are not being used, this pin can be left floating.
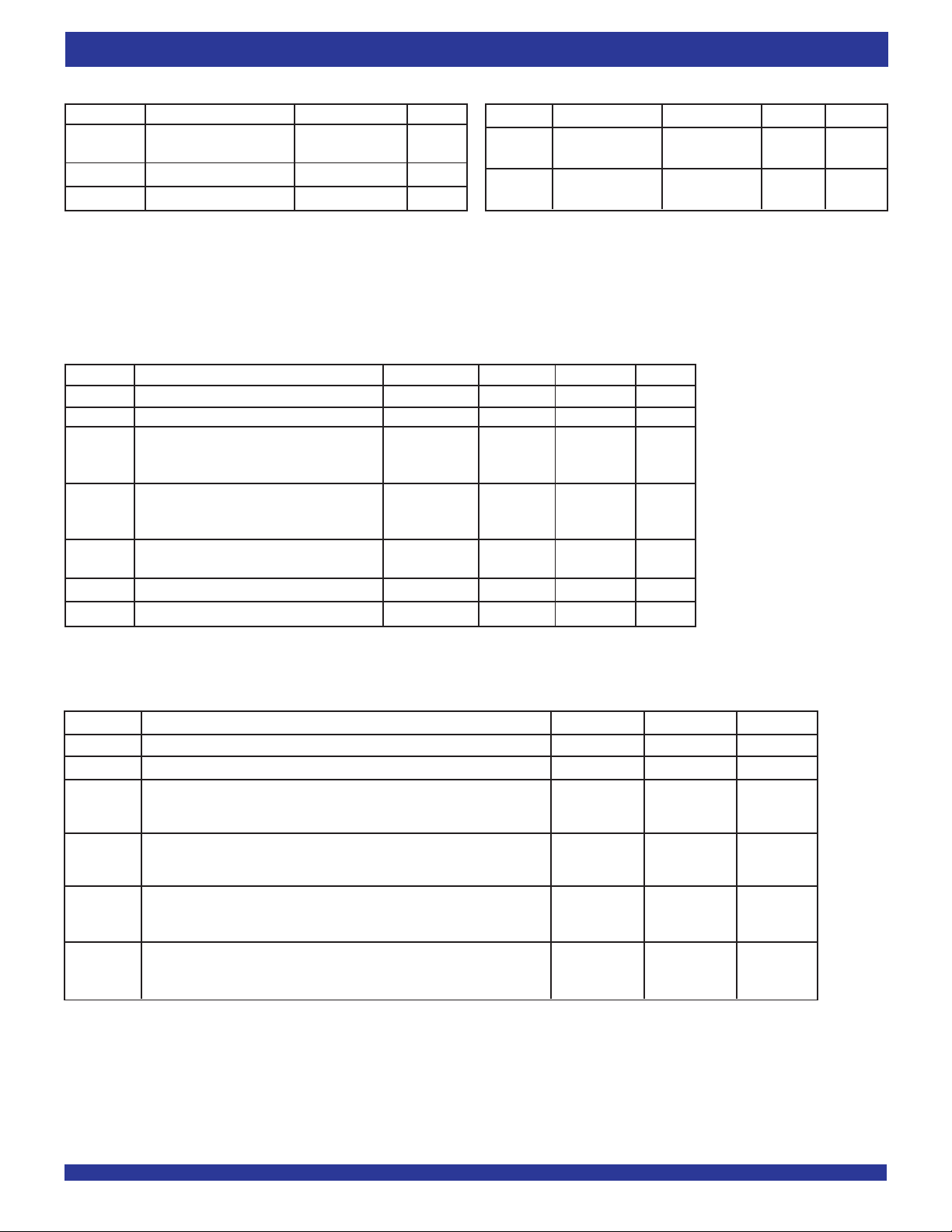
PIN NUMBER TABLE
Symbol Name I/O TYPE Pin Number
D
0-19 Data Inputs HSTL-LVTTL D0-C3, D1-A4, D2-B4, D3-C4, D4-A5, D5-B5, D6-C5, D7-A6, D8-B6, D9-A7, D10-R7, D11-T7,
INPUT D12-R6, D13-T6, D14-R5, D15-T5, D16-R4, D17-T4, D18-P3, D19-R3
0-19 Data Outputs HSTL-LVTTL Q0-B10, Q1-A10, Q2-B11, Q3-A11, Q4-B12, Q5-A12, Q6-B13, Q7-A13, Q8-B14, Q9-A14, Q10-T14
Q
OUTPUT Q11-R14, Q12-T13, Q13-R13, Q14-T12, Q15-R12, Q16-T11, Q17-R11, Q18-T10, Q19-R10
VCC +2.5V Supply INPUT A(1,2), C(6,7), D(4-7), K4, L4, M4, N(4-7), P(5-7), T(1,2)
V
DDQ O/P Rail Voltage INPUT A(15,16), C(10-13), D(10-13), E13, F(4,13), G(4,14), H(4,14), J14, K14, L14, M13, N(10-13),
P(10-13), T(15,16)
GND Ground Pin INPUT A(8,9), B(8,9), C(8,9), D(8,9), E4, G(7-10,13), H(7-10,13), J(4,7-10,13), K(7-10,13), L13, N(8,9),
P(4,8,9), R(8,9), T(8,9)
DNC Do Not Connect — A3, B(1-3,15,16), C(1,2,14-16), D(1-3,14-16), E(1,15,16), K2, M(1-3,15,16), N(1-3,14-16), P(1,2,14-16),
R(1,2,15,16)
8
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Symbol Rating Commercial Unit
VTERM Terminal Voltage –0.5 to +3.6
with respect to GND
STG Storage Temperature –55 to +125 °C
T
OUT DC Output Current –50 to +50 mA
I
NOTES:
1. Stresses greater than those listed under ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS may cause
permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation
of the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect reliability.
2. Compliant with JEDEC JESD8-5. V
CC terminal only.
(2)
V
CAPACITANCE (TA = +25°C, f = 1.0MHz)
Symbol Parameter
(2,3)
IN
C
Capacitance
(1,2)
OUT
C
Capacitance
NOTES:
1. With output deselected, (OE ≥ V
2. Characterized values, not currently tested.
IN for Vref is 20pF.
3. C
(1)
Input VIN = 0V 10
Output VOUT = 0V 10 pF
IH).
