Page 1

2
#61-164
#61-165
Intr
oduction
Utilizing patented technology, the SureTest®circuit analyzers
"look behind walls" to identify wiring problems that can lead to
personal shock hazards, electrical fires, or equipment performance issues. Personal shock
hazards stem from poor grounding, false grounds, and/or no ground fault protection.
Electrical fires are primarily caused from arc faults and high resistance points that lead to
glowing connections in the circuit wiring. And, equipment performance issues arise due to
insufficient voltage available under load, poor ground impedance, and high ground-to-neutral voltage. In fact, it’s estimated that 80% of power quality performance issues are related
to the faulty wiring issues stated above.
Product Features
• True RMS
• Measures voltage drop under 12, 15 and 20-amp loads
• Measures voltage: Line, Ground-to-Neutral, Peak, Frequency
• Measures Hot, Neutral and Ground conductor impedances
• Identifies proper wiring in 3-wire receptacles
• Identifies false (bootleg) grounds
• Tests GFCIs for proper operation
• Tests AFCIs for proper operation (61-165)
• Checks for Shared Neutrals that lead to AFCI nuisance tripping (61-165)
• Verifies dedicated circuits (with 61-176 adapter)
• Includes 1-ft. extension cord and carrying case
General Operation
The SureTest®Circuit Analyzer takes only seconds to test each outlet and circuit under a full
load. This test tool checks for various wiring conditions including: correct wiring, polarity
reversal and no ground per UL-1436. A simple menu gives access to measurements of line
voltage, voltage drop under a full load condition, ground-neutral voltage and line impedances.
The ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) test is performed separately in accordance with UL1436 and disrupts the electrical supply if a functional GFCI is present.
The SureTest®w/AFCI, #61-165, also tests arc fault circuit interrupter (AFCI) devices to
ensure that AFCI breakers protecting the circuit have been installed correctly. This test disrupts the electrical supply if a functional AFCI is present. This tool also checks for a shared
neutral condition that leads to AFCI nuisance tripping.
To maintain stated accuracies during repeated use, allow 20 seconds between insertions to
adequately dissipate any heat buildup during the load testing.
SureTest Circuit Analyzer
1. Menu Structure
2. Navigation Buttons
3. GFCI Test Button
4. AFCI Test Button
Menu Navigation
The microprocessor’s top priorities are to take live measurements and then analyze the data.
Hence, the microchip occasionally will not recognize the keypad buttons being rapidly
depressed, while it’s executing these routines. To avoid this issue, hold down the keypad
