Page 1

FC9Y-B1283
FC5A
SERIES
PID Module
User’s Manual
Page 2

Warning notices are used to emphasize that improper operation may
cause severe personal injury or death.
Caution notices are used where inattention might cause personal injury
or damage to equipment.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
• Read this user’s manual to make sure of correct operation before starting installation, wiring, operation,
maintenance, and inspection of the FC5A series MicroSmart PID modules.
• All MicroSmart modules are manufactured under IDEC’s rigorous quality control system, but users must add a
backup or failsafe provision to the control system using the MicroSmart in applications where heavy damage or
personal injury may be caused in case the MicroSmart should fail.
• In this user’s manual, safety precautions are categorized in order of importance from Warning to Caution.
Warning
• Turn off the power to the MicroSmart before starting installation, removal, wiring, maintenance, and inspection of
the MicroSmart. Failure to turn power off may cause electrical shocks or fire hazard.
• Special expertise is required to install, wire, program, and operate the MicroSmart. People without such expertise
must not use the MicroSmart.
• Emergency stop and interlocking circuits must be configured outside the MicroSmart. If such a circuit is
configured inside the MicroSmart, failure of the MicroSmart may cause a malfunction of the control system,
damage, or accidents.
• Install the MicroSmart according to the instructions described in this user’s manual. Improper installation will
result in disattachment, failure, or malfunction of the MicroSmart.
Caution
• The MicroSmart is designed for installation in a cabinet. Do not install the MicroSmart outside a cabinet.
• Install the MicroSmart in environments described in this user’s manual. If the MicroSmart is used in places where
the MicroSmart is subjected to high-temperature, high-humidity, condensation, corrosive gases, excessive
vibrations, and excessive shocks, then electrical shocks, fire hazard, or malfunction will result.
• The environment for using the MicroSmart is “Pollution degree 2.” Use the MicroSmart in environments of pollution
degree 2 (according to IEC 60664-1).
• Prevent the MicroSmart from being dropped while moving or transporting the MicroSmart, otherwise damage or
malfunction of the MicroSmart will result.
• Prevent metal fragments and pieces of wire from dropping inside the MicroSmart housing. Put a cover on the
MicroSmart modules during installation and wiring. Ingress of such fragments and chips may cause fire hazard,
damage, or malfunction.
• Use a power supply matching the rated value. Use of an incorrect power supply may cause fire hazard.
• Use an IEC 60127-approved fuse on the power line outside the MicroSmart. This is required when equipment
containing the MicroSmart is destined for Europe.
• Use an IEC 60127-approved fuse on the output circuit. This is required when equipment containing the
MicroSmart is destined for Europe.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 i
Page 3

• Use an EU-approved circuit breaker. This is required when equipment containing the MicroSmart is destined for
Europe.
• Make sure of safety before starting and stopping the MicroSmart or when operating the MicroSmart to force
outputs on or off. Incorrect operation on the MicroSmart may cause machine damage or accidents.
• If relays or transistors in the MicroSmart output modules should fail, outputs may remain on or off. For output signals
which may cause serious accidents, provide a monitor circuit outside the MicroSmart.
• Do not connect the ground wire directly to the MicroSmart. Connect a protective ground to the cabinet containing
the MicroSmart using an M4 or larger screw. This is required when equipment containing the MicroSmart is
destined for Europe.
• Do not disassemble, repair, or modify the MicroSmart modules.
• When disposing of the
MicroSmart
, do so as an industrial waste.
ii FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 4

NOTICE
1. This publication is not to be, nor any parts of it, photocopied, reprinted, sold, transferred, or rented out without
the specific written permission and consent of IDEC.
2. The contents of this user’s manual are subject to change without notice.
3. Care has been taken to ensure that the contents of this user’s manual are correct, but if there are any doubts,
mistakes or questions, please inquire our sales department.
Category
Modules
MicroSmart
(FC5A Series MicroSmart)
FC5A series MicroSmart pentra
FC5 Series
CPU Modules
All-in-One Type
FC5A-C10R2, FC5A-C10R2C, FC5A-C16R2, FC5A-C16R2C,
FC5A-C24R2, FC5A-C24R2C
Slim Type
FC5A-D16RK1, FC5A-D16RS1, FC5A-D32K3, FC5A-D32S3,
FC5A-D12K1E, FC5A-D12S1E
PID Modules
FC5A-F2MR2, FC5A-F2M2
Expansion Communication Modules
FC5A-SIF2, FC5A-SIF4
Memory Cartridge
FC4A-PM32, FC4A-PM64, FC4A-PM128
Expansion Modules
Expansion I/O module, Function module
Expansion I/O Modules
Input modules, Output modules, Mixed I/O modules
Function Modules
Analog modules, AS-Interface master module, PID module
Communication Expansion Modules
HMI base module, expansion RS232C communication module,
expansion RS485 communication module
Optional Modules
HMI module, Memory cartridge, Clock cartridge, RS232C communication
adapter, RS485 communication adapter
WindLDR
Application software [WindLDR]
IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Under no circumstances shall IDEC Corporation be held liable or responsible for indirect or consequential damages resulting
from the use of or the application of IDEC PLC components, individually or in combination with other equipment.
All persons using these components must be willing to accept responsibility for choosing the correct component to suit their
application and for choosing an application appropriate for the component, individually or in combination with other
equipment.
All diagrams and examples in this user’s manual are for illustrative purposes only. In no way does including these diagrams
and examples in this manual constitute a guarantee as to their suitability for any specific application. To test and approve all
programs, prior to installation, is the responsibility of the end user.
The PID modules is used by connecting to the FC5A series CPU module.
Use this product after thoroughly understanding the specifications of the FC5A
series CPU module.
ABOUT THIS MANUAL
Thank you for purchasing FC5A series MicroSmart PID Module. This user’s manual primarily describes system
configuration, specifications, installation, programming, application examples, and trouble shooting of the PID
module. Read this user’s manual to ensure the correct understanding of the entire functions of the PID module.
MicroSmart Modules
Caution
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 iii
Page 5

REVISION HISTORY
Date
Manual No.
Description
March, 2011
FC9Y-B1283-0
First print
Revision history of this user’s manual is described here.
iv FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 6

Type No.
Manual Name
Description
FC9Y‐B1283
FC5A Series
PID Module
User's Manual
(this manual)
Describes PID Module specifications and functions.
FC9Y‐B1268
FC5A Series
MicroSmart Pentra
User's Manual
Basic Volume
Describes module specifications, installation instructions, wiring instructions,
basic operation, special function, device addresses, instruction list, basic
instructions, analog modules, user communication, data link communication,
Modbus ASCII/RTU communication, and troubleshooting.
FC9Y‐B1273
FC5A Series
MicroSmart Pentra
User's Manual
Advanced Volume
Describes instruction list, move instructions, data comparison instructions,
binary arithmetic instructions, boolean computation instructions, shift/rotate
instructions, data conversion instructions, week programmer instructions,
interface instructions, program branching instructions, refresh instructions,
interrupt control instructions, coordinate conversion instructions, average
instructions, pulse output instructions, PID instructions, dual/teaching timer
instructions, intelligent module access instructions, trigonometric function
instructions, logarithm/power instructions, file data processing instructions, clock
instructions, computer link communication, modem communication, Modbus
TCP communication, expansion RS232C/RS485 communication modules, and
AS‐Interface master modules.
FC9Y‐B1278
FC5A Series
MicroSmart Pentra
User's Manual
Web Server CPU
Module Volume
Describes FC5A Slim Type Web Server CPU Module specifications and
functions.
RELATED MANUALS
The following manuals related to the FC5A series MicroSmart are available. Refer to them in conjunction with this
manual.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 v
Page 7

vi FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 8

TABLE OF CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1: GENERAL INFORMATION ...................................................................................... 1-1
About the PID Modules .................................................................................................................................... 1-1
Quantity of Applicable PID modules ................................................................................................................ 1-1
Applicable CPU and WindLDR version ........................................................................................................... 1-2
Confirming System Program Version .............................................................................................................. 1-2
CHAPTER 2: MODULE SPECIFICATIONS ................................................................................... 2-1
PID Module ...................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
Specifications ................................................................................................................................................... 2-3
Dimensions ...................................................................................................................................................... 2-6
CHAPTER 3: INSTALLATION AND WIRING ................................................................................. 3-1
Mounting Hole Layout for Direct Mounting on Panel Surface ......................................................................... 3-1
Terminal Connection ........................................................................................................................................ 3-3
Terminal Arrangement ..................................................................................................................................... 3-4
Type of Protection ............................................................................................................................................ 3-5
Power Supply for PID Modules ....................................................................................................................... 3-6
CHAPTER 4: PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS .......................................................................... 4-1
Temperature Control Using the PID Module .................................................................................................... 4-1
Fixed Value Control ......................................................................................................................................... 4-3
Auto-Tuning (AT)/Auto-Reset .......................................................................................................................... 4-6
Program Control .............................................................................................................................................. 4-9
Heating/Cooling Control ................................................................................................................................ 4-14
Difference Input Control ................................................................................................................................. 4-14
Cascade Control ............................................................................................................................................ 4-15
CHAPTER 5: DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE ................................................................ 5-1
Device Allocation of PID Module ..................................................................................................................... 5-1
Program Size ................................................................................................................................................... 5-2
Valid Devices ................................................................................................................................................... 5-2
Control Register ............................................................................................................................................... 5-2
Control Relay ................................................................................................................................................... 5-3
Data Register Allocation - Block 0 Read Only Parameters ............................................................................. 5-7
Data Register Allocation - Block 1 Write Only Parameters............................................................................ 5-10
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 2, 3 Basic Parameters (SHOT Action) ..................................................... 5-17
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 4, 5 Initial Setting Parameters (SHOT Action) ......................................... 5-19
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 10-19 CH0 Program Parameters (SHOT Action) ..................................... 5-22
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 30-39 CH1 Program Parameters (SHOT Action) ..................................... 5-24
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 vii
Page 9

CHAPTER 6: CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR .................................................... 6-1
Procedure to configure the PID module .......................................................................................................... 6-1
Expansion Modules Configuration Dialog Box ................................................................................................ 6-6
PID Module Configuration Dialog Box ............................................................................................................. 6-7
PID Module Configuration - Input Parameters List (CH0 and CH1) ................................................................ 6-8
PID Module Configuration - Control Parameters List (CH0 and CH1) .......................................................... 6-13
PID Module Configuration - Output Parameters List (CH0 and CH1) ........................................................... 6-17
PID Module Configuration - Program Parameters List (CH0 and CH1) ........................................................ 6-19
PID Module Configuration - I/O Function Selections ..................................................................................... 6-21
PID Module Configuration - Input Parameters Details .................................................................................. 6-24
PID Module Configuration - Control Parameters Details ............................................................................... 6-34
PID Module Configuration - Output Parameters Details ............................................................................... 6-45
PID Module Configuration - Program Parameters Details ............................................................................ 6-47
Monitoring PID Module .................................................................................................................................. 6-52
CHAPTER 7: APPLICATION EXAMPLES ..................................................................................... 7-1
Application Example 1 ..................................................................................................................................... 7-1
Application Example 2 ..................................................................................................................................... 7-8
Application Example 3 ................................................................................................................................... 7-15
CHAPTER 8: TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................ 8-1
The PID Module Power LED (PWR) is OFF or Flashing. ................................................................................ 8-1
The PID Module output does not operate normally. ........................................................................................ 8-2
Hunting phenomenon is occurring while in ON/OFF control action ................................................................ 8-3
Hunting phenomenon is occurring while in PID, PI, PD, or P control action ................................................... 8-3
The PID Module input does not operate normally. .......................................................................................... 8-4
Loop break alarm turns on even though the actuator operates normally. ....................................................... 8-6
Program control is terminated earlier than the configured time. ..................................................................... 8-6
CHAPTER 9: APPENDIX ........................................................................................................... 9-1
PID Module Function References ................................................................................................................... 9-1
Output Action ................................................................................................................................................... 9-5
Factory Default Settings of the PID Module .................................................................................................... 9-9
viii FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 10

GENERAL INFORMATION
Module Type
I/O Points
I/O Signal
Type No.
Relay Output
2 inputs
Thermocouple [K, J, R, S, B, E, T, N, PL- II, C (W/Re5-26)]
Resistance thermometer (Pt100, JPt100)
Voltage (0 to 1V DC, 0 to 5V DC, 1 to 5V DC, 0 to 10V DC)
Current (0 to 20mA DC, 4 to 20mA DC)
FC5A-F2MR2
2 outputs
Relay contact
Non-Contact Voltage
(for SSR drive)/
Current Output
2 inputs
Thermocouple [K, J, R, S, B, E, T, N, PL- II, C (W/Re5-26)]
Resistance thermometer (Pt100, JPt100)
Voltage (0 to 1V DC, 0 to 5V DC, 1 to 5V DC, 0 to 10V DC)
Current (0 to 20mA DC, 4 to 20mA DC)
FC5A-F2M2
2 outputs
Non-contact voltage(for SSR drive)/Current
Type
All-in-One Type
Slim Type
FC5A MicroSmart CPU
FC5A-C10R2
FC5A-C10R2C
FC5A-C10R2D
FC5A-C16R2
FC5A-C16R2C
FC5A-C16R2D
FC5A-C24R2D
FC5A-C24R2
FC5A-C24R2C
FC5A-D16RK1
FC5A-D16RS1
FC5A-D32K3
FC5A-D32S3
FC5A-D12K1E
FC5A-D12S1E
Number of PID Modules
4
7
1: GENERAL INFORMATION
This chapter describes general information and specifications of the FC5A series PID modules. Make effective
use of the PID modules after reading and understanding thoroughly functions and characteristics.
About the PID Modules
The PID module performs control actions to eliminate the deviation between the set point (SP) and process
variable (PV). The PID module, which is an expansion module, is required to connect to the FC5A series CPU
for use. Depending on the difference of output specifications, the PID modules are categorized into two types,
and can be used by connecting to a FC5A slim type CPU, or 24-I/O all-in-one type CPU (except 12V DC CPU).
The input channel can accept voltage, current, thermocouple or resistance thermometer signals. The output
channel generates relay output, non-contact voltage (for SSR drive), or current signals.
To configure the PID modules, the Expansion Modules Configuration dialog box in WindLDR is used.
The following table shows the PID module type numbers.
PID Module Type Numbers
Quantity of Applicable PID modules
The maximum number of PID modules that can be connected to the MicroSmart CPU differs depending on the
CPU type. The following table shows the maximum number of the PID modules.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 1-1
Page 11
GENERAL INFORMATION
Type
All-in-One Type
Slim Type
FC5A MicroSmart CPU
FC5A-C10R2
FC5A-C10R2C
FC5A-C10R2D
FC5A-C16R2
FC5A-C16R2C
FC5A-C16R2D
FC5A-C24R2D
FC5A-C24R2
FC5A-C24R2C
FC5A-D16RK1
FC5A-D16RS1
FC5A-D32K3
FC5A-D32S3
FC5A-D12K1E
FC5A-D12S1E
CPU System Program Version
230 or higher *1
WindLDR Version
6.40 or higher
Applicable CPU and WindLDR version
PID modules can be used with the following FC5A CPU module system program version and WindLDR version
as listed below.
*1: The PID module can be used with FC5A-D12K1E/-S1E with the system program version 100 or higher.
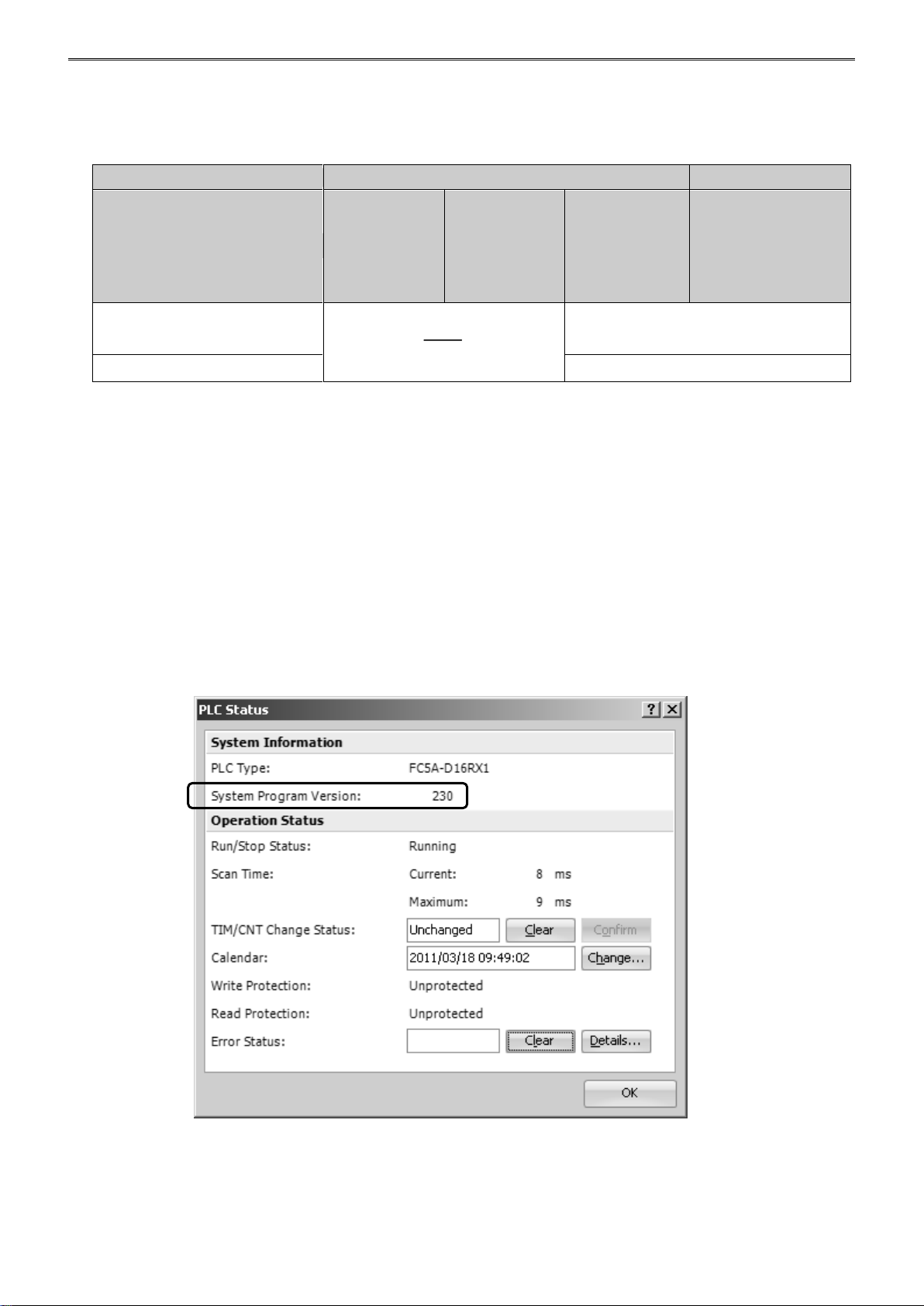
Confirming System Program Version
The system program version can be confirmed using WindLDR.
1. Connect a PC to port 1 or 2 of the FC5A CPU using serial computer link cable I/F (FC2A-KC4C) or USB
cable HG9Z-XCM2A for FC5A-D12x1E CPU.
2. From the WindLDR menu bar, select Online > Monitor.
3. From the WindLDR menu bar, select PLC > Status. The PLC Status dialog box appears and system
program version is shown.
1-2 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 12
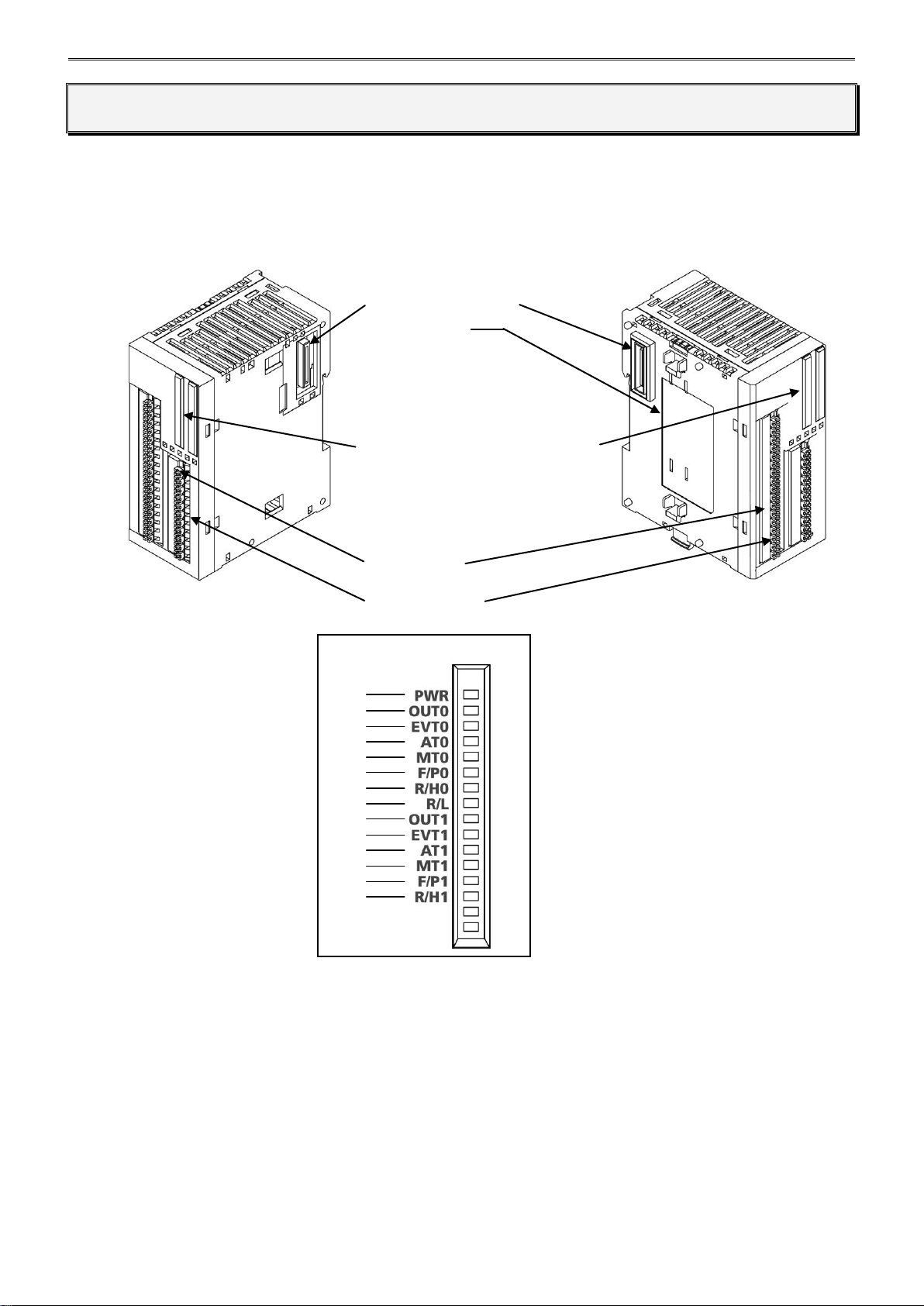
MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
(12) Expansion Connector
(1) Module Label
(2) Power LED (PWR)
(3) Control Output LED (OUT0, OUT1)
(4) Event Output LED (EVT0, EVT1)
(5) Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset LED (AT0, AT1)
(6) Manual Mode LED (MT0, MT1)
(7) Fixed Value Control Mode/Program
Control Mode LED (F/P0, F/P1)
(8) Program Control RUN/HOLD LED
(R/H0, R/H1)
(9) External SP Enable/Disable LED (R/L)
(10) Terminal No.
(11) Cable Terminal
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
2: MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
This chapter describes parts names, functions, specifications, and dimensions of the PID modules.
PID Module
Parts Description
(1) Module Label Indicates the PID module type No. and specifications.
(2) Power LED (PWR) ON : Power is normally supplied.
Flashes : External power supply (24V DC) error.
OFF : Power is not supplied.
LED Details
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 2-1
Page 13

MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
(3) Control Output LED (OUT0, OUT1)
ON : Control output is turned on.
OFF : Control output is turned off.
Flashes : When current output is used, the LED flashes in a cycle of 125 ms
according to the duty ratio of the output manipulated variable (MV).
When output manipulated variable (MV) is 20%, the LED turns on for
25 ms and off for 100 ms continuously.
(4) Event Output LED (EVT0, EVT1)
ON : Any alarm out of alarm 1 to alarm 8, loop break alarm is triggered.
OFF : None of the alarms is triggered.
(5) Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset LED (AT0, AT1)
Flashes : Auto-tuning (AT) or auto-reset is performing.
OFF : Auto-tuning (AT) or auto-reset is stopped.
(6) Manual Mode LED (MT0, MT1)
ON : Manual mode
OFF : Auto mode
(7) Fixed Value Control Mode/Program Control Mode LED (F/P0, F/P1)
ON : Program control mode
OFF : Fixed value control mode
(8) Program Control RUN/HOLD LED (R/H0, R/H1)
ON : Program control is performing, or while in fixed value control enabled.
Flashes : Program control is held, or power is restored.
OFF : Program control is stopped, or while in fixed value control disabled.
(9) External SP Enable/Disable LED (R/L)
ON : External SP input is enabled.
OFF : External SP input is disabled.
(10) Terminal No. Indicates terminal numbers.
(11) Cable Terminal Spring clamp type terminal for connecting a cable.
(12) Expansion Connector Connects to the CPU module and other expansion modules.
2-2 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 14

Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Rated Scale
Thermocouple
Type
Measurement Range
Input Value
of LSB
K
-200 to 1370°C
-328 to 2498°F
1°C (°F)
K (with decimal point)
-200.0 to 400.0°C
-328.0 to 752.0°F
0.1°C (°F)
J
-200 to 1000°C
-328 to 1832°F
1°C (°F)
R
0 to 1760°C
32 to 3200°F
1°C (°F)
S
0 to 1760°C
32 to 3200°F
1°C (°F)
B
0 to 1820°C
32 to 3308°F
1°C (°F)
E
-200 to 800°C
-328 to 1472°F
1°C (°F)
T
-200.0 to 400.0°C
-328.0 to 752.0°F
0.1°C (°F)
N
-200 to 1300°C
-328 to 2372°F
1°C (°F)
PL-II
0 to 1390°C
32 to 2534°F
1°C (°F)
C(W/Re5-26)
0 to 2315°C
32 to 4199°F
1°C (°F)
Resistance Thermometer
Type
Measurement Range
Input Value
of LSB
Pt100
-200 to 850°C
-328 to 1562°F
1°C (°F)
Pt100 (with decimal point)
-200.0 to 850.0°C
-328.0 to 1562.0°F
0.1°C (°F)
JPt100
-200 to 500°C
-328 to 932°F
1°C (°F)
JPt100(with decimal point)
-200.0 to 500.0°C
-328.0 to 932.0°F
0.1°C (°F)
Current/Voltage
Type
Measurement Range
Input Value
of LSB
4 to 20mA DC
-2000 to 10000 (12000 increments) *1
1.333μ
0 to 20mA C
-2000 to 10000 (12000 increments) *1
1.666μA
0 to 1V DC
-2000 to 10000 (12000 increments) *1
0.083mA
0 to 5V DC
-2000to 10000 (12000 increments) *1
0.416mA
1 to 5V DC
-2000 to 1000 (12000increments)
*1
0.333mA
0 to 10V DC
-2000 to 10000 (12000 increments) *1
0.833mA
*1: Linear conversion possible
Input
Input type
Thermocouple
K, J, R, S, B, E, T, N, PL-II, C (W/Re5-26)
External resistance: 100Ω maximum
However, B input, External resistance: 40Ω
maximum
Resistance
Thermometer
Pt100, JPt100, 3-wire type
Allowable conductor resistance (per wire):
10Ω maximum
Sensor (detection) current: 0.2A
Current
0 to 20mA DC, 4 to 20mA DC
Input impedance: 50Ω
Maximum permanent allowed overload (No
damage): 50mA maximum
Voltage
0 to 1V DC
Input impedance: 1MΩ minimum
Maximum permanent allowed overload (No
damage): 5V DC maximum
Allowable output impedance: 2kΩ maximum
0 to 5V DC, 1 to 5V DC, 0 to 10V DC
Input impedance: 100kΩ minimum
Maximum permanent allowed overload (No
damage): 15V DC maximum
Allowable output impedance: 100Ω maximum
Power Supply Voltage
24V DC (External power), 5V DC (Internal power)
Allowable Voltage Range
20.4 to 28.8V DC
Specifications
PID Module Specifications
Rating
MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 2-3
Page 15

MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Connector
Connector on
MotherBoard
Input : F6018-17P (Fujicon)
Output : F6018-11P (Fujicon)
Connector
Insertion/Removal
Durability
Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Maximum Error at 25°C
Thermocouple
±0.2% of full scale or ±2°C (4°F),
whichever is greater
However, R, S inputs, 0 to 200°C (0 to 400°F):
±6°C (12°F)
B input, 0 to 300°C (0 to 600°F): Accuracy is
not guaranteed.
K, J, E, T, N inputs, Less than 0°C (32°F):
±0.4% of full scale
Resistance
Thermometer
±0.1% of full scale or ±1°C (2°F), whichever is
greater
Voltage, Current
±0.2% of full scale
Input Accuracy (at 0 to 55°C)
Thermocouple
±0.7% of full scale
However, R, S input, 0 to 200°C (0 to 400°F):
±6°C (12°F)
B input, 0 to 300°C (0 to 600°F): Accuracy is
not guaranteed.
K, J, E, T, N inputs, Less than 0°C (32°F):
±0.9% of full scale
Resistance
Thermometer
±0.6% of full scale
Voltage, Current
±0.7% of full scale
Data Accuracy
Maximum error at 25°C±Minimum digital resolution of each input range
Cold Junction Temperature
Compensation Accuracy
±1°C at 0 to 55°C
Sampling Period
125 ms
Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Control Output
Relay output 1a
Rated load:
5A 250V AC (resistive load)
5A 30V DC (resistive load)
3A 250V AC (inductive load
cosφ=0.4)
Non-contact voltage (for SSR drive)
12V DC±15%
Current :
4 to 20mA DC
Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Time Setting Accuracy
±0.5% of setting time
Progressing Time Error
After Power is Restored
Maximum 6 minutes
Non-volatile Memory
Write Limit
1,000,000 times
General Specifications
Input Specifications
Output Specifications
Program Control Specifications
2-4 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 16

Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Isolation
Photocoupler-isolated between input and internal circuit
Photocoupler-isolated between input and power circuit
Photocoupler-isolated between input and internal circuit
Photocoupler-isolated between output and internal circuit
Dielectric Strength
Output terminal - External power:
1500kV AC 5mA for 1 minute
Output terminal - Internal power:
1500kV AC 5mA for 1 minute
Input power - Output power:
1500kV AC 5mA for 1 minute
FG - External power:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Input terminal - External power:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Input terminal - Internal power
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Output terminal - External power:
2500V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Output terminal - Internal power
2500V AC 5mA for 1 minute
External power -Internal power
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Input terminal - Output terminal
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
FG - External power:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
I/O terminal - External power:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
I/O terminal - Internal power:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
External power - Internal power:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Input terminal - Output terminal:
548V AC 5mA for 1 minute
Type No.
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2
Power Consumption
Approx. 3.5W maximum
Module Power
Consumption
(Interior)
5V DC
65mA
24V DC
0mA
Ambient Temperature
0 to 55°C (No icing)
Ambient Humidity
10 to 95%RH (Non-condensing)
Weight
Approx. 140g
Environmental
Specifications
Conforms to RoHS directive.
Recommended Cable
Twisted pair cable
Insulation, Dielectric Strength
Insulation, Dielectric Strength
MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
Other
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 2-5
Page 17
MODULE SPECIFICATIONS
4.5
*
Dimensions
(All dimensions in mm)
* 8.5mm when the clamp is pulled out
2-6 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 18

INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Caution • Assemble the CPU module and PID modules before installing them on a DIN rail.
Otherwise, they may break.
• Do not lay out or wire the modules while power is supplied to them. Otherwise, they
may be damaged.
• When installing modules, follow the instructions described in the FC5A MicroSmart
user’s manual. If there are flaws in the installation, it may cause disattachment,
failure or malfunction.
Direct mounting strip
FC4A-PSP1P
3: INSTALLATION AND WIRING
This chapter describes how to install and wire the PID modules. For general methods and precautions for
installation and wiring of the PID modules, see chapter 3 in the FC5A MicroSmart user’s manual (FC9Y-B1268).
Be sure to use the PID modules properly after understanding installation and wiring thoroughly.
Mounting Hole Layout for Direct Mounting on Panel Surface
To mount the PID module on a panel surface,
use the direct mounting strip and two M4 screws
(6 or 8 mm long).
For details about the direct mounting strip, see the
FC5A MicroSmart user’s manual (FC9Y-B1268).
(All dimensions in mm)
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 3-1
Page 19

INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Example: Mounting hole layout for FC5A-C24R2 and four PID modules
(All dimensions in mm)
3-2 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 20

Caution • Make sure that the operating conditions and environments are within the specified
values.
• Be sure to connect the grounding wire to a proper ground, otherwise electrical
shocks may be caused.
• Do not touch live terminals, otherwise electrical shocks may be caused.
• Do not touch terminals immediately after power is turned off, otherwise electrical
shocks may be caused.
• When using ferrules, insert a wire to the bottom of the ferrule and crimp the ferrule.
• When connecting a stranded wire or two solid wires to single-pole terminal block, be
sure to use a ferrule. Otherwise the wire may slip off the terminal block.
Phoenix Type
Cable Size
AI 1-8 RD
UL1007AWG18
AI 0.5-8 WH
UL1015AWG22
Phoenix Type
Cable Size
AI-TWIN2x0.75-8 GY
UL1007AWG18
AI-TWIN2x0.5-8 WH
UL1015AWG22
Ferrule for
Terminal block
Terminal Connection
To cramp the following ferrules, use the specified crimping tool (CRIMPFOX ZA 3).
For 1-cable connection For 2-cable connection
For 1-cable connection
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Note: The above ferrules, crimping tool, and screwdriver are made by Phoenix Contact and are available from Phoenix
For 2-cable connection
Contact.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 3-3
Page 21

INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Caution • Connect an IEC 60127-approved fuse appropriate for the applied voltage and
current draw, at the position shown in the diagram. (This is required when
equipment containing the MicroSmart is destined for Europe.)
• Do not connect a thermocouple to hazardous voltage (60V DC, 42.4V DC peak or
higher).
• Be sure to check the wiring before the power is turned on. Faulty wiring may result in
damage to the PID module.
• Applicable electric cables are listed below.
Cable size AWG16: Single-cable
Cable size AWG18, AWG22: Single-cable/Twisted cable
+
-
NC
+
NC
-
+
-
NC
-
NC -
NC NC NC -
L
L
+
FG
NC
B
-
+
-
TC
A
B
B
RTD
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
TC
A
B
B
RTD
+
-
+
-
+
-
-
-
NC
NC
+
”
+
’
+
-
NC
-
B
’
A
B
+
”
+
’
+
-B
’
A
DC DC DC
DC DC DC
24V DC
IN0
IN1
OUT1
OUT0
Channel
Terminal
No.
Terminal
No.
Channel
L
0 to 5V
4 to 20mA
1 to 5V
0 to 10V
0 to 20mA
0 to 1V
0 to 5V
4 to 20mA
1 to 5V
0 to 10V
0 to 20mA
0 to 1V
Fuse (50V-1.2A)
*1
*1
DC : Voltage/Current
RTD : Resistance thermometer
TC : Thermocouple
: Load
: Analog current input instrument
: Fuse
Terminal Arrangement
*1: OUT0 is a connection example of relay output.
OUT1 is a connection example of non-contact voltage/current output. The PID module having both outputs
is non-existent.
3-4 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 22
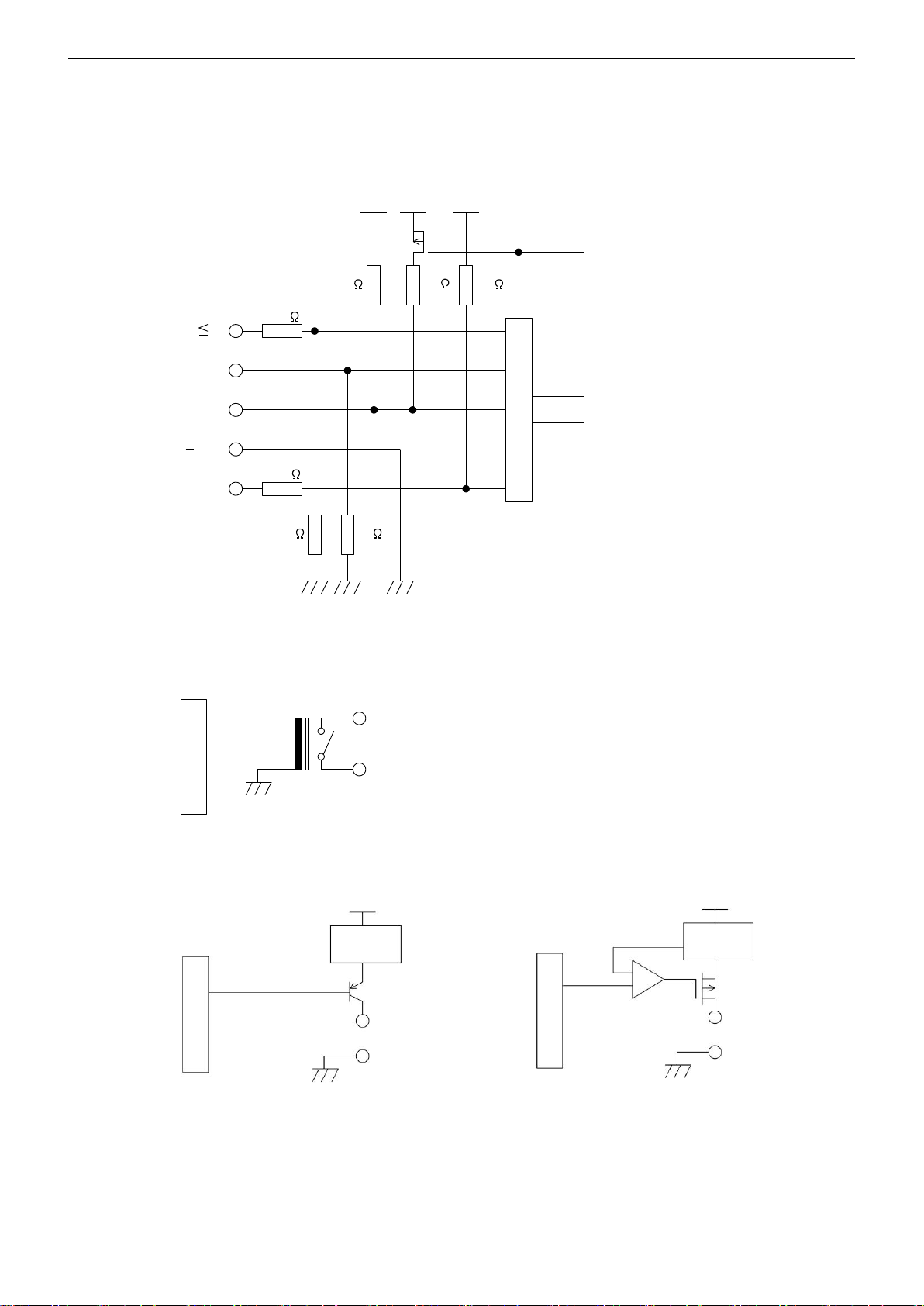
Output Circuit
(A)
(B)
(B)
+
mA
5V
160k
Multiplexer
Input Selection Signal
Input
20M 15k 15k
5040k
100
Output Circuit
Current
Detection
+
-
Output Circuit
Short Circuit
Protected
+
-
Type of Protection
Input Circuits
FC5A-F2MR2、FC5A-F2M2
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Output Circuits
FC5A-F2MR2
FC5A-F2M2 [Non-contact Voltage Output (for SSR drive)] FC5A-F2M2 (Current Output)
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 3-5
Page 23
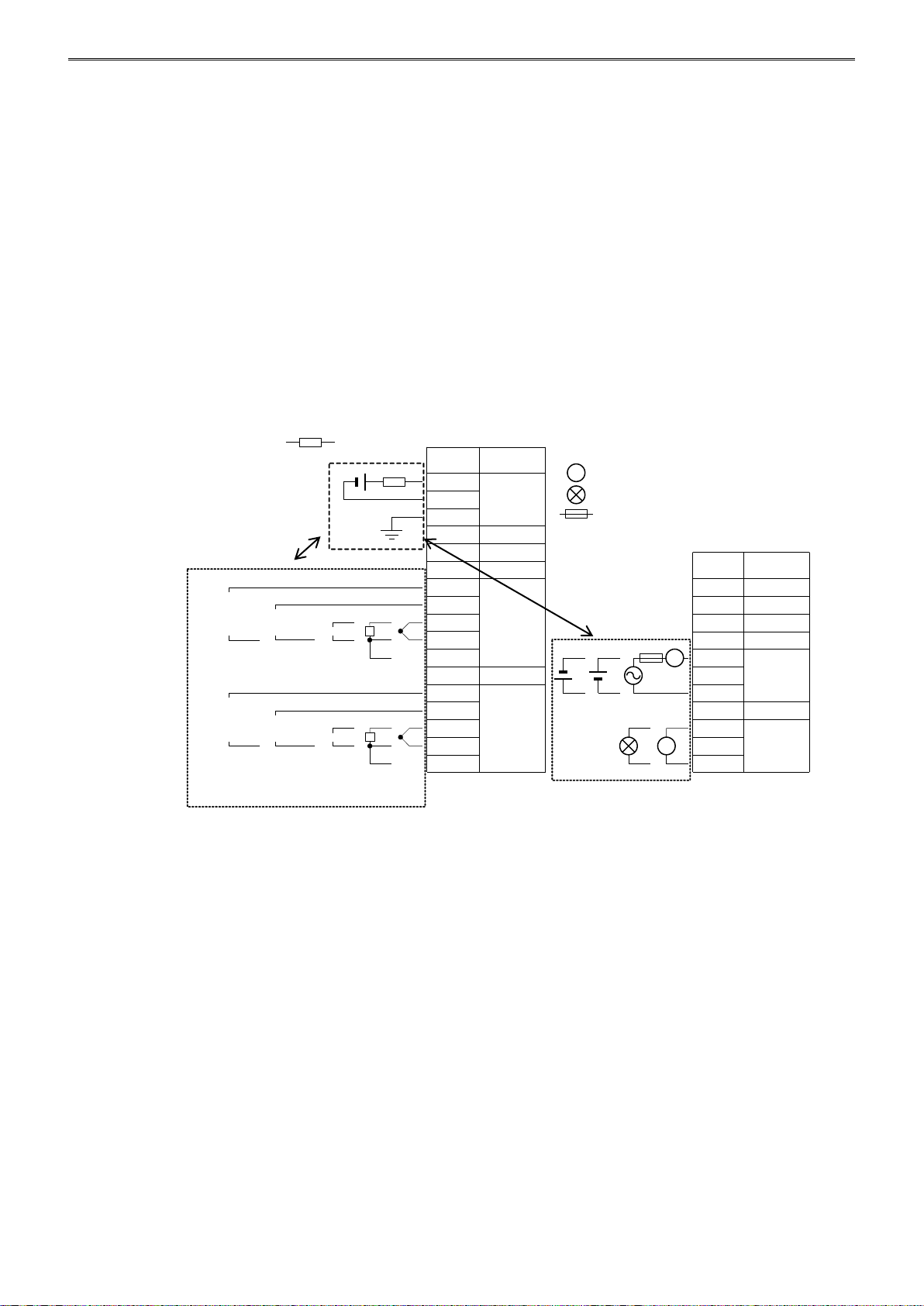
INSTALLATION AND WIRING
Separate the I/O lines
from the power line
as much as possible.
DC : Voltage/Current
RTD : Resistance thermometer
TC : Thermocouple
: Load
: Analog current input instrument
: Fuse
+
-
NC
+
NC
-
+
-
NC
-
NC -
NC NC NC -
L
L
+
FG
NC
B
-
+
-
TC
A
B
B
RTD
+
-
+
-
+
-
+
-
TC
A
B
B
RTD
+
-
+
-
+
-
-
-
NC
NC
+
”
+
’
+
-
NC
-
B
’
A
B
+
”
+
’
+
-B
’
A
DC DC DC
DC DC DC
24V DC
IN0
IN1
OUT1
OUT0
Channel
Terminal
No.
Terminal
No.
Channel
L
0 to 5V
4 to 20mA
1 to 5V
0 to 10V
0 to 20mA
0 to 1V
0 to 5V
4 to 20mA
1 to 5V
0 to 10V
0 to 20mA
0 to 1V
Fuse (50V-1.2A)
Power Supply for PID Modules
When supplying power to the PID modules, take the following into consideration.
Using the same power supply for the MicroSmart CPU and the PID module is recommended to suppress the
influence of noise. If the same power source is used for the PID module and MicroSmart CPU module, after the
MicroSmart CPU is started to run, the PID module performs initialization for a maximum of 5 seconds. During
this period, each parameter has an indefinite value. Design the user program to make sure that each parameter
is referred in the CPU module after the PID module operating status is changed to 0001h (Normal operation).
Wiring of Power Line and I/O Lines for the PID Module
Separate the I/O lines, particularly resistance thermometers, from the power line as much as possible to
suppress the influence of noise.
3-6 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 24
PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
B. PID Module
A. Thermocouple
Control Target, such
as Electric Furnace
or Constant
Temperature Oven.
Heater
C. Actuator
200V AC
Temperature
Set point (SP)
Time
Temperature
Set point (SP) B
Time
Set point (SP) A
4: PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
This chapter describes the temperature control, fixed value control, auto-tuning (AT), program control,
heating/cooling control, difference input control, and cascade control of the PID module.
Temperature Control Using the PID Module
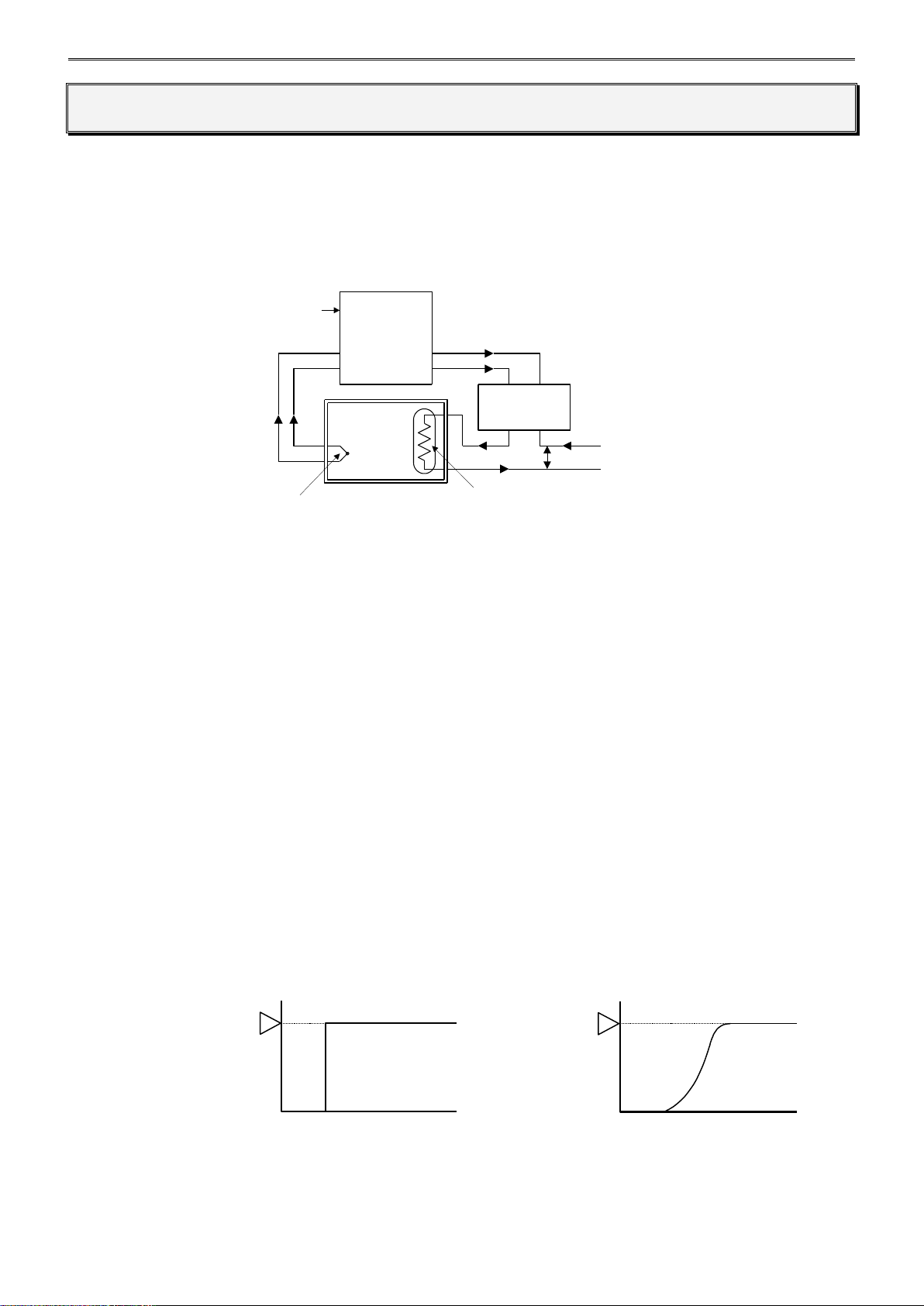
Temperature Control Configuration Example Using the PID Module
A. Sensor
Measures temperature of the control target. Thermocouple, resistance thermometer, voltage input,
or current input can be used as the sensor.
B. PID module
Receives the temperature measured by the sensor as the process variable (PV), and calculates the
output manipulated variable (MV) so that temperature difference (deviation) between the process
variable (PV) and the set point (SP) can be eliminated. The output manipulated variable (MV) is
outputted to the actuator as a control signal. Relay output, non-contact voltage output, or current
output can be used as the control signal.
C. Actuator
Receives a control signal from the PID module and turns on the load power supply to the heater.
Electromagnetic switches, SSR, or power controllers can be used as the actuator.
Optimal Temperature Control
The ideal temperature control, as shown in Figure 1, is to control the temperature to correspond with the
set point (SP) regardless of any disturbances. There should be no overshoot or response delay of time
until the temperature reaches the set point (SP).
Figure 1. Ideal Temperature Control Figure 2. Optimal Temperature Control
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-1
Page 25