RECOMMENDED DC OPERATING CONDITIONS
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
VCC Supply Voltage 2.375 2.5 2.625 V
GND Supply Voltage 0 0 0 V
IH Input High Voltage LVTTL 1 .7 — 3.45 V
V
eHSTL V
HSTL VREF+0.2 — — V
IL Input Low Voltage LVTTL -0.3 — 0.7 V
V
eHSTL — — V
HSTL — — VREF-0.2 V
REF Voltage Reference Input eHSTL 0.8 0.9 1.0 V
V
(HSTL only) HSTL 0.68 0.75 0.9 V
TA Operating Temperature Commercial 0 — 7 0 °C
A Operating Temperature Industrial -40 — 85 °C
T
NOTE:
REF is only required for HSTL or eHSTL inputs. VREF should be tied LOW for LVTTL operation.
1. V
REF+0.2 — — V
REF-0.2 V
Conditions Max. Unit
(3)
pF
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Commercial: VCC = 2.5V ± 0.125V, TA = 0°C to +70°C;Industrial: VCC = 2.5V ± 0.125V, TA = -40°C to +85°C)
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Unit
ILI Input Leakage Current –1 0 1 0 µA
ILO Output Leakage Current –1 0 1 0 µA
(5)
V
OH
OL Output Logic “0” Voltage, IOL = 8 mA @VDDQ = 2.5V ± 0.125V (LVTTL) — 0.4V V
V
(1,2)
I
CC1
(1)
I
CC2
NOTES:
1. Both WCLK and RCLK toggling at 20MHz. Data inputs toggling at 10MHz. WCS = HIGH, REN or RCS = HIGH.
2. Typical I
3. Typical I
4. Total Power consumed: PT = [(V
5. Outputs are not 3.3V tolerant.
Output Logic “1” Voltage, IOH = –8 mA @VDDQ = 2.5V ± 0.125V (LVTTL) VDDQ -0.4 — V
OH = –8 mA @VDDQ = 1.8V ± 0.1V (eHSTL) VDDQ -0.4 — V
I
IOH = –8 mA @VDDQ = 1.5V ± 0.1V (HSTL) VDDQ -0.4 — V
OL = 8 mA @VDDQ = 1.8V ± 0.1V (eHSTL) — 0.4V V
I
IOL = 8 mA @VDDQ = 1.5V ± 0.1V (HSTL) — 0.4V V
Active VCC Current (VCC = 2.5V) I/O = LVTTL — 20 mA
I/O = HSTL — 60 mA
I/O = eHSTL — 60 mA
Standby VCC Current (VCC = 2.5V) I/O = LVTTL — 1 0 mA
I/O = HSTL — 50 mA
I/O = eHSTL — 50 mA
CC1 calculation: for LVTTL I/O ICC1 (mA) = 0.6mA x fs, fs = WCLK frequency = RCLK frequency (in MHz)
DDQ calculation: With Data Outputs in High-Impedance: IDDQ (mA) = 0.15mA x fs
for HSTL or eHSTL I/O I
With Data Outputs in Low-Impedance: I
fs = WCLK frequency = RCLK frequency (in MHz), V
A = 25°C, CL = capacitive load (pf)
t
CC x ICC) + (VDDQ x IDDQ)].
CC1 (mA) = 38mA + (0.7mA x fs), fs = WCLK frequency = RCLK frequency (in MHz)
DDQ (mA) = (CL x VDDQ x fs x 2N)/2000
DDQ = 2.5V for LVTTL; 1.5V for HSTL; 1.8V for eHSTL, N = Number of outputs switching.
9
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
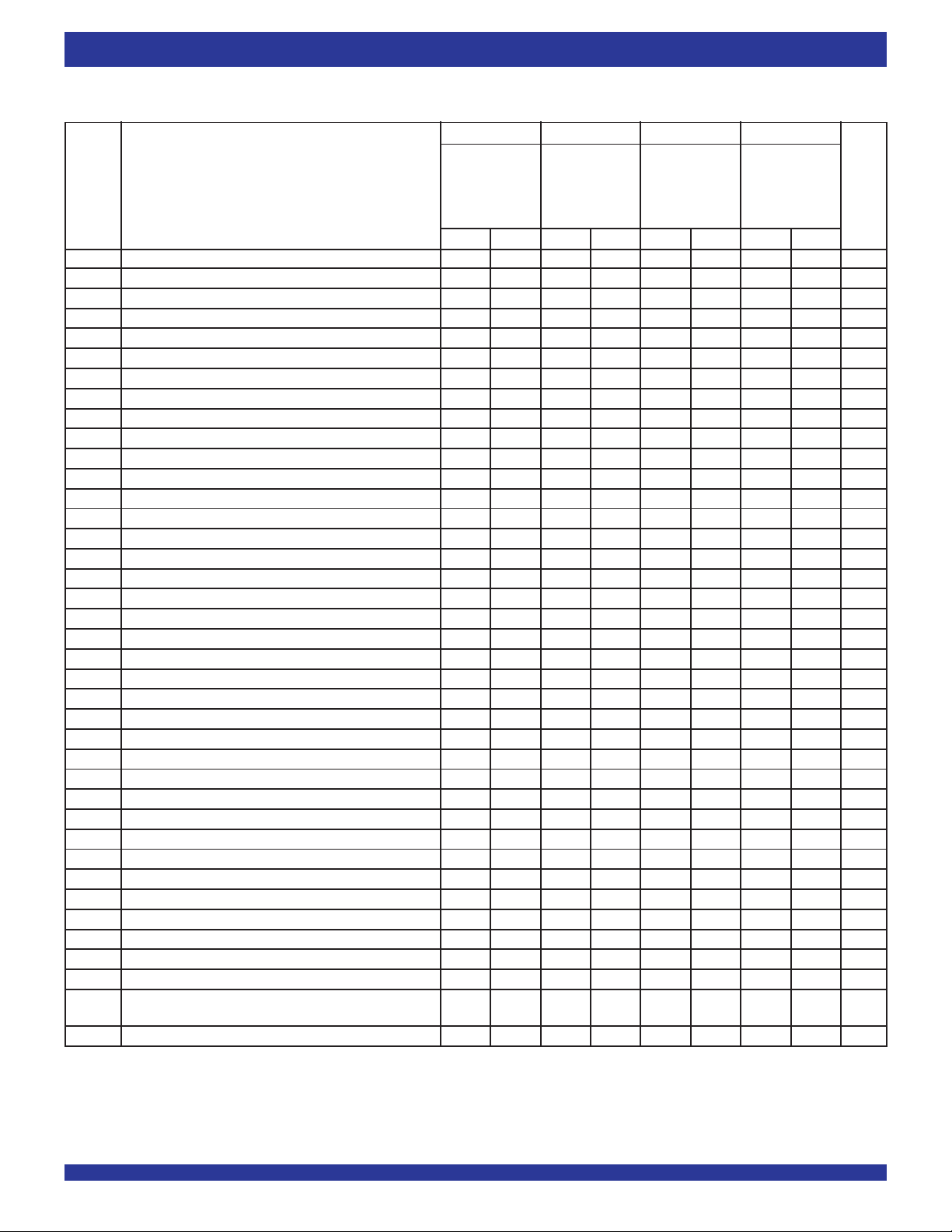
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(1)
(Commercial: VCC = 2.5V ± 5%, TA = 0°C to +70°C;Industrial: VCC = 2.5V ± 5%, TA = -40°C to +85°C)
Commercial Commercial Com’l & Ind’l
IDT72T2098L4 IDT72T2098L5 IDT72T2098L6-7 IDT72T2098L10
IDT72T20108L4 IDT72T20108L5 IDT72T20108L6-7 IDT72T20108L10
IDT72T20118L4 IDT72T20118L5 IDT72T20118L6-7 IDT72T20118L10
IDT72T20128L4 IDT72T20128L5 IDT72T20128L6-7 IDT72T20128L10