button each time until the menu changes.
The measurements taken by the SureTest are broken into five main menus positioned down
the left side of the display: Wiring Configuration (•••), Voltage (V), Voltage Drop (VD),
ASCC, and Impedance (Z). To navigate to each of the main menus, use the down arrow
button ( ).
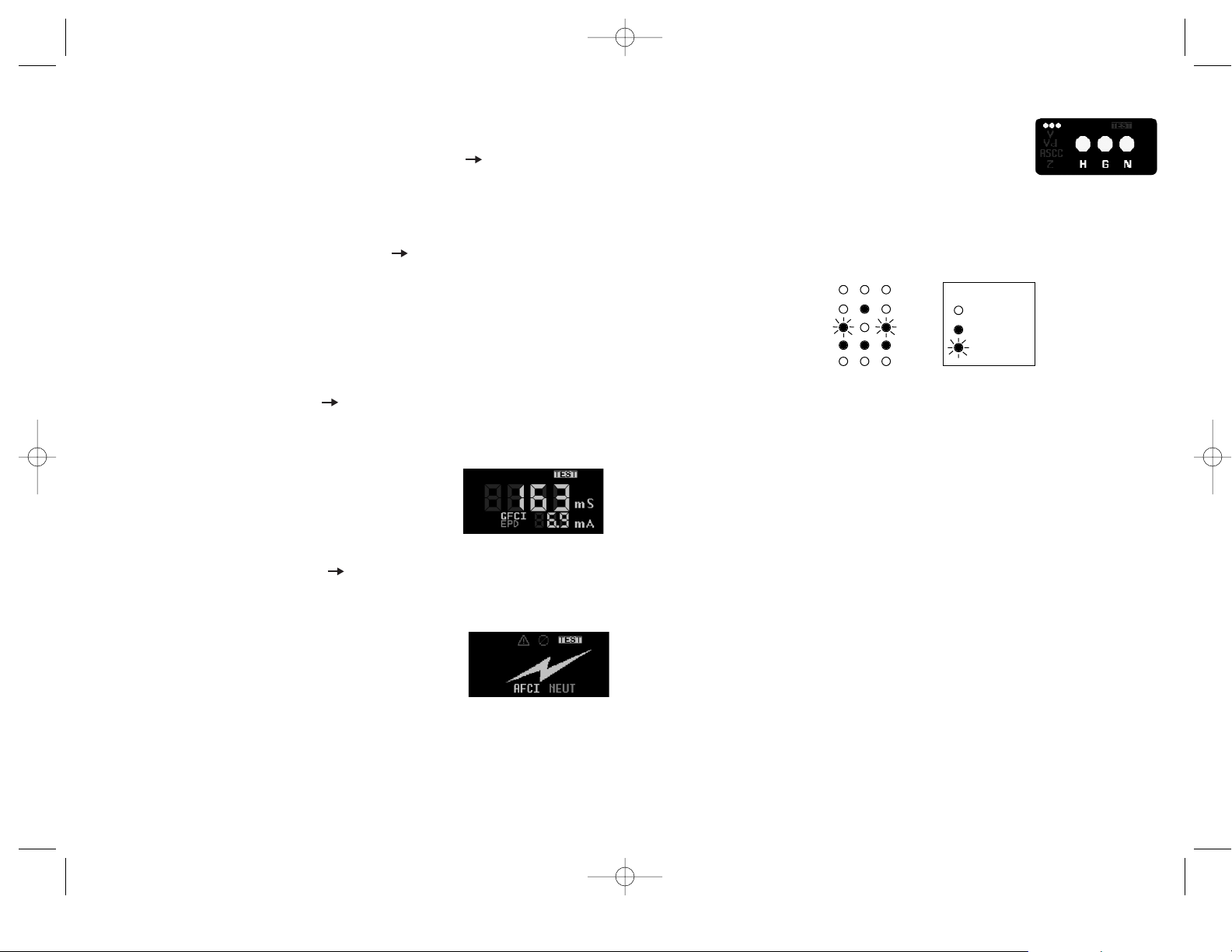
The Wiring Configuration (•••) screen indicates correct wiring, reverse polarity, hot/
ground reversal and no ground conditions by sequencing the three balls. The label on the
back of the product explains the wiring sequence indications.
#61-165
GFCI
AFCI
RM
S
True
S
u
r
e
e
T
s
t
SureTest®
Circuit Analyzer
WARNING: Do not use on outputs from UPS systems, light dimmers or square
wave generating equipment as damage to the analyzer will occur.
SureTest®Circuit Analyzer
Instruction Manual
#61-165
GFCI
AFCI
RMS
True
S
u
r
e
e
T
s
t
SureTest®
Circuit Analyzer
2
3
4
1
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 1
Page 2
3
4
The Voltage (V) menu displays the True RMS line voltage in real-time. This main menu has
a sub-menu positioned horizontally at the bottom of the screen that displays the line voltage
(RMS HN), ground-to-neutral voltage (RMS GN), Peak voltage (Peak), and Frequency
(Hz). To navigate through the submenu, use the side arrow button ( ).
The Voltage Drop (VD) screen dual displays percent voltage drop with a 15 amp load along
with the resultant loaded voltage (VL). This main menu has a submenu, which also displays the percent voltage drop and loaded voltage with 20 amp and 12 amp loads. To navigate through the submenu, use the side arrow button ( ).
The ASCC screen displays the Available Short-Circuit Current that the branch circuit can
deliver through the breaker during a bolted fault (dead-short) condition.
The Impedance (Z) main menu displays the impedance in ohms (Ω) of the hot conductor.
This main menu has a sub-menu positioned horizontally at the bottom of the screen that
also displays the neutral (N) and ground (G) conductor impedances. To navigate through
the submenu, use the side arrow button ( ). Note that testing the ground impedance will
trip a GFCI protected circuit.
GFCI Test Button
Depressing this button displays the GFCI main menu. Two tests can
be performed in this menu: GFCI and EPD. The GFCI tests Ground
Fault Circuit Interrupting devices by faulting 6-9mA from hot-toground per UL-1436. The EPD tests those breakers, which have an
Equipment Protective Device feature that trips the breaker if a ground fault of greater than 30mA
is detected. Pressing the side arrow button ( ) navigates between these two tests. Once the
desired test is highlighted, depress the GFCI test button on the keypad to activate the test.