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Temperature
Set point (SP)
Time
Time
Temperature
Set point (SP)
Characteristics of Control Target
Thermal Capacity
Static
Characteristic
Disturbance
Dynamic
Characteristic
In reality, the ideal temperature control shown in Figure 1 on the previous page is almost impossible to
achieve due to a number of complicated factors such as thermal capacity, static characteristics, dynamic
characteristics and disturbances.
Figure 2 is regarded as an optimal temperature control result. Depending on the usage and objective, for
some temperature control applications, suppression of overshoot is required even if the temperature
rises very slowly as shown in Figure 3. For some temperature control applications, it is necessary to
stabilize the temperature as quickly as possible by raising the temperature rapidly even if overshoot is
generated as shown in Figure 4. In general, however, Figure 2 is regarded as an optimal temperature
control. The PID module is designed to raise the process variable (PV) to the set point (SP) as quickly as
possible in order to stabilize the process variable (PV) at the set point (SP) so as to perform the optimal
temperature control. If the temperature fluctuates due to sudden disturbances, the PID module responds
to the fluctuation with speedy response in the shortest possible time and performs quick control to
stabilize the temperature.
Figure 3. Stable but slow temperature rise control
Figure 4. The temperature rises rapidly; however, the control stabilizes after overshoot and undershoot.
Characteristics of the Control Target
To perform optimal temperature control, it is necessary to have a good knowledge of the thermal
characteristics of the PID module, sensors, actuators as well as control targets. For example, the PID
module controls a constant temperature oven and its temperature can rise up to 100°C. Even if the set
point (SP) of the PID modules is configured as 200°C, the temperature of the constant temperature oven
rise only up to 100 °C due to its static characteristic.
The characteristic of the control target is determined by the combination of the following 4 factors.
1. Thermal capacity:
This represents how the target is easily heated, and has a relation with the volume size of the control
target.
2. Static characteristic:
This represents the capability of heating, and is determined by the size of the heater capacity.
3. Dynamic characteristic:
This represents the rising characteristic (transitional response) during initial heating. This is a
complicated process involving heater capacity, furnace capacity size and sensor location.
4. Disturbance:
Any change in control temperature causes disturbance. For example, the change of ambient
temperature or supply voltage can cause disturbance.
4-2 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 26
PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Control Output
ON
OFF
Undershoot
Overshoot
Hunting
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Proportional Band
Offset
Point A
Fixed Value Control
The PID module provides 2 control modes, one is the fixed value control and the other is the program control.
The fixed value control is a standard temperature control which performs to eliminate the deviation between
the single set point (SP) and process variable (PV). The program control allows you to define the set point
(SP) that changes as the time progresses so that the process variable (PV) can be controlled to match the set
point (SP) changing as the time progresses. For detail about the program control, see 4-9.
Control actions that can be used for fixed value control and program control are described below.
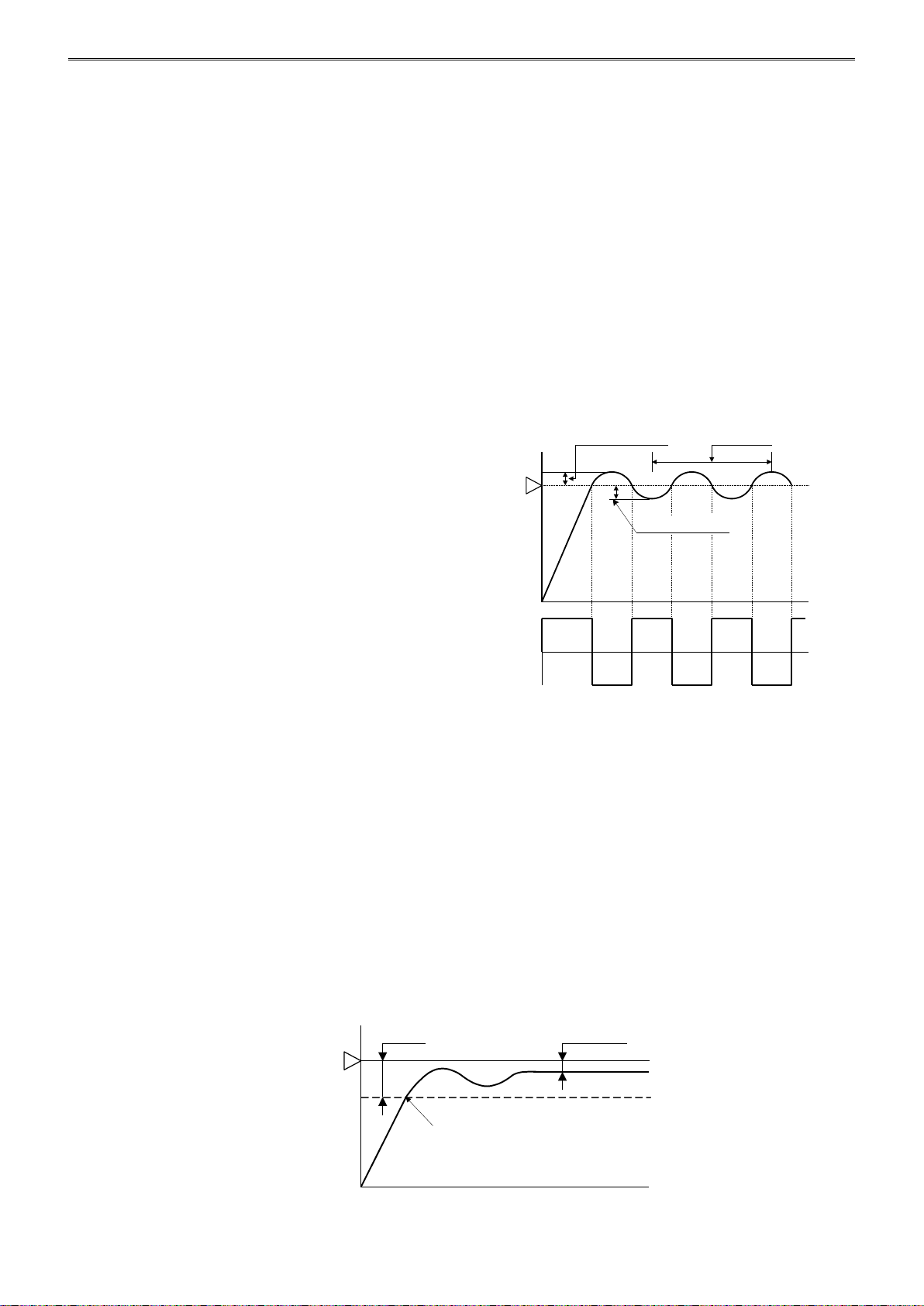
ON/OFF Control Action
In the ON/OFF control action, when the process variable (PV) is lower than the set point (SP), the control
output is turned on, and when the process variable (PV) exceeds the set point (SP), the control output is
turned off. Overshoot, undershoot, and hunting are generated. ON/OFF control is suitable for processes
which do not require accuracy.
If the proportional band or proportional gain of the PID module parameter is set to 0, the control action
becomes ON/OFF control.
Overshoot, Undershoot
As the temperature of the control target
rises as shown in the figure on the right,
the process variable (PV) sometimes
exceeds the set point (SP) greatly.
This is called overshoot. If the process
variable (PV) drops below the set point
(SP), this is called undershoot.
Hunting
The control result oscillates as shown
in the figure on the right. This is the
the hunting.
P Control Action (Proportional Action)
P control action outputs the manipulated variable (MV) in proportion to the deviation between the process
variable (PV) and the set point (SP) within the proportional band. The control output is ON until the
process variable (PV) reaches the point A that is determined by the proportional band. If the process
variable (PV) exceeds the point A (enters the proportional band), the control output starts turn on/off
according to the control period and the manipulated variable (MV). If the process variable (PV) exceeds
the set point (SP), the control output is completely turned off. While the process variable (PV) rises from
the point A to the set point (SP), the control output ON time decreases and the control output OFF time
increases. Compared to ON/OFF control action, there is no overshoot in P control action, and hunting
becomes less frequent; however, the offset is generated. The P control action is suitable for processes
such as gas pressure control or level control, in which there is no dead time.
If the integral time and derivative time of the PID module parameter are set to 0, the control action
becomes the P control action.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-3
Page 27

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Output Manipulated
Variable
100
50
0
Proportional Band
Set Point (SP)
A
B
C
Proportional band area that
can be configured with reset
function.
Offset can be corrected within
±proportional band from the
set point (SP).
Output Manipulated Variable
A: 100%
B: 50%
C: 0%
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Proportional Band
Disturbance
• If the proportional band is narrowed (Proportional gain is made larger)
Because the control output starts turning on/off at around the set point (SP), the time until the process
variable (PV) reaches the set point (SP) is shortened, and the offset is small; however, hunting is
frequent. If the proportional band is greatly narrowed, the control action becomes similar to the ON/OFF
control action.
• If the proportional band is broadened (Proportional gain is made smaller)
Because the control output starts turning on/off at the significantly low temperature from the set point
(SP), overshoot or hunting is reduced; however, it takes time for the process variable (PV) to reach to
the set point (SP), and the offset between the process variable (PV) and the set point (SP) becomes
broadened.
The offset caused by the P control action can be corrected by configuring the reset value. If the reset
value is configured, the proportional band range can be shifted as shown in the figure below. The reset
value can be automatically calculated by the auto-reset function.
PI Control Action (Proportional + Integral Action)
I (Integral) action automatically corrects the offset caused by P control action, and temperature control is
performed at the set point (SP). However, it takes time for the process variable (PV) to be stable if the
process variable (PV) is changed rapidly due to disturbance. PI control action is suitable for the
processes in which the temperature slowly changes.
If the derivative time of the PID module parameter is set to 0, the control action becomes the PI control
action.
• If the integral time is shortened too much, the integral action becomes strong. The offset can be
corrected in a shorter time; however, hunting with a long cycle may be caused.
• If the integral time is extended too much, the integral action becomes weak and it takes time to correct
the offset.
4-4 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 28
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Proportional Band
Disturbance
Set Point (SP)
Temperature
Time
Disturbance
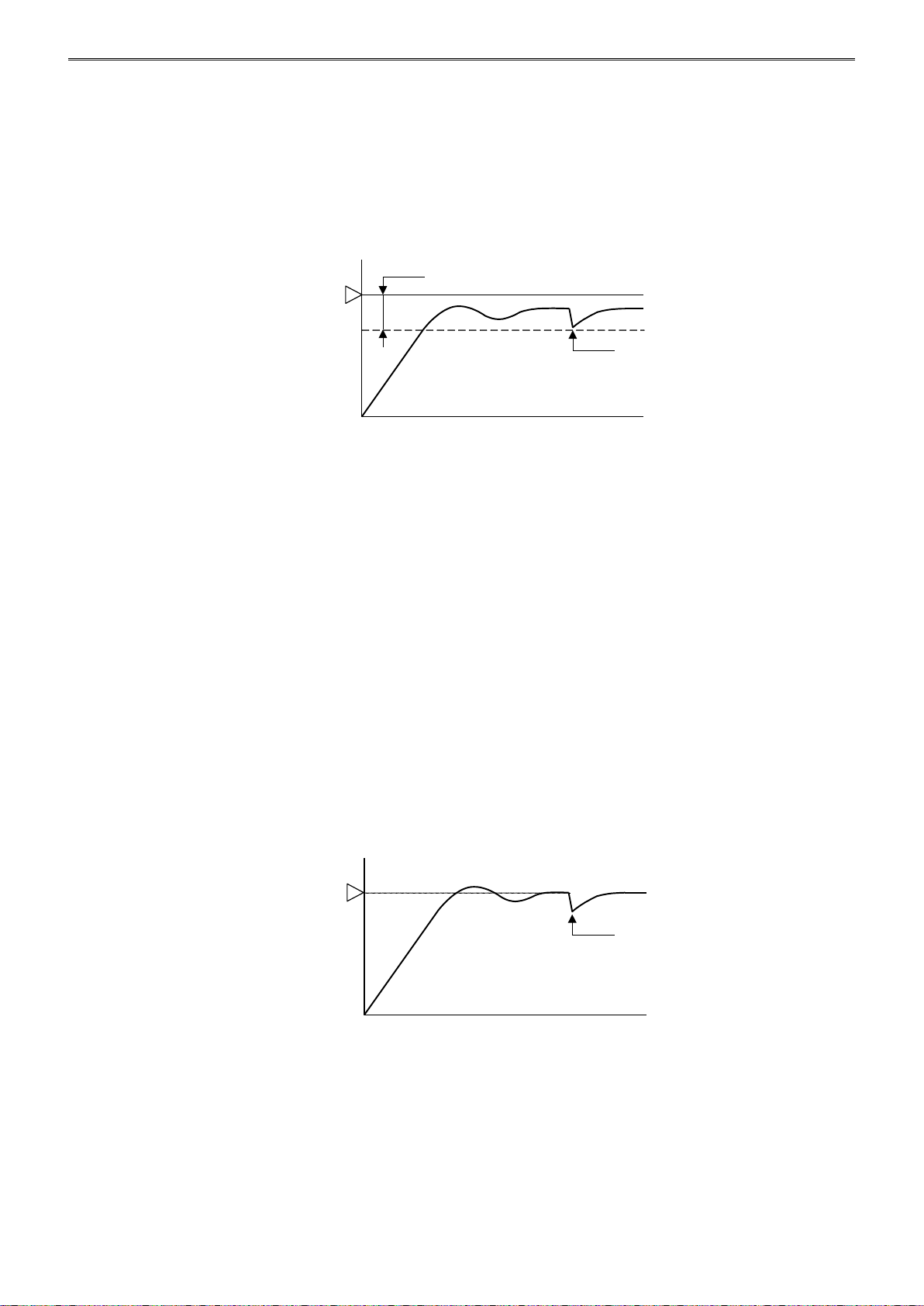
PD Control Action (Proportional + Derivative Action)
Compared with P action, the response to rapid temperature change due to disturbance is faster, the
temperature control can be stabilized in a shorter time, and transitional response characteristic can be
improved in PD control action. PD control action is suitable for the processes in which the temperature
rapidly changes.
If the integral time of the PID module parameter is set to 0, the control action becomes the PD control
action.
• If the derivative time is shortened, the derivative action becomes weak. The response to the rapid
temperature change becomes slower. Because the action to suppress the rapid temperature rises
becomes weaker, the time for the process variable (PV) to reach the set point (SP) is shortened;
however, overshoot can occur.
• If the derivative time is extended, the derivative action becomes strong. The response to the rapid
temperature change becomes faster. Because the action to suppress the rapid temperature rises
becomes strong, the time for the process variable (PV) to reach the set point (SP) is extended; however,
overshoot can be decreased.
The offset caused by the PD control action can be corrected by configuring the reset value. The reset
value can be automatically calculated by the auto-reset function.
PID Control Action (Proportional + Integral + Derivative Action)
P action suppresses the overshoot and the hunting, I action corrects the offset, and D action corrects
rapid temperature change due to disturbance in shorter time. Thus, using PID control action, optimal
temperature control can be performed. The proportional band, integral time, derivative time, and ARW
can be automatically calculated by the auto-tuning (AT).
PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-5
Page 29

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
(1) (2) (3)
SP
AT
SP+20
(4)
(4)
Time
Temperature
C
SP-20
C
SP-20
SP
AT
(1) (2) (3)
(4)
Temperature
Time
C
Caution • Perform auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset during the trial run.
• If the auto-tuning (AT) is performed near the ambient temperature, sufficient
fluctuations cannot be given to the process, and auto-tuning (AT) may fail. In
such case, configure the P, I, D, and ARW values manually.
• Perform auto-reset when the process variable (PV) is stabilized within the
proportional band.
• Once auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset is performed, it is unnecessary to perform
auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset again as long as the process is unchanged.
• When voltage or current input is selected and the auto-tuning (AT) is performed,
fluctuations are given to the process at the set point (SP) regardless of AT bias.
• During program control, fluctuations are given to the process as soon as
auto-tuning (AT) is started.
Auto-Tuning (AT)/Auto-Reset
The optimal temperature control parameters differ depending on the characteristics of the process to control.
For PID control action, the proportional band, integral time, derivative time, and ARW are automatically
configured by performing auto-tuning (AT). For P control or PD control action, the reset value is automatically
configured by performing auto-reset.
Auto-tuning (AT)
In order to configure P (proportional band), I (integral time), D (derivative time), and ARW (Anti-Reset
Windup) automatically with optimal values, the auto-tuning (AT) can be performed. The auto-tuning (AT)
gives temperature fluctuation to the process to calculate those parameters. To perform an optimal
auto-tuning (AT), temperature fluctuation is given to the process when the process variable (PV) reaches
near the set point (SP). By setting the AT bias, the temperature to start giving fluctuation can be configured.
The relation between the set point (SP), AT bias, auto-tuning (AT) starting point, and fluctuation starting point
are shown below.
[Process variable (PV) ≤ Set point (SP) - AT bias value]
When AT bias is set to 20°C, the PID module starts giving the temperature fluctuation to the process at the
temperature 20°C lower from the set point (SP).
(1) Fluctuation period. PID parameters are
measured.
(2) PID parameters are calculated and auto
tuning (AT) is finished.
(3) Temperature is controlled with the PID
parameters configured with auto-tuning (AT).
(4) AT bias value (20°C)
▲ AT: Auto-tuning (AT) perform bit is turned on
[Set point (SP) - AT bias value < Process variable (PV) < Set point (SP) + AT bias value]
The PID module starts giving the temperature fluctuation to the process when the process variable (PV)
reaches the set point (SP).
(1) Fluctuation period. PID parameters are
measured.
(2) PID parameters are calculated and auto
tuning (AT) is finished.
(3) Temperature is controlled with the PID
parameters configured with auto-tuning (AT).
(4) AT bias value (20°C)
▲ AT: Auto-tuning (AT) perform bit is turned on
4-6 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 30

SP+20
SP
AT
Temperature
(4)
Time
(1) (2) (3)
C
SP
Time
Temperature
Offset Span
Offset is Corrected.
Auto-reset is Performed.
PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
[Process variable (PV) ≥ Set point (SP) + AT bias value]
When AT bias is set to 20°C, the PID module starts giving the temperature fluctuation to the process at
the temperature 20°C higher from the set point (SP).
(1) Fluctuation period. PID parameters are
measured.
(2) PID parameters are calculated and auto
tuning (AT) is finished.
(3) Temperature is controlled with the PID
parameters configured with auto-tuning (AT).
(4) AT bias value (20°C)
▲ AT: Auto-tuning (AT) perform bit is turned on
Auto-reset
During the P control or PD control action, the deviation (offset) between the process variable (PV) and the
set point (SP) is generated when the process variable (PV) is stabilized. By performing auto-reset, the reset
value can automatically be calculated to correct the offset. It is required to perform auto-reset when the
process variable (PV) is stabilized within the proportional band. When the auto-reset is completed, the CPU
module automatically reads all parameters including the calculated reset value from the PID module and
stores those parameters in the data registers. It is unnecessary to perform the auto-reset again as long as
the process is unchanged.
When the proportional band (P) is set to 0 or 0.0, the reset value is cleared.
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset Perform/Cancel
The Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset function can be performed or cancelled by turning on/off the operation
parameter bits allocated to each channel. For the operation parameter bits, see page 5-10.
Perform Auto-tuning (AT)
To perform auto-tuning (AT), turn on the control enable/disable bit (Bit0) and auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset
bit (Bit1) of the operation parameter. P, I, D and ARW values will automatically be configured.
When auto-tuning (AT) is performed during the program control, P, I, D and ARW values of the current
step are configured. While auto-tuning (AT) is performed, the Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset LED (AT0/AT1)
flashes.
When auto-tuning (AT) is completed, the operation parameter Bit1 is automatically turned off, and the
CPU module reads all parameters of the AT performed channel from the PID module and store those
parameters in the data registers. If any parameters in the data registers of the CPU module have been
changed but have not been written to the PID module, those parameters will be overwritten with the
parameters read from the PID module when auto-turning (AT) is finished.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-7
Page 31