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Unit
fS Clock Cycle Frequency (Synchronous) — 250 — 200 — 150 — 10 0 MHz
tA Data Access Time 0. 6 3.2 0.6 3.6 0.6 3.8 0.6 4.5 ns
tASO Data Access Serial Output Time 0 .6 3.2 0.6 3.6 0.6 3.8 0.6 4.5 ns
tCLK Clock Cycle Time 4 — 5 — 6.7 — 10 — ns
tCLKH Clock High Time 1.8 — 2.3 — 2.8 — 4.5 — ns
tCLKL Clock Low Time 1.8 — 2.3 — 2.8 — 4.5 — ns
tDS Data Setup Time 1.2 — 1.5 — 2. 0 — 3.0 — ns
tDH Data Hold Time 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — ns
tENS Enable Setup Time 1.2 — 1.5 — 2. 0 — 3.0 — ns
tENH Enable Hold Time 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — ns
tWCSS WCS setup time 1.2 — 1.5 — 2.0 — 3.0 — ns
tWCSH WCS hold time 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — 0.5 — ns
fC Clock Cycle Frequency (SCLK) — 10 — 10 — 10 — 10 MH z
tSCLK Serial Clock Cycle 100 — 100 — 100 — 100 — ns
tSCKH Serial Clock High 45 — 45 — 45 — 45 — ns
tSCKL Serial Clock Low 45 — 45 — 45 — 45 — ns
tSDS Serial Data In Setup 15 — 1 5 — 15 — 15 — ns
tSDH Serial Data In Hold 5 — 5 — 5 — 5 — ns
tSENS Serial Enable Setup 5 — 5 — 5 — 5 — ns
tSENH Serial Enable Hold 5 — 5 — 5 — 5 — ns
tRS Reset Pulse Width
(3)
30 — 30 — 30 — 30 — ns
tRSS Reset Setup Time 15 — 1 5 — 15 — 15 — ns
tHRSS HSTL Reset Setup Time 4 — 4 — 4 — 4 — µs
tRSR Reset Recovery Time 1 0 — 10 — 10 — 10 — ns
tRSF Reset to Flag and Output Time — 1 0 — 12 — 15 — 15 ns
tOLZ Output Enable to Output in Low Z
(4)
0—0—0—0—ns
tOE Output Enable to Output Valid — 3.2 — 3.6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tOHZ Output Enable to Output in High Z
(4)
— 3.2 — 3.6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tWFF Write Clock to FF or IR — 3.2 — 3.6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tREF Read Clock to EF or OR — 3.2 — 3.6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tPAFS Write Clock to Programmable Almost-Full Flag — 3 .2 — 3.6 — 3 .8 — 4.5 ns
tPAES Read Clock to Programmable Almost-Empty Flag — 3.2 — 3. 6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tERCLK RCLK to Echo RCLK output — 3. 6 — 4 — 4. 3 — 5 n s
tCLKEN RCLK to Echo REN output — 3.2 — 3 .6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tRCSLZ RCLK to Active from High-Z — 3. 2 — 3.6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tRCSHZ RCLK to High-Z
(4)
— 3.2 — 3.6 — 3.8 — 4.5 ns
tSKEW1 Skew time between RCLK and WCLK for EF/OR and FF/IR 3.5—4—5—7—ns
SKEW2 Skew time between RCLK and WCLK for EF/OR and FF/IR 3.5—4—5—7—ns
t
in DDR mode
SKEW3 Skew time between RCLK and WCLK for PAE and PAF 4—5—6—8—ns
t
NOTES:
1. All AC timings apply to both IDT Standard mode and First Word Fall Through mode.
2. Industrial temperature range product for the 6-7ns speed grade is available as a standard device. All other speed grades are available by special order.