AFCI Test Button
Depressing this button displays the AFCI main menu. Two tests
can be performed in this menu: AFCI and NEUT. The AFCI tests
Arc Fault Circuit Interrupting devices by creating a 106-141 amp
short-duration arc between the hot and neutral conductors per
UL1436. The NEUT tests for a Shared Neutral or falsely grounded neutral conductor,
which causes AFCI breakers to nuisance trip with normal loads. This test applies 300mA
between hot and neutral to ensure that the AFCI breaker does not trip.
Testing Procedure
Wiring Verification
Immediately after being inserted into a receptacle, the
SureTest displays the IDEAL logo while it performs a battery
of tests. The first test result displayed is the wiring condition.
The SureTest checks for the following conditions and indicates the test result on
the display.
Wiring Condition Display Indication
HGN
Correct Wiring
No Ground
Polarity Reversal
Open/Hot Neutral
False Ground
If the wiring condition is other than normal, the SureTest is limited on its
measurements that can be performed. If a no ground condition exists, only the
line voltage and voltage drop measurements are available. In a hot/ground reversal, open neutral or open hot condition, the unit will not have any power so the
display will be blank.
Notes:
1) Will not detect two hot wires in a circuit.
2) Will not detect a combination of defects.
3) Will not detect reversal of grounded and grounding conductors.
False Ground Indication
NEC article 250-23(a) only allows for a neutral-to-ground bond to occur at the
main panel. The SureTest suggests any improper neutral-to-ground bonds within
15-20 feet upstream (towards the panel) of the tester. If this bond improperly
occurs in the branch circuit through a bootleg ground via a jumper wire at the outlet
device or inadvertent contact of the ground wire to the neutral connection, the
SureTest indicates a false ground condition. Note that if the SureTest is within 1520 feet of the main panel, the unit will indicate a false ground condition on a properly wired circuit due to its close proximity to the proper ground-neutral bond in the
main panel.
Legend
On
Off
Flashing
F
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 3
Page 3
5
Voltage Measurements
The line voltage measurement should be 120VAC +/-10% fluctuation at 60 Hz. The peak voltage should be 1.414 times the rms line voltage reading for a clean sine waveform. Ground-toneutral voltage should be less than 2 VAC. In a single-phase circuit, a higher ground-neutral
voltage indicates excessive current leakage between the neutral and ground conductors. In a 3phase circuit with a shared neutral, a high ground-neutral voltage could indicate an unbalanced
load between the three phases or harmonic distortion on the shared neutral. Excessive groundneutral voltage may result in inconsistent or intermittent equipment performance.
Troubleshooting Tips for Voltage Issues
Measurement Expected Problem Possible Possible
Result Causes Solutions
Too much load on Redistribute loads
the load on circuit. on the circuit.
High resistance Locate high resistance
connection within connection/device and
the circuit or at repair/replace.
the panel.
Supply voltage Consult power
too high/low. company.
Current leaking Identify source of leakage:
from neutral to multiple bonding points,
ground. equipment or devices.
Unbalanced 3- Check load balance
phase system. and redistribute load.
Triplen harmonics Oversize neutral to
returning on impedance. Reduce
neutral in 3-phase harmonic effect via
system. filter or other methods.
Supply voltage Consult power
too high/low. company.
High Peak Loads Evaluate number of
on line caused by electronic devices on
electronic equipment circuit and redistribute
on line. if necessary.
Supply frequency Consult power
too high/low. company.
Voltage Drop (VD) Measurements
The SureTest measures the line voltage, applies a load on the circuit, measures the loaded
voltage, then calculates the voltage drop. Results are displayed for 12A, 15A, and 20A
loads. The National Electrical Code recommends 5% as the maximum voltage drop for
branch circuits for reasonable efficiency (NEC article 210-19. FPN 4). And, the voltage
under load (VL) should not drop below 108VAC for reliable equipment operation.