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
When external input I0 is turned on, CH0
operation parameter Bit1 is set, and
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset will be started.
When external input I1 is turned on, CH0
operation parameter Bit1 is reset, and
Auto-tuning (AT) will be cancelled.
Control Enable/Disable Bit
D1022.0
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset
Perform/Cancel Bit
D1022.1
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset
Perform/Cancel Bit (Monitor)
D1009.1
Auto-tuning is started when Auto-tuning
(AT)/Auto-reset Perform/Cancel bit
(D1022.1) is turned off to on.
Auto-tuning (AT)
cannot perform
while Control is
disable.
If auto-tuning (AT) is cancelled while
it is performed, the P, I, D and ARW
values will be reverted to the original
values at the time that auto-tuning
(AT) was started.
When auto-tuning (AT) is completed:
•The P, I, D, and ARW values
will be updated.
•Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset
Perform/Cancel bit (D1022.1) will
be automatically turned off.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Cancel Auto-tuning (AT)
To cancel auto-tuning (AT) while it is performed, turn off Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset bit (Bit1) of the
operation parameter. When the operation parameter Bit1 is turned off, auto-tuning (AT) is canceled, and
the Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset LED (AT0/AT1) will go off. When auto-tuning (AT) is cancelled, P, I, D and
ARW values are reverted to the original values at the time that auto-tuning (AT) was started.
Perform Auto-reset
To perform auto-reset, turn on Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset bit (Bit1) of the operation parameter. The reset
value will automatically be configured and the offset is corrected. During auto-reset is performed, the
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset LED (AT0/AT1) flashes.
Auto-reset cannot be cancelled.
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset Program Example
The ladder program and the timing chart below describe an example of performing and canceling
auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset of CH0. In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M1000
is allocated to control relay.
Ladder Program
Timing Chart
Notes
• Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset bit is automatically turned off when Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset is completed.
• If Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset bit is kept on, Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset will be performed continuously. Use
SOTU and SET instructions to turn on Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset bit so that auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset is
performed only once.
• If auto-tuning (AT) is cancelled while it is performed, P, I, D, and ARW values will be reverted to the original values
at the time that auto-tuning (AT) was started.
• Auto-reset cannot be cancelled.
4-8 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 32

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Step
Temperature
Time
Program Control
The program control allows you to define the set point (SP) that changes as the time progresses so that the
process variable (PV) can be controlled to match the set point (SP) changing as the time progresses. The set
point (SP) and time can be configured for each step. A maximum of 10 steps can be configured and performed.
The set point (SP) can be configured as shown in the following diagram.
The program control is suitable for applications, such as electric furnaces for ceramic industries or food
machineries.
Main functions of the program control are described as follows:
Program Pattern and Steps
1 program pattern consisting of 10 steps can be performed per channel.
Program Hold Function
Suspends the progression of the program control while the program control is running and performs the fixed
value control with the set point (SP) at the time that the program control is held.
Advance Next Function
Terminates the current step while the program control is running and proceeds to the start of the next step.
Advance Previous Function
Moves back the progression of the program control while the program control is running.
Wait Function
When a step ends during program control, if the deviation between the process variable (PV) and set point
(SP) is bigger than the wait value, the program control does not move to the next step. The program control
proceeds to the next step once the deviation between the process variable (PV) and set point (SP) becomes
smaller than the wait value.
Repeat Function
When the all steps are executed and the program control is terminated, the program control can be repeated
from Step 0 as many times as the repeat number configured.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-9
Page 33

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Program Control Operation Bits and Status Monitoring
By turning on/off the operation parameter bit, program control progression can be operated. By
monitoring program run status, the current status of program control can be monitored.
For the allocation of operation parameter, program run status, operating status, see pages 5-7 to 5-10.
Program Control Start (Start the program control)
Turn on the program control bit (Bit3) of the operation parameter. Program control starts.
Program Control Stop (Terminate the program control)
Turn off the program control bit (Bit3) of the operation parameter. Program control stops and enters
standby status.
Program Hold (Suspend the program control)
Turn on the program hold bit (Bit4) of the operation parameter. Program control is held (Suspended).
While the program control is held, time progression is suspended, and fixed value control is performed
with the set point (SP) at the time that the program control is held.
While program is held, the Program Control RUN/HOLD LED (R/H0 or R/H1) of the PID module flashes.
To resume the program control, turn off the program hold bit (Bit4).
Advance Next Function (Proceed to the next step)
Turn off to on the advance next step (Bit6) of the operation parameter. The current step is terminated and
the program control is proceeded to the start of the next step. The advance next function is also effective
while the program control is in wait action.
Advance Previous Function (Move back the program control)
Turn off to on the advance previous step (Bit7) of the operation parameter. The progression of the current
step is stopped and the program control is moved back. If the elapsed time in the current step is less than
1 minute, the program control goes back to the start of the previous step. If the elapsed time in the
current step is longer than 1 minute, the program control goes back to the start of the current step.
Even when the advance previous function is executed at Step 0, the program control does not move back
to Step 9 regardless of the program end action.
Current Step Remaining Time
The remaining time of the current step is stored in the “Current Step Remaining Time” of Block 0. The
remaining time is stored in seconds or minutes according to the “Step time unit” setting.
Current Step Number
The current step number (0 to 9) is stored in the “Current Step Number” of Block 0.
Program Wait (Perform program wait)
While the program wait is functioning, the program wait bit (Bit5) of the operating status is turned on. If
the condition below is satisfied, the wait function is cancelled, the program control proceeds to the next
step, and the program wait bit (Bit5) is turned off.
Set point (SP) - Wait value ≤ Process variable (PV) ≤ Set point (SP) + Wait value
If the advance next function (Bit6) is turned from off to on or if the program control bit (Bit3) is turned off,
the wait function is canceled.
Program End Output (Program Termination)
When the program control is finished, the program end output bit (Bit6) of the operating status is turned
on. If the program control bit (Bit3) of the operation parameter is turned off, the program end output bit
(Bit6) is turned off. To start program control again, turn off to on the program control bit (Bit3) of the
operation parameter.
4-10 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 34

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Time
Set Point (SP)
100°C
60 minutes
Starts program control
Set point (SP) when program
control starts
Time
Set Point (SP)
100°C
25°C
60 minutes
45 minutes
When program control is started, the
control starts from the PV starting
point (25°C of the process variable).
PV Starting Point
Action when Program Control Starts
The program control mode start type can be selected from 3 types: PV start, PVR start, and SP start.
When SP start is selected, the program control starts from the set point (SP) configured with “Set point
(SP) when program control starts.” When PV start or PVR start is selected, and the program control starts,
the step time is advanced until the set point (SP) matches to the process variable (PV), and then the
program control starts. For details about the program control mode start type, see page 6-41.
In the following example, the set point (SP) is 100°C, the step time is 60 minutes, and the process
variable (PV) when program control starts is 25°C.
[SP Start] [PV/PVR Start]
Program End Action
Program end action can be selected from 3 types: Terminate program control, Continue program control
(Repeat), and Hold program control. When the all steps from 0 to 9 are executed and completed, the
program control is finished. When “Terminate program control” is selected, the PID module will enter
standby status after the program control is finished. While in standby status, no control is performed and
the control output is in OFF status. If “Continue program control (Repeat)” is selected, the program
control is repeated from step 0 as many times as the repeat number configured. When “Hold program
control” is selected, the program control is held (suspended) after the program control is finished, and the
fixed value control is performed with the set point (SP) of Step 9. For details about the program end
action, see page 6-43.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-11
Page 35

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Program End
Action
PID Module Status before the Power Failure
Standby
Status (*1)
Program
Control is
Performing.
Program Control is
suspended (Hold)
Program Control is
Terminated.
Terminate
Program Control
Standby
status is
maintained.
The program
control is
continued.
*2, *3
The program hold is
canceled, and the
program control is
continued. *2, *3
The program control is
started from the Step 0.
Continue
Program Control
(Repeat)
Hold Program
Control
The program hold is
maintained. Fixed value
control is performed with
the set point (SP) at the
time that the power is
turned off.
Step Number
Step Time
Program
Control Status
Saved Point
Elapsed Time
from Program
Control Start 0 1
2
3
10 min
3 min
(2)
(1)
(3)
4
15 min
6 min
10 min
24 min
28 min
6 min
12 min
25 min
30 min
34 min
18 min
0 min
Action after Power Is Restored
When the power is restored, every bit of the operation parameter excluding the program hold bit stored in
the data register is maintained. If the power is failed and restored while the PID module performs the
program control, the PID module starts its operation in accordance with the original PID module status
before the power failure as shown in the table below.
*1: The PID module is in standby status when the control enable bit is on but the program control bit is off. While in
standby status, the PID module performs no control.
*2: While the program control is running, the PID module saves the program control status every 6 minutes after the
program control is started (after the program control bit is turned on). The program control status is also saved at
the start of each step. If the power to the PID module is turned off while the program control is running, the PID
module resumes the program control from the latest saved point.
For example, if the power to the PID module is turned off in 7 minutes after the program control is started at step
0, the PID module resumes the program control at the status (1) when the power is restored. If the power to the
PID module is turned off in 4 minutes after the program control enters step 1, the PID module resumes the
program control at the status (2) when the power is restored. If the power to the PID module is turned off in 2
minutes after the program control enters step 2, the PID module resumes the program control at the status (3),
which is the start of step 2, when the power is restored.
*3: To restart the program control from the start of step 0, turn off and on the program control bit (operation
parameter Bit3).
4-12 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 36

Program Pattern
100 100 800 800
0
500
1000
60 60 300 30
10 0 10 0
0 1 2 3
10 10 10 10
200 200 200 200
50 50 50 50
50 50 50 50
0 0 0 0
0 10 0 10
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0
100 100 100 100
0 0 0 0
1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
Step No.
Set Point (SP)
Set Point
Wait Value
Proportional Term
Integral Time
ARW
Output MV Rate-of-Change
Alarm 1 Value
Output MV Upper Limit
Output MV Lower Limit
Cooling Proportional Band
Overlap/Dead Band
Time (Minutes)
C
Derivative Time
( )
Alarm 2 Value
Alarm 3 Value
Alarm 4 Value
Alarm 5 Value
Alarm 6 Value
Alarm 7 Value
Alarm 8 Value
(SP)
Program Pattern Example
The set point (SP) configured for each step is handled as the set point (SP) at the end of the step. The
time configured for each step is the process time of each step.
PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
When the program pattern is configured as shown in the above table, the following control is
performed at each step:
[Step 0]: The set point (SP) is gradually risen to 100°C in 60 minutes.
When the step 0 ends, the wait function works so that the program control does not
proceed to the step 1 until the process variable (PV) reaches 90°C.
[Step 1]: The fixed value control is performed at 100°C of the set point (SP) for 60 minutes.
[Step 2]: The set point (SP) is gradually risen to 800°C in 5 hours.
[Step 3]: The fixed value control is performed at 800°C of the set point (SP) for 30 minutes.
When the step ends, the wait function works so that the program control does not proceed
to the step 3 until the process variable (PV) reaches 790°C.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-13
Page 37

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
Cooling
Control
Target
PID
Module
Heating
PID
Module
Cabinet
Input CH1
Input CH0
Output CH0
Fan
Interior
Temperature
External
Temperature
PID
Module
Tank A
Input CH1
Input CH0
Tank B
Heating/Cooling Control
When it is difficult to control the target process with heating control only, cooling control can be added to
perform the heating/cooling control. Control results derived from the set point (SP) and process variable (PV)
are outputted to 2 outputs, heating output (CH0) and cooling output (CH1). If the process variable (PV) is
higher than the set point (SP), cooling output will be turned on. If the process variable (PV) is lower than the
set point (SP), heating output will be turned on. The area in which both heating and cooling outputs are turned
on can be configured as overlap. The area in which neither heating output nor cooling output is output can be
configured as dead band.
Example: Heating/Cooling control uses both heating and cooling outputs and is suitable for the heat producing
processes such as extruders or for temperature control at near ambient temperature such as
environment testers.
Difference Input Control
Difference input control is the control to keep the input difference between input CH0 and input CH1 at the
same level. When the difference input control is selected, input CH0 and input CH1 are independently
measured, and the difference between those inputs is used as process variable (PV). PID module controls
output so that the difference between those inputs is matched to the set point (SP).
Example 1: Controlling the liquid level difference of 2 tanks
The PID module measures the liquid levels of 2 tanks and controls output to keep liquid level difference
between Tank A and Tank constant.
Example 2: Cabinet Interior Dew Condensation Prevention
The PID module measures interior and external temperatures of the cabinet and controls output to keep the
temperature difference between interior and external cabinet constant so that dew condensation inside the
cabinet can be prevented.
4-14 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 38

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
PV (M)
SP (M)
PID (M)
MV (M)
AT (M)
PV (S)
SP (S)
PID (S)
MV (S)
AT (S)
Master (Primary Control)
Slave (Secondary Control)
PID Module (with Cascade Control)
Power Controller
Control Target
Heater
CH1 Input
CH0 Input
CH0 Output
Cooling Equipment such as Fan
CH1 Output
Single Phase
200V
Control
Target
CH0 Thermocouple
CH1 Thermocouple
+ - +
-
Power Controller
Heater
u U +
-
Power
Supply
PID Module (FC5A-F2M2)
IN0
IN1
24V DC
OUT0
OUT1
Channel
Terminal
No.
Terminal
No.
Channel
Cascade Control
The cascade control combines two PID controls to form one feedback loop to control a single target. The
cascade control is effective for applications in which the delay time or dead time is considerably large. When
delay time is large, it takes a long time for the process variable (PV) to change after the output manipulated
variable (MV) is changed. By using the cascade control, highly stable control can be realized for such
applications, though it takes time for the process variable (PV) to reach the set point (SP).
CH1 control is used as the master and CH0 control as the slave of the cascade control. The output
manipulated variable (MV) of the master (CH1 control) becomes the set point (SP) of the slave (CH0 control),
and the control result of CH0 is outputted from the CH0 output. The output manipulated variable (MV) (0 to
100%) of the master (CH1 control) is corresponded to the set point (SP) of the slave (CH0) according to the
external SP input linear conversion minimum and maximum values. For example, when the external SP input
linear conversion minimum value is 100°C and the maximum value is 400°C, the output manipulated variable
(MV) (0 to 100%) of the master (CH1 control) is converted as follows: 0% is converted to 100°C, 50% is
converted to 250°C, and 100% is converted to 400°C.
When a system using the cascade control is designed, it is required that the slave (CH0 control) have smaller
delay time and faster response comparing to the master (CH1 control).
Example: The cascade control is used for an application in which the heat quantity of a heater is controlled
using a power controller in order to control the temperature of the control target as shown in the figure below.
It is also possible to utilize the heating/cooling control to prevent a rapid temperature rise of the control target
by using a fan as the cooling output.
System Configuration and Wiring
Wiring Example of the FC5A-F2M2 [Current Output Type]
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-15
Page 39

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
How to perform auto-tuning (AT) in cascade control
Auto-tuning (AT) can be performed for the cascade control with the following procedure.
Auto-tuning (AT) for the slave (CH0)
1. Turn off the CH0 and CH1 control enable bits of the operation parameter to disable the CH0 and CH1
controls.
2. Copy the set point (SP) of the master (CH1) to the set point (SP) of the slave (CH0), the external SP
input linear conversion maximum value, and the external SP input linear conversion minimum value
in order to fix the set point (SP) of the slave (CH0).
3. Turn on the CH0 and CH1 control enable bits of the operation parameter to enable the CH0 and CH1
controls. Turn on the CH0 auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset bit of the operation parameter to start the
auto-tuning (AT) for the slave (CH0).
When auto-tuning (AT) is completed, P, I, D and ARW values of the slave (CH0) will be automatically
configured.
Auto-tuning (AT) for the master (CH1)
4. Turn off the CH1 control enable bit of the operation parameter to disable the CH1 control.
5. Store the original values in the external SP input linear conversion maximum and minimum values.
6. Turn on the CH1 control enable bit and CH1 auto-tuning (AT)/auto-reset bit of the operation parameter to enable the CH1 control and start the auto-tuning (AT) for the master (CH1).
When auto-tuning (AT) is completed, P, I, D and ARW values of the master (CH1) will be automatically configured
Notes:
• When using the cascade control, store the same set point of the master (CH1) to the set point (SP) of the slave
(CH0).
• The output manipulated variable (MV) (0 to 100%) of the master (CH1) corresponds to the set point (SP) of the
slave (CH0). The range of the set point is the external SP input linear conversion minimum value to the external
SP input linear conversion maximum value.
• Depending on each control target, optimum values of P, I, D and ARW may not be calculated with the auto-tuning
(AT). In such case, configure those parameters manually based on the P, I, D and ARW values calculated with the
auto-tuning (AT).
Program Example of Auto-tuning (AT) for Cascade Control
A sample ladder program to execute the auto-tuning (AT) for the master (CH1) and slave (CH0) in the
cascade control is described in the following page.
4-16 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 40

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
1st Scan after the completion of CH1 auto-tuning (AT)
At the falling edge of D1018.1 (CH1 auto-tuning monitor bit),
Q0 is turned on.
3rd Scan
At the rising edge of M1, the following are executed in order.
D1022.0 is turned on. CH0 control is enabled.
D1022.1 is turned on. AT for CH0 control is performed.
D1025.0 is turned on. CH1 control is enabled.
M1006 (Block 5 writing) is turned off.
2nd Scan after the completion of CH0 auto-tuning (AT)
At the falling edge of M1, the following are executed in order.
D1025.0 is turned on. CH1 control is enabled.
D1025.1 is turned on. AT for CH1 control is performed.
M1006 (Block 5 writing) is turned off.
1st Scan after the completion of CH0 auto-tuning (AT)
At the falling edge of D1009.1 (CH0 auto-tuning monitor bit),
the following are executed in order.
D1025.0 is turned off. CH1 control is disabled.
D0 and D1 are moved to D1178 and D1179, respectively.
The original values are moved to the external SP input linear
conversion max. and min. values.
M1006 (Block 5 writing) is turned on.
Values in D1178 and D1179 are written to the PID module.
M1 is turned off.
2nd Scan
At the falling edge of M0, the following are executed in order.
M1000 (reading all parameters) is turned off.
D1178 (external SP input linear conversion max. value) and
D1179 (external SP input linear conversion min. value) are
moved to D0 and D1, respectively.
D1023 is stored in D1020.
CH1 set point (SP) is copied to CH0 set point (SP).
D1023 is stored in D1178 and D1179.
CH1 set point (SP) is copied to the external SP input linear
conversion max. and min. values.
M1006 (Block 5 Writing) is turned on.
Values in D1178 and D1179 are written to the PID module.
M1 is turned on.
1st Scan
At the rising edge of M0, the following are executed in order.
D1022.0 is turned off. (CH0 control is disabled.)
D1025.0 is turned off. (CH1 control is disabled.)
M1000 (reading all parameters) is turned on.
(All parameters are read from the PID module.)
M0 is turned off.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 4-17
Page 41

PID MODULE MAIN FUNCTIONS
4-18 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 42

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Block
Number of Data
Registers
Description
Block 0
20
Read only parameters (CH0, CH1)
Block 1
6
Write only parameters (CH0, CH1)
Block 2
27
Basic parameters (CH0)
Block 3
27
Basic parameters (CH1)
Block 4
50
Initial setting parameters (CH0)
Block 5
50
Initial setting parameters (CH1)
Blocks 10 to 19
21/block
Program parameters (CH0)
Blocks 30 to 39
19/block
Program parameters (CH1)
Block data are read from/written to the
PID module according to the settings
configured in WindLDR.
CPU Module
PID Module
5: DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
This chapter describes the valid devices, control registers, control relays, and data register allocation for the
PID module.
Device Allocation of PID Module
The PID module is used by connecting to the MicroSmart CPU module. To use the PID module, allocate the
data register and internal relay to the PID module, configure the initial parameters using WindLDR, and download the user program and the parameters to the CPU module and the PID module. The initial parameters are
downloaded to the CPU module along with the user program. The CPU module reads/writes data from/to the
PID module according to the parameters configured in WindLDR.
The PID module parameters consist of 26 data blocks divided according to the function and frequency of use
of each parameter as shown in the table below. All blocks to be used are allocated to the data registers in the
CPU module. The parameters of each block can be read from/written to the PID module using the allocated
control relays.
Block 0 includes parameters such as operating status, current process variable (PV), set point (SP), and
output manipulated variable (MV) of the PID module. The CPU module reads those parameters from the PID
module every scan. The control status and alarm status of the PID module can be monitored with Block 0
parameters.
Block 1 includes the set point (SP), manual mode output manipulated variable (MV), and operation parameters
of the PID module. Those parameters are written to the PID module every scan. Operations such as changing
the set point (SP) for the fixed value control, enabling/disabling the control, or performing auto-tuning (AT) can
be carried out.
Blocks 2 and 3 include basic parameters of the PID module. By turning the control relay from off to on,
parameters can be read from/ written to the PID module.
Blocks 4 and 5 include initial setting parameters of the PID module. Parameters that are usually not changed
during the operation are stored.
Blocks 10 to 19 and 30 to 39 include parameters of each step of the program control. By turning the control
relay from off to on, parameters can be read from/written to the PID module.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-1
Page 43

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Program Size
Both CH0 and CH1 are in fixed value
control mode
CH0 or CH1 is in program control mode
All-in-one Type
1,300 bytes
4,400 bytes
Slim Type
1,200 bytes
3,900 bytes
I Q M R T C D
Constant
Control Register
– – – – – – X – Control Relay
– – X – – – –
–
Module Type
Type No.
Control Mode
Occupied
Data Register
(Word)
CH0
CH1
PID Module
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Program control mode
590
Total
2360
Module Type
Type No.
Control Mode
Occupied
Data Register
(Word)
CH0
CH1
PID Module
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Fixed value control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Fixed value control mode
590
Total
2360
Module Type
Type No.
Control Mode
Occupied
Data Register
(Word)
CH0
CH1
PID Module
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Fixed value control mode
190
Total
1960
Program Size
The user program size that the PID module uses depends on CPU module type. The table below shows the
program size required to use a PID module.
Valid Devices
The following devices can be allocated as the control register and relay for the PID module. Control register
and relay should be configured for each PID module. Duplicated device cannot be configured.
Control Register
The PID module occupies a maximum of 590 data registers (minimum 190 data registers) per PID module. The
occupied number of data registers varies between the fixed value control mode and program control mode.
When both CH0 and CH1 are in fixed value control mode, 190 data registers are occupied, including the first
data register designated. When either CH0 or CH1 is in program control mode, 590 data registers are occupied,
including the first data register designated.
Precautions when Connecting Four PID Modules to All-in-One Type CPU Module
2000 data registers (D0 to D1999) are allocated to the all-in-one type CPU module. When four PID modules
are connected to the all-in-one type CPU module, a maximum of six program controls can be conducted with
three PID modules among the four PID modules.
The configurations shown in the examples 1 and 2 are not possible because the total number of occupied data
registers exceeds 2000.
Example 1: Program control mode is selected in all four PID modules
Example 2: Program control mode is selected in all four PID modules
The configurations shown in the example 3 and 4 are possible because the total number of occupied data
registers is less than 2000.
Example 3: Program control mode is selected in three PID modules
5-2 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 44