3. Pulse widths less than minimum values are not allowed.
4. Values guaranteed by design, not currently tested.
(2)
Commercial
10
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
5996 drw04a
6
5
4
3
2
1
20 30 50 80 100 200
Capacitance (pF)
t
CD
(Typical, ns)
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
HSTL
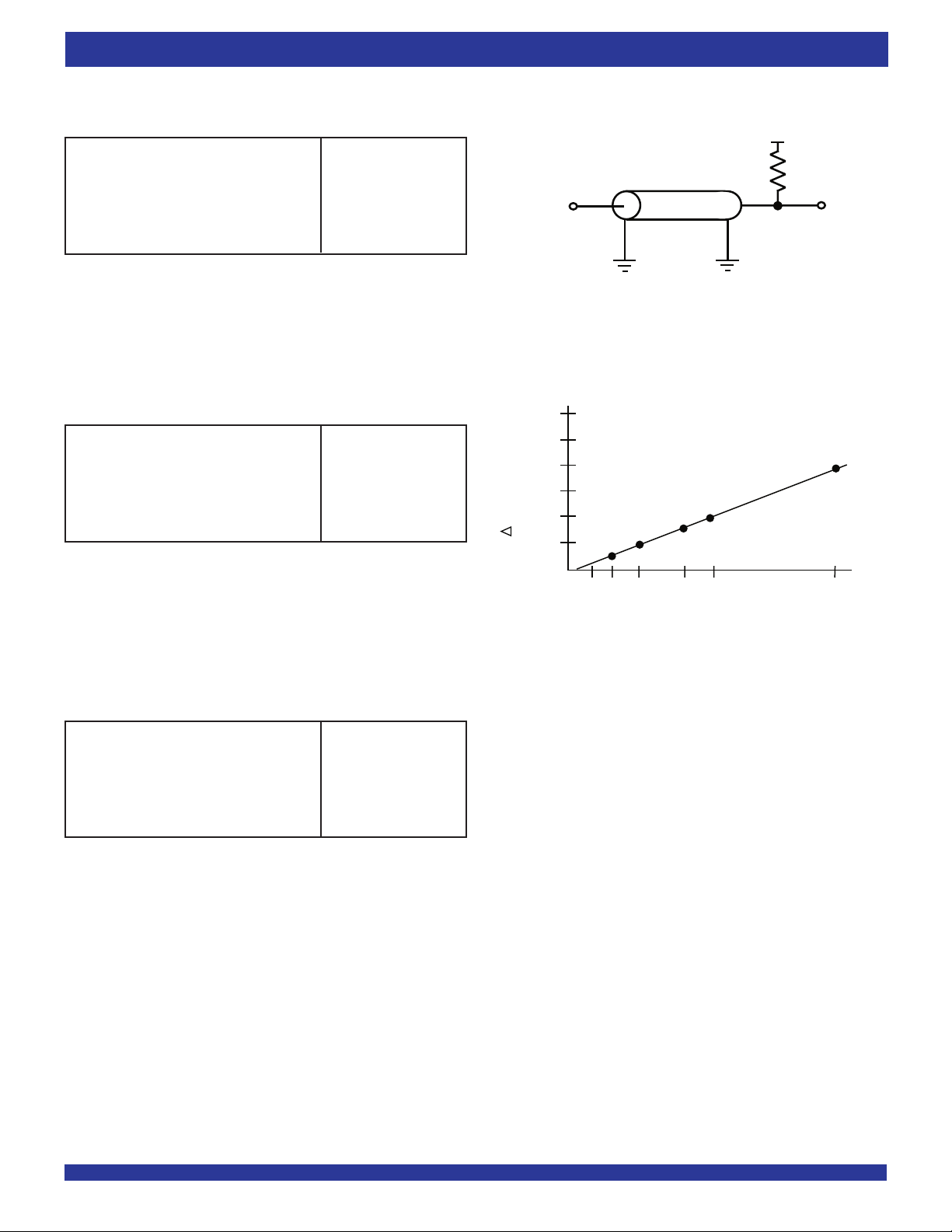
1.5V AC TEST CONDITIONS
Input Pulse Levels 0.25 to 1.25V
Input Rise/Fall Times 0.4ns
Input Timing Reference Levels 0.75
Output Reference Levels V
NOTE:
1. V
DDQ = 1.5V±.
DDQ/2
EXTENDED HSTL
1.8V AC TEST CONDITIONS
Input Pulse Levels 0.4 to 1.4V
Input Rise/Fall Times 0.4ns
Input Timing Reference Levels 0.9
Output Reference Levels V
DDQ/2
I/O
AC TEST LOADS
V
50Ω
Z0 = 50Ω
Figure 2a. AC Test Load
DDQ
5996 drw04
/2
NOTE:
1. V
DDQ = 1.8V±.
2.5V LVTTL
2.5V AC TEST CONDITIONS
Input Pulse Levels GND to 2.5V
Input Rise/Fall Times 1ns
Input Timing Reference Levels V
Output Reference Levels V
NOTE:
1. For LVTTL V
CC = VDDQ.
DDQ/2
Figure 2b. Lumped Capacitive Load, Typical Derating
CC/2
11
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
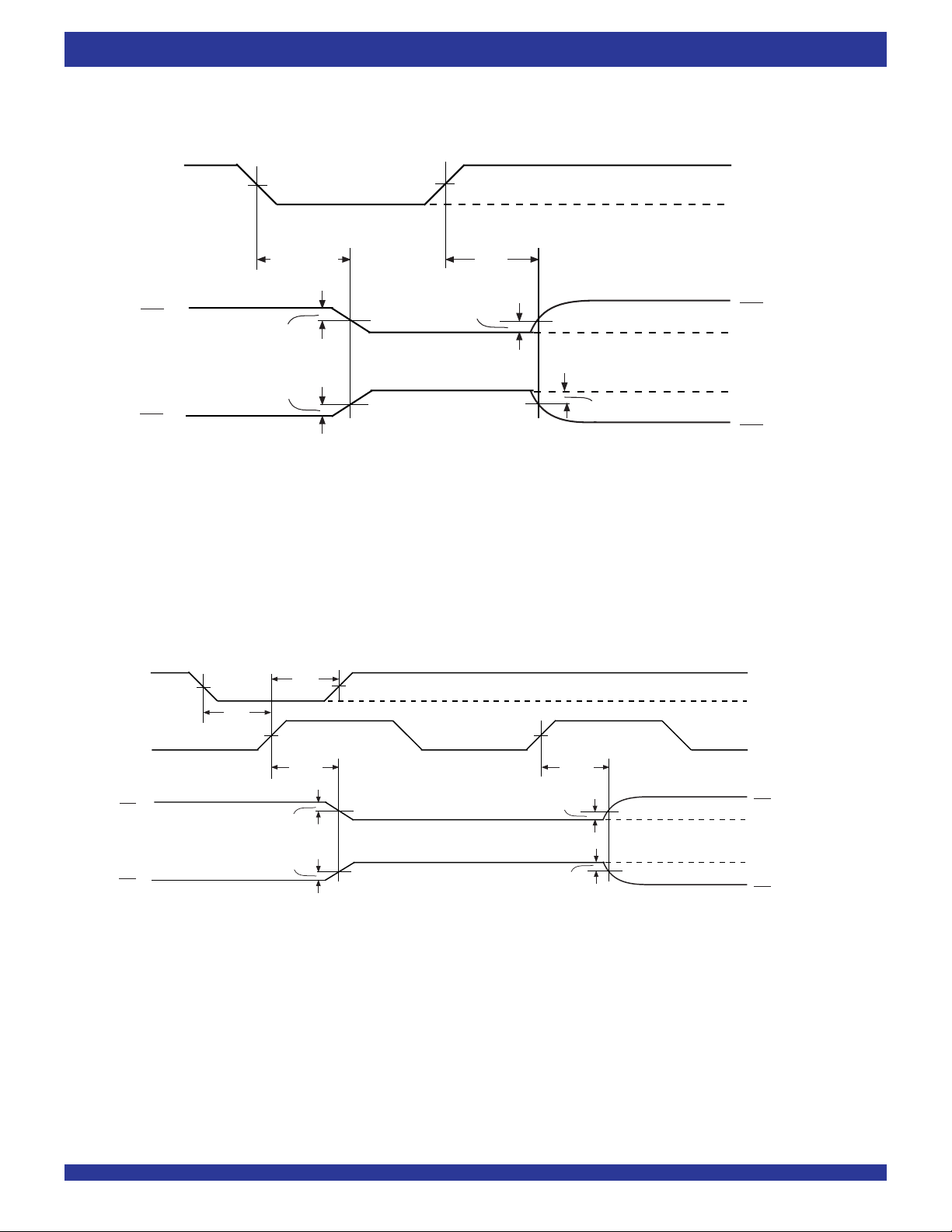
OUTPUT ENABLE & DISABLE TIMING
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
Output
Normally
LOW
Output
Normally
HIGH
NOTES:
1. REN is HIGH.
2. RCS is LOW.
Output
Enable
Output
Disable
V
IH
OE
V
IL
t
OE & tOLZ
V
CC
2
V
CC
100mV
100mV
2
t
100mV
OHZ
100mV
V
V
V
V
5996 drw04b
CC
2
OL
OH
CC
2
READ CHIP SELECT ENABLE & DISABLE TIMING
t
100mV
100mV
ENH
t
RCSLZ
100mV
RCS
RCLK
Output
V
LOW
HIGH
CC
2
V
CC
2
Normally
Output
Normally
NOTES:
1. REN is HIGH.
2. OE is LOW.
t
ENS
t
RCSHZ
100mV
5996 drw04c
V
IH
V
IL
V
CC
2
V
OL
V
OH
V
CC
2
12

IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
TIMING MODES: IDT STANDARD vs FIRST WORD FALL THROUGH
(FWFT) MODE
The IDT72T2098/72T20108/72T20118/72T20128 support two different
timing modes of operation: IDT Standard mode or First Word Fall Through
(FWFT) mode. The selection of which mode will operate is determined during
Master Reset, by the state of the FWFT input.
If, at the time of Master Reset, FWFT is LOW, then IDT Standard mode will
be selected. This mode uses the Empty Flag (EF) to indicate whether or not
there are any words present in the FIFO. It also uses the Full Flag function (FF)
to indicate whether or not the FIFO has any free space for writing. In IDT
Standard mode, every word read from the FIFO, including the first, must be
requested using the Read Enable (REN) and RCLK.
If, at the time of Master Reset, FWFT is HIGH, then FWFT mode will be
selected. This mode uses Output Ready (OR) to indicate whether or not there
is valid data at the data outputs (Q
whether or not the FIFO has any free space for writing. In the FWFT mode,
the first word written to an empty FIFO goes directly to Q
edges, REN = LOW is not necessary. Subsequent words must be accessed
using the Read Enable (REN) and RCLK.
Various signals, both input and output signals operate differently depending
on which timing mode is in effect.
IDT STANDARD MODE
In this mode, the status flags, FF, PAF, PAE, and EF operate in the manner
outlined in Table 4. To write data into to the FIFO, Write Enable (WEN) must
be LOW. Data presented to the DATA IN lines will be clocked into the FIFO on
subsequent transitions of the Write Clock (WCLK). After the first write is
performed, the Empty Flag (EF) will go HIGH. Subsequent writes will continue
to fill up the FIFO. The Programmable Almost-Empty flag (PAE) will go HIGH
after n + 1 words have been loaded into the FIFO, where n is the empty offset
value. The default setting for these values are listed in Table 2. This parameter
is also user programmable. See section on Programmable Flag Offset Loading.
Continuing to write data into the FIFO will cause the Programmable AlmostFull flag (PAF) to go LOW. Again, if no reads are performed, the PAF will go
LOW after (D-m) writes to the FIFO. If x20 Input or x20 Output bus Width is
selected, (D-m) = (32,768-m) writes for the IDT72T2098, (65,536-m) writes
for the IDT72T20108, (131,072-m) writes for the IDT72T20118 and
(262,144-m) writes for the IDT72T20128. If both x10 Input and x10 Output bus
Widths are selected, (D-m) = (65,536-m) writes for the IDT72T2098, (131,072-m)
writes for the IDT72T20108, (262,144-m) writes for the IDT72T20118 and
(524,288-m) writes for the IDT72T20128. The offset “m” is the full offset value.
The default setting for these values are listed in Table 3. This parameter is also
user programmable. See the section on Programmable Flag Offset Loading.
When the FIFO is full, the Full Flag (FF) will go LOW, inhibiting further write
operations. If no reads are performed after a reset, FF will go LOW after D writes
to the FIFO. If the x20 Input or x20 Output bus Width is selected, D = 32,768
writes for the IDT72T2098, 65,536 writes for the IDT72T20108, 131,072 writes
for the IDT72T20118 and 262,144 writes for the IDT72T20128. If both x10
Input and x10 Output bus Widths are selected, D = 65,536 writes for the
IDT72T2098, 131,072 writes for the IDT72T20108, 262,144 writes for the
IDT72T20118 and 524,288 writes for the IDT72T20128, respectively.
n). It also uses Input Ready (IR) to indicate
n after three RCLK rising
If the FIFO is full, the first read operation will cause FF to go HIGH.
Subsequent read operations will cause PAF to go HIGH at the conditions
described in Table 3. If further read operations occur, without write operations,
PAE will go LOW when there are n words in the FIFO, where n is the empty
offset value. Continuing read operations will cause the FIFO to become empty.
