Integrated Device Technology Inc IDT72264L20TF, IDT72264L15G, IDT72264L15PF, IDT72264L15TF, IDT72264L20G Datasheet
...
VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
8,192 x 18 or 16,384 x 9
16,384 x 18 or 32,768 x 9
Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
FEATURES:
• Select 8192 x 18 or 16384x 9 organization (IDT72264)
• Select 16384 x 18 or 32678 x 9 organization (IDT72274)
• Flexible control of read and write clock frequencies
• Reduced dynamic power dissipation
• Auto power down minimizes power consumption
• 15 ns read/write cycle time (10 ns access time)
• Retransmit Capability
• Master Reset clears entire FIFO, Partial Reset clears
data, but retains programmable settings
• Empty, full and half-full flags signal FIFO status
• Programmable almost empty and almost full flags, each
flag can default to one of two preselected offsets
• Program partial flags by either serial or parallel means
• Select IDT Standard timing (using EF and FF flags) or
First Word Fall Through timing (using OR and IR flags)
• Easily expandable in depth and width
• Independent read and write clocks (permits simultaneous
reading and writing with one clock signal)
• Available in the 64-pin Thin Quad Flat Pack (TQFP), 64pin Slim Thin Quad Flat Pack (STQFP) and the 68-pin
Pin Grid Array (PGA)
• Output enable puts data outputs into high impedance
• High-performance submicron CMOS technology
IDT72264
IDT72274
O
• Industrial temperature range (-40
C to +85OC) is avail-
able, tested to military electrical specifications
DESCRIPTION:
The IDT72264/72274 are monolithic, CMOS, high capacity, high speed, low power first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories
with clocked read and write controls. These FIFOs have three
main features that distinguish them among SuperSync FIFOs:
First, the data path width can be changed from 9-bits to 18bits; as a result, halving the depth. A pin called Memory Array
Select (MAC) chooses between the two options. This feature
helps reduce the need for redesigns or multiple versions of PC
cards, since a single layout can be used for both data bus
widths.
Second, IDT72264/72274 offer the greatest flexibility for
setting and varying the read and write clock (WCLK and
RCLK) frequencies. For example, given that the two clock
frequencies are unequal, the slower clock may exceed the
faster by, at most, twice its frequency. This feature is especially useful for communications and network applications
where clock frequencies are switched to permit different data
rates.
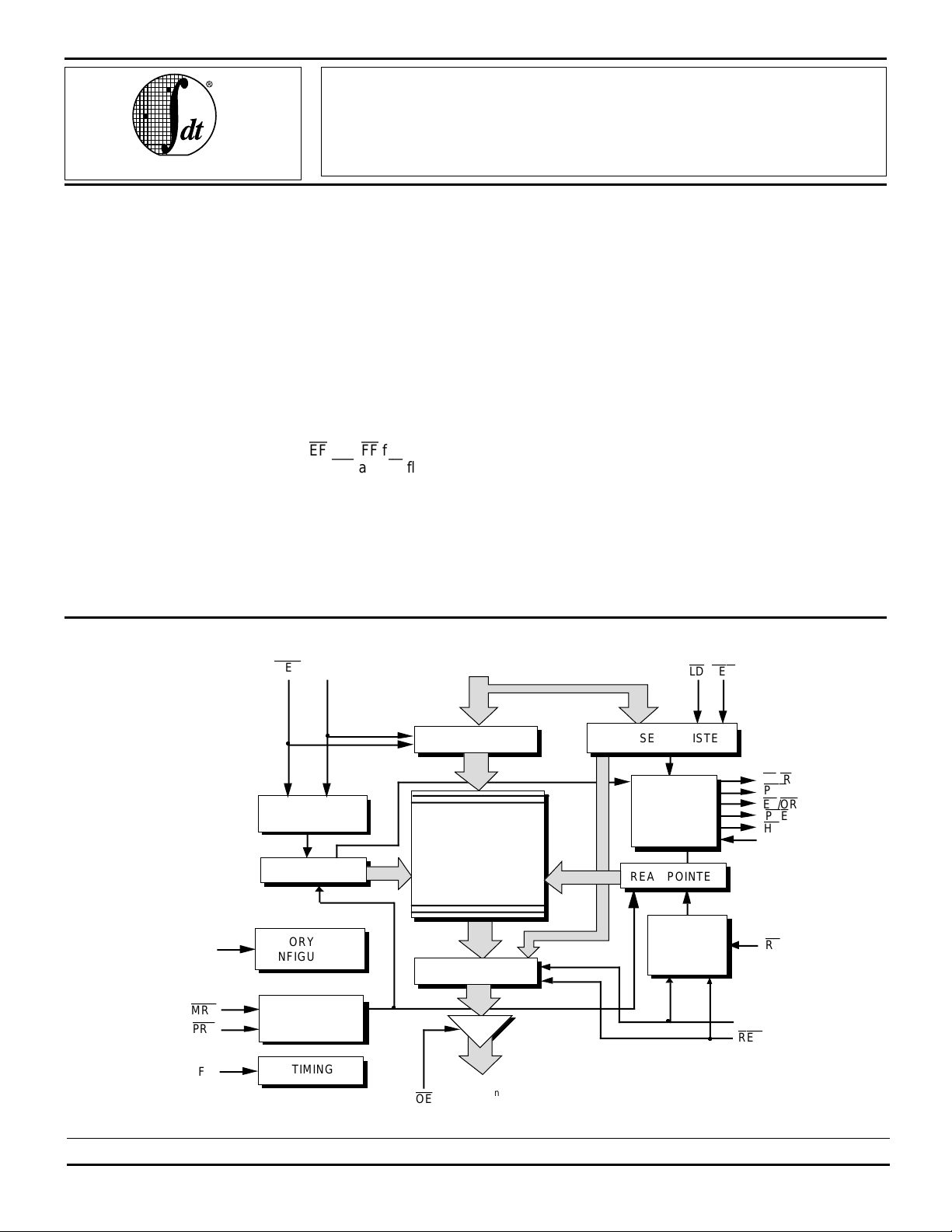
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
D
WEN
WCLK
•
•
WRITE CONTROL
LOGIC
8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9
WRITE POINTER
MAC
MRS
PRS
FS
SyncFIFO is a trademark and the IDT logo is a registered trademark of Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
MEMORY ARRAY
CONFIGURATION
RESET
LOGIC
TIMING
16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9
OUTPUT REGISTER
•
OE
COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES MAY 1997
1997 Integrated Device Technology, Inc DSC-3218/2
For latest information contact IDT's web site at www.idt.com or fax-on-demand at 408-492-8391.
0-Dn
INPUT REGISTER
•
•
RAM ARRAY
•
•
Q
0-Qn
LD
SEN
OFFSET REGISTER
FLAG
LOGIC
READ POINTER
READ
CONTROL
LOGIC
•
•
3218 drw 01
RCLK
REN
FF/IR
PAF
EF/OR
PAE
HF
FWFT/SI
RT
1
IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
Finally,of all SuperSync FIFOs, the IDT72264/72274 offer
the lowest dynamic power dissipation.
These devices meet a wide variety of data buffering needs.
In addition to those already mentioned, applications include
such as optical disk controllers, Local Area Networks (LANs),
and inter-processor communication.