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Module Type
Type No.
Control Mode
Occupied
Data Register
(Word)
CH0
CH1
PID Module
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Fixed value control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Program control mode
Program control mode
590
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Fixed value control mode
190
FC5A-F2MR2/FC5A-F2M2
Fixed value control mode
Fixed value control mode
190
Total
1560
Offset from the
Control Relay
Description
R/W
+0
Reading all parameters (PID module → CPU module data registers)
R/W
+1
Loading initial values (CPU module ROM → data registers)
R/W
+2
Writing all parameters (CPU module data registers → PID module)
R/W
+3
Block 2 (CH0 basic parameters) writing
R/W
+4
Block 3 (CH1 basic parameters) writing
R/W
+5
Block 4 (CH0 initial setting parameters) writing
R/W
+6
Block 5 (CH1 initial setting parameters) writing
R/W
+7
Reserved
R/W
Offset from the
Control Relay
Description
R/W
+0
Reading all parameters (PID module → CPU module data register)
R/W
+1
Loading initial values (CPU module ROM → Data register)
R/W
+2
Writing all parameters (CPU module data register → PID module)
R/W
+3
Block 2 (CH0 basic parameters) writing
R/W
+4
Block 3 (CH1 basic parameters) writing
R/W
+5
Block 4 (CH0 initial setting parameters) writing
R/W
+6
Block 5 (CH1 initial setting parameters) writing
R/W
+7
Reserved
R/W
+8
Block 10 (CH0 Step 0) writing
R/W
+9
Block 11 (CH0 Step 1) writing
R/W
+10
Block 12 (CH0 Step 2) writing
R/W
+11
Block 13 (CH0 Step 3) writing
R/W
+12
Block 14 (CH0 Step 4) writing
R/W
+13
Block 15 (CH0 Step 5) writing
R/W
+14
Block 16 (CH0 Step 6) writing
R/W
+15
Block 17 (CH0 Step 7) writing
R/W
+16
Block 18 (CH0 Step 8) writing
R/W
+17
Block 19 (CH0 Step 9) writing
R/W
+18
Block 30 (CH1 Step 0) writing
R/W
+19
Block 31 (CH1 Step 1) writing
R/W
+20
Block 32 (CH1 Step 2) writing
R/W
+21
Block 33 (CH1 Step 3) writing
R/W
+22
Block 34 (CH1 Step 4) writing
R/W
+23
Block 35 (CH1 Step 5) writing
R/W
+24
Block 36 (CH1 Step 6) writing
R/W
+25
Block 37 (CH1 Step 7) writing
R/W
+26
Block 38 (CH1 Step 8) writing
R/W
Example 4: Program control mode is selected in two PID modules
Control Relay
The PID module occupies a maximum of 32 internal relays (minimum 8 internal relays) per module. The
occupied number of internal relays varies between the fixed value control mode and program control mode.
When both CH0 and CH1 are in fixed value control mode, 8 internal relays are occupied. When either CH0 or
CH1 is in program control mode, 32 internal relays are occupied.
Internal Relay Allocation
When both CH0 and CH1 are in fixed value control mode, the following 8 internal relays are allocated:
When either CH0 or CH1 is in program control mode, the following 32 internal relays are allocated:
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-3
Page 45

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
+27
Block 39 (CH1 Step 9) writing
R/W
+28
Reserved
R/W
+29
Reserved
R/W
+30
Reserved
R/W
+31
Reserved
R/W
Data Register
Value
Description
0
Normal operation
1 Bus error
Turn off the MicroSmart and connect the PID module again.
3
Invalid module
number
The PID module is not connected to the configured slot number. Turn off
the MicroSmart and connect the PID module to the appropriate slot
number.
PID Module
CPU Module
ROM
RAM
(Data Registers)
2.
3.
1.
4.
For details about blocks, see page 5-7 to 5-24.
Notes about the control relays:
• The control relay +0: Reading all parameters
When this bit is turned off to on, all parameters stored in the ROM of the PID module are read out and stored in the data
registers in the CPU module.
• The control relay +1: Loading initial values
When the user program is downloaded to the CPU module, the initial values of all parameters for the PID module are
also downloaded and stored in the ROM of the CPU module. When this bit is turned off to on, the initial values stored in
the ROM are loaded into the data registers (RAM).
• The control relay +2: Writing all parameters
When this bit is turned off to on, all parameters stored in the data registers are written to the ROM of the PID module.
• The control relay +3 through +27: Writing blocks 2 to 5, 10 to 19, and 30 to 39
When the writing bit is turned off to on, the corresponding block parameters stored in the data registers are written to the
ROM of the PID module.
Data Flow of the PID module parameters
1. All parameters are read out from the PID module and stored in the data registers in the CPU module
when the reading all parameters bit is turned off to on.
2. Initial values stored in the ROM of the CPU module are loaded to the data registers when the loading
initial values bit is turned off to on.
3. All parameters stored in the data registers are written to the PID module when the writing all parameters
bit is turned off to on.
4. The block parameters stored in the data registers are written to the PID module when the block writing bit
is turned off to on.
Note:
The communication status between the CPU module and the PID module can be confirmed with the following data register.
• When both CH0 and CH1 are in fixed value control mode: First data register + 189
• When CH0 or CH1 is in program control mode: First data register + 589
5-4 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 46

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
When I0 is turned on, the new set
point 2505 is stored in D1020 [set
point (SP) of CH0].
1st Scan
At the rising edge of M100, M500 is turned on to
read all parameters from the PID module.
M100 is turned off.
2nd Scan
At the falling edge of M100, M500 is turned off.
150 is stored in D1027 (integral time of CH0).
45 is stored in D1028 (derivative time of CH0).
M503 (Block 2 writing) is turned on to write block 2
parameters stored in D1026 to D1052 to the PID
module.
Examples of changing the PID module parameters using the control relay
All parameters of block 1 to 5, 10 to 19, and 30 to 39 can be changed using a ladder program. The following
examples demonstrate how the parameters of the PID module can be changed. See pages 5-7 to 5-24 for
detail about each block parameter.
Example 1: Changing Block 1 Parameter
The set point (SP) of CH0 control (D1020) is changed to 250.5°C. In this example, D1000 is allocated to the
control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
When the new set point 2505 is stored in D1020 *1, it is automatically written to the PID module *2.
Ladder Program Example:
When external input I0 is turned on, the set point (SP) of CH0 will be changed to 250.5°C.
*1: When the input range has a decimal point, store the value multiplied by 10 in the data register.
*2: When the control register is D1000, Block 1 parameters are stored in D1020 to D1025. These values are written to
the PID module every scan.
Example 2: Changing Block 2 Parameters
The integral time (D1027) is changed to 150 seconds and the derivative time (D1028) is changed to 45
seconds for CH0 control. In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to
control relay.
Those parameters can be changed with the following procedure.
1. Turn on M500 (Reading all parameters). All PID module parameters are read out from the PID module
and stored in the data registers.
2. Store 150 in D1027 (integral time of CH0) and 45 in D1028 (derivative time of CH0).
3. Turn on M503 (Block 2 writing) *2. The integral time (150 sec) and derivative time (45 sec) will be written
to the PID module.
Ladder Program Example:
*1
*1: If the reading all parameters bit (M500) is turned on, all PID module parameters are read out from the PID module
and stored in the data registers. Block 2 parameters are stored in D1026 to D1052.
*2: Block 2 parameters stored in D1026 to D1052 are written to the PID module. The parameters of the other blocks
are not written.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-5
Page 47

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
3rd Scan
At the rising edge of M102, D1022.0 is turned on to
enable CH0 control.
M102 is turned off.
1st Scan
At the rising edge of M101, D1022.0 is turned off to
disable CH0 control.
M500 is turned on to read all parameters from the
PID module.
M101 is turned off.
2nd Scan
At the falling edge of M101, M500 is turned off.
15 is stored in D1063 (PV filter time constant of CH0).
M505 (Block 4 writing) is turned on to write block 4
parameters stored in D1053 to D1102 to the PID
module.
M102 is turned on.
Example 3: Changing Block 4 Parameter
The PV filter time constant (D1063) of CH0 is changed to 1.5 seconds. In this example, D1000 is allocated
to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
The parameter can be changed with the following procedure.
1. Turn on M500 (Reading all parameters). All PID module parameters are read out from the PID module
and stored in the data registers of the CPU module. *1
2. Turn off D1022.0 (Control enable bit of CH0). CH0 control of the PID module will be disabled.
3. Store 15 in D1063 (PV filter time constant of CH0). *2
4. Turn on M505 (Block 4 writing). *3
5. Turn on D1022.0 (Control enable bit of CH0). CH0 of the PID module will be enabled.
Ladder Program Example:
*1: If the reading all parameters (M500) is turned on, all PID module parameters are read out from the PID module and
stored in the data registers. Block 4 parameters are stored in D1053 to D1102.
*2: For a value with a decimal point, store the value multiplied by 10 in the data register.
*3: Block 4 parameters stored in D1053 to D1102 are written to the PID module. The parameters of the other blocks
are not written.
Note: If parameters of block 4 or 5 are changed while CH0 or CH1 control is enabled in the PID module, an unexpected
operation of the PID module may be caused. It is recommended that the control channel of the PID module be disabled
before changing the parameters of block 4 or 5.
5-6 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 48

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Offset from
the Control
Register
Parameter
Description
R/W
0
Common
PID Module Operating Status
0000h: Initialization
0001h: Normal operation
0002h: External power supply error
R
+1
CH0
Current Process Variable (PV)
When input is normal:
Value within the control range (see 9-4)
When input is invalid: Unknown value
R
+2
Current Heating Output
Manipulated Variable (MV)
Output manipulated variable lower limit to upper
limit
R
+3
Current Cooling Output
Manipulated Variable (MV)
Cooling output manipulated variable lower limit
to upper limit
R
+4
Current Set Point (SP)
When input is thermocouple or resistance
thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP)
upper limit
When input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion
max. R +5
Current Step Remaining Time
0 to 6000 minutes/seconds
R
+6
Current Step Number
0 to 9 R +7
Remaining Repeat Number
0 to 10000
R
+8
Reserved
0 (Fixed value)
R
+9
Operation Parameter Monitor
See 5-8 for detail about the operation parameter
monitor. R +10
Operating Status
See 5-9 for detail about the operating status.
R
+11
CH1
Current Process Variable (PV)
When input is normal:
Value within the control range (see 9-4)
When input is invalid: Unknown value
R
+12
Current Output Manipulated
Variable (MV)
Output manipulated variable lower limit to
upper limit
R
+13
Current Set Point (SP)
When input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP)
upper limit
When input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion
max. R +14
Current Step Remaining Time
0 to 6000 minutes/seconds
R
+15
Current Step Number
0 to 9 R +16
Remaining Repeat Number
0 to 10000
R
+17
Reserved
0 (Fixed value)
R
+18
Operation Parameter Monitor
See 5-8 for detail about the operation
parameter monitor.
R
+19
Operating Status
See 5-9 for detail about the operating status.
R
Data Register Allocation - Block 0 Read Only Parameters
The CPU module reads the following parameters from the PID module and store them in the data registers
every scan.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-7
Page 49

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Bit
Operation Parameter Monitor (1 word)
Parameter
Status
Description
Bit0
Control Enable Bit
0
Control is disabled
1
Control is enabled
Bit1
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-Reset Bit
0
Normal operation
1
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset is being performed
Bit2
Auto/Manual Mode Bit
0
Auto mode
1
Manual mode
Bit3
Program Control Bit
0
Program control is stopped
1
Program control is running
Bit4
Program Hold Bit
0
Normal operation
1
Program control is held
Bit5
External SP Input Enable Bit
(CH0 only)
0
External SP input is disabled
1
External SP input is enabled
Bit6
Parameter Range Error Bit (Note)
0
All parameters are within the valid range
1
All parameters are out of the valid range
Bit7
Set point (SP) Range Error Bit
0
Set point (SP) is within the valid range.
1
Set point (SP) is within the valid range.
Bit8
Manual Mode Output Manipulated
Variable Range Error Bit
0
Manual mode output manipulated variable is
within the valid range.
1
Manual mode output manipulated variable is out
of the valid range.
Bit9
Proportional Band/Integral
Time/Derivative Time/ARW/
Control Period Range Error Bit
0
Proportional band, integral Time, derivative time,
ARW, or control period is within the valid range.
1
Proportional band, integral Time, derivative time,
ARW, or control period is out of the valid range.
Bit10
Reset Setting Range Error Bit
0
Reset setting is within the valid range.
1
Reset setting is out of the valid range.
Bit11
Cooling Proportional Band/Cooling
Control Period Range Error Bit
(CH0 only)
0
Cooling proportional band or cooling control
period is within the valid range.
1
Cooling proportional band or cooling control
period is out of the valid range.
Bit12
Overlap/Dead Band Range Error
Bit (CH0 only)
0
Overlap/dead band is within the valid range.
1
Overlap/dead band is out of the valid range.
Bit13
Alarm 1 to Alarm 8 Value Range
Error Bit
0
Alarm 1 to Alarm 8 values are within the valid
range.
1
Alarm 1 to Alarm 8 values are out of the valid
range.
Bit14
PV Filter/PV Correction Range
Error Bit
0
PV Filter/PV Correction is within the valid range.
1
PV Filter/PV Correction is out of the valid range.
Bit15
Program Control Set Point (SP)
Range Error Bit
0
Program control set point (SP) is within the valid
range.
1
Program control set point (SP) is out of the valid
range.
Operation Parameter Monitor
Note: The parameter range error bit is turned on when any parameter of the PID module is out of the valid range. While
the parameter range error is occurring, the control output is turned off.
5-8 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 50

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Bit
Operating Status (1 word)
Parameter
Status
Description
Bit0
(Heating) Control Output
0
OFF
1
ON (Unknown for current output)
Bit1
Cooling Control Output
(CH0 only)
0
OFF
1
ON (Unknown for current output)
Bit2
Loop Break Alarm
0
Normal operation
1
Loop break alarm is occurring
Bit3
Over Range
0
Normal operation
1
Input value is exceeding the upper limit of the
control range (See page 9-4).
Thermocouple or resistance thermometer may be
burnt out. Voltage input (0 to 1V DC) may be
disconnected.
Bit4
Under Range
0
Normal operation
1
Input value is below the lower limit of the control
range (See page 9-4).
Voltage input (0 to 5V DC) may be disconnected.
Current input (4 to 20mA DC) may be discon-
nected.
Bit5
Program Wait
0
Normal operation
1
Program wait is functioning
Bit6
Program End Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit7
Alarm 1 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit8
Alarm 2 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit9
Alarm 3 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit10
Alarm 4 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit11
Alarm 5 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit12
Alarm 6 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit13
Alarm 7 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit14
Alarm 8 Output
0
OFF
1
ON
Bit15
Reserved
0
0 (Fixed value)
Operating Status
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-9
Page 51

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Offset from
the Control
Register
Parameter
Description
R/W
+20
CH0
Set Point (SP)
When the input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When the input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion max.
W
+21
Manual Mode Output
Manipulated Variable
When heating/cooling control is disabled:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to output manipulated
variable upper limit
When heating/cooling control is enabled:
- Cooling output manipulated variable upper limit to heating
output manipulated variable upper limit
W
+22
Operation Parameter
Refer to the table below for the operation parameters
W
+23
CH1
Set Point (SP)
When the input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When the input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion max.
W
+24
Manual Mode Output
Manipulated Variable
Output manipulated variable lower limit to output manipulated
variable upper limit
W
+25
Operation Parameter
Refer to the table below for the operation parameters
W
Bit
Operation Parameters (1 word)
Item
Status
Description
Bit0
Control Enable Bit
0
Control disable
1
Control enable
Bit1
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-Reset Bit *1
0
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset cancel
1
Auto-tuning (AT)/Auto-reset perform
Bit2
Auto/Manual Mode Bit
0
Auto mode
1
Manual mode
Bit3
Program Control Bit
0
Program control stop
1
Program control run
Bit4
Program Hold Bit *2
0
Program control run
1
Program control hold
Bit5
External SP Input Enable Bit
0
External SP input disable
1
External SP input enable
Bit6
Advance Next Step Bit *3
0
No action
1
Program control advance next step
Bit7
Advance Previous Step Bit *4
0
No action
1
Program control advance previous step
Bit8 to
Bit15
Reserved
0
Fixed value 0
Data Register Allocation - Block 1 Write Only Parameters
The CPU module writes the following parameters stored in the data registers to the PID module every scan.
Note: When the power to the PID module is turned off, Block 1 parameters are cleared to zero.
Operation Parameters
*1: Once auto-reset is performed, it cannot be cancelled during its performance.
*2: The program control is suspended while the program hold bit is on.
*3: During the program control, the current step is terminated and the program control is proceeded to the start of the
next step when the advance next step bit is turned off to on.
*4: During the program control, the progression of the program control is moved back when the advance previous step
bit is turned off to on. If the elapsed time in the current step is less than 1 minute, the program control goes back to
the start of the previous step. If the elapsed time in the current step is more than or equal to 1 minute, the program
control goes back to the start of the current step. Even when the advance previous step is executed at Step 0, the
program control does not move back to Step 9 regardless of the program end action.
5-10 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 52

0 1 1 2 0 0 1 0 1 2 0 0 1 21 21
Current step number
D1006
Control enable bit
D1022.0
Program control bit
D1022.3
Program control bit
(Monitor)
D1009.3
Program hold bit
D1022.4
Advance next step bit
D1022.6
Advance previous step bit
D1022.7
Program end output
D1010.6
The program control is started
from the start of Step 1.
The program control is held at the
40 minutes of remaining time.
The program control is proceeded to
the start of step 1 while the program
hold is maintained.
The program control is proceeded to
the start of step 2 while the program
hold is maintained.
15 sec
45 min
30 sec
30 min
20 min
30 min
5 min
The program hold is canceled, and
the program control is started from
the start of step 2.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Examples of Program Control Progress
Example 1: Terminate Program Control when Program Ends
The following diagram shows an example of the program control when terminate program control is
selected as the program end action.
Time of steps: Step 0 and 1: 60 minutes, Step 2: 30 minutes, Steps 3 to 9: 0 minute
In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
Note: The PID module executes all steps 0 to 9 even if the step times of steps are zero. When the program control is
terminated, nine is stored in the current step number of block 0.
DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-11
Page 53

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
0 01 2 0 1 2 0 1 2 0 1 2
1 0 1 0
Current step number
D1006
Number of repeats remaining
D1007
30 min
20 sec
Control enable bit
D1022.0
Program control bit
D1022.3
Program control bit
(Monitor)
D1009.3
Program hold bit
D1022.4
Advance next step bit
D1022.6
Advance previous step bit
D1022.7
Program end output
D1010.6
After the steps 0 to 2 are
executed, the program control is
repeated from the step 0.
While the program hold is executed
after the program end output is turned
on, the program hold bit has no effect.
The program control is not
moved back to step 2 even if
the advance previous step is
executed in step 0.
If the control is disabled
when step 2 is terminated,
the program end output
does not turn on.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Example 2: Continue Program Control (Repeat) when Program Ends
The following diagram shows an example of the program control when continue program control (repeat) is
selected as the program end action.
Time of steps: Step 0 and 1: 60 minutes, Step 2: 30 minutes, Steps 3 to 9: 0 minute
Number of repeats: 1
In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
5-12 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 54

0 1 1 2 0 1
1 0
2 2 222
Current step number
D1006
Number of repeats remaining
D1007
Control enable bit
D1022.0
Program control bit
D1022.3
Program control bit
(Monitor)
D1009.3
Program hold bit
D1022.4
Advance next step bit
D1022.6
Advance previous step bit
D1022.7
Program end output
D1010.6
30 min
30 min
29 min
30 min
The program control is proceeded
to the start of step 2 while the
program hold is maintained.
The program control is held at 1 minute
of the remaining time. (The program
hold works when the remaining time is
not zero.)
The program control is proceeded to the
start of step 2 while the program hold is
maintained.
The program hold is canceled,
and the program control is
started from the start of step 2.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Example 3: Continue Program Control (Repeat) when Program Ends
The following diagram shows an example of the program control when continue program control (repeat) is
selected as the program end action.
Time of steps: Step 0 and 1: 60 minutes, Step 2: 30 minutes, Steps 3 to 9: 0 minute
Number of repeats: 1
In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-13
Page 55

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
0 1 92 0 1 21 1 2 9
Current step number
D1006
Control enable bit
D1022.0
Program control bit
D1022.3
Program control bit
(Monitor)
D1009.3
Program hold bit
D1022.4
Advance next step bit
D1022.6
Advance previous step bit
D1022.7
Program end output
D1010.6
30 min
30 min
20 min
After all steps are executed, the program
control is held, and the fixed value control
is performed with the parameters of step 9.
The program hold is canceled
by executing advance next step,
and the program control is
started from the start of step 0.
The program control is held at the 30 minutes
of remaining time, and the fixed value control
is performed with the current parameters.
The program hold is canceled, and
the program control is started from
30 minutes of remaining time.
The program control is started from the
start of step 2.
After all steps are executed, the program control is
held, and the fixed value control is performed with
the parameters of step 9.
While the program hold is maintained at the
end of the program control, the program hold bit
and advance previous step bit have no effect.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Example 4: Hold Program Control when Program Ends
The following diagram shows an example of the program control when hold program control is selected as
the program end action.
Time of steps: Step 0 and 1: 60 minutes, Step 2: 30 minutes, Steps 3 to 9: 0 minute
In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
Note: The PID module executes all steps 0 to 9 even if the step times of steps are zero. When the program control is
terminated, nine is stored in the current step number of block 0.
5-14 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 56

0 0 21 1 1 12 0 211 19 9
Current step number
D1006
Control enable bit
D1022.0
Program control bit
D1022.3
Program control bit
(Monitor)
D1009.3
Program hold bit
D1022.4
Advance next step bit
D1022.6
Advance previous step bit
D1022.7
Program end output
D1010.6
30 sec
30 sec
20 min
60 min
60 min
40 min
40 min
The program control is started
from the start of step 0.
The program control is held, and
the fixed value control is performed
with the parameters of step 9.
The program control is held, and the
fixed value control is performed with
the parameters of step 9.
The control is enabled and the
program control is started.
The program hold is canceled, and the
program control is started from 40 minutes
of remaining time.
If the program hold, advance next step, and advance previous
step are executed simultaneously, they are executed as
follows:
1. Program Hold
The program control is held at 20 minutes of remaining time.
2. Advance Next Step
The program hold is canceled, and the program control is
proceeded to the start of step 2.
3. Advance Previous Step
The program control is moved back to the start of step 1.
As a result, only the execution of the advance previous step is
resulted in.
If the program hold and advance previous step
are executed simultaneously, they are executed
as follows:
1. Program Hold
The program control is held at 30 minutes (Note)
of remaining time.
2. Advance Previous Step
The program control is proceeded to the start of
step 1 while the program hold is maintained.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Example 5: Hold Program Control when Program Ends
The following diagram shows an example of the program control when hold program control is selected as
the program end action.
Time of steps: Step 0 and 1: 60 minutes, Step 2: 30 minutes, Steps 3 to 9: 0 minute
In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
Note: If minute is selected as the step time unit, the remaining time is handled with the unit of minute. If the remaining
time is between 29 minutes 1 second and 30 minutes 0 second, the remaining time will be 30 minutes.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-15
DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Page 57