When the last word has been read from the FIFO, the EF will go LOW inhibiting
further read operations. REN is ignored when the FIFO is empty.
When configured in IDT Standard mode, the EF and FF outputs are double
register-buffered outputs. IDT Standard mode is available when the device is
configured in both Single Data Rate mode and Double Data Rate mode.
Relevant timing diagrams for IDT Standard mode can be found in Figure
10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18 and 23.
FIRST WORD FALL THROUGH MODE (FWFT)
In this mode, the status flags, IR, PAF, PAE, and OR operate in the manner
outlined in Table 5. To write data into the FIFO, WEN must be LOW. Data
presented to the DATA IN lines will be clocked into the FIFO on subsequent
transitions of WCLK. After the first write is performed, the Output Ready (OR)
flag will go LOW. Subsequent writes will continue to fill up the FIFO. PAE will go
HIGH after n+2 words have been loaded into the FIFO, where n is the empty
offset value. The default setting for these values are stated in the footnote of Table
2. This parameter is also user programmable. See section on Programmable
Flag Offset Loading.
Again, if no reads are performed, the PAF will go LOW after (D-m) writes
to the FIFO. If x20 Input or x20 Output bus Width is selected, (D-m) = (32,769-m)
writes for the IDT72T2098, (65,537-m) writes for the IDT72T20108, (131,073-m)
writes for the IDT72T20118 and (262,145-m) writes for the IDT72T20128. If
both x10 Input and x10 Output bus Widths are selected, (D-m) = (65,537-m)
writes for the IDT72T2098, (131,073-m) writes for the IDT72T20108,
(262,145-m) writes for the IDT72T20118 and (524,289-m) writes for the
IDT72T20128. The offset m is the full offset value. The default setting for these
values are stated in the footnote of Table 3.
When the FIFO is full, the Input Ready (IR) flag will go HIGH, inhibiting further
write operations. If no reads are performed after a reset, IR will go HIGH after
D writes to the FIFO. If x18 Input or x18 Output bus Width is selected, D = 32,769
writes for the IDT72T2098, 65,537 writes for the IDT72T20108, 131,073 writes
for the IDT72T20118 and 262,145 writes for the IDT72T20128. If both x10 Input
and x10 Output bus Widths are selected, D = 65,537 writes for the IDT72T2098,
131,073 writes for the IDT72T20108, 262,145 writes for the IDT72T20118 and
524,289 writes for the IDT72T20128, respectively. Note that the additional word
in FWFT mode is due to the capacity of the memory plus output register.
If the FIFO is full, the first read operation will cause the IR flag to go LOW.
Subsequent read operations will cause the PAF to go HIGH at the conditions
described in Table 5. If further read operations occur, without write operations,
the PAE will go LOW when there are n+1 words in the FIFO, where n is the empty
offset value. Continuing read operations will cause the FIFO to become empty.
When the last word has been read from the FIFO, OR will go HIGH inhibiting
further read operations. REN is ignored when the FIFO is empty.
When configured in FWFT mode, the OR flag output is triple registerbuffered, and the IR flag output is double register-buffered. FWFT mode is only
available when the device is configured in Single Data Rate mode.
Relevant timing diagrams for FWFT mode can be found in Figure 19, 20,
21, 22, and 24.
13
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
TABLE 3 — DEFAULT PROGRAMMABLE
FLAG OFFSETS
IDT72T2098, 72T20108, 72T20118, 72T20128
FSEL1 FSEL0 Offsets n,m
H H 255
L H 127
HL63
LL7
NOTES:
1. n = empty offset for PAE.
2. m = full offset for PAF.
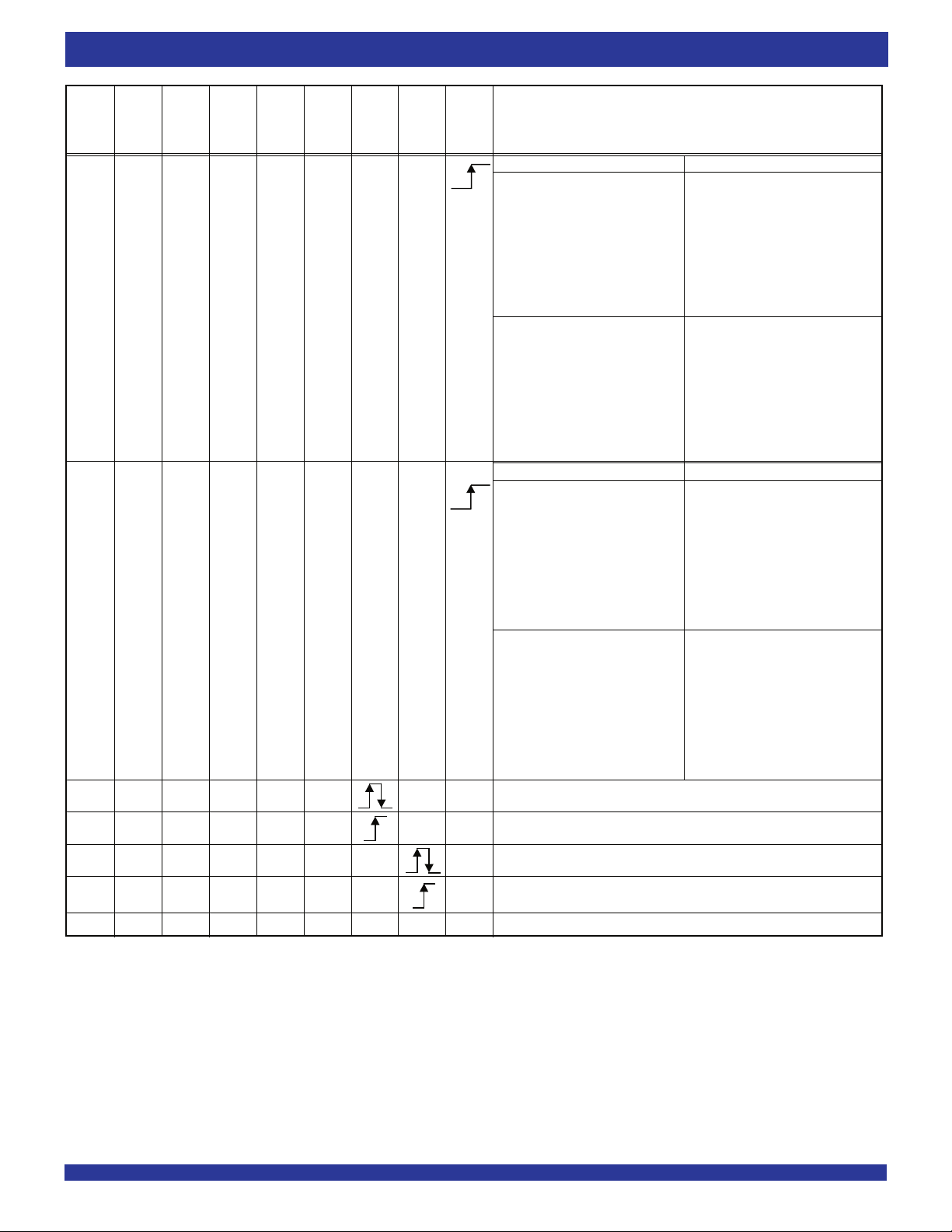
PROGRAMMING FLAG OFFSETS
Full and Empty Flag offset values are user programmable. The IDT72T2098/
72T20108/72T20118/72T20128 have internal registers for these offsets.