Both FIFOs have an 18-bit input port (Dn) and an 18-bit
output port (Qn). The input port is controlled by a free-running
clock (WCLK) and a data input enable pin (
written into the synchronous FIFO on every clock when
WEN
). Data is
WEN
is asserted. The output port is controlled by another clock pin
(RCLK) and enable pin (
REN
). The read clock can be tied to
the write clock for single clock operation or the two clocks can
run asynchronously for dual clock operation. An output
enable pin (OE) is provided on the read port for three-state
control of the outputs.
The IDT72264/72274 have two modes of operation: In the
IDT Standard Mode
, the first word written to the FIFO is
deposited into the memory array. A read operation is required
to access that word. In the
First Word Fall Through Mode
(FWFT), the first word written to an empty FIFO appears
automatically on the outputs, no read operation required. The
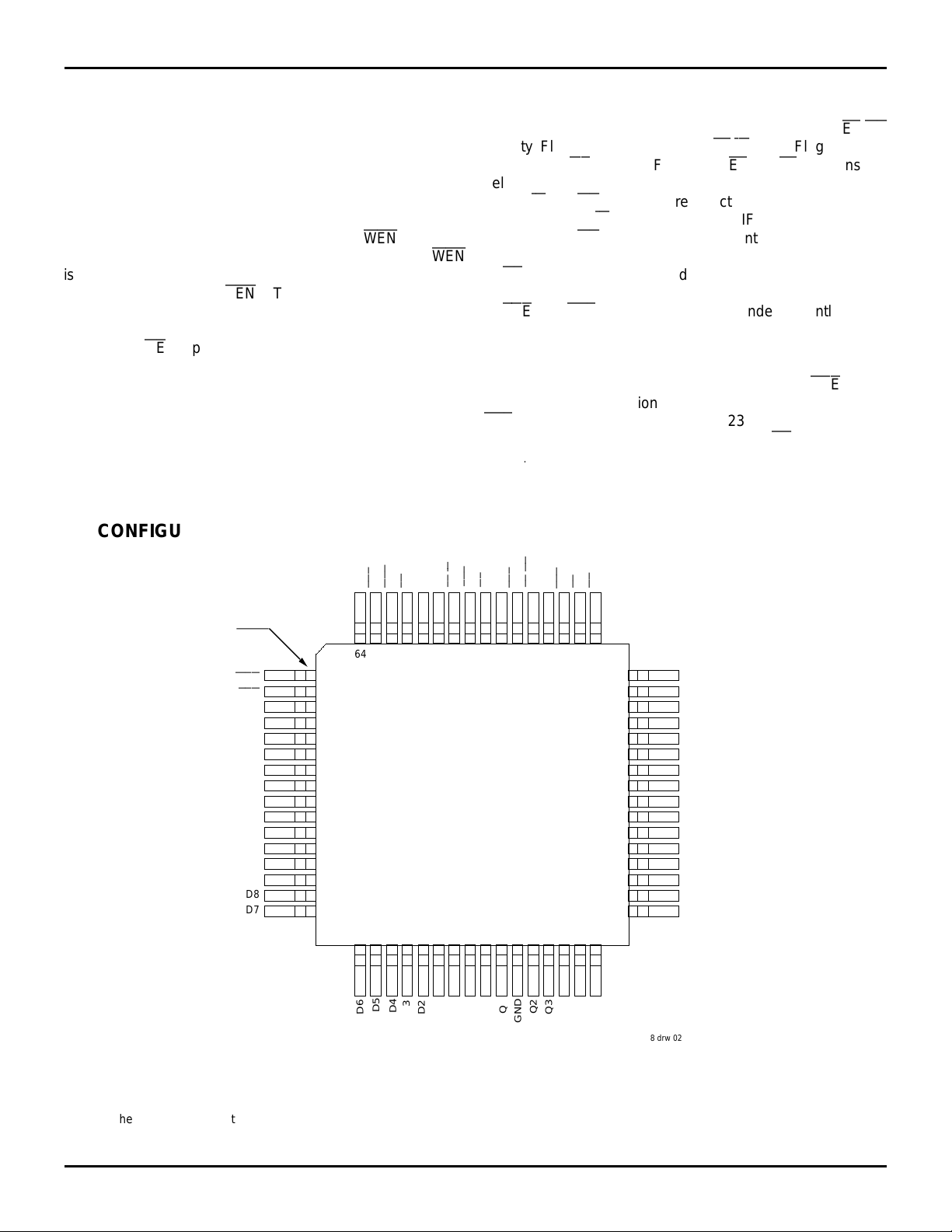
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
state of the FWFT/SI pin during Master Reset determines the
mode in use.
The IDT72264/72274 have five flag functions, EF/
OR
(Empty Flag or Output Ready), FF/IR (Full Flag or Input
Ready), and HF (Half-full Flag). The EF and FF functions are
selected in the IDT Standard Mode.
The IR and OR functions are selected in the First Word Fall
Through Mode. IR indicates that the FIFO has free space to
receive data. OR indicates that data contained in the FIFO is
available for reading.
HF
is a flag whose threshold is fixed at the half-way point in
memory. This flag can always be used irrespective of mode.
PAE
and
PAF
can be programmed independantly to any
point in memory. They, also, can be used irrespective of
mode. Programmable offsets determine the flag threshold
and can be loaded by two methods: parallel or serial. Two
default offset settings are also provided, such that
PAE
can be
set at 127 or 1023 locations from the empty boundary and the
PAF
threshold can be set at 127 or 1023 locations from the full
boundary. All these choices are made with LD during Master
Reset
.
HF
Q0
CC
V
Q1
PAE
GND
OR
/
EF
Q2
RCLK
REN
CC
Q3
V
RT
Q4
OE
Q5
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
3218 drw 02
Q17
Q16
GND
Q15
Q14
CC
V
Q13
Q12
Q11
GND
Q10
Q9
Q8
Q7
Q6
GND
PIN 1
WEN
SEN
FS
V
MAC
D17
D16
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
D7
IR
/
PAF
WCLK
PRS
MRS
LD
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49
1
2
3
CC
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
D5
D4
D6
D3
GND
FWFT/SI
D1
D2
FF
D0
GND
TQFP (PN64-1, order code: PF)
STQFP (PP64-1, order code: TF)
TOP VIEW
NOTES:
1. When the data path is selected to be 9 bits wide (MAC is HIGH), D9 - D17 may either be tied to ground or left open, Q9 - Q17 must be left open.
2
IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
In the serial method, SEN
the offset registers via the Serial Input (SI). In the parallel
method,
registers via Dn.
offsets in parallel from Qn regardless of whether serial or
parallel offset loading is selected.
set to the first location of the FIFO. The FWFT line selects IDT
Standard Mode or FWFT Mode. The LD pin selects one of two
partial flag default settings (127 or 1023) and, also, serial or
parallel programming. The flags are updated accordingly.
pointers to the first location of the memory. However, the
mode setting, programming method, and partial flag offsets
are not altered. The flags are updated accordingly.
useful for resetting a device in mid-operation, when reprogramming offset registers may not be convenient.