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
0 1 32 9 0 21 9
Current step number
D1006
Control enable bit
D1022.0
Program control bit
D1022.3
Program control bit
(Monitor)
D1009.3
Program hold bit
D1022.4
Advance next step bit
D1022.6
Advance previous step bit
D1022.7
Program end output
D1010.6
20 min
The program control is held at the ten
minutes of remaining time, and the
fixed value control is performed with
the current parameters.
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
20 min
The program control is proceeded to the start of
step 3, and the fixed value control is performed
with the parameters of step 3.
The fixed value control is performed
with the parameters of step 9.
The program hold is canceled, and
the program control is started from
the start of Step 0.
After all steps are executed, the program
control is held, and the fixed value control
is performed with the parameters of step 9.
Example 6: Hold Program Control when Program Ends
The following diagram shows an example of the program control when hold program control is selected as
the program end action.
Time of steps: Step 0 and 1: 60 minutes, Step 2: 30 minutes, Steps 3 to 9: 0 minute
In this example, D1000 is allocated to the control register and M500 is allocated to control relay.
Notes:
• The PID module executes all steps 0 to 9 even if the times of steps are zero. When the program control is terminated,
nine is stored in the current step number of block 0.
• When hold program control is selected as the program end action, the program control is held, and the fixed value
control is performed with the parameters of step 9 after all steps are executed.
5-16 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 58

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Offset from the
Control
Register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
+26
+103
Proportional Term
Proportional band:
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F)
When input is voltage or current input:
0.0 to 1000.0%
Proportional gain:
0.00 to 100.00%
R/W
+27
+104
Integral Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
+28
+105
Derivative Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
+29
+106
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
0 to 100%
R/W
+30
+107
Control Period
1 to 120 sec
R/W
+31
+108
Reset
When input range unit is Celsius:
-100.0 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-100.0 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
-1000 to 1000
R/W
+32
+109
Output Manipulated Variable
Rate-of-Change
0 to 100%/sec
R/W
+33
+110
Set Point (SP) Rise Rate
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C/min)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F/min)
When input is voltage or current input:
0 to 10000/min
R/W
+34
+111
Set Point (SP) Fall Rate
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C/min)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F/min)
When input is voltage or current input:
0 to 10000/min
R/W
+35
+112
Loop Break Alarm (LA) Time
0 to 200 minutes
R/W
+36
+113
Loop Break Alarm (LA) Span
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 150°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 150.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 150°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 150.0°F)
When input is voltage or current input:
0 to 1500
R/W
+37
+114
Alarm 1 Value
See 5-18 for the valid range of alarm 1 to alarm 8 values.
R/W
+38
+115
Alarm 2 Value
R/W
+39
+116
Alarm 3 Value
R/W
+40
+117
Alarm 4 Value
R/W
+41
+118
Alarm 5 Value
R/W
+42
+119
Alarm 6 Value
R/W
+43
+120
Alarm 7 Value
R/W
+44
+121
Alarm 8 Value
R/W
+45
+122
Reserved
R/W
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 2, 3 Basic Parameters (SHOT Action)
Block 2 (CH0) and block 3 (CH1) parameters are shown in the table below. The parameters of block 2 and 3
can be changed while the control of the PID module is enabled.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-17
Page 59

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
+46
+123
Output Manipulated Variable
Upper Limit
When output type is relay or voltage:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 100%
When output type is current:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 105%
R/W
+47
+124
Output Manipulated Variable
Lower Limit
When output type is relay or voltage:
0% to output manipulated variable upper limit
When output type is current:
-5% to output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
+48
+125
Cooling Proportional Band
(CH0 only)
0.0 to 10.0 times
(Cooling proportional band is the multiplication of heating
proportional band)
R/W
+49
+126
Cooling Control Period
(CH0 only)
1 to 120 sec
R/W
+50
+127
Overlap/Dead Band
(CH0 only)
When input range unit is Celsius:
-200.0 to 200.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-200.0 to 200.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
-2000 to 2000
R/W
+51
+128
Cooling Output Manipulated
Variable Upper Limit
(CH0 only)
When output type is relay or voltage:
Cooling output manipulated variable lower limit to 100%
When output type is current:
Cooling output manipulated variable lower limit to 105%
R/W
+52
+129
Cooling Output Manipulated
Variable Lower Limit
(CH0 only)
When output type is relay or voltage:
0% to cooling output manipulated variable upper limit
When output type is current:
-5% to cooling output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
Alarm Type
Valid Range
Upper Limit Alarm
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Lower Limit Alarm
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm
0 to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limit Range Alarm
0 to full scale *1
Process High Alarm
Input range lower limit to input range upper limit *2
Process Low Alarm
Input range lower limit to input range upper limit *2
Upper Limit Alarm with Standby
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Lower Limit Alarm with Standby
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm with Standby
0 to full scale *1
Valid Range for Alarm 1 to Alarm 8 Settings
*1: When input is voltage/current, full scale is the linear conversion span.
*2: When input is voltage/current, the valid range is the linear conversion minimum value to linear conversion
maximum value.
5-18 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 60

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Offset from the
Control
Register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
+53
+130
Control Action
0: Reverse control action (Heating)
1: Direct control action (Cooling)
R/W
+54
+131
Heating/Cooling Control
(CH0 only)
0: Disable
1: Enable
R/W
+55
+132
External SP Input
(CH0 only)
0: Disabled
1: External SP input (4 to 20mA DC)
2: External SP input (0 to 20mA DC)
3: External SP input (1 to 5V DC)
4: External SP input (0 to 1V DC)
5: Cascade control
R/W
+56
+133
Input Function
0: Input (CH0/CH1)
1: Difference input (CH0 - CH1)
2: Difference input (CH1 - CH0)
3: Addition input (CH0 + CH1)
R/W
+57
–
Output Function (CH0)
0: Output (CH0)
1: Output (CH1)
2: Both outputs (CH0, CH1)
R/W
–
+134
Output Function (CH1)
0: Output(CH1)
Output Function (CH0) has priority.
R/W
+58
+135
Input Type
See 5-21 for the input types and range
R/W
+59
+136
Set Point (SP) Upper Limit/
Linear Conversion Maximum
Value
When input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to input range upper limit
When input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion minimum to input range upper limit
R/W
+60
+137
Set Point (SP) Lower Limit/
Linear Conversion Minimum
Value
When input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Input range lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage or current input:
Input range lower limit to linear conversion maximum
R/W
+61
+138
Output ON/OFF Hysteresis
When input range unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
1 to 1000
R/W
+62
+139
PV Correction
When input range unit is Celsius:
-100.0 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-100.0 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
-1000 to 1000
R/W
+63
+140
PV Filter Time Constant
0.0 to 10.0 sec
R/W
+64
+141
Reserved
R/W
+65
+142
Alarm 1 Type
0: No alarm action
1: Upper limit alarm
2: Lower limit alarm
3: Upper/Lower limits alarm
4: Upper/Lower limit range alarm
5: Process high alarm
6: Process low alarm
7: Upper limit alarm with standby
8: Lower limit alarm with standby
9: Upper/Lower limits alarm with standby
R/W
+66
+143
Alarm 2 Type
R/W
+67
+144
Alarm 3 Type
R/W
+68
+145
Alarm 4 Type
R/W
+69
+146
Alarm 5 Type
R/W
+70
+147
Alarm 6 Type
R/W
+71
+148
Alarm 7 Type
R/W
+72
+149
Alarm 8 Type
R/W
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 4, 5 Initial Setting Parameters (SHOT Action)
Block 4 (CH0) and block 5(CH1) parameters are shown in the table below. Before changing the parameters of
block 4 or 5, it is recommended that the control of the PID module be disabled.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-19
Page 61

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
+73
+150
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
When input range unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
1 to 1000
R/W
+74
+151
Alarm 2 Hysteresis
R/W
+75
+152
Alarm 3 Hysteresis
R/W
+76
+153
Alarm 4 Hysteresis
R/W
+77
+154
Alarm 5 Hysteresis
R/W
+78
+155
Alarm 6 Hysteresis
R/W
+79
+156
Alarm 7 Hysteresis
R/W
+80
+157
Alarm 8 Hysteresis
R/W
+81
+158
Alarm 1 Delay Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
+82
+159
Alarm 2 Delay Time
R/W
+83
+160
Alarm 3 Delay Time
R/W
+84
+161
Alarm 4 Delay Time
R/W
+85
+162
Alarm 5 Delay Time
R/W
+86
+163
Alarm 6 Delay Time
R/W
+87
+164
Alarm 7 Delay Time
R/W
+88
+165
Alarm 8 Delay Time
R/W
+89
+166
AT Bias
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 50°C (0.0 to 50.0°C for input with decimal point)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 100°F (0.0 to 100.0°F for input with decimal point)
R/W
+90
+167
Control Mode
0: Fixed value control mode
1: Program control mode
R/W
+91
+168
Program Control Mode Start
Type
0: PV start
1: PVR start
2: SP start
R/W
+92
+169
Step Time Unit
0: Minute
1: Second
R/W
+93
+170
Program End Action
0: Terminate program control
1: Continue program control (Repeat)
2: Hold program control
R/W
+94
+171
Proportional Term
0: Proportional band
1: Proportional gain
R/W
+95
+172
Cooling Method
(CH0 only)
0: Air cooling
1: Oil cooling
2: Water cooling
R/W
+96
+173
Set Point (SP) when Program
Control Starts
When input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion max.
R/W
+97
+174
Number of Repeats
0 to 10000 times
R/W
+98
+175
Cooling Output ON/OFF
Hysteresis
(CH0 only)
When input range unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
1 to 1000
R/W
+99
+176
Output Type
(FC5A-F2M2 only)
0: Non-contact voltage output (for SSR drive)
1: Current output
R/W
+100
+177
External SP Input Bias
(CH1 only)
±20% of the external SP input linear conversion span
R/W
+101
+178
External SP Input Linear
Conversion Maximum Value
(CH1 only)
External SP input Linear conversion min. to input range
upper limit
R/W
+102
+179
External SP Input Linear
Conversion Minimum Value
(CH1 only)
Input range lower limit to external SP input linear conversion
max.
R/W
5-20 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 62

Input Type and Range
Unit
Range
00h
Type K Thermocouple
Celsius
-200 to 1370°C
01h
Type K Thermocouple with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 400.0°C
02h
Type J Thermocouple
-200 to 1000°C
03h
Type R Thermocouple
0 to 1760°C
04h
Type S Thermocouple
0 to 1760°C
05h
Type B Thermocouple
0 to 1820°C
06h
Type E Thermocouple
-200 to 800°C
07h
Type T Thermocouple
-200.0 to 400.0°C
08h
Type N Thermocouple
-200 to 1300°C
09h
PL-II
0 to 1390°C
0Ah
C (W/Re5-26)
0 to 2315°C
0Bh
Pt100 with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 850.0°C
0Ch
JPt100 with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 500.0°C
0Dh
Pt100
-200 to 850°C
0Eh
JPt100
-200 to 500°C
0Fh
Type K Thermocouple
Fahrenheit
-328 to 2498°F
10h
Type K Thermocouple with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 752.0°F
11h
Type J Thermocouple
-328 to 1832°F
12h
Type R Thermocouple
32 to 3200°F
13h
Type S Thermocouple
32 to 3200°F
14h
Type B Thermocouple
32 to 3308°F
15h
Type E Thermocouple
-328 to 1472°F
16h
Type T Thermocouple
-328.0 to 752.0°F
17h
Type N Thermocouple
-328 to 2372°F
18h
PL-II
32 to 2534°F
19h
C (W/Re5-26)
32 to 4199°F
1Ah
Pt100 with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 1562.0°F
1Bh
JPt100 with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 932.0°F
1Ch
Pt100
-328 to 1562°F
1Dh
JPt100
-328 to 932°F
1Eh
4 to 20mA DC
―
-2000 to 10000
1Fh
0 to 20mA DC
―
-2000 to 10000
20h
0 to 1V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
21h
0 to 5V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
22h
1 to 5V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
23h
0 to 10V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
Input Range
DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-21
Page 63

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Offset from the Control Register
Parameter
Step 0
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
+180
+201
+222
+243
+264
Set point (SP)
+181
+202
+223
+244
+265
Step time
+182
+203
+224
+245
+266
Wait value
+183
+204
+225
+246
+267
Proportional term
+184
+205
+226
+247
+268
Integral time
+185
+206
+227
+248
+269
Derivative time
+186
+207
+228
+249
+270
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
+187
+208
+229
+250
+271
Output manipulated variable rate-of-change
+188
+209
+230
+251
+272
Alarm 1 value
+189
+210
+231
+252
+273
Alarm 2 value
+190
+211
+232
+253
+274
Alarm 3 value
+191
+212
+233
+254
+275
Alarm 4 value
+192
+213
+234
+255
+276
Alarm 5 value
+193
+214
+235
+256
+277
Alarm 6 value
+194
+215
+236
+257
+278
Alarm 7 value
+195
+216
+237
+258
+279
Alarm 8 value
+196
+217
+238
+259
+280
Reserved
+197
+218
+239
+260
+281
Output manipulated variable upper limit
+198
+219
+240
+261
+282
Output manipulated variable lower limit
+199
+220
+241
+262
+283
Cooling proportional band
+200
+221
+242
+263
+284
Overlap/Dead band
Offset from the Control Register
Parameter
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
+285
+306
+327
+348
+369
Set point (SP)
+286
+307
+328
+349
+370
Step time
+287
+308
+329
+350
+371
Wait value
+288
+309
+330
+351
+372
Proportional term
+289
+310
+331
+352
+373
Integral time
+290
+311
+332
+353
+374
Derivative time
+291
+312
+333
+354
+375
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
+292
+313
+334
+355
+376
Output manipulated variable rate-of-change
+293
+314
+335
+356
+377
Alarm 1 value
+294
+315
+336
+357
+378
Alarm 2 value
+295
+316
+337
+358
+379
Alarm 3 value
+296
+317
+338
+359
+380
Alarm 4 value
+297
+318
+339
+360
+381
Alarm 5 value
+298
+319
+340
+361
+382
Alarm 6 value
+299
+320
+341
+362
+383
Alarm 7 value
+300
+321
+342
+363
+384
Alarm 8 value
+301
+322
+343
+364
+385
Reserved
+302
+323
+344
+365
+386
Output manipulated variable upper limit
+303
+324
+345
+366
+387
Output manipulated variable lower limit
+304
+325
+346
+367
+388
Cooling proportional band
+305
+326
+347
+368
+389
Overlap/Dead band
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 10-19 CH0 Program Parameters (SHOT Action)
When CH0 control is in program control mode, block 10 to 19 should be configured. A maximum of ten steps
from step 0 to step 9 can be configured. All parameters of block 10 to 19 are shown in the following tables. For
detail about each parameter, see page 5-23.
5-22 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 64

Parameter
Description
R/W
Set Point (SP)
When input is thermocouple or resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage or current input:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion max.
R/W
Step Time
When step time unit is Minute:
0 to 6000 minutes
When step time unit is Second:
0 to 6000 seconds
R/W
Wait Value
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 100°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 100.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 100°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 100.0°F)
When input is voltage or current input:
0 to 1000
R/W
Proportional Term
Proportional band:
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F)
When input is voltage or current input:
0.0 to 1000.0%
Proportional gain:
0.00 to 100.00%
R/W
Integral Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
Derivative Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
0 to 100%
R/W
Output Manipulated Variable
Rate-of-Change
0 to 100%/sec
R/W
Alarm 1 Value
See 5-18 for the valid range of alarm 1 to alarm 8 values.
R/W
Alarm 2 Value
R/W
Alarm 3 Value
R/W
Alarm 4 Value
R/W
Alarm 5 Value
R/W
Alarm 6 Value
R/W
Alarm 7 Value
R/W
Alarm 8 Value
R/W
Reserved
R/W
Output Manipulated Variable
Upper Limit
When output type is relay or voltage:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 100%
When output type is current:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 105%
R/W
Output Manipulated Variable
Lower Limit
When output type is relay or voltage:
0% to output manipulated variable upper limit
When output type is current:
-5% to output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
Cooling Proportional Band
(CH0 only)
0.0 to 10.0 times
(Cooling proportional band is the multiplication of heating proportional band)
R/W
Overlap/Dead Band
(CH0 only)
When input range unit is Celsius:
-200.0 to 200.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-200.0 to 200.0°F
When input is voltage or current input:
-2000 to 2000
R/W
Program Parameters
DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 5-23
Page 65

DEVICE ALLOCATION OF PID MODULE
Offset from the Control Register
Parameter
Step 0
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
+390
+409
+428
+447
+466
Set point (SP)
+391
+410
+429
+448
+467
Step time
+392
+411
+430
+449
+468
Wait value
+393
+412
+431
+450
+469
Proportional term
+394
+413
+432
+451
+470
Integral time
+395
+414
+433
+452
+471
Derivative time
+396
+415
+434
+453
+472
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
+397
+416
+435
+454
+473
Output manipulated variable rate-of-change
+398
+417
+436
+455
+474
Alarm 1 value
+399
+418
+437
+456
+475
Alarm 2 value
+400
+419
+438
+457
+476
Alarm 3 value
+401
+420
+439
+458
+477
Alarm 4 value
+402
+421
+440
+459
+478
Alarm 5 value
+403
+422
+441
+460
+479
Alarm 6 value
+404
+423
+442
+461
+480
Alarm 7 value
+405
+424
+443
+462
+481
Alarm 8 value
+406
+425
+444
+463
+482
Reserved
+407
+426
+445
+464
+483
Output manipulated variable upper limit
+408
+427
+446
+465
+484
Output manipulated variable lower limit
Offset from the Control Register
Parameter
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
+485
+504
+523
+542
+561
Set point (SP)
+486
+505
+524
+543
+562
Step time
+487
+506
+525
+544
+563
Wait value
+488
+507
+526
+545
+564
Proportional term
+489
+508
+527
+546
+565
Integral time
+490
+509
+528
+547
+566
Derivative time
+491
+510
+529
+548
+567
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
+492
+511
+530
+549
+568
Output manipulated variable rate-of-change
+493
+512
+531
+550
+569
Alarm 1 value
+494
+513
+532
+551
+570
Alarm 2 value
+495
+514
+533
+552
+571
Alarm 3 value
+496
+515
+534
+553
+572
Alarm 4 value
+497
+516
+535
+554
+573
Alarm 5 value
+498
+517
+536
+555
+574
Alarm 6 value
+499
+518
+537
+556
+575
Alarm 7 value
+500
+519
+538
+557
+576
Alarm 8 value
+501
+520
+539
+558
+577
Reserved
+502
+521
+540
+559
+578
Output manipulated variable upper limit
+503
+522
+541
+560
+579
Output manipulated variable lower limit
Data Register Allocation - Blocks 30-39 CH1 Program Parameters (SHOT Action)
When CH1 control is in program control mode, block 30 to 39 should be configured. A maximum of ten steps
from step 0 to step 9 can be configured. All parameters of block 30 to 39 are shown in the following tables. For
detail about each parameter, see page 5-23.
5-24 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 66

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
6: CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
This chapter describes configuration procedure of the PID modules using WindLDR, PID module configuration
dialogs, and monitoring.
Procedure to configure the PID module
1. Expansion Modules Configuration Dialog Box
To open the Expansion Modules Configuration dialog box, follow one of the procedures below.
Procedure 1:
1. From the WindLDR menu bar, select View > Project Window to open the Project Window.
2. Double-click on Expansion Modules Configuration in the Project Window.
Procedure 2:
1. From the WindLDR menu bar, select Configuration > Expansion Modules.
Expansion Modules Configuration Dialog Box
After specifying the quantity of modules and selecting the slot number to which the PID module is connected,
designate the module type number, control register (data register) and control relay (internal relay). After
designating those parameters, click on Configure Parameters button to open the PID Module
Configuration dialog.
2. PID Module Configuration Dialog Box
All parameters for the PID module can be configured in this dialog box. Configure the desired
parameters and click on OK button to close the dialog.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-1
Page 67

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
3. Download Dialog Box
From the WindLDR menu bar, select Online > Download. The Download dialog box will be opened.
Click the check box on the left of Write PID Module parameters after download and click OK button.
The user program will be downloaded. After downloading the user program, the PID module parameters
will be automatically written to the data registers in the CPU module and the PID module connected to
the CPU module.
Note: The CPU module and the connected PID module exchange data through the allocated data registers in the CPU
module. In order for the CPU module to communicate with the PID Module, it is required that the user program be
downloaded to the CPU module after configuring the PID Module in the Expansion Modules Configuration dialog box. In
order for the PID module to operate, it is required that the parameters be written to the data registers in the CPU module
and the PID module.
6-2 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 68

WindLDR
PID Module
CPU Module
ROM
RAM
(Data Register)
Flow of the parameters when executing
Write All Parameters.
Flow of the parameter when executing
Read All Parameters.
WindLDR
: Flow of the user program when executing
the user program download.
: Flow of the user program when executing
the user program upload.
PID Module
CPU Module
ROM
RAM
(Data Register)
Writing and Reading Parameters
When Write All Parameters or Read All Parameters is executed in the PID Module Configuration dialog
box, all parameters will be written to/read from the PID module as follows.
Downloading and Uploading User Program
When the user program download *1 or upload is executed, the user program is downloaded to/uploaded
from the CPU module as follows.
CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
*1: When Write PID Module parameters after download is checked in the Download dialog, writing the PID module
parameters will be executed after the user program is downloaded to the CPU module. The PID module parameters
are written to the data registers in the CPU module and all PID modules configured in the Expansion Modules
Configuration dialog box. For details, see the following page.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-3
Page 69

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
User Program Download
The user program contains the user program and the PID module parameters (initial values) configured
in the PID Module Configuration dialog box. After the user program is downloaded to the CPU module,
the CPU module can communicate with the PID Modules through the allocated data registers.
After the user program download, the following actions will be taken depending on whether Write PID
Module parameters after download in the Download dialog box is checked or not.
When Write PID Module parameters after download is checked:
After the user program is downloaded to the CPU module, the PID module parameters configured in the
PID Module Configuration dialog box are written to the CPU module and the connected PID modules.
When Write PID Module parameters after download is not checked:
After the user program is downloaded to the CPU module, the PID module parameters are not written to
the PID module.
When Write PID Module parameters after download is checked, after the user program is downloaded
to the CPU module, the PID module parameters configured in the PID Module Configuration dialog box
will be written to the data registers in the CPU module and all PID modules configured in the Expansion
Modules Configuration dialog box. However, if a PID module is not connected to the configured slot,
writing parameters to the PID module will fail. Even after writing parameters to one PID module failed,
WindLDR continues to write the parameters to all PID modules configured in the Expansion Modules
Configuration dialog box.
If writing parameters fails, connect the PID module to the CPU module and write parameters to the PID
module again.
To write the PID module parameters without downloading the user program to the CPU module, take the
following steps:
1. Connect the PID module to the CPU module.
2. Open the PID Module Configuration dialog box for the slot.
3. Click on Write All Parameters button.
All the configured parameters will be written to the data registers in the CPU module and the PID
module.
6-4 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 70