There are four selectable default offset values during Master Reset. These offset
values are shown in Table 3. The offset values can also be programmed serially
into the FIFO. To load offset values, set SEN LOW and the rising edge of SCLK
will load data from the SI input into the offset registers. SCLK runs at a nominal
speed of 10MHz at the maximum. The programming sequence starts with one
bit for each SCLK rising edge, starting with the Empty Offset LSB and ending
with the Full Offset MSB. The total number of bits per device is listed in Figure
3, Programmable Flag Offset Programming Sequence. See Figure 25,
Loading of Programmable Flag Registers, for the timing diagram for this mode.
The PAE and PAF can show a valid status only after the complete set of bits (for
all offset registers) has been entered. The registers can be reprogrammed as
long as the complete set of new offset bits is entered.
In addition to loading offset values into the FIFO, it is also possible to read
the current offset values. Similar to loading offset values, set SREN LOW and
the rising edge of SCLK will send data from the offset registers out to the SO output
port. When initializing a read to the offset registers, data will be read starting from
the first location in the register, regardless of where it was last read.
Figure 3, Programmable Flag Offset Programming Sequence, summarizes
the control pins and sequence for programming offset registers and reading and
writing into the FIFO.
The offset registers may be programmed (and reprogrammed) any time
after Master Reset. Valid programming ranges are from 0 to D-1.
TABLE 4 STATUS FLAGS FOR IDT STANDARD MODE
IW = OW = x10
IW
≠
OW or
IW = OW = x20
Number of
Words in
FIFO
IDT72T2098
00 0
(1)
1 to n
(16,385) to (32,768-(m+1))
(32,768-m) to 32,767 (65,536-m) to 65,535 (131,072-m) to 131,071
32,768
NOTE:
1. See table 3 for values for n, m.
IDT72T20108
(1)
1 to n
(32,769) to (65,536-(m+1))
65,536 131,072
IDT72T20108IDT72T2098 IDT72T20118 IDT72T20128
IDT72T20118 IDT72T20128
(65,537) to (131,072-(m+1))
TABLE 5 STATUS FLAGS FOR FWFT MODE
IW = OW = x10
IW
≠
OW or
IW = OW = x20
Number of
Words in
FIFO
IDT72T2098
00 0
(1)
1 to n
(16,386) to (32,764-(m+1))
(32,764-m) to 32,768 (65,537-m) to 65,536 (131,073-m) to 131,072
32,769 65,537 131,073
IDT72T20108
(1)
1 to n
(32,770) to (65,537-(m+1))
NOTE:
1. See table 3 for values for n, m.
2. Number of Words in FIFO = FIFO Depth + Output Register.
3. FWFT mode available only in Single Data Rate mode.
IDT72T20108IDT72T2098 IDT72T20118 IDT72T20128
IDT72T20118 IDT72T20128
(65,538) to (131,073-(m+1))
1 to n
1 to n
FF PAF PAE EF
(1)
(131,073) to (262,144-(m+1))
(1)
(131,074) to (262,145-(m+1)) (262,146) to (524,289-(m+1))
00
(1)
1 to n
(262,144-m) to 262,143
262,144
00
(1)
1 to n
(262,145-m) to 262,144
262,145
(262,145) to (524,288-(m+1))
(524,288-m) to 524,287
(524,289-m) to 524,288
1 to n
524,288
1 to n
524,289
(1)
(1)
HHLL
HHLH
HHHH
HLHH
LLHH
IR PAF PAE OR
LHLH
LHLL
LHHL
LLHL
HL
HL
5996 drw05
14
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
WSDR
X
X
RSDR
X
X
WEN
1
1
REN
1
1
SEN
SREN
WCLK RCLK
0
1X
1
0
X
X
SCLK
X
X11 XX X01
x10 to x10 Mode All Other Modes
Serial Write to registers:
In SDR Mode:
32 bits for the IDT72T2098
34 bits for the IDT72T20108
36 bits for the IDT72T20118
38 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
Serial Write to registers:
In DDR Mode:
30 bits for the IDT72T2098
32 bits for the IDT72T20108
34 bits for the IDT72T20118
36 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
x10 to x10 Mode All Other Modes
Serial Read From registers:
In SDR Mode:
32 bits for the IDT72T2098
34 bits for the IDT72T20108
36 bits for the IDT72T20118
38 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
Serial Read from registers:
In DDR Mode:
30 bits for the IDT72T2098
32 bits for the IDT72T20108
34 bits for the IDT72T20118
36 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
Write Memory (DDR)
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
IDT72T2098
IDT72T20108
IDT72T20118
IDT72T20128
Serial Write to registers:
In SDR Mode:
30 bits for the IDT72T2098
32 bits for the IDT72T20108
34 bits for the IDT72T20118
36 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
Serial Write to registers:
In DDR Mode:
28 bits for the IDT72T2098
30 bits for the IDT72T20108
32 bits for the IDT72T20118
34 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
Serial Read from registers:
In SDR Mode:
30 bits for the IDT72T2098
32 bits for the IDT72T20108
34 bits for the IDT72T20118
36 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
Serial Read from registers:
In DDR Mode:
28 bits for the IDT72T2098
30 bits for the IDT72T20108
32 bits for the IDT72T20118
34 bits for the IDT72T20128
1 bit for each rising SCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
X01 XX X01
X11 XX X10
X10 XX X10
XXX X11 XXX
NOTES:
Write Memory (SDR)
Read Memory (DDR)
Read Memory (SDR)
No Operation
5996 drw06
1. The programming sequence applies to both IDT Standard and FWFT modes.
2. When the input or output ports are in DDR mode, the depth is reduced by half but the overall density remains the same. For example, the IDT72T2098 in SDR mode is
32,768 x 20/65,536 x 10 = 655,360, in DDR mode the configuration becomes 16,384 x 40/32,768 x 20 = 655,360. In both cases, the total density are the same.