to the first location in the RAM array. It is synchronized to
WEN
together with LD can be used to load the offset
REN
During Master Reset (
The Partial Reset (
The Retransmit function allows the read pointer to be reset
together with LD are used to load
together with LD can be used to read the
MRS
), the read and write pointers are
PRS
) also sets the read and write
PRS
is
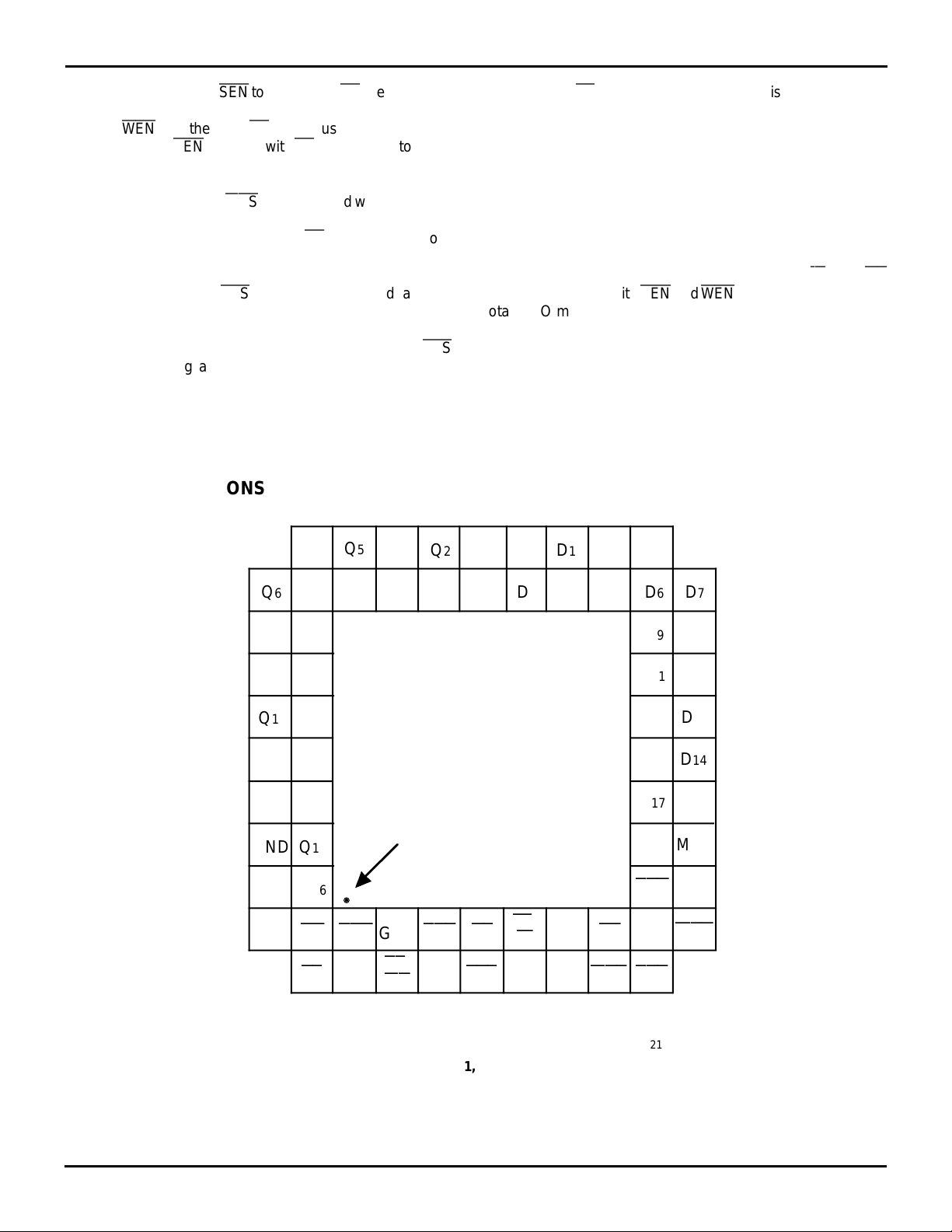
PIN CONFIGURATIONS (CONT.)
RCLK when RT is LOW. This feature is convenient for
sending the same data more than once.
If, at any time, the FIFO is not actively performing a function,
the chip will automatically power down. This occurs if neither
a read nor a write occurs within 10 cycles of the faster clock,
RCLK or WCLK. During the Power Down state, supply current
consumption (ICC2) is at a minimum. Initiating any operation
(by activating control inputs) will immediately take the device
out of the Power Down state.
The IDT72264/72274 are depth expandable. The addition
of external components is unnecessary. The IR and
functions, together with
total FIFO memory capacity.
The FS line ensures optimal data flow through the FIFO. It
is tied to GND if the RCLK frequency is higher than the WCLK
frequency or to Vcc if the RCLK frequency is lower than the
WCLK frequency
The IDT72264/72274 is fabricated using IDT’s high speed
submicron CMOS technology.
REN
and
WEN
, are used to extend the
OR
11
10
09
08
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
DNC
GND
Q6
Q
8 Q7
Q10
Q9
Q
11
GND
Q13 Q12
Q14
V
Q15
GND
Q17
Q16
DNC
RT
CC
Q5
RENOE
RCLK
CC
V
Q
3Q4 GND
Q2
Pin 1 Designator
GND
EF
OR
/
PAE
VCC
HF
PAF
Q1
Q0 D2
D0
FF
/
DNC
IR
FWFT/
GND
MRS
SI
D3D1
D
LD
4
D5GND
D9
D11
D13
D
15
D
17
V
CC
SEN
WCLK
PRS
D7D6
D8
D10
D12
D14
D16
MAC
FS
WEN
ABCDEFGHJKL
3218 drw 03
PGA (G68-1, order code: G)
TOP VIEW
NOTES:
1. When the data path is selected to be 9 bits wide (MAC is HIGH), D9 - D17 may be tied to ground or left open, Q9 - Q17 must be left open.
2. DNC = Do not connect
3
IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
PIN DESCRIPTION
Symbol Name I/O Description
0–D17 Data Inputs I Data inputs for a 18-bit bus.
D
MRS
PRS
RT
FWFT/SI First Word Fall I During Master Reset, selects First Word Fall Through or IDT Standard mode.
WCLK Write Clock I When enabled by
WEN
RCLK Read Clock I When enabled by
REN
OE
SEN
LD
MAC Memory Array I MAC selects 8192 x 18 or 16384x 9 memory array organization for the IDT72264.
FS Frequency Select I FS selects selects WCLK or RCLK, whichever is running at a higher frequency,
FF/IR
EF/OR
PAF
PAE
HF
Q
0–Q17 Data Outputs O Data outputs for a 18-bit bus.
CC Power +5 volt power supply pins.
V
GND Ground Ground pins.
Master Reset I
MRS
initializes the read and write pointers to zero and sets the output register to
all zeroes. During Master Reset, the FIFO is configured for either FWFT or IDT
Standard Mode, one of two programmable flag default settings, and serial or
parallel programming of the offset settings.
Partial Reset I
PRS
initializes the read and write pointers to zero and sets the output register to
all zeroes. During Partial Reset,the existing mode (IDT or FWFT), programming
method (serial or parallel), and programmable flag settings are all retained.
Retransmit I Allows data to be resent starting with the first location of FIFO memory.
Through/Serial In After Master Reset, this pin functions as a serial input for loading offset registers
WEN
, the rising edge of WCLK writes data into the FIFO and
offsets into the programmable registers.
Write Enable I
WEN
enables WCLK for writing data into the FIFO memory and offset registers.
REN
, the rising edge of RCLK reads data from the FIFO
memory and offsets from the programmable registers.
Read Enable I
Output Enable I OE controls the output impedance of Q
Serial Enable I
REN
enables RCLK for reading data from the FIFO memory and offset registers.
n.
SEN
enables serial loading of programmable flag offsets.