A good branch circuit should start out with less than 5% voltage drop at the furthest receptacle from the panel at the end of the cable run. Then, each receptacle tested in sequence
towards the panel should show a steady decrease in voltage drop. If the voltage drop is
above 5% and does not noticeably decrease as you get closer to the first device on the circuit, then the problem is between the first device and the panel. Visually check the terminations at the first device, the wiring between the device and the panel, and the circuit breaker
connections. High resistance points can usually be identified as hot spots using an infrared
thermometer or by measuring the voltage across the breaker. If the voltage drop exceeds
5% but noticeably decreases as you nearer the panel, the circuit may have undersized wire,
too long of a cable run, or too much current on the circuit. Check the wire to ensure that it
is sized per code and measure the current on the branch circuit. If a voltage drop reading
changes significantly from one receptacle to the next, then the problem is a high impedance
point at or between two receptacles. It is usually located at a termination point, such as a
bad splice or loose wire connection, but it might also be a bad receptacle.
Troubleshooting Tips for Voltage Drop
Measurement Expected Problem Possible Possible
Result Causes Solutions
Too much Redistribute the
load on load on
the circuit. the circuit.
Undersized wire for Check code requirements
length of run. and re-wire if necessary.
High resistance Locate high
connection within resistance connection/
the circuit or at device and
the panel. repair/replace.
ASCC Measurement
The SureTest calculates the Available Short-Circuit Current (ASCC) that the branch circuit
can deliver through the breaker during a bolted fault (dead-short) condition.
The ASCC is calculated by dividing the line voltage by the circuit’s line impedance (hot +
neutral). Depressing the side arrow ( ) displays the worst-case scenario where all three
conductors (hot, neutral, ground) are shorted together -- the neutral and ground provide a
lower impedance via a parallel return path. Note that this second test will trip a GFCI. See
the following equations for clarification.
Line Voltage
120VAC
220VAC
Neutral-Ground
Voltage
Peak Voltage
120VAC
220VAC
Frequency
108-132VAC
198-242VAC
<2VAC
Voltage
153-185VAC
280-342VAC
60HZ
High/low
High G-N
>2VAC
High/low
peak voltage
High/low
frequency
Voltage Drop <5%
High Voltage
Drop
WARNING: Do not exceed the unit’s maximum voltage rating of 250VAC.
6
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 5
Page 4
8
7
ASCC1= Line Voltage (VHN)/ (Hot Ω + Neu Ω)
ASCC2= Line Voltage (VHN)/ (Hot Ω + 1/(1/Neu Ω + 1/ Grd Ω)
Impedance (Z) Measurements
If the voltage drop measurement exceeds 5%, analyze the hot and neutral impedances. If
one is significantly higher than the other, the problem is with the conductor with the much
higher impedance. Then, check all connections on that conductor back to the panel. If
both impedances appear high, the source can be undersized wire for the length of run, a
bad device, or poor connections at the pigtails, devices, or panel.
The ground impedance measured should be less than 1 ohm as a rule of thumb to ensure
that fault current has a sufficient path back to the panel. IEEE states the ground impedance
should be less than 0.25 ohms to ensure the ground conductor can safely return any fault
current which could damage equipment on the circuit. Surge suppression systems require
a good ground to adequately protect equipment from transient overvoltages. Note that a
small amount of current is applied to the ground conductor to accurately measure its
impedance. By the inherent nature of this test, a GFCI protected circuit will trip unless the
device is temporarily removed from the circuit.
Troubleshooting Tips - Impedances
Measurement Expected Problem Possible Possible
Result Causes Solutions
<0.048Ω/foot Too much load Redistribute the load
of 14 AWG wire on branch circuit. on the circuit.
<0.03Ω/ foot Undersized wire Check code requirements
of 12 AWG wire for length of run. and rewire if necessary.
<0.01Ω/ foot High resistance Locate high resistance
or 10 AWG wire connection within connection/device
the circuit or at and repair/replace.
the panel.
< 1 Ω to
protect people
High resistance Locate high resistance
connection within connection/device
the circuit or at and repair/replace.
the panel.
GFCI Testing
To test the GFCI device, the SureTest®creates an imbalance between the hot and neutral conductors by leaking a small amount of current from hot to ground using a fixed value resistor.
The test current applied by the SureTest®should not be less than 6mA or greater than 9mA
per UL-1436. A functional GFCI should sense the imbalance and disconnect the power. The
SureTest displays the actual test current in milliamps and trip time in milliseconds.
To conduct a GFCI test, press the GFCI button to enter the GFCI main menu. The GFCI
symbol in the display should be highlighted as the default test. If EPD is lit, then use the
side arrow ( ) to highlight the GFCI symbol. Then, press the GFCI button to activate the
test. The actual current being leaked to ground is displayed. The TEST icon and hourglass
symbol appear on the display to let the user know that the GFCI test is being performed.
