Integrated Device Technology Inc IDT71F432S75, IDT71F432L66, IDT71F432L75 Datasheet
Integrated Device Technology, Inc.
COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE DECEMBER 1996
©1996 Integrated Device Technology, Inc. DSC-3555/3
13.1 1
fundamentally compatible with standard PBSRAM, with additional features to accommodate the internal DRAM operation
of the memory. These additional features are defined so that
71F432 compatible system controllers and properly implemented PC boards can work transparently with either the
71F432 or PBSRAM in cache memory applications.
Six pins, identified as No Connect (NC) on the standard
PBSRAM specifications, are used to support 71F432 operation. These pins are 5V supply (2), host bus W/R#, RESET#
and two proprietary functions labeled F0 and F1. When using
standard PBSRAM, these pins have no effect and the associated functions in the 71F432-compatible chipset are not
activated.
The 71F432 supports PBSRAM operating modes, including burst read (3-1-1-1), burst write (3-1-1-1) and pipelined
burst read or write (3-1-1-1-1-1...). As with all DRAM devices,
refresh is required. The memory is not accessible during the
refresh interval. Refresh occupies 0.5% of the clock cycles,
resulting in a system performance reduction of less than 0.1%.
DESCRIPTION:
The IDT71F432 MCache is a high-performance, low-power
replacement for standard 32K x 32 pipelined burst SRAM
(PBSRAM) in cache applications. The 71F432 is built using
IDT's Fusion Memory technology, which combines the performance of SRAM with the cost structure of DRAM. It is
How does the performance of Fusion Memory cache RAMs
compare with synchronous burst SRAMS?
• The Fusion Memory devices equal the performance of the
SRAMs they are designed to replace.
Are Fusion Memory and PBSRAMs interchangeable?
• A system designed to use the Fusion Memory cache RAMs
can use standard PBSRAMs instead.
What is the difference between MoSys MCache™ and IDT’s
Fusion Memory?
• MCache is MoSys’ trademark for their cache memory
devices. Fusion Memory is IDT’s trademark for the underlying technology. IDT will use the technology in other
products besides cache RAMs. The IDT71F432 and
MoSys' MCache devices are interchangeable.
ABOUT IDT'S Fusion Memory TECHNOLOGY:
What is Fusion Memory?
• Fusion Memory is a new kind of memory technology that
combines the high performance and ease-of-use of SRAM
with the manufacturing costs of DRAM.
Why are Fusion Memory chips so much smaller than SRAM?
• Traditional SRAM uses four or six transistors to make each
memory cell. Fusion Memory uses only one transistor for
each memory cell, so the memory array itself is only about
1/4 the size of an SRAM.
Is Fusion Memory the same as Dynamic Memory?
• Not exactly. While both Fusion Memory and DRAMs use
single-transistor dynamic cells for storage, Fusion Memories use much different designs for all the surrounding
circuitry, such as address drivers, sense amps, and control
circuitry. This gives Fusion Memory a performance level
that is much higher than DRAM.
If Fusion Memory uses dynamic storage, are there refresh
cycles?
• Yes, but the refresh control is handled automatically and
nearly invisibly, using either on-chip circuitry or circuitry in
the chip set used with the memory device. The performance penalty is typically less than 0.1%.
Cost
Performance
Fusion
Memory
DRAM
SRAM
FEATURES:
• Uses IDT's Fusion Memory technology
• 66 and 75 MHz speed grades
• 3-1-1-1 Pipelined Burst Read
• 3-1-1-1 Pipelined Burst Write
• 3-1-1-1-1-1-1-1... extended pipelined operation
• Refresh overhead consumes less than 0.5% of cycles
• Pinout is superset of industry standard PBSRAM
• Interchangeable with PBSRAM in new designs
• Compatible with MoSys MCache™ devices
• Low operating and standby power consumption
1/3 the power of standard PBSRAM
• Packaged in a JEDEC Standard 100-pin rectangular plastic
thin quad flatpack (TQFP)
The IDT logo is a registered trademark and Fusion Memory and CacheRAM are trademarks of Integrated Device Technology
Pentium is a trademark of Intel Corp.
MCache is a trademark of MoSys, Inc.