Load I During Master Reset, LD selects one of two partial flag default offsets (127 and
1023) and determines programming method, serial or parallel. After Master
Reset, this pin enables writing to and reading from the offset registers.
Configuration It selects 16384 x 18 or 32678 x 9 memory array organization for the IDT72274.
to synchronize the FIFO's internal state machine.
Full Flag/ O In the IDT Standard Mode, the FF function is selected. FF indicates whether or
Input Ready not the FIFO memory is full. In the FWFT mode, the IR function is selected.
IR
indicates whether or not there is space available for writing to the FIFO memory.
Empty Flag/ O In the IDT Standard Mode, the EF function is selected.
EF
indicates whether or
Output Ready not the FIFO memory is empty. In FWFT mode, the OR function is selected.
OR
indicates whether or not there is valid data available at the outputs.
Programmable O
Almost Full Flag offset m which is stored in the Full Offset register.
PAF
goes HIGH if the number of free locations in the FIFO memory is more than
PAF
goes LOW if the
number of free locations in the FIFO memory is less than m.
Programmable O
Almost Empty which is stored in the Empty Offset register.
PAE
goes LOW if the number of words in the FIFO memory is less than offset n
PAE
goes HIGH if the number of
Flag words in the FIFO memory is greater than offset n.
Half-full Flag O
HF
indicates whether the FIFO memory is more or less than half-full.
4
IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
Symbol Rating Commercial Unit
V
TERM Terminal Voltage –0.5 to +7.0 V
with respect to GND
T
A Operating 0 to +70 °C
Temperature
T
BIAS Temperature Under –55 to +125 °C
Bias
STG Storage –55 to +125 °C
T
Temperature
I
OUT DC Output Current 50 mA
NOTE:
1. Stresses greater than those listed under ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only
and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above
those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not implied.
Exposure to absolute maimum rating conditions for extended periods may
affect reliabilty.
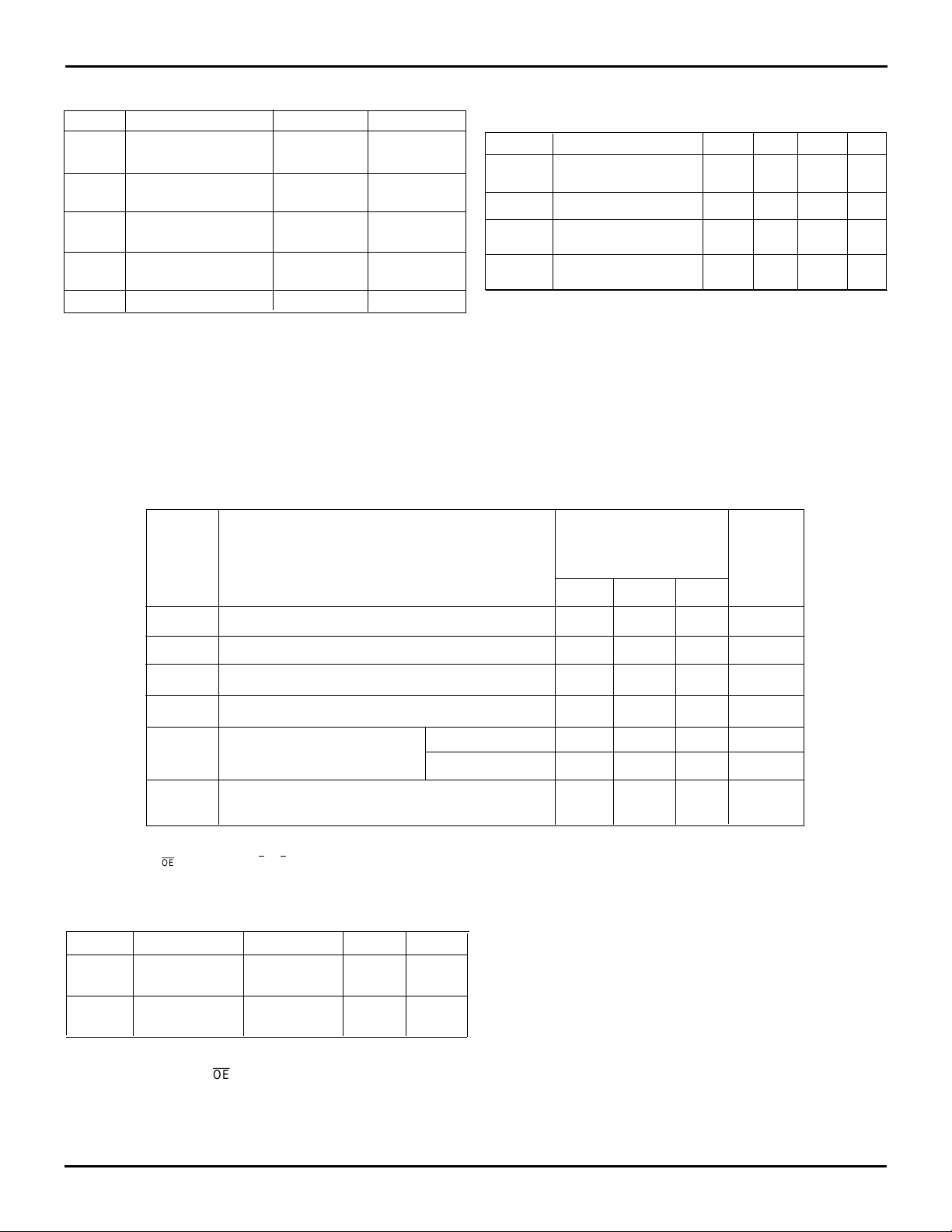
DC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Commercial: VCC = 5V ± 10%, TA = 0°C to +70°C)
Symbol Parameter Min. Type Max Unit
(1)
I
LI
(2)
I
LO
V
OH
V
OL
(3)
I
CC1
(3,4)
I
CC2
Input Leakage Current (any input except MAC) -1 — 1 µA
Output Leakage Current -10 — 10 µA
Output Logic "1" Voltage, IOH = -2mA 2.4 — — V
Output Logic "0" Voltage, IOL = 8mA — — 0.4 V
MAS = V
Active Power Supply Current
MAS = GND — — 135 mA
Power Down Current (All inputs = VCC - 0.2V or — — 115 mA
GND + 0.2V, RCLK and WCLK are free-running)
RECOMMENDED DC
OPERATING CONDITIONS
Symbol Parameter Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
CCC
GND Supply Voltage 0 0 0 V
V
IH
V
IL
NOTE:
1.Does not apply to MAC which can only be tied to Vcc or GND.
2.1.5V undershoots are allowed for 10ns once per cycle.
CC
Commercial Supply 4.5 5.0 5.5 V
Voltage
Input High Voltage 2.0 — — V
Commercial
(1,2)
Input Low Voltage — — 0.8 V
Commercial
IDT72264L
IDT72274L
Commercial
= 15, 20ns
t
CLK
— — 115 mA
NOTES:
1. Measurements with 0.4
2. OE + V
IH
3. Tested at f = 20 MHz with outputs uploaded.
4. No data written or read for more than 10 cycles.
< VIN < V
CC.