User Program Upload
When the user program containing the initial parameters of the PID modules is uploaded from the CPU
module, the initial values will be restored. The parameters saved in the PID module will not be read.
How to restore data register values when a keep data error has occurred
If more than 30 days pass since the power to the CPU module is turned off, values stored in the data
registers will be lost. When the data register values are lost, after the power is turned on, restore the PID
module parameters in the data registers of the CPU module using either of the following methods, and
then enable the control of the PID module.
Method 1: Use the parameters stored in the PID module
The parameters stored in the PID module can be read out and stored in the data registers of the CPU
module with one of the following procedures:
Procedure 1: Using WindLDR
1. Open Expansion Modules Configuration dialog box in WindLDR.
2. Select the slot number of the connected PID module and open the PID Module Configuration dialog
box.
3. Click on Read All Parameters button to read all parameters from the PID module.
4. Configure the set point (SP) and the manual mode output manipulated variable in the PID Module
Configuration dialog box. *1
5. Click on Write All Parameters button.
When the control of the PID module is enabled, the PID module will start operating with the
downloaded parameters.
Procedure 2: Using the user program
1. Turn off to on the reading all parameters relay (control relay + 0).
2. Configure the set point (SP) and the manual mode output manipulated variable if necessary. *1
When the control of the PID module is enabled, the PID module will start operating with the
configured parameters.
*1: Because the block 1 parameters are not saved in the PID module, it is required to configure those parameters.
Method 2: Use the default parameters stored in the ROM of the CPU module
When the PID module parameters are configured in the PID Module Configuration dialog box and the
user program is downloaded to the CPU module, the PID module parameters (initial values) will be
saved in ROM of the CPU module. Those initial values can be loaded to the data registers in the CPU
module, and the PID module can be operated with those initial values with the following procedure:
1. Turn off to on the loading initial values relay (control relay + 1).
2. Turn off to on the writing all parameters relay (control relay + 2).
When the control of the PID module is enabled, the PID module will start operating with the default
values.
CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-5
Page 71

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Item
Description
(1)
Quantity
of
Modules
Configure the quantity of modules to be expanded. The quantity of PID modules can be
connected varies with the CPU module type. A maximum of four PID modules can be
connected to the all-in-one type CPU modules. A maximum of seven PID modules can be
connected to the slim type CPU modules.
(2)
Slot
Number
Select a slot number to configure the PID module.
(3)
Module
Type
No.
Select the type number of the PID module to configure.
(4)
Data
Register
Designate the control register for the PID module. Data register can be designated. A
maximum of 590 data registers (minimum 190 data registers) are occupied, including the first
data register designated.
(5)
Internal
Relay
Designate the control relay for the PID module. Internal relay can be designated. A maximum
of 32 internal relays (minimum 8 internal relays) are occupied, including the first internal relay
designated.
Button
Description
(6)
Configure Parameters
The PID Module Configuration dialog box is opened.
(7)
Copy Parameters To
The PID module parameters of the current slot can be copied to another slot.
(8)
OK
All parameters are saved and the dialog is closed.
(9)
Cancel
All changes made are discarded and the dialog is closed.
(1)
(2)
(3)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
Expansion Modules Configuration Dialog Box
Settings
Buttons
6-6 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 72

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Button
Description
(1)
OK
All parameters are saved and the dialog is closed.
(2)
Cancel
All changes made to the parameters are discarded and the dialog is closed.
(3)
Write All Parameters
Current parameters configured in the PID Module Configuration dialog box
are written to the data registers (RAM) in the CPU module and the PID
module.
(4)
Upload All Parameters
All parameters stored in the PID module mounted on the slot selected in the
Expansion Modules Configuration dialog box are read, and all parameters in
the dialog box are updated.
(5)
Monitor
The PID module mounted on the slot selected in the Expansion Modules
Configuration dialog box can be monitored.
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
PID Module Configuration Dialog Box
The buttons in the PID module configuration dialog box are described.
Buttons
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-7
Page 73

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(1)
+56
–
Input CH0 Function
0: Input CH0
1: Difference input (Input CH0 - Input CH1)
2: Difference input (Input CH1 - Input CH0)
3: Addition input (Input CH0 + Input CH1)
R/W
(2)
–
+133
Input CH1 Function
0: Input CH1
1: Difference input (Input CH0 - Input CH1)
2: Difference input (Input CH1 - Input CH0)
3: Addition input (Input CH0 + Input CH1)
R/W
+55
–
External SP Input
0: Disabled
1: External SP input (4 to 20mA DC) (Note)
2: External SP input (0 to 20mA DC)
3: External SP input (1 to 5V DC)
4: External SP input (0 to 1V DC)
5: Cascade control (Note)
Note: When External SP input is selected in Input CH1
Function, “1: External SP input (4 to 20mA DC)” is
selected as the default. When Cascade Control is
selected in Input CH1 Function, “5: Cascade control” is
selected.
R/W
(3)
+57
–
Output CH0 Function
0: Output CH0
1: Output CH1
2: Both outputs (Output CH0, Output CH1)
R/W
(4) – +134
Output CH1 Function
0: Output CH1
(The selection of Output CH0 Function has priority.)
R/W
(5)
+58
+135
Input Range
See page 6-10 for the detail about the input range.
R/W
(6)
+59
+136
Set Point (SP) Upper Limit/
Linear Conversion
Maximum Value
When input is thermocouple/resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to input range upper limit
When input is voltage/current:
Linear conversion minimum to input range upper limit
R/W
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
PID Module Configuration - Input Parameters List (CH0 and CH1)
The input parameters for CH0 and CH1 controls are described here.
Control Registers
6-8 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 74

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(7)
+60
+137
Set Point (SP) Lower Limit/
Linear Conversion
Minimum Value
When input is thermocouple/resistance thermometer:
Input range lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage/current:
Input range lower limit to linear conversion maximum
R/W
(8)
+62
+139
PV Correction
When input range unit is Celsius:
-100.0 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-100.0 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage/current:
-1000 to 1000
R/W
(9)
+63
+140
PV Filter Time Constant
0.0 to 10.0 sec
R/W
(10)
+65
+142
Alarm 1 Type
0: No alarm action
1: Upper limit alarm
2: Lower limit alarm
3: Upper/Lower limits alarm
4: Upper/Lower limit range alarm
5: Process high alarm
6: Process low alarm
7: Upper limit alarm with standby
8: Lower limit alarm with standby
9: Upper/Lower limits alarm with standby
R/W
+66
+143
Alarm 2 Type
+67
+144
Alarm 3 Type
+68
+145
Alarm 4 Type
+69
+146
Alarm 5 Type
+70
+147
Alarm 6 Type
+71
+148
Alarm 7 Type
+72
+149
Alarm 8 Type
(11)
+37
+114
Alarm 1 Value
See page 6-10 for the detail about alarm value range.
R/W
+38
+115
Alarm 2 Value
+39
+116
Alarm 3 Value
+40
+117
Alarm 4 Value
+41
+118
Alarm 5 Value
+42
+119
Alarm 6 Value
+43
+120
Alarm 7 Value
+44
+121
Alarm 8 Value
(12)
+73
+150
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
When the unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When the unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage/current:
1 to 1000
R/W
+74
+151
Alarm 2 Hysteresis
+75
+152
Alarm 3 Hysteresis
+76
+153
Alarm 4 Hysteresis
+77
+154
Alarm 5 Hysteresis
+78
+155
Alarm 6 Hysteresis
+79
+156
Alarm 7 Hysteresis
+80
+157
Alarm 8 Hysteresis
(13)
+81
+158
Alarm 1 Delay Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
+82
+159
Alarm 2 Delay Time
+83
+160
Alarm 3 Delay Time
+84
+161
Alarm 4 Delay Time
+85
+162
Alarm 5 Delay Time
+86
+163
Alarm 6 Delay Time
+87
+164
Alarm 7 Delay Time
+88
+165
Alarm 8 Delay Time
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-9
Page 75

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Input Type and Range
Unit
Range
00h
Type K Thermocouple
Celsius
-200 to 1370°C
01h
Type K Thermocouple with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 400.0°C
02h
Type J Thermocouple
-200 to 1000°C
03h
Type R Thermocouple
0 to 1760°C
04h
Type S Thermocouple
0 to 1760°C
05h
Type B Thermocouple
0 to 1820°C
06h
Type E Thermocouple
-200 to 800°C
07h
Type T Thermocouple with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 400.0°C
08h
Type N Thermocouple
-200 to 1300°C
09h
P L-II
0 to 1390°C
0Ah
C (W/Re5-26)
0 to 2315°C
0Bh
Pt100 with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 850.0°C
0Ch
JPt100 with Decimal Point
-200.0 to 500.0°C
0Dh
Pt100
-200 to 850°C
0Eh
JPt100
-200 to 500°C
0Fh
Type K Thermocouple
Fahrenheit
-328 to 2498°F
10h
Type K Thermocouple with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 752.0°F
11h
Type J Thermocouple
-328 to 1832°F
12h
Type R Thermocouple
32 to 3200°F
13h
Type S Thermocouple
32 to 3200°F
14h
Type B Thermocouple
32 to 3308°F
15h
Type E Thermocouple
-328 to 1472°F
16h
Type T Thermocouple with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 752.0°F
17h
Type N Thermocouple
-328 to 2372°F
18h
PL-II
32 to 2534°F
19h
C (W/Re5-26)
32 to 4199°F
1Ah
Pt100 with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 1562.0°F
1Bh
JPt100 with Decimal Point
-328.0 to 932.0°F
1Ch
Pt100
-328 to 1562°F
1Dh
JPt100
-328 to 932°F
1Eh
4 to 20mA DC
―
-2000 to 10000
1Fh
0 to 20mA DC
―
-2000 to 10000
20h
0 to 1V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
21h
0 to 5V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
22h
1 to 5V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
23h
0 to 10V DC
―
-2000 to 10000
Alarm Type
Valid Range
Upper Limit Alarm
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Lower Limit Alarm
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm
0 to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limit Range Alarm
0 to full scale *1
Process High Alarm
Input range lower limit to input range upper limit *2
Process Low Alarm
Input range lower limit to input range upper limit *2
Upper Limit Alarm with Standby
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Lower Limit Alarm with Standby
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm with Standby
0 to full scale *1
Input Range
Each input setting range is described.
Valid Range for Alarm 1 to Alarm 8 Value
The valid range of each alarm type is described in the following table.
*1: When input is voltage/current, full scale is the linear conversion span.
*2: When input is voltage/current, the valid range is the linear conversion minimum value to linear conversion maximum
value.
6-10 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 76

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
(1)
+55
Input Range
(External SP input)
0: Disabled (Note)
1: 4 to 20mA DC
2: 0 to 20mA DC
3: 1 to 5V DC
4: 0 to 1V DC
5: Cascade control (Note)
Note: Disabled and Cascade control cannot be selected
in the input range.
R/W
(2)
+139
PV Correction
-1000 to 1000
R/W
(3)
+140
PV Filter Time Constant
0.0 to 10.0 sec
R/W
(4)
+178
External SP Input Linear
Conversion Maximum
Value
External SP Input linear conversion min. to input range
upper limit of CH0
R/W
(5)
+179
External SP Input Linear
Conversion Minimum
Value
Input range lower limit of CH0 to external SP input linear
conversion max.
R/W
(6)
+177
External SP Input Bias
±20% of the external SP input linear conversion span
R/W
(7)
+142
Alarm 1 Type
0: No alarm action
1: No alarm action
2: No alarm action
3: No alarm action
4: No alarm action
5: Process high alarm
6: Process low alarm
7: No alarm action
8: No alarm action
9: No alarm action
R/W
+143
Alarm 2 Type
+144
Alarm 3 Type
+145
Alarm 4 Type
+146
Alarm 5 Type
+147
Alarm 6 Type
+148
Alarm 7 Type
+149
Alarm 8 Type
(8)
+114
Alarm 1 Value
See page 6-10 for the detail about alarm value range.
R/W
+115
Alarm 2 Value
+116
Alarm 3 Value
+117
Alarm 4 Value
+118
Alarm 5 Value
+119
Alarm 6 Value
+120
Alarm 7 Value
+121
Alarm 8 Value
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
Input Parameters List when External SP Input is Selected
Control Registers
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-11
Page 77

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(9)
+150
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
When input range unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current:
1 to 1000
R/W
+151
Alarm 2 Hysteresis
+152
Alarm 3 Hysteresis
+153
Alarm 4 Hysteresis
+154
Alarm 5 Hysteresis
+155
Alarm 6 Hysteresis
+156
Alarm 7 Hysteresis
+157
Alarm 8 Hysteresis
(10)
+158
Alarm 1 Delay Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
+159
Alarm 2 Delay Time
+160
Alarm 3 Delay Time
+161
Alarm 4 Delay Time
+162
Alarm 5 Delay Time
+163
Alarm 6 Delay Time
+164
Alarm 7 Delay Time
+165
Alarm 8 Delay Time
6-12 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 78

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(1)
+90
+167
Control Mode
0: Fixed value control mode
1: Program control mode
When the cascade control is selected as Input CH1
Function, only the fixed value control mode can be
selected for CH0 control.
If program control is selected, external SP input will not
work.
R/W
(2)
+53
+130
Control Action
0: Reverse control action (Heating)
1: Direct control action (Cooling)
R/W
(3)
+54
–
Heating/Cooling Control
0: Disable
R/W
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(21)
(22)
(17)
(18)
(20)
(19)
(15)
(16)
(23)
(24)
(25)
(26)
(27)
PID Module Configuration - Control Parameters List (CH0 and CH1)
The control parameters for CH0 and CH1 are described here.
Control Parameters when Program Control Mode is Selected
When the program control mode is selected, parameters (23) to (27) are enabled. Parameters for the fixed
value control mode, such as the set point (SP), proportional band/proportional gain, or integral time, are
disabled.
Control Registers
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-13
Page 79

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
1: Enable
(4)
+20
+23
Set Point (SP)
When input is thermocouple/resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage/current:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion max.
R/W
(5)
+94
+171
Proportional Term
0: Proportional band
1: Proportional gain
R/W
(6)
+26
+103
Proportional Band/
Proportional Gain
Proportional band:
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F)
When input is voltage/current:
0.0 to 1000.0%
Proportional gain:
0.00 to 100.00%
R/W
(7)
+27
+104
Integral Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
(8)
+28
+105
Derivative Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
(9)
+29
+106
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
0 to 100%
R/W
(10)
+89
+166
AT Bias
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 50°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 50. 0 °C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 100°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 100. 0 °F)
R/W
(11)
+31
+108
Reset
When input range unit is Celsius:
-100.0 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-100.0 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current:
-1000 to 1000
R/W
(12)
+33
+110
Set Point (SP) Rise Rate
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C/min)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F/min)
When input is voltage or current:
0 to 10000/min
R/W
(13)
+34
+111
Set Point (SP) Fall Rate
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C/min)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F/min
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F/min)
When input is voltage or current:
0 to 10000/min
R/W
6-14 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 80

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Setting Range
R/W
CH0
CH1
(14)
+32
+109
Output Manipulated
Variable Rate-of-Change
0 to 100%/sec
R/W
(15)
+61
+138
Output ON/OFF
Hysteresis
When input range unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current:
1 to 1000
R/W
(16)
+21
+24
Manual Mode Output
Manipulated Variable
When heating/cooling control is disabled:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to output
manipulated variable upper limit
When heating/cooling control is enabled:
- Cooling output manipulated variable upper limit to
heating output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
(17)
+35
+112
Loop Break Alarm (LA)
Time
0 to 200 minutes
R/W
(18)
+36
+113
Loop Break Alarm (LA)
Span
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 150°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 150.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 150°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 150.0°F)
When input is voltage or current:
0 to 1500
R/W
(19)
+95
–
Cooling Method
0: Air cooling
1: Oil cooling
2: Water cooling
R/W
(20)
+48
–
Cooling Proportional
Band
0.0 to 10.0 times
(Cooling proportional band is the product of this value
and the heating proportional band)
R/W
(21)
+98
–
Cooling Output ON/OFF
Hysteresis
When input range unit is Celsius:
0.1 to 100.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0.1 to 100.0°F
When input is voltage or current:
1 to 1000
R/W
(22)
+50
–
Overlap/Dead Band
When input range unit is Celsius:
-200.0 to 200.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-200.0 to 200.0°F
When input is voltage or current:
-2000 to 2000
R/W
(23)
+91
+168
Program Control Mode
Start Type
0: PV start
1: PVR start
2: SP start
R/W
(24)
+96
+173
Set Point (SP) when
Program Control Starts
When input is thermocouple/resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage or current:
Linear conversion min. to linear conversion max.
R/W
(25)
+92
+169
Step Time Unit
0: Minute
1: Second
R/W
(26)
+93
+170
Program End Action
0: Terminate program control
1: Continue program control (Repeat)
2: Hold program control
R/W
(27)
+97
+174
Number of Repeats
0 to 10000 times
R/W
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-15
Page 81

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Setting Range
R/W
(1)
+178
External SP Input Linear
Conversion Maximum
Value
External SP Input linear conversion min. value to input
range upper limit of CH0
R/W
(2)
+179
External SP Input Linear
Conversion Minimum
Value
Input range lower limit of CH0 to external SP Input linear
conversion max. value
R/W
(1)
(2)
Control Parameters when Cascade Control is Enabled
Control Registers
6-16 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 82

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(1)
+99
+176
Output Type
0: Non-contact voltage output (for SSR drive)
1: Current output
R/W
(2)
+30
+107
Control Period
1 to 120 sec
R/W
(3)
+46
+123
Output Manipulated
Variable Upper Limit
When output type is voltage:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 100%
When output type is current:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 105%
R/W
(4)
+47
+124
Output Manipulated
Variable Lower Limit
When output type is voltage:
0% to output manipulated variable upper limit
When output type is current:
-5% to output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
(5)
+49
–
Cooling Control Period
1 to 120 sec
R/W
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
PID Module Configuration - Output Parameters List (CH0 and CH1)
The output parameters for CH0 and CH1 are described here.
Output Parameters when Heating/Cooling Control is Enabled
Control Registers
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-17
Page 83

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(6)
+51
–
Cooling Output
Manipulated Variable
Upper Limit
When output type is voltage:
Cooling output manipulated variable lower limit to 100%
When output type is current:
Cooling output manipulated variable lower limit to 105%
R/W
(7)
+52
–
Cooling Output
Manipulated Variable
Lower Limit
When output type is voltage:
0% to cooling output manipulated variable upper limit
When output type is current:
-5% to cooling output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
6-18 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 84

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(1)
+180
+390
Set Point (SP)
When input is thermocouple/resistance thermometer:
Set point (SP) lower limit to set point (SP) upper limit
When input is voltage or current:
Linear conversion min. to linear con- version max.
R/W
(2)
+181
+391
Step Time
When step time unit is Minute:
0 to 6000 minutes
When step time unit is Second:
0 to 6000 seconds
R/W
(3)
+182
+392
Wait Value
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 100°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 100.0°C)
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 100°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 100.0°F)
When input is voltage or current:
0 to 1000
R/W
(4)
+183
+393
Proportional Band/
Proportional Gain
Proportional band:
When input range unit is Celsius:
0 to 10000°C
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°C )
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
0 to 10000°F
(Range with a decimal point: 0.0 to 1000.0°F)
When input is voltage or current:
0.0 to 1000.0%
Proportional gain:
0.00 to 100.00%
R/W
(5)
+184
+394
Integral Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
(6)
+185
+395
Derivative Time
0 to 10000 sec
R/W
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
(19)
(20)
PID Module Configuration - Program Parameters List (CH0 and CH1)
Program parameters for CH0 and CH1 are described here.
Control Registers
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-19
Page 85

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Offset from
the control
register
Parameter
Description
R/W
CH0
CH1
(7)
+186
+396
ARW (Anti-Reset Windup)
0 to 100%
R/W
(8)
+187
+397
Output Manipulated
Variable Rate-of-Change
0 to 100%/sec
R/W
(9)
+188
+398
Alarm 1 Value
Refer to the valid range for alarm 1 to alarm 8 values
shown in the following table.
R/W
(10)
+189
+399
Alarm 2 Value
(11)
+190
+400
Alarm 3 Value
(12)
+191
+401
Alarm 4 Value
(13)
+192
+402
Alarm 5 Value
(14)
+193
+403
Alarm 6 Value
(15)
+194
+404
Alarm 7 Value
(16)
+195
+405
Alarm 8 Value
(17)
+197
+407
Output Manipulated
Variable Upper Limit
When output type is voltage:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 100%
When output type is current:
Output manipulated variable lower limit to 105%
R/W
(18)
+198
+408
Output Manipulated
Variable Lower Limit
When output type is voltage:
0% to output manipulated variable upper limit
When output type is current:
-5% to output manipulated variable upper limit
R/W
(19)
+199
–
Cooling Proportional
Band
0.0 to 10.0 times
(Cooling proportional band is the multiplication of
heating proportional band)
R/W
(20)
+200
–
Overlap/Dead Band
When input range unit is Celsius:
-200.0 to 200.0°C
When input range unit is Fahrenheit:
-200.0 to 200.0°F
When input is voltage or current:
-2000 to 2000
R/W
Alarm Type
Valid Range
Upper Limit Alarm
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Lower Limit Alarm
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm
0 to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limit Range Alarm
0 to full scale *1
Process High Alarm
Input range lower limit to input range upper limit *2
Process Low Alarm
Input range lower limit to input range upper limit *2
Upper Limit Alarm with Standby
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Lower Limit Alarm with Standby
–(Full scale) to full scale *1
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm with Standby
0 to full scale *1
Valid Range for Alarm 1 to Alarm 8 Value
*1: When input is voltage/current, full scale is the linear conversion span.
*2: When input is voltage/current, the valid range is the linear conversion minimum value to linear conversion maximum
value.
6-20 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 86

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
PID Module Configuration - I/O Function Selections
(1) Control Register+56: Input CH0 Function
The one of the following input functions can be selected as the Input CH0 Function.
Input CH0:
Input CH0 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH0 control.
Difference (CH0-CH1):
The difference between input CH0 and input CH1 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH0 control.
Process variable (PV) of CH0 control = Input CH0 input value - Input CH1 input value
Difference (CH1-CH0):
The difference between input CH1 and input CH0 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH0 control.
Process variable (PV) of CH0 control = Input CH1 input value - Input CH0 input value
Addition (CH0+CH1):
The addition of input CH0 and input CH1 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH0 control.
Process variable (PV) of CH0 control = Input CH0 input value + Input CH1 input value
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-21
Page 87

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Current
Voltage
Input Type
4 to 20mA DC or 0 to 20mA DC
1 to 5V DC or 0 to 1V DC
Allowable Input
50mA DC maximum
0 to 1V DC: 5V DC maximum
1 to 5V DC: 10V DC maximum
Input Impedance
50Ω
100kΩ
(2) Control Register+133: Input CH1 Function
Control Register+55: External SP Input
The one of the following input functions can be selected as the Input CH1 Function.
Input CH1:
Input CH1 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH1 control.
Difference (CH0-CH1):
The difference between input CH0 and input CH1 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH1 control.
Process variable (PV) of CH1 control = Input CH0 input value - Input CH1 input value
Difference (CH1-CH0):
The difference between input CH1 and input CH0 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH1 control.
Process variable (PV) of CH1 control = Input CH1 input value - Input CH0 input value
Addition (CH0+CH1):
The addition of input CH0 and input CH1 is used as the process variable (PV) for CH1 control.
Process variable (PV) of CH1 control = Input CH0 input value + Input CH1 input value
External SP Input:
Input CH1 is used as the set point (SP) for CH0 control.
When the external SP input bias is configured, the external SP input bias is added to the input CH1 value, and
then the input CH1 value is used as the set point (SP) for CH0 control. One of the analog input types shown in
the table blow can be selected for the external SP input.
Cascade Control:
The cascade control is an advanced control that uses 2 inputs [CH1 as a master (primary control) and CH0 as
a slave (secondary control)] to control a single process.
Master (CH1) calculates the output manipulated variable (MV) according to the process variable (PV) and the
set point (SP). The output manipulated variable (MV) of the master (CH1) is used as the set point (SP) of the
slave (CH0). With the obtained set point (SP), the slave (CH0) calculates the output manipulated variable (MV)
and controls the output CH0.
6-22 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 88

