MK74CB214
Dual 1 to 7 Buffalo™ Clock Driver
Description
The MK74CB214 Buffalo™ is a monolithic
CMOS high speed clock driver which is ideal for
Pentium™, 486, and RISC processor systems. It
consists of two identical single input to seven lowskew output, non-inverting clock drivers. When
combined with MicroClock’s MK14xx series of
low jitter clock synthesizers, the two chips form an
unequaled high performance clocking scheme for
new processors. This is the only solution on the
market that meets Intel’s specs for skew and jitter.
Many new Pentium systems require up to seven
outputs each of two low-skew clocks. This
monolithic solution eliminates any concern for
part-to-part skew matching. The MK74CB214 is
packaged in the tiny 20 pin SSOP, which uses the
same board space as the narrow 14 pin SOIC. An
added feature of the chip is the ability to produce
both 3.3V and 5V amplitude clocks by connecting
different voltages to VDDA and VDDB. See
MAN03 for dual voltage operation.
Features
• Tiny 20 pin SSOP (150 mil) package
• Dual one input to seven output clock drivers
• Outputs are skew matched to within 250ps
• A outputs and B outputs matched to 500ps
• 3.3V±10% and/or 5V±10% supply voltage
• Each set of seven clock drivers can run from
different supply voltages, making it possible to
have 3.3V and 5V amplitude clock outputs from
the same chip
• Clock speeds up to 66.67 MHz
Family of MicroClock Parts
The MK74CB214 Buffalo™ is designed to be
used with MicroClock’s clock synthesizer devices,
which will produce the CPU, memory, and local
bus clocks. The inputs of the Buffalo are matched
to the outputs of MicroClock clock synthesizers.
Consult MicroClock for applications support.
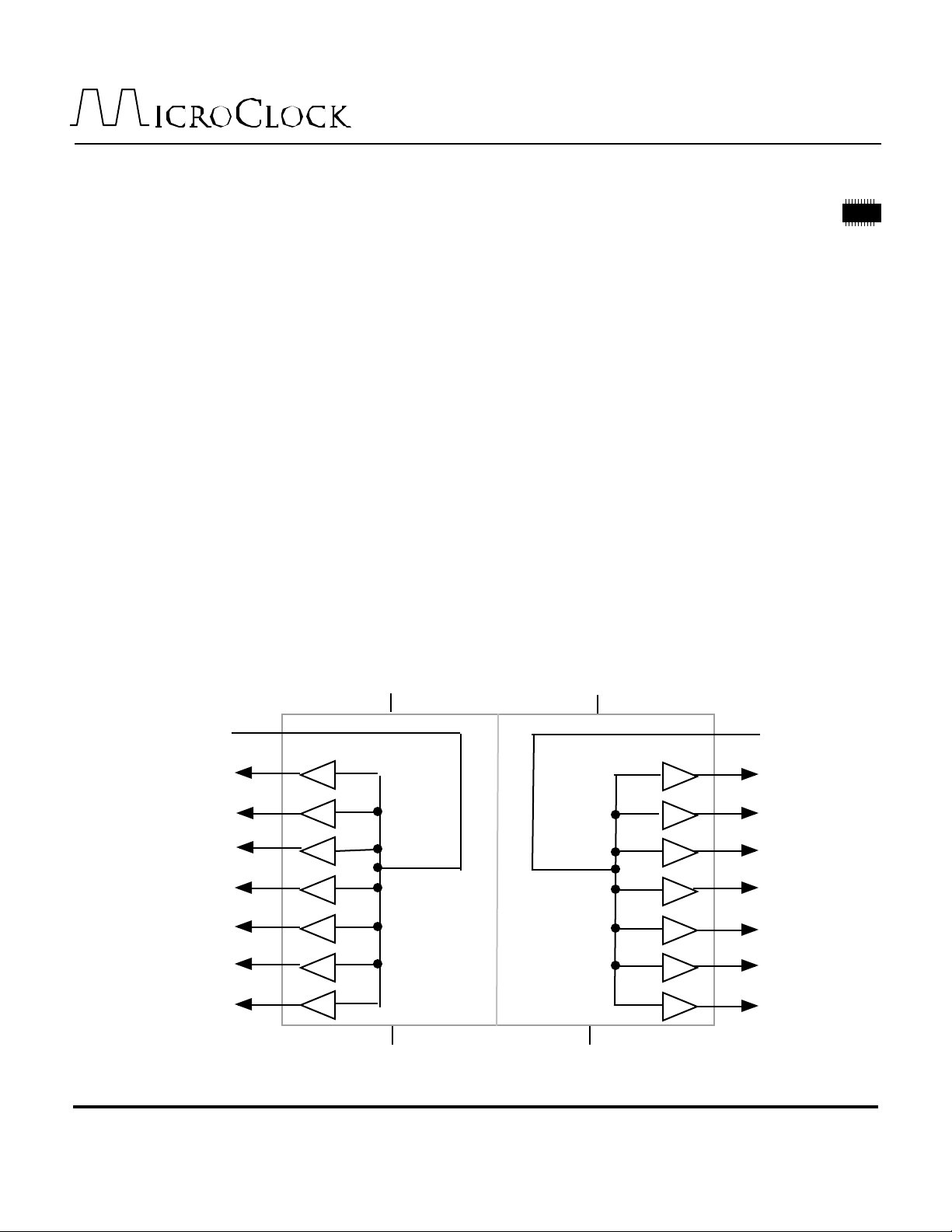
Block Diagram
INA
QA0
QA1
QA2
QA3
QA4
QA5
QA6
VDDA
GNDA
VDDB
INB
QB0
QB1
QB2
QB3
QB4
QB5
QB6
GNDB
MDS 74CB214 B 1 Revision 051396 Printed 11/16/00
MicroClock Incorporated•1171 North Fourth St.•San Jose•CA•95112•(408)295-9800tel•(408)295-9818fax

MK74CB214
Dual 1 to 7 Buffalo™ Clock Driver
Pin Assignment
INA
QA0
QA1
VDDA
QA2
QA3
GNDA
QA4
QA5
QA6
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
INB
QB0
QB1
VDDB
QB2
QB3
GNDB
QB4
QB5
QB6
Suggested Layout
V
0.1µF
G
For simplicity, terminating resistors (if needed) are not
shown for the outputs, but should be placed as close to the
device as possible. It is most critical to have the 0.1µF
decoupling capacitors closest.
= connect to VDD
V
= connect to GNDG
V
0.1µF
G
Pin Descriptions
Number Name Type Description
1 INA I Clock input for seven A outputs.
2, 3 QA0, QA1 O Clock A outputs.
4 VDDA P Power supply for seven A buffers. Connect to +3.3V or +5V. Clock amplitude will match.
5, 6 QA2, QA3 O Clock A outputs.
7 GNDA P Connect to ground.
8, 9, 10 QA4, QA5, QA6 O Clock A outputs.
11, 12, 13 QB6, QB5, QB4 O Clock B outputs.
14 GNDB P Connect to ground.
15, 16 QB3, QB2 O Clock B outputs.
17 VDDB P Power supply for seven B buffers. Connect to +3.3V or +5V. Clock amplitude will match.
18, 19 QB1, QB0 O Clock B outputs.
20 INB I Clock input for sevent B outputs.
Type: I = Input, O = output, P = power supply connection
MDS 74CB214 B 2 Revision 051396 Printed 11/16/00
MicroClock Incorporated•1171 North Fourth St.•San Jose•CA•95112•(408)295-9800tel•(408)295-9818fax
 Loading...
Loading...