CAPACITANCE (TA = +25°C, f = 1.0MHz)
Symbol Parameter
(2)
C
IN
Input VIN = 0V 10 pF
Capacitance
(1,2)
C
OUT
Output VOUT = 0V 10 pF
Capacitance
NOTES:
1. With output deselected, (OE=HIGH).
2. Characterized values, not currently tested.
(1)
Conditions Max. Unit
5
IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
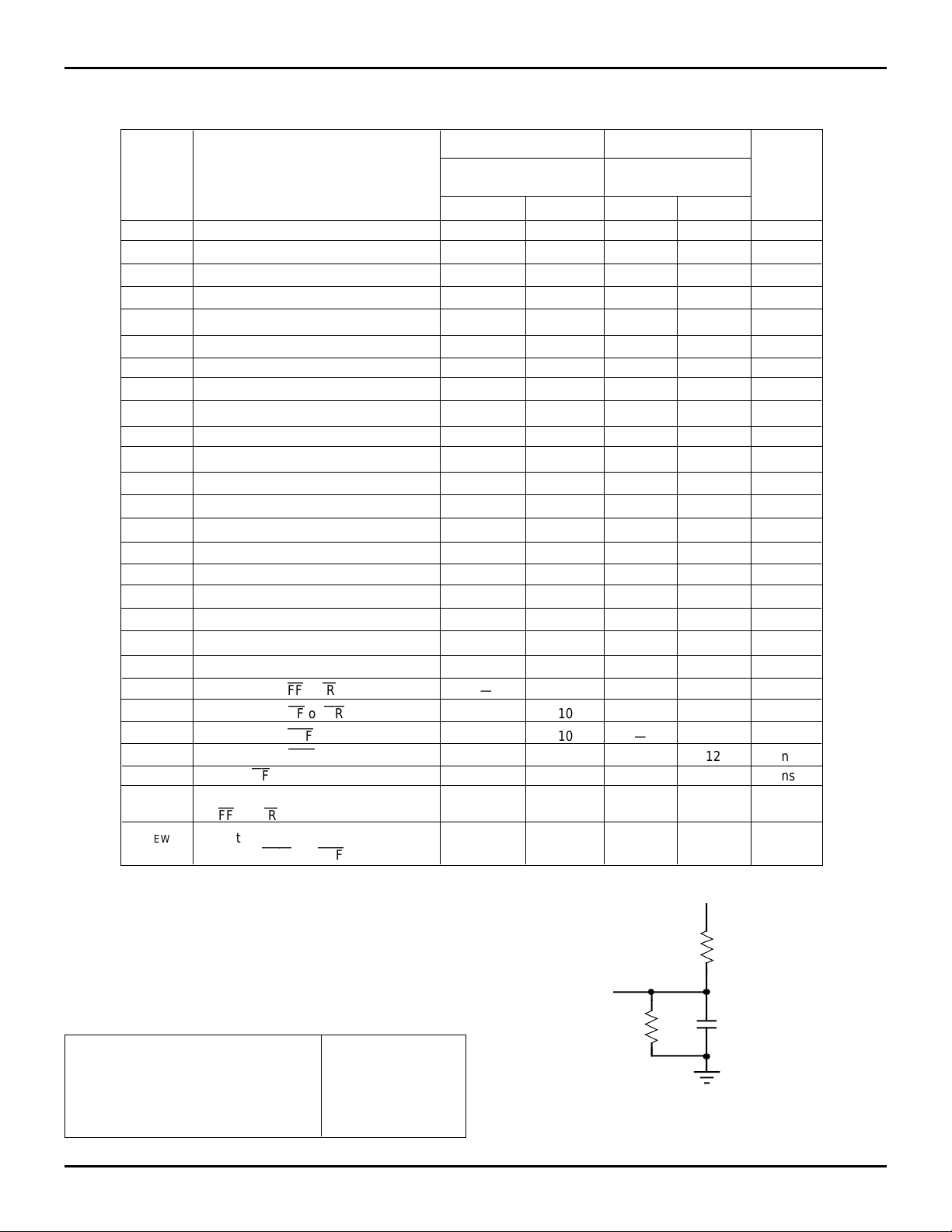
AC ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(1)
(Commercial: VCC = 5V ± 10%, TA = 0°C to +70°C)
Symbol Parameter Min. Max. Min. Max. Unit
f
S Clock Cycle Frequency — 66.7 — 50 MHz
A Data Access Time 2 10 2 12 ns
t
CLK Clock Cycle Time 15 — 20 — ns
t
t
CLKH Clock High Time 6 — 8 — ns
CLKL Clock Low Time 6
t
DS Data Set-up Time 4 — 5 — ns
t
t
DH Data Hold Time 1 — 1 — ns
ENS Enable Set-up Time 4 — 5 — ns
t
ENH Enable Hold Time 1 — 1 — ns
t
t
LDS Load Set-up Time 4 — 5 — ns
LDH Load Hold Time 10 — 10 — ns
t
FF
EF
PAF
PAE
and
or
or
(3)
IR
OR
PAF
RS Reset Pulse Width
t
RSS Reset Set-up Time 15 — 20 — ns
t
t
RSR Reset Recovery Time 15 — 20 — ns
RSF Reset to Flag and Output Time — 15 — 20 ns
t
FWFT Mode Select Time 0 — 0 — ns
t
t
RTS Retransmit Set-Up Time 4 — 5 — ns
OLZ Output Enable to Output in Low Z
t
OE Output Enable to Output Valid 3 8 3 10 ns
t
t
OHZ Output Enable to Output in High Z
WFF Write Clock to
t
REF Read Clock to
t
t
PAF Write Clock to
t
PAE Read Clock to
t
HF Clock to
SKEW1 Skew time between RCLK and WCLK 12 — 15 — ns
t
for FF and
t
SKEW2 Skew time between RCLK and 21 — 25 — ns
WCLK for
HF
IR
PAE
Commercial Commercial
72264L15 72264L20
72274L15 72274L20
(2)
—8—ns
15 — 20 — ns
(4)
(4)
0—0—ns
38310ns
—10—12ns
—10—12ns
—10—12ns
—10—12ns
—20—22ns
NOTES:
1. All AC timings apply to both Standard IDT Mode and First Word Fall
Through Mode.
2. For the RCLK line: t
the programmable flag registers; otherwise, use the table value. For the
WCLK line, use the t
3. Pulse widths less than minimum values are not allowed.
4. Values guaranteed by design, not currently tested.
CLKL (min.) = 7 ns only when reading the offsets from
CLKL (min.) value given in the table.
AC TEST CONDITIONS
Input Pulse Levels GND to 3.0V
Input Rise/Fall Times 3ns
Input Timing Reference Levels 1.5V
Output Reference Levels 1.5V
Output Load See Figure 1
3037 tbl 08
5V
1.1K
D.U.T.
680Ω
Figure 1. Output Load
* Includes jig and scope capacitances.
30pF*
3218 drw 04
6

IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS:
INPUTS:
DATA IN (D
All 18 data inputs (D0 - D17) function when the Memory
Array Configuration input (MAC) is tied to ground. Only 9-data
inputs ( D
other data inputs (D9 - D17) do not function and may either be
tied to ground or left open.
CONTROLS:
MEMORY ARRAY CONFIGURATION (MAC)
The MAC line determines whether the FIFO will operate
with a nine-bit-wide data bus or an 18-bit wide data bus. A
FIFO is configured for 18-bit wide operation has half the
memory depth of the same FIFO configured for 9-bit wide
operation. MAC must be tied to either GND or Vcc. Connecting MAC to Vcc will configure the FIFO's input and output data
buses to be 9 bits wide. In this case, the IDT72264 will have
a 16384x 9 organization, and the IDT72274 will have a 32678
x 9 organization.