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Input CH0
Input CH1
Input CH1
Difference
(CH0-CH1)
Difference
(CH1-CH0)
Addition
(CH0+CH1)
External
SP Input
Cascade
Control
Input CH0
O O O O O
O
Difference (CH0-CH1)
O O O O X
X
Difference (CH1-CH0)
O O O O X
X
Addition (CH0+CH1)
O O O O X
X
When the cascade control is used, the output CH1 is unused. When the output type is current, the output CH1
is 4 mA. When the output type is voltage, the output CH1 is 0 V. When the output type is relay, Output CH1 is
turned off. When heating/cooling control is enabled, output CH1 is used as the cooling output.
Output manipulated variable (MV) (0 to 100%) of the master (CH1) is converted using the external SP input
linear conversion minimum and maximum values and is used as the set point (SP) of the slave (CH0).
Example: When the external SP input linear conversion minimum value is 0°C and the external SP input linear
conversion maximum value is 1000°C, the set point (SP) of the slave (CH0) is decided as follows:
When master (CH1) output manipulated variable (MV) is 0%: 0°C
When master (CH1) output manipulated variable (MV) is 50%: 500°C
When master (CH1) output manipulated variable (MV) is 100%: 1000°C
Combination of Input CH0 and Input CH1 Functions
The possible combinations of Input CH0 and CH1 Functions are shown below. (O: Possible, X: Impossible)
(3) Control Register+57: Output CH0 Function
The one of the following output functions can be selected as the Output CH0 Function.
Output (CH0): The output of the CH0 control is outputted from output CH0
Output (CH1): The output of the CH0 control is outputted from output CH1
When Output (CH1) is selected, CH1 parameters are used for the control period and the output manipulated
variable (MV) upper and lower limits. CH0 parameters are used for all other parameters, such as the output
manipulated variable rate-of-change, output on/off hysteresis, and manual mode output manipulated variable.
When Output (CH1) is selected, output CH0 is unused. When output type is relay, the output CH0 is turned off.
When output type is voltage/current, output CH0 is 0V/4mA.
Both Outputs (CH0, CH1): The output of the CH0 control is outputted from both outputs CH0 and CH1
The control period and output manipulated variable (MV) upper and lower limits of CH0 and CH1 are used for
the corresponding output. CH0 parameters are used for all other parameters, such as, the output manipulated
variable rate-of-change, output on/off hysteresis, and manual mode output manipulated variable.
(4) Control Register+134: Output CH1 Function
Output (CH1) is always selected as Output CH1 Function. The output of the CH1 control is outputted from
output CH1. Output CH0 Function has priority.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-23
Page 89

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
PID Module Configuration - Input Parameters Details
Input parameters for CH0 control are described here. Input parameters for CH1 control are the same as those
of CH0 control. However, the position from the control register for each parameter differs. For details about the
positions from the control register for CH1 control, see 5-17 to 5-20.
(1) Control Register+58: Input Range
Select input type and input range unit (Celsius or Fahrenheit). For details about the input range, see 6-10.
(2) Control Register+62: PV Correction
If the sensor cannot be installed to the location of the control target, the temperature measured by the sensor
may deviate from the actual temperature of the control target. When a target is controlled with multiple PID
modules, the measured temperatures may not match due to the differences in sensor accuracy or dispersion
of load capacities even though the set points (SP) of those PID modules are the same. In such cases, the
process variable (PV) of the PID module can be adjusted to the desired temperature by using the PV
Correction. The process variable (PV) after the PV correction should be within the control range (See 9-4). For
example, when type K thermocouple (-200 to 1370°C) is selected as input type, configure an appropriate PV
correction value so that the process variable (PV) after the PV correction does not exceed the control range
(-250 to 1420°C) [(Input range lower limit - 50°C) to (Input range upper limit + 50°C)].
When the process variable (PV) after the PV correction is within the control range, the PID module controls the
temperature based on the process variable (PV) after the PV correction. When the process variable (PV) after
the PV correction is out of the control range, the under or over range error occurs and the control output is
turned off
The process variable (PV) after the PV correction can be calculated using the following formula:
Process variable (PV) after the PV correction = Process variable (PV) + (PV correction value)
Example 1: When process variable (PV) is 198°C
If the PV correction value is 2.0°C, the process variable (PV) will be 200.0°C (198°C + 2.0°C).
If the PV correction value is -2.0°C, the Process variable (PV) will be 196.0°C (198°C - 2.0°C).
6-24 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 90

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
10000
5000
0
-2000
4mA
20mA
Input range
Current
Linear conversion is conducted
within this range.
Sensor
Electric Furnace
PV correction value: 10.0°C
PID Module
Process
Variable (PV)
200°C
T
Time (Second)
Process
Variable
(PV)
Time (Second)
Process
Variable
(PV)
Example 2: By setting the PV correction value for the PID module to 10.0°C, the process variable (PV) of the
PID module is adjusted from 190°C to 200°C.
(3) Control Register +63: PV Filter Time Constant
The PV filter function is a software filter to stabilize the process variable (PV) affected by fluctuating processes,
such as the pressure or flow rate, by calculating first-order lag of the process variable (PV). Even if the process
variable (PV) changes as shown in the Figure 1, when the PV filter time constant is configured, the process
variable (PV) changes as shown in the Figure 2. After the PV filtering process, the process variable (PV)
reaches 63% of the process variable (PV) in T seconds.
If the PV filter time constant is too large, it adversely affects the control results due to the delay of response.
Example: If the least significant digit of the process variable (PV) is fluctuating, the fluctuation can be
suppressed by using the PV filter time constant.
Figure 1. Process variable (PV) Figure 2. Process variable (PV)
before PV filtering process after PV filtering process
(4) Control Register+59: Set Point (SP) Upper Limit/Linear Conversion Maximum Value
(5) Control Register+60: Set Point (SP) Lower Limit/Linear Conversion Minimum Value
Linear Conversion Function
The diagram below shows an example of the linear conversion. When the linear conversion maximum value is
5000 and the linear conversion minimum value is 0, the current input (4 to 20mA DC) is linearly-converted as
shown in the diagram.
Set Point (SP) Upper Limit/Linear Conversion Maximum Value
When input type is thermocouple or resistance thermometer, the linear conversion is disabled. The linear
conversion maximum value is used as the upper limit of the set point (SP). When input type is voltage/current,
configure the maximum value of input CH0 as the linear conversion maximum value. Any value within the valid
input range can be configured.
Set Point (SP) Lower Limit/Linear Conversion Minimum Value
When input type is thermocouple or resistance thermometer, the linear conversion is disabled. The linear
conversion minimum value is used as the lower limit of the set point (SP). When input type is voltage/current,
configure the minimum value of input CH0 as the linear conversion minimum value. Any value within the valid
range can be configured.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-25
Page 91

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
OFF
ON
SP
SP
SP
OFF
ON
SP
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
200
205
5
203
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
200
205203
195
197
OFF
ON
200
207205
193
195
Alarm Hysteresis
-Alarm Value +Alarm Value+Alarm Value-Alarm Value
Alarm Hysteresis
Alarm Hysteresis
Alarm Value
Alarm Value Alarm ValueAlarm Value
C
2.0
C
C C C
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: -5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
[Alarm Action]
[Setting Example]
[Setting Example]
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: 5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
[Alarm Action]
C205 Process Variable (PV): Alarm Output ON
Process Variable (PV)
203 : Alarm Output OFFC
C197
Process Variable (PV)
195 : Alarm Output ONC
-5
C
2
C
195C197C200
C
[Setting Example]
[Alarm Action]
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: 5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
Process Variable (PV)
203 : Alarm
Output OFF
C
197
C
Process Variable (PV)
195 : Alarm Output ONC
C205
Process Variable (PV) or
[Alarm Action]
205 : Alarm
Output ON
[Setting Example]
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: 5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
Process Variable (PV) or 207
C
Process Variable (PV)
193 : Alarm Output OFFC
C195
Process Variable (PV)
C
C
2.0
C
2.0
C
C
5 C
5 C
C
C C
CCCC
C
2.0
C
5 C5 C
2.0
C
Upper Limit Alarm Lower Limit Alarm
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm Upper/Lower Limit Range Alarm
Alarm Hysteresis
Process Variable (PV) : Alarm Output OFF
(6) Control Register+65: Alarm 1 Type
Control Register+66: Alarm 2 Type
Control Register+67: Alarm 3 Type
Control Register+68: Alarm 4 Type
Control Register+69: Alarm 5 Type
Control Register+70: Alarm 6 Type
Control Register+71: Alarm 7 Type
Control Register+72: Alarm 8 Type
Select one of the alarm types from upper limit alarm, lower limit alarm, upper/lower limits alarm, upper/lower
limit range alarm, process high alarm, process low alarm, upper limit alarm with standby, lower limit alarm with
standby, upper/lower limits alarm with standby, and no alarm action. The same alarm type can be selected in
multiple alarms.
Alarm Actions
6-26 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 92

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
SP
OFF
ON
SP
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
205203
OFF
ON
197195
OFF
ON
200
205
5
203
OFF
ON
195
200197
Alarm ValueAlarm Value
Alarm Hysteresis
Alarm Hysteresis
Alarm Hysteresis
[Setting Example]
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 205
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
[Alarm Action]
C205 Process Variable (PV): Alarm Output ON
Process Variable (PV)
203 : Alarm Output OFFC
[Setting Example]
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 195
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
[Alarm Action]
C197 Process Variable (PV): Alarm Output OFF
Process Variable (PV)
195 : Alarm Output ONC
2.0
C
C C
C
C
Alarm Hysteresis
Upper Limit Alarm with Standby Lower Limit Alarm with Standby
[Setting Example]
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: 5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
[Alarm Action]
C205 Process Variable (PV): Alarm Output ON
Process Variable (PV)
203 : Alarm Output OFFC
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: -5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
[Alarm Action]
[Setting Example]
197
Process Variable (PV) : Alarm Output OFF
Process Variable (PV)
195 : Alarm Output ONC
+Alarm Value-Alarm Value
+Alarm Value-Alarm Value
2.0 C
C
2.0 C
-5
C
C
CCCCC
C
: Standby functions.
Process High Alarm
Process Low Alarm
2.0
C
Note: When the set point (SP) is changed, the standby function is enabled. Once the process variable (PV)
enters the alarm output off range, the standby function is canceled.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-27
Page 93

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
SP
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
5 5
200
205
203
195
197
Alarm Hysteresis
Upper/Lower Limits Alarm with Standby
Alarm Value Alarm Value
: Standby functions.
[Setting Example]
Set Point (SP)
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 200 C
: 5
C
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
C
Process Variable (PV)
203 : Alarm
Output OFF
C
197
C
Process Variable (PV)
195 : Alarm Output ONC
C205
Process Variable (PV) or
C C
2.0 2.0
C C
C
C C
C
C
[Alarm Action]
Alarm Type
Alarm Value
Alarm Action
Deviation
Alarm
Upper/Lower limit range alarm
Deviation from the set
point (SP) is the alarm
value.
The alarm output turns off if the
process variable (PV) exceeds
the range.
Upper limit alarm,
Lower limit alarm,
Upper/Lower limits alarm,
Upper limit alarm with standby,
Lower limit alarm with standby,
Upper/Lower limits alarm with
standby
The alarm output turns on if the
process variable (PV) exceeds
the range.
Process
Alarm
Process high alarm
Process low alarm
The alarm action point is
the alarm value.
The alarm output turns on if the
process variable (PV) exceeds
the alarm value.
Notes:
· When the set point (SP) is changed, the standby function is enabled. Once the process variable (PV)
enters the alarm output off range, the standby function is canceled.
· Even when an alarm output is triggered, the PID module continues its control. To stop the control when an
alarm is triggered, ladder programming is needed. For a ladder program example, see 7-6.
(7) Control Register+37: Alarm 1 Value
Control Register+38: Alarm 2 Value
Control Register+39: Alarm 3 Value
Control Register+40: Alarm 4 Value
Control Register+41: Alarm 5 Value
Control Register+42: Alarm 6 Value
Control Register+43: Alarm 7 Value
Control Register+44: Alarm 8 Value
There are two types of alarms: Deviation alarm and process alarm.
6-28 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
When the alarm value is 0, the alarm action is disabled except process high alarm and process low alarm.
If the input type or input unit type is changed, confirm the valid range of the alarm value and configure
appropriate values.
Page 94

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(8) Control Register+73: Alarm 1 Hysteresis
Control Register+74: Alarm 2 Hysteresis
Control Register+75: Alarm 3 Hysteresis
Control Register+76: Alarm 4 Hysteresis
Control Register+77: Alarm 5 Hysteresis
Control Register+78: Alarm 6 Hysteresis
Control Register+79: Alarm 7 Hysteresis
Control Register+80: Alarm 8 Hysteresis
When an alarm turns from on to off and vice versa, the span between on and off is called alarm hysteresis. If
the alarm hysteresis is narrowed, the alarm output switches to on or off even by a slight variation of
temperature at around the alarm action point. This frequent on/off of an alarm may negatively affect the
connected equipment. To prevent that harmful effect, configure the alarm hysteresis for alarm on/off action.
(9) Control Register+81: Alarm 1 Delay Time
Control Register+82: Alarm 2 Delay Time
Control Register+83: Alarm 3 Delay Time
Control Register+84: Alarm 4 Delay Time
Control Register+85: Alarm 5 Delay Time
Control Register+86: Alarm 6 Delay Time
Control Register+87: Alarm 7 Delay Time
Control Register+88: Alarm 8 Delay Time
The alarm is not triggered until the configured time elapses after the process variable (PV) enters the alarm
output range. The input fluctuation due to noise may result in alarm output turning on. This can be prevented
by configuring the alarm delay time. When an alarm output is changed from on to off status, the alarm output
turns off and the alarm action delay time is reset. When the alarm output is changed from off to on status, the
time counting starts.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-29
Page 95

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(10)
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(8)
(9)
(5)
(6)
(7) T Time (Second)
Process
Variable
(PV)
Time (Second)
Process
Variable
(PV)
Input Parameters when External SP Input is Selected
The input CH1 parameters when External SP input is selected as the Input CH1 Function are described here.
(1) Control Register+55: Input Range
Select input type for the external SP input. Current (4 to 20mA DC or 0 to 20mA DC) or voltage (0 to 1V DC or 1
to 5V DC) can be selected.
(2) Control Register+62: PV Correction
If the sensor cannot be installed to the location of the control target, the temperature measured by the sensor
may deviate from the actual temperature of the control target. When a target is controlled with multiple PID
modules, the measured temperatures may not match due to the differences in sensor accuracy or dispersion
of load capacities even though the set points (SP) of those PID modules are the same. In such cases, the
process variable (PV) of the PID module can be adjusted to the desired temperature by using the PV
Correction.
The process variable (PV) after PV correction can be calculated using the following formula.
Process variable (PV) after PV correction = Process variable (PV) + (PV correction value)
(3) Control Register +63: PV Filter Time Constant
The PV filter function is a software filter to stabilize the process variable (PV) affected by fluctuating processes
such as pressure or flow rate by calculating first-order lag of the process variable (PV). Even if the process
variable (PV) changes as shown in the Figure 1, when the PV filter time constant is configured, the process
variable (PV) changes as shown in the Figure 2. After the PV filtering process, the process variable (PV)
reaches 63% of the process variable (PV) in T seconds.
If the PV filter time constant is too large, it adversely affects the control results due to the delay of response.
Example: If the least significant digit of the process variable (PV) is fluctuating, the fluctuation can be
suppressed by using the PV filter time constant.
6-30 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Figure 1. Process variable (PV) Figure 2. Process variable (PV)
before PV filtering process after PV filtering process
Page 96

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(4) Control Register+178: External SP Input Linear Conversion Maximum Value
Configure the linear conversion maximum value for the external SP input. When input type is current (4 to
20mA DC or 0 to 20mA DC), configure the value corresponding to 20mA for input CH1. When input type is
voltage (0 to 1V DC or 1 to 5V DC), configure the value corresponding to 1V or 5V for input CH1.
Example: When input type is current (4 to 20mA DC), if the external SP input linear conversion maximum value
is 1000°C, external SP input 20mA corresponds to the set point (SP) 1000°C for CH0 control. When input type
is voltage (0 to 1V DC), if external SP input linear conversion maximum value is 1200°C, external SP input 1V
corresponds to the set point (SP) 1200°C for CH0 control.
(5) Control Register+179: External SP Input Linear Conversion Minimum Value
Configure the linear conversion minimum value for the external SP input. When input type is current (4 to
20mA DC or 0 to 20mA DC), configure the value corresponding to 4mA or 0mA for input CH1. When input type
is voltage (0 to 1V DC or 1 to 5V DC), configure the value corresponding to 0V or 1V for input CH1.
Example: When input type is current (4 to 20mA DC), if external SP input linear conversion minimum value is
0°C, external SP input 4mA corresponds to the set point (SP) 0°C for CH0 control. When input type is voltage
(0 to 1V DC), if external SP input linear conversion maximum value is set to -20°C, external SP input 0V
corresponds to the set point (SP) -20°C for CH0 control.
(6) Control Register+177: External SP Input Bias
The external SP input bias is added to the set point (SP) obtained after the linear conversion for the external
SP input. The set point (SP) is then used as the set point (SP) for CH0 control.
Examples:
When the input type is current (4 to 20mA DC), the linear conversion maximum value is 1000°C, the linear
conversion minimum value is 0°C, and the external SP input bias is 50°C, the set point (SP) of CH0 control
corresponding to 12mA of external SP input will be 550°C.
When the input type is voltage (0 to 1V DC), the linear conversion maximum value is 1000°C, the linear
conversion minimum value is 0°C, and the external SP input bias is 50°C, the set point (SP) of CH0 control
corresponding to 0.5V of external SP input will be 550°C.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-31
Page 97

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
205203
OFF
ON
197195
Alarm Value
Alarm Value
Alarm HysteresisAlarm Hysteresis
[Setting Example]
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value
: 205
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
[Alarm Action]
205 Process Variable (PV): Alarm Output ON
Process Variable (PV)
203: Alarm Output OFF
[Setting Example]
: 2.0
Alarm 1 Value : 195
Alarm 1 Hysteresis
[Alarm Action]
197 Process Variable (PV): Alarm Output OFF
Process Variable (PV)
195: Alarm Output ON
2.0
Process High Alarm
Process Low Alarm
2.0
Alarm Type
Alarm Value
Alarm Action
Process
Alarm
Process high alarm
Process low alarm
The alarm action point is
the alarm value.
The alarm output turns on if the
process variable (PV) exceeds
the alarm value.
(7) Control Register+65: Alarm 1 Type
Control Register+66: Alarm 2 Type
Control Register+67: Alarm 3 Type
Control Register+68: Alarm 4 Type
Control Register+69: Alarm 5 Type
Control Register+70: Alarm 6 Type
Control Register+71: Alarm 7 Type
Control Register+72: Alarm 8 Type
Select one of the alarm types from process high alarm, process low alarm, and no alarm action. The same
alarm type can be selected in multiple alarms.
Alarm Actions
(8) Control Register+37: Alarm 1 Value
Control Register+38: Alarm 2 Value
Control Register+39: Alarm 3 Value
Control Register+40: Alarm 4 Value
Control Register+41: Alarm 5 Value
Control Register+42: Alarm 6 Value
Control Register+43: Alarm 7 Value
Control Register+44: Alarm 8 Value
6-32 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 98

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(9) Control Register+73: Alarm 1 Hysteresis
Control Register+74: Alarm 2 Hysteresis
Control Register+75: Alarm 3 Hysteresis
Control Register+76: Alarm 4 Hysteresis
Control Register+77: Alarm 5 Hysteresis
Control Register+78: Alarm 6 Hysteresis
Control Register+79: Alarm 7 Hysteresis
Control Register+80: Alarm 8 Hysteresis
When an alarm turns from on to off and vice versa, the span between on and off is called alarm hysteresis. If
the alarm hysteresis is narrowed, the alarm output switches to on or off even by a slight variation of
temperature at around the alarm action point. This frequent on/off of an alarm may negatively affect the
connected equipment. To prevent that harmful effect, configure the alarm hysteresis for alarm on/off action.
(10) Control Register+81: Alarm 1 Action Delay Time
Control Register+82: Alarm 2 Action Delay Time
Control Register+83: Alarm 3 Action Delay Time
Control Register+84: Alarm 4 Action Delay Time
Control Register+85: Alarm 5 Action Delay Time
Control Register+86: Alarm 6 Action Delay Time
Control Register+87: Alarm 7 Action Delay Time
Control Register+88: Alarm 8 Action Delay Time
The alarm is not triggered until the configured time elapses after the process variable (PV) enters the alarm
output range. The input fluctuation due to noise may result in alarm output turning on. This can be prevented
by configuring the alarm delay time. When an alarm output is changed from on to off status, the alarm output
turns off and the alarm action delay time is reset. When the alarm output is changed from off to on status, the
time counting starts.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-33
Page 99

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
(5)
(6)
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
(11)
(12)
(13)
(14)
(16)
(21)
(22)
(17)
(18)
(20)
(19)
(15)
(23)
(24)
(25)
(26)
(27)
PID Module Configuration - Control Parameters Details
Control Parameters when Program Control Mode Is Selected
Control parameters of CH0 control are described here. When the program control mode is selected as the
control mode, parameters for the fixed value control mode, such as the set point (SP), proportional
band/proportional gain, or integral time, are disabled. The parameters for the program control mode (23) to
(27) are enabled.
Control parameters for CH1 control are the same as those of CH0 control except cascade control parameters.
However, the position from the control register for each parameter differs. For details about the positions from
the control register for CH1 control, see pages 5-17 to 5-20.
(1) Control Register+90: Control Mode
Either fixed value control mode or program control mode can be selected. When the external SP input or the
cascade control is selected in Input CH1 Function, the program control mode cannot be used for CH0 control.
Select fixed value control mode for control mode of CH0 control. If the program control mode is selected, the
external SP input does not function.
6-34 FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283
Page 100

CONFIGURING PID MODULE USING WINDLDR
Step
Temperature
Set point (SP)
Time
Temperature
Time
Output Manipulated
Variable (MV)
High
Low
Set Point (SP)
Process Variable (PV)
Output Manipulated
Variable (MV)
High
Low
Set Point (SP)
Process Variable (PV)
The fixed value control is a normal temperature control that the PID module controls the output to eliminate the
deviation between a single set point (SP) and the process variable (PV). The following diagram shows an
example of the fixed value control.
The program control allows you to define the set point (SP) that changes as the time progresses so that the
process variable (PV) can be controlled to match the set point (SP) changing as the time progresses. The set
point (SP) and time can be configured for each step. A maximum of 10 steps can be configured and performed.
The set point (SP) can be configured as shown in the following diagram.
(2) Control Register+53: Control Action
Selects either direct control action or reverse control action.
In direct control action, the output manipulated variable (MV) increases when the process variable (PV) is
higher than the set point (SP) (positive deviation). For example, freezers perform the direct control (cooling)
action.
In reverse control action, the output manipulated variable (MV) increases when the process variable (PV) is
lower than the set point (SP) (negative deviation). For example, electric furnaces perform the reverse control
(heating) action.
FC5A MicroSmart PID Module User’s Manual FC9Y-B1283 6-35
 Loading...
Loading...