Figure 3. Programmable Flag Offset Programming Sequence
15
IDT72T2098/108/118/128 2.5V HIGH-SPEED TeraSync™ DDR/SDR FIFO 20-BIT/10-BIT CONFIGURATIONS
32K x 20/64K x 10, 64K x 20/128K x 10, 128K x 20/256K x 10, 256K x 20/512K x 10
COMMERCIAL AND INDUSTRIAL
TEMPERATURE RANGES
RETRANSMIT FROM MARK OPERATION
The Retransmit from Mark feature allows FIFO data to be read repeatedly
starting at a user-selected position. The FIFO is first put into retransmit mode
that will “mark” a beginning word and also set a pointer that will prevent
ongoing FIFO write operations from over-writing retransmit data. The retransmit data can be read repeatedly any number of times from the “marked”
position. The FIFO can be taken out of retransmit mode at any time to allow
normal device operation. The “mark” position can be selected any number of
times, each selection over-writing the previous mark location.
In Double Data Rate, data is always marked in pairs. That is, the unit of data
read on the rising and falling edge of WCLK. If the data marked was read on
the falling edge of RCLK, then the marked data will be the unit of data read from
the rising and falling edge of that particular RCLK edge. Refer to Figure 23,
Retransmit from Mark in Double Data Rate Mode, for the timing diagram in
this mode. Retransmit operation is available in both IDT standard and FWFT
modes.
During IDT standard mode the FIFO is put into retransmit mode by a Lowto-High transition on RCLK when the MARK input is HIGH and EF is HIGH.
The rising RCLK edge marks the data present in the FIFO output register as
the first retransmit data. Again, the data is marked in pairs. Thus if the data
marked was read on the falling edge of RCLK, the first part of retransmit will
read out the data read on the rising edge of RCLK, followed by the data on the
falling edge (the marked data). The FIFO remains in retransmit mode until a
rising edge on RCLK occurs while MARK is LOW.
Once a marked location has been set, a retransmit can be initiated by a
rising edge on RCLK while the Retransmit input (RT) is LOW. REN must be
HIGH (reads disabled) before bringing RT LOW. The device indicates the start
of retransmit setup by setting EF LOW, also preventing reads. When EF goes
HIGH, retransmit setup is complete and read operations may begin starting
with the first unit of data at the MARK location. Since IDT standard mode is
selected, every word read including the first “marked” word following a retransmit setup requires a LOW on REN.
Note, write operations may continue as normal during all retransmit functions,
however write operations to the “marked” location will be prevented. See Figure
23, Retransmit from Mark in Double Data Rate Mode, for the relevant timing
diagram.
During FWFT mode the FIFO is put into retransmit mode by a rising RCLK
edge when the MARK input is HIGH and OR is LOW. The rising RCLK edge
marks the data present in the FIFO output register as the first retransmit data.
The data is marked in pairs. The FIFO remains in retransmit mode until a
rising RCLK edge occurs while MARK is LOW.
Once a marked location has been set, a retransmit can be initiated by a
rising RCLK edge while the Retransmit input (RT) is LOW. REN must be
HIGH (reads disabled) before bringing RT LOW. The device indicates the
start of retransmit setup by setting OR HIGH, preventing read operations.
When OR goes LOW , retransmit setup is complete and on the next rising
RCLK edge (RT goes HIGH), the contents of the first retransmit location are
loaded onto the output register. Since FWFT mode is selected, the first word
appears on the outputs regardless of REN, a LOW on REN is not required for
the first word. Reading all subsequent words requires a LOW on REN to
enable the rising RCLK edge. See Figure 24, Retransmit from Mark (FWFT
mode) for the relevant timing diagram.
Before a retransmit can be performed, there must be at least 1280 bits (or
160 bytes) of data between the write pointer and mark location.That is, 20 bits
x64 for the x20 mode and 10 bits x128 for the x10 mode. Also, once the Mark
is set, the write pointer will not increment past the marked location, preventing
overwrites of retransmit data.
HSTL/LVTTL I/O
This device supports both LVTTL and HSTL logic levels on the input and
output signals. If LVTTL is desired, a LOW on the HSTL pin will set the inputs
and outputs to LVTTL mode. If HSTL is desired, a HIGH on the HSTL pin will
set the inputs and outputs to HSTL mode. VREF is the input voltage reference
used in HSTL mode. Typically a logic HIGH in HSTL would be Vref + 0.2V and
a logic LOW would be VREF – 0.2V. Table 6 illustrates which pins are and are
not associated with this feature. Note that all “Static Pins” must be tied to Vcc or
GND. These pins are LVTTL only and are purely device configuration pins.
TABLE 6 — I/O CONFIGURATION
HSTL SELECT STATIC PINS
HIGH = HSTL LVTTL ONL Y
LOW = LVTTL
Write Port Read Port Signal Pins Static Pins
Dn (I/P) Qn (O/P) EF/OR (O/P) SCLK (I/P) TRST (I/P) IW (I/P)
WCLK (I/P) RCLK (I/P) PAF (O/P) SI (I/P) TDI (I/P) OW (I/P)
WEN (I/P) REN (I/P) PAE (O/P) SO (O/P) TDO (O/P) HSTL (I/P)
WCS (I/P) RCS (I/P) FF/IR (O/P) MRS (I/P) SEN (I/P) FSEL1 (I/P)
MARK (I/P) ERCLK (O/P) PRS (I/P) SREN (I/P) FSEL0 (I/P)
OE (I/P) EREN (O/P) TCK (I/P) FWFT (I/P)
RT (I/P) TMS (I/P) WSDR (I/P)
RSDR (I/P)
16
 Loading...
Loading...