Connecting MAC to GND will configure the FIFO's input
and output data buses to be 18 bits wide. In this case, the
IDT72264 will have a 8192 x 18 organization, and the IDT72274
will have a 16384 x 18 organization. MAC must be set before
Master Reset; afterwards, it cannot be dynamically varied.
MASTER RESET (
A Master Reset is accomplished whenever the
is taken to a LOW state. This operation sets the internal read
and write pointers to the first location of the RAM array.
will go LOW,
If FWFT is LOW during Master Reset then the IDT
Standard Mode, along with EF and FF are selected. EF will
go LOW and FF will go HIGH. If FWFT is HIGH, then the First
Word Fall through Mode (FWFT), along with IR and OR, are
selected. OR will go HIGH and IR will go LOW.
If LD is LOW during Master Reset, then
threshold 127 words from the empty boundary and
assigned a threshold 127 words from the full boundary; 127
words corresponds to an offset value of 07FH. Following
Master Reset, parallel loading of the offsets is permitted, but
not serial loading.
If LD is HIGH during Master Reset, then
a threshold 1023 words from the empty boundary and
assigned a threshold 1023 words from the full boundary;
1023 words corresponds to an offset value of 3FFH. Following
Master Reset, serial loading of the offsets is permitted, but not
parallel loading.
Regardless of whether serial or parallel offset loading has
been selected, parallel reading of the registers is always
permitted. (See section describing the LD line for further
details).
During a Master Reset, the output register is initialized to
all zeroes. A Master Reset is required after power up, before
a write operation can take place.
0 - D17)
0 - D8) function when MAC is connected to Vcc. The
MRS
)
MRS
MRS
input
PAE
PAF
will go HIGH, and HF will go HIGH.
PAE
is assigned a
PAF
is
PAE
is assigned
PAF
is
MRS
is asynchronous
PARTIAL RESET (
A Partial Reset is accomplished whenever the
PRS
PRS
)
PRS
input
is taken to a LOW state. As in the case of the Master Reset,
the internal read and write pointers are set to the first location
of the RAM array,
PAE
goes LOW,
PAF
goes HIGH, and
HF
goes HIGH.
Whichever mode is active at the time of partial reset, IDT
Standard Mode or First Word Fall-through, that mode will
remain selected. If the IDT Standard Mode is active, then
FF
will go HIGH and EF will go LOW. If the First word Fall-through
Mode is active, then OR will go HIGH, and IR will go LOW.
Following Partial Reset, all values held in the offset registers remain unchanged. The programming method (parallel
or serial) currently active at the time of Partial Reset is also
retained. The output register is initialized to all zeroes.
PRS
is asynchronous.
A Partial Reset is useful for resetting the device during the
course of operation, when reprogramming flag settings may
not be convenient.
RETRANSMIT (
RTRT)
The Retransmit operation allows data that has already
been read to be accessed again. There are two stages: first,
a setup procedure that resets the read pointer to the first
location of memory, then the actual retransmit, which consists
of reading out the memory contents, starting at the beginning
of memory.
Retransmit Setup is initiated by holding RT LOW during a
rising RCLK edge.
bringing
RT
LOW. At least one word, but no more than Full - 2
REN
and
WEN
must be HIGH before
words should have been written into the FIFO between Reset
(Master or Partial) and the time of Retransmit Setup. (For the
IDT72264, 8,192 when MAC is LOW, 16,384 when MAC is
HIGH; For the IDT72274, Full = 16,384 words when MAC is
LOW, 32,768 when MAC is LOW).
If IDT Standard mode is selected, the FIFO will mark the
beginning of the Retransmit Setup by setting EF LOW. The
change in level will only be noticeable if EF was HIGH before
setup. During this period, the internal read pointer is initialized
to the first location of the RAM array.
When EF goes HIGH, Retransmit Setup is complete and
read operations may begin starting with the first location in
memory. Since IDT Standard Mode is selected, every word
read including the first word following Retransmit Setup requires a LOW on
REN
to enable the rising edge of RCLK.
Writing operations can begin after one of two conditions have
been met: EF is HIGH or 14 cycles of the faster clock (RCLK
or WCLK) have elapsed since the RCLK rising edge enabled
by the RT pulse.
The deassertion time of EF during Retransmit Setup is
variable. The parameter t
RTF1, which is measured from the
rising RCLK edge enabled by RT to the rising edge of EF is
described by the following equation:
t
RTF1 max. = 14*Tf + 3*TRCLK (in ns)
where Tf is either the RCLK or the WCLK period, whichever is
shorter, and TRCLK is the RCLK period.
7

IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
Regarding FF: Note that since no more than Full - 2 writes
are allowed between a Reset and a Retransmit Setup, FF will
remain HIGH throughout the setup procedure.
For IDT Standard mode, updating the
flags begins with the "first"
REN
-enabled rising RCLK edge
following the end of Retransmit Setup (the point at which
PAE, HF
, and
PAF
EF
goes HIGH). This same RCLK rising edge is used to access
the "first" memory location. HF is updated on the first RCLK
rising edge.
PAF
is updated after the "first" rising RCLK edge, followed by
PAE
is updated after two more rising RCLK edges.
the next two rising WCLK edges. (If the tskew2 specification
is not met, add one more WCLK cycle.)
If FWFT mode is selected, the FIFO will mark the beginning
of the Retransmit Setup by setting OR HIGH. The change in
level will only be noticeable if OR was LOW before setup.
During this period, the internal read pointer is set to the first
location of the RAM array.
When OR goes LOW, Retransmit Setup is complete; at the
same time, the contents of the first location are automatically
displayed on the outputs. Since FWFT Mode is selected, the
first word appears on the outputs, no read request necessary.
Reading all subsequent words requires a LOW on
REN
to
enable the rising edge of RCLK. Writing operations can begin
after one of two conditions have been met: OR is LOW or 14
cycles of the faster clock (RCLK or WCLK) have elapsed since
the RCLK rising edge enabled by the RT pulse.
The assertion time of OR during Retransmit Setup is
variable. The parameter t
RTF2, which is measured from the
rising RCLK edge enabled by RT to the falling edge of OR is
described by the following equation:
t
RTF2 max. = 14*Tf + 4*TRCLK (in ns)
where T
f is either the RCLK or the WCLK period, whichever is
shorter, and TRCLK is the RCLK period. Note that a Retransmit
Setup in FWFT mode requires one more RCLK cycle than in
IDT Standard mode.
Regarding IR: Note that since no more than Full - 2 writes
are allowed between a Reset and a Retransmit Setup, IR will
remain LOW throughout the setup procedure.
For FWFT mode, updating the
PAE, HF
, and
PAF
flags
begins with the "last" rising edge of RCLK before the end of
Retransmit Setup. This is the same edge that asserts OR and
automatically accesses the first memory location. Note that,
in this case,
is updated on the "last" RCLK rising edge.
after two more rising RCLK edges.
REN
is not required to initiate flag updating.
PAE
PAF
is updated after the
HF
is updated
"last" rising RCLK edge, followed by the next two rising WCLK
edges. (If the tSKEW2 specification is not met, add one more
WCLK cycle.)
RT
is synchronized to RCLK. The Retransmit operation is
useful in the event of a transmission error on a network, since
it allows a data packet to be resent.
FIRST WORD FALL THROUGH/SERIAL IN (FWFT/SI)
This is a dual purpose pin. During Master Reset, the state
of the FWFT/SI input helps determine whether the device will
operate in IDT Standard mode or First Word Fall Through
(FWFT) mode.