The GFCI device should trip within the UL established guideline causing the display to
blank out with the loss of power. When the GFCI device is reset, the unit displays the actual
trip time that the GFCI took to respond to the current imbalance and open the circuit.
Pressing the down arrow button ( ) returns it to the wiring verification mode. If the GFCI
fails to trip, the SureTest terminates the test after 6.5 seconds. Further inspection should
determine whether the GFCI circuitry is faulty, the GFCI is installed incorrectly, or if the circuit is protected by a GFCI device.
UL Guideline
for trip time:
Notes:
1) In order to test a GFCI in a 2-wire system (no ground), the #61-175 ground continuity
adapter must be used. Connect the alligator clip on the adapter to a ground source,
such as to a metal, water or gas pipe.
2) All appliances or equipment on the ground circuit being tested should be unplugged to
help avoid erroneous readings.
In addition to performing a GFCI test for evaluating personal protection from shock hazards,
the SureTest can also conduct testing to ensure equipment protection from ground faults
exceeding 30mA. The method of operation is the same as the GFCI test noted in the first
paragraph above but uses a different resistor to create a 30mA leakage current from hot-toground. To conduct an EPD test on an Equipment Protective Device, press the GFCI button
to enter the GFCI main menu. The GFCI symbol in the display should be highlighted as the
default test. Press the side arrow ( ) button to highlight the EPD symbol. Then, press
the GFCI button to activate the test. The actual current being leaked to ground is displayed.
The TEST icon and hourglass symbol appear on the display to let the user know that the
Hot and Neutral
Impedance
Ground
Impedance
<0.25Ω to
protect
equipment
Undersized wire
for length of run.
Check code requirements
and re-wire if necessary.
High conductor
impedance
High ground
impedance
Where: T = seconds (s)
I = milliamps (mA)
I
T
=(
20)1.43
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 7
Page 5
9
EPD test is being performed. The EPD should trip causing the display to blank out with the
loss of power. When the EPD is reset and power is restored, the unit displays the actual
trip time that the EPD took to respond to the current imbalance and open the circuit.
Pressing the down arrow button ( ) returns it to the wiring verification mode. If the EPD
fails to trip, the SureTest terminates the test after 6.5 seconds. Further inspection should
determine whether the EPD circuitry is faulty, the EPD is installed incorrectly, or if the circuit is protected by an EPD.
Troubleshooting Tips
Measurement Expected Problem Possible Possible
Result Causes Solutions
Check wiring for proper
installation in accordance
with manufacturer’s
instructions and NEC.
GFCI doesn’t trip.
GFCI may be Check wiring and ground.
defective. Replace GFCI if necessary.
AFCI Testing (#61-165 only)
The SureTest®w/AFCI applies 8-12 current pulses in less than a half second across hot-toneutral with each pulse no longer than 8.3ms in duration, and having an amplitude of 106141 amps in accordance with UL1436. A functional AFCI breaker should recognize these
current pulses as a dangerous arc and disconnect the power to the circuit. To restore
power, reset the breaker at the panel.
To properly test the AFCI, execute the following steps:
1) Consult the AFCI manufacturer's installation instructions to determine that the AFCI is
installed in accordance with the manufacturer's specifications.
2) Plug in the SureTest and check for correct wiring of receptacle and all remotely connected receptacles on the branch circuit. Then, go to the panel and operate the test button on the AFCI installed in the circuit. The AFCI must trip. If it does not, do not use the
circuit - consult an electrician. If the AFCI does trip, reset the AFCI.
3) Return to the tester and press the AFCI button on the tester to enter the AFCI main
menu. The AFCI symbol in the display should be highlighted as the default test. If
NEUT is lit, then use the side arrow ( ) to highlight the AFCI symbol. Then, press
the AFCI button to activate the test. The TEST icon and lightning bolt symbol light
brightly on the display to let the user know that the AFCI test is being performed. The
AFCI device should trip causing the display to blank out with the loss of power. If the
AFCI fails to trip, the SureTest®will not lose power and the display shows a dimly lit
GFCI Test
GFCI trips
within trip time
GFCI doesn’t
trip within proper
trip time.
GFCI maybe
installed
improperly.
10
lightning bolt. This non-trip condition would suggest:
a) A wiring problem with a totally operable AFCI, or
b) Proper wiring with a faulty AFCI.