Fusion Memory™ Provides SRAM Performance at DRAM Cost
32K x 32 MCache
SYNCHRONOUS PIPELINED
CACHE RAM
IDT71F432
IDT71F432 32Kx32 MCache SYNCHRONOUS PIPELINED CACHE RAM COMMERCIAL TEMPERATURE RANGE
13.1 2
PIN DESCRIPTION SUMMARY
SYMBOL DESCRIPTION TYPE PIN NUMBER
A14 – A0 Address Inputs Input 48, 47, 46, 45, 44, 81, 82, 99,
100, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37
CE# Chip Enable Input 98
CS0, CS1# Chip Selects Input 97, 92
OE# Output Enable Input 86
GW# Global Write Enable Input 88
BWE# Byte Write Enable Input 87
BW1#, BW2#, BW3#, BW4# Individual Byte Write Selects Input 93, 94, 95, 96
CLK Clock Input 89
ADV# Burst Address Advance Input 83
ADSC# Address Status (Cache Controller) Input 85
ADSP# Address Status (Processor) Input 84
I/O31-I/O0 Data Input/Output I/O 29, 28, 25, 24, 23, 22, 19, 18, 13, 12,
9, 8, 7, 6, 3, 2, 79, 78, 75, 74, 73, 72,
69, 68, 63, 62, 59, 58, 57, 56, 53, 52
NC Reserved for LBO# (burst order) NC 31
NC Reserved for ZZ (sleep) NC 64
RESET# Host Bus Reset Signal Input 38
W/R# Host Bus W/R# Input 39
F0 Function 0 Special 43
F1 Function 1 Special 42
VDD5 5V Power Pwr 16, 66
VDD 3.3V Power Pwr 4, 11, 15, 20, 27, 41, 54, 61, 65, 70, 77, 91
VSS Ground Gnd 5, 10, 17, 21, 26, 40, 55, 60, 67, 71, 76, 77
3555 tbl 01
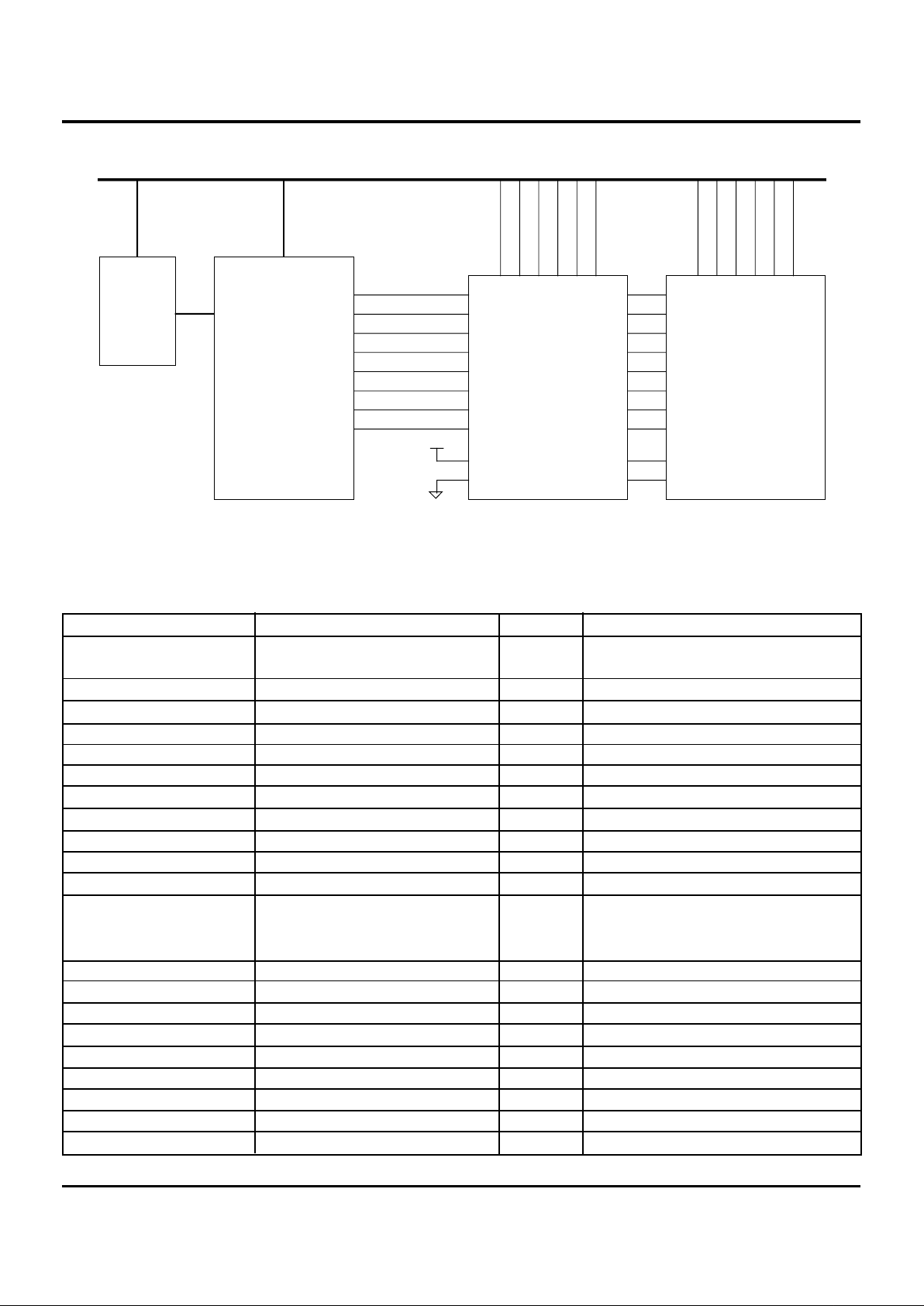
256KB CACHE BLOCK DIAGRAM
CLK
ADSC#
OE#
ADV#
CS0
CS1#
CE#
GW#
F0, F1
BWE#
CPU A[17:3]
CPU D[31:0]
CPU W/R#
RESET#
CPU ADS#
CPU A[17:3]
CPU D[63:32]
CPU W/R#
RESET#
CPU ADS#
BE#[4:1]
BE#[8:5]
CHIPSET
CACHE
CONTROLLER
TAG
SRAM
IDT71F432
32Kx32
IDT71F432
32Kx32
PROCESSOR BUS
 Loading...
Loading...