If, at the time of Master Reset, FWFT/SI is LOW, then IDT
Standard mode will be selected. This mode uses the Empty
Flag (EF) to indicate whether or not there are any words
present in the FIFO memory. It also uses the Full Flag function
(FF) to indicate whether or not the FIFO memory has any free
space for writing. In IDT Standard mode, every word read
from the FIFO, including the first, must be requested using the
Read Enable (
REN
) line.
If, at the time of Master Reset, FWFT/SI is HIGH, then
FWFT mode will be selected. This mode uses Output Ready
(OR) to indicate whether or not there is valid data at the data
outputs (Qn). It also uses Input Ready (IR) to indicate whether
or not the FIFO memory has any free space for writing. In the
FWFT mode, the first word written to an empty FIFO goes
directly to Qn, no read request necessary. Subsequent words
must be accessed using the Read Enable (
REN
) line.
After Master Reset, FWFT/SI acts as a serial input for
loading
PAE
and
PAF
offsets into the programmable registers.
The serial input function can only be used when the serial
loading method has been selected during Master Reset.
FWFT/SI functions the same way in both IDT Standard and
FWFT modes.
WRITE CLOCK (WCLK)
A write cycle is initiated on the rising edge of the WCLK
input. Data set-up and hold times must be met with respect to
the LOW-to-HIGH transition of the WCLK. The write and read
clocks can either be asynchronous or coincident.
WRITE ENABLE (
When the
WEN
)
WEN
WEN
input is LOW, data can be loaded into the
input register on the rising edge of every WCLK cycle. Data
is stored in the RAM array sequentially and independently of
any on-going read operation.
When
WEN
is HIGH, the input register holds the previous
data and no new data is loaded into the FIFO.
To prevent data overflow in the IDT Standard Mode, FF will
go LOW , inhibiting further write operations. Upon the completion of a valid read cycle, FF will go HIGH allowing a write to
occur.
WEN
is ignored when the FIFO is full.
To prevent data overflow in the FWFT mode, IR will go
HIGH, inhibiting further write operations. Upon the completion
of a valid read cycle, IR will go LOW allowing a write to occur.
WEN
is ignored when the FIFO is full.
READ CLOCK (RCLK)
Data can be read on the outputs, on the rising edge of the
RCLK input, when Output Enable (OE) is set LOW. The write
and read clocks can be asynchronous or coincident.
READ ENABLE (
REN
REN
)
When Read Enable is LOW, data is loaded from the RAM
array into the output register on the rising edge of the RCLK.
8
IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
When the
REN
input is HIGH, the output register holds the
previous data and no new data is loaded into the output
register.
In the IDT Standard Mode, every word accessed at Q
including the first word written to an empty FIFO, must be
requested using
REN
. When all the data has been read from
the FIFO, the Empty Flag (EF) will go LOW, inhibiting further
read operations.
Once a write is performed, EF will go HIGH after t
REN
is ignored when the FIFO is empty.
FWL1 +tREF
and a read is permitted.
In the FWFT Mode, the first word written to an empty FIFO
automatically goes to the outputs Qn, no need for any read
request. In order to access all other words, a read must be
executed using
REN
. When all the data has been read from
the FIFO, Output Ready (OR) will go HIGH, inhibiting further
read operations.
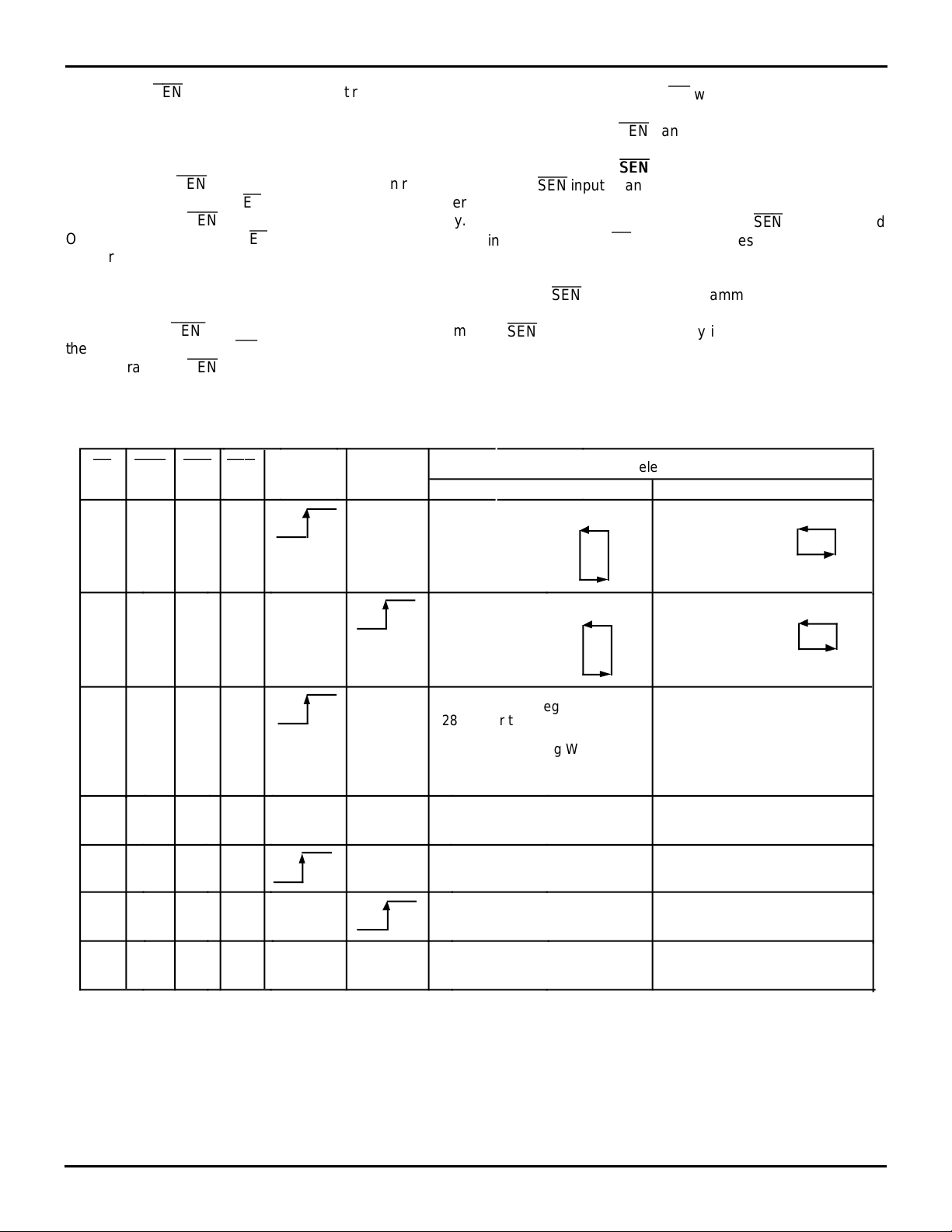
LD
WEN
0
REN
is ignored when the FIFO is empty.
SEN
REN
0
1
1
WCLK RCLK Selection
X Parallel write to registers:
Empty Offset (LSB)
Empty Offset (MSB)
Full Offset (LSB)
Full Offset (MSB)
Once a write is performed, OR will go LOW after tFWL2 +tREF,
when the first word appears at Qn ; if a second word is written
into the FIFO, then
n,
SERIAL ENABLE (
The
SEN
input is an enable used only for serial program-
REN
can be used to read it out.