Consult with an electrician to check the condition of the wiring and AFCI.
4) CAUTION: AFCIs recognize characteristics unique to arcing, and AFCI testers produce
characteristics that mimic some forms of arcing. Because of this, the tester may give a
false indication that the AFCI is not functioning properly. If this occurs, recheck the
operation of the AFCI using the test and reset buttons. The AFCI’s test button function
should demonstrate proper operation.
Note: The AFCI circuitry is protected by a thermal sensor to assure long life. If a
thermometer icon appears in the display during repeated AFCI testing, the sensor
delays further testing until the circuitry cools. At that point, the testing will automatically
continue.
Shared Neutral Test (#61-165 only)
AFCI breakers are prone to nuisance tripping when wired with a shared neutral or when the
neutral conductor is accidentally grounded before the panel. The AFCI tripping occurs
because it senses an imbalance between the current going out on the hot and the current
returning on the neutral. A shared neutral between two hot conductors creates this imbalance. See the illustration below to see how this imbalance can occur.
The SureTest can test for these conditions by applying a small load of 300mA between hot
and neutral to simulate a normal load and ensure that the AFCI breaker does not trip. To
conduct a shared neutral test, press the AFCI button to enter the AFCI main menu. Press
the side arrow ( ) to highlight the NEUT symbol. Then, press the AFCI button to activate
the test. The TEST icon will light brightly while the test is being conducted. The AFCI
breaker should not trip. If the breaker does trip, a shared neutral is the probable cause.
Illustration:
SureTest Shared Neutral Test w/300mA load
3A H1
3.3A N
300mA H2
)
)
)
)
Lights
Outlet
Circuit #1: Breaker
Circuit #2: Breaker
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 9
Page 6
Troubleshooting Tips
Measurement Expected Problem Possible Possible
Result Causes Solutions
Check wiring and re-
wire device according
to manufacturer’s
instructions.
AFCI defective. Replace AFCI.
High source of Check for
line impedance high voltage
or resistance. drop.
Re-wire circuit
per AFCI
manufacturer’s
Instructions.
Optional Accessories
#61-183 Alligator Clip Adapter
This adapter allows the SureTest to analyze non-outlet based circuits for branch circuit
safety and performance. Simply plug the alligator clip adapter into the IEC connection on
the front of the SureTest. Then, properly connect the hot (black), neutral (white) and ground
(green) alligator clips onto the circuit. Correct test results are dependent on making good
connections with the alligator clips onto the circuit.
WARNING: The SureTest is designed for 120/240VAC circuits only. Do not
exceed the rating of the SureTest with this adapter.
This adapter also allows the operator to use the SureTest (#61-165 only) to verify AFCI
protection on non-outlet based circuits in bedrooms, such as on circuits used for lighting,
ceiling fans, and smoke detectors.
#61-175 Ground Continuity Adapter
This adapter allows the operator to verify that a cabinet or equipment chassis has been
properly bonded to the system ground. Plugging the SureTest into the ground continuity
adapter isolates the SureTest from the electrical ground. If the equipment is properly
grounded, then connecting the alligator clip from the ground continuity adapter to the cabinet or equipment chassis should provide a pathway to ground, and consequently a normal
wiring condition on the SureTest.
After the ground continuity adapter has been connected, the SureTest can be used to measure the ground impedance of the cabinet or equipment chassis back to the panel. See the
section on Line Impedance Measurements for test instructions for ground impedance.
This adapter can also be used to test GFCI receptacles on 2-wire circuits. Connect the alligator
clip on the adapter to a ground, such as a metal water or gas pipe prior to testing the GFCI.
#61-176 Isolated Gr
ound Adapter
This adapter allows the operator to verify that a receptacle is completely isolated from the
system ground that is bonded to other devices on the branch circuit. Test the ground
impedance of the receptacle and record the ohms value. (See the section on Line
Impedance Testing for details on obtaining the ground impedance value). Remove the
SureTest and plug it into the isolated ground adapter. Attach the alligator clip to the center
receptacle screw or metal junction box, and re-insert the SureTest into the receptacle and
record the ohms value.
The isolated ground adapter creates a parallel pathway to ground, which results in a lower
ground impedance reading with the adapter versus with the receptacle with the isolated
ground. If the two readings are the same, then the receptacle does not have an isolated
ground. If the reading taken with the isolated ground adapter is lower, then the receptacle
has an isolated ground.