SEN
)
SEN
ming of the offset registers. The serial programming method
must be selected during Master Reset.
SEN
is always used
in conjunction with LD. When these lines are both LOW, data
at the SI input can be loaded into the input register one bit for
each LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK.
When
SEN
is HIGH, the programmable registers retains
the previous settings and no offsets are loaded.
SEN
functions the same way in both IDT Standard and
FWFT modes.
MAC = Vcc MAC = GND
Parallel write to registers:
Empty Offset
Full Offset
0
0
X
1
1
1
NOTES:
1. Only one of the two offset programming methods, serial or parallel, is available for use at any given time.
2. The programming method can only be selected at Master Reset.
3. Parallel reading of the offset registers is always permitted regardless of which programming method has been selected.
4. The programming sequence applies to both IDT Standard and FWFT modes.
1
1
1
0
X
X
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
X
X
0
X
1
X Parallel read from registers:
X Serial shift into registers:
XX
X
X
XX
Empty Offset (LSB)
Empty Offset (MSB)
Full Offset (LSB)
Full Offset (MSB)
28 bits for the 72264
30 bits for the 72274
1 bit for each rising WCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
No Operation
Write Memory
Read Memory
No Operation
Parallel read from registers:
Empty Offset
Full Offset
Serial shift into registers:
26 bits for the 72264
28 bits for the 72274
1 bit for each rising WCLK edge
Starting with Empty Offset (LSB)
Ending with Full Offset (MSB)
No Operation
Write Memory
Read Memory
No Operation
3218 tbl 01
Figure 2. Partial Flag Programming Sequence
9

IDT72264/72274 VARIABLE WIDTH SUPERSYNC FIFO
(8192 x 18 or 16384 x 9) and (16384 x 18 or 32768 x 9) COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGES
OUTPUT ENABLE (
OEOE)
When Output Enable is enabled (LOW), the parallel output
buffers receive data from the output register. When OE is
HIGH, the output data bus (Q
n) goes into a high impedance
state.
LOAD (
LDLD)
This is a dual purpose pin. During Master Reset, the state
of the LD input determines one of two default values (127 or
1023) for the
PAE
and
PAF
flags, along with the method by
which these flags can be programmed, parallel or serial. After
Master Reset, LD enables write operations to and read
operations from the registers. Only the offset loading method
currently selected can be used to write to the registers. Aside
from Master Reset, there is no other way change the loading
method. Registers can be read only in parallel; this can be
accomplished regardless of whether serial or the parallel
loading has been selected.
Associated with each of the programmable flags,
PAF
, is one register which can either be written to or read from.
PAE
and
Offset values contained in these registers determine how
many words need to be in the FIFO memory to switch a partial
flag. A LOW on LD during Master Reset selects a default
PAE
offset value of 07FH ( a threshold 127 words from the empty
boundary), a default
PAF
offset value of 07FH (a threshold 127
words from the full boundary), and parallel loading of other
offset values. A HIGH on LD during Master Reset selects a
default
the empty boundary), a default
PAE
offset value of 3FFH (a threshold 1023 words from
PAF
offset value of 3FFH (a
threshold 1023 words form the full boundary), and serial
loading of other offset values.
The act of writing offsets (in parallel or serial) employs a
dedicated write offset register pointer. The act of reading
offsets employs a dedicated read offset register pointer. The
two pointers operate independently; however, a read and a
write should not be performed simultaneously to the offset
registers. A Master Reset initializes both pointers to the
Empty Offset (LSB) register. A Partial Reset has no effect on
the position of these pointers.
It is important to note that the MAC setting configures the
offset register architecture to suit the memory array dimensions being selected. Therefore, the way offsets are programmed will vary according to whether MAS is tied to Vcc or
GND.
Consider the case where serial offset loading has been
selected. If MAC = GND (18-bit operation), then programming
PAE
and
PAF
proceeds as follows: When LD and
SEN
are set
LOW, data on the SI input are written, one bit for each WCLK
rising edge, starting with the Empty Offset (13 bits for the
72264, 14 bits for the 72274) and ending with the Full Offset
(13 bits for the 72264, 14 bits for the 72274). A total of 26 bits
are necessary to program the 72264; a total of 28 bits are
necessary to program the 72274.
If serial offset loading has been selected and MAC = Vcc
(9-bit operation), then programming
as follows: When LD and
SEN
PAE
and
PAF
proceeds
are set LOW, data on the SI
input are written, one bit for each WCLK rising edge, starting
with the Empty Offset LSB (8 bits for both the 72264 and
72274), then the Empty Offset MSB (6 bits for the 72264, 7 bits
for the 72274) , then the Full Offset LSB (8 bits for both the
72264 and 72274), ending with the Full Offset MSB (6 bits for
the 72264, 7 bits for the 72274). A total of 28 bits are
necessary to program the 72264; a total of 30 bits are
necessary to program the 72274.
For either MAC setting, individual registers cannot be
loaded serially; rather, all offsets must be programmed in
sequence, no padding allowed.
PAE
and
PAF
can show a
valid status only after the full set of bits have been entered.
The registers can be re-programmed as long as all offsets are
loaded. When LD is LOW and
SEN
is HIGH, no serial write to
the registers can occur.
Consider the case where parallel offset loading has been
selected. If MAC = GND (18-bit operation), then programming
PAE
and
PAF
proceeds as follows: When LD and
WEN
are
set LOW, data on the inputs Dn are written into the Empty
Offset Register on the first LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK.
Upon the second LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK, data at
the inputs are written into the Full Register. The third transition
of WCLK writes, once again, to the Empty Offset Register.
If parallel offset loading has been selected and MAC = Vcc
(9-bit operation), then programming
as follows: When LD and
inputs D
n are written into the LSB Empty Offset Register on the
WEN
PAE
and
PAF
proceeds
are set LOW, data on the
first LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK. Upon the second
LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK, data at the inputs are
written into the MSB Empty Offset Register. Upon the third
LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK, data at the inputs are
written into the LSB Full Offset Register. Upon the fourth
LOW-to-HIGH transition of WCLK, data at the inputs are
written into the MSB Full Offset Register. The fifth transition of
WCLK writes, once again, to the LSB Empty Offset Register.
To ensure proper programming (serial or parallel) of the
offset registers, no read operation is permitted from the time
of reset (master or partial) to the time of programming. (During
this period, the read pointer must be pointing to the first
location of the memory array.) After the programming has
been accomplished, read operations may begin.
Write operations to memory are allowed before and during
the parallel programming sequence. In this case, the programming of all offset registers does not have to occur at one
time. One or two offset registers can be written to and then,
by bringing LD HIGH, write operations can be redirected to the
FIFO memory. When LD is set LOW again, and
WEN
is LOW,
the next offset register in sequence is written to. As an
alternative to holding
WEN
LOW and toggling LD, parallel
programming can also be interrupted by setting LD LOW and
toggling
WEN
.
Write operations to memory are allowed before and during
the serial programming sequence. In this case, the programming of all offset bits does not have to occur at once. A select
number of bits can be written to the SI input and then, by
bringing LD and
memory via D
with LD and
SEN
HIGH, data can be written to FIFO
n by toggling
SEN
restored to a LOW, the next offset bit in
WEN
. When
WEN
is brought HIGH
sequence is written to the registers via SI. If a mere interruption of serial programming is desired, it is sufficient either to set
10
 Loading...
Loading...