Maintenance
Clean case with a damp cloth and mild detergent. Do not use abrasives or solvents.
Service and Replacement Parts:
This unit has no user-serviceable parts. To inquiry about service information, call Technical
Support at 877 201-9005 or visit our website at www.testersandmeters.com.
Repair address is:
IDEAL INDUSTRIES, INC.
Attention: Repair Dept.
1000 Park Ave.
Sycamore, IL 60178
AFCI Test
AFCI installed
incorrectly.
Shared neutral
exists.
Shared Neutral
Test
AFCI does
not trip
AFCI does
trip.
AFCI trips
AFCI does
not trip.
1211
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 11
Page 7
1413
General Specifications
Characteristics Description
Display 128 x 64 OLED with backlight
Display update for Volt Less than 2.5 times Second.
Over-range Indication on all functions Display "OL"
Operating Environment,
Relative Humidity 32°F to 122°F (0°C to 50°C) at <80%RH
Storage Environment: 32°F to 122°F (0°C to 50°C) at <80% RH
Case Construction: ABS UL 94V/0/5VA rated
Altitude: 6561.7 ft (2000m)
Dimensions: 6.4" (L) x 3" (W) x 1.4" (D)
162mm (L) x 76mm (W) x 36mm (D)
Weight: 9.4 oz (267g)
Safety: UL61010B-1, Cat III-300V
UL-1436 for AFCI, GFCI & Outlet
Accessories: Includes 1’ plug adapter, carrying case,
instruction manual. Optional alligator clip
adapter available.
Double Insulation
Instrument has been evaluated and complies with insulation category III (overvoltage category III). Pollution degree 2 in accordance with IEC-644. Indoor use.
Measurement Specifications:
All specifications are at 23°C ± 5°C at less than 80% relative humidity.
Accuracy is state as ± ([% of range] + [counts]).
AC converter is true rms sensing.
Measurement Ranges Resolution Accuracy
Line Voltage 85.0 - 250.0 VAC 0.1V 1.0% ± .2V
Peak Line Voltage 121.0 - 354.0 VAC 0.1V 1.0% ± .2V
Frequency 45.0 - 65.0 Hz 0.1Hz 1.0% ± .2Hz
% Voltage Drop 0.1% - 99.9% 0.1% 2.5% ± .2%
Voltage Loaded 10.0 - 250.0 VAC 0.1V 2.5% ± .2V
Neutral-Ground V 0.0 - 10.0 VAC 0.1V 2.5% ± .2V
Impedance - Hot 0.00 Ω - 3.00 Ω 0.01Ω 2.5% ± .02Ω
Neutral, & Ground > 3 Ω Unspecified.
GFCI Trip Time 1mS to 6.500S counter. 1 mS 1.0% ± 2mS
GFCI Trip Current 6.0 - 9.0 mA 0.1 mA 1.0% ± .2mA
EPD Trip Current 30.0 - 37.0 mA 0.1 mA 1.0% ± .2mA
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 13
CUS
Page 8

15
Limited Warranty
This meter is warranted to the original purchaser against defects in material or workmanship for two years from the date of purchase. During this warranty period, IDEAL INDUSTRIES, INC. will, at its option, replace or repair the defective unit, subject to verification of
the defect or malfunction. This warranty does not apply to defects resulting from abuse,
neglect, accident, unauthorized repair, alteration, or unreasonable use of the instrument.
Any implied warranties arising out of the sale of an IDEAL product, including but not limited
to implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, are limited to
the above. The manufacturer shall not be liable for loss of use of the instrument or other
incidental or consequential damages, expenses, or economic loss, or for any claim or
claims for such damage, expenses or economic loss.
State laws vary, so the above limitations or exclusions may not apply to you. This warranty
gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other rights, which vary from state to
state.
Warranty limited solely to repair or replacement; no warranty of merchantability, fitness for a
particular purpose or consequential damages.
IDEAL INDUSTRIES, INC.
Sycamore, IL 60178, U.S.A.
800-435-0705 Customer Assistance / Service d'assistance à la clientèle au / Asistencia al Cliente
www.idealindustries.com
ND 5481-4 Made in U.S.A. / Fabriqué aux USA / Fabricado en EE.UU.
ND 5481-4 61-164 165 Ins 11/21/06 1:28 PM Page 15
 Loading...
Loading...